Breeding method of Chinese cabbages resistant to clubroot
A technology against clubroot and clubroot, which is applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, and microbial determination/inspection, etc. application and other issues to achieve rapid screening, shorten the breeding cycle, and avoid the spread of germs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] In mid-April 2014, the target parent Y1 (clubroot resistance genotype rr) and the source CRA-2 (DH line, clubroot resistance genotype RR) were crossed to obtain F1 generation seeds.
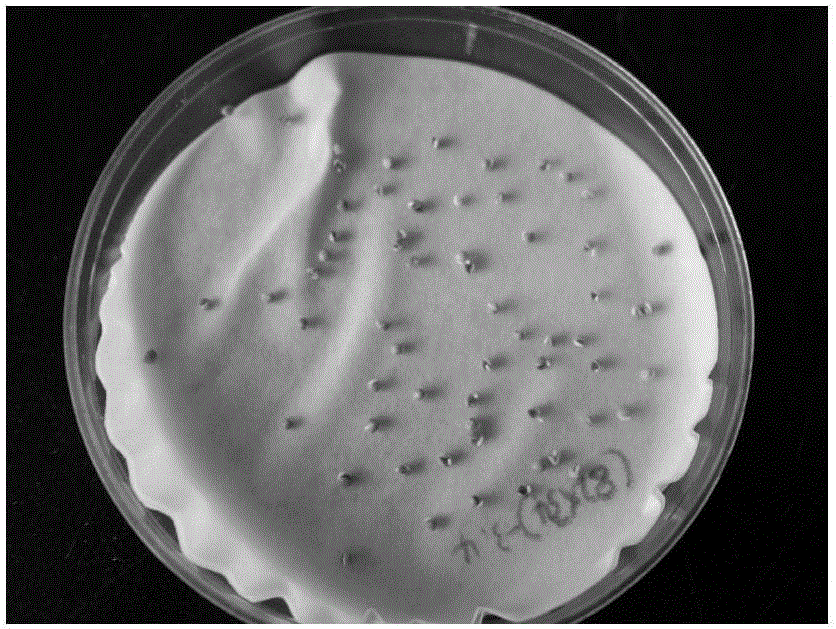
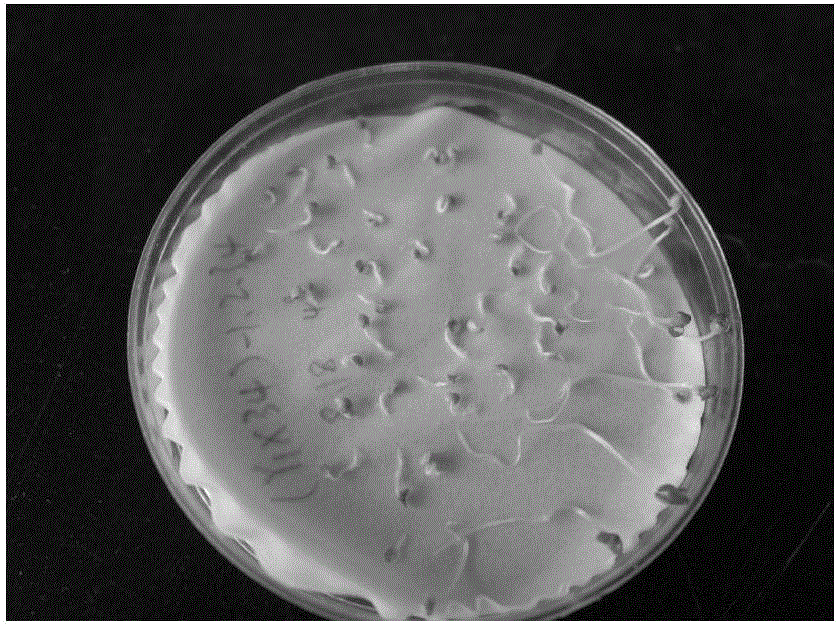
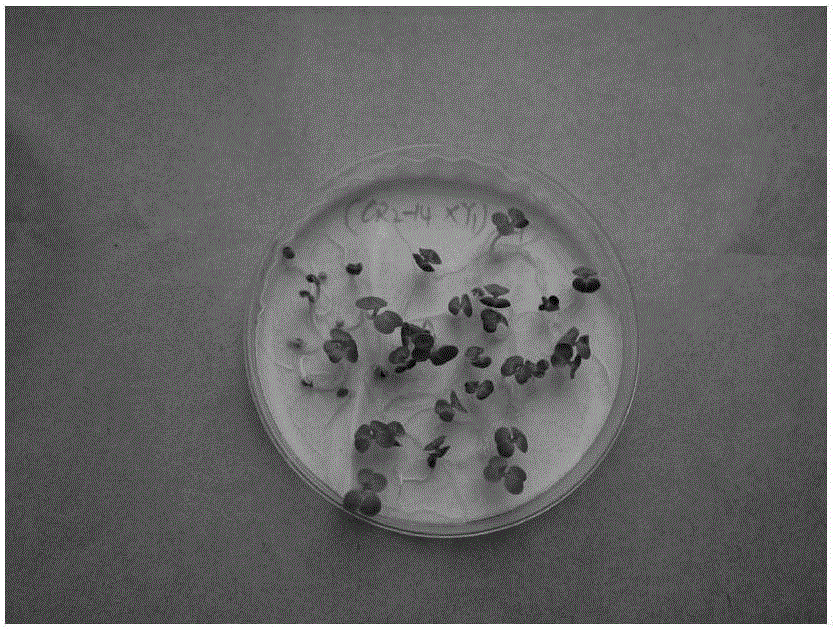
[0048] The seed pods of F1 were picked in early May, and the immature embryos were peeled off and placed in a petri dish covered with moist filter paper (see figure 1 ), germinated in a 24°C incubator, and the germinated immature embryos (see figure 2 ) in a refrigerated incubator (SANYO MEDICALCOOL) at 4°C for vernalization under low light (see image 3 ), sowed in June, cultivated in an artificial climate box (see Figure 4 ), the culture temperature is 24°C, the humidity is 69%, and the light is 24 hours. The BC1 generation seeds are obtained by backcross pollination in July, and the BC1 generation seeds are peeled off in August and germinated at 25°C for 6 days.
[0049] The immature embryos of the BC1 generation after germination were vernalized at 5°C for 3 weeks, sown in Septembe...
Embodiment 2
[0057] In mid-April 2014, the target parent Y1 (clubroot resistance genotype rr) and the source CRA-2 (DH line, clubroot resistance genotype RR) were crossed to obtain F1 generation seeds.
