Patents
Literature
78results about How to "Flexible limit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
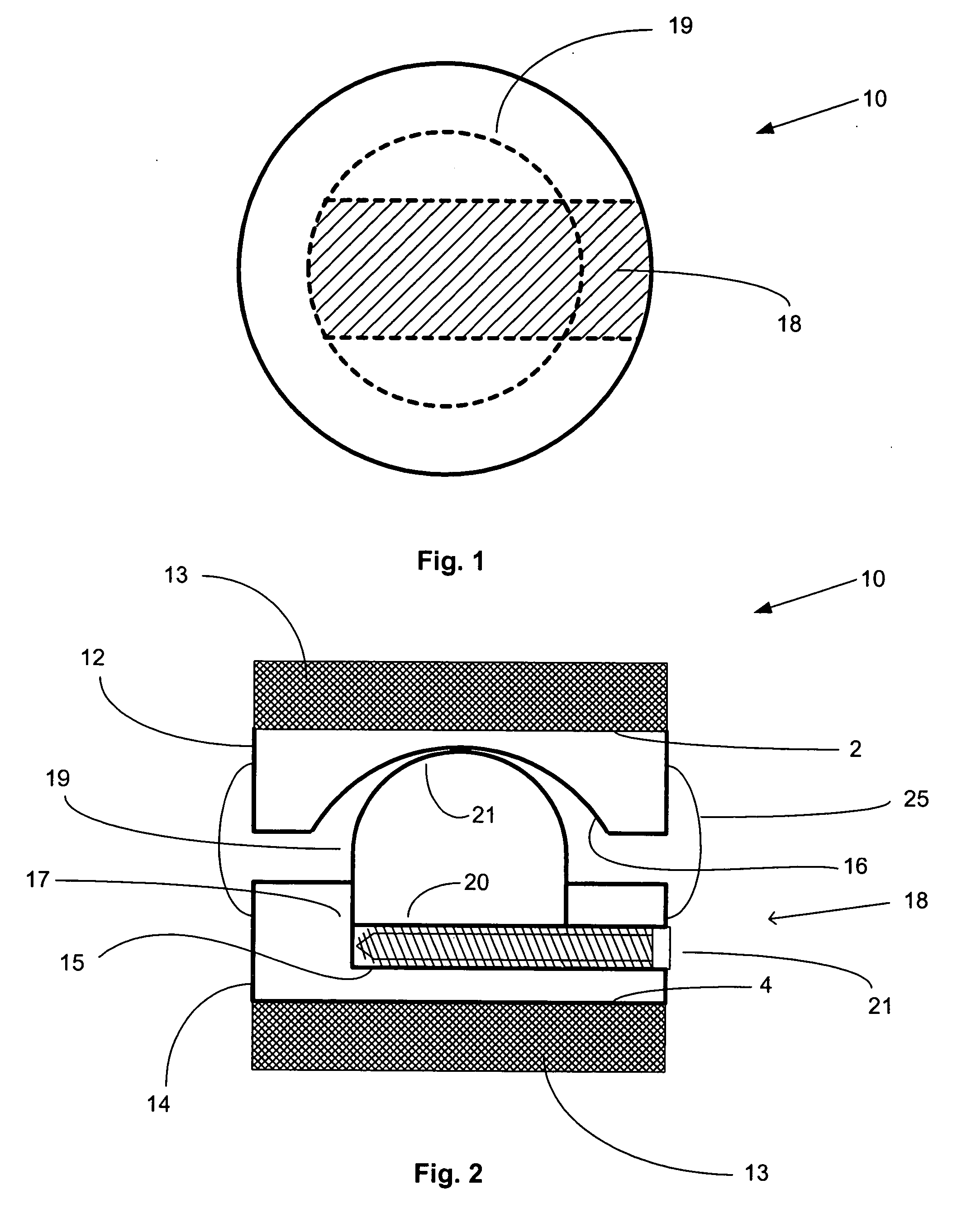
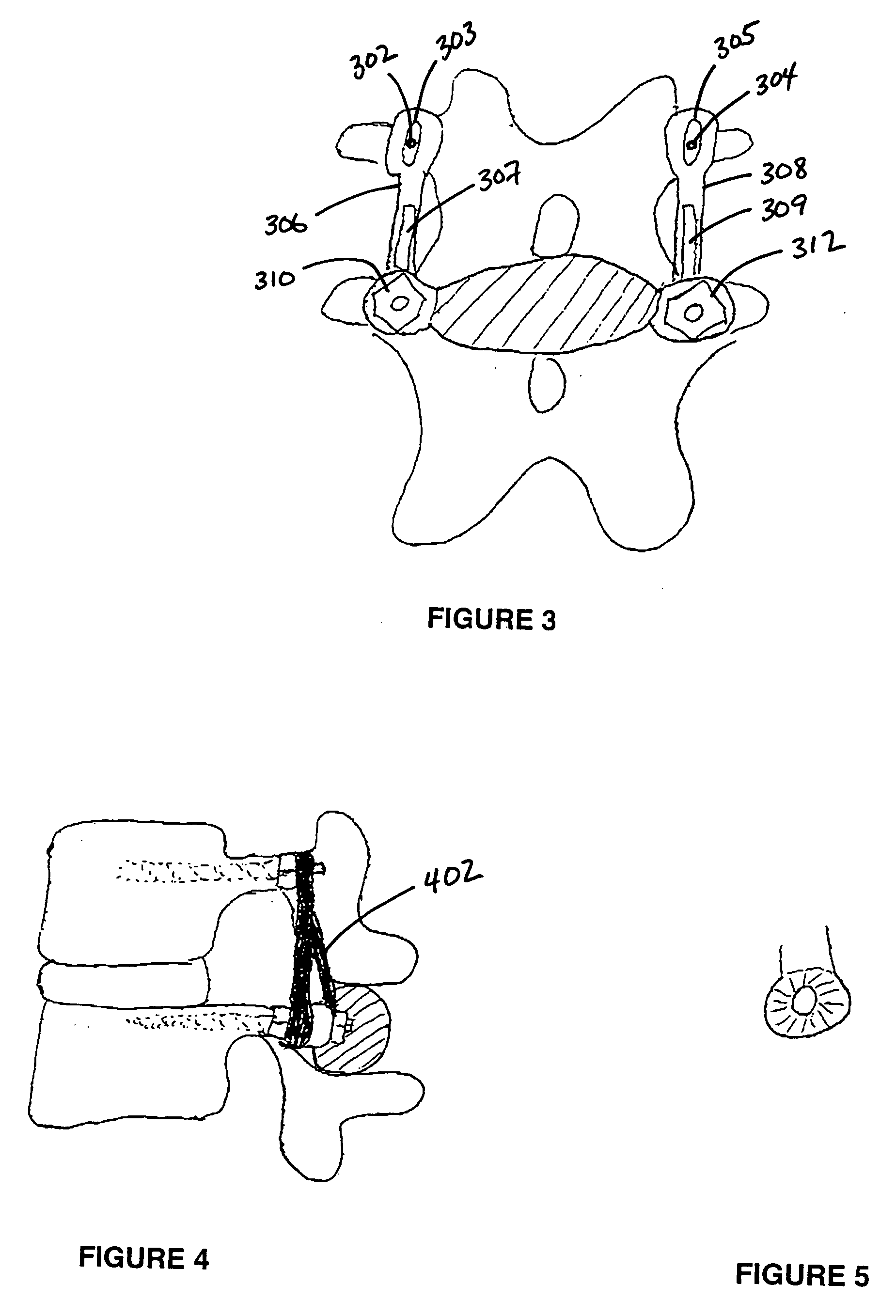
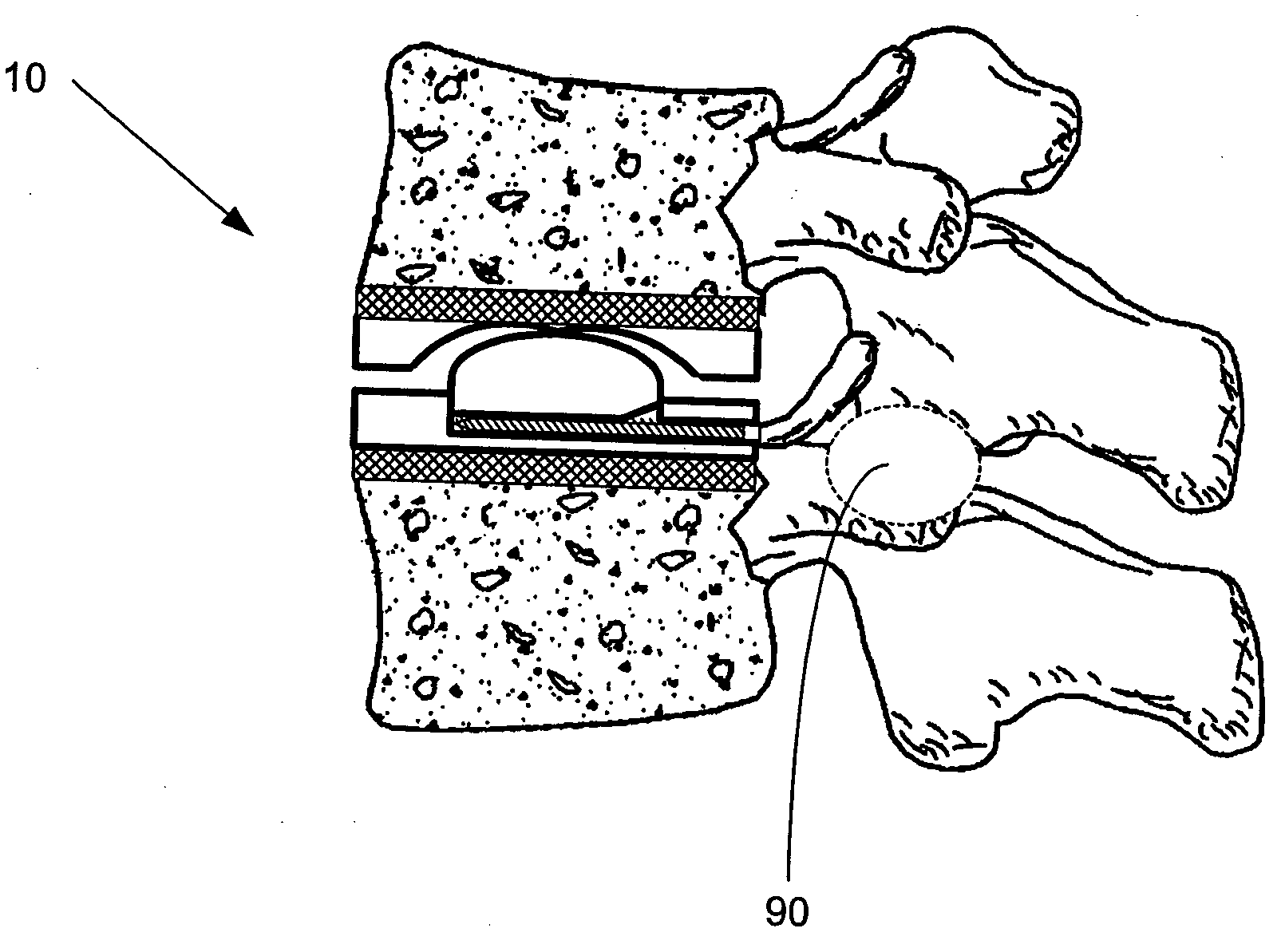
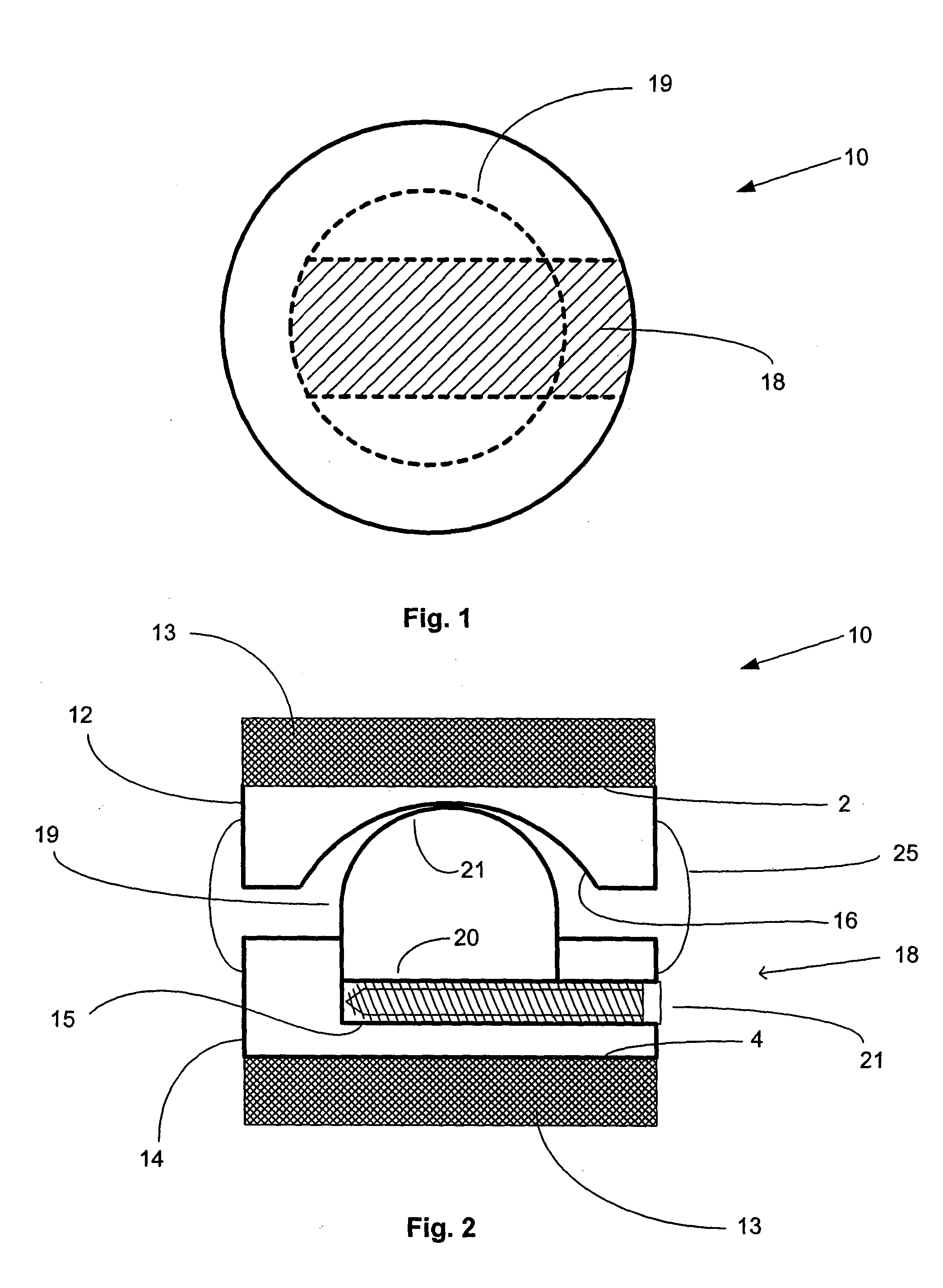
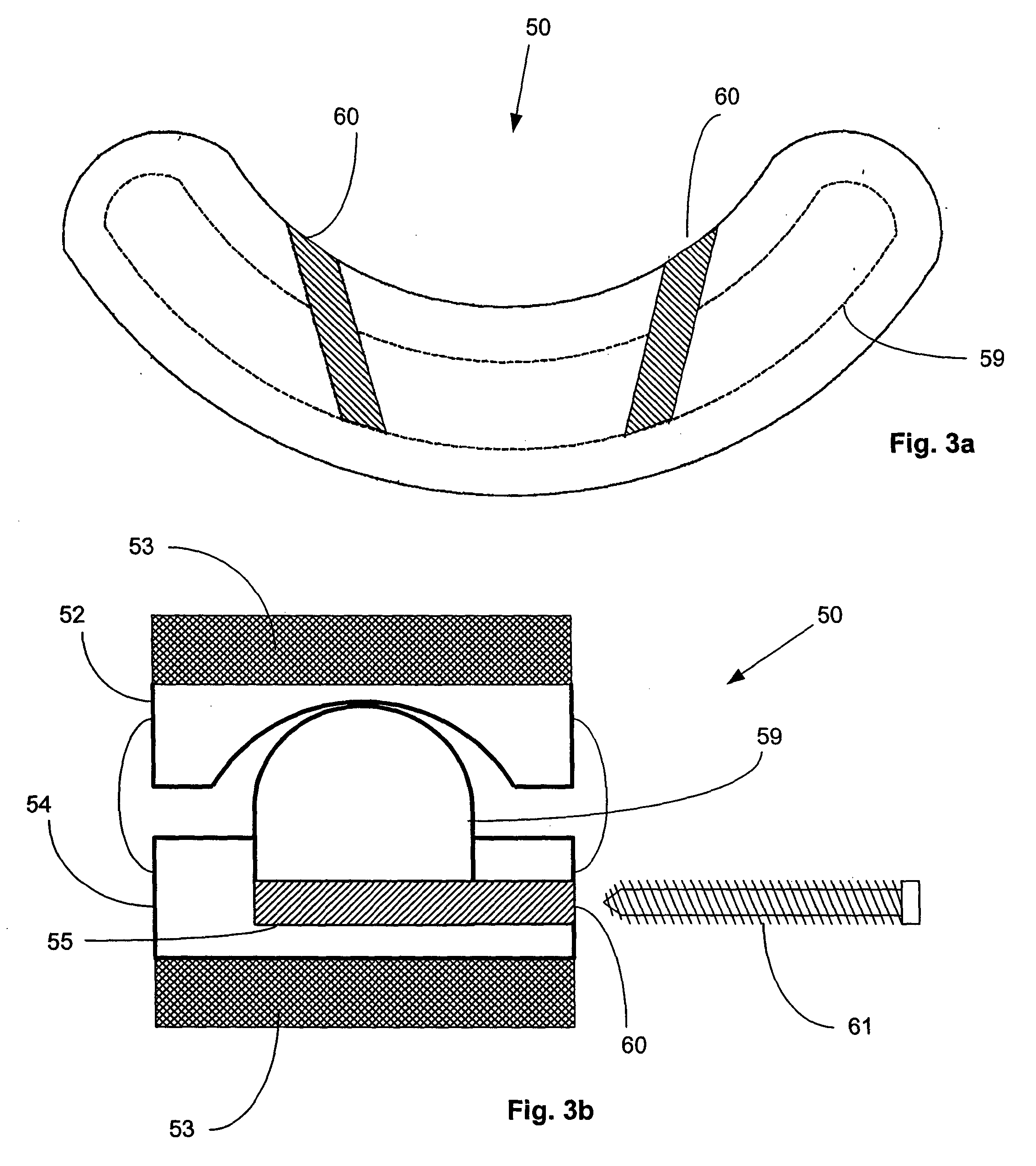
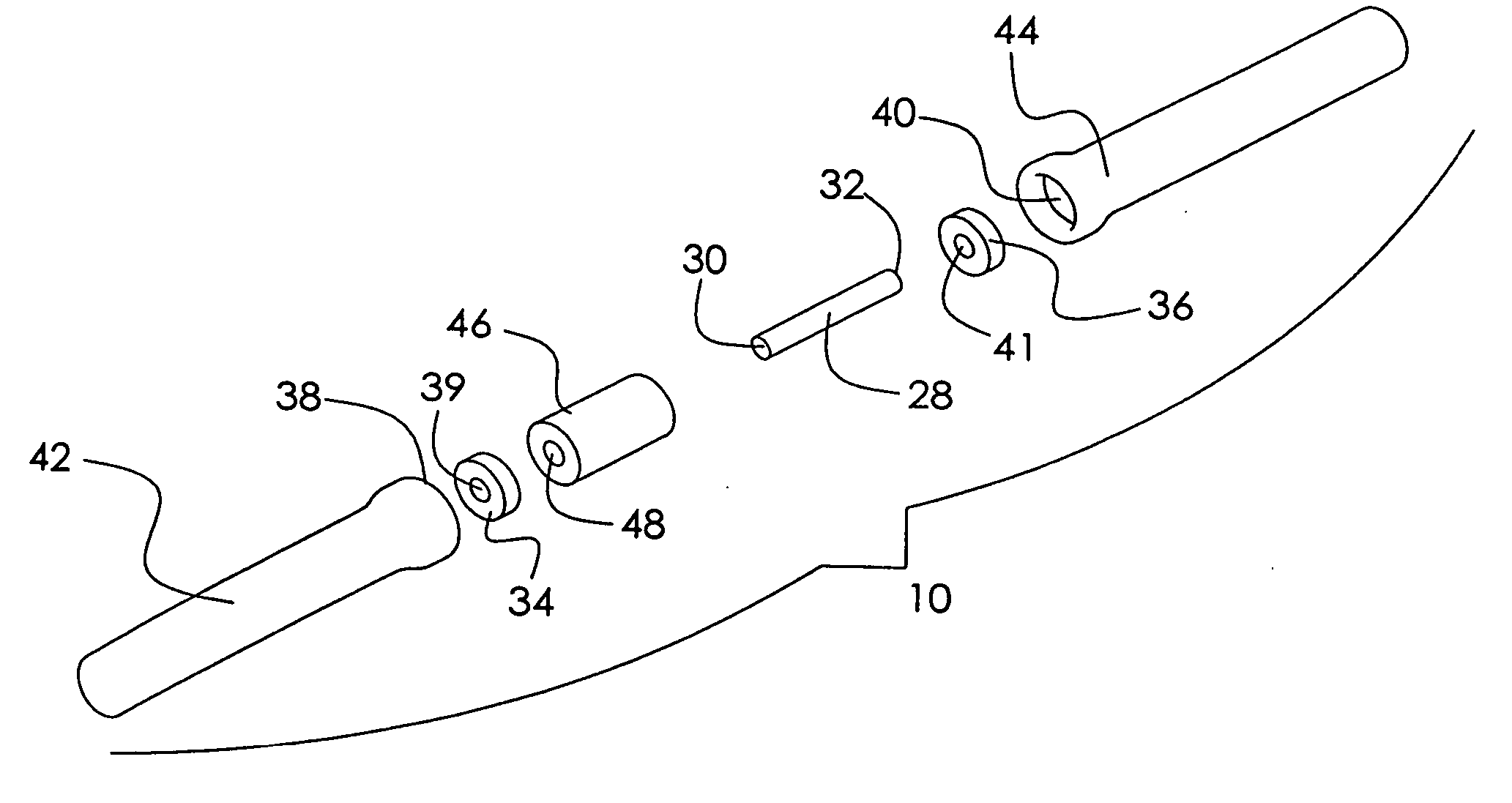
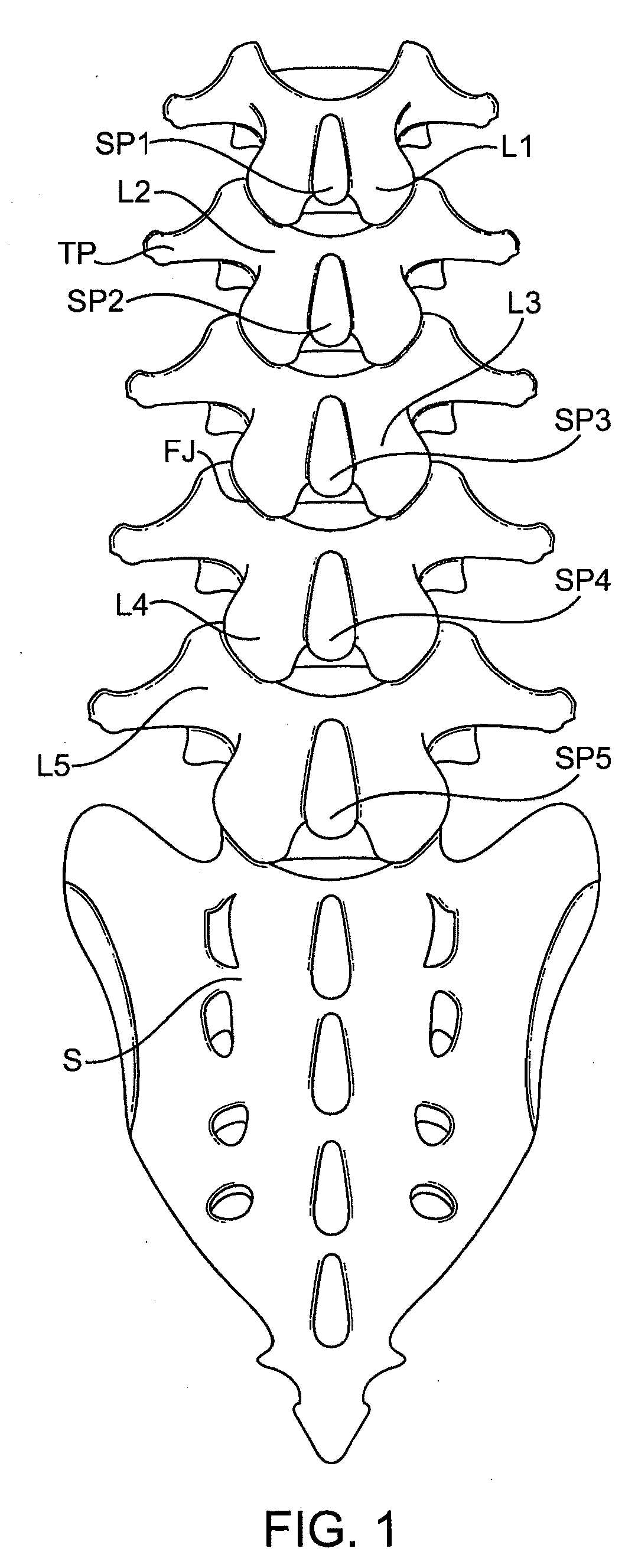
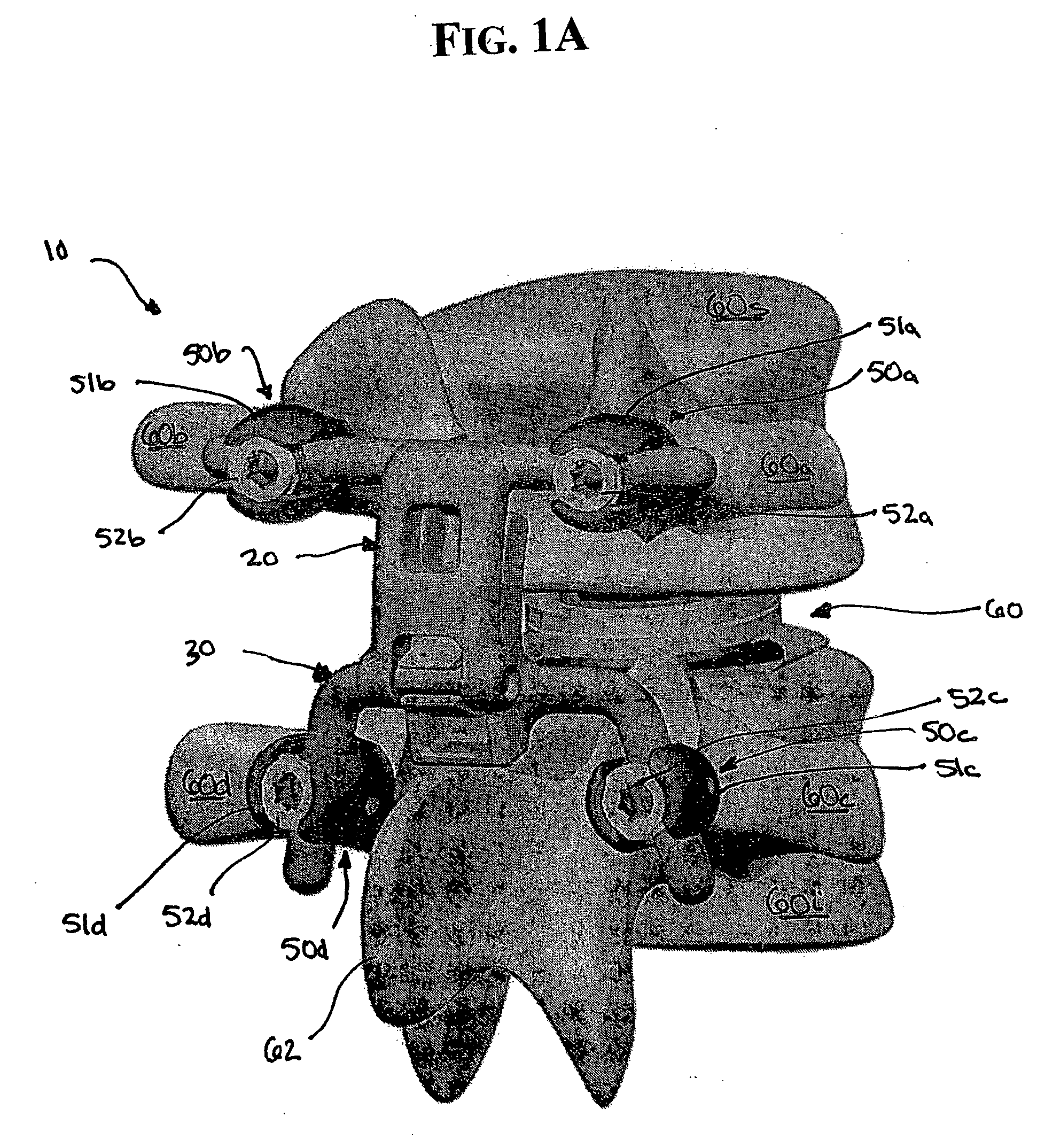
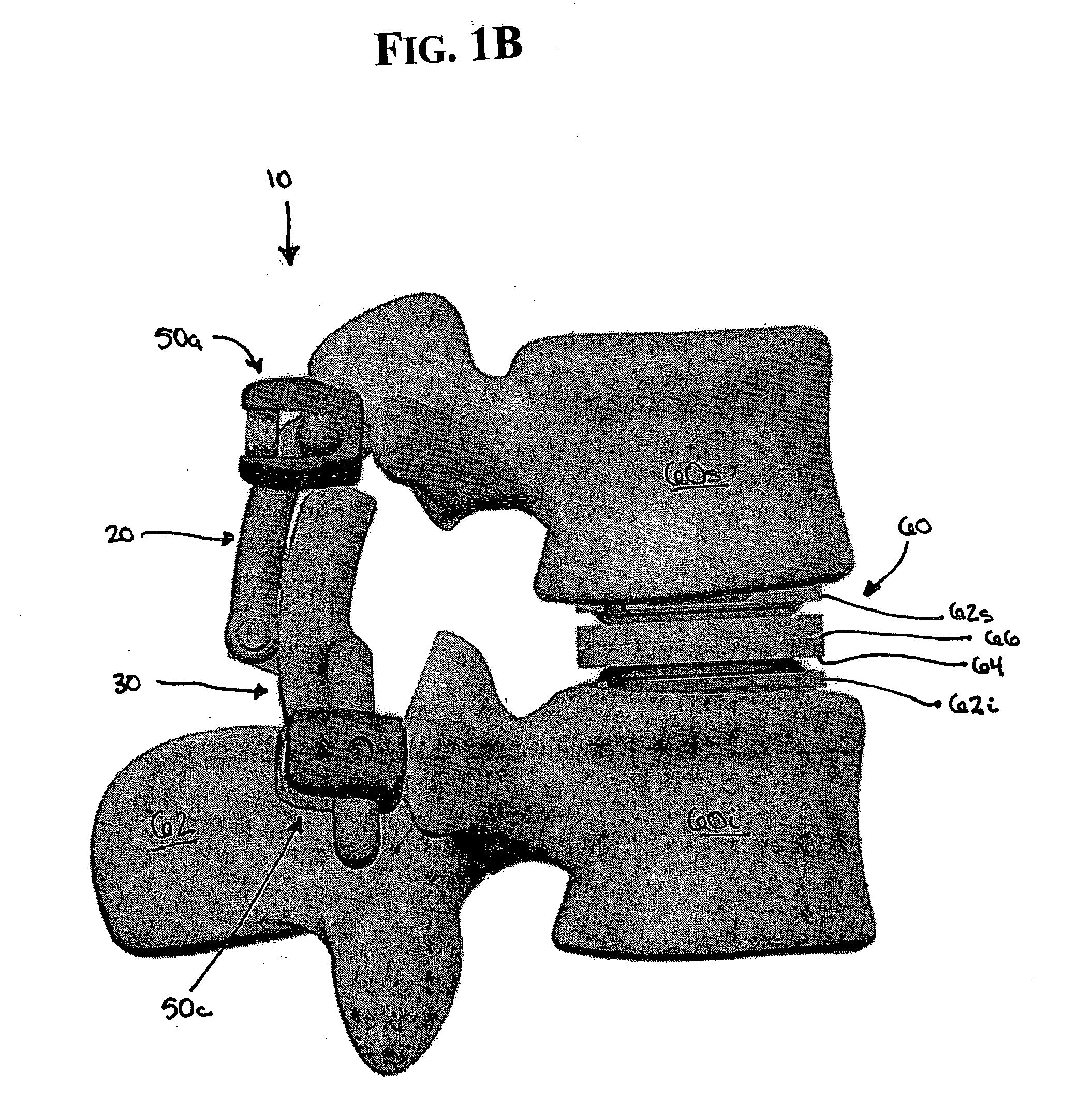
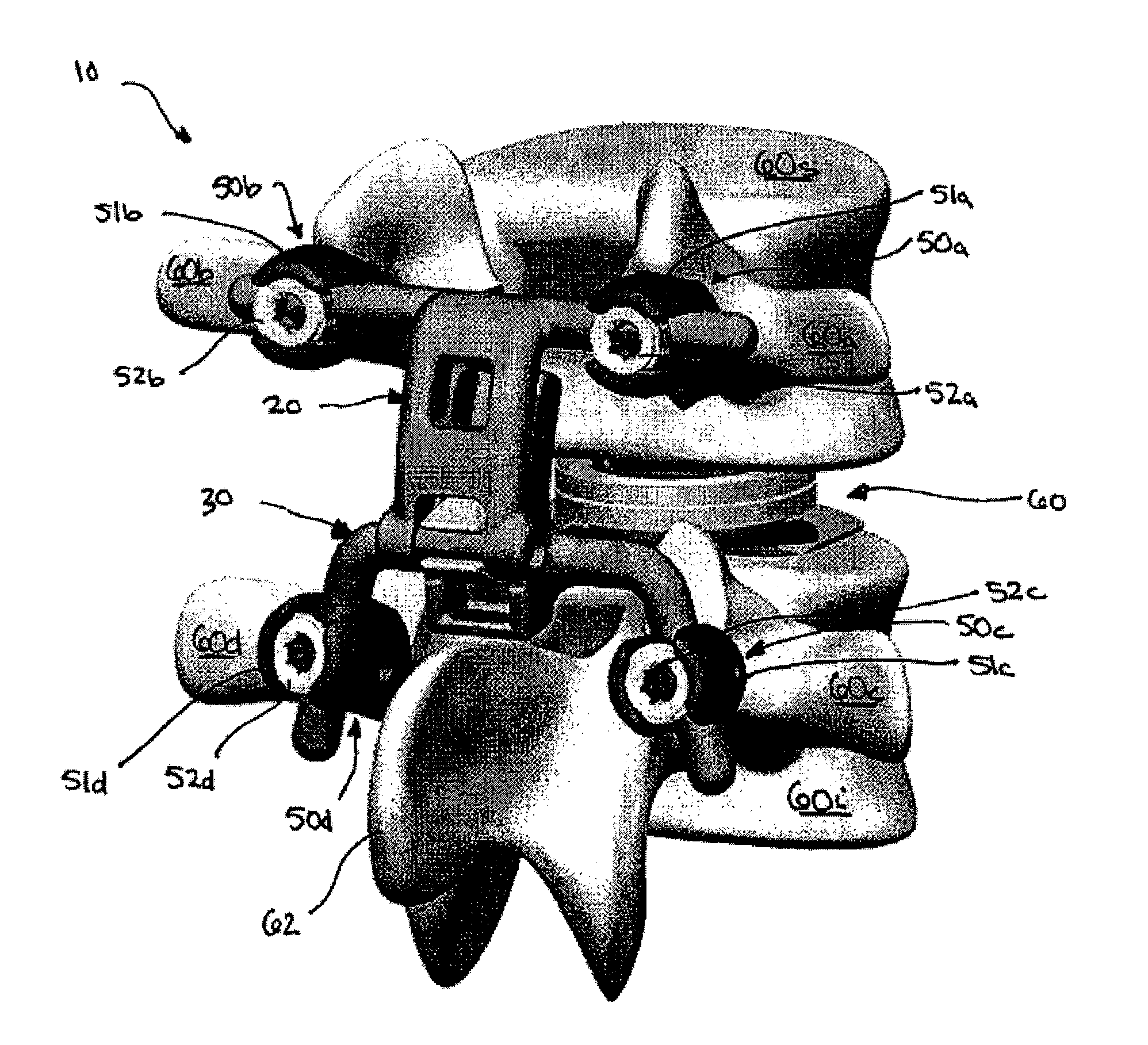
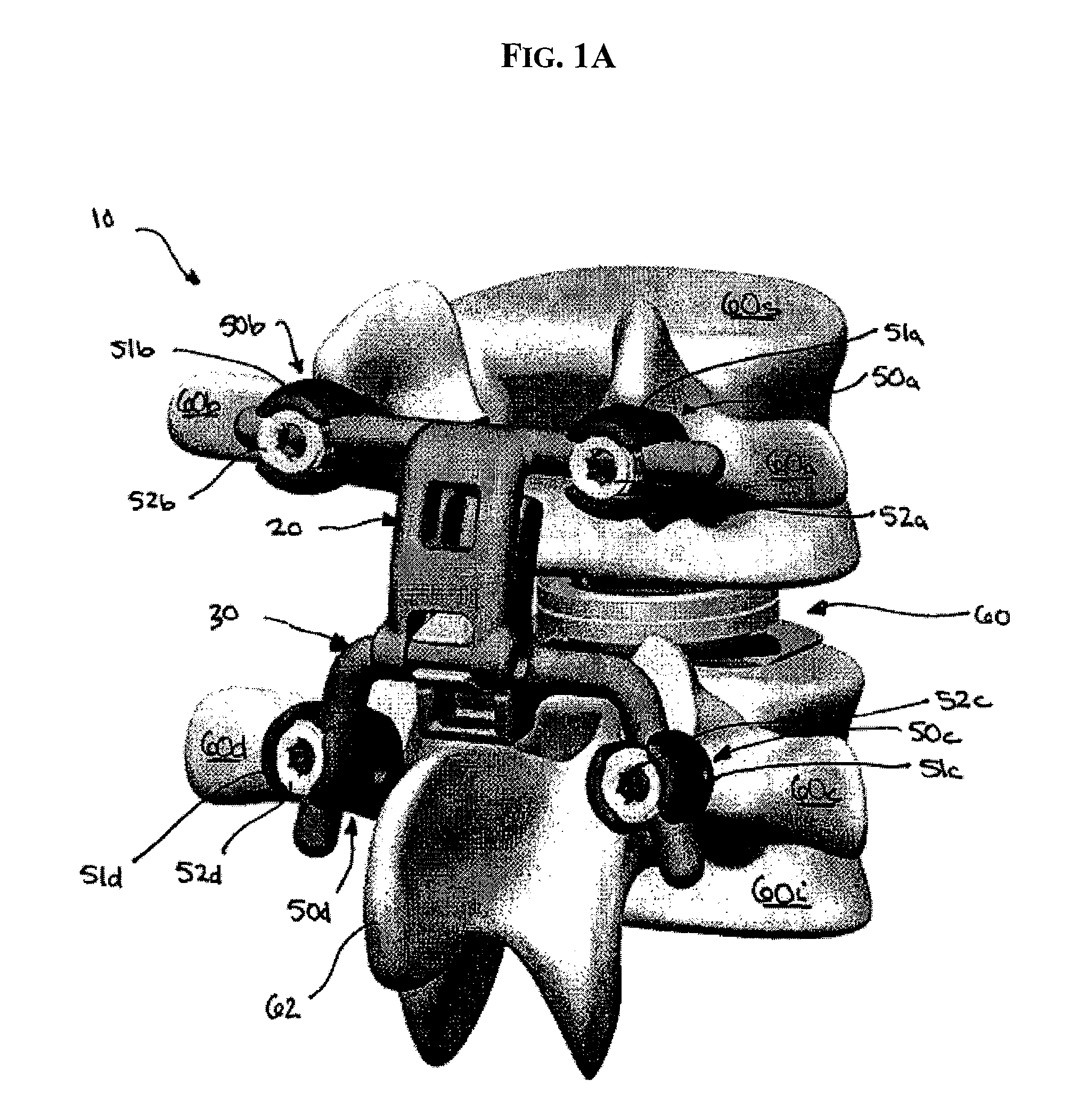
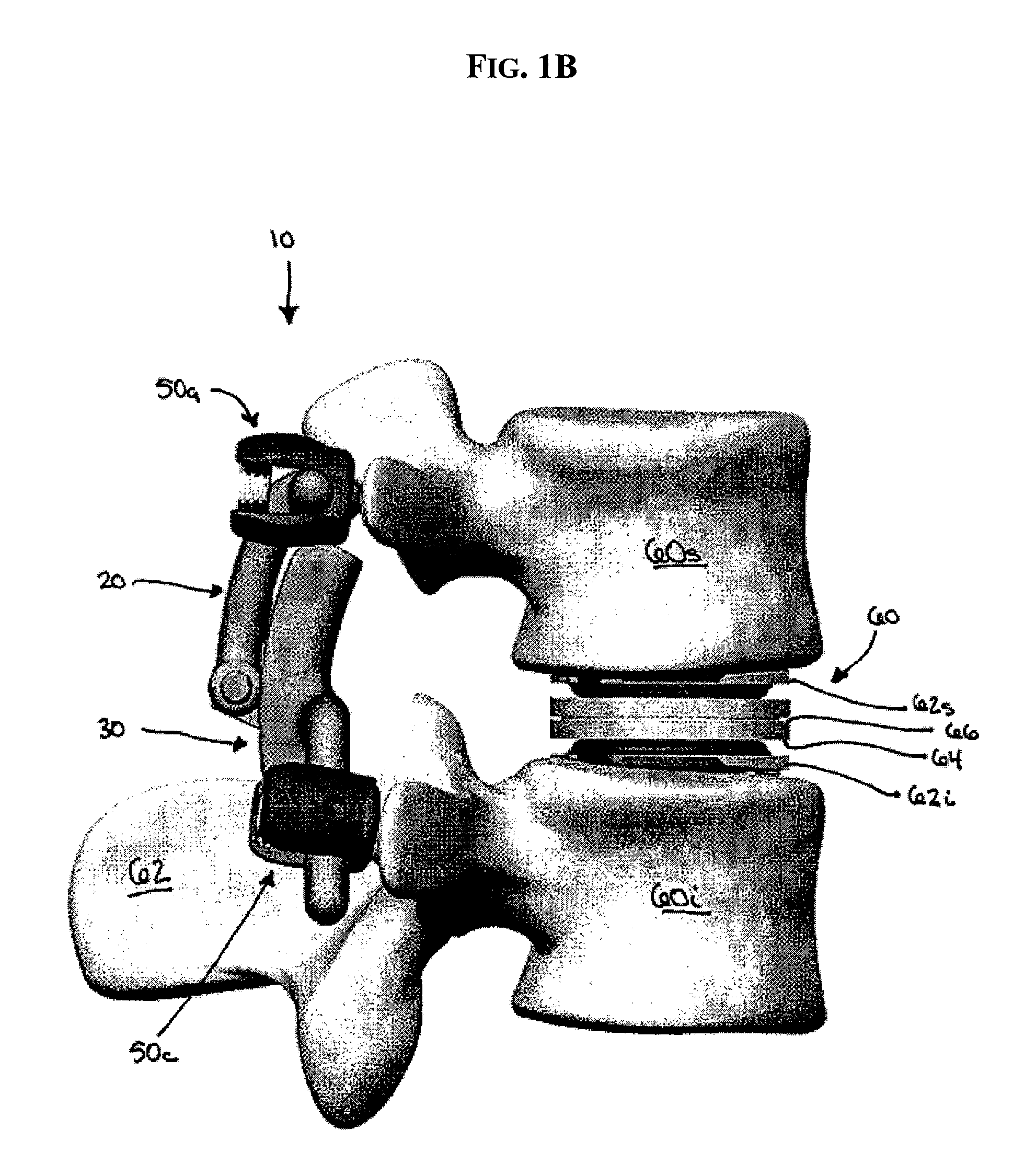
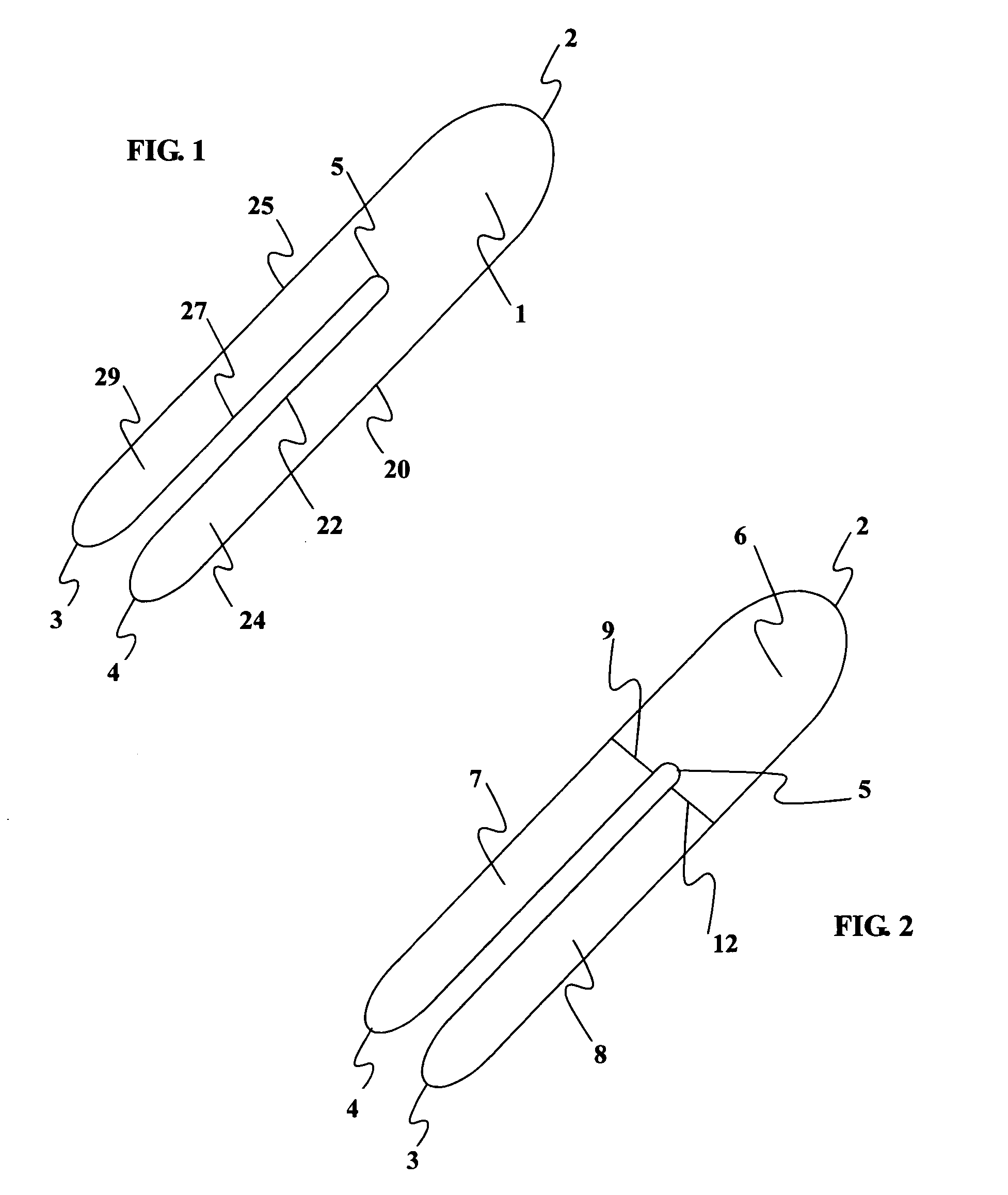
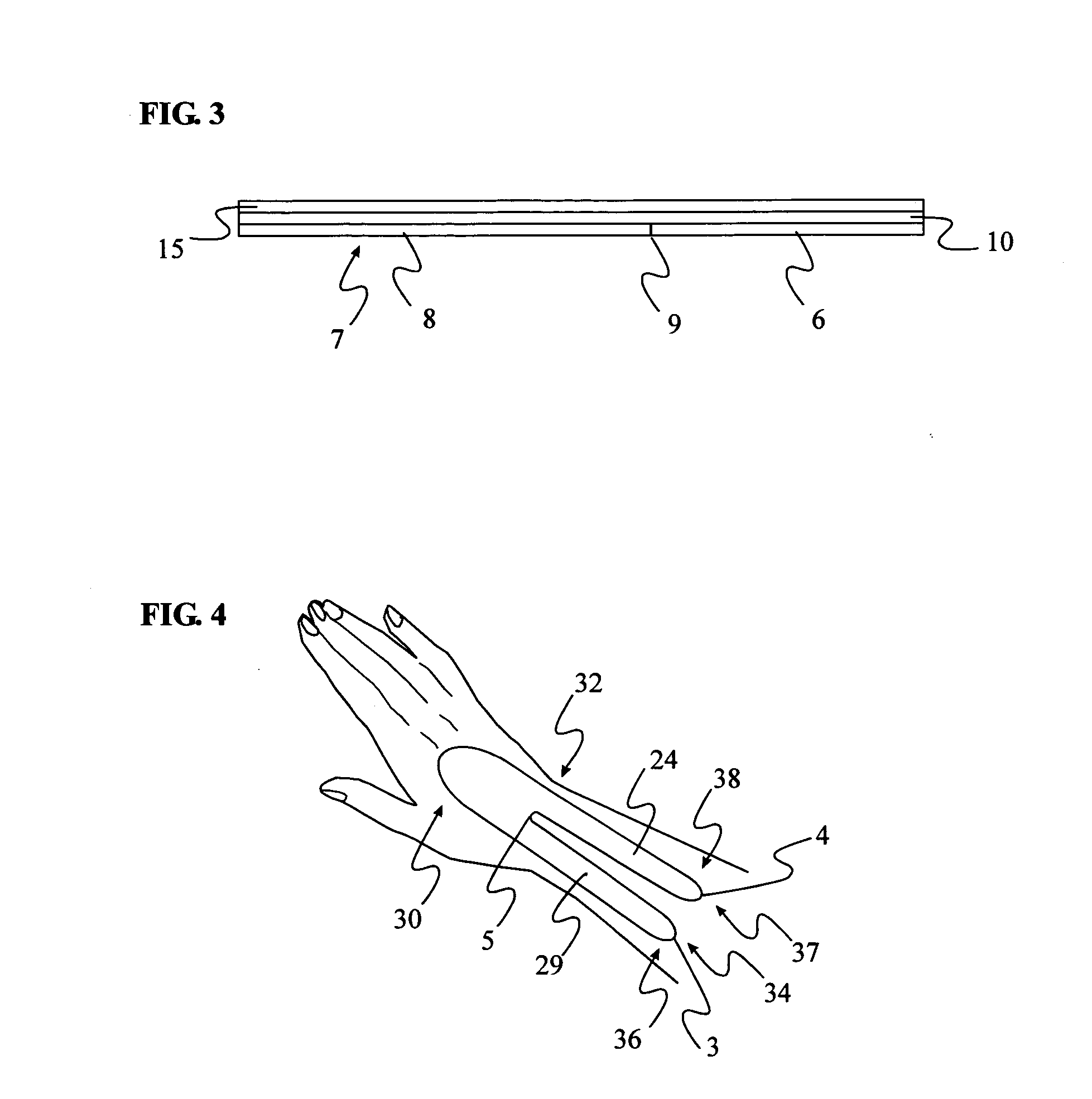
Artificial functional spinal unit assemblies
InactiveUS7316714B2Promote growthPromoting bony end growthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSurgical operationSurgical approach
An artificial functional spinal unit is provided comprising, generally, an expandable artificial intervertebral implant that can be placed via a posterior surgical approach and used in conjunction with one or more artificial facet joints to provide an anatomically correct range of motion. Expandable artificial intervertebral implants in both lordotic and non-lordotic designs are disclosed, as well as lordotic and non-lordotic expandable cages for both PLIF (posterior lumber interbody fusion) and TLIF (transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion) procedures. The expandable implants may have various shapes, such as round, square, rectangular, banana-shaped, kidney-shaped, or other similar shapes. By virtue of their posteriorly implanted approach, the disclosed artificial FSU's allow for posterior decompression of the neural elements, reconstruction of all or part of the natural functional spinal unit, restoration and maintenance of lordosis, maintenance of motion, and restoration and maintenance of disc space height.
