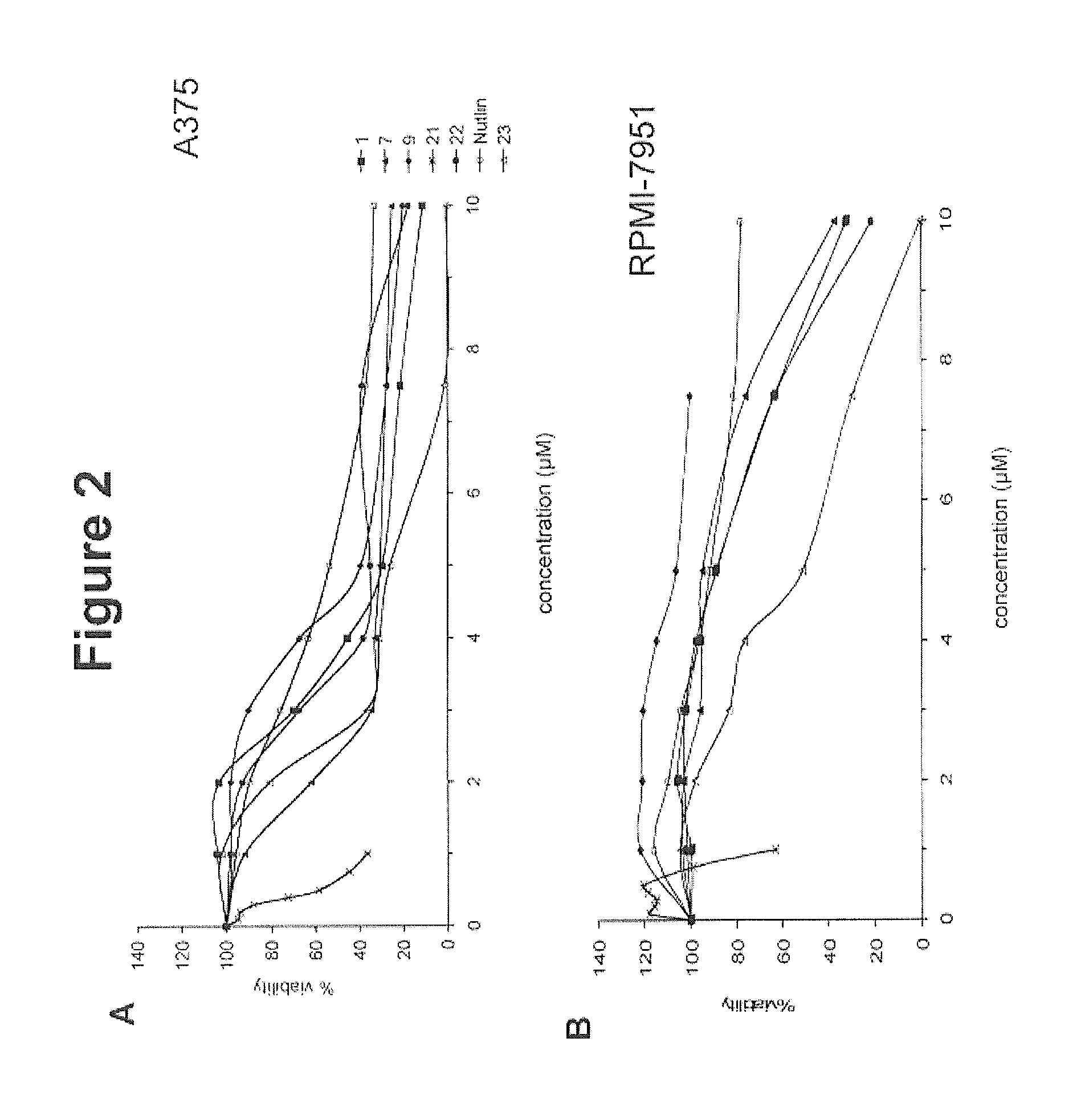
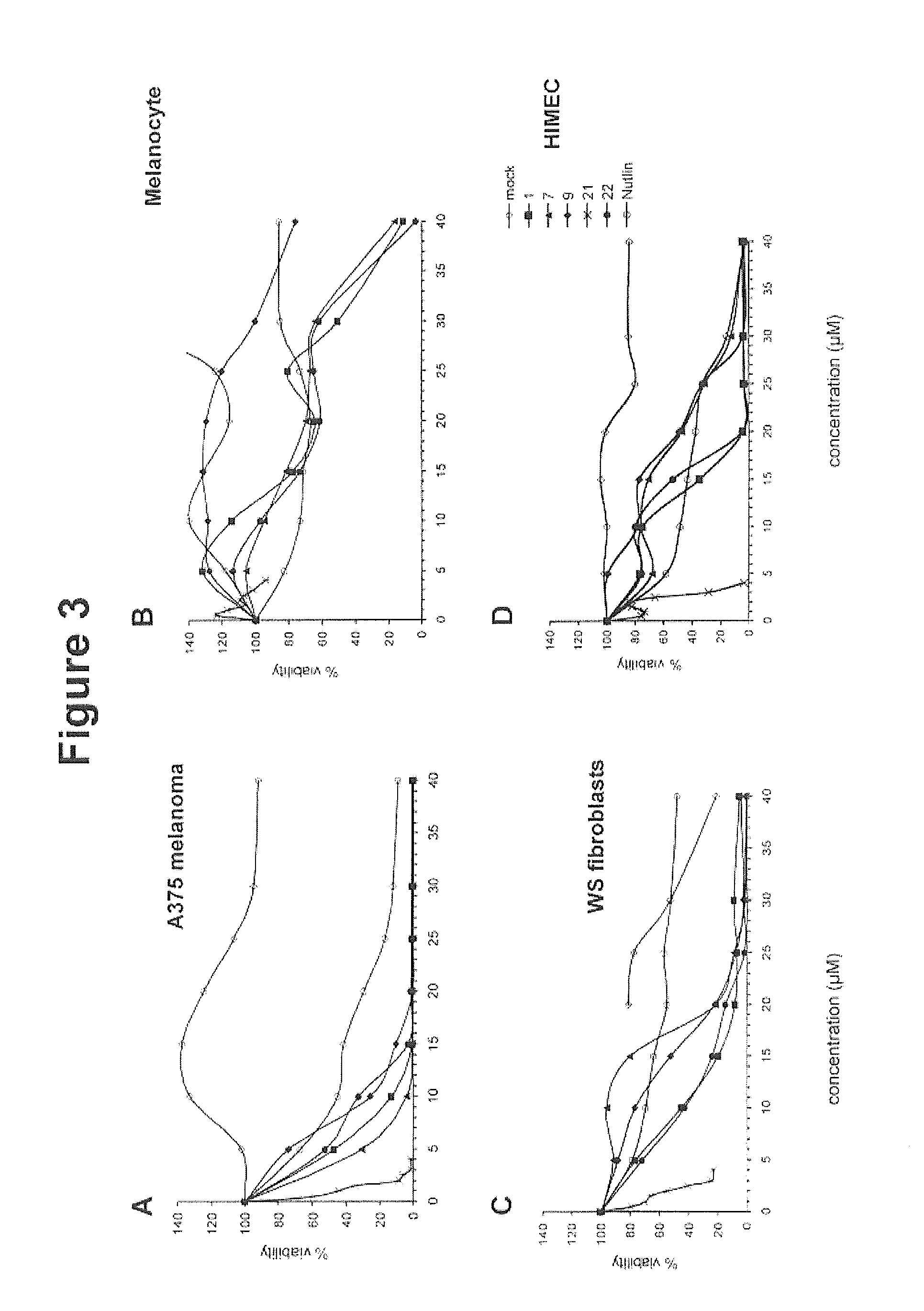
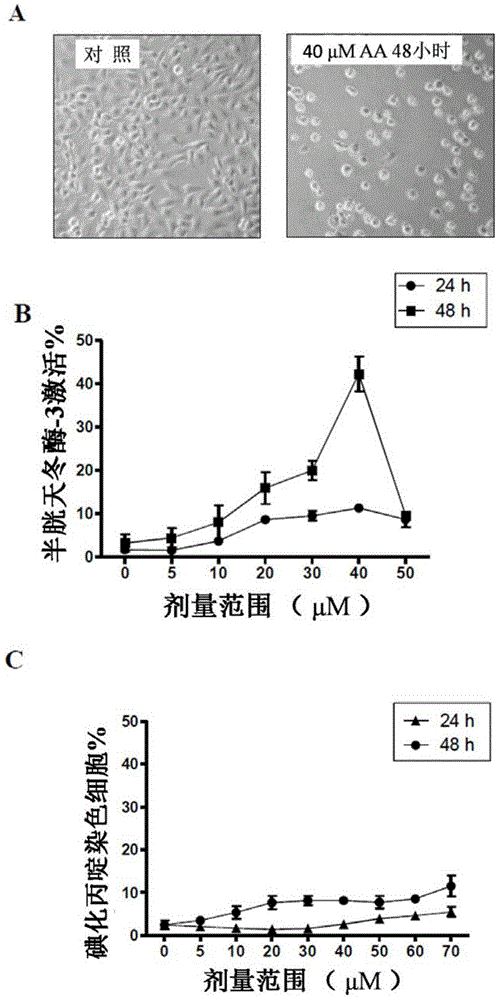
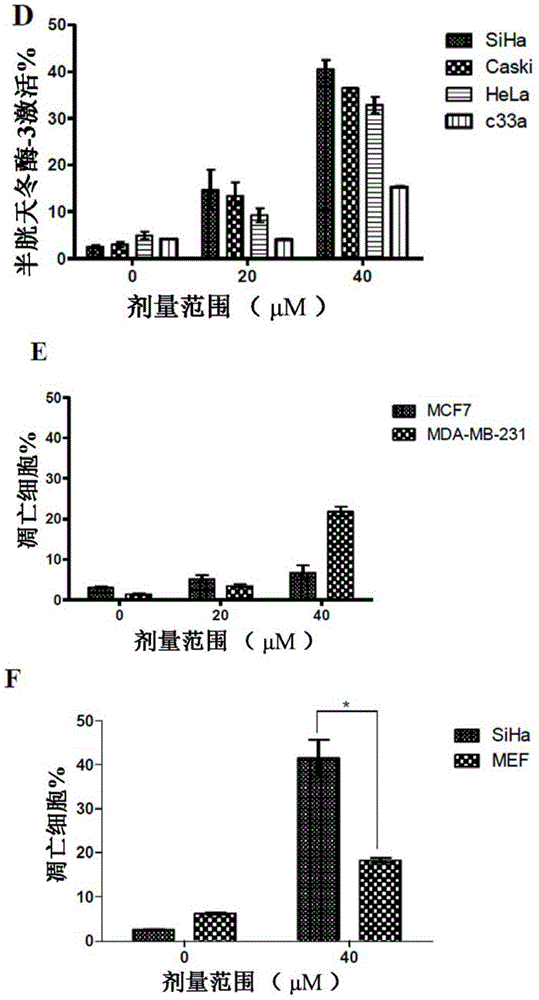
Patents
Literature
33 results about "P53 pathway" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of efficiently establishing induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20110223669A1Improve setup efficiencyEfficient productionGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsNuclear reprogrammingBiology
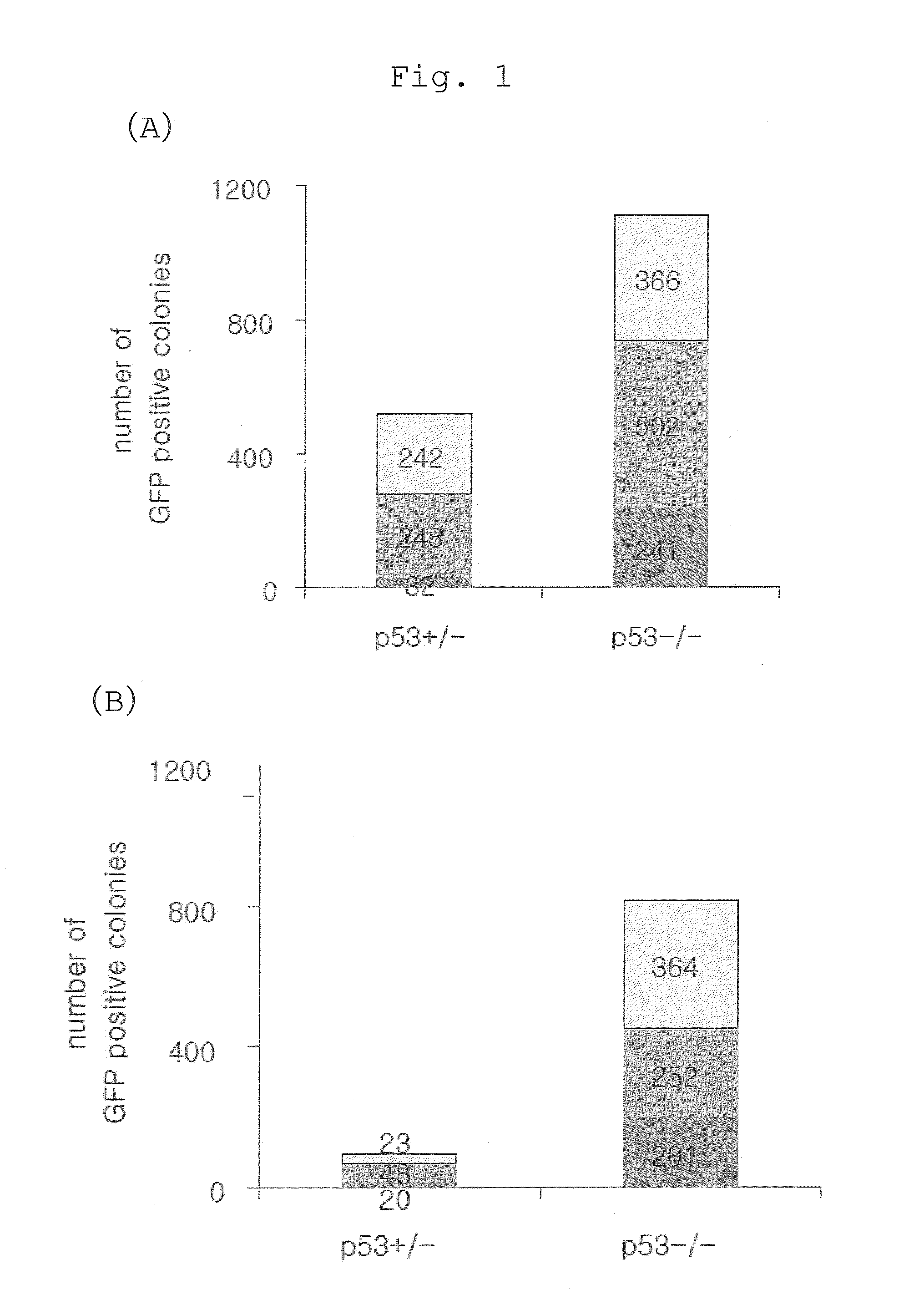
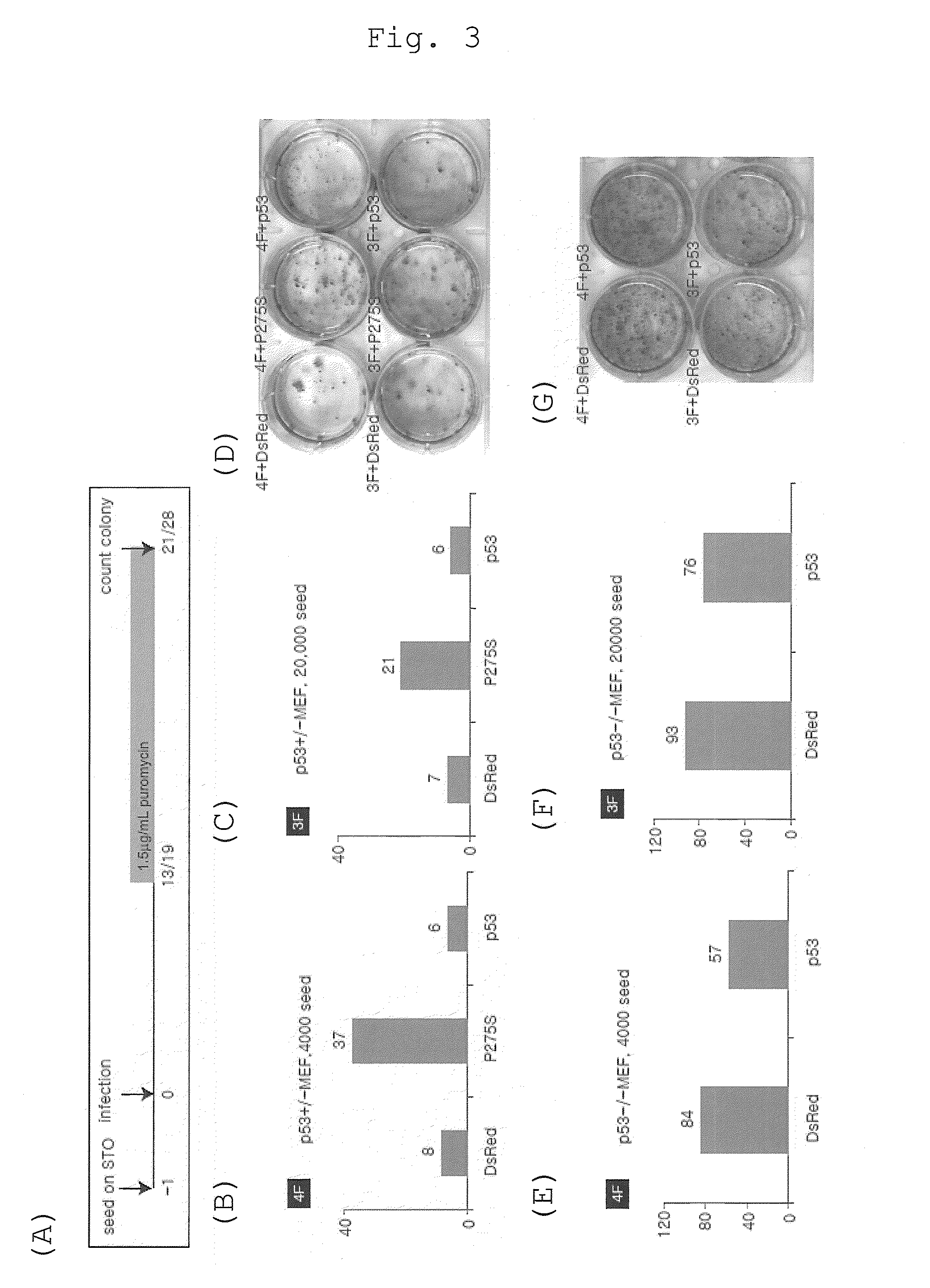
The present invention provides a method of improving the efficiency of establishment of induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, comprising inhibiting the p53 function in the step of somatic cell nuclear reprogramming. The inhibition of p53 function is achieved by bringing a substance selected from the group consisting of (1) chemical inhibitors of p53, (2) dominant negative mutants of p53 and nucleic acids that encode the same, (3) siRNAs and shRNAs against p53 and DNAs that encode the same, and (4) p53 pathway inhibitors, into contact with a somatic cell, and the like. The present invention also provides an agent for improving the efficiency of establishment of iPS cells, the agent comprising an inhibitor of p53 function, particularly (1) chemical inhibitors of p53, (2) dominant negative mutants of p53 and nucleic acids that encode the same, (3) siRNAs and shRNAs against p53 and DNAs that encode the same, and (4) p53 pathway inhibitors. The present invention further provides a method of producing an iPS cell, comprising bringing a nuclear reprogramming substance and an inhibitor of p53 function into contact with a somatic cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Molecular chemotherapy enhancement of radiotherapy
InactiveUS6552005B1Tumour growth inhibitionCurrent is limitedBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsWhole bodyCytotoxicity
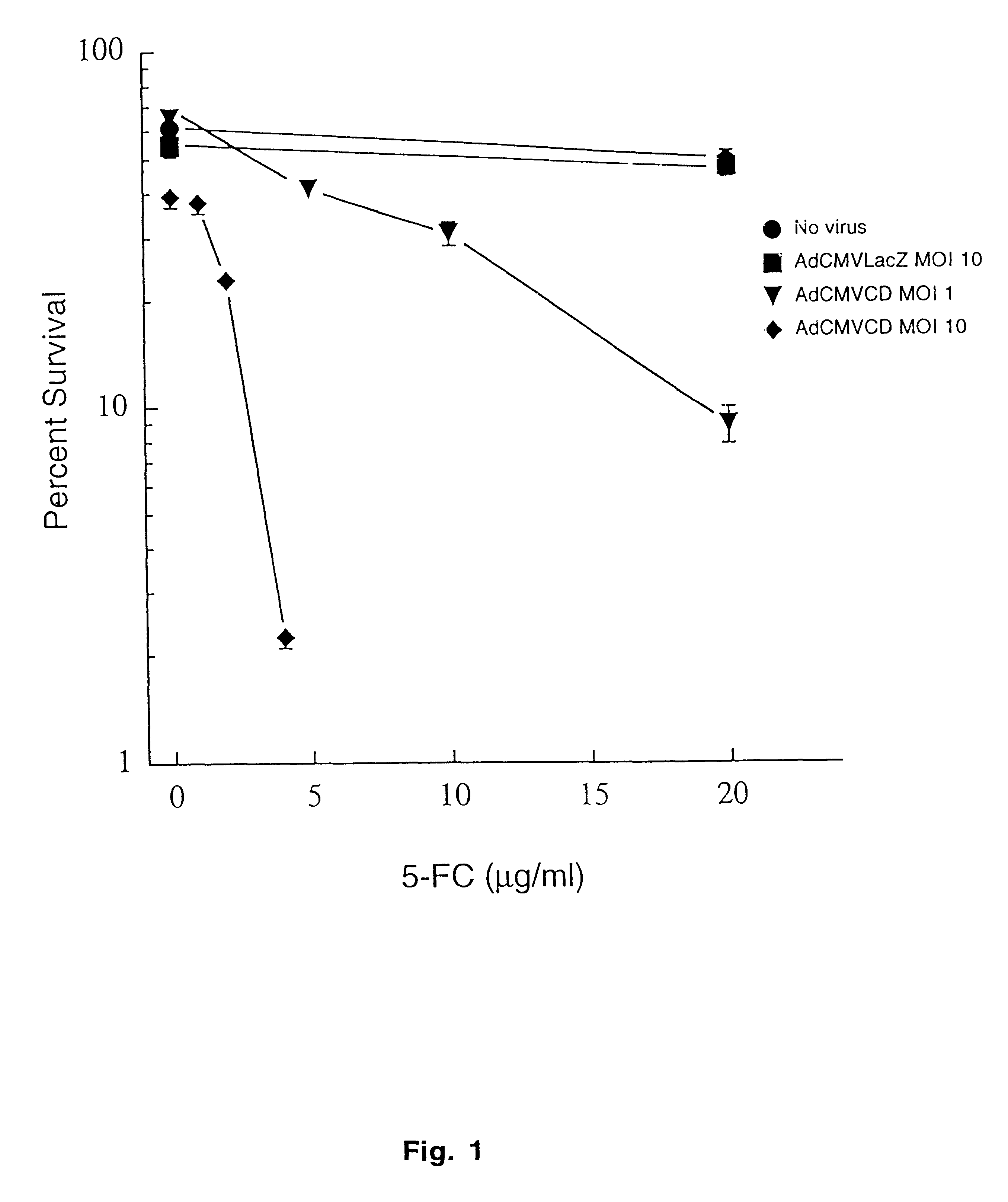
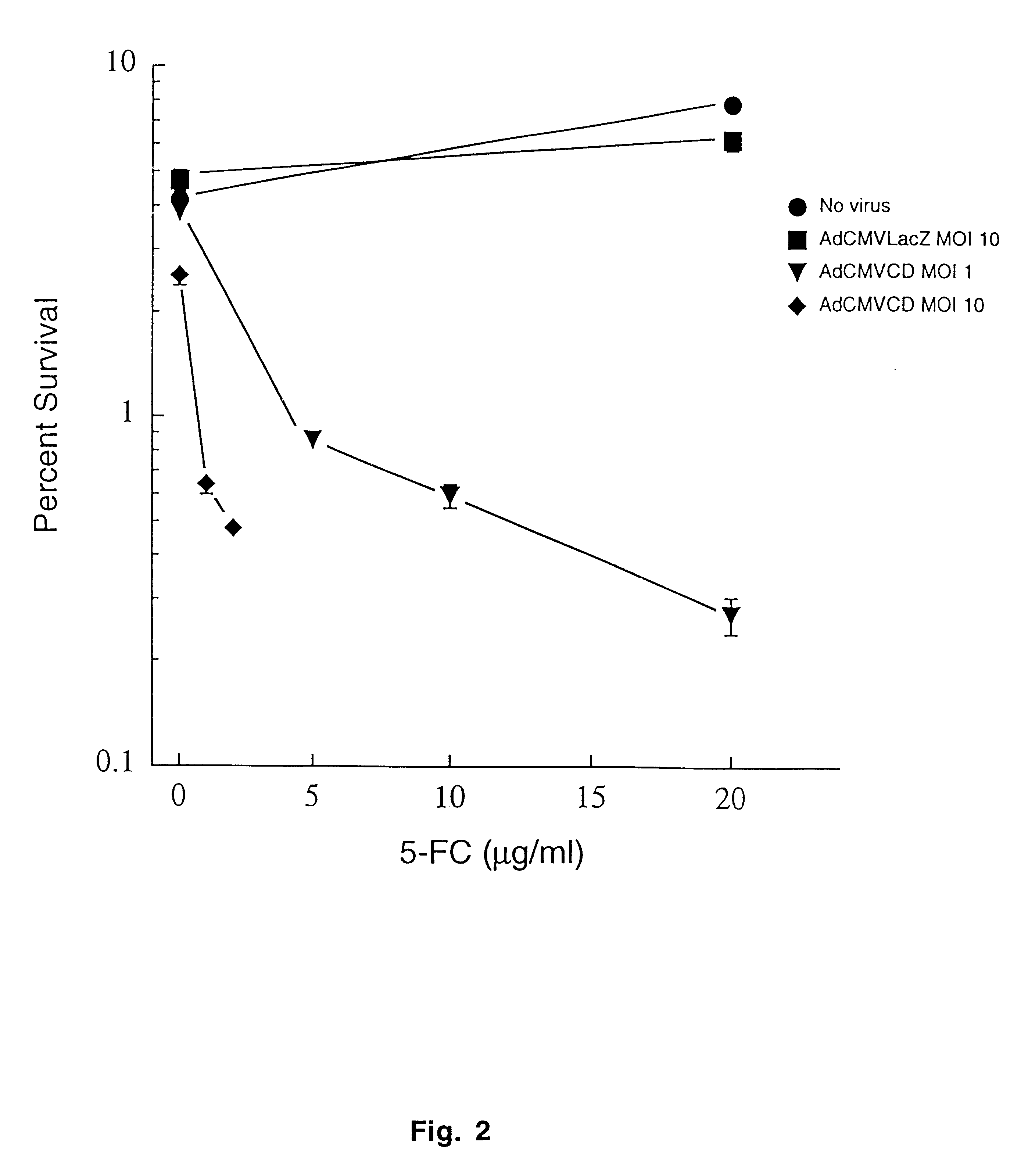
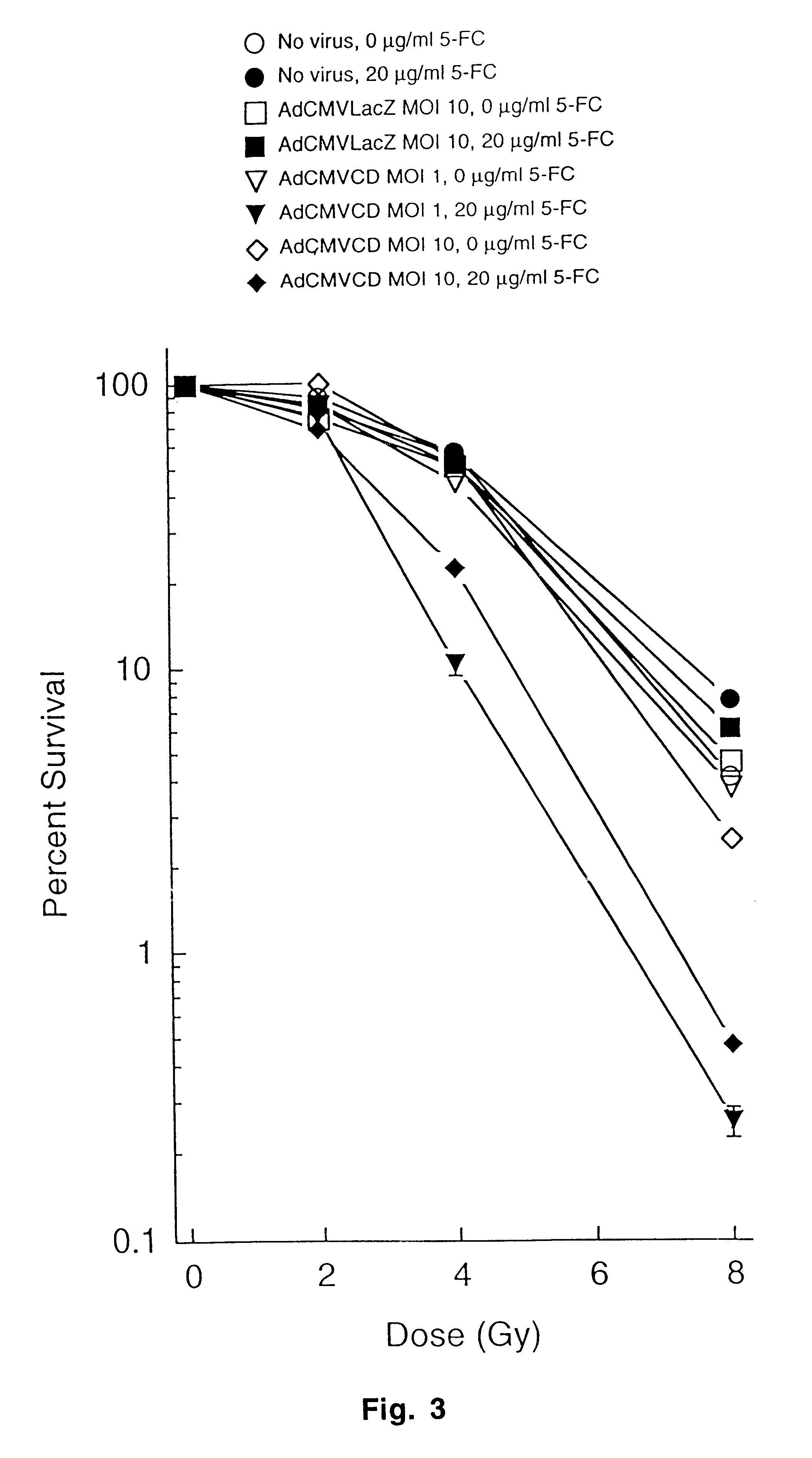
The present invention provides a new approach for cancer treatment by utilizing gene therapy combined with radiation therapy to enhance cytotoxicity in malignant cells. Specifically, the present invention demonstrates that molecular chemotherapy with the cytosine deaminase gene and 5-fluorocytosine is an effective radiosensitizing strategy which may lead to substantial improvement in tumor control, with less normal tissue toxicity than conventional systemic administration of 5-fluorouracil, that would translate into improved cure rates and better survival. A noninvasive method is described for continuous in vivo monitoring of 5-fluorouracil production via magnetic resonance spectroscopy. An adenovirus encoding cytosine deaminase gene which selectively replicates in tumor cells with a defective p53 pathway was constructed. Also provided is an adenovirus which encodes a fusion protein of cytosine deaminase and uracil phosphoribosyltransferase.
