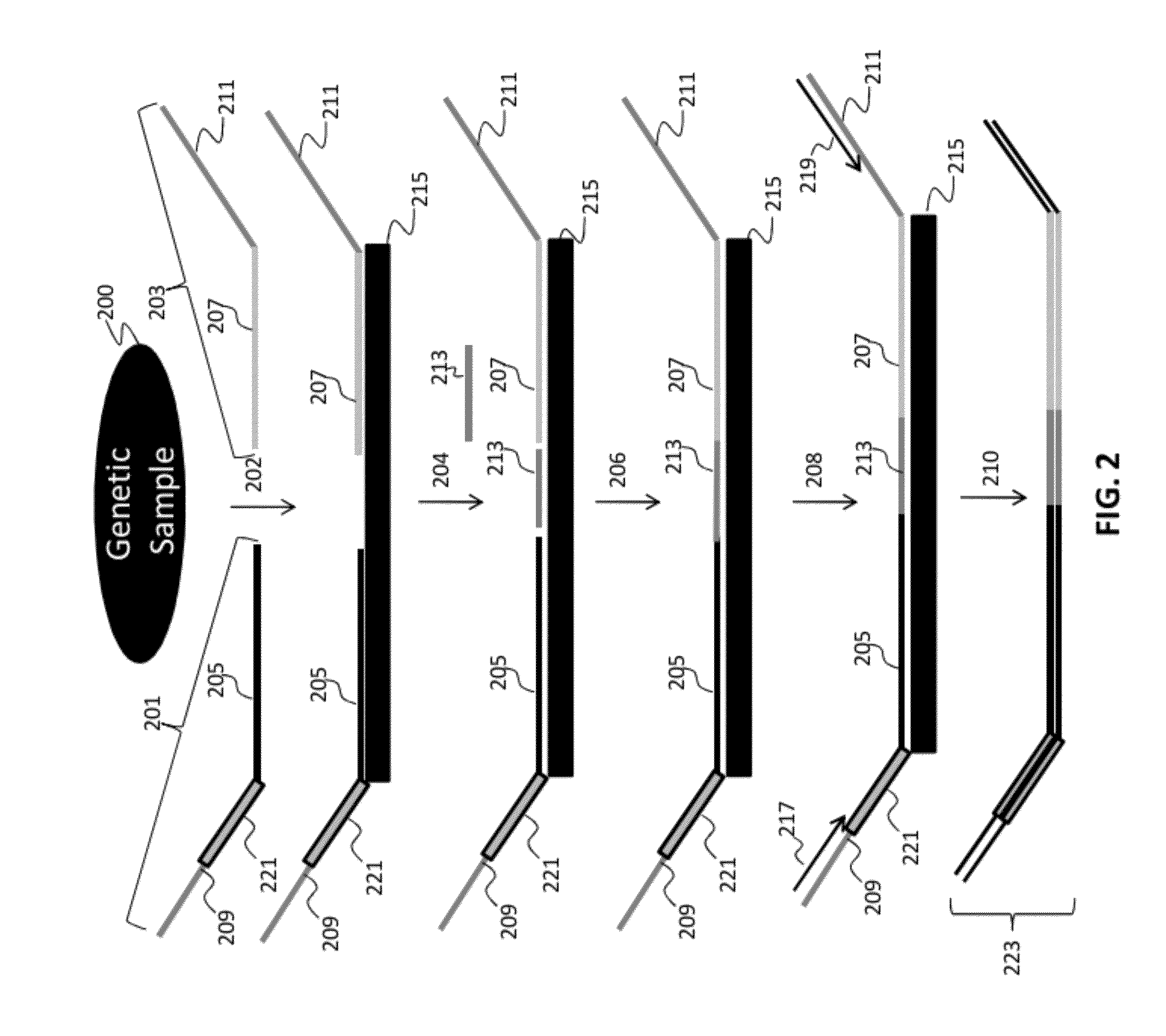
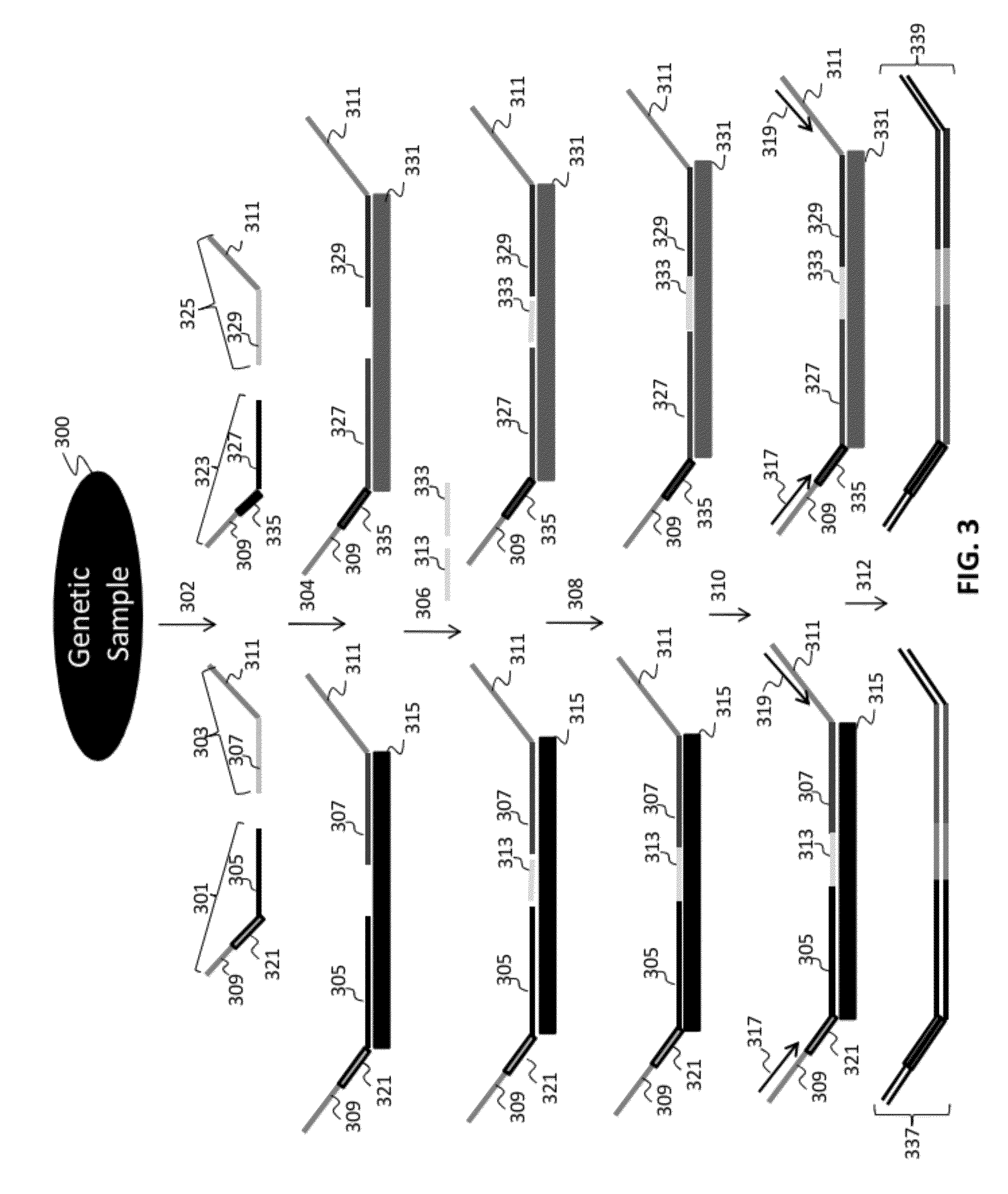
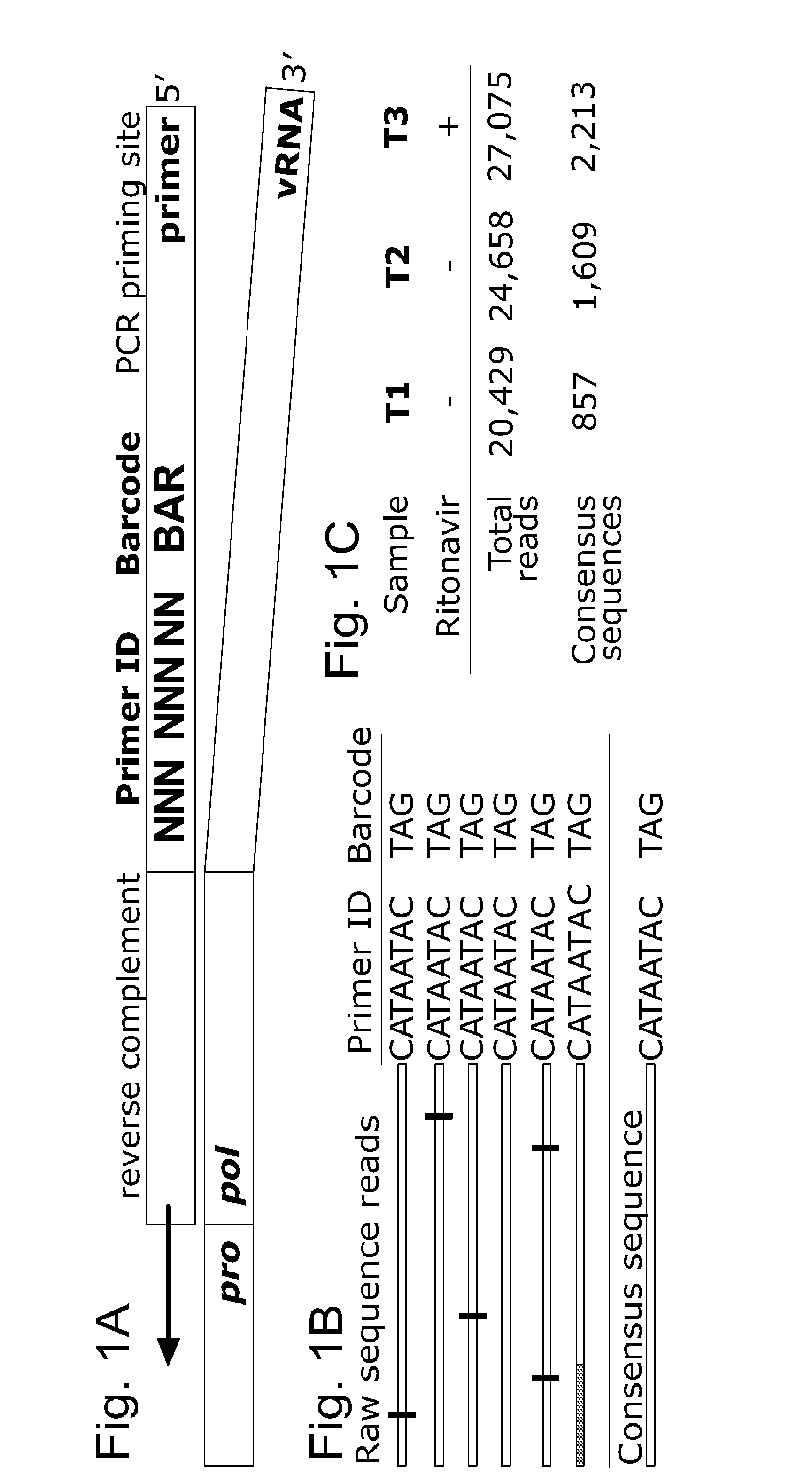
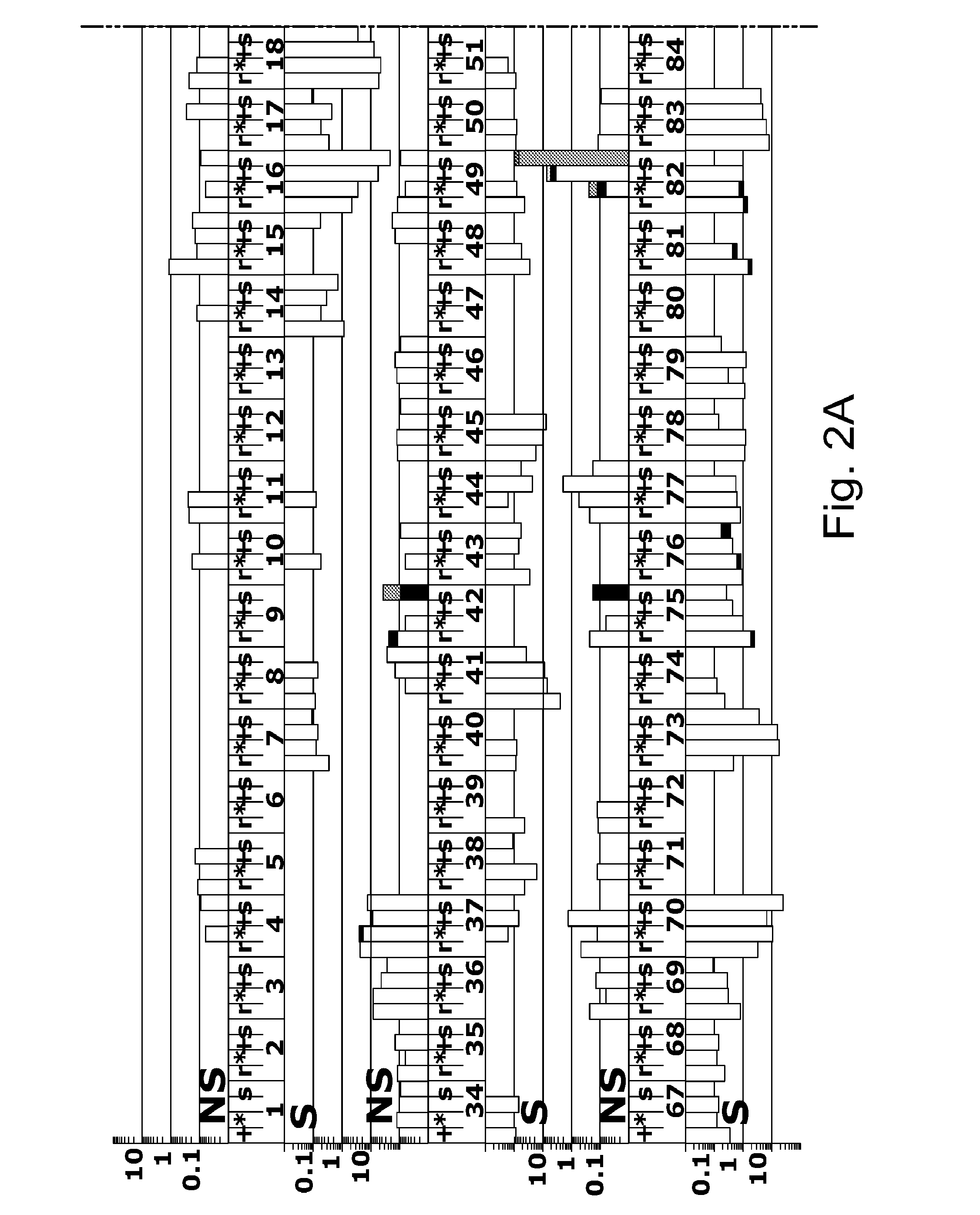
Patents
Literature
361 results about "Variation (Genetics)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genetic variation is brought about, fundamentally, by mutation, which is a permanent change in the chemical structure of chromosomes. Genetic recombination also produces changes within alleles. Genetic variation among individuals within a population can be identified at a variety of levels.
