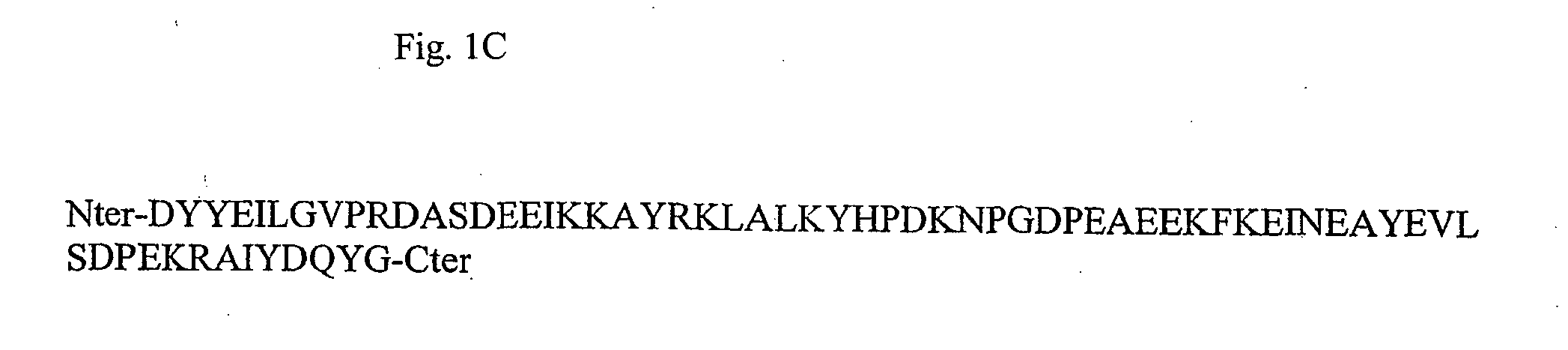Patents
Literature
30 results about "Dominant-Negative Mutant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A dominant-negative mutation usually means that the resulting protein is has lost a certain part of its function (negative), but it can out-compete the endogenous protein in some way (dominant).
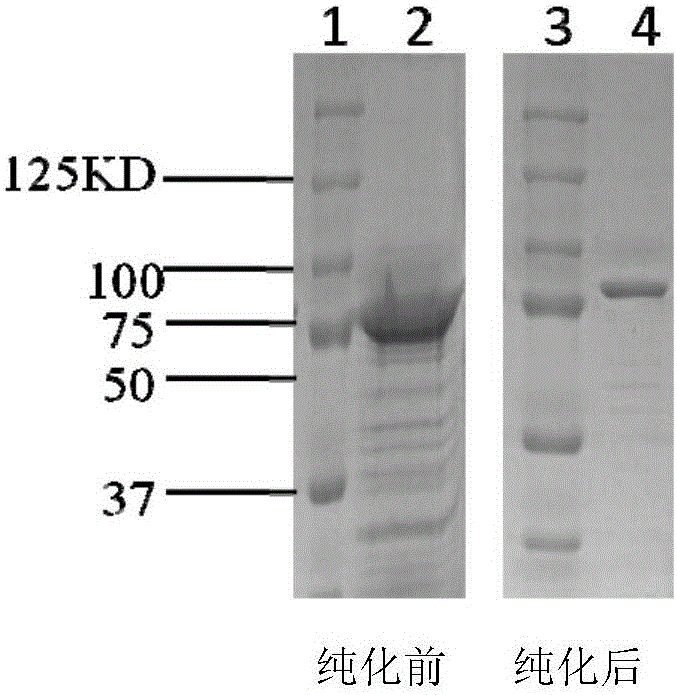
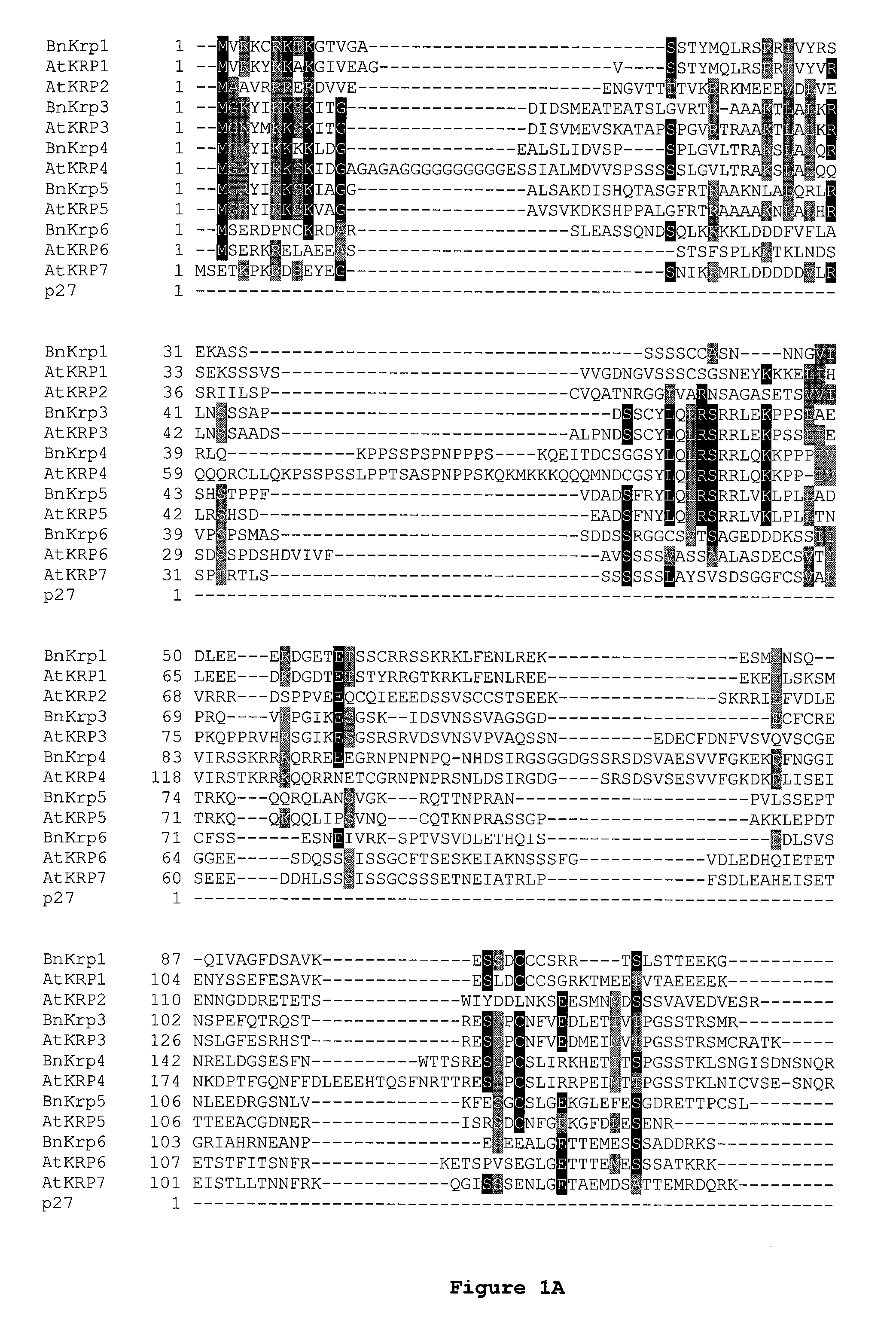
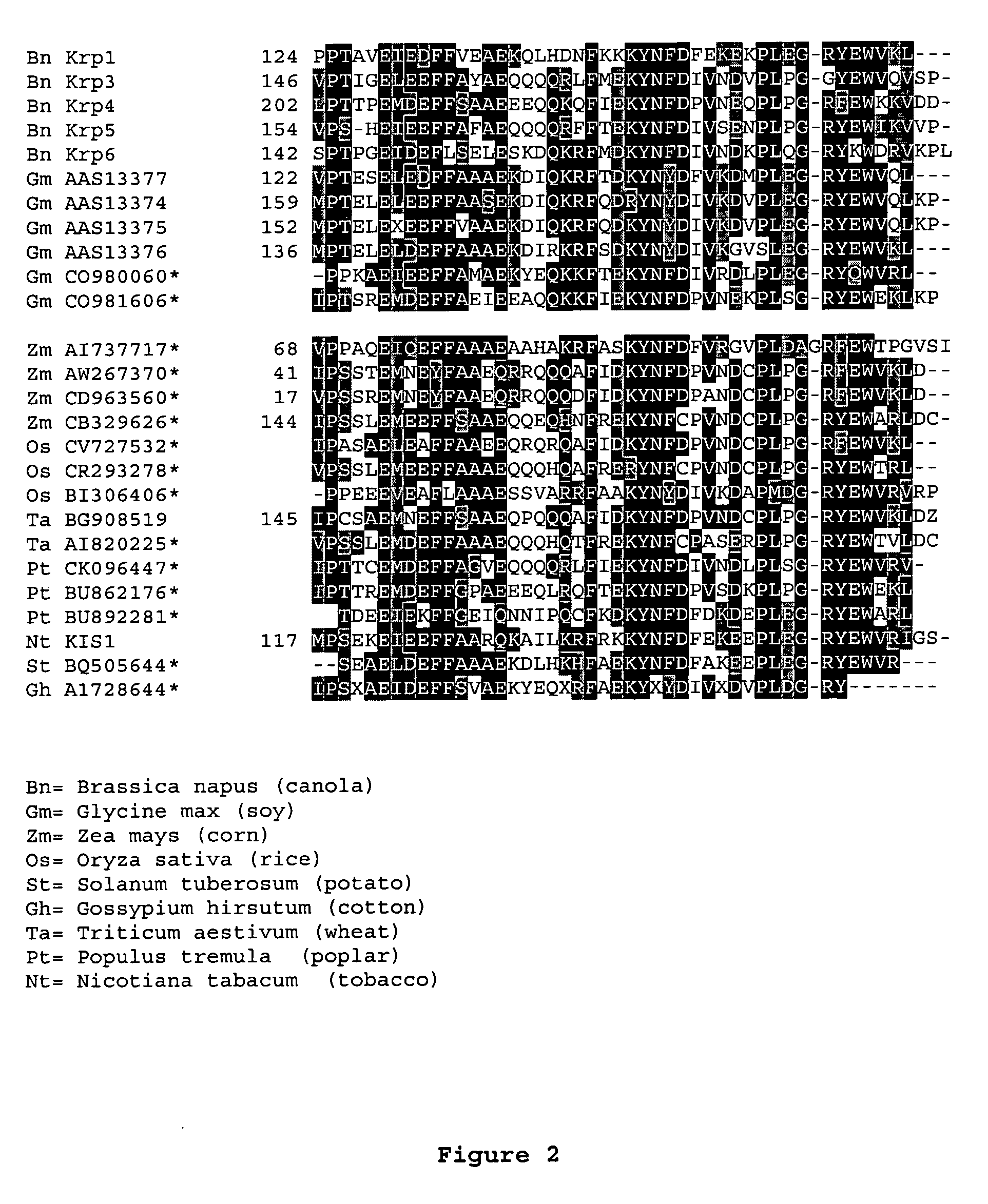
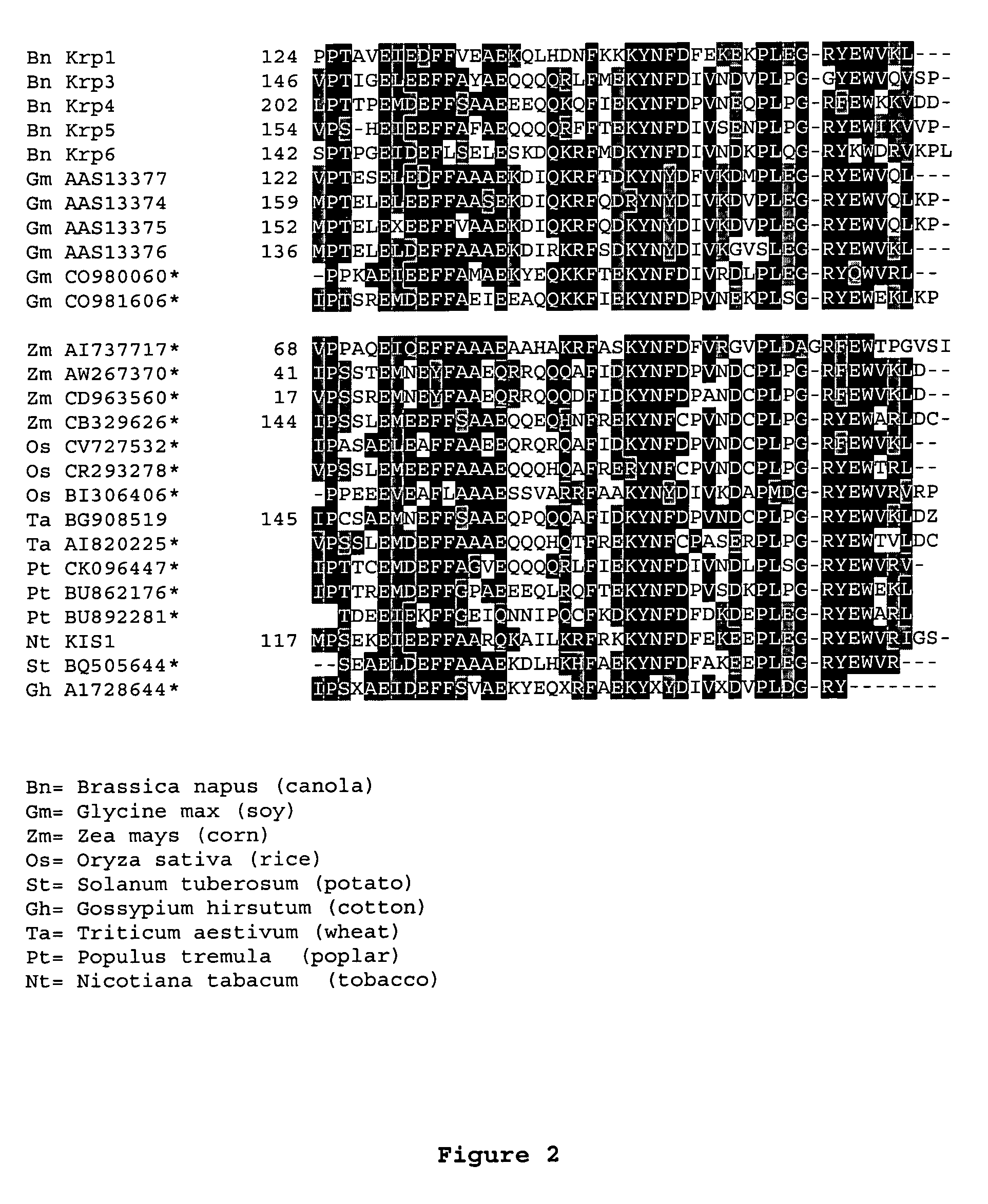
Dominant negative mutant krp protein protection of active cyclin-cdk complex inhibition by wild-type krp
InactiveUS20070056058A1Speed upIncreasing cell proliferationBacteriaSugar derivativesMutated proteinPlant cell
Disclosed are mutant CDK inhibitor (CKI) polypeptides having dominant negative antagonist activity against wild-type CKI proteins, as well as related compositions, including nucleic acids and vectors encoding the mutant CKI polypeptides and transformed host cells and transgenic plants comprising such nucleic acids and vectors. Also disclosed are related methods for using the mutant proteins to modulate cell division in cells, particularly plant cells.
Owner:TARGETED GROWTH
Method of efficiently establishing induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20110223669A1Improve setup efficiencyEfficient productionGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsNuclear reprogrammingBiology
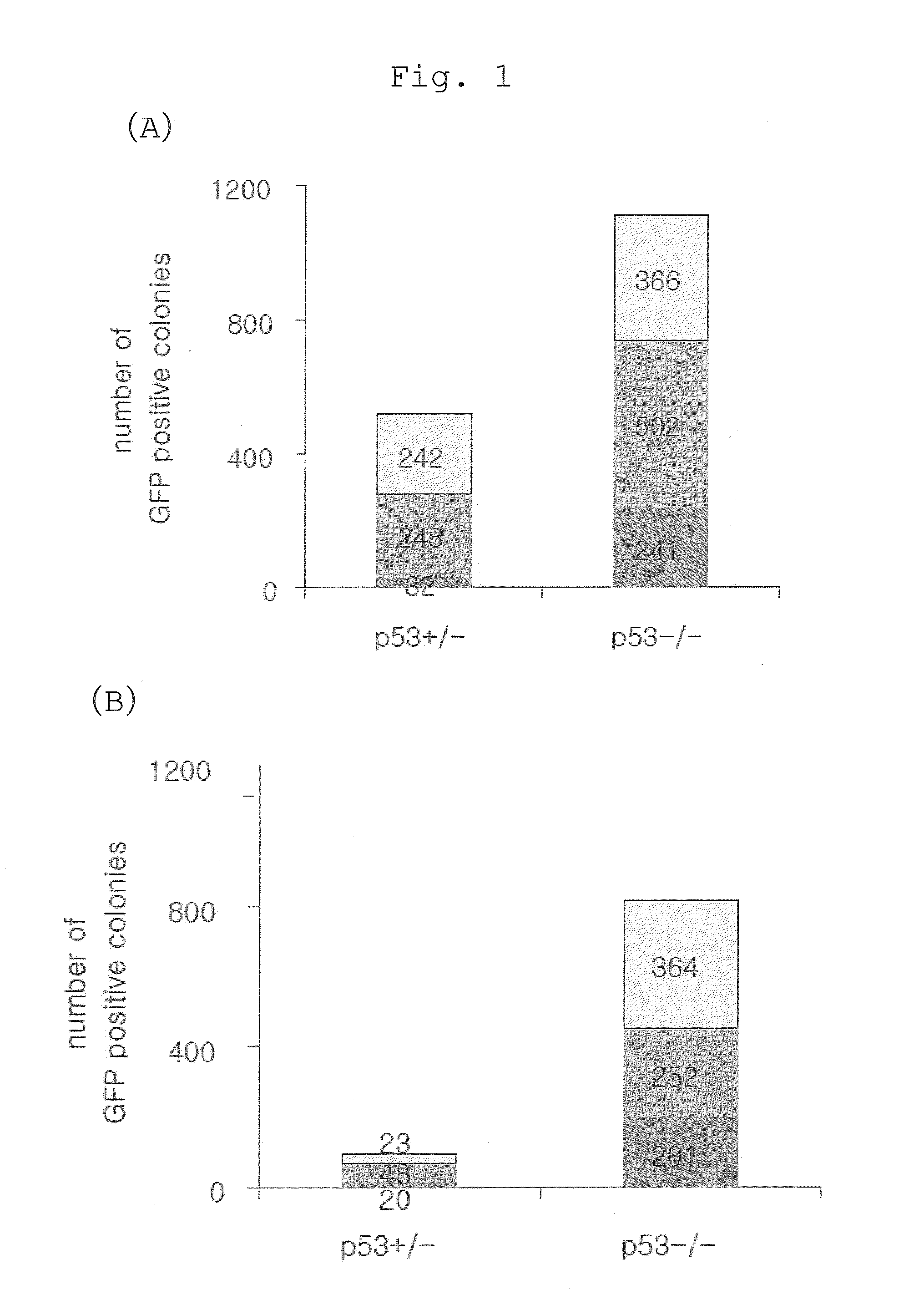
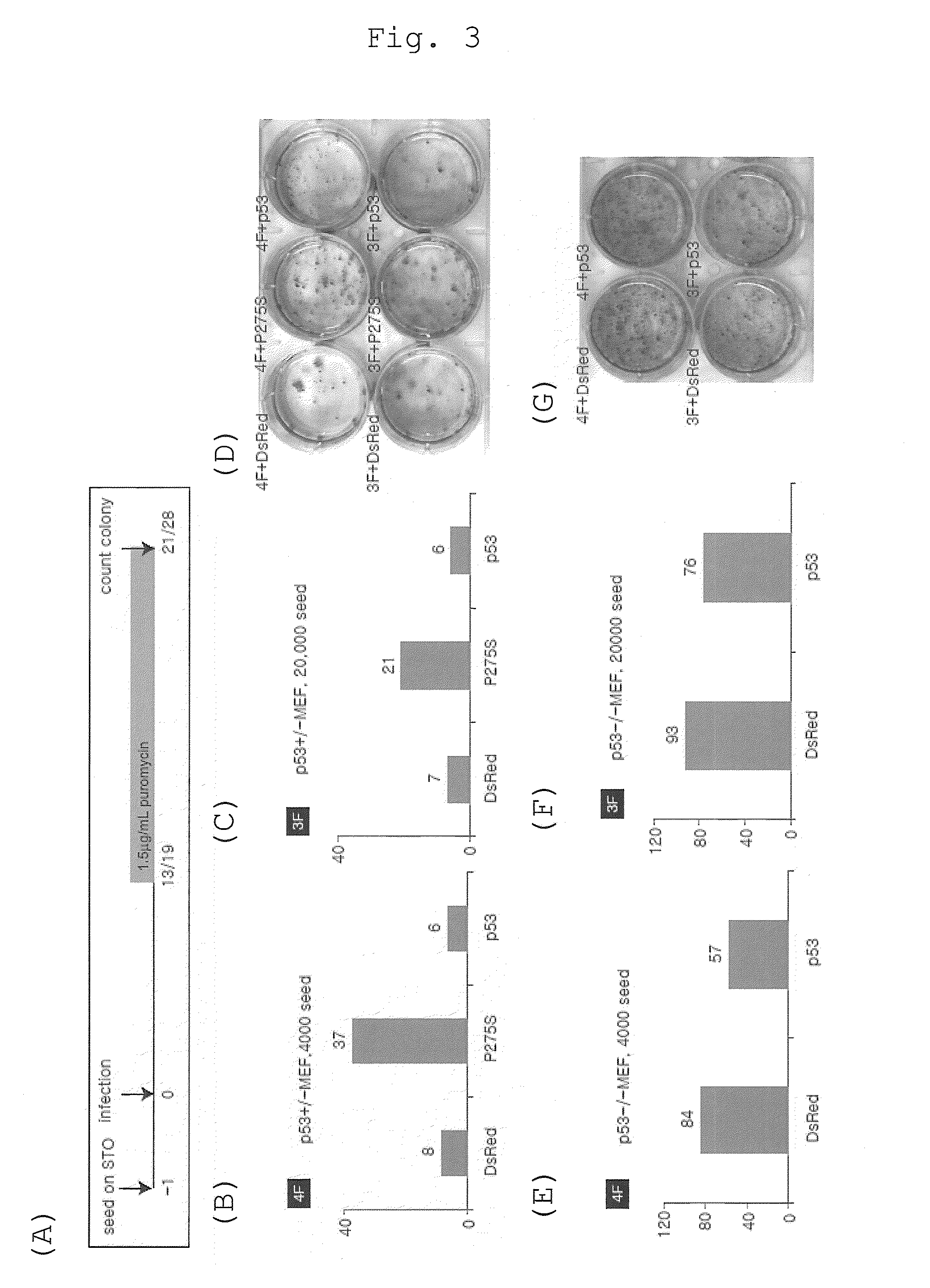
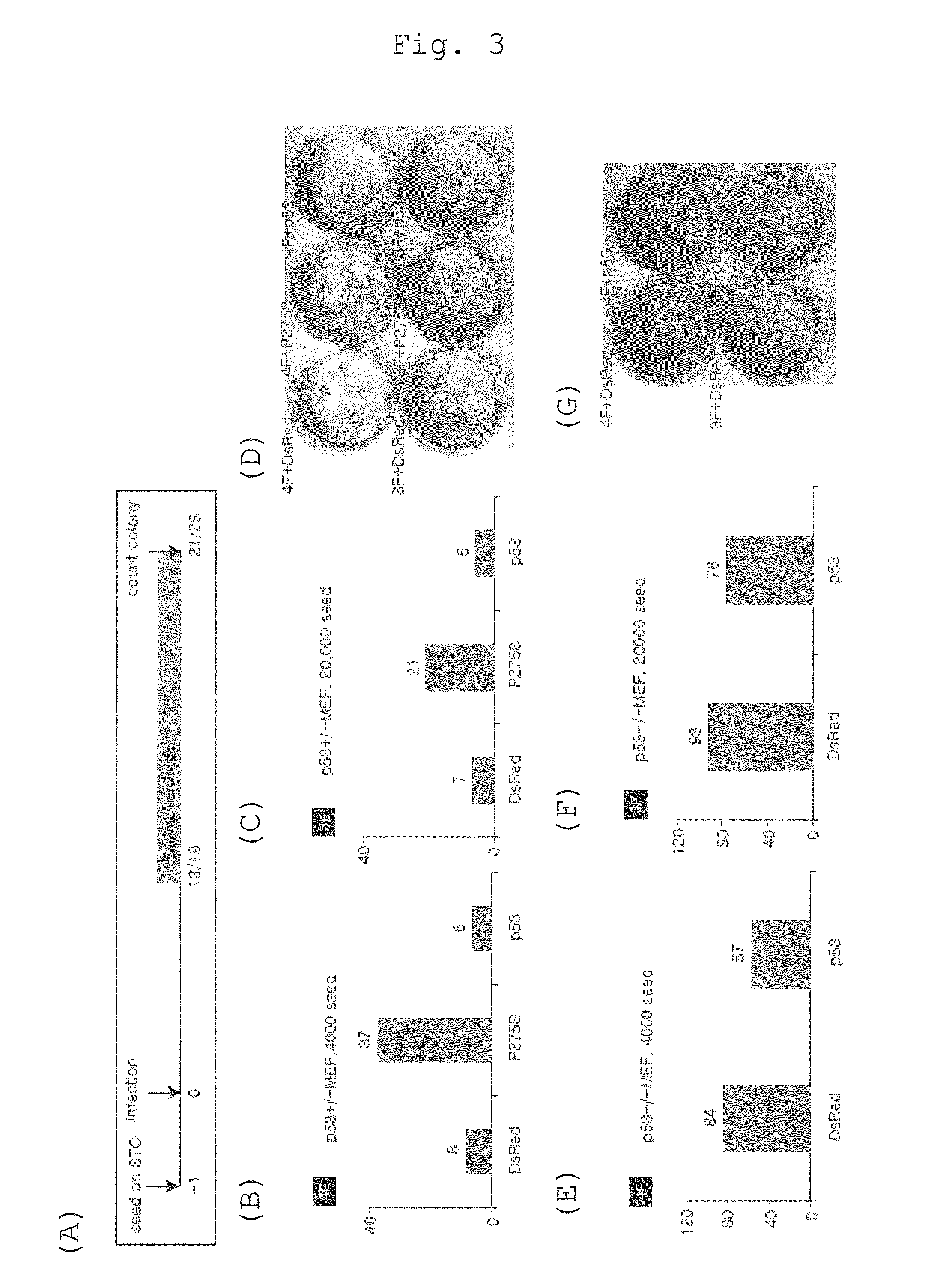
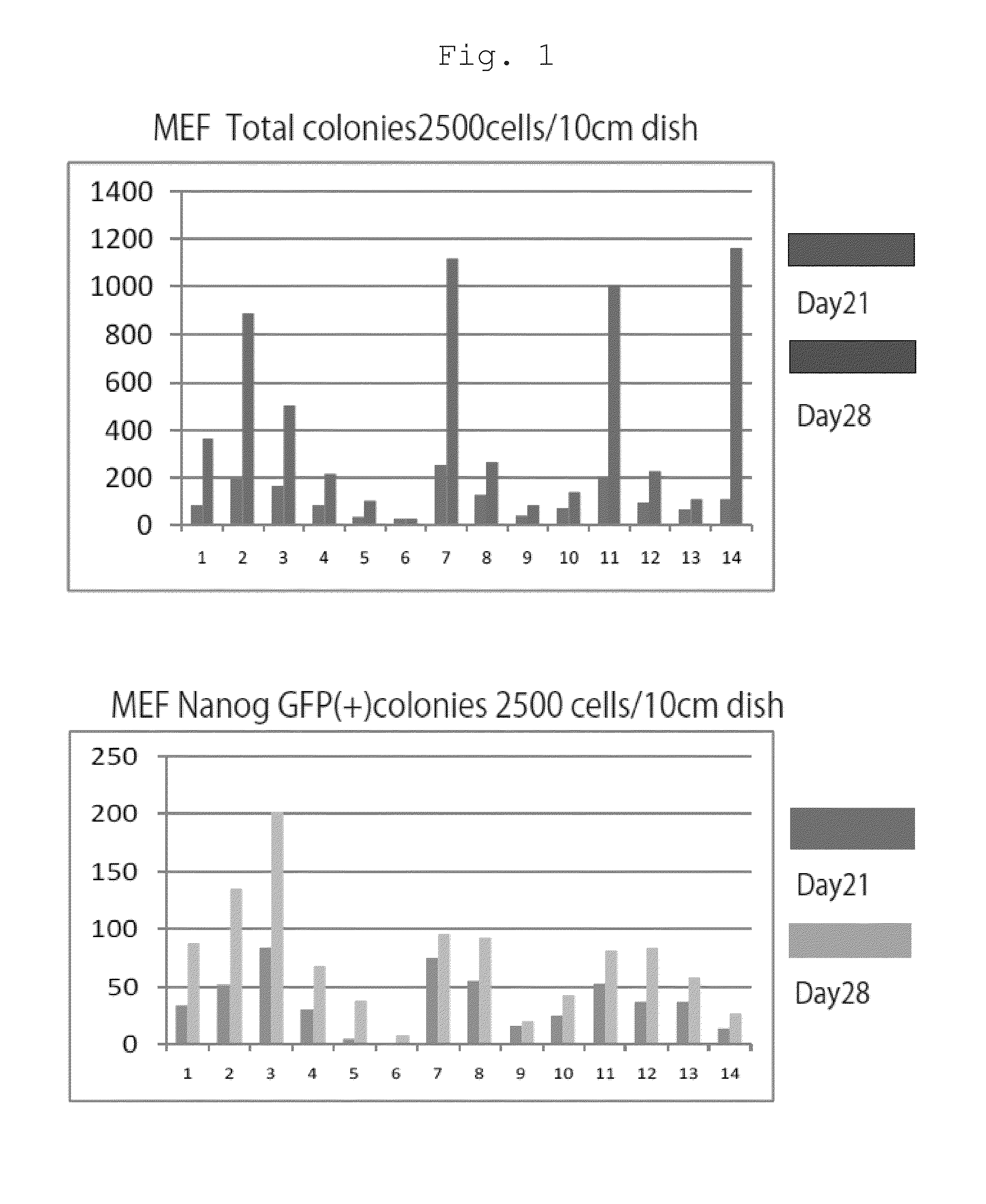
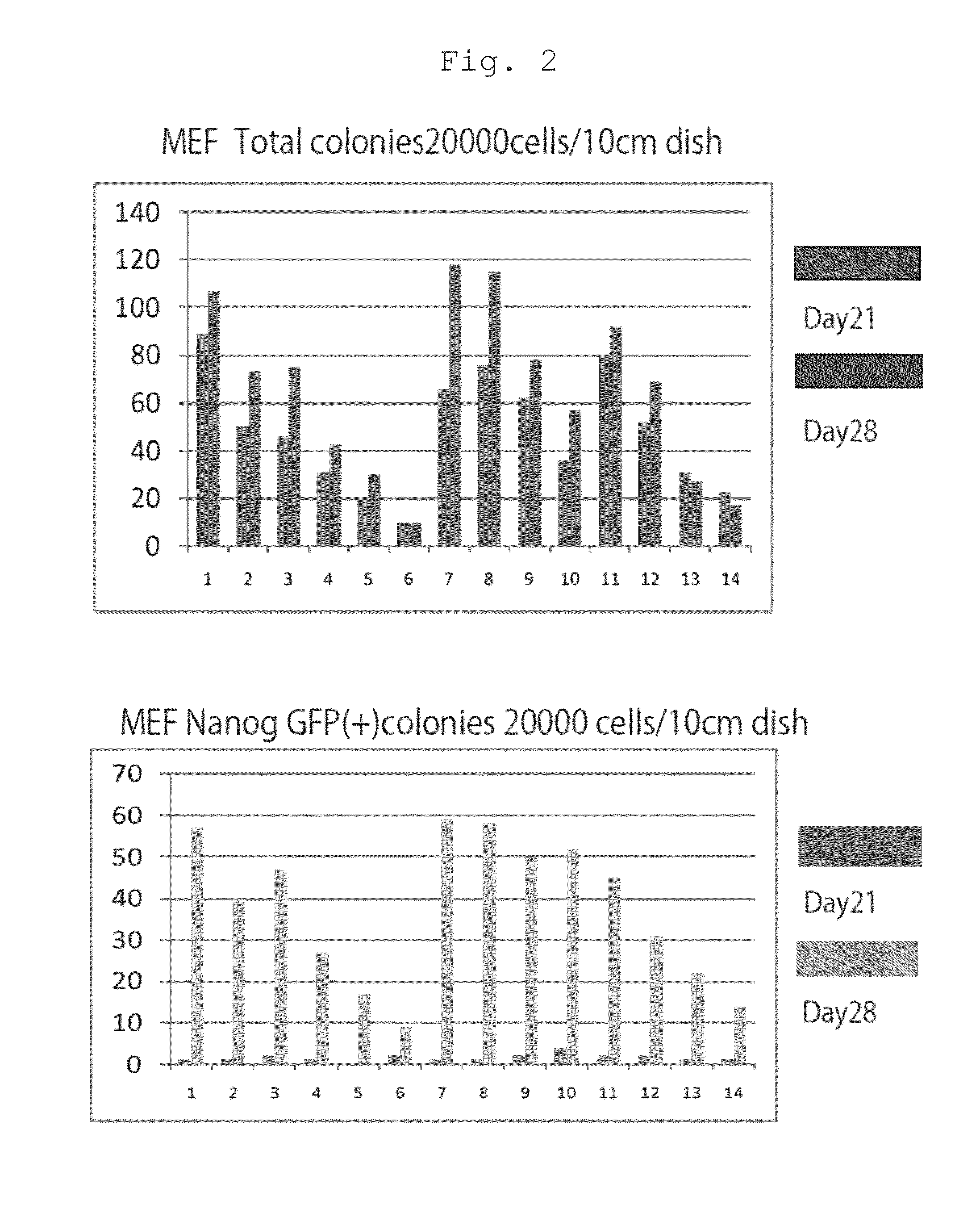
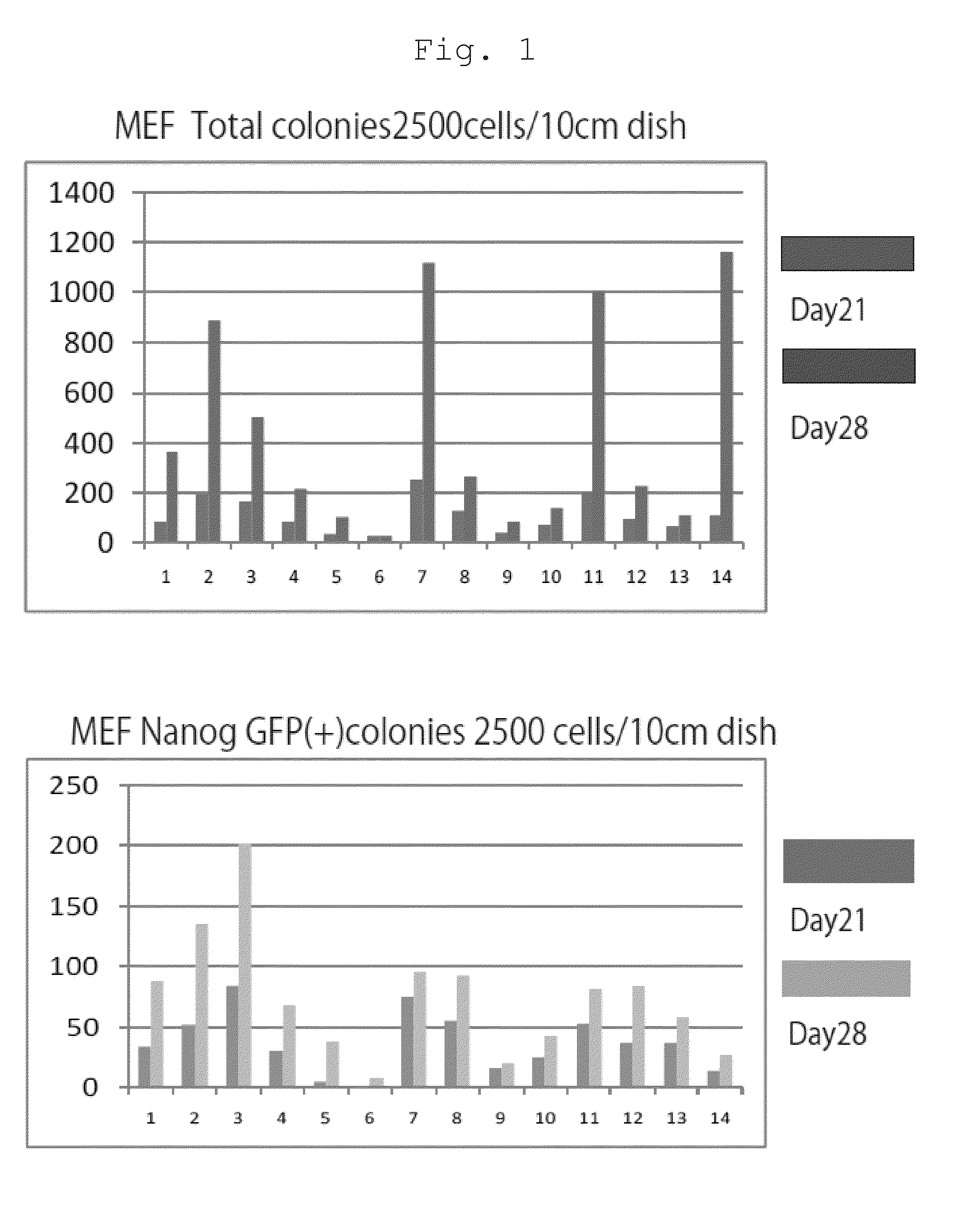
The present invention provides a method of improving the efficiency of establishment of induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, comprising inhibiting the p53 function in the step of somatic cell nuclear reprogramming. The inhibition of p53 function is achieved by bringing a substance selected from the group consisting of (1) chemical inhibitors of p53, (2) dominant negative mutants of p53 and nucleic acids that encode the same, (3) siRNAs and shRNAs against p53 and DNAs that encode the same, and (4) p53 pathway inhibitors, into contact with a somatic cell, and the like. The present invention also provides an agent for improving the efficiency of establishment of iPS cells, the agent comprising an