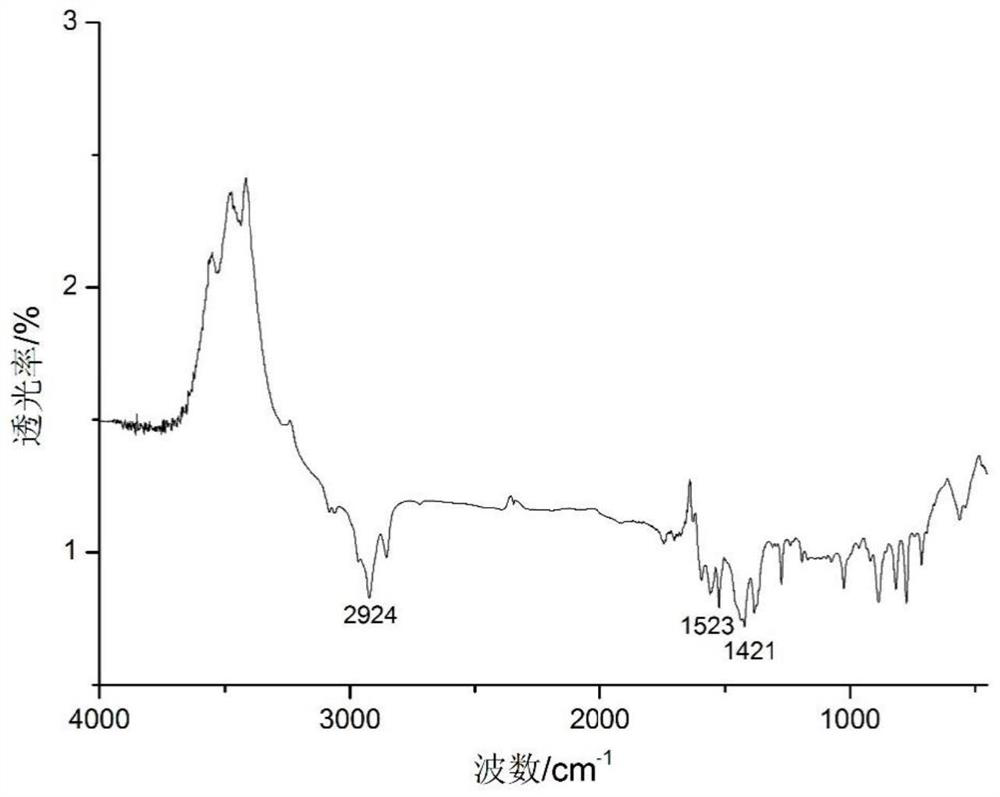
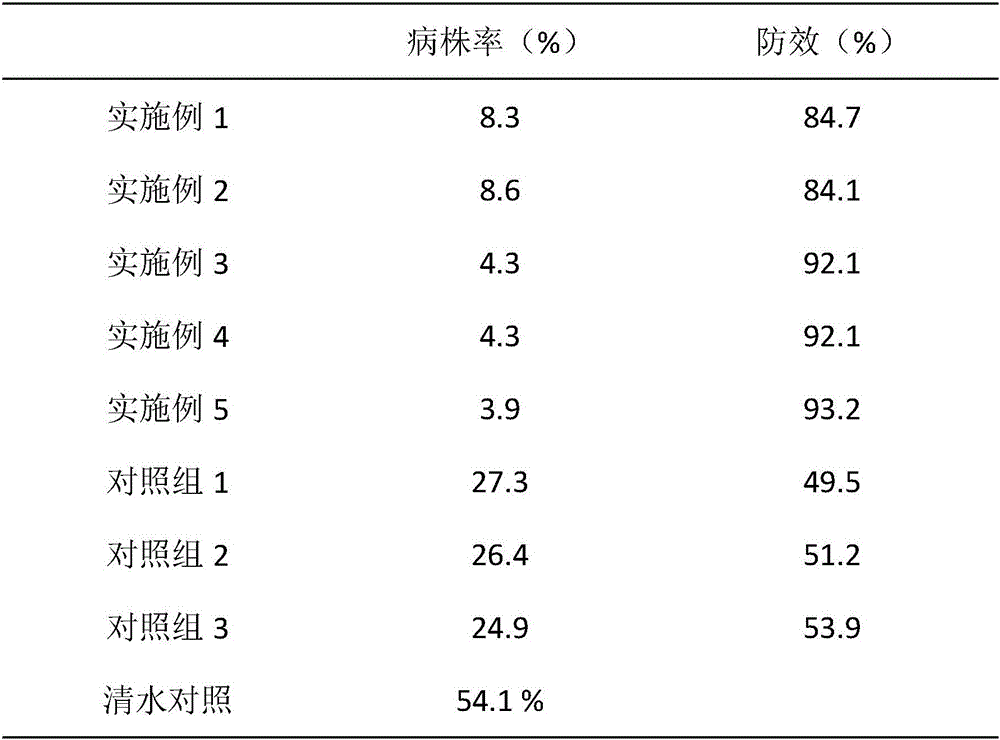
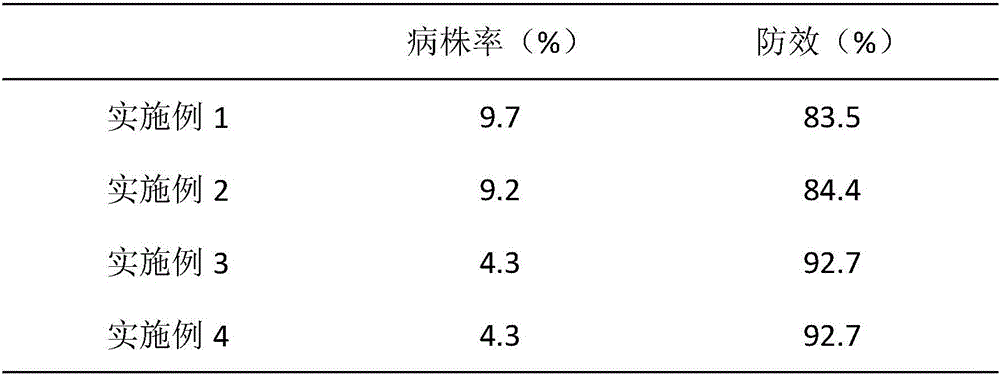
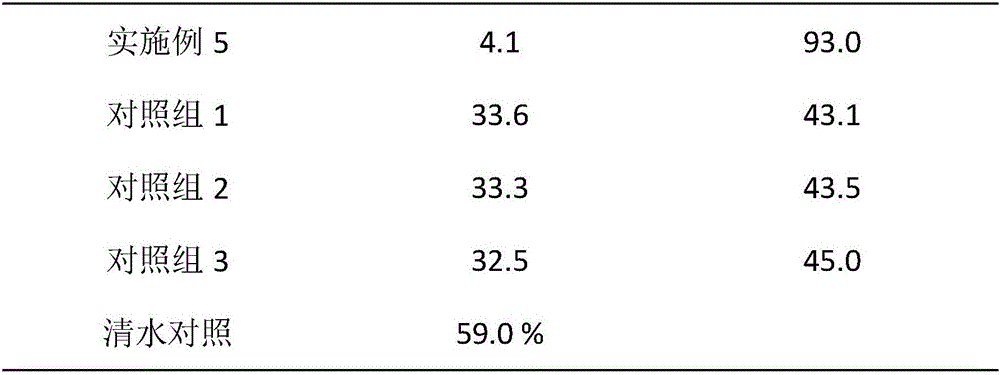
Patents
Literature
67 results about "Russulaceae" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Russulaceae are a diverse family of fungi in the order Russulales, with roughly 1,900 known species and a worldwide distribution. They comprise the brittlegills and the milk-caps, well-known mushroom-forming fungi that include some edible species. These gilled mushrooms are characterised by the brittle flesh of their fruitbodies.
Biological preparation capable of preventing and treating cruciferae club root and use thereof
InactiveCN101416641AGood control effectSolve prevention and control problemsBiocideBacteriaSucroseRussulaceae
The invention relates to a biological agent against crucifer club root and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of bio-pesticide. The strain for production is Bacillus subtilis XF-1, whose preserving number is CGMCC NO.2357. The stain has the characteristics as follows: (1) the primary colony on the LB culture substrate is white and round having a wet surface; the later colony is light yellow having uneven edge with dry and crimple surface; observed from the microscope, the strain is short-bar shaped and movable with spore, peritricha and dimension of 0.7 - 0.8 * 2.0-2.4 mum; (2) the strain is Gram-positive and aerobic and makes use of glycogen, sugar, citrate, gelatin hydrolysate, starch and casein, but does not make use of cellulose, tyrosine and catalase positive; (3) the stain has the function of sterilization, disease prevention, and yield improvement. The embodiment of the invention is as follows: using the test tube of Bacillus subtilis XF-1 stain, shake cultivation, and culture solution for fermentation to prepare biological agent, then applying the biological agent to the rhizosphere soil of crucifer crops, thereby having good effect in preventing and treating, and simple production.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for producing edible fungi flavoring powder
The invention discloses a method for producing edible fungi flavoring powder, and belongs to the field of novel biological products. For solving the technical problems, the invention provides the method for producing the edible fungi flavoring powder for keeping the nutritional and functional components of fungi and keeping original flavor and form. The method comprises the following steps of: a, raw material treatment: cleaning and slicing at least one of fresh tricholoma matsutake, toadstool, bolete, sarcodon quel, hericium erinaceus, lentinus edodes, pleurotus cornucopiae, pleurotus eryngii, cantharellus cibarius, termitomyces albuminosus, agrocybe cylindracea, lactarius deliciosus and russulaceae and fresh truffle, and drying the surface moisture in air; b, freezing; c, vacuum drying; d, resolving and drying; e, crushing; and f, sterile packing. The flavoring powder produced by using the method can keep original flavor and form, the nutritional and functional components are not lost, the indexes of the stored flavoring powder are in accordance with the regulation of edible fungi health standard GB7096-2003, and the water content index of the flavoring powder is lower than 1 / 3 of the national standard.