[0058] In the first ten days of May, the seed pods of F1 were picked, and the immature embryos were removed and germinated in a 24°C incubator on a petri dish covered with wet filter paper, and the germinated immature embryos were placed in a refrigerated incubator (SANYO MEDICALCOOL) at 4-5°C with low light Cultivate vernalization, sow in June, cultivate in an artificial climate box, culture temperature 24°C, humidity 66%, 24 hours light, backcross pollination in July to obtain BC1 generation seeds, August BC1 generation seeds to peel off embryos, 25°C to accelerate germination 6 sky.
[0059] The immature embryos of the BC1 generation after germination were vernalized at 5°C for 3 weeks, sown in September, and identified by the KBrH129J18R molecular marker in October, from which the BC1 ...
Embodiment 3
[0067] In mid-April 2014, the target parent Y1 (clubroot resistance genotype rr) and the source CRA-2 (DH line, clubroot resistance genotype RR) were crossed to obtain F1 generation seeds.
[0068] In the first ten days of May, the seed pods of F1 were picked, and the immature embryos were stripped and germinated in a culture dish covered with wet filter paper in a 24°C incubator. Planted in June, cultured in an artificial climate box at 24°C, 68% humidity, 24 hours of light, backcross pollination in July to obtain BC1 generation seeds, in August BC1 generation seeds were stripped of embryos and germinated at 25°C for 6 days.
[0069] The immature embryos of the BC1 generation after germination were vernalized at 5°C for 3 weeks, sown in September, and identified by the KBrH129J18R molecular marker in October, from which the BC1 generation resistant single plant with the clubroot resistance gene Rr was screened out. In November, the BC1 generation The disease-resistant single ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com