inhibitor of p53 function, particularly (1) chemical inhibitors of p53, (2) dominant negative mutants of p53 and nucleic acids that encode the same, (3) siRNAs and shRNAs against p53 and DNAs that encode the same, and (4) p53 pathway inhibitors. The present invention further provides a method of producing an iPS cell, comprising bringing a nuclear reprogramming substance and an inhibitor of p53 function into contact with a somatic cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Compounds and methods for the treatment and prevention of bacterial infection
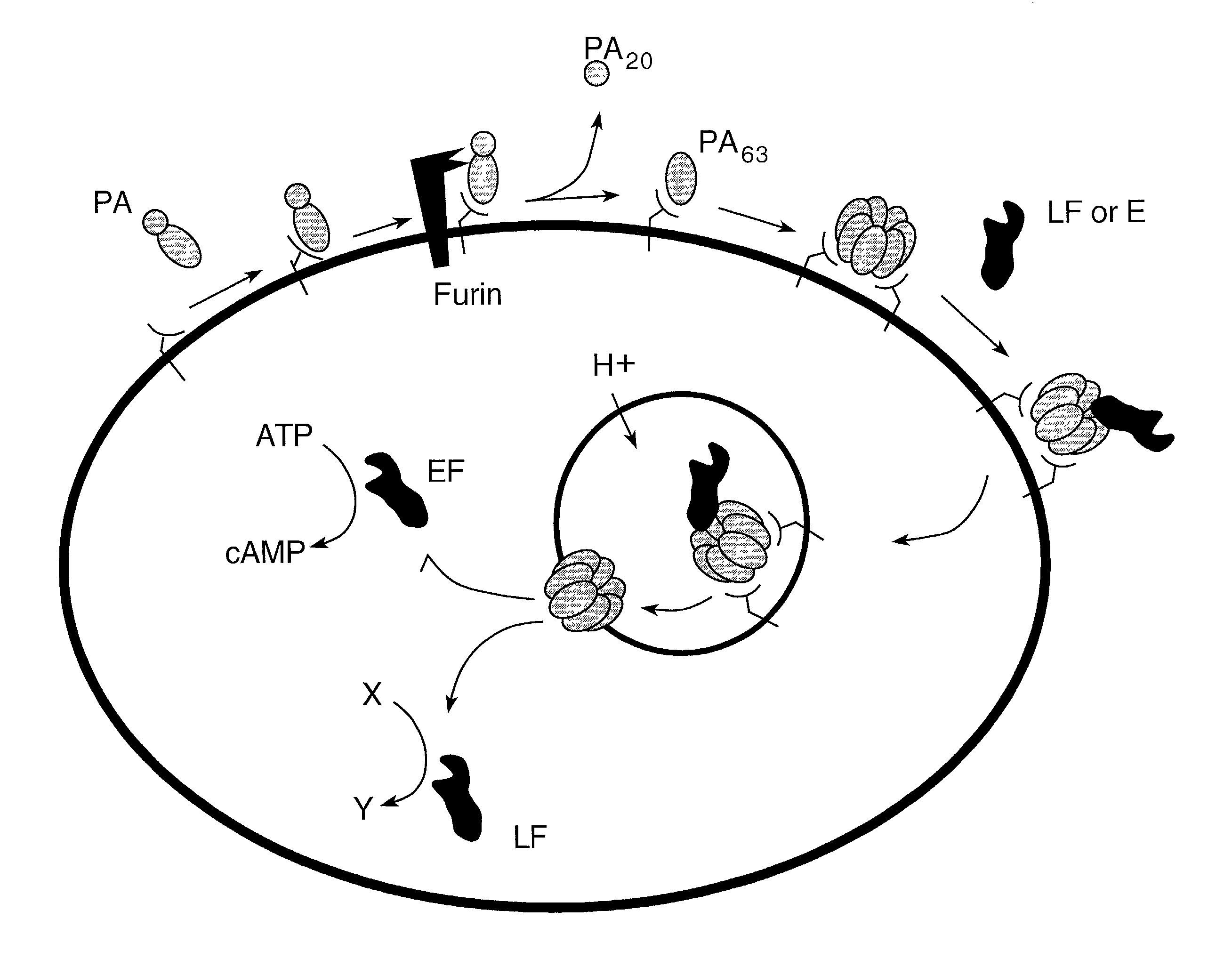
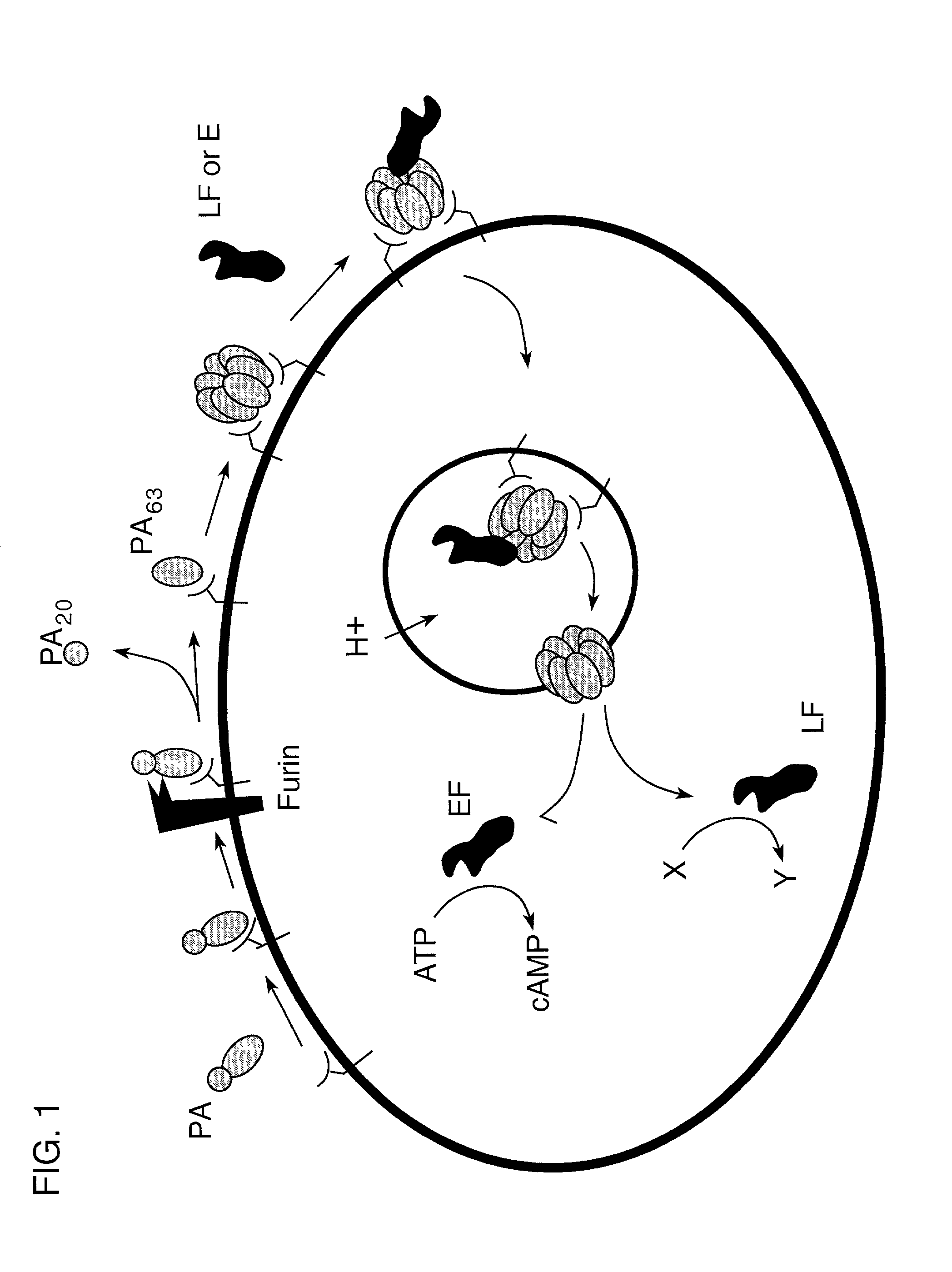
InactiveUS7037503B2Reduced ability to form poreInhibit pore-forming abilityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsDominant-Negative MutantDominant negative
The invention provides mutant forms of pore-forming toxins. These mutant toxins may be used in vaccines for the prevention of bacterial infection. Additionally, dominant negative mutants may be administered as therapeutics for the treatment of bacterial infection.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method of efficiently establishing induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS8530238B2Genetically modified cellsBlood/immune system cellsNuclear reprogrammingCancer research
The present invention provides a method of improving the efficiency of establishment of induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, comprising inhibiting the p53 function in the step of somatic cell nuclear reprogramming. The inhibition of p53 function is achieved by bringing a substance selected from the group consisting of (1) chemical inhibitors of p53, (2) dominant negative mutants of p53 and nucleic acids that encode the same, (3) siRNAs and shRNAs against p53 and DNAs that encode the same, and (4) p53 pathway inhibitors, into contact with a somatic cell, and the like. The present invention also provides an agent for improving the efficiency of establishment of iPS cells, the agent comprising an inhibitor of p53 function, particularly (1) chemical inhibitors of p53, (2) dominant negative mutants of p53 and nucleic acids that encode the same, (3) siRNAs and shRNAs against p53 and DNAs that encode the same, and (4) p53 pathway inhibitors. The present invention further provides a method of producing an iPS cell, comprising bringing a nuclear reprogramming substance and an inhibitor of p53 function into contact with a somatic cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