Method and compositions for detection and enumeration of genetic variations
ActiveUS20070065823A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSpecific populationFluorescence
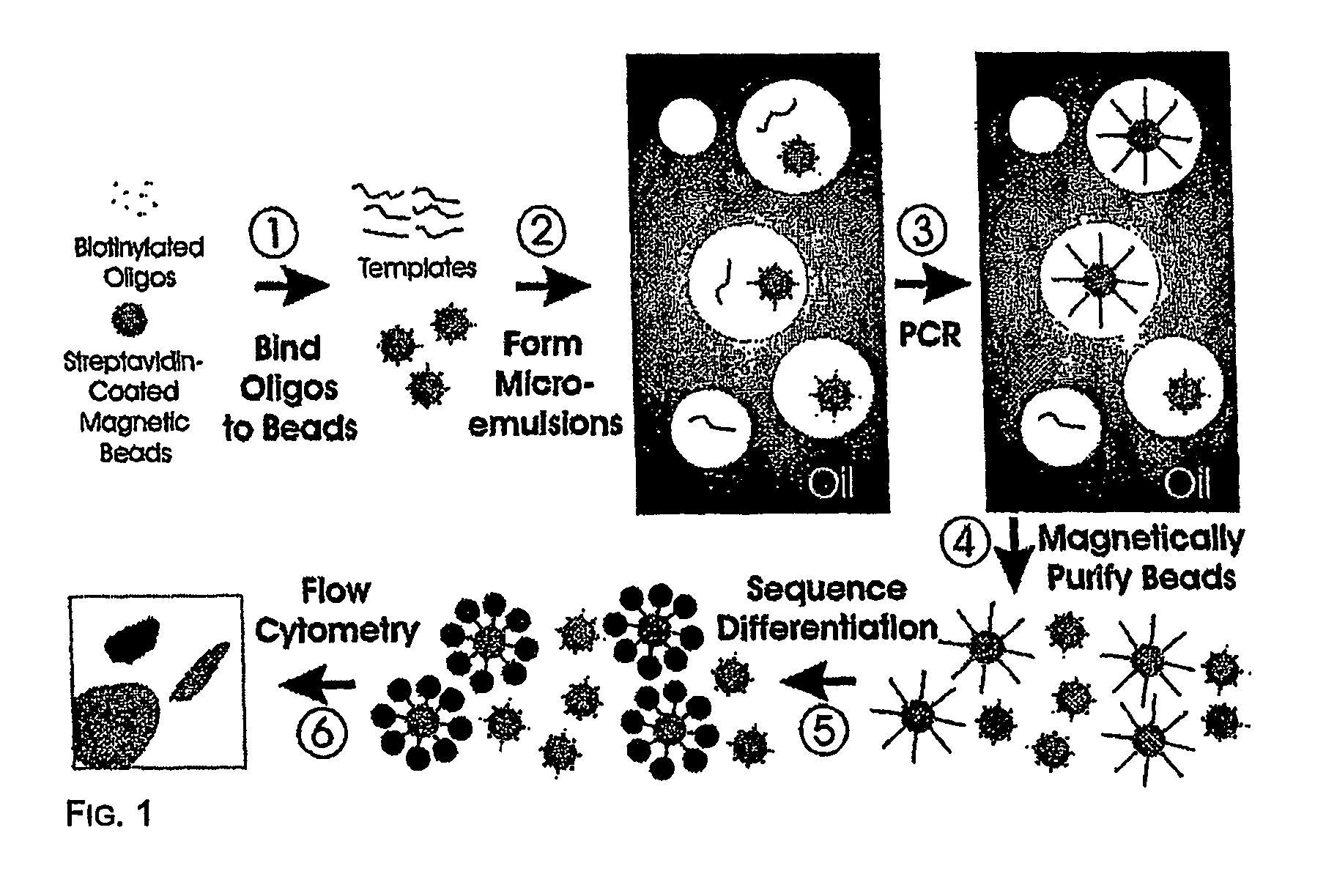
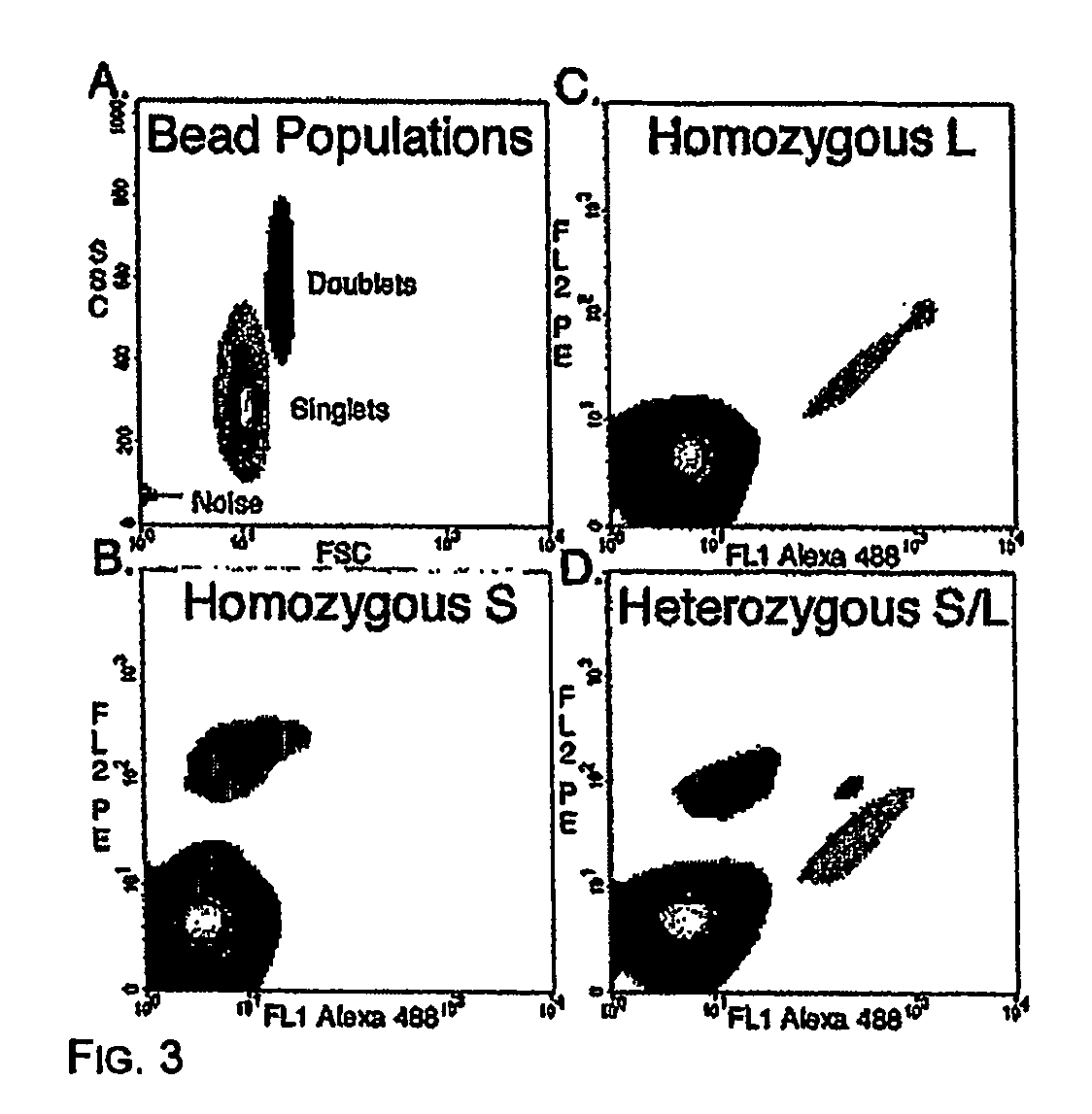
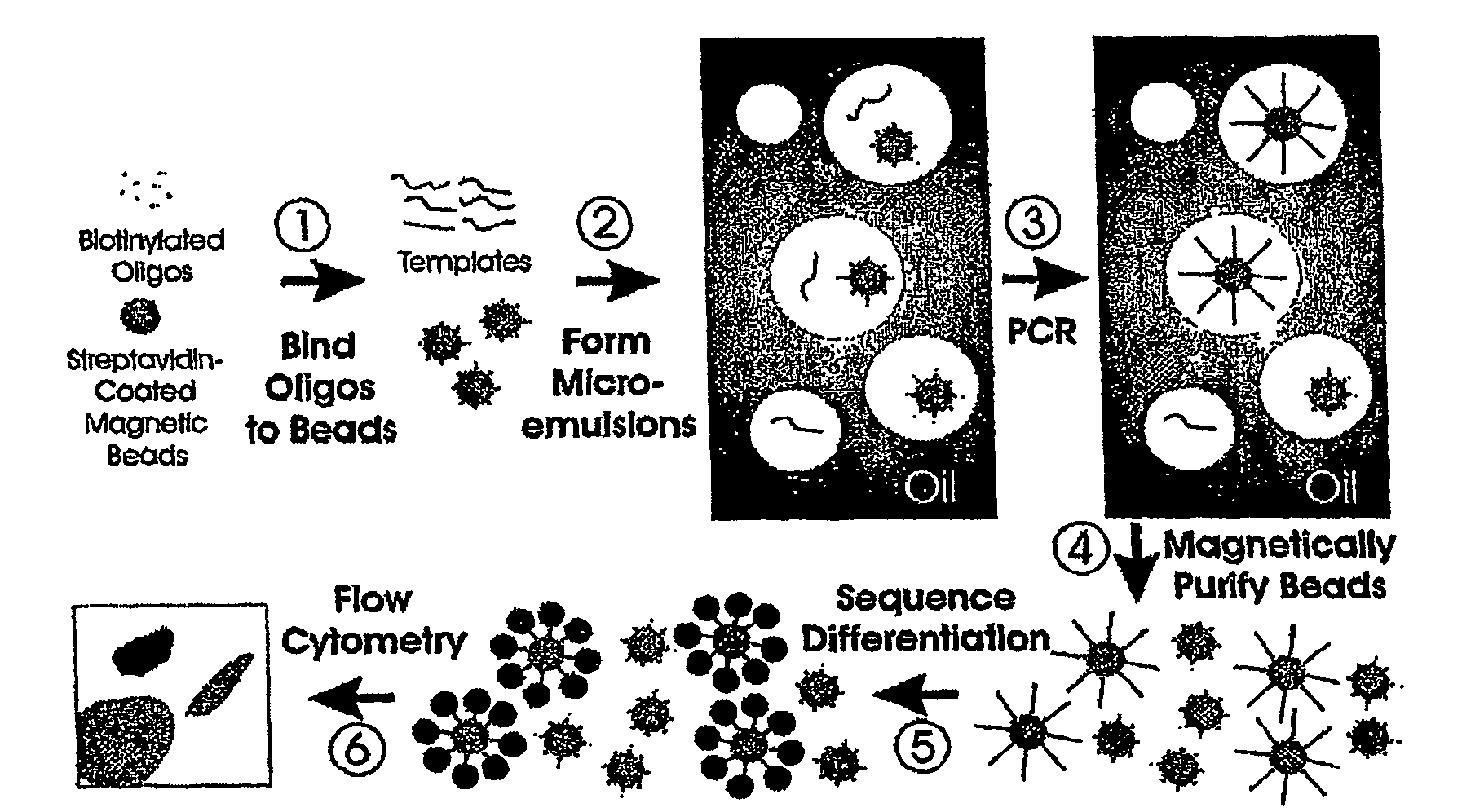
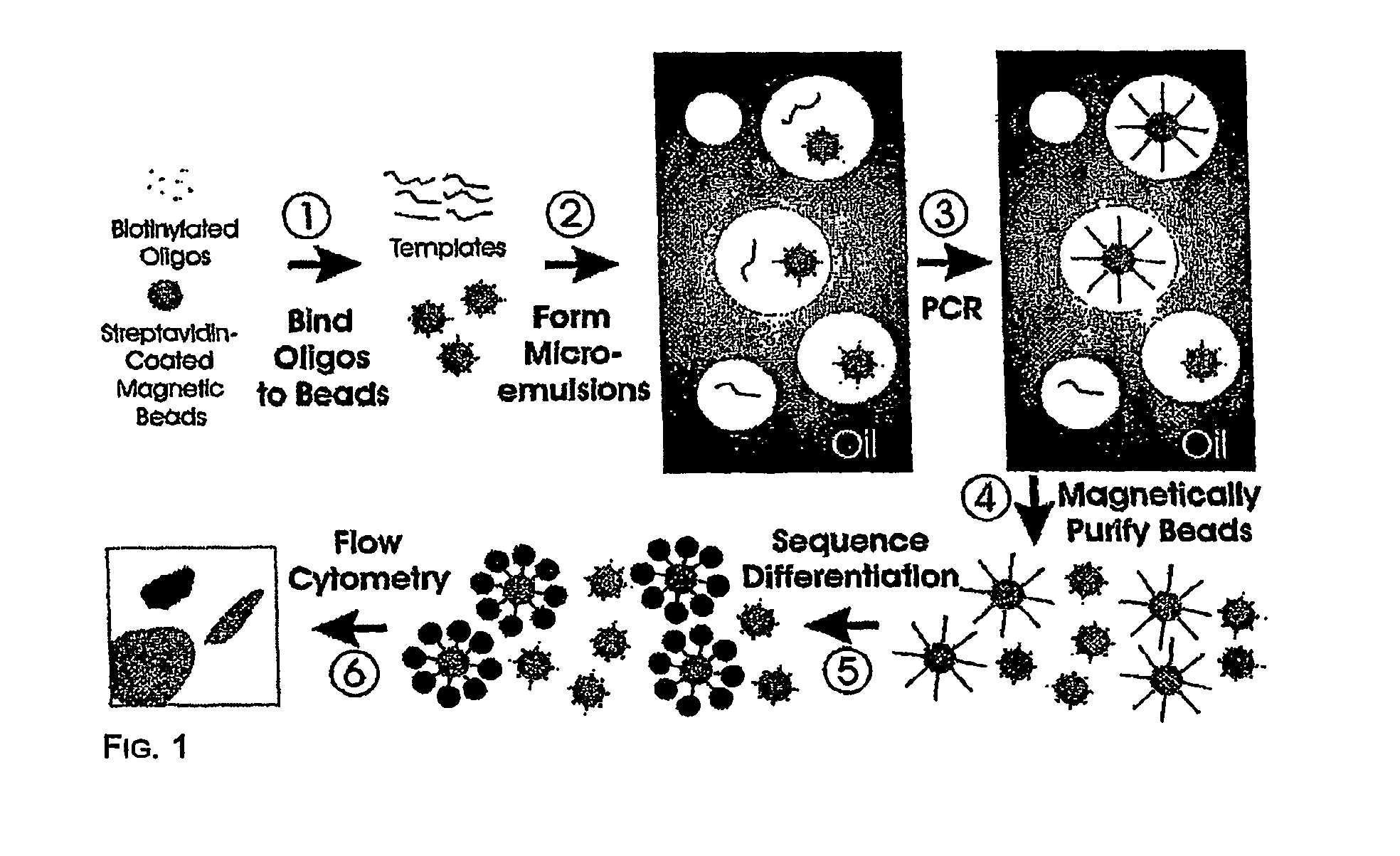
Many areas of biomedical research depend on the analysis of uncommon variations in individual genes or transcripts. Here we describe a method that can quantify such variation at a scale and ease heretofore unattainable. Each DNA molecule in a collection of such molecules is converted into a single particle to which thousands of copies of DNA identical in sequence to the original are bound. This population of beads then corresponds to a one-to-one representation of the starting DNA molecules. Variation within the original population of DNA molecules can then be simply assessed by counting fluorescently-labeled particles via flow cytometry. Millions of individual DNA molecules can be assessed in this fashion with standard laboratory equipment. Moreover, specific variants can be isolated by flow sorting and employed for further experimentation. This approach can be used for the identification and quantification of rare mutations as well as to study variations in gene sequences or transcripts in specific populations or tissues.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Ligation-based detection of genetic variants
InactiveUS20120034603A1Eliminate needElimination contentMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsOligonucleotide
The present invention provides assays systems and methods for detection of genetic variants in a sample, including copy number variation and single nucleotide polymorphisms. The invention preferably employs the technique of tandem ligation, i.e. the ligation of two or more fixed sequence oligonucleotides and one or more bridging oligonucleotides complementary to a region between the fixed sequence oligonucleotides.
Owner:TANDEM DIAGNOSTICS
Methods and uses for molecular tags
ActiveUS20160026758A1Overcome limitationsImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationGenetic analysisComputational biology
Methods and uses for molecular tags are disclosed. Molecular tags may be attached to nucleic acid molecules. The attachment of the nucleic acid molecules prior to PCR amplification and sequencing improves the accuracy of genetic analysis and detection of genetic variations and diversity. Molecular tags may also be used for detection of drug-resistant variants. Methods for using molecular tags for determining and correcting PCR errors and / or sequencing error are also disclosed.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Method and Compositions for Detection and Enumeration of Genetic Variations
InactiveUS20090286687A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecific populationIndividual gene
Many areas of biomedical research depend on the analysis of uncommon variations in individual genes or transcripts. Here we describe a method that can quantify such variation at a scale and ease heretofore unattainable. Each DNA molecule in a collection of such molecules is converted into a single particle to which thousands of copies of DNA identical in sequence to the original are bound. This population of beads then corresponds to a one-to-one representation of the starting DNA molecules. Variation within the original population of DNA molecules can then be simply assessed by counting fluorescently-labeled particles via flow cytometry. Millions of individual DNA molecules can be assessed in this fashion with standard laboratory equipment. Moreover, specific variants can be isolated by flow sorting and employed for further experimentation. This approach can be used for the identification and quantification of rare mutations as well as to study variations in gene sequences or transcripts in specific populations or tissues.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Dual resonance energy transfer nucleic acid probes
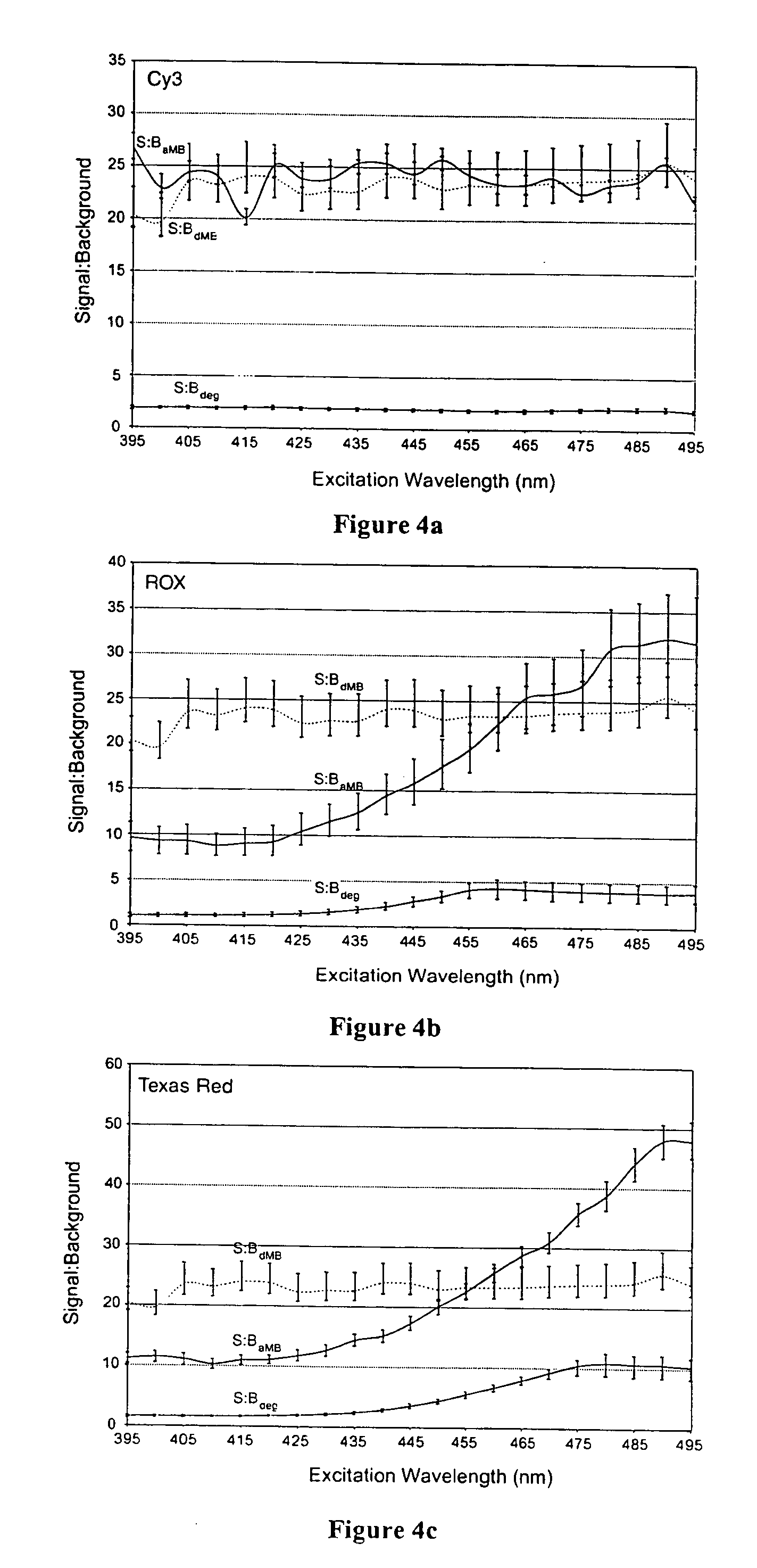
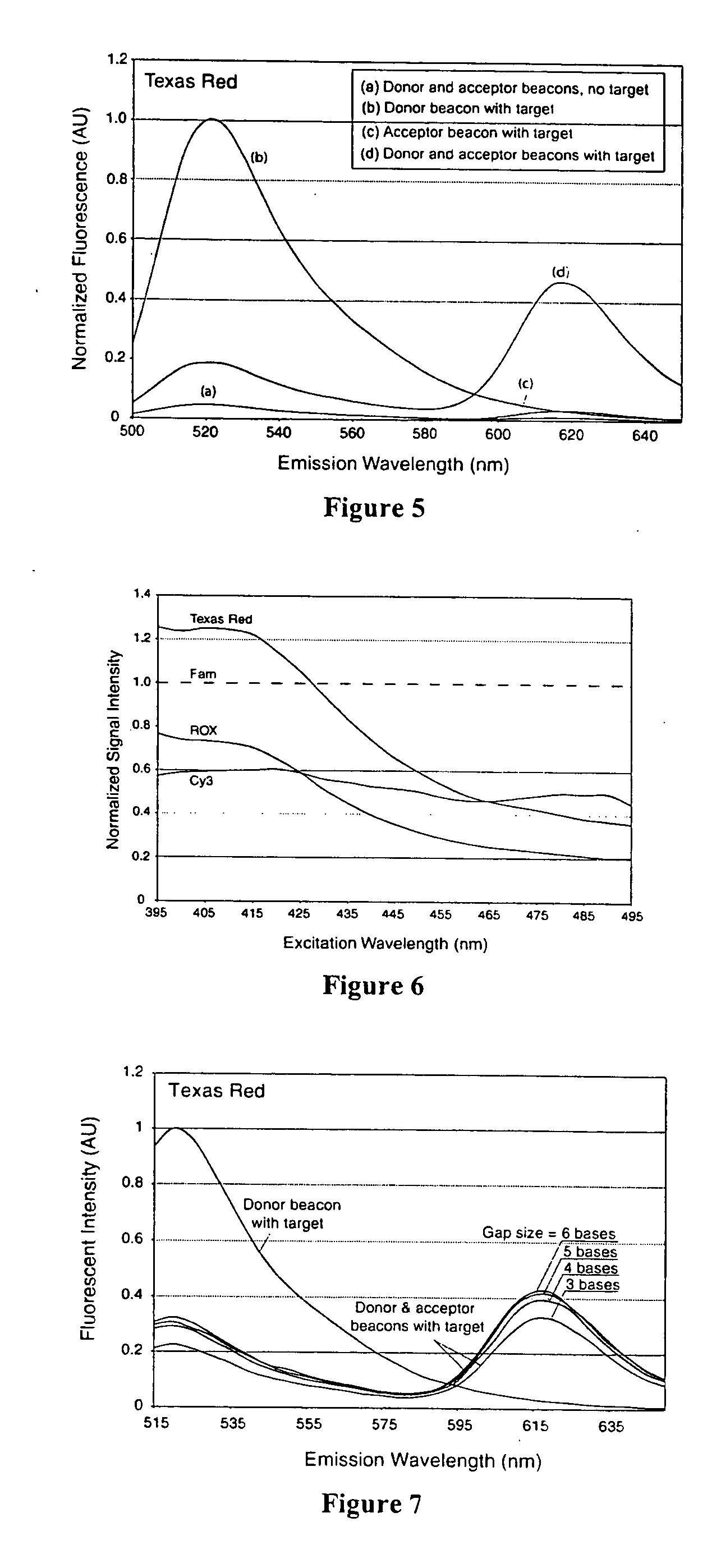
InactiveUS7081336B2Quick checkEasy to useSugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDiseaseCell specific
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Methods and compositions for screening and treatment of disorders of blood glucose regulation
InactiveUS20080280955A1High frequencyIncrease appetiteBiocideSenses disorderInsulin resistanceScreening Result
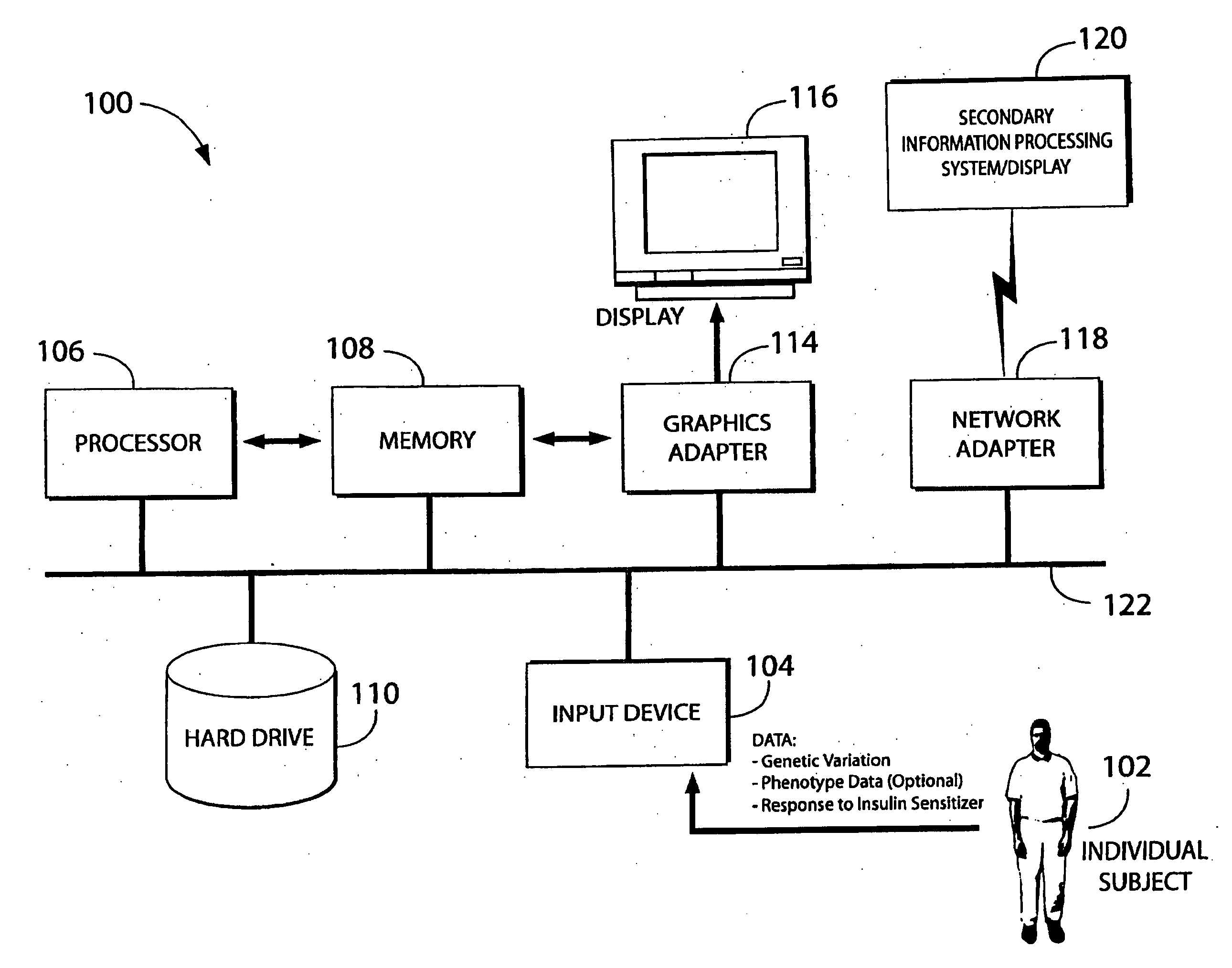
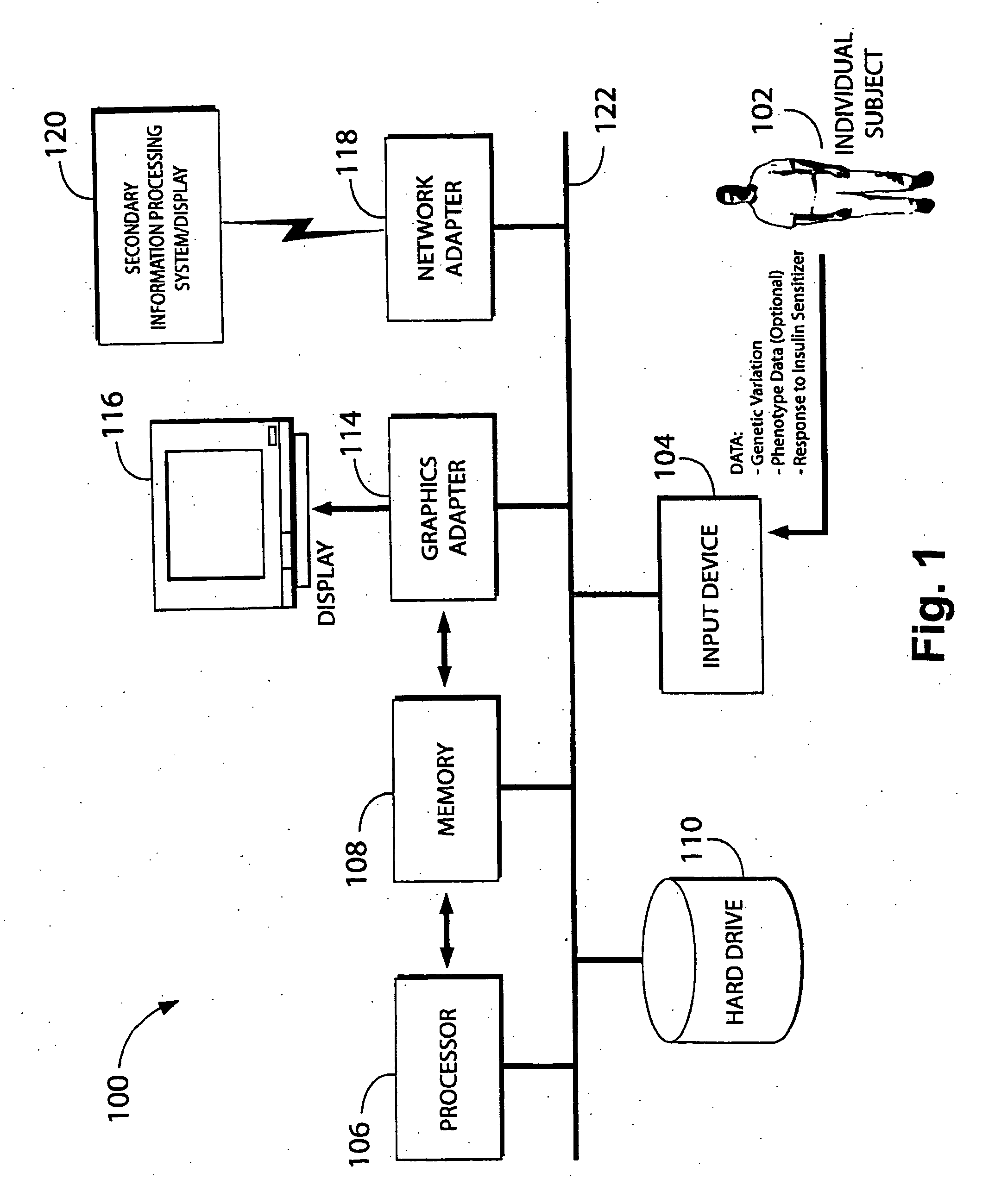
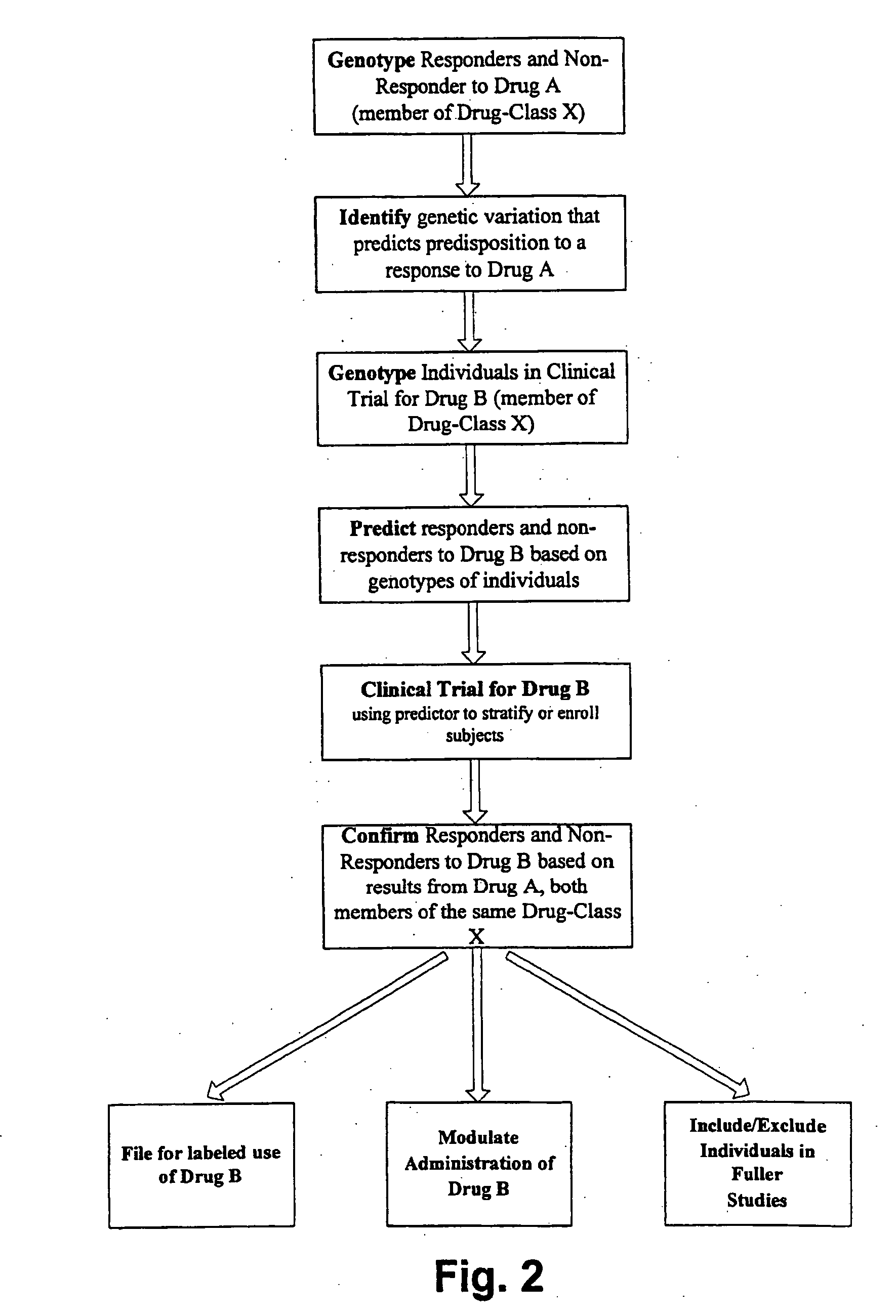