Owner:PANZHIHUA CHENFENG FORESTRY
Methods and means for delaying seed shattering in plants
ActiveUS20060248612A1Reduce seed shatterIncrease pod shatter resistanceSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBrassicaceaeRussulaceae
The invention relates to methods and compositions for modulating properties of fruit dehiscence in plants such Brassicaceae plants, specifically to improved methods and means for reducing seed shattering in Brassicaceae plants, particularly the Brassicaceae plants grown for oil production, to a degree which is agronomically important.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC +1
Cabbage vegetable storage and preservation technology
InactiveCN103329987AReduce mildewExtend freshnessFruits/vegetable preservation by freezing/coolingHorticultureRoom temperatureBud
The invention relates to a cabbage vegetable storage and preservation technology. Cauliflower and asparagus broccoli both belong to cruciferae cabbage vegetables and are native to the coast of the Mediterranean; the cauliflower is also named cavolfiore or broccolo; the cauliflower is reduced in quality by probably generating ball looseness and ball-flower browning during storage due to picking time delay or improper storage environments, such as high temperature, low temperature, and the like, after picking; the asparagus broccoli is also named broccoli, broccoliflorets or sprouting broccoli, because the edible part of the asparagus broccoli is a tender peduncle and a small flower bud, and the flower bud is extremely easy to open and yellow after picking at room temperature, the asparagus broccoli is more difficult to preserve compared with the cauliflower. The cabbage vegetable storage and preservation technology disclosed by the invention solves the problem of the traditional vegetable storage mode, solves the technical problem on the links of picking, precooling, packaging and transportation, reduces the rottenness during the storage and prolongs the preservation time.
Owner:韩浩良
Biological preparation capable of preventing and treating cruciferae club root and use thereof
InactiveCN101416641BGood control effectSolve prevention and control problemsBiocideBacteriaSucroseRussulaceae
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Fermentation method of bacillus amyloliquefaciens Bam22 for preventing and treating cruciferae plasmodiophora brassicae
ActiveCN105296392AHigh activityEasy to carry out prevention workBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesMicroorganism
The invention provides a fermentation method of bacillus amyloliquefaciens Bam22 for preventing and treating cruciferae plasmodiophora brassicae. The method comprises the following steps: (1) picking up a bacillus amyloliquefaciens Bam22 colony cultivated on a solid culture medium, and carrying out shake culture in a liquid culture medium at 30-32 DEG C for 10-12 hours, wherein the rotating speed is 200-220rpm; and the product is taken as a seed solution; (2) fermenting the seed solution obtained in the step (1) in a fermentation tank for 40-50 hours, wherein the access amount of the seed solution is 8%-10%; the temperature of the tank is 27-30 DEG C; the stirring speed of the fermentation