Owner:CDEPT
Method of efficiently establishing induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS8530238B2Genetically modified cellsBlood/immune system cellsNuclear reprogrammingCancer research
The present invention provides a method of improving the efficiency of establishment of induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, comprising inhibiting the p53 function in the step of somatic cell nuclear reprogramming. The inhibition of p53 function is achieved by bringing a substance selected from the group consisting of (1) chemical inhibitors of p53, (2) dominant negative mutants of p53 and nucleic acids that encode the same, (3) siRNAs and shRNAs against p53 and DNAs that encode the same, and (4) p53 pathway inhibitors, into contact with a somatic cell, and the like. The present invention also provides an agent for improving the efficiency of establishment of iPS cells, the agent comprising an inhibitor of p53 function, particularly (1) chemical inhibitors of p53, (2) dominant negative mutants of p53 and nucleic acids that encode the same, (3) siRNAs and shRNAs against p53 and DNAs that encode the same, and (4) p53 pathway inhibitors. The present invention further provides a method of producing an iPS cell, comprising bringing a nuclear reprogramming substance and an inhibitor of p53 function into contact with a somatic cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Method for Treating Ocular Cancer
Owner:FLANDERS INTERUNIV INST FOR BIOTECH VIB +3
Activators and therapeutic applications thereof
The invention presents methods of identifying small molecule compounds that are activators of tumor suppressor protein p53 pathway, and its associated family members p63 and p73, function. The invention is further drawn to methods of killing tumor cells and treating cancers or other conditions requiring activation of the p53 family member pathways and DNA damage response pathways with the small molecules.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Pharmaceutical compositions of anisomelic acid and the use thereof
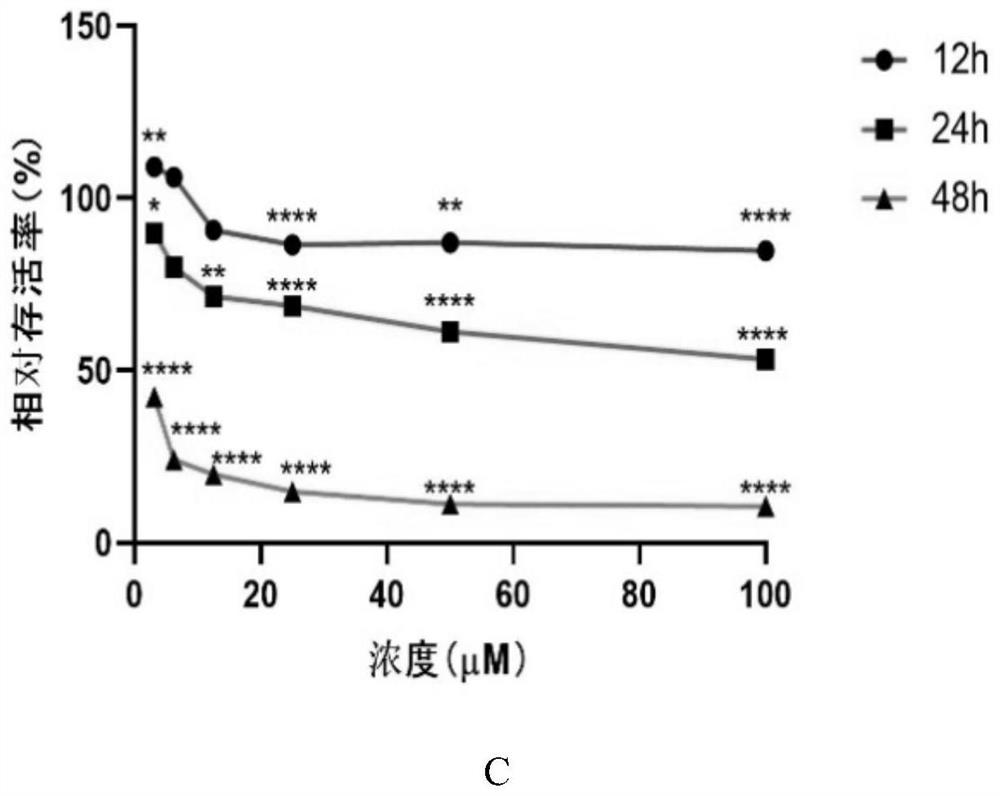
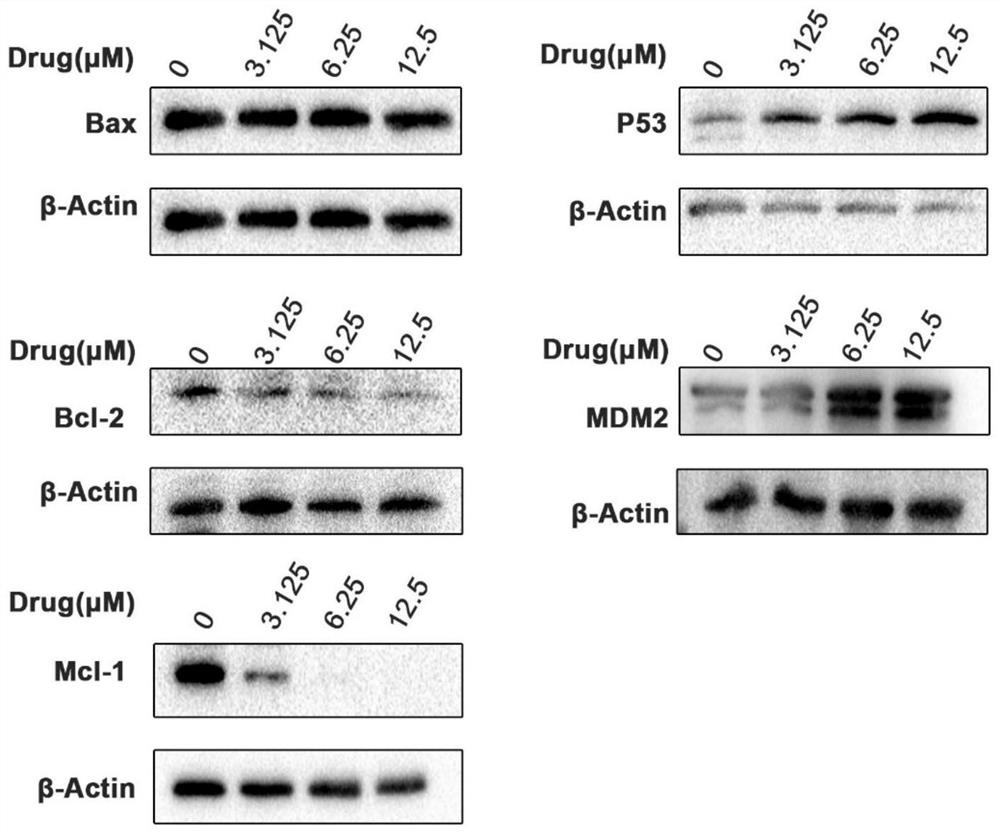
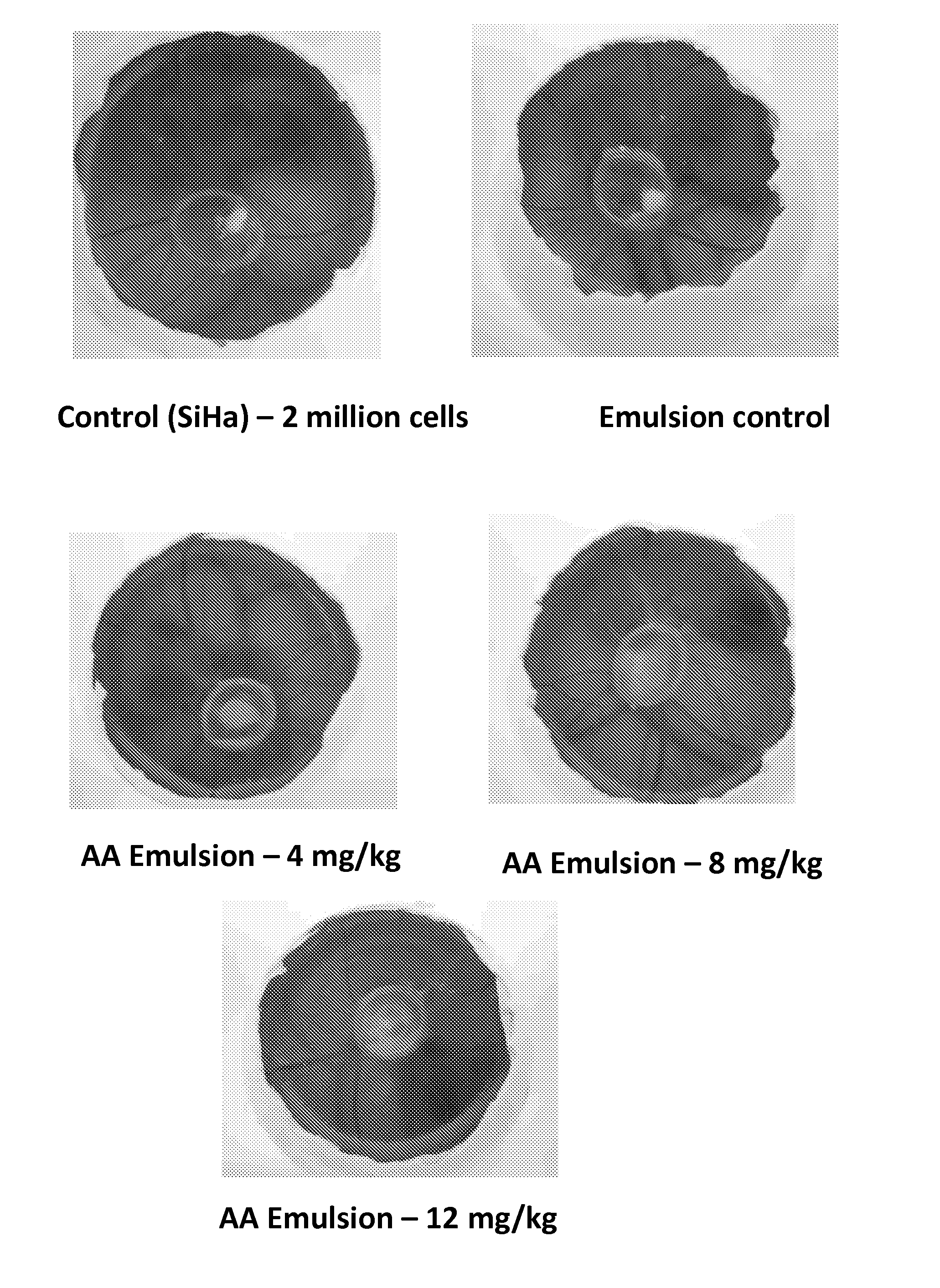
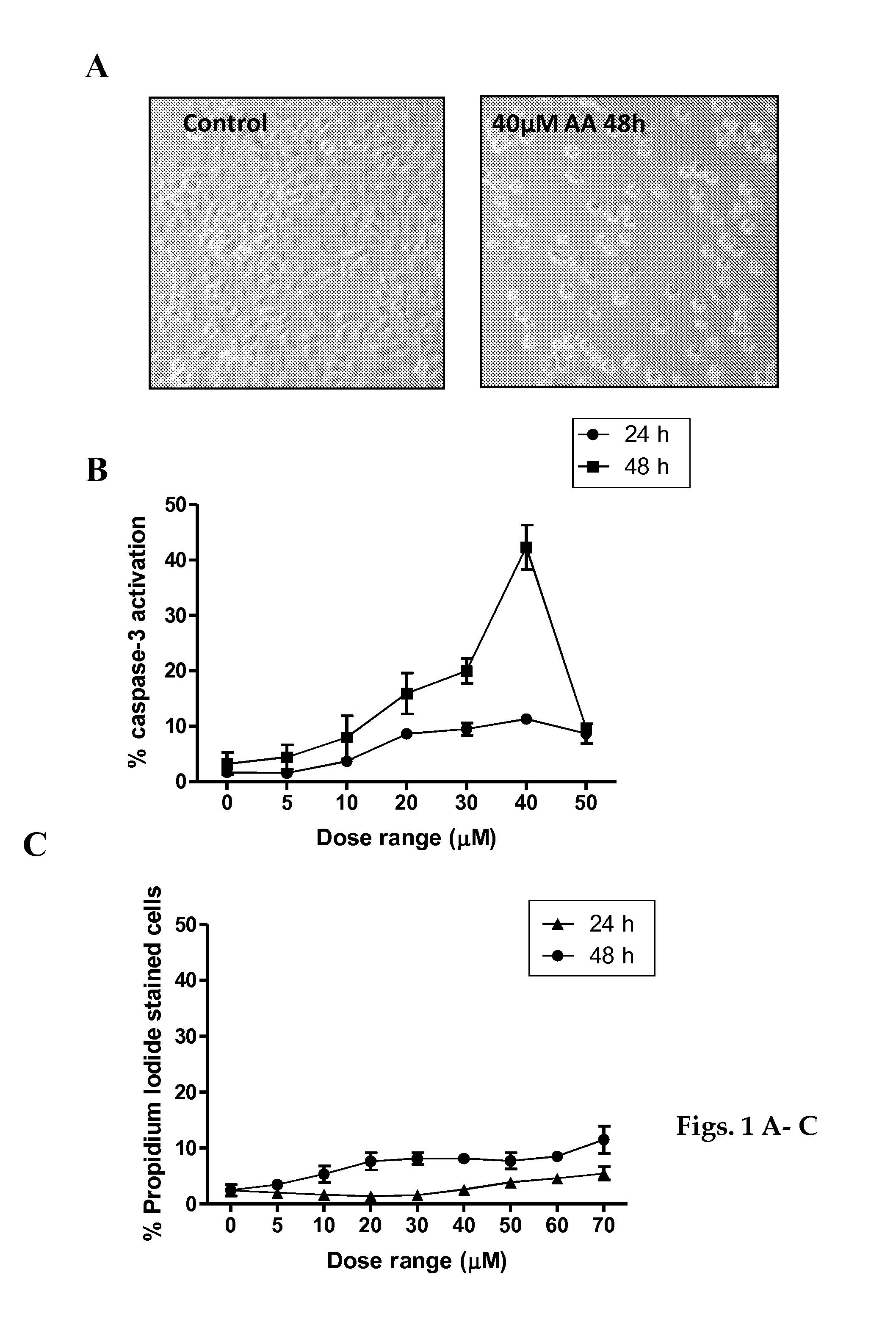
ActiveCN104869991APrevent proliferationPrevent killOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsActive agentSurface-active agents
