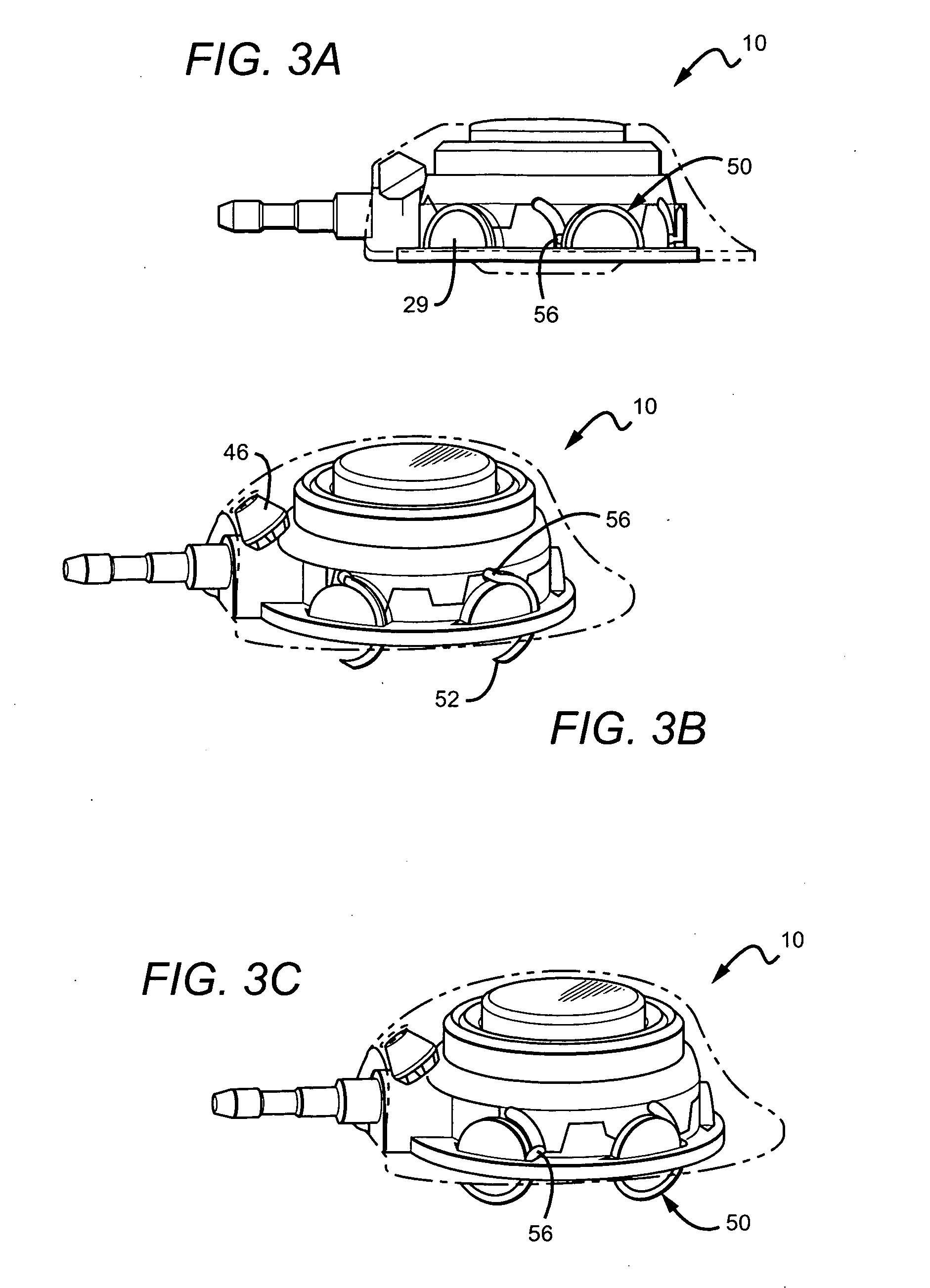
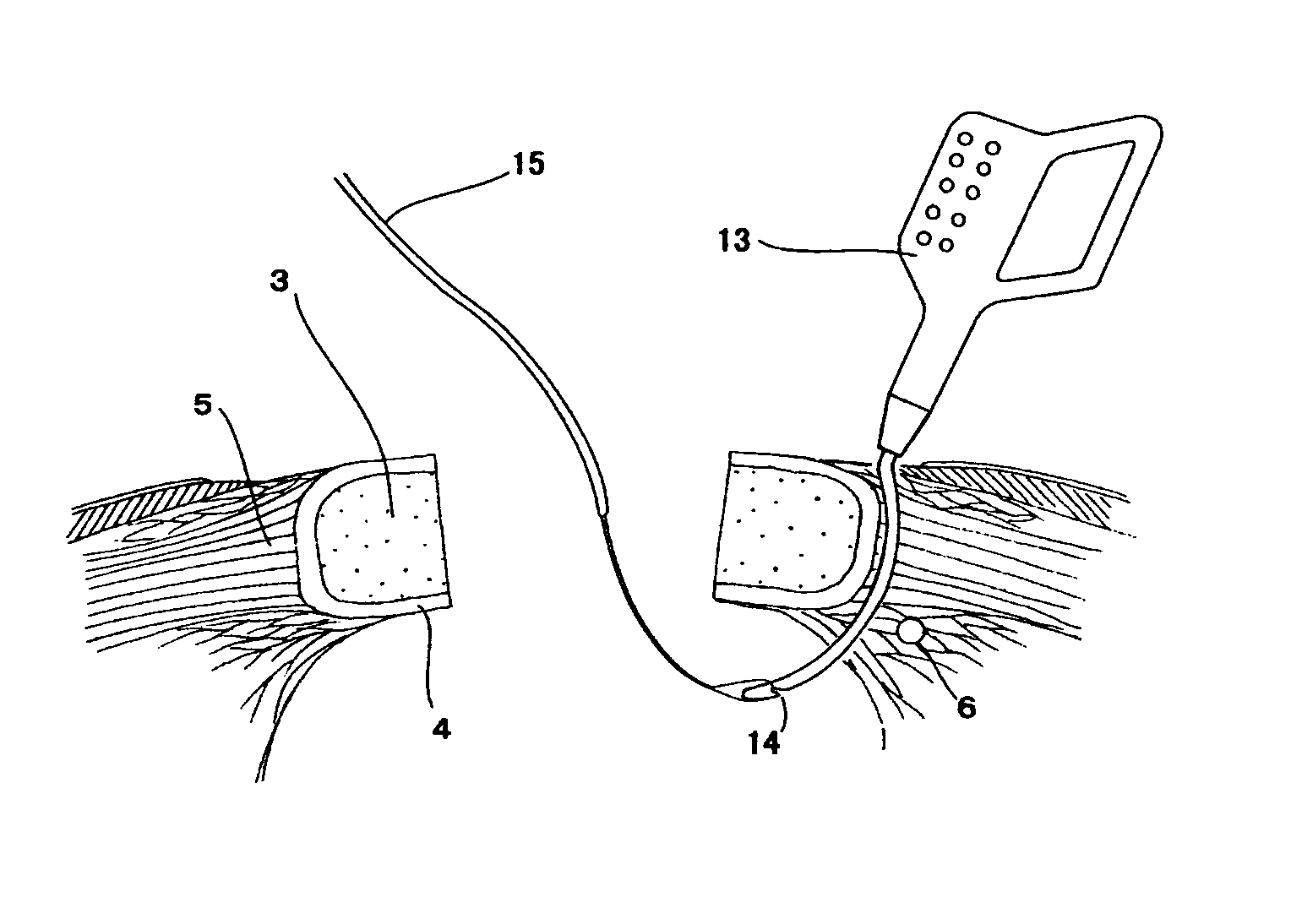