Owner:FLEXUSPINE INC
Artificial spinal unit assemblies
ActiveUS20050033432A1Prohibit some movementPrevent movementInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnSurgical approach
An artificial functional spinal unit is provided comprising, generally, an expandable artificial intervertebral implant that can be placed via a posterior surgical approach and used in conjunction with one or more artificial facet joints to provide an anatomically correct range of motion. Expandable artificial intervertebral implants in both lordotic and non-lordotic designs are disclosed, as well as lordotic and non-lordotic expandable cages for both PLIF (posterior lumber interbody fusion) and TLIF (transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion) procedures. The expandable implants may have various shapes, such as round, square, rectangular, banana-shaped, kidney-shaped, or other similar shapes. By virtue of their posteriorly implanted approach, the disclosed artificial FSU's allow for posterior decompression of the neural elements, reconstruction of all or part of the natural functional spinal unit, restoration and maintenance of lordosis, maintenance of motion, and restoration and maintenance of disc space height.
Owner:FLEXUSPINE
Devices to prevent spinal extension
InactiveUS20050288672A1Avoid painPreventing other complicationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsPreventing painSpinal column
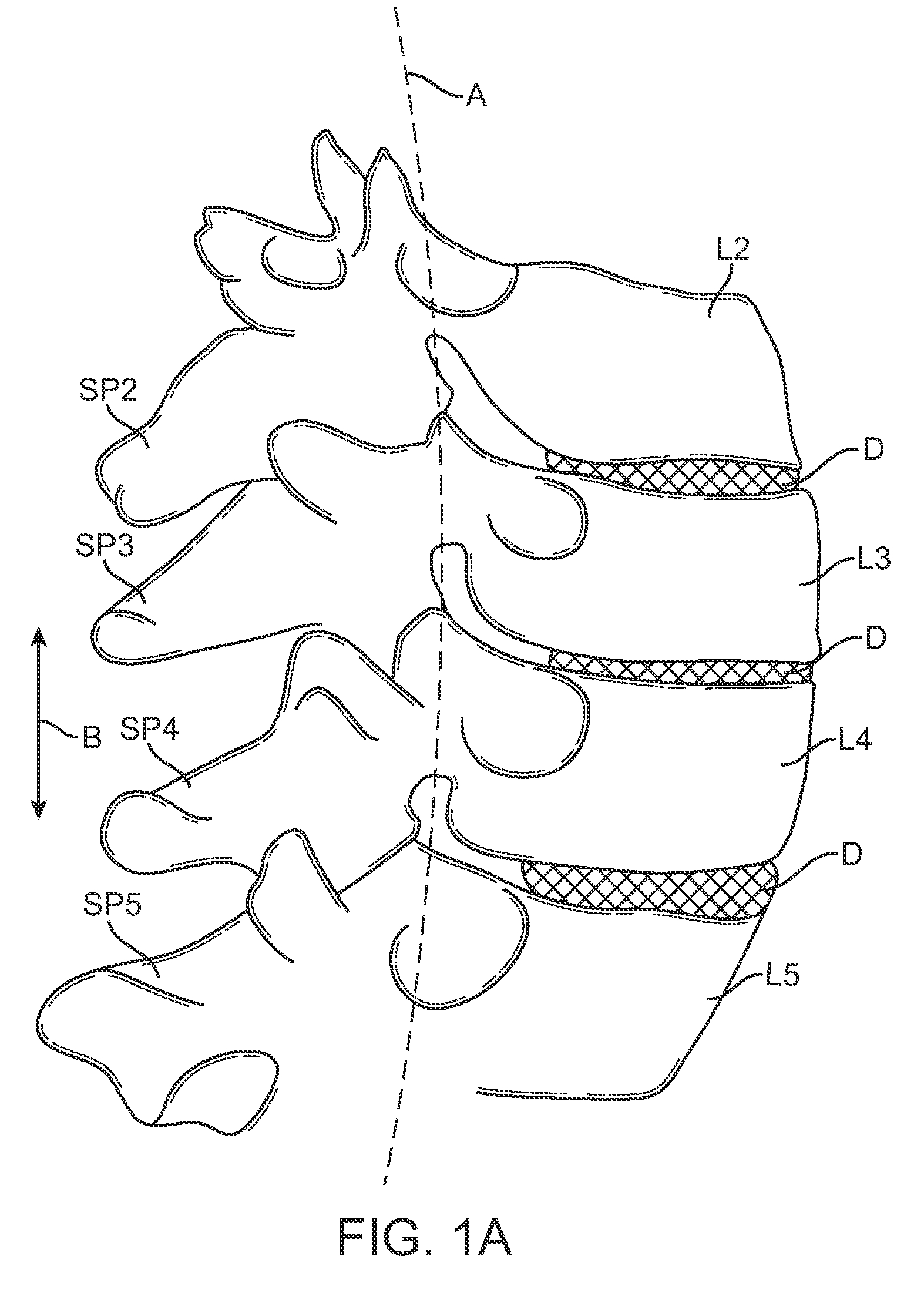
This invention resides in an apparatus for inhibiting full extension between upper and lower vertebral bodies, thereby preventing pain and other complications associated with spinal movement. In the preferred embodiment, the invention provides a generally transverse member extending between the spinous processes and lamina of the upper and lower vertebral bodies, thereby inhibiting full extension. Various embodiments of the invention may limit spinal flexion, rotation and / or lateral bending while preventing spinal extension. In the preferred embodiment, the transverse member is fixed between two opposing points on the lower vertebral body using pedicle screws, and a cushioning sleeve is used as a protective cover. The transverse member may be a rod or cable, and the apparatus may be used with a partial or full artificial disc replacement. To control spinal flexion, rotation and / or lateral bending one or more links may be fastened to an adjacent vertebral body, also preferably using a pedicle screw. Preferably a pair of opposing links are used between the upper and lower vertebral bodies for such purposes.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Artificial functional spinal unit assemblies
ActiveUS20050033439A1Promote growthPromoting bony end growthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSurgical approachFunctional spinal unit
An artificial functional spinal unit is provided comprising, generally, an expandable artificial intervertebral implant that can be placed via a posterior surgical approach and used in conjunction with one or more artificial facet joints to provide an anatomically correct range of motion. Expandable artificial intervertebral implants in both lordotic and non-lordotic designs are disclosed, as well as lordotic and non-lordotic expandable cages for both PLIF (posterior lumber interbody fusion) and TLIF (transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion) procedures. The expandable implants may have various shapes, such as round, square, rectangular, banana-shaped, kidney-shaped, or other similar shapes. By virtue of their posteriorly implanted approach, the disclosed artificial FSU's allow for posterior decompression of the neural elements, reconstruction of all or part of the natural functional spinal unit, restoration and maintenance of lordosis, maintenance of motion, and restoration and maintenance of disc space height.
Owner:FLEXUSPINE INC
Artificial functional spinal unit assemblies
InactiveUS20050033431A1Promote growthPromoting bony end growthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSurgical approachFunctional spinal unit
An artificial functional spinal unit is provided comprising, generally, an expandable artificial intervertebral implant that can be placed via a posterior surgical approach and used in conjunction with one or more artificial facet joints to provide an anatomically correct range of motion. Expandable artificial intervertebral implants in both lordotic and non-lordotic designs are disclosed, as well as lordotic and non-lordotic expandable cages for both PLIF (posterior lumber interbody fusion) and TLIF (transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion) procedures. The expandable implants may have various shapes, such as round, square, rectangular, banana-shaped, kidney-shaped, or other similar shapes. By virtue of their posteriorly implanted approach, the disclosed artificial FSU's allow for posterior decompression of the neural elements, reconstruction of all or part of the natural functional spinal unit, restoration and maintenance of lordosis, maintenance of motion, and restoration and maintenance of disc space height.
Owner:FLEXUSPINE INC
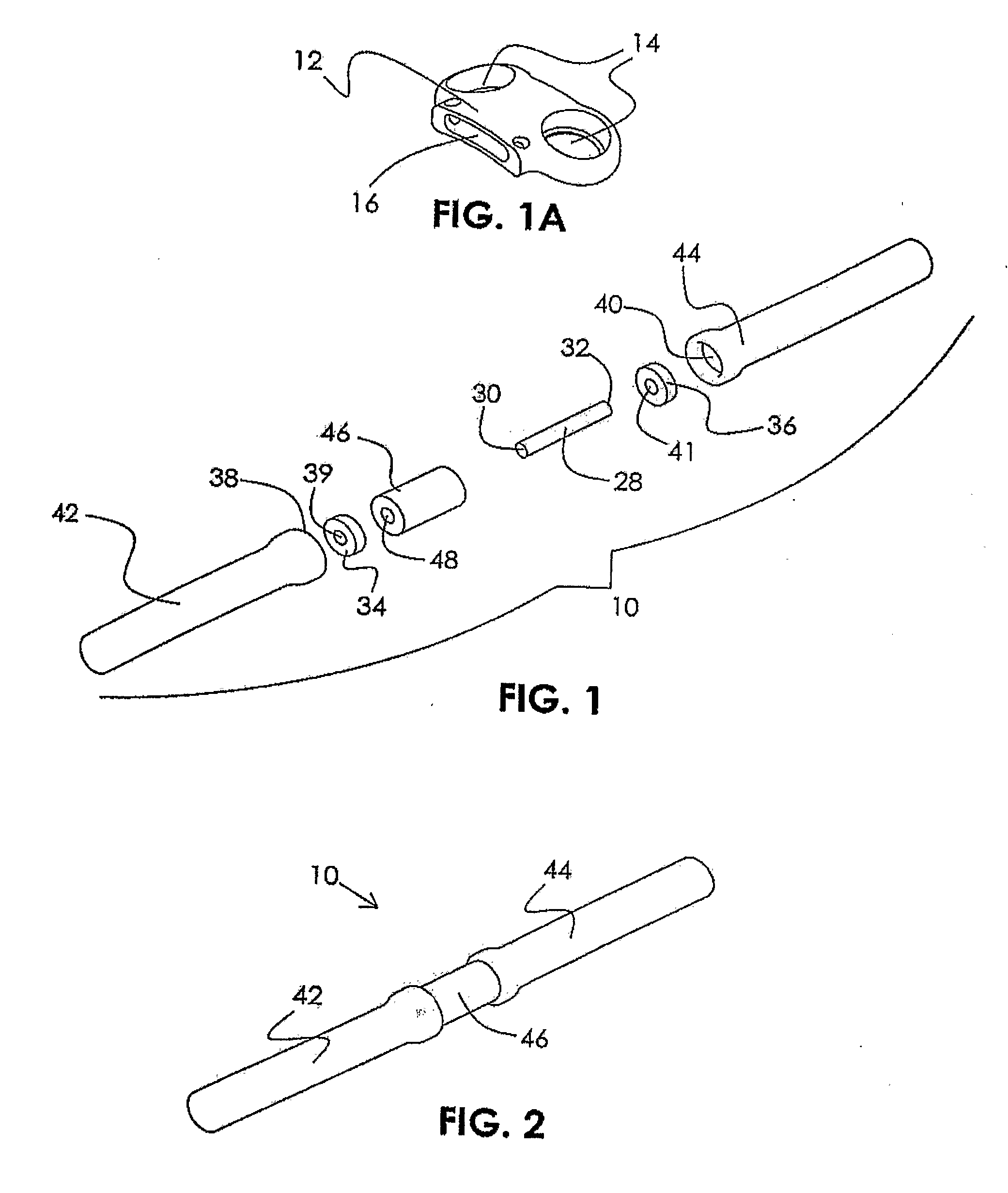
Mobile spine stabilization device
InactiveUS20060264937A1Limit range of motionConstraining bending forceInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnMedicine
An orthopedic device is described for stabilizing the spinal column between first and second vertebral bodies. The device has first and second screws adapted for fixation to the first and second vertebral bodies, respectively. The device further includes an elongated ligament with a first end connected to the first screw and the second end operatively connected with the second screw. The ligament is made preferably of a nickel titanium alloy selected to have ductile inelastic properties at body temperature and is capable of continuous plastic deformation to allow relative constrained motion between the vertebral bodies. In a preferred embodiment the second pedicle screw includes a bearing for receiving the ligament in a slideably engageable relationship. The device further includes optional first and second dampening members surrounding the ligament for restraining the spinal column during flexion and extension. Other preferred devices and kits containing such devices are also described.
Owner:WHITE PATRICK
Artificial functional spinal unit assemblies
InactiveUS20060195192A1Promote growthPromoting bony end growthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSurgical approachFunctional spinal unit
An artificial functional spinal unit is provided comprising, generally, an expandable artificial intervertebral implant that can be placed via a posterior surgical approach and used in conjunction with one or more artificial facet joints to provide an anatomically correct range of motion. Expandable artificial intervertebral implants in both lordotic and non-lordotic designs are disclosed, as well as lordotic and non-lordotic expandable cages for both PLIF (posterior lumber interbody fusion) and TLIF (transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion) procedures. The expandable implants may have various shapes, such as round, square, rectangular, banana-shaped, kidney-shaped, or other similar shapes. By virtue of their posteriorly implanted approach, the disclosed artificial FSU's allow for posterior decompression of the neural elements, reconstruction of all or part of the natural functional spinal unit, restoration and maintenance of lordosis, maintenance of motion, and restoration and maintenance of disc space height.
Owner:FLEXUSPINE INC
Artificial spinal unit assemblies
ActiveUS7909869B2Promote growthPromoting bony end growthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnSurgical operation
An artificial functional spinal unit is provided comprising, generally, an expandable artificial intervertebral implant that can be placed via a posterior surgical approach and used in conjunction with one or more artificial facet joints to provide an anatomically correct range of motion. Expandable artificial intervertebral implants in both lordotic and non-lordotic designs are disclosed, as well as lordotic and non-lordotic expandable cages for both PLIF (posterior lumber interbody fusion) and TLIF (transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion) procedures. The expandable implants may have various shapes, such as round, square, rectangular, banana-shaped, kidney-shaped, or other similar shapes. By virtue of their posteriorly implanted approach, the disclosed artificial FSU's allow for posterior decompression of the neural elements, reconstruction of all or part of the natural functional spinal unit, restoration and maintenance of lordosis, maintenance of motion, and restoration and maintenance of disc space height.
Owner:FLEXUSPINE INC
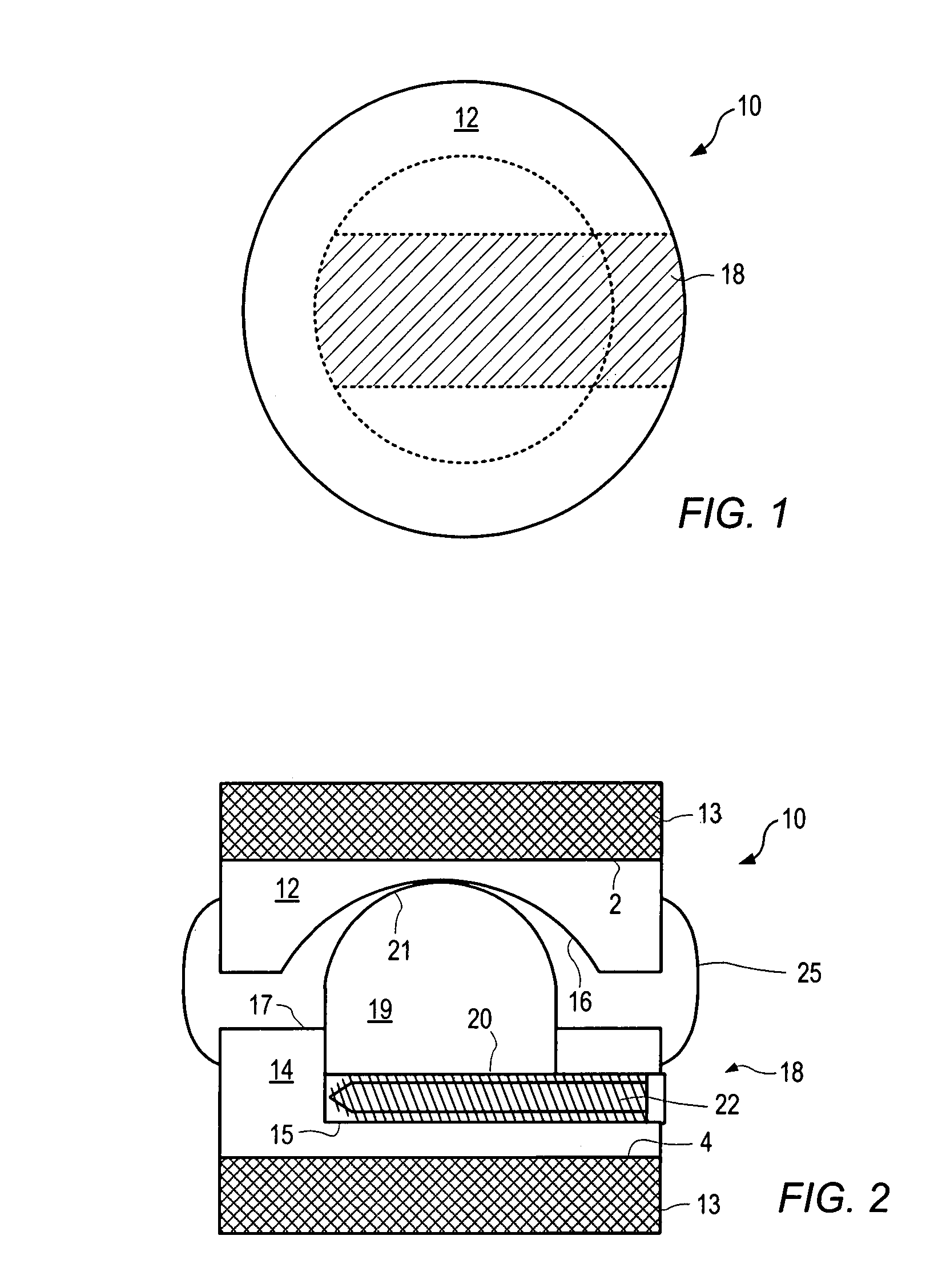
Force feedback and texture simulating interface device
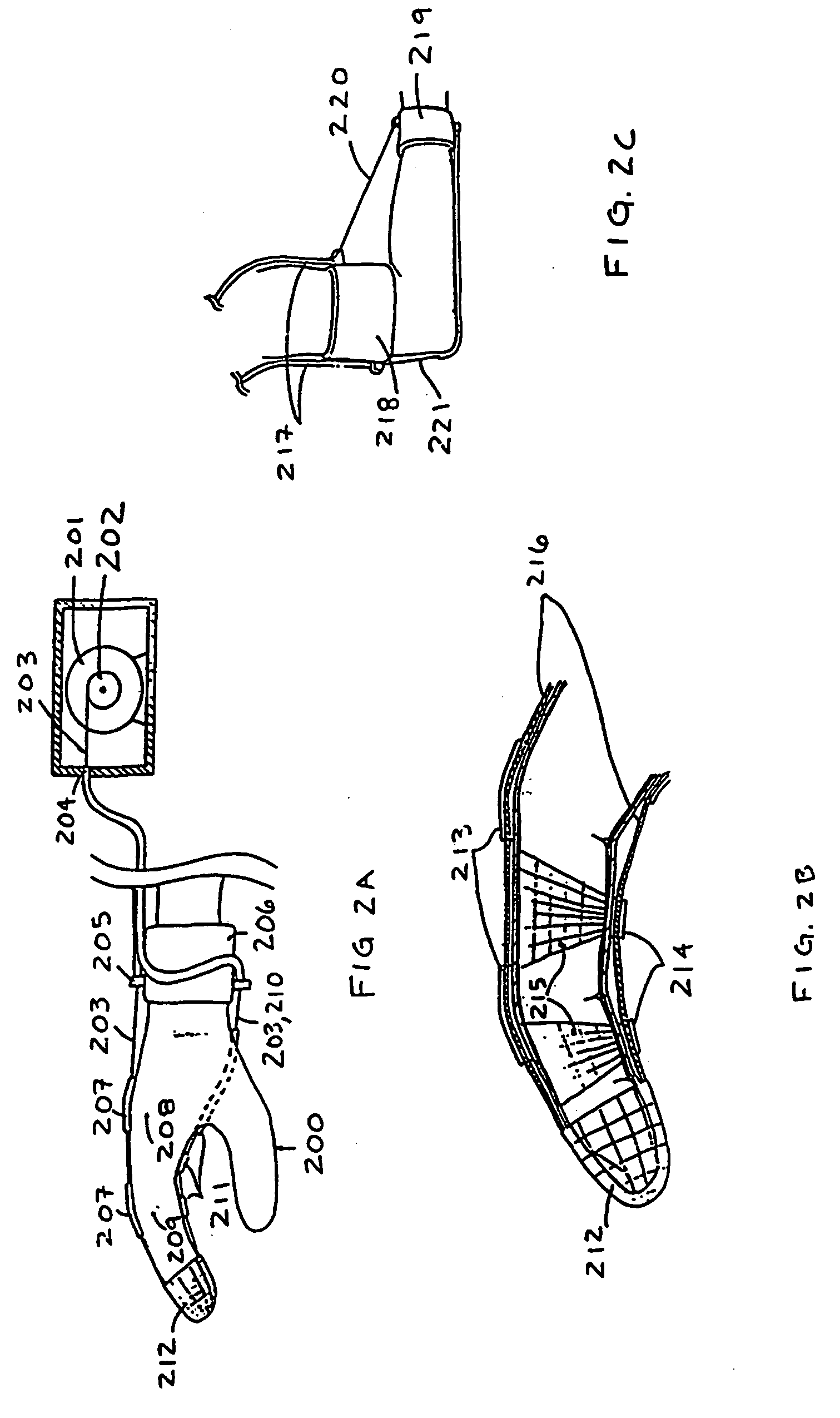
InactiveUS6979164B2Facilitate taskReliably grasp and manipulateProgramme controlInput/output for user-computer interactionBody regionHuman–machine interface
A man-machine interface is disclosed which provides force, texture, pressure and temperature information to sensing body parts. The interface is comprised of a force-generating device (900) that produces a force which is transmitted to a force-applying device (902) via force-transmitting means (908). The force-applying device applies the generated force to a sensing body part. A force sensor (909) associated with the force-applying device measures the actual force applied to the sensing body part, while angle sensors (917) measure the angles of relevant joint body parts. A computing device (911) uses the joint body part position information to determine a desired force value to be applied to the sensing body part. The computing device combines the joint body part position information with the force sensor information to calculate the force command which is sent to the force-generating device. In this manner, the computing device may control the actual force applied to a sensing body part to a desired force which depends upon the positions of related body parts. In addition, the interface is comprised of a displacement-generating device (901) which produces a displacement which is transmitted to a displacement-applying device (902) (e.g., a texture simulator) via displacement-generating means (920). The displacement-applying device applies the generated displacement to a sensing body part. The force-applying device and displacement-applying device may be combined to simultaneously provide force and displacement information to a sensing body part. Furthermore, pressure and temperature-applying devices may be combined to also provide pressure and temperature sensations to a sensing body part. In addition, a force-applying device may be attached to a sensing body part and apply force to the sensing body part, where the force is applied relative to a reference location not rigidly affixed to the living body.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
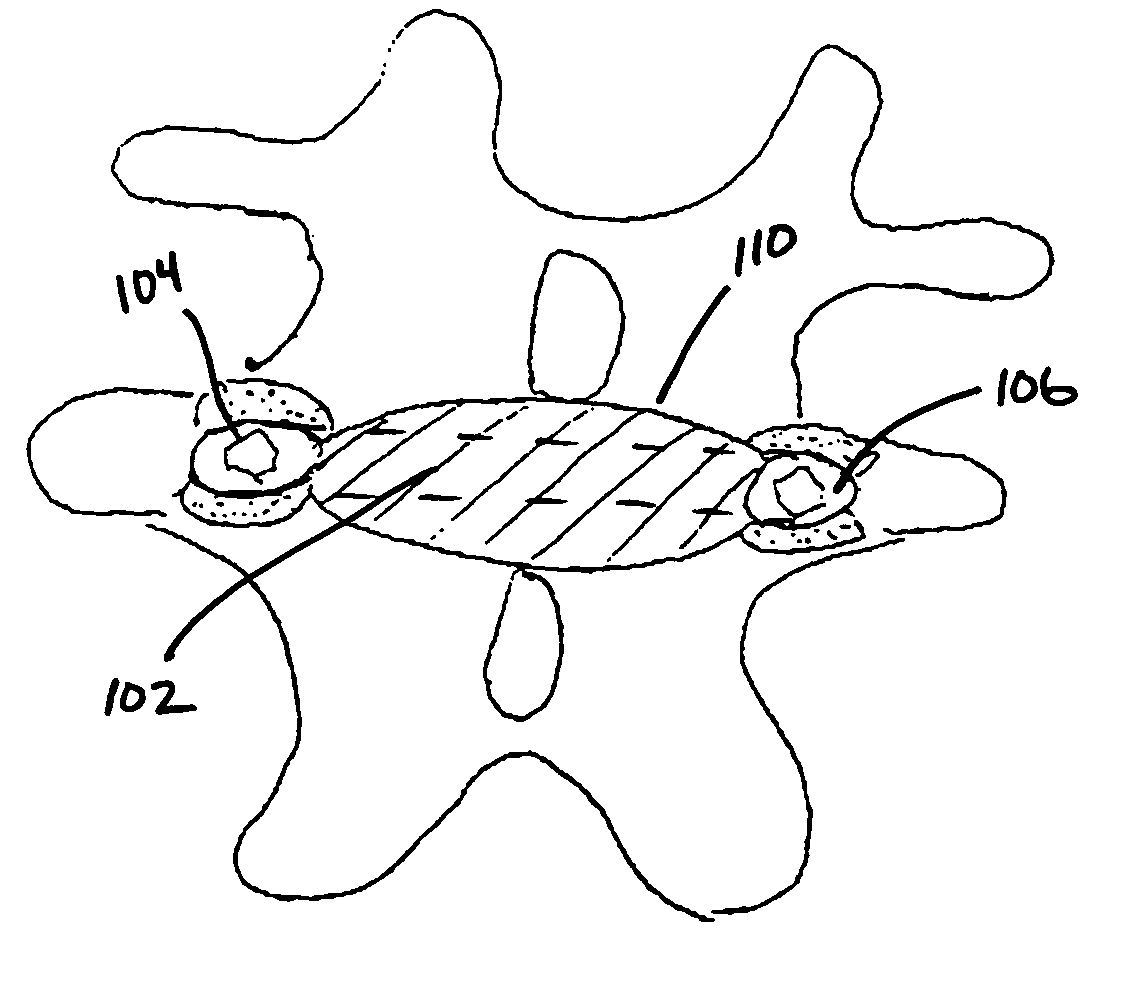
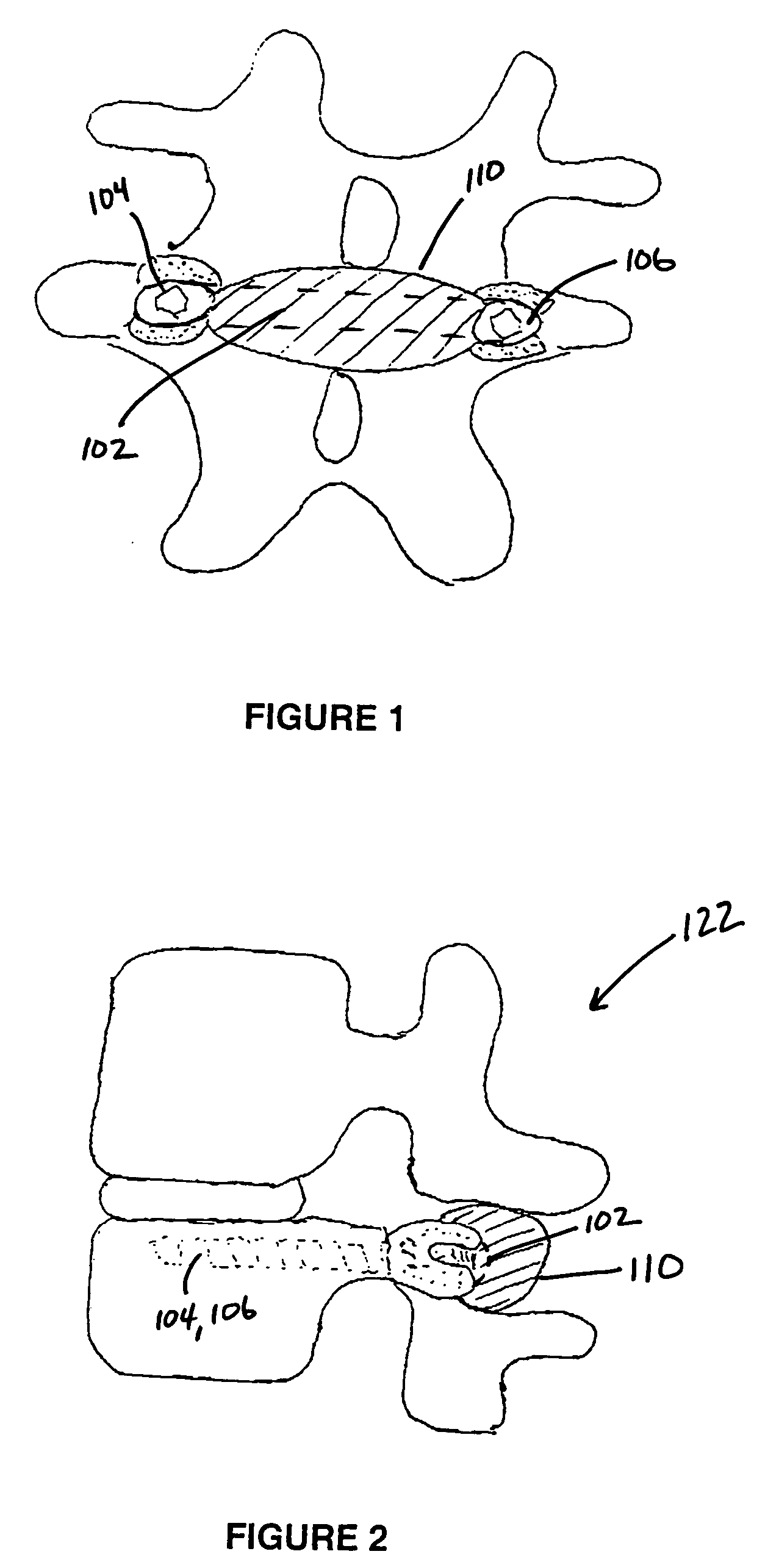
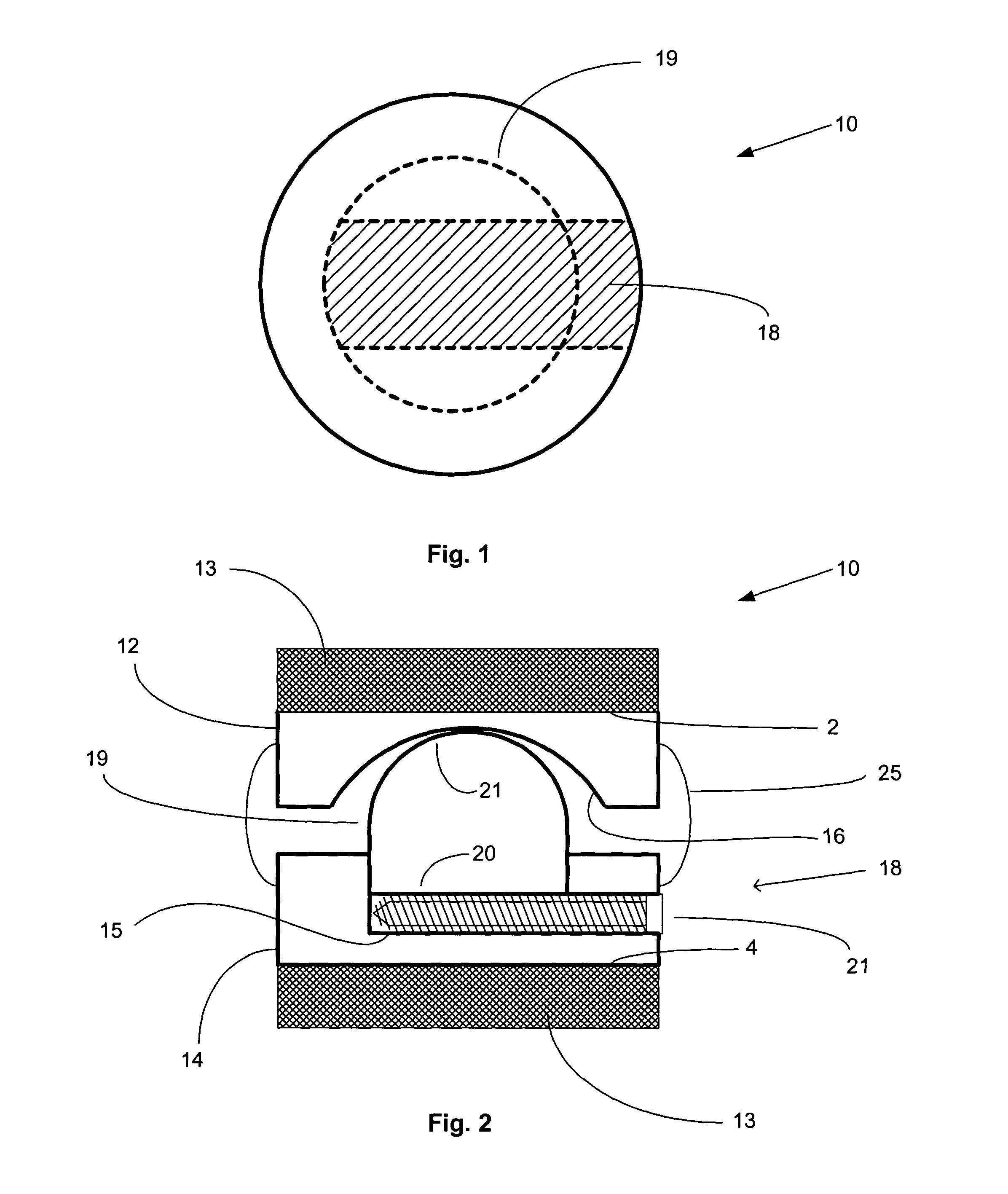
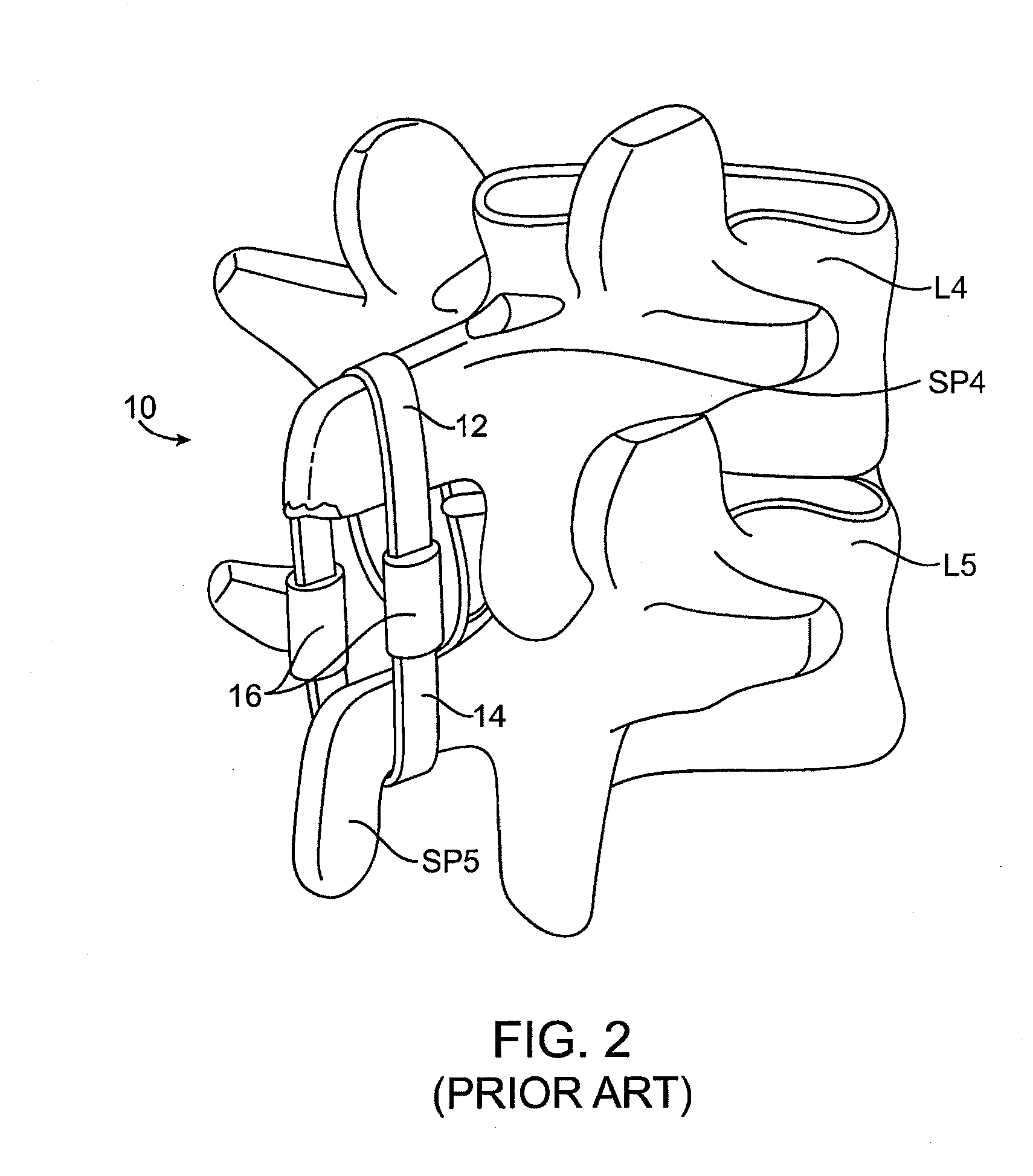
Structures and methods for constraining spinal processes with single connector
ActiveUS20090264929A1Simplify alignmentImplantation be simplifyInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinous processEngineering
Spinous process constraint structures include a first attachment element for placement over a first spinous process and a second attachment element for placement over a second spinous process. The attachment elements are joined by a single connector which may optionally include a compliance member for providing controlled elasticity between the spinous processes.
