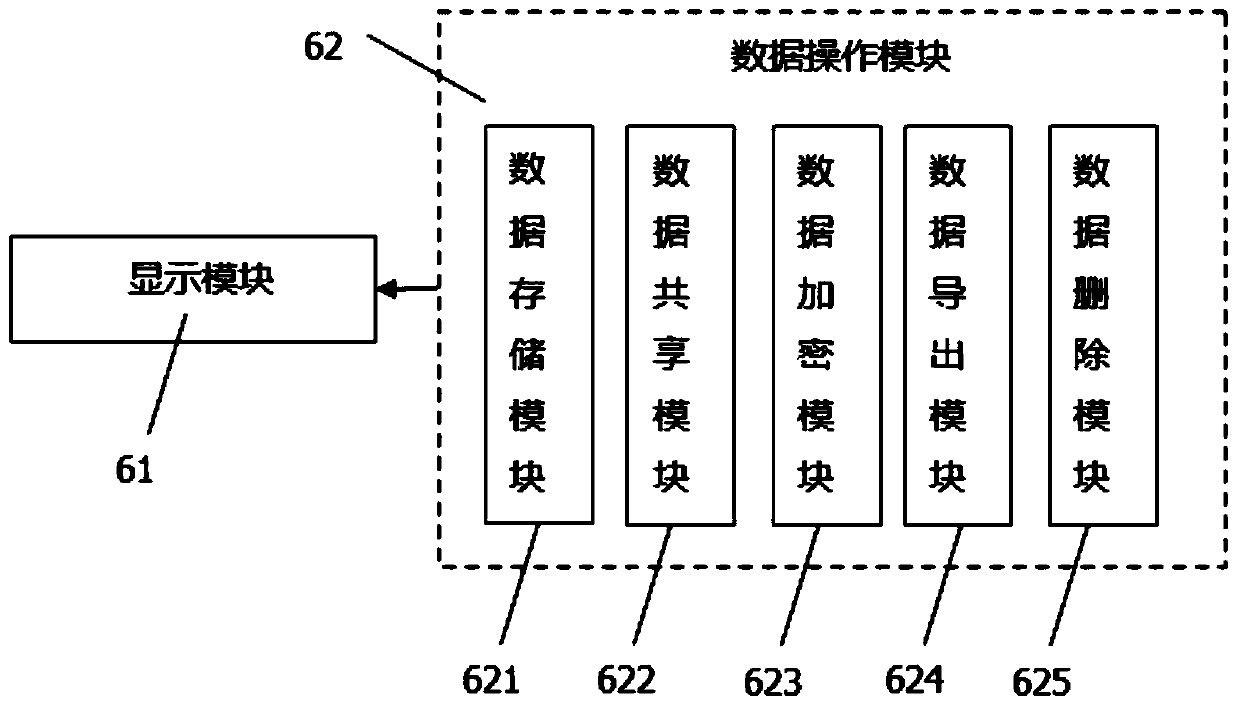
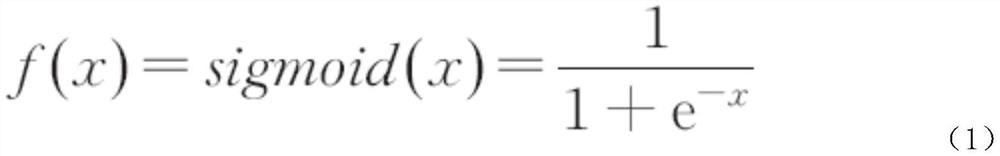Patents
Literature
117 results about "Laboratory safety" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Many laboratories contain significant risks, and the prevention of laboratory accidents requires great care and constant vigilance. Examples of risk factors include high voltages, high and low pressures and temperatures, corrosive and toxic chemicals, and biohazards including infective organisms and their toxins.
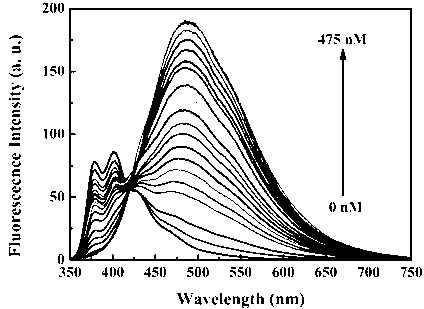
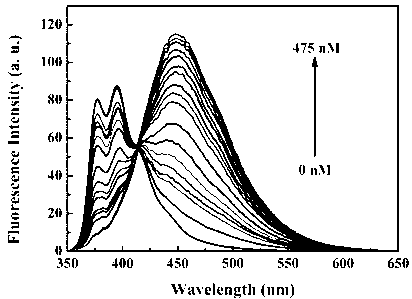
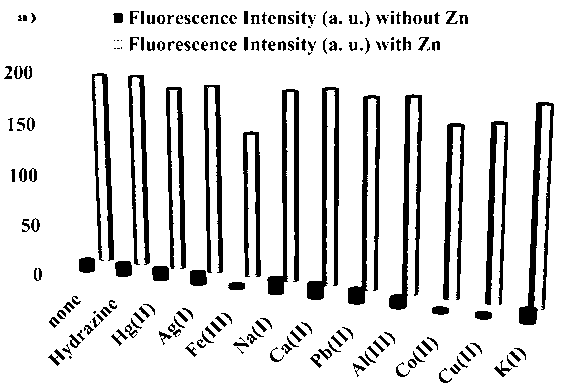
Fluorescent probe: benzothiazole-terpyridine compound used for distinguishing and detecting zinc ions and cadmium ions, preparation method and application method thereof
ActiveCN103265539ASimple preparation processConjugate plane largeOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceSolubilityDisease
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe: a benzothiazole-terpyridine compound used for distinguishing and detecting zinc ions and cadmium ions. The probe has a structural formula as shown in (I). The compound is prepared by using bromobenzaldehyde and O-aminothiophenol as raw materials, and performing a dehydration cyclization reaction, a coupling reaction and a terpyridine derivative reaction. According to the invention, the raw materials are cheap and easily available, a synthesis route is simple, a yield is relatively high, and the fluorescent probe is high in fluorescence quantum efficiency, and relatively high in heat stability and dissolvability. The probe uses a photoinduced charge transfer mechanism, has different luminescence response for the zinc ions and the cadmium ions, has characteristics of rapid response, high sensitivity and high selectivity, is suitable for food safety inspection, laboratory safety inspection, and especially industrial wastewater monitoring, and has a wide application prospect in environment monitoring, ecological protection, disease diagnosis, industrial production and sewage inspection.
Owner:浙江富昇科技有限公司
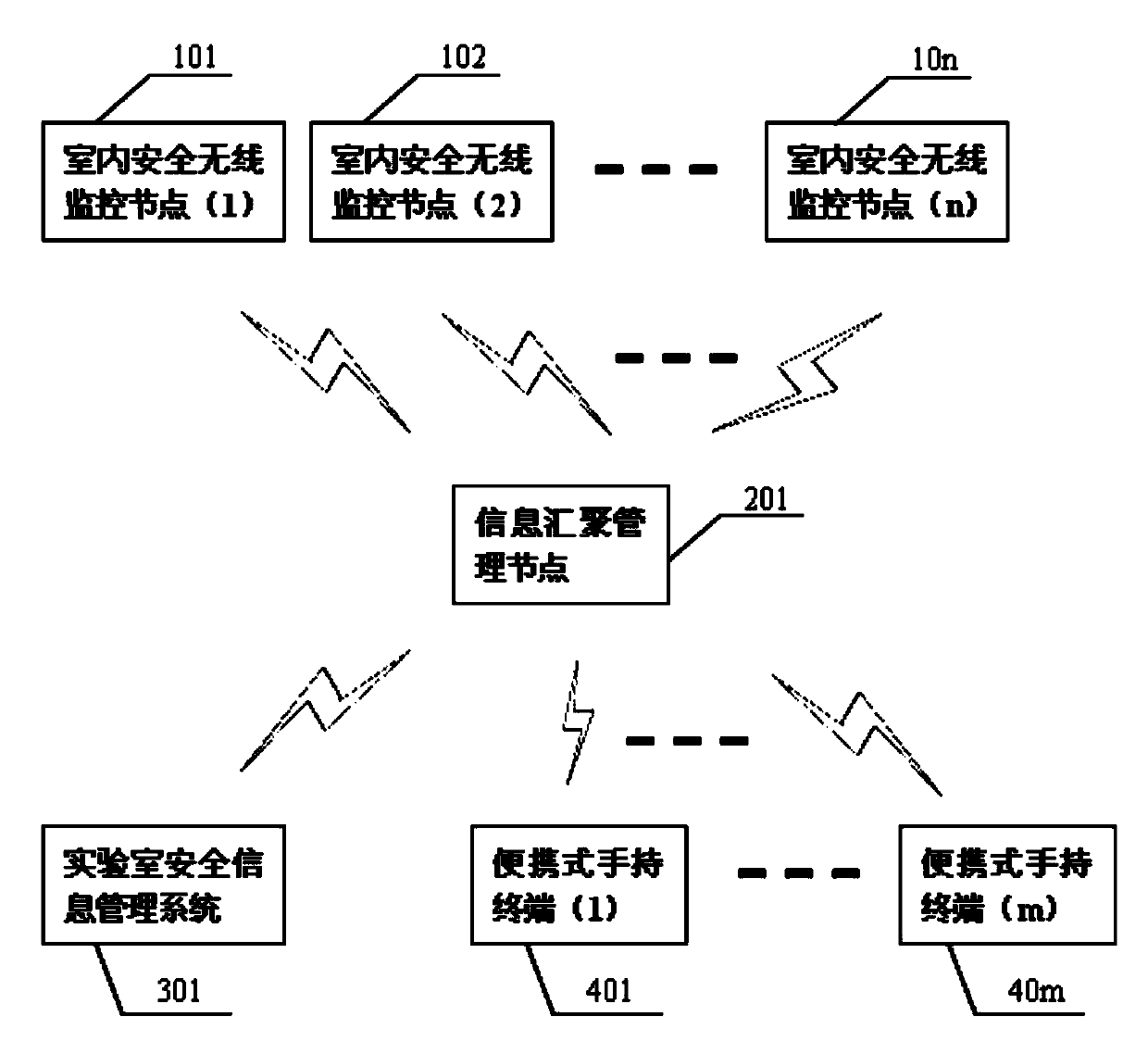
Laboratory safety wireless monitoring method and system
InactiveCN103744357AReduce labor intensityContinuous scientific researchProgramme total factory controlEngineeringLaboratory safety
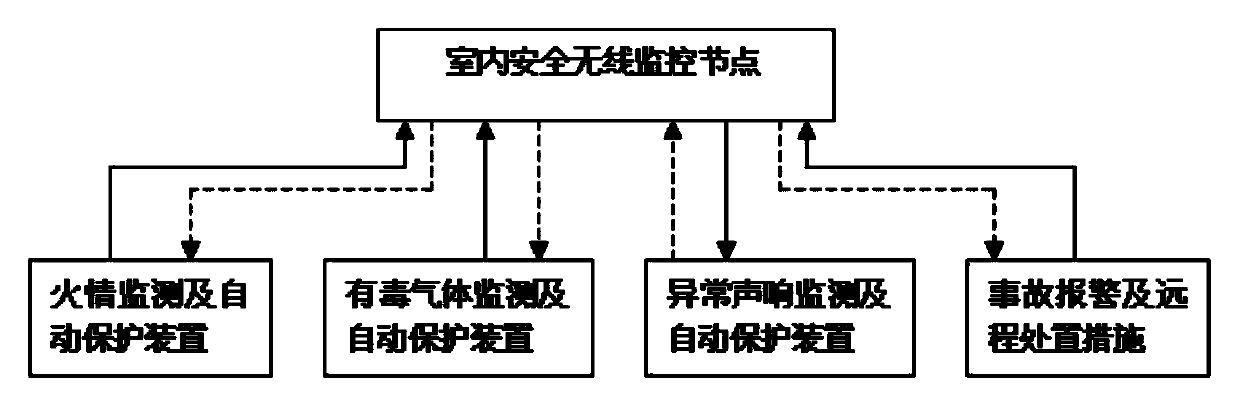
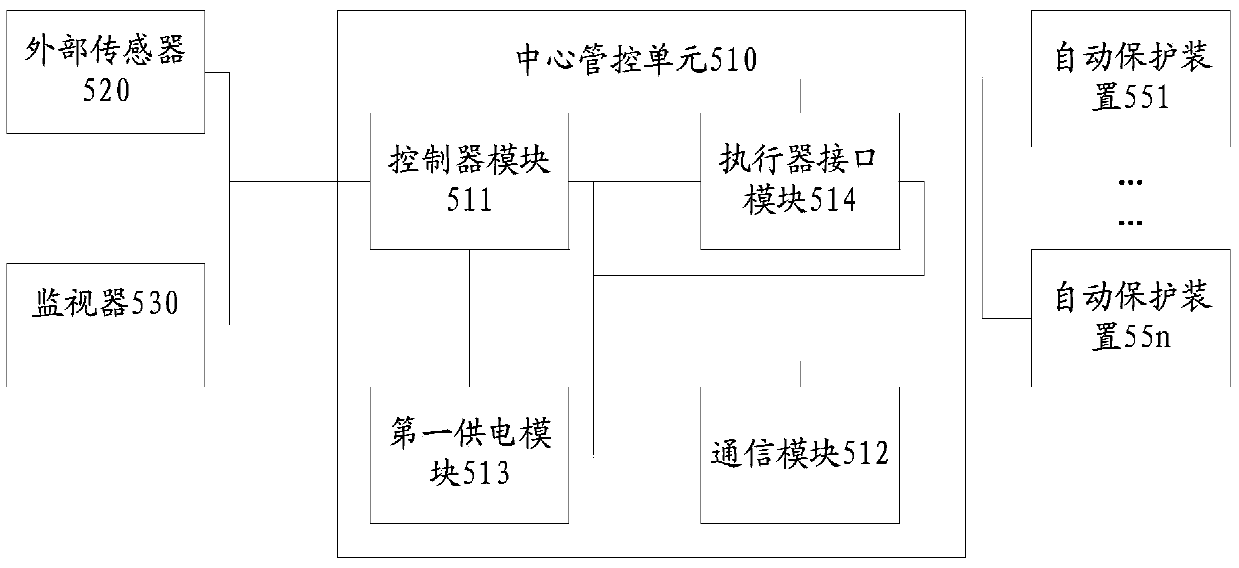
The application provides a laboratory safety wireless monitoring method and a system thereof and belongs to the field of measuring and controlling technology and instrument and detection technology and automation equipment. The system comprises at least an indoor safety wireless monitoring node, an information aggregation and management node, at least a portable handheld terminal and a laboratory safety information management system. Each indoor safety wireless monitoring node can monitor indoor safety states (such as fire, poisonous gas, unusual sounds and the like). The portable handheld terminal can be adopted to guarantee safety of a laboratory, remind people who are responsible for safety to carry out remote check and control and start an automatic safety device corresponding to the indoor safety wireless monitoring node according to an instruction that the portable handheld terminal sends. According to the invention, all-weather online monitoring of indoor safety information can be realized, continuity and safety of scientific experiments are guaranteed; and labor intensity of laboratory administrative staff is mitigated greatly. The location of an accident and field state can be reported accurately, and losses caused by accidents can be minimized.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Smart laboratory cloud platform
InactiveCN108961884AImprove teaching qualityData processing applicationsElectrical appliancesVideo recordingBroadcasting
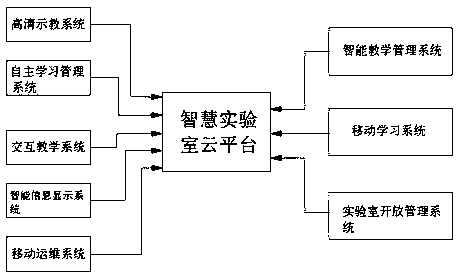
The invention discloses a smart laboratory cloud platform, comprising a high-definition demonstration system, an autonomous learning management system, an interactive teaching system, an intelligent information display system, a mobile operation and maintenance system, a laboratory open management system, an intelligent teaching management system and a mobile learning system. The high-definition demonstration system includes a demonstration video recording and synchronous live broadcasting module. The autonomous learning management system includes an autonomous video uploading module, a synchronous redisplay and self-diagnosis module and an autonomous on-demand module. By organically integrating cloud computing, big data, mobile Internet and other information technologies, the smart laboratory cloud platform promoting the innovation of experimental management means and the improvement of teaching quality through high-definition demonstration, autonomous learning, interactive teaching,laboratory management, intelligent teaching management, teaching resources, mobile learning, laboratory safety management, data analysis and data maps is built.
