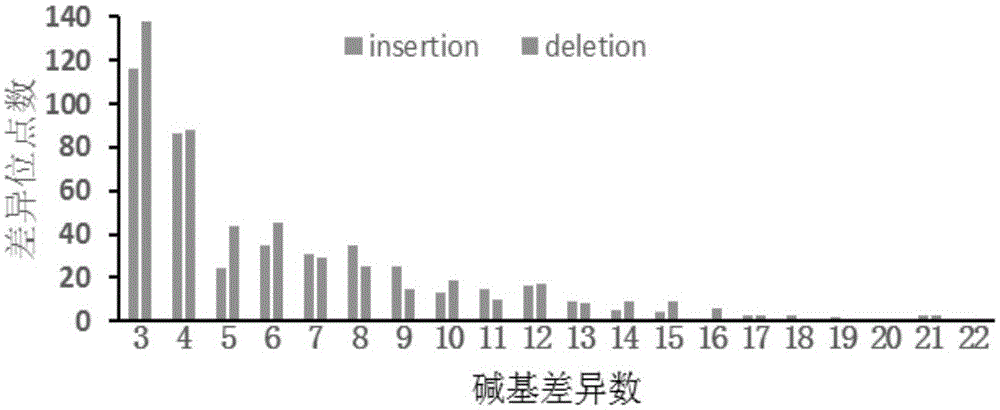
Molecular marker of brassica napus anti-clubroot gene and application of molecular marker to anti-clubroot breeding
A cabbage type rape, clubroot disease resistance technology, applied in the direction of microbial determination/inspection, DNA/RNA fragment, recombinant DNA technology, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of improving breeding efficiency and shortening the breeding process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Acquisition and identification of a marker closely linked to the clubroot resistance gene PbBa8.1 in Brassica napus
[0026] 1. Construction of isolated groups
[0027]Turnip ECD04 (Identification of novel QTLs for isolate-specific partial resistance to Plasmodiophora brassicae in Brassicarapa.[J].PlosOne,2013,8(12):e85307-e85307) containing the PbBa8.1 locus resistant to race 4 was used as the male parent, which was susceptible to conventional Brassica oleracea Rapeseed Huashuang 5 was used as the female parent to cross to obtain F1. The disease resistance of F1 was identified with the Huangshan physiological race in Anhui, and all F1 showed disease resistance. Next, we continued to backcross F1 with Huashuang 5 for three generations, and obtained backcross populations of BC1, BC2, and BC3 respectively. At the same time, we used the SSR markers cum_m090a and sau_um353a linked to the PbBa8.1 site to start Genotype analysis was performed on the BC1 population, and indi...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The application of the molecular marker A08-300 closely linked to the clubroot resistance gene PbBa8.1 in the auxiliary selection of Brassica napus resistant to clubroot. The application process includes:
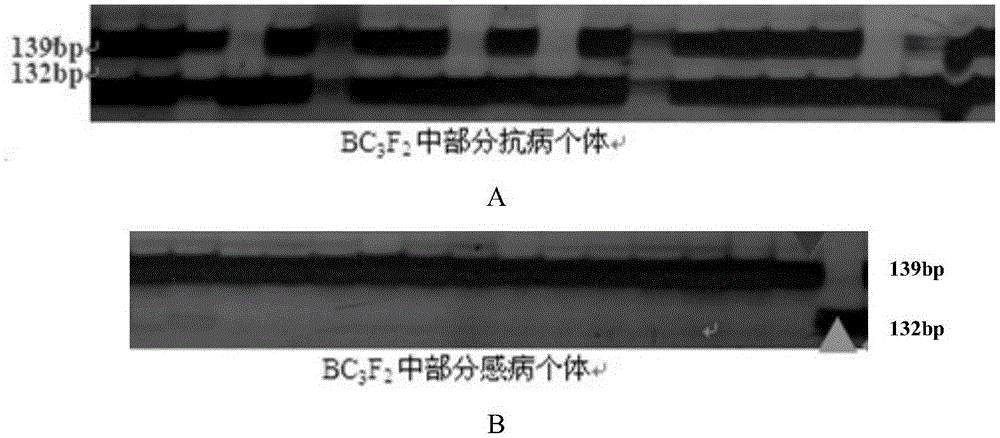
[0043] From the BC3F2 population prepared in Example 1, 35 resistant individual plants and 27 susceptible individual plants were randomly selected, and genotype identification was performed on them using two pairs of SSR primers cun_m090a, sau_um353a and Indel marker A08-300.