Owner:SIMPIRICA SPINE
Force feedback and texture simulating interface device
InactiveUS20060115348A1Reduce tensionFlexible limitInput/output for user-computer interactionProgramme controlMan machineEngineering
A man-machine! interface is disclosed which provides force, texture, pressure and temperature information to sensing body parts. The interface is comprised of a force-generating device (900) that produces a force which is transmitted to a force-applying device (902) via force-transmitting means (908). The force-applying device applies the generated force to a sensing body part A force sensor (909) associated with the force-applying device measures the actual force applied to the sensing body part, while angle sensors (9171 measure the angles of relevant joint body parts. A computing device (911) uses the joint body part position information to determine a desired force value to be applied to the sensing body part. The computing device combines the joint body part position information with the force sensor information to calculate the force command which is sent to the force-generating device. In this manner, the computing device may control the actual force applied to a sewing body part to a desired force which depends upon the positions of related body parts. In addition, the interface is comprised of a displacement-generating device (901) which produces a displacement which is transmitted to a displacement-applying device (902) (e.g., a texture simulator) via displacement-generating means (920). The displacement-applying device applies the generated displacement to a sensing body part. The force-applying device and displacement-applying device may be combined to simultaneously provide force and displacement information to a sensing body part. Furthermore, pressure and temperature-applying devices may be combined to also provide pressure and temperature sensations to a sensing body part. In addition, a force-applying device may be attached to a sensing body part and apply force to the sensing body part, where the force is applied relative to a reference location not rigidly affixed to the living body.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
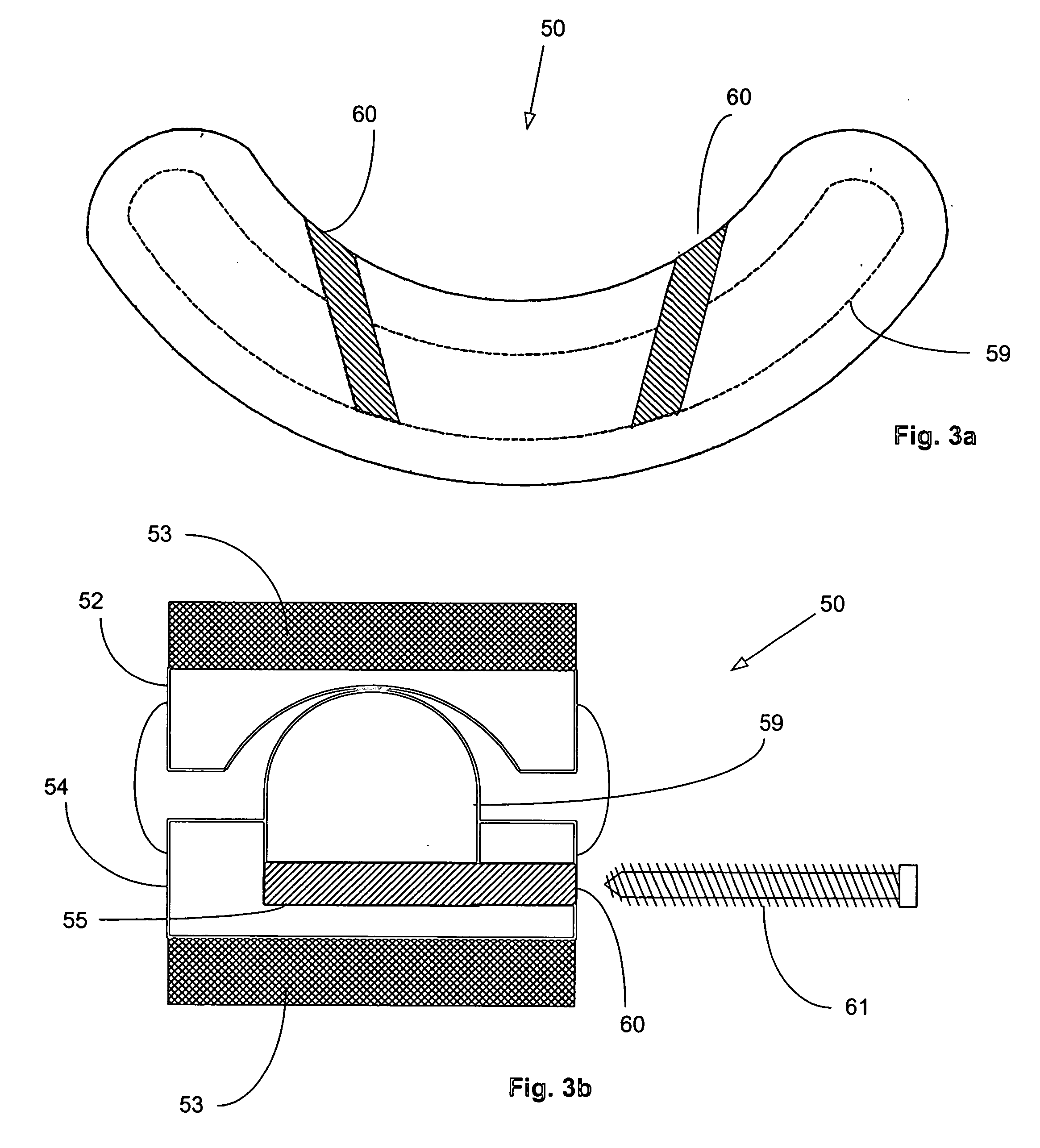
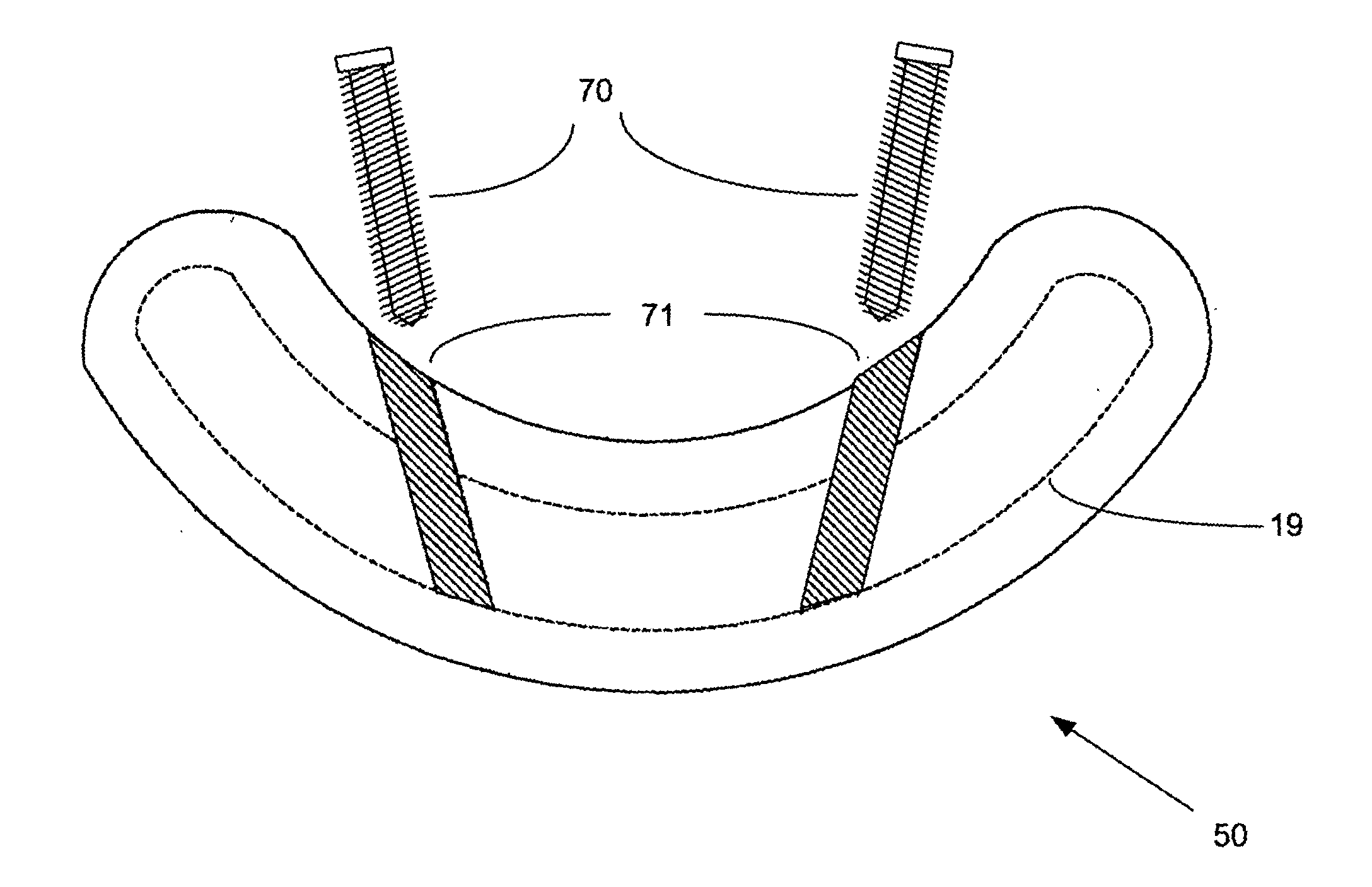
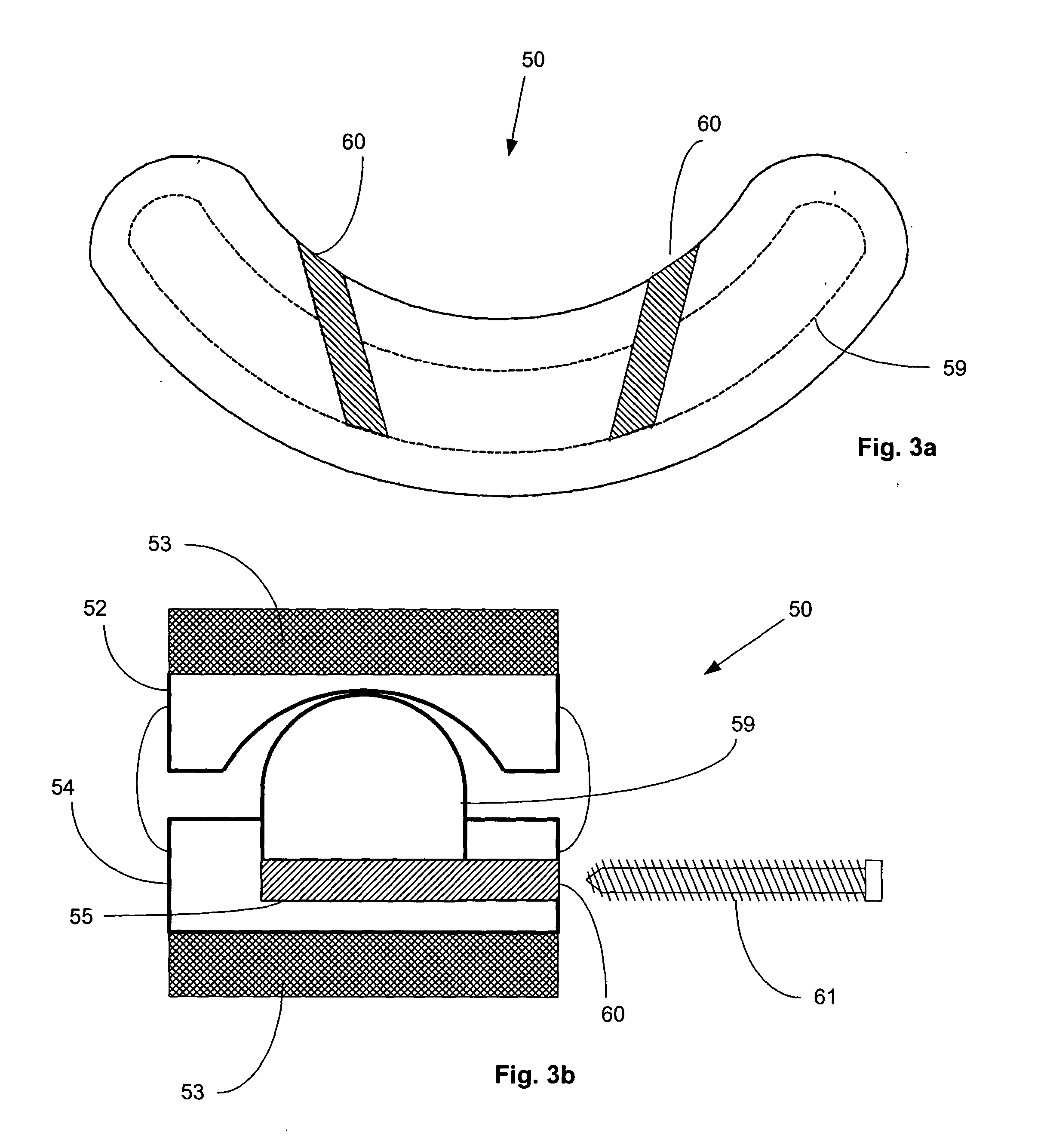
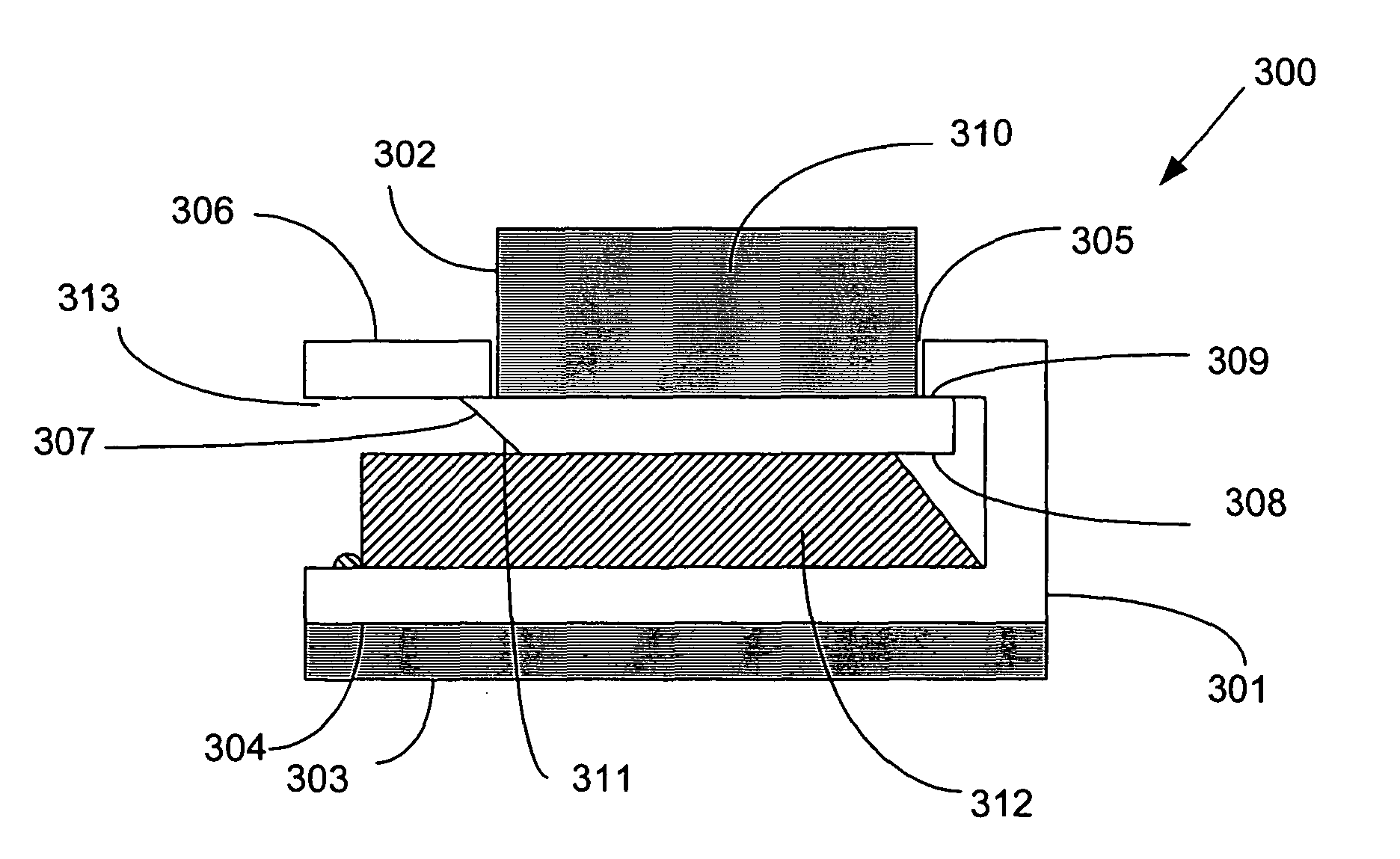
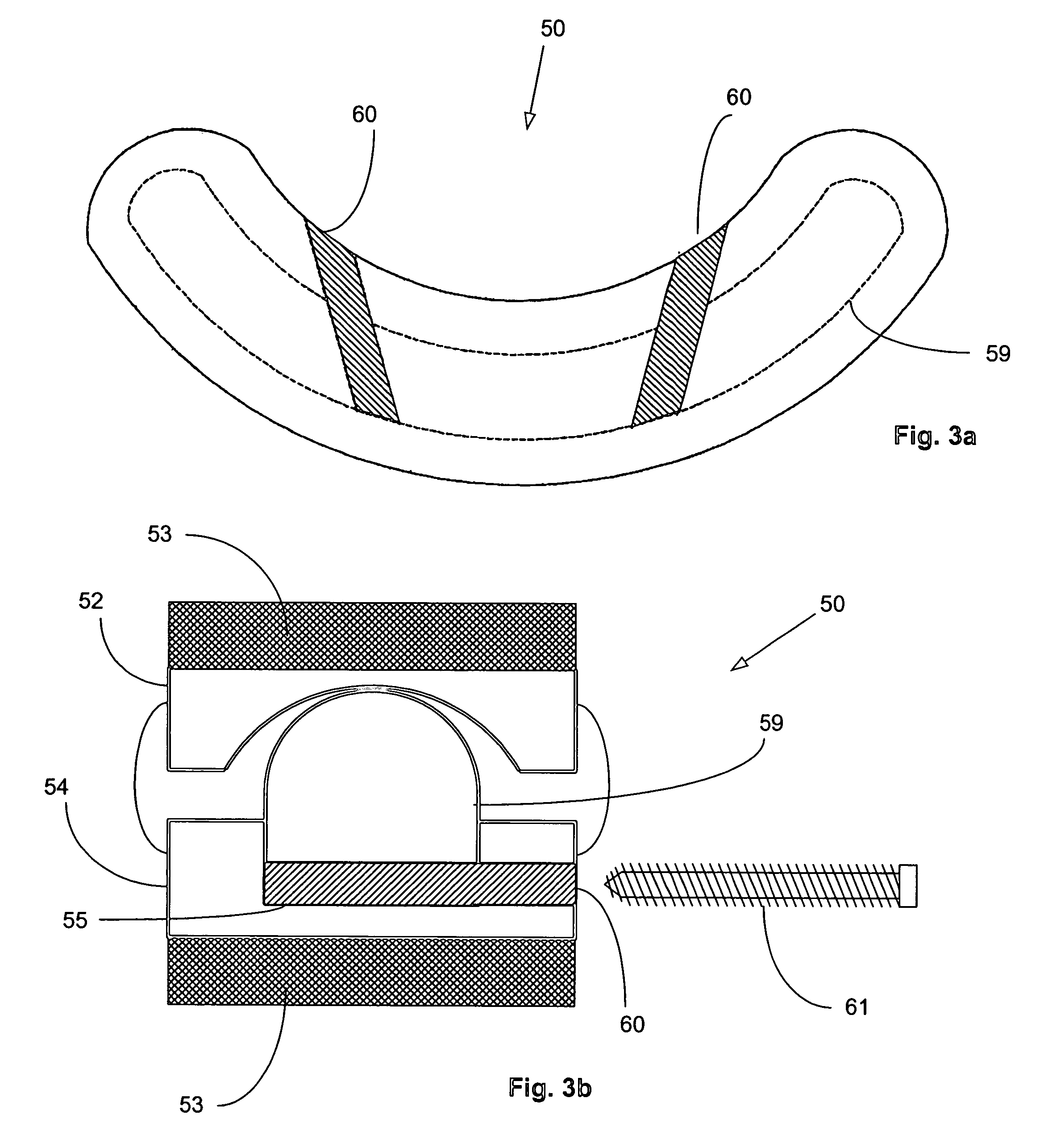
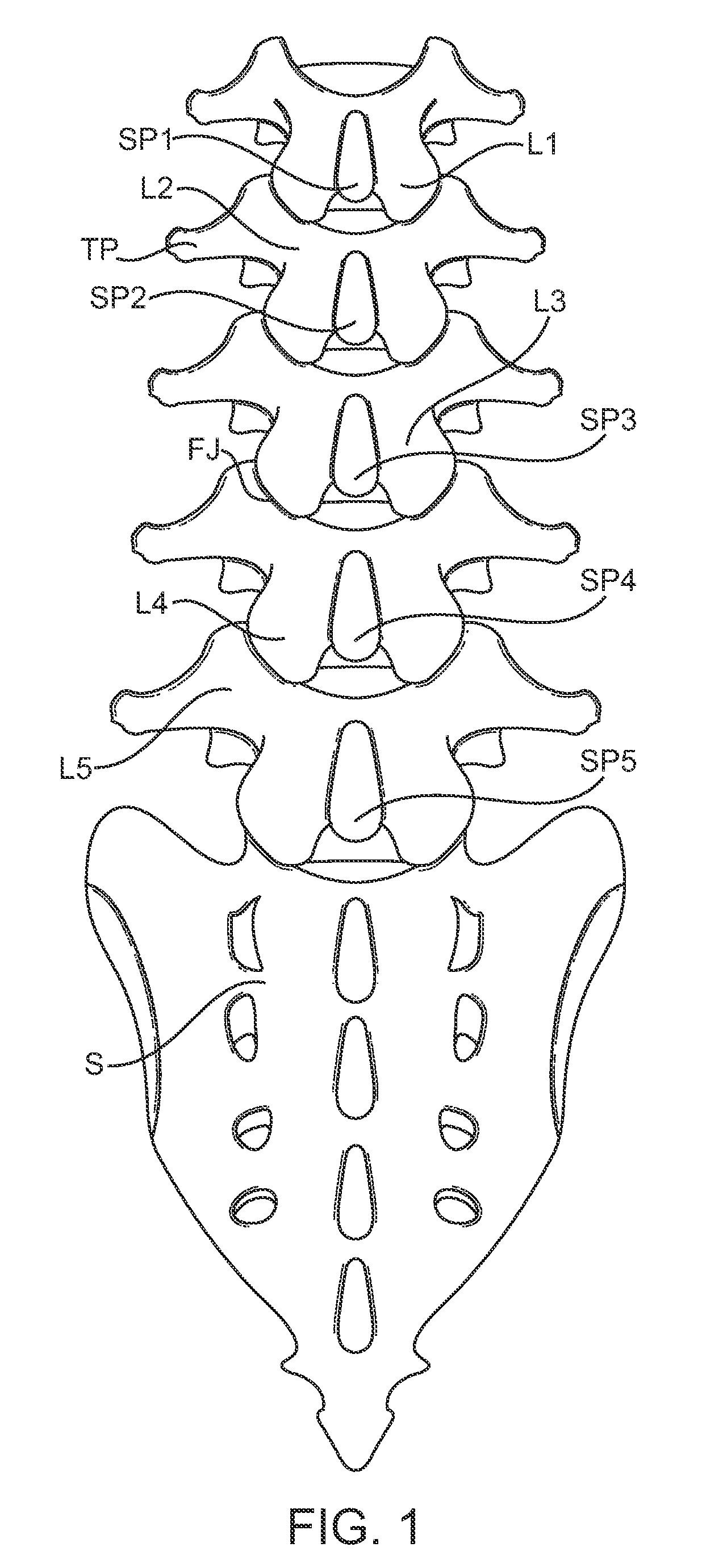
Methods and systems for increasing the bending stiffness and constraining the spreading of a spinal segment
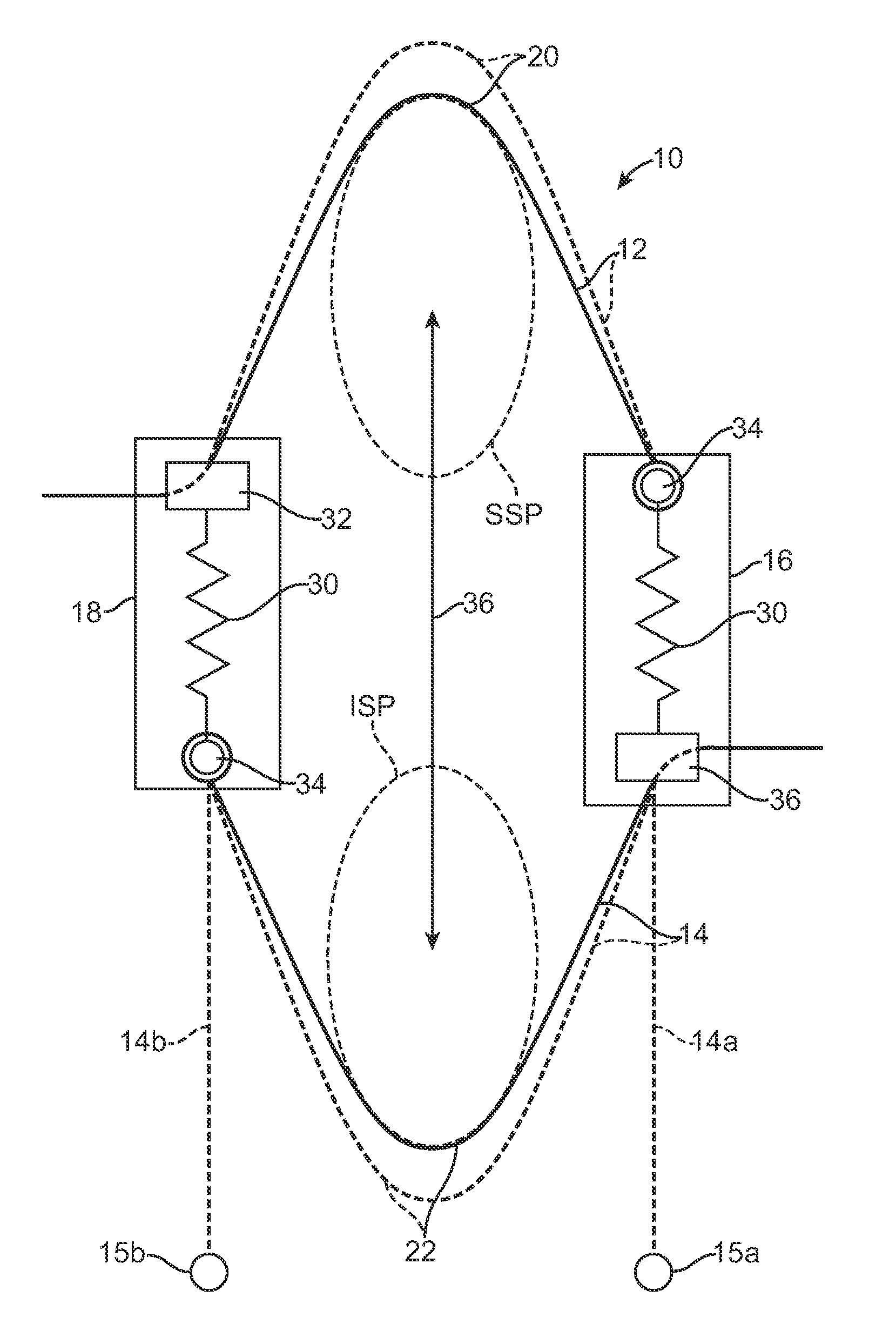
InactiveUS20100036424A1Increased bending stiffnessRelieve instabilityInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsMedicineTension member
A system for restricting spinal flexion includes superior and inferior tether structures joined by a pair of compliance members. Compliance members comprise tension members which apply a relatively low elastic tension on the tether structures. By placing the tether structures on or over adjacent spinous processes, flexion of a spinal segment can be controlled in order to reduce pain.
Owner:SIMPIRICA SPINE
Posterior Dynamic Stabilization System With Flexible Ligament
InactiveUS20090326583A1Limit excessive motionFlexible limitSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisLigament structure
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
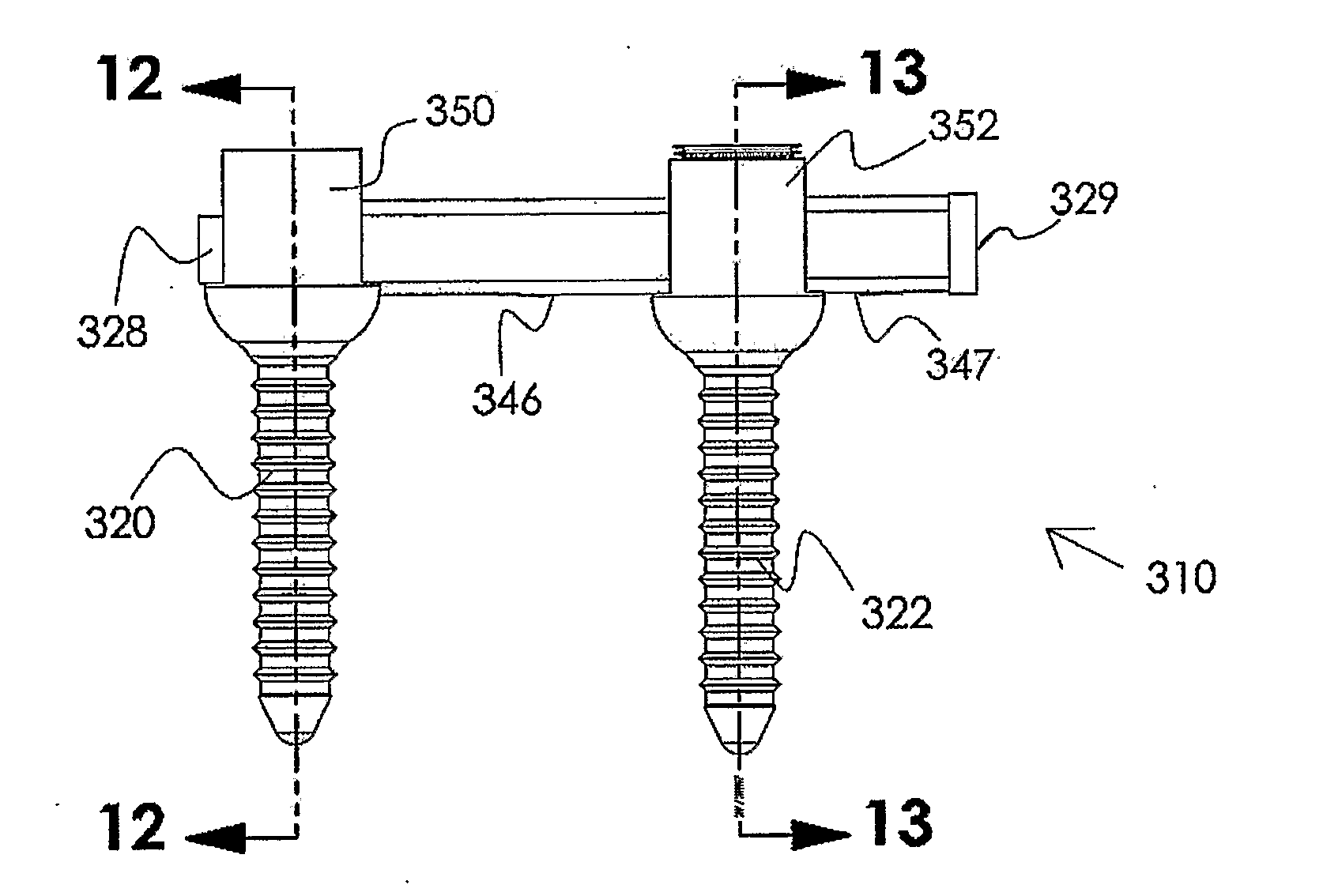
Posterior stabilization system
ActiveUS20060149230A1Limit axial rotationPrevent axial rotationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsPosterior stabilizationVertebra
Various methods and devices for replacing damaged, injured, diseased, or otherwise unhealthy posterior elements, such as the facet joints, the lamina, the posterior ligaments, and / or other features of a patient's spinal column, are provided. In one exemplary embodiment, a posterior implant is provided and it can be adapted to control movement of two or more adjacent vertebrae. In particular, the implant can be adapted to control extension, flexion, and lateral bending of the adjacent vertebrae. The implant can also be adapted to substantially prevent rotation of the adjacent vertebrae. In another exemplary embodiment, the implant can have an envelope of motion that is within an envelope of motion of a disc, either natural or artificial, that is disposed between the adjacent vertebrae. In other words, the implant can be configured to allow flexion, extension, lateral bending of the vertebrae to within the amount of flexion, extension, and lateral bending allowed by the particular disc. The implant can also be adapted to substantially prevent rotation of the vertebrae relative to one another.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Mobile spine stabilization device
InactiveUS20090131981A1Limited rangeFlexible limitSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSpinal columnMedicine
An orthopedic device is described for stabilizing the spinal column between first and second vertebral bodies. The device has first and second screws adapted for fixation to the first and second vertebral bodies, respectively. The device further includes an elongated ligament with a first end connected to the first screw and the second end operatively connected with the second screw. The ligament is made preferably of a nickel titanium alloy selected to have ductile inelastic properties at body temperature and is capable of plastic deformation to allow relative constrained motion between the vertebral bodies. The preferred nickel titanium has a martensite / austenite transition temperature above body temperature. In a preferred embodiment, the second pedicle screw includes a bearing for receiving the ligament in a slidably engageable relationship. The device further includes optional first and second dampening members surrounding the ligament for restraining the spinal column during flexion and extension.