Owner:南京览众智能科技有限公司
Device and method for detecting total cyanide and sulfide in water solution by employing direct conversion
ActiveCN104280509APrevent oxidationSolve the problem of scattering loss light intensityComponent separationLiquid wasteSolvent
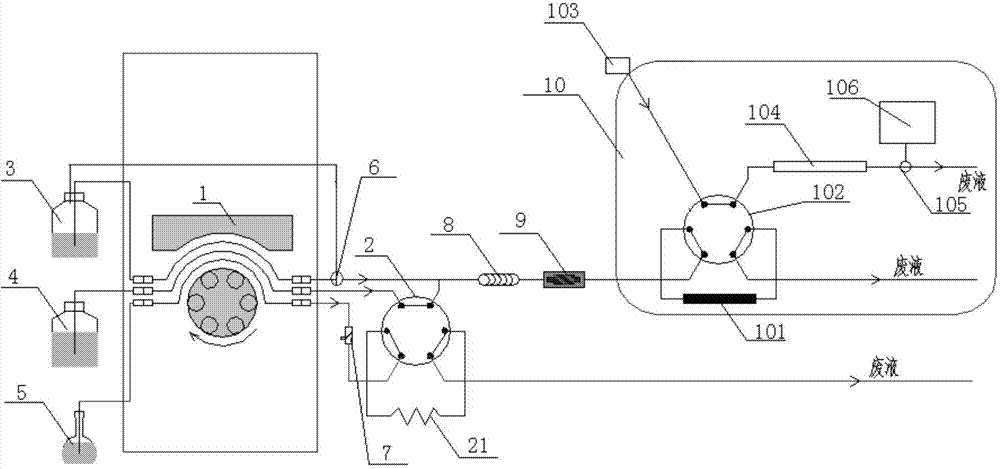
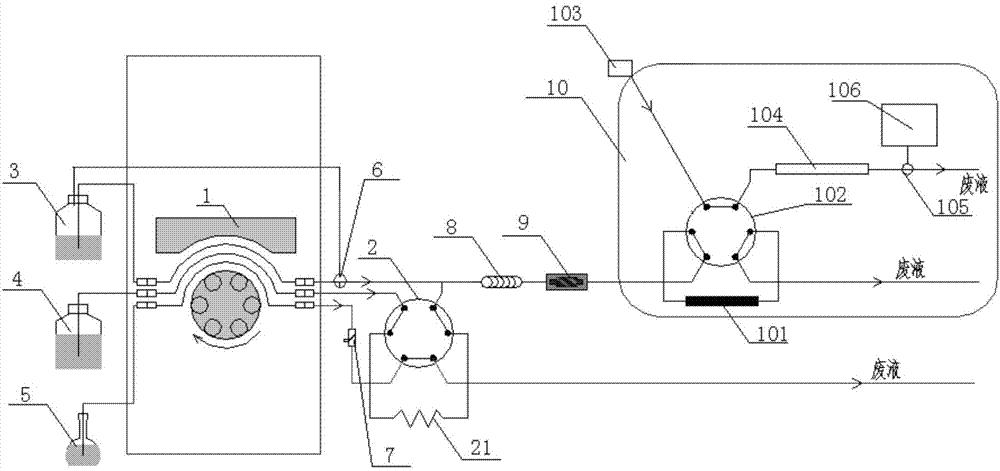
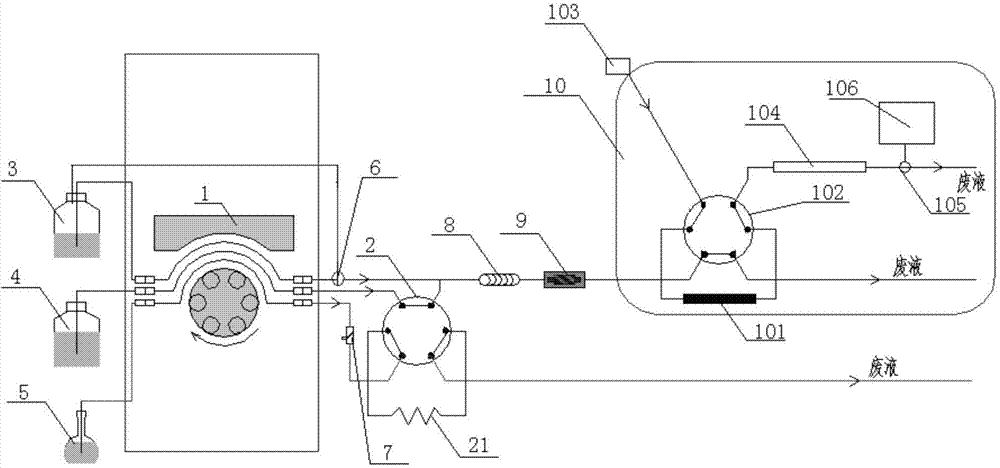
The invention discloses a device and a method for detecting total cyanide and sulfide in a water solution by employing direct conversion. The method comprises the following steps: feeding a sample solution of which the pH is greater than or equal to 11 into a six-way valve quantitative loop to quantify through an online filter, feeding excessive sample solution into a liquid waste bottle; switching a six-way valve, pumping a pure water solvent as a carrying current, pushing out the sample solution, and pumping a water solution containing a stabilizer and an exchanger in advance; after mixing with the sample coming from quantitative loop samples, switching a three-way valve, and refluxing into a storage bottle, further pushing the solution to be mixed evenly in a mixing pipe by virtue of the pure water solvent; entering a photolysis device to carry out photolysis until reaching a capture column in the six-way valve in an ion chromatograph; locking a to-be-detected object, feeding a non-to-be-detected object into the liquid waste bottle; rising the capture column by using an eluting solution, and entering a separation post; sequentially discharging the sulfide and cyanide; and respectively detecting the sulfide and the cyanide by virtue of an ampere detector, and then rinsing the separation column in a reinforcing manner. Compared with an existing national standard method, the method disclosed by the invention is green, safe, environment-friendly, and little in interference; the analysis time, the laboratory safety and the cost are obviously improved; and use of a toxic reagent is also reduced.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
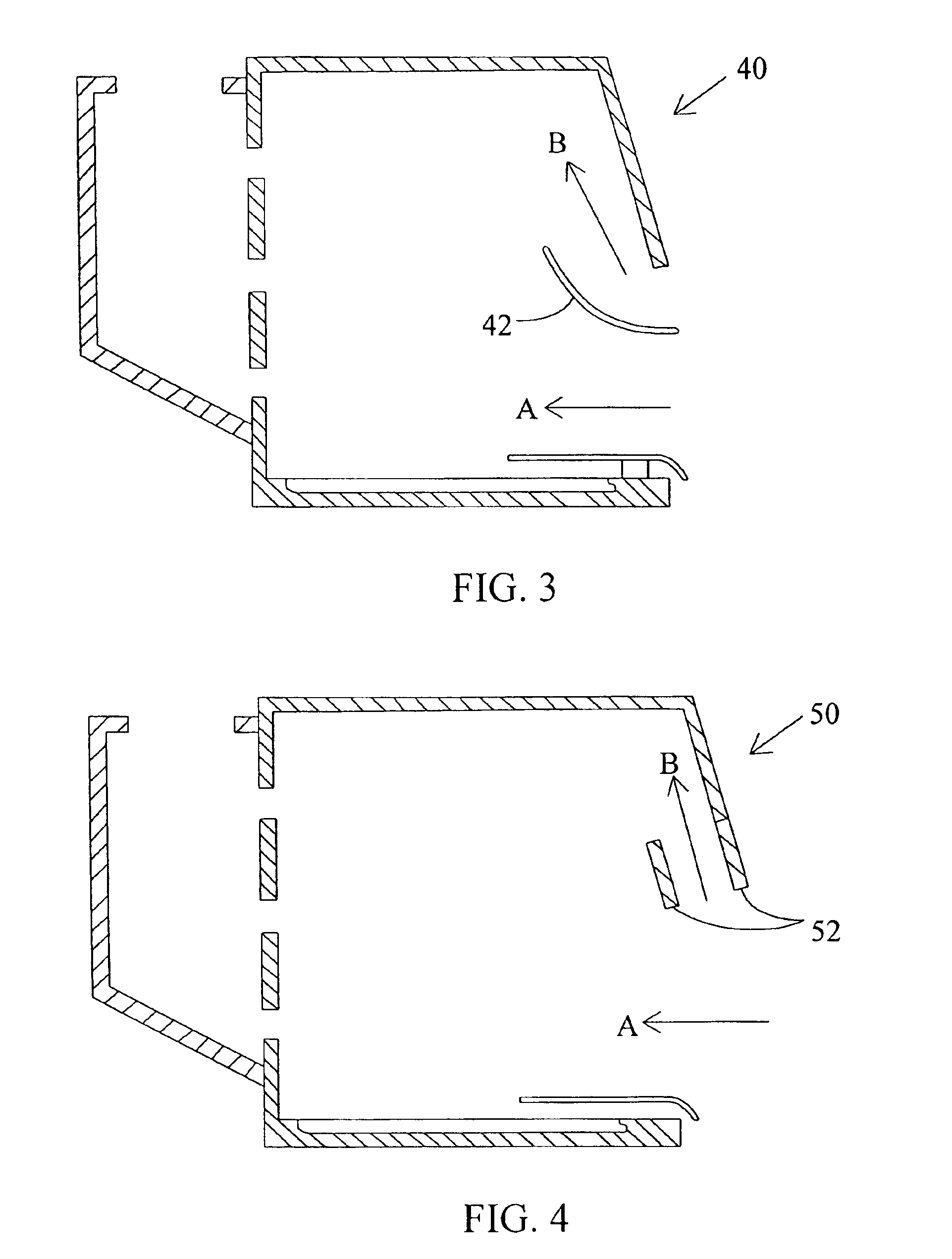
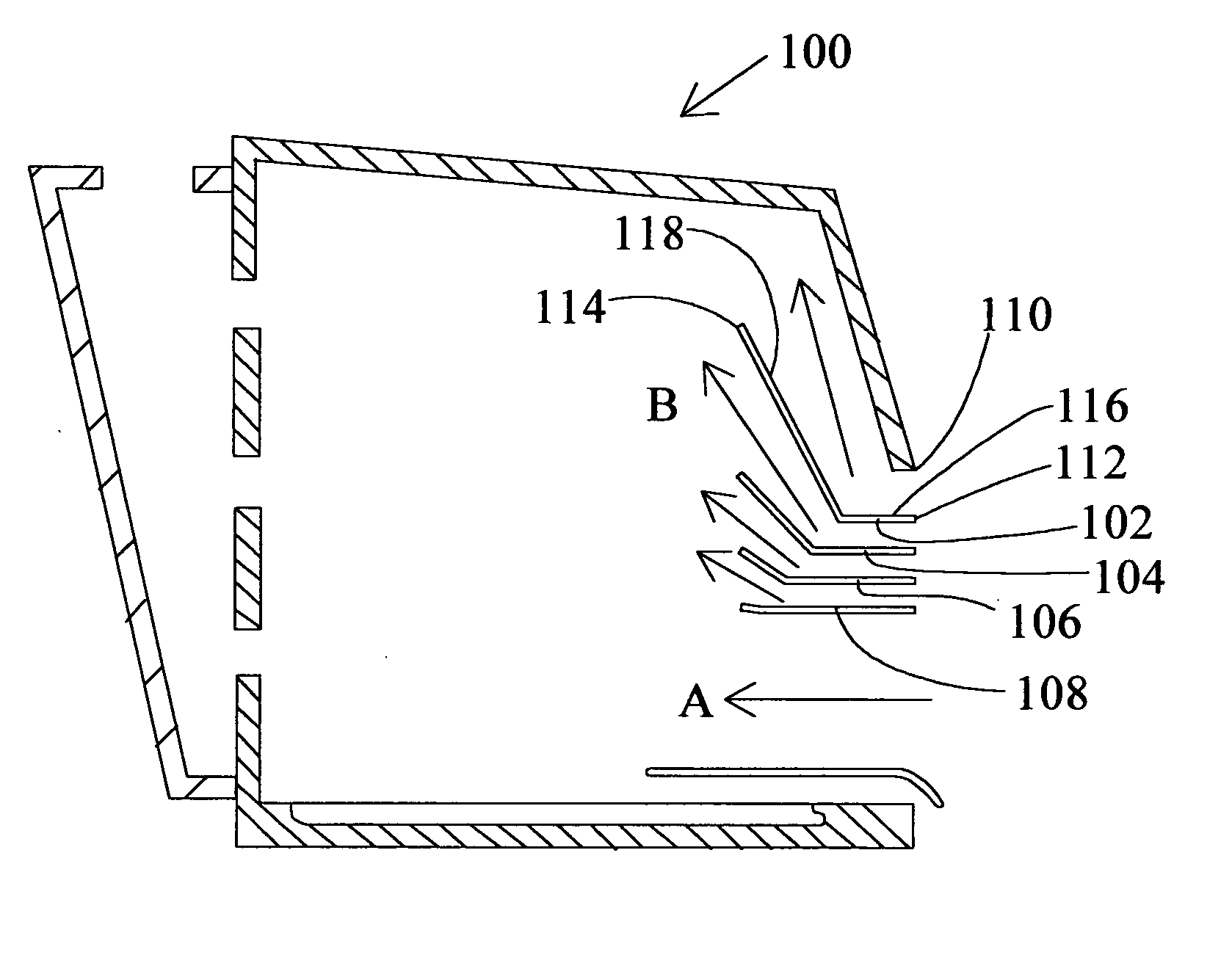
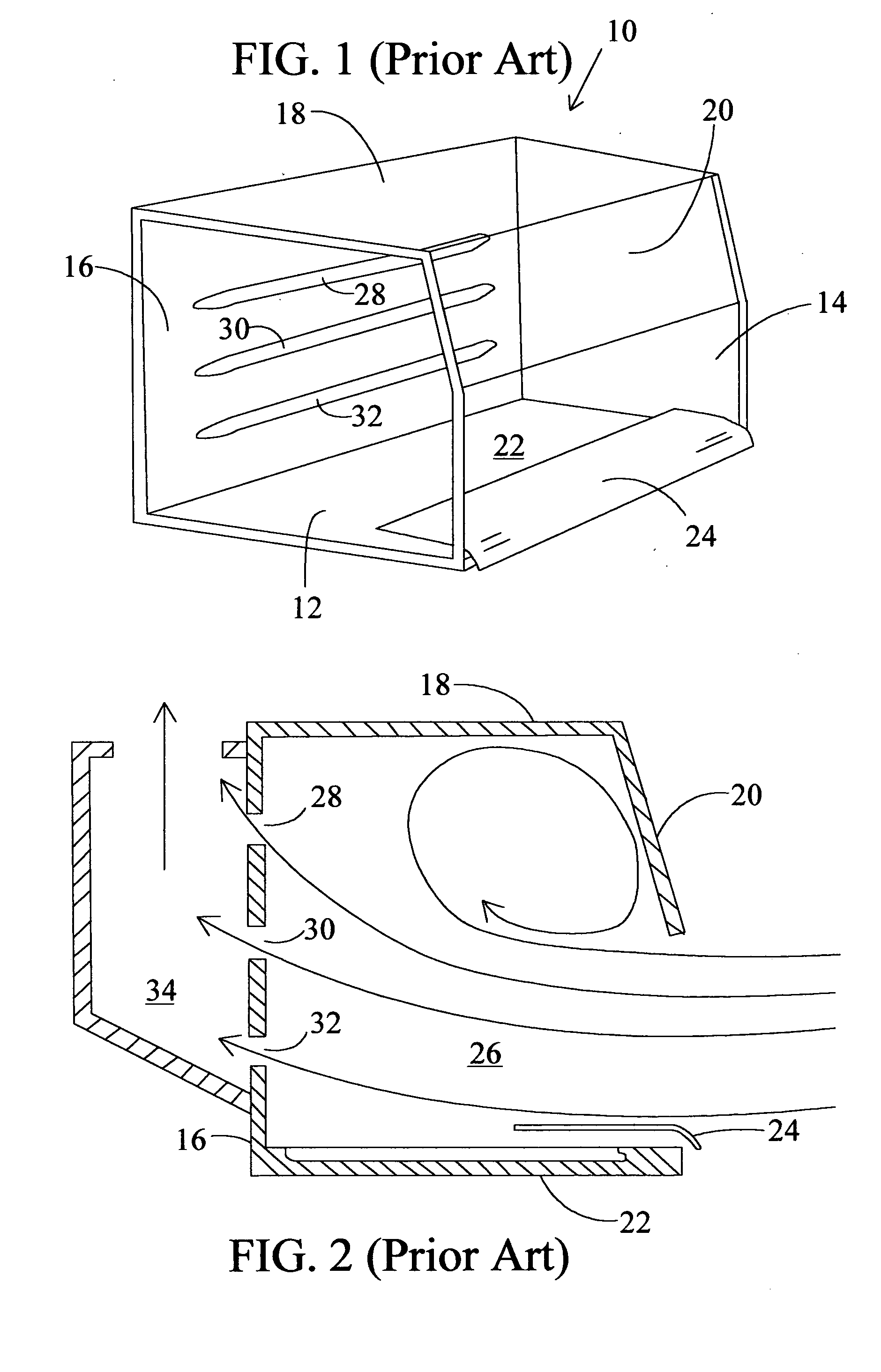
Turbulence-free laboratory safety enclosure
InactiveUS6871170B2Most efficientIncreased turbulenceMechanical apparatusDomestic stoves or rangesEddy currentFume hood
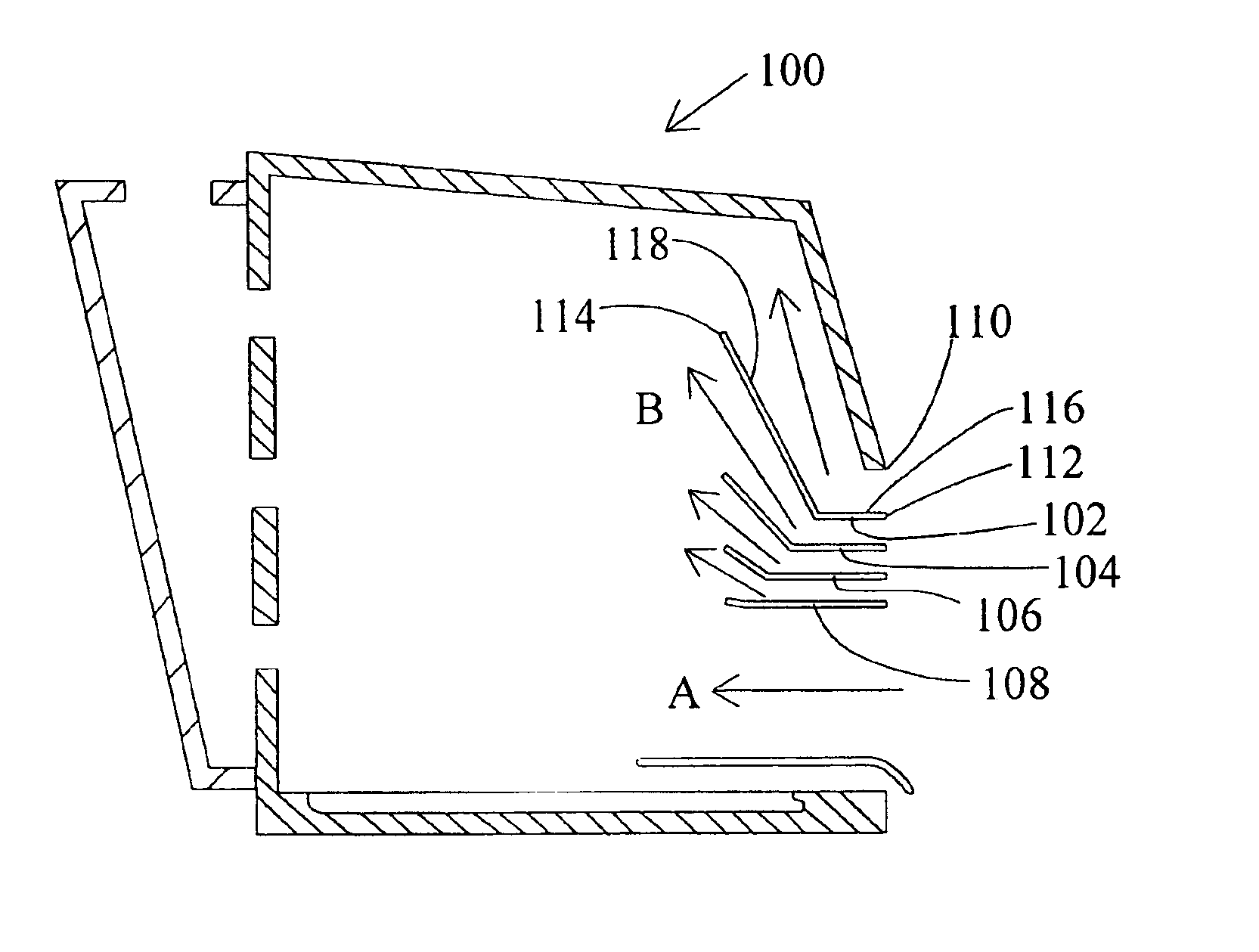
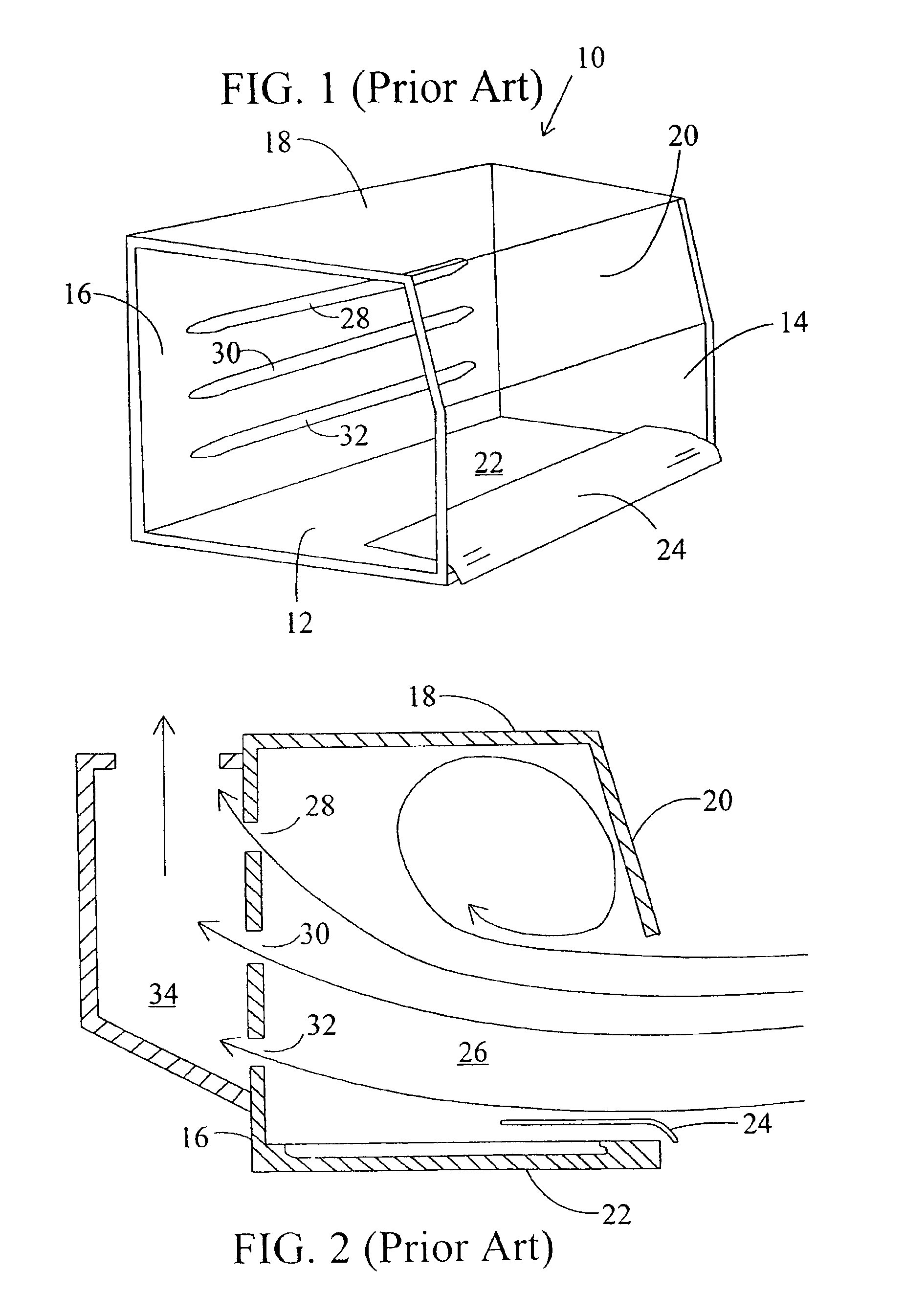
The present invention relates to controlled airflow and air distribution within a laboratory safety enclosure and in particular, to turbulence-free airflow within a laboratory fume hood. The fume hood of the present invention has a work chamber and an access opening having an upper edge. A horizontal air deflector structure is positioned adjacent to the upper edge of the access opening to divert a portion of air entering the access opening upwardly within the chamber, whereby the diverted air eliminates an airflow eddy current.
