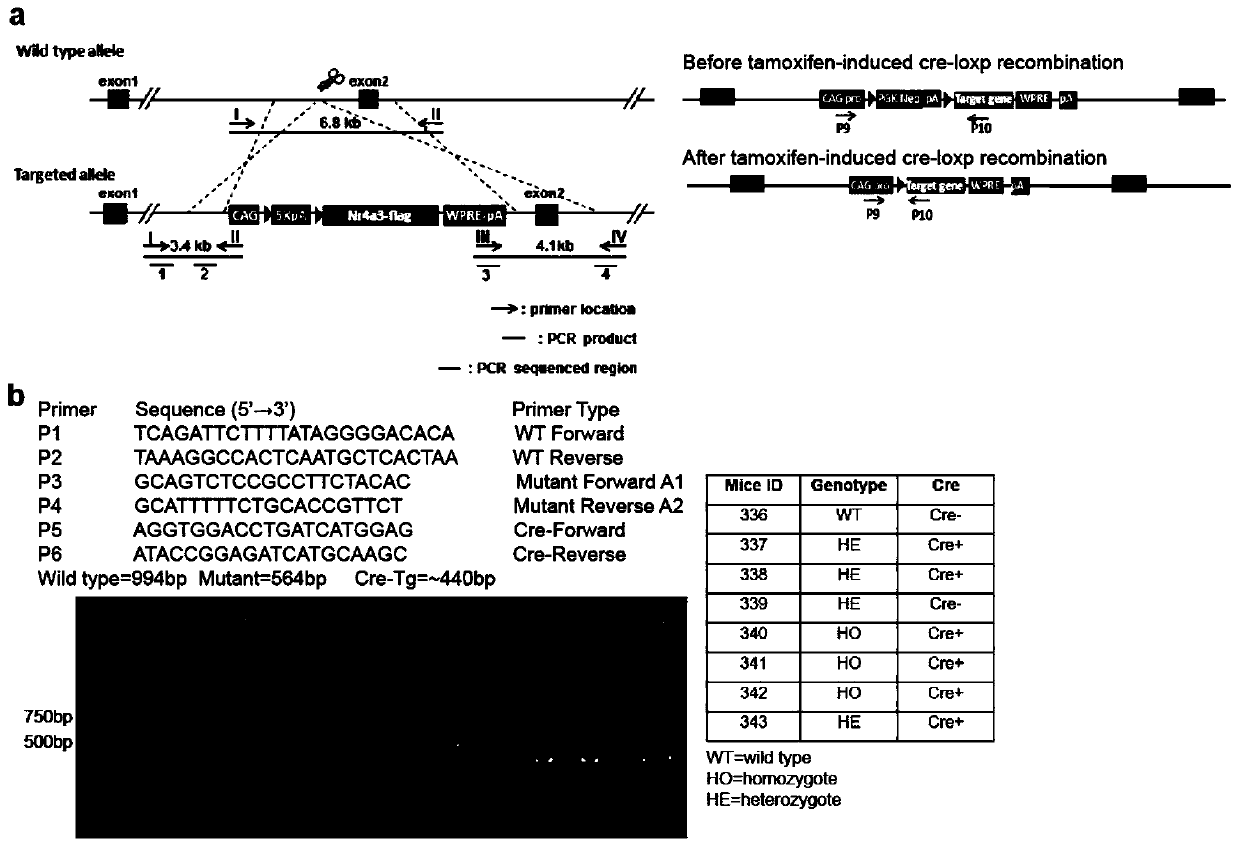
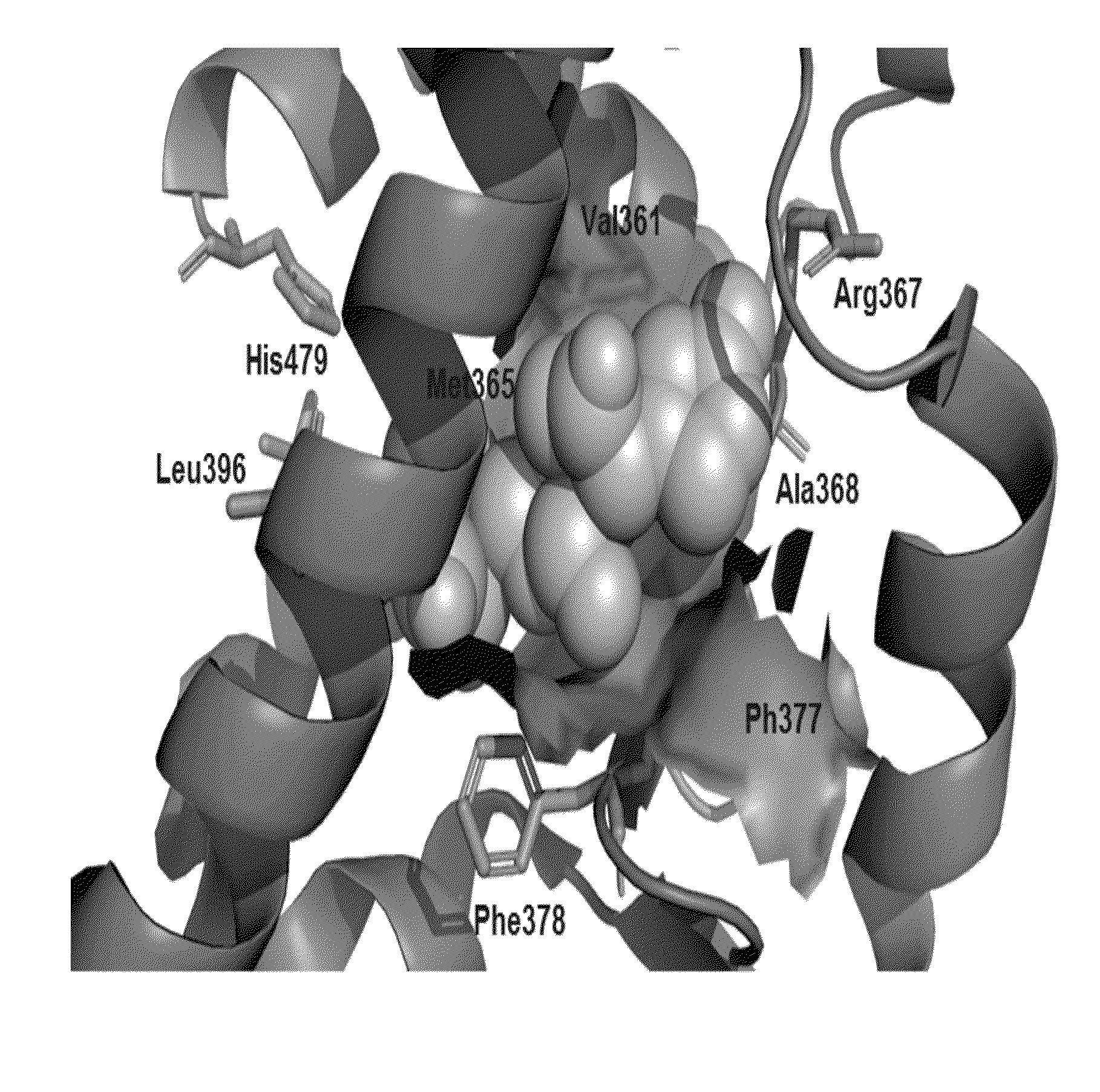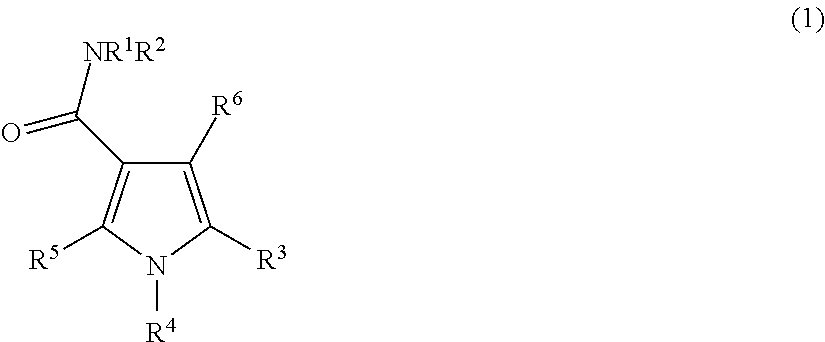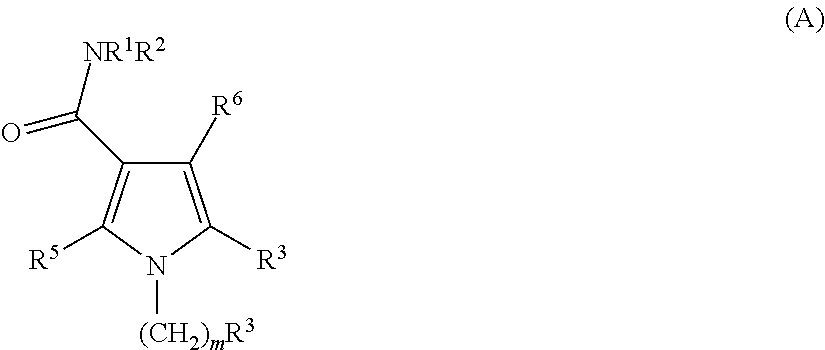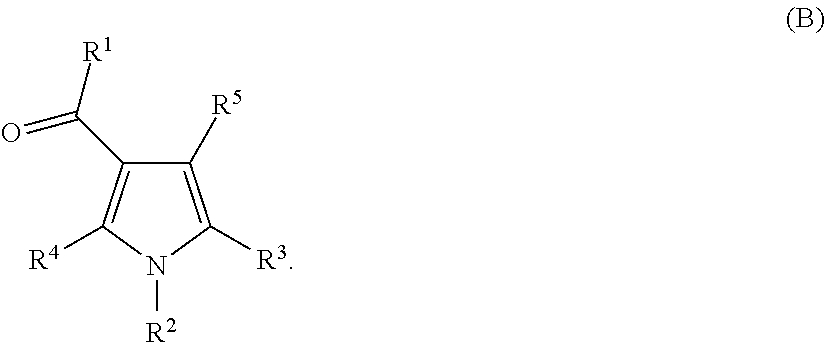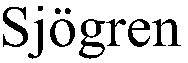Patents
Literature
50 results about "Orphan Nuclear Receptors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Examples of orphan receptors are found in the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) and nuclear receptor families. GPCR orphan receptors are usually given the name "GPR" followed by a number, for example GPR1. If an endogenous ligand is found, the orphan receptor is "adopted".
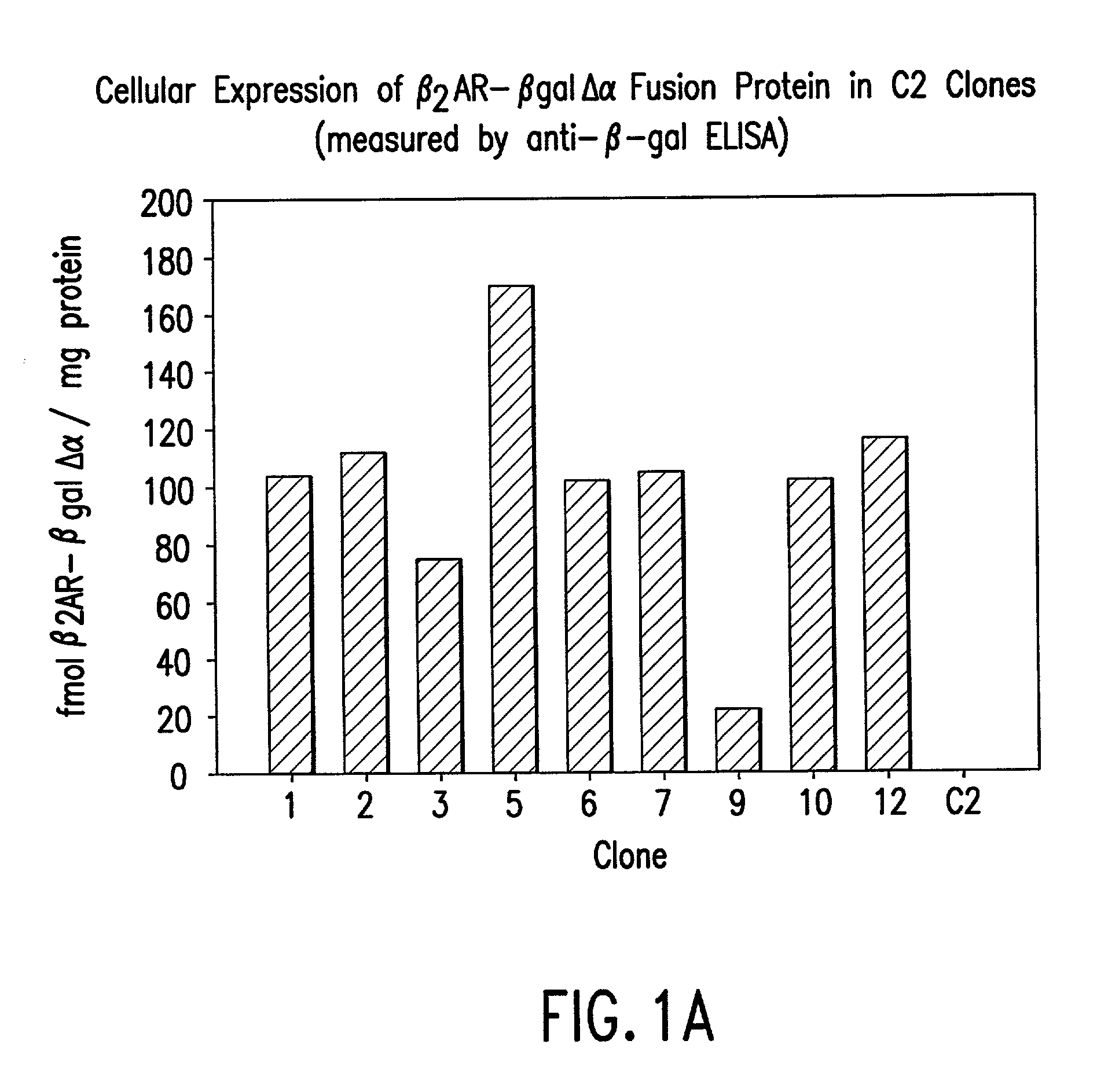
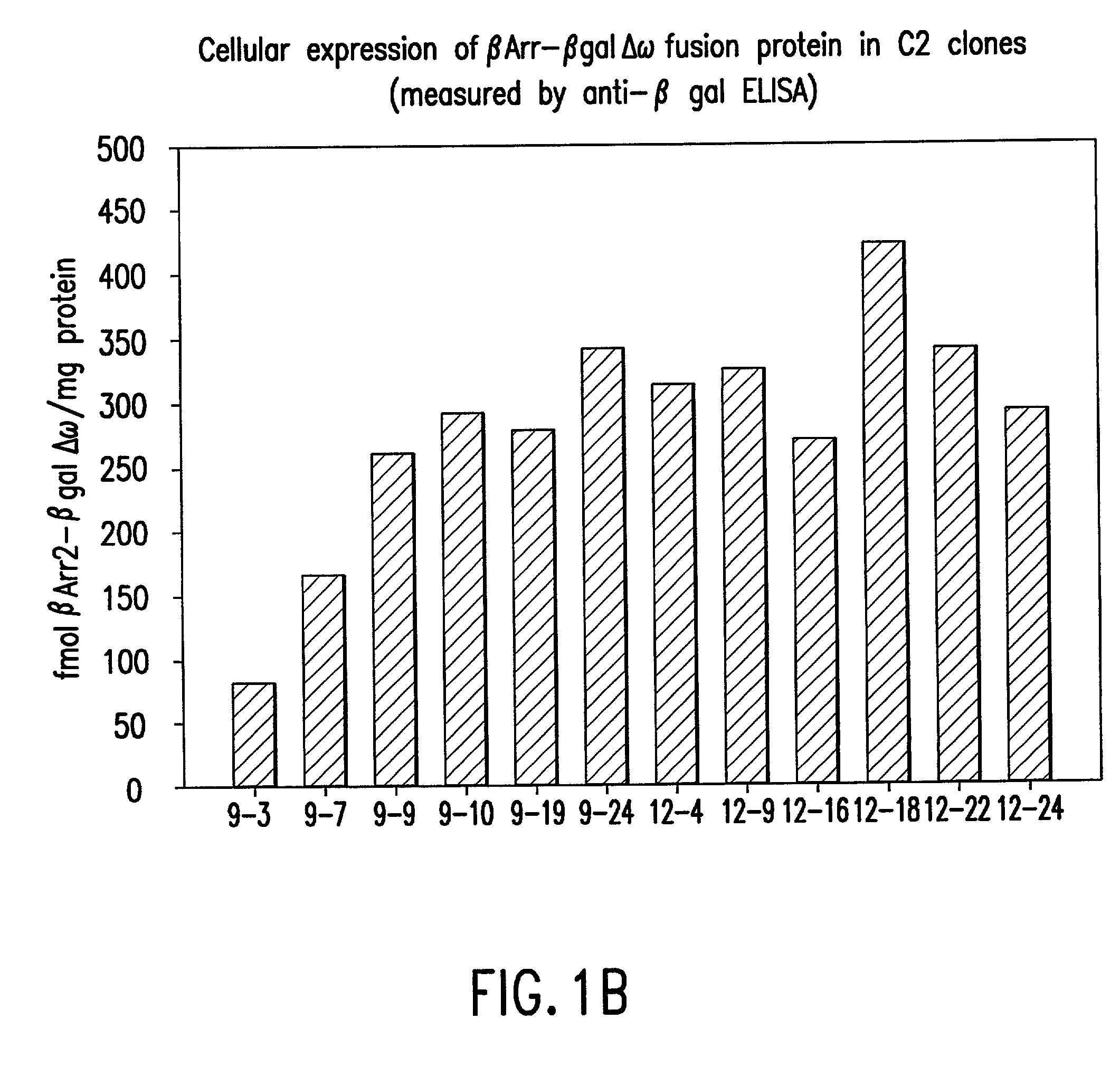
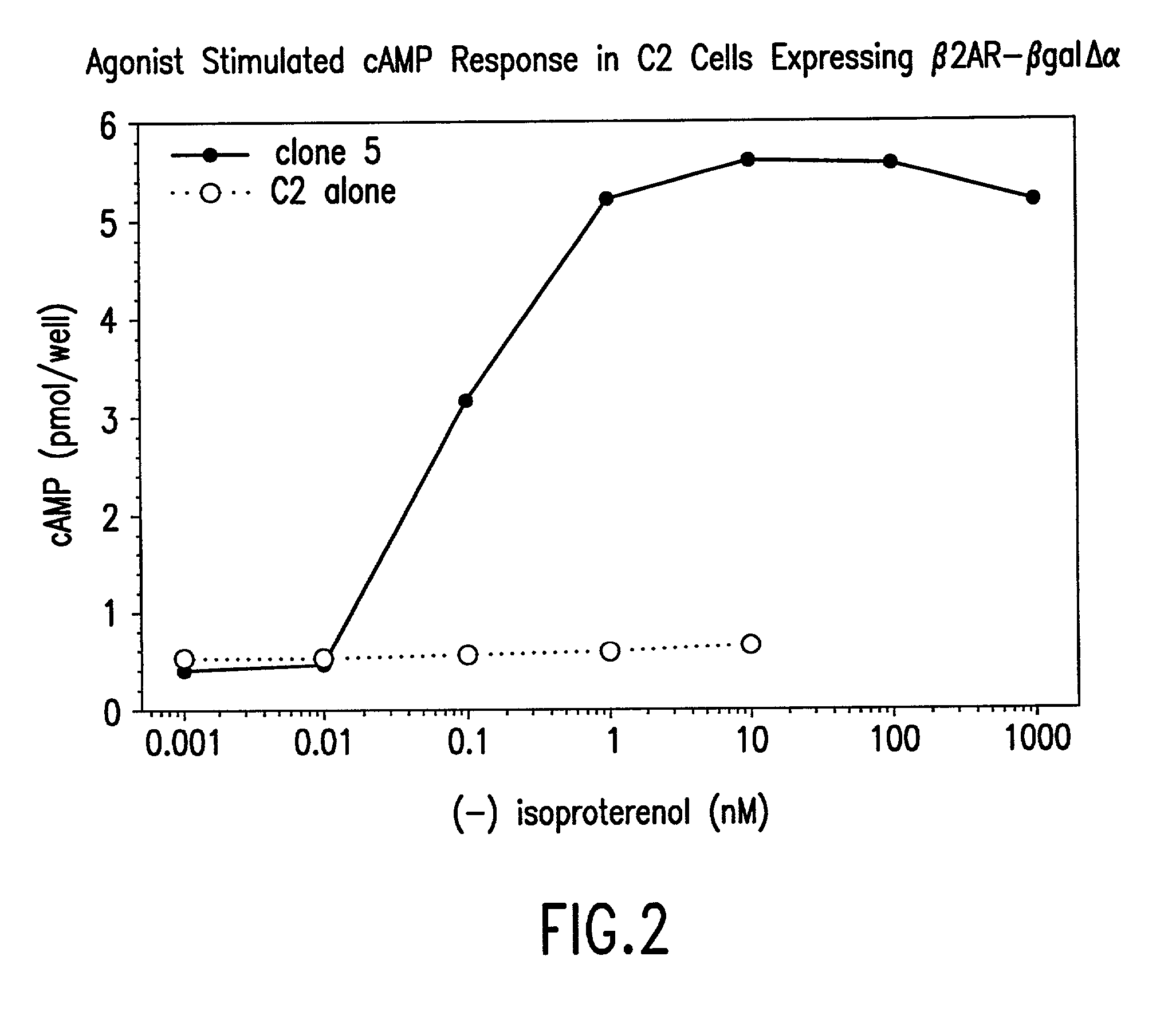
Systems for sensitive detection of G-protein coupled receptor and orphan receptor function using reporter enzyme mutant complementation
Methods for detecting G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) activity; methods for assaying GPCR activity; and methods for screening for GPCR ligands, G-protein-coupled receptor kinase (GRK) activity, and compounds that interact with components of the GPCR regulatory process are described. Included are methods for expanding ICAST technologies for assaying GPCR activity with applications for ligand fishing, and agonist or antagonist screening. These methods include: engineering seronine / threonine phosphorylation sites into known or orphan GPCR open reading frames in order to increase the affinity of arrestin for the activated form of the GPCR or to increase the reside time of arrestin on the activated GPCR; engineering mutant arrestin proteins that bind to activated GPCRs in the absence of G-protein coupled receptor kinases which may be limiting; and engineering mutant super arrestin proteins that have an increased affinity for activated GPCRs with or without phosphorylation. These methods are intended to increase the robustness of the GPCR / ICAST technology in situations in which G-protein coupled receptor kinases are absent or limiting, or in which the GPCR is not efficiently down-regulated or is rapidly resensitized (thus having a labile interaction with arrestin). Included are also more specific methods for using ICAST complementary enzyme fragments to monitor GPCR homo- and hetero-dimerization with applications for drug lead discovery and ligand and function discovery for orphan GPCRs.