In one aspect, the invention provides a method of screening and, optionally, treatment of an individual suffering from an insulin resistance disorder by screening an individual in need of treatment for an insulin resistance disorder for one or more genetic variations indicating a predisposition to a response to an insulin sensitizer; and, optionally, administering or not administering an insulin sensitizer to the individual based on the results of the screening. The insulin sensitizer for which the individual is screened and the insulin sensitizer that is administered or not administered may be the same or different. In another aspect, the invention provides methods comprising identifying one or more genetic variations, e.g., one or more single nucleotide polymorphisms, that at least partly differentiate between a subset of a plurality of individuals who experience a response when administered an insulin sensitizer, and a subset of said plurality of individuals who do not experience a response when administered the insulin sensitizer. The invention also provides nucleic acids, polypeptides, antibodies, kits, and business methods associated with these screening and association methods.
Owner:PERLEGEN SCIENCES INC
Disease-associated genetic variations and methods for obtaining and using same
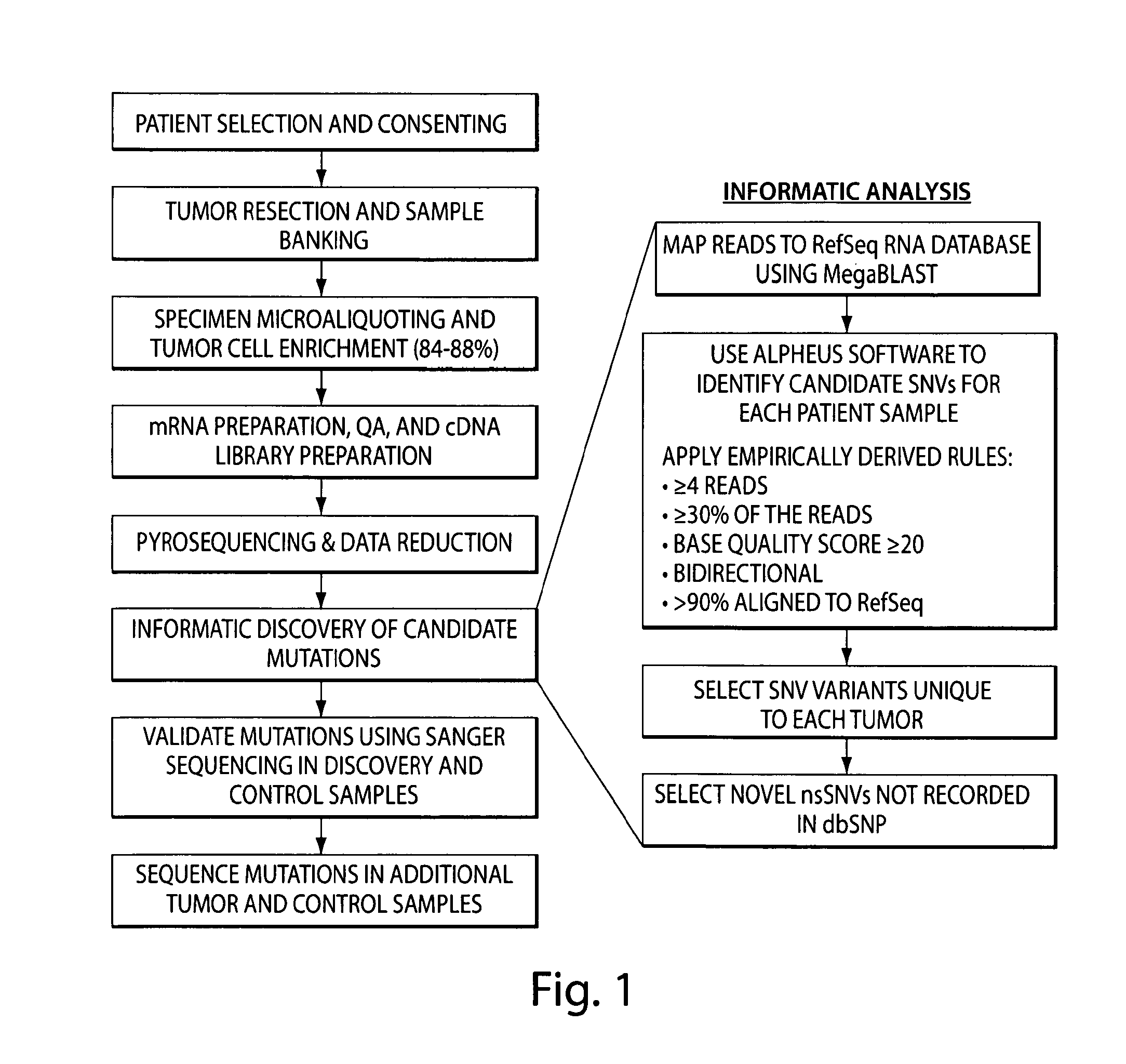
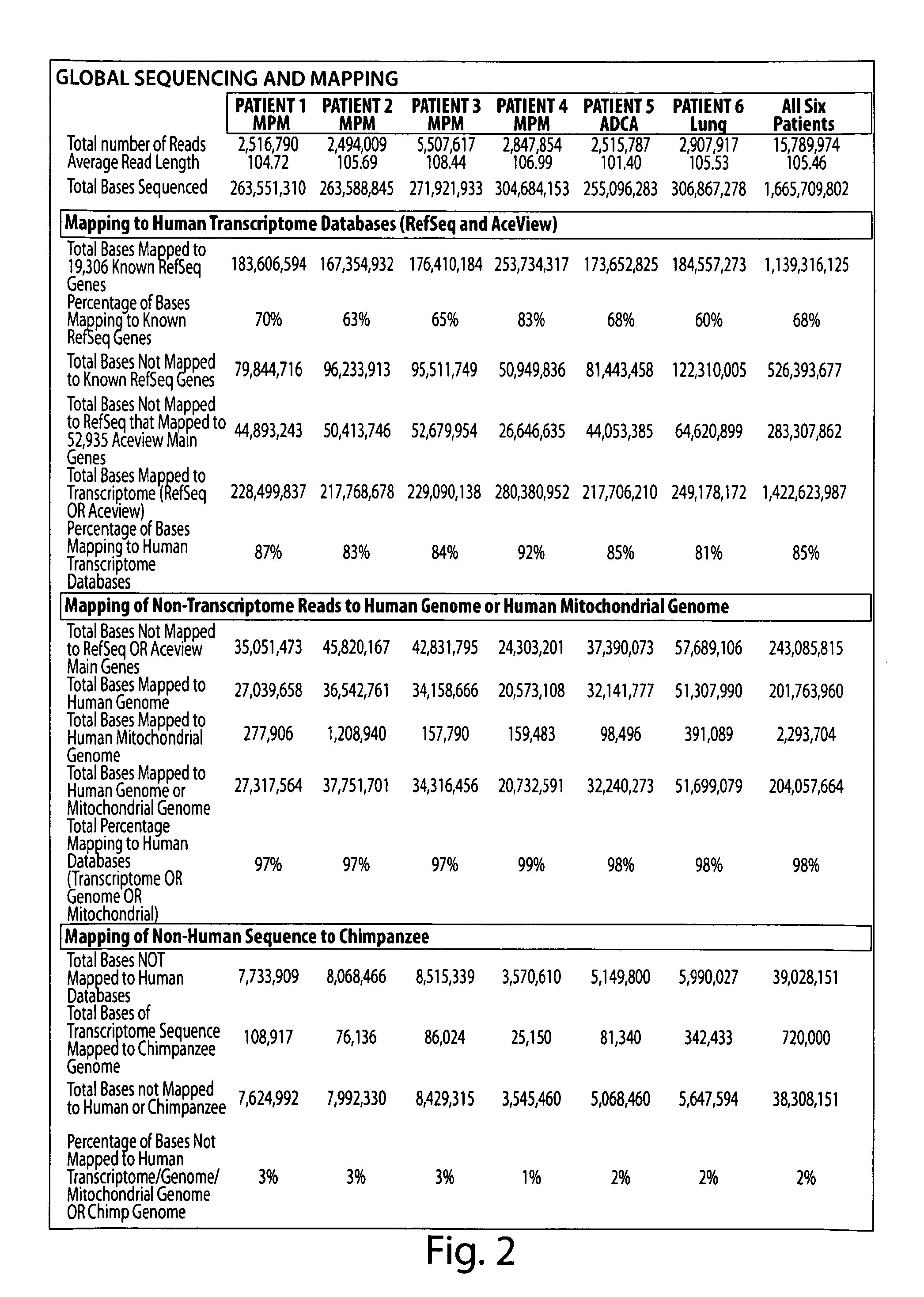
InactiveUS20100196898A1Rapid, unbiased, and accurateTumor rejection antigen precursorsMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease causeVariation (Genetics)
The invention provides a comprehensive, rapid, unbiased, and accurate method for identifying and / or discovering disease-associated genetic variations, e.g., disease-associated variations. The present invention further provides novel disease-associated genetic variations for use as genetic markers of disease, e.g., cancer. The invention further provides methods for assessing an individual's risk for developing a disease, e.g., cancer, by detecting the presence the novel disease-associated genetic variations of the invention.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Disease-associated genetic variations and methods for obtaining and using same
InactiveUS20120214163A1Rapid, unbiased, and accurateFungiTumor rejection antigen precursorsCvd riskVariation (Genetics)
The invention provides a comprehensive, rapid, unbiased, and accurate method for identifying and / or discovering disease-associated genetic variations, e.g., disease-associated variations. The present invention further provides novel disease-associated genetic variations for use as genetic markers of disease, e.g., cancer. The invention further provides methods for assessing an individual's risk for developing a disease, e.g., cancer, by detecting the presence the novel disease-associated genetic variations of the invention.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Method for evaluating correlations between structured and normalized information on genetic variations between humans and their personal clinical patient data from electronic medical patient records
InactiveUS20070294113A1Medical data miningData processing applicationsClinical informationClinical psychology
Various embodiments of the presently described invention provide a method for evaluating correlations between genetic variations and clinical information. The method includes normalizing one or more of genotypic data and clinical data associated with each of a plurality of patients in a population of patients, receiving one or more clinical conditions from a user, selecting a subset of patients from the population based on the clinical conditions, and determining one or more correlations between at least one of the clinical conditions and one or more of the genotypic and clinical data for the patient subset.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for single cell classification and screening and device therefor
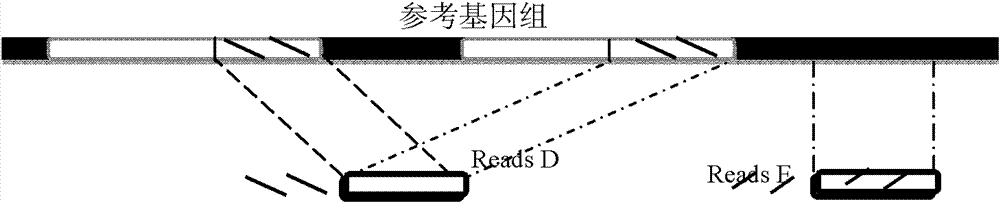
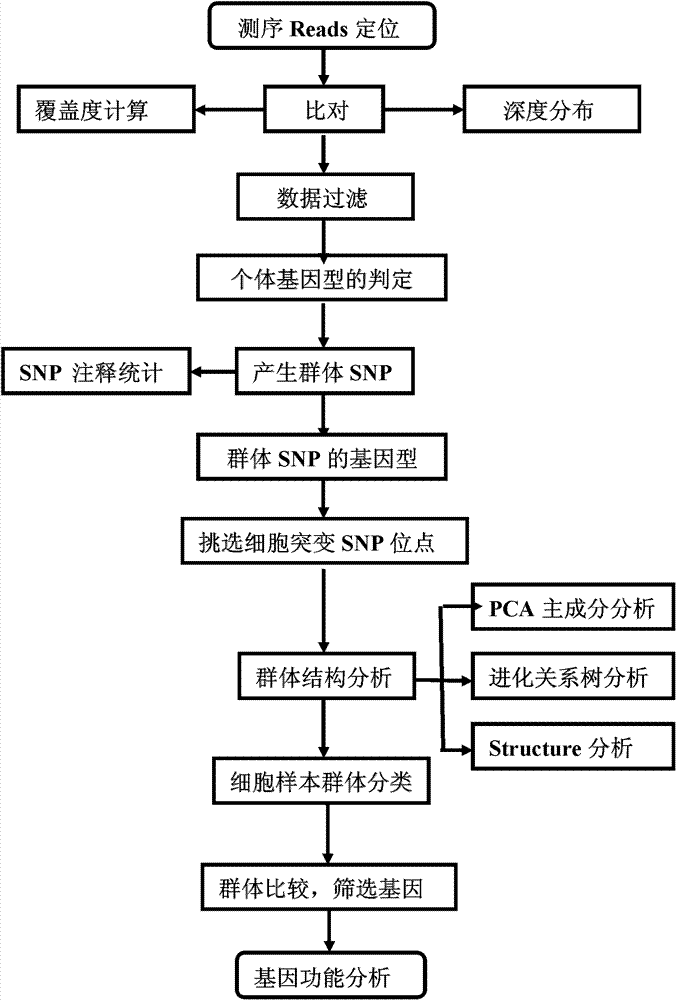
ActiveCN102952854AAvoid marked actionsImprove accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReference genesData set
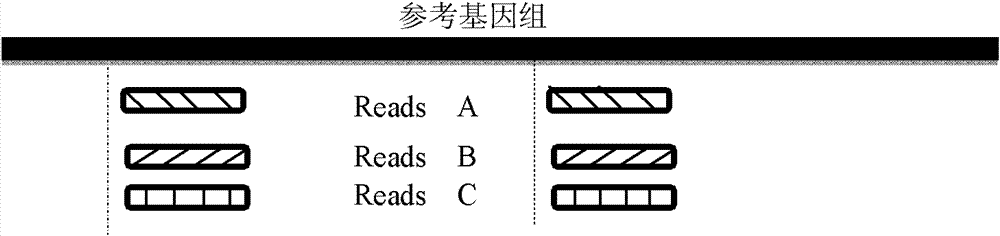
The invention provides a method for single cell classification and screening and a device therefor. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out comparison of reads obtained by sample sequencing and a reference genome, carrying out data filtration of a comparison result, determining a consistent genotype of all single cell samples according to filtered data, saving the consistent genotype of the all single cell samples into a SNP data set, extracting genotype files of loci corresponding to reference genome SNP data set positions from the saved SNP data set, selecting a cell mutation SNP locus, and carrying out cell classification and functional gene screening according to a genotype file of the cell mutation SNP locus. The method and the device avoid cell marking, solve the problem that the traditional single cell classification method can not realize classification of a certain cell subset having no corresponding specific markers, realize complete analysis of genetic variation information of a single cell genome, and greatly improve the accuracy of cell subset classification.