Owner:FLOW SCI INC
Laboratory safety management system based on Internet of Things
PendingCN112034766AImprove intelligenceImprove reliabilityProgramme controlRadiation pyrometryLaboratory deviceThe Internet
The invention discloses a laboratory safety management system based on the Internet of Things. The system comprises a sensing layer, a network transmission layer and an application layer, and the sensing layer comprises a data collector which is used for monitoring the environmental parameters of a laboratory and the operation parameters of all laboratory equipment, and the application layer comprises a cloud monitoring platform which receives and processes the operation parameters through the network transmission layer and a remote control center which is in communication connection with thecloud monitoring platform. On the basis of combination of big data, the Internet of Things information technology and traditional electrical fire hazard monitoring, the cloud monitoring platform is provided with multiple sensors for omnibearing real-time monitoring, and early fire hazard potential safety hazards can be quickly and accurately identified on the basis of the neural network model. Inaddition, alarms of different degrees can be processed respectively, so that harm caused by an electrical fire can be reduced, and accident loss can be reduced.
Owner:广州邦禾检测技术有限公司
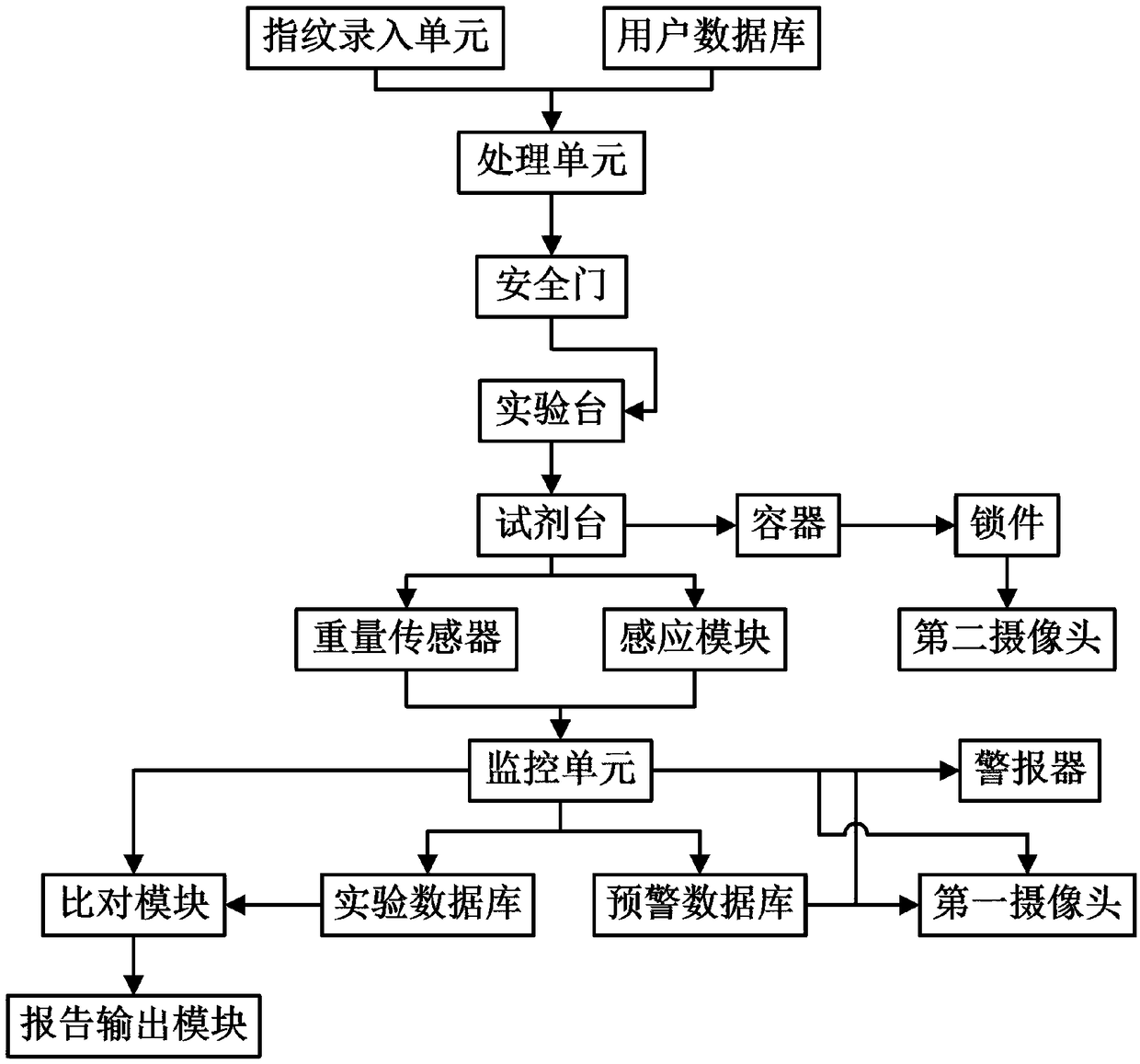
Safety monitoring and early warning system for laboratory
ActiveCN109147264AEnsure safetyEasy to manageClosed circuit television systemsIndividual entry/exit registersEarly warning systemLaboratory safety
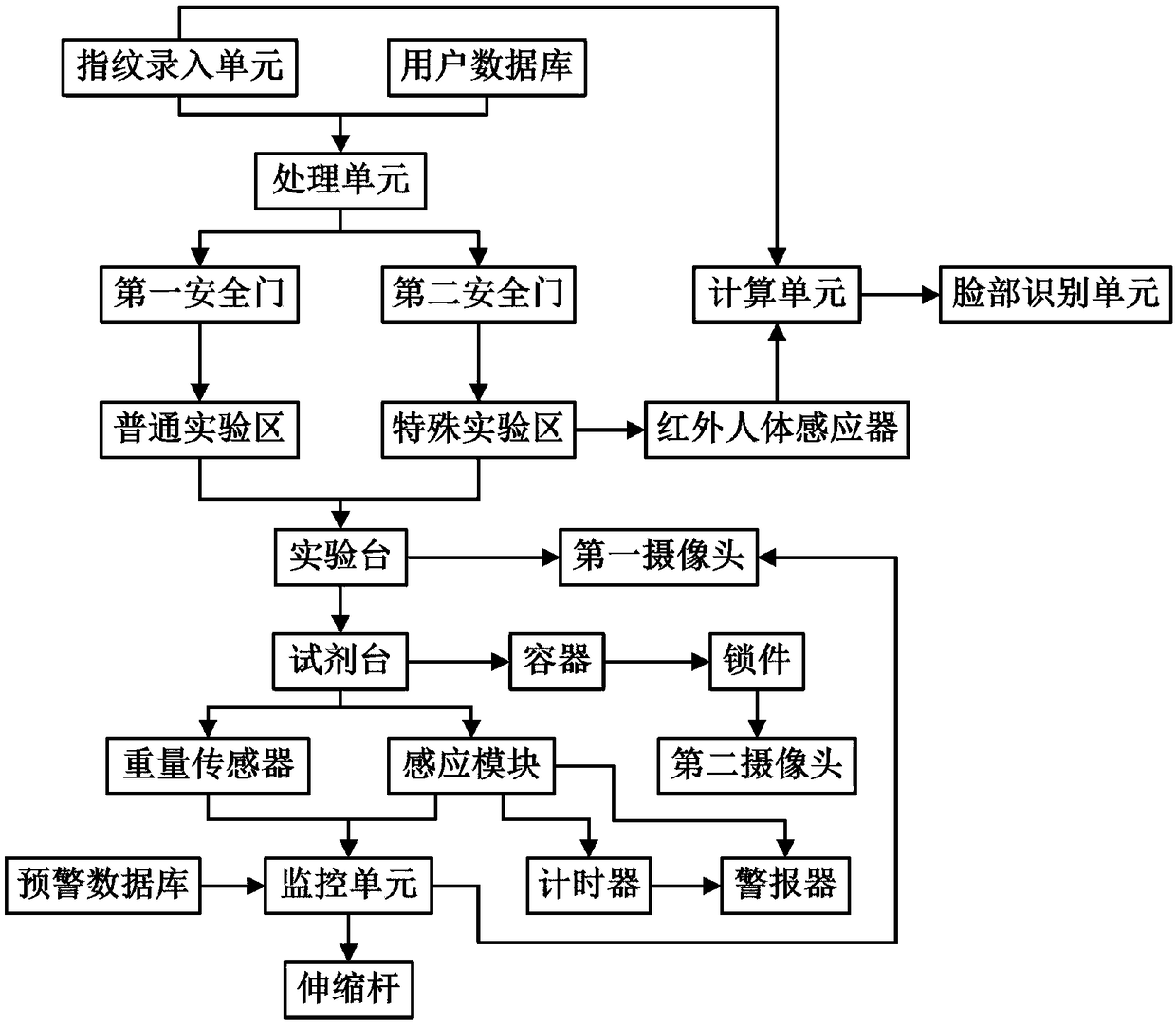
The invention discloses a safety monitoring and early warning system for a laboratory. The system includes a laboratory body, identity authentication modules, and an experiment table. The laboratory body is divided into a general experimental area and a special experimental area; each of the identity authentication modules includes a fingerprint entry unit, a user database, and a processing unit;the experiment table includes a reagent platform, a monitoring unit, and an early warning unit; an early warning database and an alarm are disposed in the early warning unit; a combination mode of experimental reagents that are dangerous is stored in the early warning database; when any one of the experimental reagents in dangerous experimental reagent combination contained in the early warning database is taken and utilized, the monitoring unit controls and restricts access of other experimental reagents that are in the same dangerous experimental reagent combination with the taken experimental reagents; and the alarm is connected to a sensing module and gives an alarm when the experimental reagents that are restricted to be taken are taken. The system can limit the access of the experimental reagents mixed with danger, avoids the occurrence of the danger, and timely emits warnings when potential dangers occur to ensure the safety of personnel and property.
Owner:广州应达环境工程设备有限公司
Safe transportation device for high-pressure combustible experimental gas and gas supply method thereof
PendingCN109654375AMeet the experimental requirementsEasy to operatePipeline systemsGas cylinderEngineering
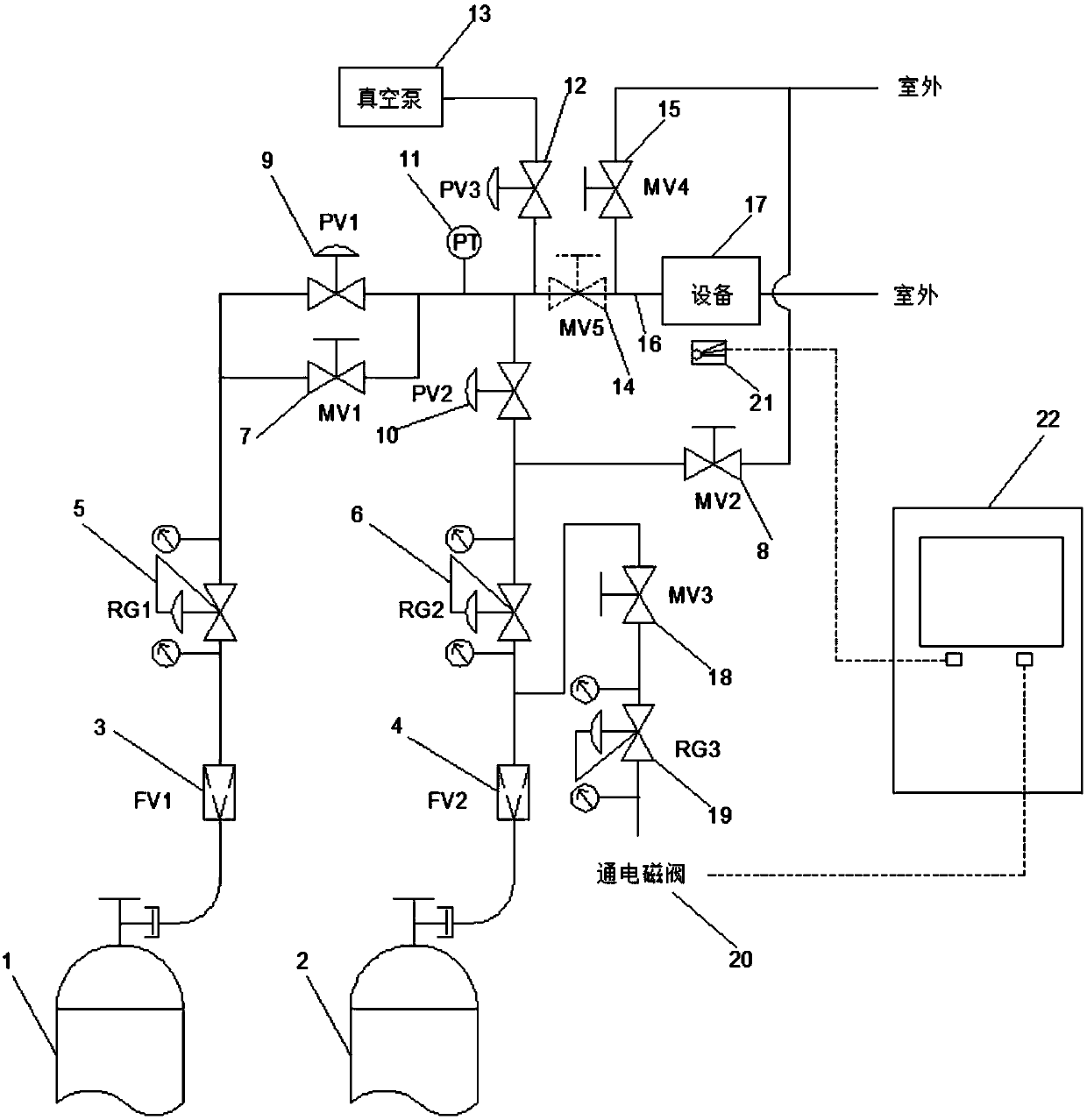
The invention discloses a safe transportation device for high-pressure combustible experimental gas and a gas supply method thereof. The device comprises a combustible experimental gas cylinder, an inert gas cylinder, a filter, a pipeline pressure reducing valve, a manual stop valve, a pneumatic stop valve, a pressure transmitter, a vacuum pump, a pressure gauge, a vacuum gauge, an electromagneticvalve, a combustible gas detector, a combustible gas alarm controller, a metal pipeline and the like. The device can be used for: 1) transporting the combustible gas to experimental equipment safely;2) adjusting the gas pressure in full range during the using process; 3) supplying gas continuously or intermittently for laboratory equipment; 4) conduting air tightness inspection to the equipmentbefore the experiment and supplying gas for cleaning tail gas after the experiment; 5) replacing the high-pressure gas cylinder safely and conveniently; 6) detecting combustible gas concentration in real time to maintain laboratory safety. With good air tightness, high cleanliness, high durability and safety reliability, the transportation device and method provided by the invention can meet the requirements of continuous gas supply and intermittent gas supply for the laboratory equipment.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
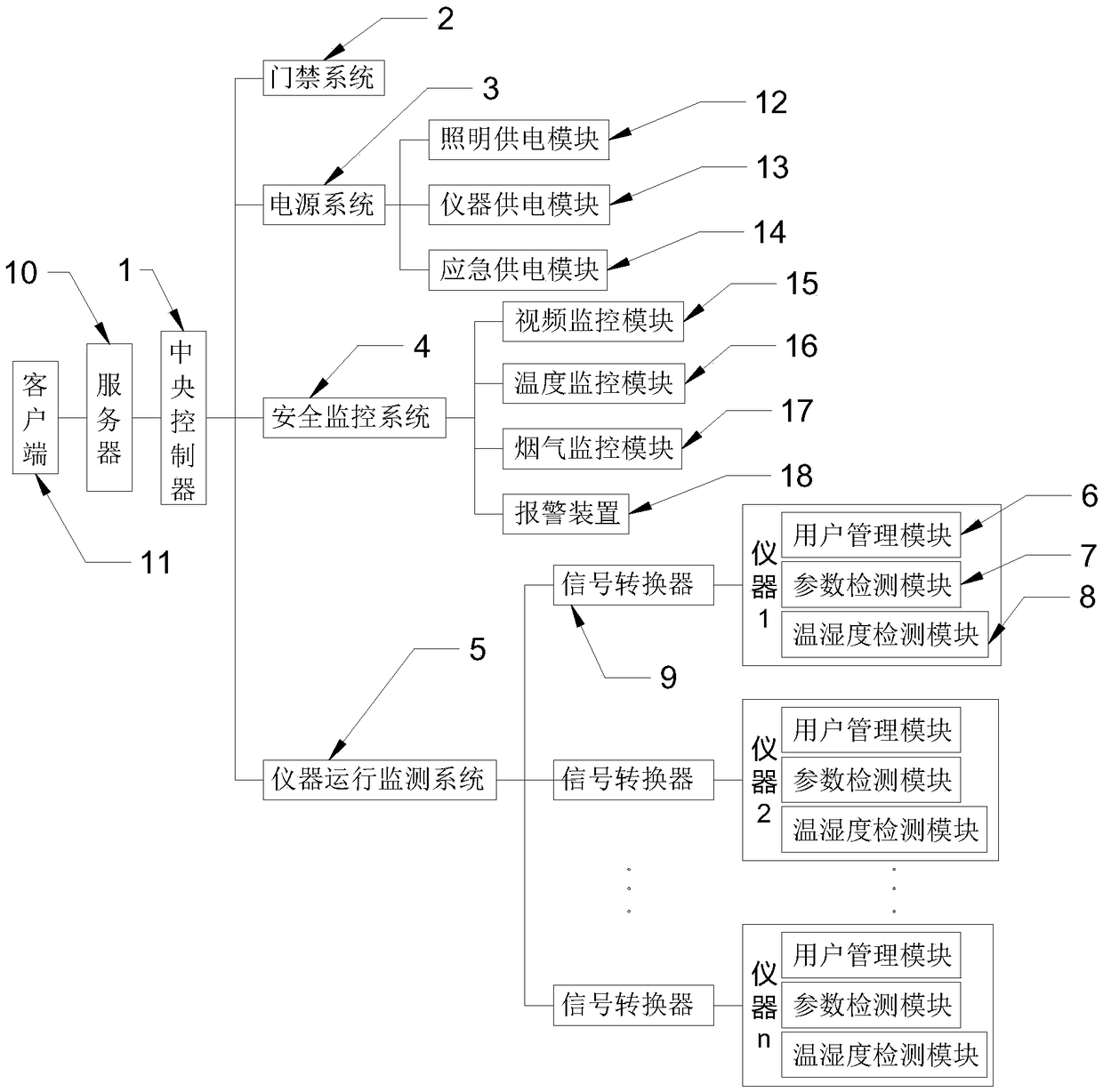
Safety management system of laboratory
InactiveCN109032088AReal-time monitoring of usageReal-time monitoring of runabilityTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlSafety management systemsMonitoring system
The invention relates to the technical field of safety management of a laboratory, and discloses a safety management system of the laboratory. The safety management system comprises an access controlsystem, a power system, a safety monitoring system and an instrument running monitor, wherein the access control system is controlled by a central controller, the instrument running monitor is used for monitoring all instruments in the laboratory, and the central controller is connected to a server and is used for timely sending an abnormal condition to a client by the server. By the safety management system, access control, laboratory lightning, instrument running and safety monitoring are met; meanwhile, all instruments in the laboratory are connected to an instrument running monitoring system, the instrument application condition, a running parameter and an experiment environment are monitored in real time, an abnormal result is timely sent to the client by the server, so that a manageris reminded of timely checking and adjusting.