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
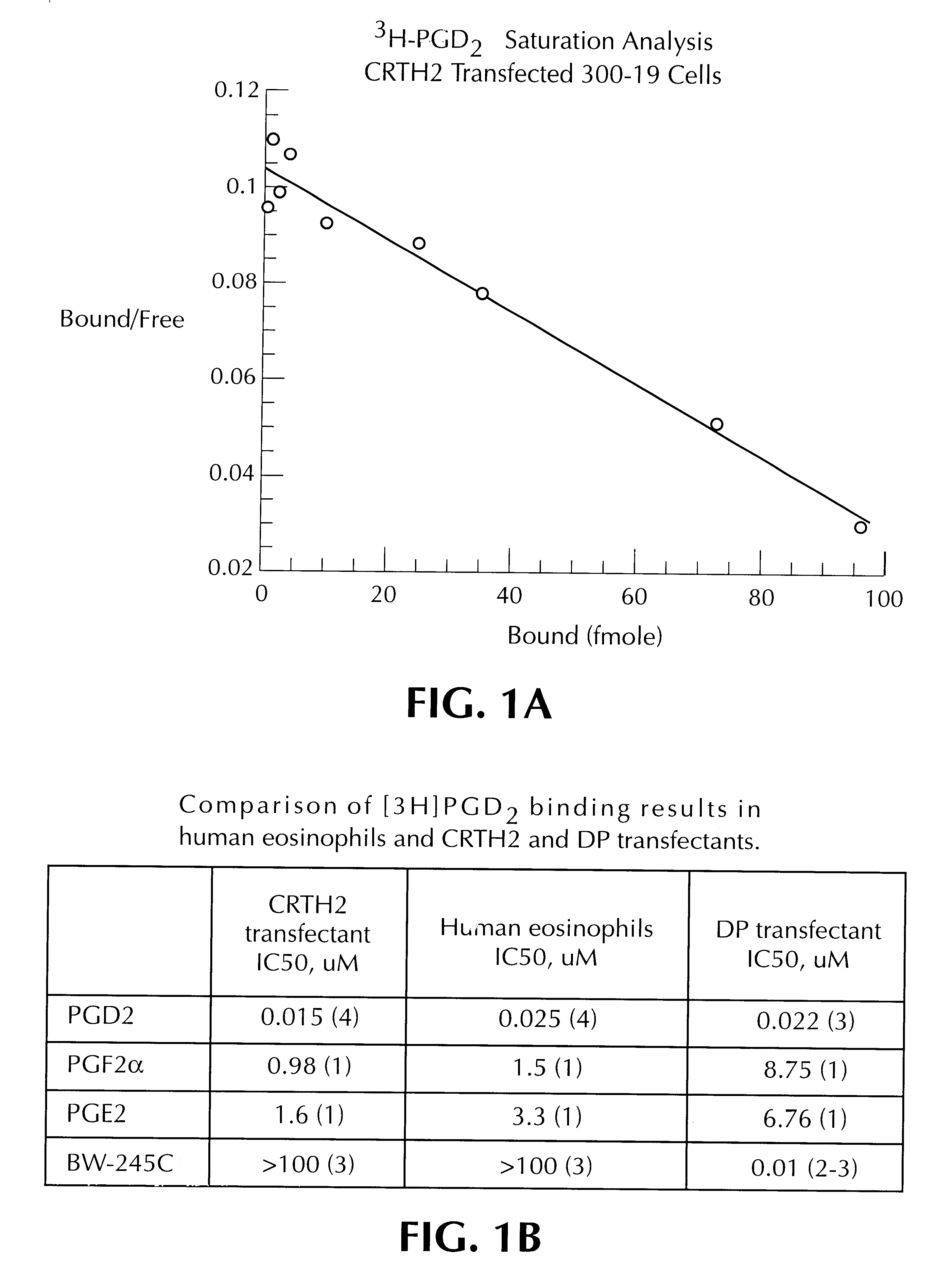
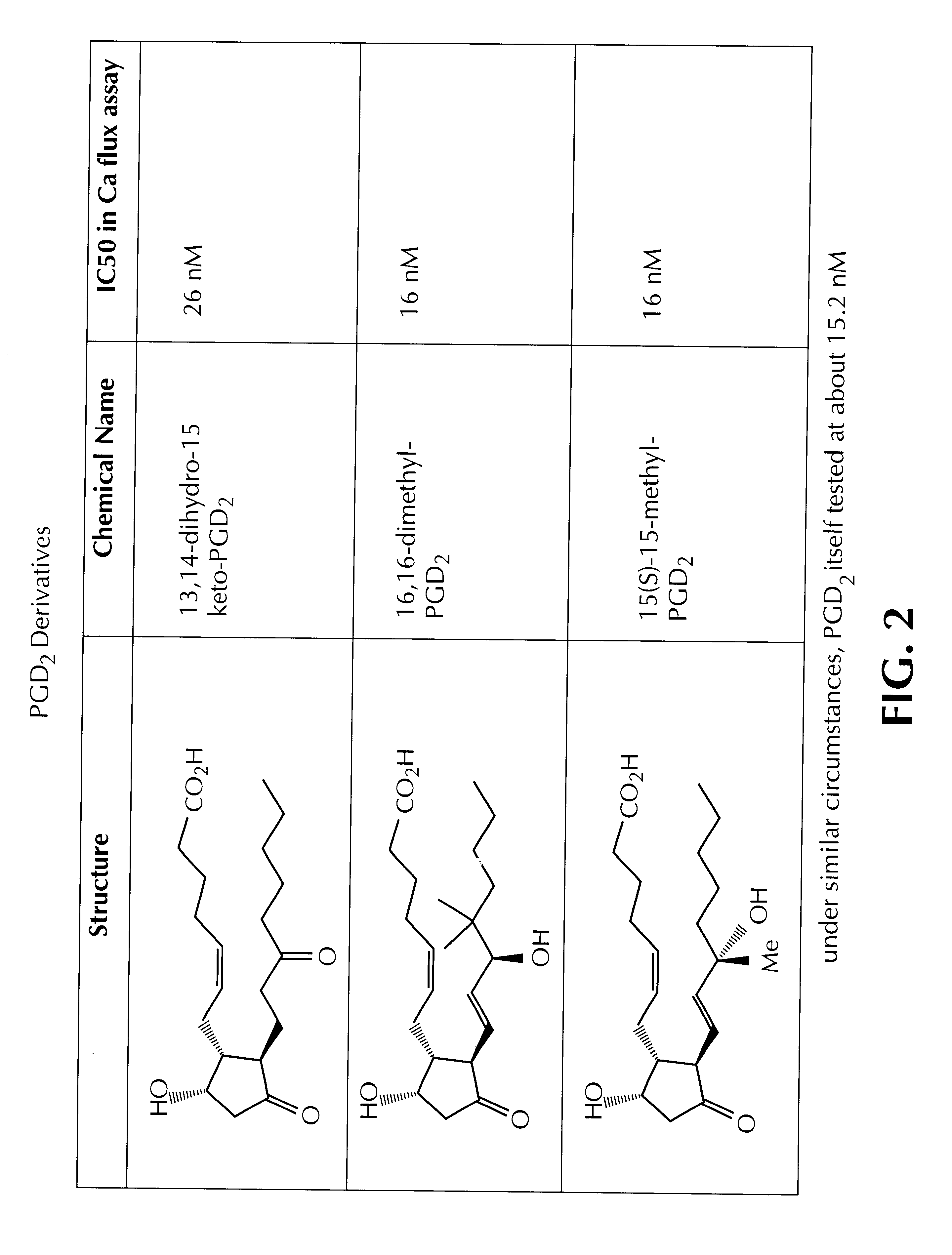
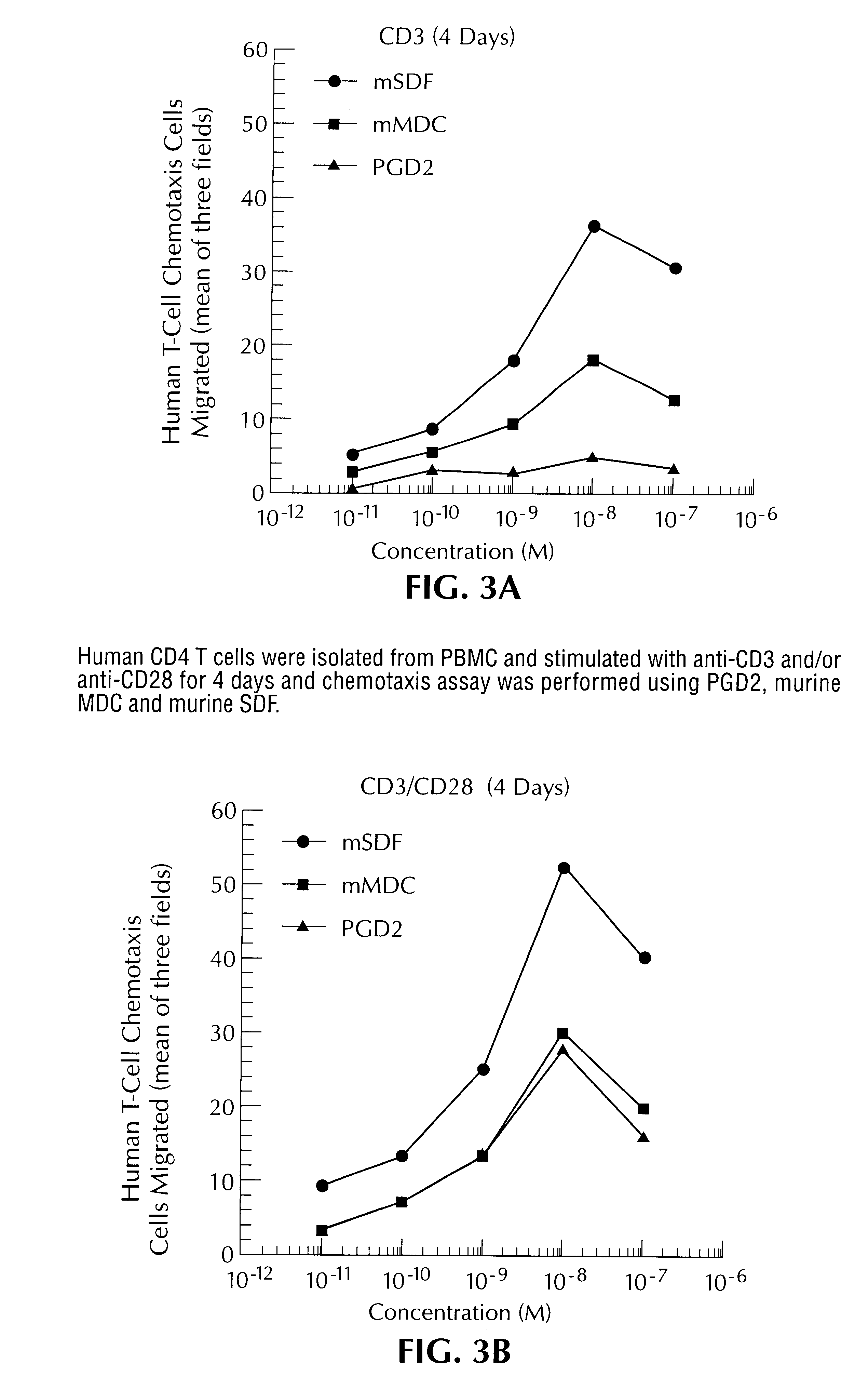
Methods for the identification of compounds useful for the treatment of disease states mediated by prostaglandin D2
The present invention relates to the discovery that PDG2 is the nautral ligand for orphan receptor CRTH2, which interaction, it will now immediately be recognized, is important in the development of valuable pharmaceuticals. The present invention is therefore related to methods for screening for therapeutic compounds useful in the treatment of PGD2-related disorders such as allergy, asthma and inflammation. Appropriate assay methodology is also disclosed.
Owner:PFIZER INC +1
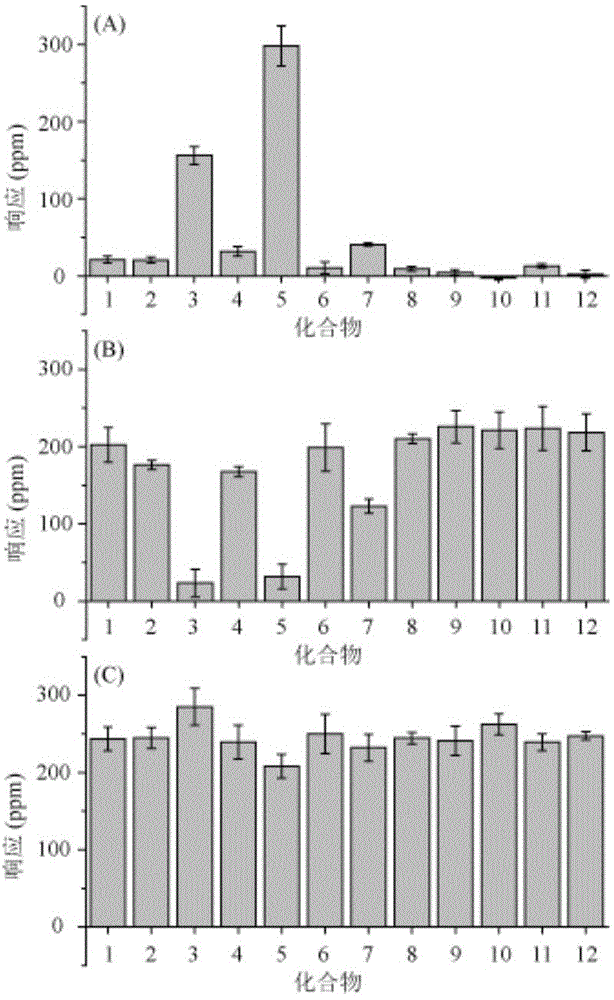
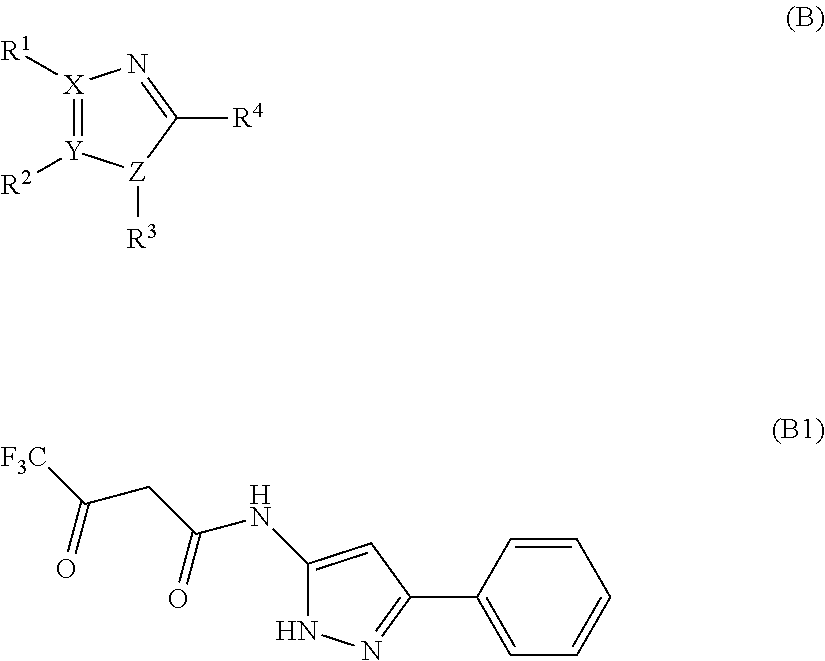
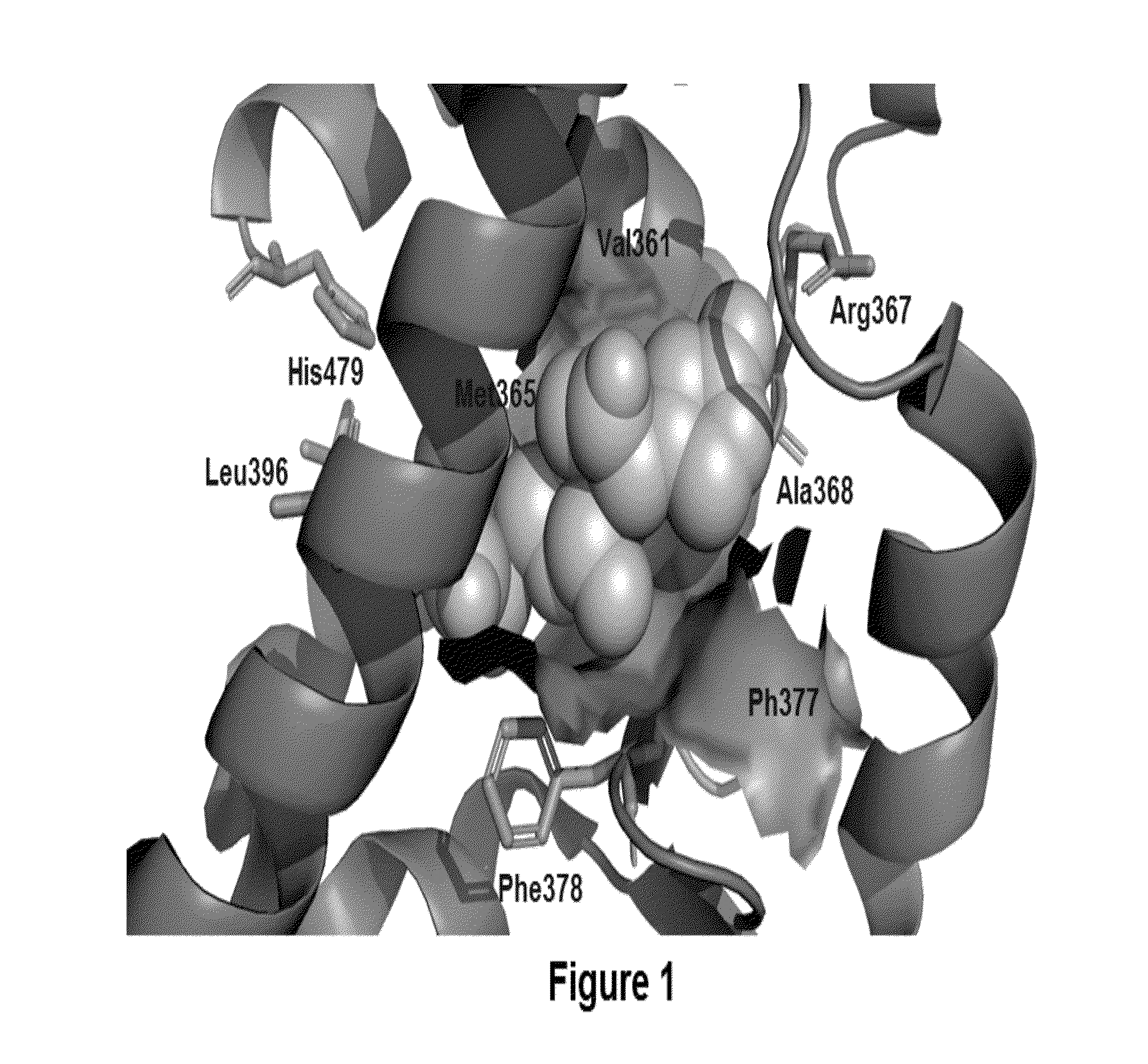
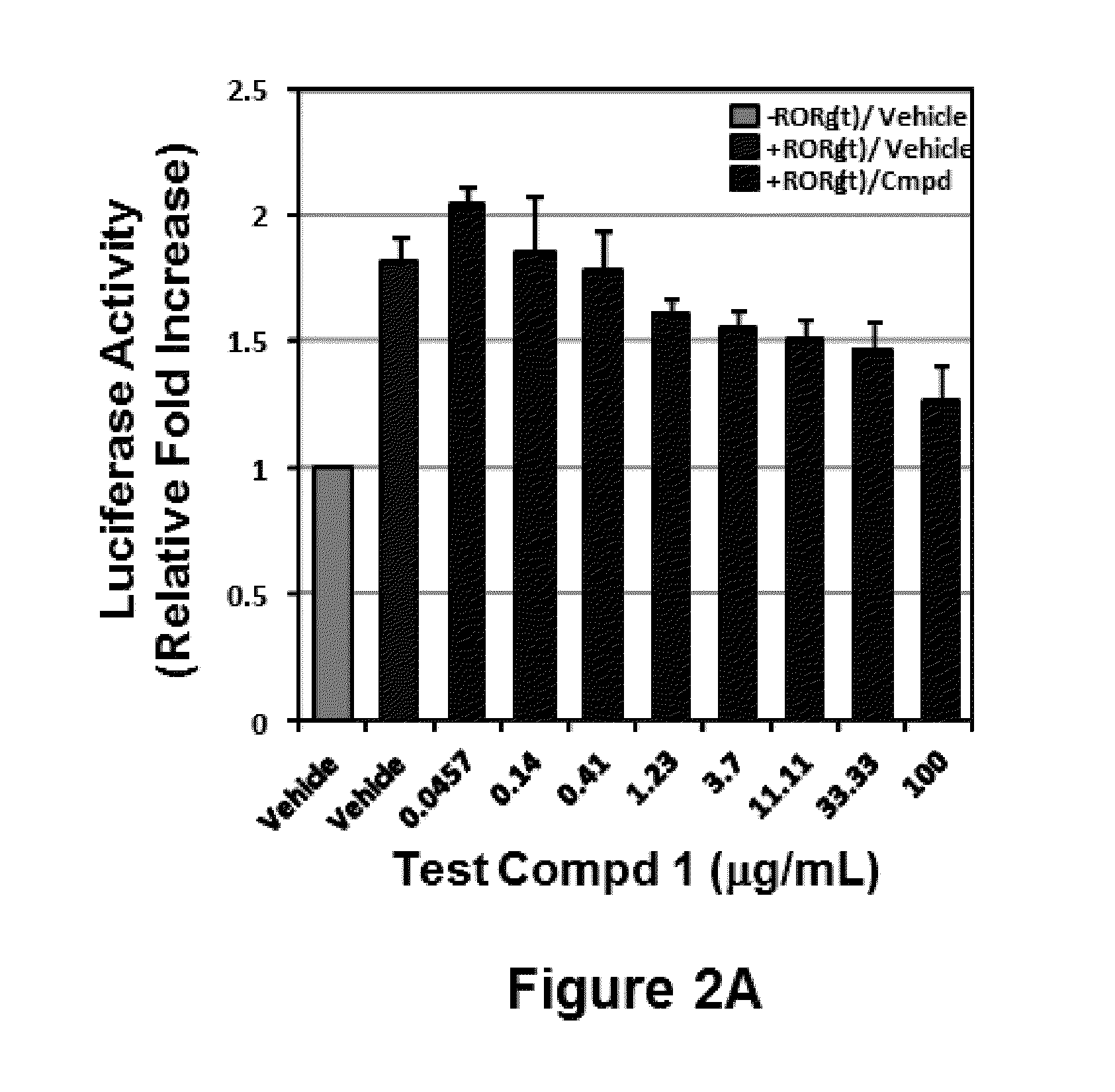
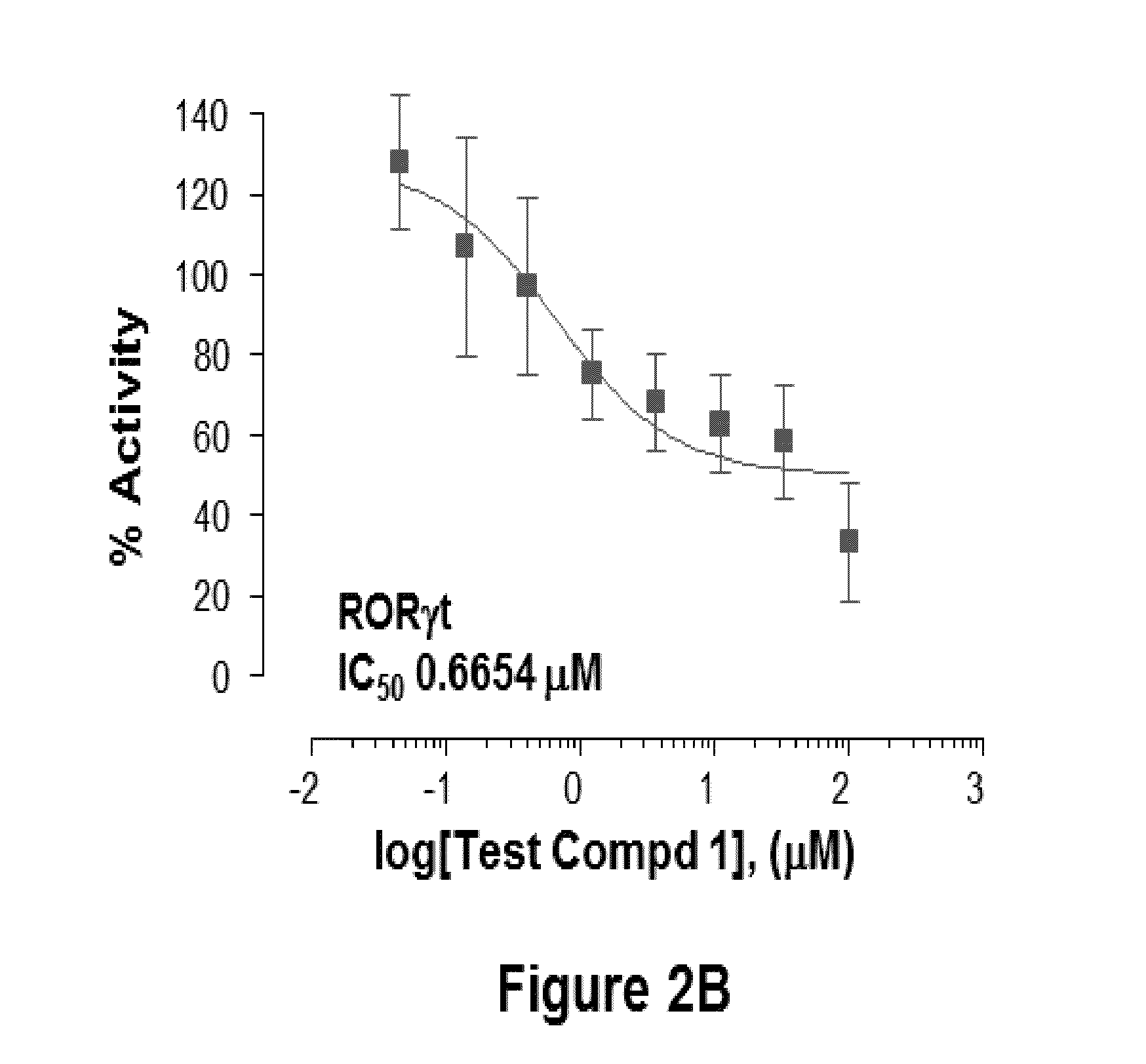
2-oxo-1,2-dihydrobenzo[cd] indole-6-sulfamide compound and composition and application thereof
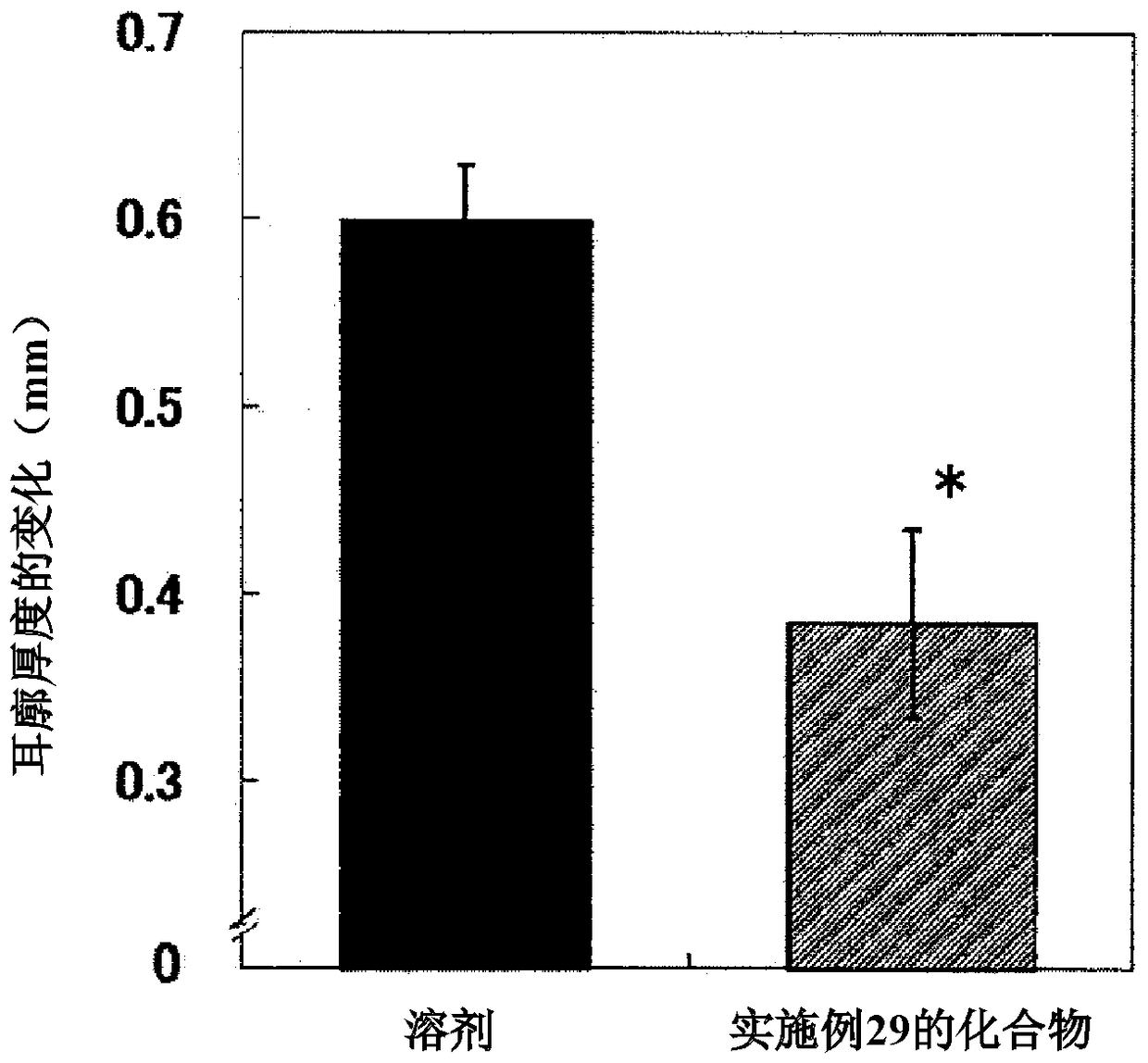
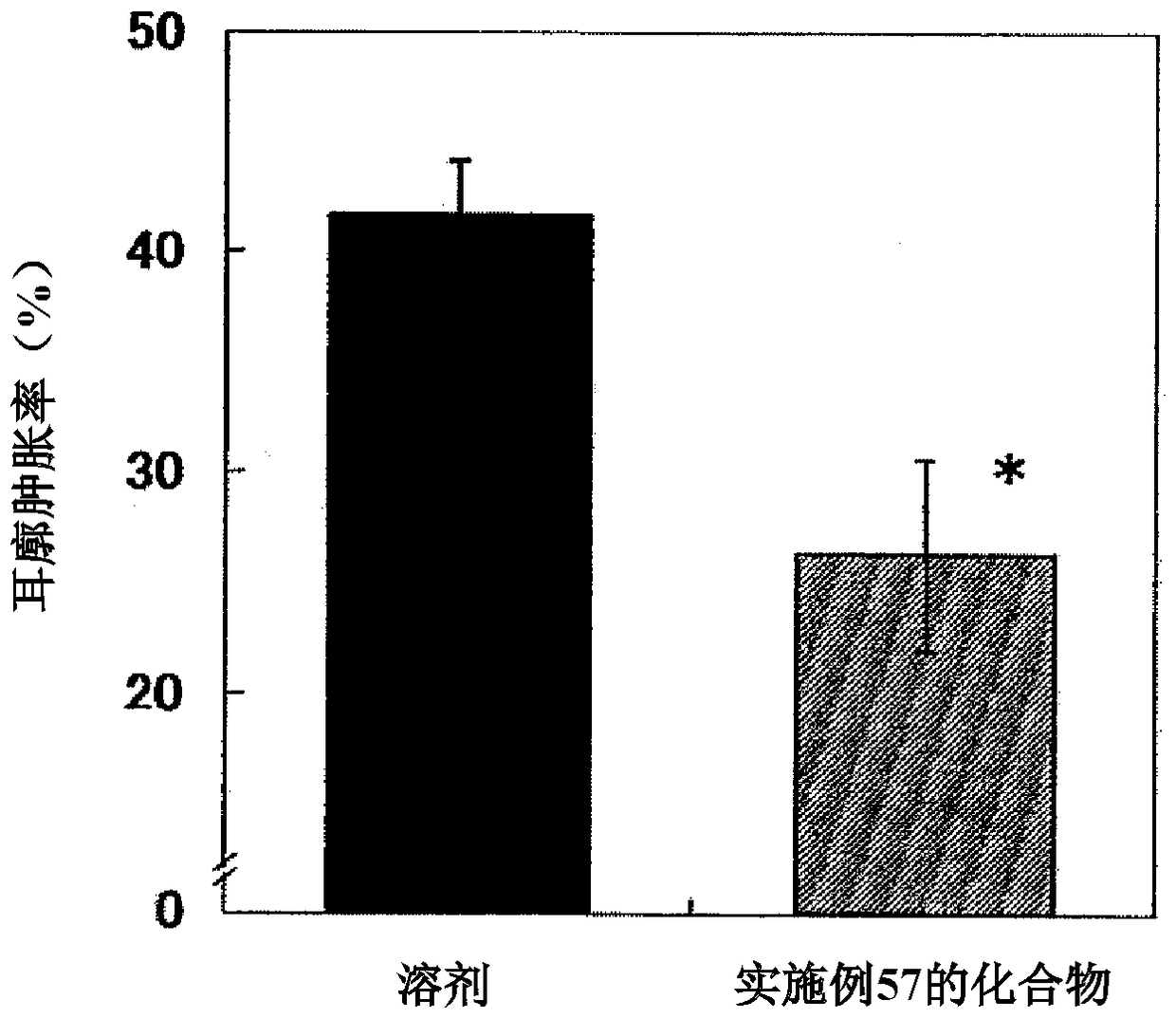
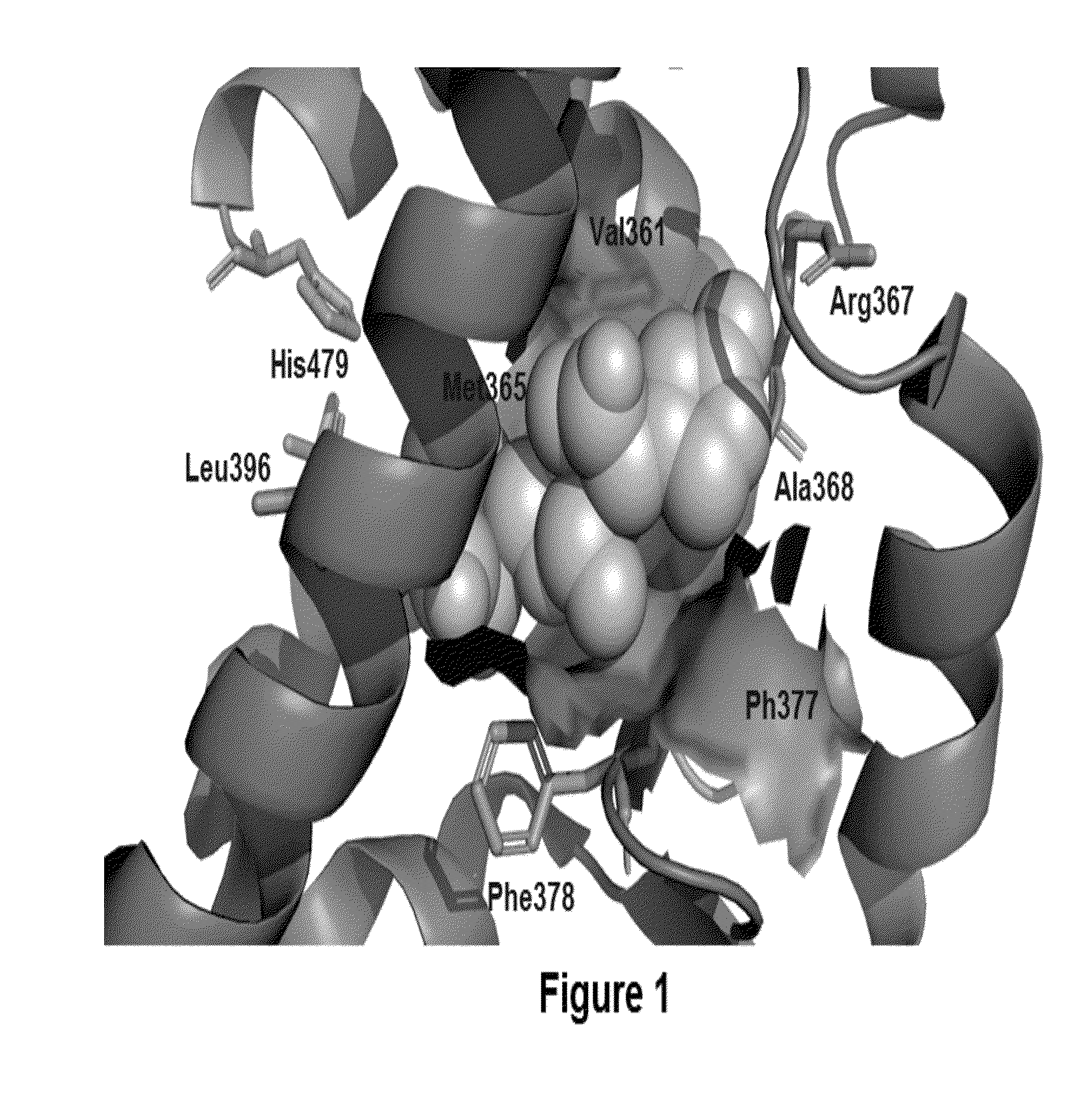
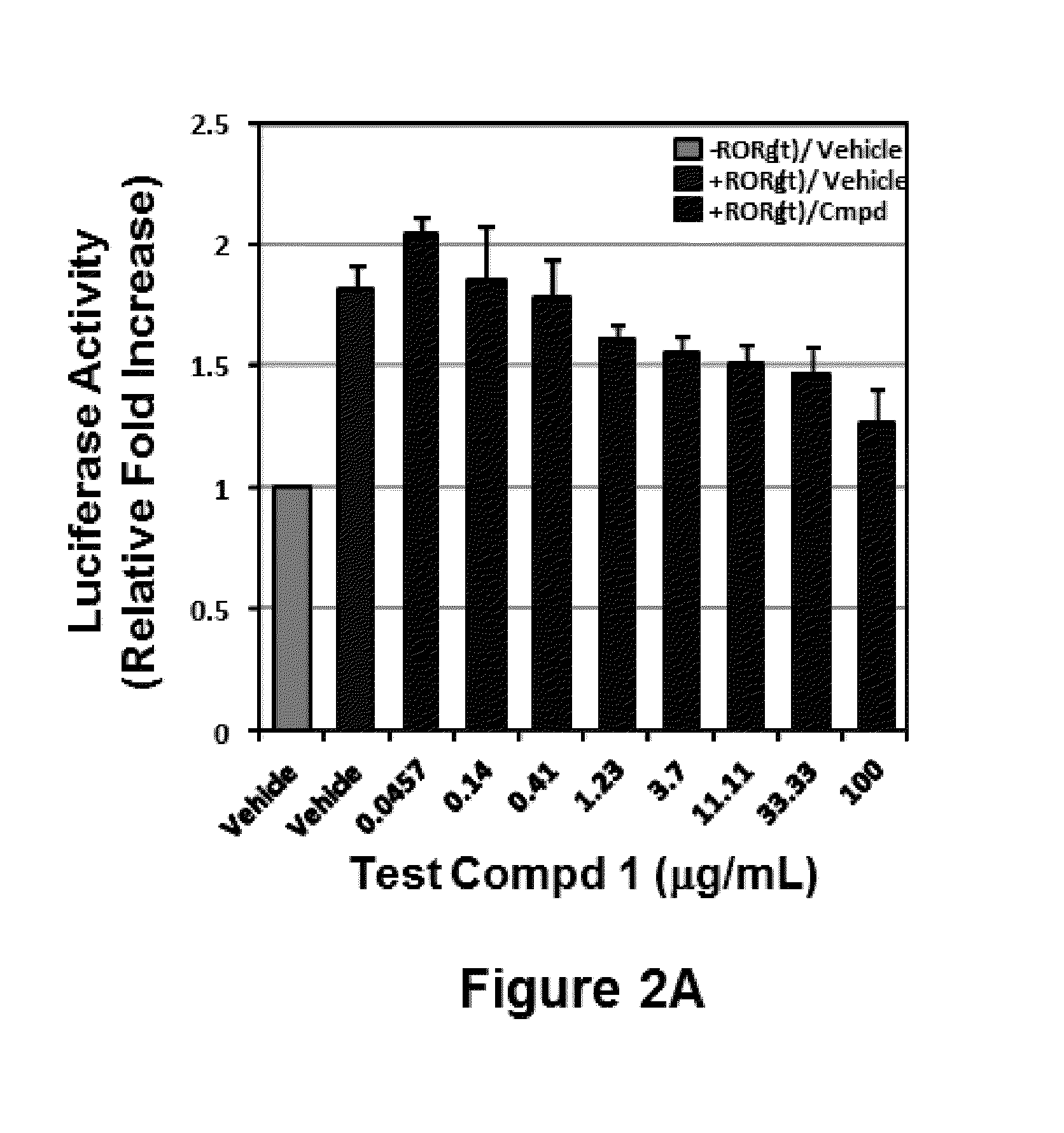
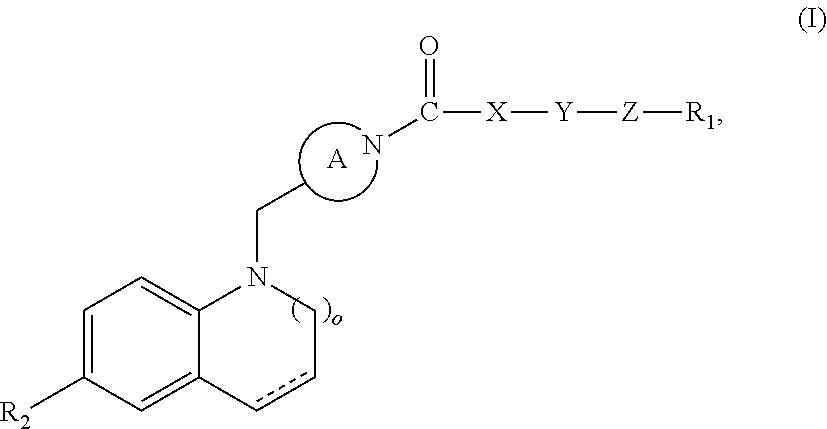
The invention relates to a 2-oxo-1,2-dihydrobenzo[cd] indole-6-sulfamide compound and a composition and application thereof. The invention provides a compound with the structural characteristics of the general formula I in the specification serving as a novel retinoic acid orphan nuclear receptor gamma subtype (RORgamma) inhibitor, as well as an application of the compounds and pharmaceutically acceptable salts, isomers, racemes, pro-drug co-crystallization compounds, hydrates and solvates thereof in medicines for treating or preventing RORgamma-regulated related diseases. More importantly, the compounds are possibly used for reducing generation of immune factors related to immunological diseases and alleviating symptoms of immunologic derangement and cancers.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