Owner:BGI SHENZHEN CO LTD +1
Systems and Methods for Reconstructing Gene Networks in Segregating Populations
ActiveUS20080294403A1Predictive capabilitySimple technologyAnalogue computers for chemical processesBiostatisticsLiving systemsReconstruction algorithm
The reconstruction of genetic networks in mammalian systems is one of the primary goals in biological research, especially as such reconstructions relate to elucidating not only common, polygenic human disease, but living systems more generally. The present invention provides novel gene network reconstruction algorithms that utilize naturally occurring genetic variations as a source of perturbations to elucidate the networks. The algorithms incorporate relative transcript abundance and genotypic data from segregating populations by employing a generalized scoring function of maximum likelihood commonly used in Bayesian network reconstruction problems. The utility of these novel algorithms can be demonstrated via application to gene expression data from a segregating mouse population. The network derived from such data using the novel network reconstruction algorithm is able to capture causal associations between genes that result in increased predictive power, compared to more classically reconstructed networks derived from the same data.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
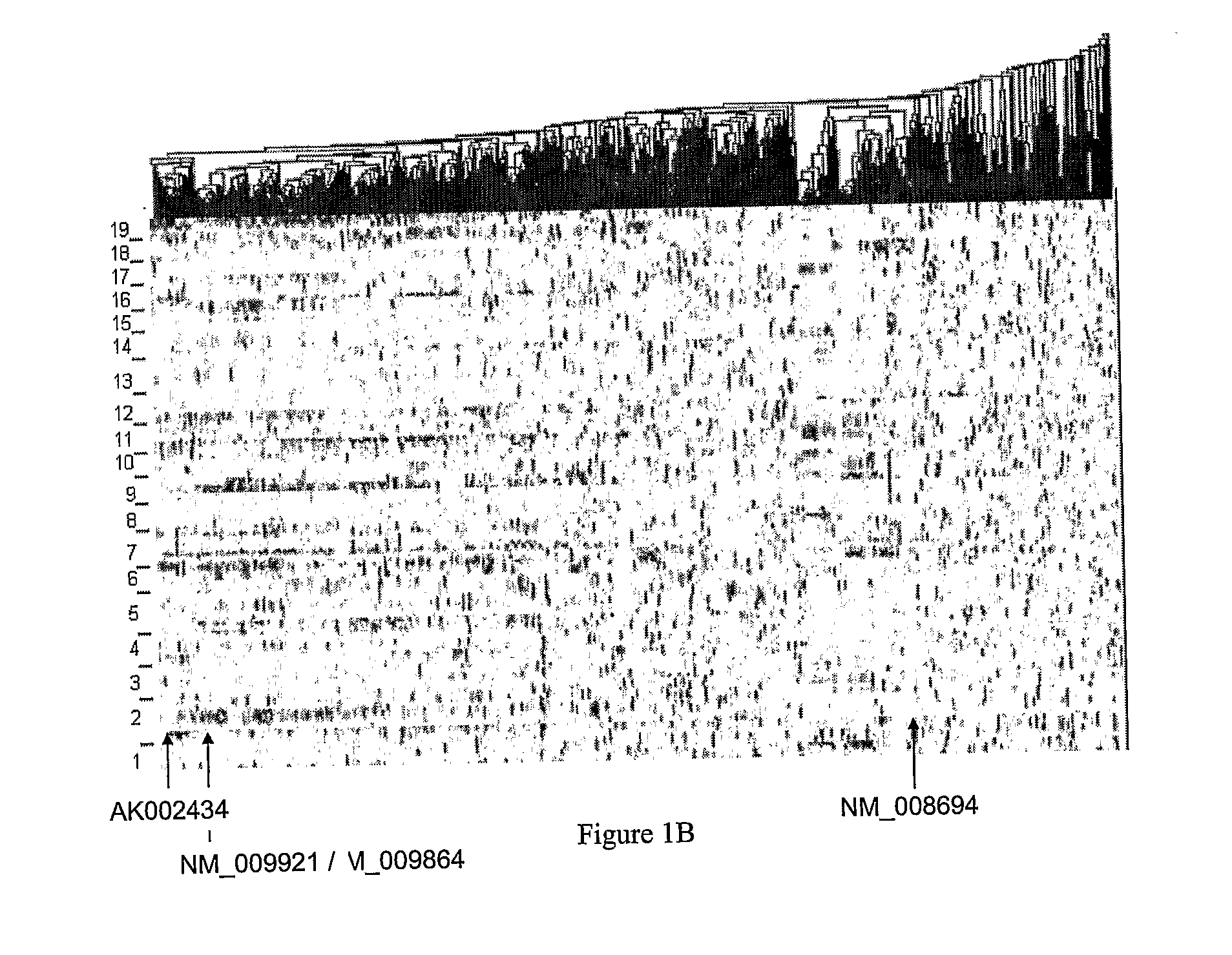
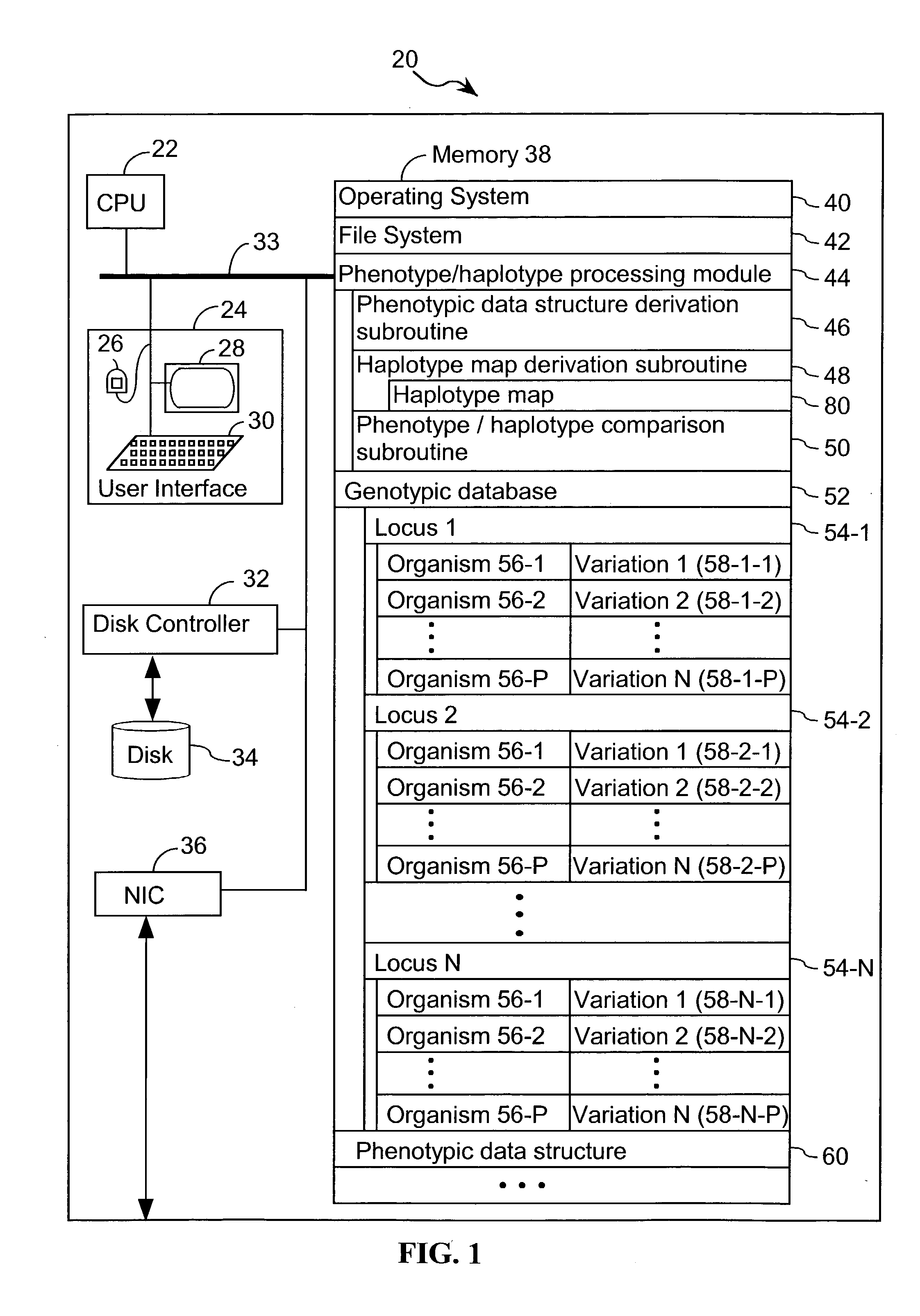
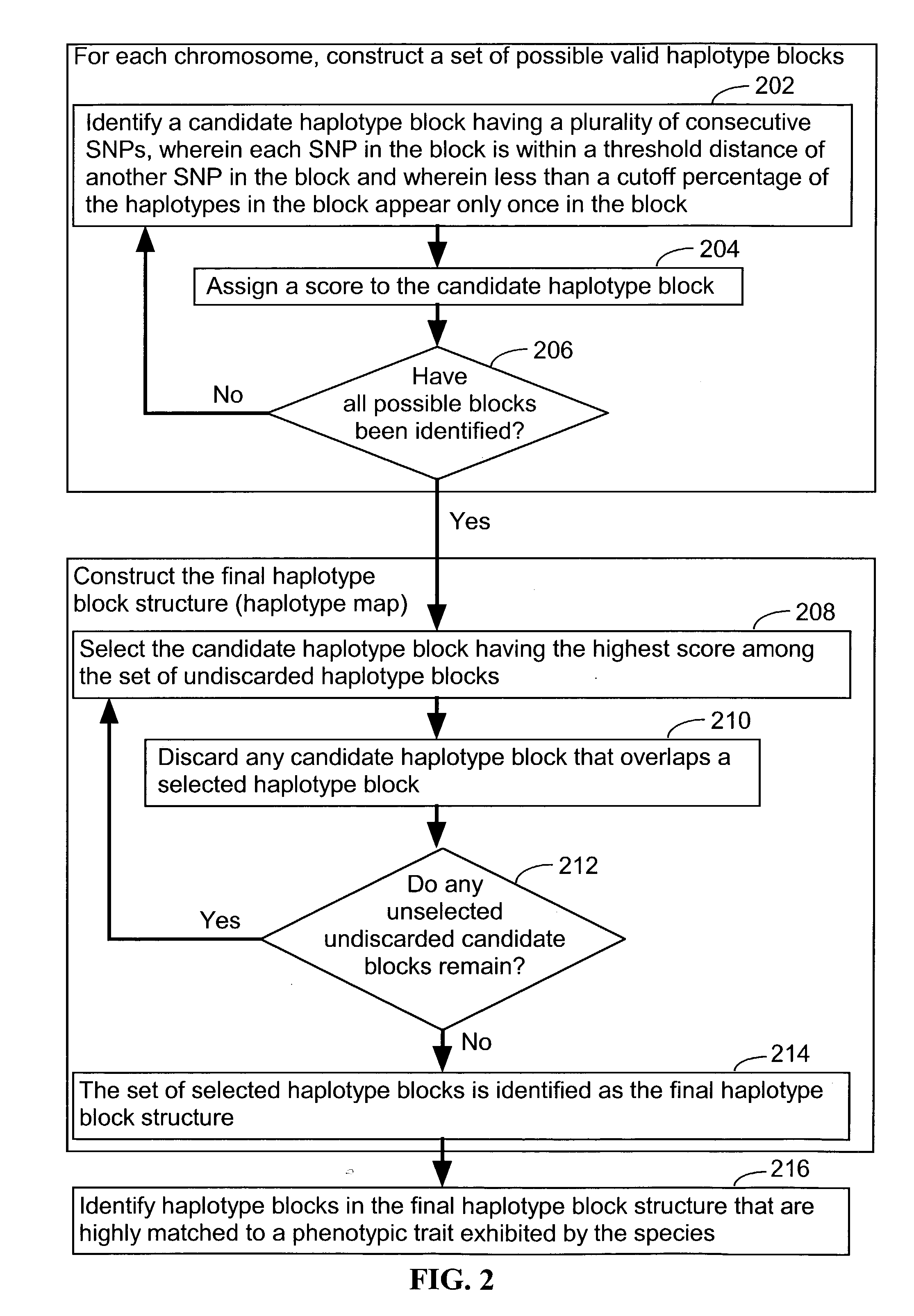
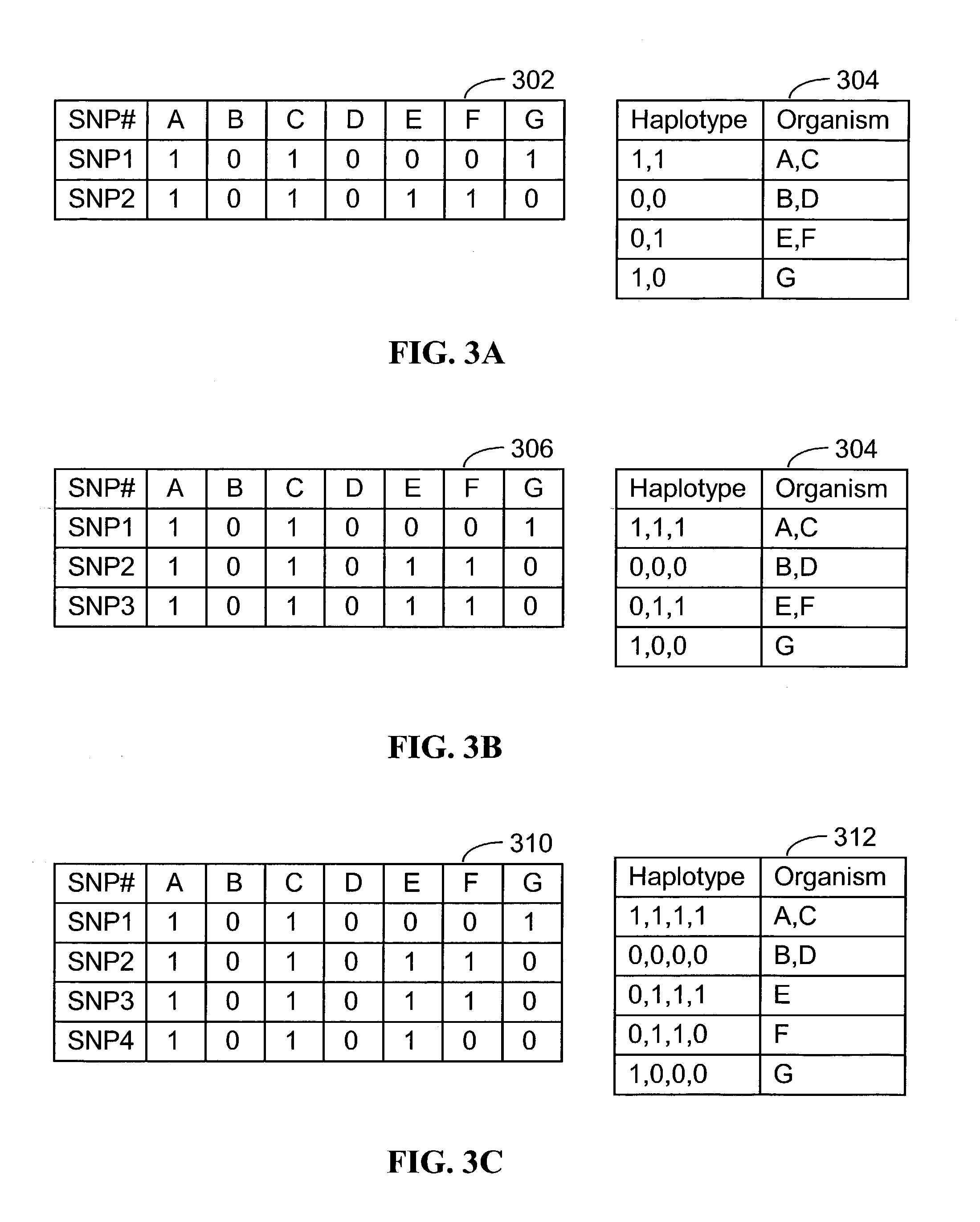
Systems and methods for predicting specific genetic loci that affect phenotypic traits
A database of genetic variations is analyzed to produce a haplotype map of the genome for strains of a single species. A computational method is used to rapidly map complex phenotypes onto the haplotype blocks within the haplotype map. The specific genetic locus regulating three different biologically important phenotypic traits in mice is identified using these systems and methods.