A pharmaceutical composition for anti-viral cancer treatment in mammals, comprising a therapeutically effective amount of Anisomelic acid or salts thereof. The pharmaceutical composition may comprise Anisomelic acid or salt thereof in an oil-in-water emulsion, for example in an isotropic mixture of at least one oil and at least one surfactant or, alternatively, in a hydrophilic solvent and a co-solvents or surfactant or a combination thereof. A method of treating or preventing of cancer in a mammal, wherein the p53 pathway is deregulated by viral oncoproteins, is also provided.
Owner:ANISON THERAPEUTICS OY
Application of shikonin in preparing drug for treating lung cancer
InactiveCN107137384AInduced agingPlay a role in the treatment of lung cancerOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCancer cellStructural formula
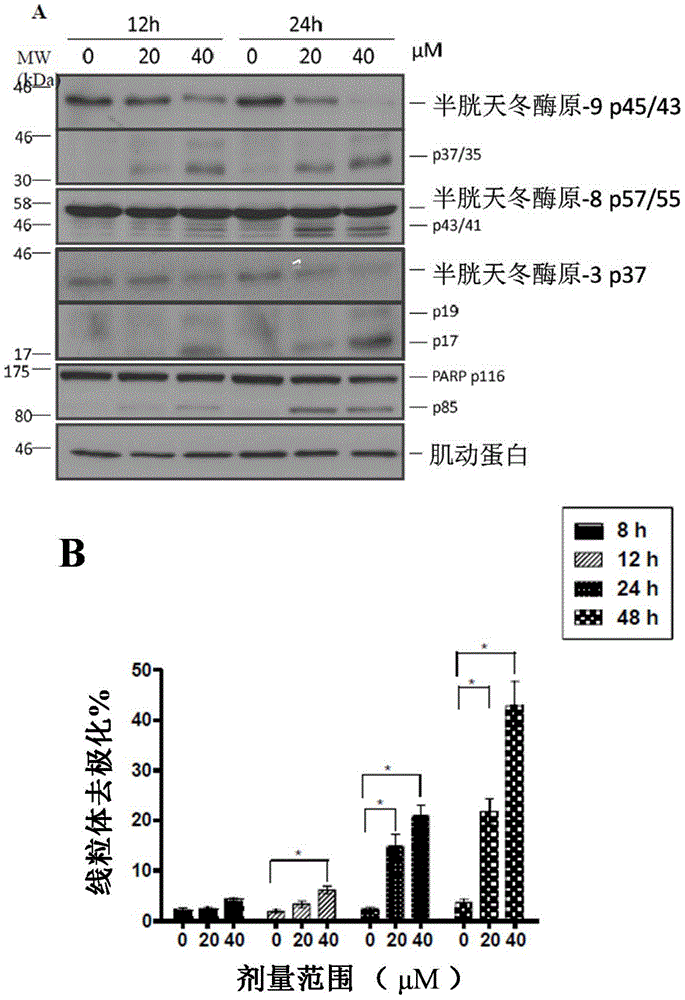
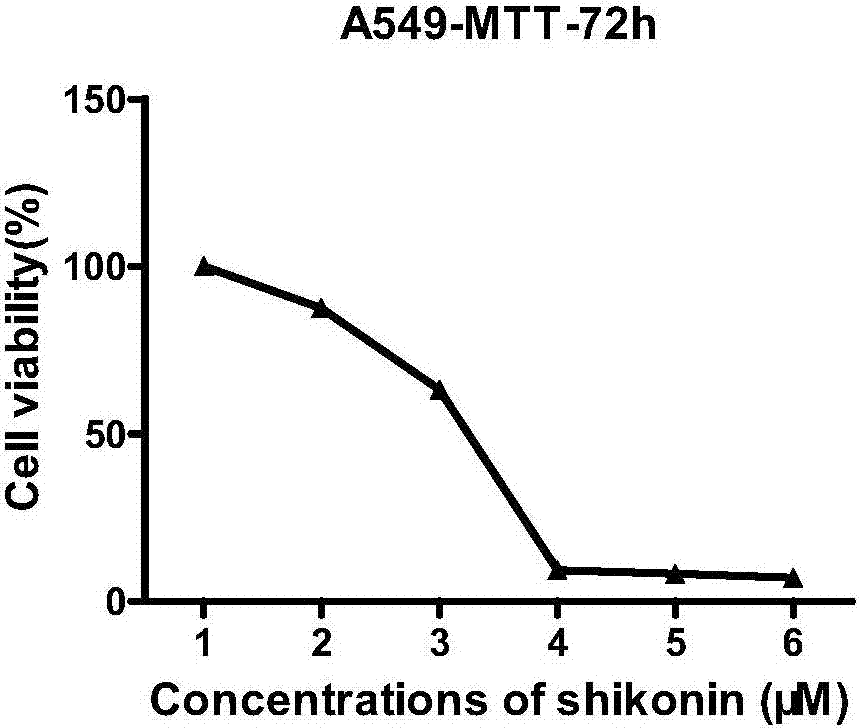
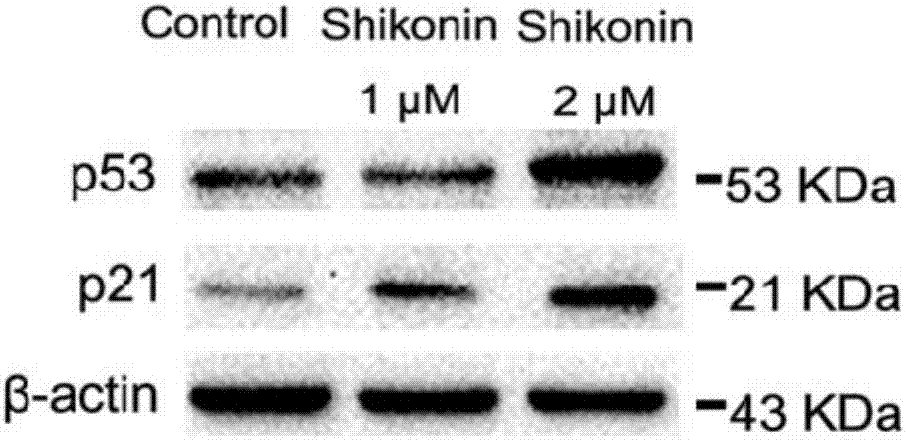
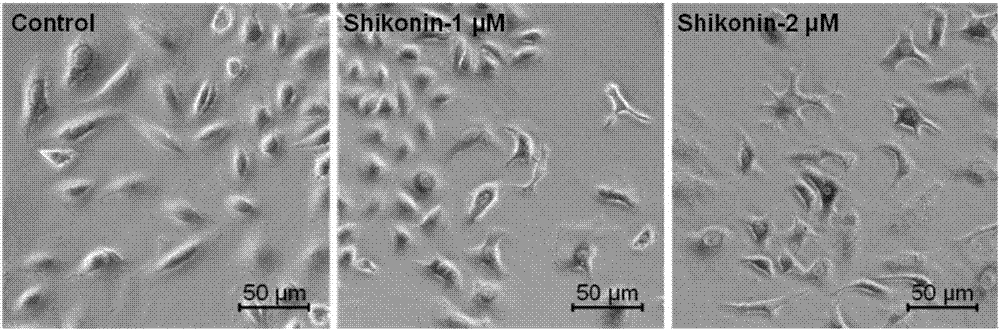
The invention relates to application of shikonin in preparing drug for treating lung cancer. The chemical structural formula of shikonin is shown as a following formula (I). Shikonin can effectively activate P53 pathways in cancer cells, induce senescence of the cancer cells and play a role in treating the lung cancer.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Reconstituted human breast tumor model
Reconstituted human breast tumor models are disclosed. The models, which are incorporated into mice, provide actual tumors that arise spontaneously, thereby mimicking naturally occurring breast cancer. The tumors are genetically human, because they arise from human mammary tissues that develop from human mammary epithelial cells implanted into host mice. Prior to implantation, the mammary epithelial cells are genetically modified to contain either: (a) a recombinant human oncogene and an SV40er; or (b) a recombinant human oncogene, a transgene or shRNA that inhibits the p53 pathway, and a transgene or shRNA that inhibits the Rb pathway.
Owner:AVEO PHARM INC
Pharmaceutical compositions of anisomelic acid and the use thereof
ActiveUS9345687B2Improve commercial useIncreasing therapeutic usageOrganic chemistryPeptide/protein ingredientsAnisomelic acidCancer treatment
A pharmaceutical composition for anti-viral cancer treatment in mammals, comprising a therapeutically effective amount of Anisomelic acid or salts thereof. The pharmaceutical composition may comprise Anisomelic acid or salt thereof in an oil-in-water emulsion, for example in an isotropic mixture of at least one oil and at least one surfactant or, alternatively, in a hydrophilic solvent and a co-solvents or surfactant or a combination thereof. A method of treating or preventing of cancer in a mammal, wherein the p53 pathway is deregulated by viral oncoproteins, is also provided.