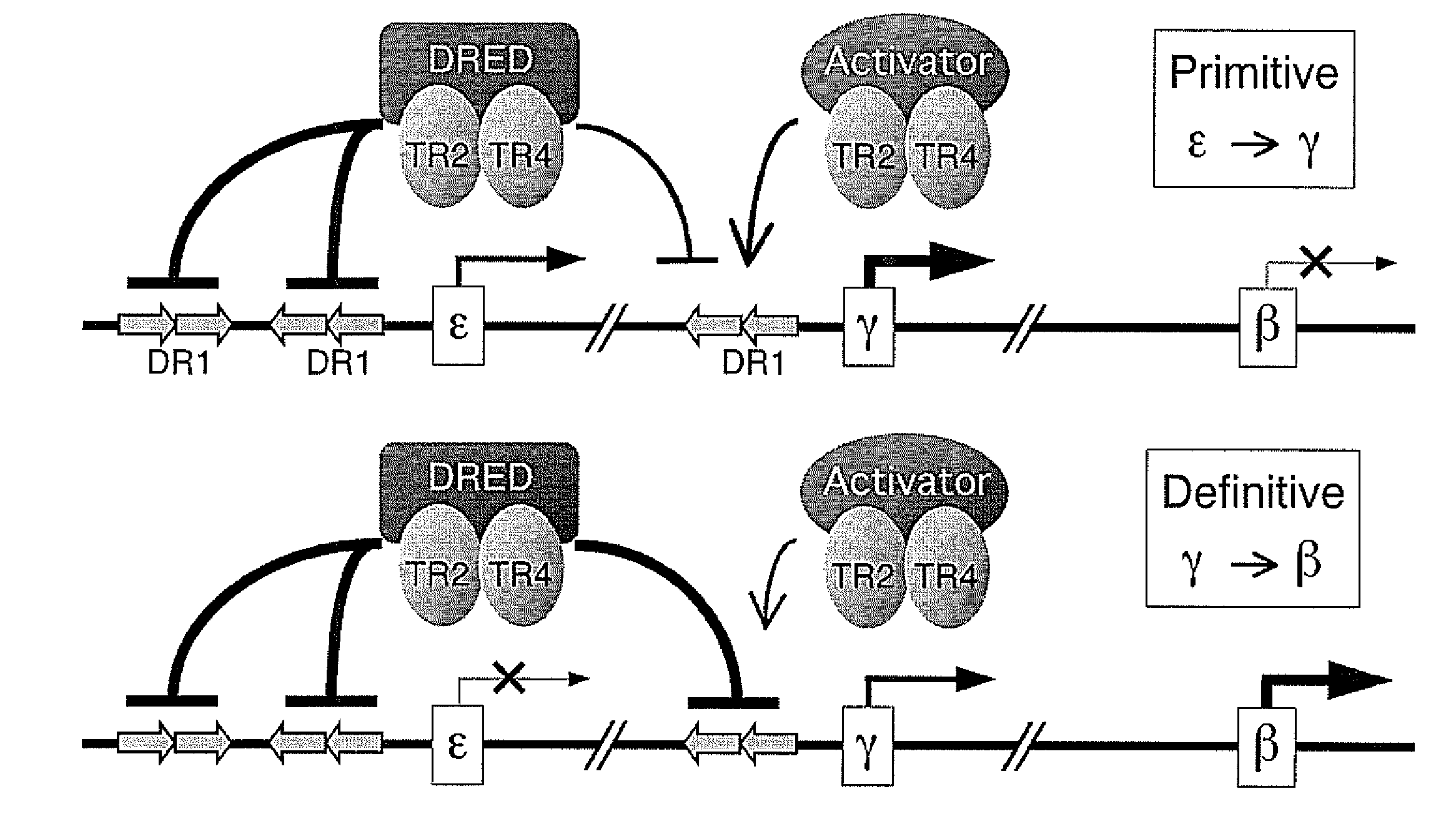
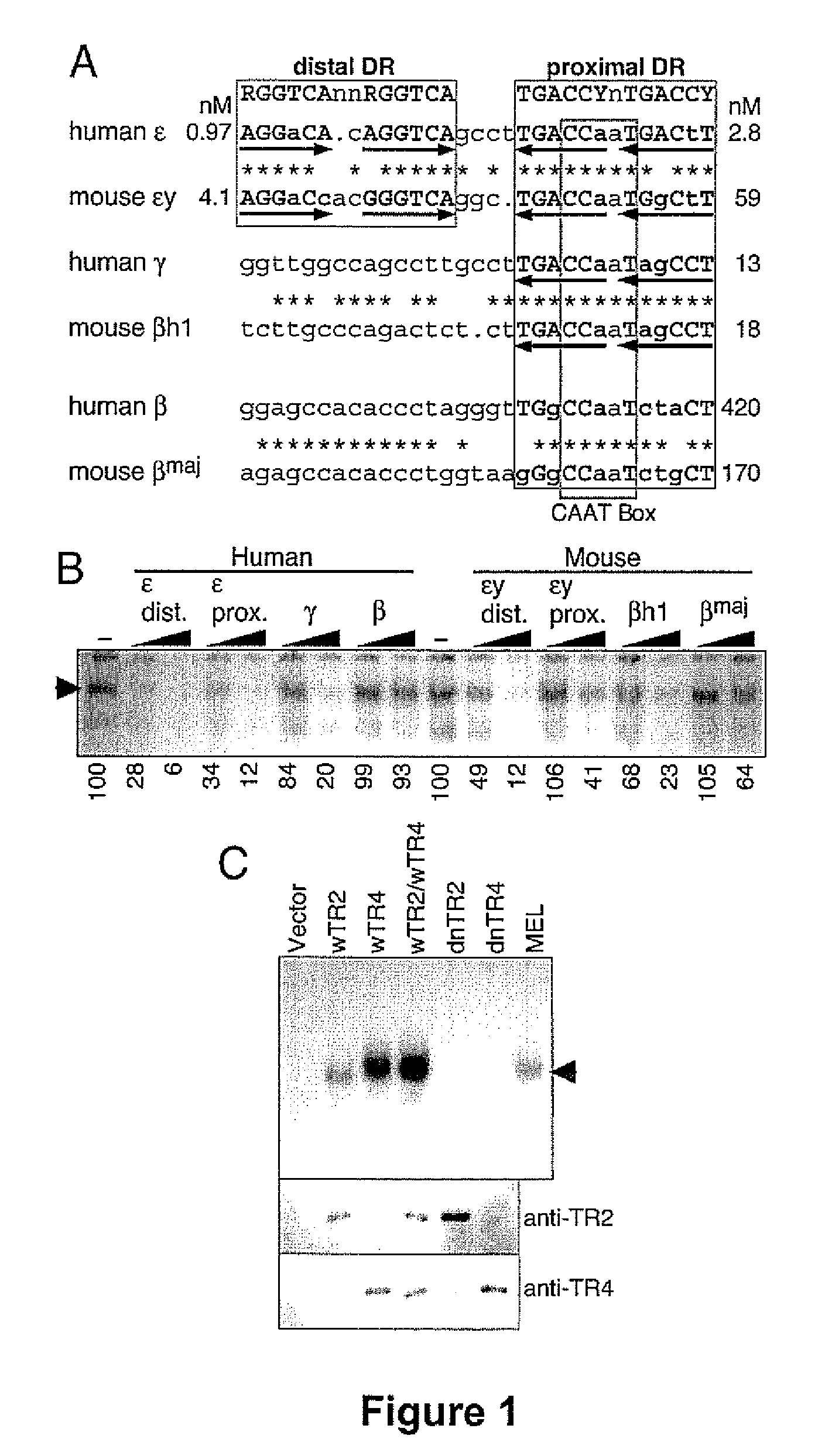
Screening Methods and Transgenic Animals for the Treatment of Beta-Globin Related Disease and Conditions
InactiveUS20080008651A1High expressionIncrease transcriptionBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementDevelopmental stageBeta globin
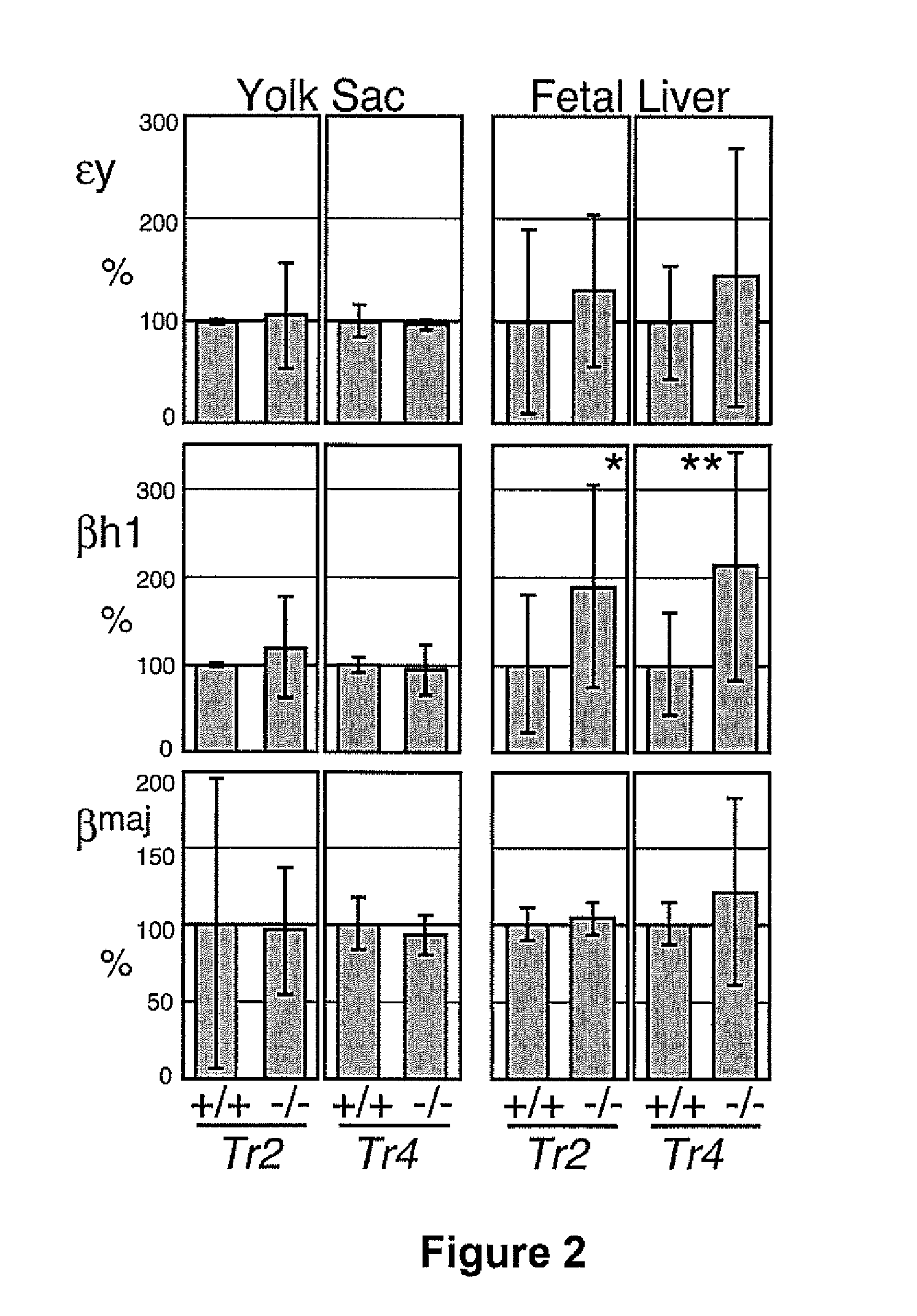
The orphan nuclear receptors TR2 and TR4 together constitute the DNA binding core of the 540 kDa DRED complex, a putative repressor of the human embryonic ε- and fetal γ-globin genes. Here the functional consequences of TR2 and TR4 germ line loss of function were examined, transgenic gain of function and dominant negative gain of function on human and murine β-type globin gene expression throughout development. ε-globin transcription responded in a manner consistent with the hypothesis that TR2 / TR4 is a constitutive erythroid ε-globin repressor. In contrast, parallel experiments show that TR2 / TR4 is a definitive stage-selective γ-globin repressor. This developmental stage-specific, gene-selective repression of the ε- and γ-globin genes by TR2 / TR4 establishes, when considered in concert with the competition hypothesis, a coherent molecular rationale for hemoglobin switching (temporally specific, sequential activation of all the β-type globin genes) during vertebrate development.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
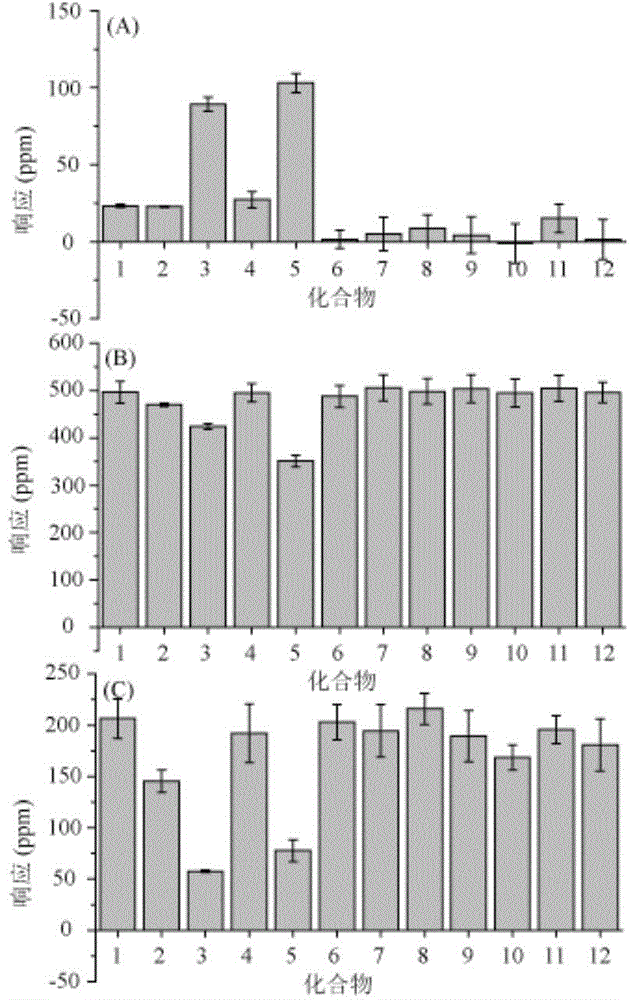
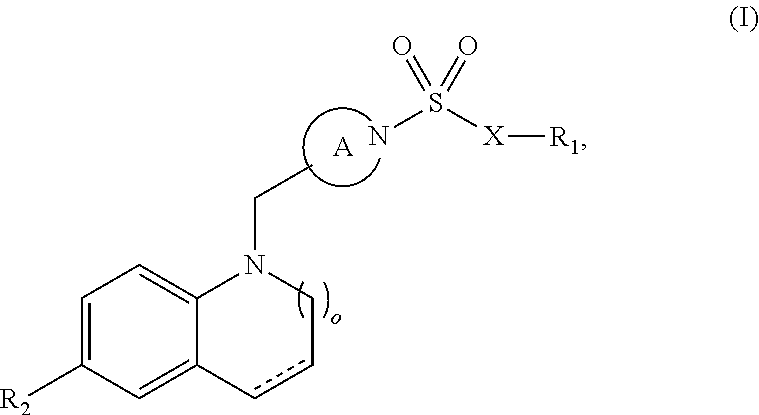
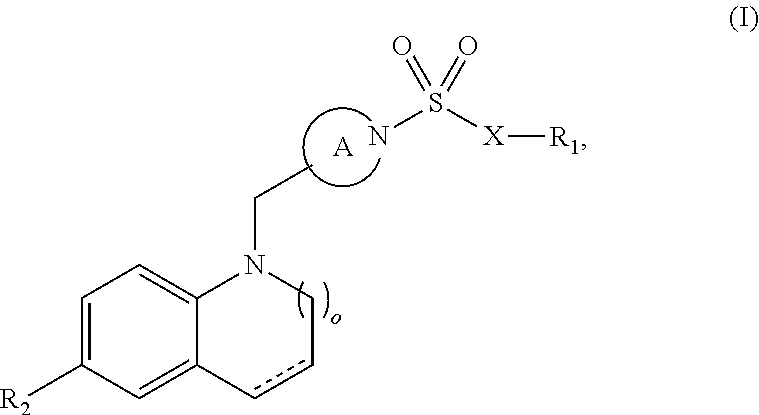
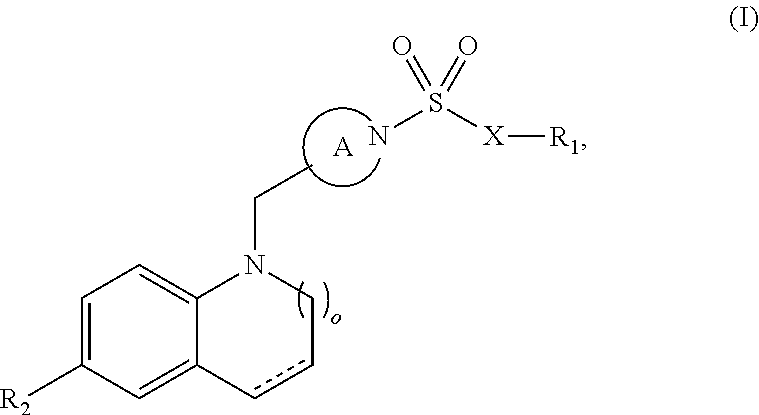
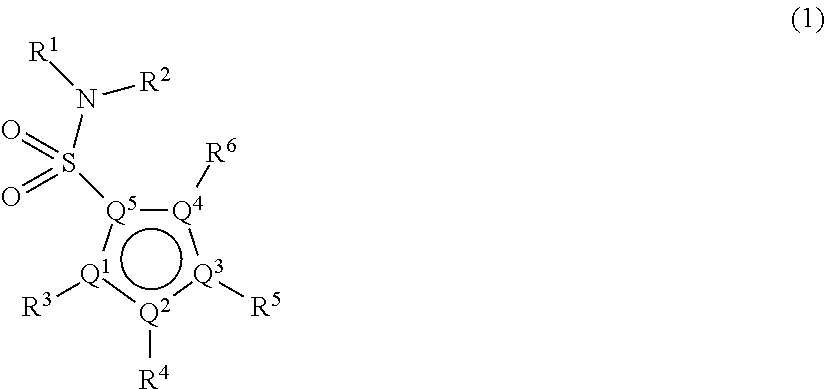
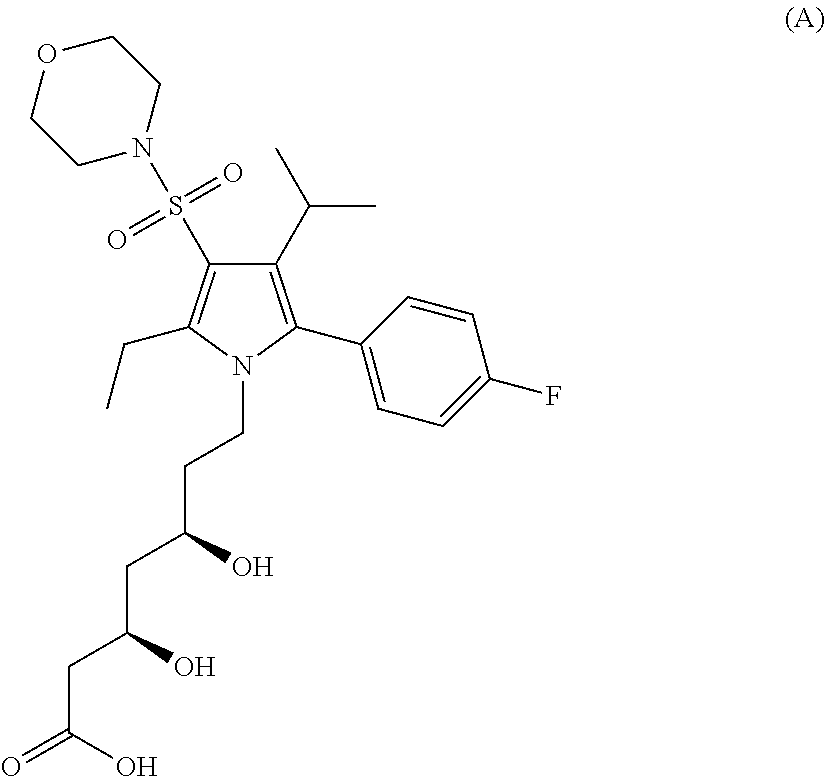
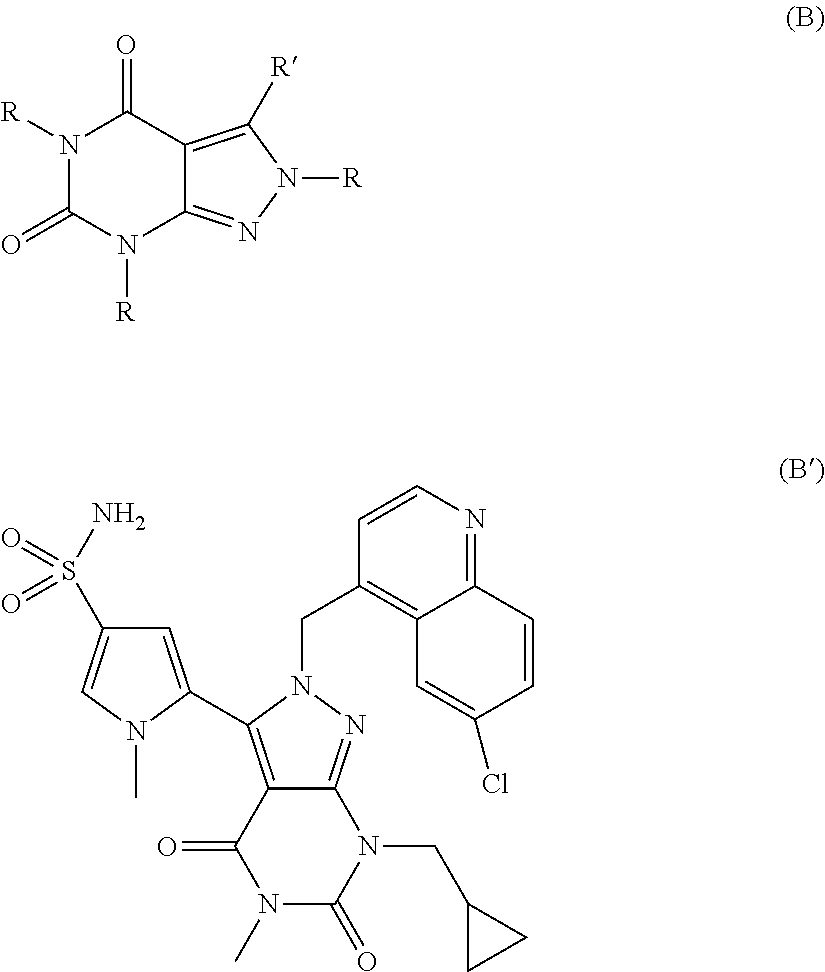
Carboxamide or sulfonamide substituted thiazoles and related derivatives as modulators for the orphan nuclear receptor ror[gamma]