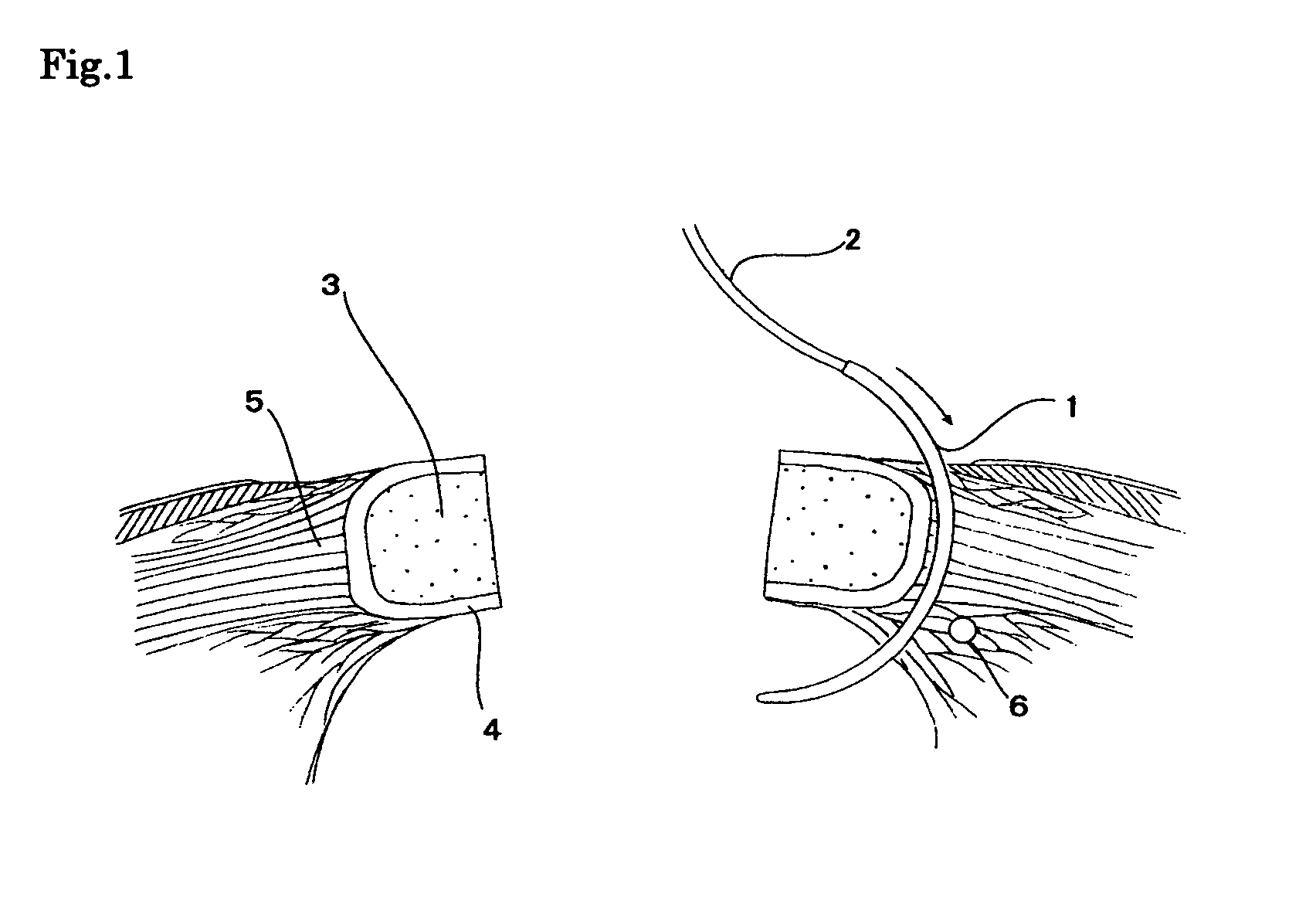
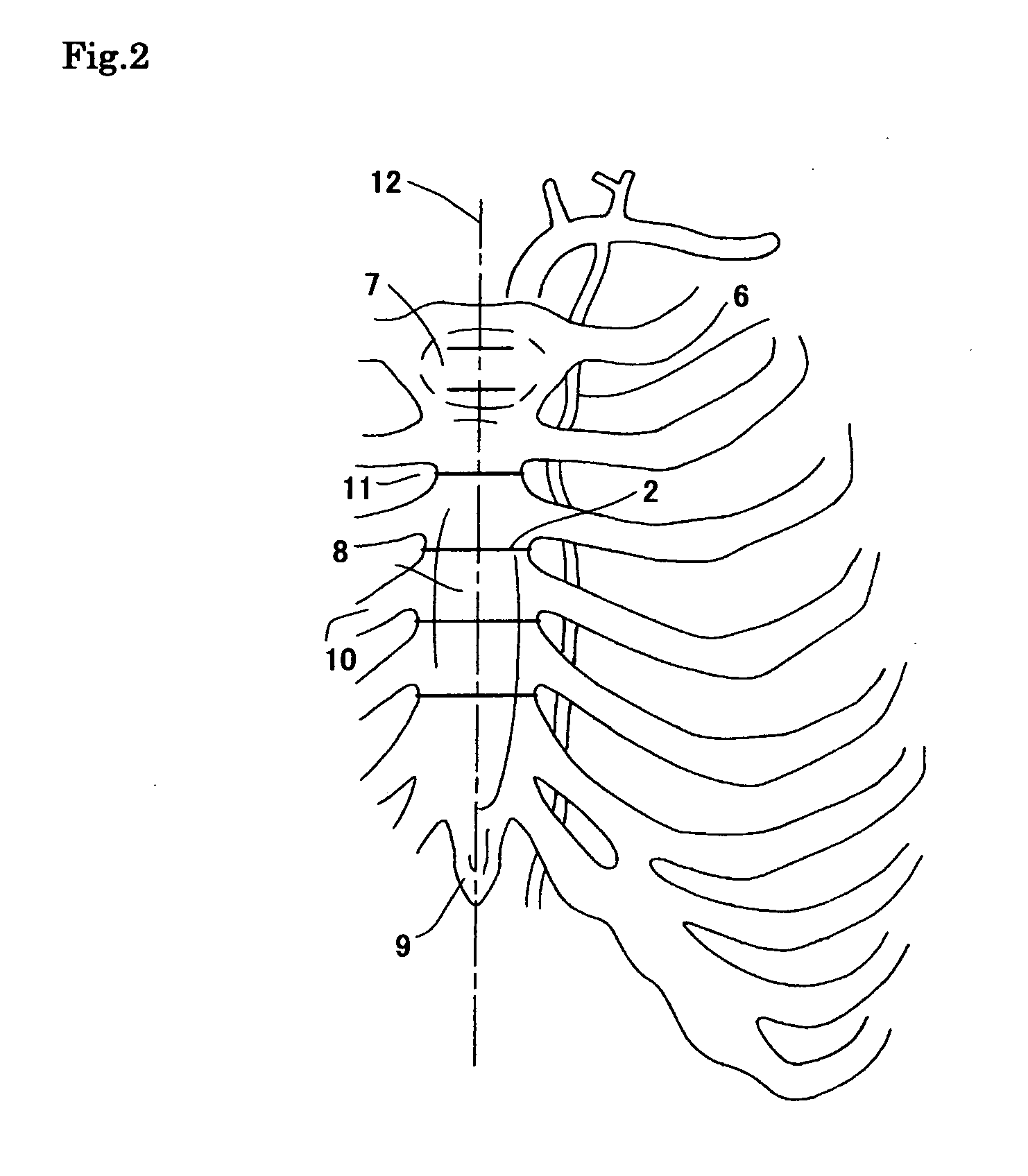
Patents
Literature
849 results about "Suturing needle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A suturing needle is usually held by a surgeon using a needle driver, which resemble scissors. A suture needle is used to apply sutures.