Owner:SHENZHEN INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
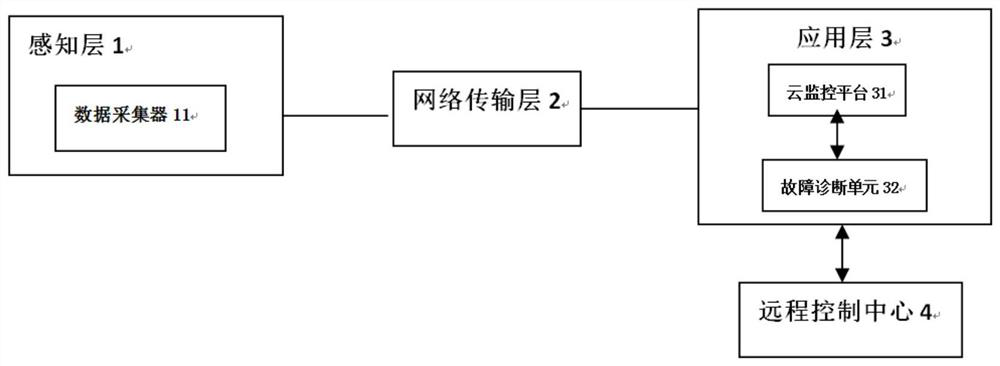
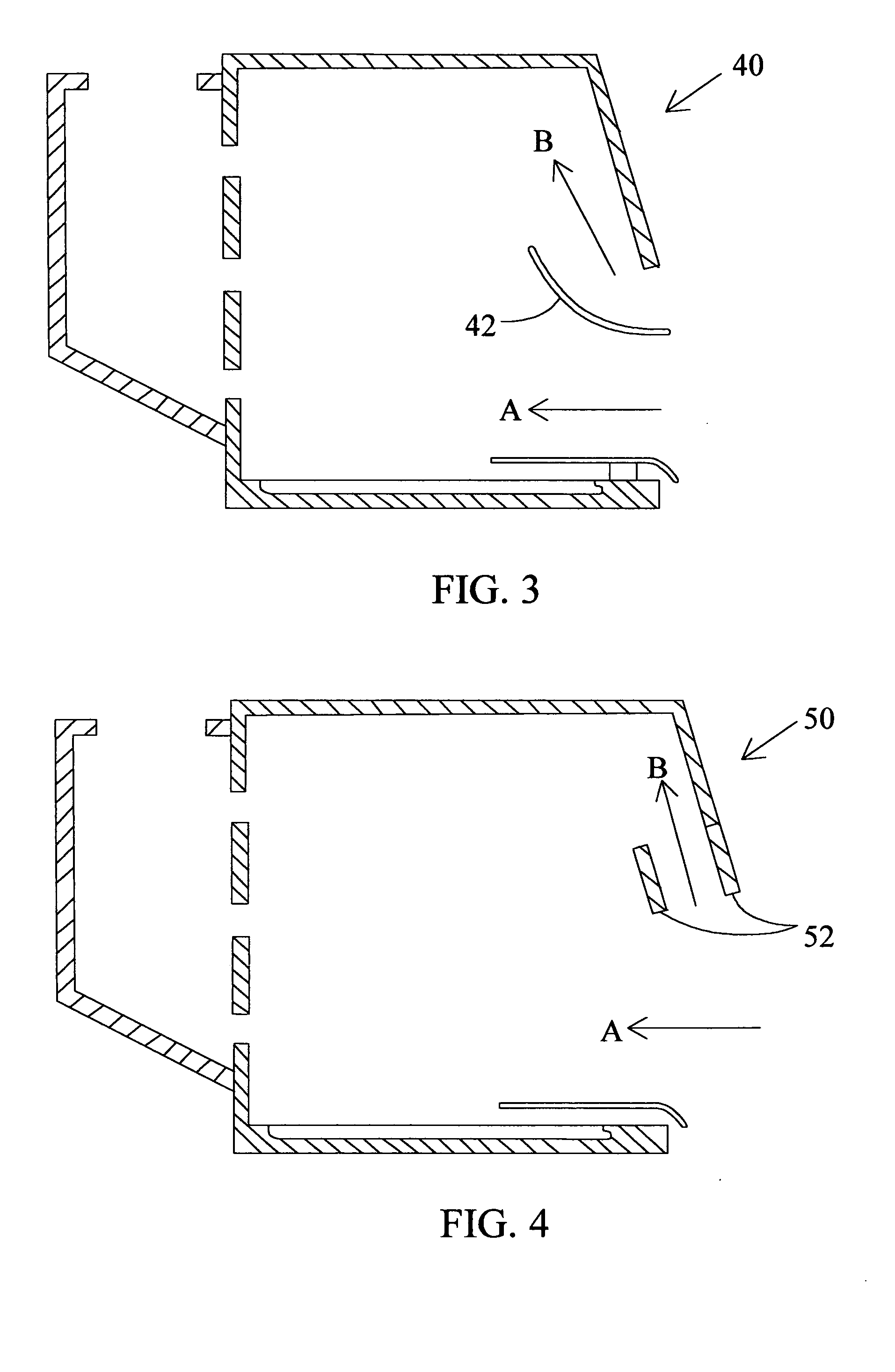
Turbulence-free laboratory safety enclosure
InactiveUS20050164622A1Maintains turbulence-free operationEasy to liftMechanical apparatusDomestic stoves or rangesEddy currentFume hood
The present invention relates to controlled airflow and air distribution within a laboratory safety enclosure and in particular, to turbulence-free airflow within a laboratory fume hood. The fume hood of the present invention has a work chamber and an access opening having an upper edge. A horizontal air deflector structure is positioned adjacent to the upper edge of the access opening to divert a portion of air entering the access opening upwardly within the chamber, whereby the diverted air eliminates an airflow eddy current.
Owner:FLOW SCI INC
A laboratory safety monitoring system and method based on Internet of Things
ActiveCN108956875AFlexible settingsGuaranteed accuracyTransmission systemsAlarmsElectricityMonitoring system
A laboratory safety monitoring system and method based on Internet of Things are disclosed. The system includes a background server and a monitoring device disposed in a laboratory. The monitoring device includes a control device and a harmful toxic gas detection device. The harmful toxic gas detection device includes a plurality of gas detection modules disposed at different positions of the roofof the laboratory. The gas detection modules include bases. The lower surfaces of the bases are provided with a plurality of gas sensors forming a round shape and equally spaced along the round shape. The bases are also provided with microprocessors and first wireless communication modules. The control device includes a controller, an alarm module and a second wireless communication module. The microprocessors are electrically connected to the gas sensors and the first wireless communication modules respectively. The controller is electrically connected to the alarm module and the second wireless communication module separately. Safety of a laboratory can be effectively monitored through the system and the method, and when leakage of harmful toxic gas is detected in the laboratory, an alarm is given in time.
Owner:重庆七彩虹数码科技有限公司
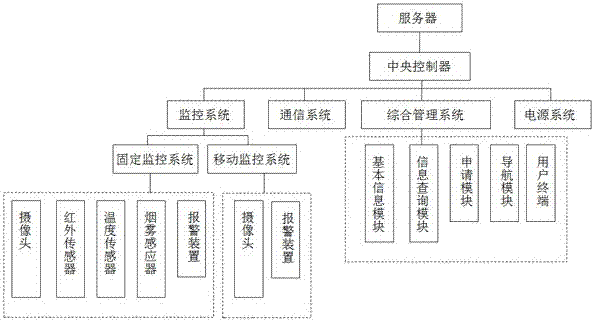
Campus laboratory safety management system
InactiveCN107291033AEnsure safe developmentEliminate potential safety hazardsProgramme controlComputer controlApplication moduleSafety monitoring
The invention provides a campus laboratory safety management system which comprises a central control unit, a server, an integrated management system, a monitoring system, a communication system and a power supply system for providing power for whole monitoring system, the server comprises a local server and a network server, and the central control unit is separately connected with the server and the systems; the integrated management system comprises a basic information module, an information query module, an application module, a navigation module and a user terminal; the information query module is used for querying matched information; the monitoring system comprises a fixed monitoring device and a movable monitoring device, and the fixed monitoring device comprises a camera, an infrared sensor, a temperature sensor, a smog detector and a warning device. The campus laboratory safety management system performs all-around safety monitoring and management on a laboratory and strengthens monitoring and management on experiment with hazardous material and overnight experiment, once an abnormal condition occurs, the alarm raises in time, the safety of the experiment is ensured, and the economic loss is avoided.
Owner:SUZHOU BAJITE INFORMATION CONSULTING CO LTD
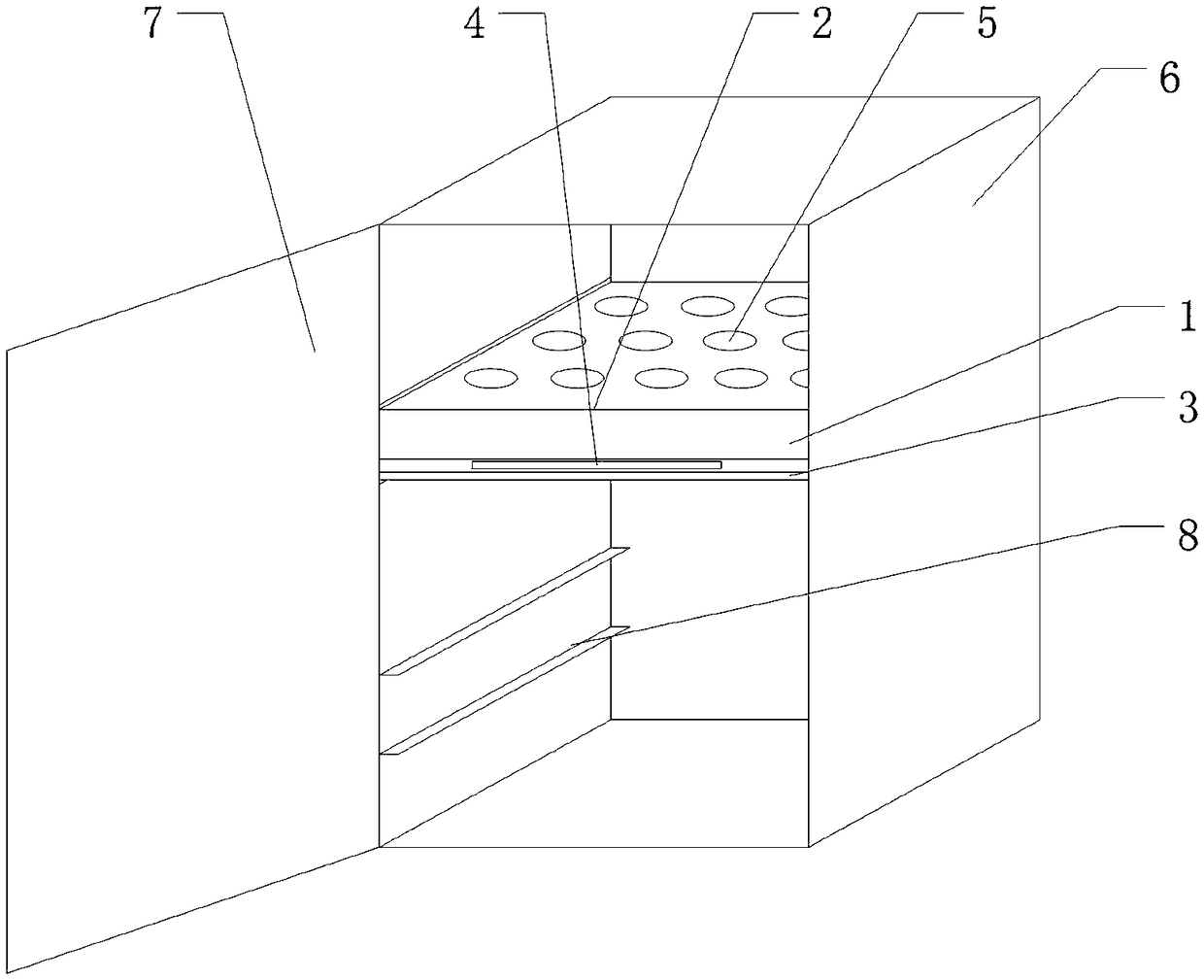
Test tube cleaning device
PendingCN111940439APrevent overflowPrevent spillageHollow article cleaningStructural engineeringLaboratory safety
The invention relates to a cleaning device, in particular to a test tube cleaning device. According to the test tube cleaning device, test tubes can be automatically fixed in batches and then cleaned,the cleaning angle is comprehensive, and the cleaning efficiency and the laboratory safety are improved. The test tube cleaning device comprises a mounting frame and a placing mechanism, and the placing mechanism is arranged between the lower sides in the mounting frame; a lifting cleaning mechanism is also included, and the side, close to the placing mechanism, of the mounting frame is connectedwith the lifting cleaning mechanism; and a rotating mechanism is further included and is arranged on the lifting cleaning mechanism, and the rotating mechanism is connected with the inner top wall ofthe mounting frame. Through cooperation between the placing mechanism and the lifting cleaning mechanism, the test tubes can be placed in a test tube rack to be fixed, an air cylinder is started to drive a lifting plate to slide up and down and drive a connecting rod and a brush to accurately move up and down in the test tubes, the test tubes are automatically and quickly cleaned instead of the hands, and test tube fragmentation and content overflow to injure people due to stress can be effectively avoided.
Owner:郑稳翠
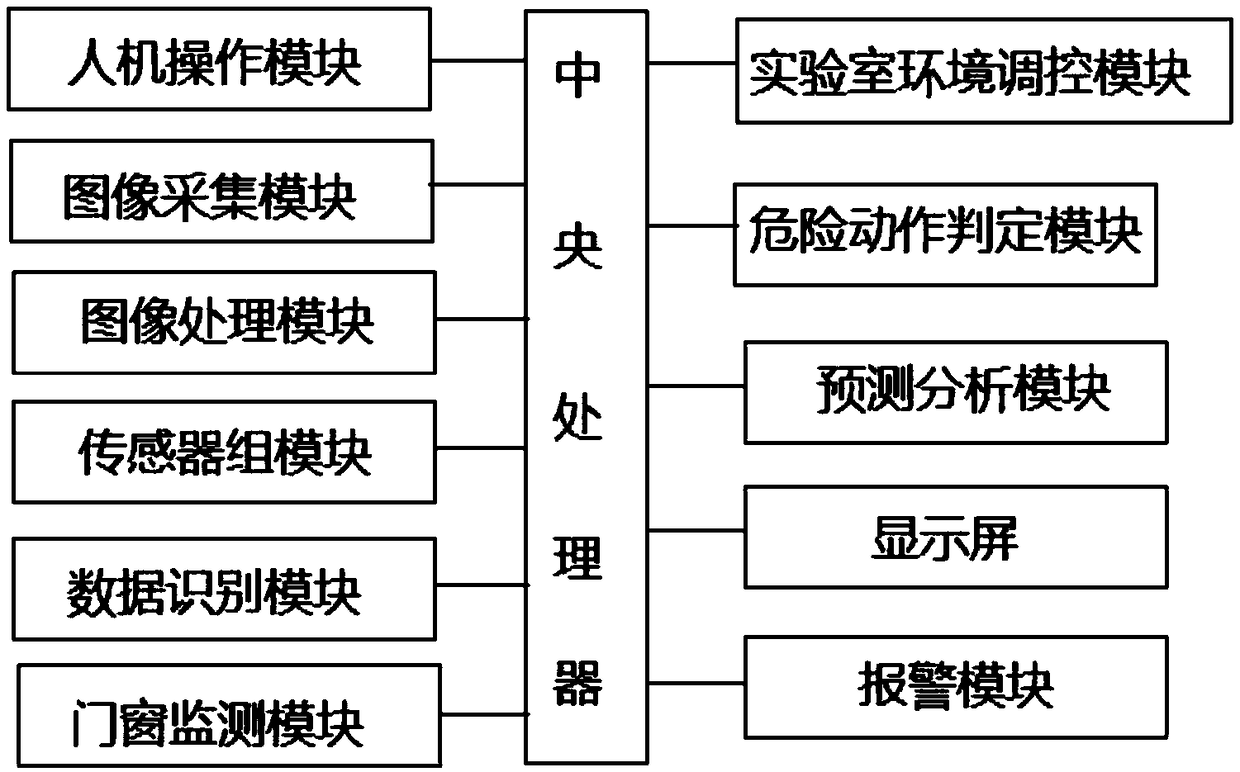
Laboratory safety monitoring system
InactiveCN108829158ARealize all-round monitoringMeasurement devicesSimultaneous control of multiple variablesImaging processingMonitoring system
The invention discloses a laboratory safety monitoring system comprising an image acquisition module, a sensor group module, an image processing module, a danger motion determination module, a prediction analysis module, a central processor and a laboratory environment regulation and control module; the image acquisition module and the sensor group module can work in synergy to omnibearingly monitor the environment in the laboratory; the system has an environment adjusting function, thus ensuring the environmental parameters in the laboratory to be always in a proper scope as possible.