InactiveUS20150175562A1Developmental harmReduce in quantityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseasePharmaceutical medicine
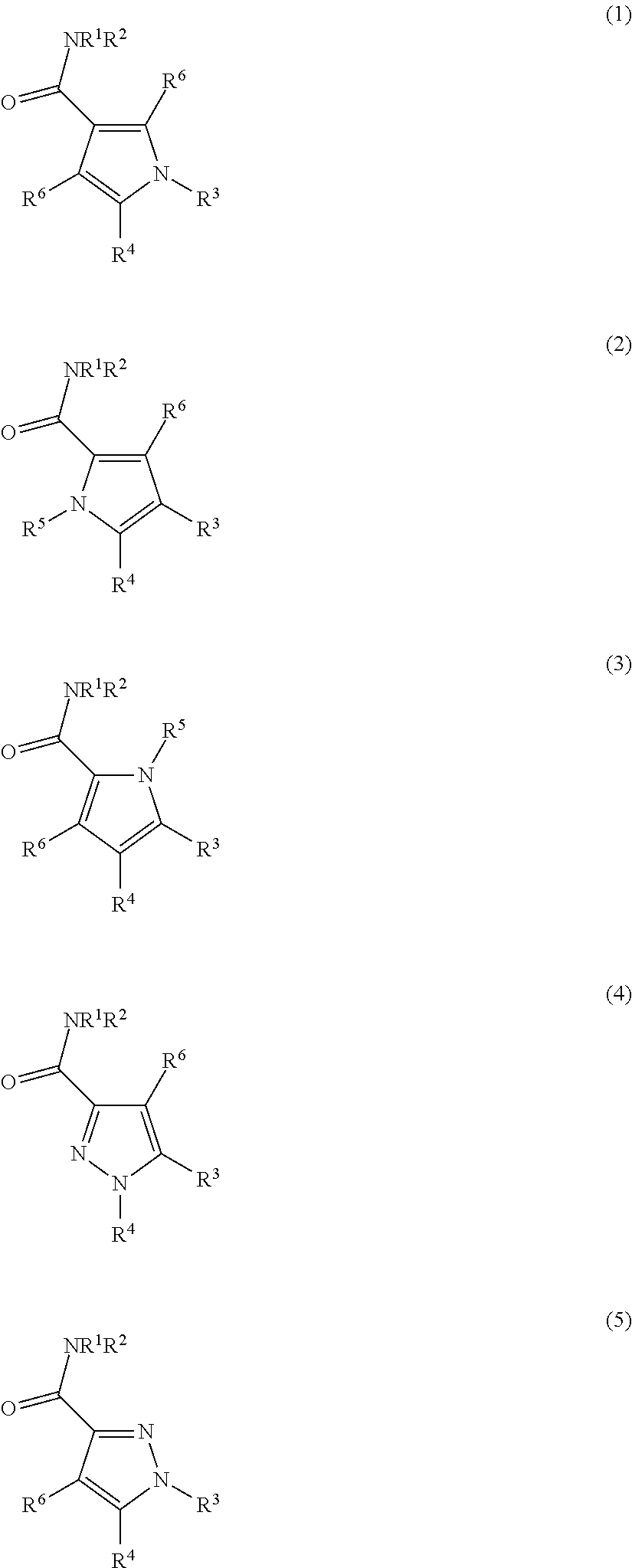
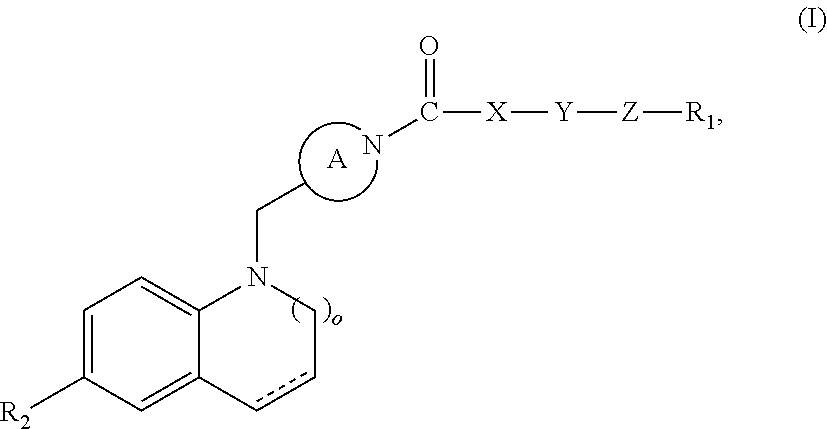
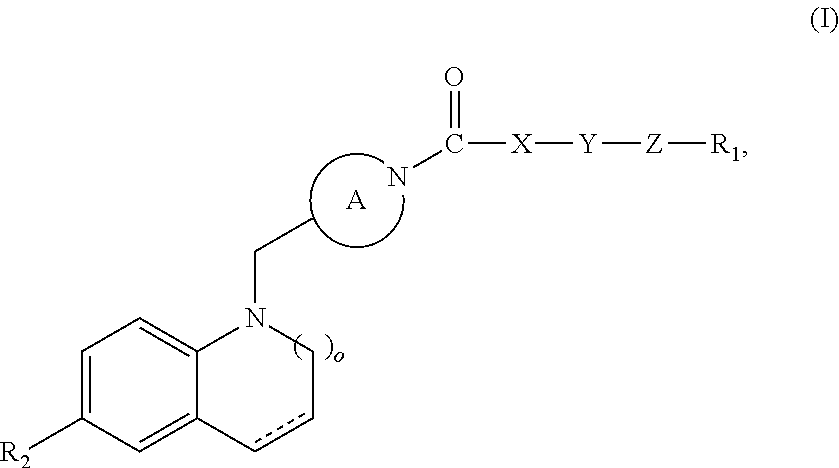
The invention provides modulators for the orphan nuclear receptor RORy and methods for treating RORy mediated diseases by administering these novel RORy modulators to a human or a mammal in need thereof. Specifically, the present invention provides carboxamide or sulfonamide containing cyclic compounds of Formula (1), (1′), (100), (100′), (200) and (200′) and the enantiomers, diastereomers, tautomers, / V-oxides, solvates and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
Owner:PHENEX PHARMA
Novel class of sterol ligands and their uses in regulation of cholesterol and gene expression
ActiveUS20060121024A1Modulate activityEfficient modulationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsKetoneOxysteroid
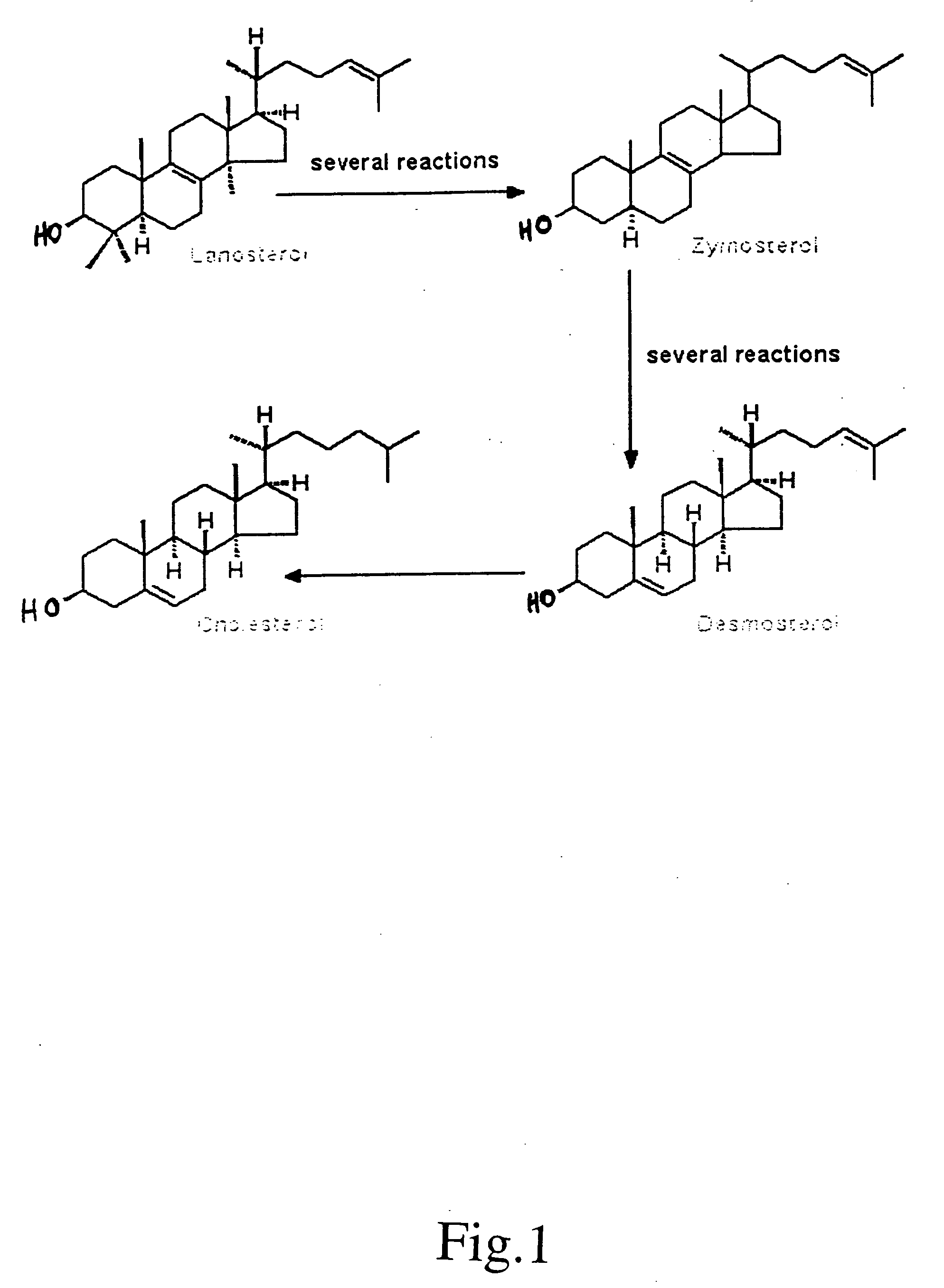
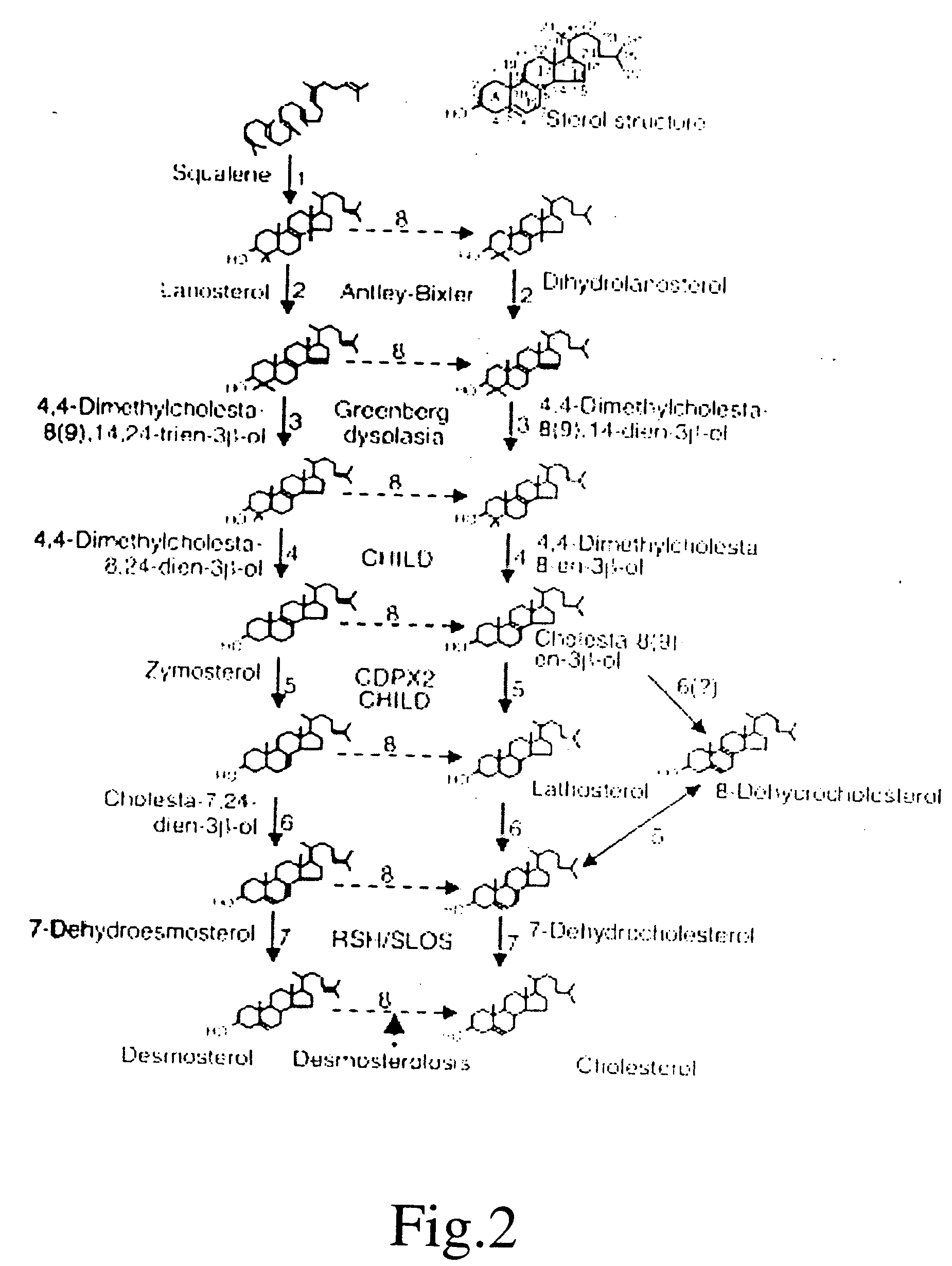
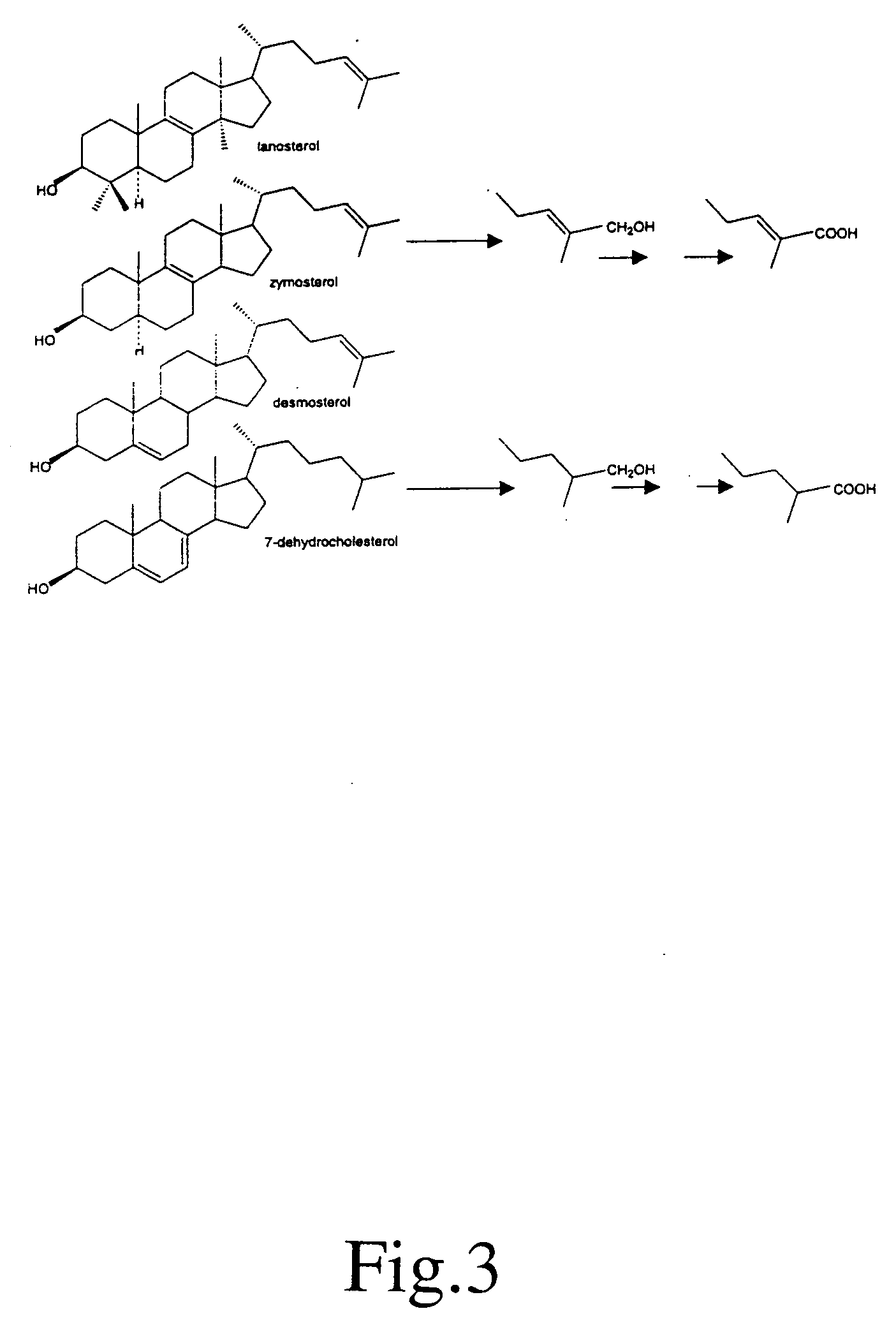
This invention relates to oxysteroids and oxysteroid hormones which have been identified. These oxysteroids are C27 modified sterols, particularly derivatives of intermediates in cholesterol synthesis, including lanosterol, zymosterol and desmosterol, including C27 diol and C27 acid derivatives, as well as related compounds and analogs thereof. The oxysteroids are capable of binding to or otherwise interacting with orphan nuclear receptors to result in modulation of gene expression. The invention further relates to methods of modulating the rate of cholesterol synthesis in a mammal. More specifically, the invention relates to treatment of cholesterol-related conditions which are improved or ameliorated by modulating the rate of cholesterol synthesis or cholesterol metabolism in a human in need thereof by administration of these oxysteroids, analogs or antagonists thereof. The invention includes methods for ameliorating, treating or preventing macular degeneration in a mammal comprising administering to said