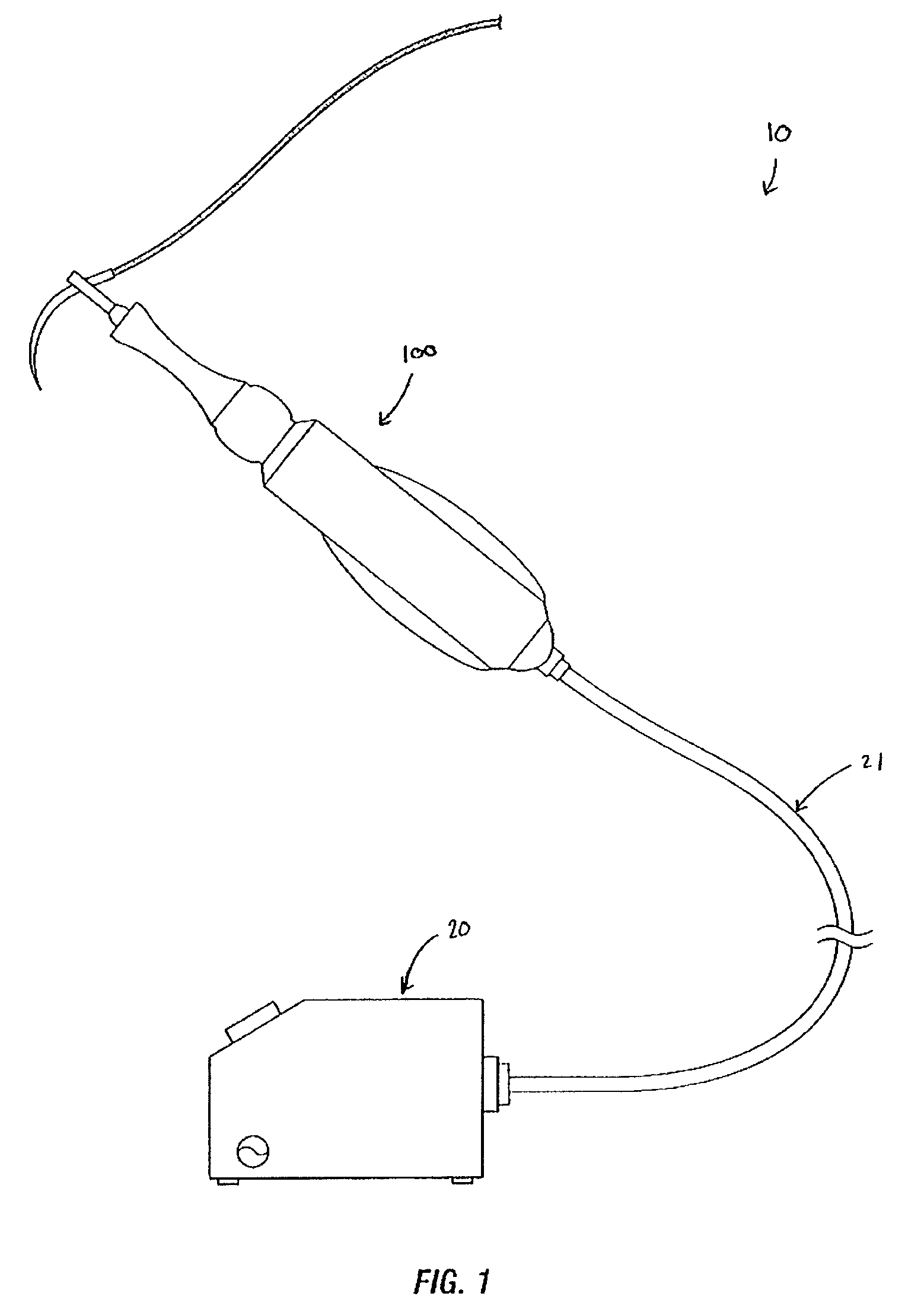
