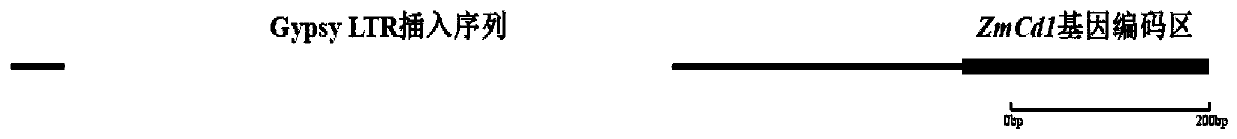Molecular marker of low-cadmium-accumulation control gene ZmCd1 of corn kernel and application
A molecular marker, low accumulation technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, and microbial assay/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as limited application, and achieve the effect of accelerating genetic improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
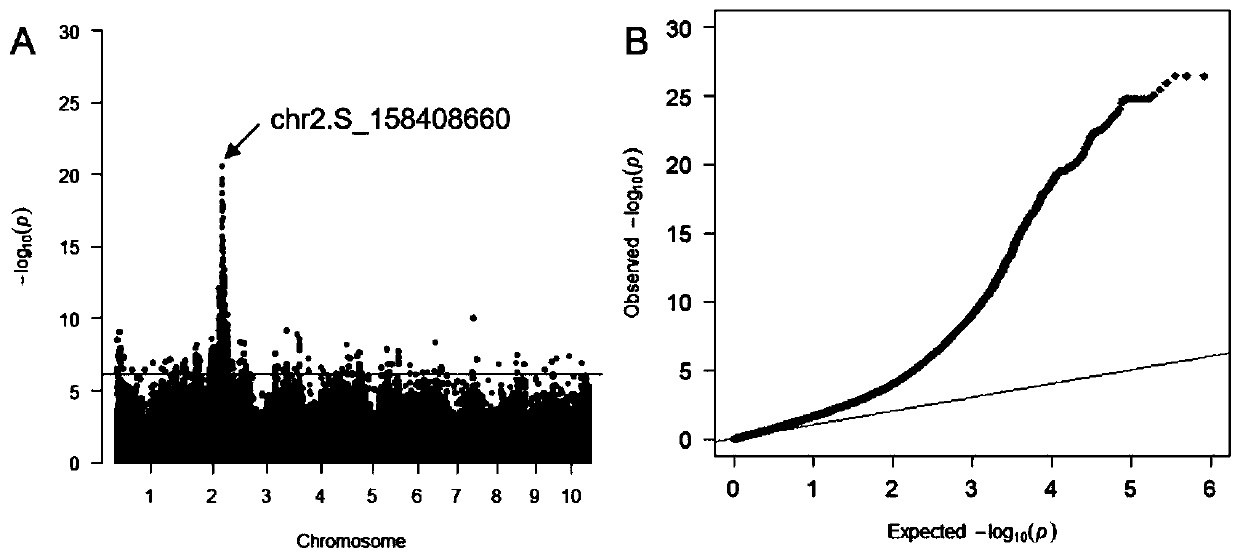
[0035] Example 1 Using genome-wide association analysis to locate key regulatory genes for low grain cadmium accumulation
[0036] An associated group consisting of 436 maize inbred lines was planted in cadmium-contaminated farmland (cadmium content was 1.8±0.3mg / kg). The experiment was conducted in randomized block design with two independent repetitions. For each replicate, each maize inbred line was planted in a row with 10 plants in each row. Each row is 3m long and the row spacing is 60cm. Grain cadmium content was determined after maize was harvested. The average value of the cadmium content in the grains of the inbred lines corresponding to two replicates was used as the phenotype value of the inbred lines. Genotypes of associated populations were combined with reduced genome sequencing (GBS), high-density array technology, and deep RNA-sequencing data from 368 different maize inbred lines, identifying 1.25M SNPs with an allele frequency (MAF) greater than 0.05 ( Liu e...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2 Candidate Gene Screening
[0040] According to the LD attenuation distance of the population in Example 1 (Liu et al., 2017, Molecular Plant, 10:414-426), the candidate genes regulating the cadmium content of maize grains were screened within 100 kb of the flanking sequence of the significant SNP site. According to gene function annotation, a candidate gene was locked and named ZmCd1. The gene is located within 100kb of the flanking sequence of the most significant SNP site (chr2.S_158408660).
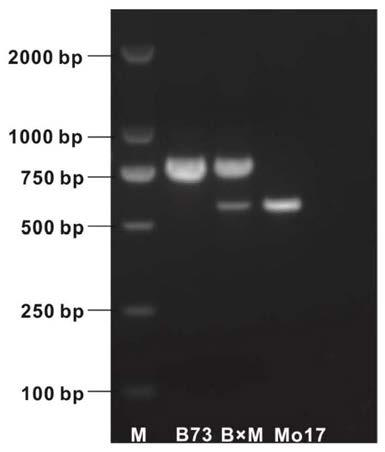
[0041] Four high cadmium accumulating maize inbred lines Zheng 58 (0.26 mg / kg), Ye478 (0.21 mg / kg), P178 (0.44 mg / kg) and Mo17 (0.14 mg / kg) and four low cadmium accumulating maize inbred lines The ZmCd1 genes of cross-lines B73 (0.008mg / kg), Huangzaosi (0.009mg / kg), Jing 92 (0.014mg / kg) and Jing 724 (0.008mg / kg) were sequenced, and the sequences were compared and analyzed. , the four high cadmium accumulating maize inbred lines Zheng 58, Ye478, P178 and Mo17 all had ...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3 Candidate gene ZmCd1 functional verification
[0047] Obtain the EMS mutant with termination mutation (EMS4-038f45) and missplicing (EMS4-038f36) in the ZmCd1 (Zm00001d005190) gene coding region from the corn mutant database MEMD (http: / / www.elabcaas.cn / memd / ) , each planted 5 rows in cadmium-contaminated farmland, and planted 10 plants in each row. After the corn was mature, mixed threshing was used to determine the cadmium content in the grain, and three biological replicates were measured. The measurement results showed that there was no significant difference in the cadmium content among the grains of the same mutant, and the cadmium content in the mutant grains was 0.26±0.16mg / kg and 0.24±0.07mg / kg, which were significantly higher than that of the wild-type material B73 (the cadmium content in the grain was 0.008mg / kg).
[0048] EMS4-038f45 and EMS4-038f36 were crossed with high cadmium accumulation maize inbred line Mo17 (with LTR retrotransposon inse...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com