Owner:SANDHILL BIO CORP +1
Industrial control protocol vulnerability mining system based on fuzzy test
InactiveCN105721255AImprove hit rateImprove digging efficiencyData switching networksSession managementTest script
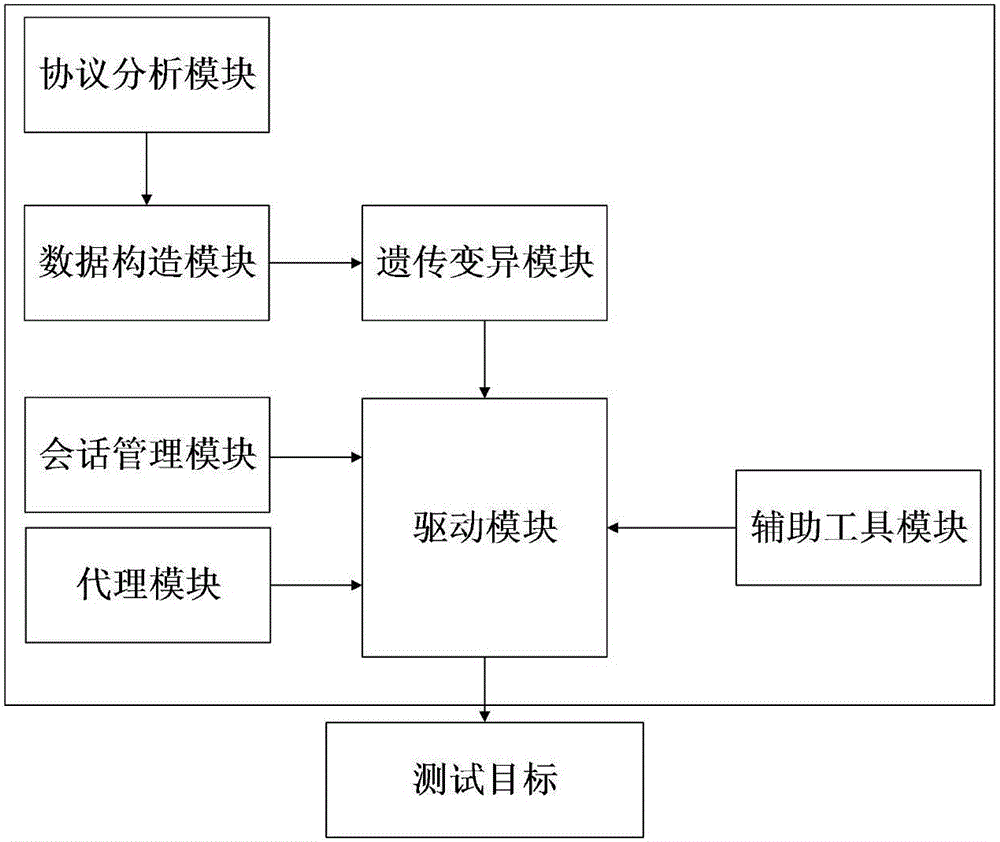
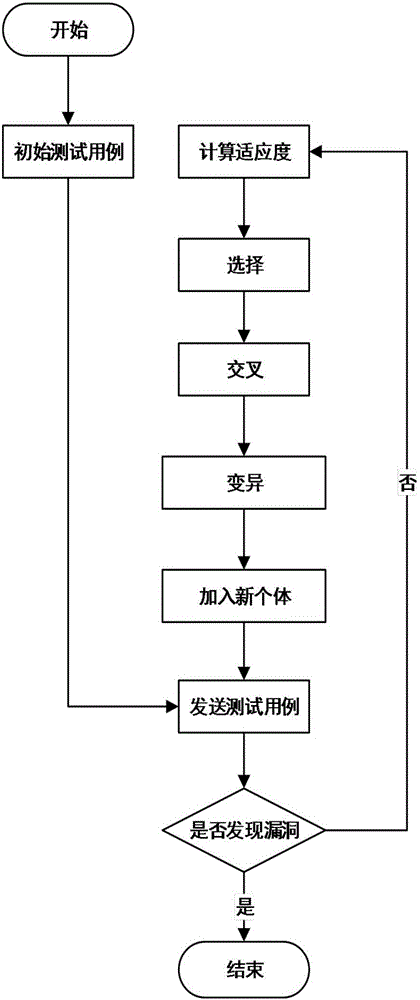
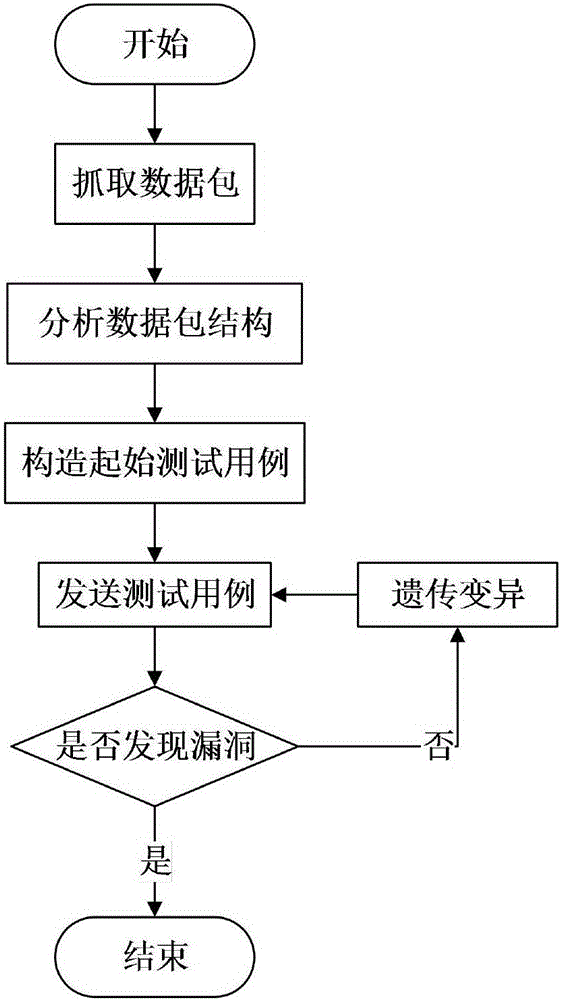
The invention discloses an industrial control protocol vulnerability mining system based on a fuzzy test. The system comprises a protocol analyzing module, a data construction module, a genetic variation module, a session management module, an agent module, a drive module and an auxiliary tool module; the genetic variation module, the session management module and the agent module are connected with the drive module; the protocol analyzing module is connected with the data construction module and then is connected with the genetic variation module; and the drive module is used for connecting a test target. According to the system, the conditions of the tested target can be learned and analyzed; related data such as test scripts and a test case are specifically constructed according to the analyzed information; the hit rate of the test case is increased through analyzing the tested target; in a test process, the generation method or variation direction of the test case is adjusted specifically according to the information such as the current state of the tested target and the feedback of the test case; the vulnerability mining efficiency is improved through an efficient adjusting algorithm; and moreover, the system adaptation is increased.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Genetic diagnosis using multiple sequence variant analysis
The present invention is in the field of nucleic acid-based genetic analysis. More particularly, it discloses novel insights into the overall structure of genetic variation in all living species. The structure can be revealed with the use of any data set of genetic variants from a particular locus. The invention is useful to define the subset of variations that are most suited as genetic markers to search for correlations with certain phenotypic traits. Additionally, the insights are useful for the development of algorithms and computer programs that convert genotype data into the constituent haplotypes that are laborious and costly to derive in an experimental way. The invention is useful in areas such as (i) genome-wide association studies, (ii) clinical in vitro diagnosis, (iii) plant and animal breeding, (iv) the identification of micro-organisms.
Owner:METHEXIS GENOMICS
Associations using genotypes and phenotypes
The present invention discloses methods for combining data on genetic variations and phenotypes of individuals to predict a phenotype-of-interest. The present invention also discloses kits that can be used to determine if an individual has or does not have a phenotype-of-interest. The kit can include at least one diagnostic tool and written instructions.
Owner:NORVIEL VERNON A
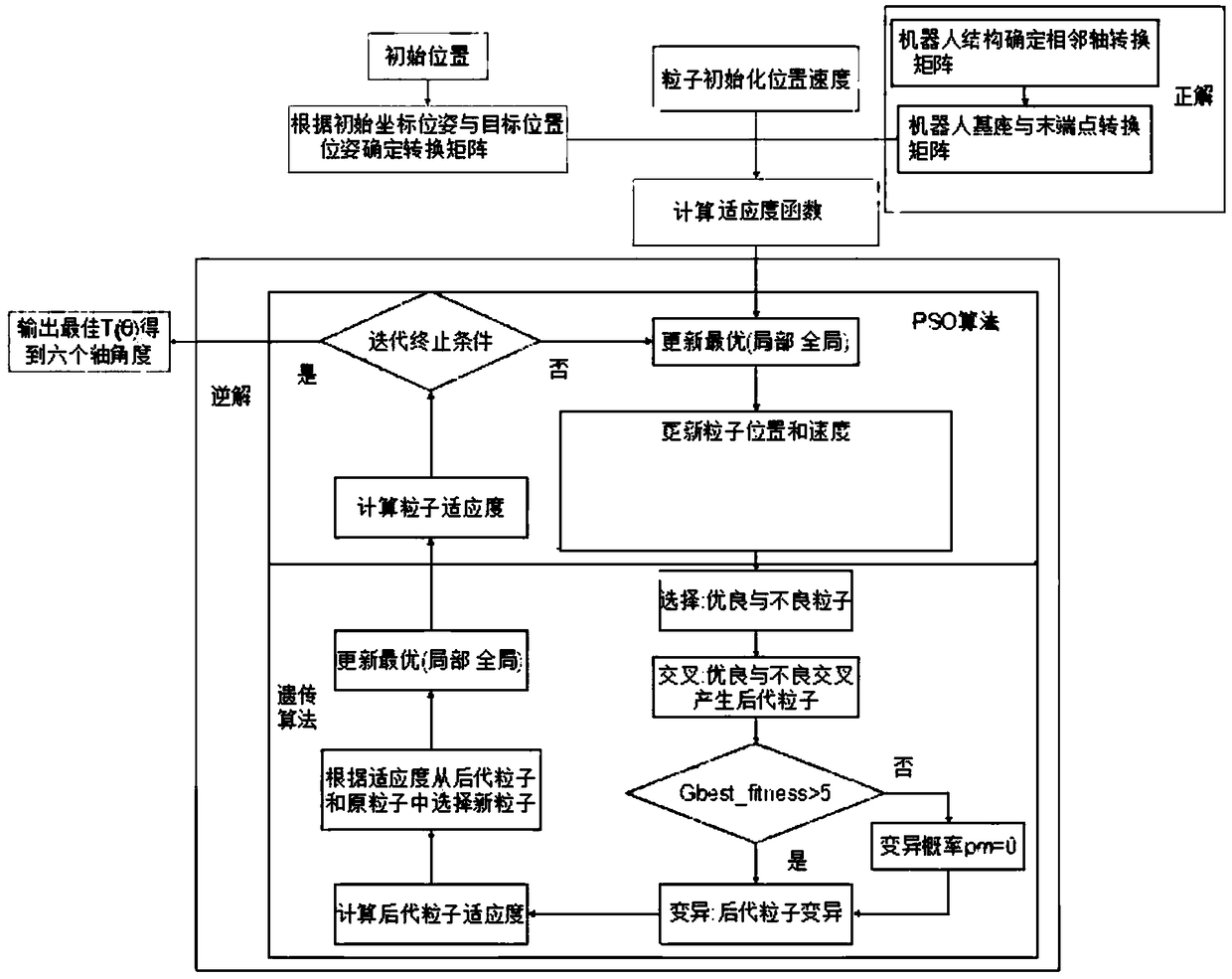
Method for solving robot inverse kinematics based on particle swarm optimization algorithm
ActiveCN108932216ASolve the shortcomings of easy to fall into local optimumReduce the number of iterationsArtificial lifeComplex mathematical operationsLocal optimumInverse kinematics
The invention relates to a method for solving robot inverse kinematics based on a particle swarm optimization algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: 1) establishing a kinematic model according to joint parameters of a robot, obtaining a kinematic positive solution formula, setting positions of target points and an attitude matrix, determining a fitness function; 2) initializing a particle population, calculating an individual fitness value of an initial population, obtaining an individual optimal value and a global optimal value; 3) updating the position and speed of the particlepopulation using dynamic inertia weight which changes with the number of iterations, calculating a new fitness value, and determining whether to update; 4) performing genetic variation operation on the particle population, calculating the fitness value; 5) determining whether a termination condition is satisfied according to the fitness value and the number of iterations. Compared with the priorart, the method solves a shortcoming that a traditional PSO algorithm easily falls into local optimal values, and can enhance local search capability and improve convergence speed and precision by reducing the number of iterations.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF ENG SCI