tank is 220-250rpm; the air flow is 0.8:1 to 1:1 (V / V.m); the efficient bacillus amyloliquefaciens Bam22 for cruciferae plasmodiophora brassicae is preserved at the General Microbiology Center of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on September 6, 2015; and the preservation number is CGMCC No.11329. The fermentation method provided by the invention is very favorable to cultivation of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens Bam22; and multiple bacteria are obtained and have good activity.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION SICHUAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Pickle and purple cabbage trigenomic species allohexaploid vegetable germplasm and acquisition method
ActiveCN103651111AShorten the timeEasy to operateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureGermplasmOperability
The invention discloses a pickle and purple cabbage tri-genome species allohexaploid vegetable germplasm and an acquisition method, which fill in the blank of lack of brassica trigenomic species allohexaploid vegetable germplasm. The acquisition method comprises the steps that pickle and purple cabbages of brassica vegetable germplasm are cross-fertilized; an ovary is picked at the seventh day after pollination; mature seeds are obtained by embryo rescue; a large quantity of propagated progenies are obtained through subculture and propagation after seed germination; duplication treatment is carried out on a haploid by a liquid culture medium with colchicine to obtain the multi-genome allohexaploid vegetable germplasm. The pickle and purple cabbage tri-genome species allohexaploid vegetable germplasm and the acquisition method, disclosed by the invention, have the advantages of strong operability, simpleness and practicality, save the time for obtaining multi-genome polyploidy material, can be widely used for embryo rescue for interspecies cross of cruciferous brassica vegetable germplasm, and have great significance to cultivation and breeding of new species of special plants.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Selective breeding method preserved sichuan pickle cytoplasm male sterile line
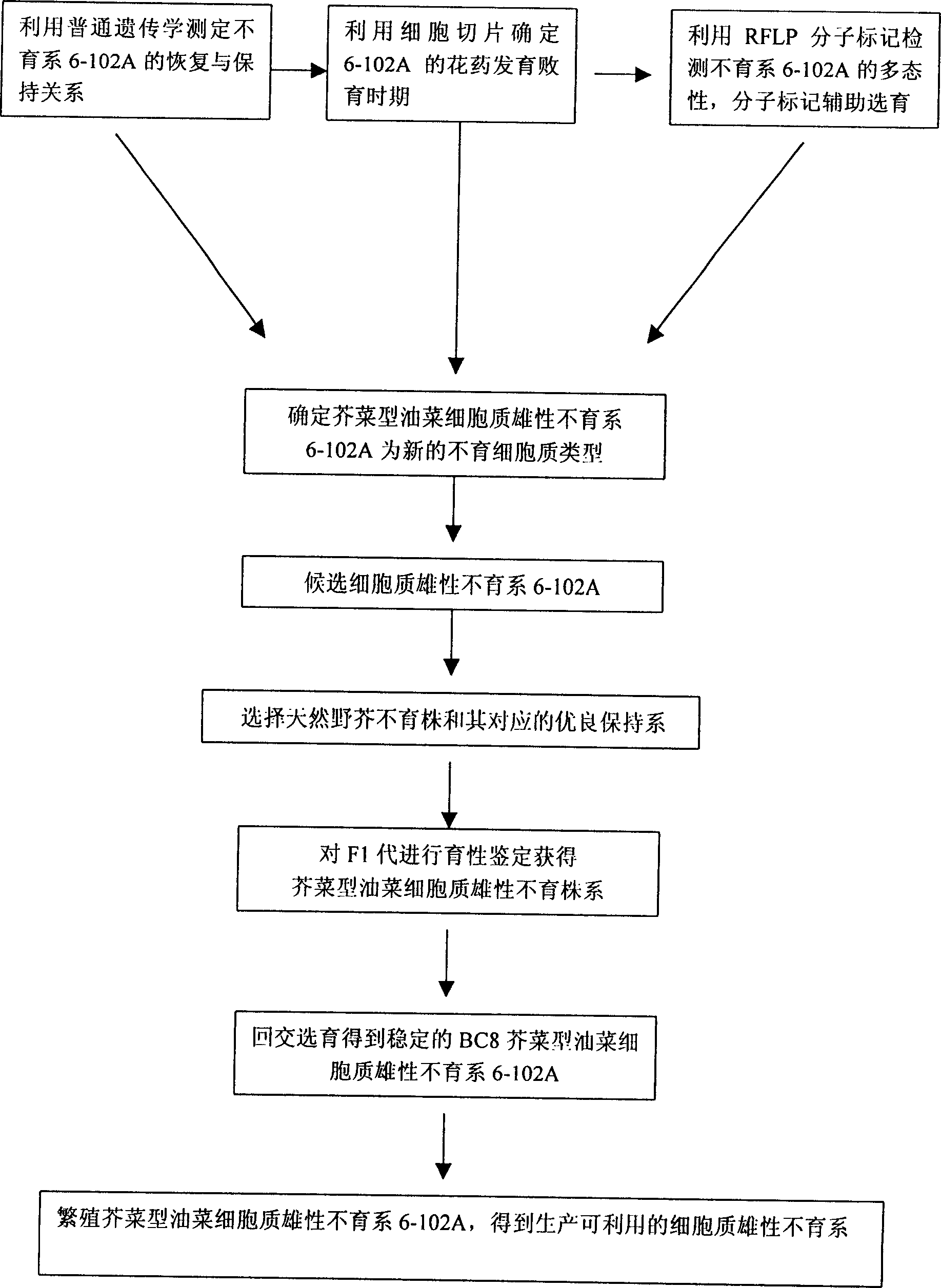
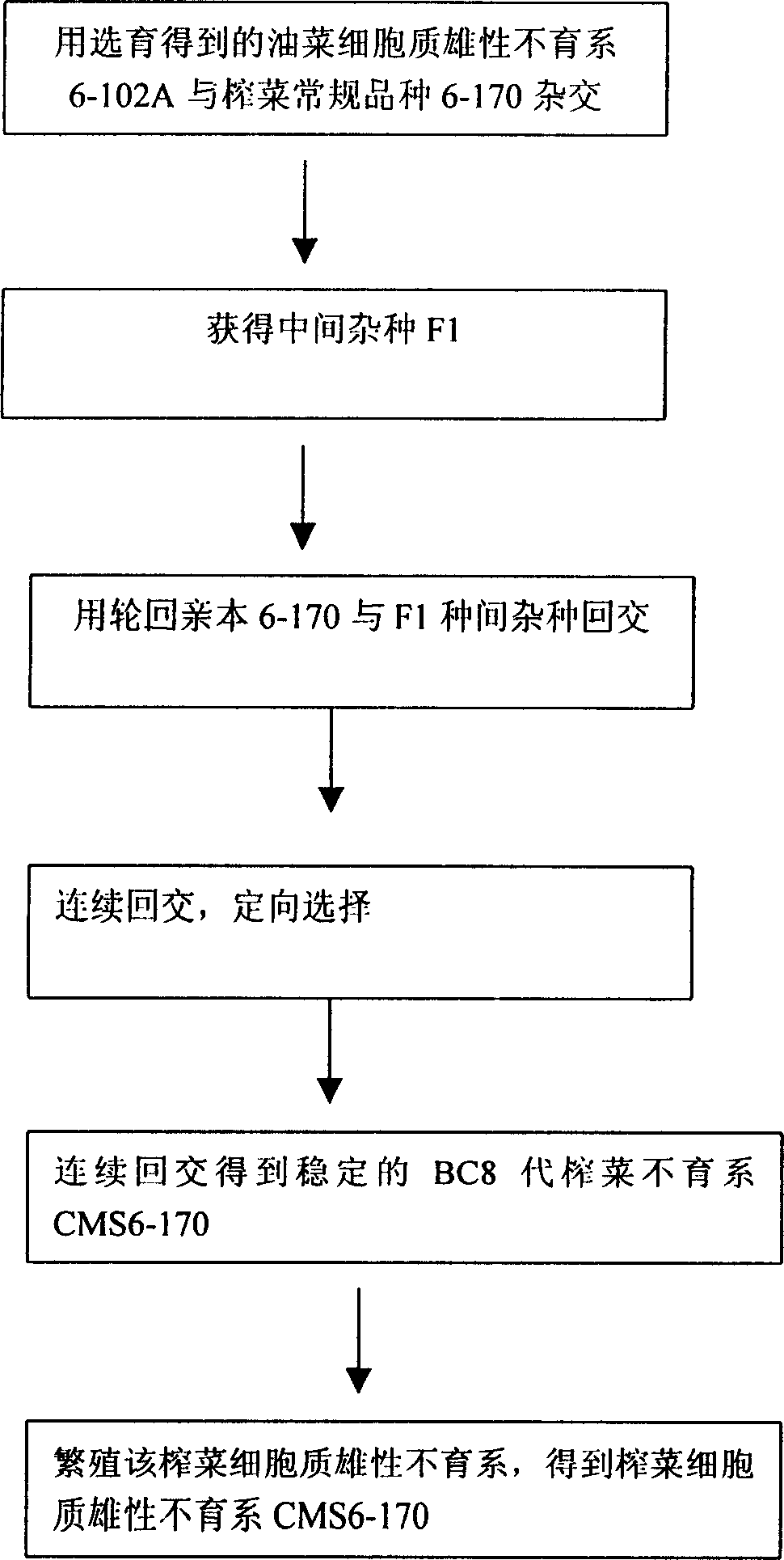
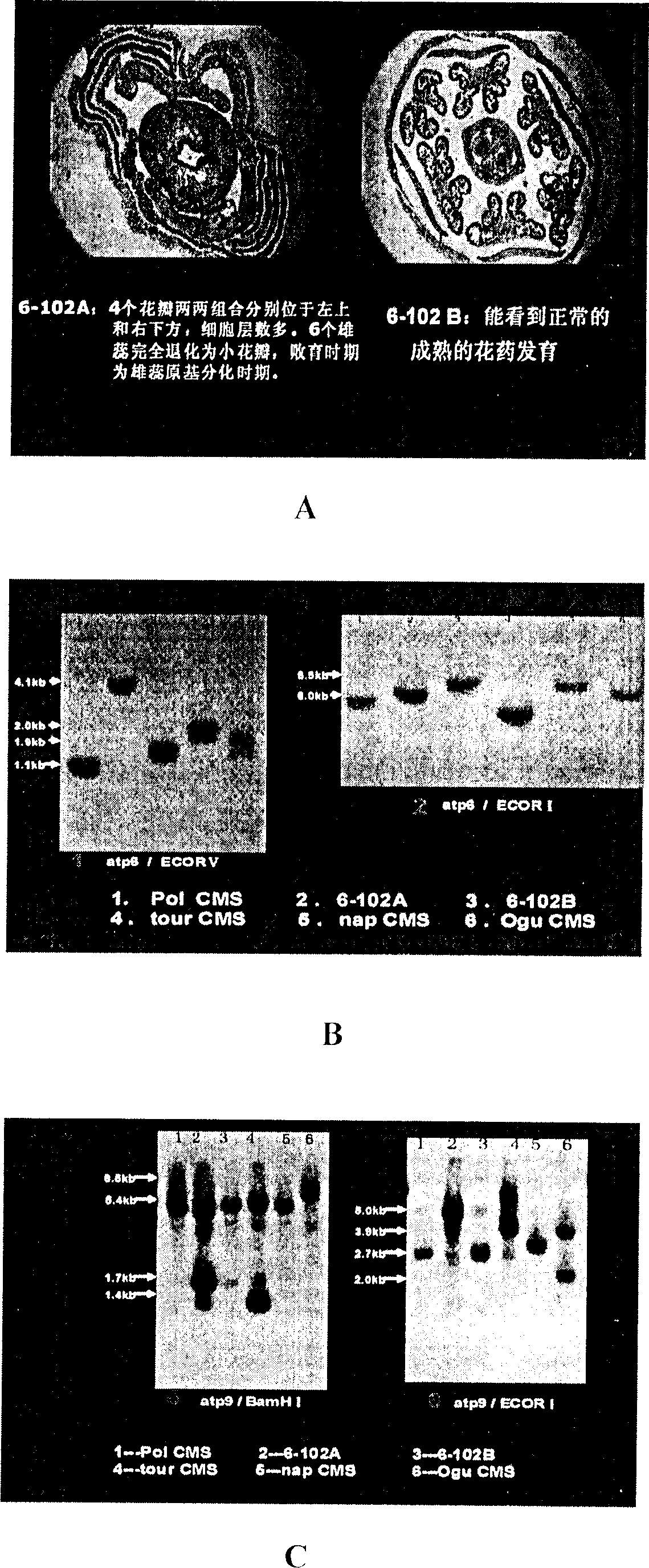
InactiveCN1849879ASterility is stable and completeNo dead budsVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationRussulaceaePlant Tubers
The present invention relates to a method for selecting and breeding tuber muslard cytoplasmic male sterile line. It is characterized by that it uses natural mustard rape cytoplasmic male sterile line 6-102A as female parent, uses high-quality tuber mustard 6-170 as maintainer line, utilizes continuous backcross and molecular making auxiliary selection to obtain genetic stable tuber mustard cytoplasmic male sterile line CMS 6-170, breeding said sterile line so as to obtain the tuber mustard cytoplasmic male sterile line for production application.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Photosynthetic bacterium strain and its use in prevention and treatment on clubroot of cruciferous crops