Owner:ANISON THERAPEUTICS OY
Activators and therapeutic applications thereof
The invention presents methods of identifying small molecule compounds that are activators of tumor suppressor protein p53 pathway, and its associated family members p63 and p73, function. The invention is further drawn to methods of killing tumor cells and treating cancers or other conditions requiring activation of the p53 family member pathways and DNA damage response pathways with the small molecules.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
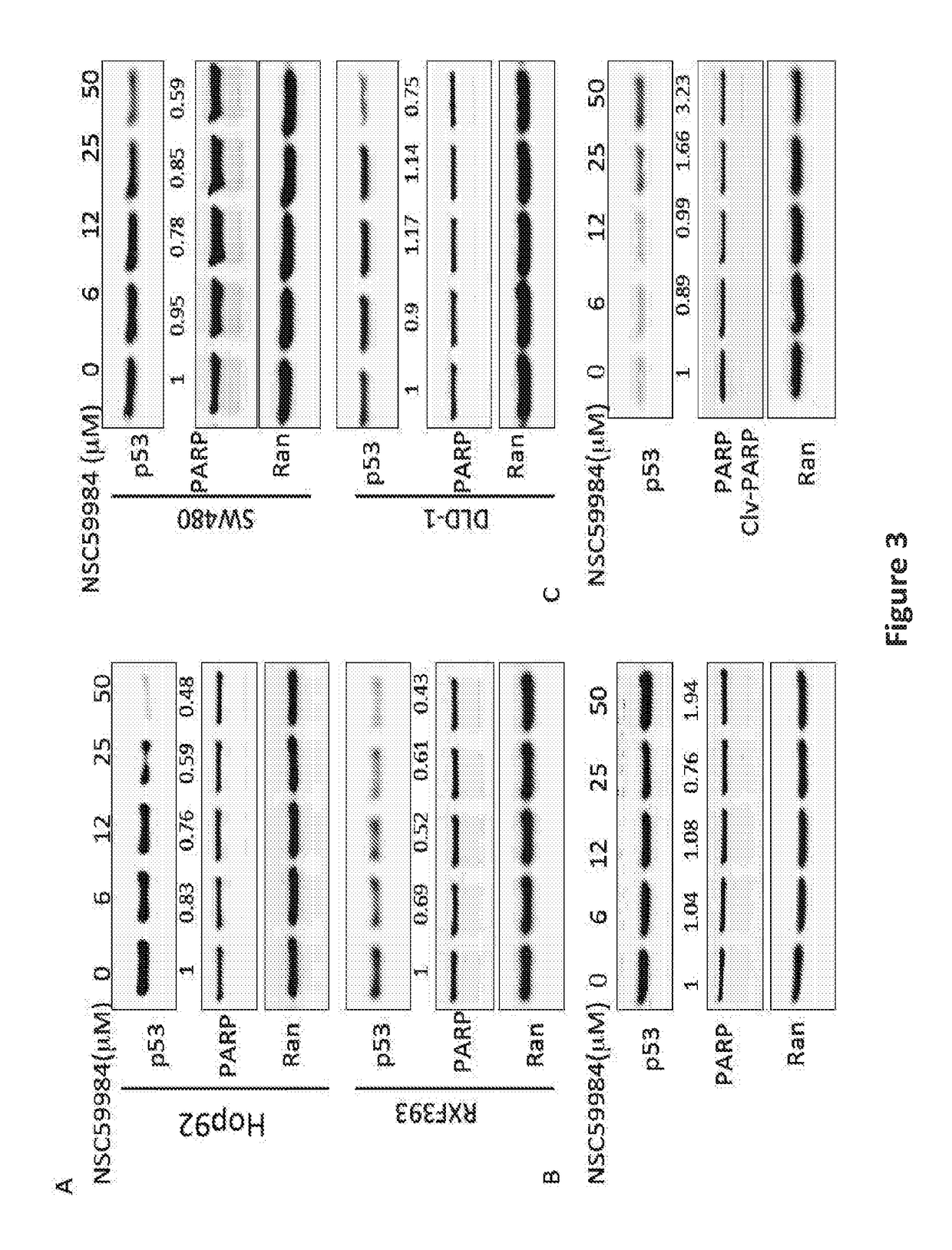
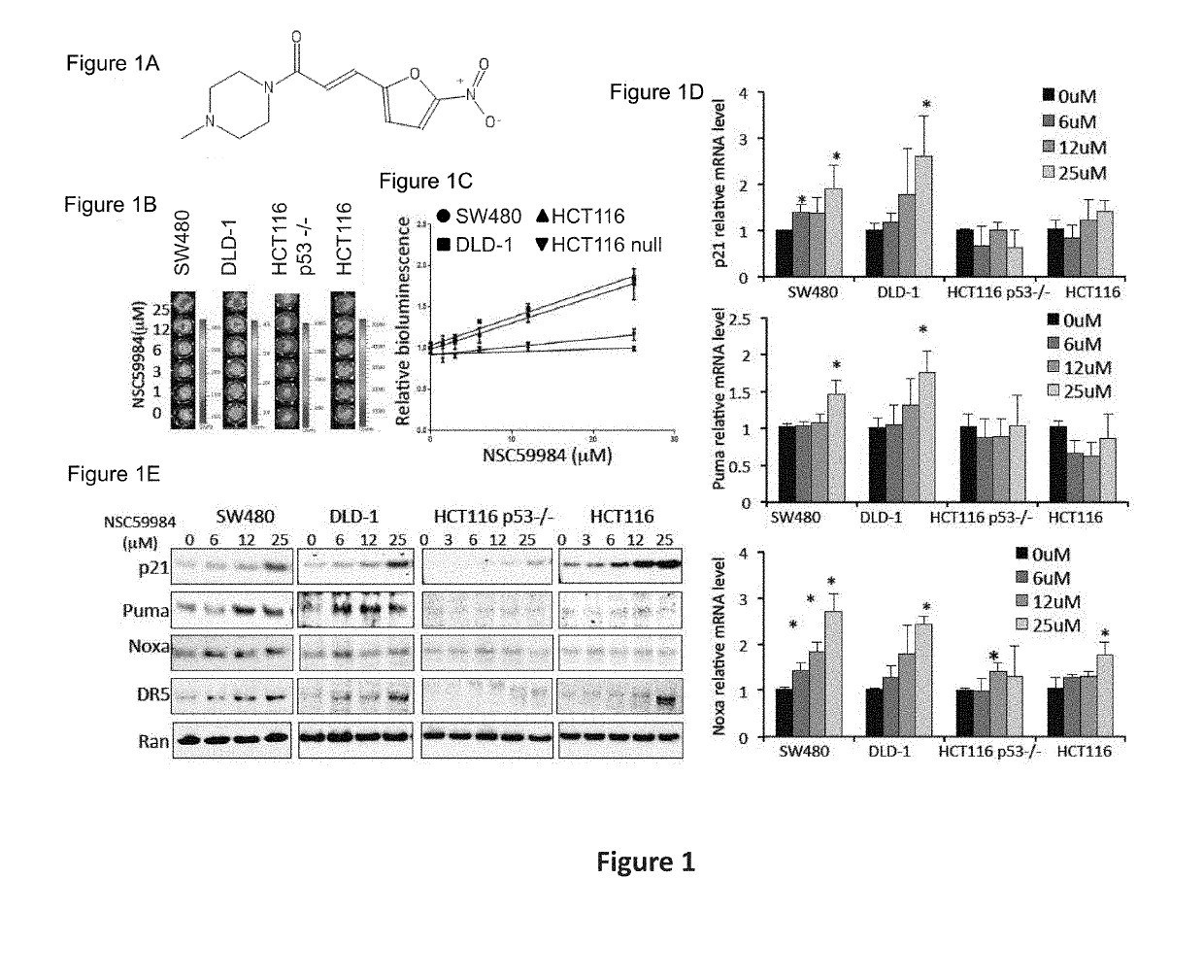
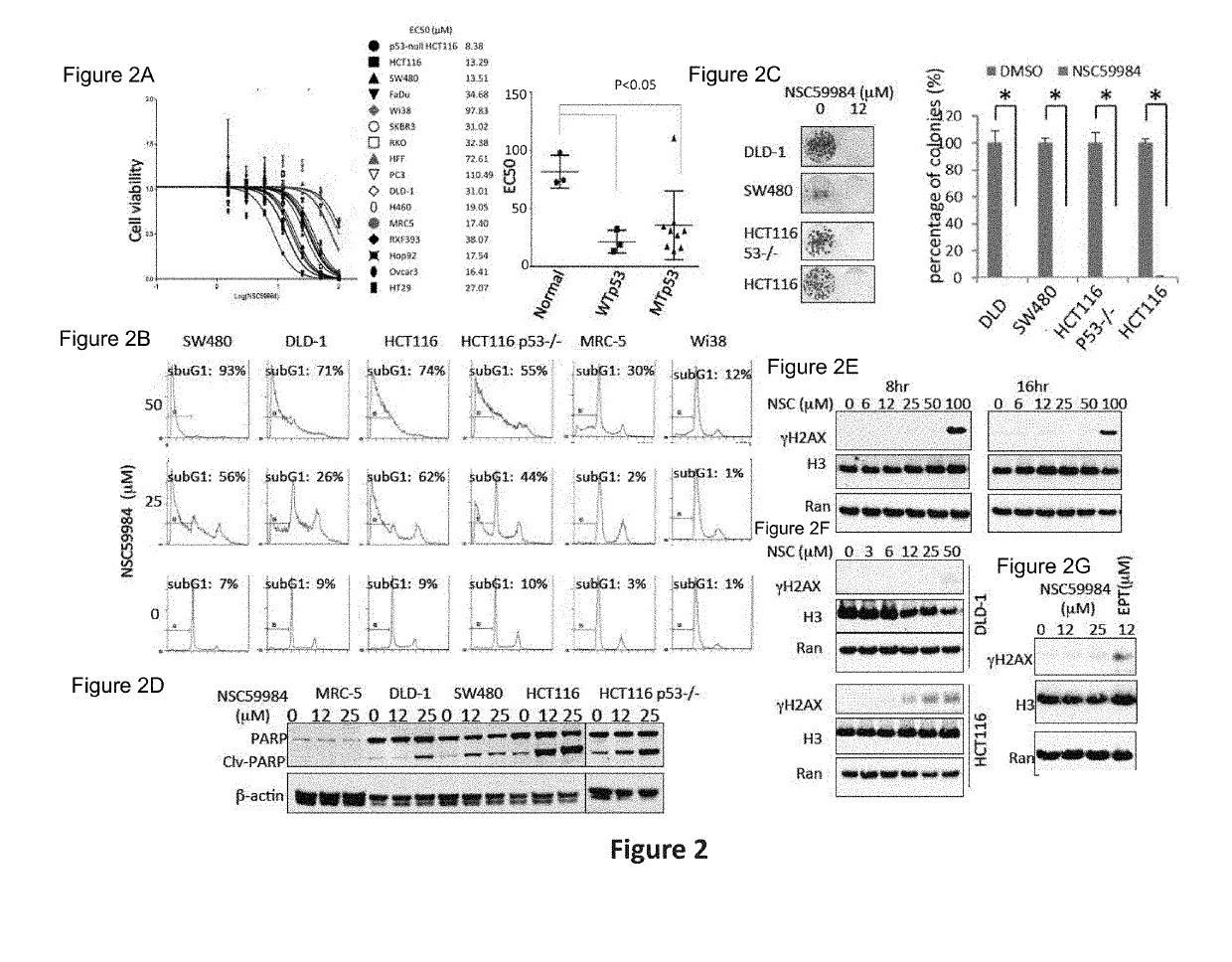
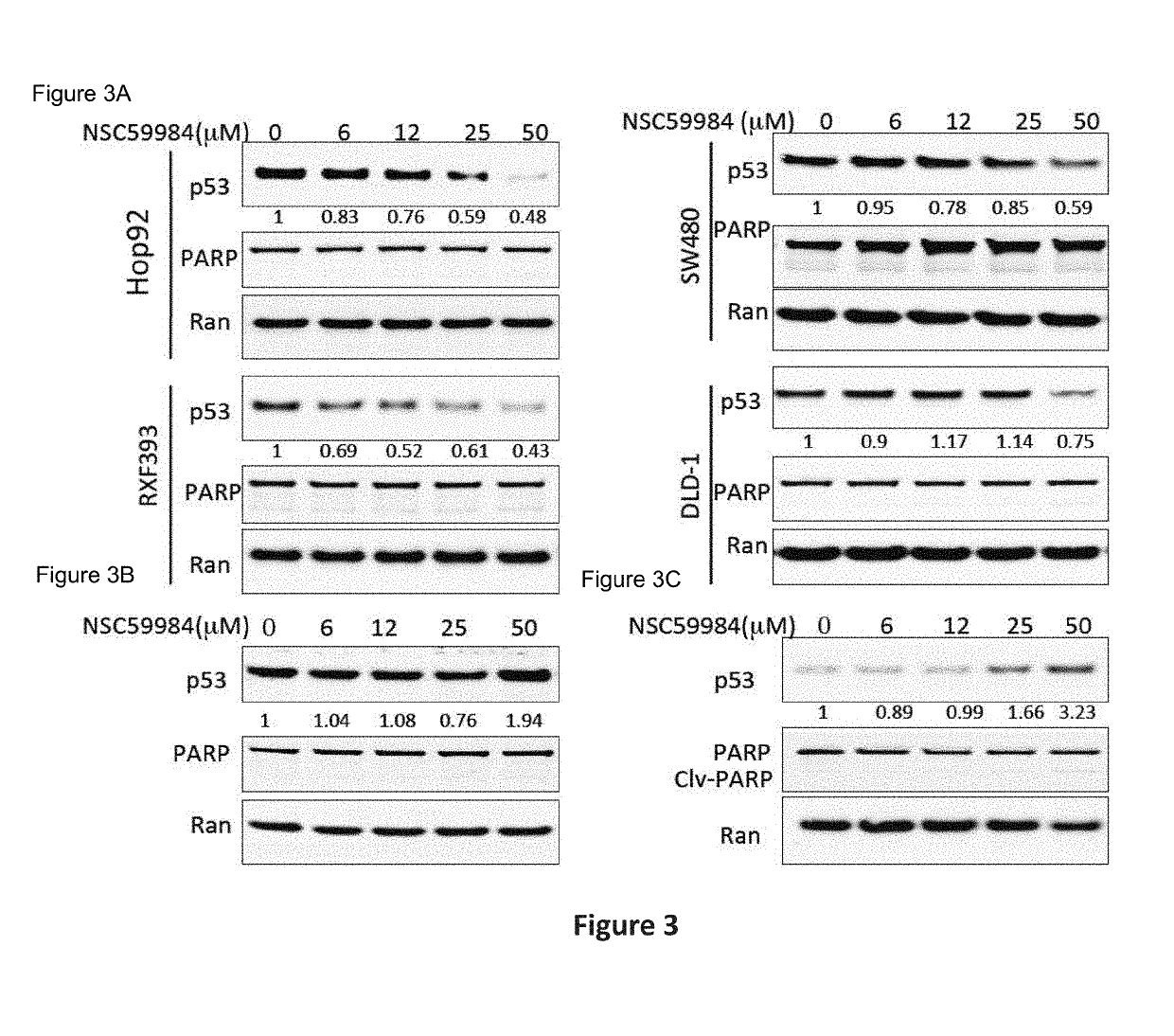
Compound for anti-cancer therapy that acts by targeting GOF mutant P53 and stimulates P73 to restore the P53 pathway signaling
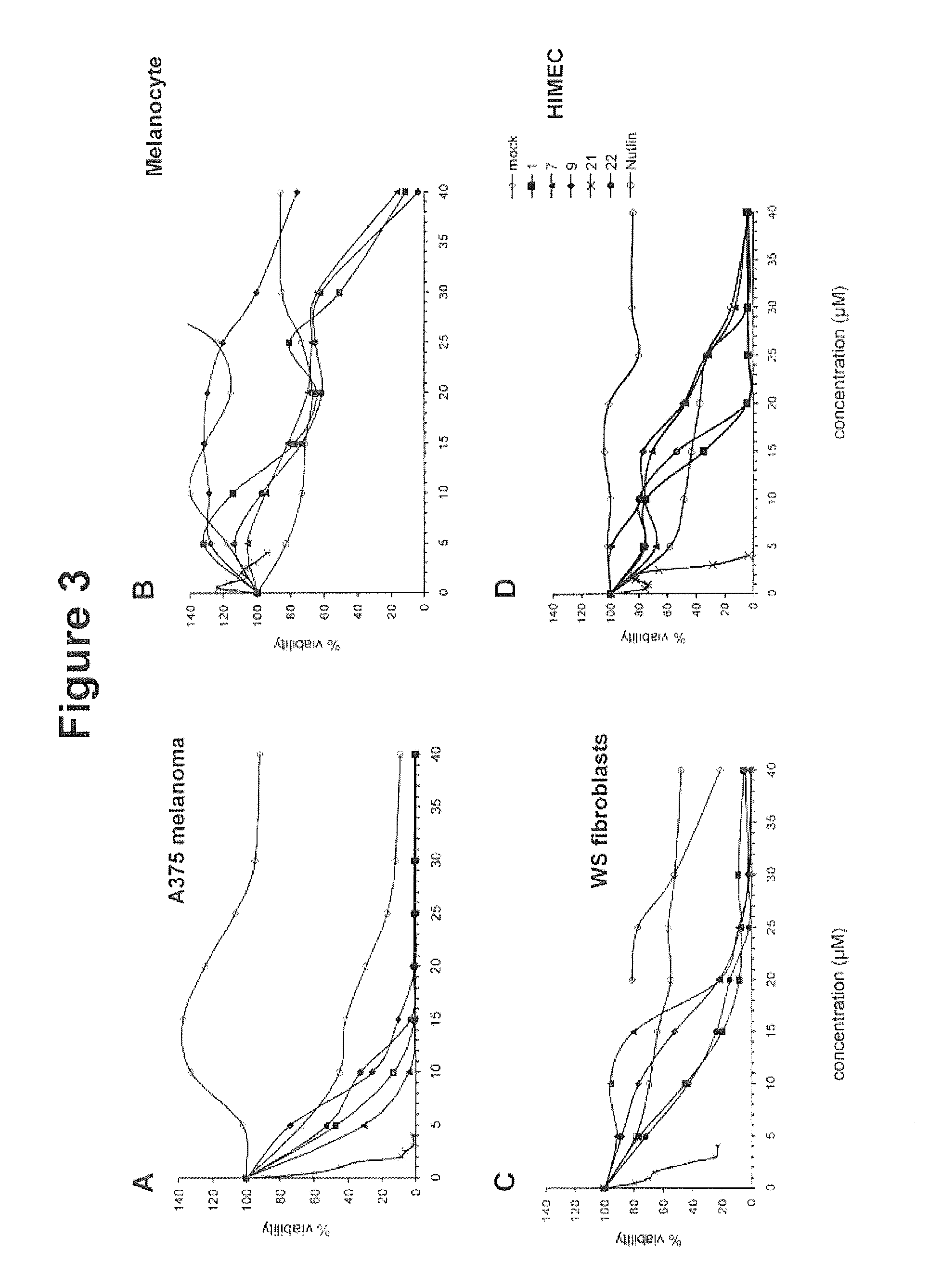
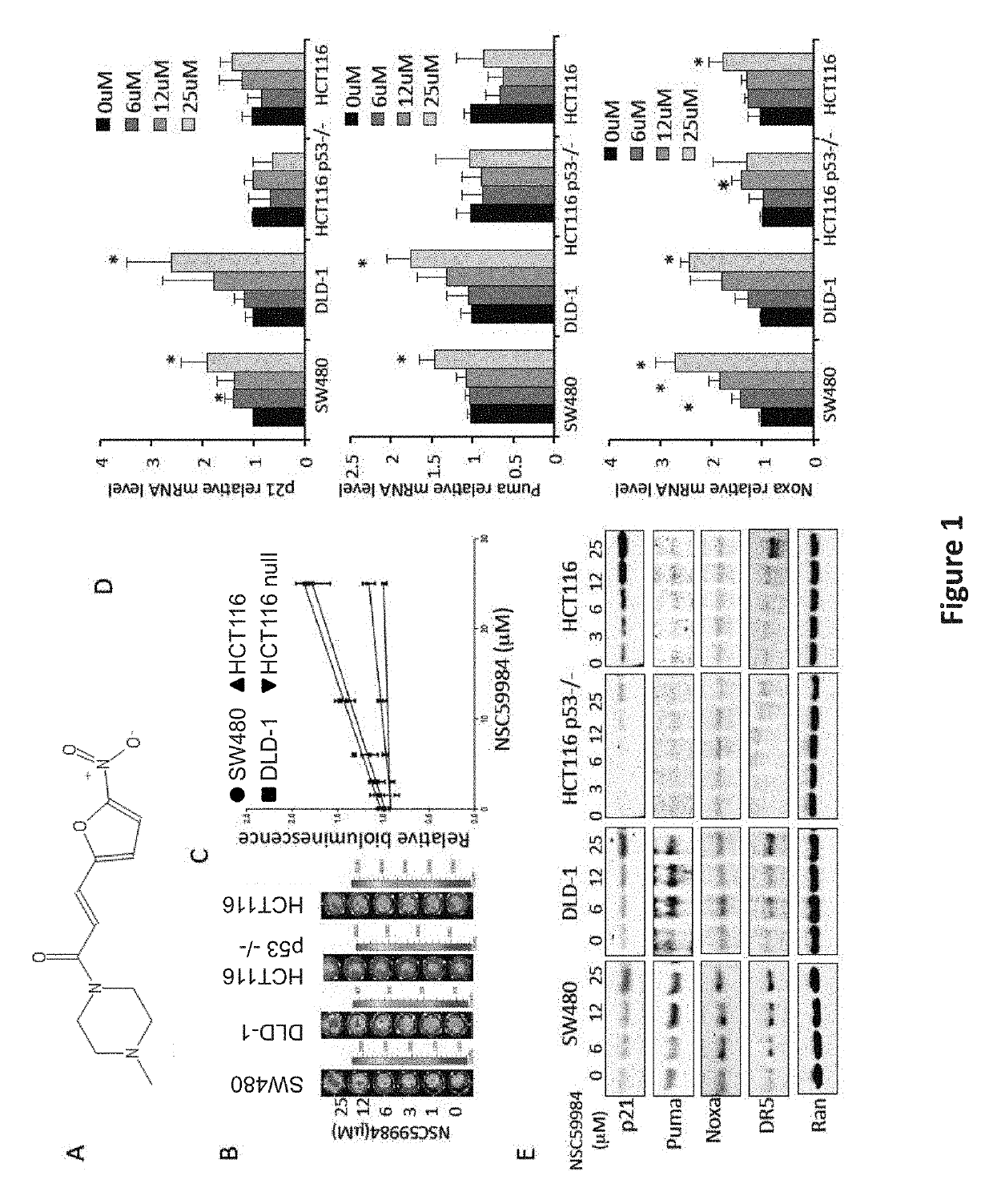
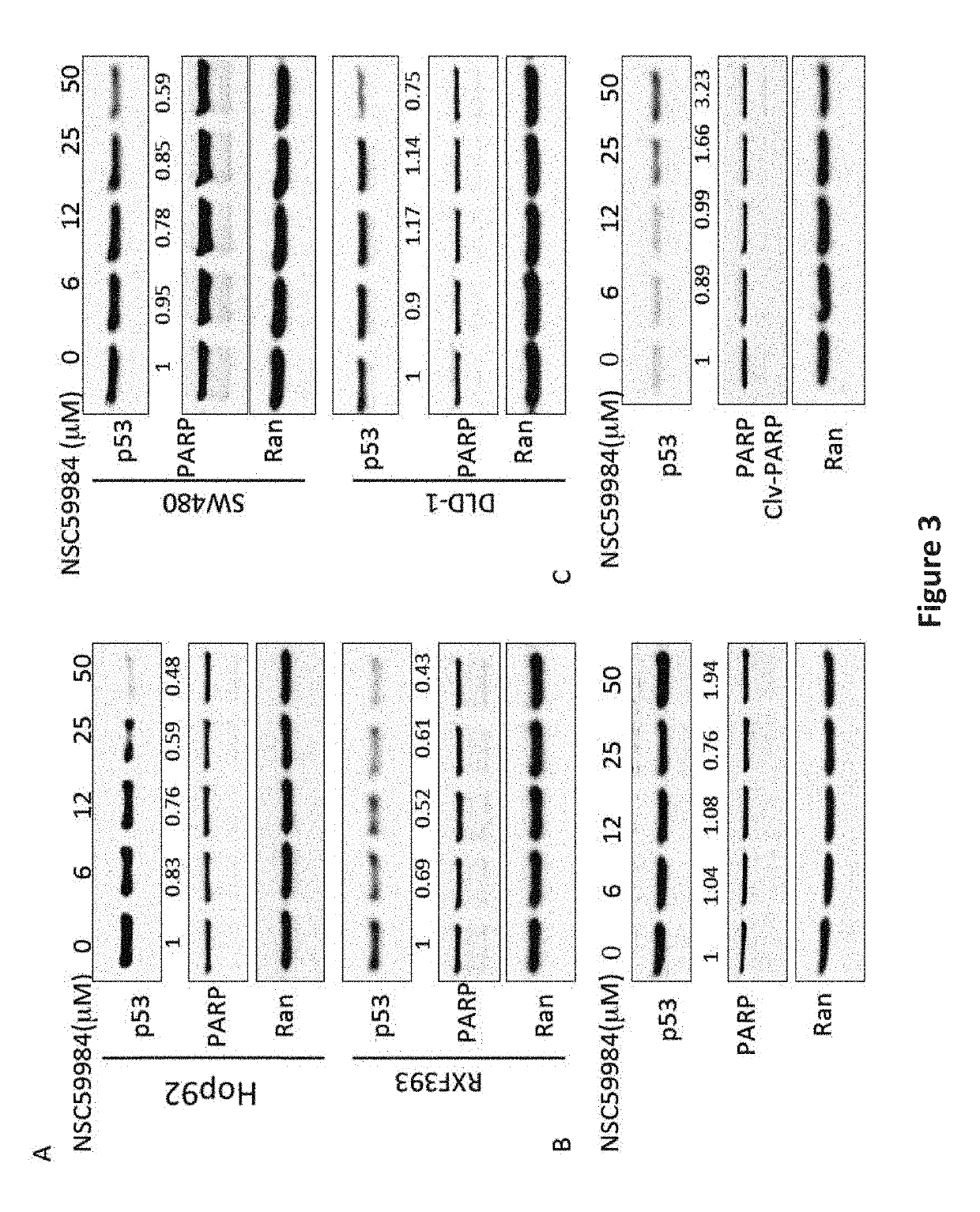
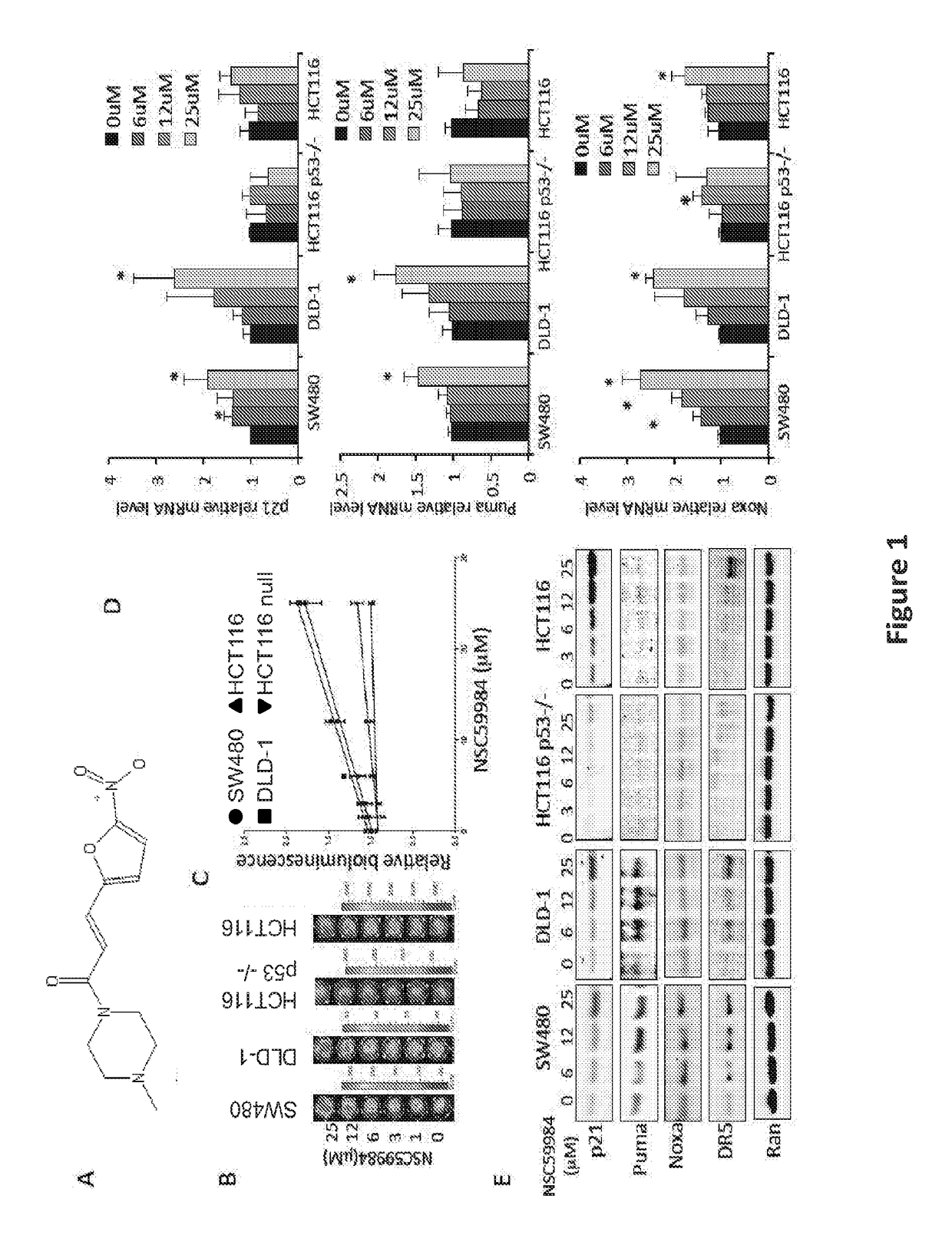
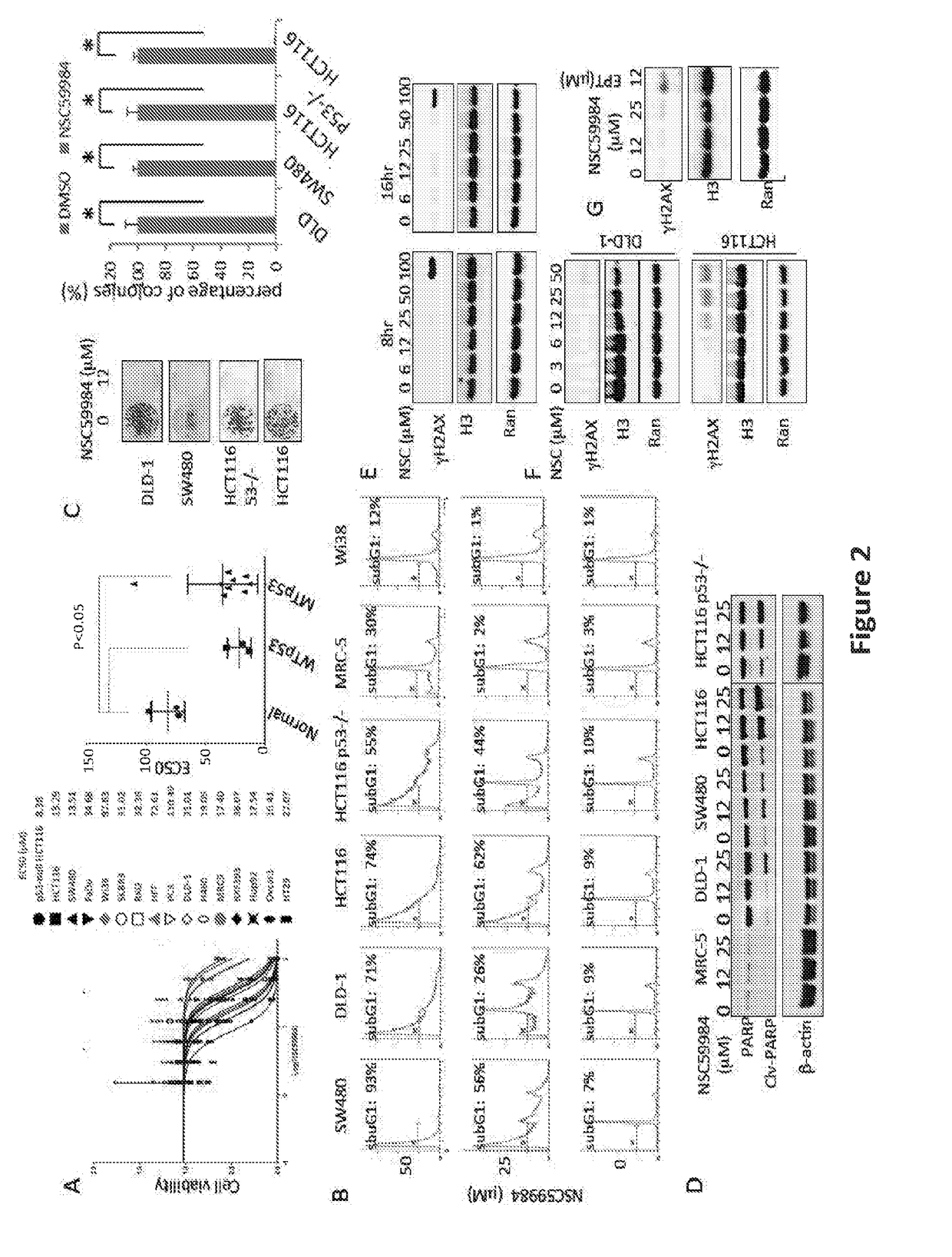
The invention includes compositions comprising NSC59984 or a derivative or analog thereof and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The invention further includes methods of treating or preventing cancer in a subject, comprising the step of administering to the subject the compositions contemplated within the invention.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Medicine for treating or preventing human cervical cancer as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN112870185ANovel mechanism of actionNon-addictiveInorganic non-active ingredientsEther/acetal active ingredientsMechanism of actionCervical ca
The invention discloses a medicine for treating or preventing human cervical cancer as well as a preparation method and application thereof, belongs to the technical field of medicines, and particularly relates to a medicine for treating or preventing human cervical cancer based on an MDM2-p53 protein and protein interaction signal channel and a target mechanism as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The invention finds that the action mechanism of the compound 1, 5, 6-trimethoxy-2, 7-dihydroxyphenanthrene is a new mechanism based on an MDM2-p53 protein and protein interaction signal