Owner:WHITE PATRICK
Articulated Two-piece Wheeled Sport Board with Rigid Flexible Connector
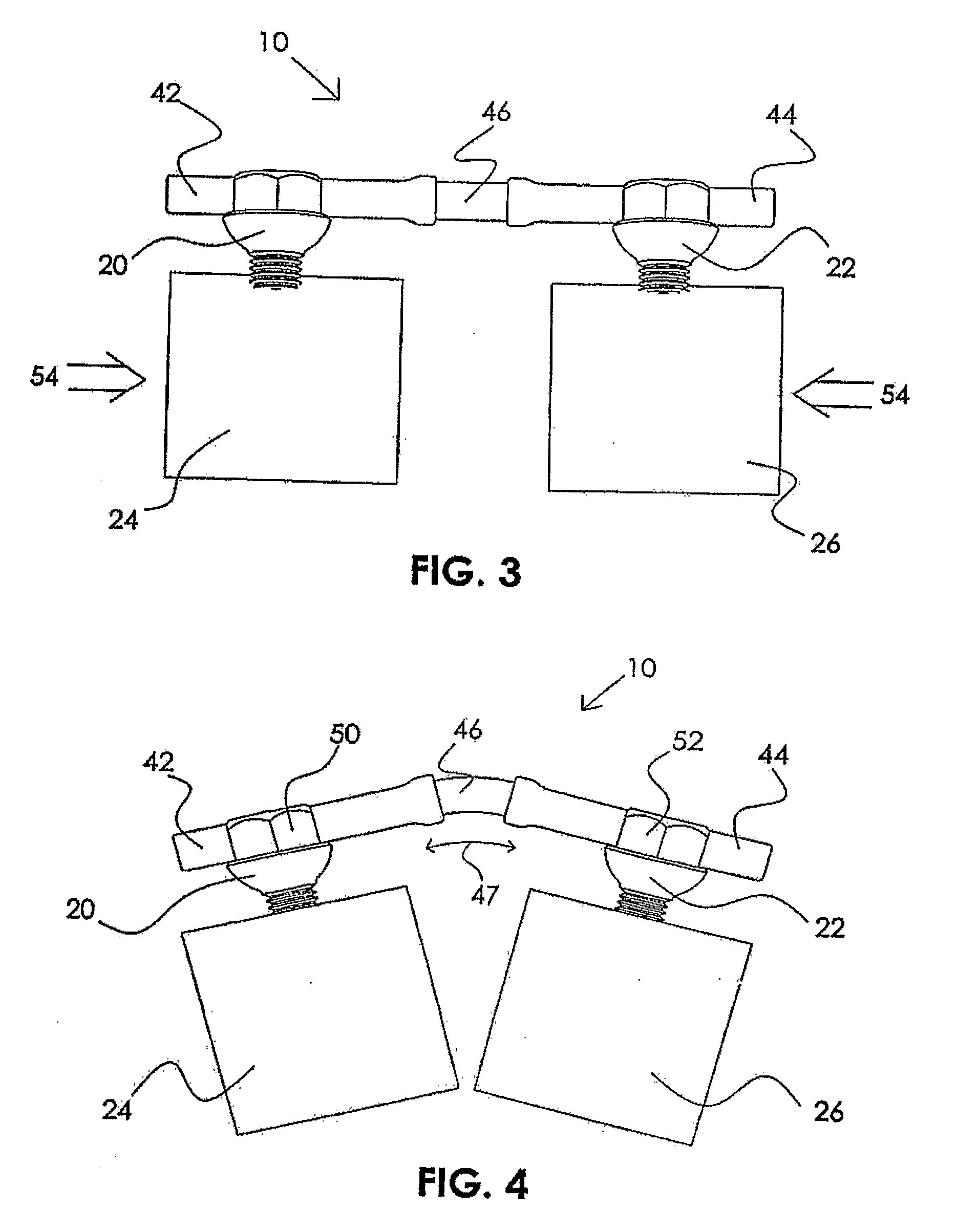
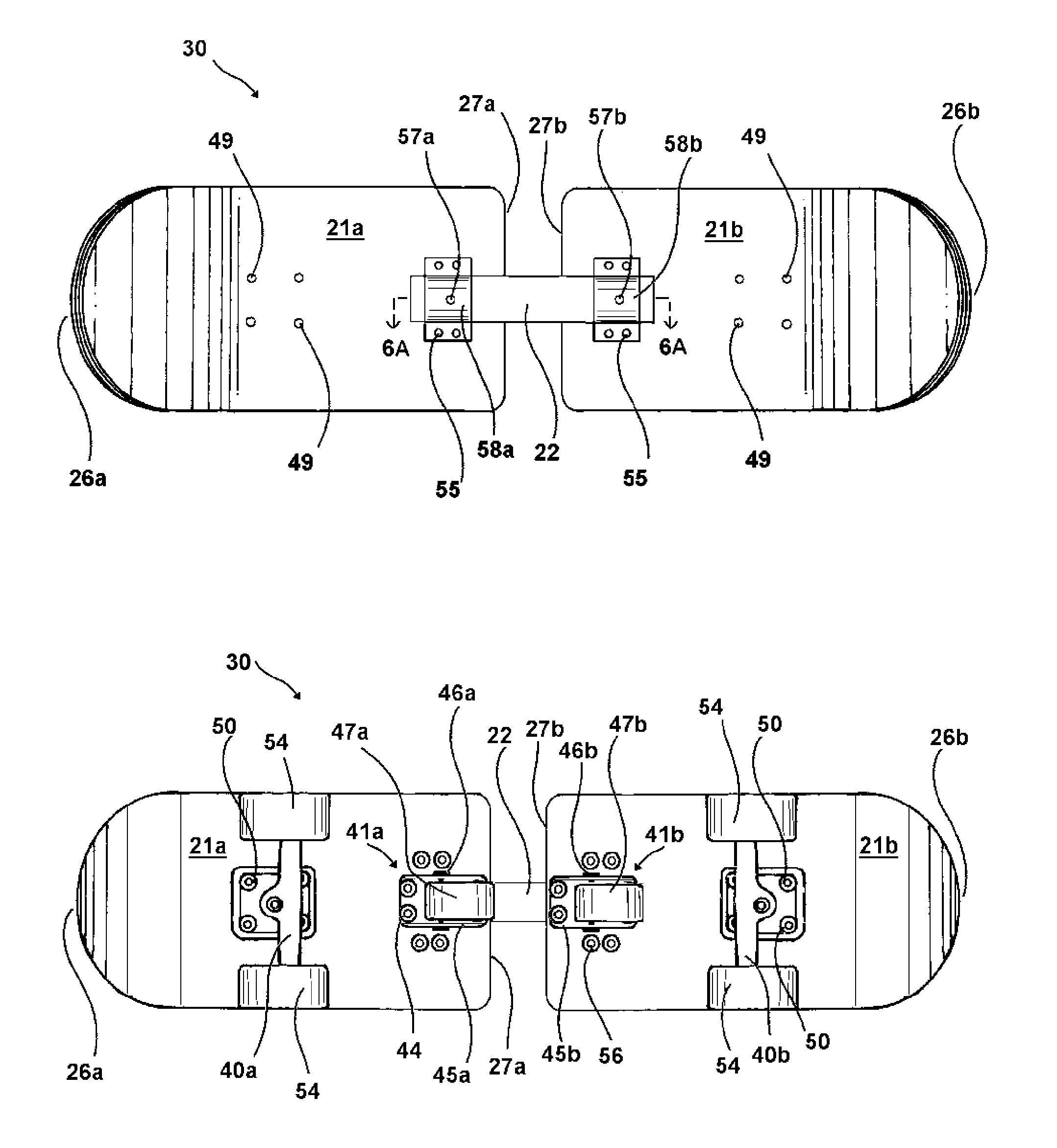
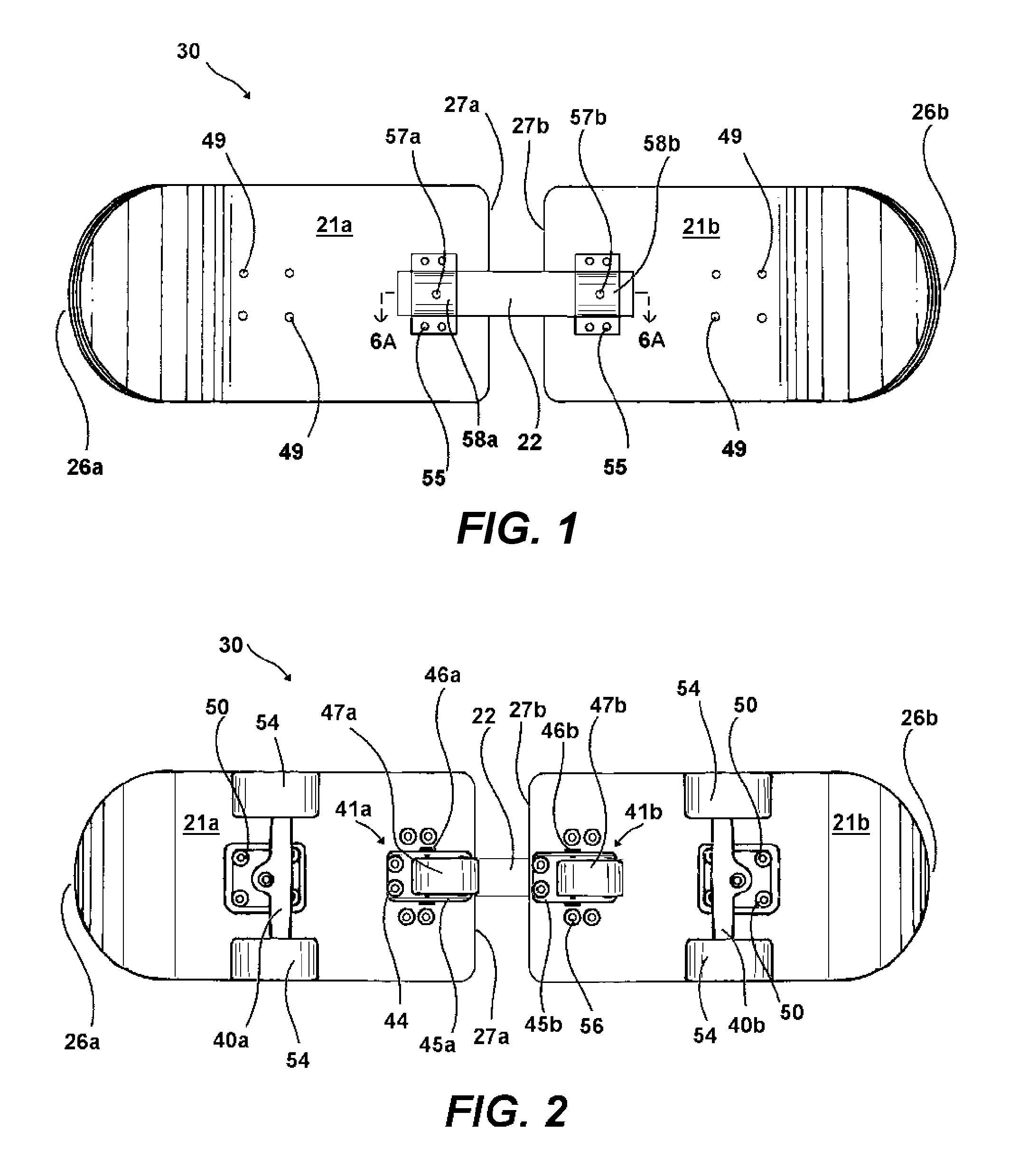
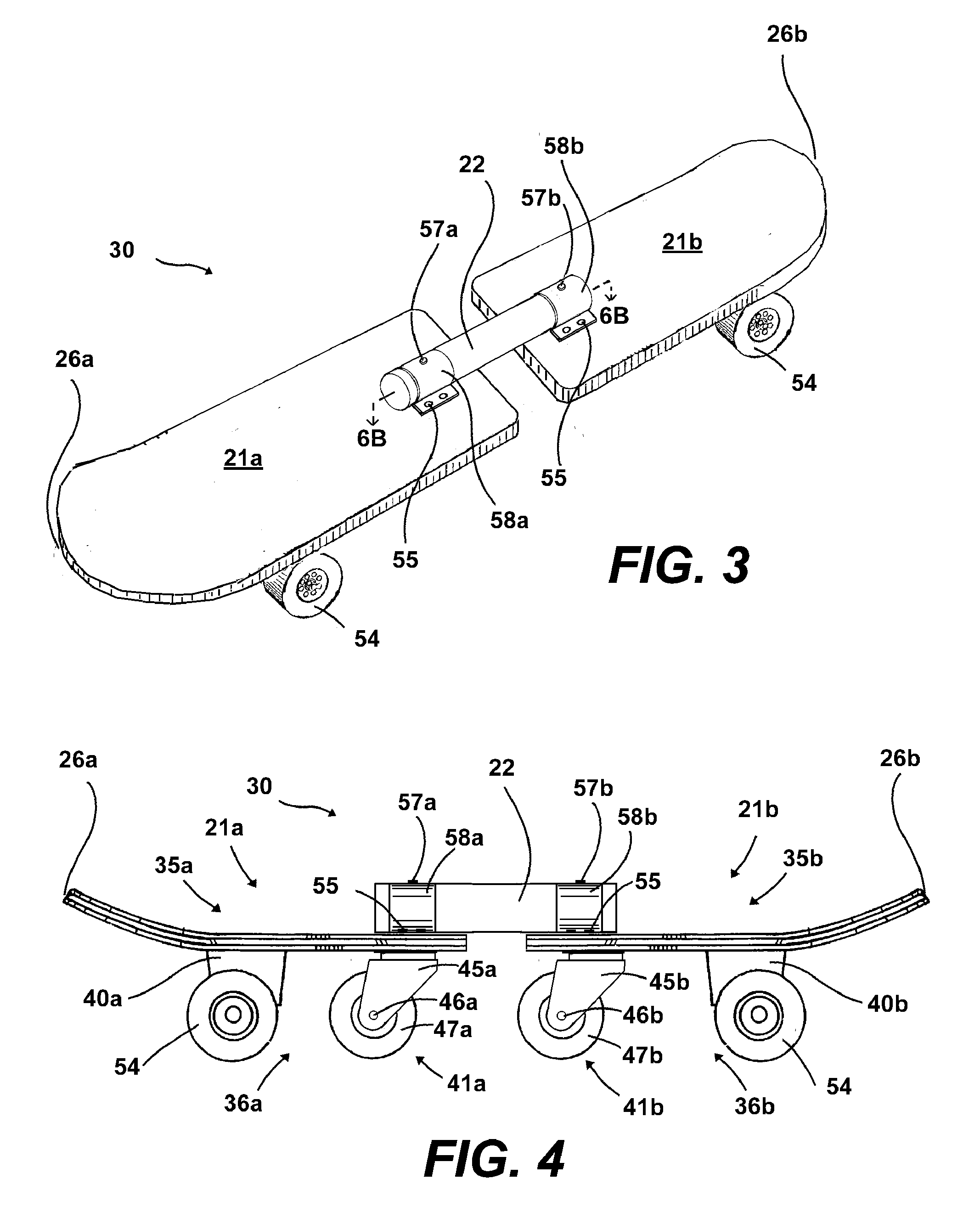
InactiveUS20100225080A1Ability to bend the boardFacilitate turn and stopRider propulsionSkate-boardsSlide plateEngineering
A two-piece articulated skateboard includes two sections connected by a connector. Standard skateboard trucks and wheels are attached to the sections at opposite ends of the articulated skateboard and swiveling casters are attached to the bottom of each section and positioned towards the connector. When riding like a one-piece skateboard, the rider's feet are placed over the trucks and the swiveling casters do not touch the ground. The connector only allows enough vertical movement around the lateral axis so that when the rider shifts his weight towards the connector, the swiveling casters are lowered to the ground and engaged, enabling the two-piece articulated skateboard to slide sideways. The connector provides for a small amount of left-to-right motion around the vertical axis, providing the ability to bend the board while in a slide and to facilitate turns and stops.
Owner:SMITH SHANE
Posterior stabilization system
ActiveUS7766940B2Prevent axial rotationFlexible limitInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsPosterior stabilizationLateral bending
Various methods and devices for replacing damaged, injured, diseased, or otherwise unhealthy posterior elements, are provided. In one exemplary embodiment, a posterior implant is provided and can be adapted to control movement of two or more adjacent vertebrae. In particular, the implant can be adapted to control extension, flexion, and lateral bending of adjacent vertebrae. The implant can also be adapted to substantially prevent rotation of the adjacent vertebrae. In another exemplary embodiment, the implant can have an envelope of motion that is within an envelope of motion of a disc, either natural or artificial, that is disposed between adjacent vertebrae. In other words, the implant can be configured to allow flexion, extension, lateral bending of the vertebrae to within the amount of flexion, extension, and lateral bending allowed by the particular disc. The implant can also be adapted to substantially prevent rotation of the vertebrae relative to one another.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
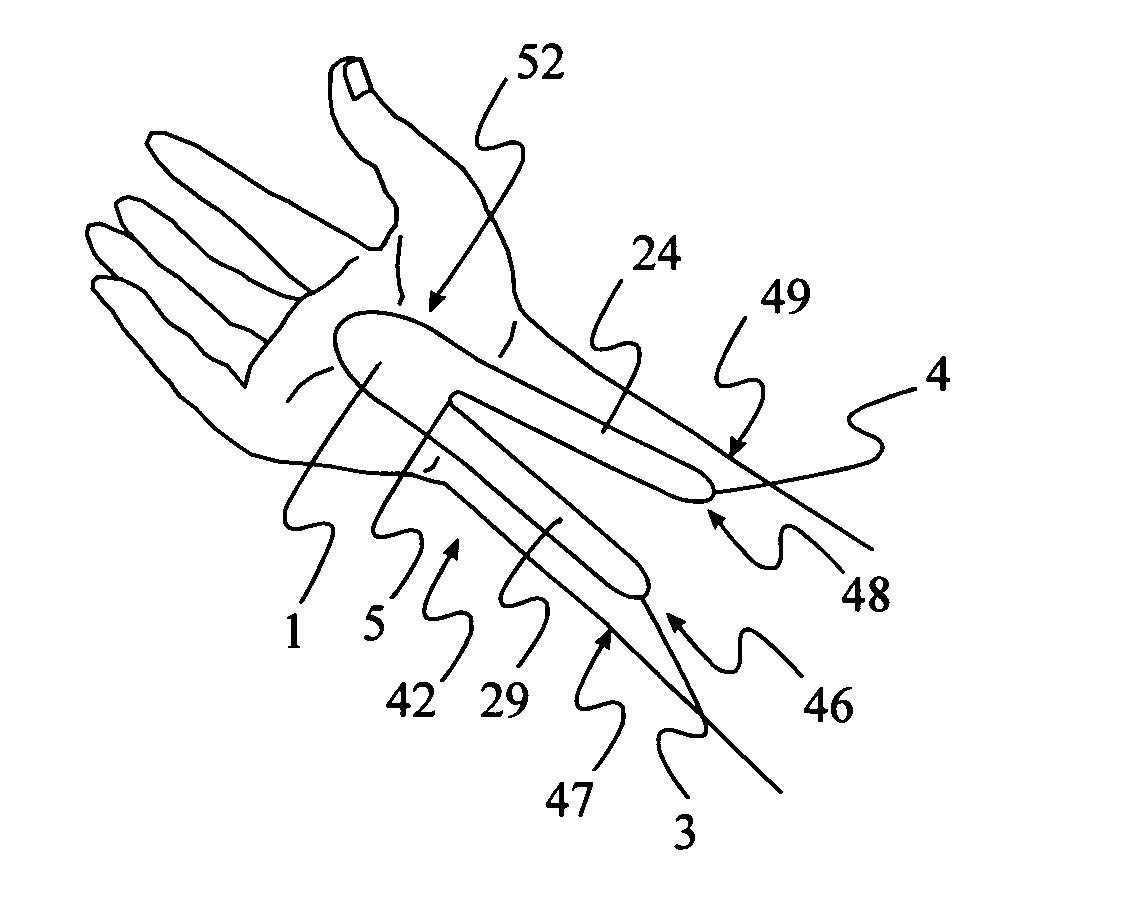
Method and application of a self adhesive splint
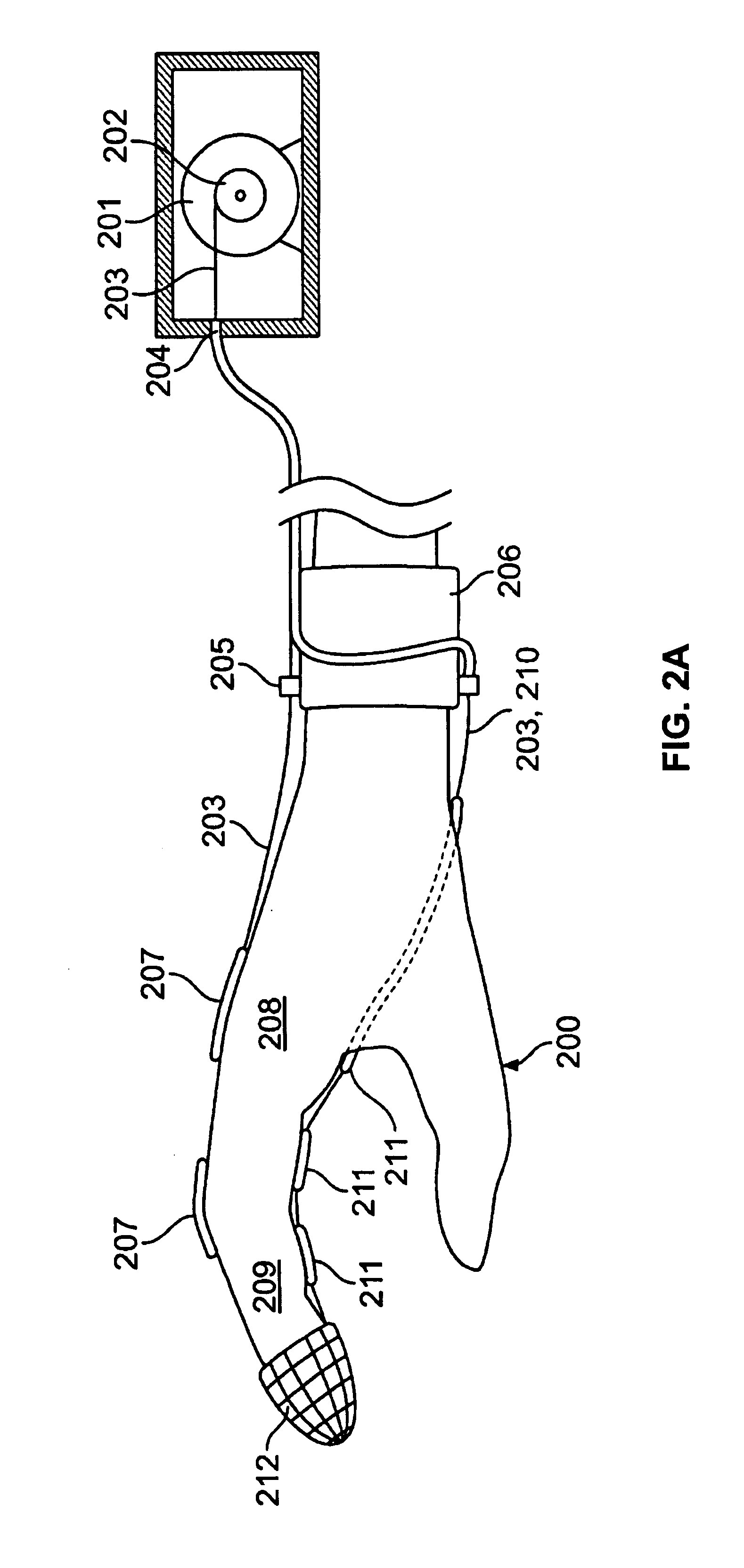
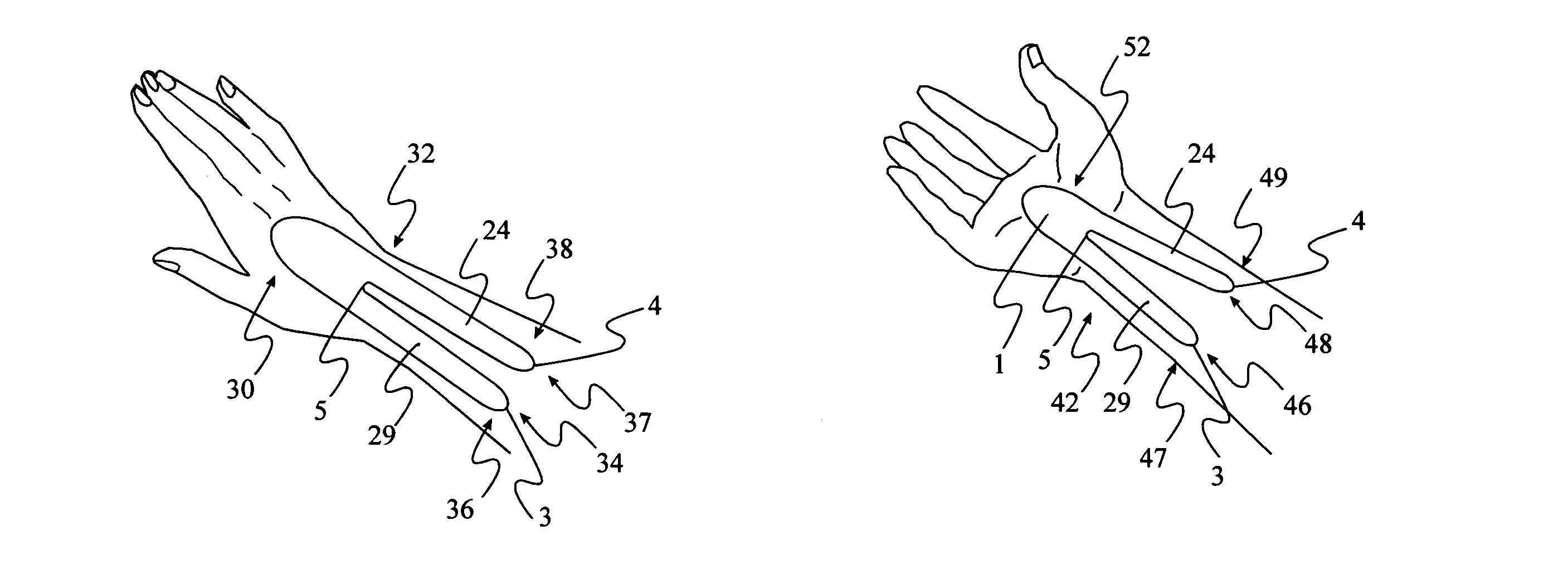
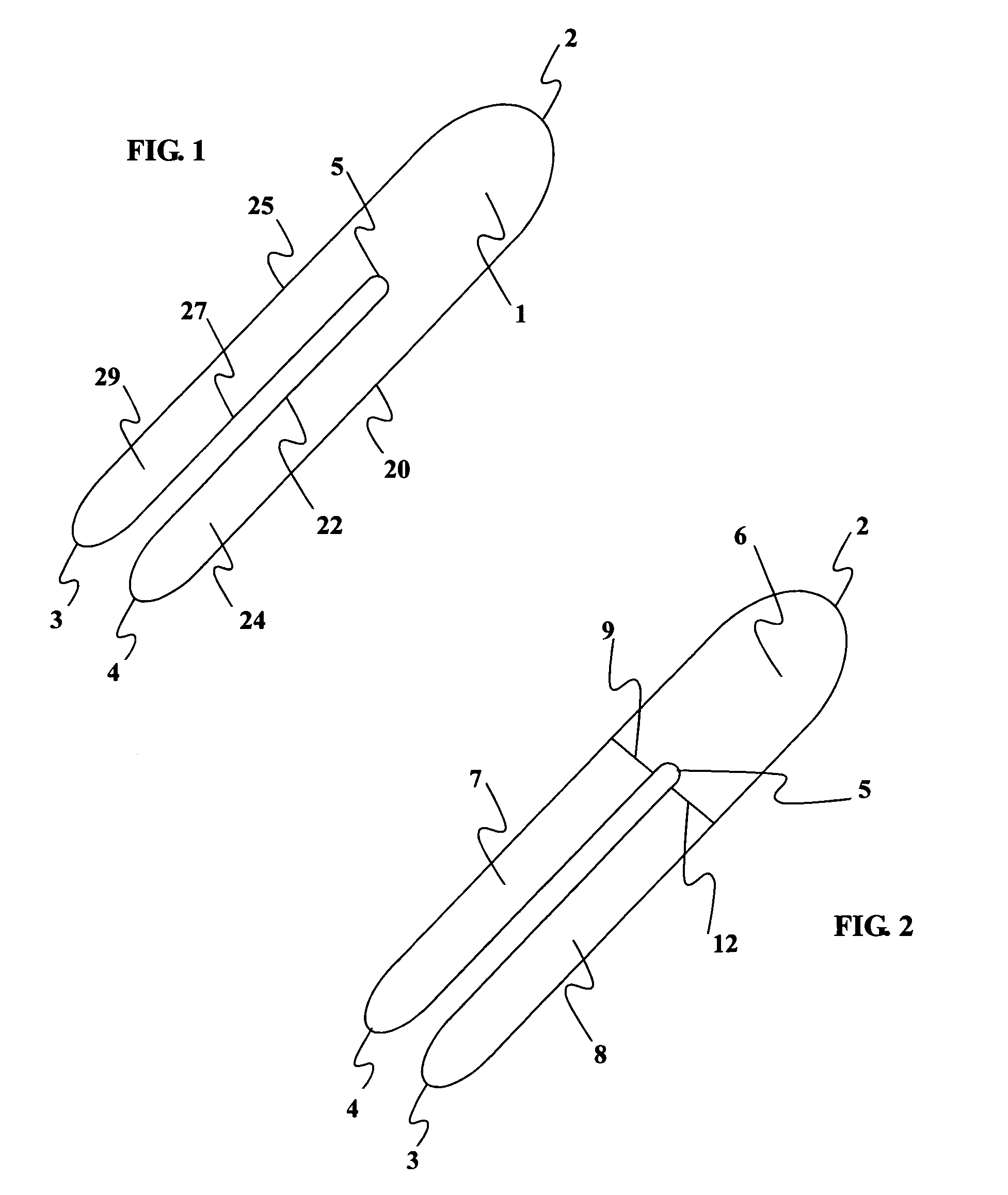
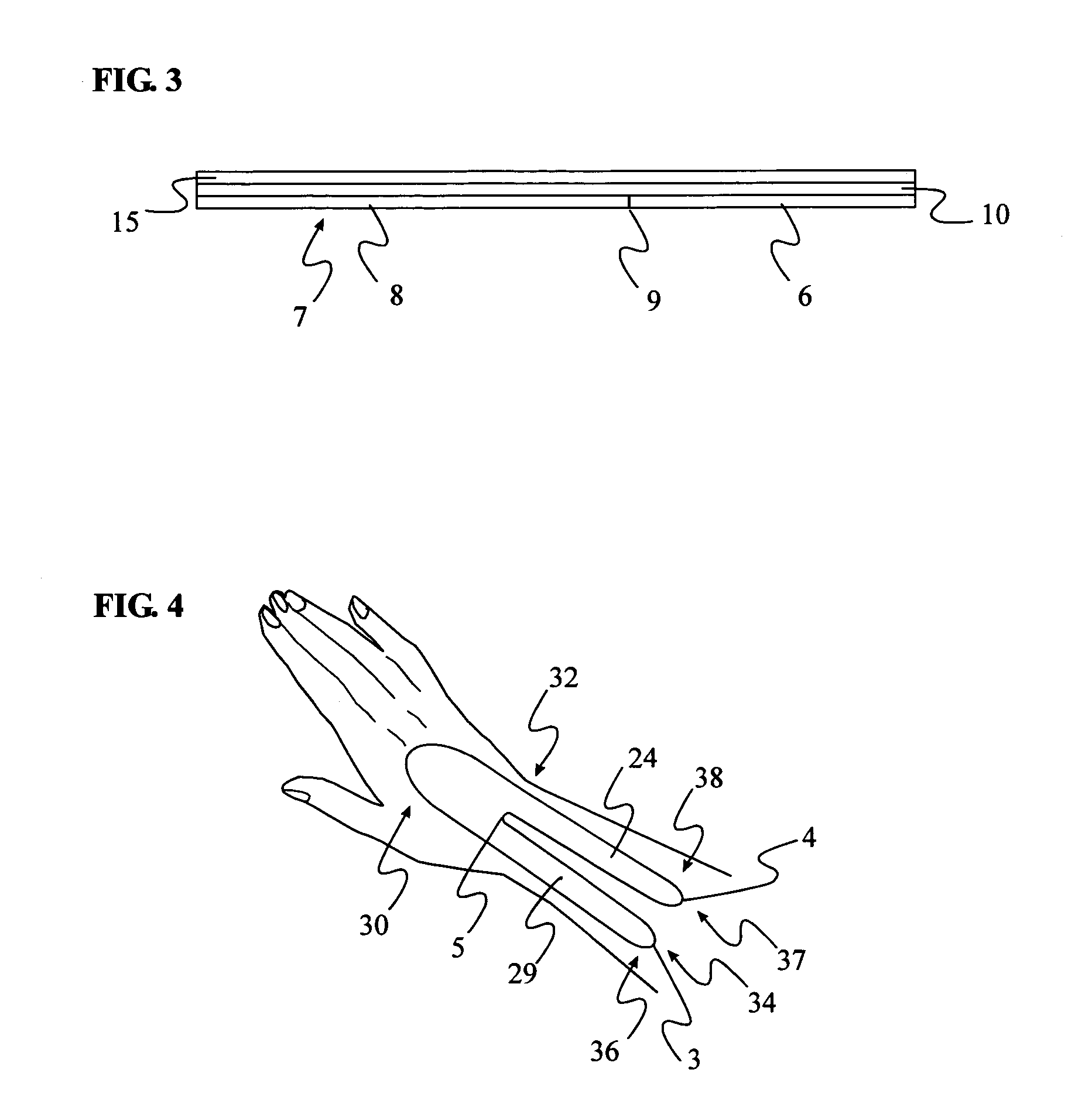
InactiveUS20050228323A1Reduce elasticityReduce abilityFeet bandagesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesMedian nerveSkin elasticity
The device is a thin, self-adhesive non-stretch splint, having the capability to flex. This device is intended for the treatment of repetitive stress injuries such as Carpal Tunnel Syndrome with elements that provide user adjustable limitation of movement within acceptable medical parameters. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome symptoms include pain and numbness in the thumb, index, and middle fingers, that are aggravated by compression of the median nerve. This device limits flexion, extension, ulnar and radial deviation movements of the wrist without compressing the median nerve The device limits movement by reducing skin elasticity on the surface skin above or below the wrist and up the forearm. The application provides biomechanical feedback to the wearer in the form of the tugging sensation on the skin around the perimeter of the device assisting the user in maintaining a more neutral wrist position without imposing wrist immobilization. The design elements allow the use of the device in such a manner that produces no additional pressure to the median nerve while in use. Furthermore the method of application provides a means for the user to regulate the amount of wrist movement to provide a greater comfort level while still limiting movement within medically proven parameters. The adhesive nature of the device eliminates the need for external straps that normally wrap completely around the forearm and hand to hold a splint in place. The application of the device limits movement by greatly reducing the ability of the skin to stretch by placing a self-adhesive non-stretch splint directly on the skin. The device, and how it is placed utilizes the wearers skin elasticity to provide biomechanical feedback to the user to promote better wrist posture.