The invention relates to a photosynthetic bacterium strain for preventing and treating clubroot of cruciferous crops and its application and belongs to the technical field of plant protection. The photosynthetic bacterium belongs Lampropedia sp, is named as photosynthetic bacterium GH-1, is preserved in the China center for type culture collection on November 25, 2016 and has a preservation number of CCTCC NO: M 2016680. The strain has high ability to effectively prevent and treat clubroot of cruciferous crops, can be used for preventing and treating clubroot of cruciferous crops, reduces clubroot morbidity to about 10%, observably reduces a plant disease index, effectively improves a crop yield, has a yield increasing rate of 150% or more, is environmentally friendly and safe, does not produce residues and broadens the application field of photosynthetic bacteria.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION SICHUAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for preparing novel downy-mildew-resistant common head cabbage germplasm through protoplast asymmetric fusion
InactiveCN102181424AImprove economyExcellent agronomic traitsGenetic engineeringFermentationHigh resistanceResistant genes
The invention discloses a method for creating a novel downy-mildew-resistant common head cabbage germplasm through a protoplast asymmetric fusion technology, solves the problems that a common head cabbage variety which has high resistance against downy mildew of cruciferae and is even immune is substantially not available in production at present and overcomes the defects of incompatible distant hybridization, large difficulty and high investment of a genetic engineering technology and the like. The method for preparing the novel downy-mildew-resistant common head cabbage germplasm through the protoplast asymmetric fusion is characterized in that: a brussels sprout carrying downy-mildew-resistant gene is used as a donor; protoplast of the donor is treated through UV (Ultraviolet) ray; the common head cabbage which is sensitive to the downy mildew and has other superior economical and agronomic characters is used as a receptor; and the novel downy-mildew-resistant common head cabbage germplasm is created through a protoplast asymmetric fusion method. In the method, the downy-mildew-resistant gene of the brussels sprout is transferred into a common head cabbage, so that a system for quickly breeding the novel disease-resistant germplasm is established by using a protoplast fusion technology, and a modern cabbage germplasm resource innovation and disease-resistant breeding high-efficiency technical platform is established.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
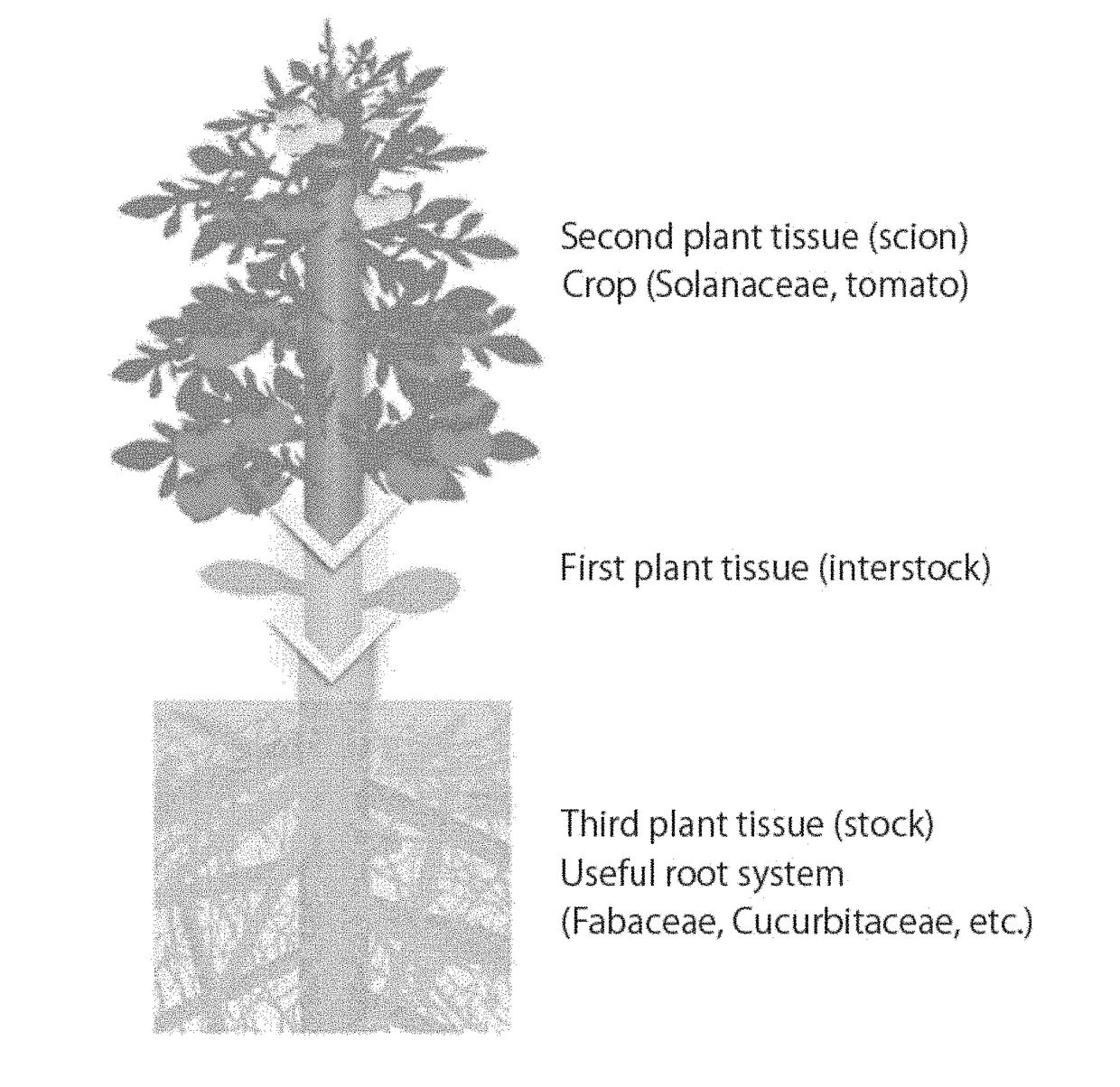
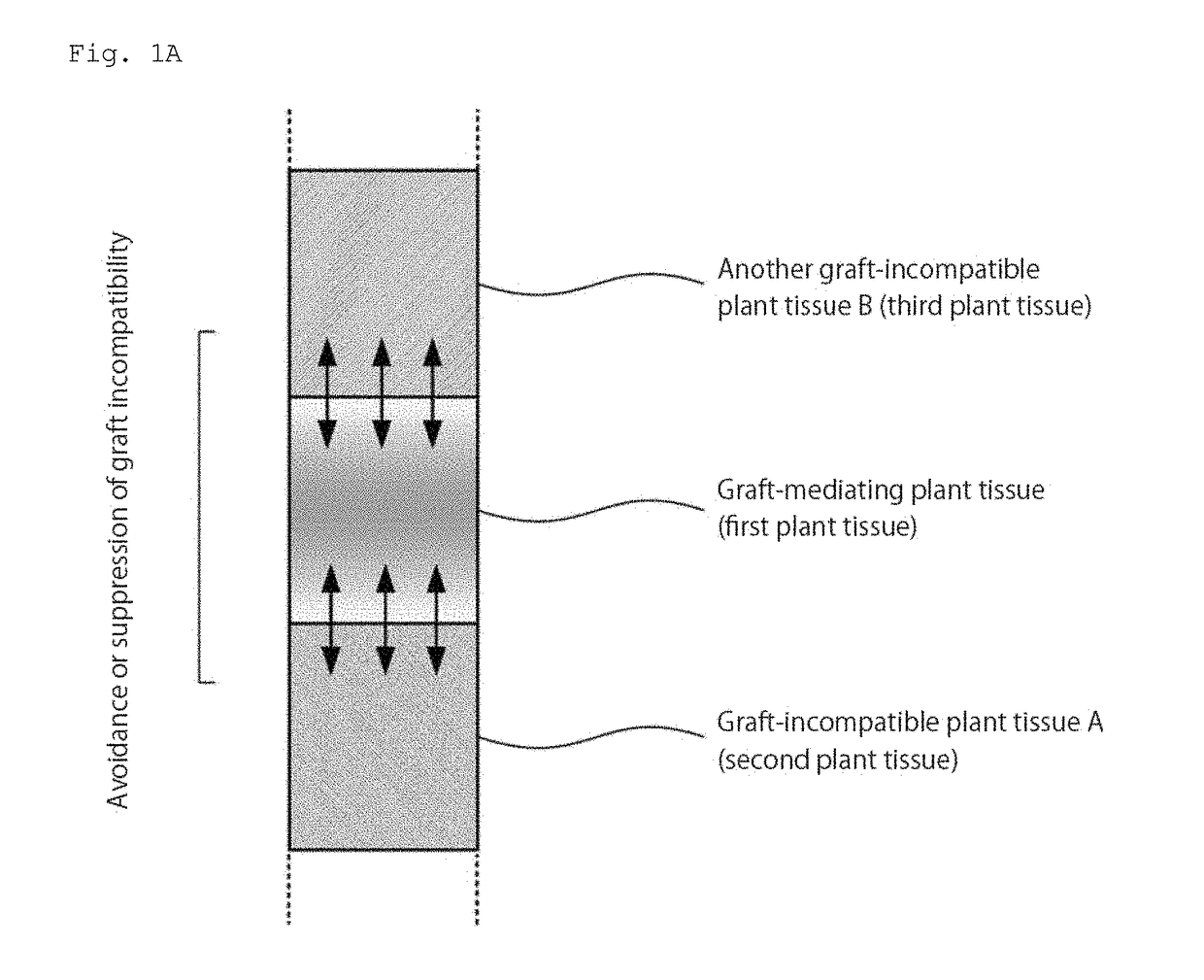
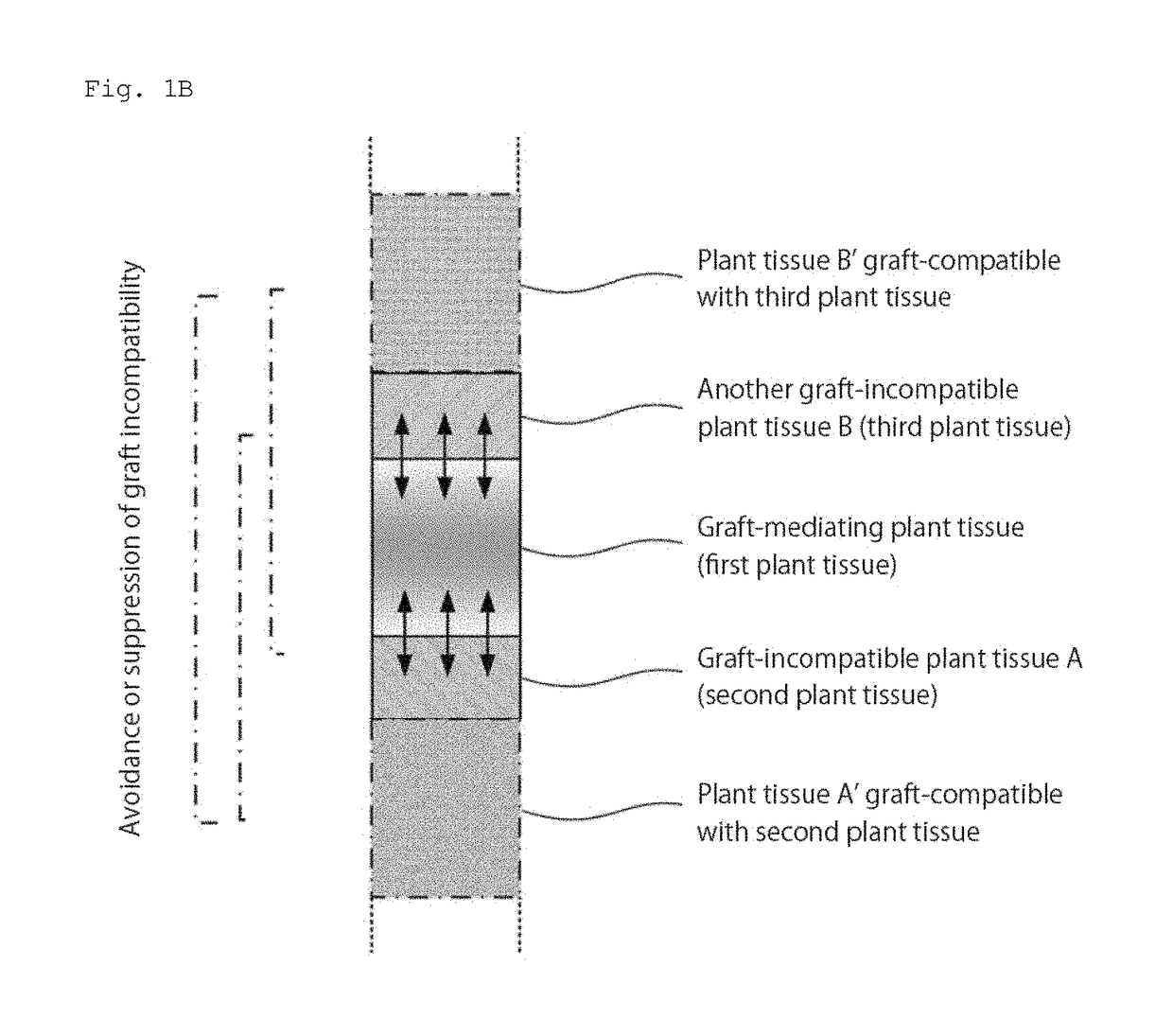
Grafted plant body and method for producing same
ActiveUS20170347531A1Avoid and suppress graft incompatibilityIncrease freedomGraftingWood testingBrassicaceaePlant tissue
Provided is a novel plant body comprising a plant tissue of a plant belonging to the family Solanaceae, Brassicaceae, Lamiaceae, or Orobanchaceae, wherein graft incompatibility is avoided or suppressed by using a graft medium between different-family plants.