Owner:XIAN AERONAUTICAL POLYTECHNIC INST
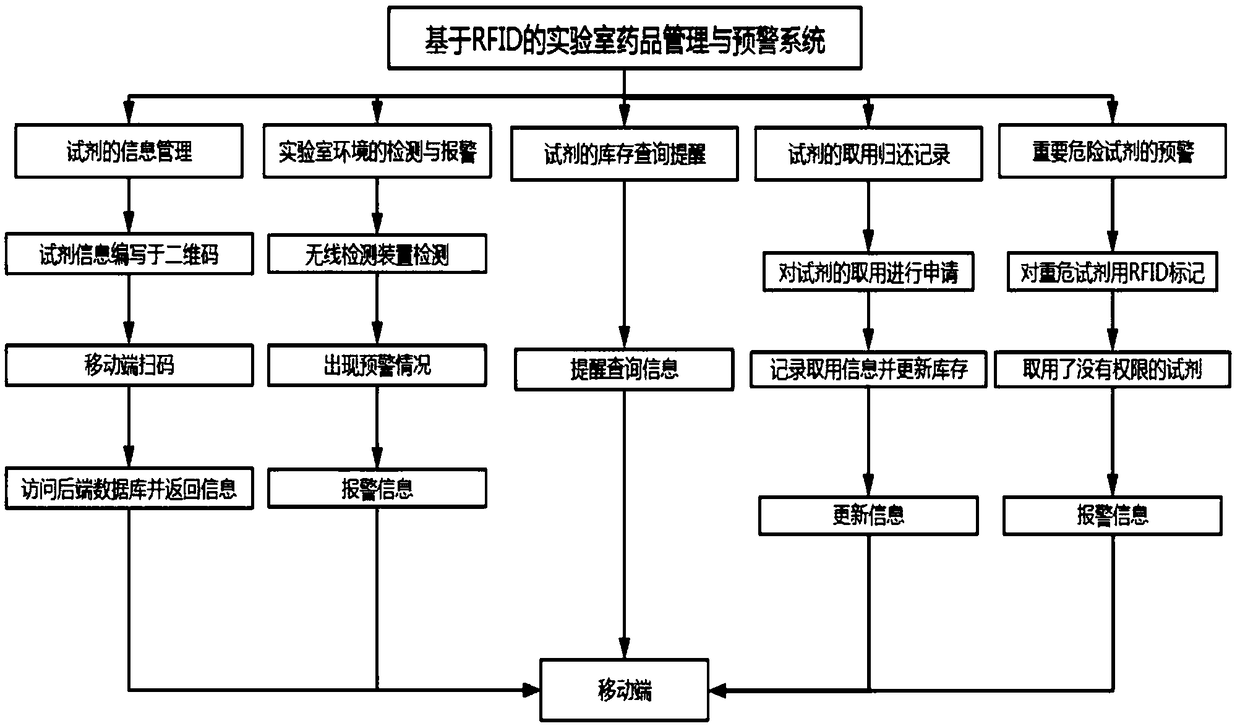
RFID-based laboratory drug intelligent management and early warning system
InactiveCN108898193AImprove securityAvoid lossCo-operative working arrangementsEarly warning systemIntelligent management
The invention relates to an RFID-based laboratory drug intelligent management and early warning system comprising two-dimensional code tags which are used for compiling laboratory drug information; RFID tags which are used for marking the important and dangerous laboratory drugs; a drug management system which records access and the information of the laboratory drugs in real time and realizes thedrug quantity prompting function; a mobile client side which scans the two-dimensional code tags to obtain the laboratory drug information; and an RFID system which binds the specific location of theimportant and dangerous laboratory drugs with the RFID tag reader alerts the mobile client side when the marked laboratory drugs are removed from the location of the specified RFID tag reader. The system is reasonable in design and triggers alarming when the dangerous drugs are taken out of the laboratory so as to prevent loss of the important and dangerous laboratory drugs. The intelligent, accurate and safe laboratory drug management function is realized, the burden of manual management is reduced, the management efficiency is enhanced and the laboratory safety factor is enhanced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
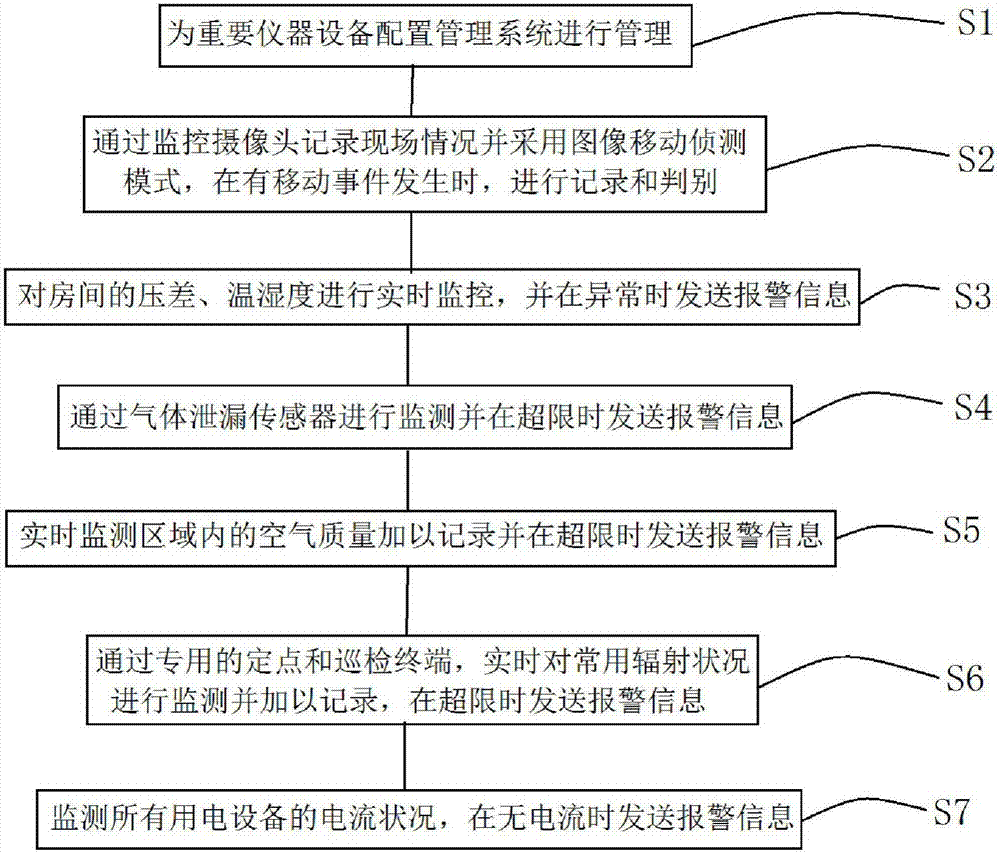
Laboratory safety intelligent management method
InactiveCN107450422AImprove management efficiencyProgramme controlComputer controlResource utilizationElectrical devices
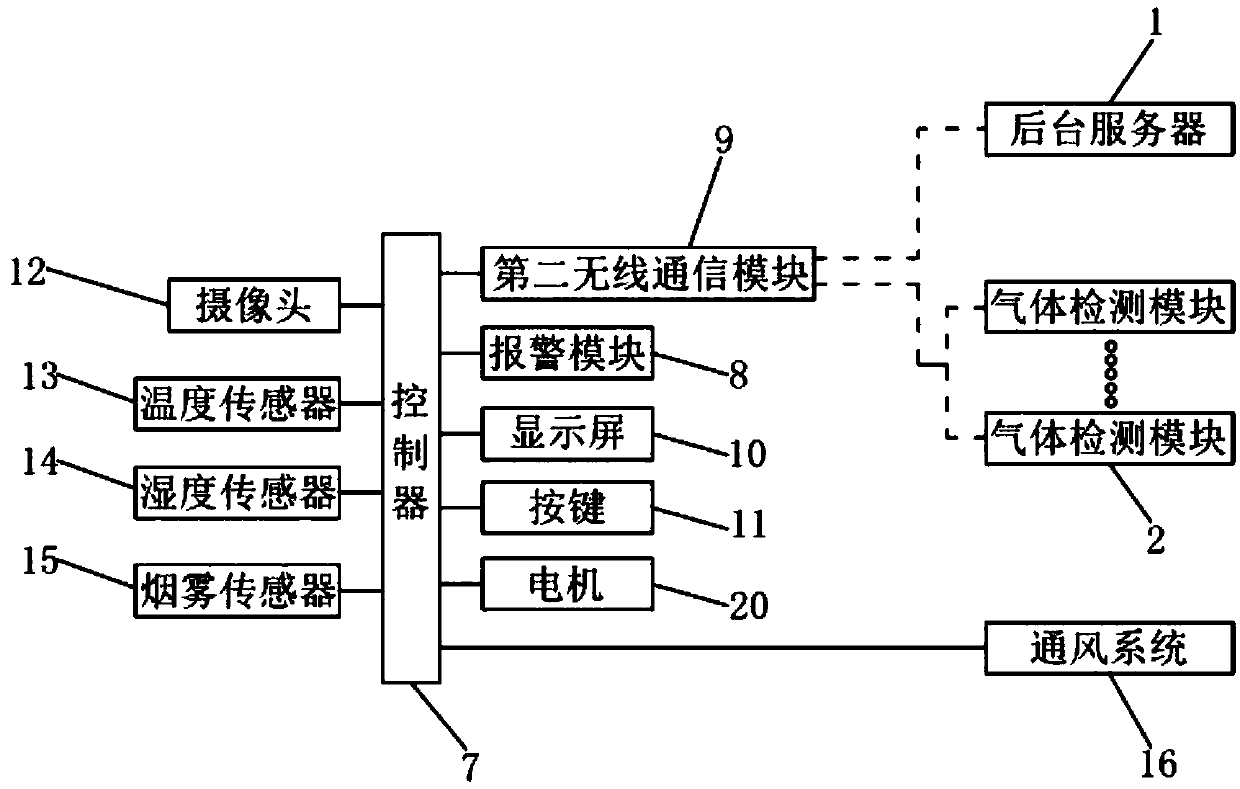
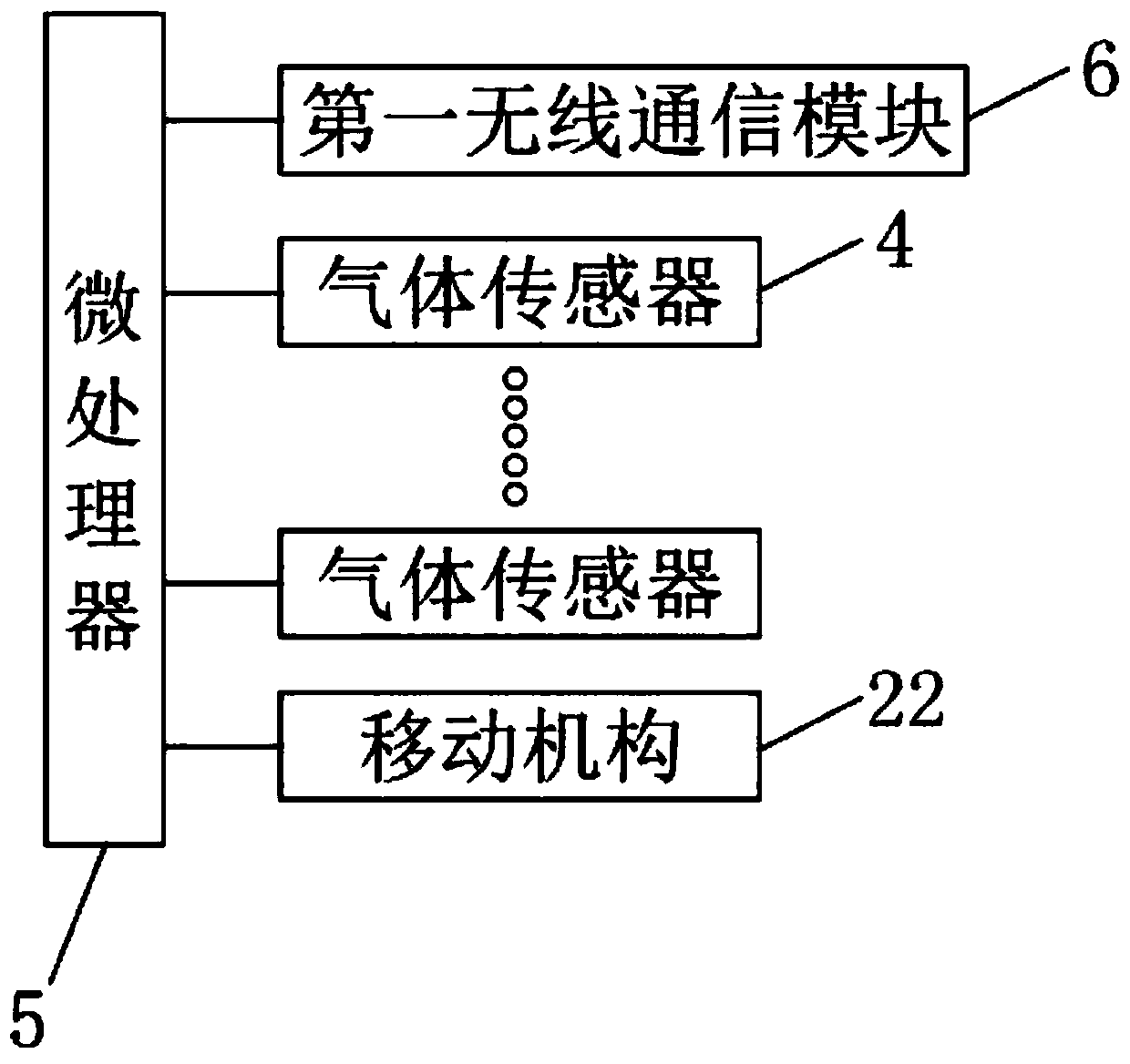
The invention discloses a safety intelligent management method for a laboratory, which includes: configuring a management system for important instruments and equipment for management; recording on-site conditions through a monitoring camera and adopting an image movement detection mode to record and judge when a movement event occurs ;Real-time monitoring of the pressure difference, temperature and humidity of the room, and send an alarm message when it is abnormal; monitor through the gas leakage sensor and send an alarm message when it exceeds the limit; record the air quality in the real-time monitoring area and send an alarm when it exceeds the limit Information; monitor and record common radiation conditions in real time through dedicated fixed-point and inspection terminals, and send alarm messages when the limit is exceeded; monitor the current status of all electrical equipment, and send alarm messages when there is no current; guarantee the laboratory Safety, fully improve management efficiency and resource use efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI QUADJOIN ELECTRONICS TECH
Laboratory safety monitoring system and working method thereof
ActiveCN109030731AEffectively Monitor Security SituationsAvoid harmTransmission systemsMaterial analysisMonitoring systemEngineering
The invention discloses a laboratory safety monitoring system and a working method thereof. The system comprises a background server and a monitoring device, wherein the monitoring device is arrangedin a laboratory and comprises a control device and a hazardous gas detection device, the hazardous gas detection device comprises a railway network and a plurality of gas detection modules, the railway network is arranged at the top of the laboratory in a lattice shape, the plurality of gas detection modules are arranged on the railway network and can move along the railway network, each gas detection module comprises a base, a plurality of different gas sensors are arranged on a lower surface of the base, the gas sensors are encircled in a round shape and are arranged along the round shape atequal distance, a moving mechanism is arranged at the top of the base and can move along a guide rail, a microprocessor and a first wireless communication module are further arranged on the base, andthe control device comprises a controller, a warning module and a second wireless communication module. By the system, the safety condition of the laboratory can be effectively monitored, and warningcan be timely given out when that hazardous gas is leaked from the laboratory is detected.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
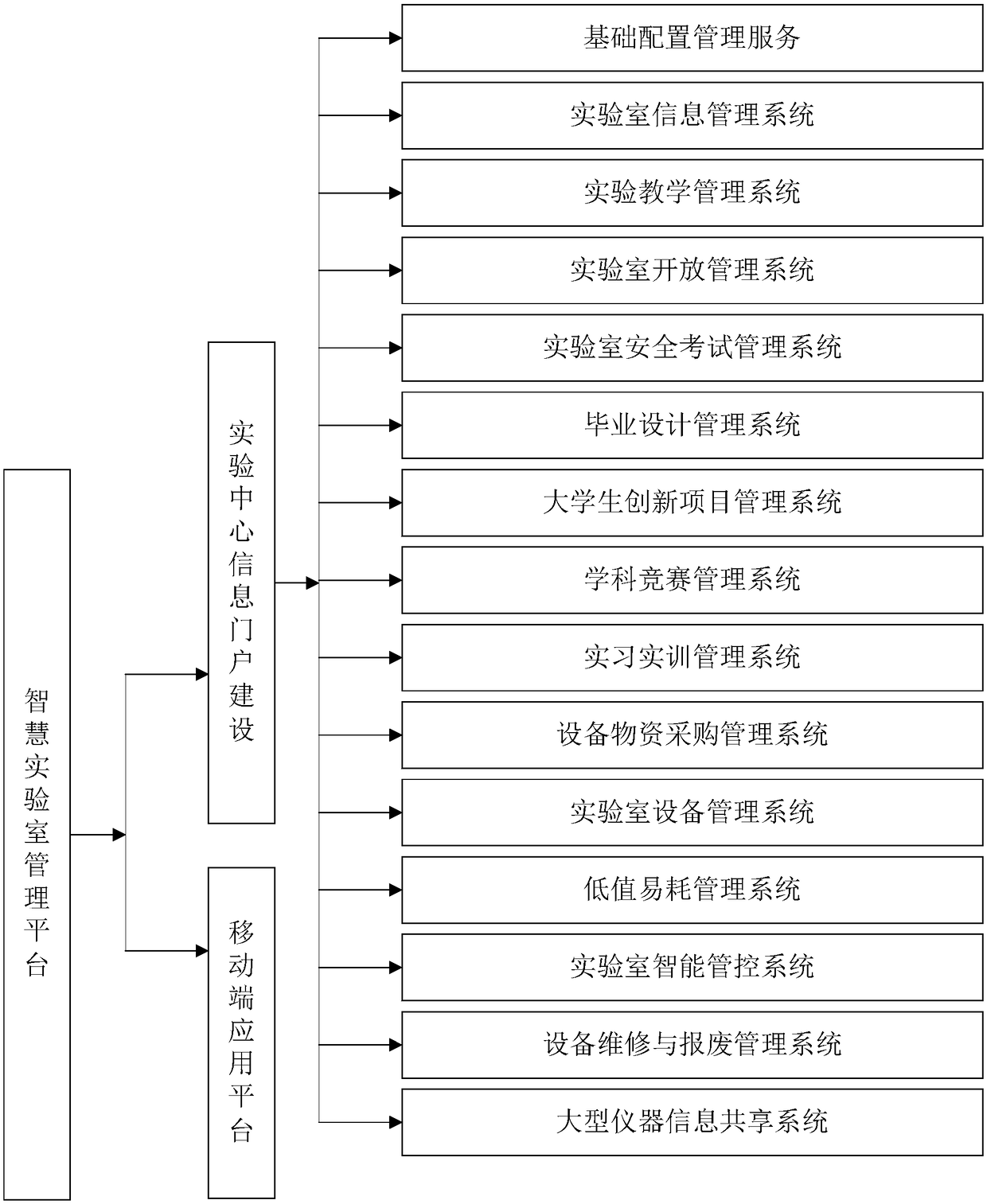
Intelligent laboratory management platform
InactiveCN109191339ARealize data-oriented managementData processing applicationsIndividual entry/exit registersInstrumentationInformation sharing system
The invention discloses an intelligent laboratory management platform, which includes basic configuration management services, a laboratory information management system, an experimental teaching management system, a laboratory open management system, a laboratory safety examination management system, a graduation design management system, an undergraduate innovative project management system, a discipline competition management system, a practice training management system, an equipment and material procurement management system, a laboratory equipment management system, a low-value and easy-to-consume management system, a laboratory intelligent management and control system, an equipment maintenance and scrap management system, a large-scale instrument information sharing system, a laboratory center information portal construction and a mobile application platform based on the same set of basic data and the same management interface. By constructing an intelligent laboratory information management platform, the invention promotes the combination of on-line analysis and off-line management of the laboratory work, realizes the data-oriented management without omission in the practice of all laboratories and teachers and students, and facilitates the later big data analysis.