Owner:TORNAI RICHARD MANUEL
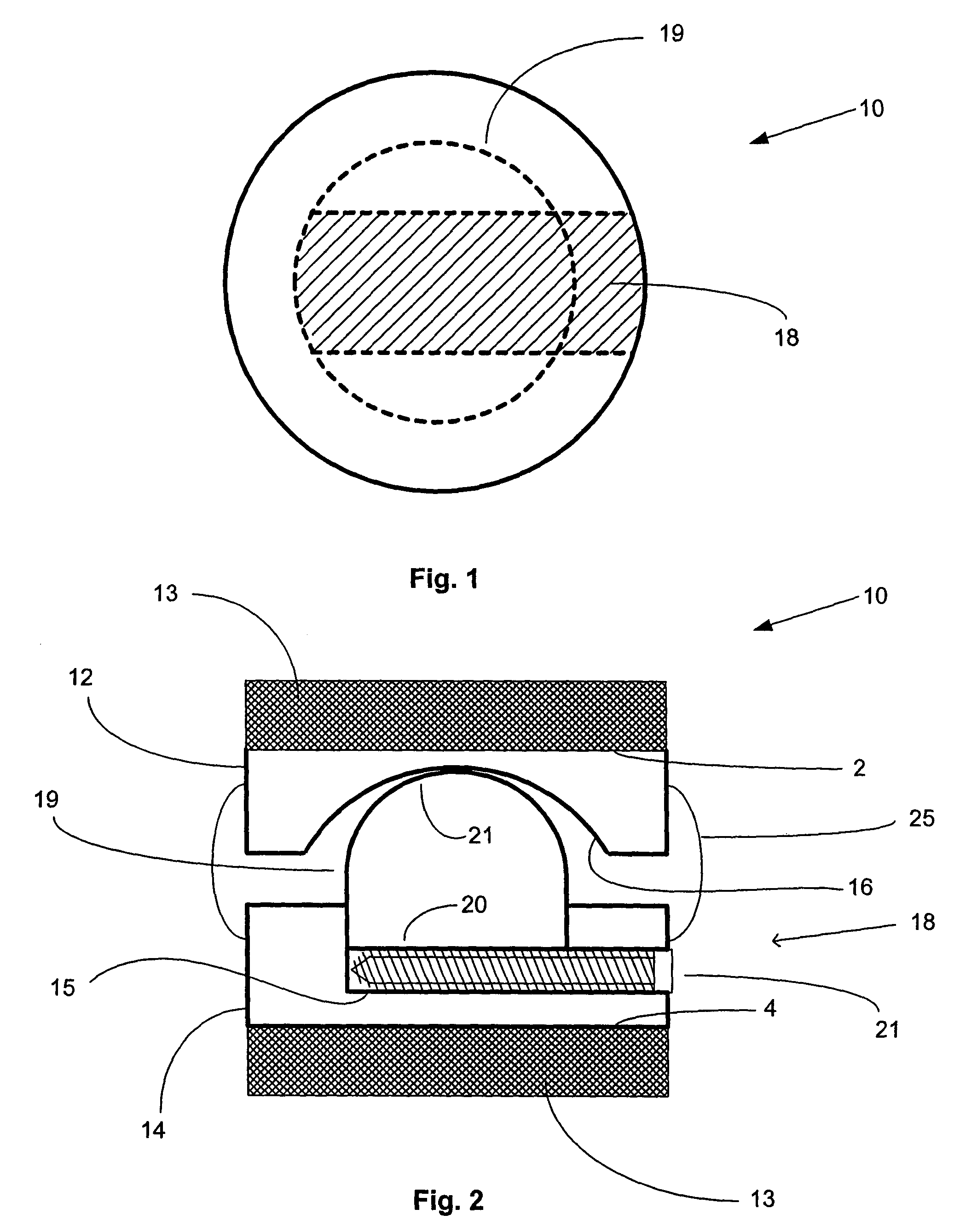
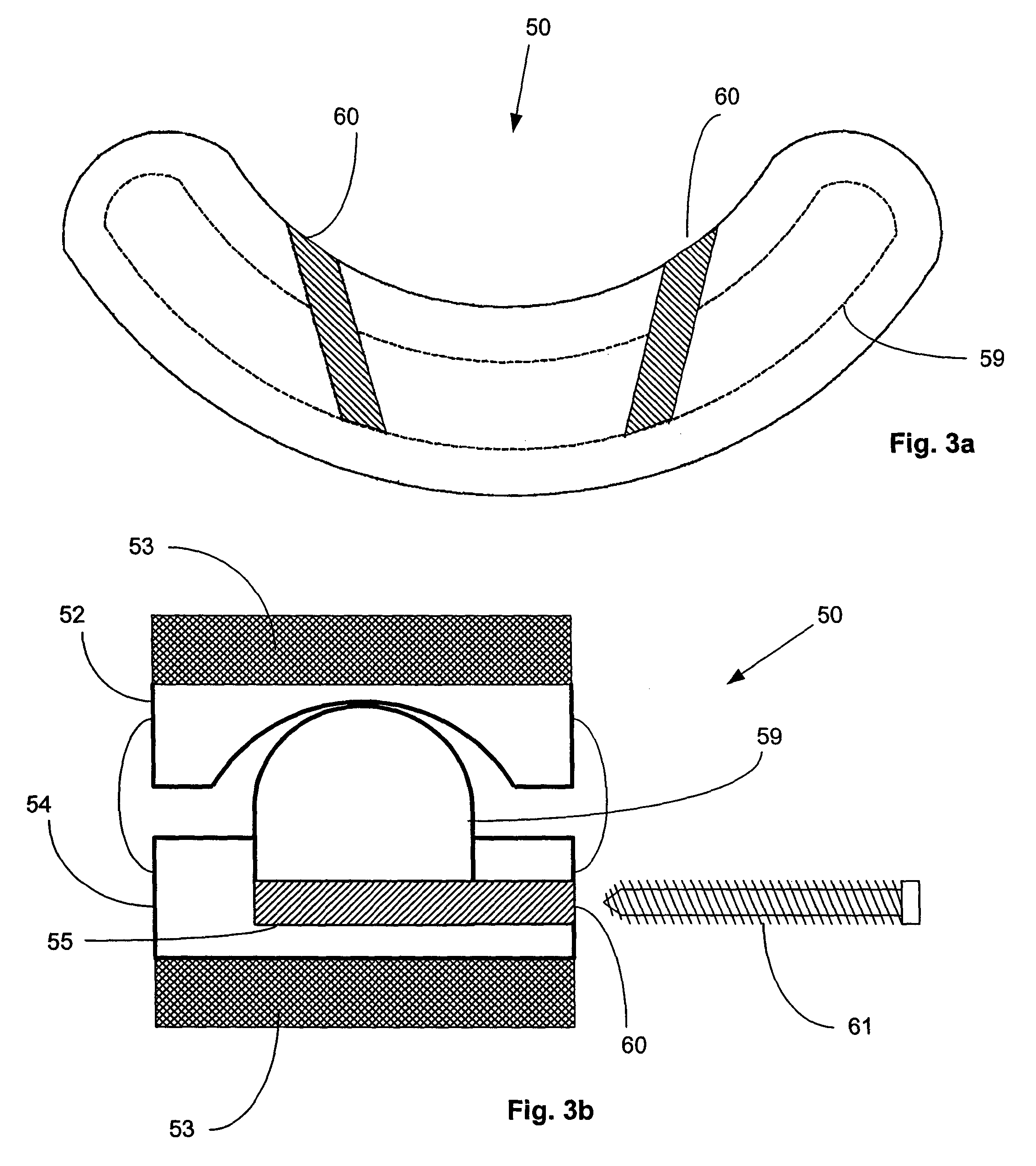
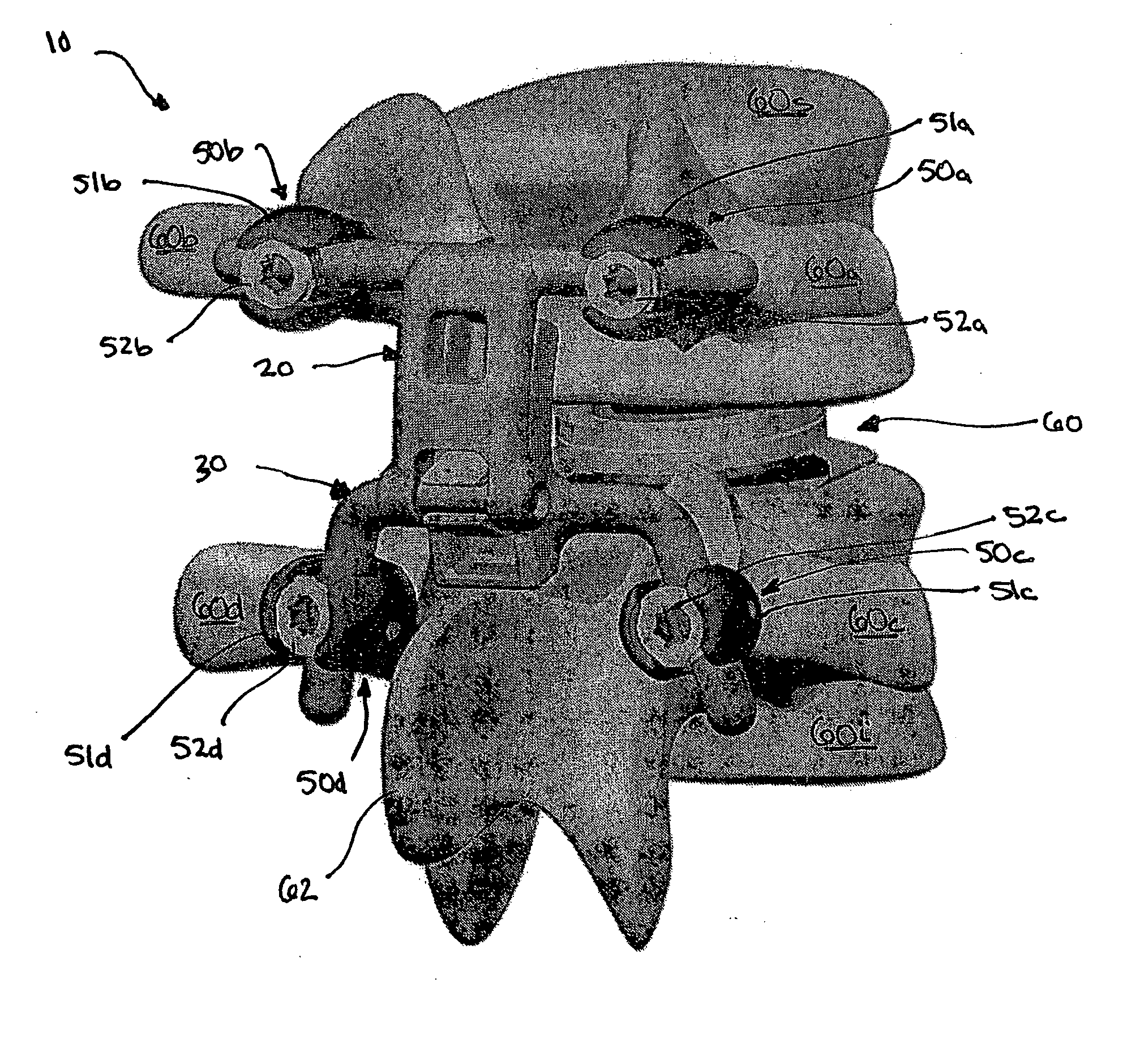
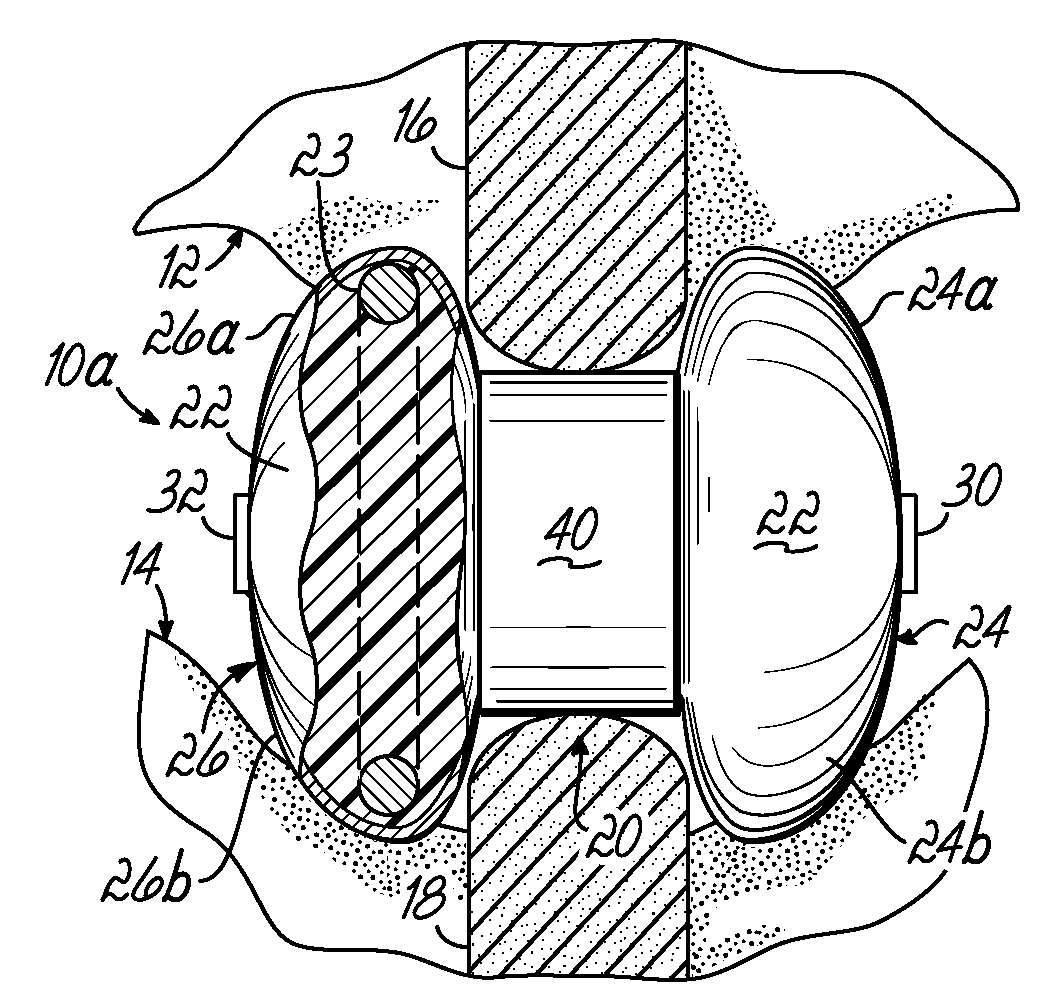
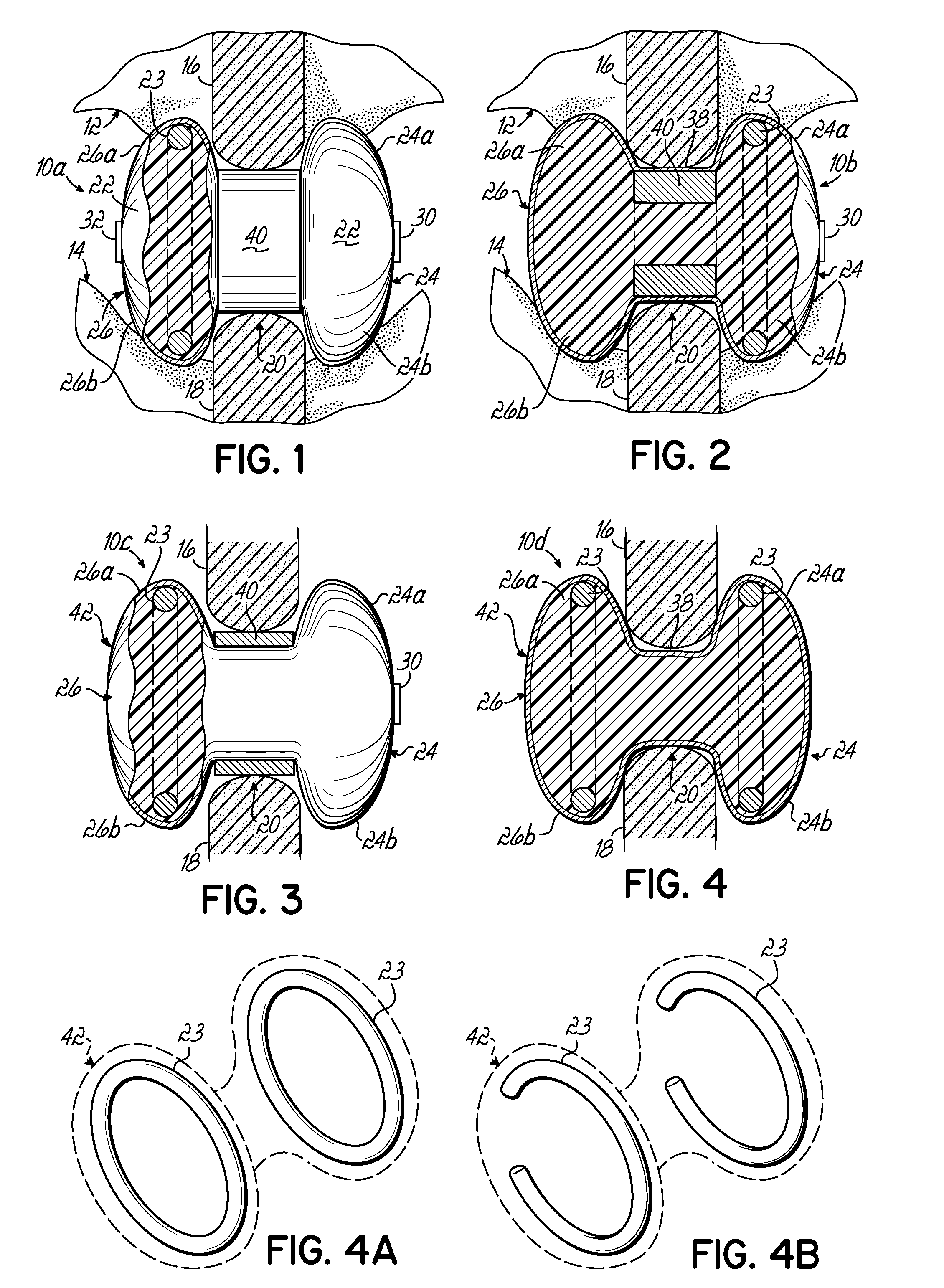
Expandable interspinous process spacer with lateral support and method for implantation
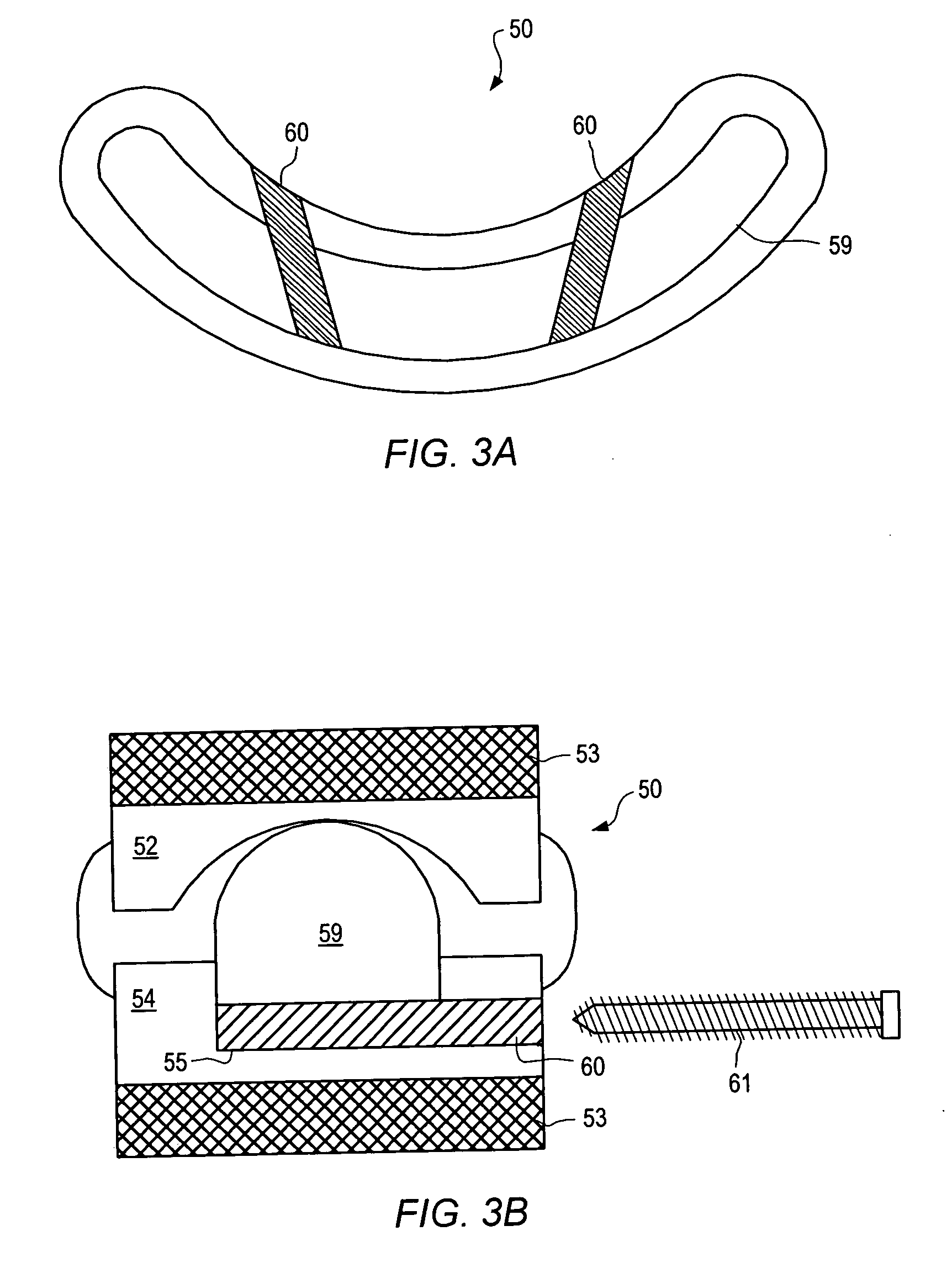
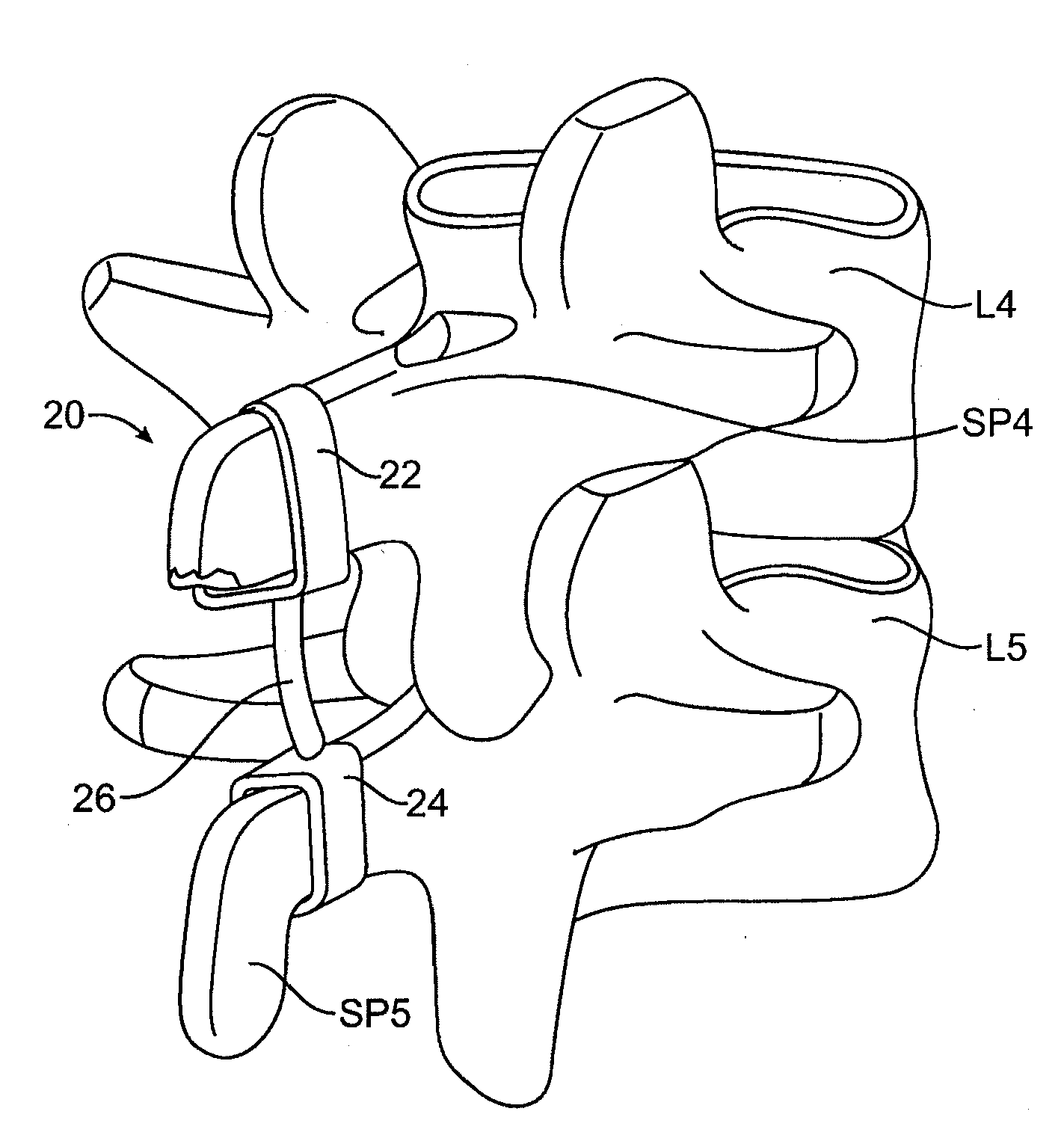
ActiveUS20090216274A1Relieve pressureRelief the painInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinous process
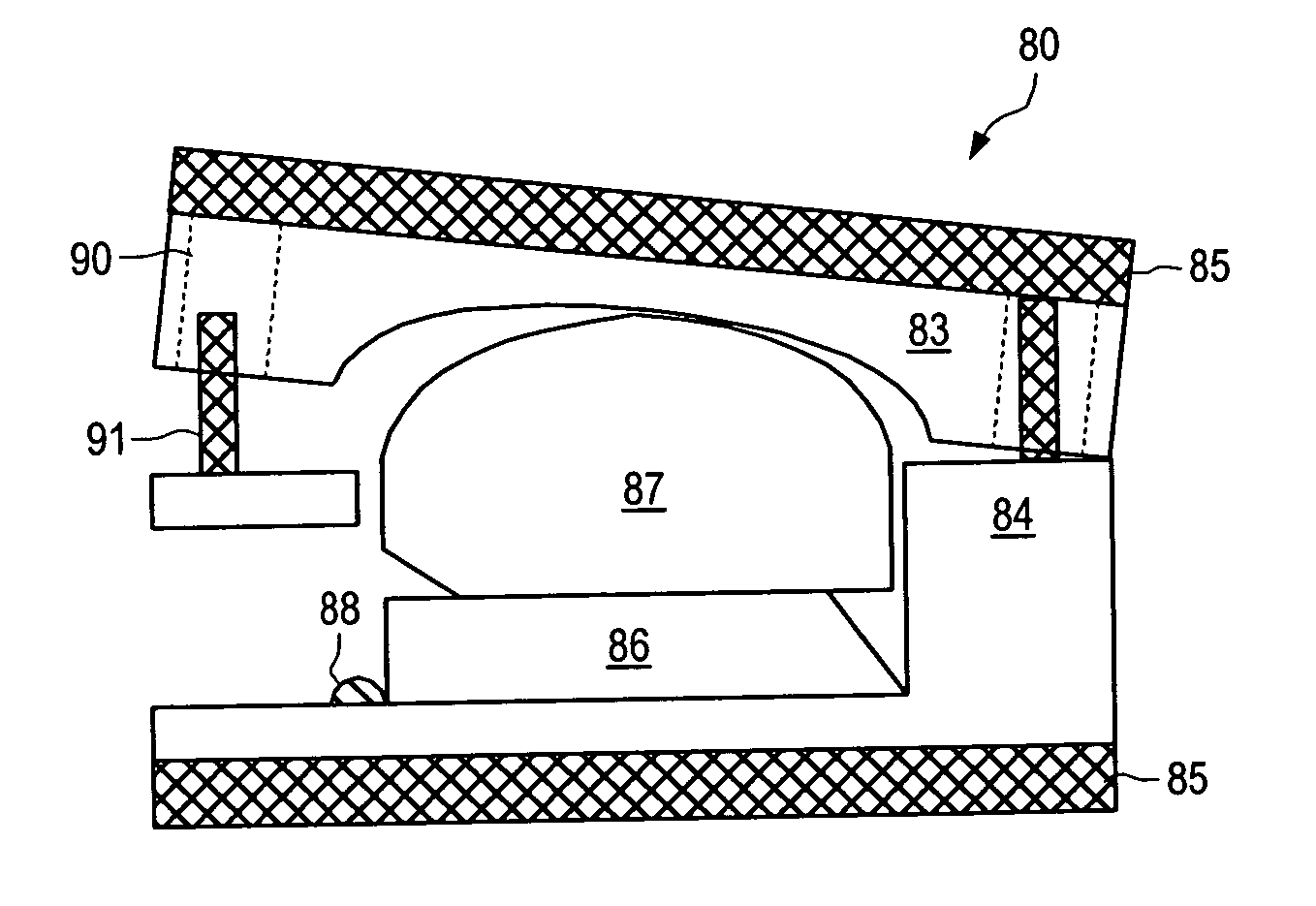
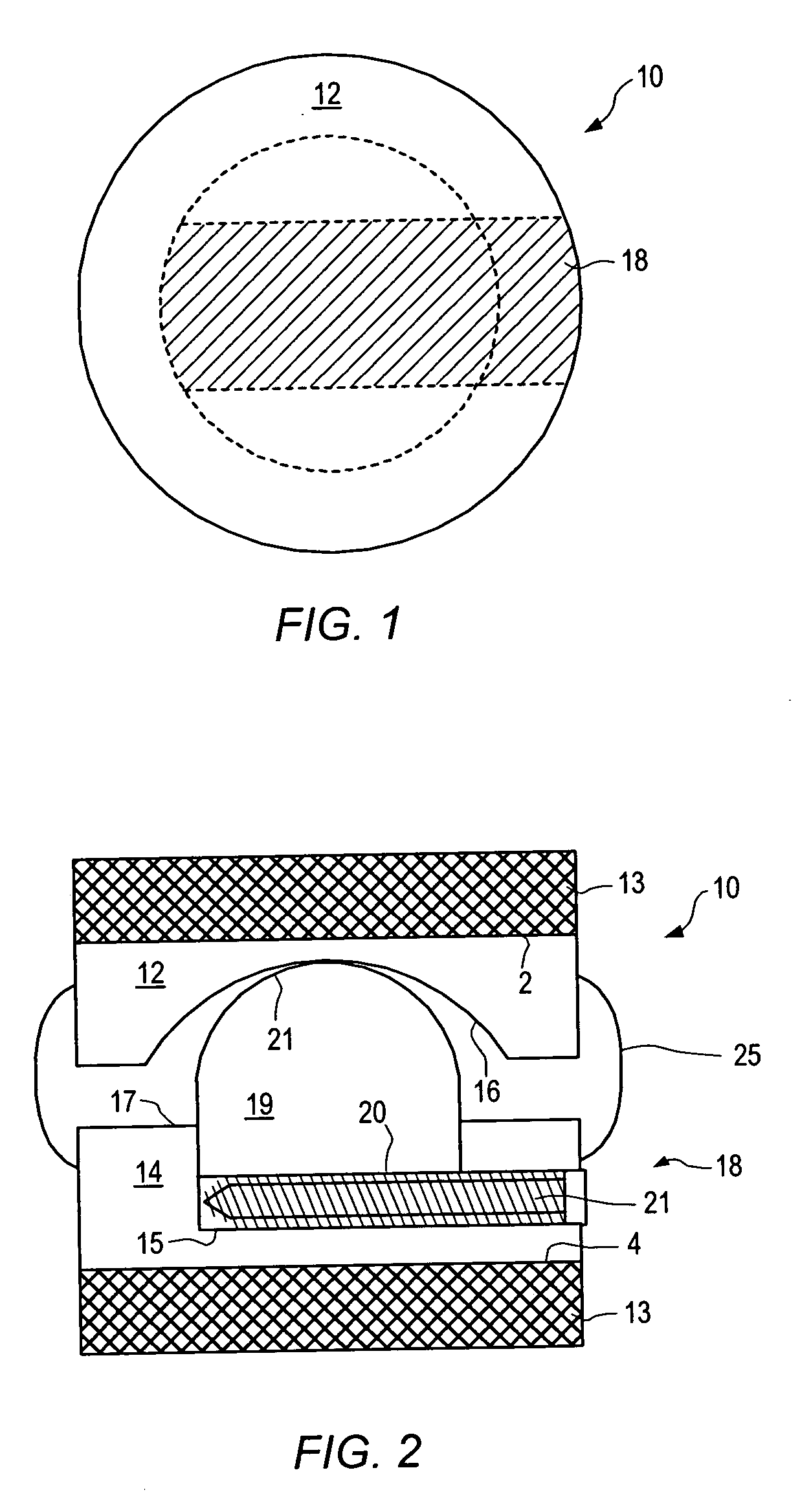
An interspinous process spacer and method of implanting same is provided for maintaining separation between adjacent spinous processes of adjacent vertebrae. The spacer has two lateral portions and a medial portion therebetween, the medial portion adapted to reside between the adjacent superior and inferior spinous processes in the deployed configuration to maintain separation therebetween. The lateral portions each comprise a superior lateral portion and an inferior lateral portion adapted to reside on the lateral side of the respective superior and inferior spinous process in the deployed configuration to maintain positioning of the interspinous process spacer between the two adjacent vertebrae. The lateral portions each comprise an expandable lateral member that is expandable from an insertion configuration to the deployed configuration, and at least one of the lateral portions includes within it a lateral support member configured to be deformable for the insertion configuration and expanded in the deployed configuration. The method includes introducing the spacer through a tubular delivery device to the region between the spinous processes and positioning therein, followed by retraction of the delivery device and expansion of the expandable lateral members and lateral support members.
Owner:ZIMMER GMBH
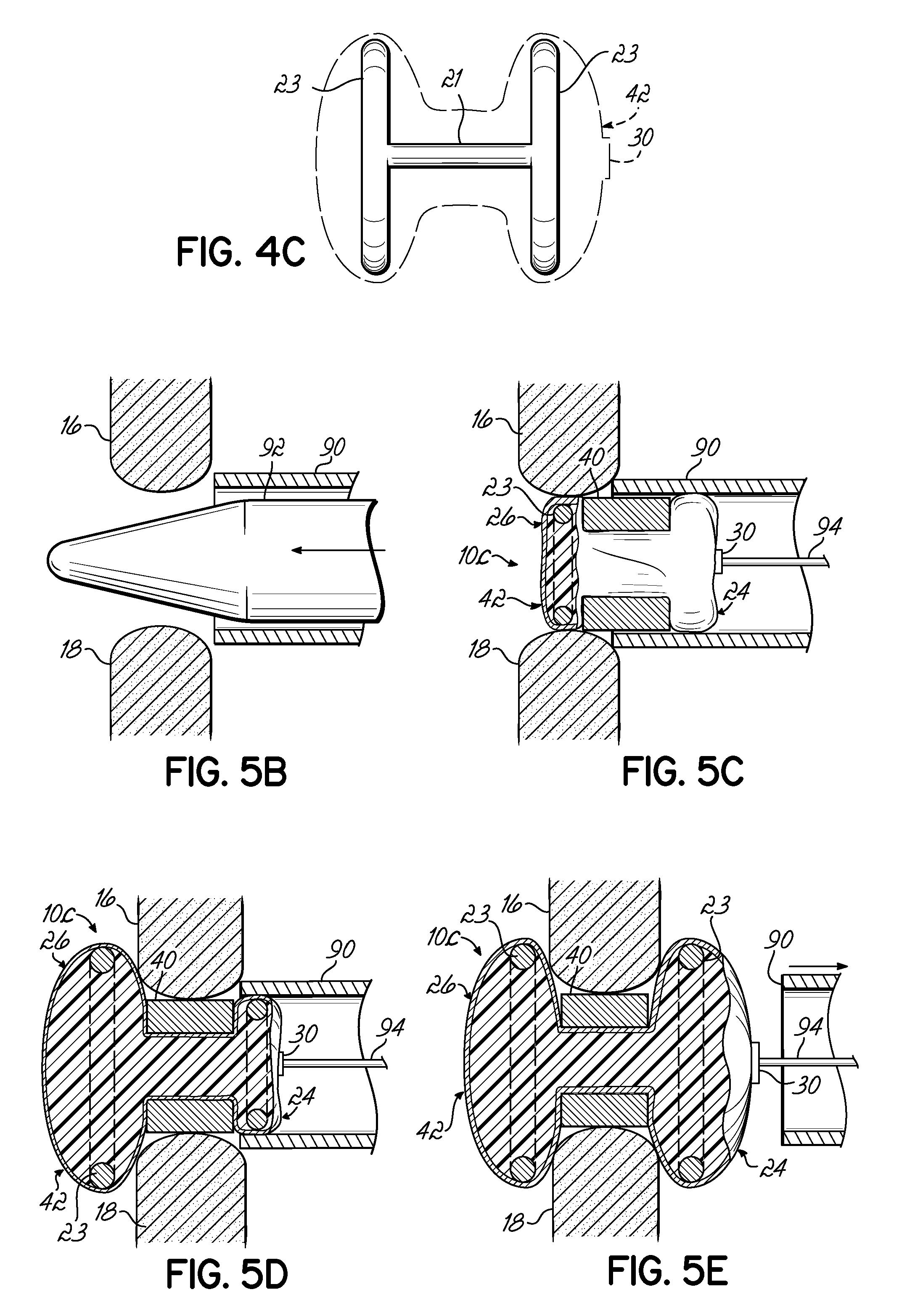
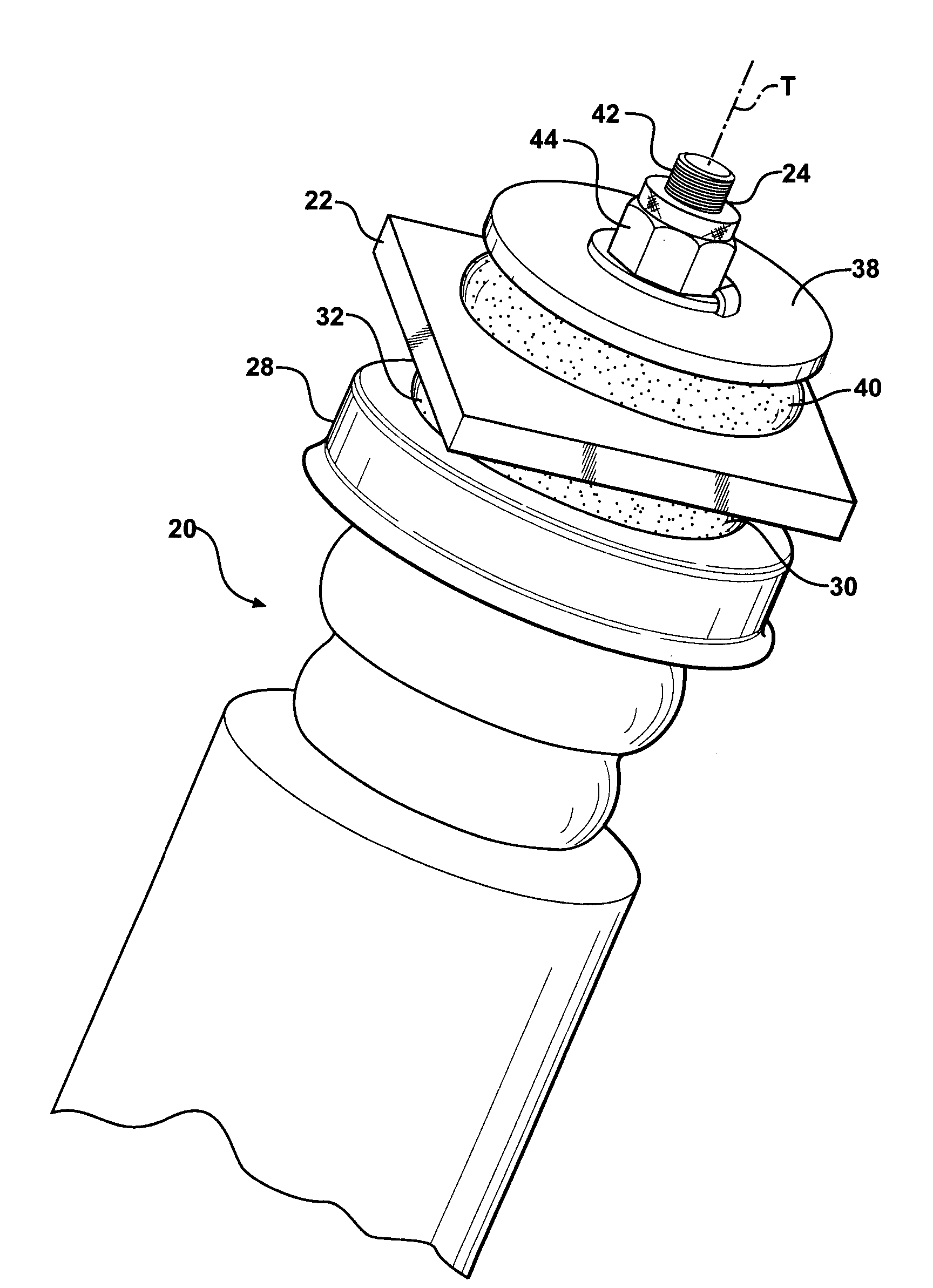
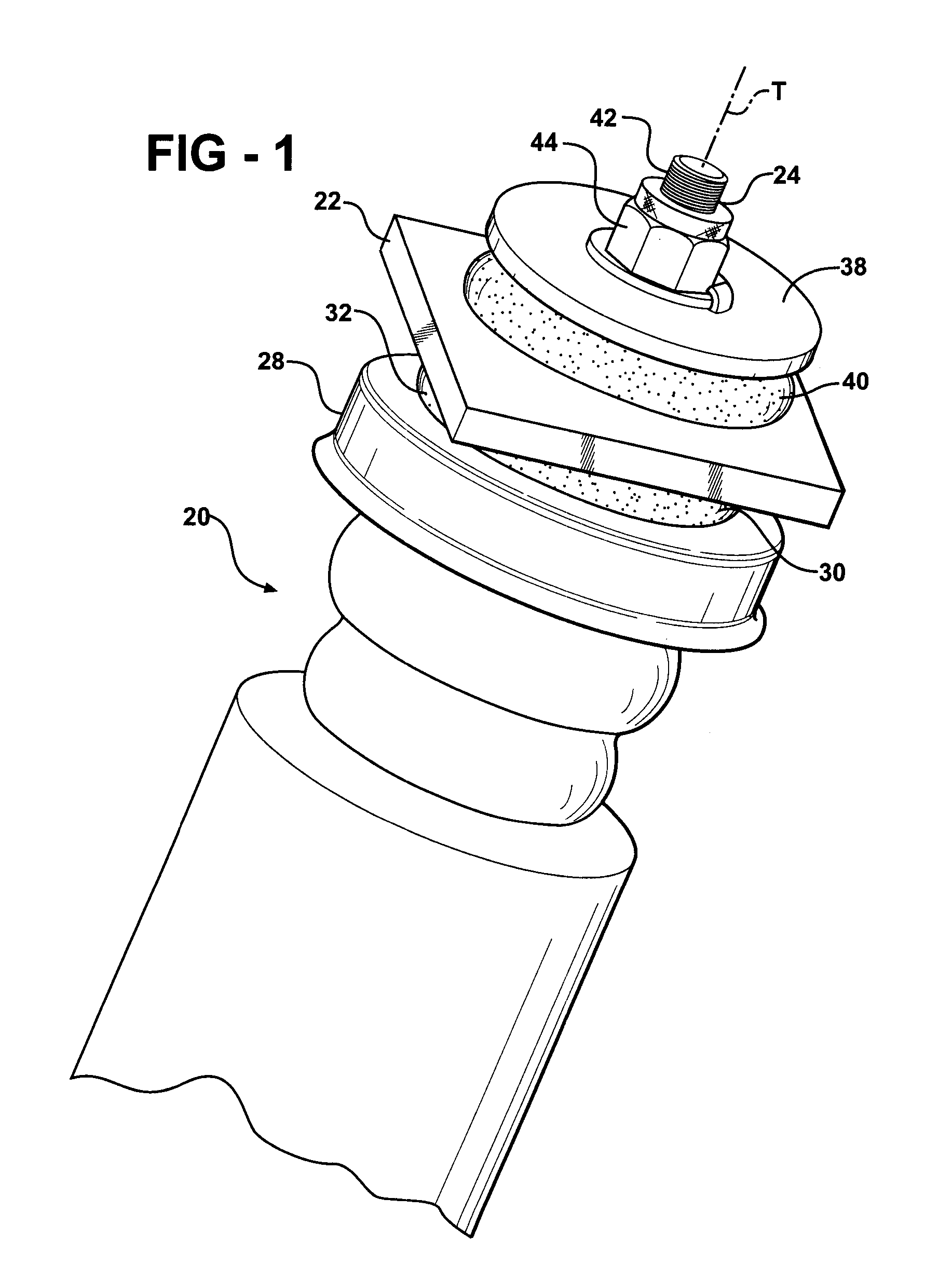
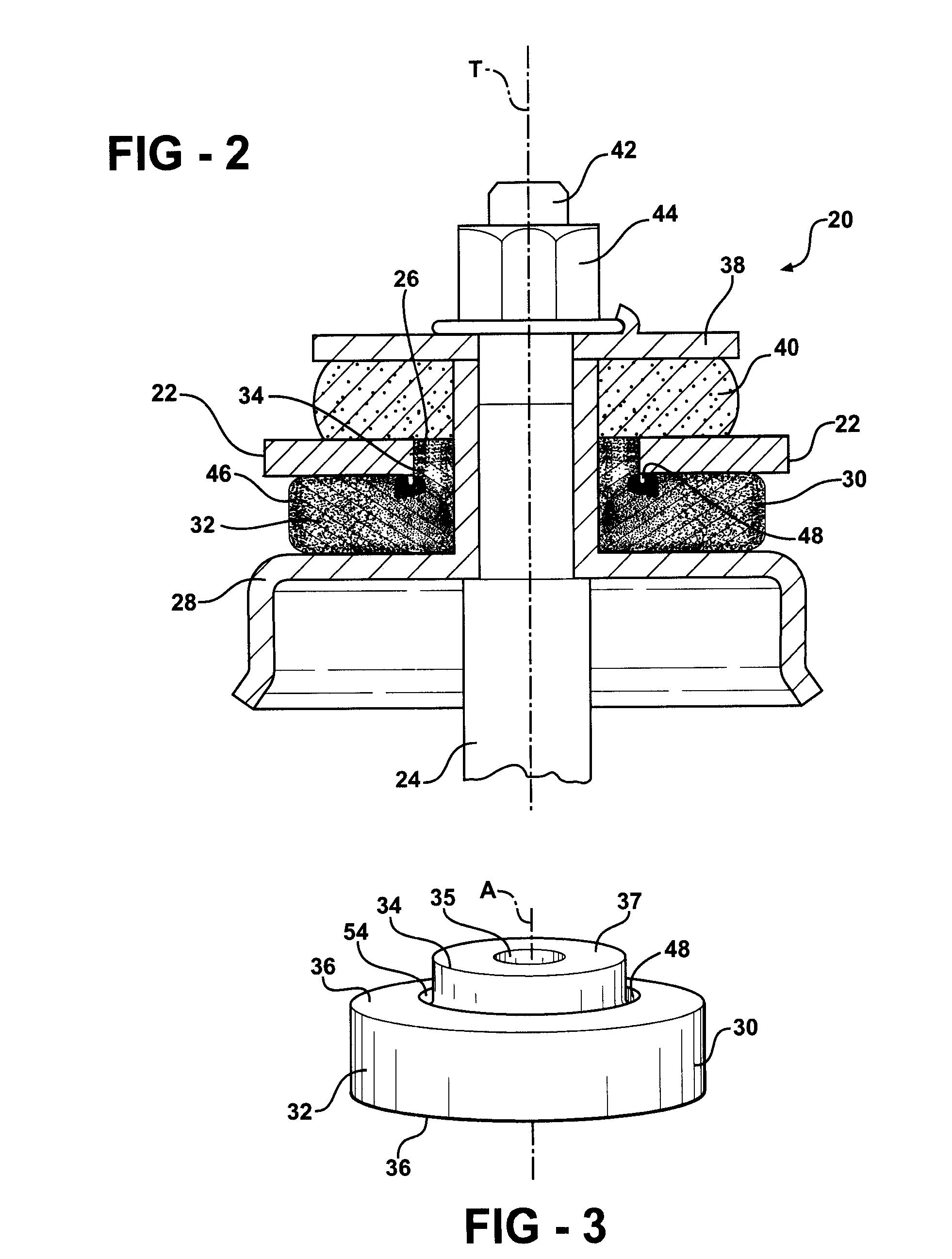
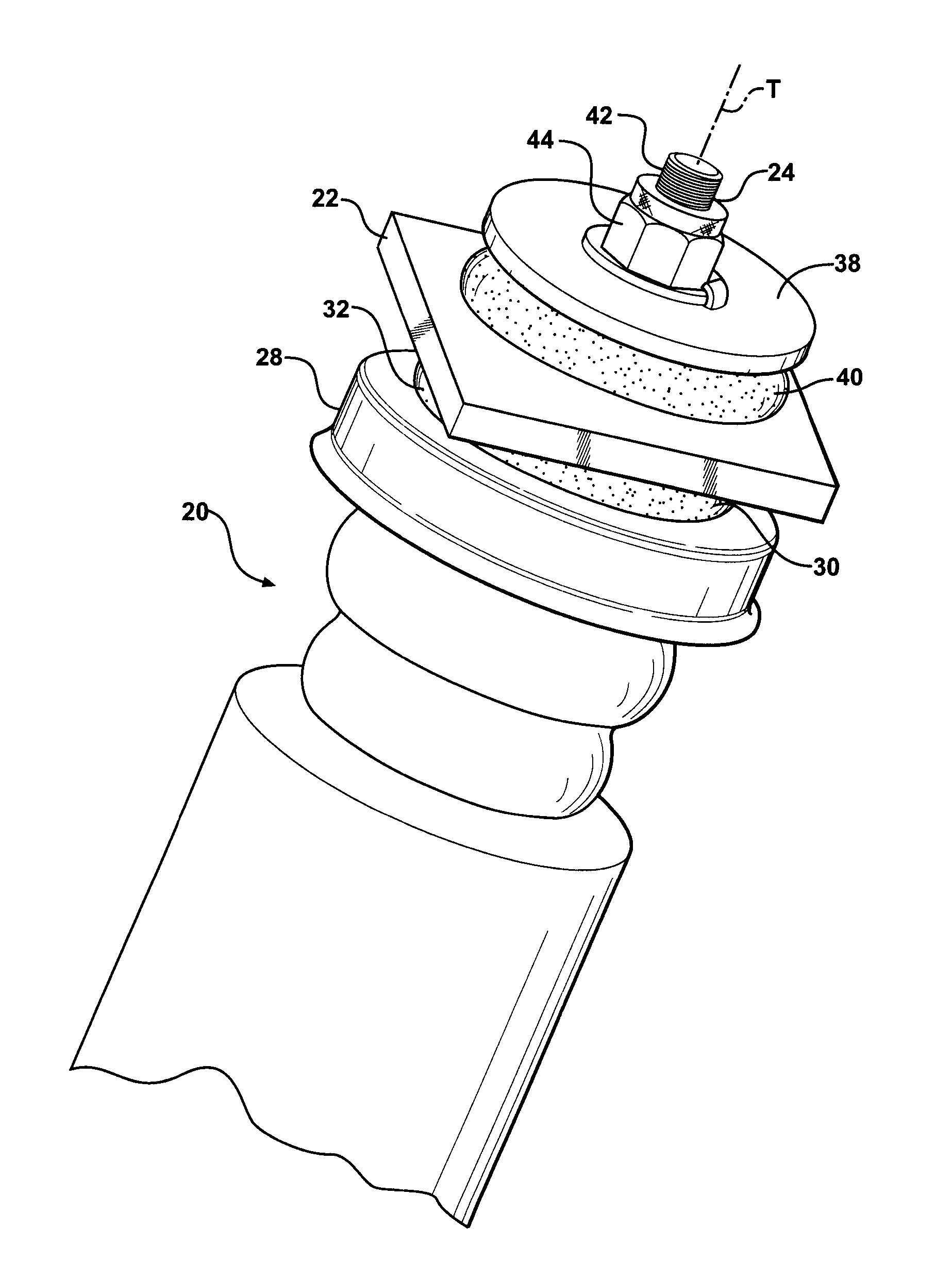
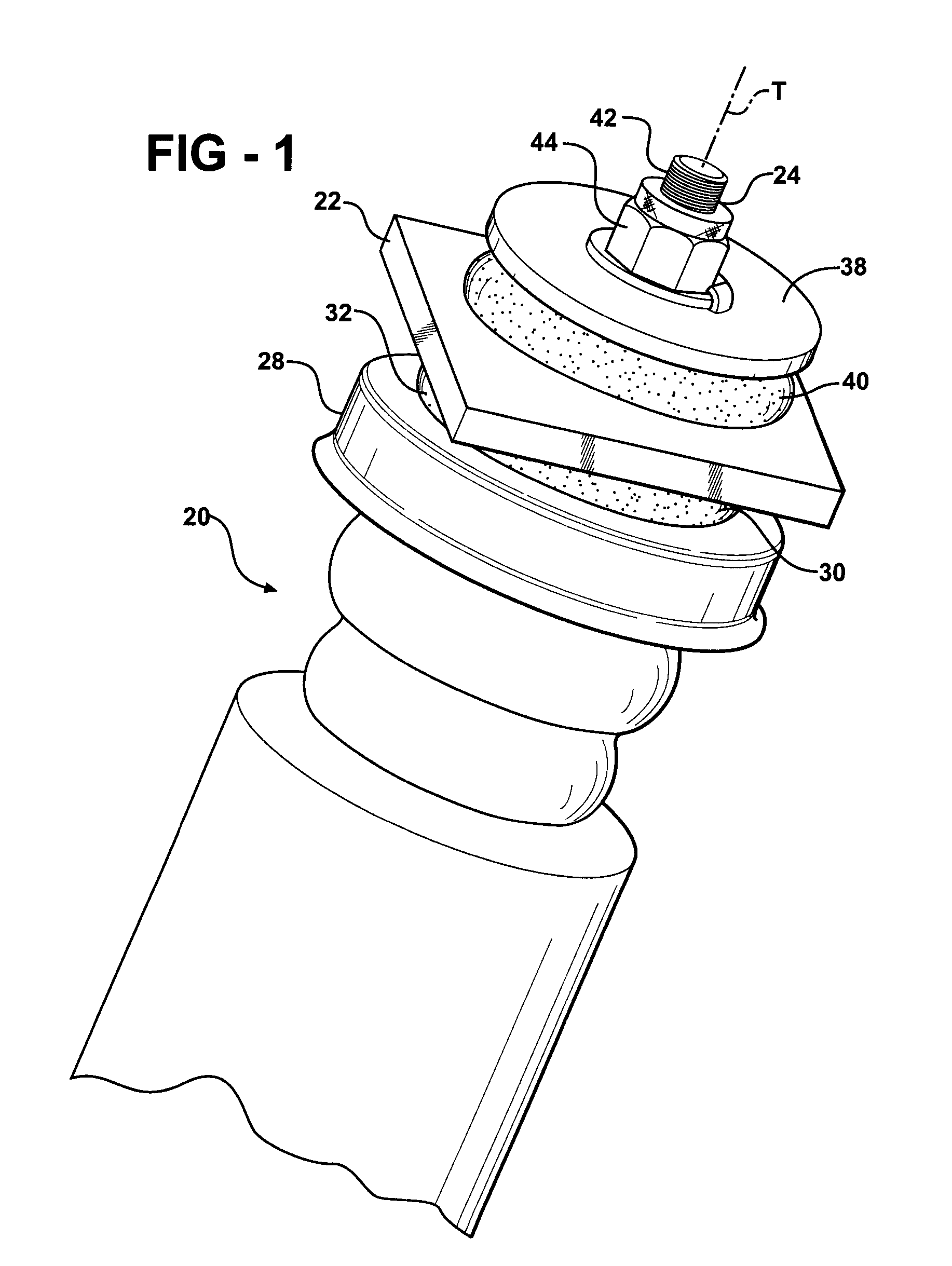
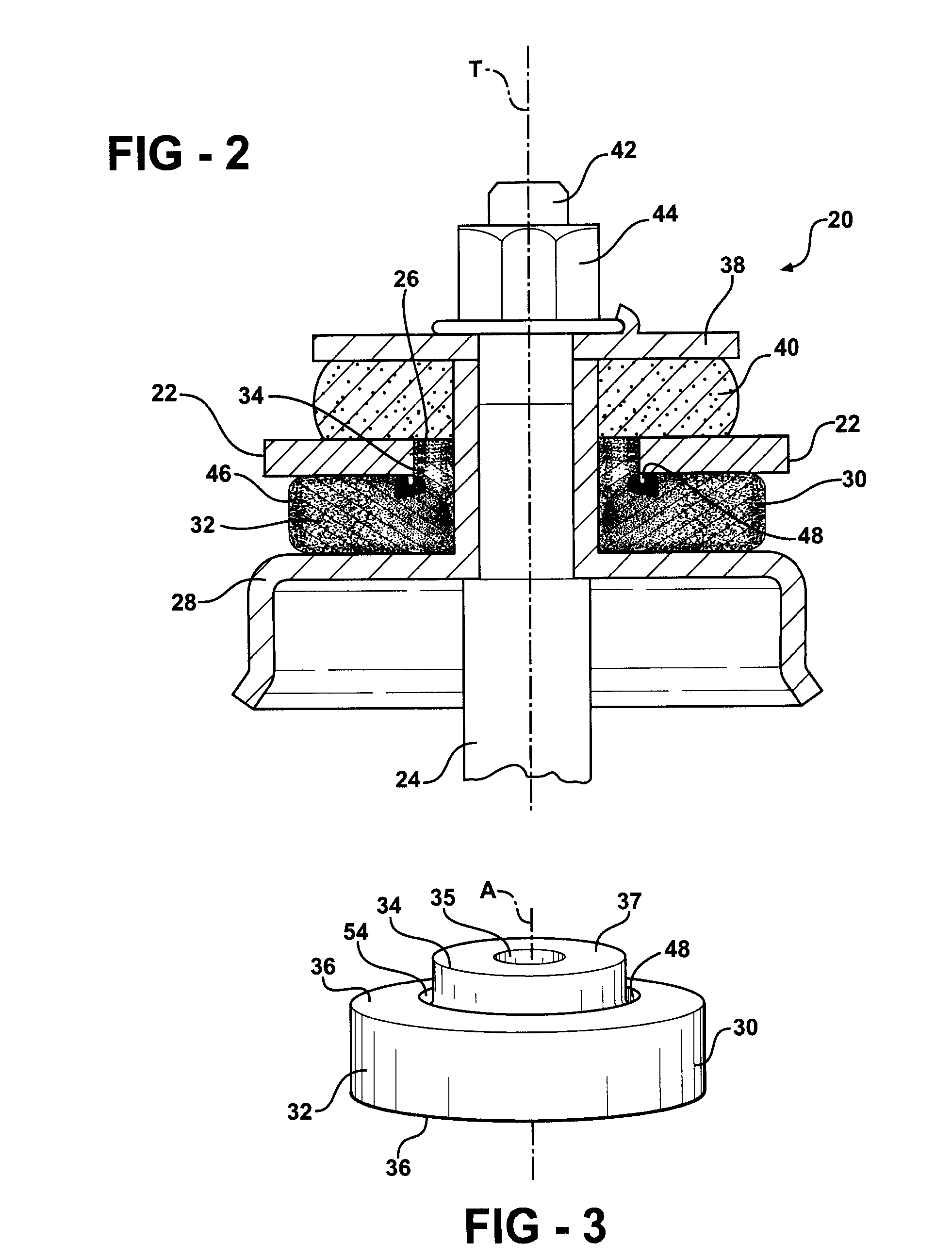
Insulator For A Wheel Suspension System
InactiveUS20080012263A1Increase flexibilityIncreased durabilityElectrical apparatusPipesElastomerEngineering
An insulator for a wheel suspension system of a vehicle is formed of an elastomeric material. The elastomeric material defines a channel that provides increased flexibility to the insulator and defines an increased density about the channel that increases the durability of the insulator. The suspension system includes a support structure adapted to be mounted to the vehicle, a piston rod disposed within the aperture and displaceable relative to the support structure along a line of travel, and a plate mounted to the piston rod. The insulator is compressibly disposed between the support structure and the plate. The exterior channel increases the flexibility of the insulator to distribute localized stress on the insulator by the support structure and the plate. The increased density about the channel increases the durability of the insulator about the channel when the support structure and the plate exert a compressive force on the insulator.
