Molecular marker of major QTL (Quantitative Trait Locus) of soybean seed protein content and application thereof
A technology of protein content and molecular markers, which is applied in the field of genetic breeding and achieves good application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1. Acquisition of main effect QTL for soybean grain protein content
[0039] (1), 'NJRSXG' group construction
[0040] Hybrid F 1 , through the "single-seed transmission" method to construct the population and obtain 147 F 2:7 Generation recombinant inbred line ('NJRSXG').
[0041] The steps of the "single-seed transmission" method are as follows: a seed harvested from the female parent plant in the parental hybrid generation grows into a F1 generation single plant, and its self-crossing (that is, self-pollination) yields 1 F plant 2 generation seeds, the latter is planted to grow into a F2 generation line containing segregation traits, and each individual plant of it is self-fertile and harvests F 3 For generation seeds, the isolated plants of the same traits are harvested and threshed into bags, and each seed is planted separately in the next year. 3 F 4 Generation seeds, ... until the characters of different plants in each family are completely stable and ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2. Acquisition of major QTL tight marker Z56 for protein content in soybean grain
[0050] (1) Molecular marker development
[0051] Using the published soybean physical map information and the sequence information of the sequencing materials of the National Soybean Improvement Center, multiple molecular markers were designed in the Gm08:13000kb-17000kb region of chromosome 8.
[0052] (2) Phenotype determination of local materials
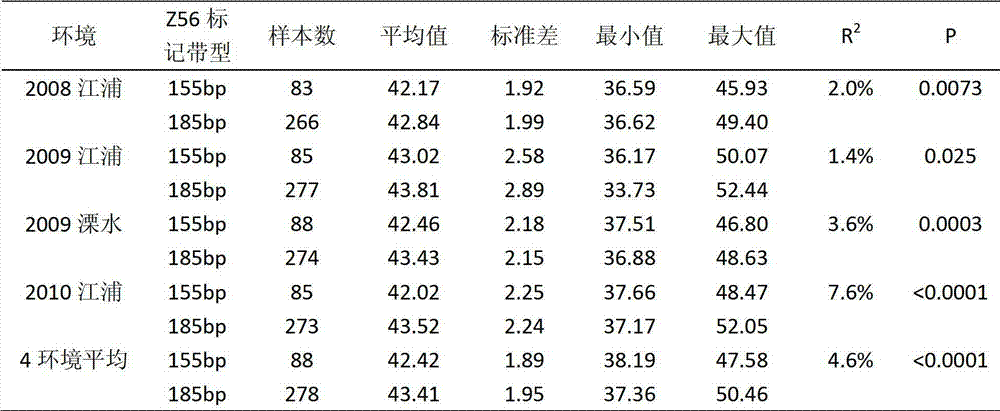
[0053] Soybean local materials for analysis consisted of 366 accessions from 6 ecological regions of the country, and dried soybean seeds were milled using a 1095 Knifetec sample mill (FOSS Tecator, Switzerland). Using VECTOR 22 / N Fourier transform infrared spectrometer to measure the spectrum of soybean seed powder, and use the established soybean protein content model to predict the protein content of soybean seeds.
[0054] (3) Molecular marker identification of local materials
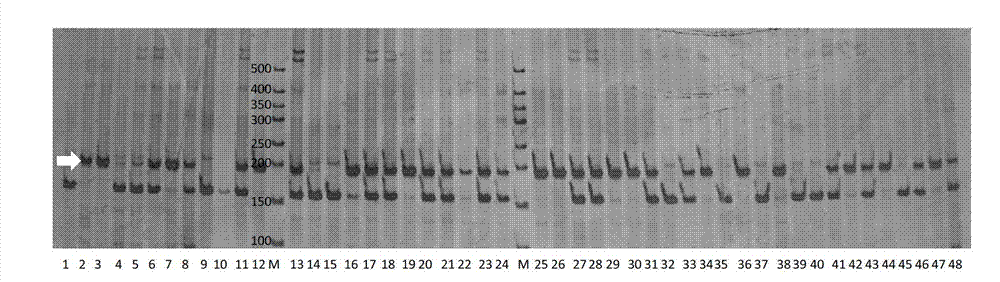
[0055] Using CTAB method to extract genomic DNA...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Example 3. Application of Z56 Molecular Marker in Selection of Protein Content in Soybean Grain
[0061] (1) Genome amplification detection of both parents
[0062] The parents used to verify the QTL for soybean grain protein content were parent WT133 (Z56 allele band is 155bp, soybean seed protein content is 49.9%), parent XG30 (Z56 allele band is 185bp, soybean seed protein content is 46.9%), XG30 Although the seed protein content is smaller than that of WT133, it contains a potentiating site at the Z56 site.
[0063] (2), population amplification detection and marker analysis
[0064] Using the above two parents to cross, get F 1 After the seed is planted, it grows into a F 1 Generation single plant, its self-crossing is fruitful, and one F2 generation seed is harvested, and the latter grows into a F2 generation containing segregation traits. 2 Generation line, on F 2 Harvesting seeds from a single plant F 2:3 The adult plant row was planted, two replicates wer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com