Corrosive agent for displaying 9% Cr steel original austenite grain boundary and application thereof
A technology of austenite grain boundaries and corrosive agents, which is applied in the preparation of test samples, etc., can solve the problems of invisible grain boundaries, influence on grain size rating, and inconvenience of material detection and analysis, and achieve good results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] 3g FeCl 3 Put it in a container, then add 0.5g of picric acid, then add 6ml of hydrochloric acid (36% by weight concentration), add 75ml of water, then add 1.5g of sodium dodecylsulfonate, and mix well to obtain a corrosive agent. Process the 9% Cr steel into a sample to be corroded. After polishing, at room temperature, use a cotton ball dipped in corrosive agent to gently rub the metal surface for about 11 seconds, clean it with water, rinse it with alcohol, and dry it with a hair dryer. The metallographic structure was observed with a metallographic microscope.
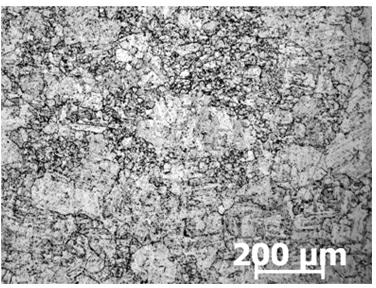
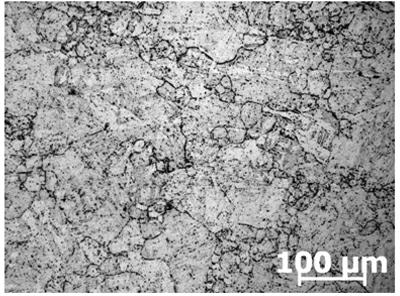
[0022] The grain boundary morphology of the sample is as figure 1 and image 3 As shown, among them, figure 1 is the grain boundary morphology observed by a metallographic microscope (×100), image 3 It is the grain boundary morphology observed by metallographic microscope (×200).
Embodiment 2
[0024] 2g FeCl 3 Put it in a container, then add 0.2g of picric acid, then add 4ml of hydrochloric acid (36% concentration by weight), add 60ml of water, then add 1.0g of sodium dodecylsulfonate, and mix well to obtain a corrosive agent. Process the 9% Cr steel into a sample to be corroded. After polishing, at room temperature, use a cotton ball dipped in corrosive agent to gently rub the metal surface for about 13 seconds, clean it with water, rinse it with alcohol, and dry it with a hair dryer. The metallographic structure was observed with a metallographic microscope.
[0025] The grain boundary morphology of the sample is as Figure 5 As shown, among them, Figure 5 It is the grain boundary morphology observed by metallographic microscope (×100).
Embodiment 3
[0027] First add 4g FeCl 3 In the container, add 0.5g of picric acid, then add 8ml of hydrochloric acid (36% concentration by weight), add 80ml of water, then add 2.0g of sodium dodecylsulfonate, and mix well to obtain a corrosive agent. Process the 9% Cr steel into a sample to be corroded. After polishing, at room temperature, use a cotton ball dipped in corrosive agent to gently rub the metal surface for about 10 seconds, clean it with water, rinse it with alcohol, and dry it with a hair dryer. The metallographic structure was observed with a metallographic microscope.
[0028] The grain boundary morphology of the sample is as Figure 6 As shown, among them, Figure 6 It is the grain boundary morphology observed by metallographic microscope (×100).
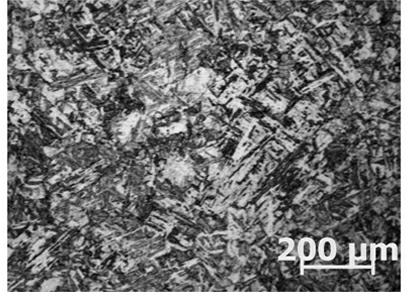
[0029] The same mixed crystal sample was corroded with conventional etchant Vickers reagent, the structure was clear, but the grain boundaries were not obvious, and the appearance was as follows: figure 2 and Figure 4 sho...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com