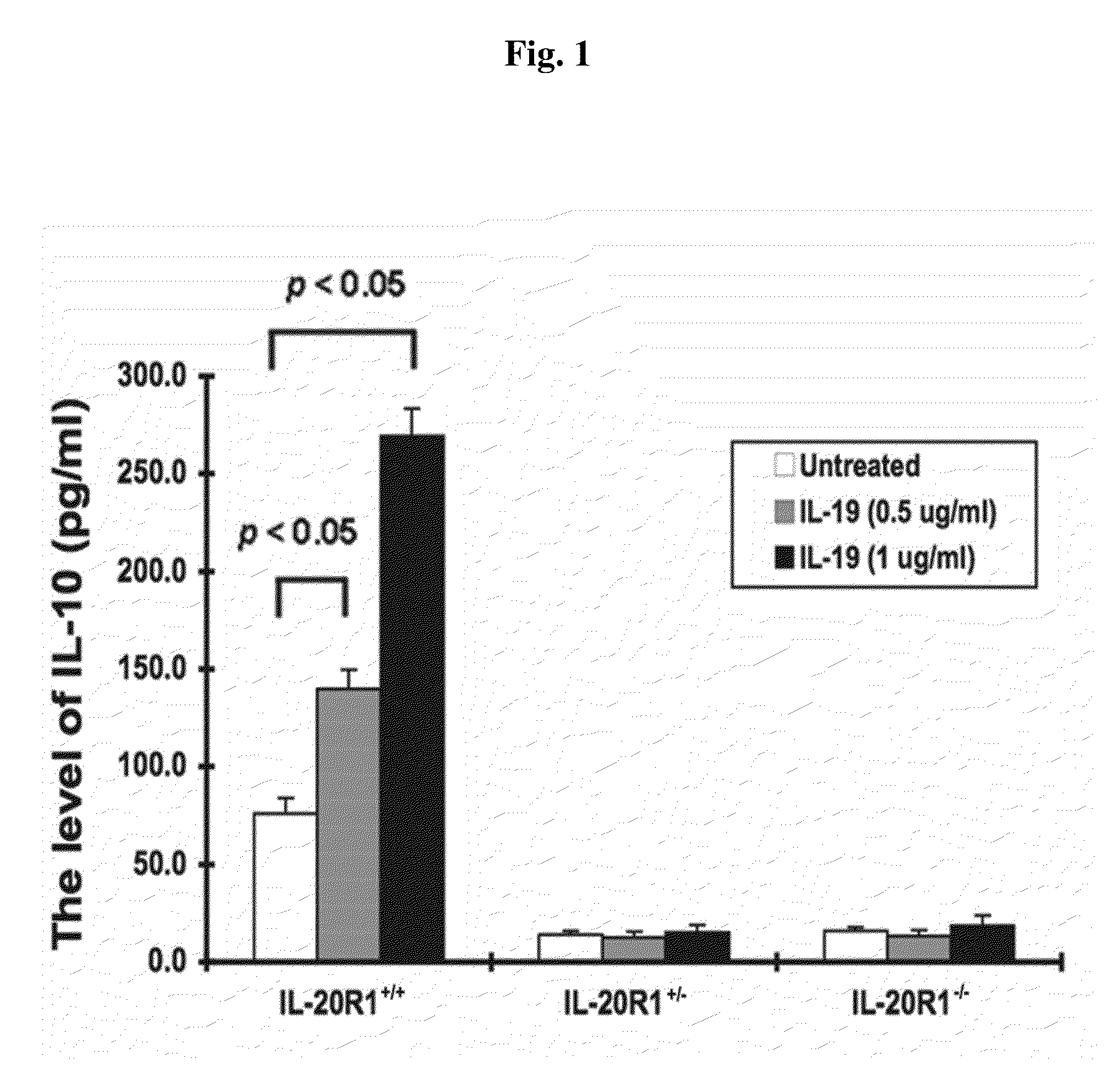
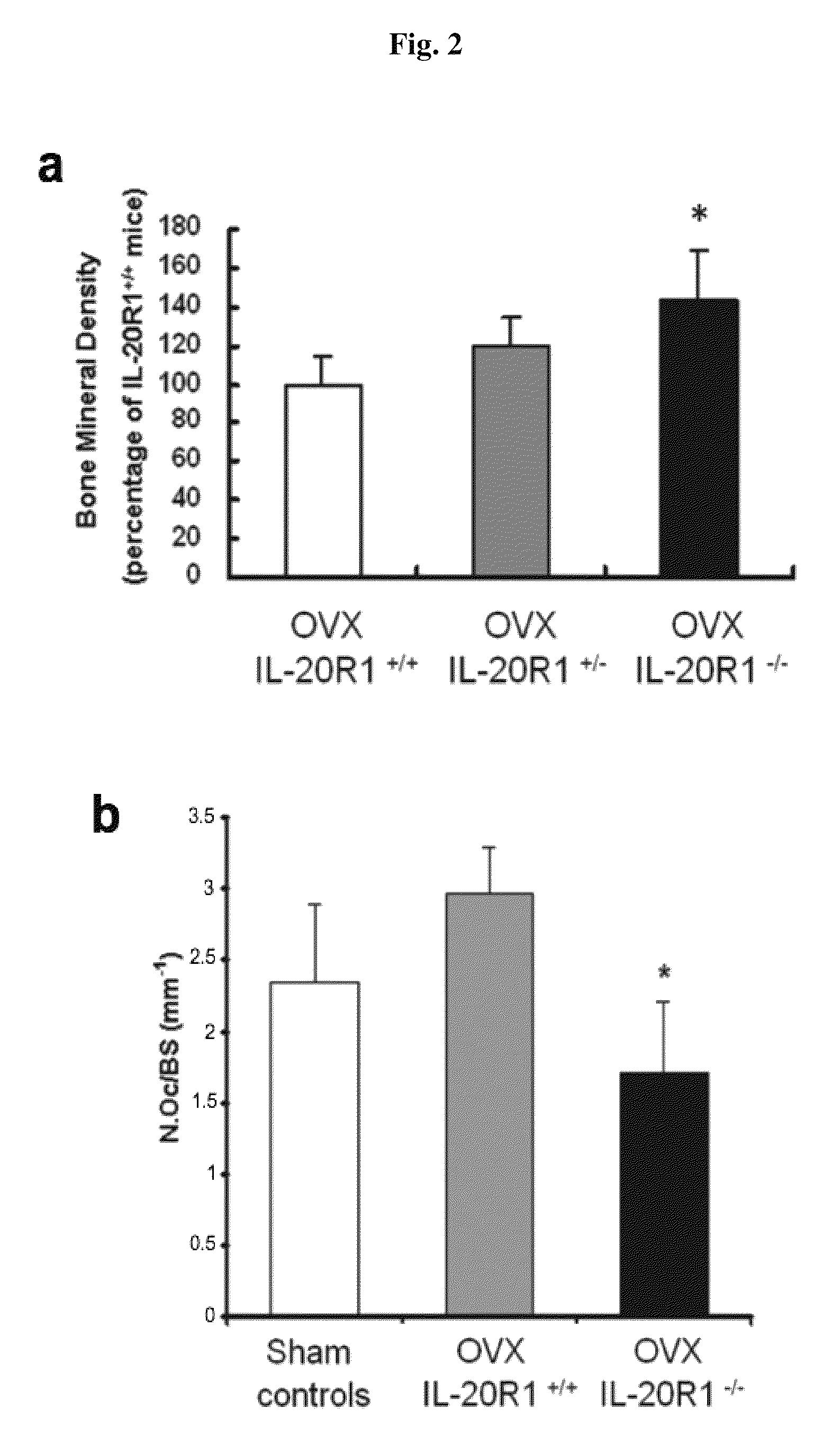
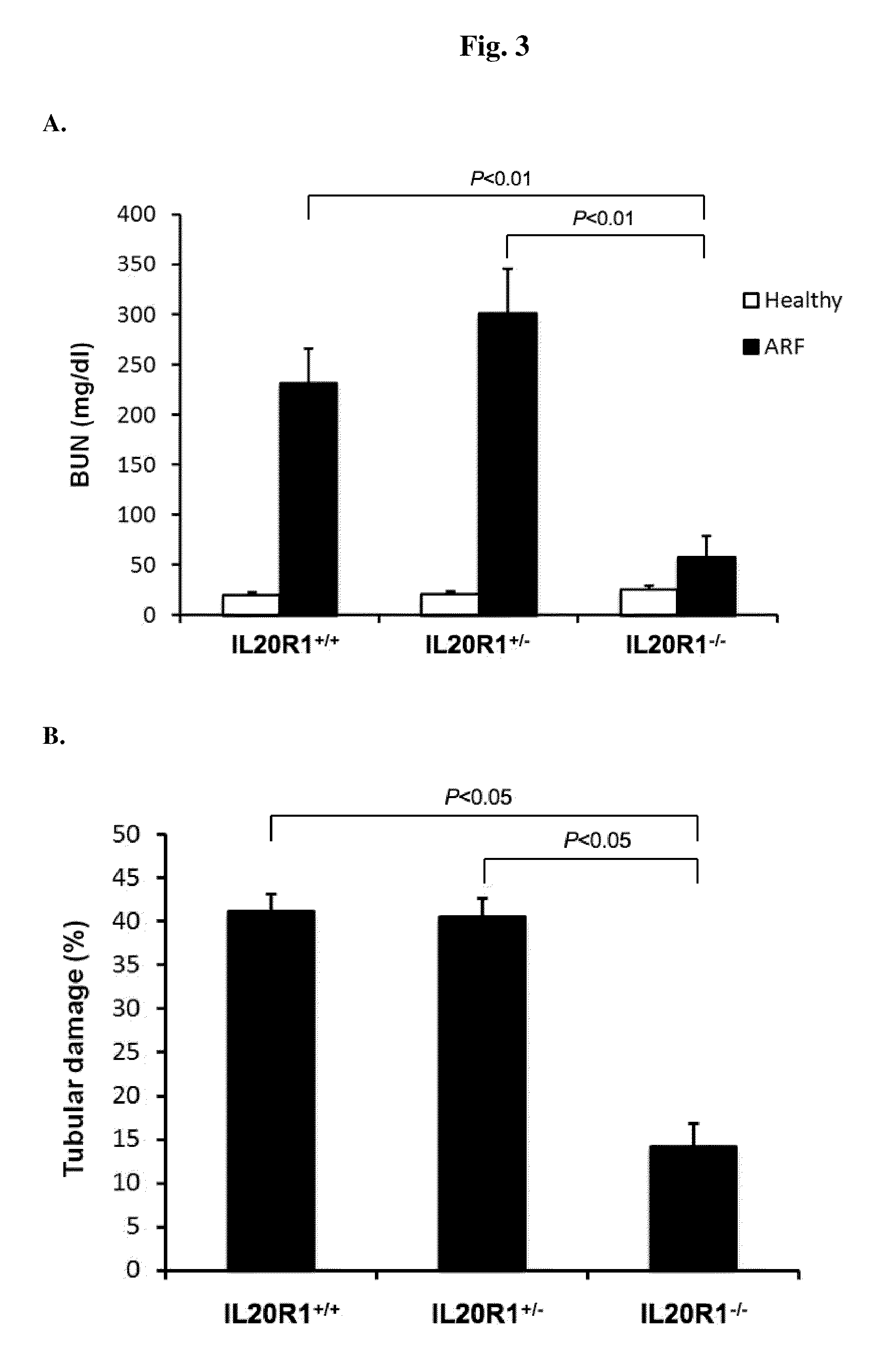
Treating Disorders Associated with IL-20 Receptor-Mediated Signaling Pathway by Blocking IL-20 Receptor Activity
ActiveUS20110256093A1Less severe osteoporosisLess severe renal failureOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAntisense nucleic acid
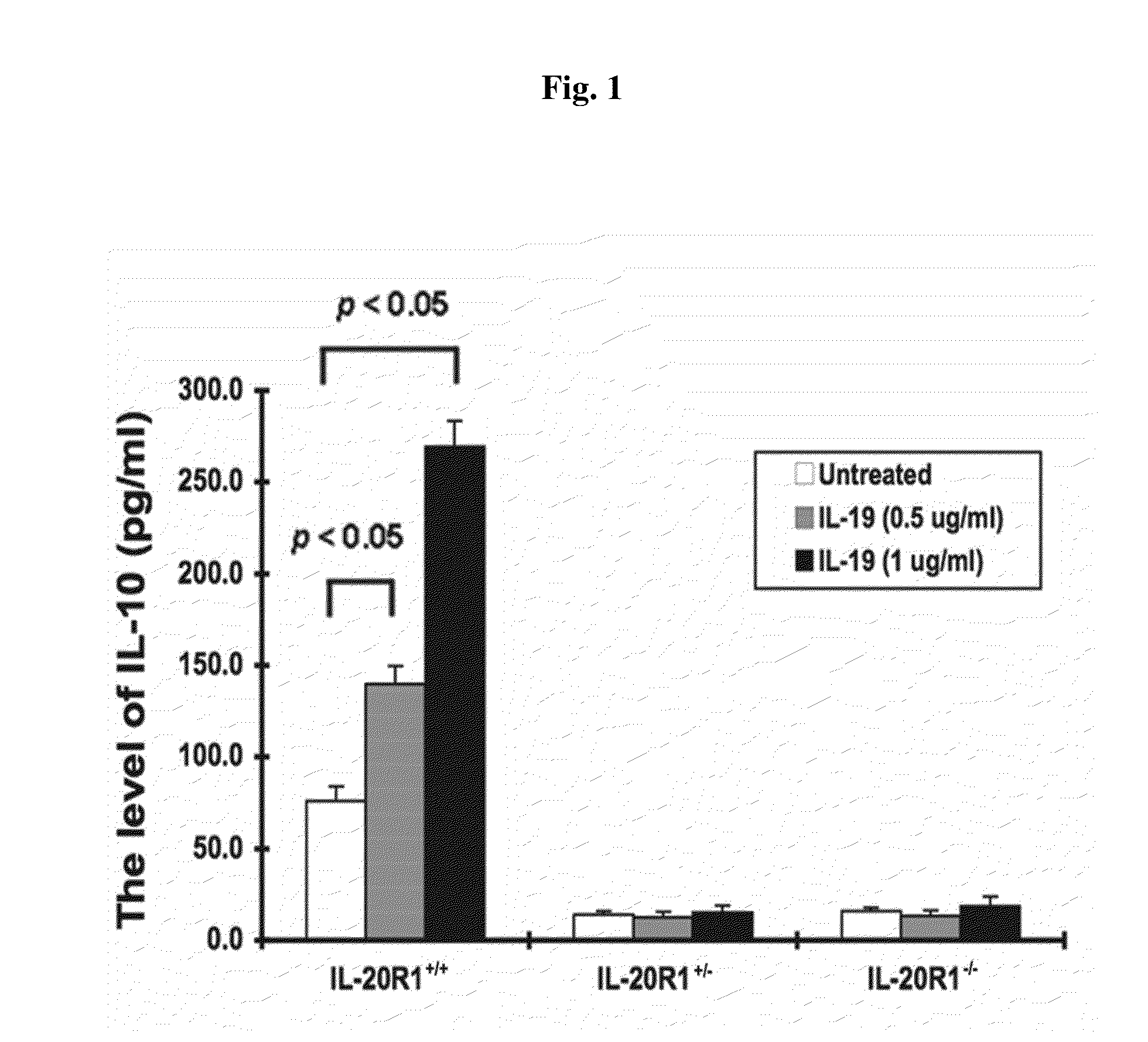
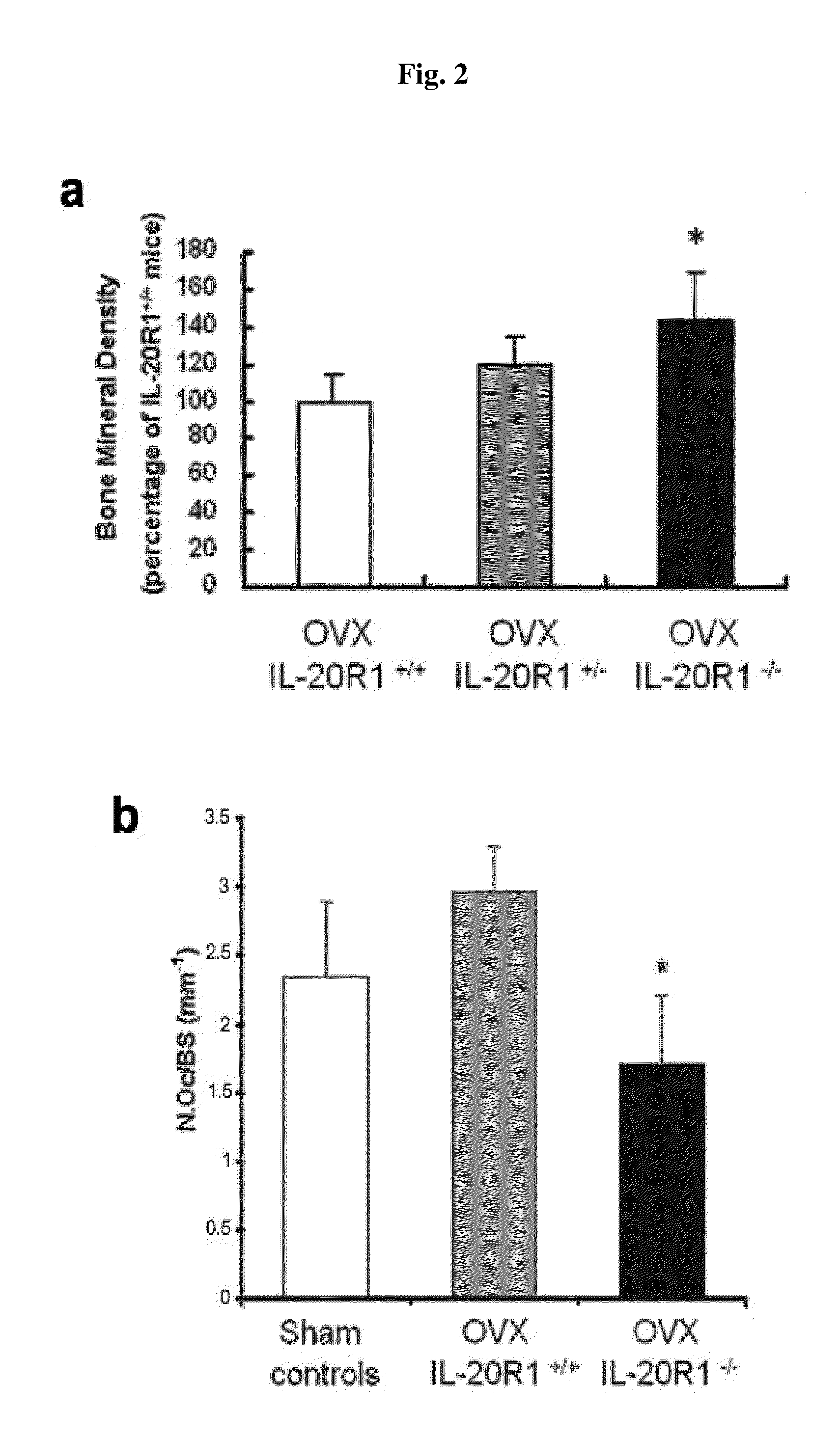
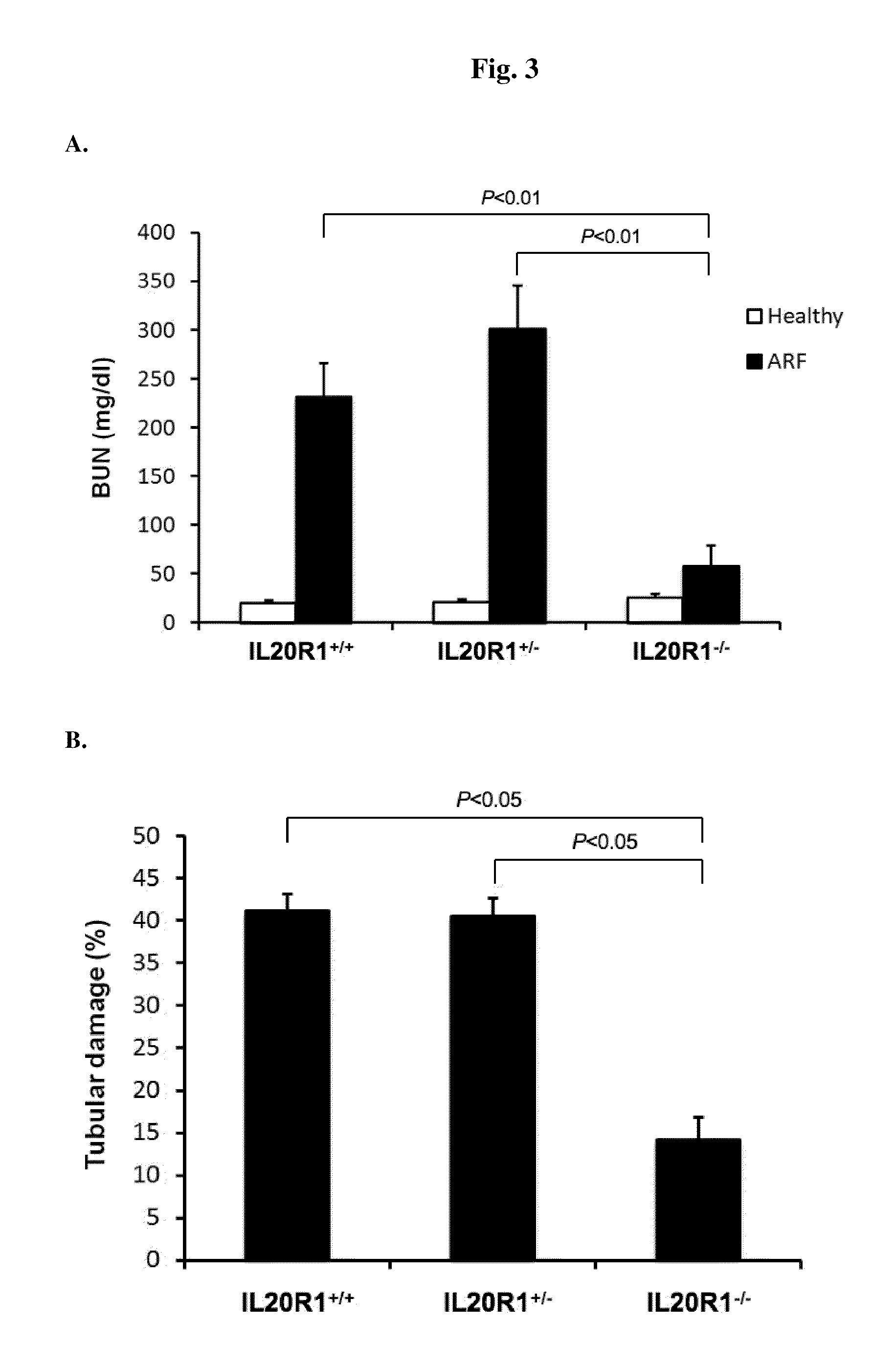
Treating a disorder (e.g., osteoporosis, renal failure, or diabetic nephropathy) associated with a signaling pathway mediated by IL-20 receptor with an agent that suppresses IL-20 receptor activity, e.g., an antibody that neutralizes IL-20 receptor via binding to IL-20R1, an antisense nucleic acid that suppresses expression of IL-20R1, a small molecule that inhibits IL-20 receptor activity, or a dominant negative mutant of IL-19, IL-20, or IL-24.
Owner:LBL BIOTECH INC
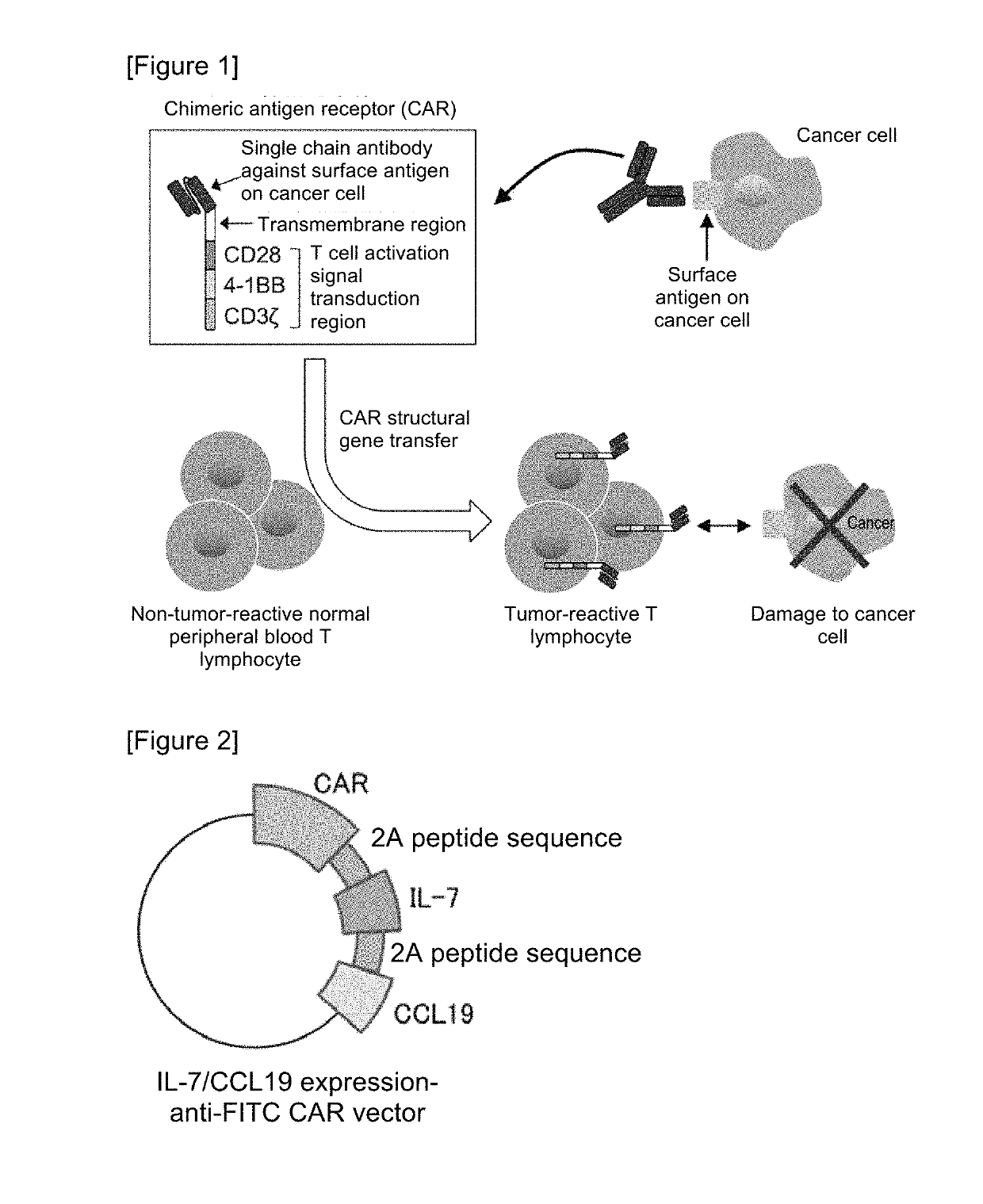
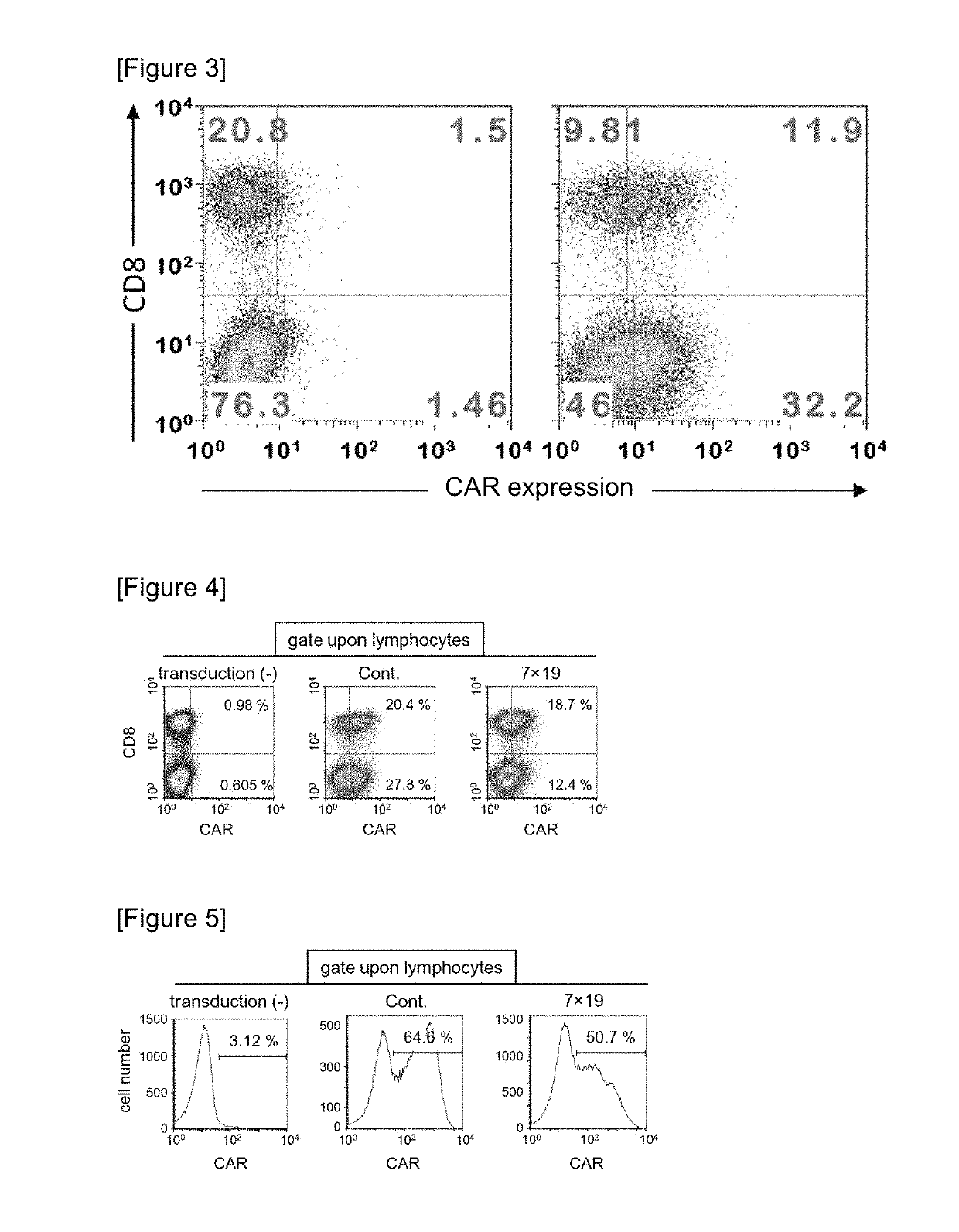
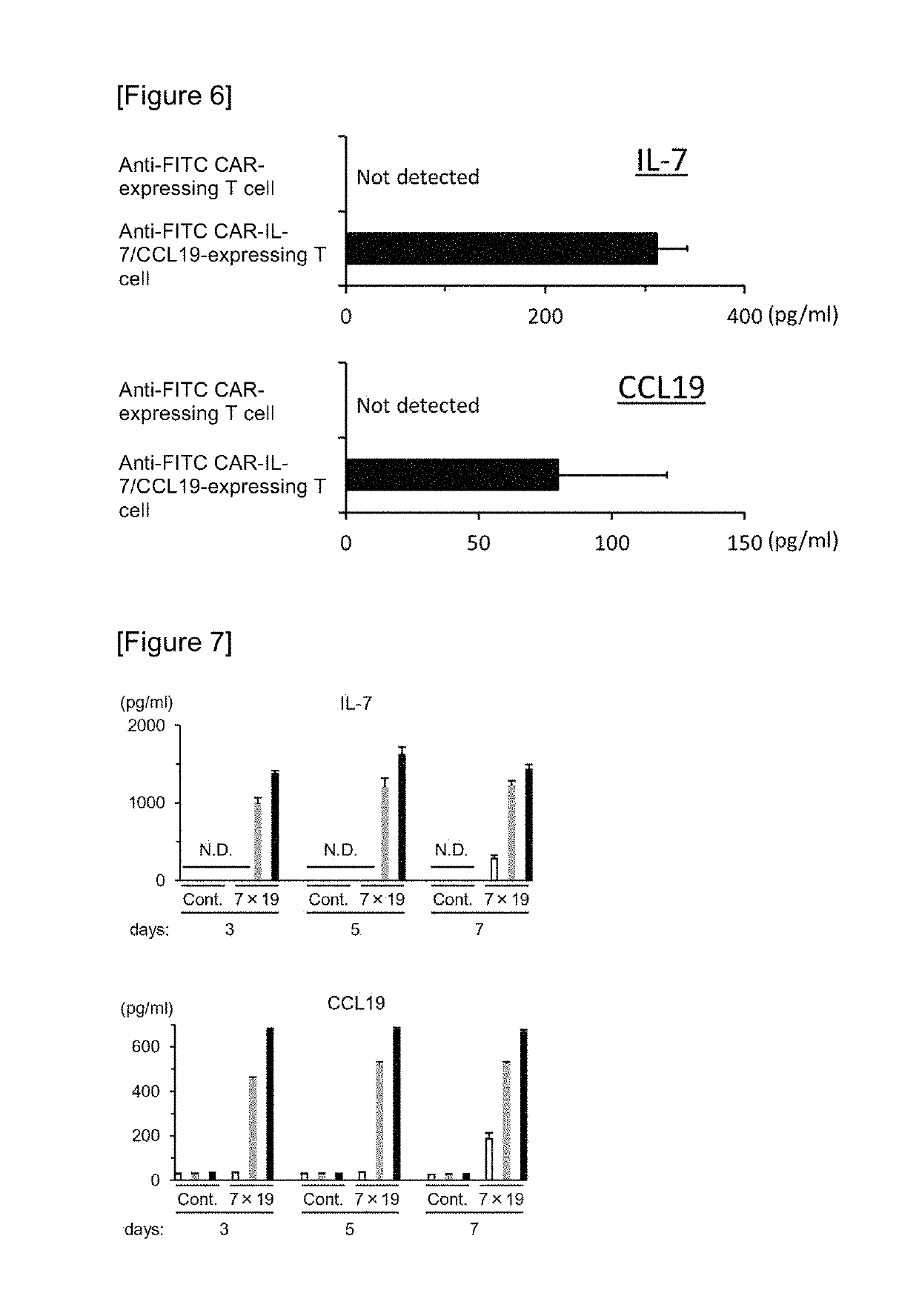
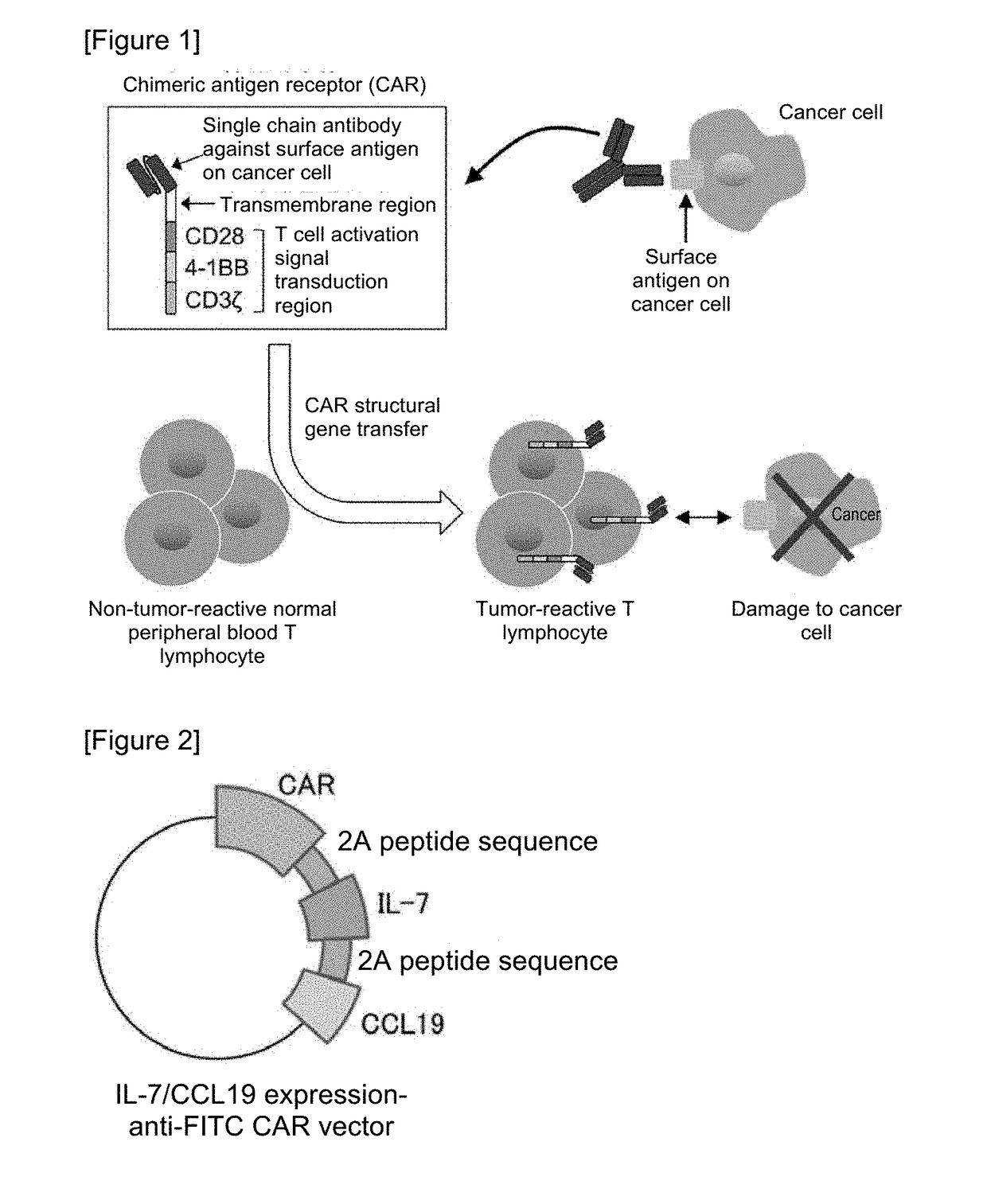
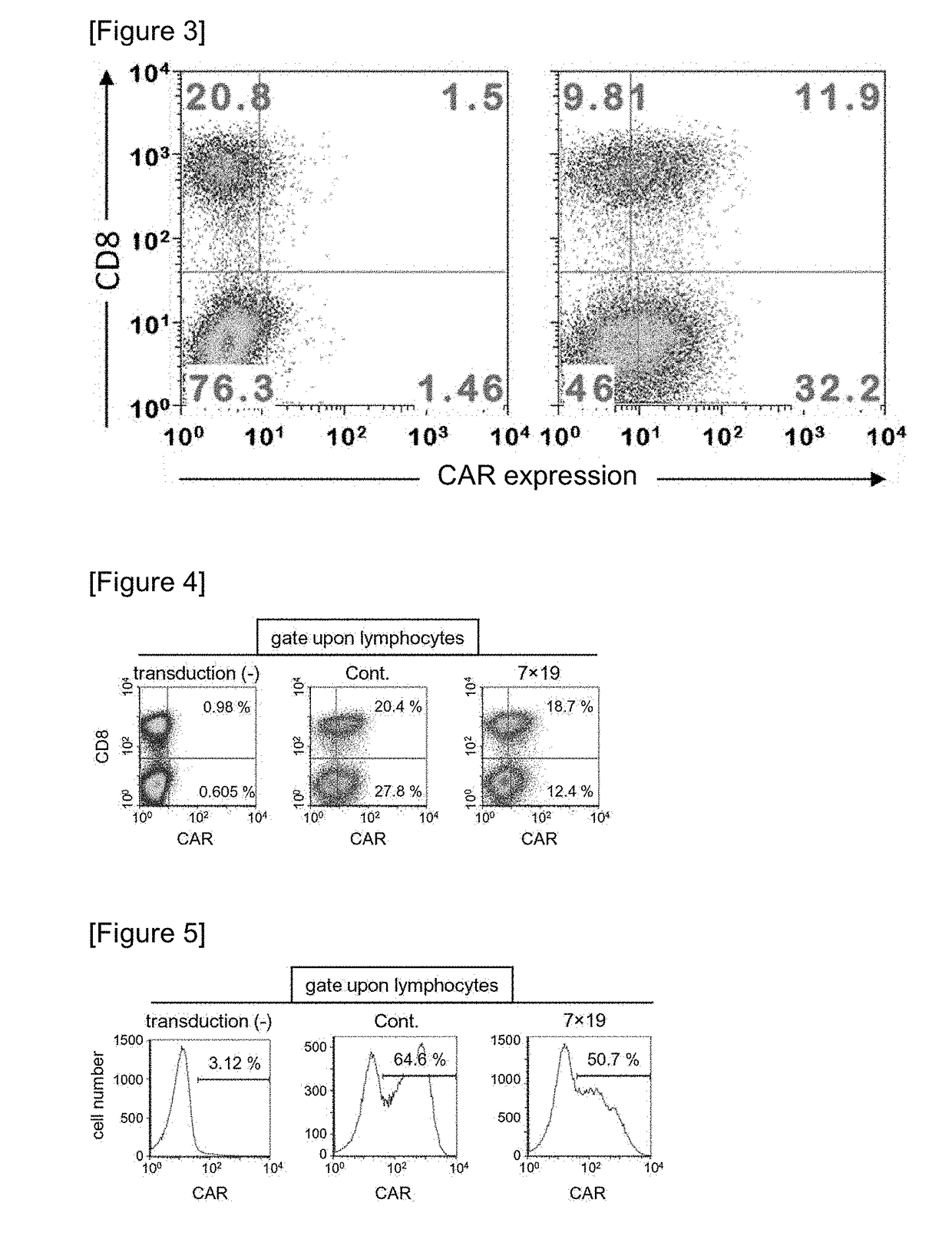
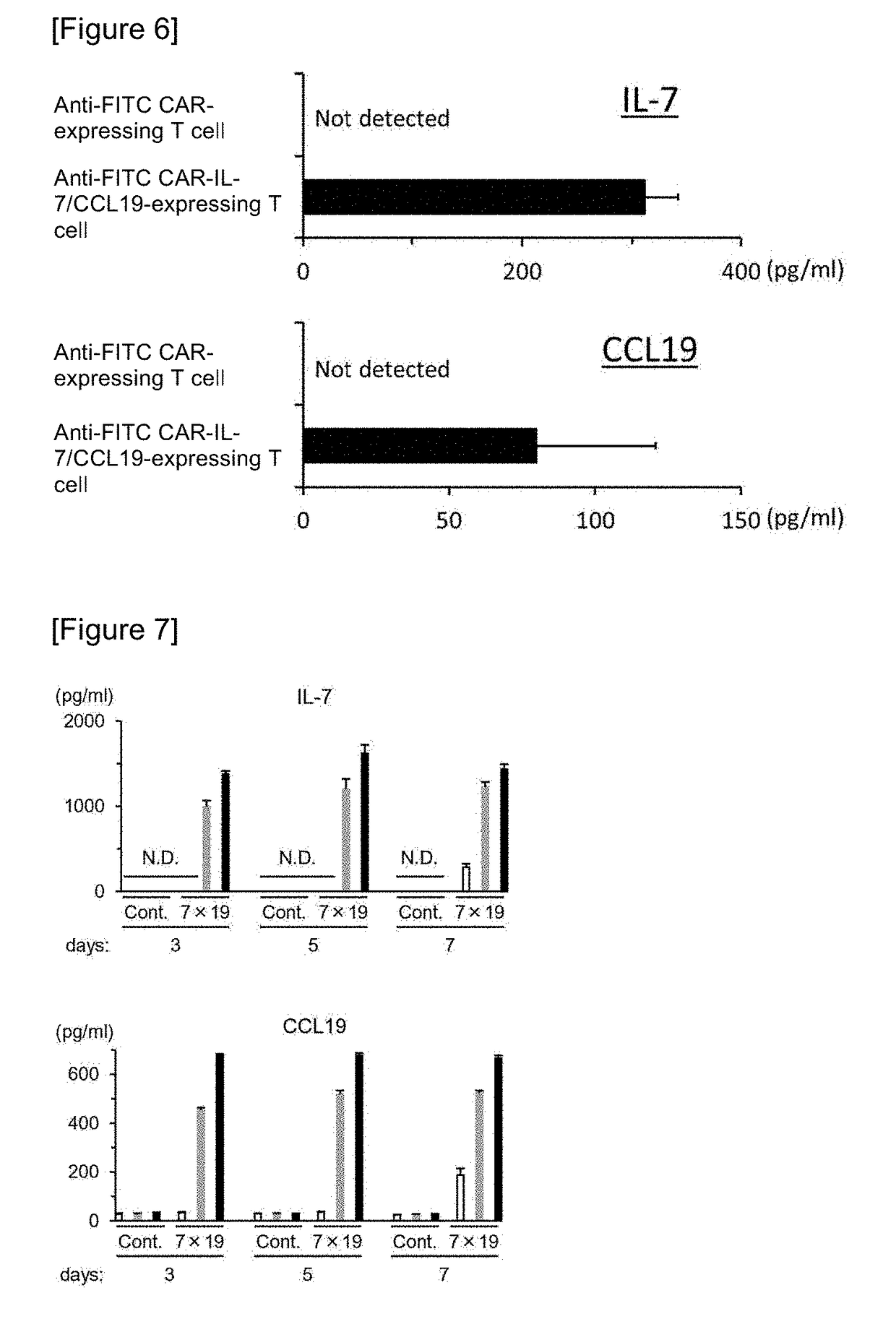
Car expression vector and car-expressing T cells
ActiveUS10316102B2Good treatment effectVirusesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigen receptorsChimeric antigen receptor
Owner:YAMAGUCHI UNIV
Car expression vector and car-expressing t cells
Owner:YAMAGUCHI UNIV
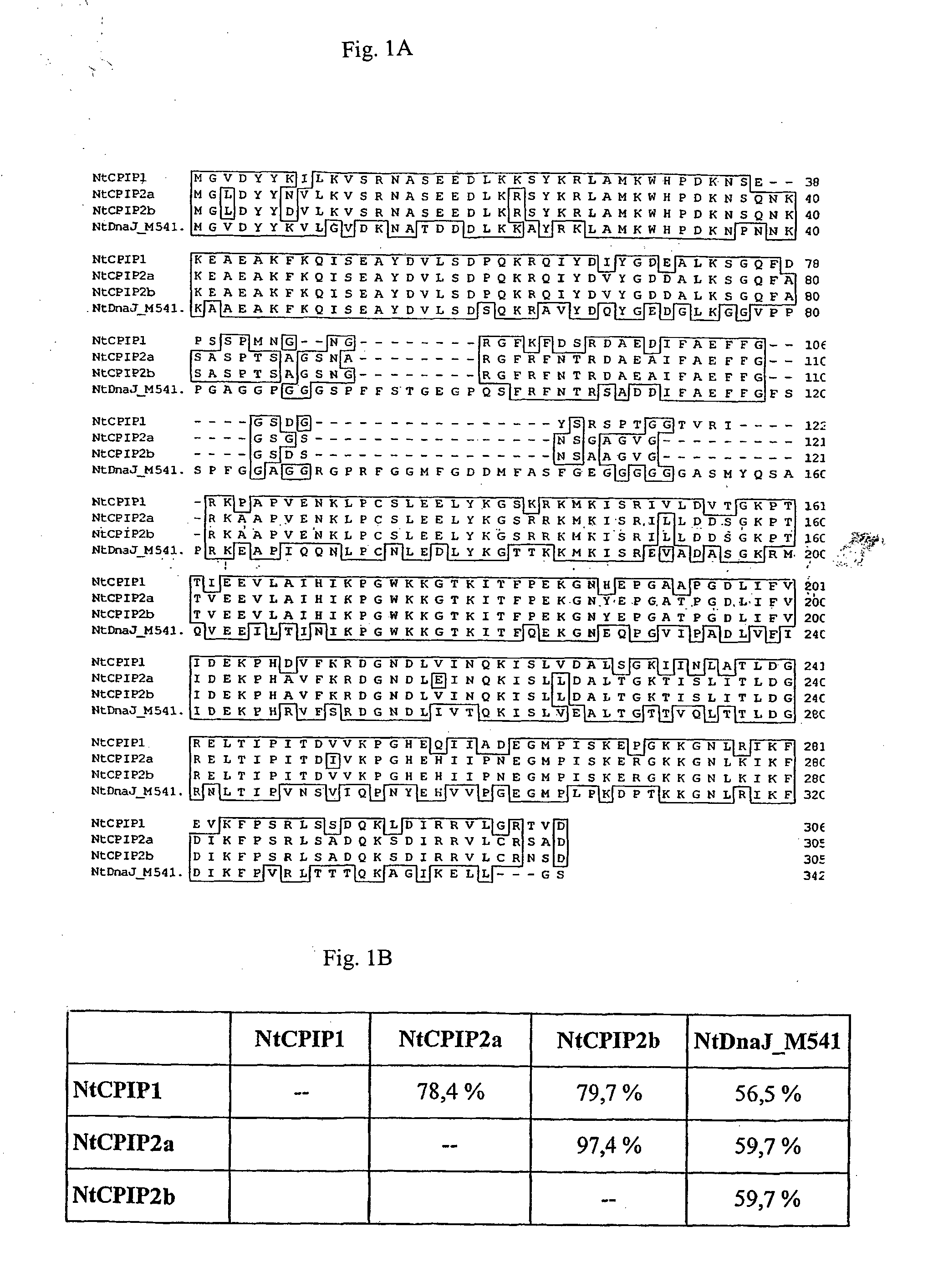
Method for the production of transgenic plants with increased virus resistance by silencing vegetable DnaJ-like proteins
InactiveUS20050251879A1Good antiviral effectEasily put into practiceOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationPlant cellGMO Plants
The invention relates to plants and plant cells which have a transient or permanent virus resistance as a result of modulation of the gene expression and / or binding behavior of vegetable DnaJ-like proteins. The invention also relates to methods for the production of transgenic plants with increased virus resistance, wherein the expression of vegetable DnaJ-like proteins which interact with viral components is substantially prevented by silencing the DnaJ-like