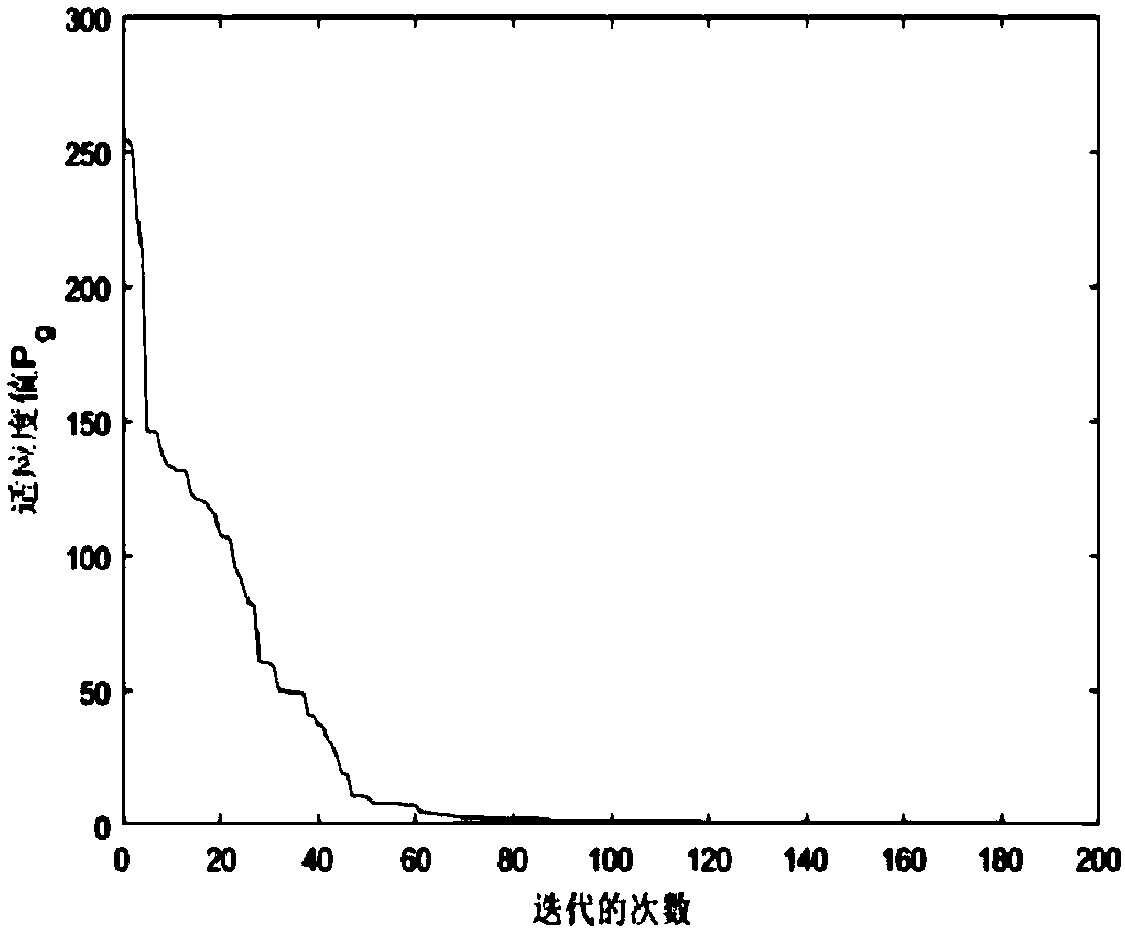
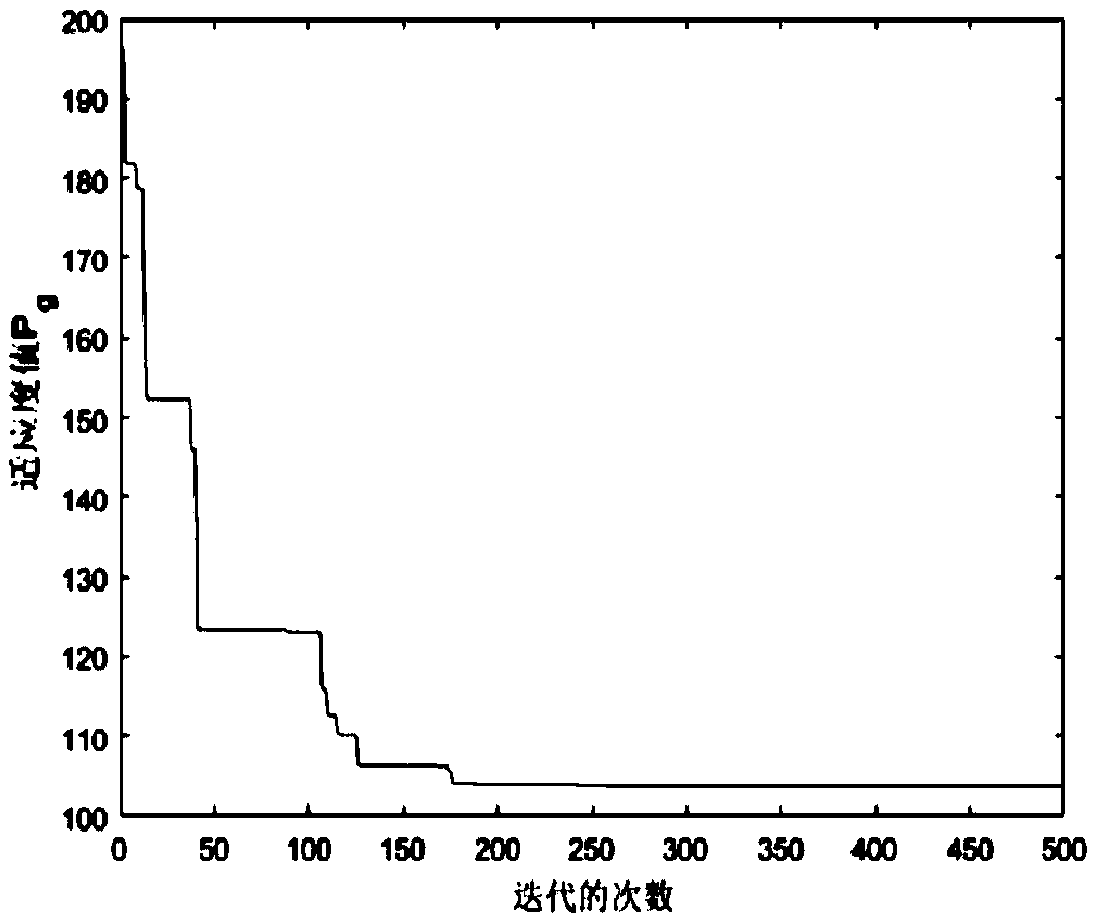
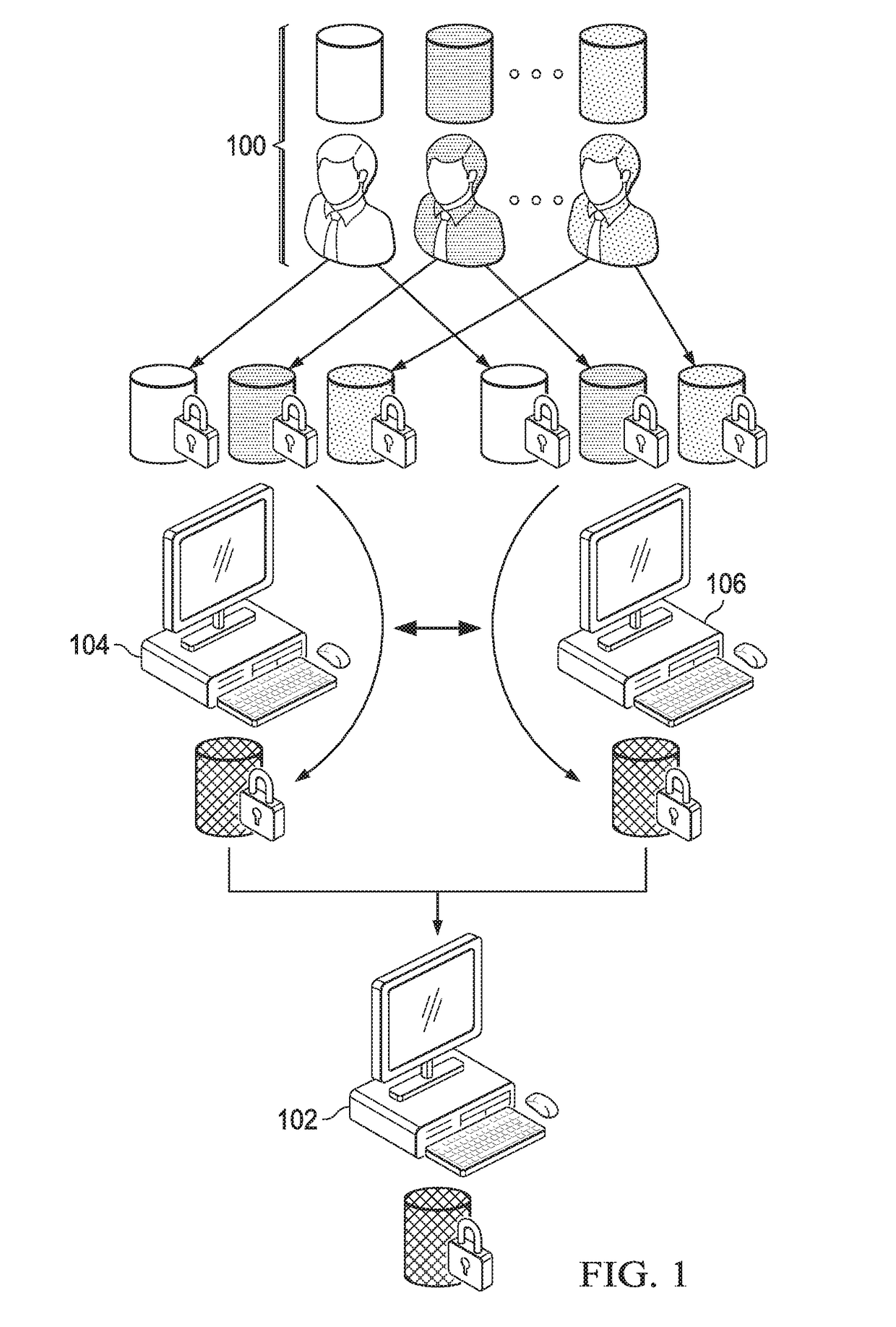
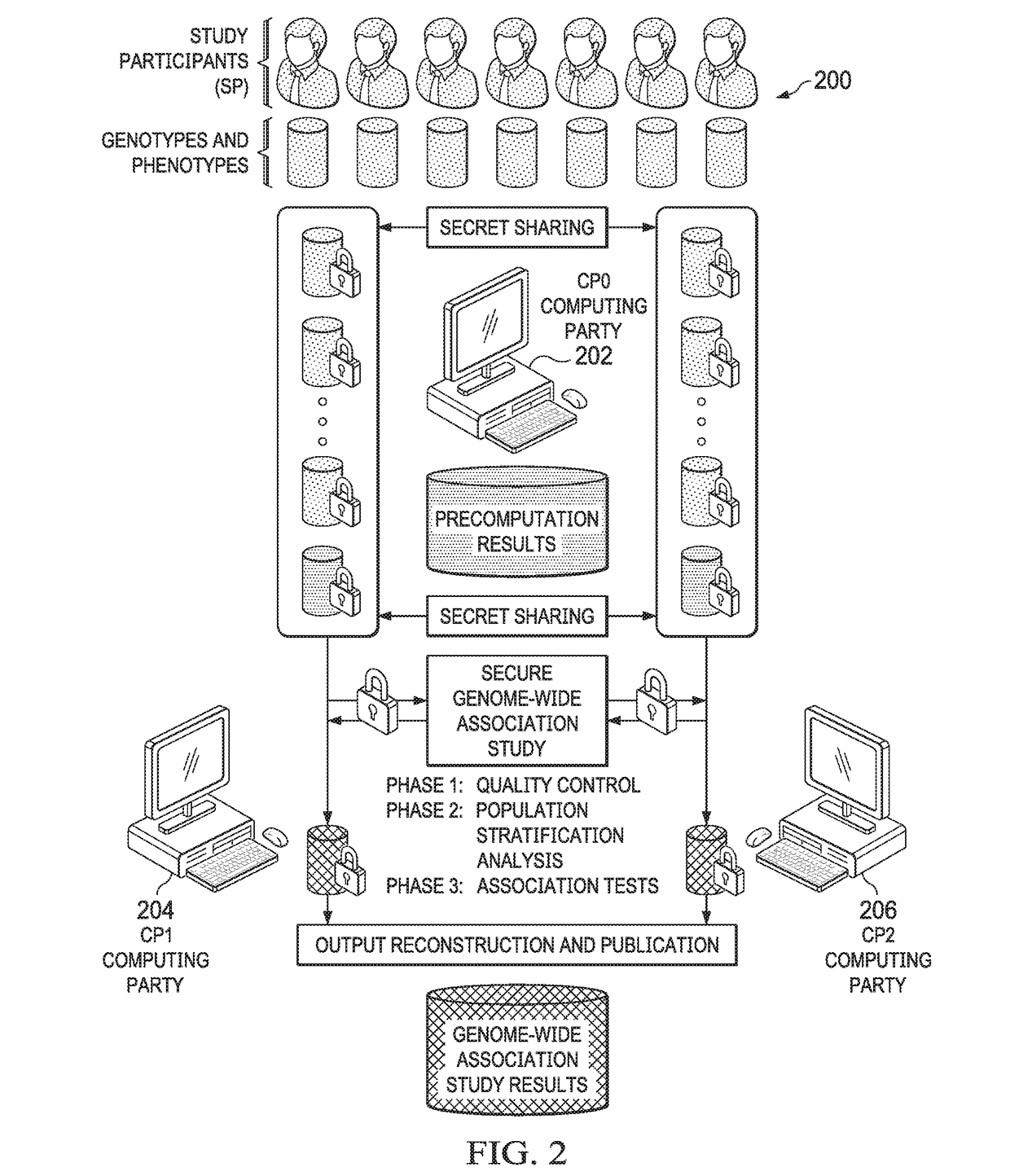
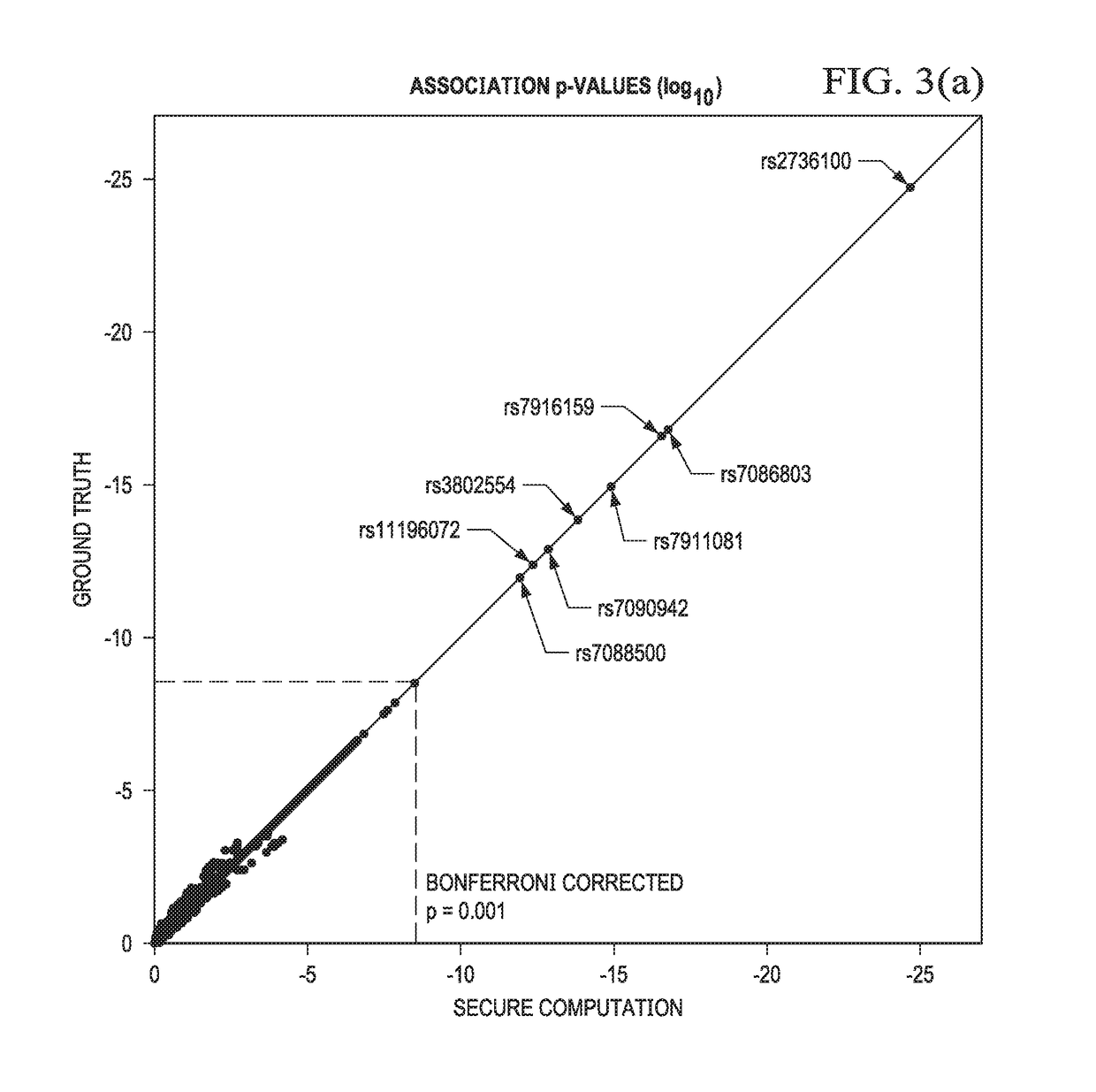
Secure genome crowdsourcing for large-scale association studies
ActiveUS20180373834A1Secure crowdsourcingPrivacy protectionProteomicsGenomicsData setIndividual study
Computationally-efficient techniques facilitate secure crowdsourcing of genomic and phenotypic data, e.g., for large-scale association studies. In one embodiment, a method begins by receiving, via a secret sharing protocol, genomic and phenotypic data of individual study participants. Another data set, comprising results of pre-computation over random number data, e.g., mutually independent and uniformly-distributed random numbers and results of calculations over those random numbers, is also received via secret sharing. A secure computation then is executed against the secretly-shared genomic and phenotypic data, using the secretly-shared results of the pre-computation over random number data, to generate a set of genome-wide association study (GWAS) statistics. For increased computational efficiency, at least a part of the computation is executed over dimensionality-reduced genomic data. The resulting GWAS statistics are then used to identify genetic variants that are statistically-correlated with a phenotype of interest.
Owner:CHO HYUNGHOON +2
Molecular marker related with wheat thousand grain weight and applications thereof
InactiveCN104342484AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceGrain weight
The invention discloses a molecular marker related with wheat thousand grain weight and applications thereof. Through the heritable variation analysis on 6-SFT gene of a wheat natural variation group, people find that the 6-SFT gene has two SNPs corresponding to the 1371st and 2450th positions in the tail ends from 1 to 5' in the sequence one. Three haplotypes exist in the two SNP, namely haplotype A (G,G) haplotype B (G,A), and haplotype C (A,G). Through correlation analysis, the wheat thousand grain weights of the three homozygous haplotypes are accord with a relationship as follows: the wheat thousand grain weight of homozygous haplotype C > the wheat thousand grain weight of homozygous haplotype B > the wheat thousand grain weight of homozygous haplotype C. The invention also provided a CAPS label for detecting the two SNPs. Experiments have proved that the wheat with a higher thousand grain weight can be found through detecting the two SNPs. A novel method is provided for the wheat breeding assisted by a molecular labeling technology, and the provided molecular maker has an important meaning for the breeding and researches of wheat species with a high yield.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for detecting embryo chromosome abnormalities by using blastula-stage embryo cells
InactiveCN104711362AAvoid harmA large amountMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh cellCell separation
The invention discloses a method for performing genome amplification by using embryo blastula-stage cells, performing chromosome detection on the preimplantational embryo by combining a high-flux sequencing technique and screening out the chromosome normal embryo. The method can comprehensively and completely analyze the genetic variation information of the embryo genome, thereby instructing the preimplantational embryo selection, reducing the hereditary diseases and enhancing the success rate of test tube babies. The method comprises the following steps: blastula-stage trophocyte separation; genome amplification; DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) segmentation; and Proton library establishment, mounting sequencing and sequencing data analysis. By using the blastula-stage embryo to perform trophocyte separation detection, the method avoids the injuries of cleavage-stage cell separation to the embryo, obtains higher cell quantity than the cleavage stage, and enhances the success rate and amplification effect of genome amplification. After the blastula-stage embryos are subjected to the natural elimination process, the high-quality blastula-stage embryo is selected for detection, thereby saving the cost.
Owner:SUZHOU BASECARE MEDICAL DEVICE CO LTD
Genome-Wide Association Study Identifying Determinants Of Facial Characteristics For Facial Image Generation
InactiveUS20130039548A1Promote generationBiometric pattern for forensic purposeImage enhancementA-DNAOrganism