Owner:BASF CORP
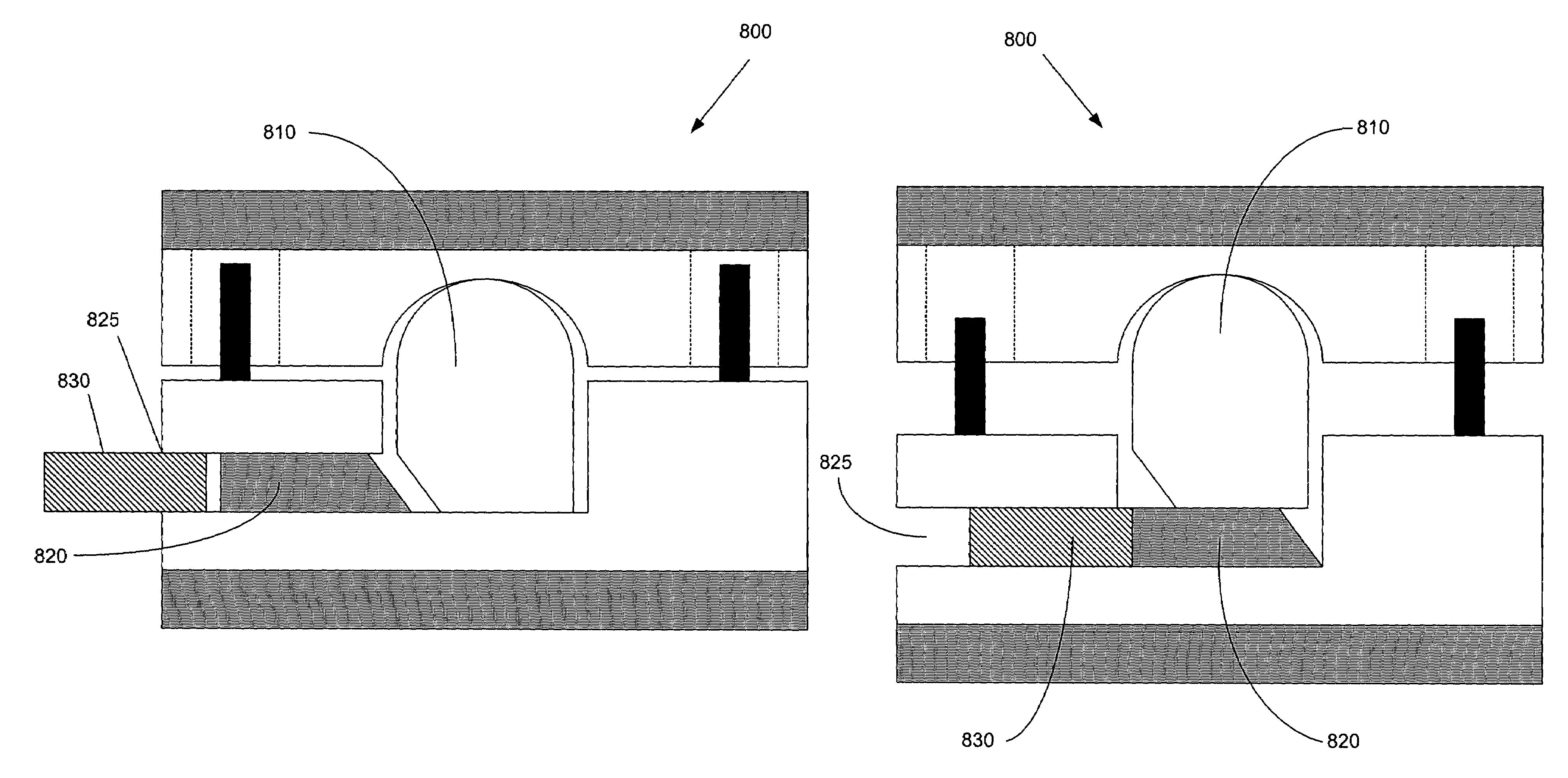
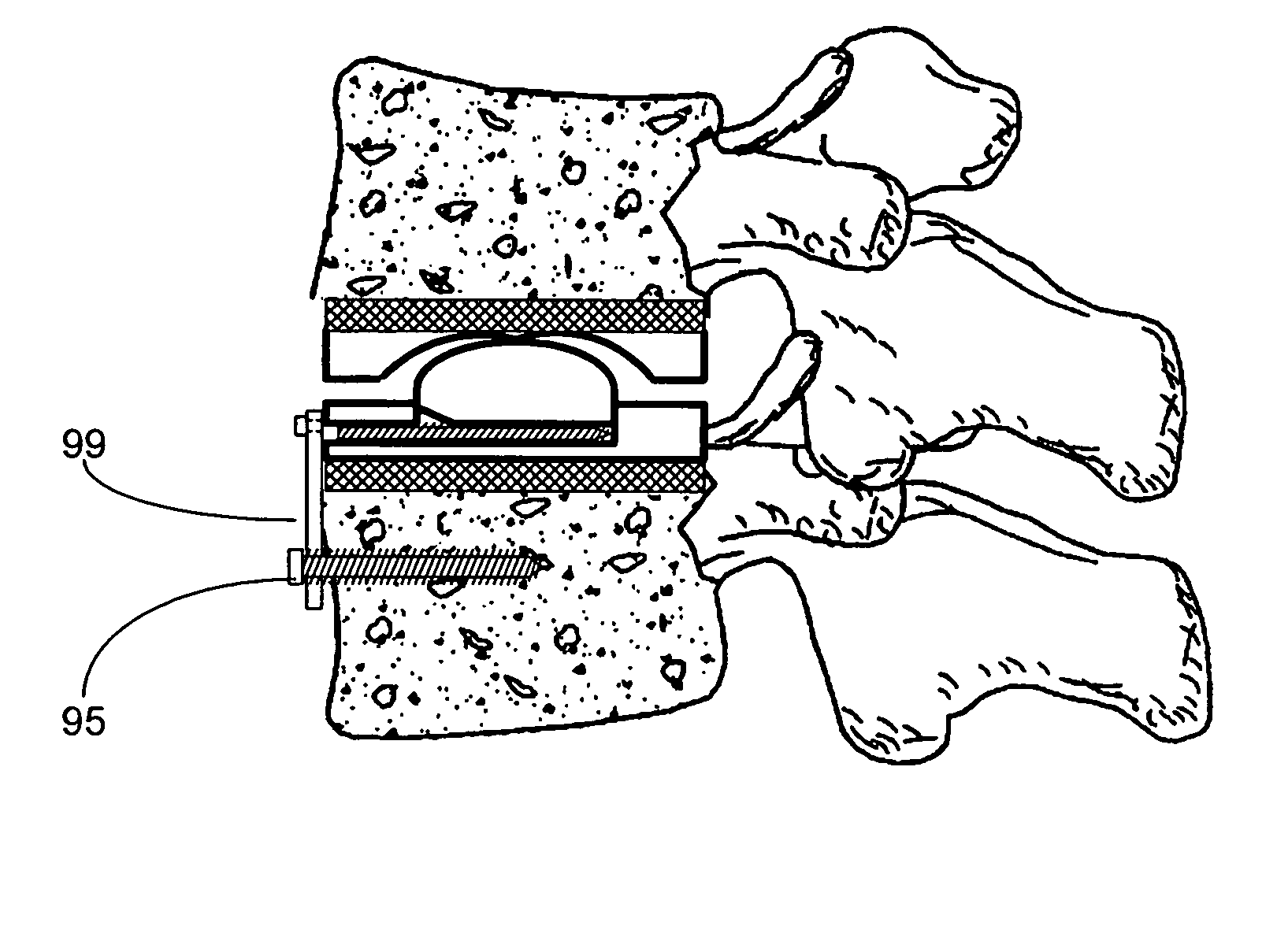
Cross-coupled vertebral stabilizers incorporating spinal motion restriction
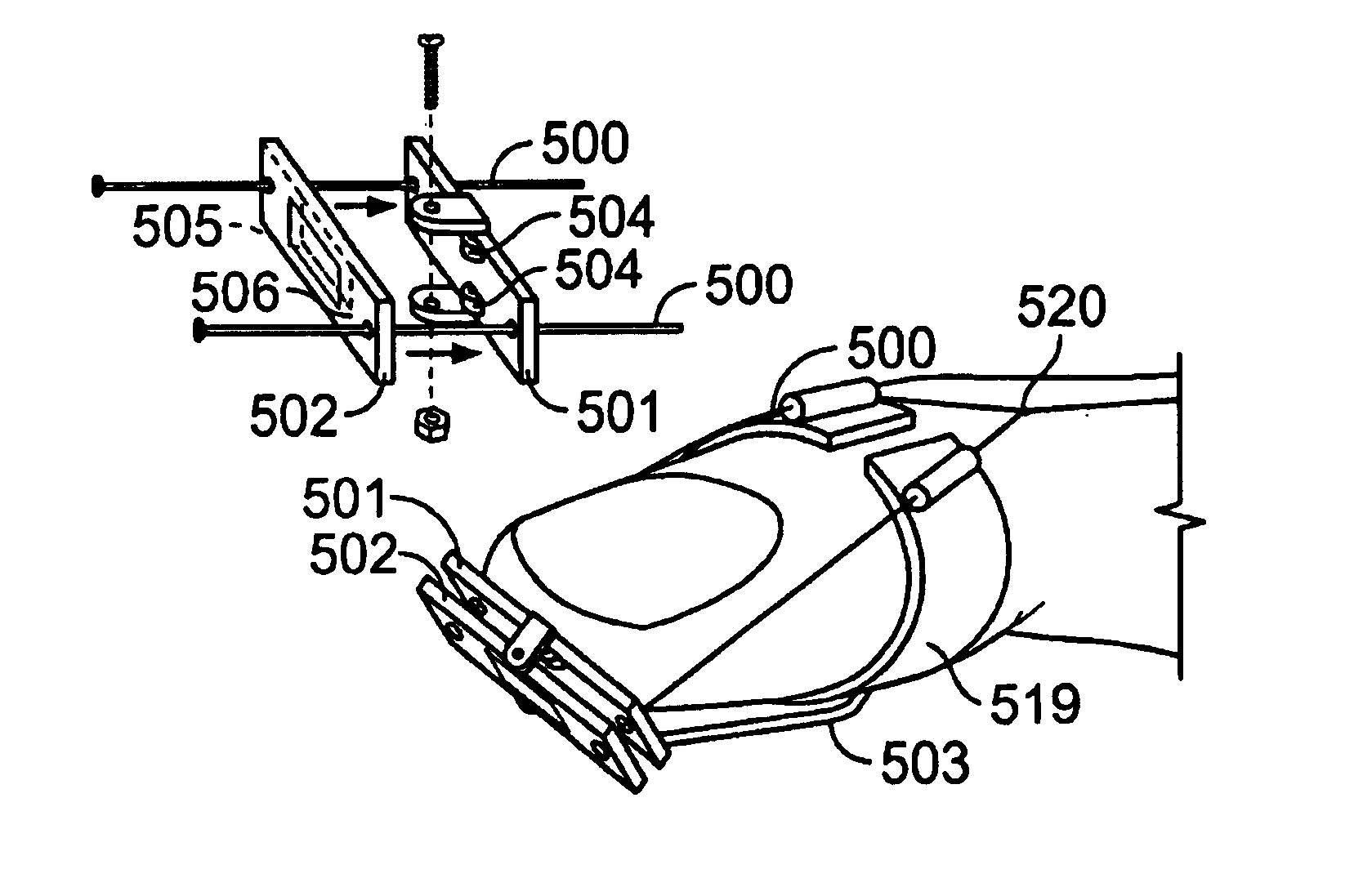
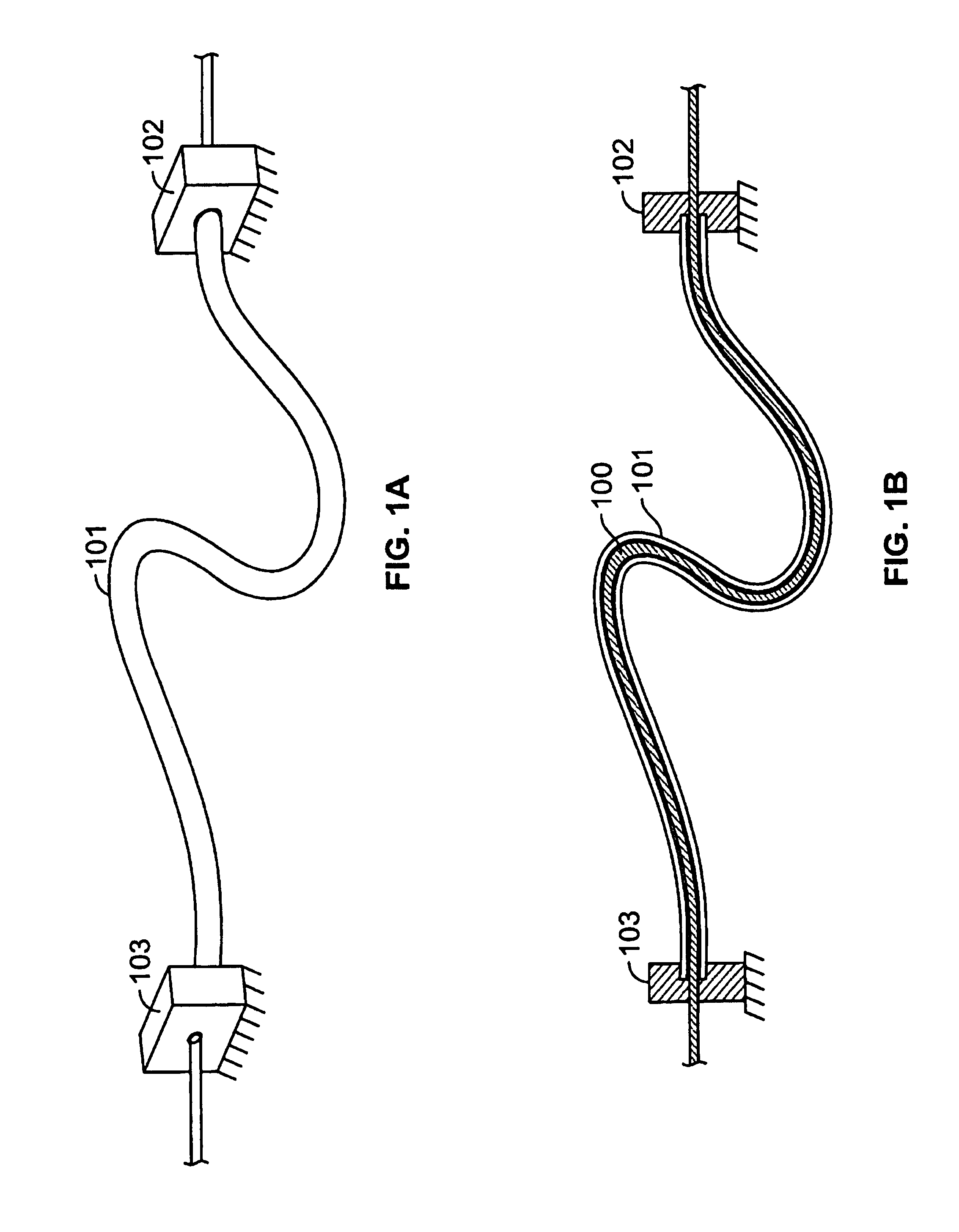
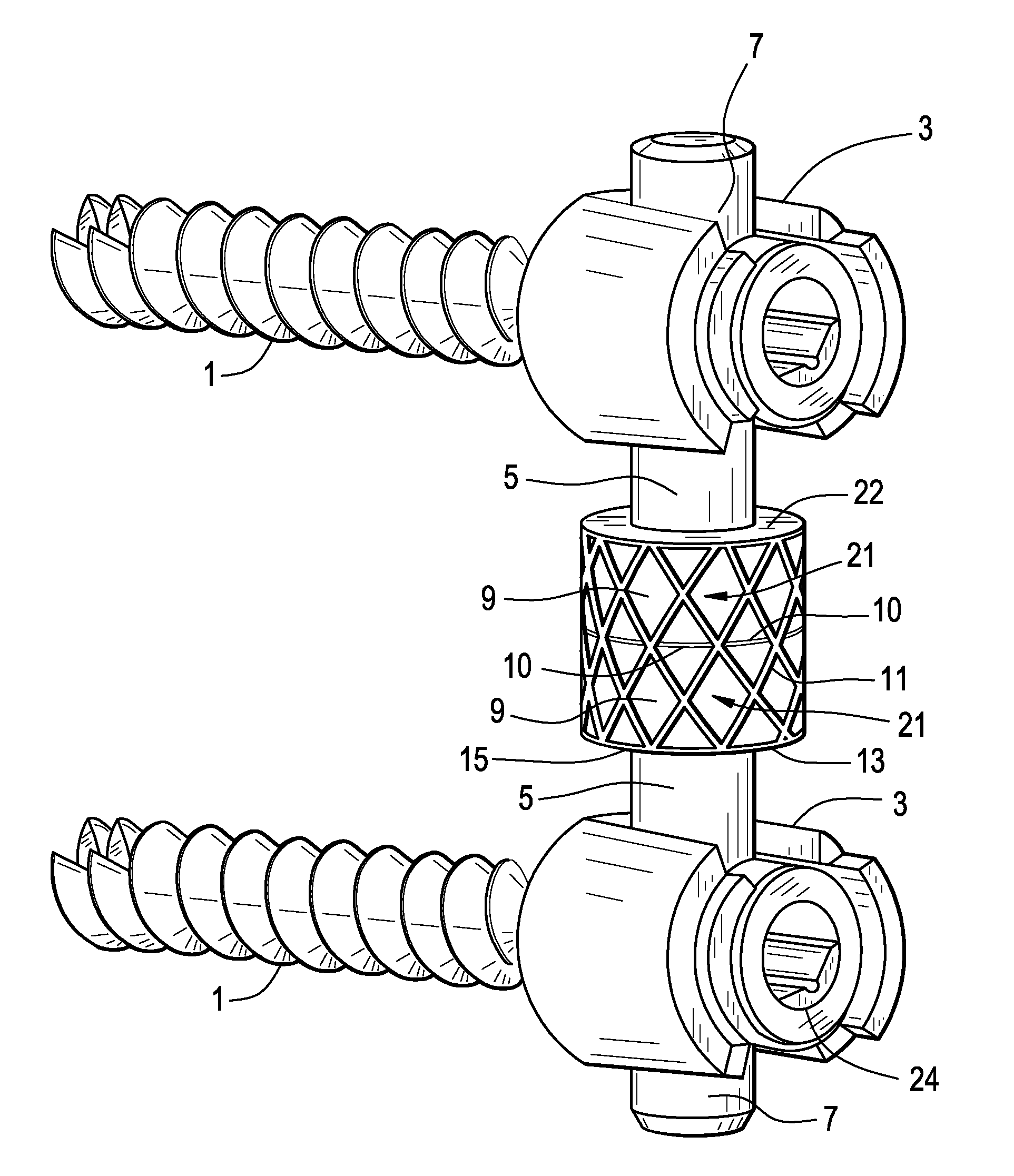
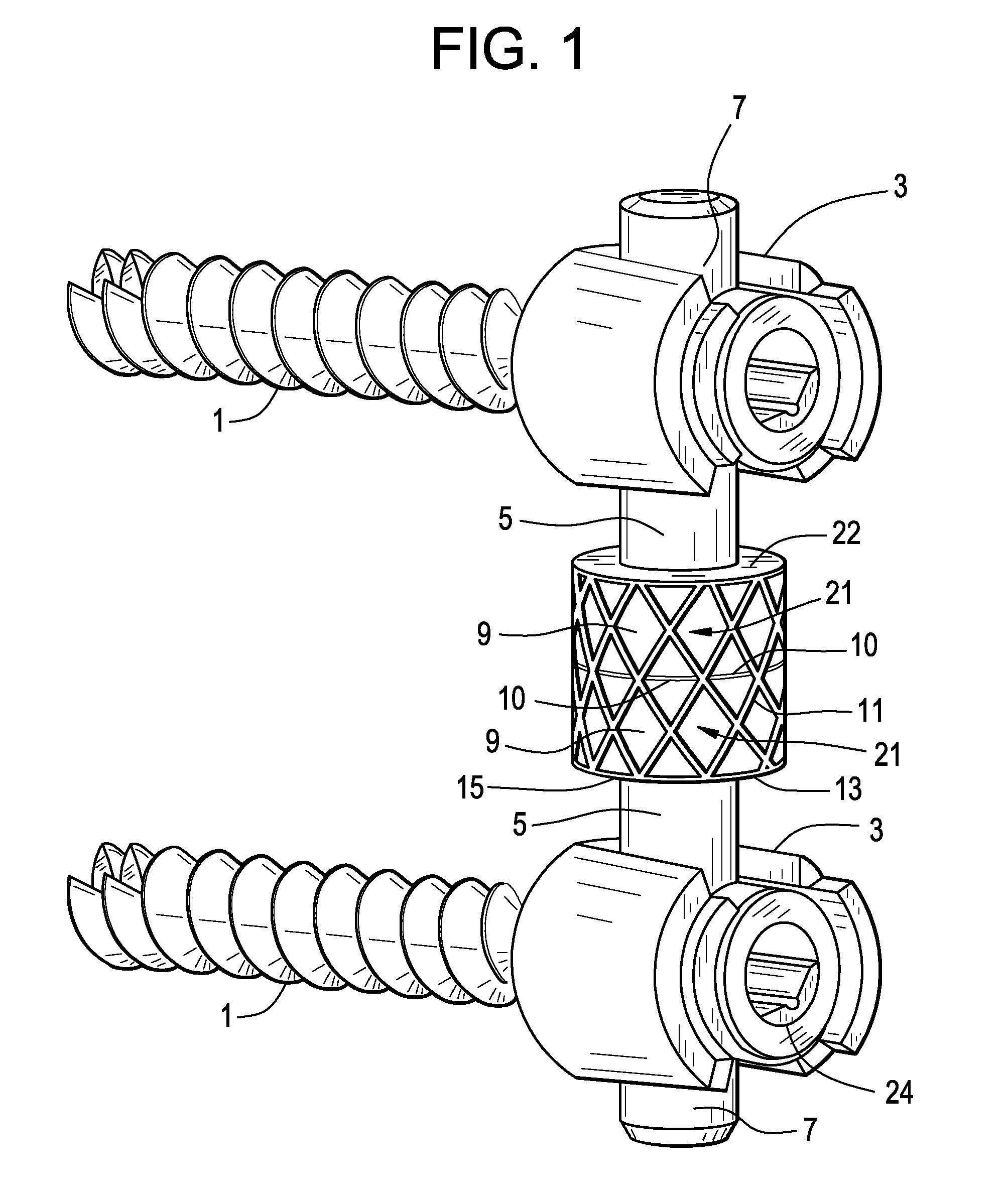
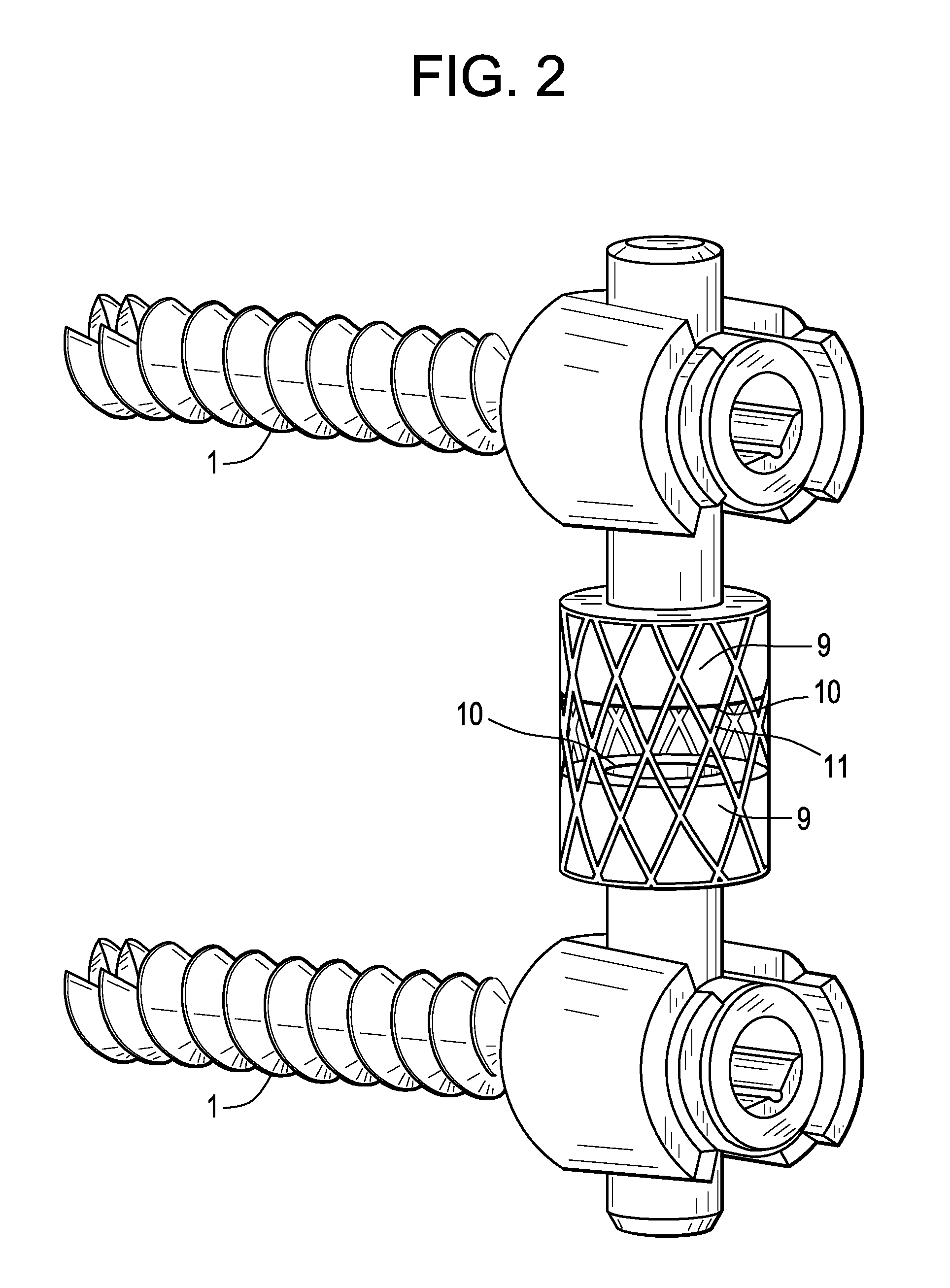
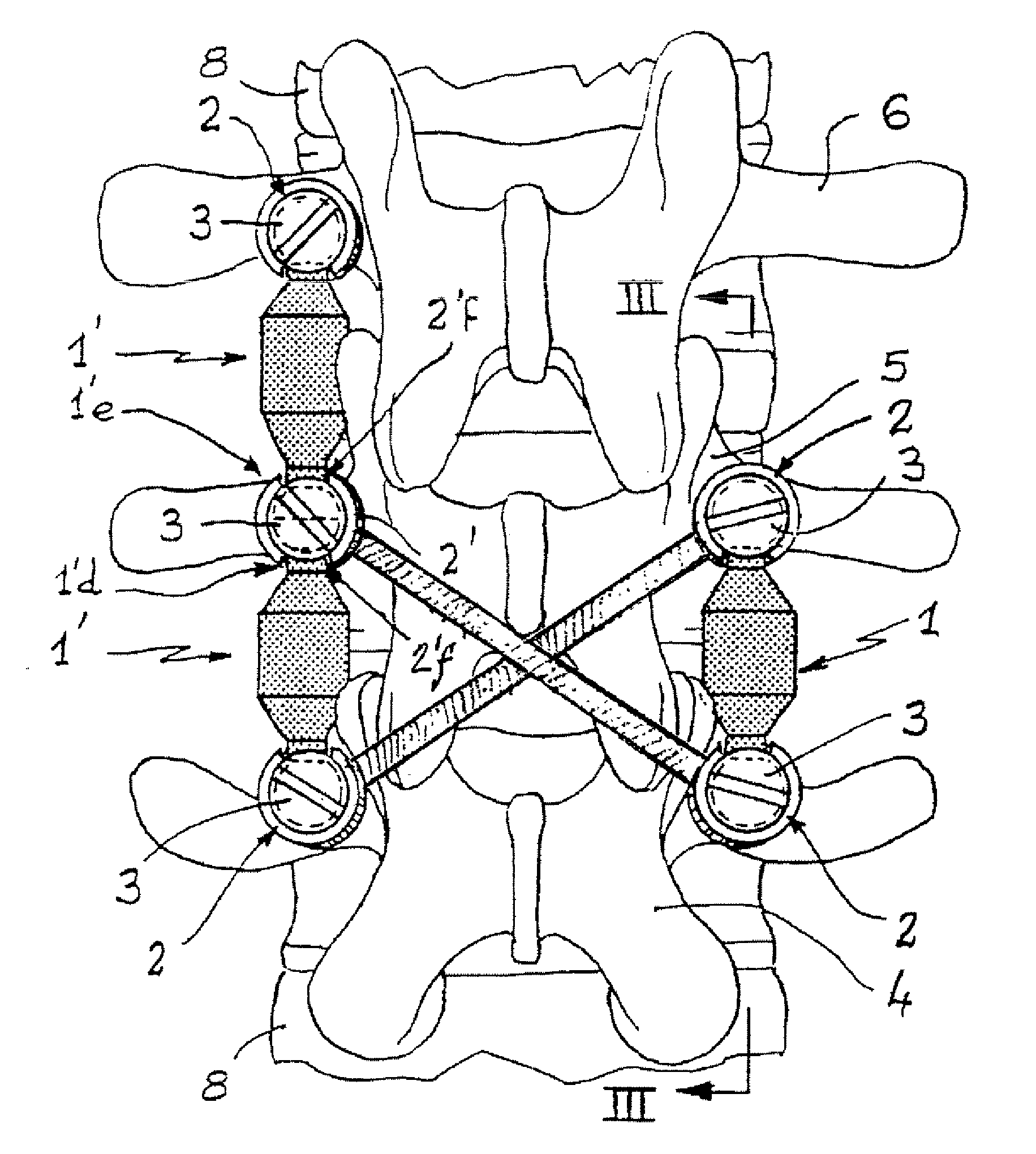
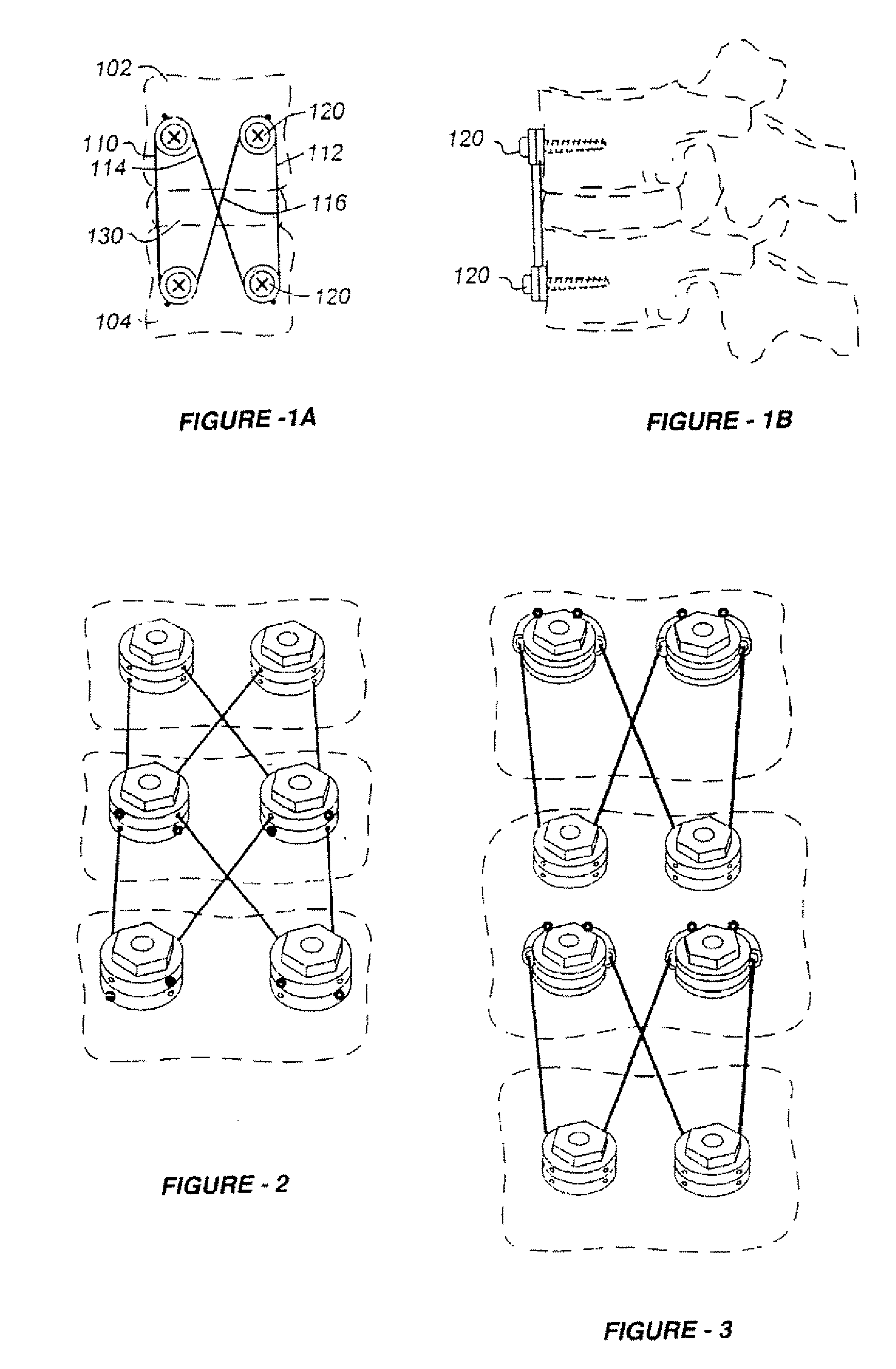
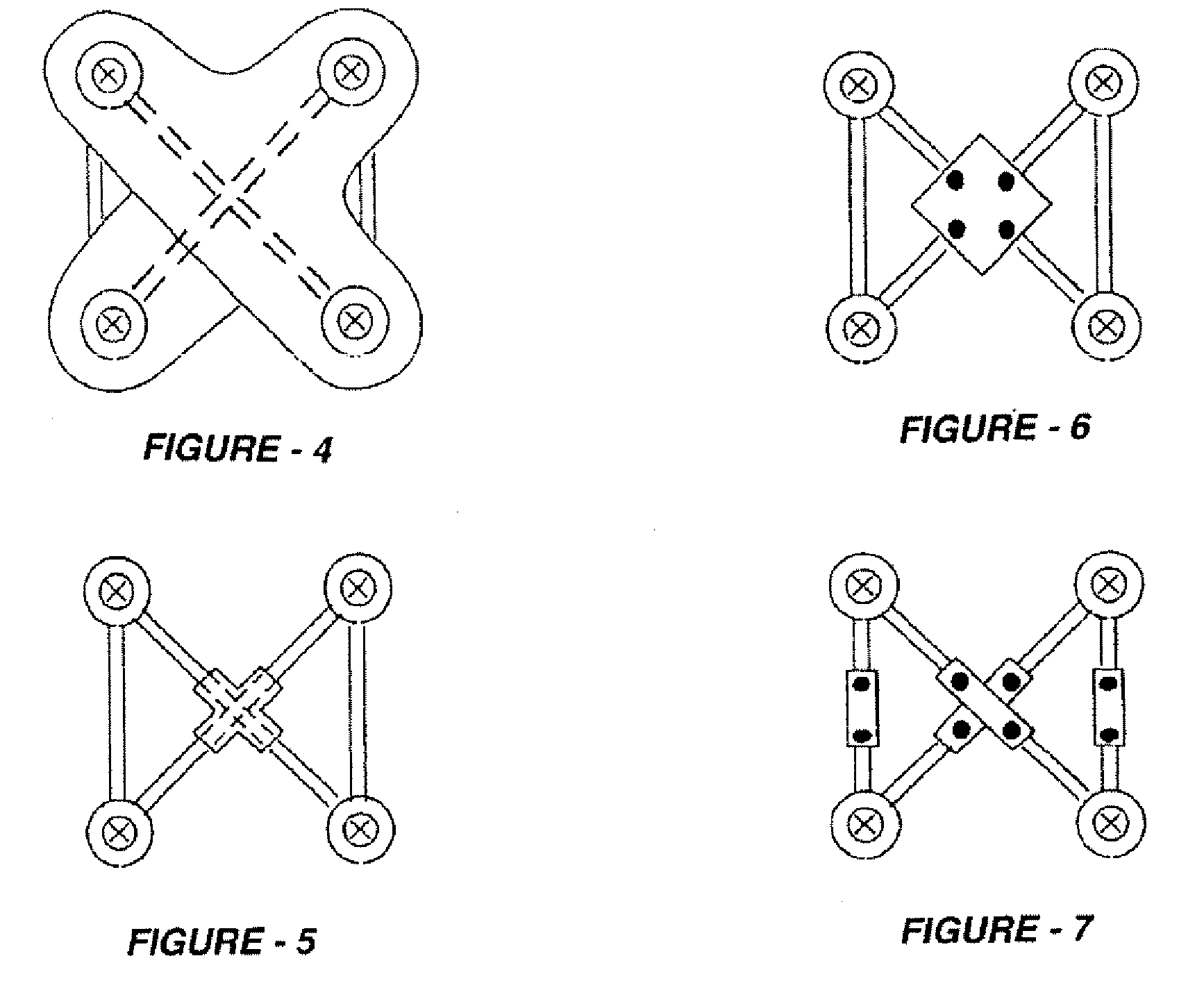
InactiveUS20080262550A1Flexible limitDampen forceSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSpinal columnMOTION LIMITATION
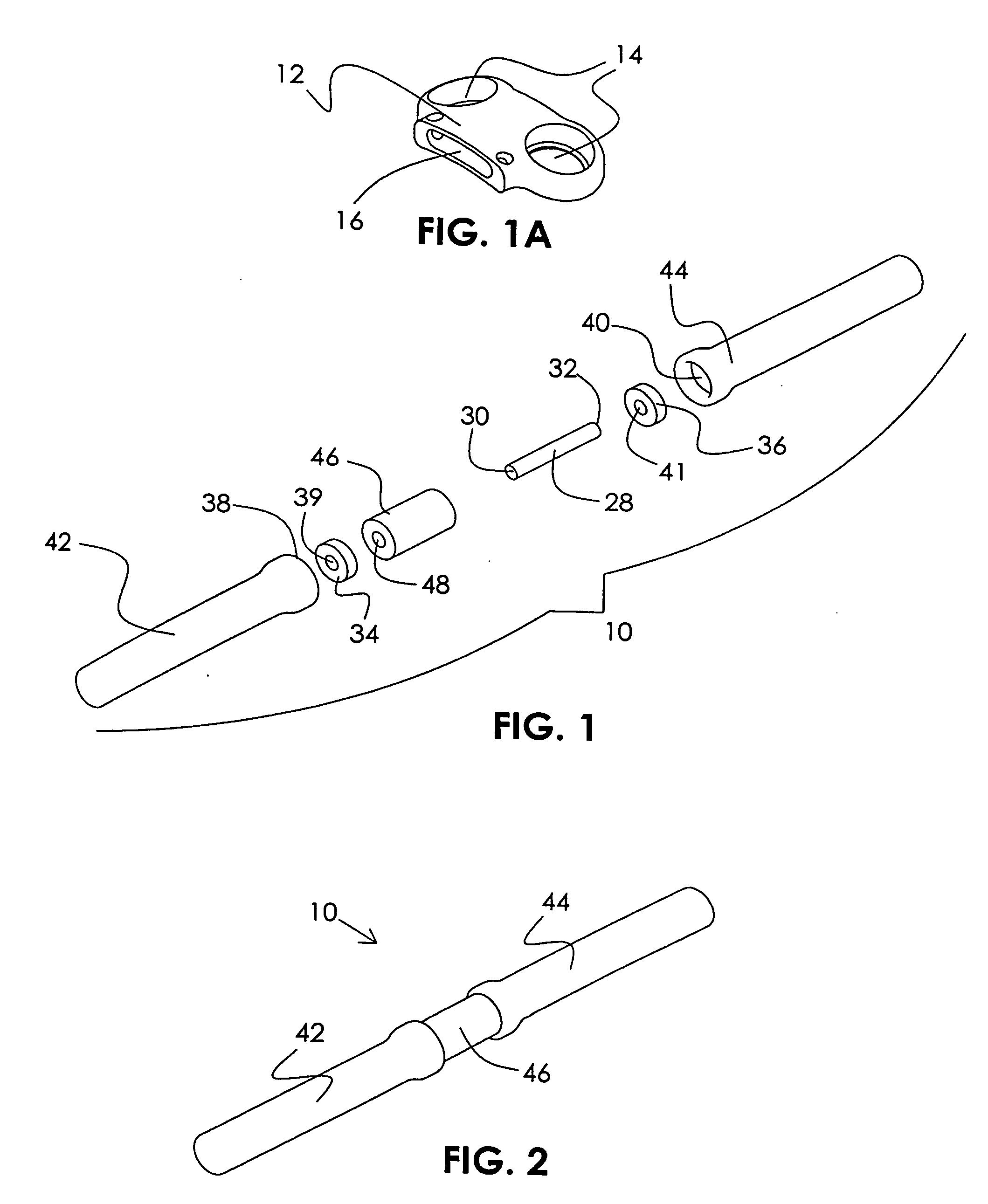
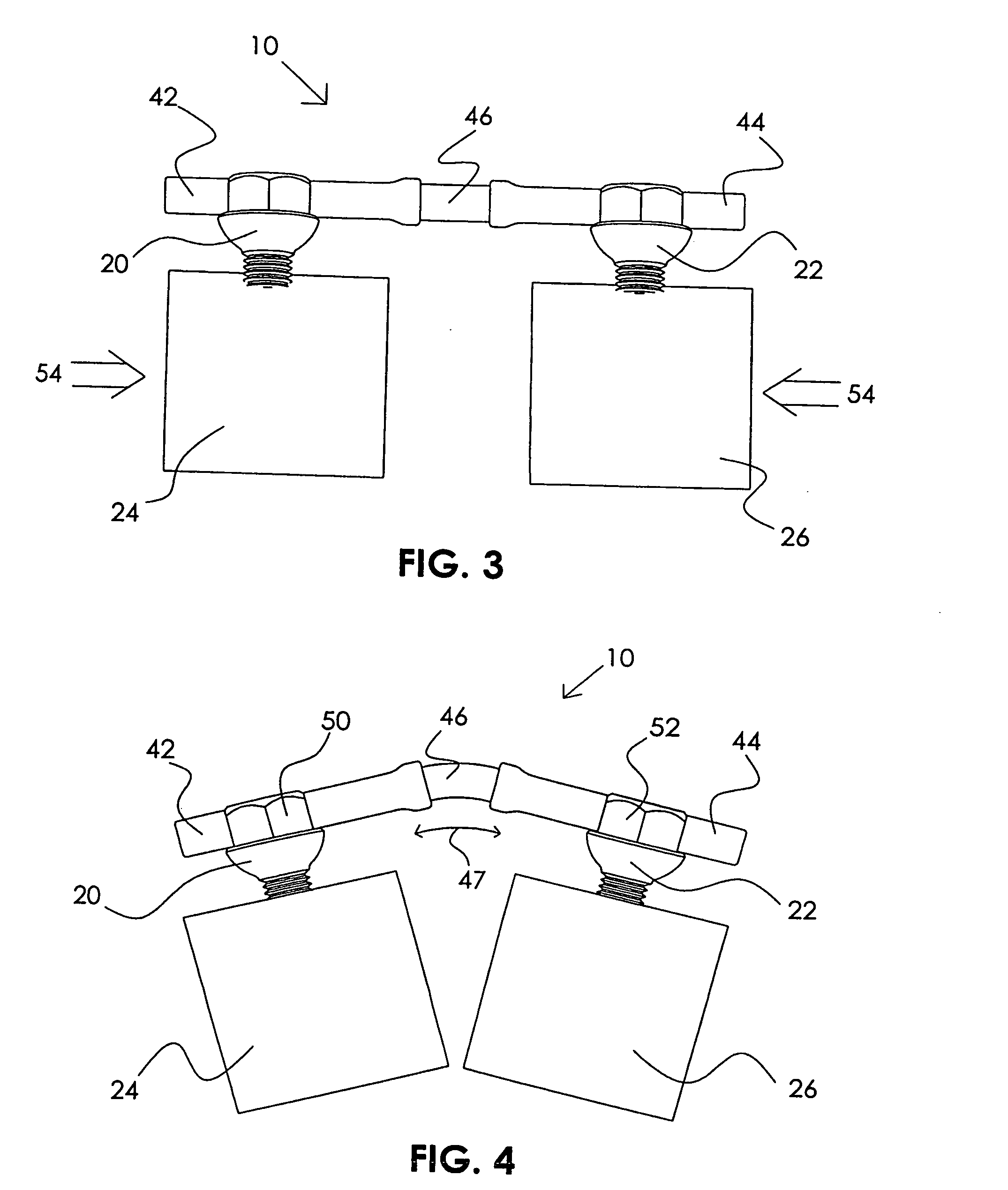
Methods for stabilizing upper and lower spinal vertebrae having a disc situated between the upper and lower vertebrae are described. First and second fasteners are inserted into the upper vertebra. Third and fourth fasteners are inserted into the lower vertebra. At least two of the first, second, third, and fourth fasteners are connected with an elongate element. In an alternative embodiment, at least three of the first, second, third, and fourth fasteners are connected with the elongate element. The elongate element may be an elastic connector or a cable. The elongate element may also have first and second ends that are connected by a crimp.
