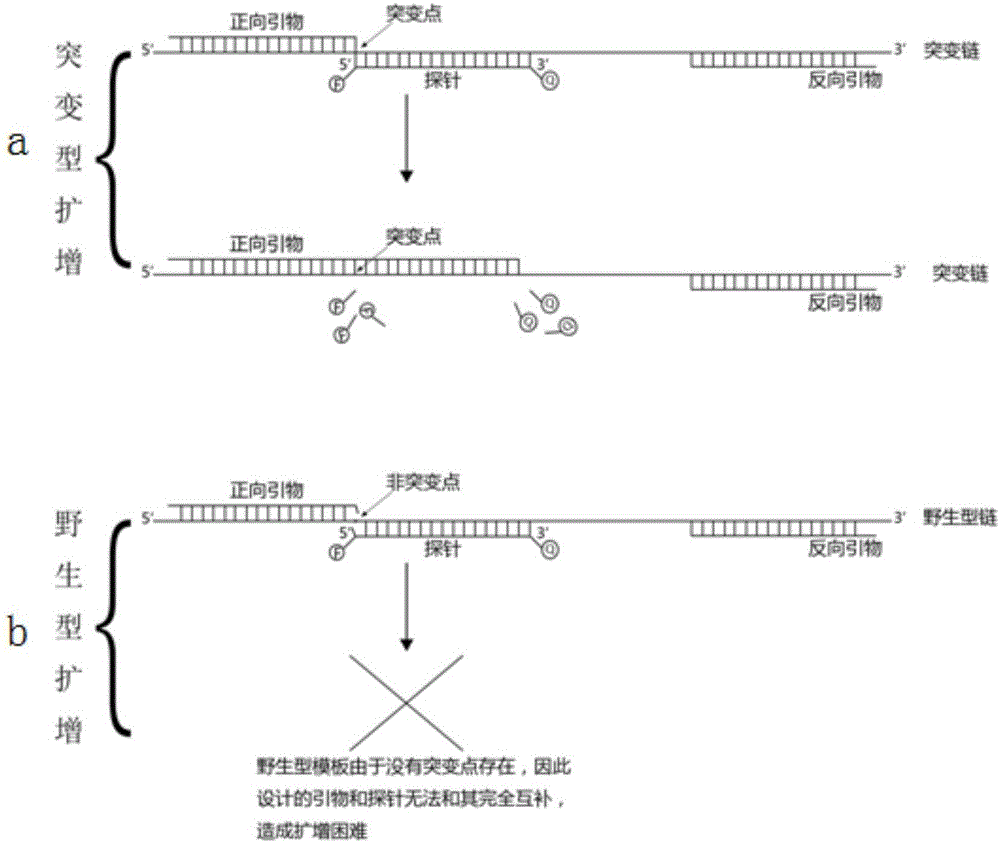
Design method for primers and probe for amplifying low-concentration mutation target sequence
A design method and target sequence technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of limited detection ability, poor selectivity, false negative detection, etc., to increase the specificity of amplification, ensure specificity and efficiency, process optimized effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
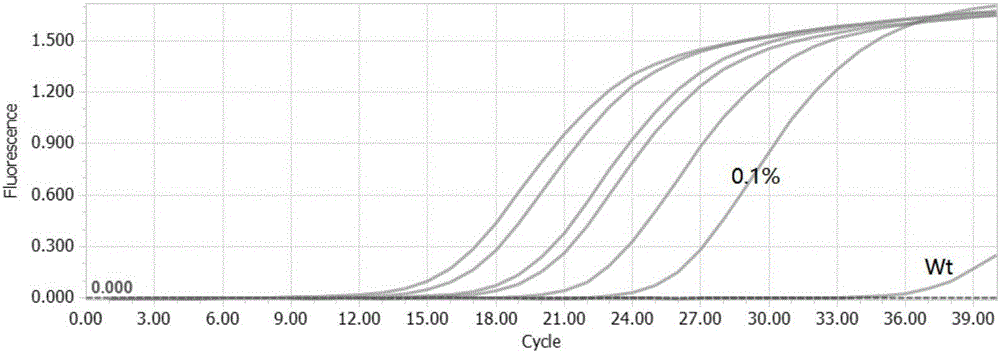
[0062] 1. Use the method of the present invention to design primers and probes, and carry out G on the 12th codon of Kras gene G T>G C Fluorescence PCR amplification assay of different gradients of T mutant and control wild-type samples.