proteins. The invention further relates to methods for the production of transgenic plants with increased virus resistance, wherein the interaction of viral components with vegetable DnaJ-like proteins is substantially prevented by expression of dominant-negative mutants of the DnaJ-like proteins, by antibodies against DnaJ-like proteins or by specific inhibitors.
Owner:HOFIUS DANIEL +2
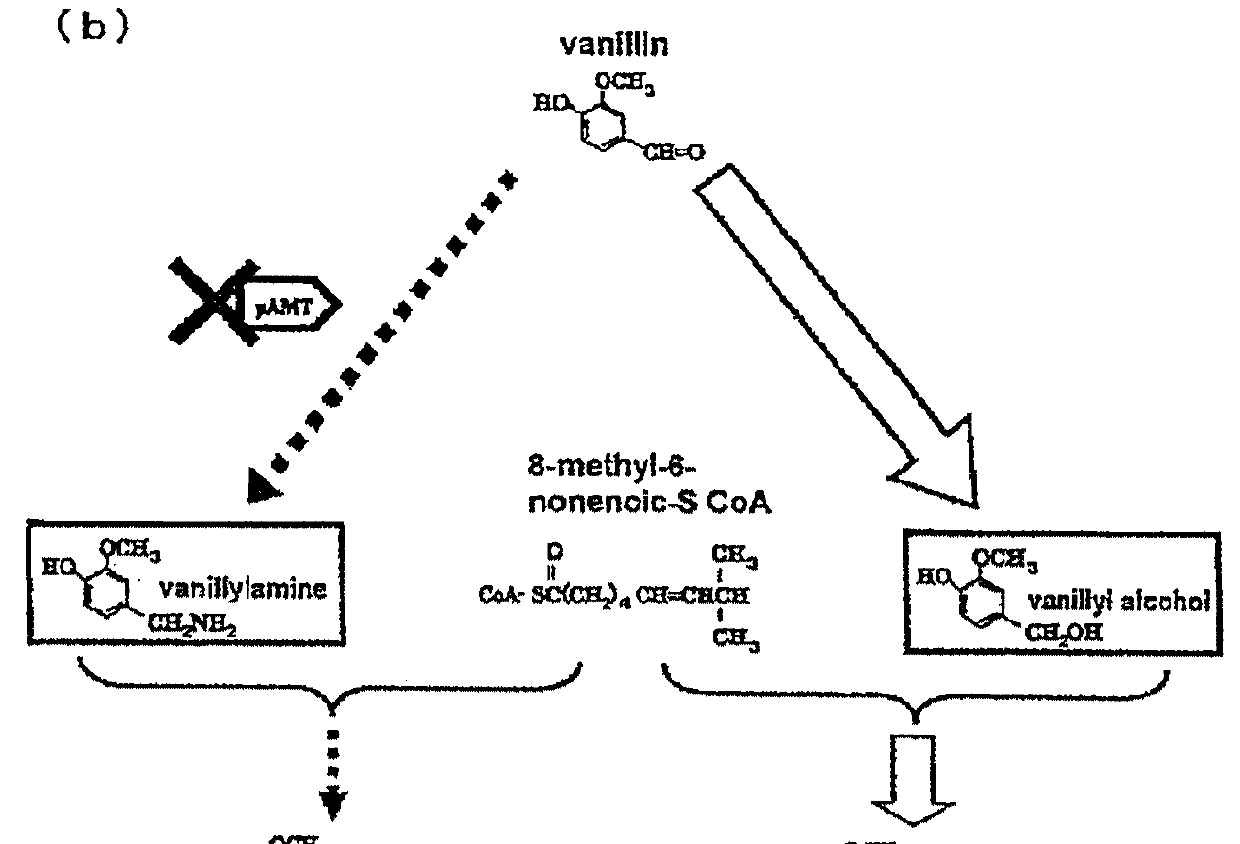
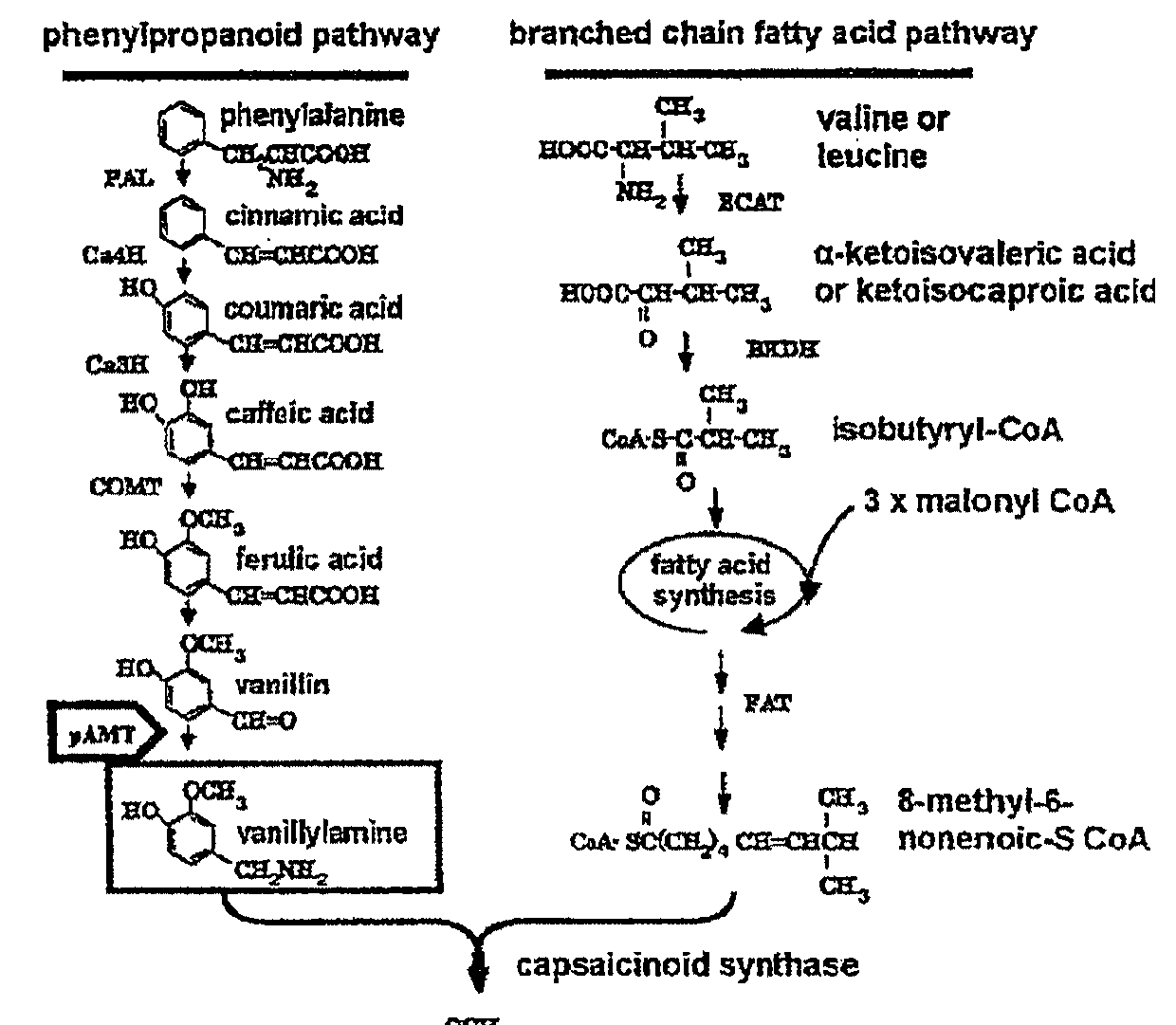
Genetically modified plant capable of biosynthesizing capsinoid
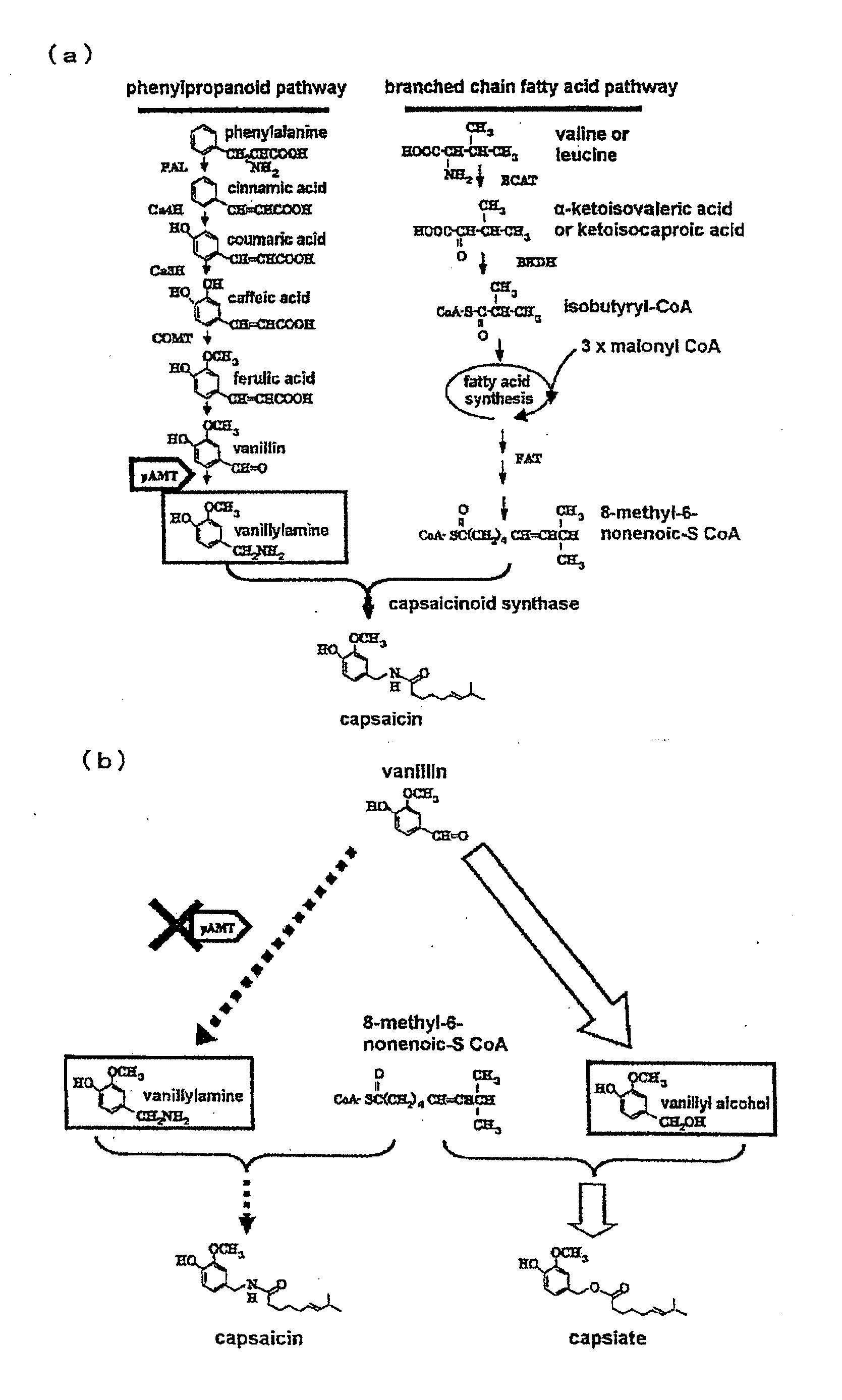
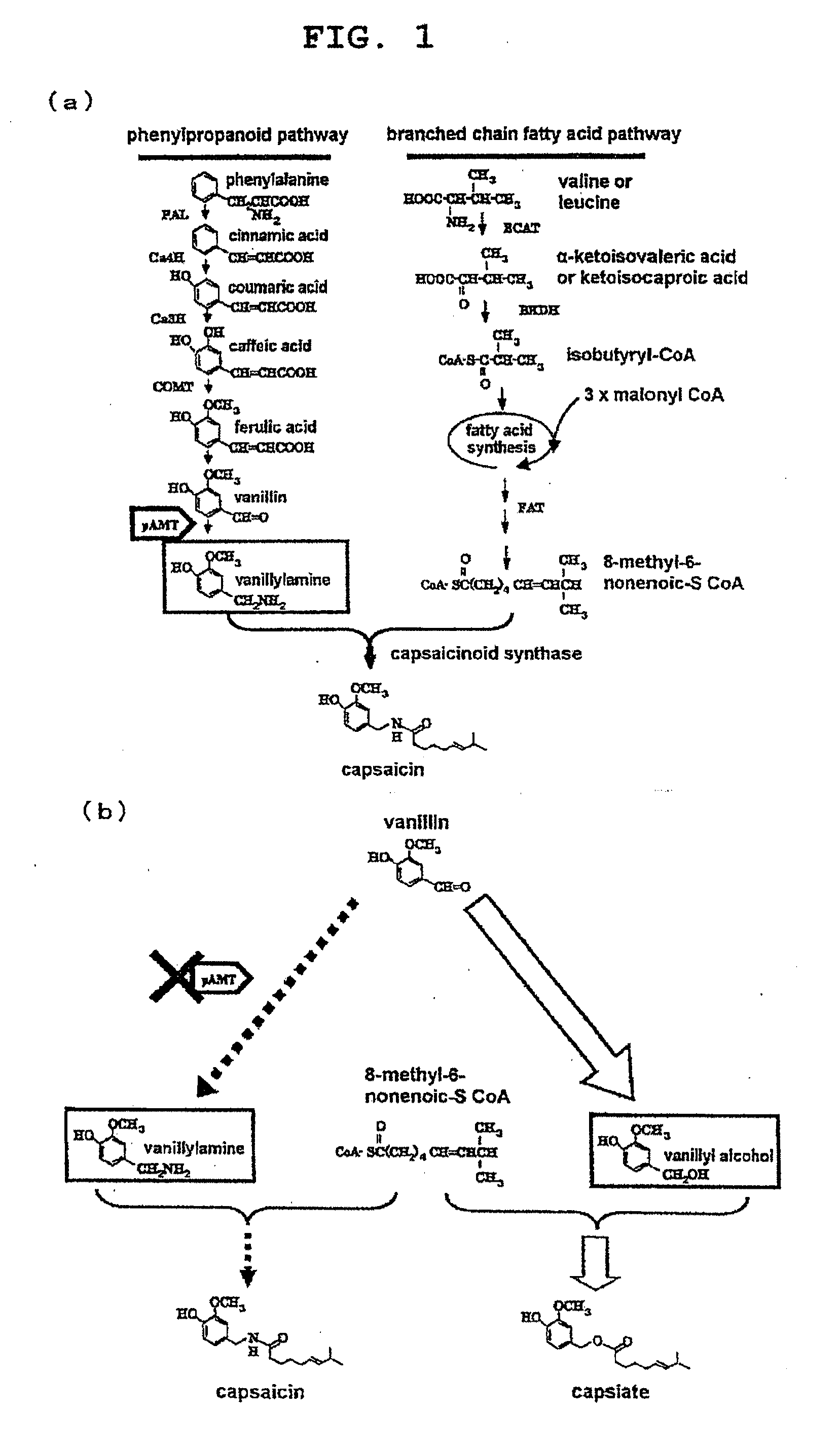
ActiveUS20110166371A1Increase productionClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesCapsaicinOrganism
The present invention provides a genetically modified plant that biosynthesizes an increased amount of capsinoids, a method of producing the genetically modified plant, and a production method of capsinoids from the genetically modified plant. More particularly, the present invention provides a genetically modified plant capable of producing capsinoids, which shows a decreased expression or activity of an enzyme that catalyzes an amino group conversion reaction from vanillin to vanillylamine as compared to wild strains, and the like. As a method of suppressing expression or activity of an enzyme, an introduction of DNA encoding an antisense RNA, iRNA, ribozyme or dominant-negative mutant for the target gene, a destruction of the gene by a knockout method, mutagen treatment or transposon insertion, an introduction of a gene encoding an antibody against the enzyme and the like can be mentioned.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Dominant negative mutant KRP protein protection of active cyclin-CDK complex inhibition by wild-type KRP
InactiveUS8742205B2Maintaining binding affinity for a cyclin proteinDominant negative antagonist activitySugar derivativesBacteriaCell divisionMutated protein
Disclosed are mutant CDK inhibitor (CKI) polypeptides having dominant negative antagonist activity against wild-type CKI proteins, as well as related compositions, including nucleic acids and vectors encoding the mutant CKI polypeptides and transformed host cells and transgenic plants comprising such nucleic acids and vectors. Also disclosed are related methods for using the mutant proteins to modulate cell division in cells, particularly plant cells.