Owner:广州市昊意科技有限公司
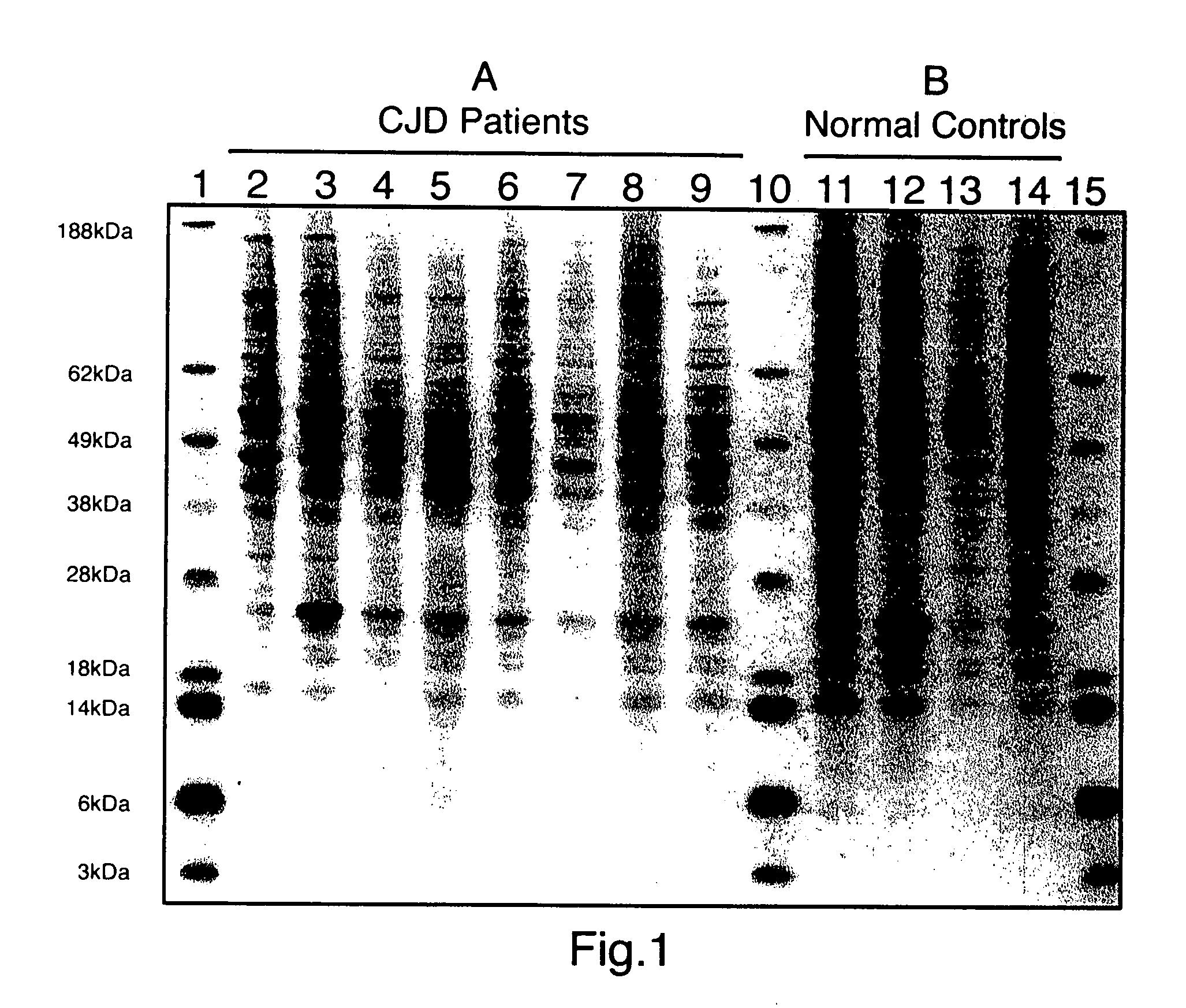
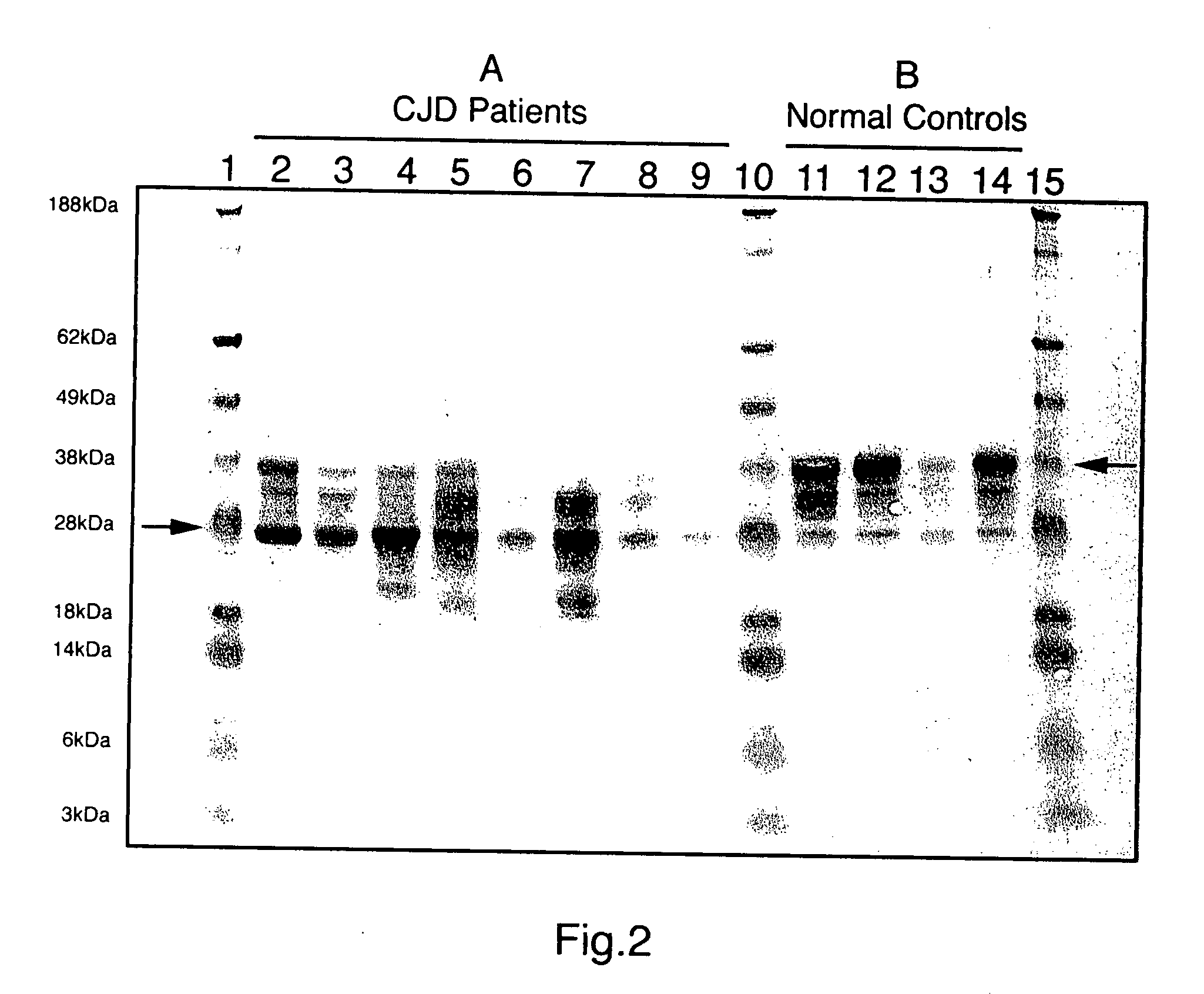
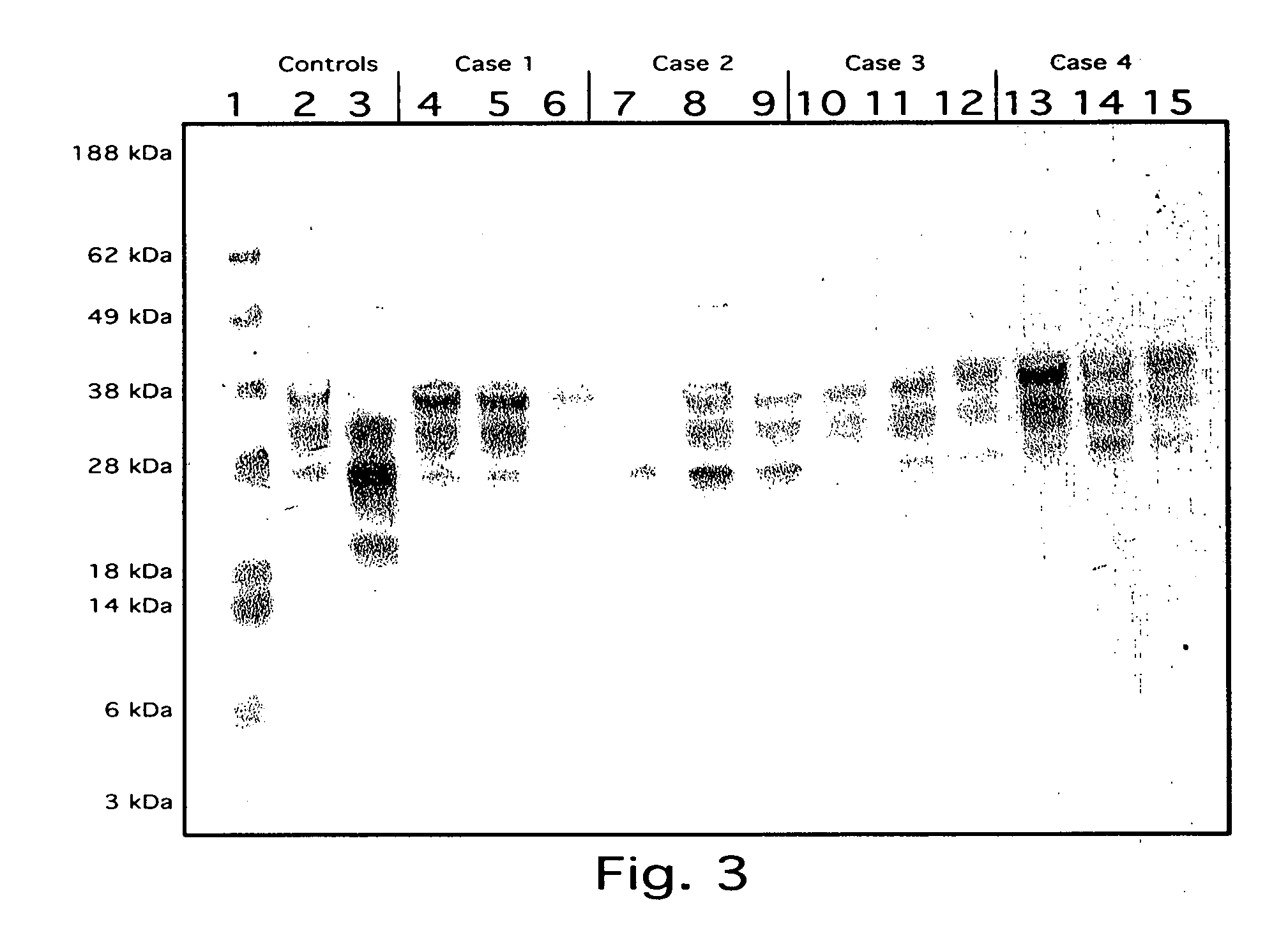
Safe method for isolation of prion protein and diagnosis of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies
InactiveUS20050255525A1Easy to distinguishEffectively infectivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisWestern blotBiology
Provided is a safe novel method for detecting Transmissible Spongiform encephalopathies (TSE). The method comprises: selecting a sample from a subject to determine whether the subject has transmissible spongiform encephalopathy; and detecting abnormal prion protein (Prpes) in the sample. The method detects PrPres without Proteinase-K treatment by disrupting the sample in guanidine thiocyanate lysis solution followed by phenol purification of proteins, and demonstration of the abnormal prion isoform by Western blotting using monoclonal antibodies against prion protein structure. Guanidine salts effectively kill TSE infectivity providing a laboratory safe environment and stabilize biomolecules so TSE samples can be procured in the field and transported to the laboratory in guanidine lysis solution for processing at a later date. This method provides for rapid detection of the abnormal prion isoform diagnostic of TSE and results are easily interpretable based upon very different Western blot patterns for abnormal prion isoform versus the normal prion.
Owner:BASTIAN FRANK OWEN
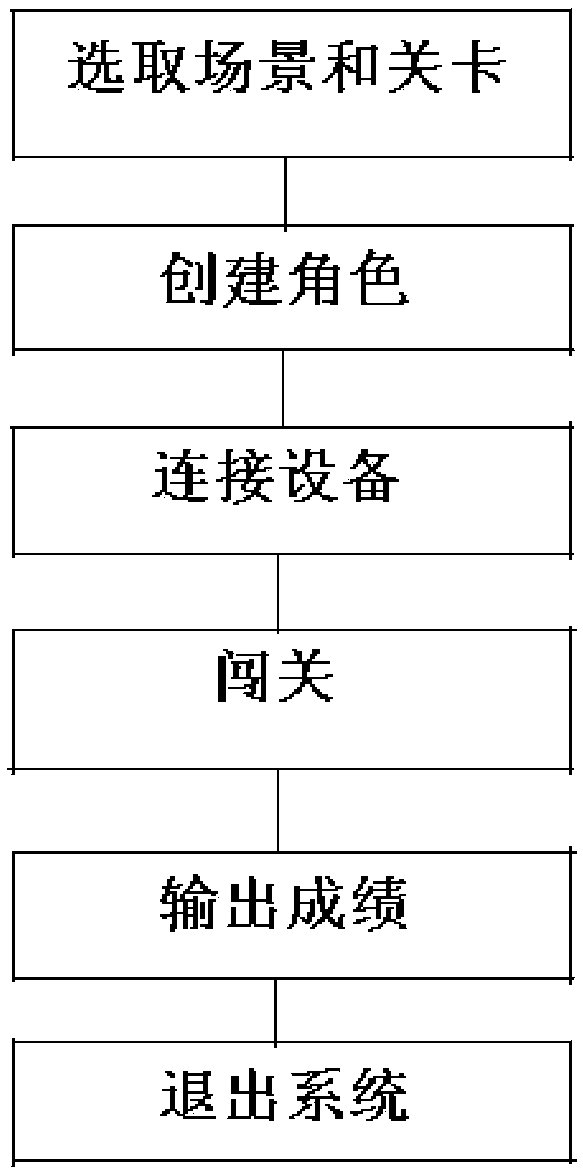
Immersive laboratory security access method
InactiveCN108389457AImprove learning efficiencyIncrease interest in learningInput/output for user-computer interactionCosmonautic condition simulationsAccess methodLaboratory safety
The invention relates to a security access method. An immersive laboratory security access method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting a scene and a level, (2) creating a role, (3) connectinga device, (4) defeating the level, (5) outputting a result, and (6) logging out a system. The method introduces a game mode into teaching, and immerses the user in a three-dimensional laboratory scenethrough VR technology, thereby bringing a real sense of manipulation to the students. Therefore, the learning efficiency of students is improved through hands-on operation, students' interest in learning is stimulated, the drawbacks of traditional teaching modes are tackled, and the quality of students' learning is greatly improved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
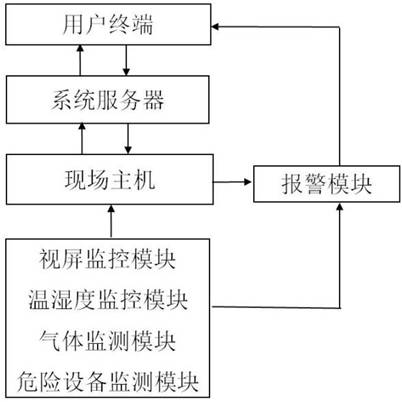
Intelligent safety early warning system for laboratory
PendingCN112904785AImprove safety management efficiencyEffective judgmentProgramme controlComputer controlVideo monitoringServer
The invention relates to an intelligent safety early warning system for a laboratory. The intelligent safety early warning system comprises a video monitoring module, a temperature and humidity monitoring module, a gas monitoring module, a dangerous equipment monitoring module, a system server, an on-site host, a computer program of the on-site host and an alarm device. According to the invention, a traditional on-site checking mode depending on a laboratory administrator is changed, the laboratory dangerous situation can be effectively judged through real-time dynamic data of videos and environment and equipment parameters, multi-level linkage intelligent safety early warning based on laboratory video monitoring, environment monitoring and dangerous equipment monitoring is realized, the early warning capability is improved, the risk is avoided in adavance, and the safety management efficiency of the laboratory is greatly improved.