pathway and a target spot. The medicine disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of novel action mechanism, no addiction and small dosage, and has the effect of inhibiting the growth of Hela cells. The IC50 on Hela cells for 48 hours is 0.42 [mu]M. And cell apoptosis can be caused by acting on an MDM2-p53 pathway, and meanwhile, mitochondrial apoptosis is caused.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Pharmaceutical compositions of Anisomelic acid and the use thereof
ActiveUS20150202180A1Improve commercial useIncreasing therapeutic usageBiocideOrganic chemistryAnisomelic acidSURFACTANT BLEND
A pharmaceutical composition for anti-viral cancer treatment in mammals, comprising a therapeutically effective amount of Anisomelic acid or salts thereof. The pharmaceutical composition may comprise Anisomelic acid or salt thereof in an oil-in-water emulsion, for example in an isotropic mixture of at least one oil and at least one surfactant or, alternatively, in a hydrophilic solvent and a co-solvents or surfactant or a combination thereof. A method of treating or preventing of cancer in a mammal, wherein the p53 pathway is deregulated by viral oncoproteins, is also provided.
Owner:ANISON THERAPEUTICS OY
Chds as modifiers of the p53 pathway and methods of use
Owner:EXELIXIS INC
Activators and therapeutic applications thereof
The invention presents methods of identifying small molecule compounds that are activators of tumor suppressor protein p53 pathway, and its associated family members p63 and p73, function. The invention is further drawn to methods of killing tumor cells and treating cancers or other conditions requiring activation of the p53 family member pathways and DNA damage response pathways with the small molecules.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method for treating ocular cancer
It has now been found that the p53 pathway is inactivated in ocular cancers such as retinoblastoma. As such, the present invention is a method for inducing ocular cancer cell death using a p53 activator. In particular embodiments, the p53 activator blocks the interaction between DM2 or DMX and p53. As the p53 activator induces ocular cancer cell death, a method for preventing or treating ocular cancer is also provided.