Owner:TARGETED GROWTH INC
Methods and compositions for the treatment of cancer
ActiveUS20160122415A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsCancer researchDominant-Negative Mutant
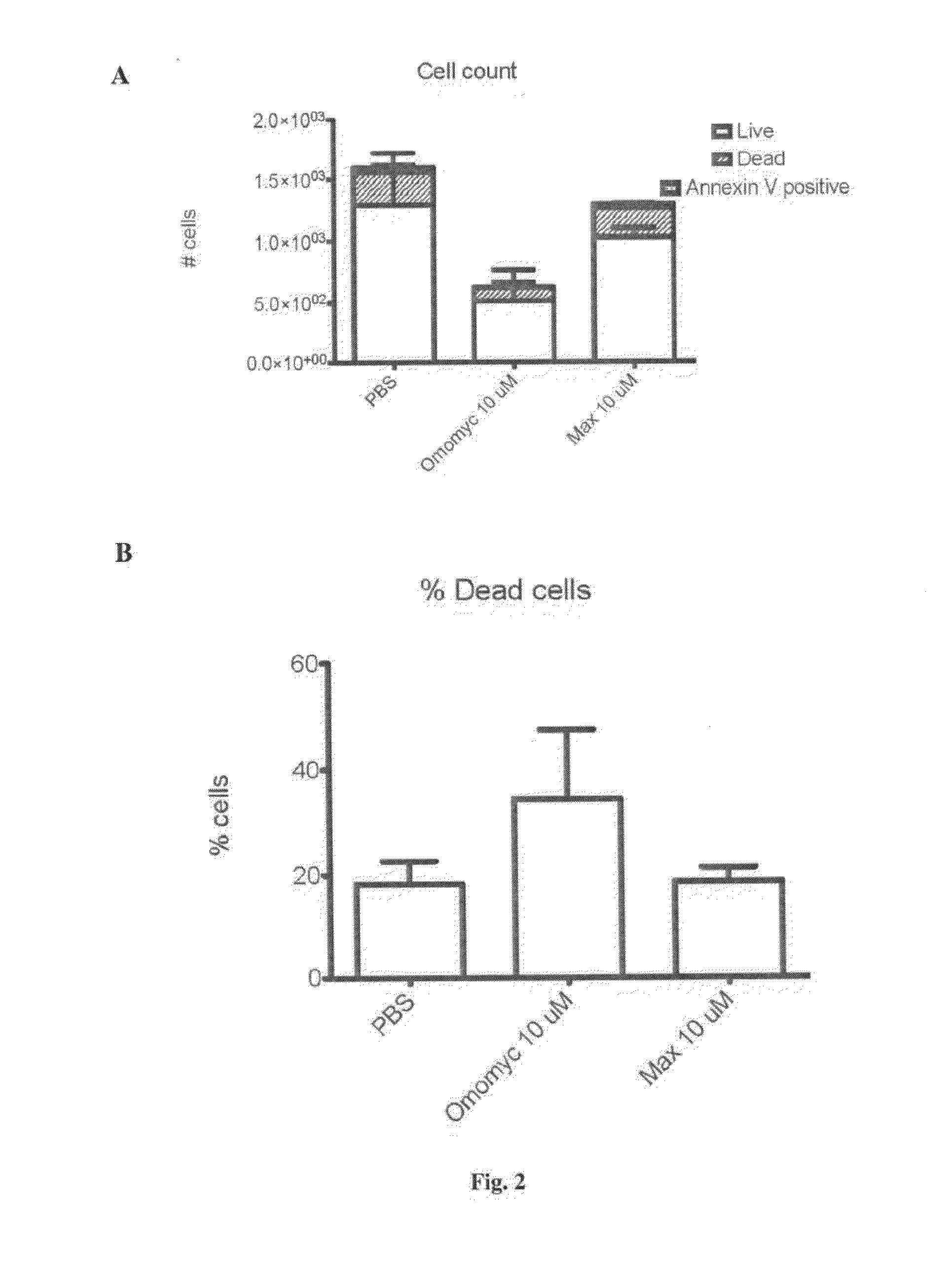
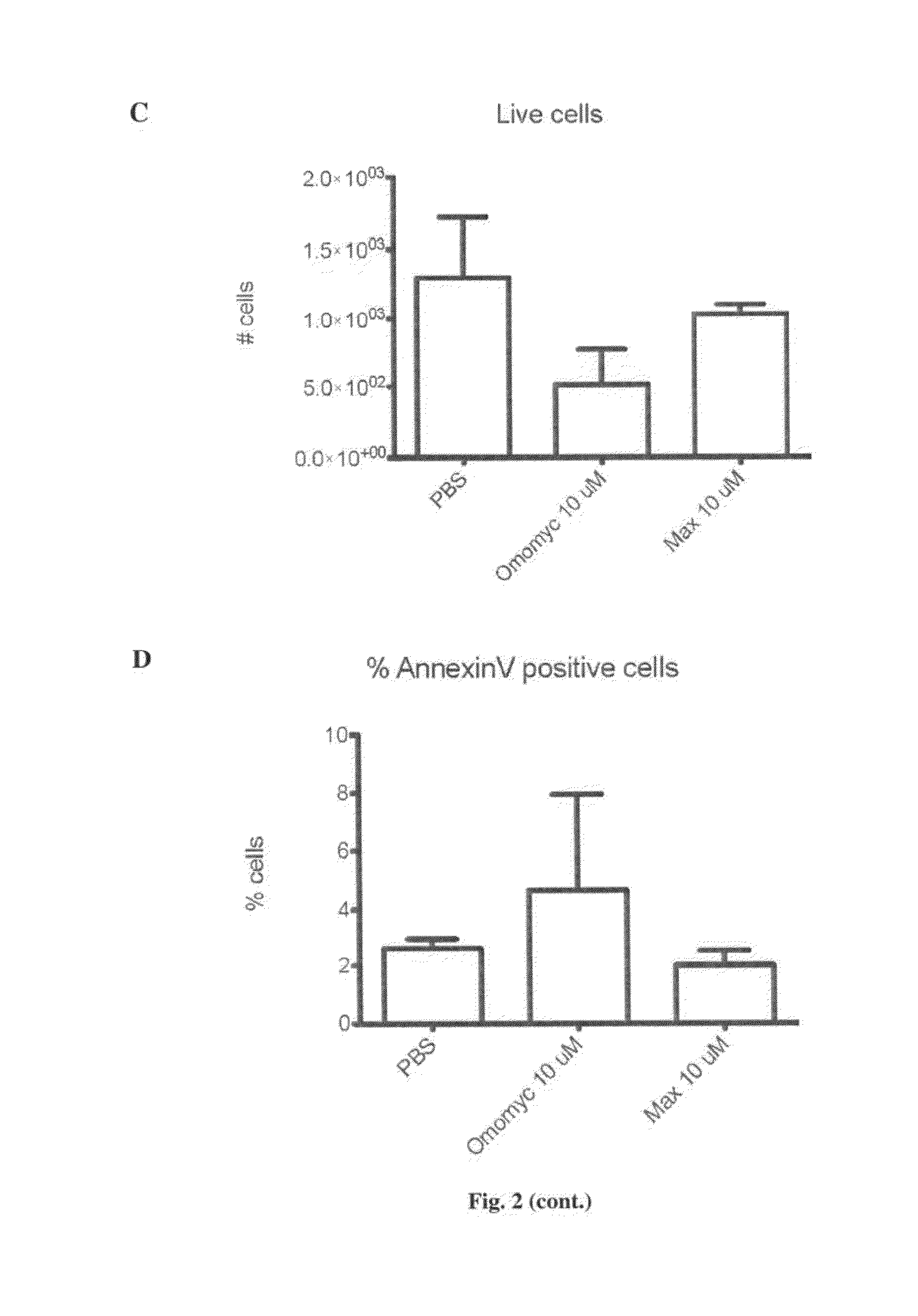
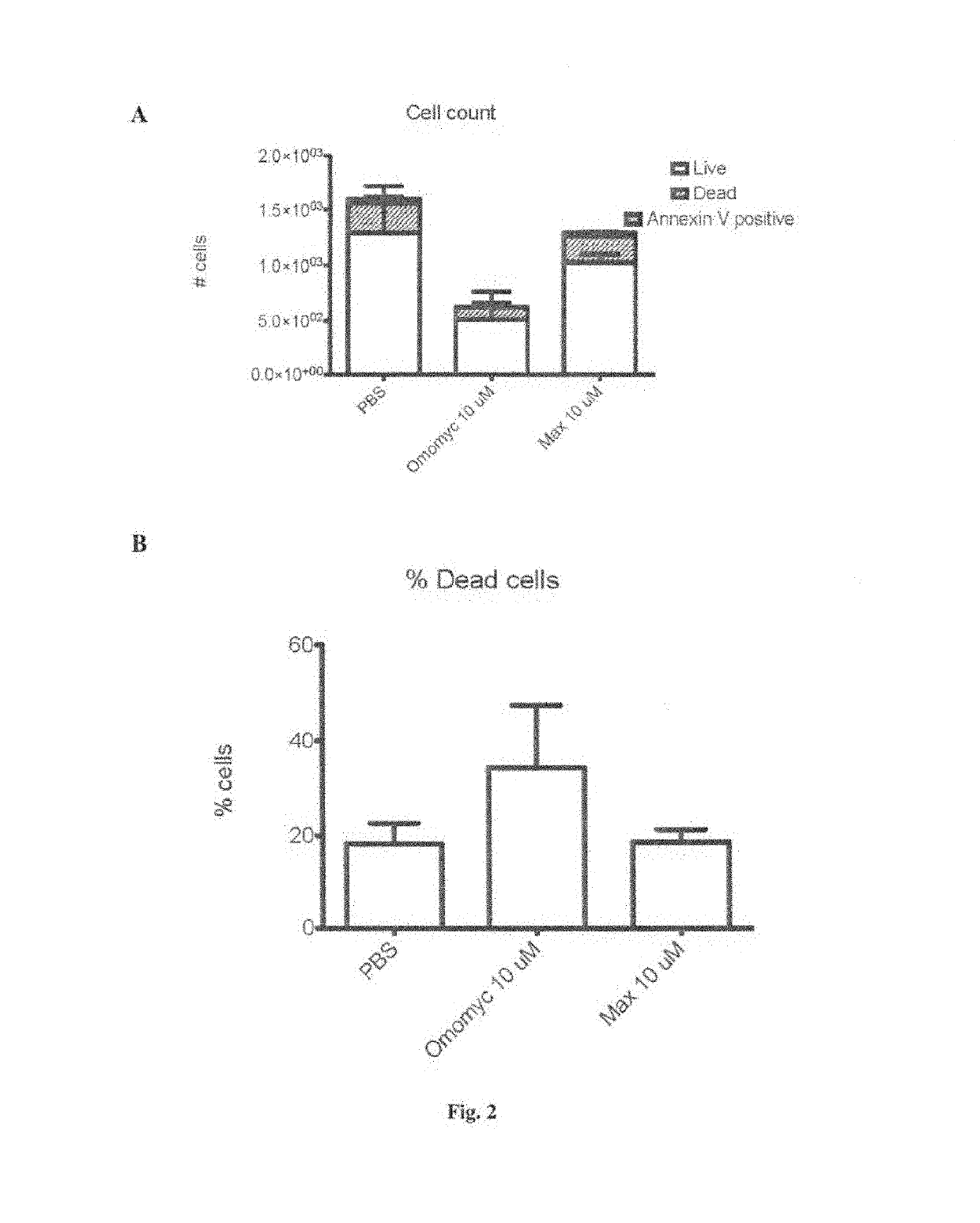
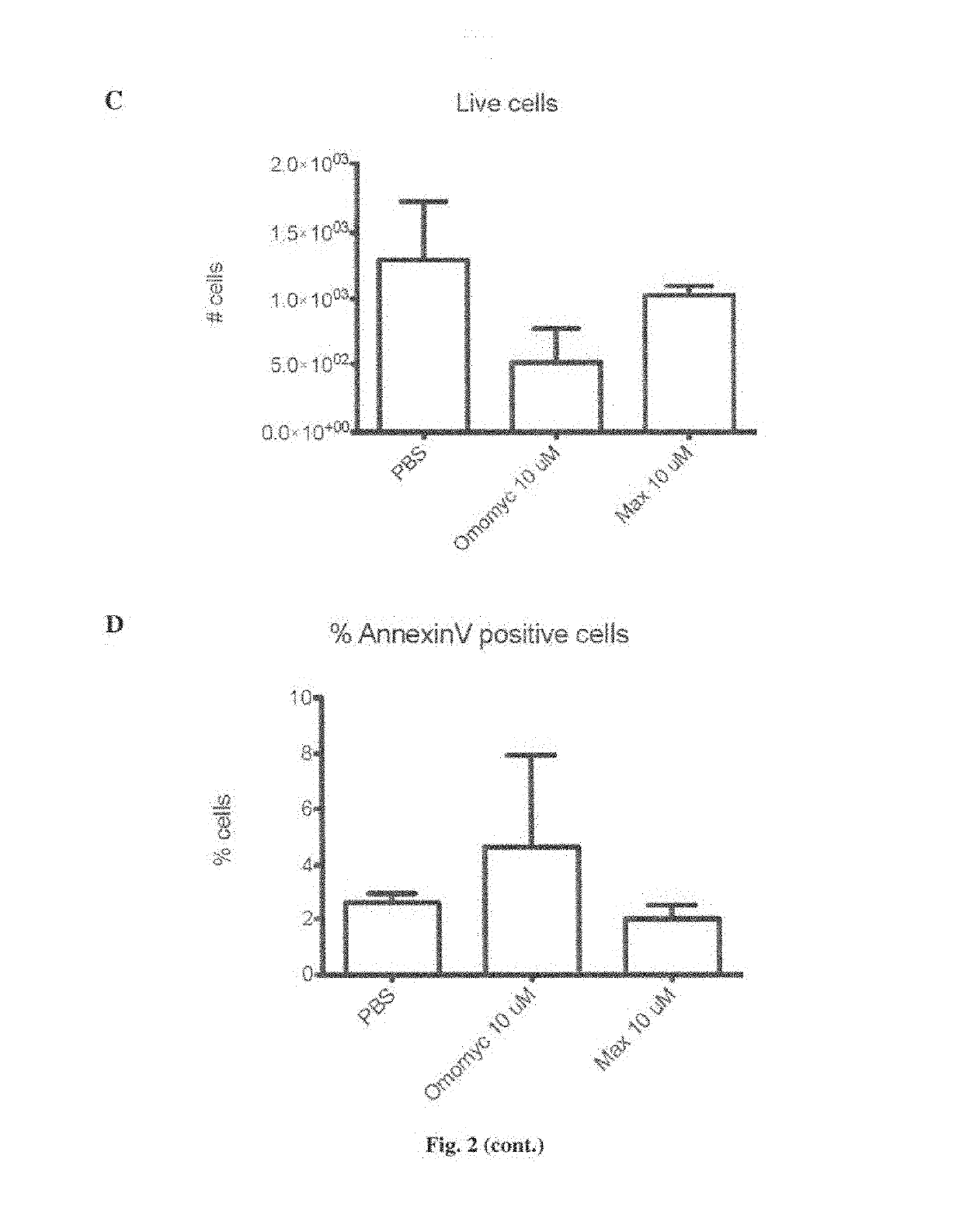
The invention relates to a Myc dominant negative mutant, called Omomyc, for use in medicine and for use in the prevention and / or treatment of cancer. The invention also refers to a fusion protein comprising Omomyc and pharmaceutical composition thereof and their use in medicine and, in particular, for treatment of cancer.
Owner:FUNDACIO PRIVADA INST DINVESTIGACIO ONCOLOGICA DE VALL DHEBRON (VHIO)
Method of efficiently establishing induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS9447408B2Improve setup efficiencyEfficient productionMutant preparationArtificially induced pluripotent cellsNuclear reprogrammingIsrapafant
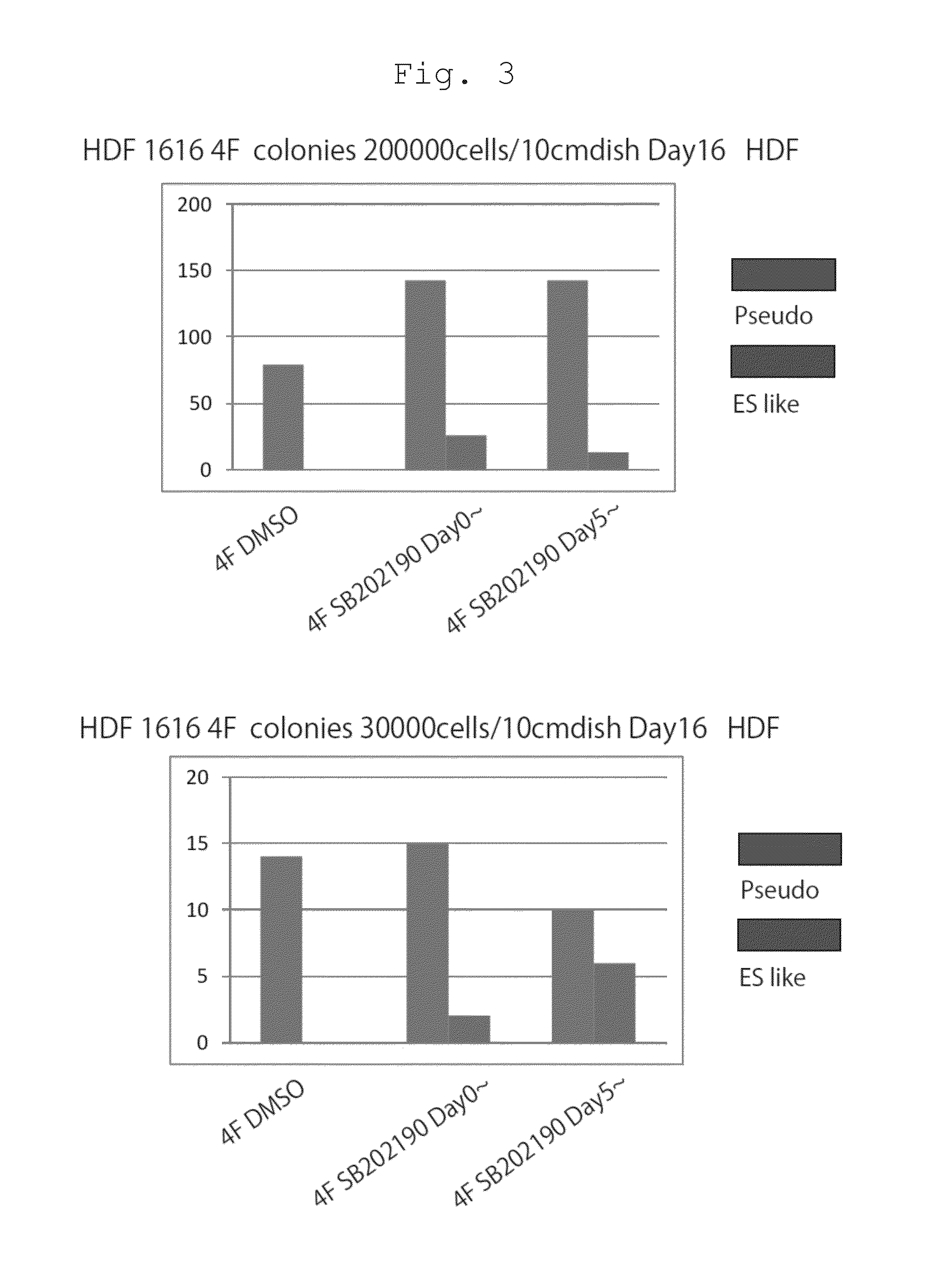
The present invention provides a method of improving the efficiency of establishment of induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells by inhibiting p38 function in the step of somatic cell nuclear reprogramming. The 38 function can be inhibited by bringing an inhibitor selected from the group consisting of (1) a chemical inhibitor of p38 (2) a dominant negative mutant of p38 or a nucleic acid that encodes the same, (3) a nucleic acid selected from the group consisting of siRNAs and shRNAs targeted to p38 and DNAs that encode the same and (4) an inhibitor of p38 pathway into contact with a somatic cell and the like. The present invention also provides an agent for improving the efficiency of establishment of induced pluripotent stem cells, which contains an inhibitor of p38 function, particularly an inhibitor selected from the group consisting of (1) a chemical inhibitor of p38 (2) a dominant negative mutant of p38 or a nucleic acid that encodes the same, (3) a nucleic acid selected from the group consisting of siRNAs and shRNAs targeted to p38 and DNAs that encode the same and (4) an inhibitor of p38 pathway. Moreover, the present invention provides a production method of iPS cells, which includes bringing a nuclear reprogramming substance and an inhibitor of p38 function into contact with a somatic cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Method of efficiently establishing induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20130183759A1Improve setup efficiencyLow establishment efficiencyMutant preparationCell culture active agentsNuclear reprogrammingIsrapafant
The present invention provides a method of improving the efficiency of establishment of induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells by inhibiting p38 function in the step of somatic cell nuclear reprogramming. The p38 function can be inhibited by bringing an inhibitor selected from the group consisting of (1) a chemical inhibitor of p38 (2) a dominant negative mutant of p38 or a nucleic acid that encodes the same, (3) a nucleic acid selected from the group consisting of siRNAs and shRNAs targeted to p38 and DNAs that encode the same and (4) an inhibitor of p38 pathway into contact with a somatic cell and the like. The present invention also provides an agent for improving the efficiency of establishment of induced pluripotent stem cells, which contains an inhibitor of p38 function, particularly an inhibitor selected from the group consisting of (1) a chemical inhibitor of p38 (2) a dominant negative mutant of p38 or a nucleic acid that encodes the same, (3) a nucleic acid selected from the group consisting of siRNAs and shRNAs targeted to p38 and DNAs that encode the same and (4) an inhibitor of p38 pathway. Moreover, the present invention provides a production method of iPS cells, which includes bringing a nuclear reprogramming substance and an inhibitor of p38 function into contact with a somatic cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Methods and compositions for the treatment of cancer
ActiveUS10370434B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsCancer researchDominant-Negative Mutant
The invention relates to a Myc dominant negative mutant, called Omomyc, for use in medicine and for use in the prevention and / or treatment of cancer. The invention also refers to a fusion protein comprising Omomyc and pharmaceutical composition thereof and their use in medicine and, in particular, for treatment of cancer.
Owner:FUNDACIO PRIVADA INST DINVESTIGACIO ONCOLOGICA DE VALL DHEBRON (VHIO)
Methods for treating osteoporosis with anti-IL-20 receptor antibodies
Treating a disorder (e.g., osteoporosis, renal failure, or diabetic nephropathy) associated with a signaling pathway mediated by IL-20 receptor with an agent that suppresses IL-20 receptor activity, e.g., an antibody that neutralizes IL-20 receptor via binding to IL-20R1, an antisense nucleic acid that suppresses expression of IL-20R1, a small molecule that inhibits IL-20 receptor activity, or a dominant negative mutant of IL-19, IL-20, or IL-24.