Owner:LUOYANG TMAXTREE BIOTECH CO LTD
Intelligent terminal control system for laboratory safety
InactiveCN108536066AReliable Connection Guarantee MechanismGuaranteed real-time data transmissionProgramme controlComputer controlRadio frequencyTerminal system
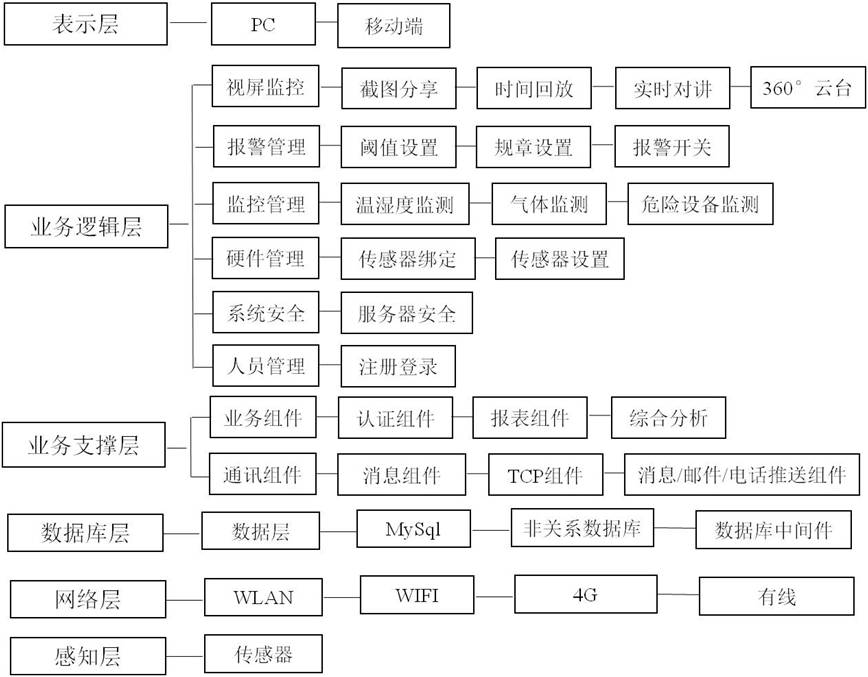
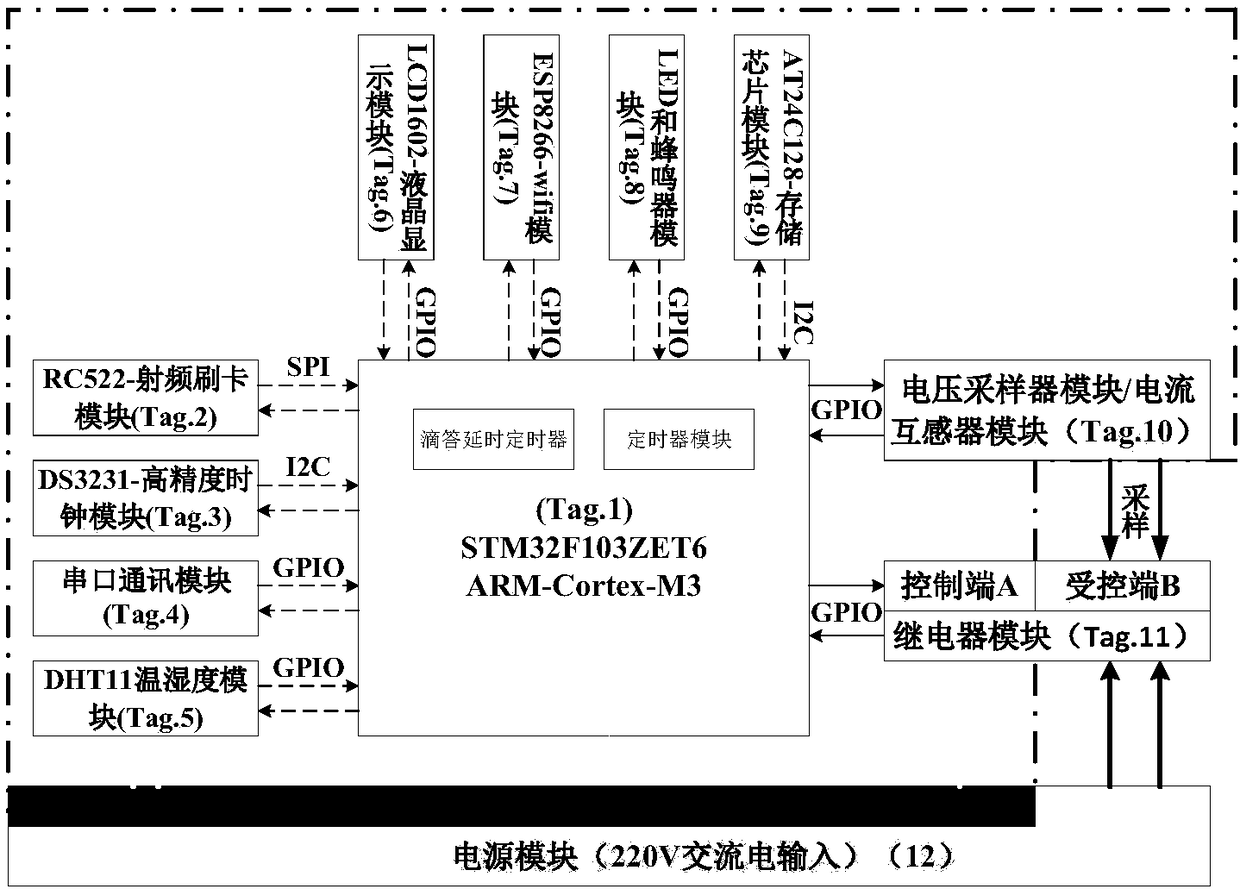
The invention relates to an intelligent terminal control system for laboratory safety. The terminal system is an intelligent terminal control system which is designed based on an ARM processor and achieves centralized server control and accurate multi-sensor data sampling according to the principle of on-demand service. The control system comprises a main control chip module with ARM-CortexM3 as the core as well as a radio frequency card reading module, a high-precision clock module, a serial communication module, a temperature and humidity module, a liquid crystal display module, a wireless WIFI module, an LED and buzzer module, a storage module, an alternating voltage sampler module and current transformer module and a relay module which are connected with the main control chip module respectively. Compared with the prior art, the system has the advantages that the laboratory management level is intelligently improved and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Internet of things based safety management device for school laboratory
InactiveCN109507919AEasy to understandQuick understandingProgramme controlComputer controlVideo monitoringOperational system
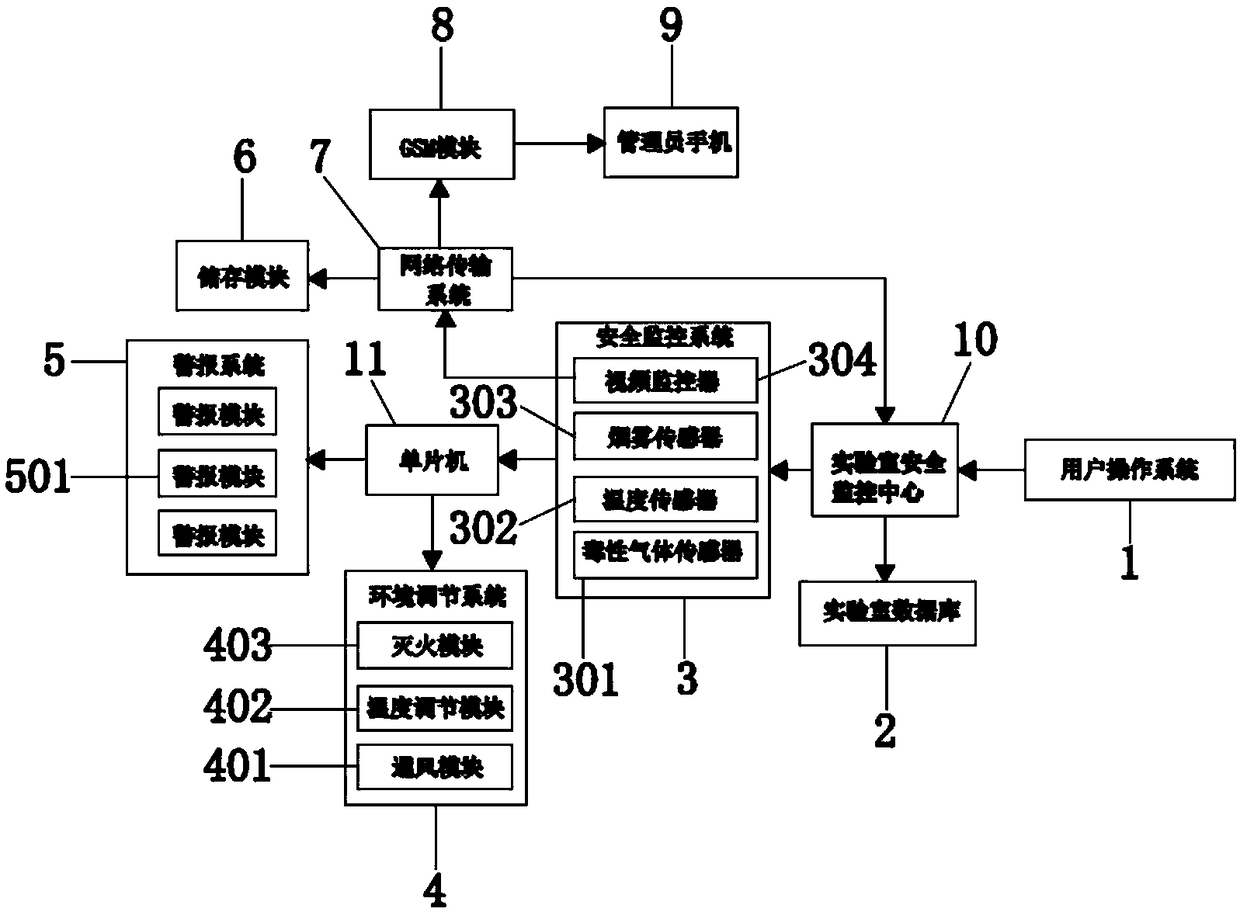
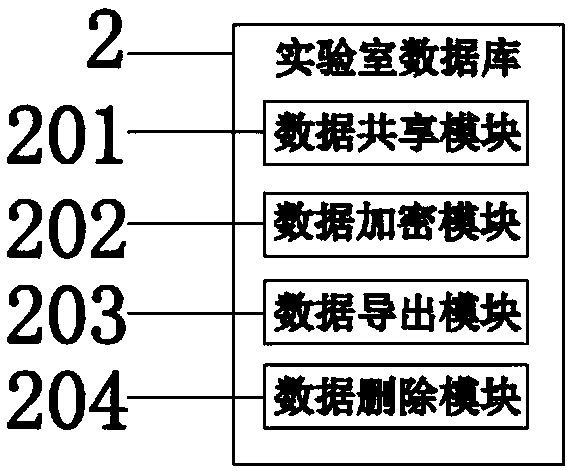
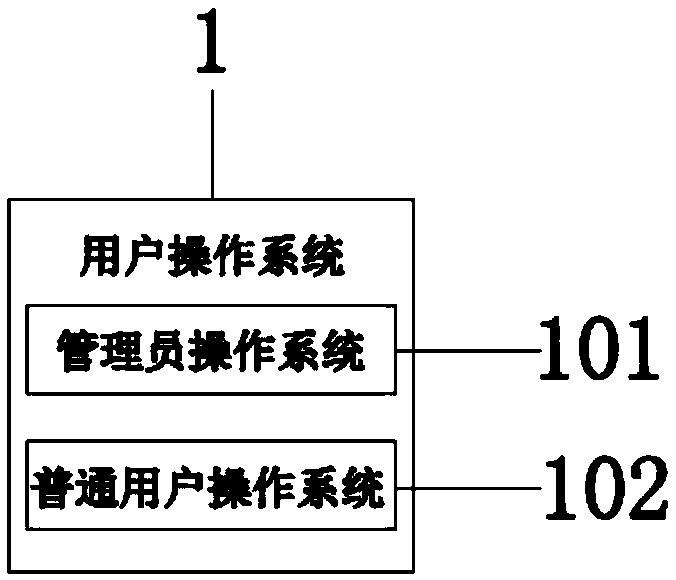
The invention relates to the technical field of laboratory management, and particularly relates to an Internet of things based safety management device for a school laboratory. The device comprises alaboratory safety monitoring center, wherein an output end of the laboratory safety monitoring center is connected with a user operating system, a laboratory data base and an input end of a safety monitoring system in a circuit manner; the safety monitoring system comprises a toxic gas sensor, a temperature sensor, a smoke sensor and a video monitor; an output end of the video monitor is connectedwith an input end of a network transmission system in the circuit manner; and an output end of the network transmission system is connected with an input end of a GSM (Global System for Mobile communication) module in the circuit manner. The device is used for reliably carrying out real-time monitoring and management through multiple monitoring and transmission ways; a manager is enabled to be capable of conveniently and quickly knowing the safety protection state information of the laboratory, is used for greatly improving the management efficiency of the laboratory, and can be used for managing the environment of the laboratory; thus, the utilization of the laboratory is more scientized; and the quality of experimental teaching is effectively promoted.
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
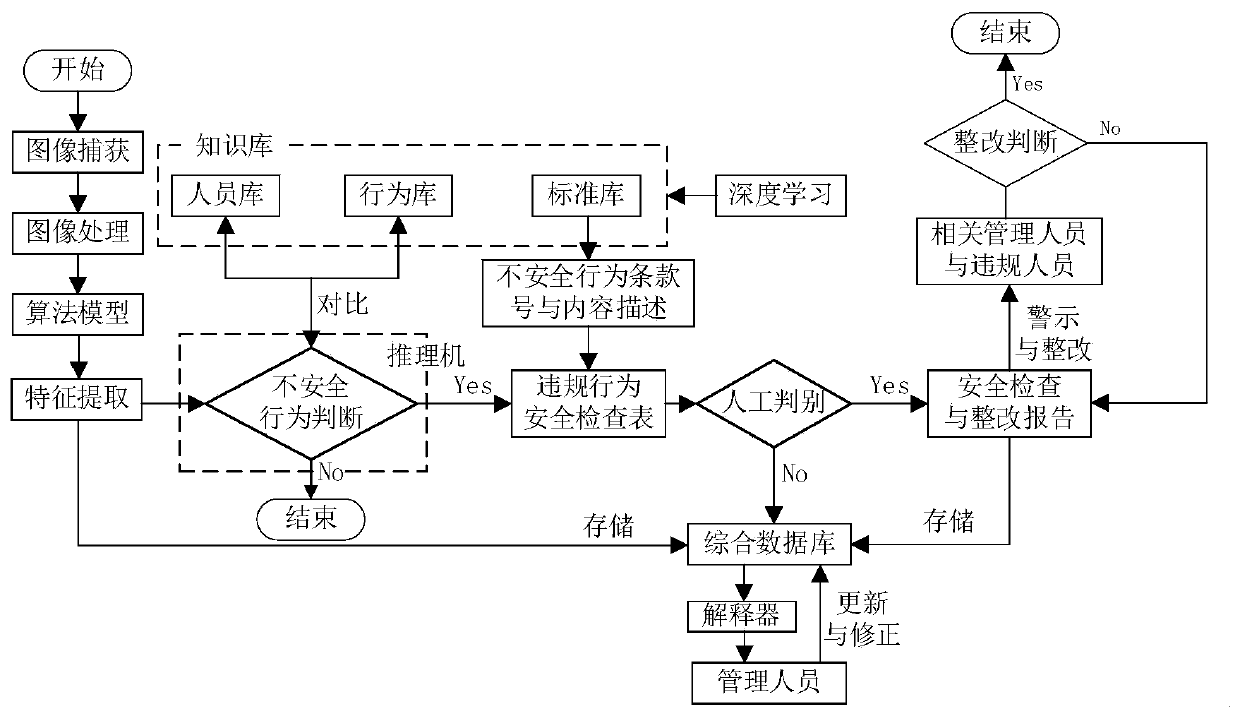
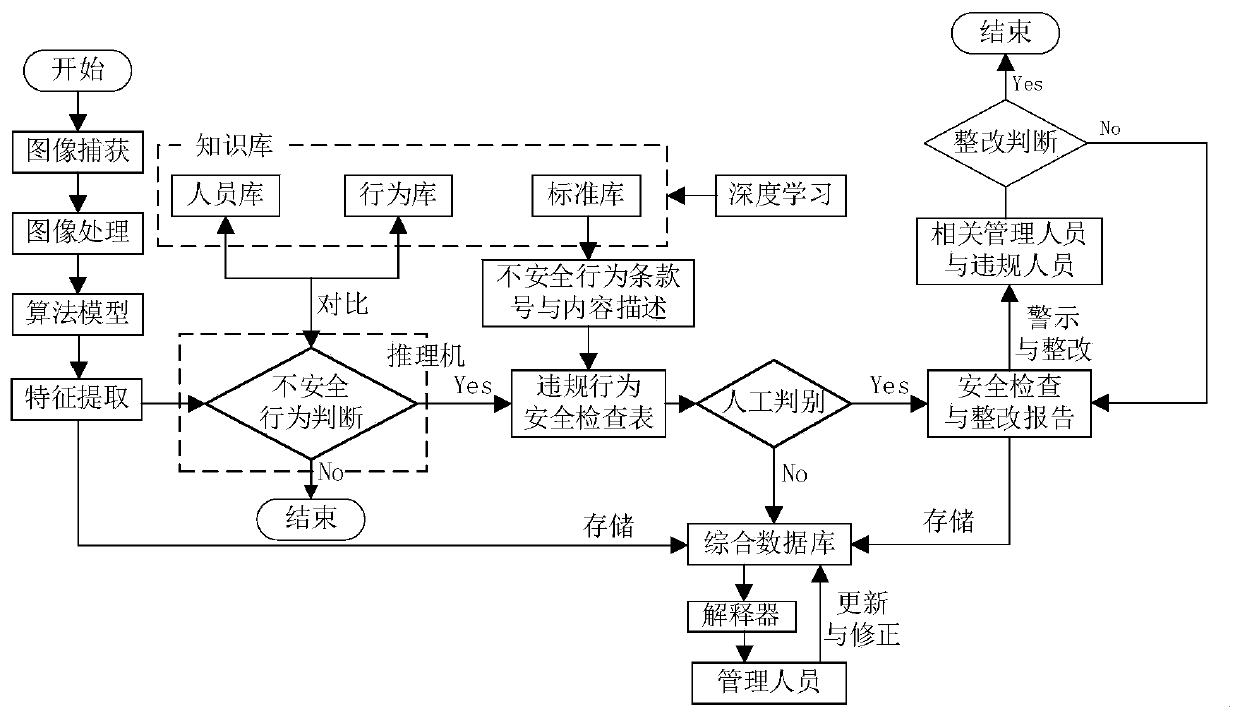
Laboratory personnel unsafe behavior safety inspection method based on machine vision
InactiveCN111177468AImplement automated security checksCheck in real time 24/7Digital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman bodyFeature set
The invention provides a laboratory personnel unsafe behavior safety inspection method based on machine vision. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, determining the identity of laboratory personnel and whether the laboratory personnel meet laboratory safety admission conditions by adopting a face recognition system; using an image sensor for collecting video images of the laboratorypersonnel; after image processing, extracting a human body behavior feature set, and determining whether the laboratory personnel performs a unsafe operation or has unsafe behaviors or not according to the human body behavior feature set; if yes, a searching for a corresponding unsafe behavior term number in a laboratory safety inspection standard library database, and giving the content description of the unsafe behaviors; generating a safety inspection table of the violation behaviors of the laboratory personnel, sending the safety inspection table to the management personnel, generating a formal safety inspection report after confirmation, sending the formal safety inspection report to the violation personnel and the related management personnel, and carrying out warning and responsibility rectification; and continuously supervising and inspecting the unsafe behaviors of the violation personnel within a specified rectification period until the rectification is finished.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Automatic face identification safety examination system
ActiveCN107967660AIncrease stringencyData processing applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionPersonalizationData information
The invention provides an automatic face identification safety examination system. The system comprises a monitoring camera and a test device, wherein the monitoring camera and the test device are both in communication connection with a cloud server, the monitoring camera is used for shooting faces of students and acquiring face characteristic data of the students in a fixed time and transmittingthe face characteristic data to the cloud server, the face characteristic data corresponds to the students in a one-to-one correspondence, and the cloud server is used for searching examinee identifiers according to the face characteristic data information, automatically acquiring question keywords according to the examinee identifiers and constructing test questions issued to the students. The system is advantaged in that a problem that the current laboratory safety test can not achieve adequate room conditions, personalization and differentiation in the prior art is solved, targeted and morespecific safety exam training can be organized, and problems of poor monitoring of online security exams, easily-generated surrogate exam-taking phenomena, frauds and other issues are solved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHINESE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Intelligent management system for laboratory safety
ActiveCN108107778AEfficient discoveryAvoid safety hazardsProgramme controlMeasurement devicesPower usageIntelligent management
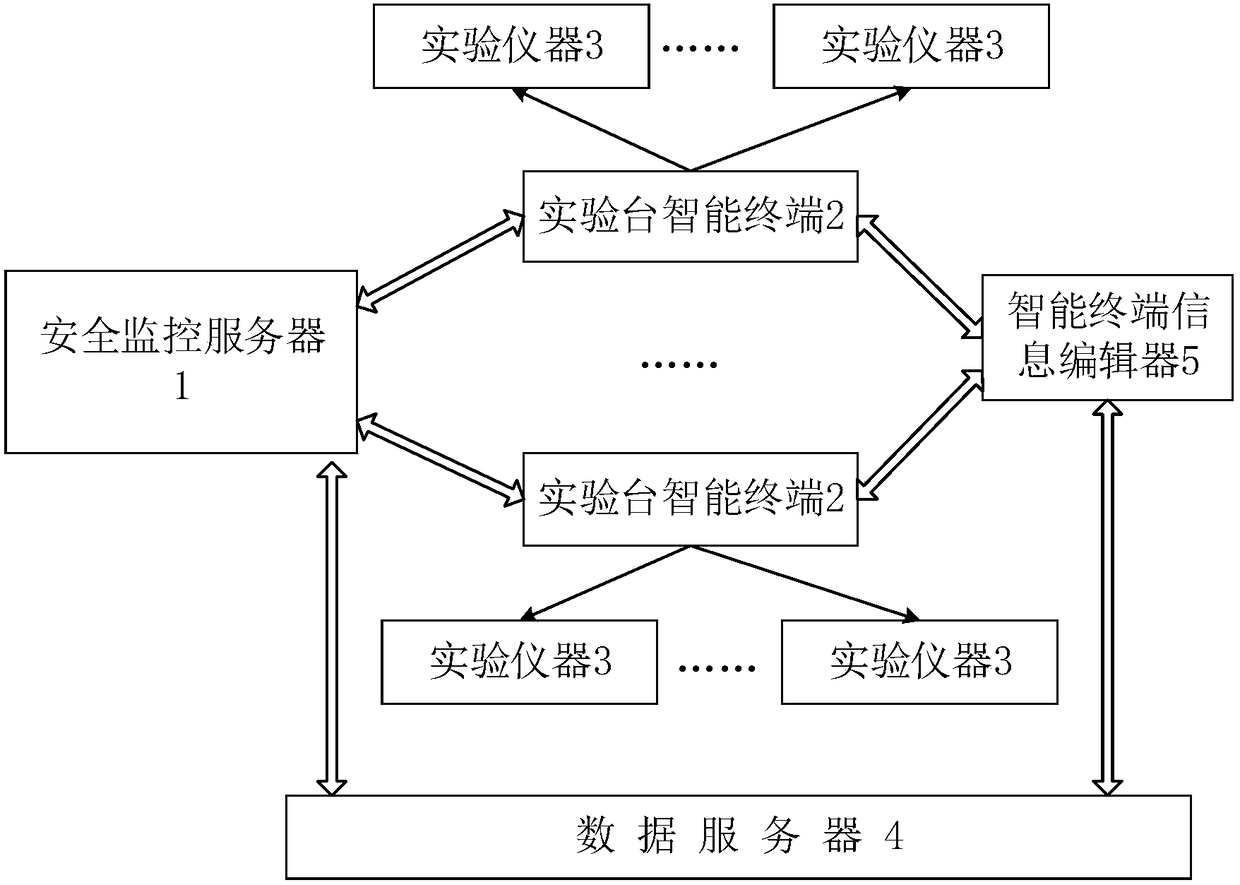
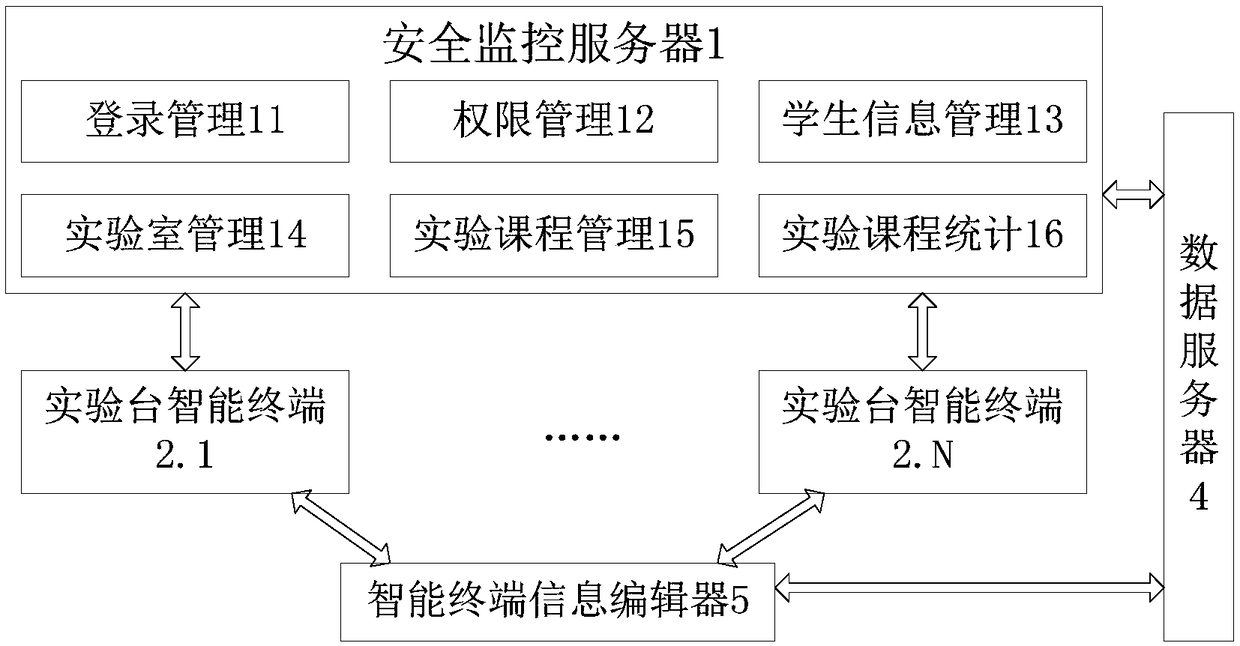