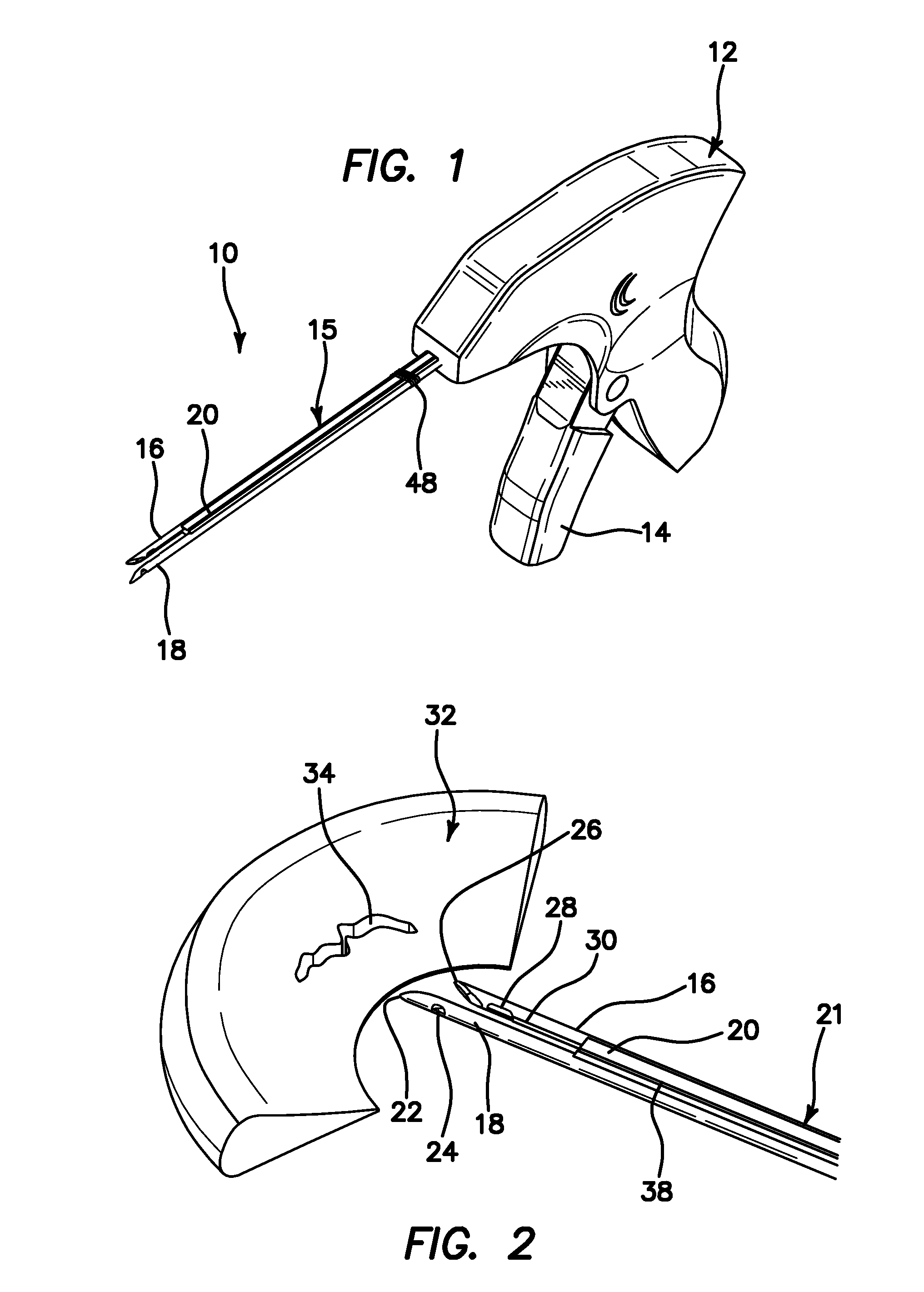
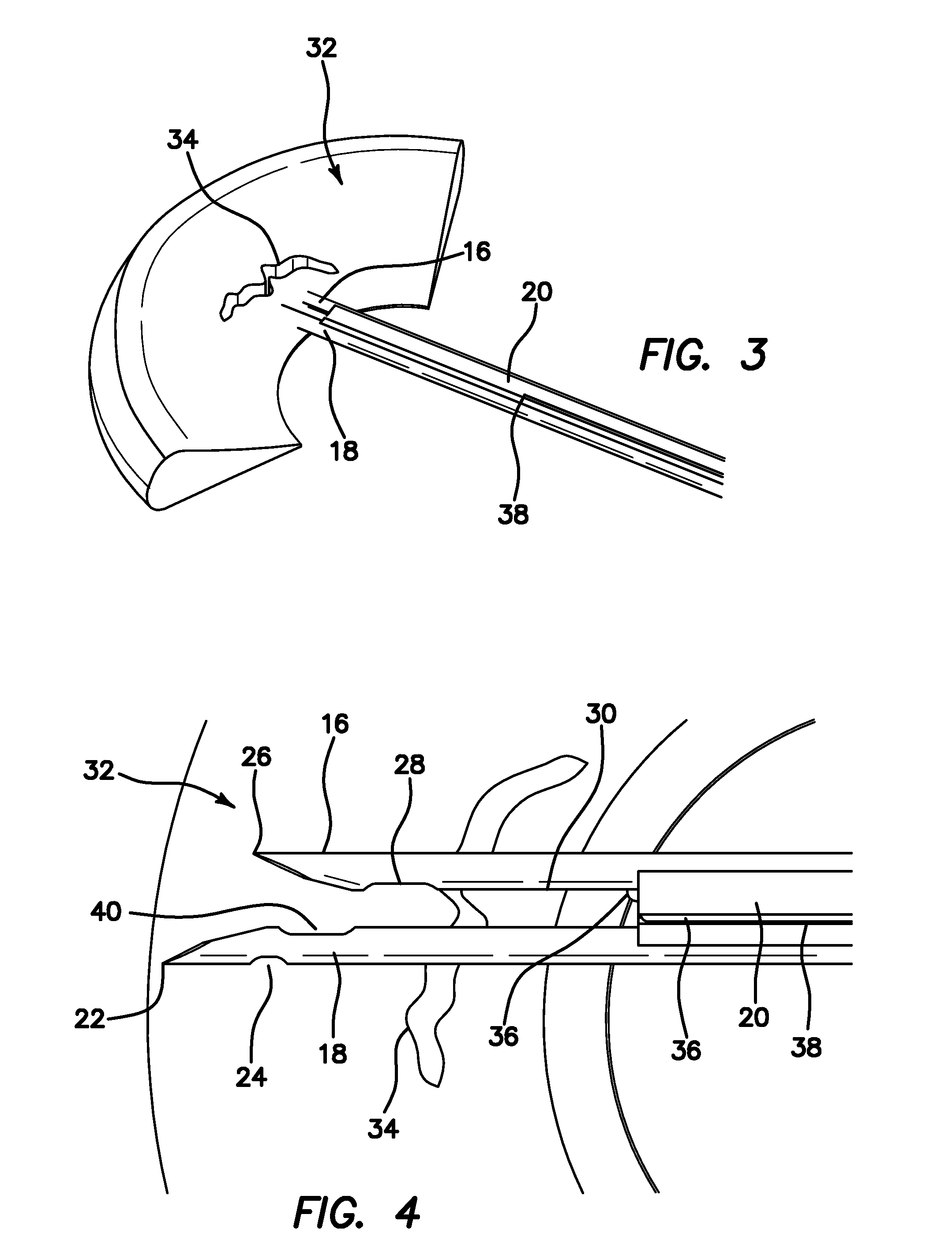