Owner:LBL BIOTECH INC
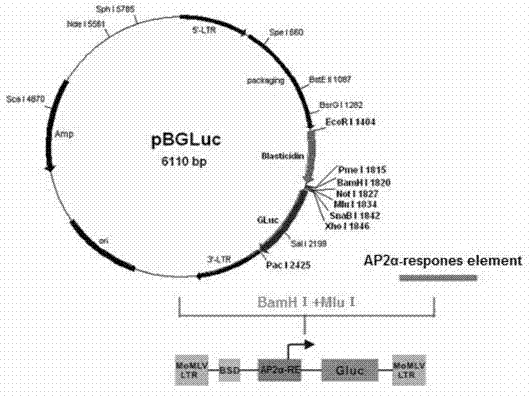
Reporter gene carrier for detecting activity of AP2alpha transcription factor
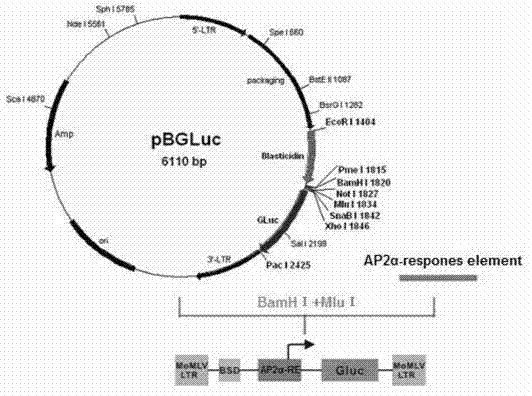
InactiveCN103305550AReliable detection methodActivity downregulationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationTranscription factor activityNucleotide
The invention provides a reporter gene carrier which comprises an AP2alpha specific cis acting element. The carrier is characterized in that the AP2alpha specific cis acting element consists of four GCCCGCGG nucleotide sequences connected in series, wherein the four GCCCGCGG nucleotide sequences are connected in series through a nucleotide sequence TT. The reporter gene carrier designed by the invention is easy to prepare, simple to operate and good in repeatability, and can effective transfect different mammalian cells. The carrier is more accurate and reliable than EMSA (Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay) when is used to detect activity change of a dominant negative mutant-mediated transcription factor. The carrier is suitable for in vitro study of biological activity of the AP2alpha transcription factor in various mammalian cells.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIV
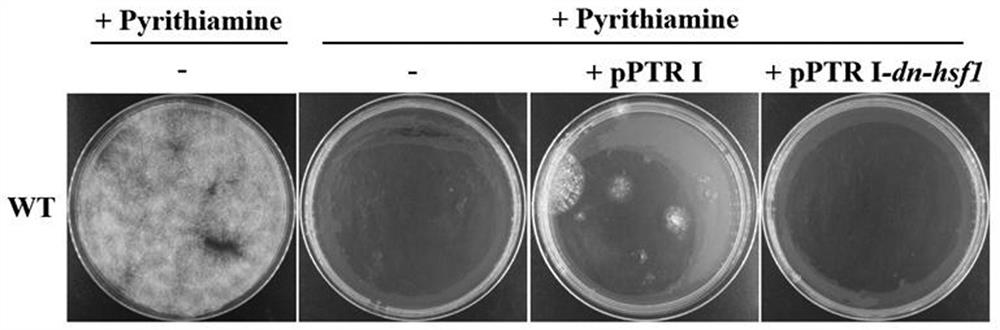
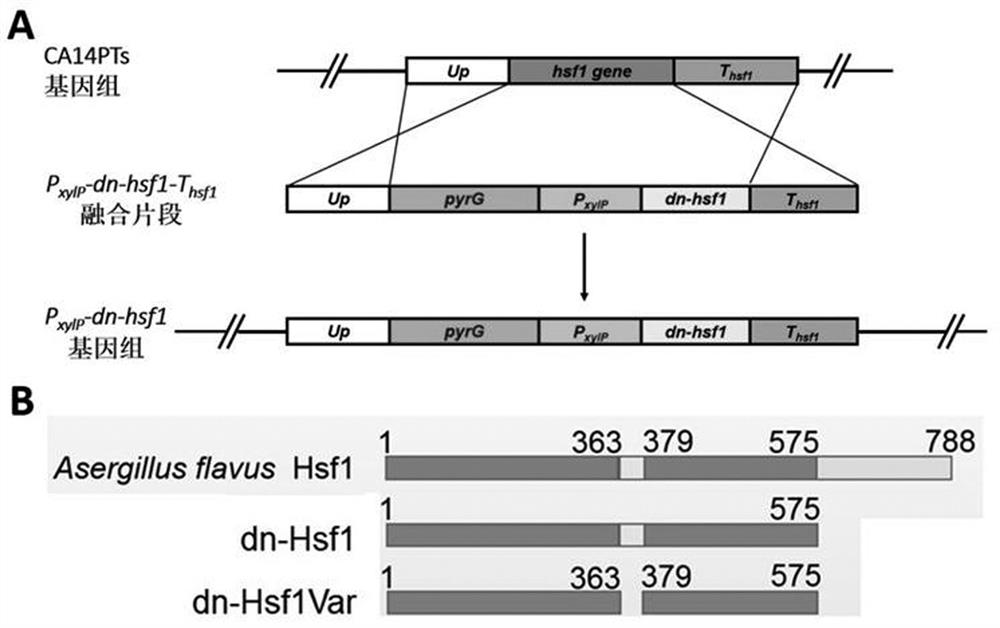
A dominant negative effect mutant of heat shock transcription factor 1 and its application
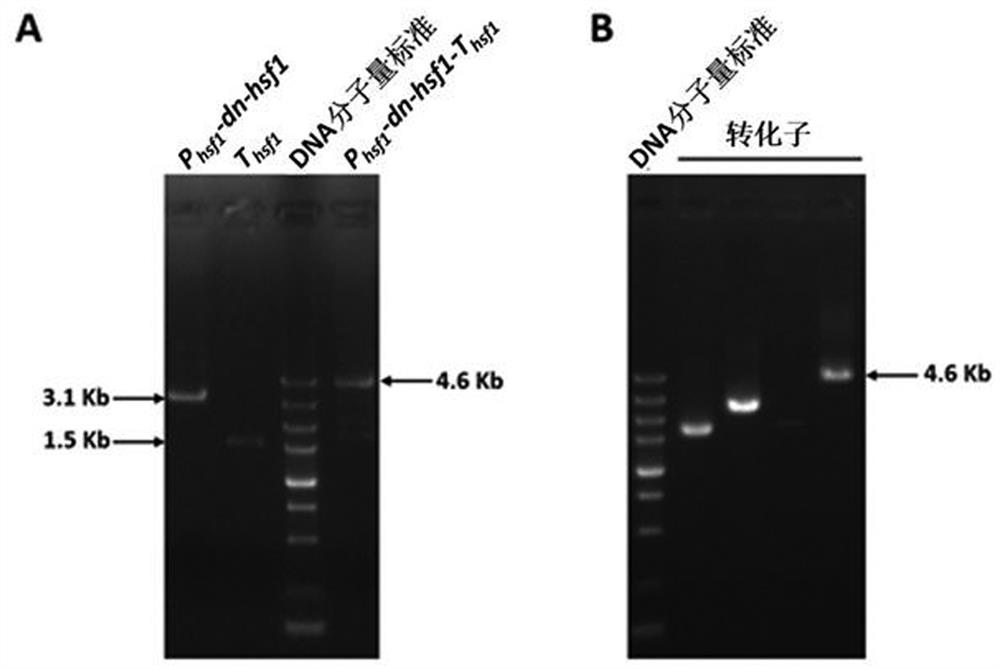
ActiveCN111087454BGrowth inhibitionLow homologyFungiAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleotideAspergillus flavus
The invention discloses a heat shock transcription factor 1 dominant negative effect mutant dn-Hsf1 and its application, belonging to the field of biotechnology. Human and A. flavus ( Aspergillus flavus ) in the heat shock transcription factor 1 HSF1 protein, and a total of 213 amino acid residues from the 576th to the 788th position of the C-terminal of the Aspergillus flavus Hsf1 protein were deleted to obtain the heat shock transcription factor 1 dominant negative mutant dn in Aspergillus flavus The amino acid sequence of the -Hsf1 protein is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the coding nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The dominant-negative mutant dn-Hsf1 can inhibit the function of normal Hsf1 in fungi, thereby inhibiting the growth of fungi, and is used in the prevention and control of fungal pollution.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
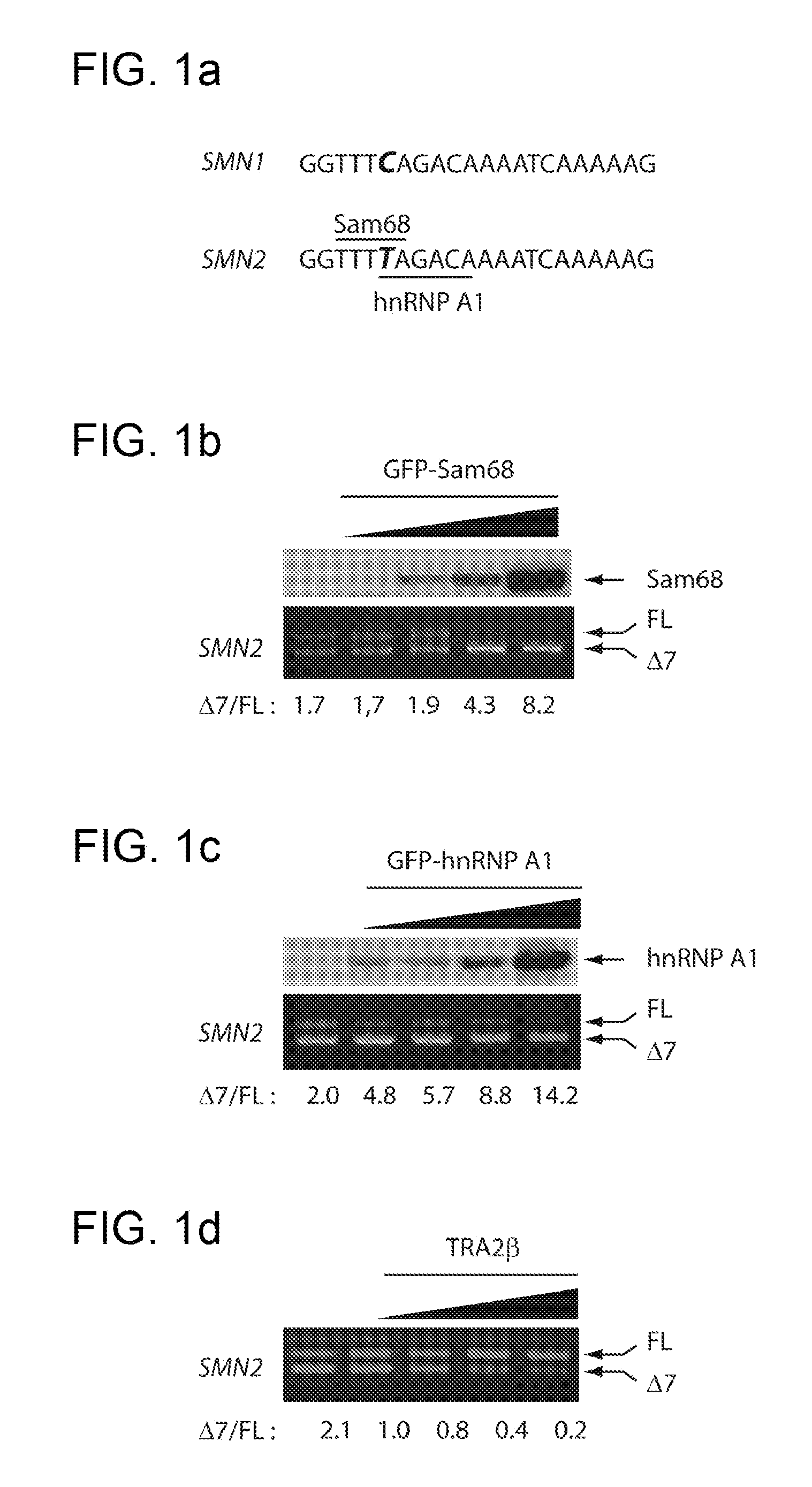
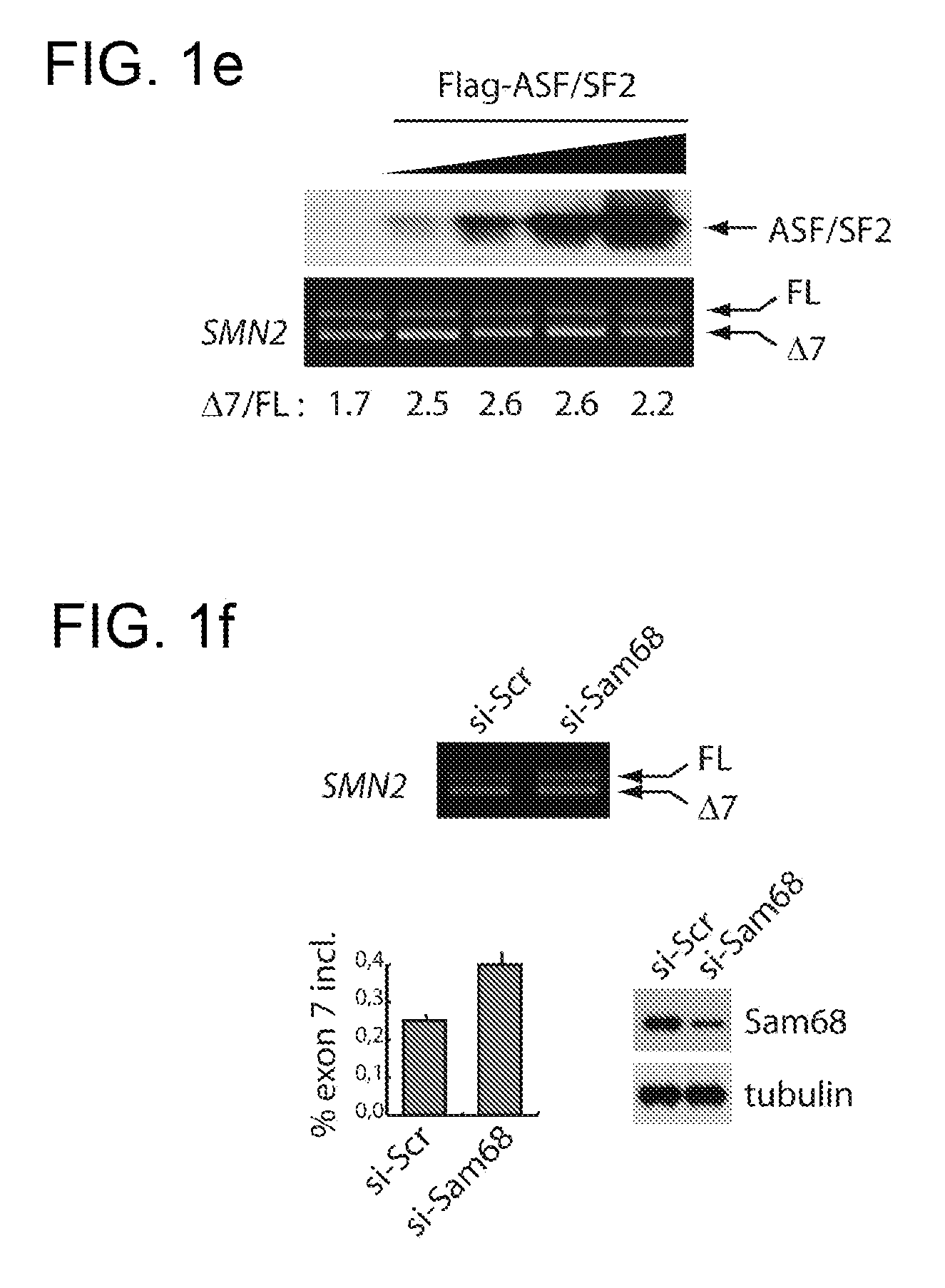
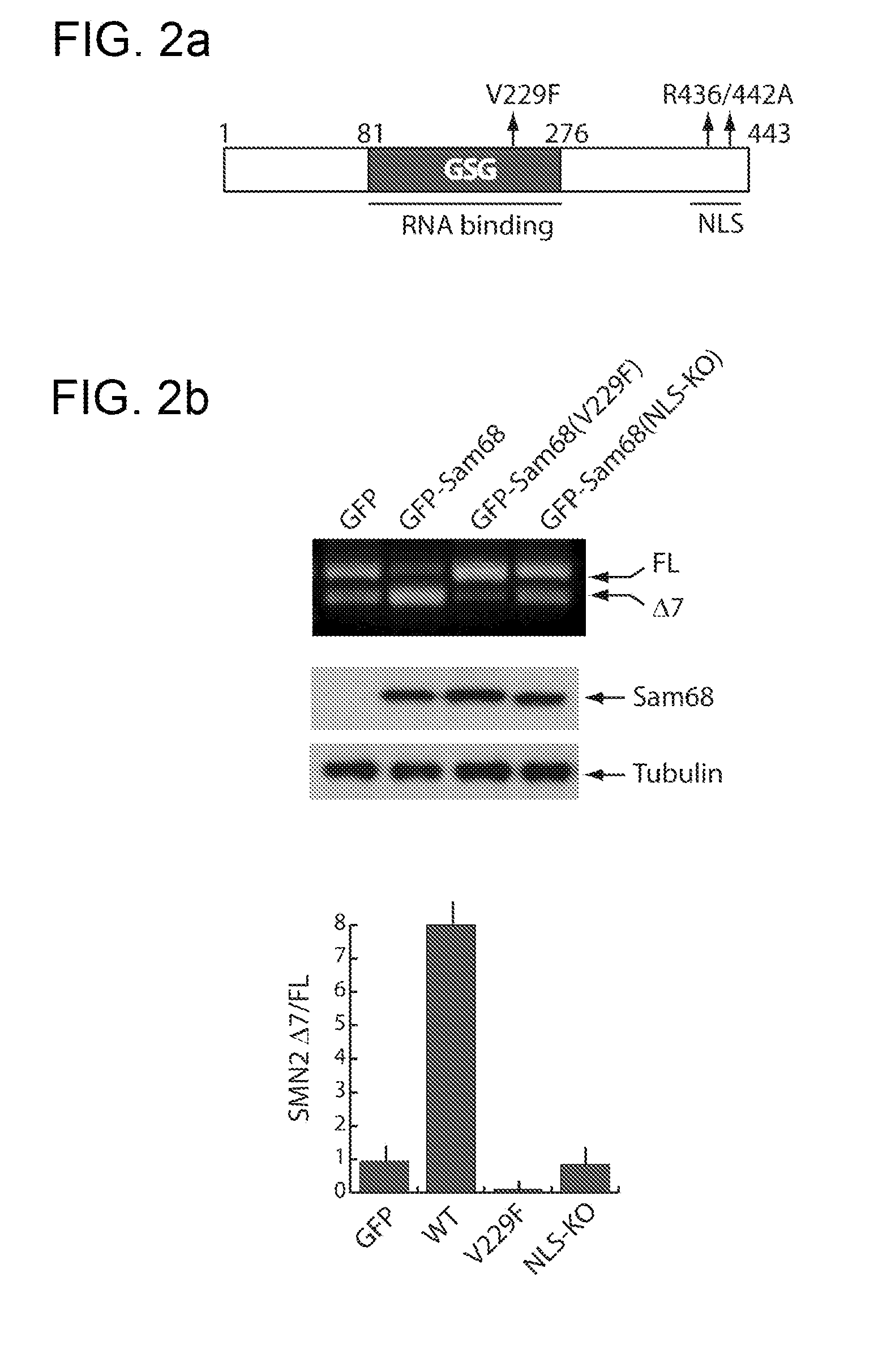
Dominant negative mutants of sam68 for use in the treatment of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA)
InactiveUS20120071415A1Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDominant-Negative MutantDominant negative
The present invention relates to the use of dominant negative mutants of Sam68 for the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment of spinal muscular atrophy, to nucleic acids coding for such mutants and to vectors and methods related thereto.
Owner:FOND SANTA LUCIA
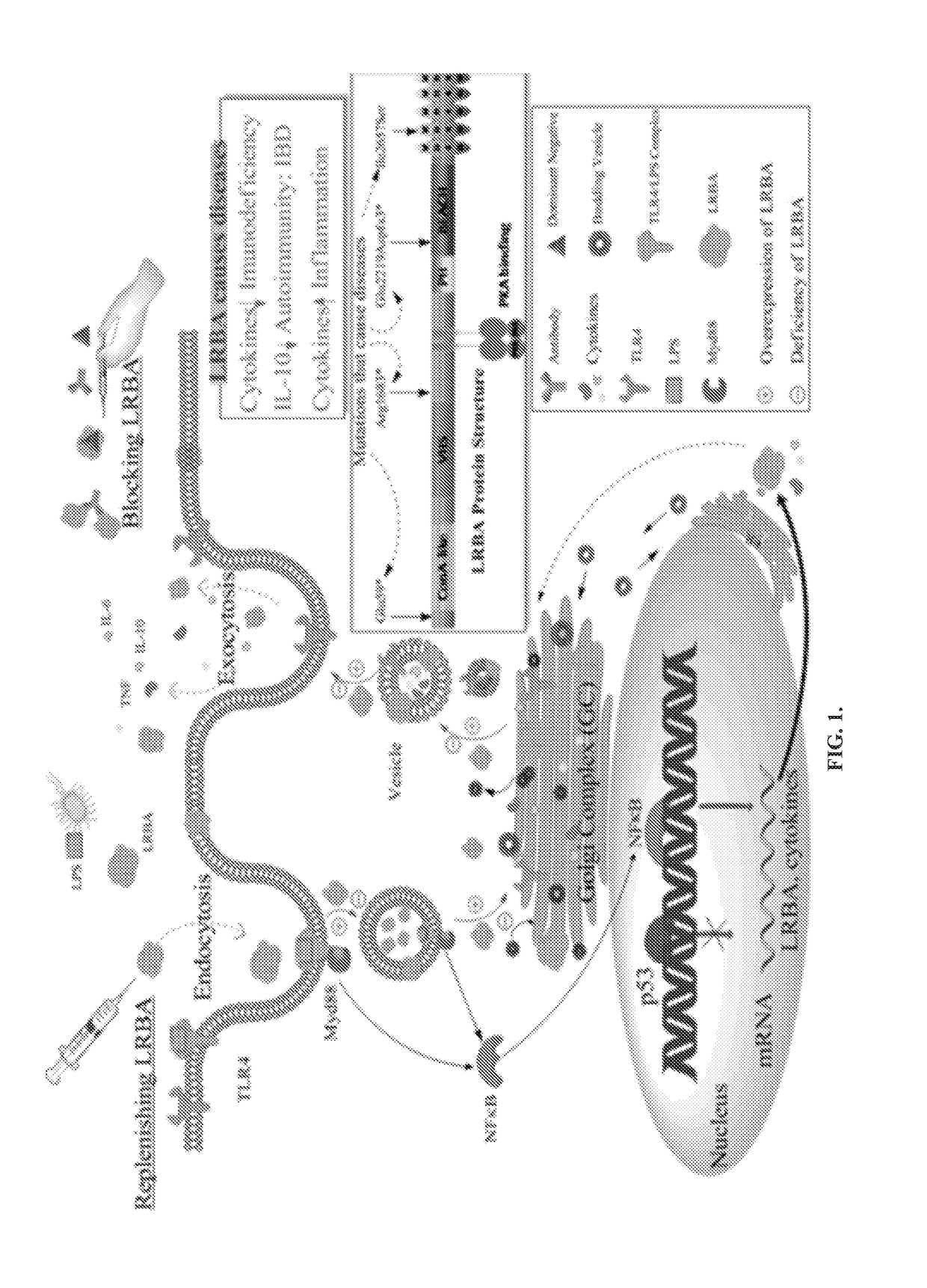
Inflammatory disease diagnosis and methods of treatment using lipopolysaccharide-responsive beige-like anchor
ActiveUS20180002413A1Risk of hospitalization for infectionPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansLRBAAutoimmune responses
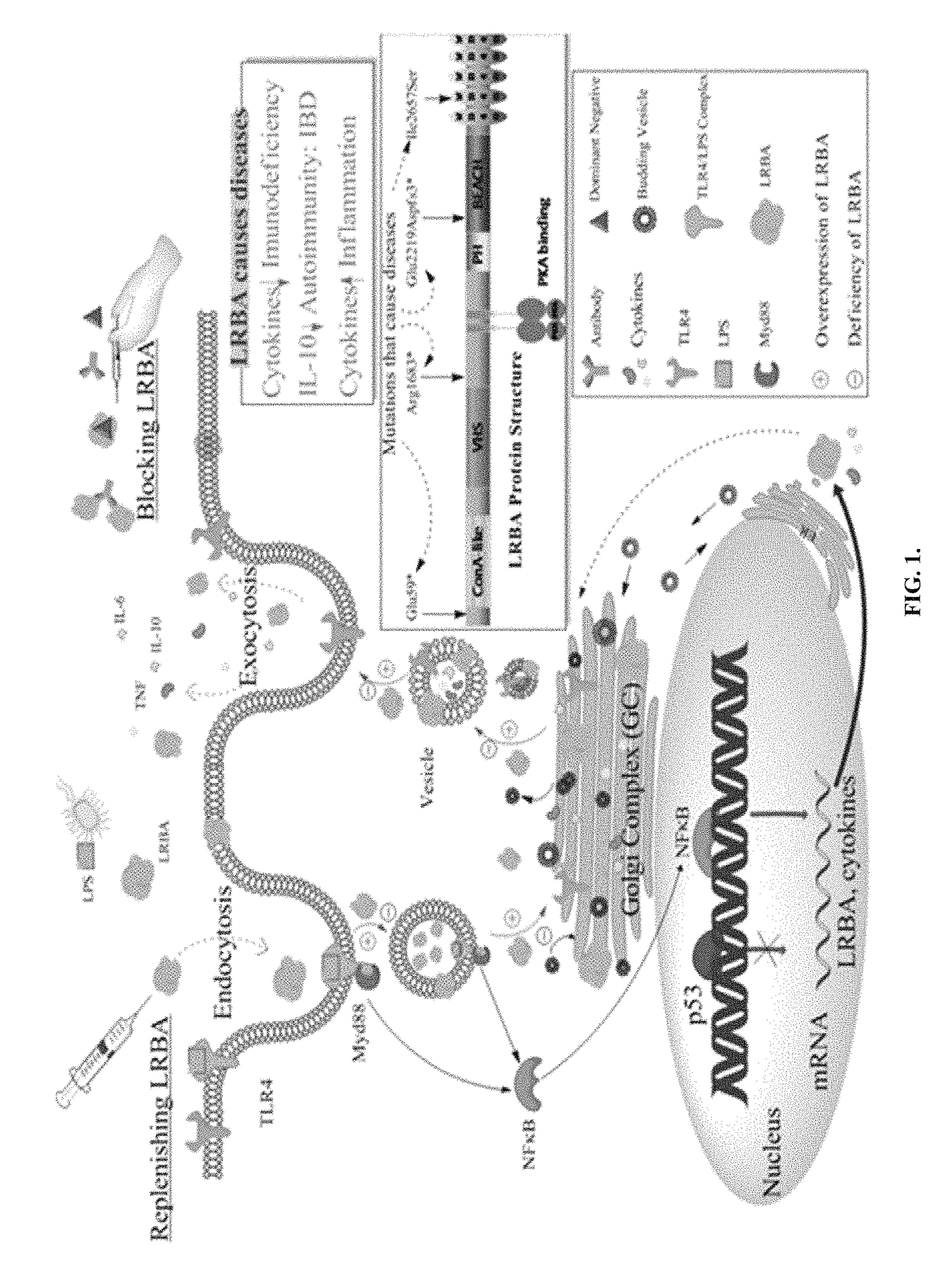
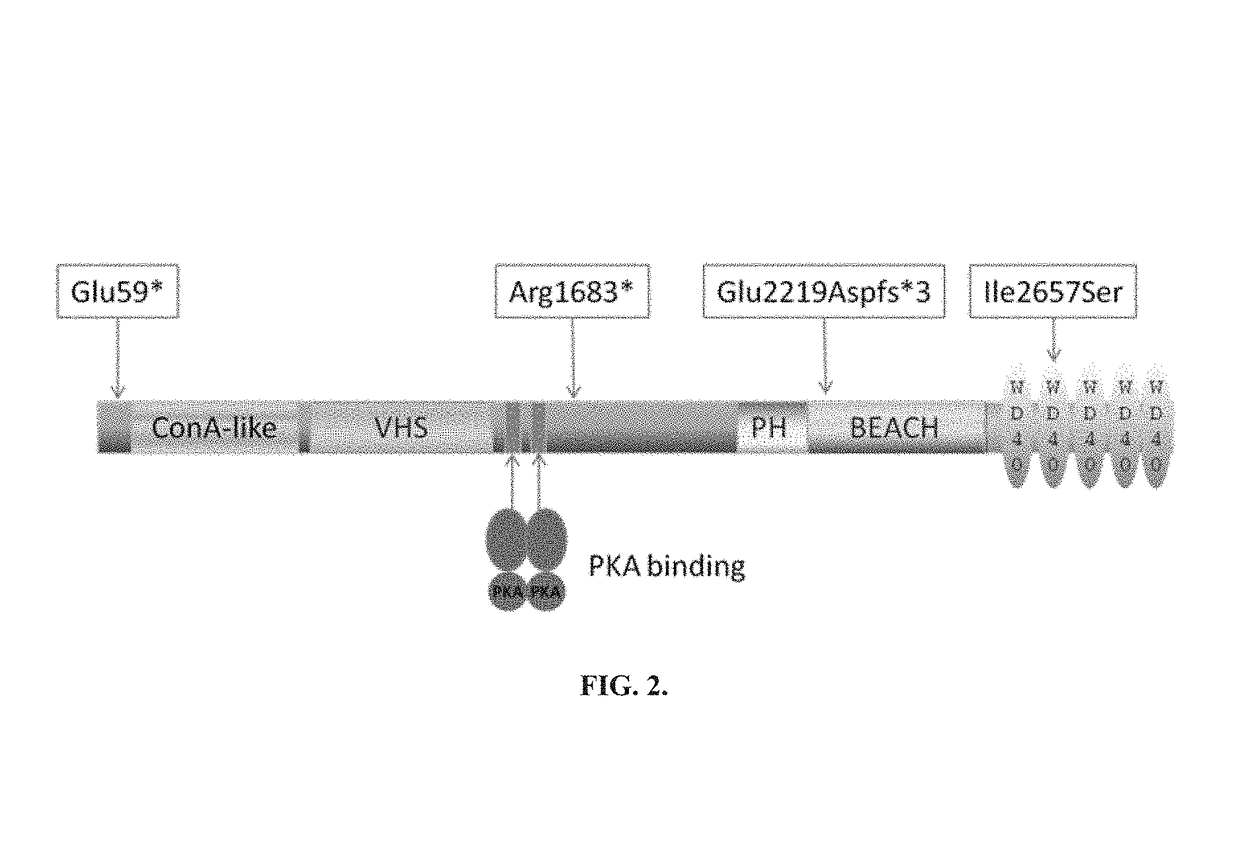
Anti-cytokine therapy has revolutionized immunological disease treatment, but is not always effective and subject to treatment resistance as the cytokine cascade is highly redundant and multiple cytokines are involved in inflammation. Targeting a critical common regulator of inflammatory effectors is desirable. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-responsive beige-like anchor (LRBA) is a master regulator of multiple genes important for inflammation. Subcellular localization shows that LRBA translocated to the nucleus upon LPS stimulation and colocalized with multiple proteins associated with the endosome membrane system, indicating a critical role in membrane / vesicle trafficking essential for deposition, secretion and signal transduction of immune effectors. Deregulation, deficiency, down-regulation and overexpression of LRBA causes defective trafficking and signaling of immune effector molecules, resulting in immunodeficiency and autoimmunity diseases associated with a broader spectrum of severe symptoms when compared to other CVID genes. Modulating LRBA through antibodies, dominant negative mutants, or small interference RNA can be used to treat inflammatory diseases.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