The invention relates to an intelligent management system for laboratory safety. The intelligent management system comprises a safety monitoring server, an experimental table intelligent terminal, anexperimental apparatus, a data server and an intelligent terminal information editor. The safety monitoring server interacts with the experimental table intelligent terminal so as to timely acquire the current experimental states of respective experimental tables in a laboratory, including the student's experiment state, the power usage state, the temperature and humidity states of the experimental tables and the like, and store the information in the data server. The experimental table intelligent terminal timely acquires the student sign-in and sign-out information of the current experimental table, the current power usage states and the current temperature and humidity states of respective experimental apparatuses on the experimental table, and on the one hand, reports the state information to the safety monitoring server, and on the other hand, obtains the instructions of the safety monitoring server, and then operates the current experimental table. Compared with the prior art, the intelligent management system can efficiently and timely find out an abnormally operating device and avoid the safety hazards.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
College laboratory safety management device based on Internet of Things
PendingCN110868454ASafe and efficient managementGuaranteed reliabilityData processing applicationsAlarmsThe InternetSecurity alarm
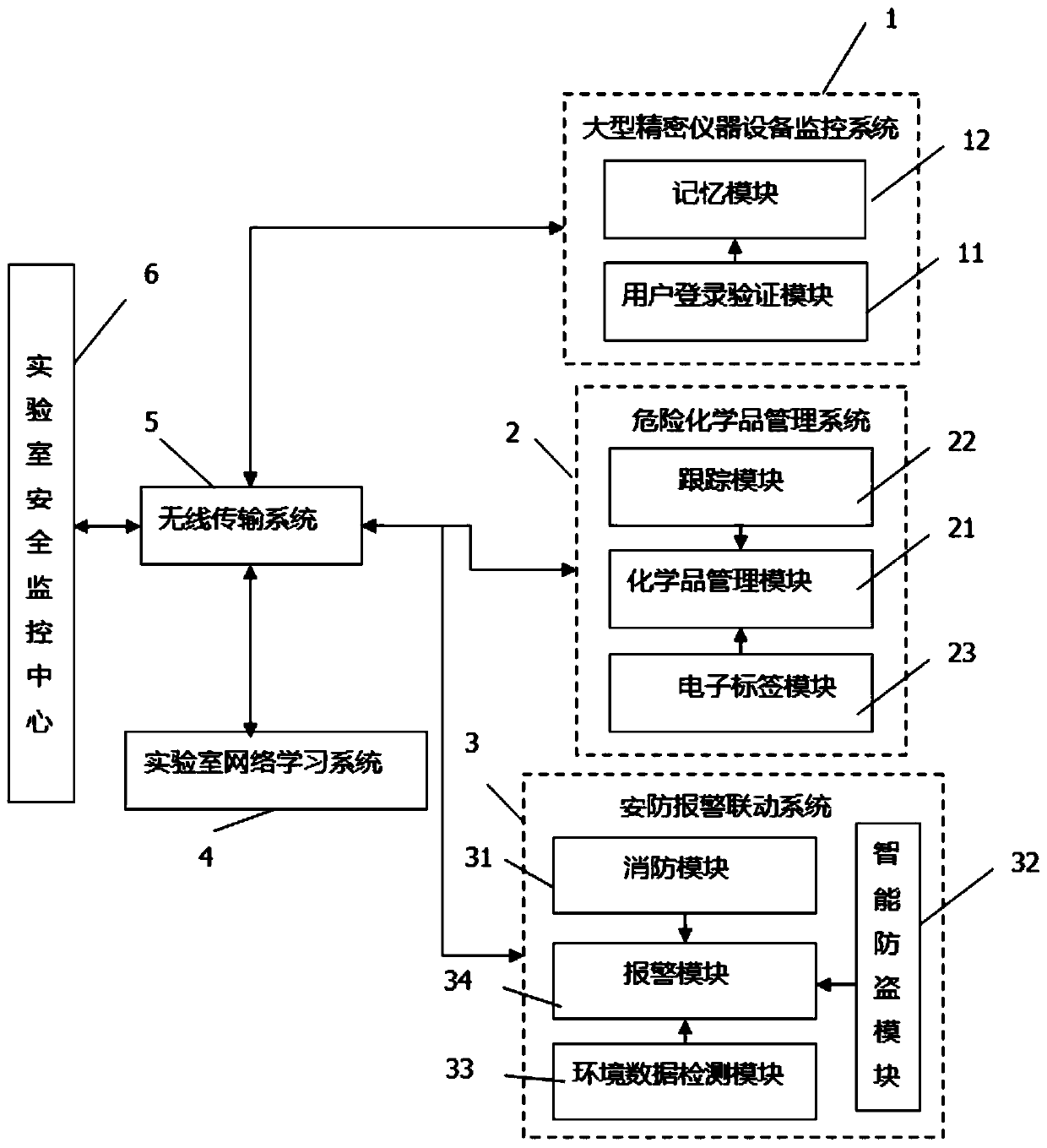
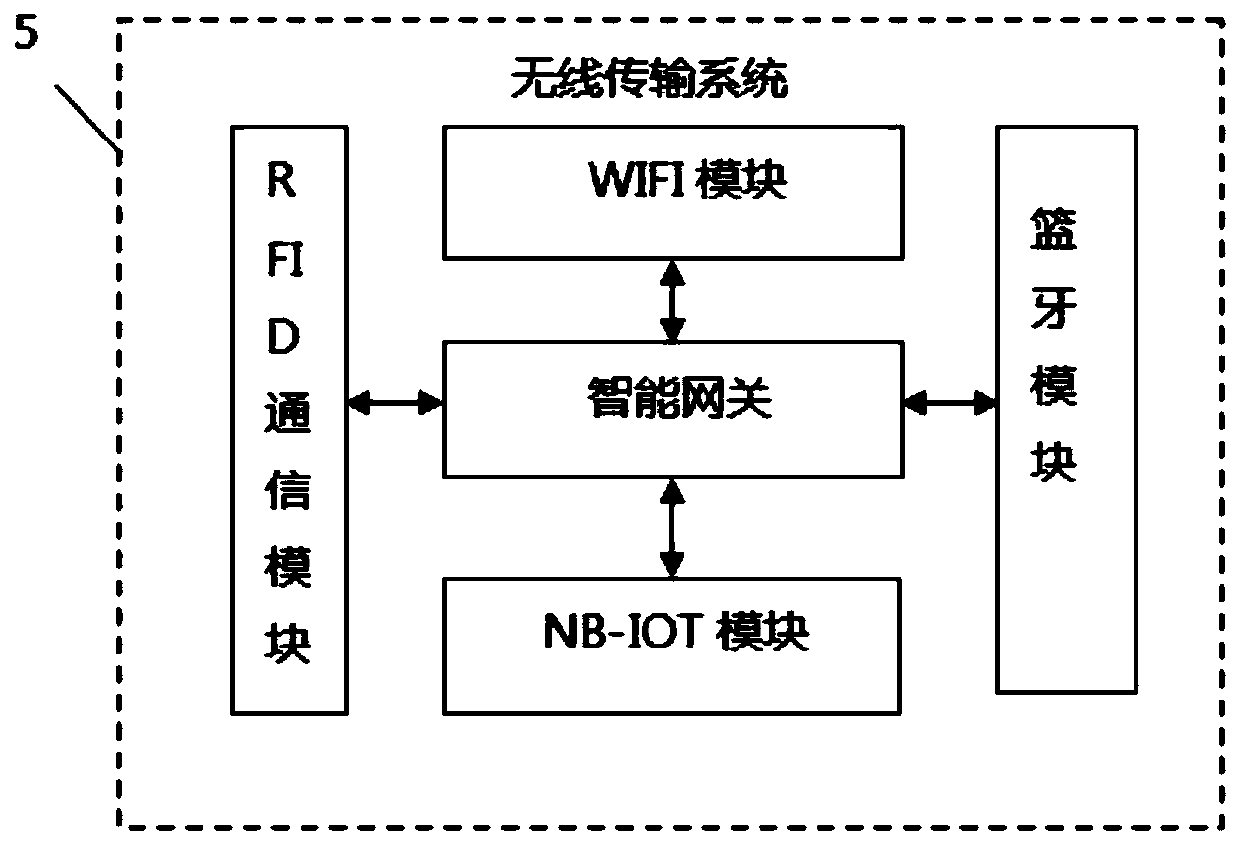
The invention provides a college laboratory safety management device based on the Internet of Things. The college laboratory safety management device comprises a large precise instrument equipment monitoring system, a dangerous chemical management system, a security alarm linkage system, a laboratory network learning system, a wireless transmission system and a laboratory safety monitoring center.The large precise instrument equipment monitoring system is used for monitoring the operation state and the use time of the large precise instrument equipment; the dangerous chemical management system comprises a chemical management module and a tracking module used for recording the whole life cycle process of dangerous chemicals from use to destruction. The security alarm linkage system comprises a fire protection module, an intelligent anti-theft module, an environment data detection module and an alarm module, all the systems are in linkage cooperation, so that the laboratory management process is safer and more efficient, and meanwhile the resource use benefit is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG IND & TRADE VACATIONAL COLLEGE
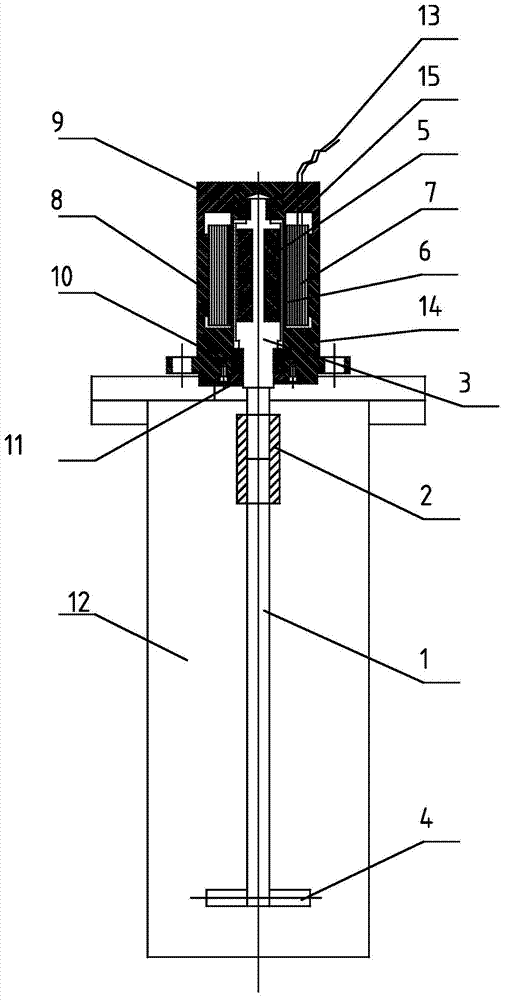
Permanent magnet coupling sealing motor stirring device
InactiveCN103585914AImprove securityReasonable designRotary stirring mixersMechanical energy handlingCouplingEngineering
The invention discloses a permanent magnet coupling sealing motor stirring device. The permanent magnet coupling sealing motor stirring device comprises a stirring shaft, a cavity body and an inner rotor, wherein the stirring shaft is positioned in the cavity body; the lower end of the stirring shaft is provided with a stirrer, and the upper end of the stirring shaft is connected with the inner rotor through a coupler; the periphery of the inner rotor is provided with a permanent magnet, the upper end of the inner rotor is sleeved on an upper bearing, the lower end of the inner rotor is sleeved on a lower bearing, and an isolation hood is arranged outside the permanent magnet; a coil is arranged outside the isolation hood, the coil is connected with a power line, and a positioning sleeve is arranged outside the coil. The permanent magnet coupling sealing motor stirring device disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the design is reasonable, the practicability is good, the coil and the inner rotor can realize full isolation through the isolation hood, a sealing cavity body and the exterior are fully isolated, the permanent magnet coupling sealing motor stirring device can realize well mixing and stirring, a condition that a chemical article leaks to cause serious damage is prevented, and the laboratory safety is strengthened.
Owner:张良光
Laboratory safety monitoring and guidance system
ActiveCN109116794AEnsure safetyAvoid lossProgramme controlComputer controlGuidance systemLaboratory safety
The invention discloses a laboratory safety monitoring and guidance system comprising a laboratory body, an identity verification module, and an experimental platform. A safety door is arranged at theentrance of the laboratory body. The identity verification module includes a fingerprint inputting unit, a user database and a processing unit; the processing unit controls the safety door to be opened after fingerprint comparison success. The experimental platform includes a reagent bench, a monitoring unit and an early warning unit; the monitoring unit monitors types and usage amounts of used reagents in an experiment; an early warning database, an alarm device and a first camera are arranged inside the early warning unit; the first camera starts shooting to shoot an image in front of the reagent bench when any one of dangerous experimental reagent combination unit or a certain dangerous reagent is used; and the alarm device carries out alarming when the any one of dangerous experimental reagent combination unit is used or the usage amount of the dangerous reagent exceeds a limit. Therefore, the experimental process is monitored; and when any potential hazard occurs, early warning is carried out timely to protect the safety of the personnel and property.
Owner:贵州众创仪云科技有限公司
Method and system for monitoring and early warning experimental device based on artificial intelligence
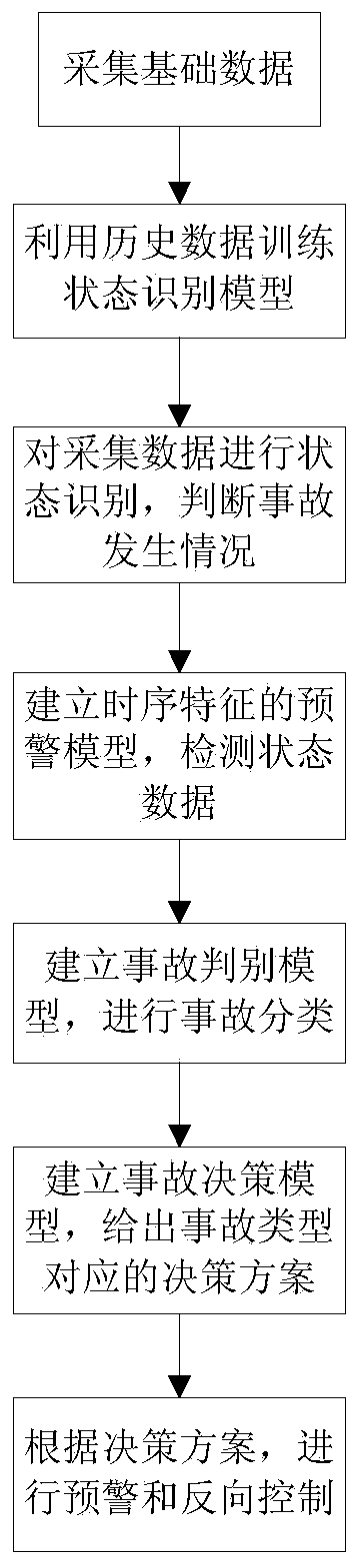
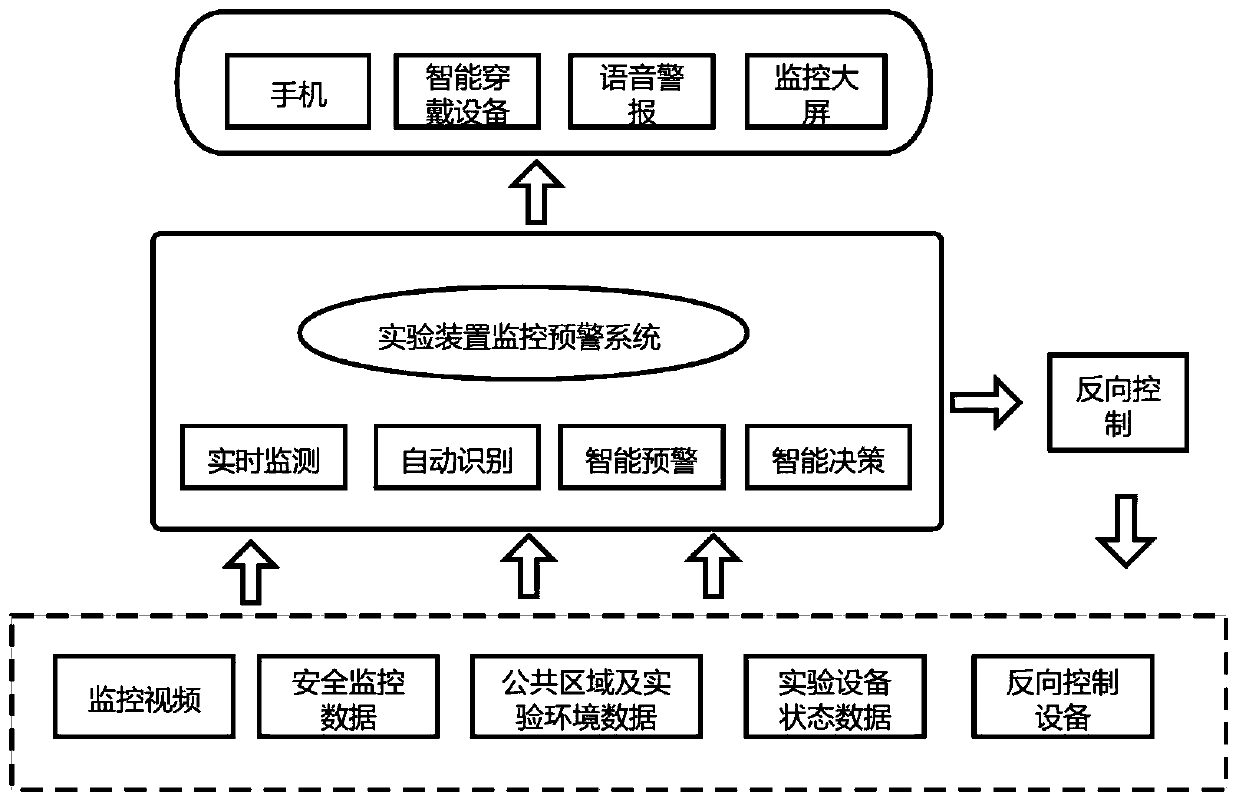
ActiveCN111464793ARespond quicklyComprehensive monitoring rangeStill image data indexingCharacter and pattern recognitionAutomatic controlEngineering
The invention discloses a method and a system for monitoring and early warning an experimental device based on artificial intelligence, and the method comprises the steps: judging the type of an accident according to monitoring contents, and giving an early warning to an administrator; and making and providing auxiliary decisions and intelligent control decisions for laboratory managers and central control center managers. According to the invention, the influence of the current state of the experimental device and the abnormal experimental data on the laboratory safety is considered, the monitoring range is more comprehensive, and the monitoring and early warning accuracy is more accurate; the artificial intelligence technology is introduced into the experiment monitoring and early warning process, automatic early warning can be conducted on accidents which do not happen on the basis of historical data, auxiliary decisions can be given, automatic control can be conducted in time in emergency, damage can be stopped in time, and personal safety can be guaranteed; in addition, various early warning modes such as a mobile phone, an intelligent wearable device, a voice alarm and a large monitoring screen are adopted, and an administrator can be assisted in quickly making a response.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com