The present invention relates to a method for the generation of a facial composite from the genetic profile of a DNA-donor. The method comprises the steps of a) subjecting a biological sample to genotyping thereby generating a profile of genetic markers associated to numerical facial descriptors (NFD) for said sample, b) reverse engineer a NFD from the profile of the associated genetic variants and constructing a facial composite from the reverse engineered numerical facial descriptors (NFDs). The present invention also relates to a method for identifying genetic markers and / or combinations of genetic markers that are predictive of the facial characteristics, (predictive facial markers) of a person, said method comprising the steps of: a) capturing images of a group of individual faces; b) performing image analysis on facial images of said group of individual faces thereby extracting phenotypical descriptors of the faces; c) obtaining data on genetic variation from said group of individual and d) performing a genome-wide association study (GWAS) to identify said predictive facial markers.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Method of Simulation Reproductive Creatures
The present invention is an interactive simulation of animate creatures. This program is a computerized method of simulating reproductive virtual pets that display complex patterns of genetic variation, but which will not consume excessive amounts of system resources. This program is comprised of computerized simulations, manufacturers, compositions of matter and processes including reproducing objects, such as pets.
Owner:SARGENT CANDACE +1
Dual resonance energy transfer nucleic acid probes
InactiveUS20060127940A1Rapid and specific and sensitive hybridization detectionEasy to useSugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDiseaseCell specific
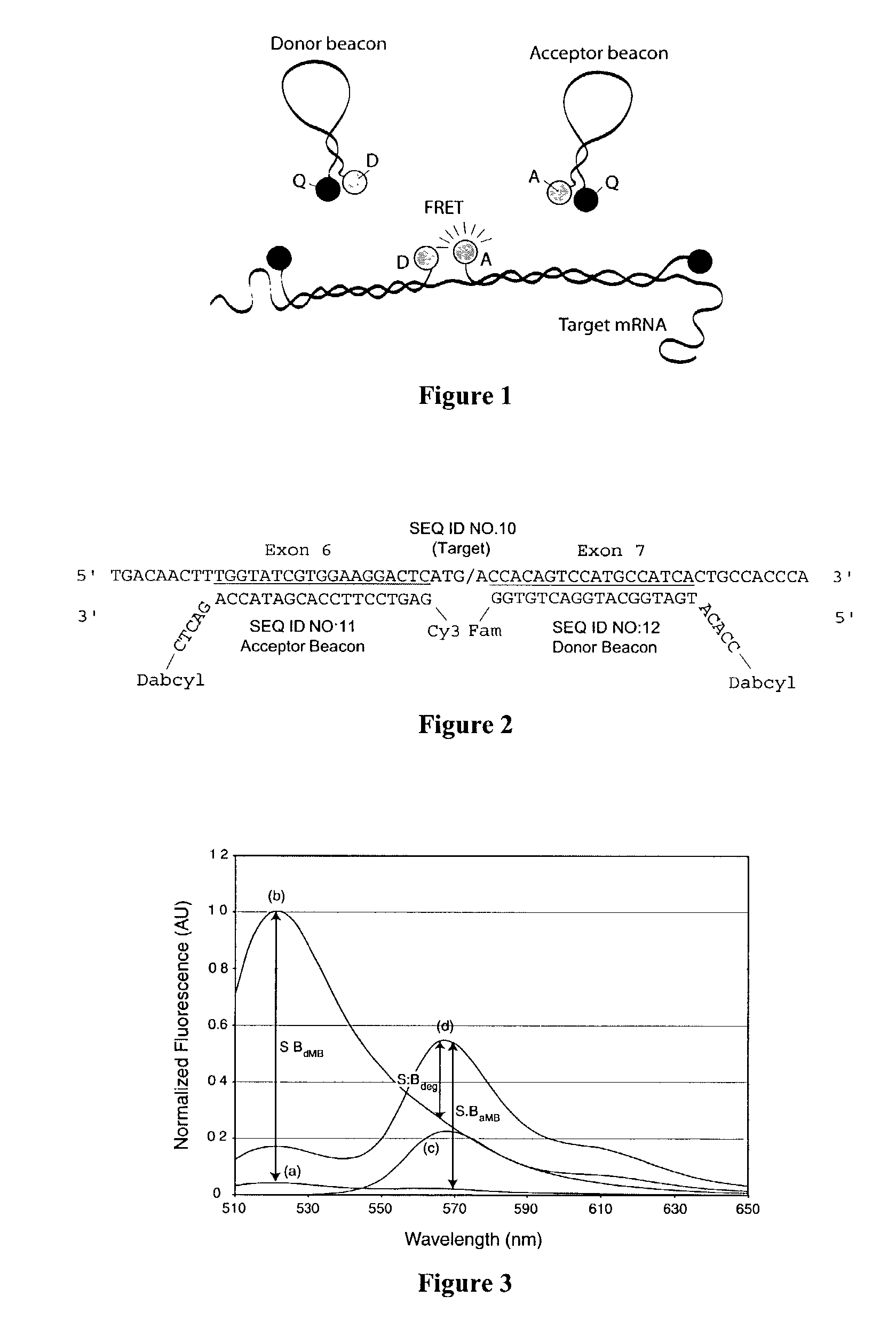
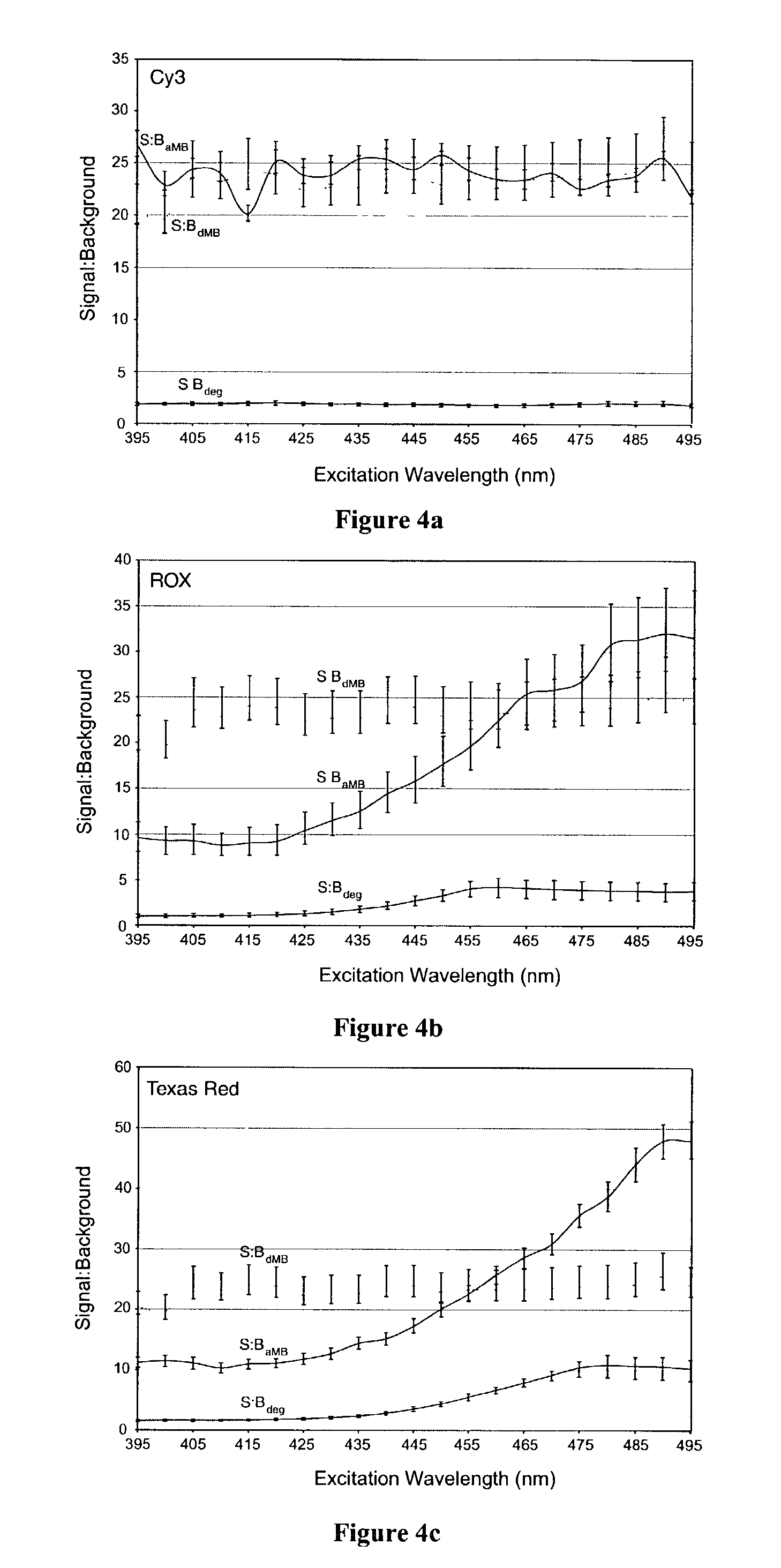
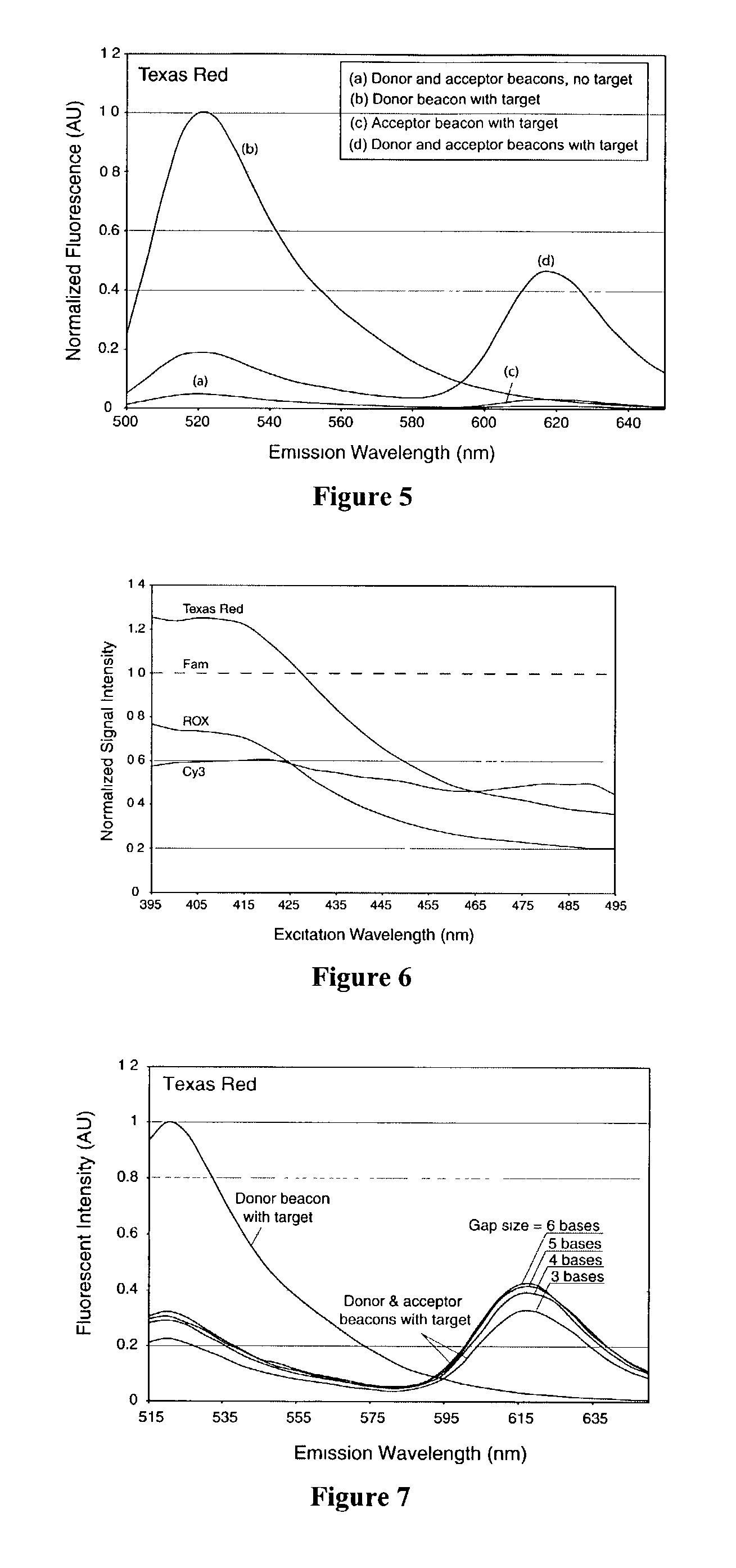
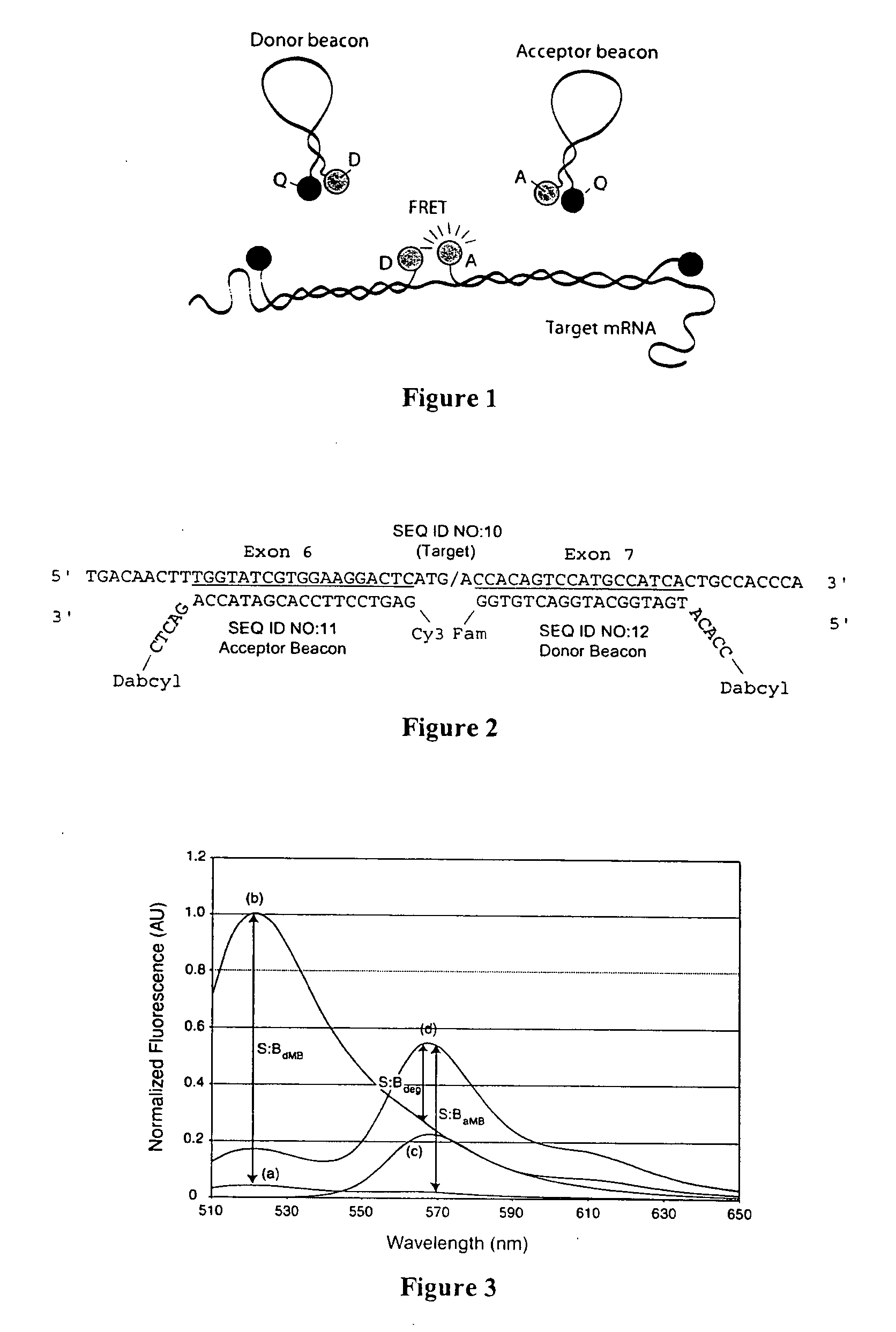
Dual nucleic acid probes with resonance energy transfer moieties are provided. In particular, fluorescent or luminescent resonance energy transfer moieties are provided on hairpin stem-loop molecular beacon probes that hybridize sufficiently near each other on a subject nucleic acid, e.g. mRNA, to generate an observable interaction. The invention also provides lanthanide chelate luminescent resonance energy transfer moieties on linear and stem-loop probes that hybridize sufficiently near each other on a subject nucleic acid to generate an observable interaction. The invention thereby provides detectable signals for rapid, specific and sensitive hybridization determination in vivo. The probes are used in methods of detection of nucleic acid target hybridization for the identification and quantification of tissue and cell-specific gene expression levels, including response to external stimuli, such as drug candidates, and genetic variations associated with disease, such as cancer.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
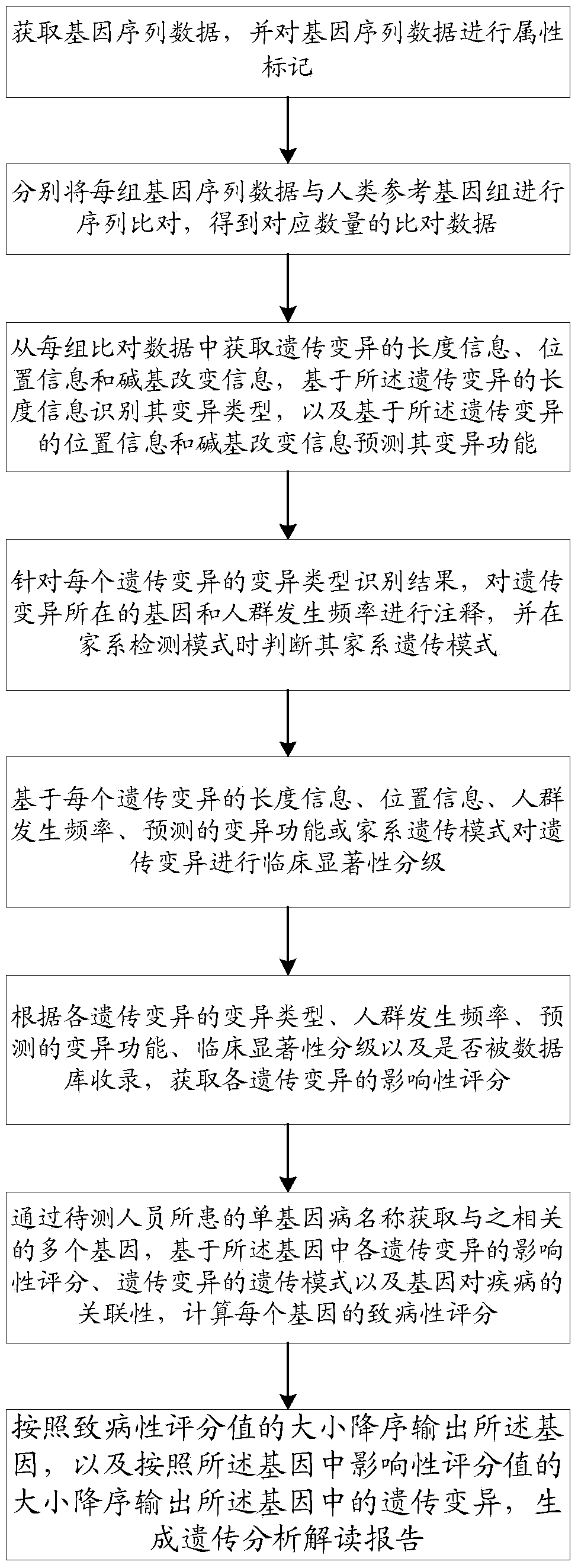
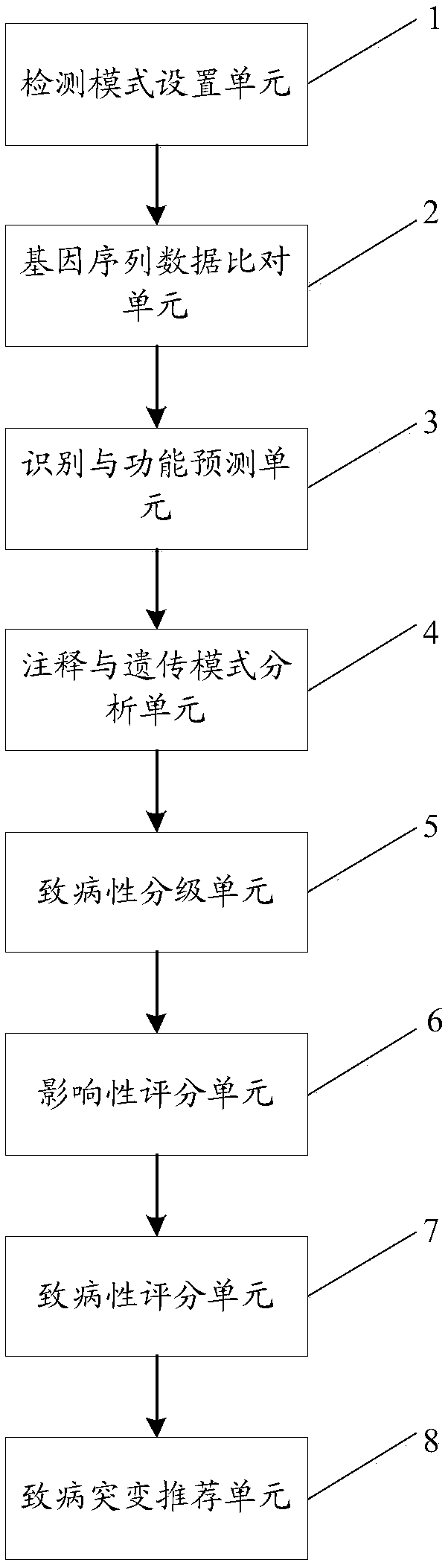
A method and system for intelligently interpreting and reporting genetic variation of monogenic diseases
ActiveCN109086571ARealize full automationReduce workloadSpecial data processing applicationsCrowdsSequence alignment
The invention discloses a method and a system for intelligently interpreting and reporting the genetic variation of a single gene disease, which can automatically analyze the genetic variation resultbased on the original sequence data of a gene of a patient, and provide a professional genetic variation analysis report, thereby improving the diagnosis and treatment efficiency of the genetic variation. The method comprises the following steps of: gene sequence data is acquired and attribute marking is performed on the gene sequence data; sequence alignment of each set of gene sequence data withhuman reference genome is performed to obtain corresponding amount of alignment data; based on the length information of genetic variation, the variation type is identified, and the variation function is predicted based on the position information and base change information of genetic variation. According to the identification results of each genetic variation type, the gene and population frequencies of genetic variation were annotated, and the family genetic pattern was judged when the family detection mode was used. The system comprises the method proposed in the technical proposal.