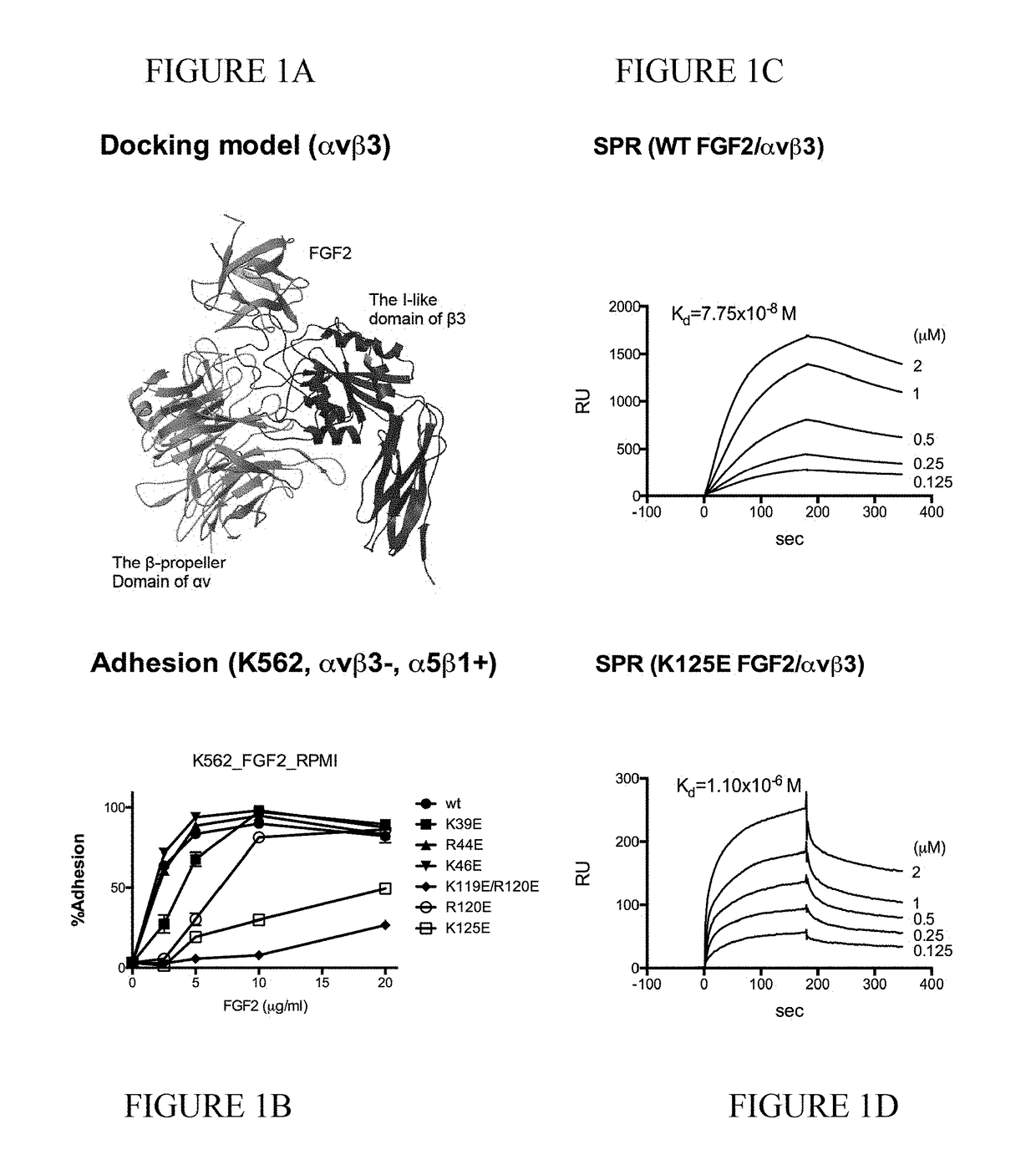
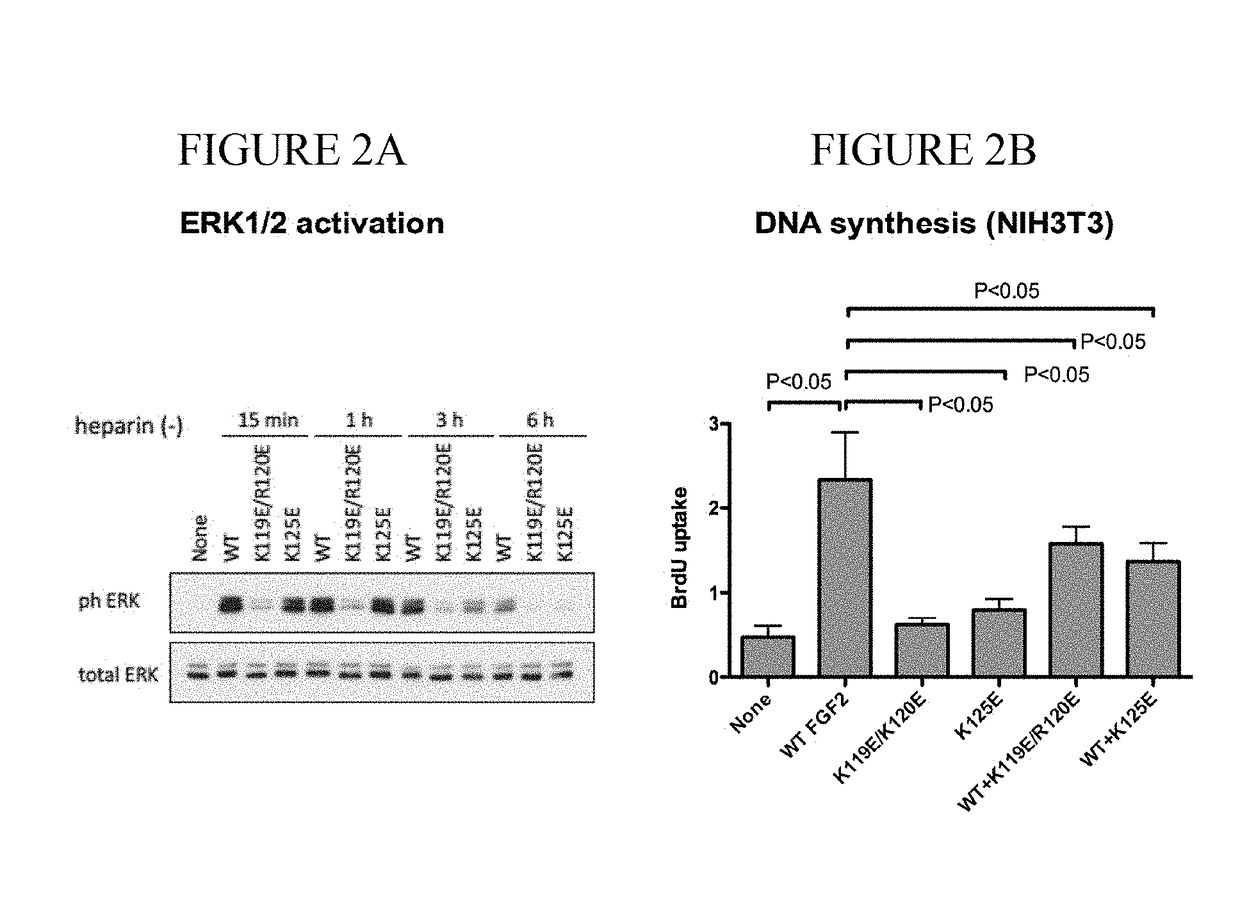
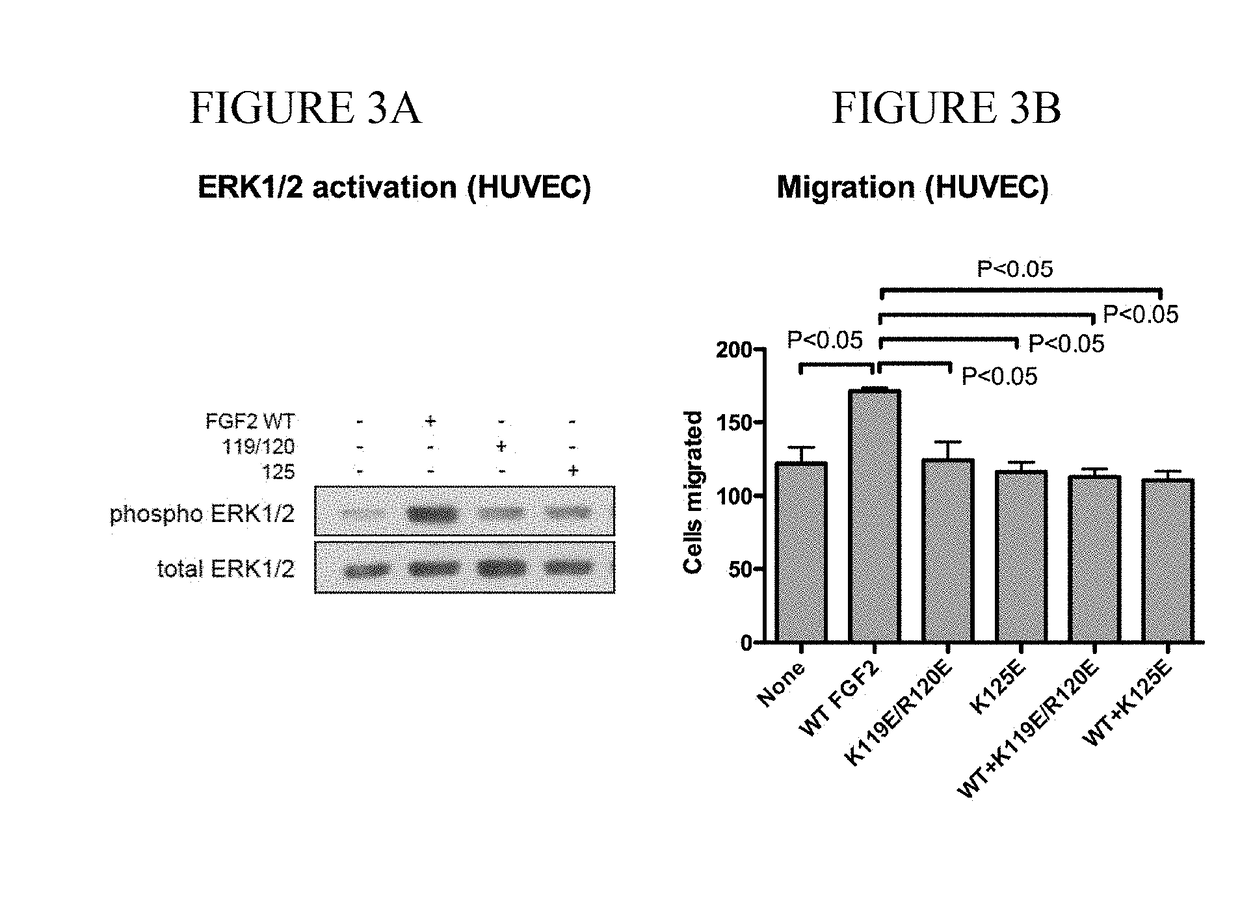
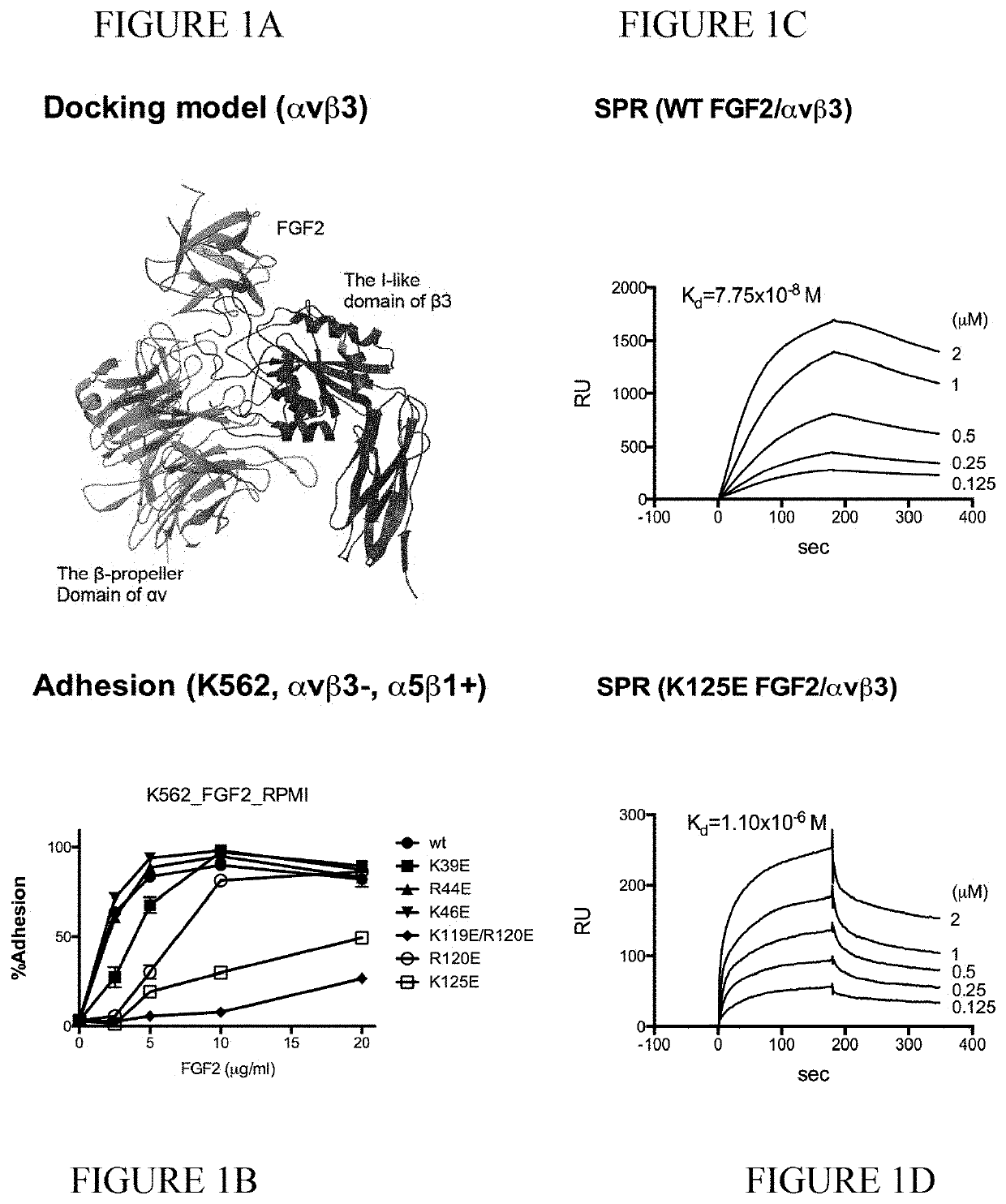
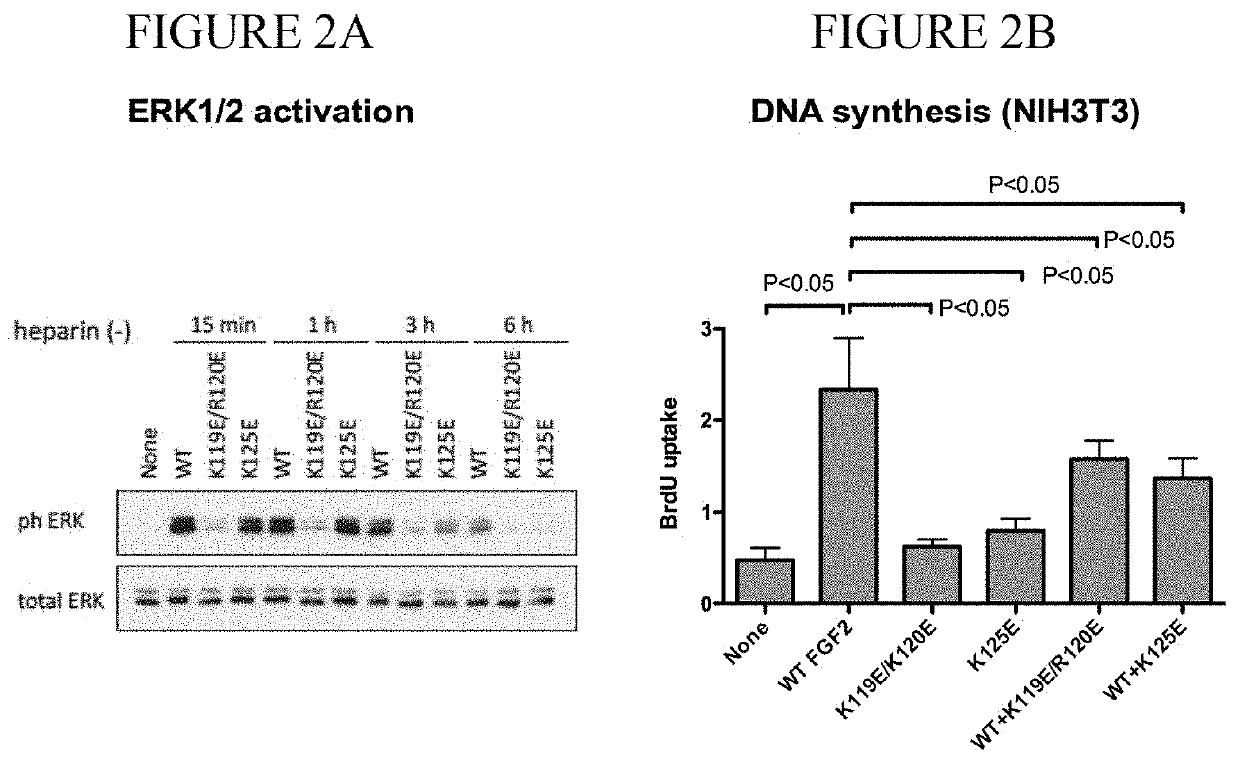
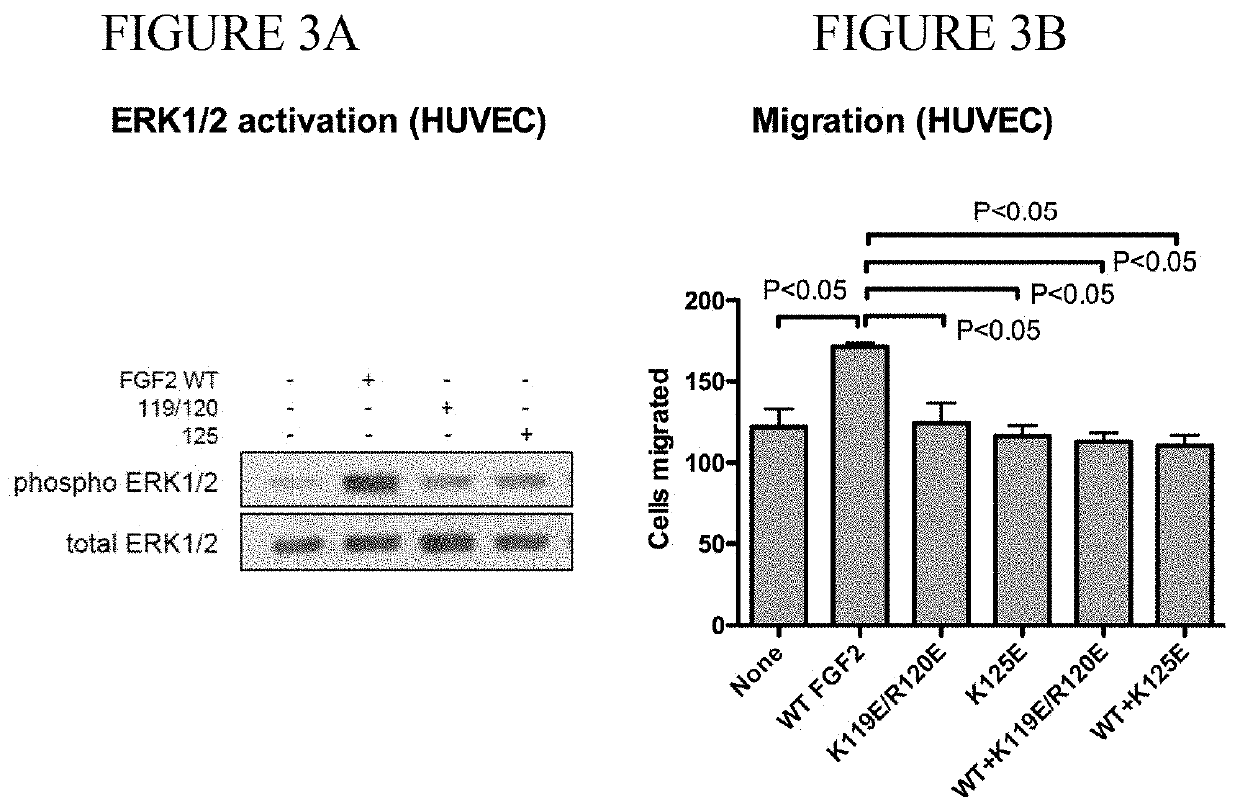
Dominant-negative fgf2 antagonists
ActiveUS20190015478A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiochemistryDominant-Negative Mutant
The present invention provides dominant negative mutants of FGF2 for suppressing FGF-mediated cellular signaling. Related compositions, methods, and kits are disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Genetically modified plant capable of biosynthesizing capsinoid
ActiveUS9340795B2Increase productionClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesGMO PlantsCapsazepine
The present invention provides a genetically modified plant that biosynthesizes an increased amount of capsinoids, a method of producing the genetically modified plant, and a production method of capsinoids from the genetically modified plant. More particularly, the present invention provides a genetically modified plant capable of producing capsinoids, which shows a decreased expression or activity of an enzyme that catalyzes an amino group conversion reaction from vanillin to vanillylamine as compared to wild strains, and the like. As a method of suppressing expression or activity of an enzyme, an introduction of DNA encoding an antisense RNA, iRNA, ribozyme or dominant-negative mutant for the target gene, a destruction of the gene by a knockout method, mutagen treatment or transposon insertion, an introduction of a gene encoding an antibody against the enzyme and the like can be mentioned.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
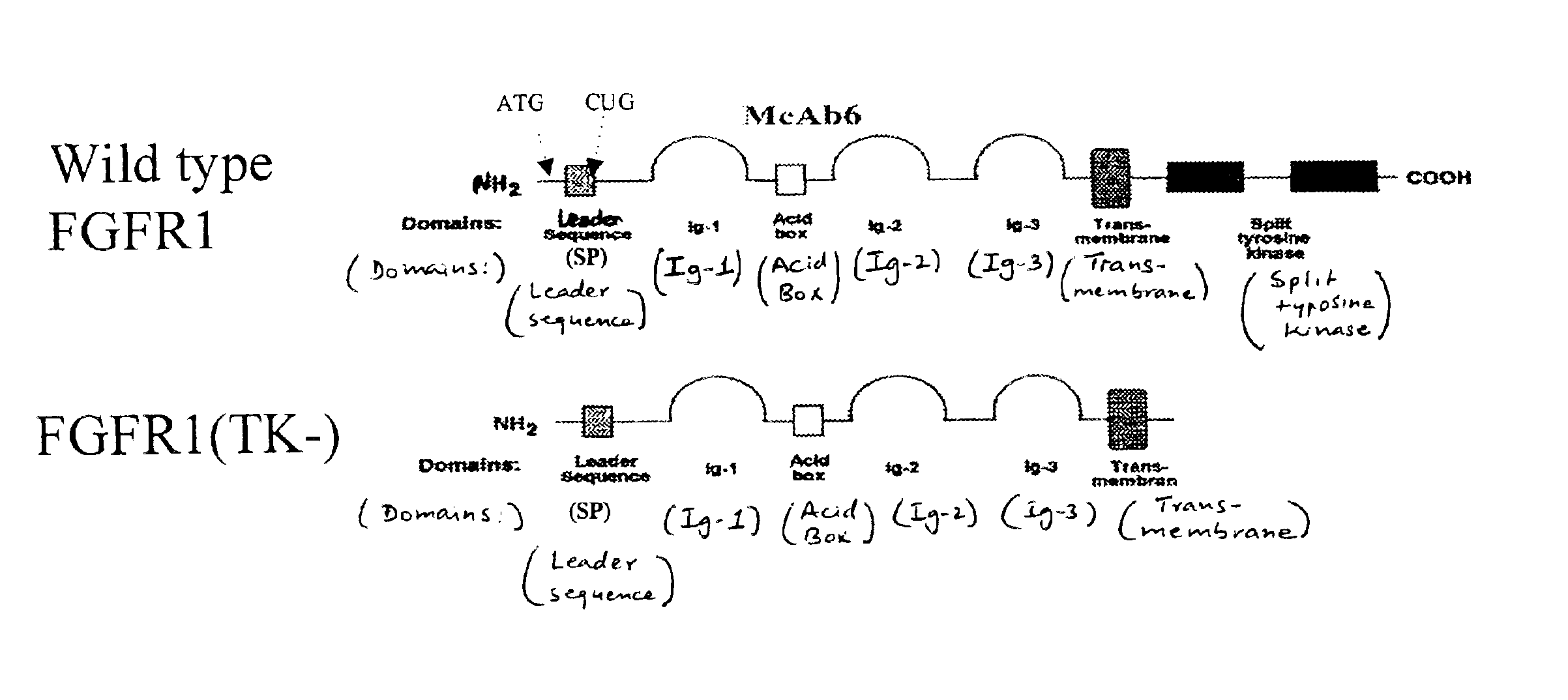
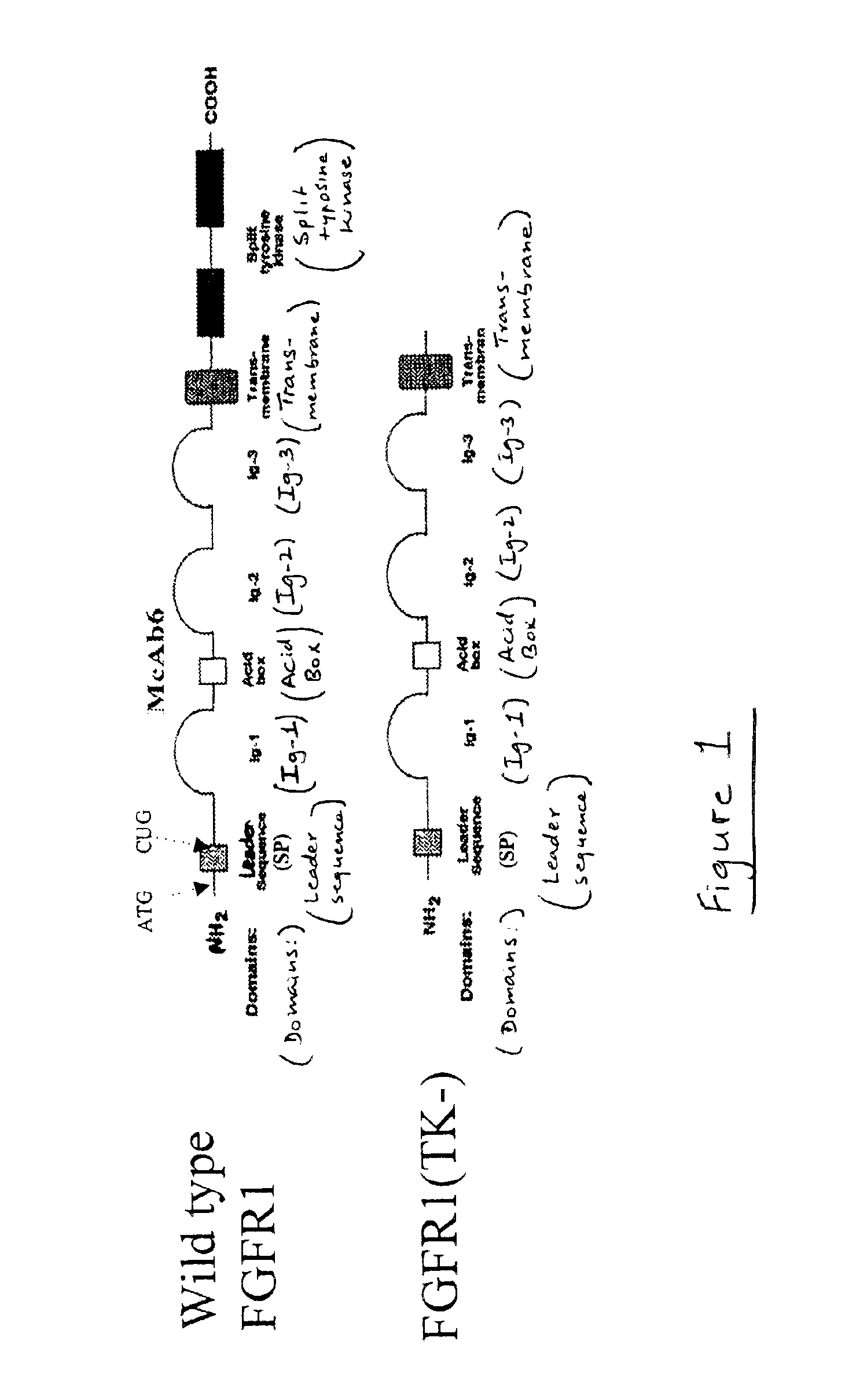
Rodent model for Parkinson's Disease
InactiveUS6878858B2Genetic material ingredientsCarbohydrate active ingredientsRodent modelJuvenile parkinson's disease
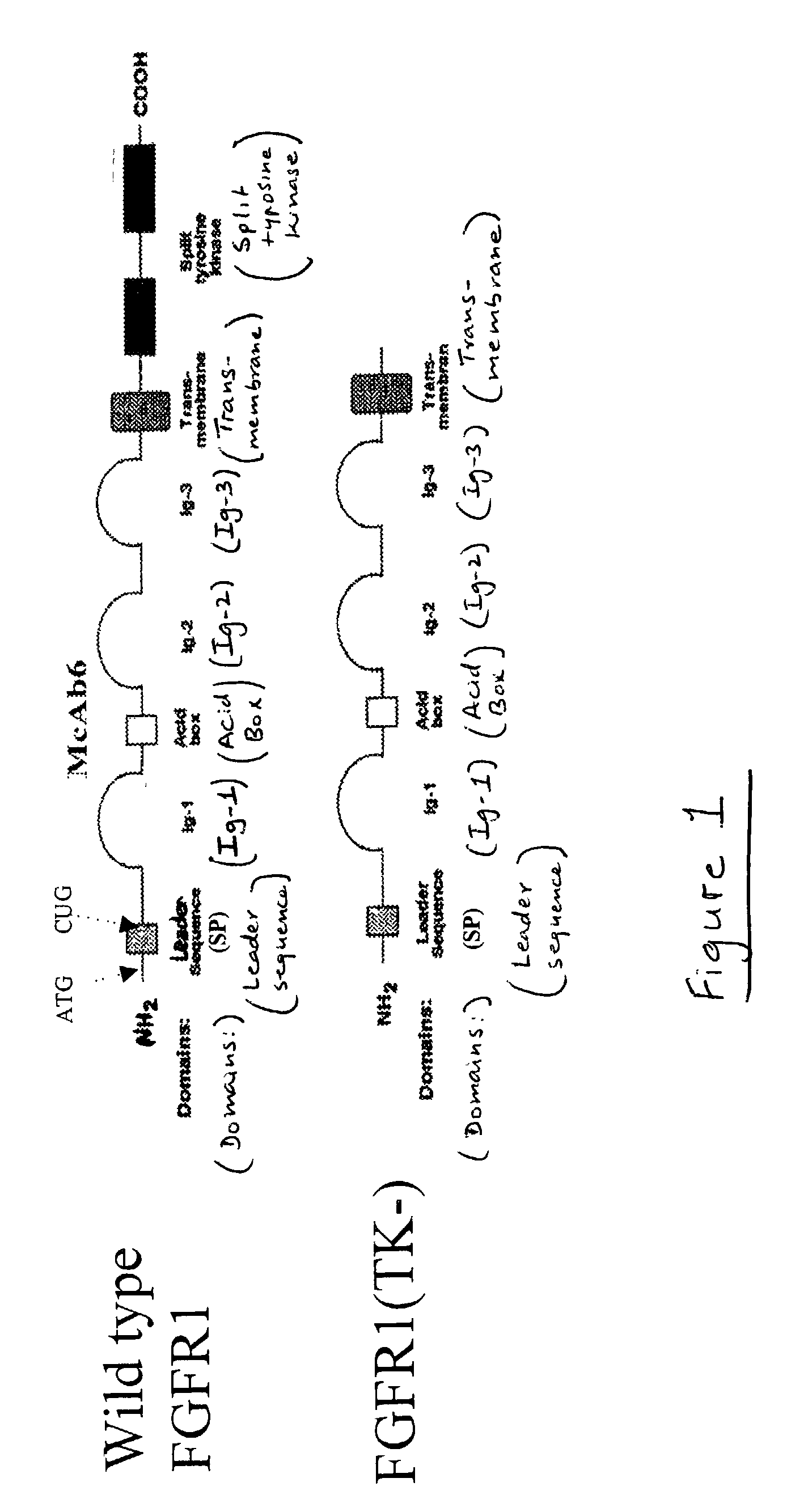
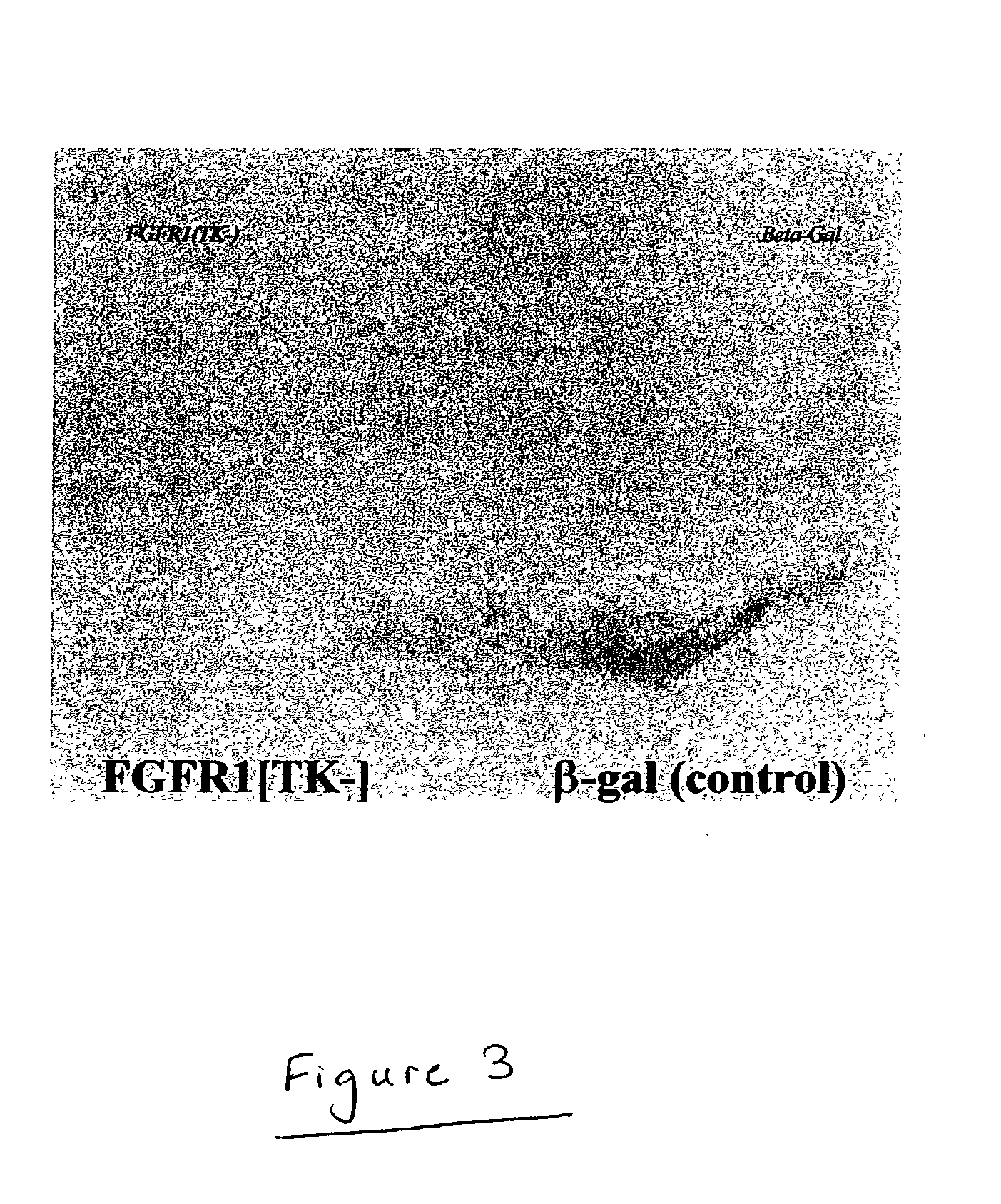
The present invention provides an animal model for Parkinson's Disease and a method for generating such a model. The method comprises the steps of transfecting dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra with a dominant negative mutant of FGFR1 with deleted tyrosine kinase domain. The animals are characterized by a reduction in the number of tyrosine hydroxylase neurons in the SNc area.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Dominant-negative FGF2 antagonists
The present invention provides dominant negative mutants of FGF2 for suppressing FGF-mediated cellular signaling. Related compositions, methods, and kits are disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
A kind of avirulent live anthrax vaccine and avirulent anthrax strain
Owner:ICDC CHINA CDC
Nontoxic anthrax live vaccine and nontoxic anthrax strain
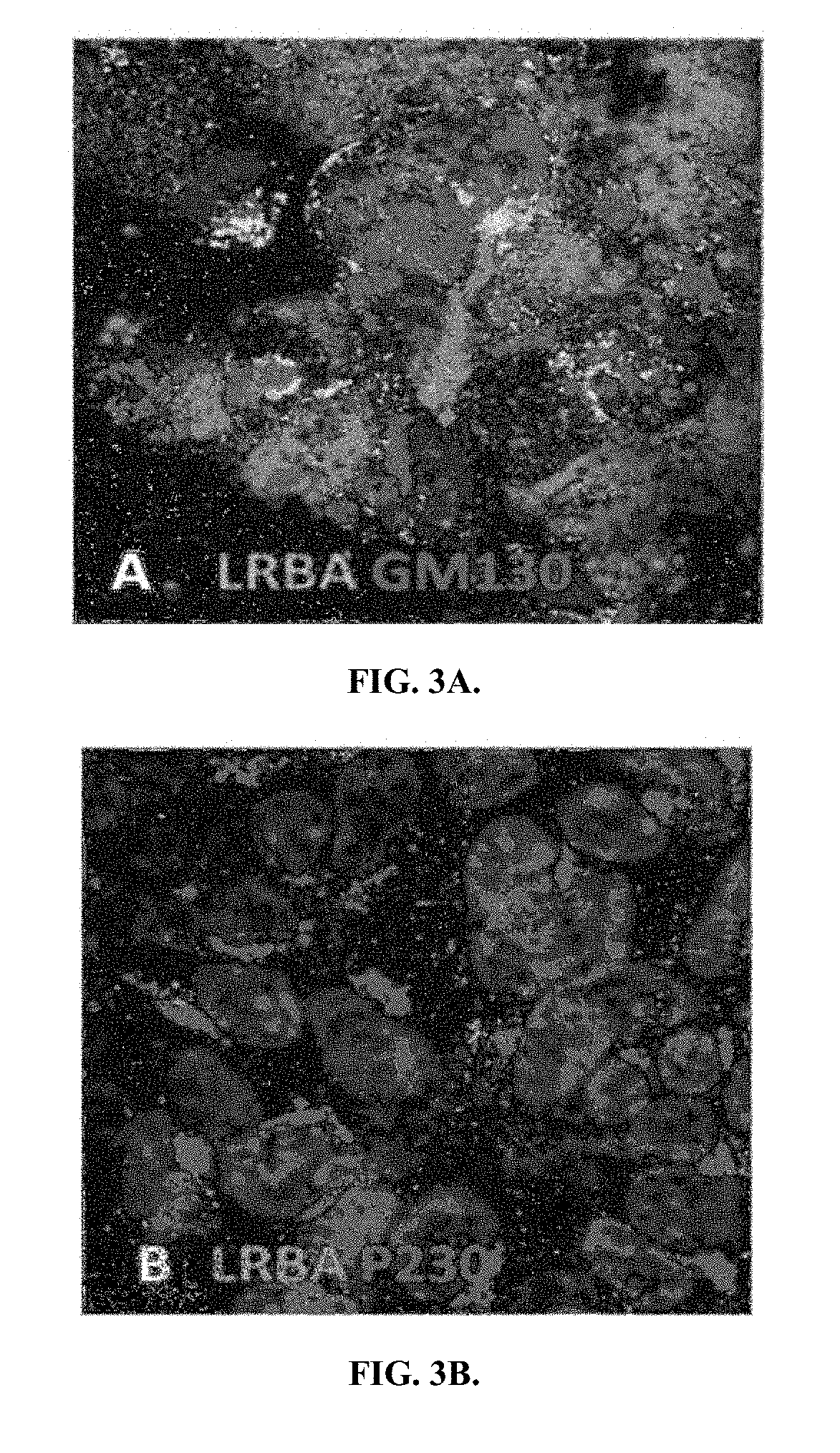
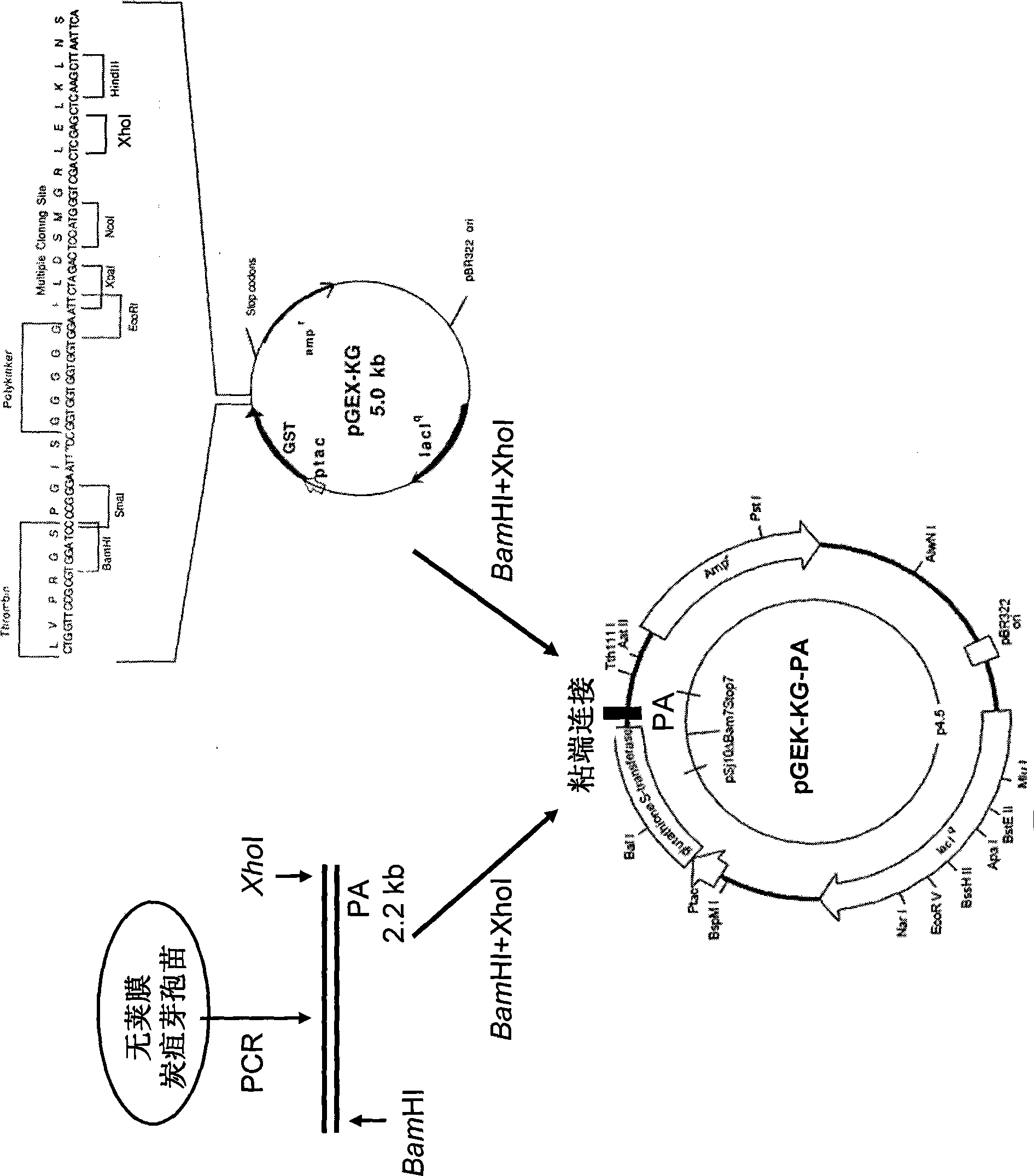
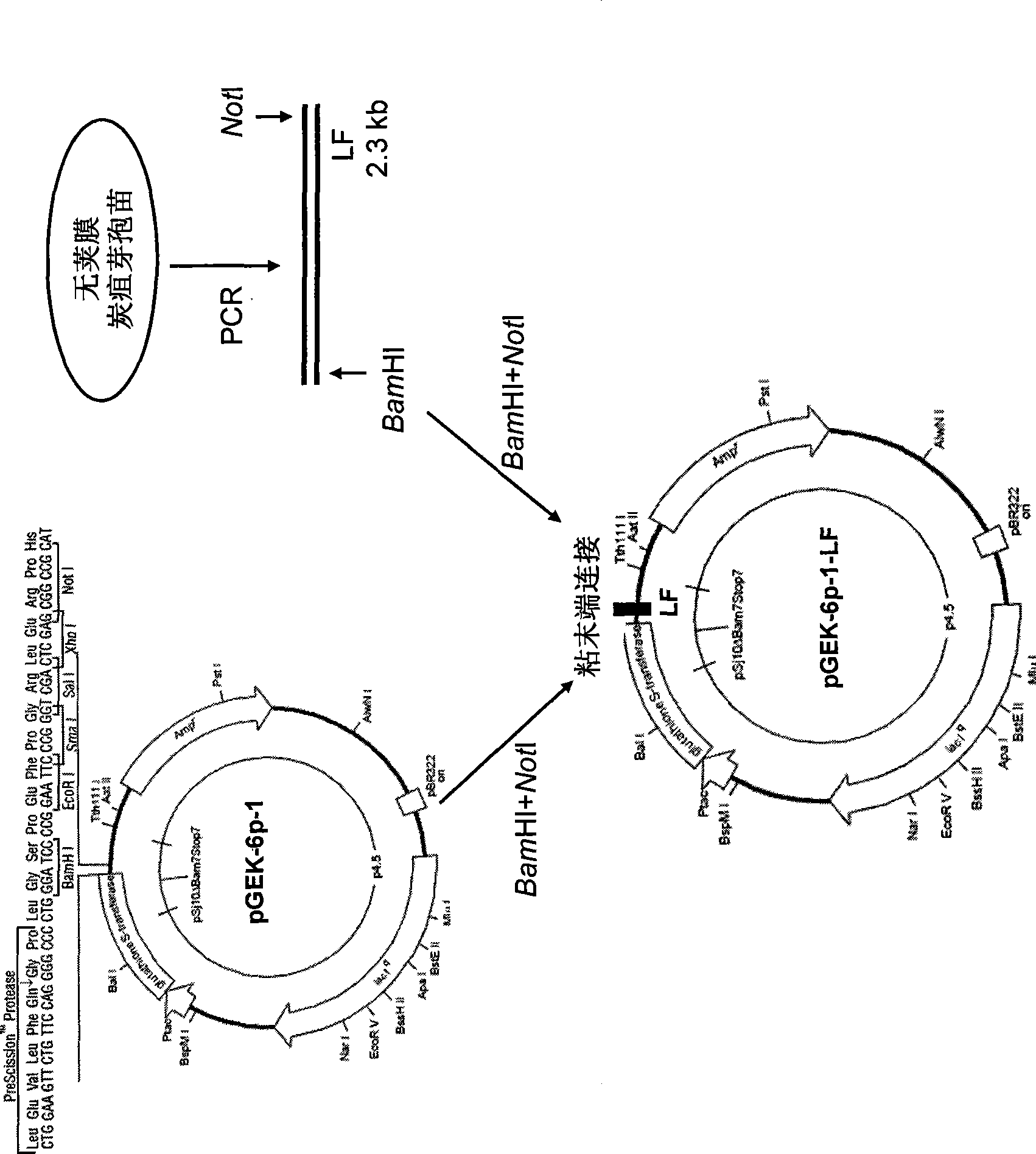
The invention provides a nontoxic anthrax live vaccine.The active ingredient of the nontoxic anthrax live vaccine includes a nontoxic anthrax strain for expressing anthrax protective antigen mutant protein (rPA).The nontoxic anthrax strain is obtained by performing locus mutation on pXO1 plasmid of an original Sterne vaccine strain, and locus mutation covers R178A and K197A double-locus mutants of a protective antigen.The live vaccine is prepared from the strain including the PA dominant negative mutants of the protective antigen, and has the advantages that the live vaccine loses the capability of being combined with lethal factors and edema factors, toxins cannot be generated, and it is proved that the immunogen of the live vaccine is not changed at all; meanwhile, biologically-inactivated rPA can be in competitive combination with cell receptors, and the purpose of neutralizing anthrax toxins can be achieved.The mutant strain completely loses the sporeforming function, the vaccine standard requirements for not harming operators and not causing environment pollution are met, subcutaneous injection and oral administration can be selected as administration routes, and the defect that a Sterne vaccine strain is not suitable for certain livestock due to large residual toxicity is overcome.
Owner:ICDC CHINA CDC
Animal model for parkinson's disease and method of making same
InactiveUS20030033620A1In-vivo testing preparationsReceptors for growth factors/regulatorsJuvenile parkinson's diseaseTyrosine hydroxylase