Owner:FLANDERS INTERUNIV INST FOR BIOTECH VIB +3
Application of Exenatide in preparing medicament for reversing activation of FFA to P53
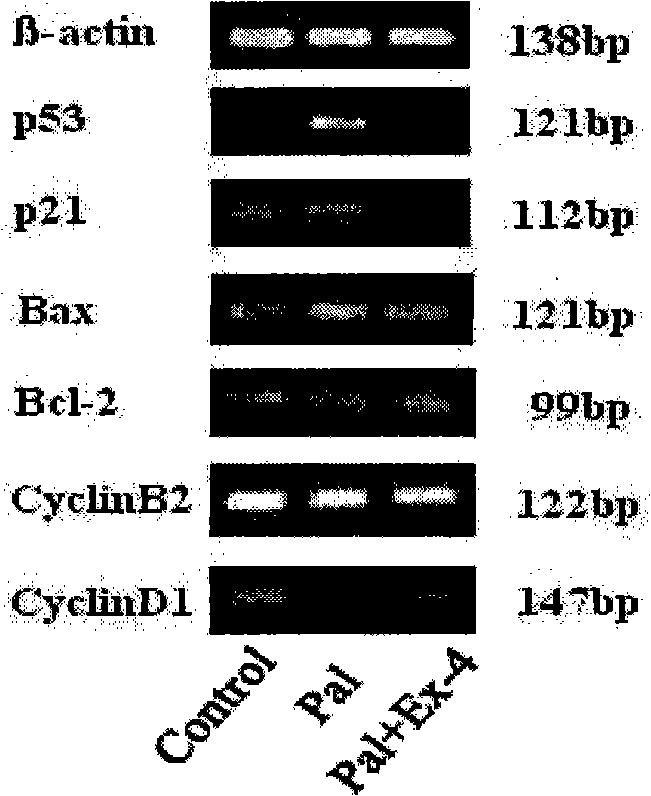
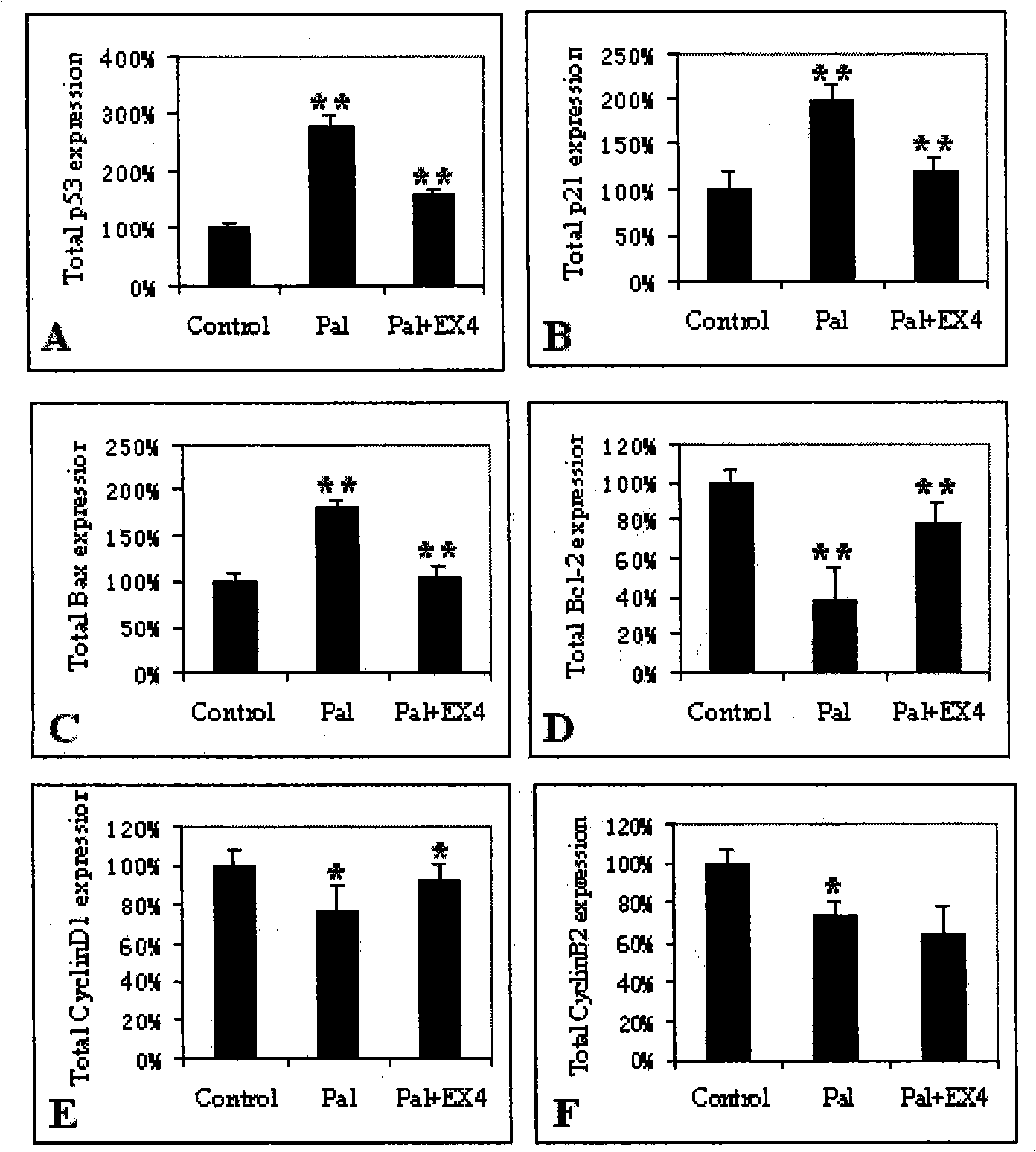
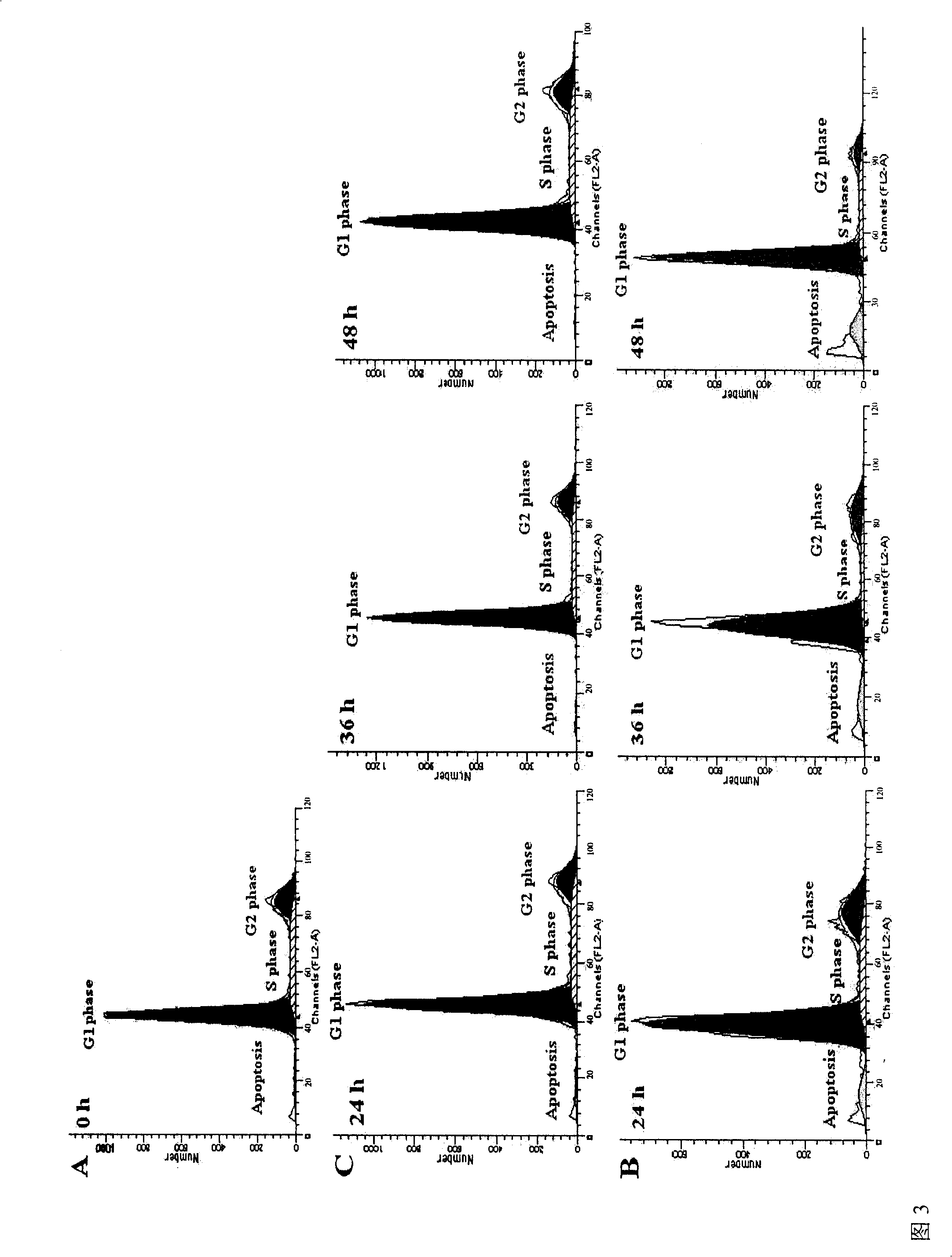
InactiveCN101293090AInhibit apoptosisPrevent diabetesPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderFactor iiBiological activation
The invention relates to an application of Exenatide in the preparation of drugs for reversing the activation of FFA on P53, which pertains to the field of medicine. The application of the Exenatide in the preparation of the drugs for reversing the activation of FFA on the sequence specific transcription factor P53 can inhibit the increases of P53, P21 and bax mRNA expressions and the decreases of bcl-2, CyclinD1 and CyclinB2 mRNA expressions caused by FFA. The Exenatide can prevent the occurrence of type II diabetes caused by P53 pathway during the early stage of obesity.
Owner:长春百克生物科技有限公司
Pharmaceutical compositions of Anisomelic acid and the use thereof
ActiveUS20160136126A1Improve commercial useIncreasing therapeutic usageBiocideAnimal repellantsAnisomelic acidSURFACTANT BLEND
A pharmaceutical composition for anti-viral cancer treatment in mammals, comprising a therapeutically effective amount of Anisomelic acid or salts thereof. The pharmaceutical composition may comprise Anisomelic acid or salt thereof in an oil-in-water emulsion, for example in an isotropic mixture of at least one oil and at least one surfactant or, alternatively, in a hydrophilic solvent and a co-solvents or surfactant or a combination thereof. A method of treating or preventing of cancer in a mammal, wherein the p53 pathway is deregulated by viral oncoproteins, is also provided.
Owner:ANISON THERAPEUTICS OY
Reconstituted human breast tumor model
InactiveUS20070157330A1VectorsArtificial cell constructsAbnormal tissue growthHuman Mammary Epithelium
Reconstituted human breast tumor models are disclosed. The models, which are incorporated into mice, provide actual tumors that arise spontaneously, thereby mimicking naturally occurring breast cancer. The tumors are genetically human, because they arise from human mammary tissues that develop from human mammary epithelial cells implanted into host mice. Prior to implantation, the mammary epithelial cells are genetically modified to contain either: (a) a recombinant human oncogene and an SV40er; or (b) a recombinant human oncogene, a transgene or shRNA that inhibits the p53 pathway, and a transgene or shRNA that inhibits the Rb pathway.
Owner:WU MIN +2
Methods for in vitro expansion of adult tissue stem cells
PendingUS20210147811A1Increased proliferationIncrease in sizeCulture processArtificial cell constructsP53 signalingPharmacometrics
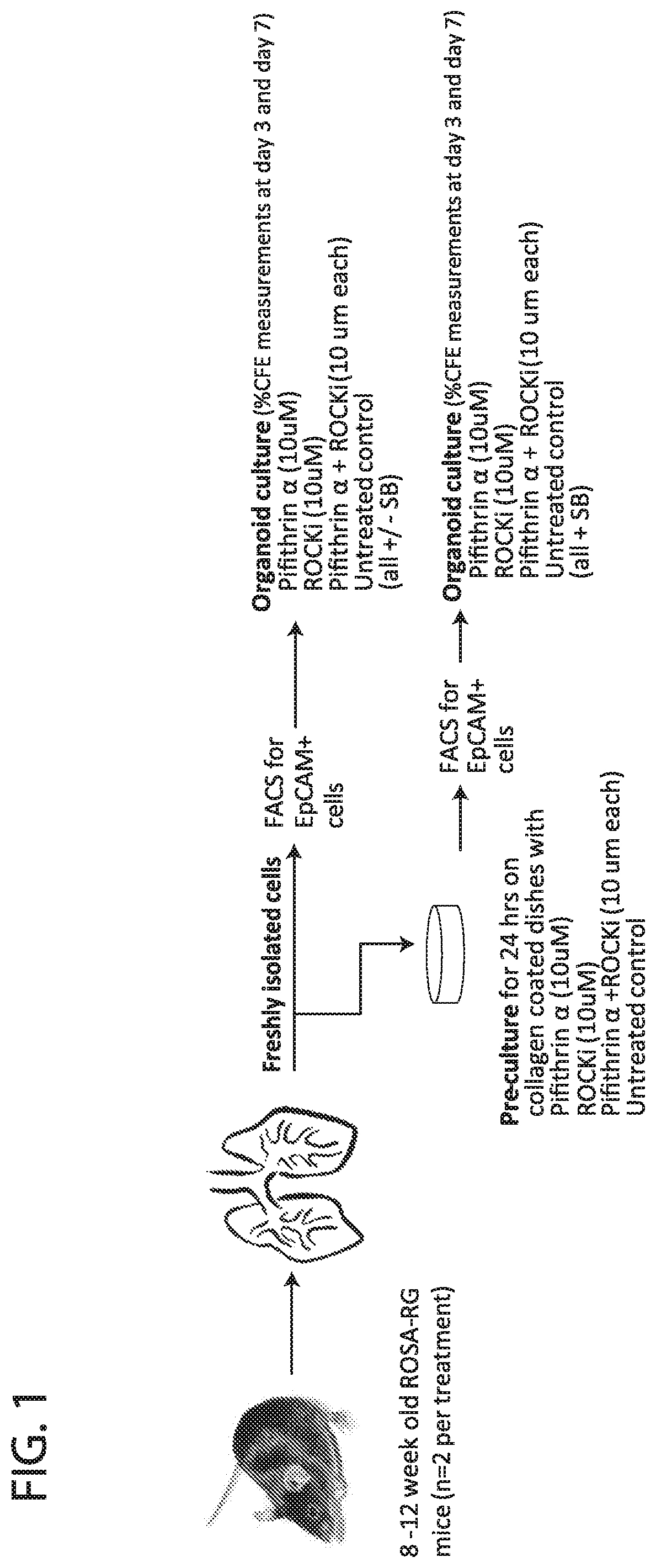
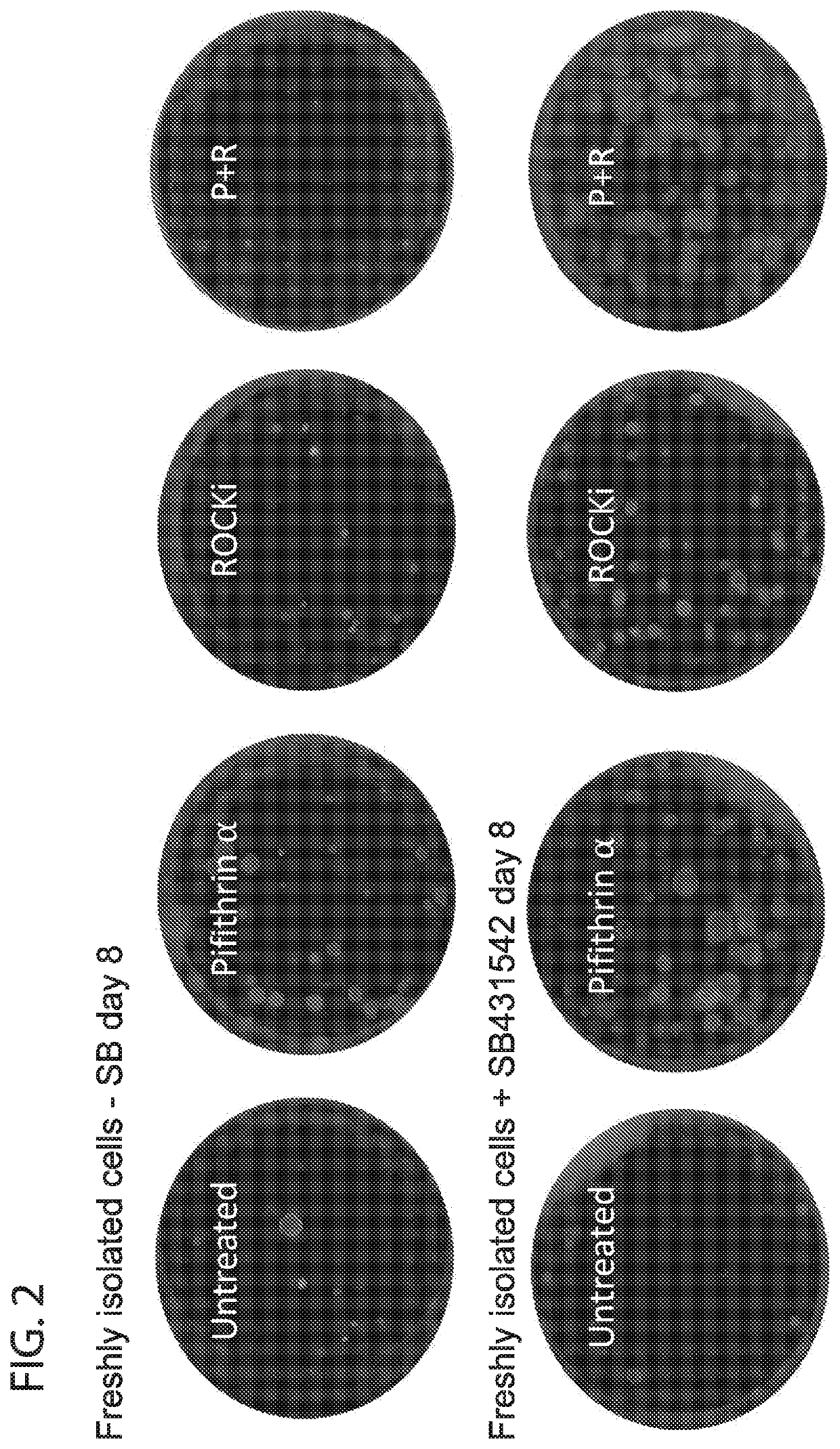
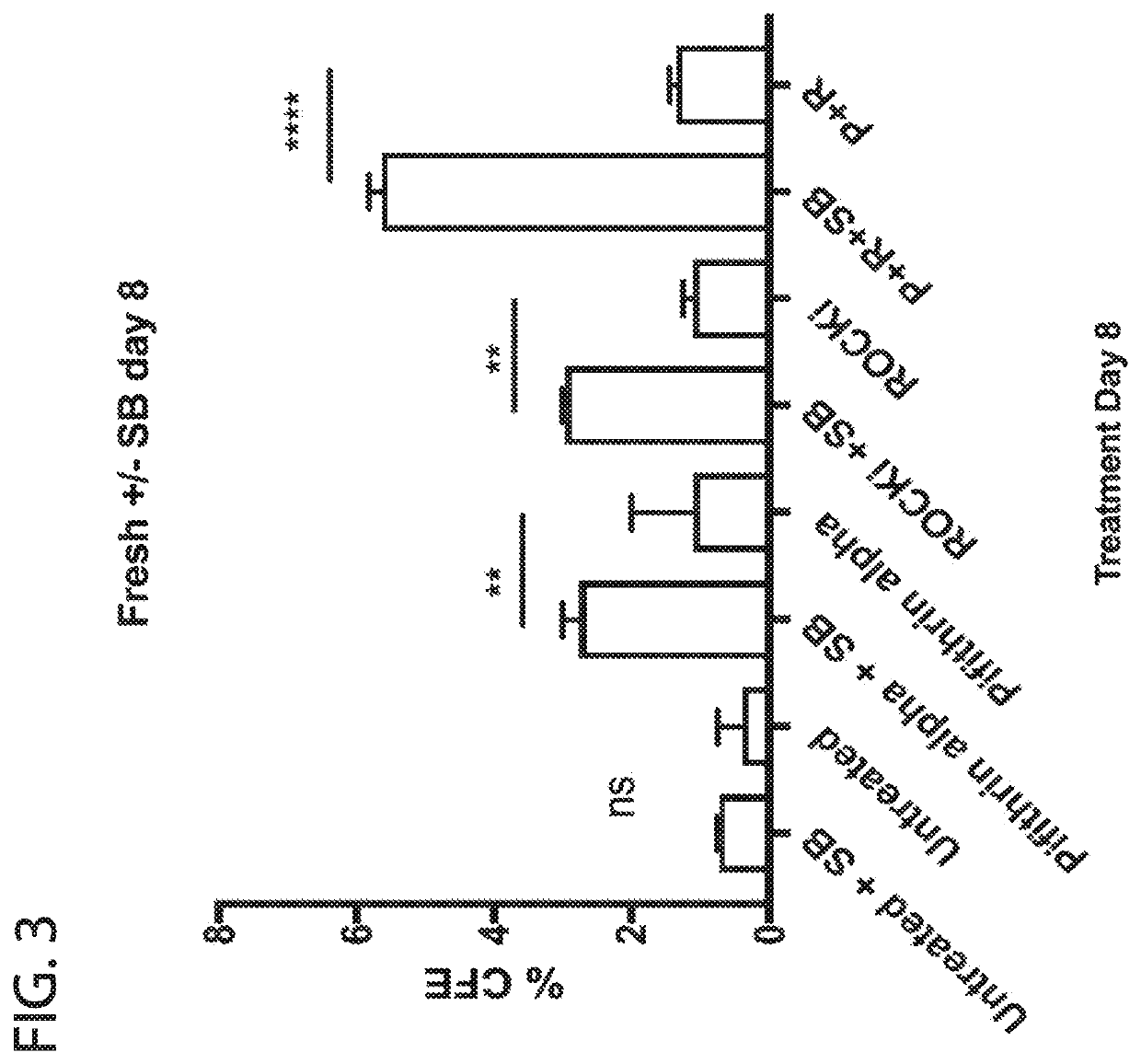