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY
Method for breeding hybrid of rape or cruciferae vegetables by using wild leaf mustard sterile cytoplasm
InactiveCN101044837AImprove identification efficiencyNormal fertilityClimate change adaptationFused cellsHybrid seedRussulaceae
A process for preparing the hybrid seeds of rape and the vegetables in the mustard family by using the sterile cytoplasm of charlock includes such steps as separating the protoplast from leaf pulp, purifying it, pre-treating, fusing, culturing, discriminating the hybrid, reproduction, selectively culturing the male sterility recovery line of charlock cytoplasm, transferring the male sterility and recovery characters from the charlock cytoplasm to rape or the vegetables in mustard family, and hybridizing between the charlock cytoplasm male sterility line of rape or the said vegetables and the male fetile rape or the said vegetables.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for indoor quick amplification propagation of cruciferous vegetable lepidoptera pest parasitic wasps
The invention relates to a method for indoor quick amplification propagation of cruciferous vegetable lepidoptera pest parasitic wasps. The method includes the following steps: (1) acquiring parasiticwasp cocoons from a field; (2) performing verification on parasitic wasps for use after the parasitic wasps are hatched out from the acquired parasitic wasp cocoons; (3) planting radish seedlings inplanting pots in the condition of plant growth light sources; (4) performing indoor propagation on Plutella xylostella by using a suspension method; (5) allowing the acquired parasitic wasps from thestep (2) to perform mating; (6) selecting and putting the 2th-3th-age-group Plutella xylostella acquired from the step (4) in parasitic cups, and leading the parasitic wasps acquired from the step (5)to the parasitic cups to perform parasitism; (7) collecting parasitic wasp cocoons acquired from the parasitic cups, and cleaning the parasitic cups; and (8) repeating the above steps (2)-(7), and performing successive propagation on the Plutella xylostella and the parasitic wasps. The method is easy to operate, is efficient and convenient, is low in cost, can achieve indoor quick amplification propagation of the cruciferous vegetable lepidoptera pest parasitic wasps, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Method for acquiring novel species of brassicaceous vegetables and application method of novel specie of brassicaceous vegetables
InactiveCN103798125AShort breeding cycleImprove efficiencyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSporeHybrid seed
The invention discloses a method for acquiring novel species of brassicaceous vegetables and an application method of the novel species of the brassicaceous vegetables. According to the method, free microspore culture is carried out between hybrid seeds of the brassicaceous vegetables of 'celery cabbage species*small cabbage species' or 'small cabbage species*variants' to obtain regenerated plants so as to create the novel species. The method is applied to breeding and comprises the main steps of carrying out vegetable hybridization on 'celery cabbage species*'small cabbage species' and 'small cabbage species*variants', inducing embryoid by virtue of the free microspore culture, acquiring the regenerated plants through the germination of embryoid, carrying out ploidy determination on the regenerated plants acquired through the culturing of the microspore culture, reserving seeds of double haploid and high haploid, carrying out morphological identification and nutritive index identification on descendants of the planted regenerated plants, and preparing cross composition. The method has the advantages of short period and high efficiency, provides materials for the efficient breeding of Chinese cabbage vegetables and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN ZIFENG SEED IND
Method for breeding prematurity good-quality high-yield hybrid tumorous stem mustard (hot pickled mustard tube)
InactiveCN101467514ASolve supply problemsPlant genotype modificationAngiosperms/flowering plantsStem barkRussulaceae
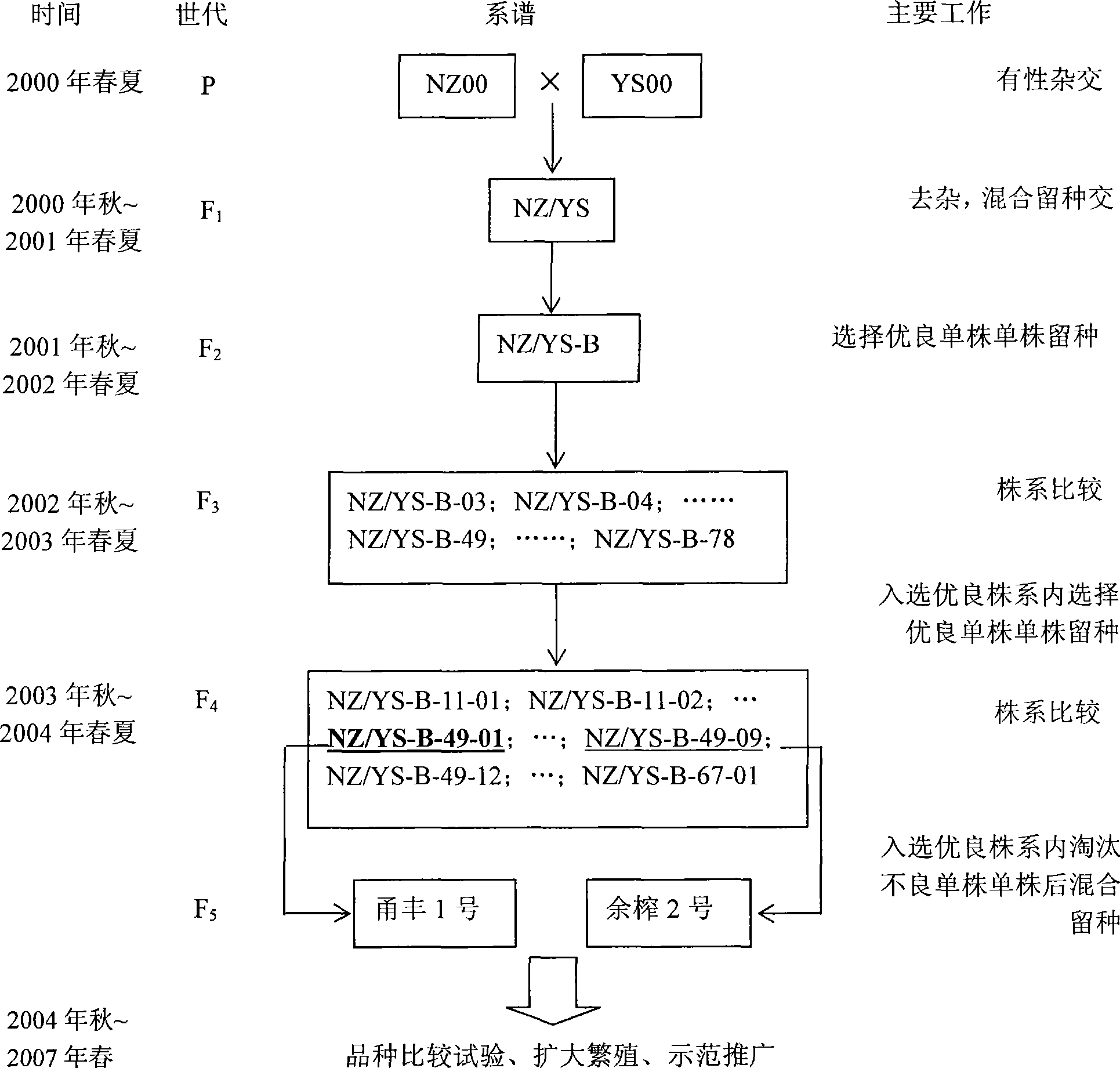
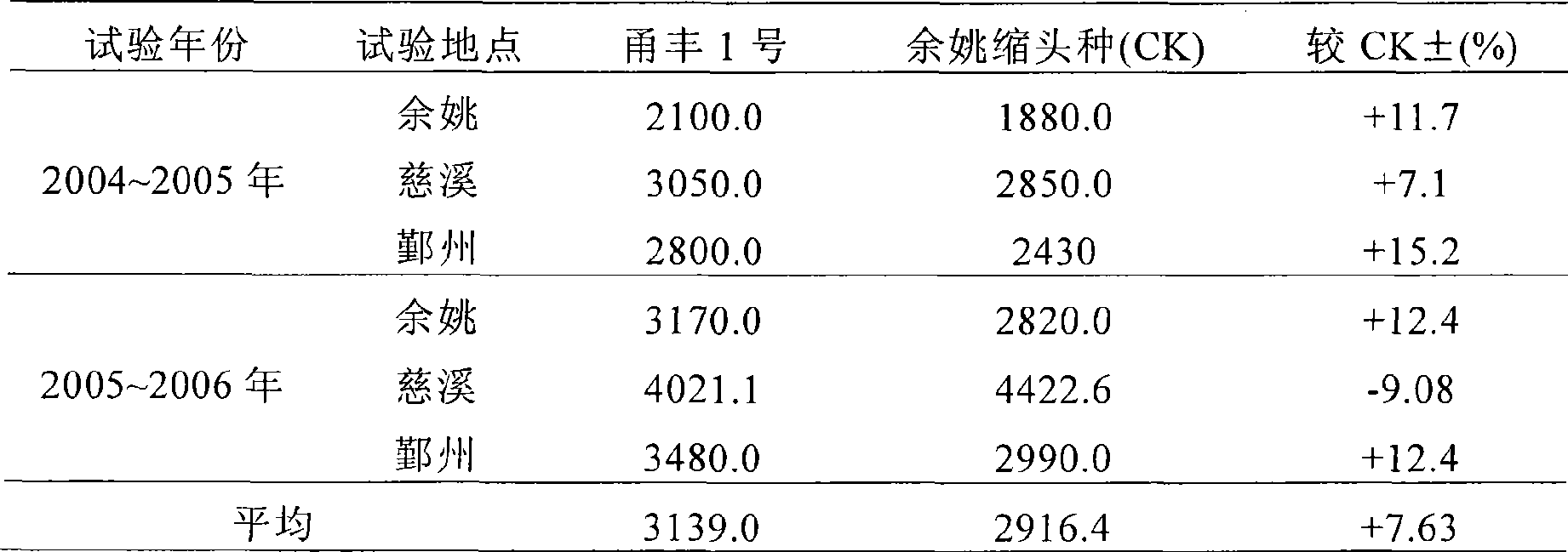
The invention pertains to the cruciferous vegetable breeding technique field. The stable inbred line of the plate leaf type tuber mustard(code: NZ00) stemming from Szechwan is used as female parent; the stable inbred line(semi-leaf piece type) of Yuyao local species(code: YS00) is used as male parent; the female parent and the male parent are hybridized to acquire the hybrid between species F1, and the filial generation is bred through genealogical breeding. The breeding tuber mustard in the invention agrees with the breeding target, has relatively early picking time, light green knotty bark, more knotty projections, non-concave top, and is not easy to accumulating water in rainy days; the knotty bark is thin and has low water content, faster dehydration speed and crisp flesh; the invention is especially suitable for rice winter fallow field planting.