mammal an agent which stimulates or enhances the expression or activity of steroid sulphotransferase (SLUT2), particularly SLUT2B1b, or which stimulates or enhances the expression or activity of CYP27A1 or sterol 27-hydroxylase or otherwise increasing the sulfonation or 27-hydroxylation of cholesterol intermediates, including 7-ketocholesterol. Assays for identification of analogs, antagonists or modulators of these oxysteroids or of sterol 27-hydroxylase are also provided.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV MEDICAL CENT
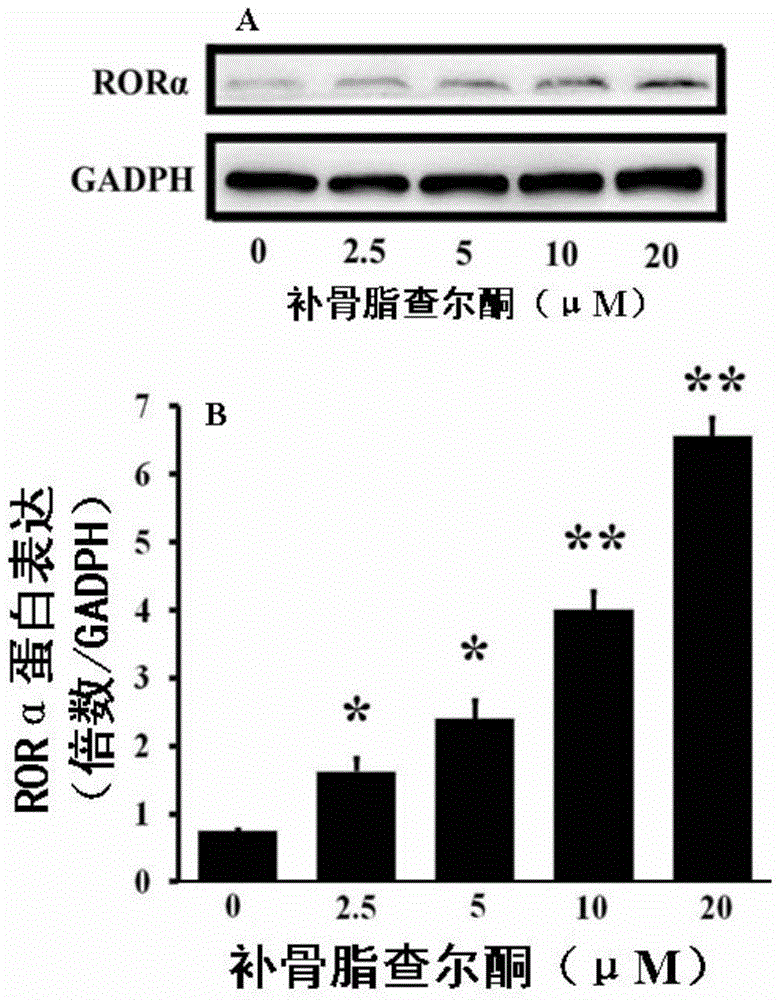
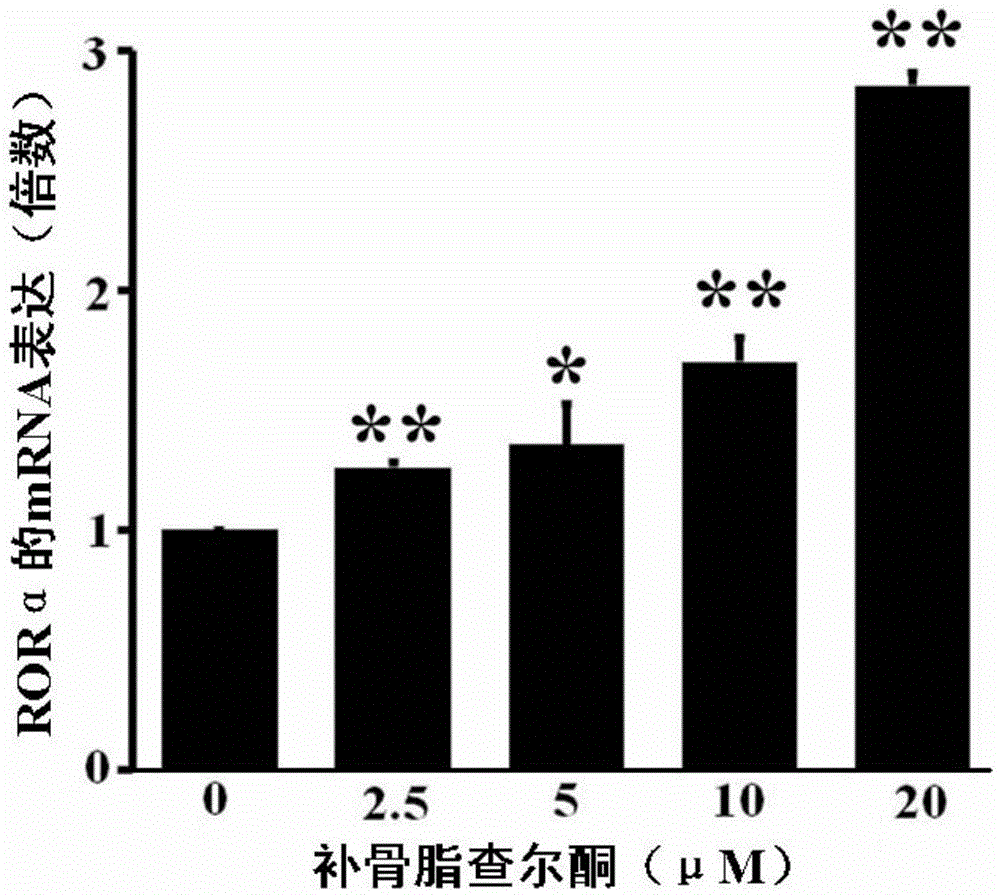
Application of bavachalcone and analogues thereof
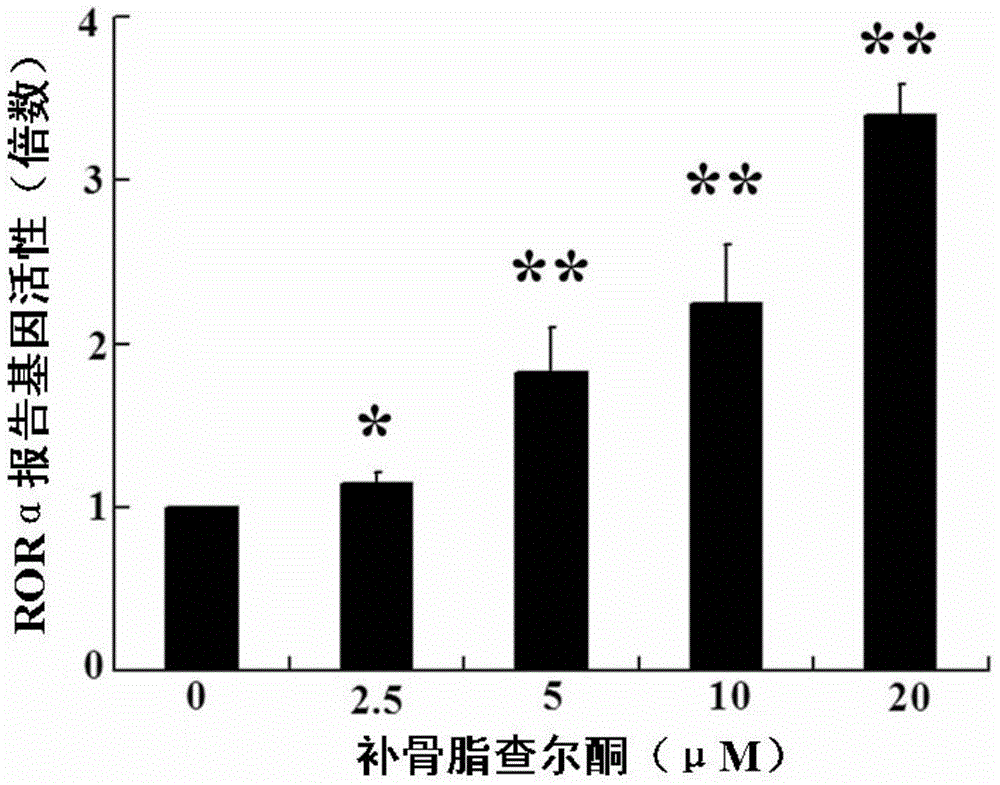
The invention discloses a use of psoralen chalcone and its analogues. The use refers to the use of psoralen chalcone or / and its analogues as active ingredients for the preparation of activating retinoic acid-related orphan nuclear receptors. Body-alpha composition. The research results of the present invention show that psoralen chalcone and its analogs can directly activate the activity of RORα in a dose-dependent manner, and activate the expression of RORα protein and RORα mRNA in a concentration-dependent manner, and can effectively regulate its downstream biological clock genes The expression of BMAL1 indicates that psoralen chalcone and its analogues are good positive activators of RORα, which can be used to prevent or treat related diseases mediated by RORα, and have broad application prospects.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
Application of alkannin derivant
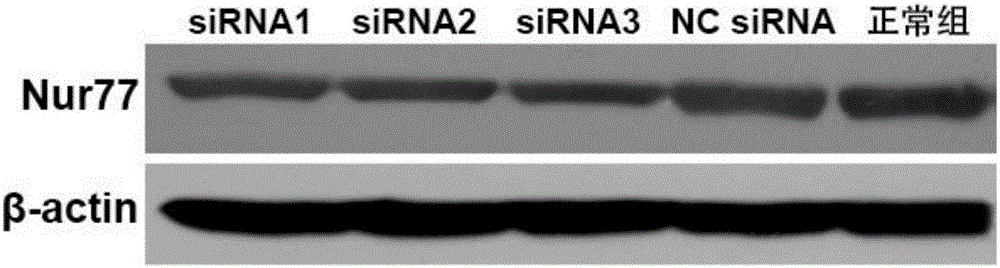
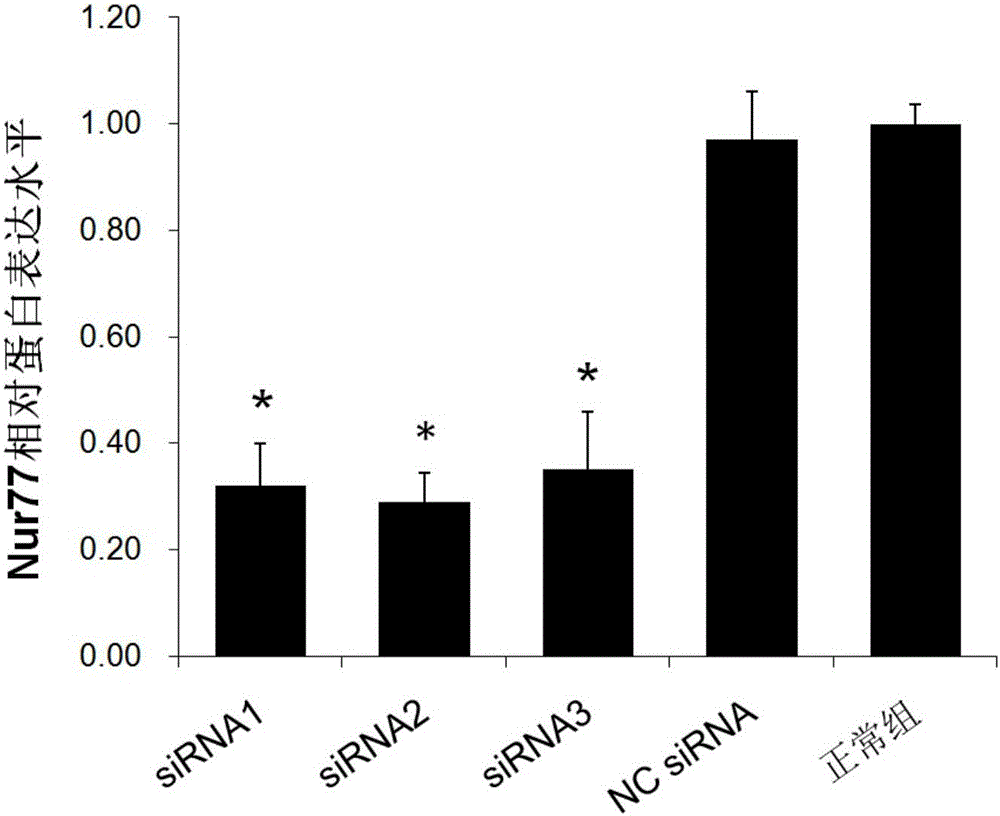
InactiveCN101683331AHas antitumor activityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsTumor cell apoptosisAlkannin
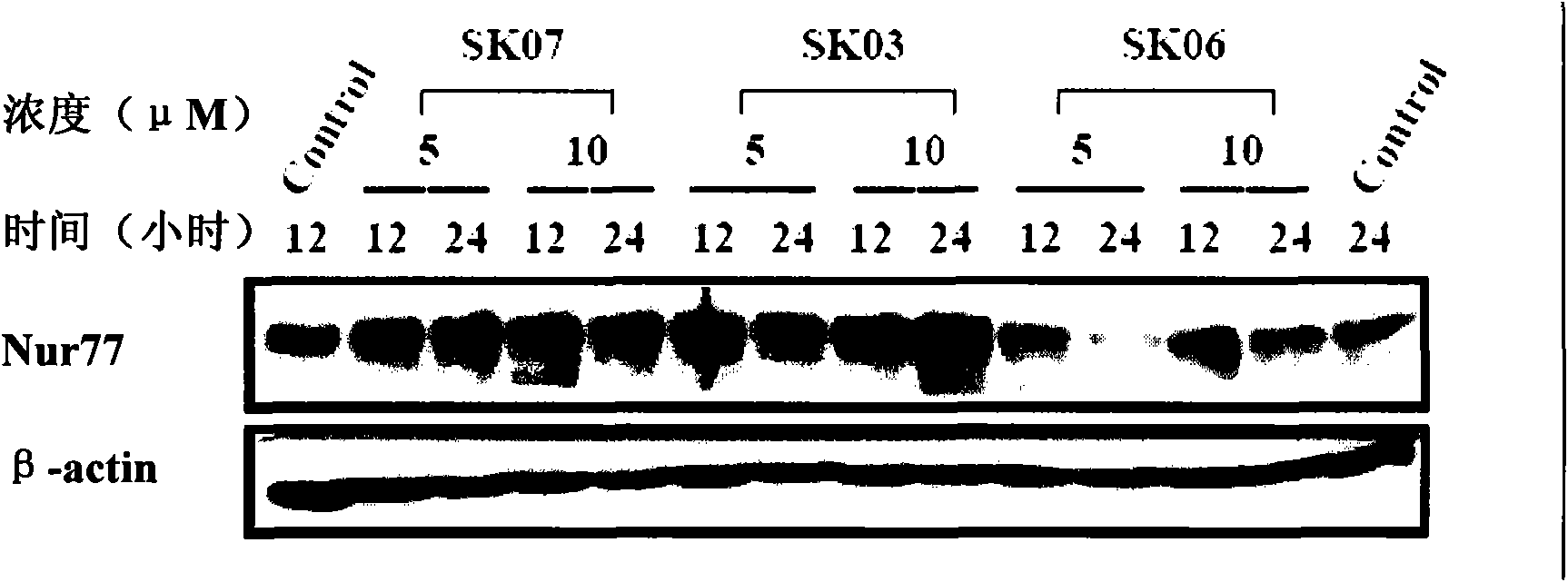
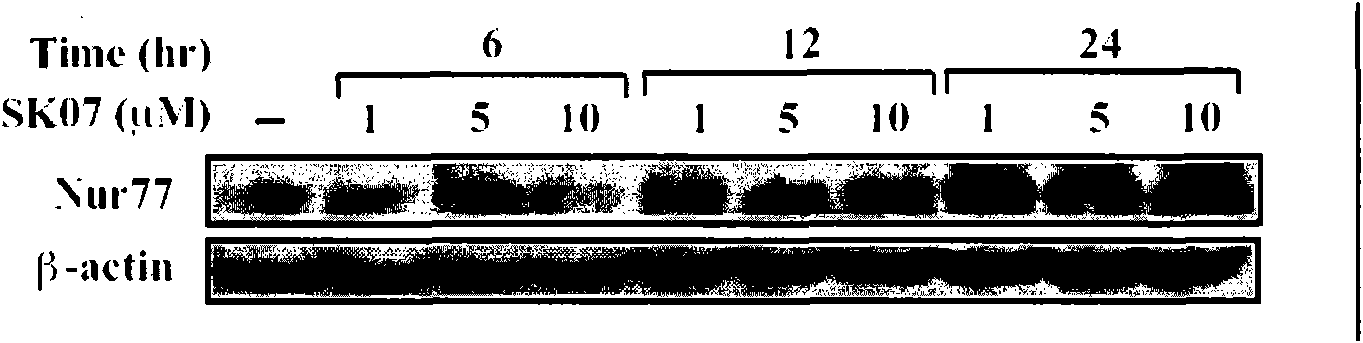