[0063] The wild-type gene sequence and G G T>G C For T mutant gene sequence, a probe was designed as Kras-Pb; primers were respectively Kras-Fp and Kras-Rp.
[0064] Specifically, the primer and probe sequences designed according to the method of the present invention are as follows:
[0065] Kras-0Fp: CACTCTTGCCTACGCCTG;
[0066] Kras-0Pb: TGCAGTCCAACTACCAC;
[0067] Kras-ORp: GGCCTGCTGAAAATGACTG.
[0068] The primers and probes designed according to the general conventional primer and probe design method are as follows:
[0069] Kras-1Fp: CACTCTTGCCTACGCCTG;
[0070] Kras-1Pb: GCTCCAACTACCACAAGTT;
[0071] Kras-1Rp: GGCCTGCTGAAAATGACTG.
[0072] 2. Sample preparation:
[0073] Artificially synthesized a section with G G T>G C ...
Embodiment 2
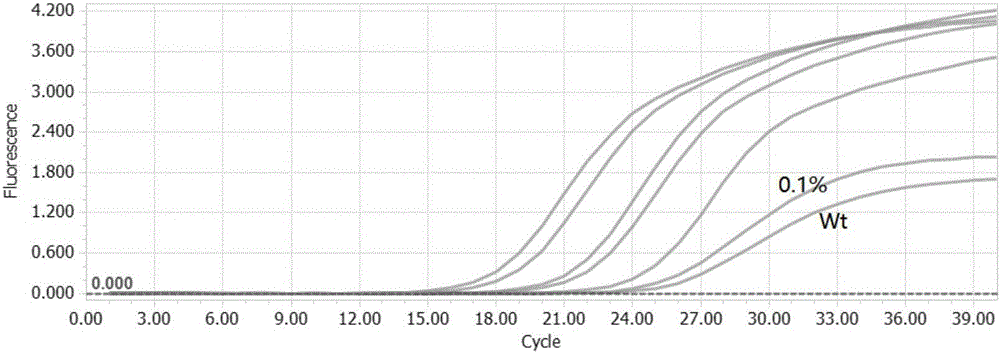
[0089] 1. Use the primers and probes designed by the patent of the present invention to detect the BRAF V600E mutation.
[0090] According to the wild-type and mutant sequences of the BRAF gene queried from the cosmic data, the following primers and probes were designed:
[0091] BRAFV600E primers and probes designed according to the inventive method:
[0092] BRAF-0Fp: CCCACTCCATCGAGATGTCT;
[0093] BRAF-0Rp: TGAAGACCTCACAGTAAAA;
[0094] BRAF-OPb:CTCTGTAGCTAGACCA.
[0095] BRAFV600E primer and probe sequences designed according to common methods:
[0096] BRAF-1Fp: CCCACTCCATCGAGATTTCT;
[0097] BRAF-1Rp: TGAAGACCTCACAGTAAAA;
[0098] BRAF-1Pb:CTGTAGCTAGACCAA.
[0099] 2. Sample preparation:
[0100] Artificially synthesize a sequence with BRAFV600E mutation and the corresponding BRAF wild sequence, and load these two sequences into plasmids for amplification. Use the enzyme digestion system to digest the synthetic plasmid and obtain 10^4 copies of the restriction fr...
Embodiment 3
[0116] 1. Use the primers and probes designed by the method of the present invention and the primers and probes designed according to the common method to detect the mutation of PIK3CA gene c.3140A>G and compare the effects.
[0117] According to the wild-type and mutant sequences of the PIK3CA gene queried from the cosmic data, the following primers and probes were designed:
[0118] PIK3CAc.3140A>G primers and probes designed according to the method of the present invention:
[0119] PIK-0Fp: AACAAATGAATGATGCGCG
[0120] PIK-0Rp: TGCATGCTGTTTAATTGTGTGG
[0121] PIK-0Pb: CGTCATGGTGGCTGGACAACA
[0122] PIK3CAc.3140A>G primer and probe sequences designed according to common methods:
[0123] PIK-1Fp: CAAATGAATGATGCACG
[0124] PIK-1Rp: TGCATGCTGTTTAATTGTGTGG
[0125] PIK-1Pb: ATGGTGGCTGGACAACA
[0126] 2. Sample preparation:
[0127] A sequence with a PIK3CA c.3140A>G mutation and the corresponding wild sequence of PIK3CA were artificially synthesized, and the two sequen...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-denatured | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com