Owner:FERREE BRET A
Method and application of a self adhesive splint
InactiveUS7393334B2Reduce pressureComfortable to wearFeet bandagesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesCTS - Carpal tunnel syndromeStress injury
The device is a thin, self-adhesive non-stretch splint, having the capability to flex. This device is intended for the treatment of repetitive stress injuries such as Carpal Tunnel Syndrome with elements that provide user adjustable limitation of movement within acceptable medical parameters. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome symptoms include pain and numbness in the thumb, index, and middle fingers, that are aggravated by compression of the median nerve. This device limits flexion, extension, ulnar and radial deviation movements of the wrist without compressing the median nerve The device limits movement by reducing skin elasticity on the surface skin above or below the wrist and up the forearm. The application provides biomechanical feedback to the wearer in the form of the tugging sensation on the skin around the perimeter of the device assisting the user in maintaining a more neutral wrist position without imposing wrist immobilization. The design elements allow the use of the device in such a manner that produces no additional pressure to the median nerve while in use. Furthermore the method of application provides a means for the user to regulate the amount of wrist movement to provide a greater comfort level while still limiting movement within medically proven parameters. The adhesive nature of the device eliminates the need for external straps that normally wrap completely around the forearm and hand to hold a splint in place. The application of the device limits movement by greatly reducing the ability of the skin to stretch by placing a self-adhesive non-stretch splint directly on the skin. The device, and how it is placed utilizes the wearers skin elasticity to provide biomechanical feedback to the user to promote better wrist posture.
Owner:TORNAI RICHARD MANUEL
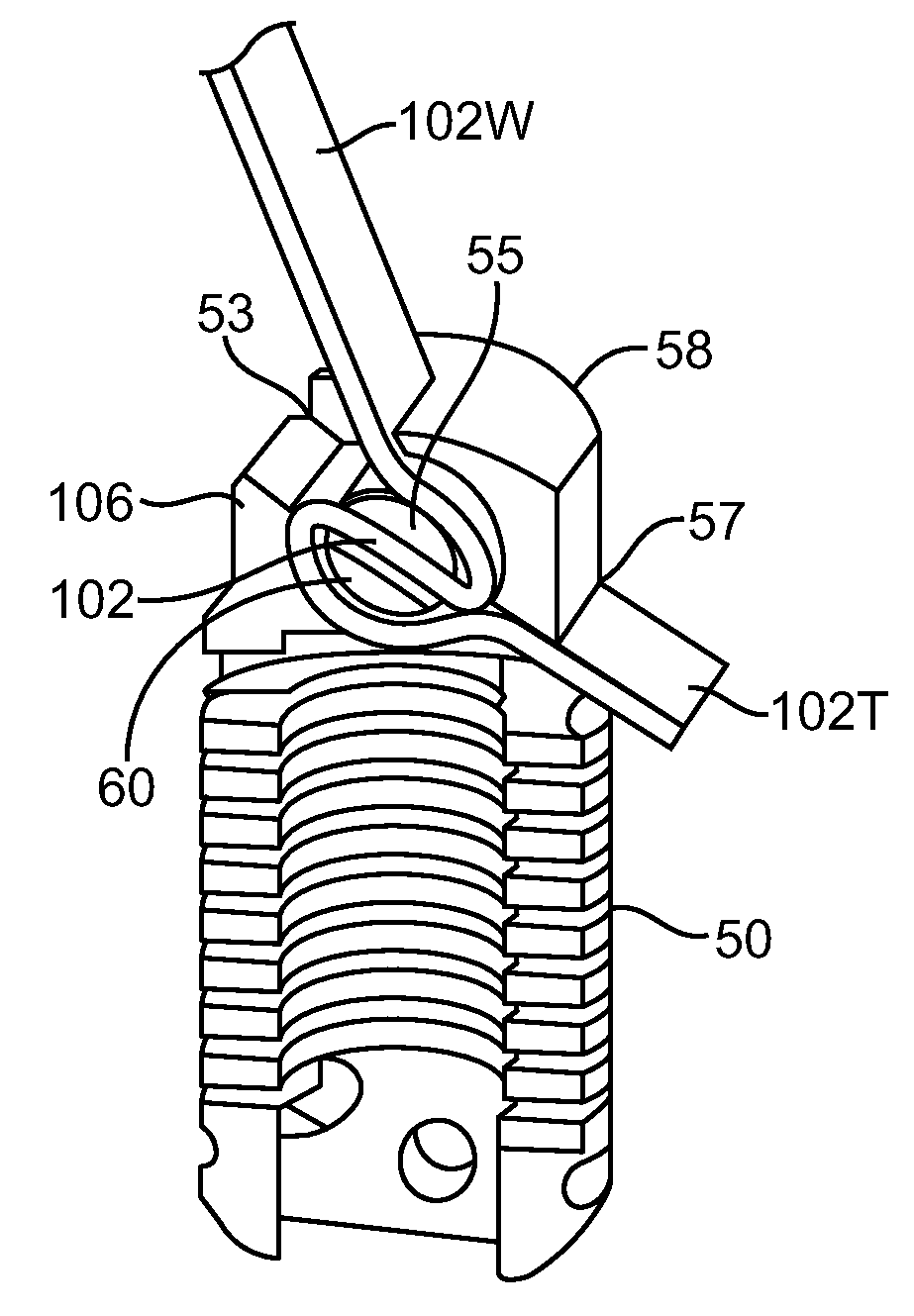
Methods and apparatus for locking a band
ActiveUS8308771B2Flexible limitEasy to operateInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsLocking mechanismEngineering
A surgical fastening mechanism for releasably locking an implantable tether includes a housing having a central channel. The housing has an entry aperture, an exit aperture and a side channel extending therebetween. A roller element has a sidewall with an aperture therethrough and the roller is slidably disposed at least partially in the central channel such that the entry and exit apertures are at least partially aligned with the roller aperture. This permits passage of the tether therethrough. Rotation of the roller element in a first direction winds the tether around the roller thereby creating a friction interface between the roller element, the housing and the tether. A locking mechanism is operably connected with either the housing or the roller element and is adapted to prevent rotation of the roller in the central channel and also adapted to prevent release of the tether from the roller.
Owner:SIMPIRICA SPINE
Shoe with energy storage and delivery device
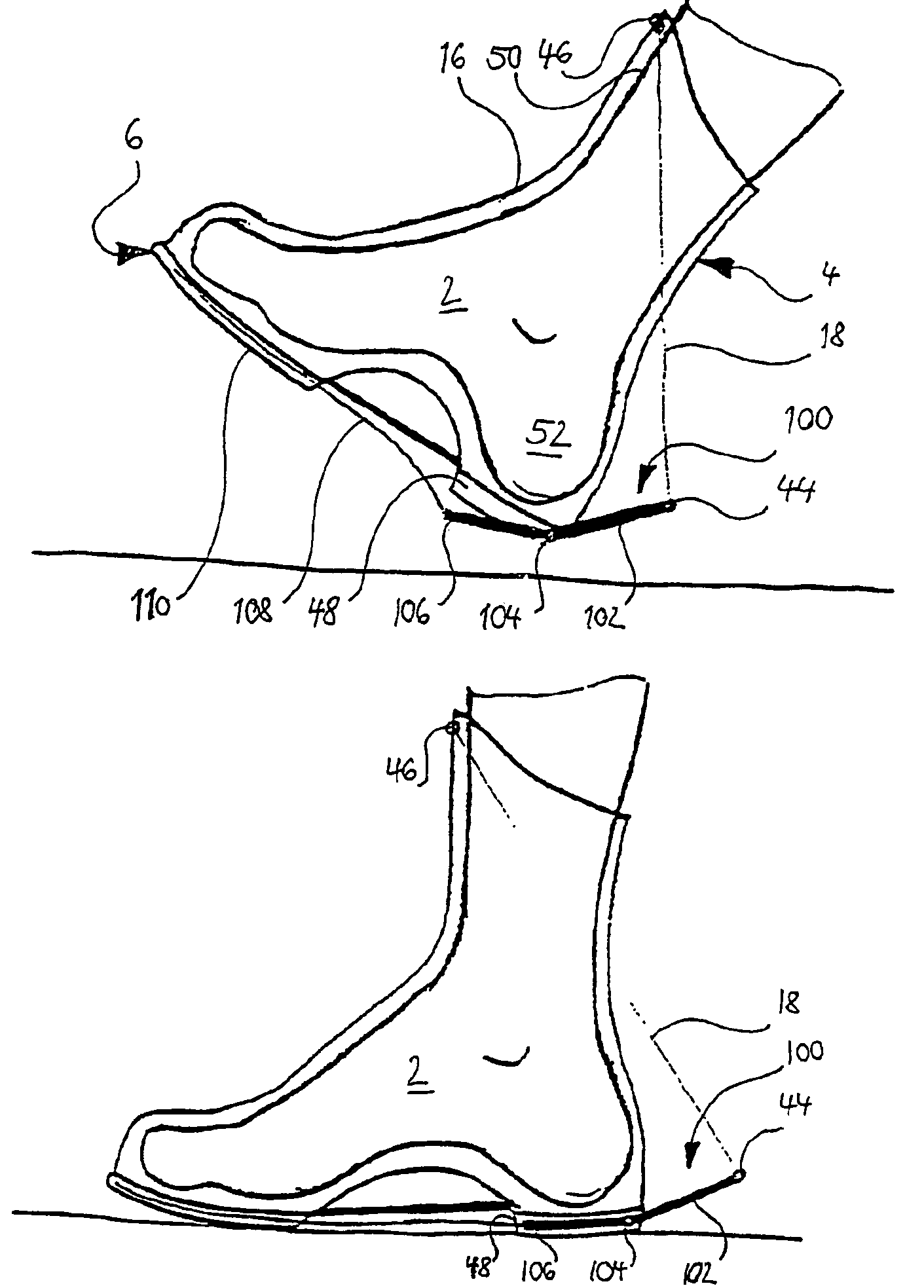
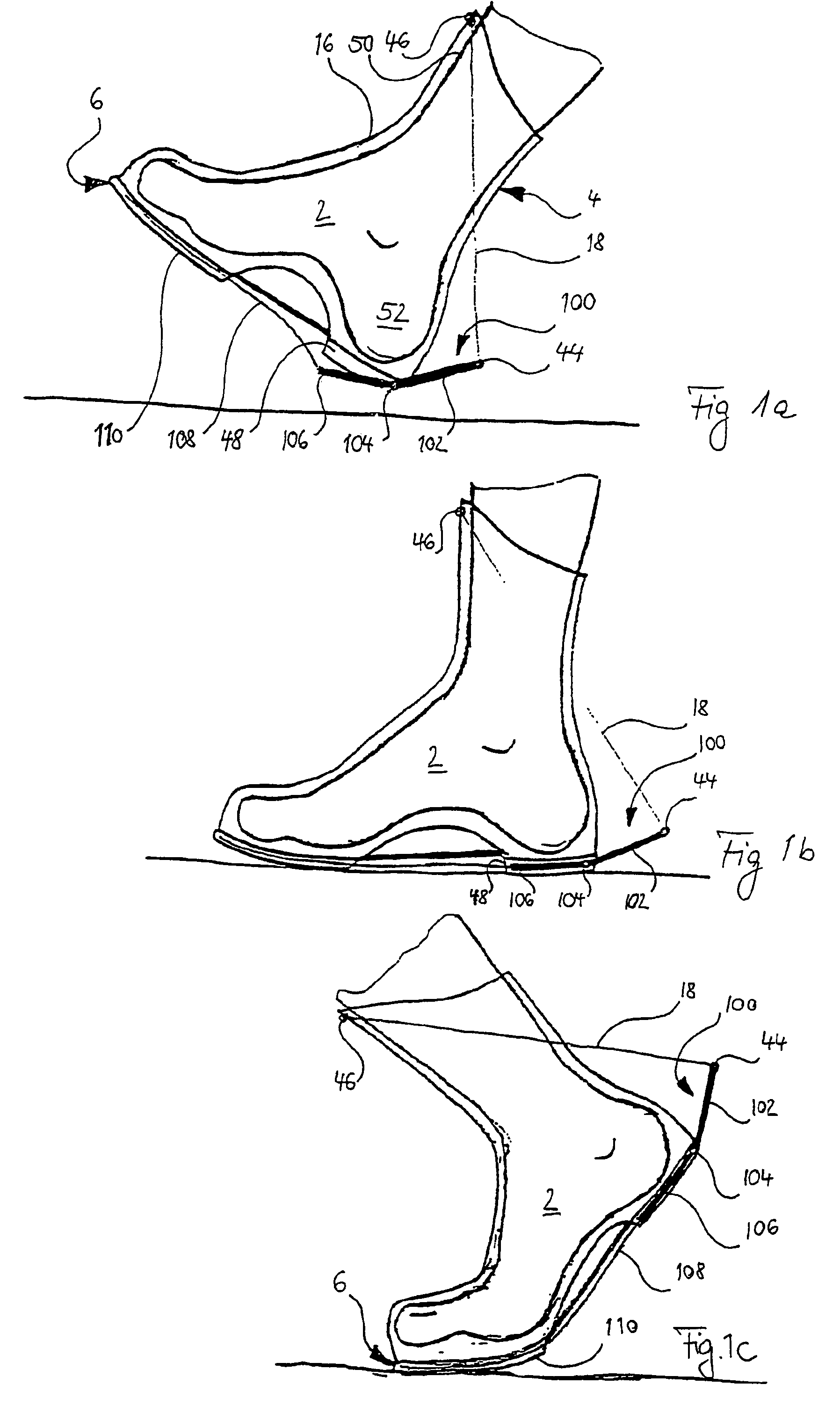
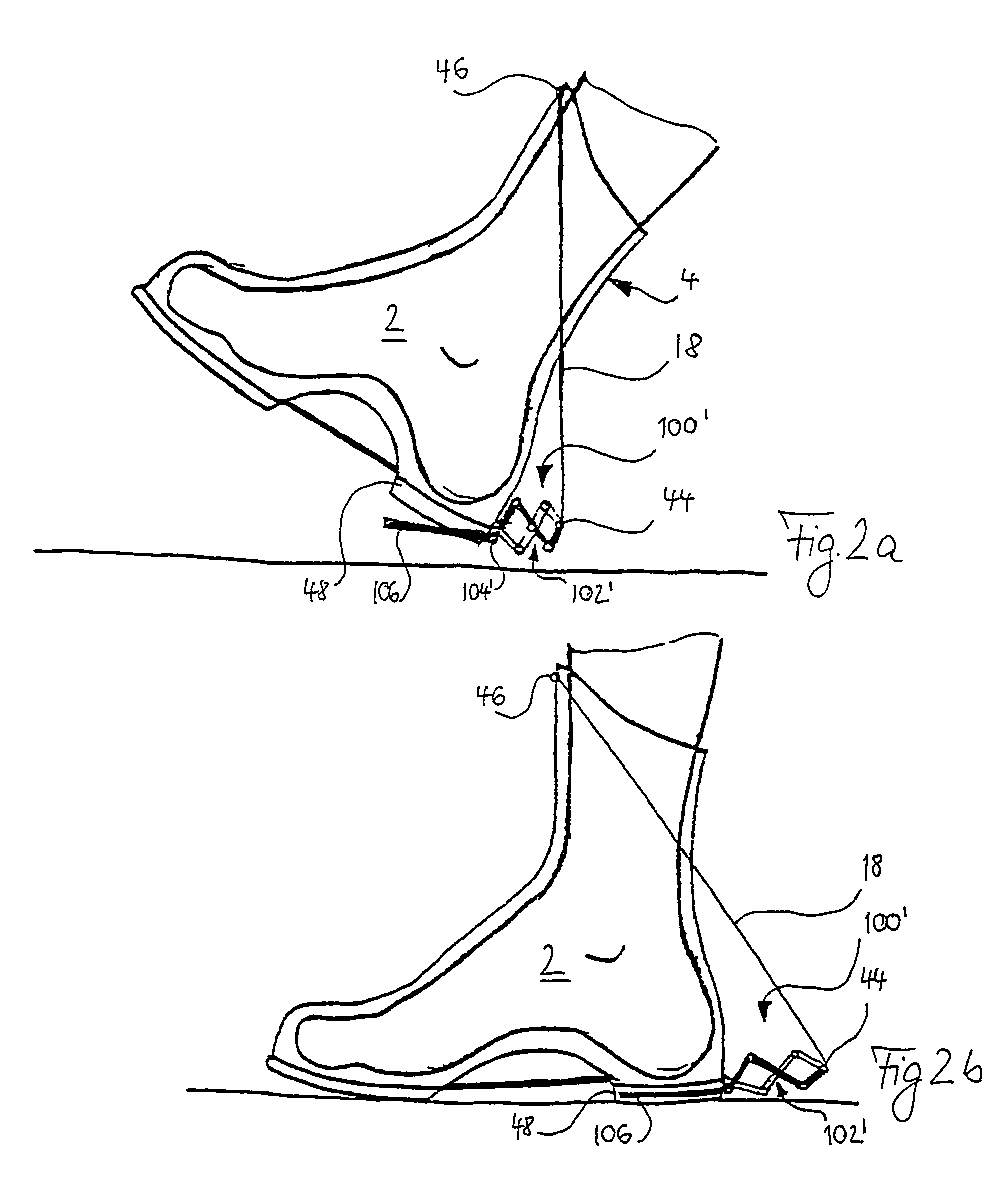
InactiveUS7510538B2Improving surface gripImproving impact dampingSolesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesTibiaEngineering
According to the invention, a shoe having at least one base spring element, which is arranged between appendages at a heel zone of the shoe and at a shaft zone taking support at the front edge of the shin bone and which stretches in the course of an ambulation phase, characterized in that a tensioning assembly moves the appendage of the base spring element at the heel zone away from the appendage at the shaft zone upon planting of the shoe, for stretching of the base spring element.
Owner:DIETMAR WOLTER
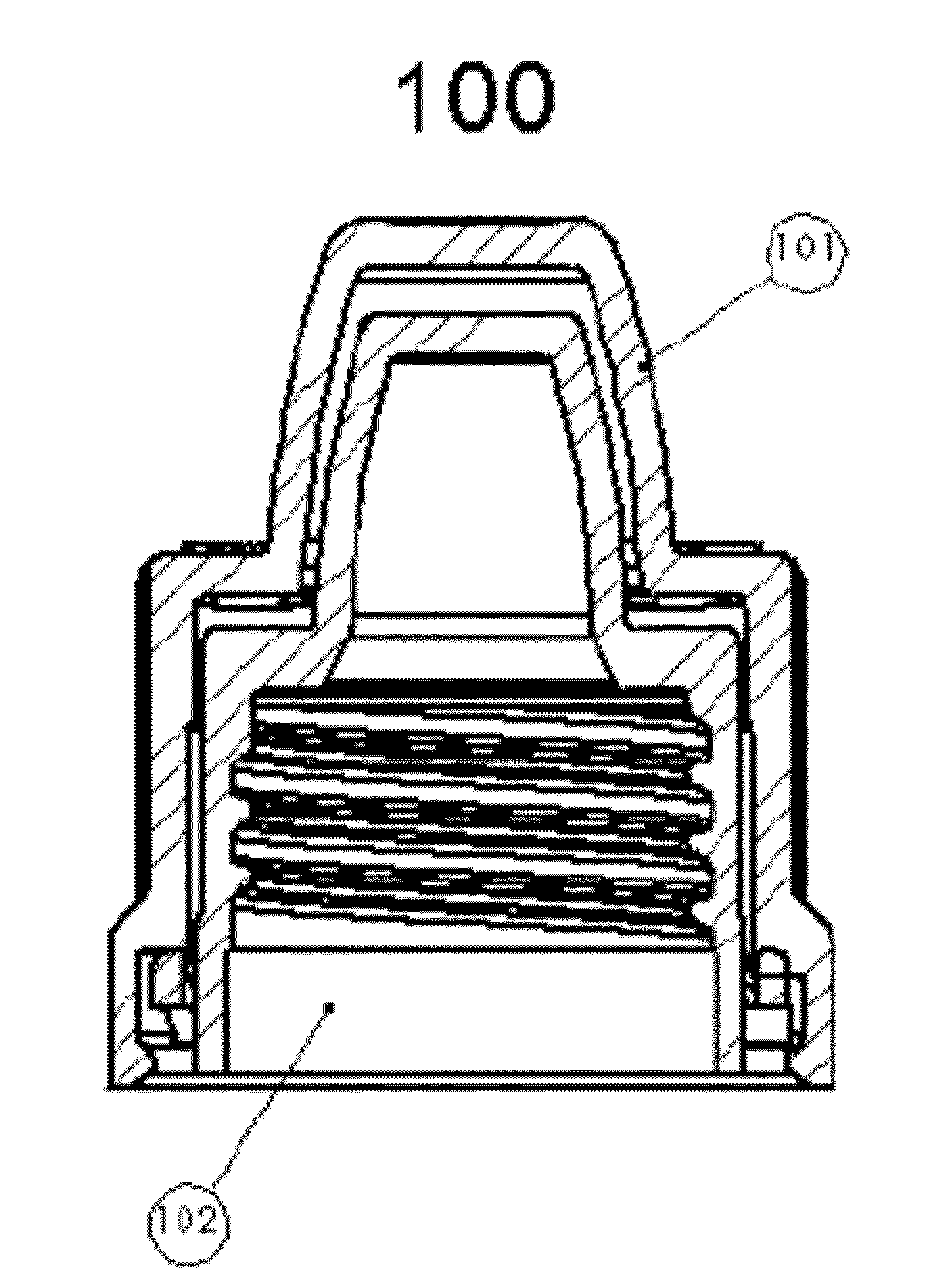
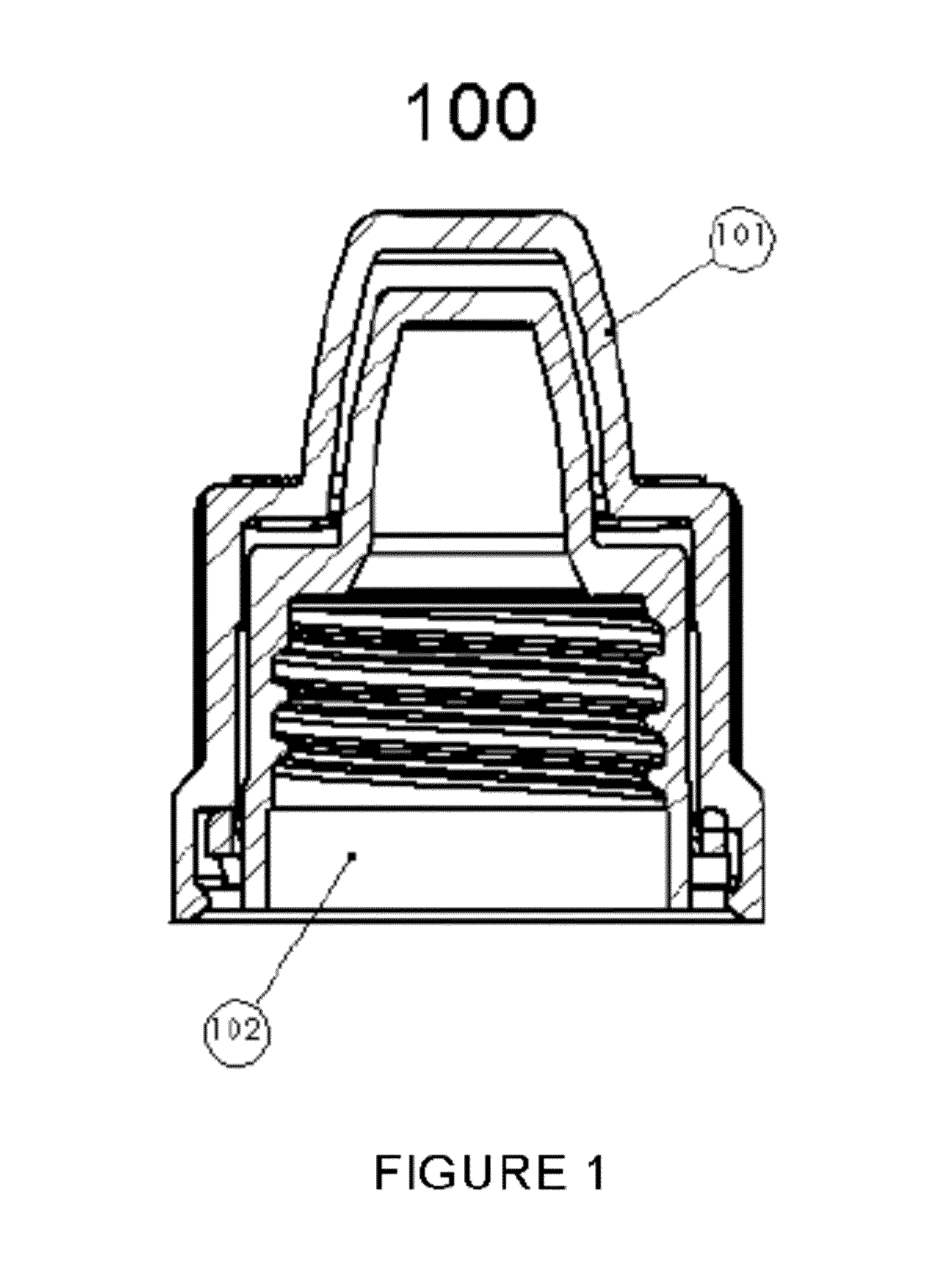
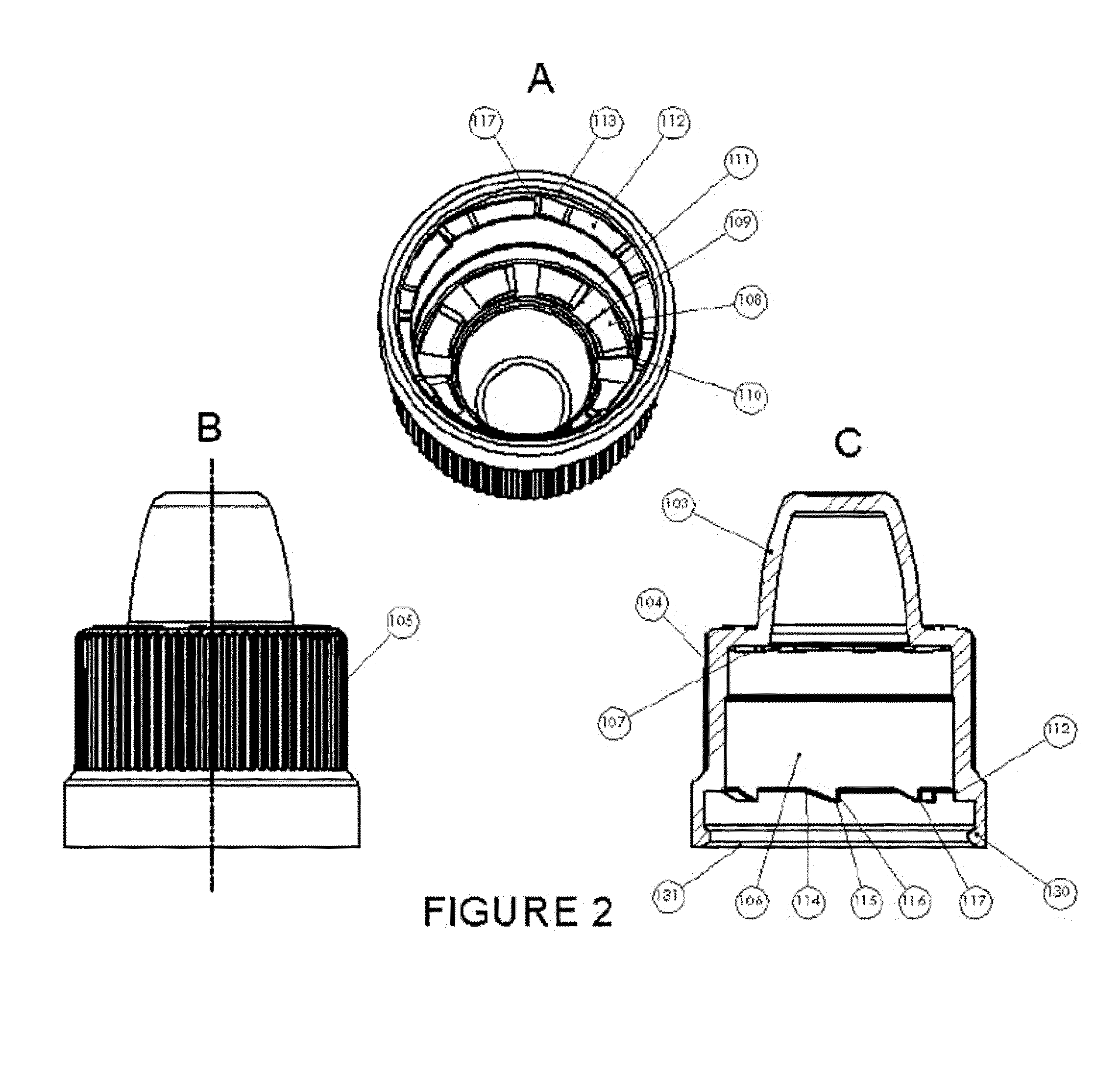
Child-Resistant Cap for Liquid Medicaments
InactiveUS20140014611A1Efficient use ofImprove propertiesOpening closed containersBottle/container closureEngineeringBottle
An improved child-resistant closure for dispensers of liquid medicaments, the closure being of a two-part construction. The closure has an outer cap with a quantity of shoulder lugs and skirt lugs and an inner cap with a quantity of shoulder lugs and flexible beams. The closure has equal quantities of shoulder lugs on the inner and outer caps, equal quantities of skirt lugs and flexible beams, flexible beams having an arcuate underside, shoulder lugs having a depth to prevent hyper-flexion of the flexible beams, and an ideal overlap when the faces of the shoulder lugs are aligned. Additionally, provided are methods for attaching and removing the cap from a pre-existing bottle.