The invention provides an application of alkannin derivant for preparing drug treating cancers, and the drug takes orphan receptor Nur77 as an effect target. The invention also provides the application of the orphan receptor Nur77 which serves as an effect target to screen alkannin derivant. The alkannin derivant of the invention clarifies the mechanism of the anti-tumour effect of alkannin derivant via a great discovery that tumour cells are induced to apoptosis by acting on the orphan receptor Nur77, and provides effective target spots for decorating and optimizing the structure.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
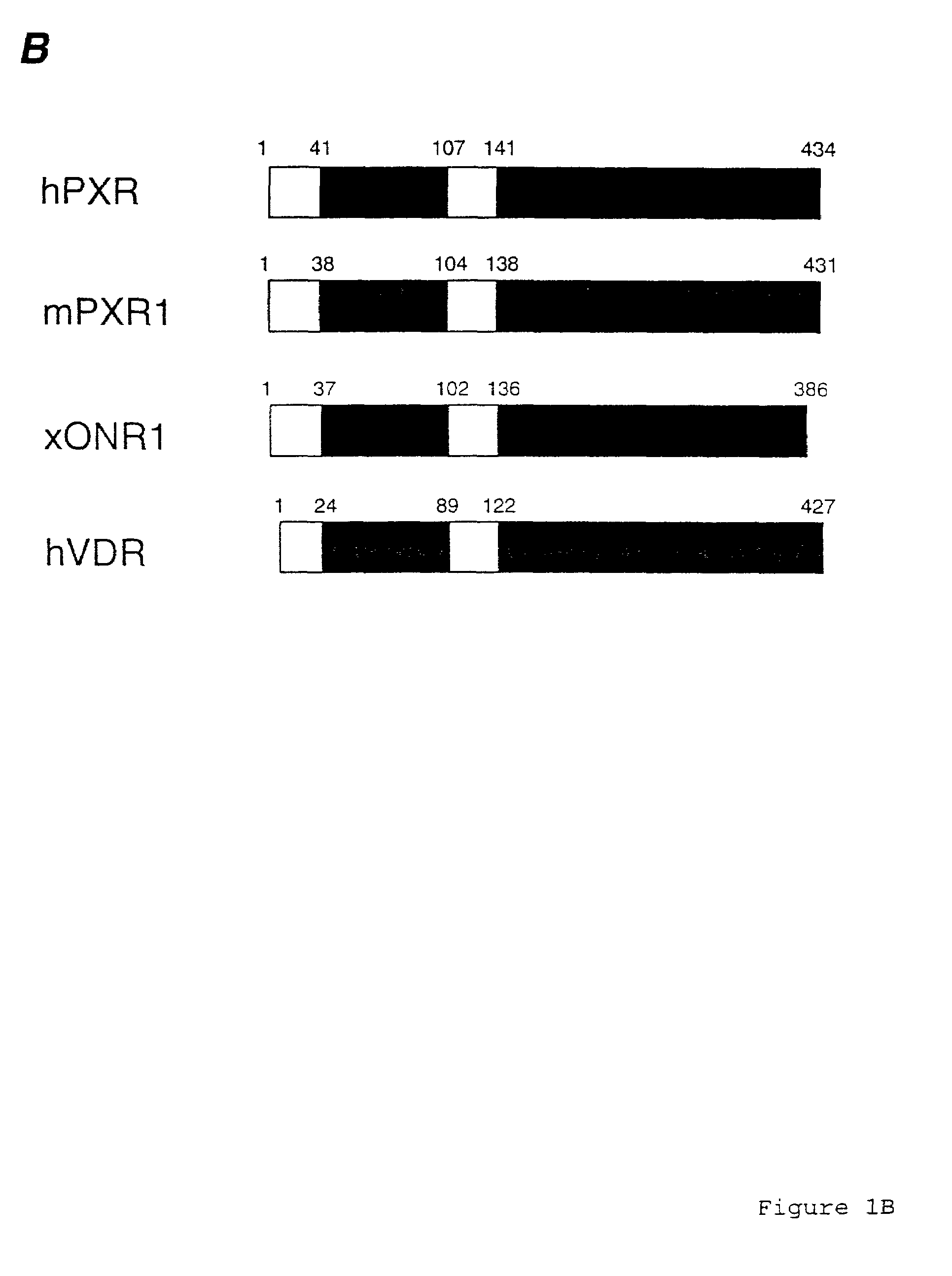
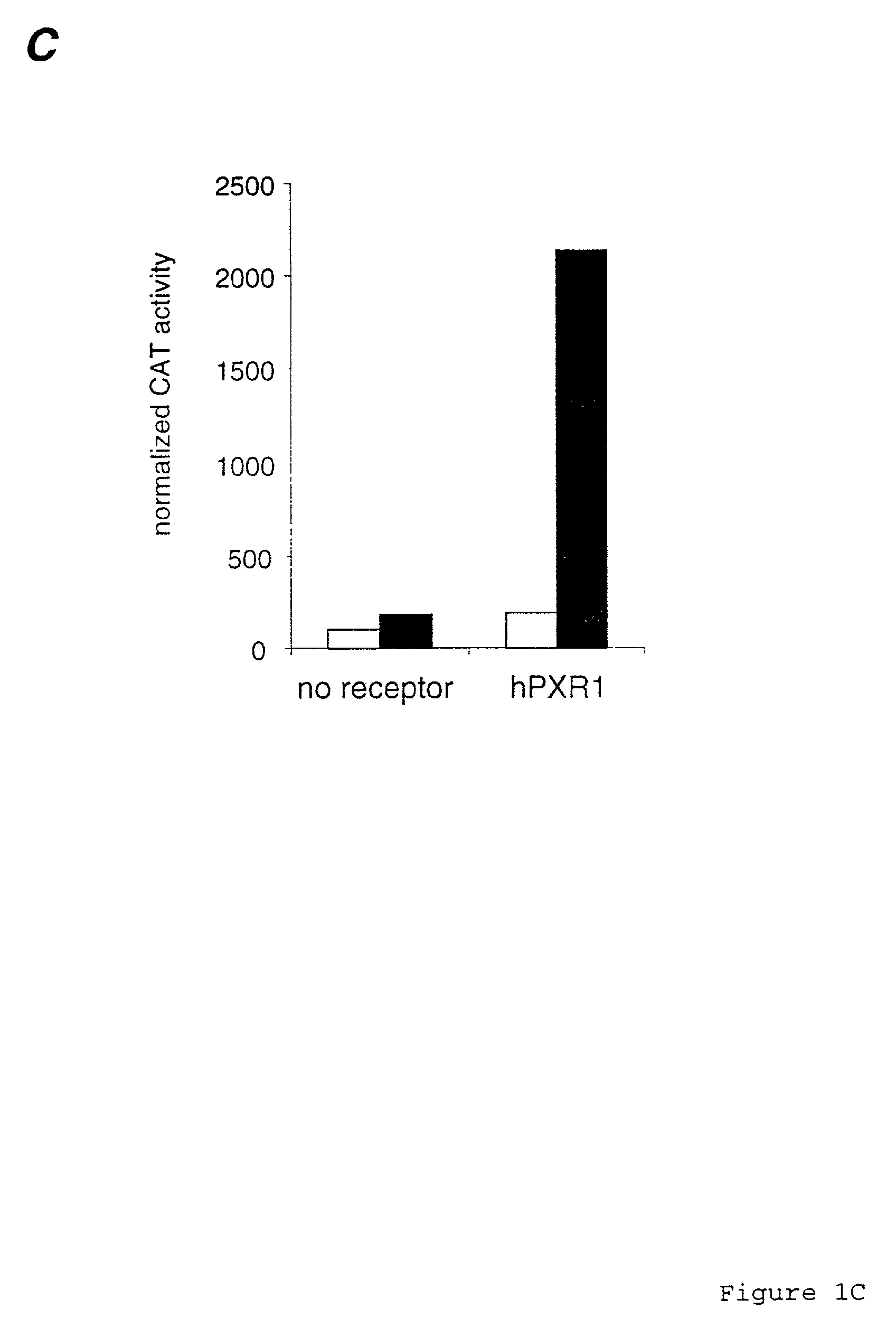
Pregnane X receptor method
The present invention relates to a novel human orphan nuclear receptor that binds to a cytochrome P-450 monooxygenase (CYP) promoter and that is activated by compounds that induce CYP gene expression. The invention further relates to nucleic acid sequences encoding such a receptor, to methods of making the receptor and to methods of using the receptor and nucleic acid sequences encoding same. The invention also relates to non-human animals transformed to express the human receptor and to methods of using such animals to screen compounds for drug interactions and toxicities.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
Modulators of ROR-gamma Receptors, Composition and Use Thereof
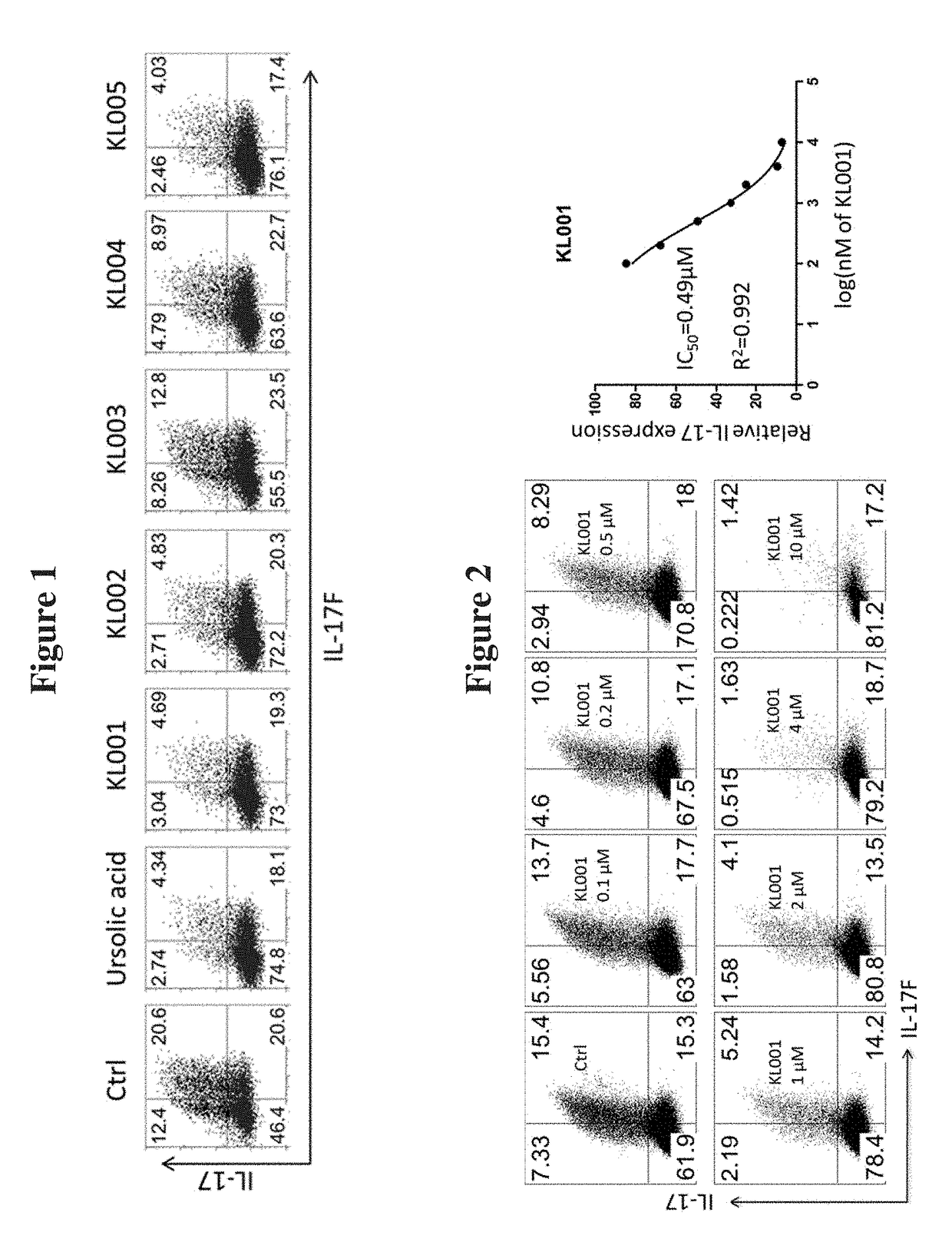
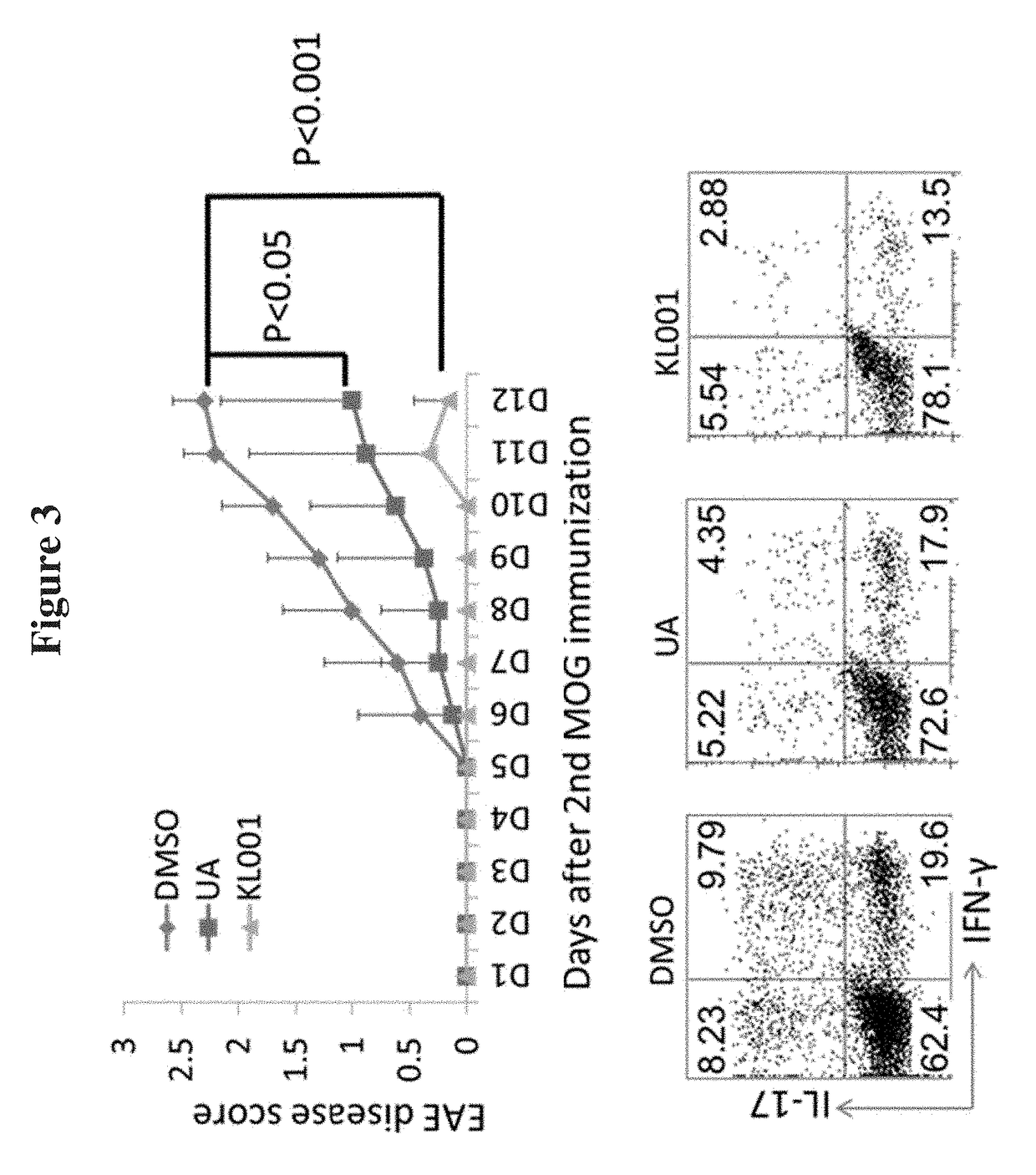
InactiveUS20170298090A1Good metabolic stabilityProlong half-life in vivoSteroidsAmide active ingredientsRetinoidUrsolic acid
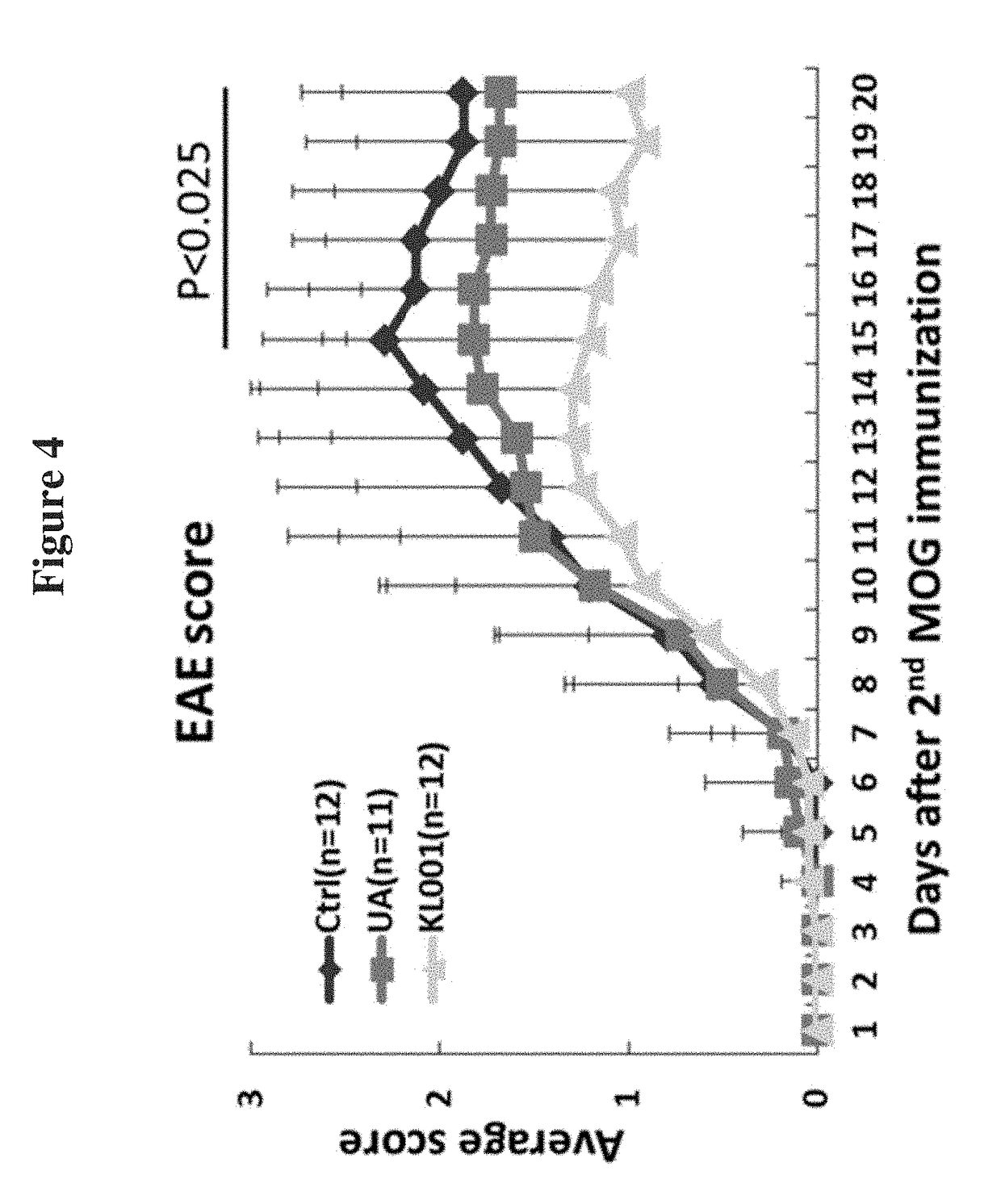
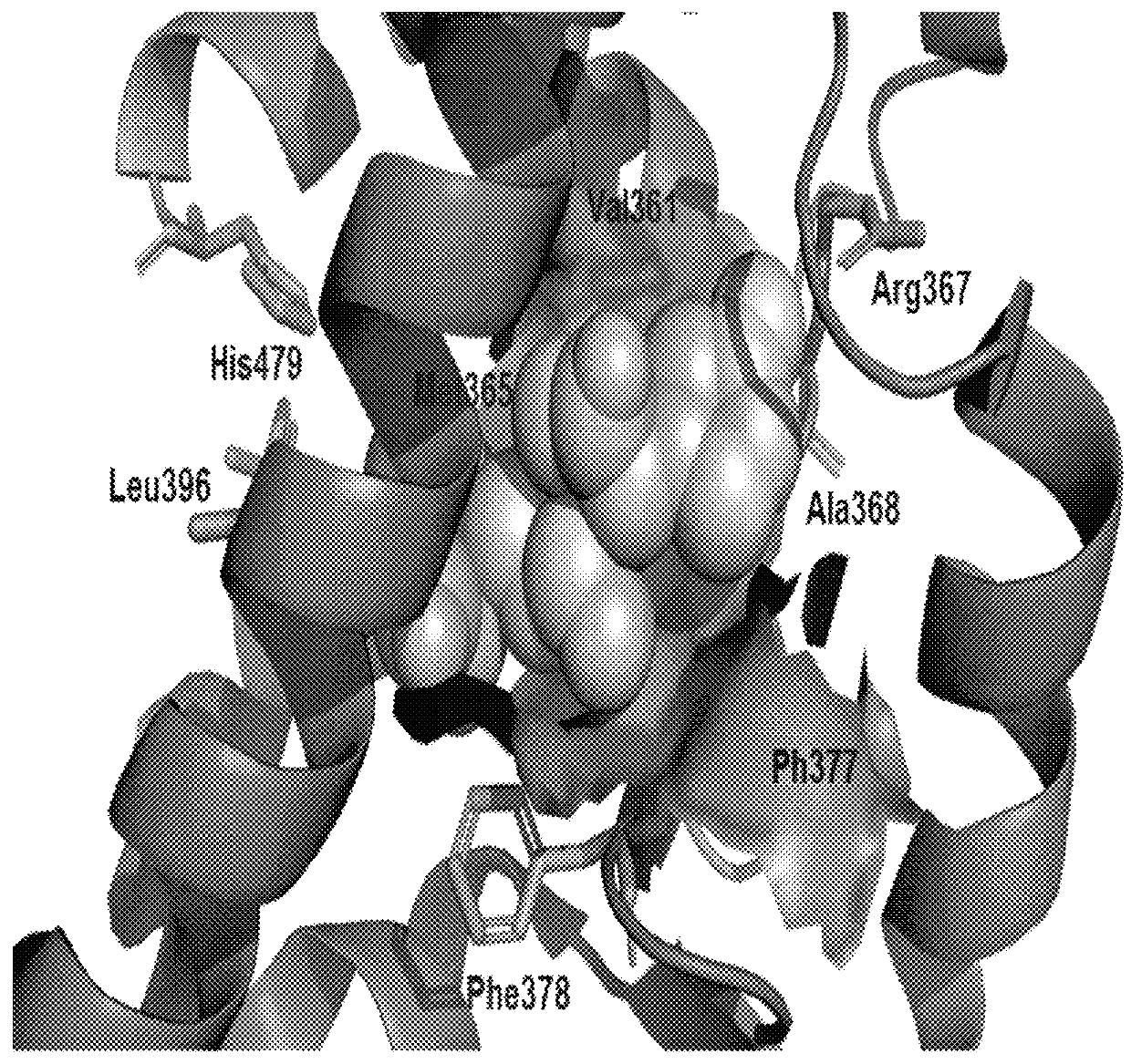
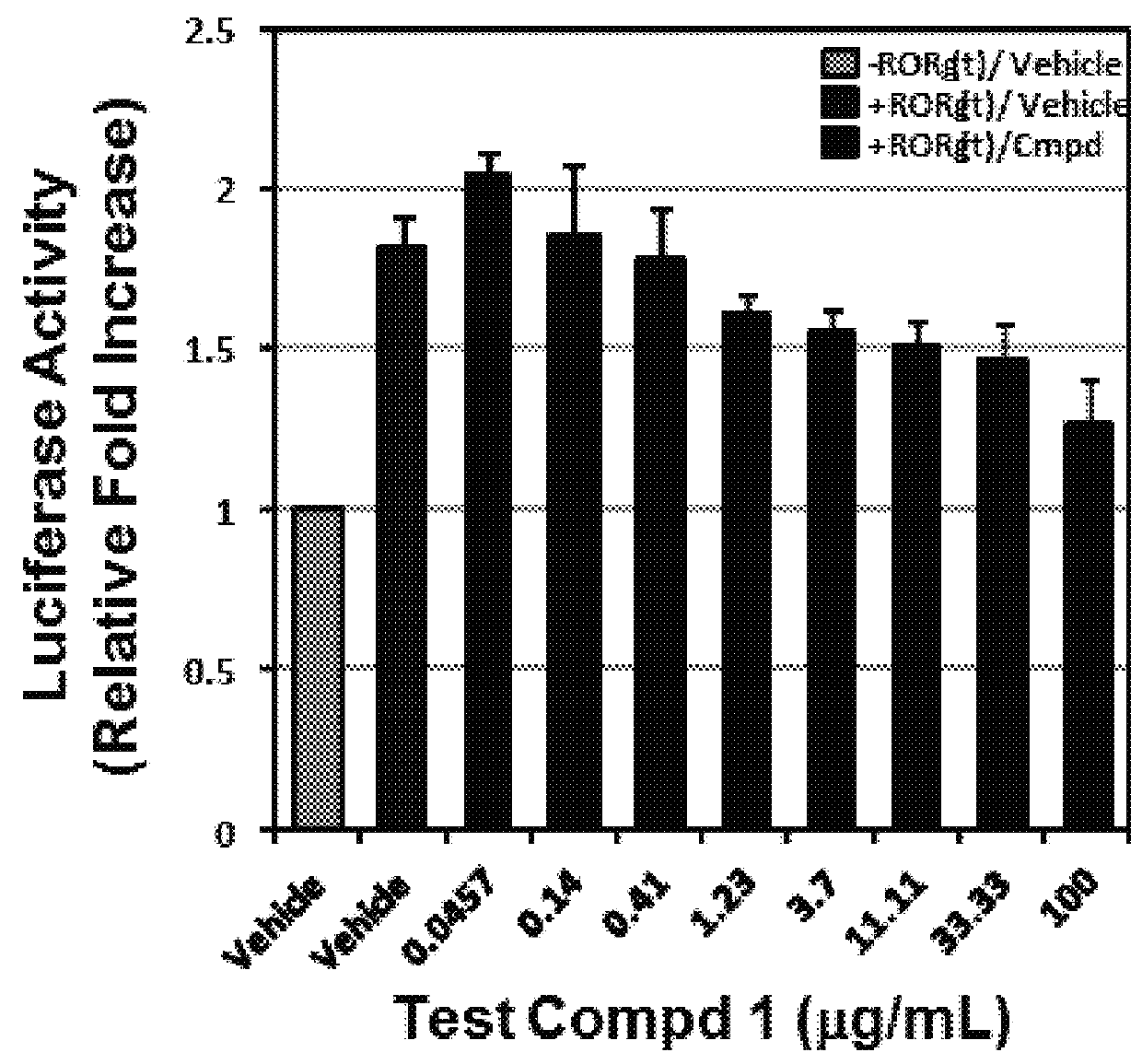
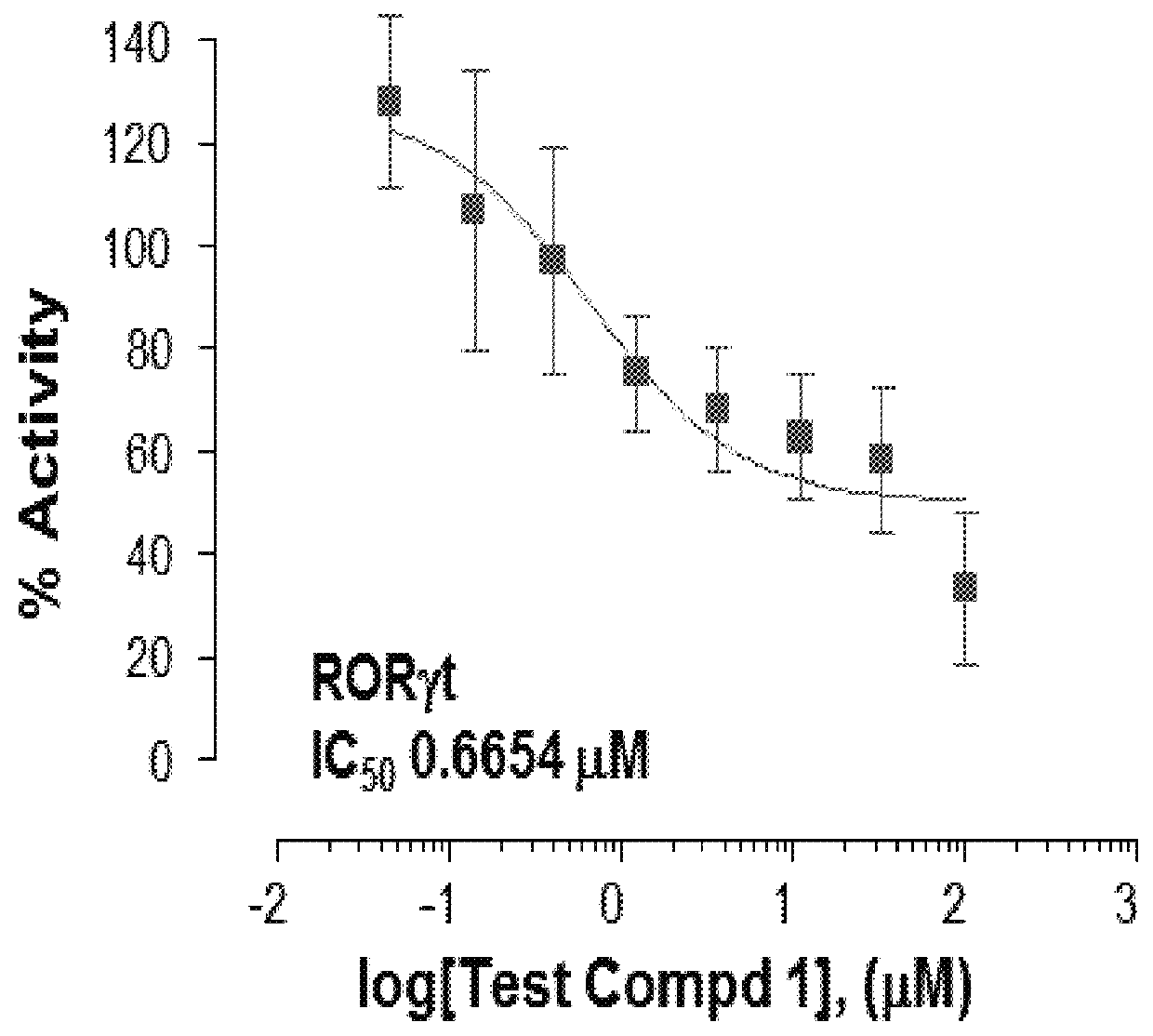
The present invention provides novel methods to treat disease by modulating retinoid-related orphan receptor gamma (ROR-gamma) in vitro and in vivo with ursolic acid analogs, and compositions thereof. The methods and compounds disclosed herein are useful for inhibiting the differentiation of a population of T cells, or treating a disease related to Th17 cell responses in a subject. Examples of such diseases include, but are not limited to, autoimmune diseases, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis and diabetes.
