Insertion deletion marker site for identifying shape of watermelon fruit, primer and application
A technology of indels and marker sites, which is applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problems of low breeding efficiency, etc. Product stability and high accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1 Obtaining of indel sites
[0033] 1. Whole genome resequencing
[0034]In the present invention, 315 watermelon germplasm resources selected from the middle-term bank of melon germplasm resources of Zhengzhou Fruit Tree Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences are used as samples, and the DNA of the samples is extracted by the conventional CTAB method, and the 315 watermelon species are analyzed by an Illumina Hi Seq 2000 sequencer. The quality was resequenced to obtain 2.3T data, with an average coverage of 85.42% of the watermelon genome and an average sequencing depth of 9.24X. According to the 50-150 reads obtained by sequencing, compared with the watermelon reference genome 97103 (http: / / cucurbitgenomics.org / organism / 1), 4,661,625 SNP sites were identified, and these 315 watermelon germplasms were used for GWAS (Genome-wide association analysis), the candidate interval related to the shape of watermelon fruit is obtained between the 2...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Embodiment 2 Utilizes the method for identification of watermelon fruit shape by this indel site
[0040] 1. DNA extraction from watermelon tissue
[0041] The DNA of the watermelon sample tissue was extracted by the conventional CTAB method, and the RNA was removed, and the DNA sample volume was not less than 50 μL. Measure the OD value of the DNA sample at 260nm and 280nm with an ultraviolet spectrophotometer, and calculate the DNA content and the ratio of OD260 / 280. The OD260 / 280 value of DNA sample purity should be 1.8-2.0, and the concentration should be diluted to 100ng / μL.
[0042] 2. Primer design
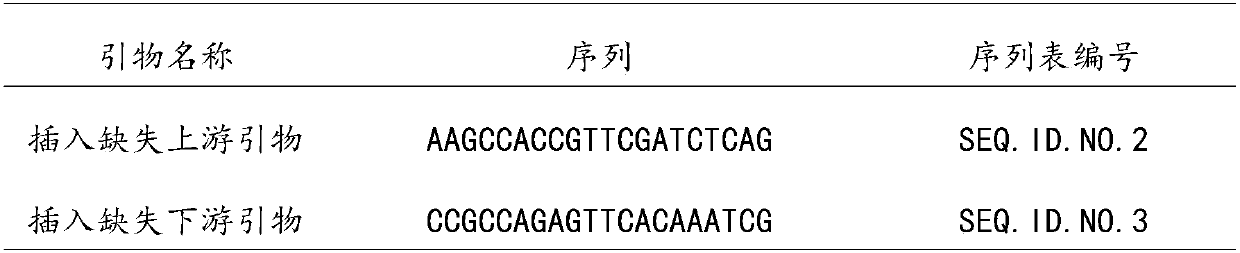
[0043] According to the 300 bp sequence upstream of the 26847023 nucleotide of the watermelon genome chromosome 3, the upstream primer was designed, and the downstream primer was designed for the 300 bp sequence downstream of the 26847181 nucleotide. See sequence listing for sequence information.
[0044] Primers were synthesized by a biotechnology company and di...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Example 3 Using the indel marker locus to verify the fruit shape phenotype identification of two hybrid populations
[0063] 1. Selection of experimental materials
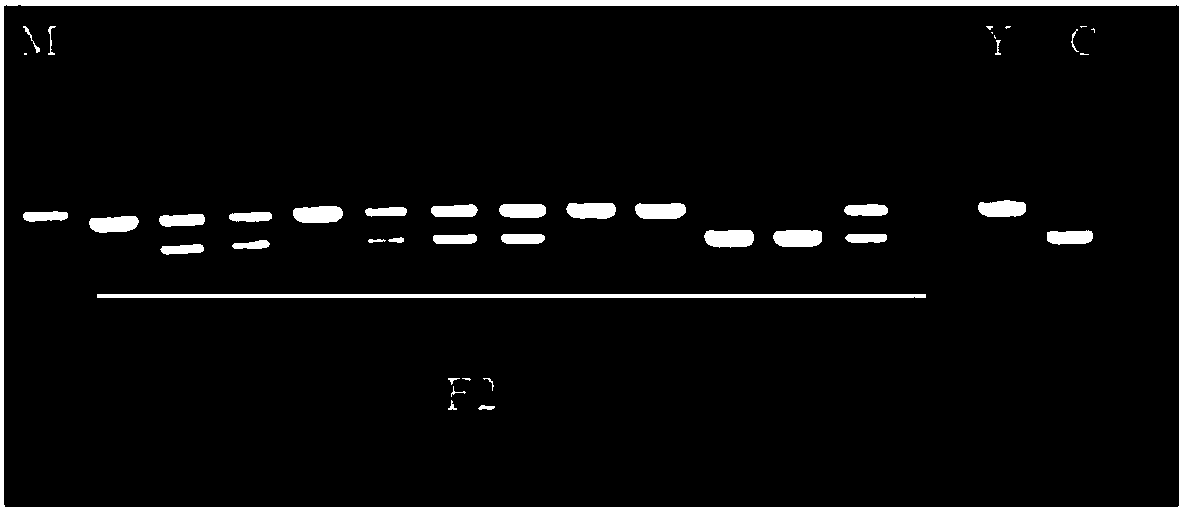
[0064] A total of 778 individual plants of the F2 populations of two hybrid combinations prepared by the polyploid watermelon breeding project of the Zhengzhou Pomology Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences for many years were used as experimental materials, as shown in Table 4.
[0065] Table 4 The name and population size information of the hybrid population
[0066]
[0067] 2. Use the indel marker locus to identify the two populations
[0068] The fruit shape of 778 F2 individual plants was identified by using the indel markers on chromosome 3 of watermelon obtained in the present invention related to the shape of watermelon fruit, and the specific identification method refers to the method in Example 2. Some results of agarose gel electrophoresis detection are shown in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com