The present invention provides an animal model for Parkinson's Disease and a method for generating such a model. The method comprises the steps of transfecting dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra with a dominant negative mutant of FGFR1 with deleted tyrosine kinase domain. The animals are characterized by a reduction in the number of tyrosine hydroxylase neurons in the SNc area.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Inflammatory disease diagnosis and methods of treatment using lipopolysaccharides-responsive beige-like anchor
ActiveUS9738706B2Risk of hospitalization for infectionPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAutoimmune responsesImmunodeficiency
Anti-cytokine therapy has revolutionized immunological disease treatment, but is not always effective and subject to treatment resistance as the cytokine cascade is highly redundant and multiple cytokines are involved in inflammation. Targeting a critical common regulator of inflammatory effectors is desirable. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-responsive beige-like anchor (LRBA) is a master regulator of multiple genes important for inflammation. Subcellular localization shows that LRBA translocated to the nucleus upon LPS stimulation and colocalized with multiple proteins associated with the endosome membrane system, indicating a critical role in membrane / vesicle trafficking essential for deposition, secretion and signal transduction of immune effectors. Deregulation, deficiency, down-regulation and overexpression of LRBA causes defective trafficking and signaling of immune effector molecules, resulting in immunodeficiency and autoimmunity diseases associated with a broader spectrum of severe symptoms when compared to other CVID genes. Modulating LRBA through antibodies, dominant negative mutants, or small interference RNA can be used to treat inflammatory diseases.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Application of dominant negative mutant F427N as anthrax toxin inhibitor and vaccine
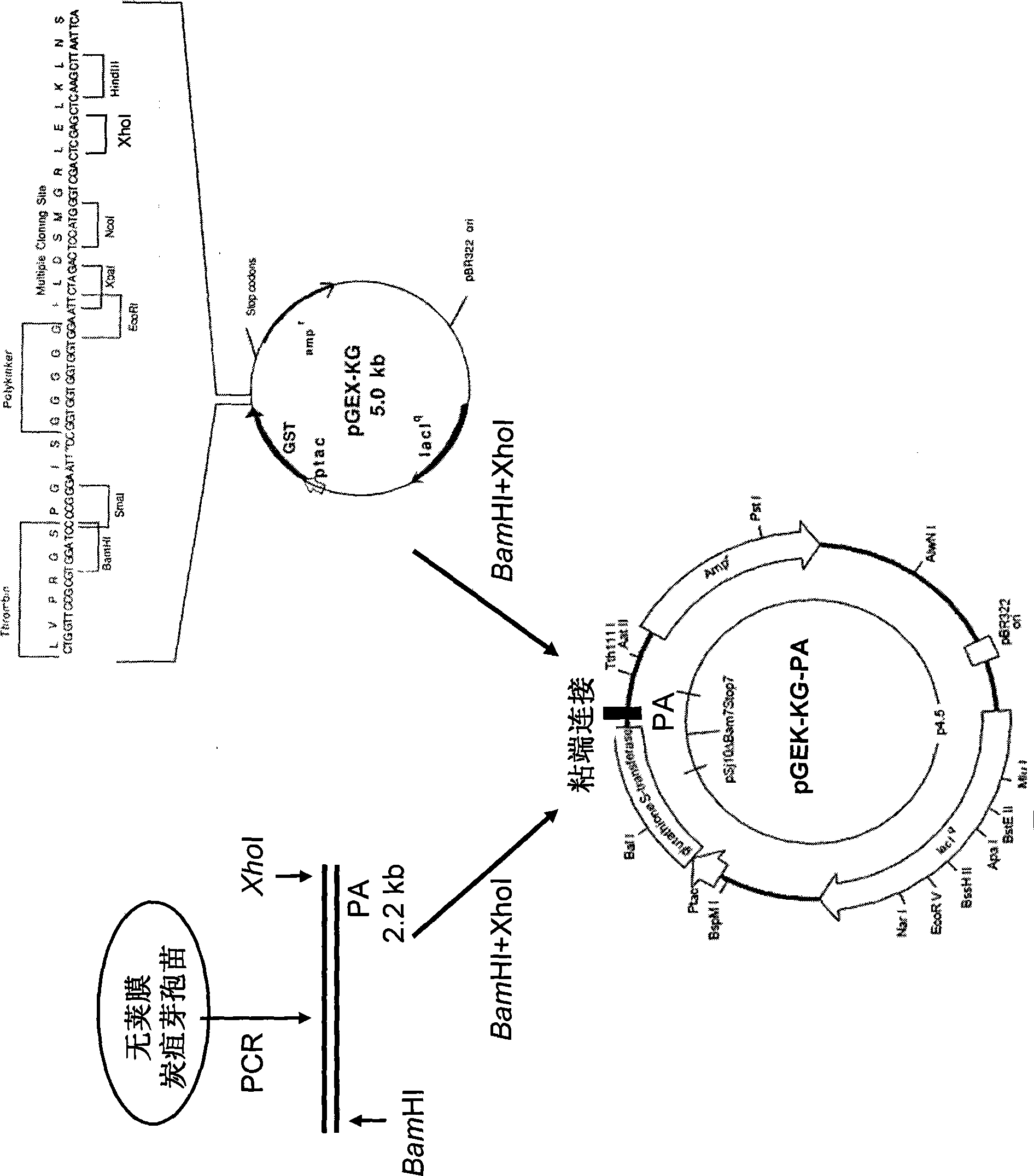
InactiveCN101445789BImproving immunogenicityNo risk of latent infectionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAntigenEscherichia coli
The invention relates to the technical field of animal bacteriology and anthropozoonosis science, in particular to the application of dominant negative mutant F427N as bacillus anthracis toxin inhibitor and vaccine. In the invention, by the methods of bacillus anthracis lethal toxin gene clone, protein expression and purification, gene fixed point saturation mutation and the like, the protective antigen protein of the bacillus anthracis (namely, dominant negative mutant F427N) is obtained. The mutant is successfully cloned to bacterial expression vector pGEX-KG, thus forming recombinant plasmid pGEX-KG-PA (F427N). The colon bacillus containing the recombinant plasmid is named as Escherichia coli DH5 alpha / pGEX-KG-PA (F427N) and preserved at China Center for Type Culture Collection. The preservation code is CCTCC-M208159. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the antigen protein, a method for preparing the anthrax toxin inhibitor and subunit vaccine with the antigen protein and the application thereof.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Application of dominant negative mutant F427N as anthrax toxin inhibitor and vaccine
InactiveCN101445789AImproving immunogenicityNo risk of latent infectionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsEscherichia coliAntigen
The invention relates to the technical field of animal bacteriology and anthropozoonosis science, in particular to the application of dominant negative mutant F427N as bacillus anthracis toxin inhibitor and vaccine. In the invention, by the methods of bacillus anthracis lethal toxin gene clone, protein expression and purification, gene fixed point saturation mutation and the like, the protective antigen protein of the bacillus anthracis (namely, dominant negative mutant F427N) is obtained. The mutant is successfully cloned to bacterial expression vector pGEX-KG, thus forming recombinant plasmid pGEX-KG-PA (F427N). The colon bacillus containing the recombinant plasmid is named as Escherichia coli DH5 alpha / pGEX-KG-PA (F427N) and preserved at China Center for Type Culture Collection. The preservation code is CCTCC-M208159. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the antigen protein, a method for preparing the anthrax toxin inhibitor and subunit vaccine with the antigen protein and the application thereof.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Reporter gene carrier for detecting activity of AP2alpha transcription factor
InactiveCN103305550BReliable detection methodActivity downregulationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationTranscription factor activityNucleotide
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com