Owner:KULING THERAPEUTICS
Substituted 2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-one retinoic acid-related orphan nuclear receptor antagonists for treating multiple sclerosis
Owner:XENTHERA INC
Novel compounds for modulation of orphan nuclear receptor RAR-related orphan receptor-gamma (RORgamma, NR1F3) activity and for the treatment of chronic inflammatory and autoimmune disease
The invention provides modulators for the orphan nuclear receptor RORγ and methods for treating RORγ mediated diseases by administrating these novel RORγ modulators to a human or a mammal in need thereof. Specifically, the present invention provides compounds of Formula (1) and the enantiomers, diastereomers, tautomers, solvates and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
Owner:PHENEX PHARMA
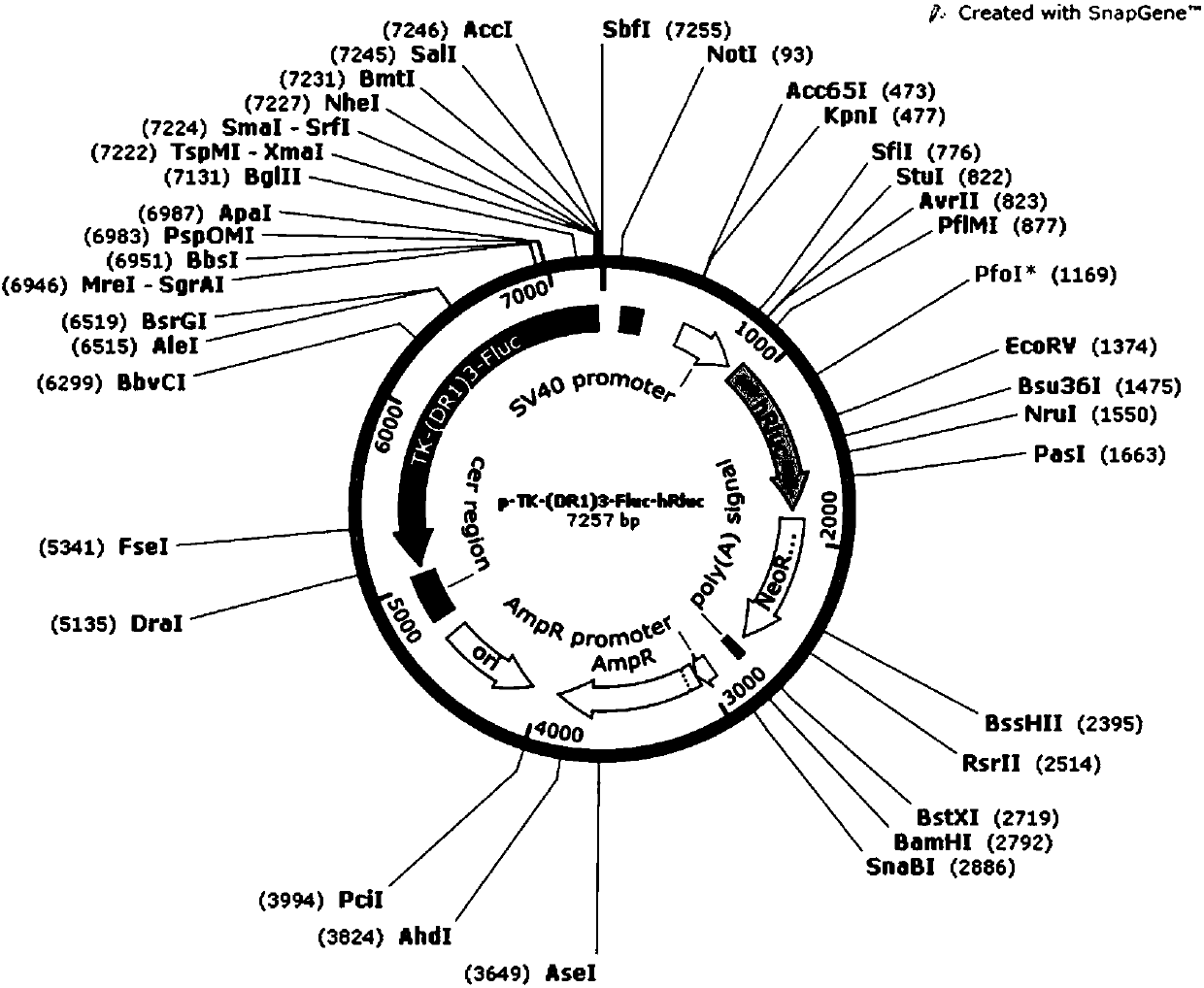
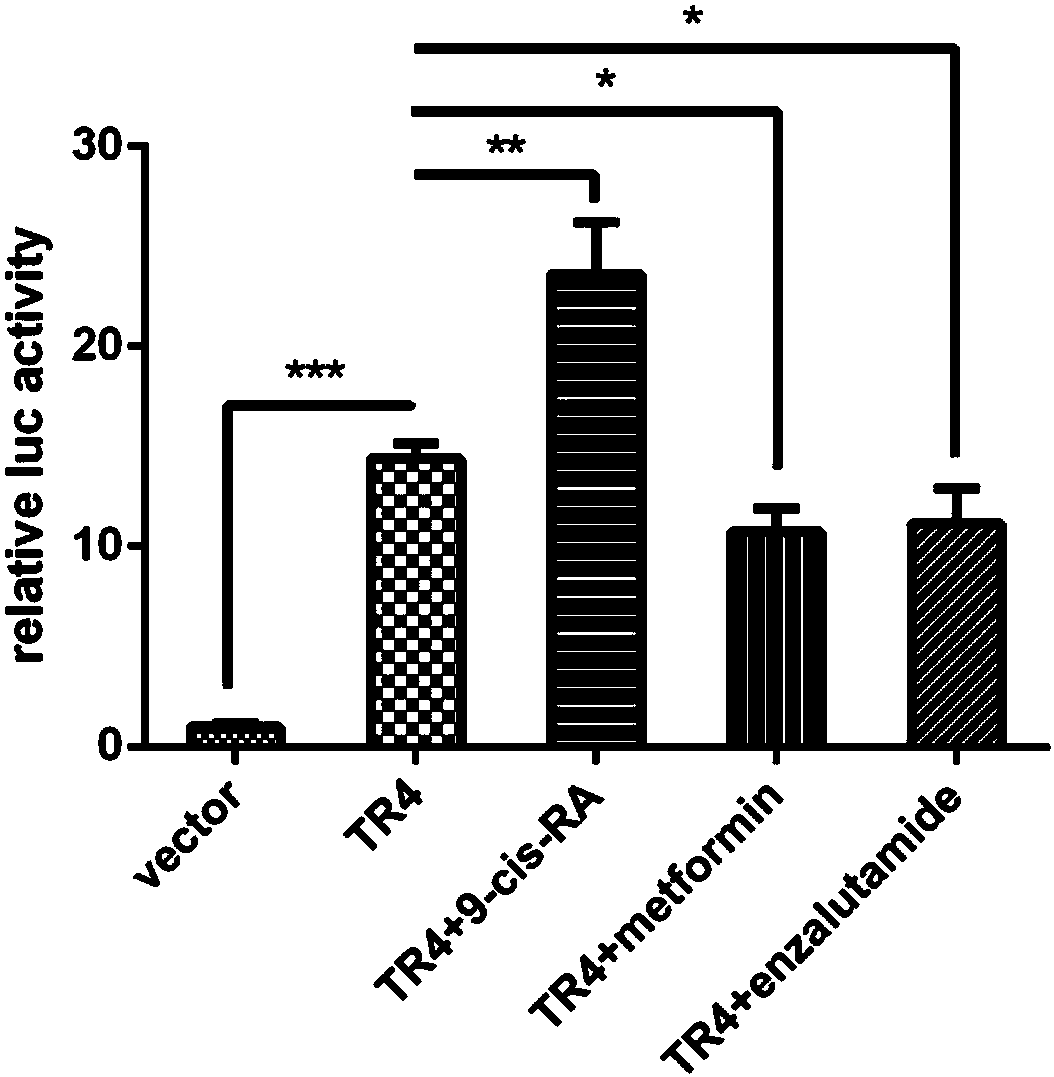
Dual-luciferase reporter gene plasmid applicable to screening of orphan nuclear receptor activity regulating agent, and construction and application thereof
ActiveCN107893085ASimple and fast operationHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionRenilla luciferaseLuciferases
The invention discloses a dual-luciferase reporter gene plasmid applicable to screening of an orphan nuclear receptor activity regulating agent. The plasmid is a chimeric plasmid (p-TK(DR1)<3>-Fluc-hRluc) of DR1-containing firefly luciferase and the internal reference renilla luciferase. A construction method for the plasmid is to insert a fragment as shown in SEQ ID No. 1 into a hRluc-containingframework plasmid obtained after NheI / BglII double-digestion of the commercial plasmid pmirGLO. High-efficiency screening of the orphan nuclear receptor activity regulating agent can be realized through cotransfection of cells with the plasmid and an orphan nuclear receptor-overexpressed plasmid and activity detection via dual luciferases. The method is simple to operate, and the dual-luciferase reporter gene plasmid has high sensitivity and good specificity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
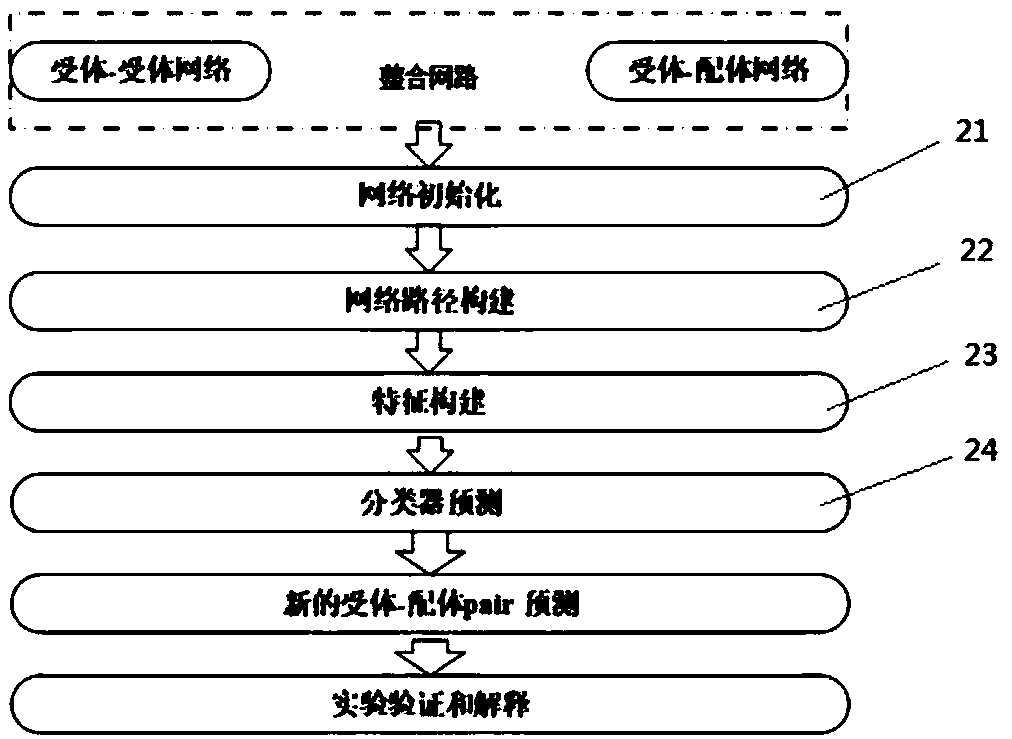
Prediction method and prediction system for G-protein-coupled receptor-ligand interaction relationship
The invention discloses a multi-information integration-based prediction method for G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR)-ligand interaction. The method comprises the steps of constructing a GPCR-ligand interaction network structure graph of a non orphan receptor; embedding a receptor-receptor relationship between an orphan receptor and the non orphan receptor into a receptor-ligand relationship network; and based on a distance relationship between nodes in the network, constructing a feature relationship of a receptor-ligand interaction pair, and in combination with an ensemble learning method, realizing effective prediction of a potential receptor-ligand relationship. The prediction method suitable for prediction of a GPCR-ligand interaction relationship and prediction of a potential ligandof an orphan GPCR is established and realized for bio-features of the GPCR and the ligand of the GPCR; and an experiment shows that the method is good in prediction effect and has a relatively wide application prospect. The invention furthermore discloses a multi-information integration-based prediction system for the GPCR-ligand interaction.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Nucleosome-based biosensor
InactiveUS20090062130A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsHistone octamer
A nucleosome-based biosensor can detect events of transcriptional activity. The biosensor includes a nucleosome-forming DNA that contains at least one nuclear responsive DNA sequence; a core histone octamer and at least two labels. In one version, the two labels are placed on the DNA. In another version, one of the labels is attached to the DNA, while the other to the core histone octamer. The sensor function is effected by measuring an emission signal, associated with the labels, which is sensitive to whether the nucleosome-forming DNA is or is not in nucleosomal configuration. The biosensor finds application, for example, in high-throughput screening for ligands to known and orphan nuclear receptors, respectively.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
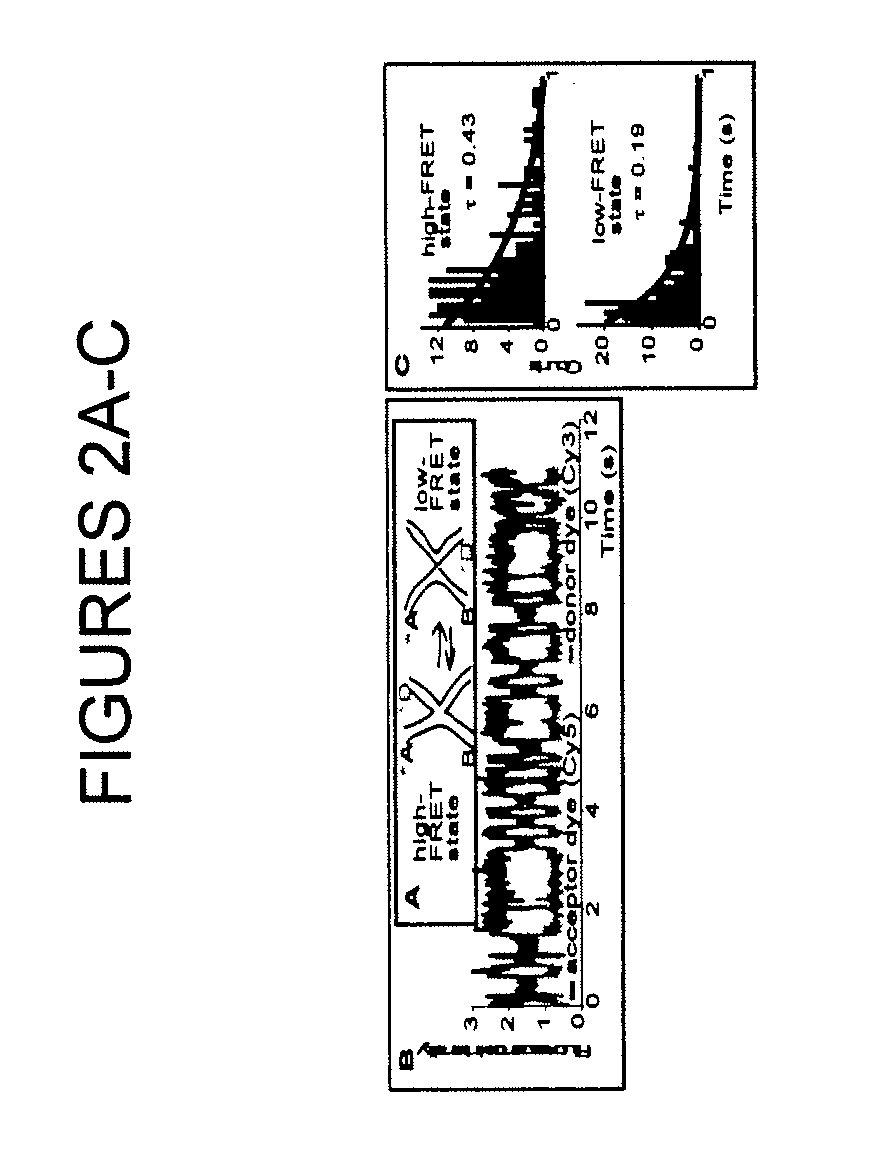
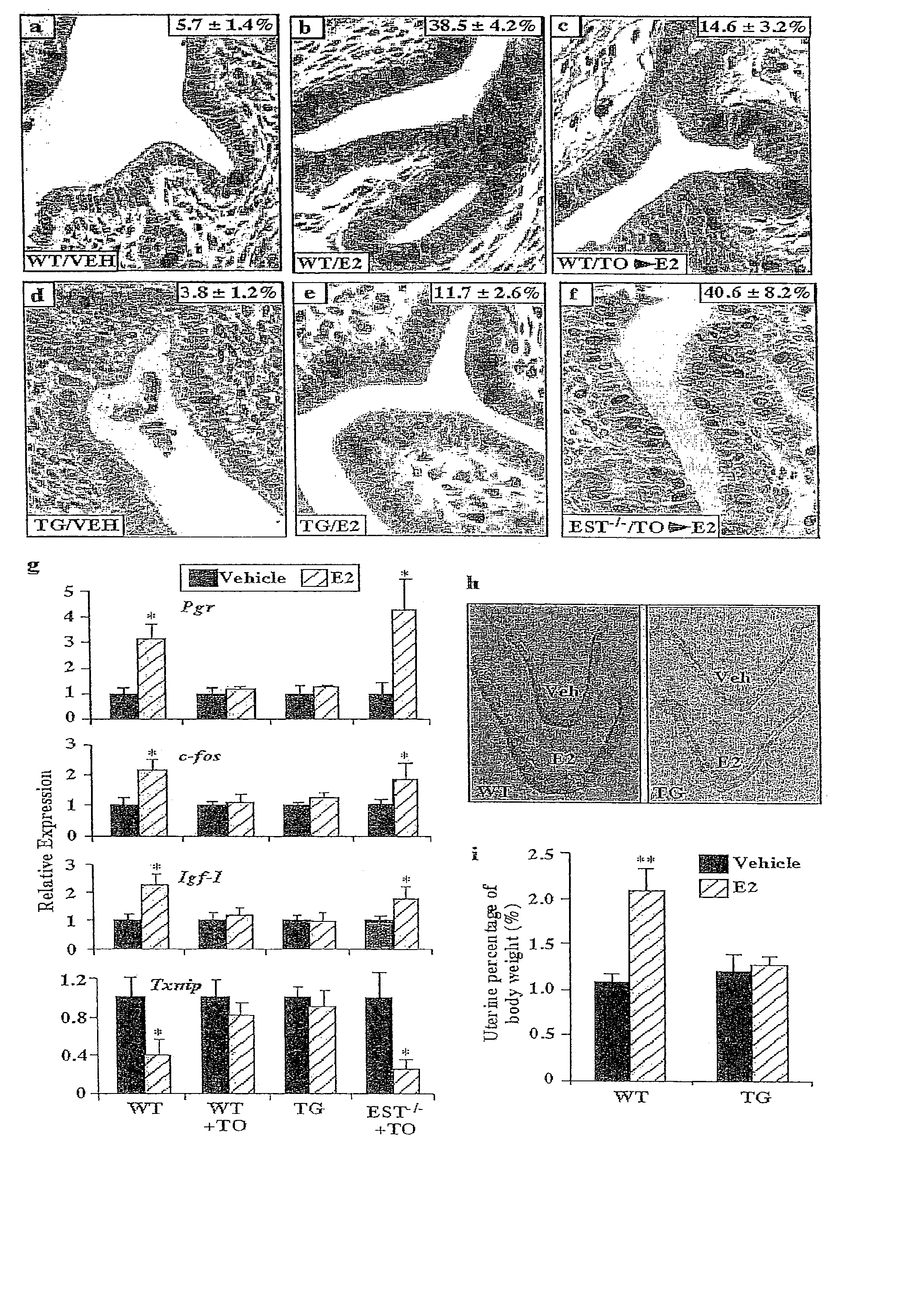
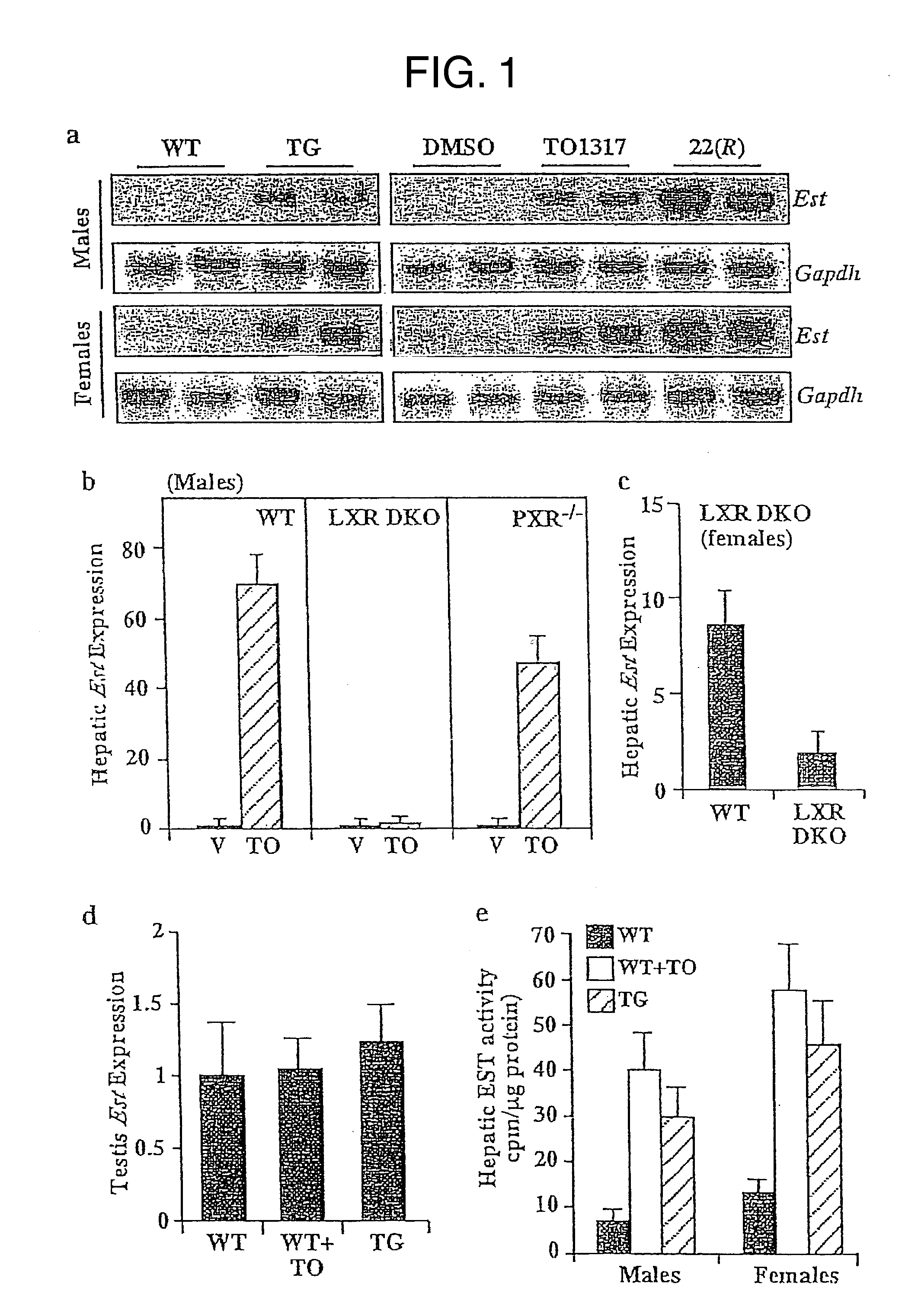
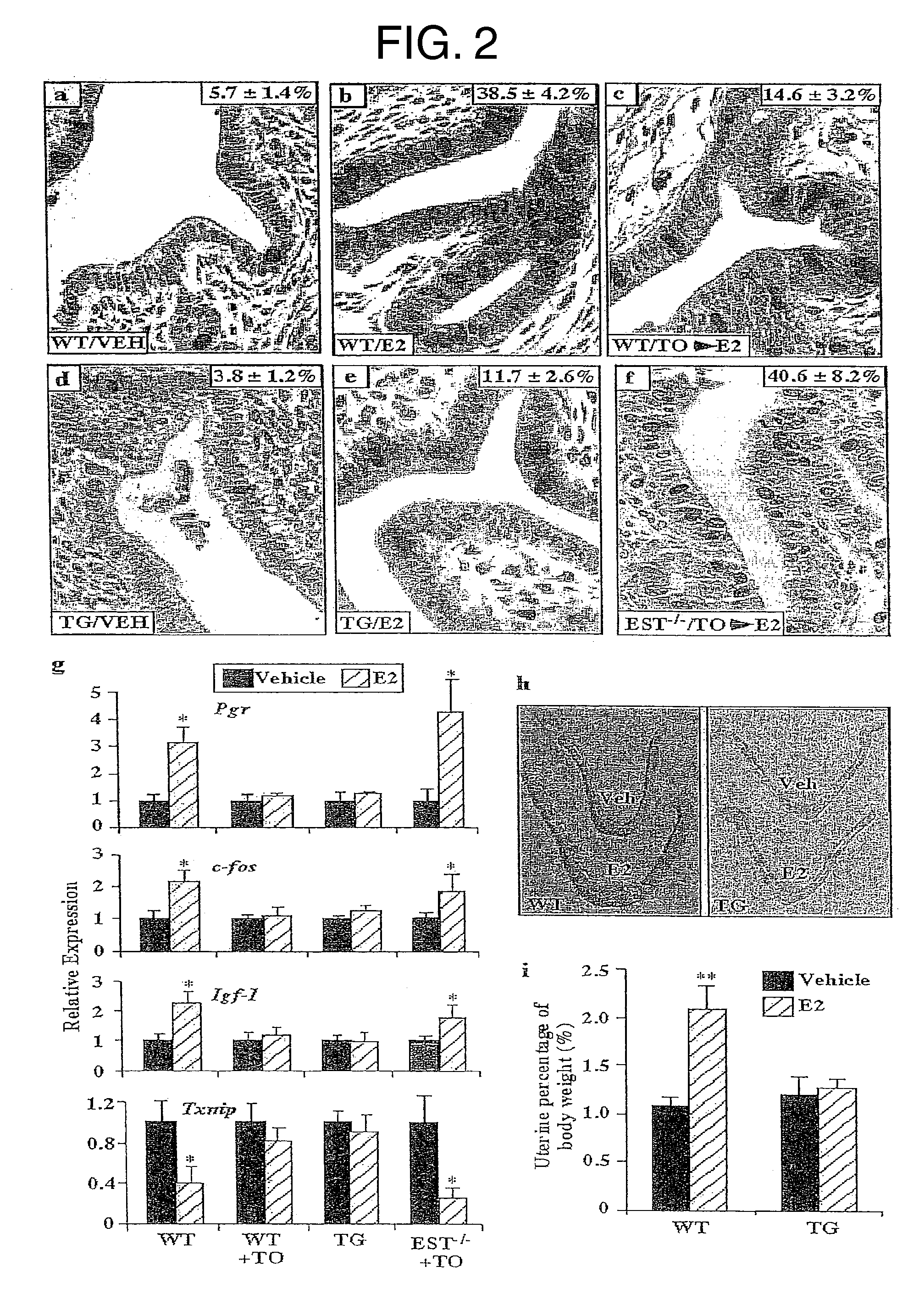
Methods of treating estrogen-responsive conditions by orphan nuclear receptor activation
InactiveUS20080085879A1Small sizeInhibitory activityAmide active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsAbnormal tissue growthAgonist
The invention provides a method of treating an estrogen responsive condition comprising administration of an agonist of an orphan nuclear receptor, wherein activation of the orphan nuclear receptor inhibits estrogen activity. The invention also provides a method of reducing the size of an estrogen responsive tumor comprising administration of an agonist of an orphan nuclear receptor, wherein activation of the orphan nuclear receptor inhibits estrogen activity. The invention also provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising an agonist of an orphan nuclear receptor and a pharmaceutically acceptable vehicle, wherein activation of the orphan nuclear receptor inhibits estrogen activity.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
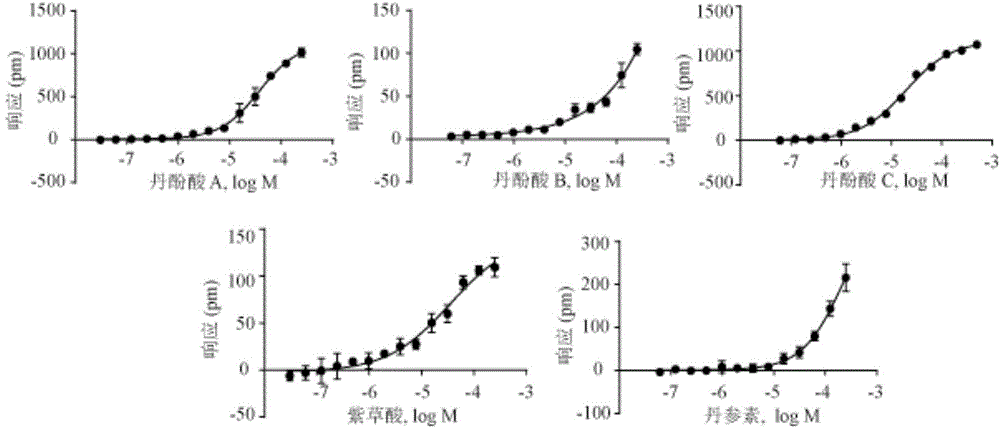
GPR35 receptor stimulant in salviae miltiorrhizae, inhibitor of Ca2+-ATPase and application
InactiveCN105521016AExpand the scope of clinical applicationNervous disorderAntipyreticATPaseSalvianolic acid B
The invention relates to the discovering of the action targets of traditional Chinese medicine salviae miltiorrhizae and widening of clinical application range, in particular to discovering of the new action targets of phenolic acid compounds in the salviae miltiorrhizae and new clinical application of the phenolic acid compounds. The phenolic acid compounds include similar-structured compounds such as protocatechuic aldehyde, tanshinol, caffeic acid, alkannic acid, salvianolic acid A, salvianolic acid B, salvianolic acid C and salvianolic acid D, the derivatives of the similar-structured compounds and the pharmaceutically-acceptable salt-forming compounds of the similar-structured compounds. In vitro cell experiments show that the compounds act on the orphan receptor GPR35 and current researches show that the orphan receptor GPR35 is related to diseases such as cardiac failure, hypertension, coronary heart disease, metabolic syndrome, asthma, pain, inflammation and cancer, so that the clinical application range of the compounds can be widened. In addition, the fact that the compounds have a double-target effect is discovered, and certain guidance is provided for the new clinical application.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cyclic amine derivative and pharmaceutical use thereof
ActiveCN108473426AInhibitory functionOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderAllergic dermatitisRetinoid-Related Orphan Receptor
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a novel compound having antagonist activity against retinoid-related orphan receptor [gamma], and exhibiting a therapeutic effect or a preventive effect for an autoimmune disease such as multiple sclerosis or psoriasis, or an allergic disease such as contact dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, or other allergic dermatitis. The present invention provides a cyclic amine derivative represented by the formula, or a pharmacologically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Carboxamide or sulfonamide substituted nitrogen-containing 5-membered heterocycles as modulators for the orphan nuclear receptor RORγ
ActiveUS9458104B2High metabolismDecreases in serum and liver triglycerideNervous disorderOrganic chemistryDiseaseCyclic compound
The invention provides modulators for the orphan nuclear receptor RORy and methods for treating RORy mediated diseases by administering these novel RORy modulators to a human or a mammal in need thereof. Specifically, the present invention provides carboxamide containing cyclic compounds of Formula (1) to Formula (5) and the enantiomers, diastereomers, tautomers, / V-oxides, solvates and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
Owner:PHENEX PHARMA
Sulfonamide retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor modulators and uses thereof
ActiveUS9701663B2Organic chemistryHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsRetinoic acid receptorReceptor for activated C kinase 1
Owner:INNOV17
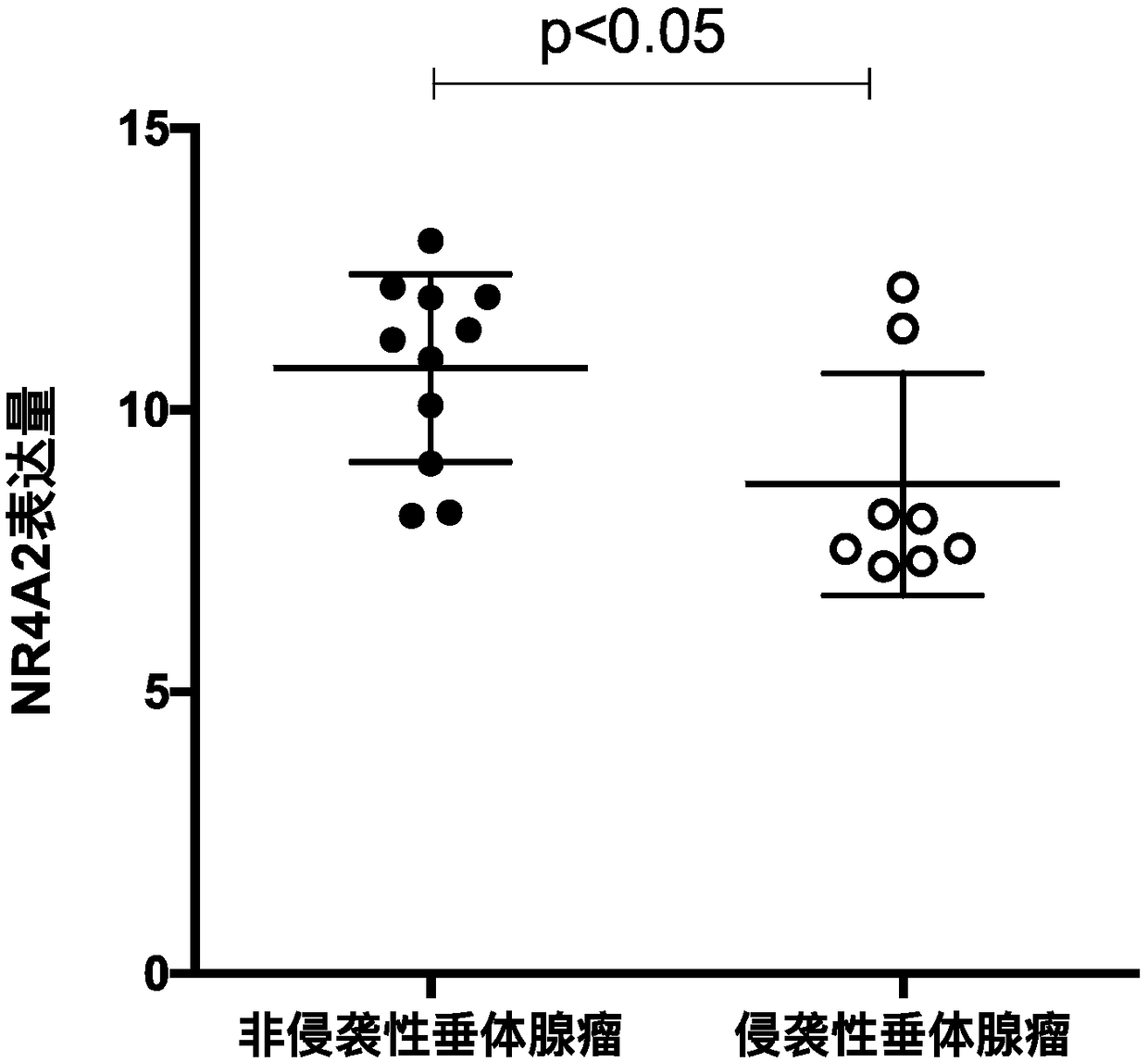
Application and expression of NR4A2 gene in pituitary adenoma biomarker
The invention discloses an application and an expression of an NR4A2 gene in a pituitary adenoma biomarker, in particular to the technical field of applications of natural ribonucleotide. An NR4A2 gene belongs to an orphan nuclear receptor subfamily in a nuclear receptor family and is used for identifying an object probably suffering from pituitary adenoma or invasiveness of pituitary adenoma. Theexpression of NR4A2 from a pituitary adenoma tissue sample of the object is detected, wherein NR4A2 with higher expression shows that the invasiveness of the pituitary adenoma of the object is high and is related with increase of the possibility of bad prognosis of the object. The invention provides the application of the NR4A2 gene. The expressions of the NR4A2 gene in tissue of invasive pituitary adenoma and non-invasive pituitary adenoma patients are different, and therefore, the NR4A2 gene has the application prospects of becoming the pituitary adenoma biomarker.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL OF DALIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Substituted 2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-one Retinoic acid-related orphan nuclear receptor Antagonists for Treating Multiple Sclerosis