Described herein are methods and compositions for regulation of the p53 pathway, providing intrinsic “sternness” allowing for their efficient in vitro expansion following isolation. Pharmacologic approaches to modulate p53 signaling supports expansion of stem cells, including greater clonal expansion of lung stem cells when compared to use of other small molecules such as ROCK inhibitor Y27632 alone. Effects of combined treatment with Pifithrin-α and Y27632 are additive. The current invention involves use of drugs that target the p53 pathway to reversibly regulate stem cell expansion in vitro for banking of stem cells and for pre-conditioning of stem cells prior to orthotopic transplantation.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Application of theabrownin in preparation of medicine for treating liver cancer
ActiveCN111870638BGrowth inhibitionGrowth inhibitory effectAntineoplastic agentsPlant ingredientsSignalling pathwaysPharmacology
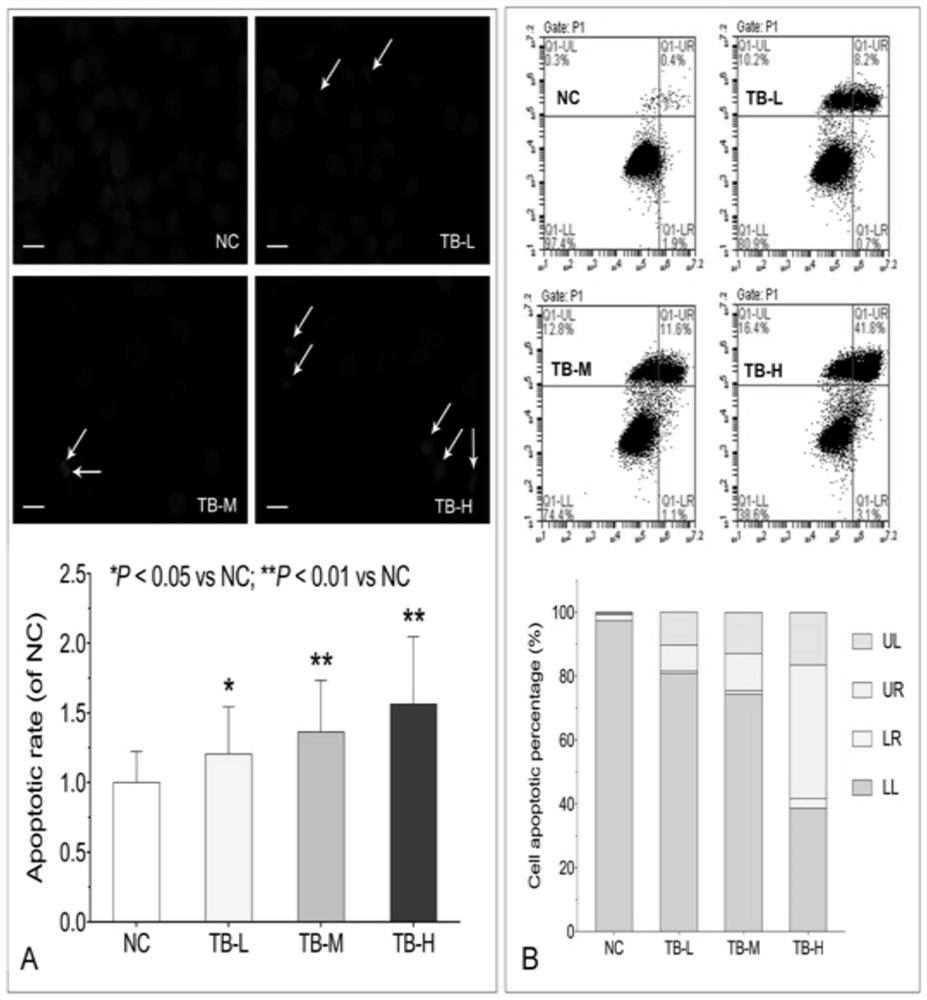
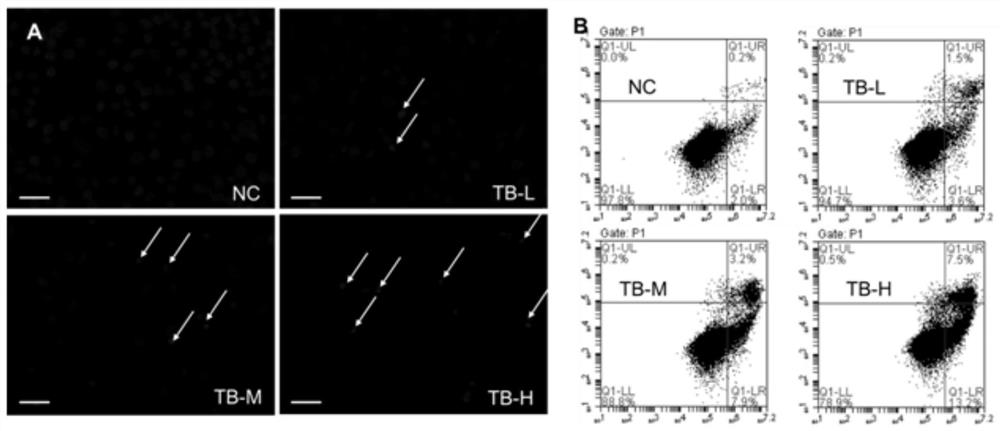
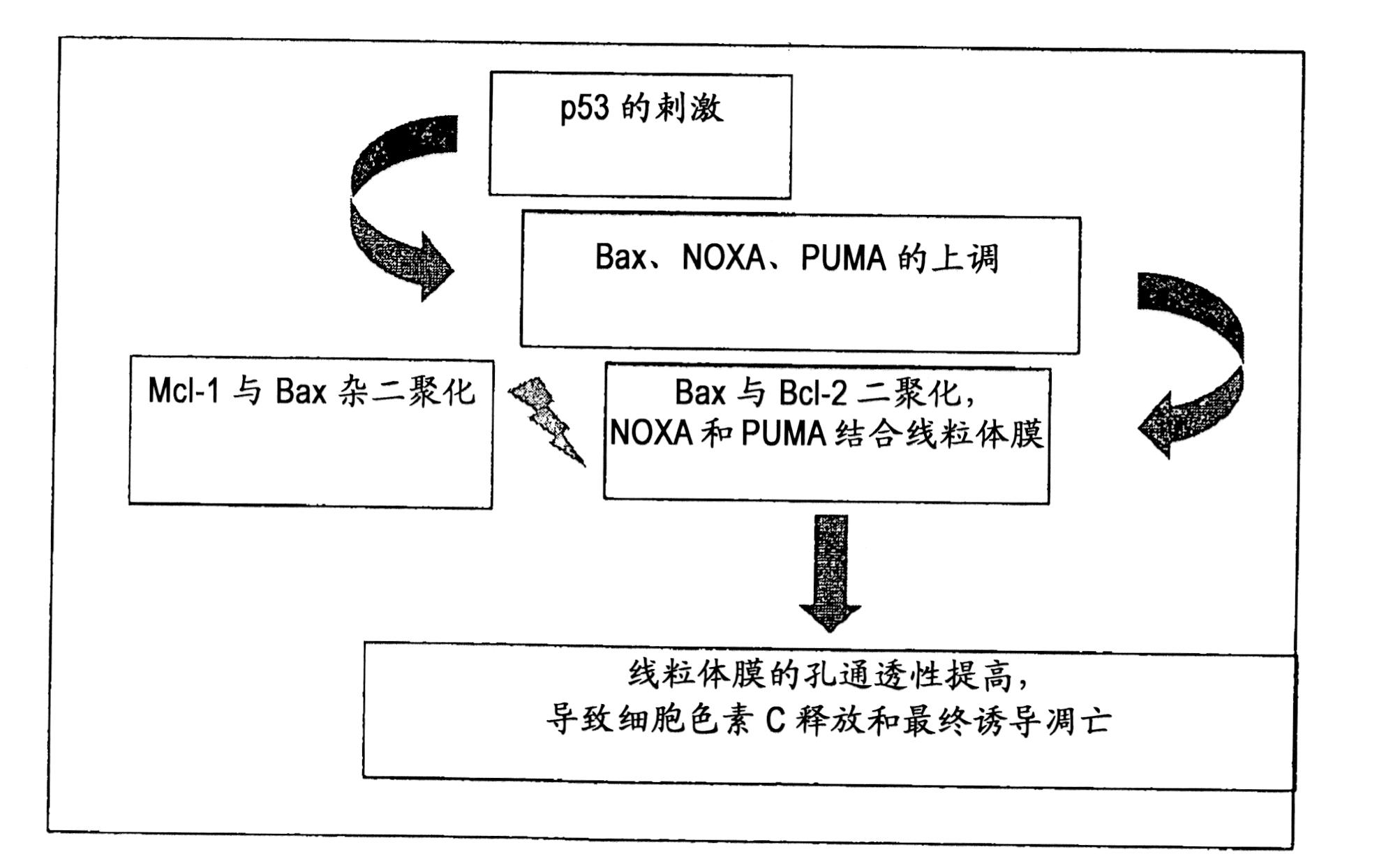
The application of theabrownin in the preparation of drugs for treating liver cancer belongs to the technical field of theabrownin use. Specifically include: the application of theabrownin in the preparation of drugs for treating liver cancer, theabrownin promotes the apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma Huh7 cells by activating the JNK signaling pathway, and inhibits the growth of liver cancer xenografts. The present invention proves through various tests that theabrownin has significant anti-proliferation and pro-apoptotic effects on Huh7 cells, and has dose-dependent effects. Theabrownin promotes the apoptosis of Huh7 cells and inhibits the growth of zebrafish liver cancer xenografts by activating the JNK signaling pathway. Theabrownin can inhibit tumor by 48.1%. Moreover, theabrownin regulates downstream apoptosis-related genes by activating the P53 pathway PUMA, NOXA, Bax, and Bcl‑2 and so on to promote the apoptosis of P53 wild Sk‑hep1 cells.
Owner:杭州茗褐生物科技有限公司
Methods and use of inducing apoptosis in cancer cells
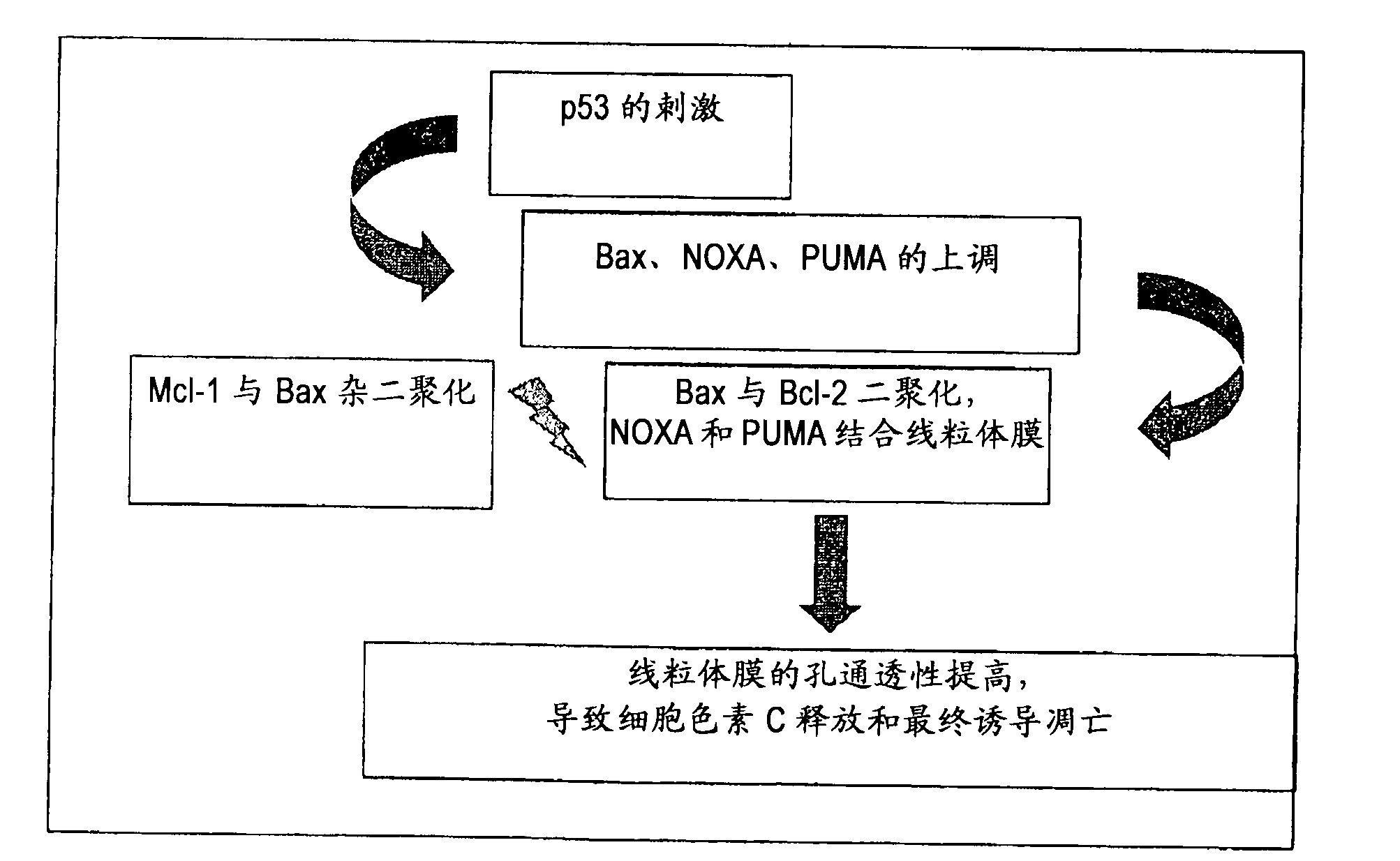
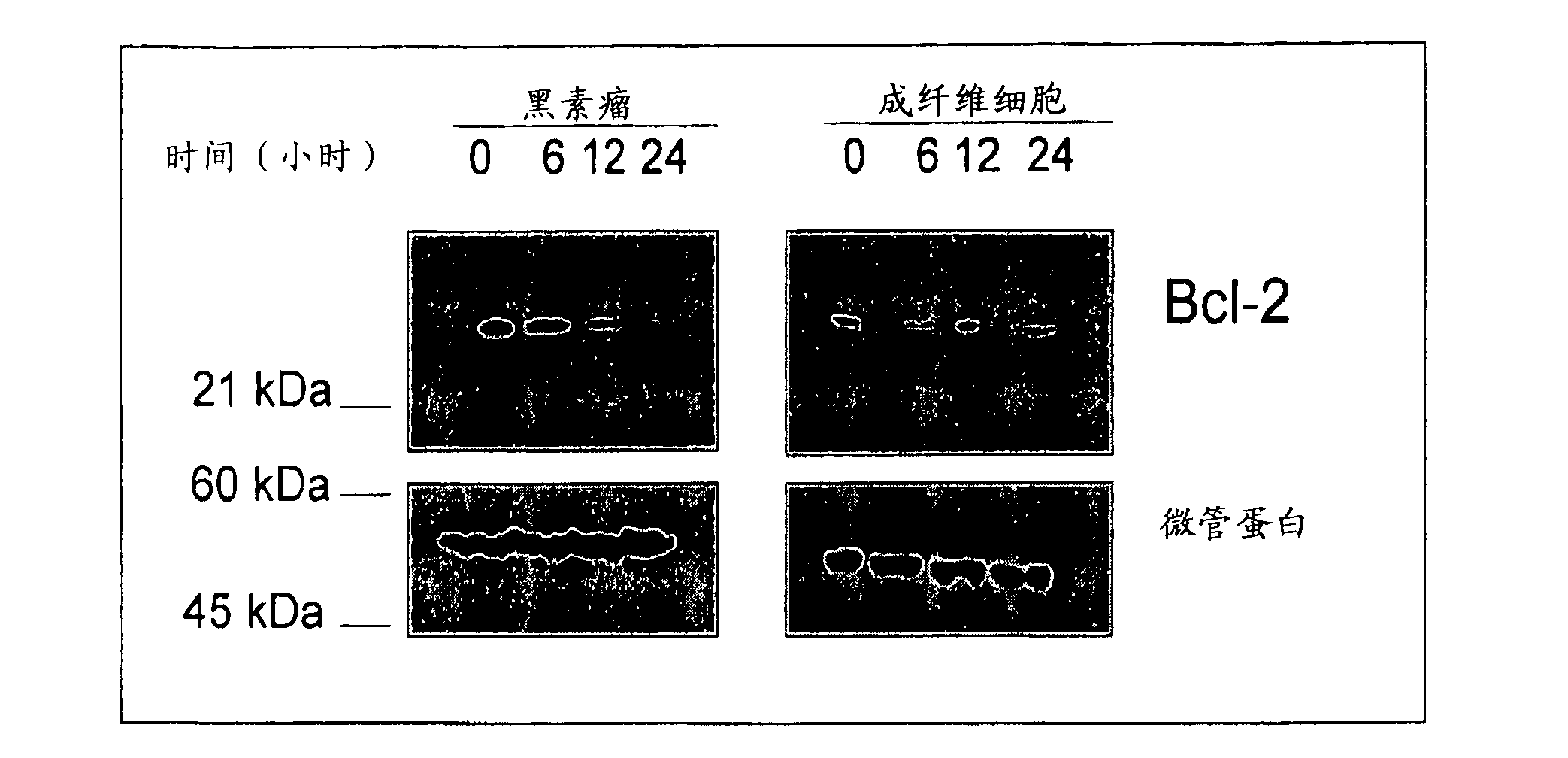
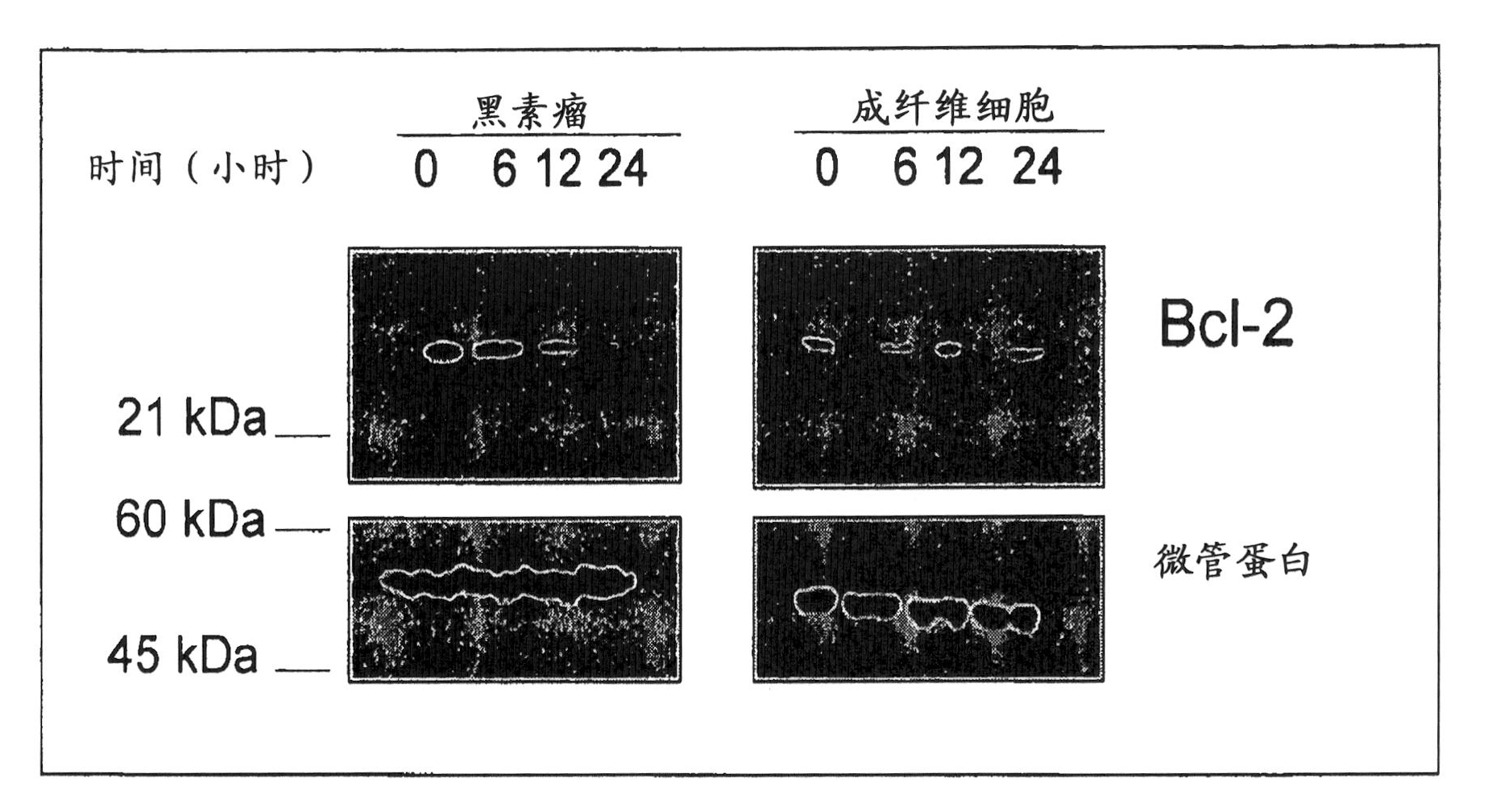
The present disclosure relates to a method of inducing apoptosis in a cancer cell by delivery of exogenous Coenzyme Q1O or its metabolites thereof in a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier to effectuate cell contact of endogenous Coenzyme Q1O or its metabolites thereof in addition to but not limited to mevalonic acid and oleic acid to form an intracellular complex. The present disclosure also provides a method of modulating the p53 pathway and Bcl-2 protein family in a manner that restores the apoptotic potential to a cancer cell by delivery of Coenzyme Q1O in a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present disclosure further provides a method to specifically normalize the ratio of pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2 gene family in a proportion to re-program a cancer cell to undergo apoptosis.