Owner:NINGBO ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Food-intake preventer and preparing method thereof for striped flea beetle
ActiveCN101223889AInhibition of feedingFeeding inhibitors can inhibitBiocideArthropodicidesRussulaceaeLantana
Owner:广州瑞丰生物科技有限公司
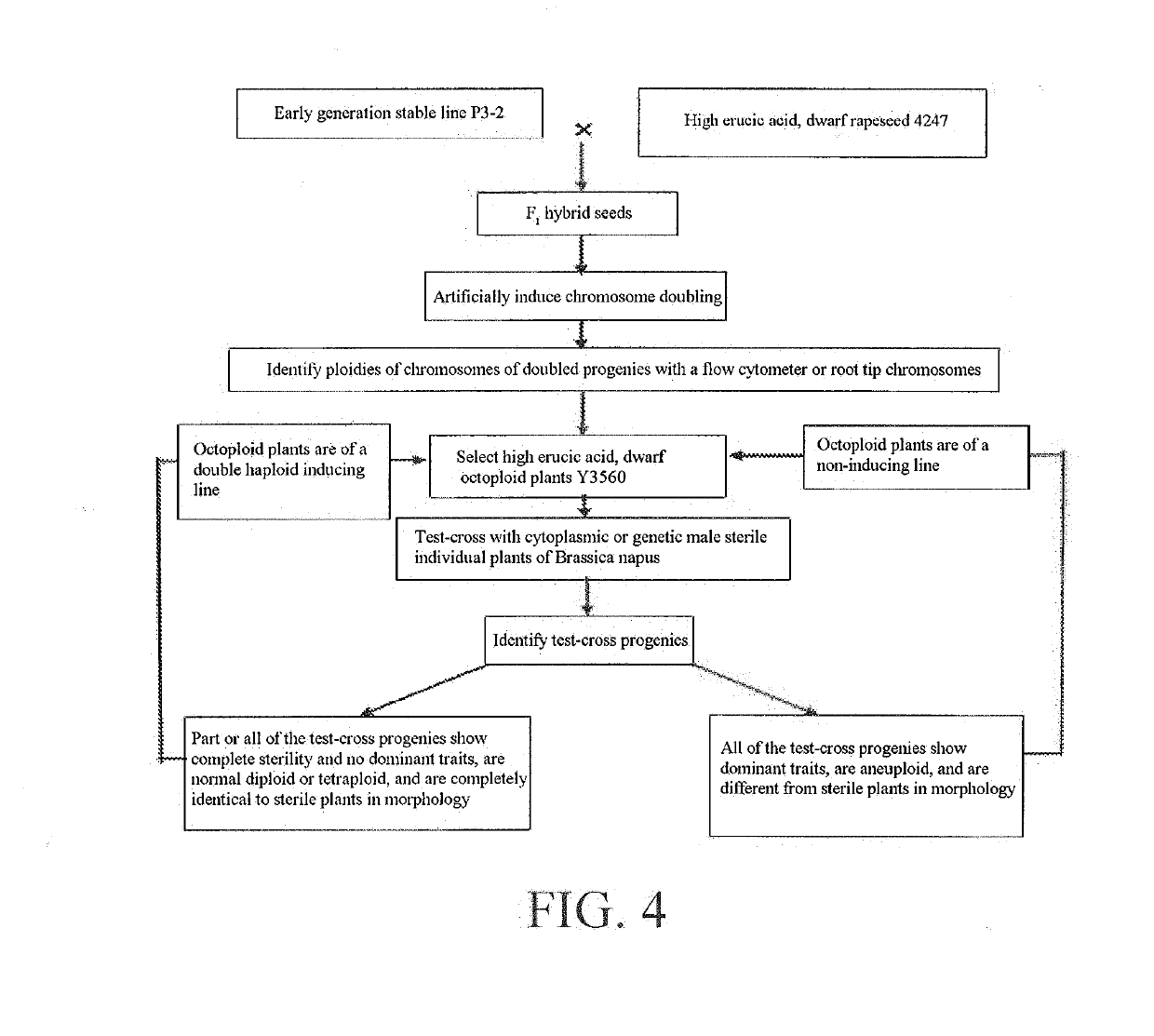
Method for breeding cruciferous vegetable materials and varieties with double haploid induction line of rapeseed
InactiveUS20190327923A1Rapid and efficient reproductionImprove efficiencyBiocideAnimal repellantsAgricultural scienceMaterial resources
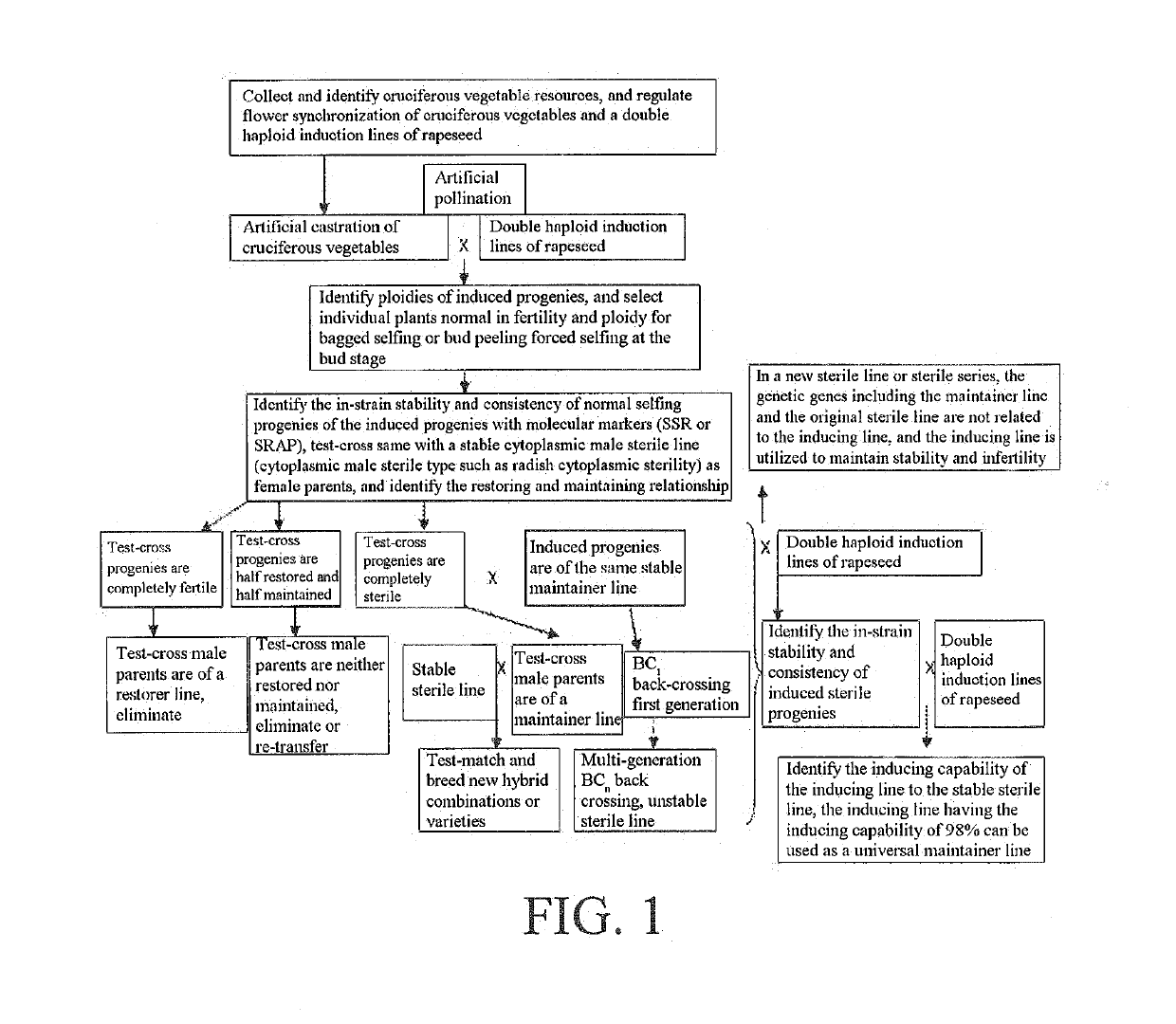
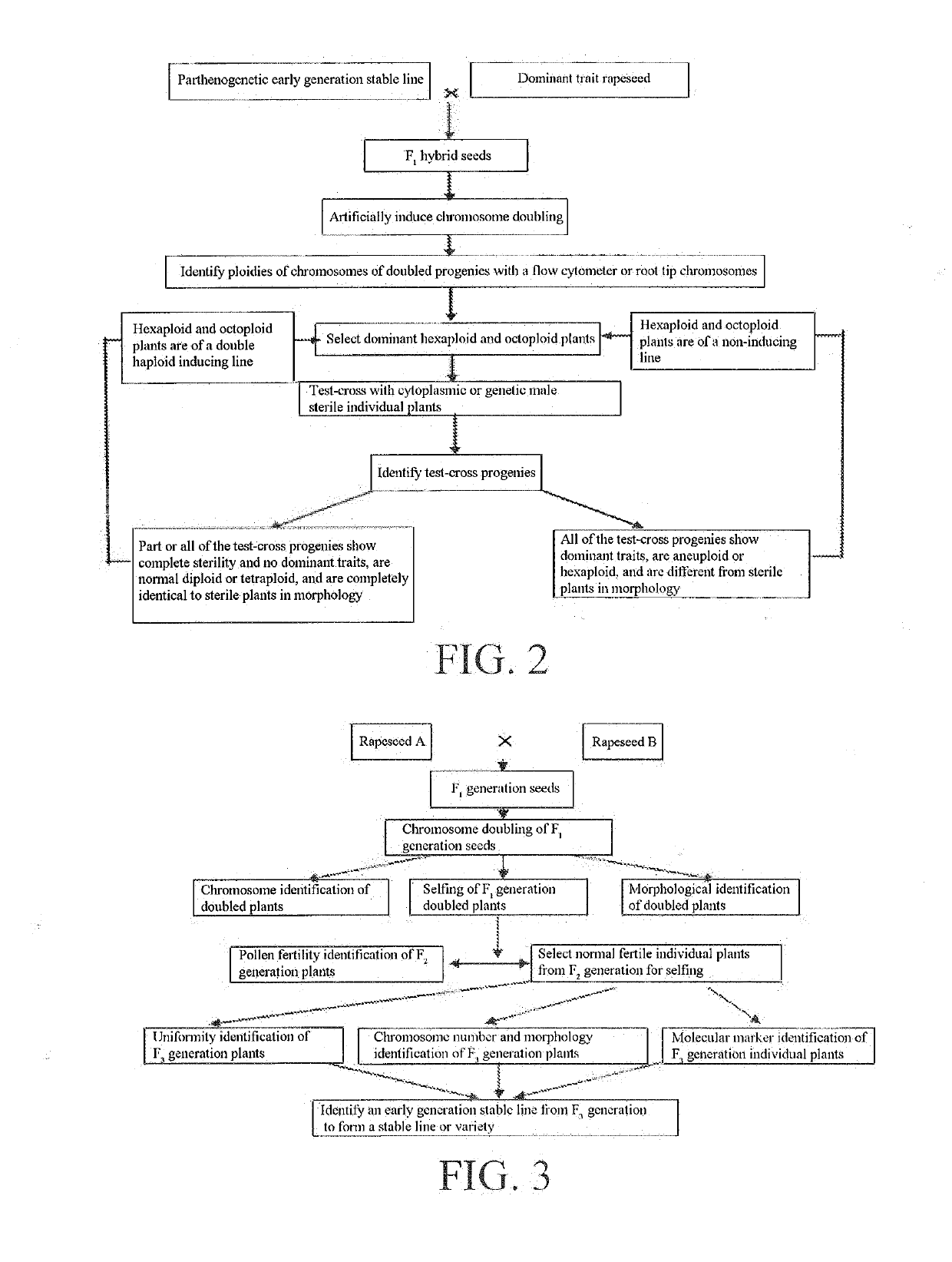
The present invention discloses a method for breeding cruciferous vegetable materials and varieties with a double haploid induction line of rapeseed, including: 1) collecting resources of cruciferous vegetables, identifying and classifying same, and regulating the sowing time of the double haploid induction line of rapeseed to ensure flower synchronization; 2) pollinating the cruciferous vegetables with the double haploid induction line of rapeseed; 3) performing bagged selfing or bud peeling forced selfing at a bud stage on the induced progeny individual plants; 4) identifying the strain stability of the induced selfing progenies; 5) test-crossing stable strains with sterile lines; 6) investigating the sterile degree of test-cross progenies to breed excellent maintainer lines; 7) pollinating sterile plants of the test-cross progenies with the double haploid induction line of rapeseed; 8) investigating the fertility of the induced progenies, and continuing to pollinate sterile individual plants with the inducing line to breed new sterile lines; and 9) test-matching the sterile lines with the maintainer lines to breed new hybrid combinations or new hybrid varieties. The method of the present invention can be flexibly applied in cruciferous vegetables, and can greatly improve the breeding efficiency of cruciferous vegetables and reduce the cost of manpower and material resources.