The present invention is directed to compounds, their synthesis, and their use as antagonists, inverse agonists, modulators and or inhibitors of the Retinoic acid-related orphan nuclear receptor γt (RORγt) / RORγ. The compounds of the present invention are useful for modulating RORγt) / RORγ activity and for treating diseases or conditions mediated by RORγt) / RORγ such as for example, disease states associated with immunopathology of human autoimmune diseases such as Multiple Sclerosis (MS), Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), Inflammatory Colitis, Psoriasis, COPD, Pain, Obesity, Diabetes, Dyslipidemia, Osteoporosis, Asthma, Neurodegenerative diseases and Cancer.
Owner:XENTHERA INC
Substituted 2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-one Retinoic acid-related orphan nuclear receptor Antagonists for Treating Multiple Sclerosis
The present invention is directed to compounds, their synthesis, and their use as antagonists, inverse agonists, modulators and or inhibitors of the Retinoic acid-related orphan nuclear receptor γt (RORγt) / RORγ. The compounds of the present invention are useful for modulating RORγt) / RORγ activity and for treating diseases or conditions mediated by RORγt) / RORγ such as for example, disease states associated with immunopathology of human autoimmune diseases such as Multiple Sclerosis (MS), Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), Inflammatory Colitis, Psoriasis, COPD, Pain, Obesity, Diabetes, Dyslipidemia, Osteoporosis, Asthma, Neurodegenerative diseases and Cancer.
Owner:XENTHERA INC
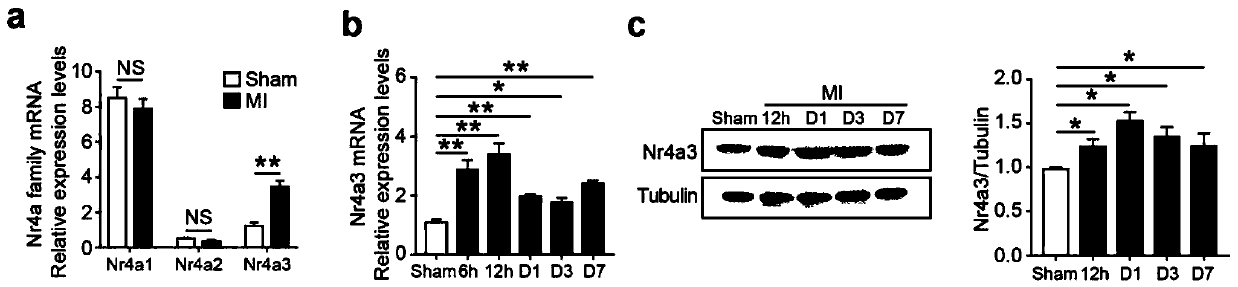
Application of ribosome S6 kinase inhibitor SL0101 in preparation of drug for treating cardiovascular diseases
InactiveCN110237087AInhibit phosphorylationReduce mortalityCompounds screening/testingOrganic active ingredientsVascular diseaseRibosomal s6 kinase
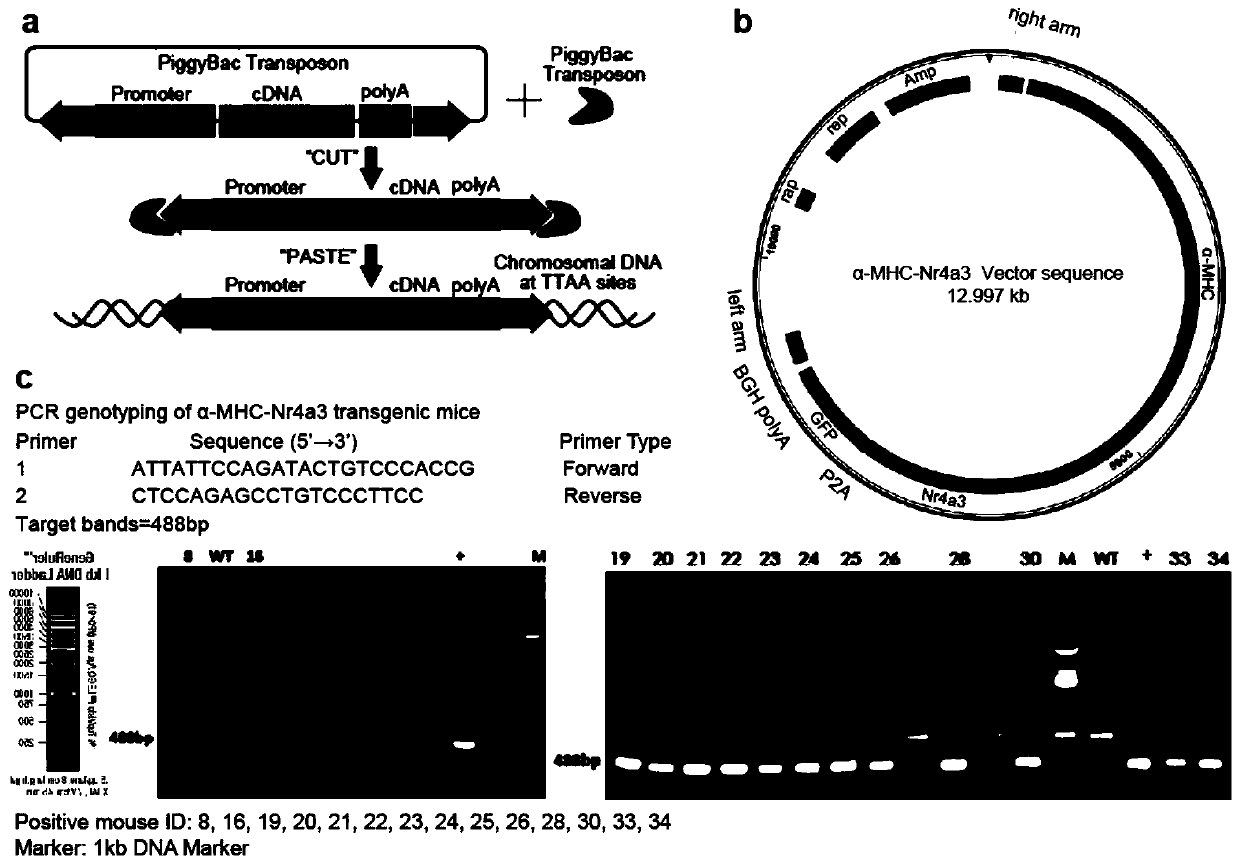
The invention belongs to the field of drug preparation and application, and particularly relates to application of a ribosome S6 kinase inhibitor SL0101 in the preparation of a drug for treating cardiovascular diseases. The invention aims at providing the drug for treating the cardiovascular diseases, wherein the drug contains a substance for performing treatment by taking an orphan nuclear receptor Nr4a3 as a drug target. Preferably, the effective component of the substance comprises the ribosome S6 kinase inhibitor SL0101. The application of the orphan nuclear receptor Nr4a3 as a target in the preparation of a drug for screening the cardiovascular diseases provides a very wide prospect and important significance for drug application of the ribosome S6 kinase inhibitor SL0101.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Pyrrolo carboxamides as modulators of orphan nuclear receptor RAR-related orphan receptor-gamma (RORγ, NR1F3) activity and for the treatment of chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases
InactiveUS9815851B2High metabolismDecreases in serum and liver triglycerideNervous disorderOrganic chemistryAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
The invention provides modulators for the orphan nuclear receptor RORγ and methods for treating RORγ mediated diseases by administrating these novel RORγ modulators to a human or a mammal in need thereof. Specifically, the present invention provides pyrrolo carboxamide compounds of Formula (1) and the enantiomers, diastereomers, N-oxides, tautomers, solvates and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
Owner:PHENEX PHARMA AG
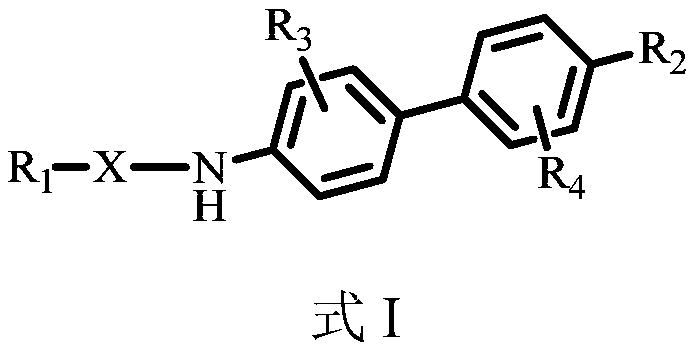
Benzidine compound and application thereof
ActiveCN109879784AEnhanced inhibitory effectEasy to prepareOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseRetinoid
The invention relates to a benzidine compound and application thereof. The benzidine compound has a structure disclosed in the following formula I. The invention also provides the pharmaceutically acceptable salt, the isomer, the raceme, the pro-drug cocrystallization compound, the hydrate and the solvate of the compound, and the application thereof for preparing medicines for treating or preventing ROR (Retinoid-related Orphan nuclear Receptor) gamma regulation and control relevant diseases. More importantly, the class of compound can be used for treating medicines used for treating inflammation, immunological diseases, cancers and neurological diseases.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor modulators and uses thereof
InactiveUS20150252051A1BiocideOrganic chemistryReceptor for activated C kinase 1Retinoic acid receptor alpha
Provided herein are compounds of the formula (I):as well as pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein the substituents are as those disclosed in the specification. These compounds, and the pharmaceutical compositions containing them, are useful for the treatment of Retinoic Acid Receptor-Related Orphan Receptor regulated diseases and disorders.
Owner:INNOV17
Small nucleic acid molecule capable of inhibiting vascular restenosis and applications of small nucleic acid molecule
InactiveCN106367417APrevent restenosisOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCytosinePercent Diameter Stenosis
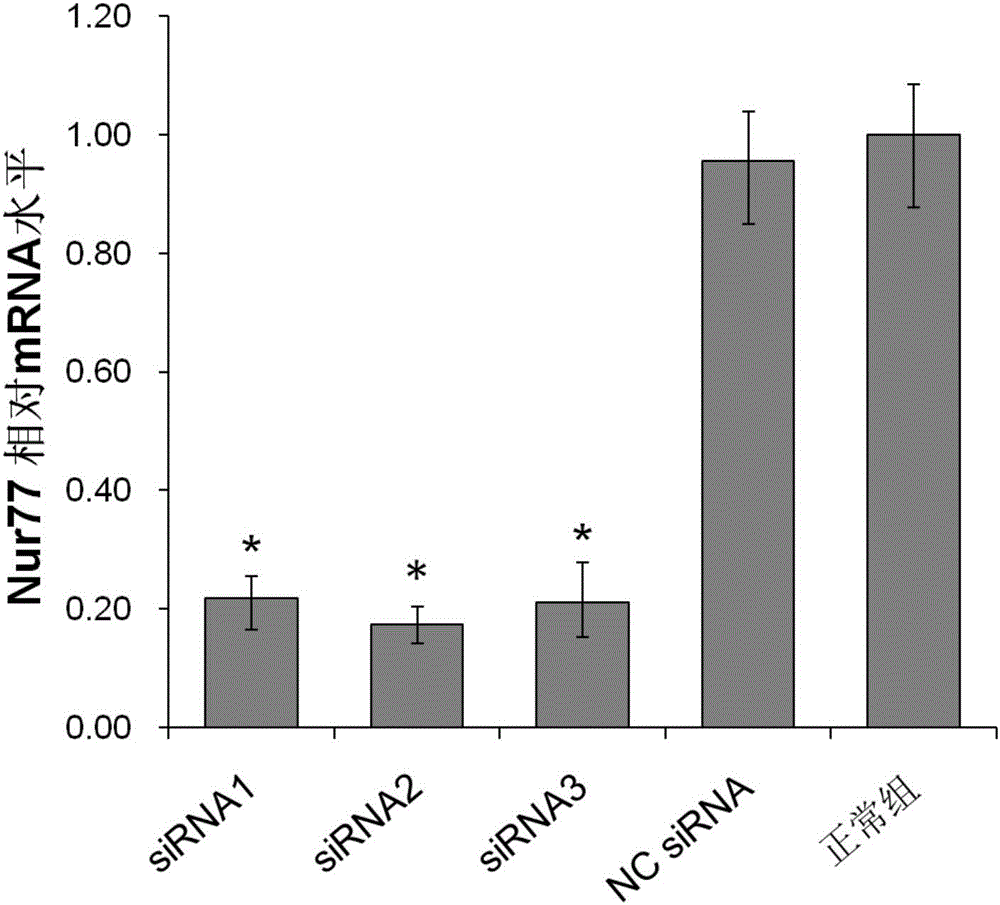
The invention discloses a small nucleic acid siRNA molecule capable of inhibiting the expression of orphan nuclear receptor Nur77. The small nucleic acid siRNA molecule is composed of a positive-sense strand and an antisense strand with the following sequences: the positive-sense strand: 5'-GCUCAGGCCUGGUGCUACANn-3' (SEQ ID NO:13), and the antisense strand: 5'-UGUAGCACCAGGCCUGAGCNn-3' (SEQ ID NO:14), N in the positive-sense strand and N in the antisense strand are the same or different, and cytosine C, uracil U, guanine G, adenine A, deoxycytosine dC, deoxyguanine dG, deoxyadenine dA or deoxythymine dT is independent; n is the number of N, and is 0, 1 or 2. The siRNA molecule provided by the invention can be used for inhibiting the grafted vascular restenosis.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF NANTONG UNIV
Pyrrolo sulfonamide compounds for modulation of orphan nuclear receptor RAR-related orphan receptor-γ (ROR-γ, NR1F3) activity and for the treatment of chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases
The invention provides modulators for the orphan nuclear receptor RORy and methods for treating RORy mediated diseases by administrating these novel RORy modulators to a human or a mammal in need thereof. Specifically, the present invention provides pyrrolo sulfonamide compounds of Formula (1) and the enantiomers, diastereomers, tautomers, solvates and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
Owner:PHENEX PHARMA
Bicyclic compounds, compositions and medicinal applications thereof
The present disclosure relates to a class of substituted bicyclic compounds of formula (I), their tautomers, polymorphs, stereoisomers, prodrugs, solvates, hydrates, N-oxides, co-crystals, pharmaceutically acceptable salts and pharmaceutical compositions containing them. The disclosure also relates to the process of preparation of compounds of Formula (I). These compounds are useful in the treatment, prevention, prophylaxis, management, or adjunct treatment of all medical conditions related to inhibition of retinoic acid-related orphan receptor [gamma] (ROR[gamma]) such as inflammatory and / or autoimmune disorder, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, allergic diseases, asthma, COPD, cancer, cell proliferation, type 1 diabetes, myasthenia gravis, hematopoetic disfunction, systemic lupus, erythematosus or other disorders.
Owner:ADVINUS THERAPEUTICS PVT LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![2-oxo-1,2-dihydrobenzo[cd] indole-6-sulfamide compound and composition and application thereof 2-oxo-1,2-dihydrobenzo[cd] indole-6-sulfamide compound and composition and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/41d2a09f-eb9c-4663-9a46-49cf1ce360ef/DEST_PATH_IMAGE001.PNG)
![2-oxo-1,2-dihydrobenzo[cd] indole-6-sulfamide compound and composition and application thereof 2-oxo-1,2-dihydrobenzo[cd] indole-6-sulfamide compound and composition and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/41d2a09f-eb9c-4663-9a46-49cf1ce360ef/DEST_PATH_IMAGE002.PNG)
![2-oxo-1,2-dihydrobenzo[cd] indole-6-sulfamide compound and composition and application thereof 2-oxo-1,2-dihydrobenzo[cd] indole-6-sulfamide compound and composition and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/41d2a09f-eb9c-4663-9a46-49cf1ce360ef/DEST_PATH_IMAGE003.PNG)
![Carboxamide or sulfonamide substituted thiazoles and related derivatives as modulators for the orphan nuclear receptor ror[gamma] Carboxamide or sulfonamide substituted thiazoles and related derivatives as modulators for the orphan nuclear receptor ror[gamma]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/44db4e58-e71b-4dce-a6bd-600b0cf762b3/US20150175562A1-20150625-C00001.PNG)
![Carboxamide or sulfonamide substituted thiazoles and related derivatives as modulators for the orphan nuclear receptor ror[gamma] Carboxamide or sulfonamide substituted thiazoles and related derivatives as modulators for the orphan nuclear receptor ror[gamma]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/44db4e58-e71b-4dce-a6bd-600b0cf762b3/US20150175562A1-20150625-C00002.PNG)
![Carboxamide or sulfonamide substituted thiazoles and related derivatives as modulators for the orphan nuclear receptor ror[gamma] Carboxamide or sulfonamide substituted thiazoles and related derivatives as modulators for the orphan nuclear receptor ror[gamma]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/44db4e58-e71b-4dce-a6bd-600b0cf762b3/US20150175562A1-20150625-C00003.PNG)