Owner:BERG
Lces as modifiers of the p53 pathway and methods of use
Owner:EXELIXIS INC
Compound For Anti-Cancer Therapy That Acts By Targeting GOF Mutant P53 And Stimulates P73 To Restore The P53 Pathway Signaling
The invention includes compositions comprising NSC59984 or a derivative or analogue thereof and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The invention further includes methods of treating or preventing cancer in a subject, comprising the step of administering to the subject the compositions contemplated within the invention.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Methods for identifying novel therapeutics and diagnostics in the p53 pathway
InactiveUS7196242B2Extend your lifeShortened life-spanSugar derivativesAnimals/human peptidesRegimenHuman tumor
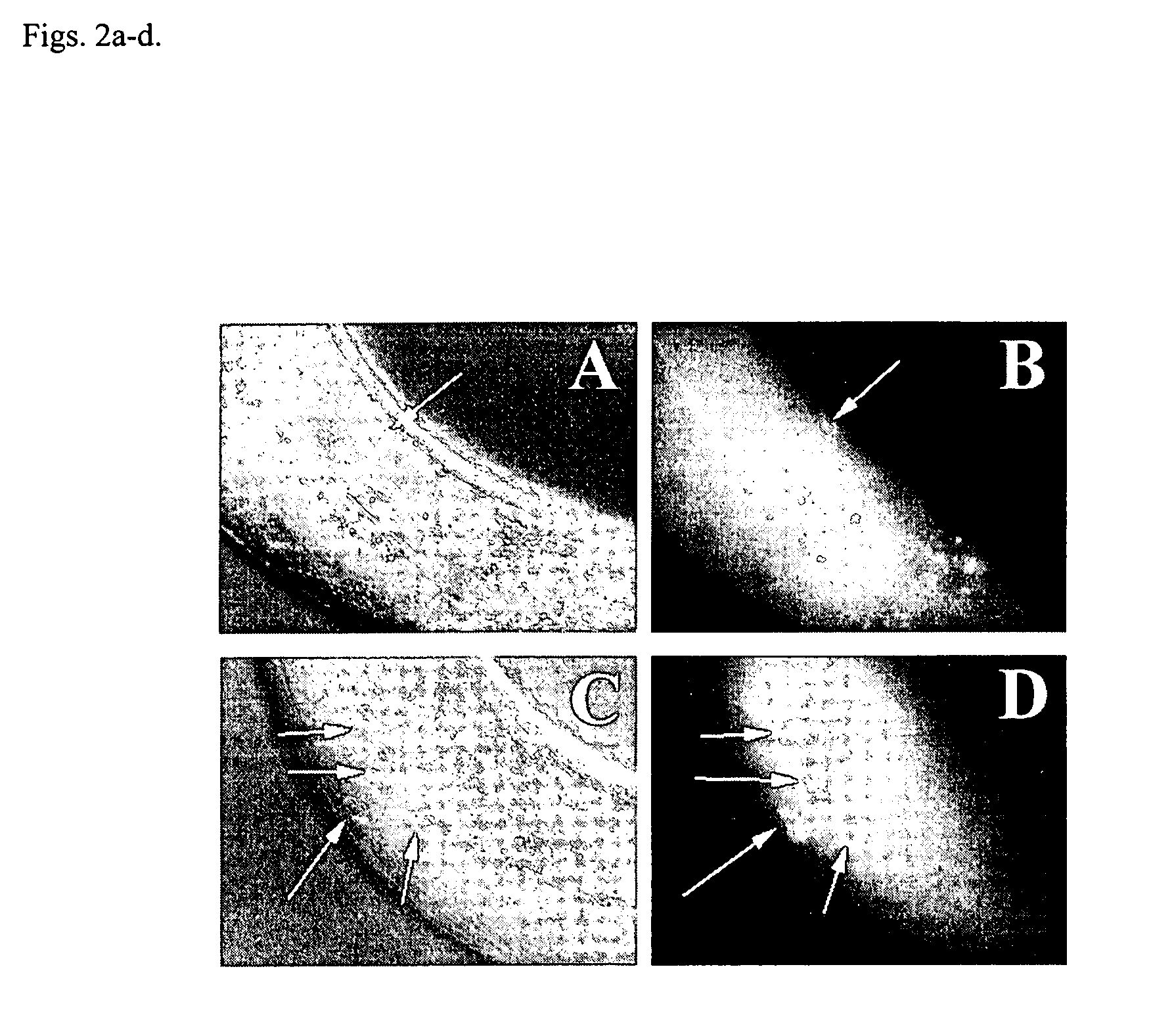
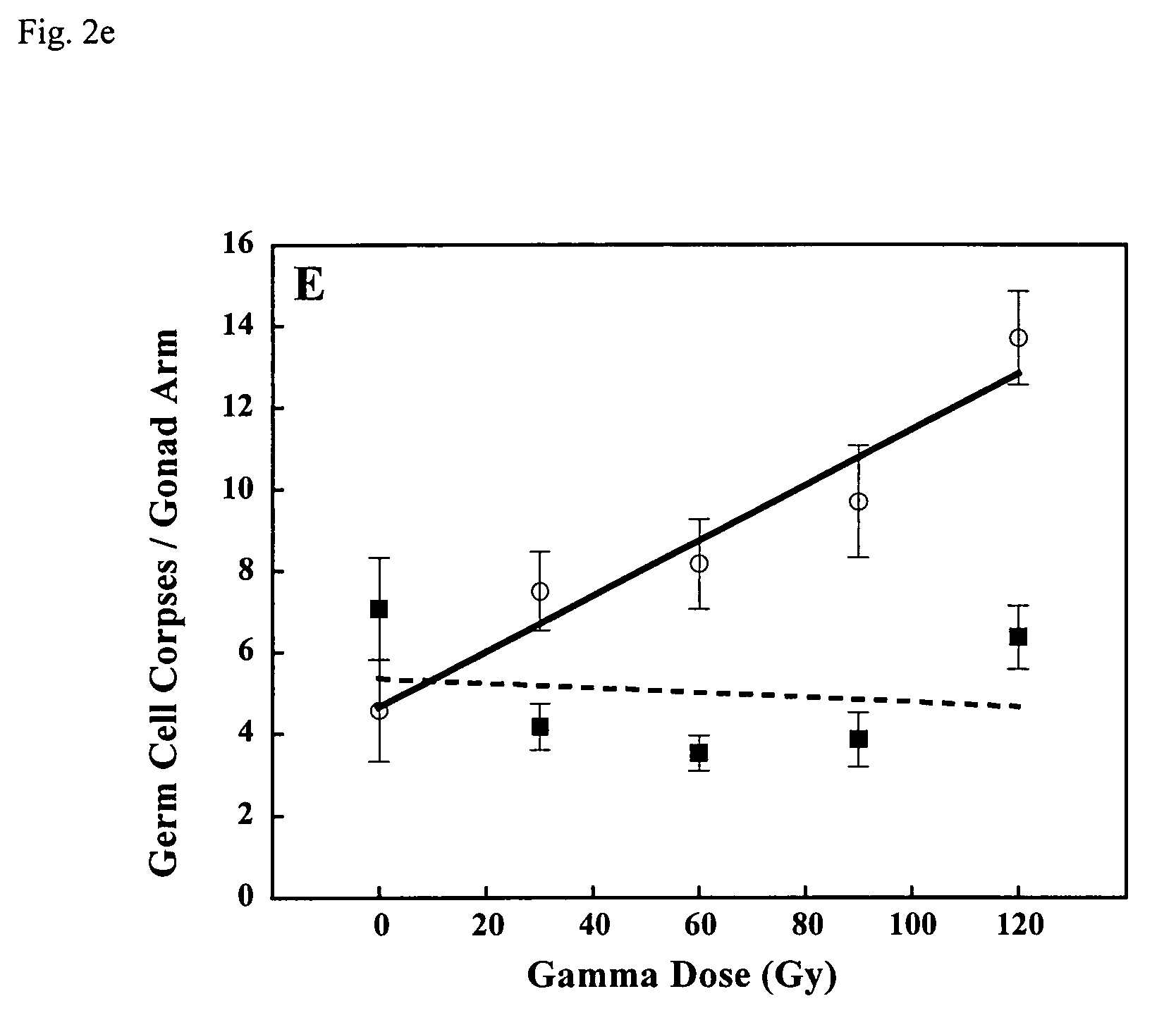
The present invention identifies a p53 homolog gene, cep-1, and mutations thereof in the nematode C. elegans which allows for the application of molecular genetic methods to identify new components of the p53 pathway as well as genes that act in parallel to the p53 pathway. cep-1 mutants show elevated physiological germ cell death during normal development. The present invention also provides a simple system with which to perform high-throughput screens for pharmacological agents that suppress the effects of eliminating the cep-1 gene or that enhance its effectiveness when in a mutant state. This strategy should identify agents that selectively kill p53-deficient cells that are resistant to traditional chemotherapeutic regimens and thus block the formation of human tumors that arise when p53 function is compromised.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods and use of inducing apoptosis in cancer cells
The present disclosure relates to a method of inducing apoptosis in a cancer cell by delivery of exogenous Coenzyme QlO or its metabolites thereof in a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier to effectuate cell contact of endogenous Coenzyme QlO or its metabolites thereof in addition to but not limited to mevalonic acid and oleic acid to form an intracellular complex. The present disclosure also provides a method of modulating the p53 pathway and Bcl-2 protein family in a manner that restores the apoptotic potential to a cancer cell by delivery of Coenzyme QlO in a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present disclosure further provides a method to specifically normalize the ratio of pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2 gene family in a proportion to re-program a cancer cell to undergo apoptosis.
Owner:BERG
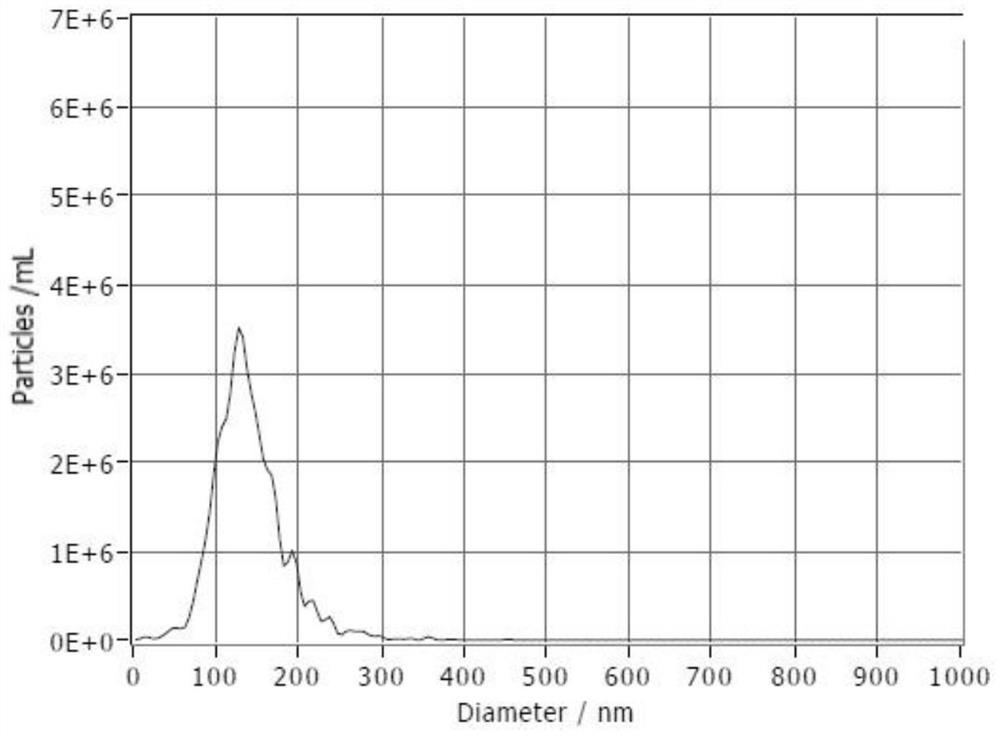
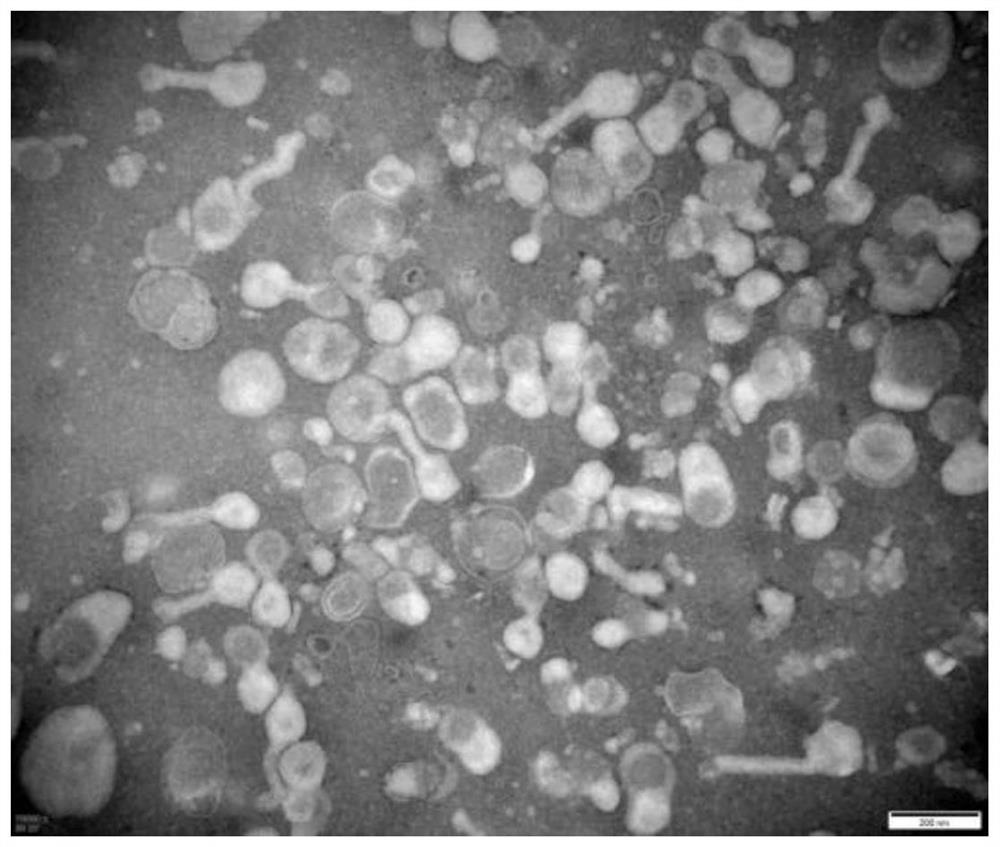
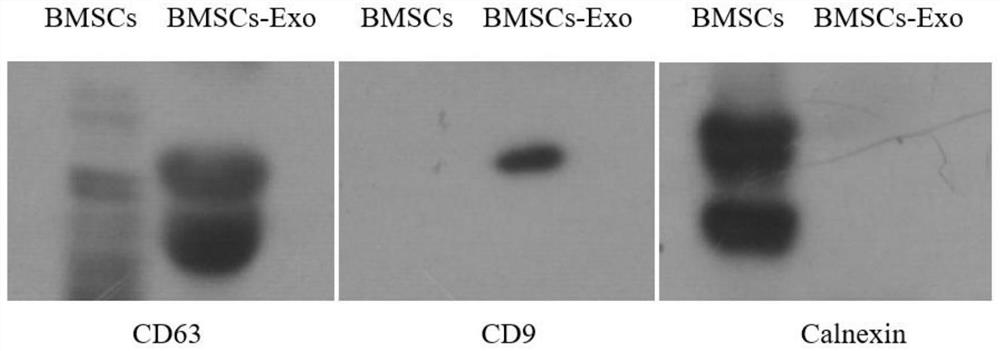
Application of mesenchymal stem cell exosome
PendingCN114748505APrevent hypoxic damageAlleviate hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injuryOrganic active ingredientsUnknown materialsSignal PathwaysP53 pathway
The invention provides an application of a bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell exosome. After BMSCs-Exo is injected into HIRI Kunming mice, liver function impairment can be relieved, and transcriptome sequencing finds that a p53 signal channel participates in the process. The miR-25-3p is significantly down-regulated in an HIRI liver, while the BMSCs and the BMSCs-Exo both contain the miR-25-3p. After the miR-25-3p simulant is transferred, the expression quantity of the miR-25-3p is increased. Bioinformatics analysis and dual luciferase reporter gene experiments show that PTEN is a target gene of miR-25-3p. After the miR-25-3p simulant is transferred into an HIRI mouse and hypoxia / reoxygenation AML12 hepatocytes, the PTEN expression quantity is reduced, the p53 pathway is inhibited, the apoptosis is reduced, the cell activity is improved, and the liver injury is relieved. Therefore, the mechanism of the miR-25-3p for relieving the HIRI is clarified, and a new thought is provided for stem cell treatment of the HIRI.
Owner:GUILIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Multi-target anti-tumor small molecule and derivative, preparation method, pharmaceutical composition and application thereof
ActiveCN113831346AEfficient anti-tumor effectHigh tumor inhibition rate in vivoOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryTopoisomerase activityChemical structure
The invention discloses a multi-target anti-tumor small molecule and a derivative, a preparation method, a pharmaceutical composition and application thereof. The chemical structure of the small molecule is shown as a formula I, and the derivative relates to a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of the small molecule. The small molecule and the derivative thereof have efficient tumor inhibition effects in vivo and in vitro, have low toxicity to cells and organisms, and do not generate genotoxicity; the anti-tumor activity is achieved through the multi-target effect, the HDAC inhibition activity is provided, the p53 pathway can be effectively activated, the topoisomerase activity can be effectively inhibited, and the small molecule can be used for preparing anti-tumor drugs; the preparation method is simple and easy to operate.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Methods for treating cognitive deficits associated with fragile X syndrome
ActiveUS9962380B2Improve and enhanceIncrease neurogenesisOrganic active ingredientsFragile X chromosomeMdm2 p53
Provided herein are methods of treating a cognitive deficit, including cognitive deficits associated with a Fmr1 genetic defect. More particularly, provided herein are methods in which an effective amount of a MDM2-p53 pathway inhibitor is administered to a subject afflicted with at least one cognitive deficit, whereby administration of the inhibitor improves, enhances, or rescues at least one cognitive deficit in the subject.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
A Compound For Anti-Cancer Therapy That Acts By Targeting GOF Mutant P53 And Stimulates P73 To Restore The P53 Pathway Signaling
The invention includes compositions comprising NSC59984 or a derivative or analogue thereof and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The invention further includes methods of treating or preventing cancer in a subject, comprising the step of administering to the subject the compositions contemplated within the invention.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com