[0044] The identification process utilizing the primer FA08-300 / RA08-300 provided by the present invention comprises:
[0045] 1. Genomic DNA extraction
[0046] 1. Add 498uL 1×CTAB extract (2% CTAB, 100mmol / LTris-HCl, 20mmol / LEDTA, 1.4mol / LNaCl,) and 2uL β-mercaptoethanol to a 1.5ml centrifuge tube and shake well;
[0047] 2. Take 0.2g of young leaves, grind them to powder under liquid nitrogen conditions, add them to a centrifuge tube containing CTAB extract and β-mercaptoethanol, and shake...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Application of molecular marker A08-300 primer closely linked to clubroot resistance gene PbBa8.1 in auxiliary selection of Brassica napus resistant to clubroot:
[0068] Using the disease-resistant molecular marker primers provided by the present invention, the BC3F2 generation plants derived from the BC3 single plant of ZHE-226 in Example 1 were subjected to genotype analysis and agronomic trait selection, and a homozygous disease-resistant locus (i.e. Using primers FA08-300 / RA08-300 to amplify 132bp single plant), 200 single plants with relatively consistent growth period and good agronomic traits were obtained by selfing BC3F3 mixed population.
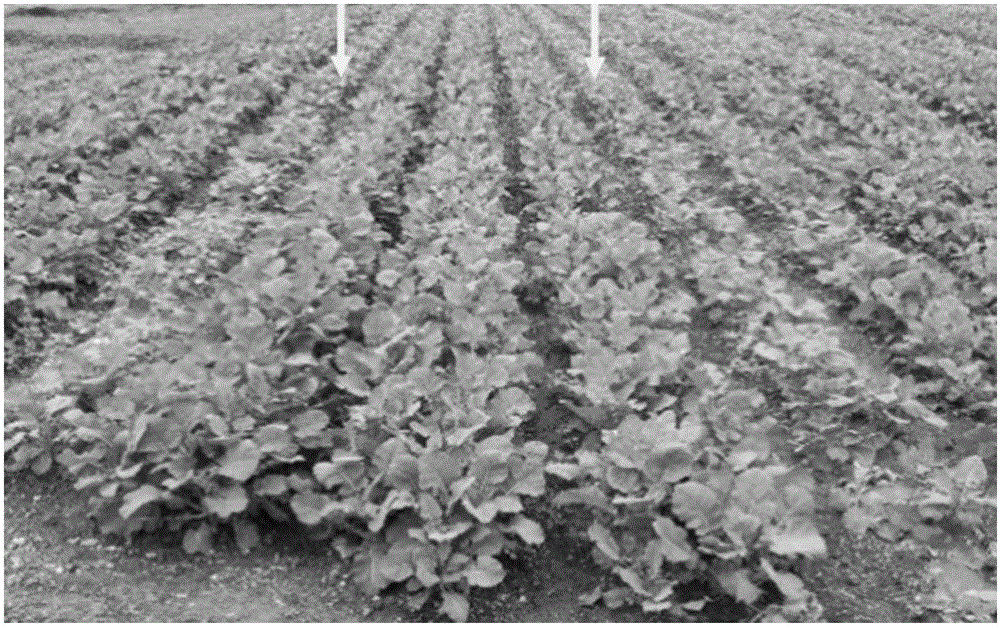
[0069] In May 2015, field disease resistance identification was carried out again in the clubroot disease area in Badong, Enshi, Hubei, and field phenotype investigation was carried out 45 days after sowing. From the perspective of the overall effect in the field, compared with the new disease-resistant strain we transferre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com