Owner:CHENGDU ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
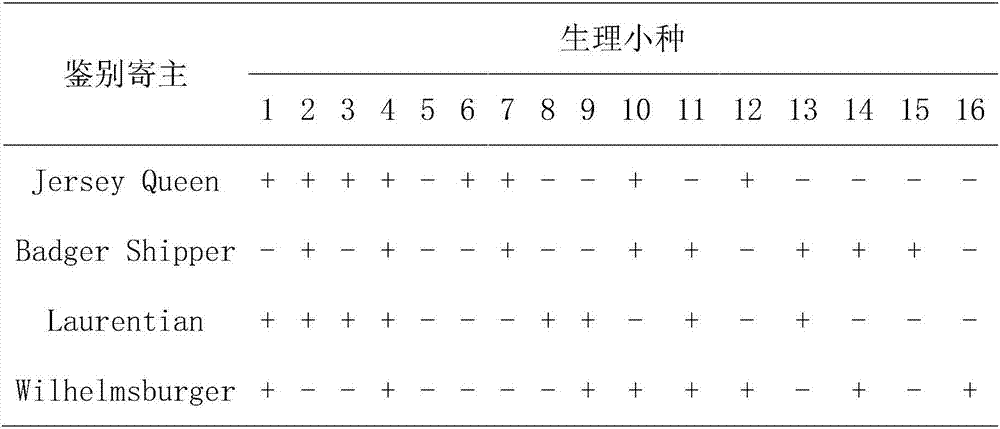
Inoculation identification method for clubroot of cruciferous crops
InactiveCN107058460AReduce consumptionStable source of bacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementCultivating equipmentsSmall samplePlasmodiophora
The invention discloses an inoculation identification method for clubroot of cruciferous crops, belongs to the technical field of plant protection, and provides the inoculation identification method for clubroot of cruciferous crops. Aseptic dried sphagnum is used as a carrier for culturing Plasmodiophora by inoculating. The method of the invention has the advantages that the consumption of bacterial sources is low, inoculating efficiency is high, operability is high, pathogenesis is uniform, result stability is good, disease determination is highly sensitive, the method is applicable to the identification of physiological races of small samples and the identification of disease resistance in large-batch varieties, and the method serves for breeding novel disease-resistant varieties and reasonably laying out disease-resistant varieties.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION JIANGXI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
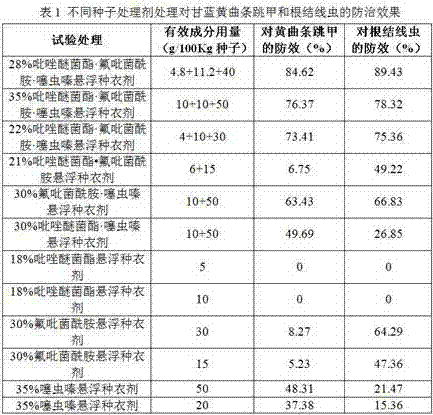
Suspended seed coating agent for controlling brassicaceous vegetable phyllotreta striolata fabricius
ActiveCN106922728ARoot Knot Nematode ControlSimple preparation processBiocideDead animal preservationDiseaseActive component
The invention discloses a suspended seed coating agent for controlling brassicaceous vegetable phyllotreta striolata fabricius. The suspended seed coating agent can effectively control cabbage phyllotreta striolata fabricius, and meanwhile a cabbage root knot nematode disease can be controlled. The suspended seed coating agent contains pyraclostrobin, fluopyram and thiamethoxam, and the rest are ordinary auxiliary components in preparation processing, wherein the weight ratio of the pyraclostrobin to the fluopyram to the thiamethoxam is (2-10):(2-12):(10-30), and the weight ratio is preferably 2.4:5.6:20. By means of the suspended seed coating agent, the pesticide active component usage amount can be reduced, the control efficiency can be improved, the use cost can be reduced, and pollution to the environment can be reduced.
Owner:PLANT PROTECTION RES INST OF GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for inducing wild cabbage type cole in vitro microspores and screening mutant
InactiveCN101250516AStrong mutagenic effectEfficient use ofMutant preparationElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentSaccharumPlant cell
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant cell engineering and in particular relates to a method for screening brassica napus in vitro microspores ultraviolet mutation and mutants, which is characterized in that the method comprises: using aqueous sucrose solution to separate brassica napus microspores, suspending the microspores on NLN culture medium which is modified through adding colchicine to be irradiated with ultraviolet and to be doubled with chromosome, transferring doubled microspores on the NLN culture medium which is modified to induce embryoid, then, transferring the embryoid on B5 culture medium to be induced into double haploid plants, transplanting the plants into filed to indentify, and screening out the mutants. The morphological character mutant rate is 10.53-21.57%, and the variant rates of sulfuric glucoside, the oil content and the erucic acid content are respectively 25.53-78.7%, 22.22-59.09% and 38.89-46.97%. The method of the invention has the advantages that the operation procedure is convenient, the time is saved, the cost is low, and the like. The method is suitable for screening the microspores ultraviolet mutation and mutants of cruciferae crops.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for accelerating transformed brassica juncea sterile line by using vernalization and generation-adding
InactiveCN101897291ALow priceThe method is practical and feasiblePlant genotype modificationPollenRussulaceae
The invention belongs to the technical field of cruciferous vegetable breeding, disclosing a method for accelerating transformed brassica juncea sterile line by using vernalization and generation-adding. The method comprises the following steps: taking cytoplasmic male sterile line of hot pickled mustard tuber as a female parent; taking brassica juncea self-bred line 05g-01 as an recurrent parent; by using the vernalization and generation-adding, selecting inert sterile plants of all flowers and pollens to carry out backcross transformation after hybridizing, and cultivating brassica juncea sterile line 09G-01 through six generated transformation. The recurrent parent is maintainer line of corresponding cytoplasmic male sterile line.