Owner:COMAR
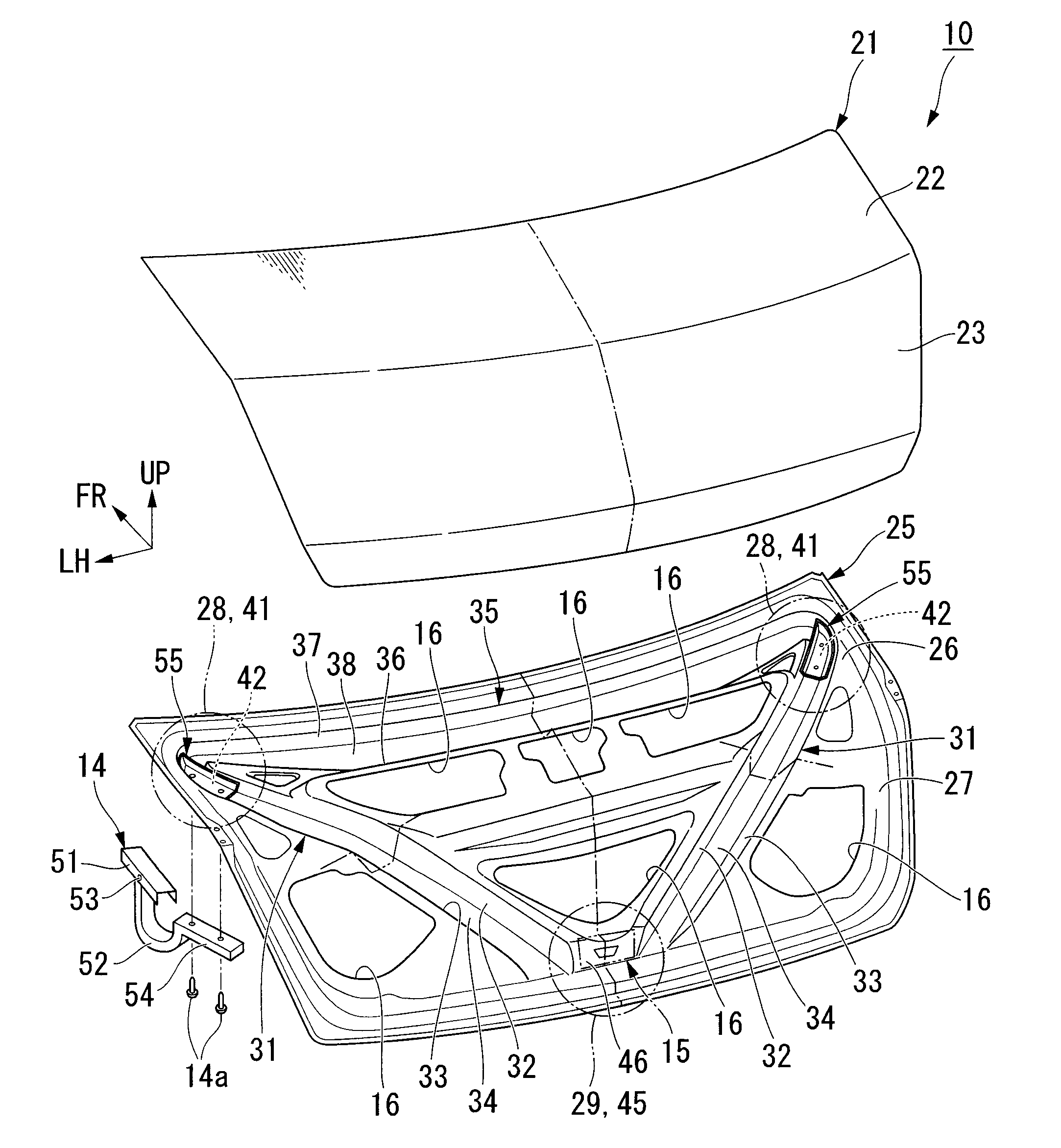
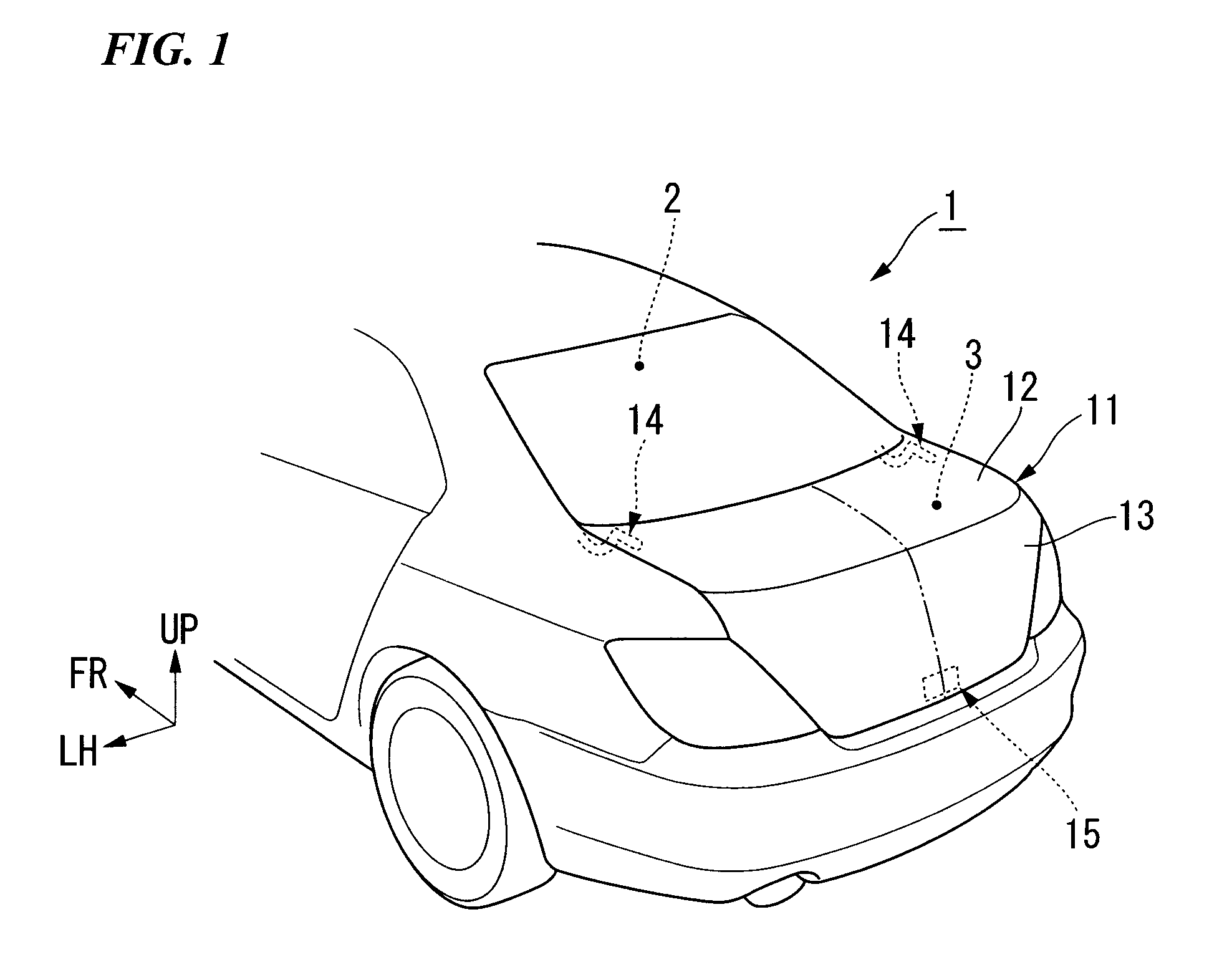
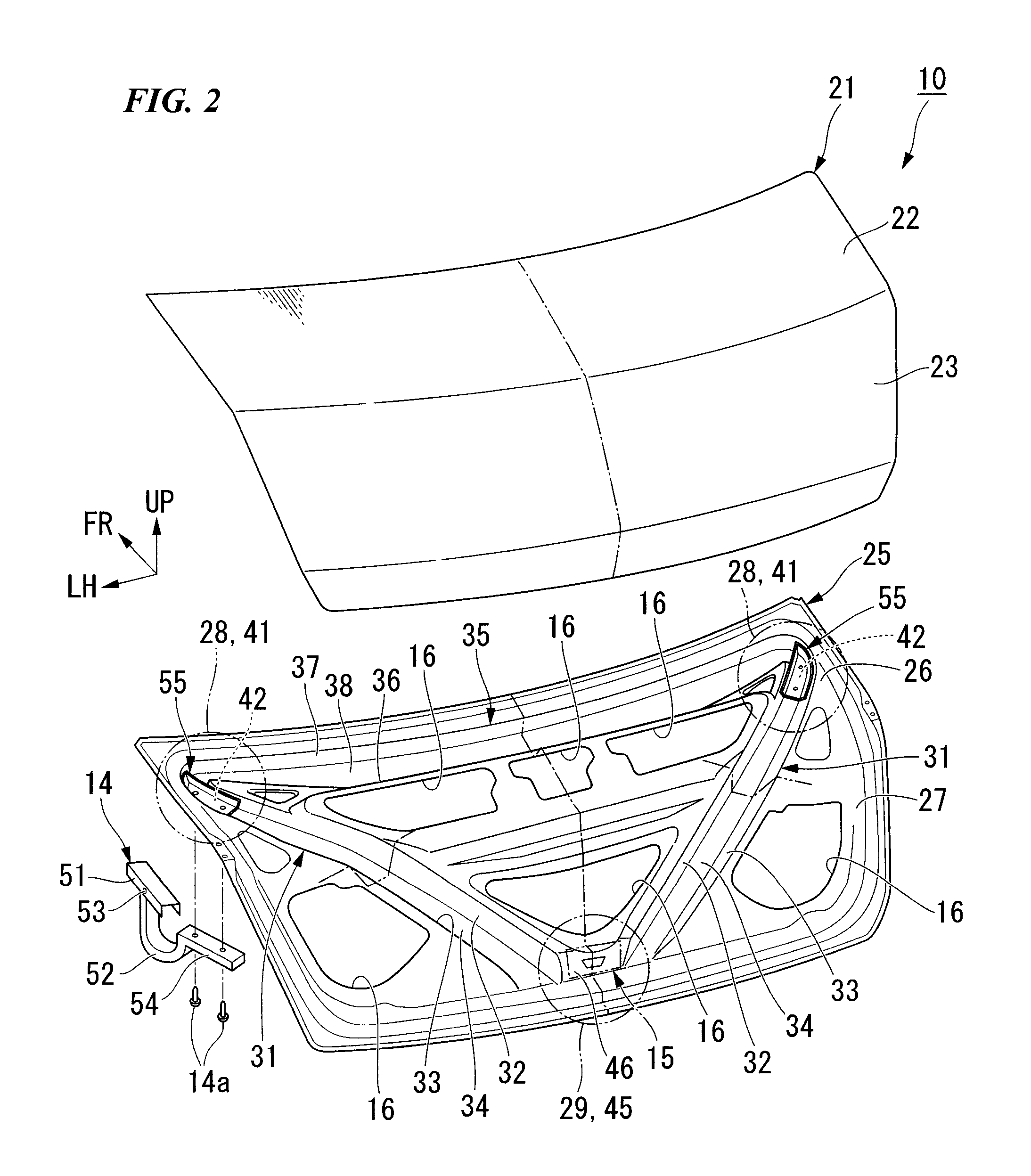
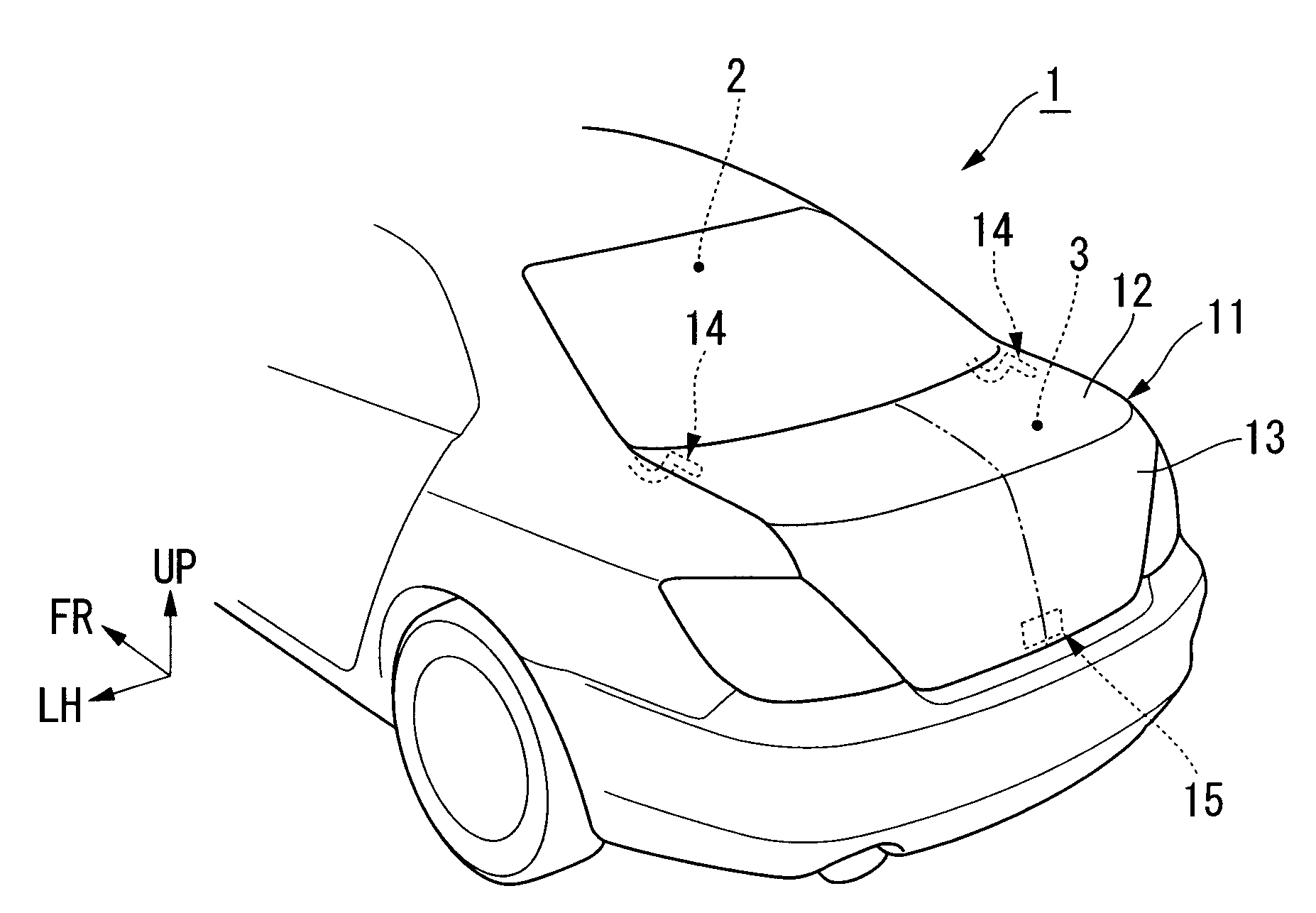
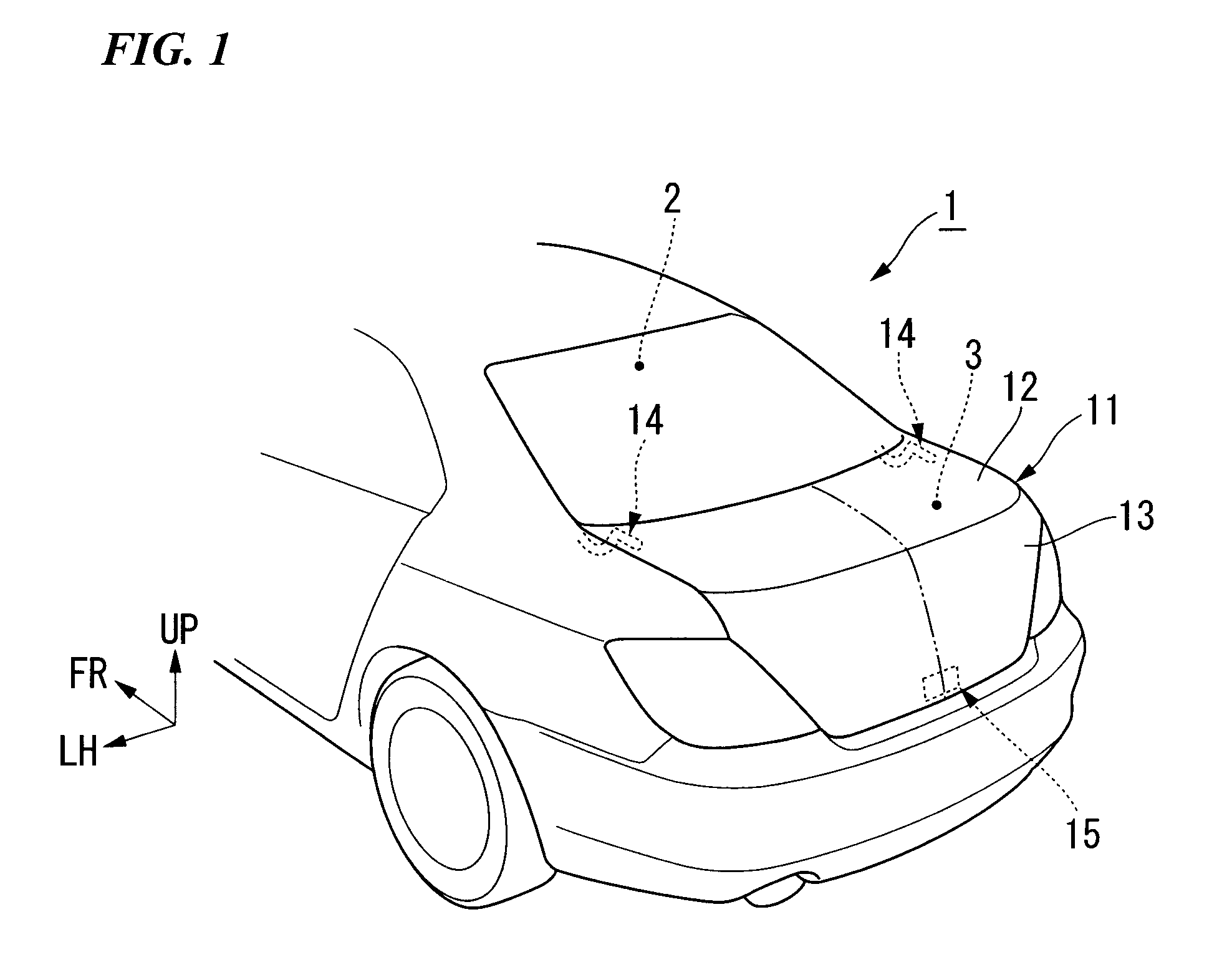
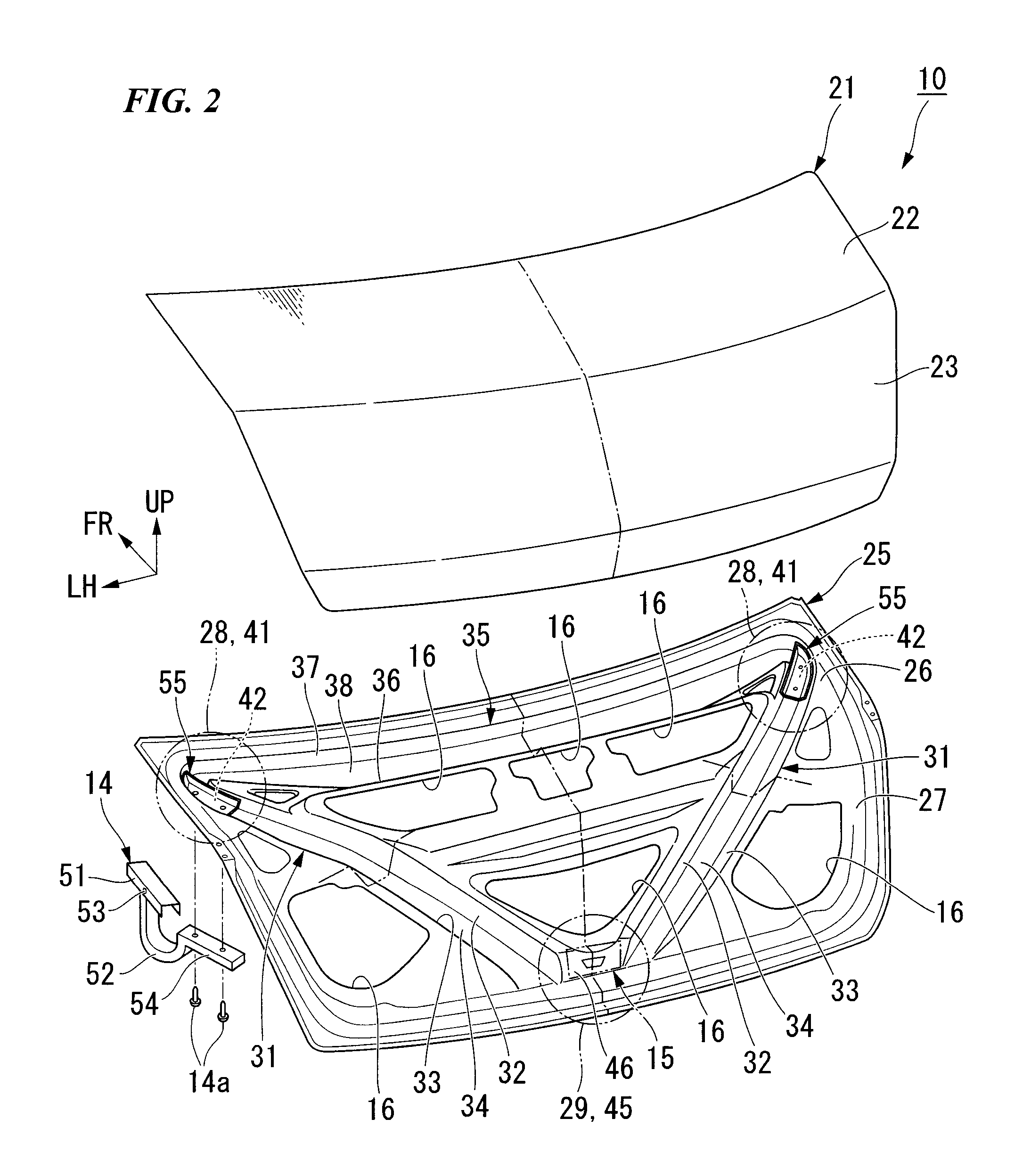
Trunk lid frame structure
ActiveUS7597378B2Flexible limitIncrease stiffnessSuperstructure subunitsMonocoque constructionsEngineeringTrunk closure
In the present frame structure of a trunk lid: the trunk lid has an outer panel and an inner panel, and is formed such that its cross-section is approximately L-shaped, with a top face part and a rear face part; left and right hinge installation sections are provided, and a lock installation section is provided in the left to right center of the rear face part; left and right beading parts are provided on the inner panel; and fastening parts of hinge arms are arranged diagonally along the lengthwise direction of the left and right beading parts.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
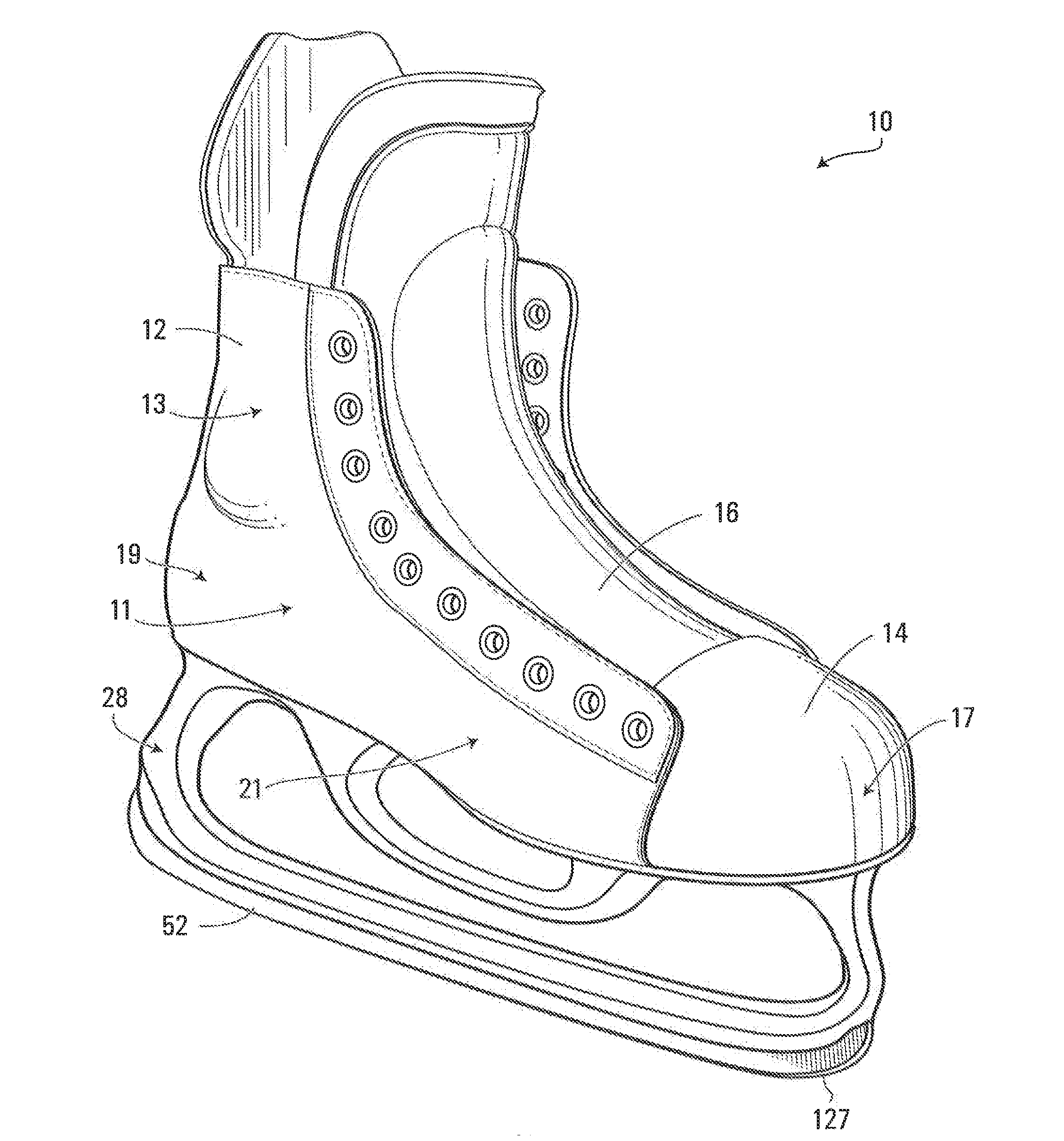
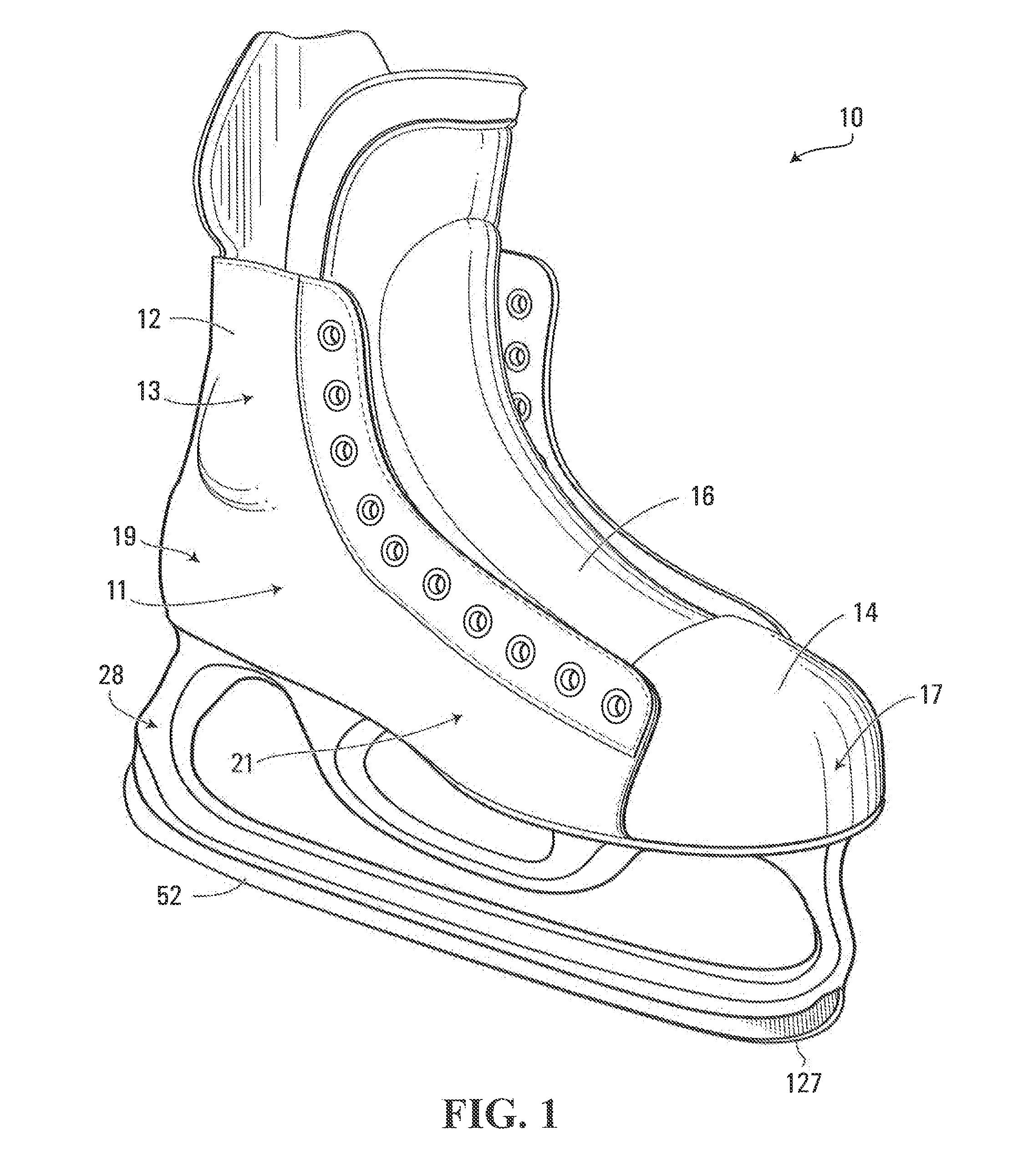
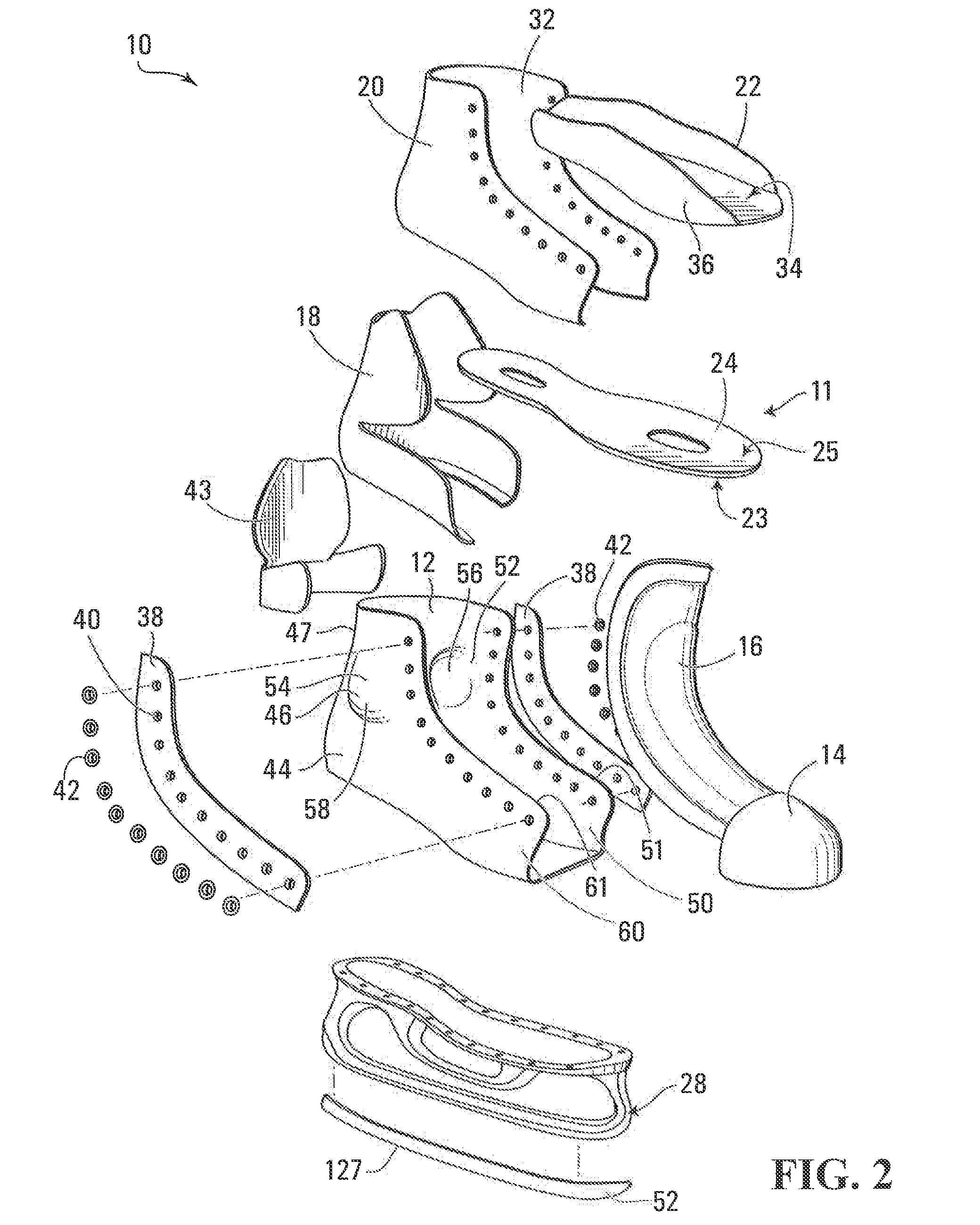
Ice skate
An ice skate comprising a blade holder having U-shaped inner and outer members that are spaced apart to define a hollow space therebetween. The U-shaped outer member has an elongated blade-supporting base and front and rear pillars that are spaced apart in a longitudinal direction of the blade holder. At least part of the elongated blade-supporting base, front pillar and rear pillar is made of a composite material such as a fiber-matrix composite material. The ice skate also has a blade comprising a runner and a body made of composite material with a matrix and a plurality of fibers embedded in the matrix.
Owner:BAUER HOCKEY LLC
Trunk lid frame structure
ActiveUS20090026793A1Avoid it happening againFlexible limitSuperstructure subunitsMonocoque constructionsEngineeringHinge angle
In the present frame structure of a trunk lid: the trunk lid has an outer panel and an inner panel, and is formed such that its cross-section is approximately L-shaped, with a top face part and a rear face part; left and right hinge installation sections are provided, and a lock installation section is provided in the left to right center of the rear face part; left and right beading parts are provided on the inner panel; and fastening parts of hinge arms are arranged diagonally along the lengthwise direction of the left and right beading parts.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
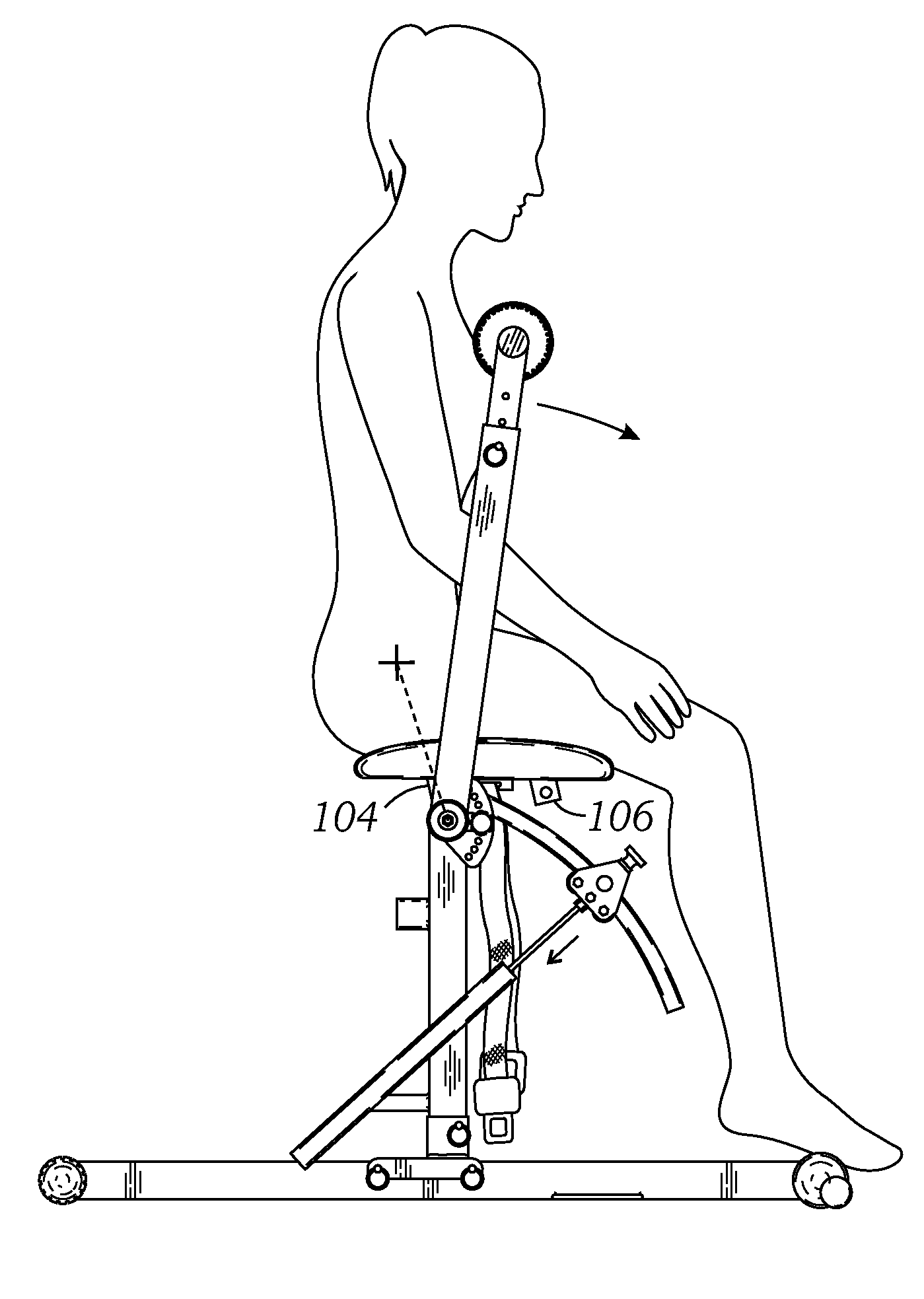
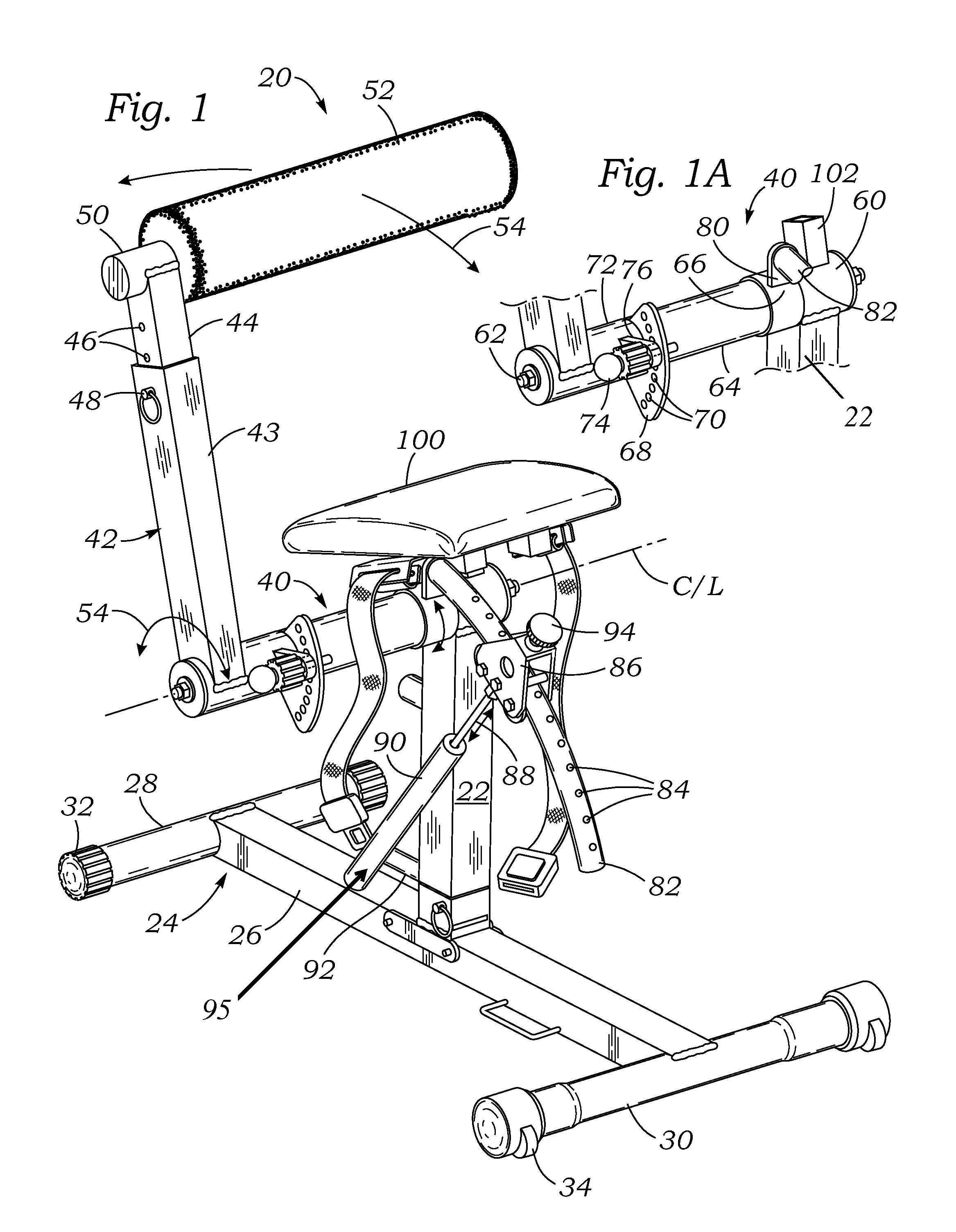
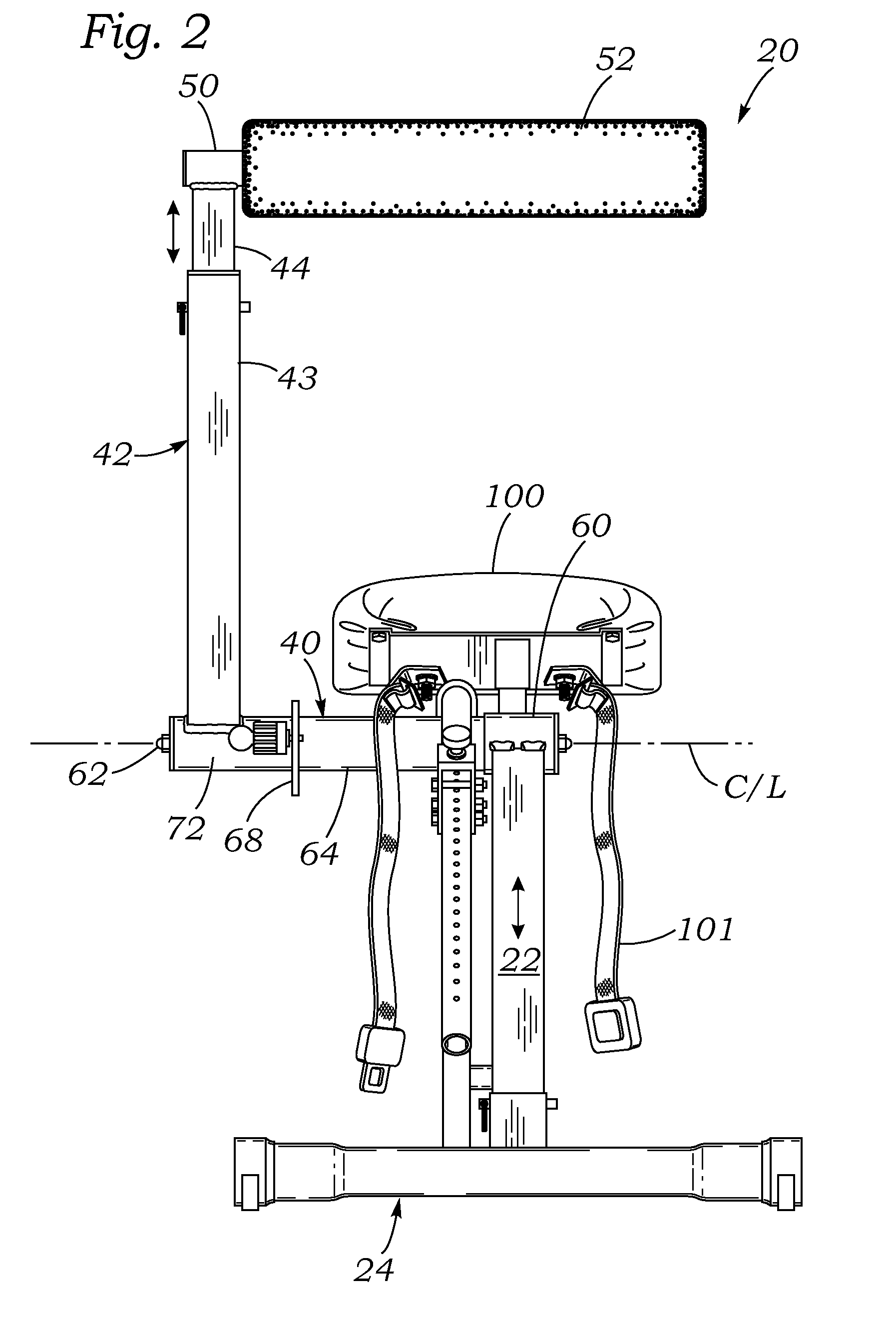
Core exercising machine
InactiveUS20140296042A1Flexible limitAvoid discomfortSpace saving gamesMuscle exercising devicesRotational axisExternal obliques
A collapsible exercise machine for strengthening the core muscles (transverse abdominal, internal obliques, external obliques, rectus abdominis, and erector spinae) includes a frame mounted on a base on which a user sits and manipulates an upstanding lever arm. A seat is convertible between two differently-angled positions for back extension or abdominal exercises. The lever arm rotates a curved tube having a plurality of force adjustment holes. The tube passes through a frame at the upper end of a gas spring, and engaging an adjustment pin on the frame with different adjustment holes changes the amount of resistance. The entire frame above the base can be vertically adjusted to accommodate different sizes of user without altering the relative position between the seat (and user's hips) and the axis of rotation of the lever arm thus not affecting / changing the designated resistance between users of different heights (resistance is affected when the lever arm is lengthened). The connection between the frame and the base enables the unit to be collapsed to a profile small enough to fit under a bed.
Owner:SNYDER MICHAEL J
Insulator for a wheel suspension system
InactiveUS8333269B2Increase flexibilityIncreased durabilityResilient suspensionsRubber-like material springsElastomerEngineering
An insulator for a wheel suspension system of a vehicle is formed of an elastomeric material. The elastomeric material defines a channel that provides increased flexibility to the insulator and defines an increased density about the channel that increases the durability of the insulator. The suspension system includes a support structure adapted to be mounted to the vehicle, a piston rod disposed within the aperture and displaceable relative to the support structure along a line of travel, and a plate mounted to the piston rod. The insulator is compressibly disposed between the support structure and the plate. The exterior channel increases the flexibility of the insulator to distribute localized stress on the insulator by the support structure and the plate. The increased density about the channel increases the durability of the insulator about the channel when the support structure and the plate exert a compressive force on the insulator.
Owner:BASF CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com