Owner:国家卫生健康委科学技术研究所
In vitro conservation method of churysanthemum by reducing macroelements in the medium
InactiveCN101006774ANormal growthKeep material stableDead plant preservationHorticulture methodsAxillary budNormal growth
The invention relates to a method for conserving chrysanthemum in vitro through reducing major element in the medium, which is special for the in vitro conservation of the chrysanthemum germplasm resource. The invention comprises the steps of: taking the suckers of the chrysanthemum as the explants, and axillary buds for subculture, and conserving on the 1 / 2MS, 1 / 2MS (1 / 2NH4+) or 1 / 4MS medium containing 6-BA0.3mg / L and NAA0.1mg / L. The survival rate for a 12-month conservation is 100%, 8 months longer than that of conservation on the normal MS medium. After the conservation material recovers to normal growth, the descendant is proved to have no genetic variance through the detection of POD, EST and ISSR. The invention uses the method of conserving chrysanthemum test-tube plantlet through reducing major element in the medium and identifies the genetic stability of the descendant, which proves that the plants grow normally after one-year conservation and the descendant has no genetic variation.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
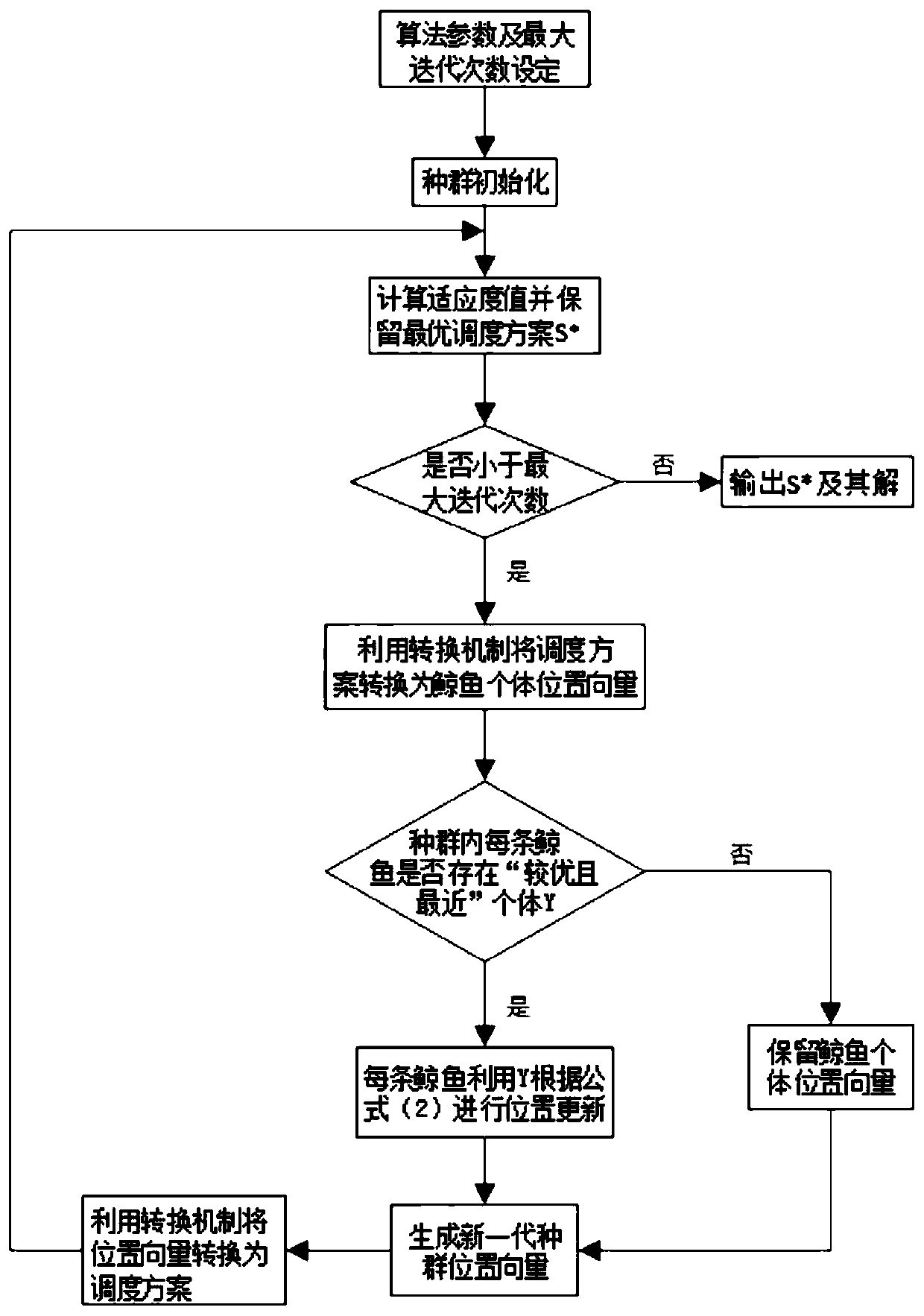
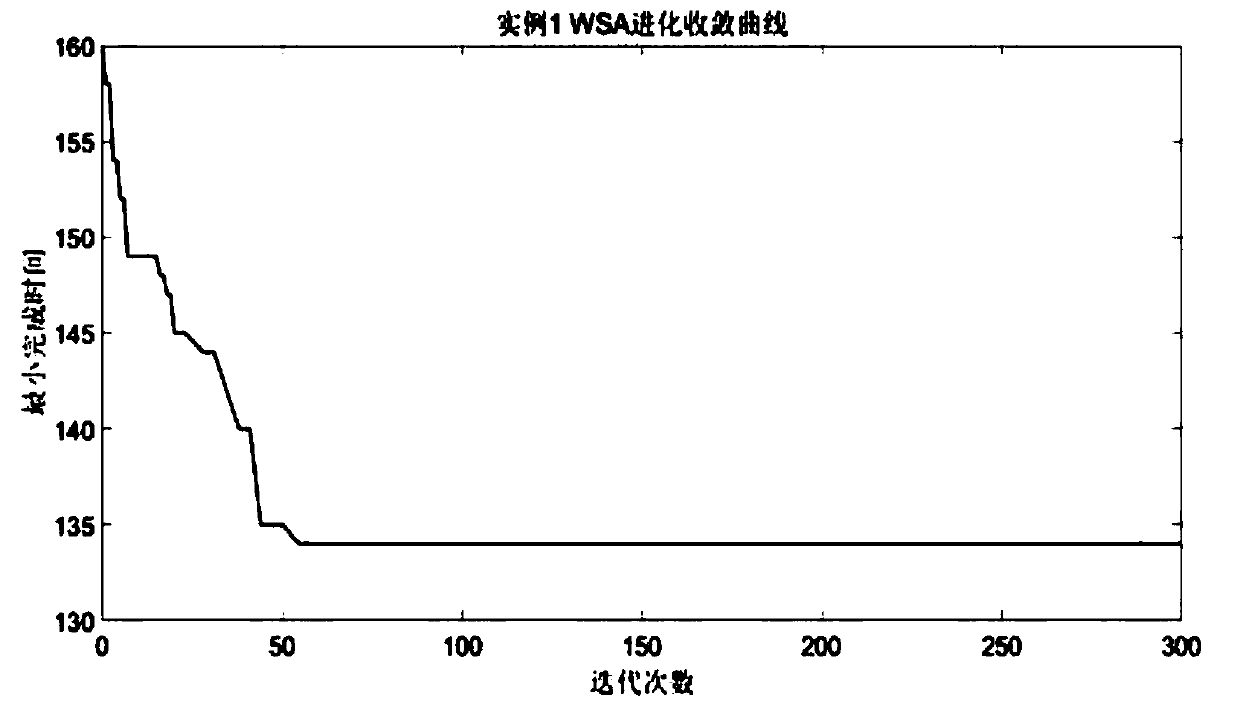
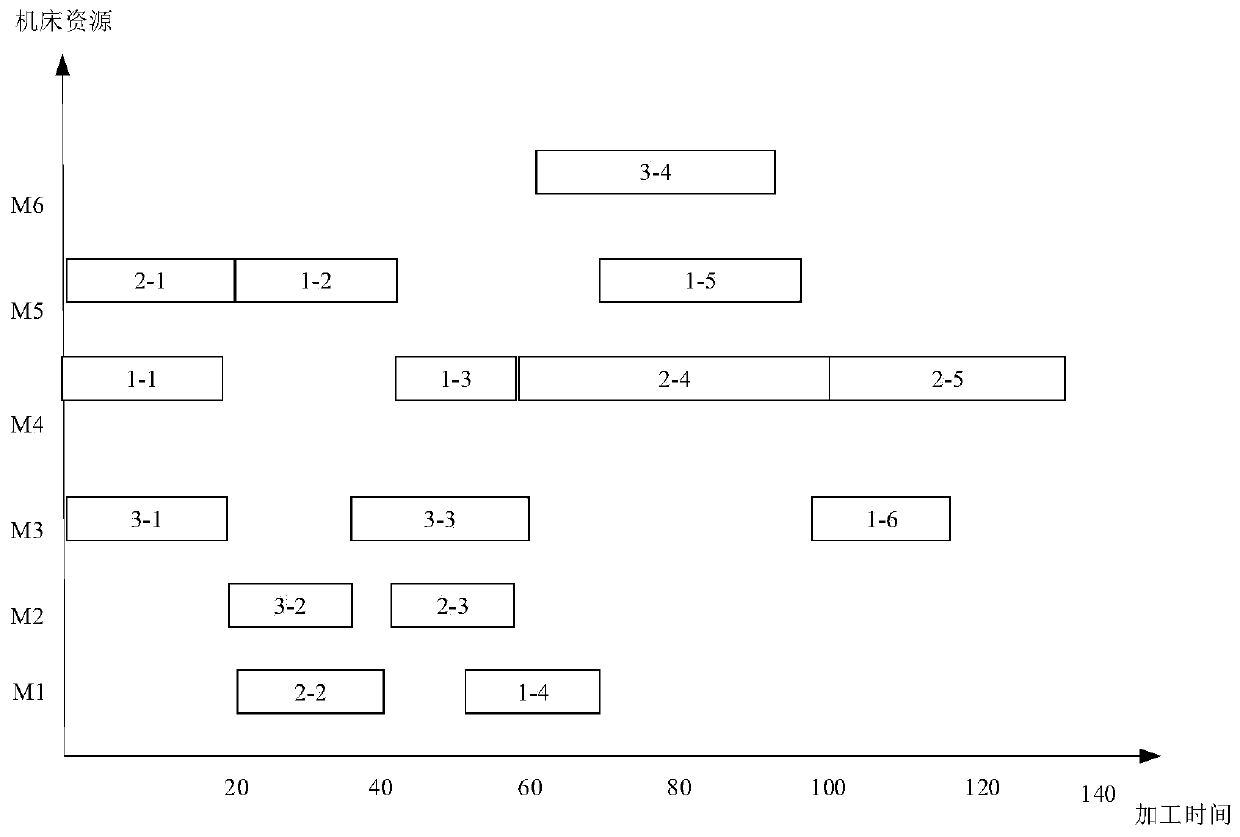
A method for solving flexible job shop scheduling based on a hybrid whale swarm algorithm
The invention discloses a method for solving flexible job shop scheduling based on a hybrid whale swarm algorithm, and the method comprises the steps: firstly defining the coding mode of flexible jobshop scheduling as two-stage random key coding, and then carrying out the mapping conversion through employing a conversion mechanism; Defining the shortest total processing time for solving the fitness function as an optimization target; Secondly, initializing parameters and whale population in the flexible job shop scheduling problem by adopting a whale group algorithm, wherein initialization isdivided into a sorting scheme of a random generation process and a genetic variation mode of an improved genetic algorithm to generate a better machine distribution scheme corresponding to the sorting scheme of the process, and then a better initial population is generated; Calculating the fitness value of each scheduling scheme, and finding and reserving the best scheduling solution; And finally, outputting the optimal scheduling solution and the corresponding fitness function value to obtain a solved optimal scheduling scheme, and solving the problems of low solution precision and low convergence rate in the existing flexible job shop scheduling problem.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Cotton breeding method
InactiveCN101707963ASimple Breeding MethodBroad Breeding PathwayPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAgricultural scienceGossypium
The invention relates to a cotton breeding method. In the method, a combination part of genetic variation generated by cotton graft is used as an explant for inducing to culture callus; the cultured callus is subjected to propagation, subculturing and differentiated culture to obtain cotton seedlings; and after hardening off, the cotton seedlings are grafted for transplantation or directly transplanted. The cotton breeding method has the advantages that: by utilizing graft to create genetic variation, the method not only improves plant quality, yield, stress resistance, and the like, but also obtains distant variation which cannot be obtained through sexual hybridization, and has simple operation, high seed selection efficiency and low cost; the method provides a novel cotton transgenic means and can transfer target gene to a breed to be improved to generate a variation type combining the merits of parental stock and cion parents; and the creation of genetic variation by utilizing graft can be taken as a supplementary means of general breeding and modern gene engineering breeding and is an important breeding means with broad prospects.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
System and methods for detecting genetic variation
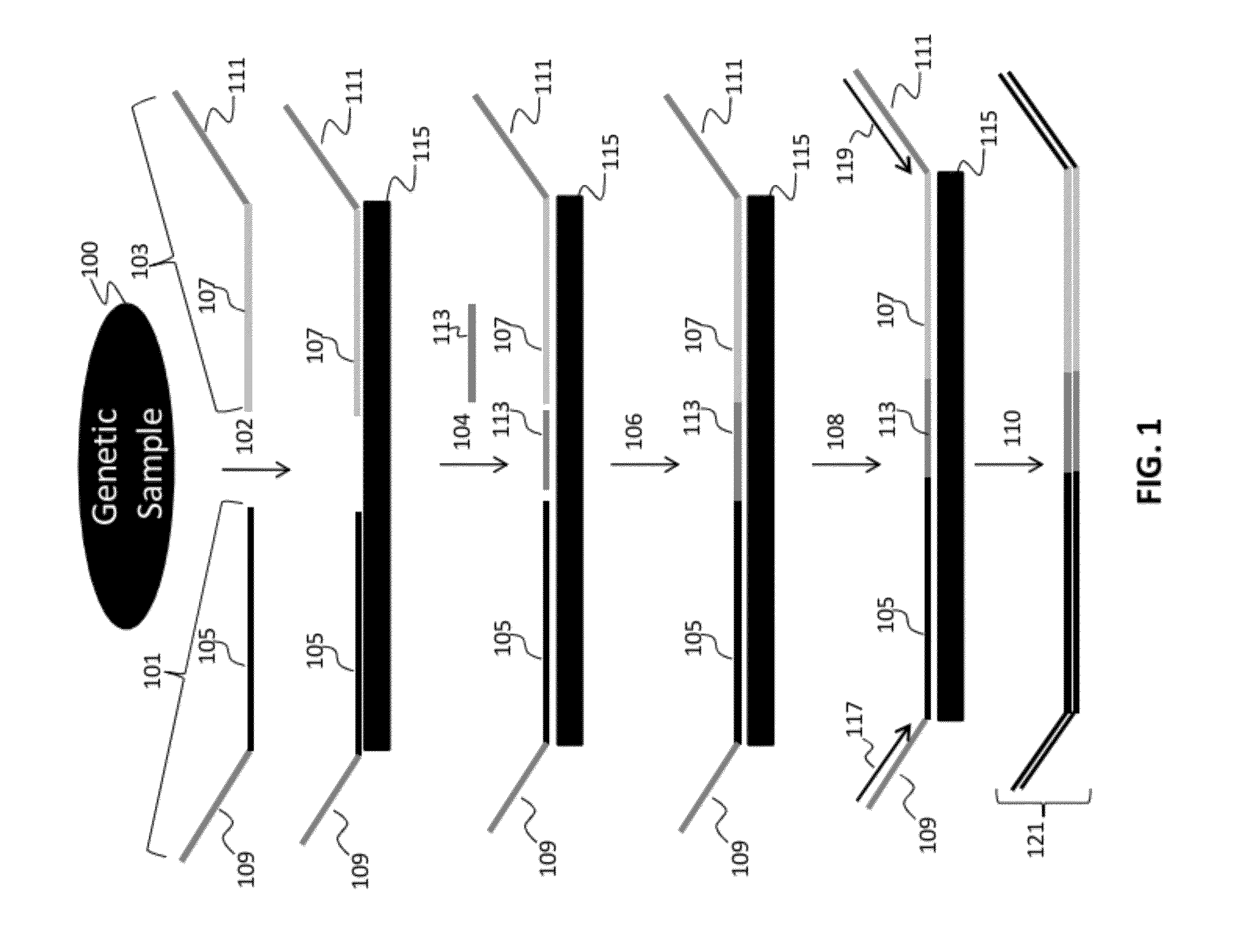
The invention provides methods, apparatuses, and compositions for high- throughput amplification sequencing of specific target sequences in one or more samples. In some aspects, barcode-tagged polynucleotides are sequenced simultaneously and sample sources are identified on the basis of barcode sequences. In some aspects, sequencing data are used to determine one or more genotypes at one or more loci comprising a causal genetic variant. In some aspects, systems and methods of detecting genetic variation are provided.
Owner:COUNSYL INC
Porcine circovirus I type infectious clone and virus rescued thereby and application thereof
InactiveCN101423836ASimple and fast operationInfectious cloneViruses/bacteriophagesFermentationViral antibodyPorcine circovirus type 1
The invention discloses infective clone for porcine circovirus type 1 and rescued virus and application thereof. Two genomes of the porcine circovirus type 1 are connected in cis and inserted into a vector to construct and obtain an infective molecular clone. A Sal I enzyme cutting site as a molecular target is inserted in the infective molecular clone. A rescued recombinant virus (PCV1 / G strains) carries a molecular marker, and the preservation number of the rescued recombinant virus is CGMCC NO.2658. An antigen of the recombinant virus is only reacted with a univalent specific antibody of PCV1 / Cap protein, but has no cross with an antibody against PCV2 / Cap protein. The recombinant virus and a parental virus are identified by combination of PCR and RFLP. The virus strain cultured in vitro has stable propagation property and high virus titer, and the rescued virus strain can be used for detecting the antibody of the virus. The invention lays a foundation for research such as genesis and evolution, genetic variation rule, molecular differential diagnosis, and the like for porcine circovirus in future.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
High Amylopectin Maize
The present invention is directed to compositions and methods for producing a dominant high-amylopectin starch trait in cereal grain and methods for screening grain for genetic variation in hydrolysis and fermentation time.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
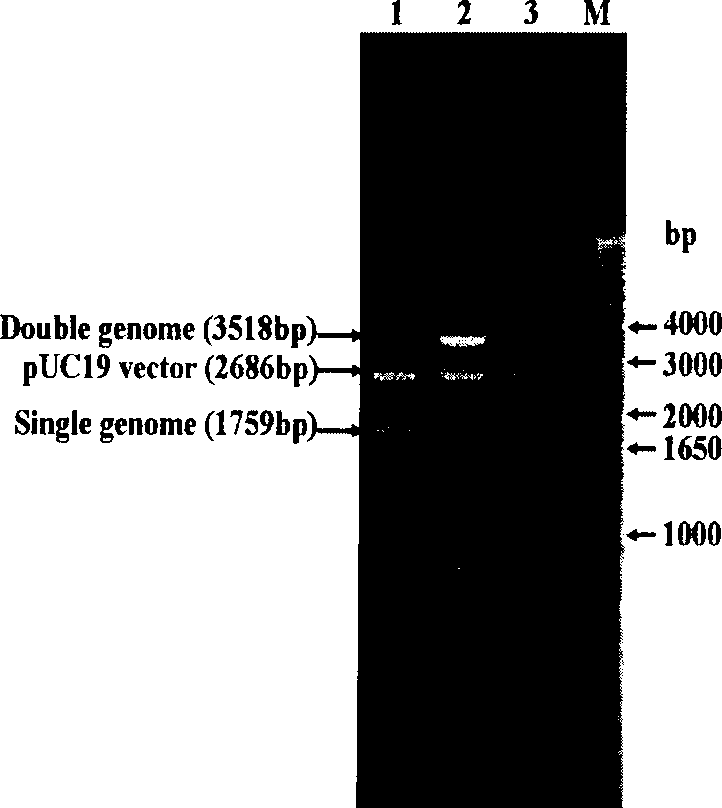
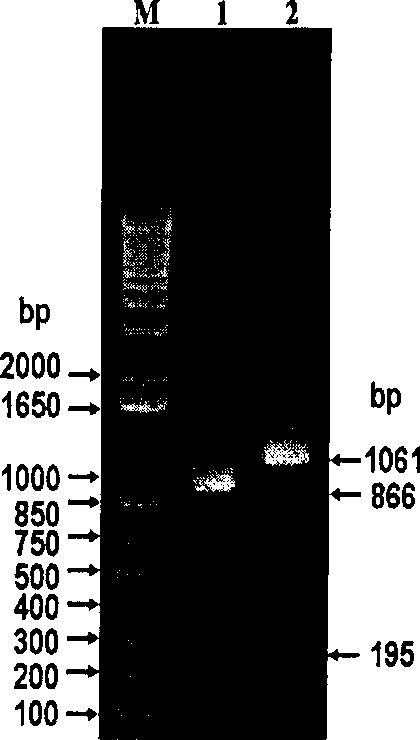
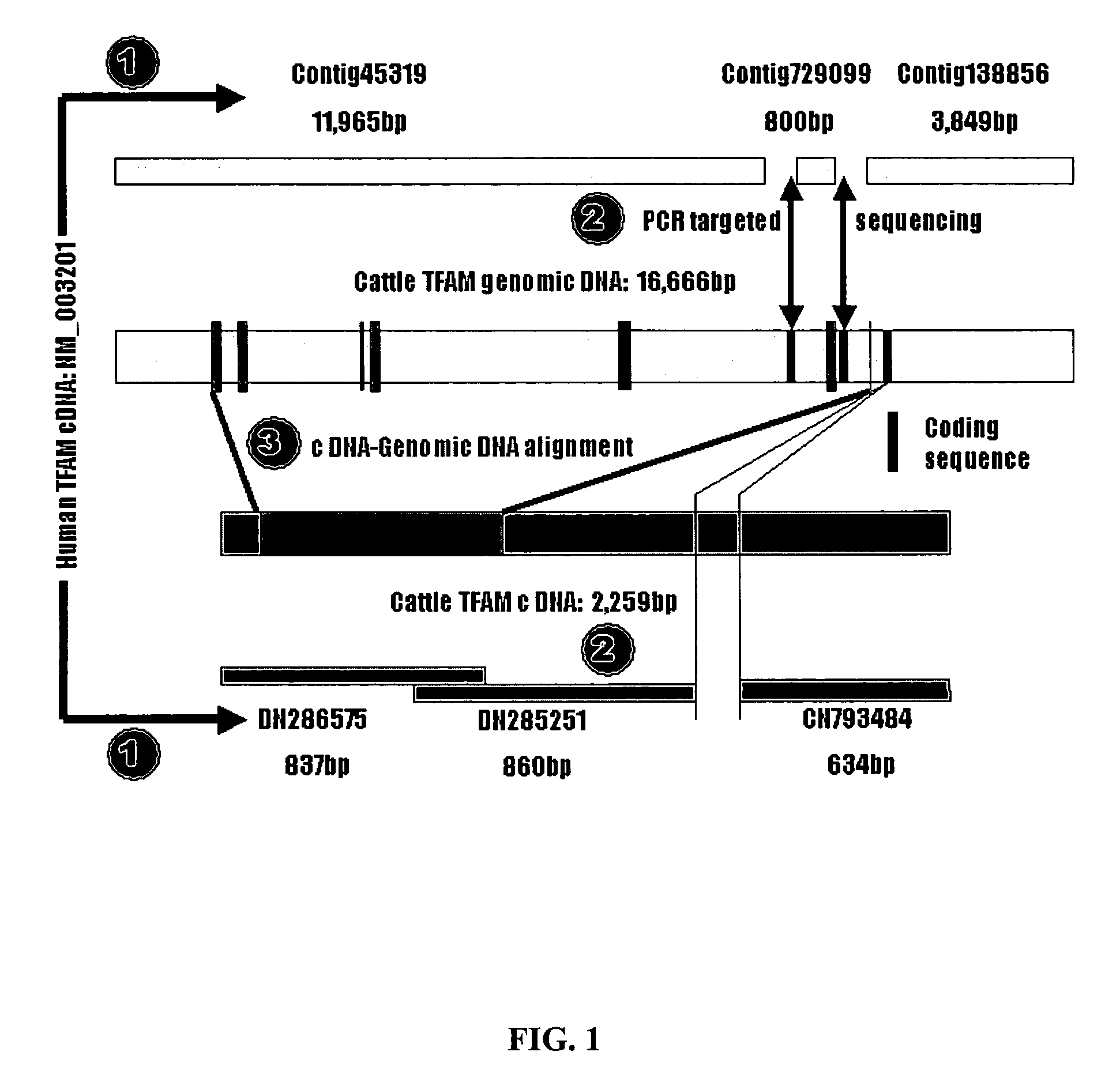
Polymorphisms in mitochondrial transcription factor A ("TFAM") gene and their associations with measures of marbling and subcutaneous fat depth in beef cattle
ActiveUS20070065843A1Increase productivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationZooidMitochondrial transcription
The physiological regulation of intake, growth and energy partitioning in animals is under the control of multiple genes, which may be important candidates for unraveling the genetic variation in economically relevant traits in beef production. The present invention relates to the identification of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within the bovine gene encoding mitochondrial transcription factor A (“TFAM”) and their associations with economically relevant traits in beef production. The invention further encompasses methods and systems, including network-based processes, to manage the SNP data and other data relating to specific animals and herds of animals, veterinarian care, diagnostic and quality control data and management of livestock which, based on genotyping, have predictable meat quality traits, husbandry conditions, animal welfare, food safety information, audit of existing processes and data from field locations.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com