Owner:NINGBO ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Breeding method of brassica vegetable hybrid
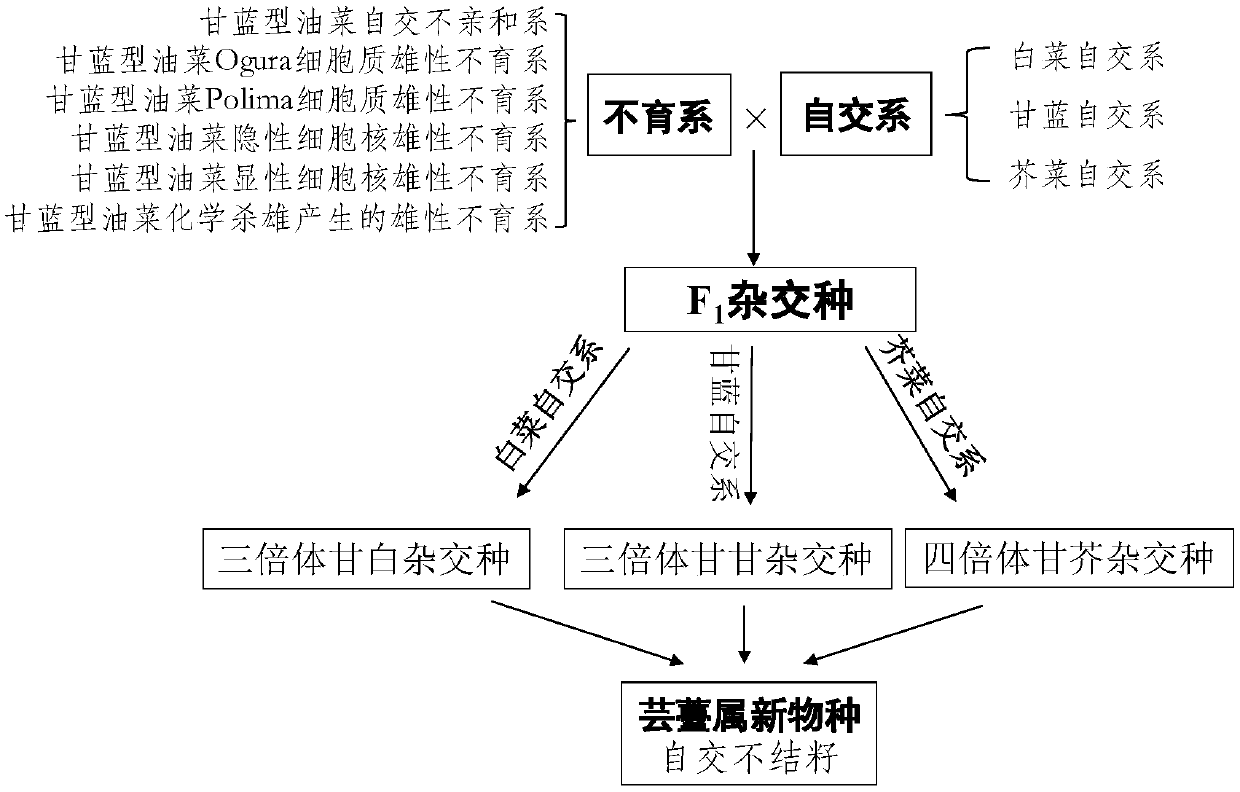
The invention belongs to the technical field of vegetable breeding, and discloses a breeding method of a brassica vegetable hybrid. A cabbage type rape sterile line as a female parent is mated with acabbage / Chinese cabbage / leaf mustard inbreeding line as a male parent into a hybrid, and a hybrid between brassica plant species is obtained; the male parent is diploid Chinese cabbage AA, the diploid Chinese cabbage AA is mated with tetraploid cabbage type rape AACC into a hybrid, and the hybrid is a triploid AAC cabbage and Chinese cabbage hybrid; the male parent is diploid cabbage CC, the diploid cabbage CC is mated with the tetraploid cabbage type rape into a hybrid, and the hybrid is a triploid ACC cabbage and cabbage hybrid; the male parent is tetraploid AABB, the tetraploid leaf mustard AABB is mated with the tetraploid cabbage type rape into a hybrid, and the hybrid is a tetraploid AABC cabbage and leaf mustard hybrid. The breeding method of the brassica vegetable hybrid createsnew species to promote breeding and utilization of brassicaceae brassica vegetable new species.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Instant noodle sauce packet with dried small shrimps and pork
InactiveCN104855945AGood for healthNatural extract food ingredientsFood ingredient functionsManihotAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses an instant noodle sauce packet with dried small shrimps and pork. The instant noodle sauce packet mainly comprises the components of hibiscus manihot flower powder, pork lean, pickled Chinese cabbages, duck tongues, the dried small shrimps, russulaceae, caraways, fermented soya beans, potatoes, Chinese chives, grapes, sweet oranges, Chinese angelica, radix curcumae, jasmines, meadowrue root and rhizome, honeysuckle stems and the like. The instant noodle sauce packet with the dried small shrimps and the pork, which is disclosed by the invention, not only has the flavor of a conventional pickled Chinese cabbage sauce packet, but also the flavor of grapes and sweet oranges as well as nutrients of the duck tongue and the dried small shrimps; besides, Chinese herbal medicines of jasmines, meadowrue root and rhizome and the like as well as components of needle mushrooms, kelps and the like in the health additive further have the effects of invigorating stomach, moistening lungs and reducing weight, so that the instant noodle sauce packet is beneficial to body health after being eaten.
Owner:蚌埠市楠慧川味食品厂
Common vetch herbage cultivation method
InactiveCN105165324AAvoid deathImprove germination ratePlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsEconomic benefitsLight exposure
A common vetch herbage cultivation method comprises the following steps: 1, using common vetch and cruciferous rape or broad bean for mixed spawning, wherein common vetch and cruciferous rape mixed spawning plant ratio is 10:0.6-3, and common vetch and broad bean mixed spawning plant ration is 4:1-2; 2, broadcast spawning the seeds into field, immediately using clear water to irrigate, and a mud pile is placed in a field water inlet so as to stir the water for irrigation. The method can effectively prevent lodging of the common vetch plants in a growth anaphase, can prevent the common vetch seeds from being picked up by birds in broadcast spawning, and the seeds cannot be dead because of strong light exposure, thus improving emergence rate, and economic benefit is obvious.
Owner:AGRI RESOURCE & ENVIRONMENT RES INST TIBET AUTONOMOUS REGION ACADEMY OF AGRI & ANIMAL HUSBANDRY
Lactarazulene as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113200811AIncrease typeGood anti-inflammatory activityOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticPharmaceutical drugLactarius deliciosus
The invention relates to the technical field of natural extracts, in particular to lactarazulene and a preparation method and application thereof. The structural formula of the lactarazulene is shown in the specification. The lactarazulene is extracted from lactarius deliciosus of russulaceae, has excellent anti-inflammatory activity and can be used for preparing anti-inflammatory drugs.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Earthworm cast bio-fertilizer capable of controlling clubroot of cruciferae crops and application technology
InactiveCN106831145AReduce usageGood control effectBio-organic fraction processingExcrement fertilisersRussulaceaeFermentation
The invention provides an earthworm cast bio-fertilizer capable of controlling clubroot of cruciferae crops remarkably. The bio-fertilizer is prepared from components in parts by weight as follows: 1,000-1,200 parts of an earthworm cast and crop straw fermentation product and 1-3 parts of an antibacterial agent, wherein the weight ratio of the earthworm cast to crop straw is (5-8):1; the antibacterial agent contains at least one of Flowncide and Segway; pH of the bio-fertilizer is 6.8-7.2. The invention further provides a preparation method and an application method of the bio-fertilizer. The earthworm cast and the crop straw as two kinds of agricultural and breeding waste are taken as raw materials, and the cost is low; the formula and the preparation process of the bio-fertilizer are simple; the bio-fertilizer has a good control effect on clubroot of the cruciferae crops, and the control efficiency can reach 92%-93%; besides, the required application amount of the bio-fertilizer is small.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION SICHUAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for improving hybrid seed production yield of cabbages in facility
ActiveCN108142279AGuaranteed purityGrowth inhibitionLeaf crop cultivationPlant genotype modificationHybrid seedGreenhouse
The invention relates to a method for improving the hybrid seed production yield of cabbages in facility, and belongs to the technical field of vegetable farming. The method includes the steps of seeding and seedling raising, land preparation and bedding, field planting of parent materials, bolting, bee depositing for fertilization, harvesting and the like. According to the method, seed productionof hybrid seeds of the cabbages in the facility is adopted, exotic other-cabbage pollen is effectively avoided, and the purity of the hybrid seeds is ensured; in the facility, black mulching film islaid, the growth of weeds can be effectively inhibited, the method also plays the roles of cooling and moisturizing the ground, and in this way, farm operation such as weeding and watering during beepollination can be reduced as far as possible; bees and mason bees are adopted to conduct matched pollination, and the mason bees are used for solving the problem that in a facility greenhouse, illumination is deficient, the temperature is high, the activity space is small, and bee pollination is deficient; the method not only can improve the yield of hybrid seed production, but also is low in cost, and reference is provided for facility seed production of other cruciferous crops.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Breeding method of male sterile cytoplasm NAU1A of rapeseed
InactiveCN101647396AConducive to cultivationSolve the problems of single sterile cytoplasm and unstable fertilityPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyRapeseed
The invention discloses a creating method and characteristics of male sterile cytoplasm NAU1A of Brassica napus, belonging to the fields of genetic engineering and plant breeding. The protoplast technology of Brassica napus is employed to obtain a blending progeny, and a sterile plant is found in the blending progeny. An NAU1B maintainer line is crossed and backcrossed with the sterile plant to obtain a stable sterile line NAU1A. Mitochondrial DNA of the sterile line NAU1A is extracted and the PCR technology is employed to clone and identify the sterile cytoplasm to obtain a characteristic sequence SEQ ID NO.1 and an amino acid sequence SEQ ID NO.2 of the mitochondrial DNA of the sterile line NAU1A. The cytoplasm and the characteristic gene sequence of the invention are reported for the first time. The NAU1A cytoplasm can be widely applied to heterosis utilization of cruciferae and has good application prospect.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Episyrphus balteaus breeding method and use of episyrphus balteaus in pollinating seed-production cruciferae crop
InactiveCN104255670AMining highImprove pollination efficiencyPlant genotype modificationAnimal husbandryPollenHabit
The invention discloses an episyrphus balteaus breeding method. The episyrphus balteaus breeding method comprises the steps of 1) breeding next generation episyrphus balteaus in a breeding cage, 2) obtaining the next generation episyrphus balteaus, and 3) enabling episyrphus balteaus to collect pollen and carry out pollination. The invention also discloses a use of the episyrphus balteaus in pollinating a seed-production cruciferae crop; the adult episyrphus balteaus out of pupae flies in the cruciferae crop greenhouse, collects the pollen of the cruciferae crop and pollinates the cruciferae crop. The episyrphus balteaus breeding method is simple and easy to implement; the episyrphus balteaus highly adapts to the environment in the greenhouse, can be hardly affected by temperatures and humidity and can grow, develop and reproduce as along as sufficient light is supplied. The pollen collection and pollination efficiency of the episyrphus balteaus is obviously higher than that of bees, and the seed production yield is about 10% higher than that of bee pollination. The adults also have the habit of preying on aphids, and therefore, an obvious effect on controlling aphids on the crop in the greenhouse can be achieved.
Owner:ZHENJIANG SUIHAN AGRI
Method for cultivating black rot resisting cabbage vegetable
InactiveCN101126087AOvercoming barriers to interspecies hybridizationFused cellsGenetic engineeringDiseaseGene cluster
The invention discloses a culture method of anti-black-rot cabbage vegetable, which comprises the steps: 1) cells of an anti-blact-rot Brassica nigra and cells of cabbage vegetable are cell fused to obtain hybridized cells; 2) the hybridized cells are in vitro cultured, and regenerated plant is obtained, so the anti-black-rot cabbage vegetable is obtained. The method of the invention adopts cell hybridization technique, overcomes the interspecific hybridization obstacles in breeding, transplants the disease-fighting gene in cruciferae wild Brassica nigra into the gene cluster of cabbage vegetable, and thus culturing the disease-fighting cabbage vegetable such as anti-black-rot cauliflower.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com