Suture passer and method of passing suture material
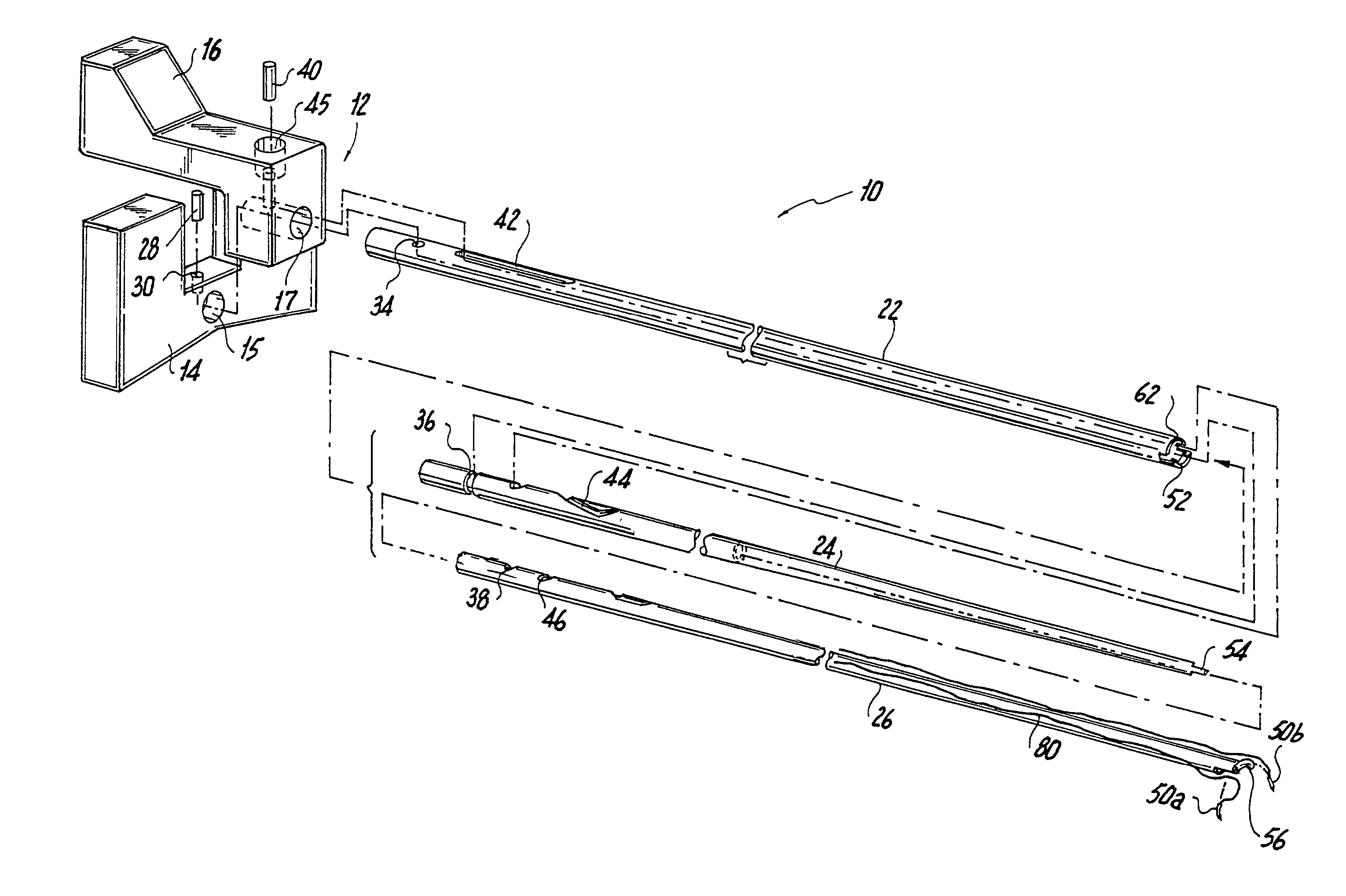
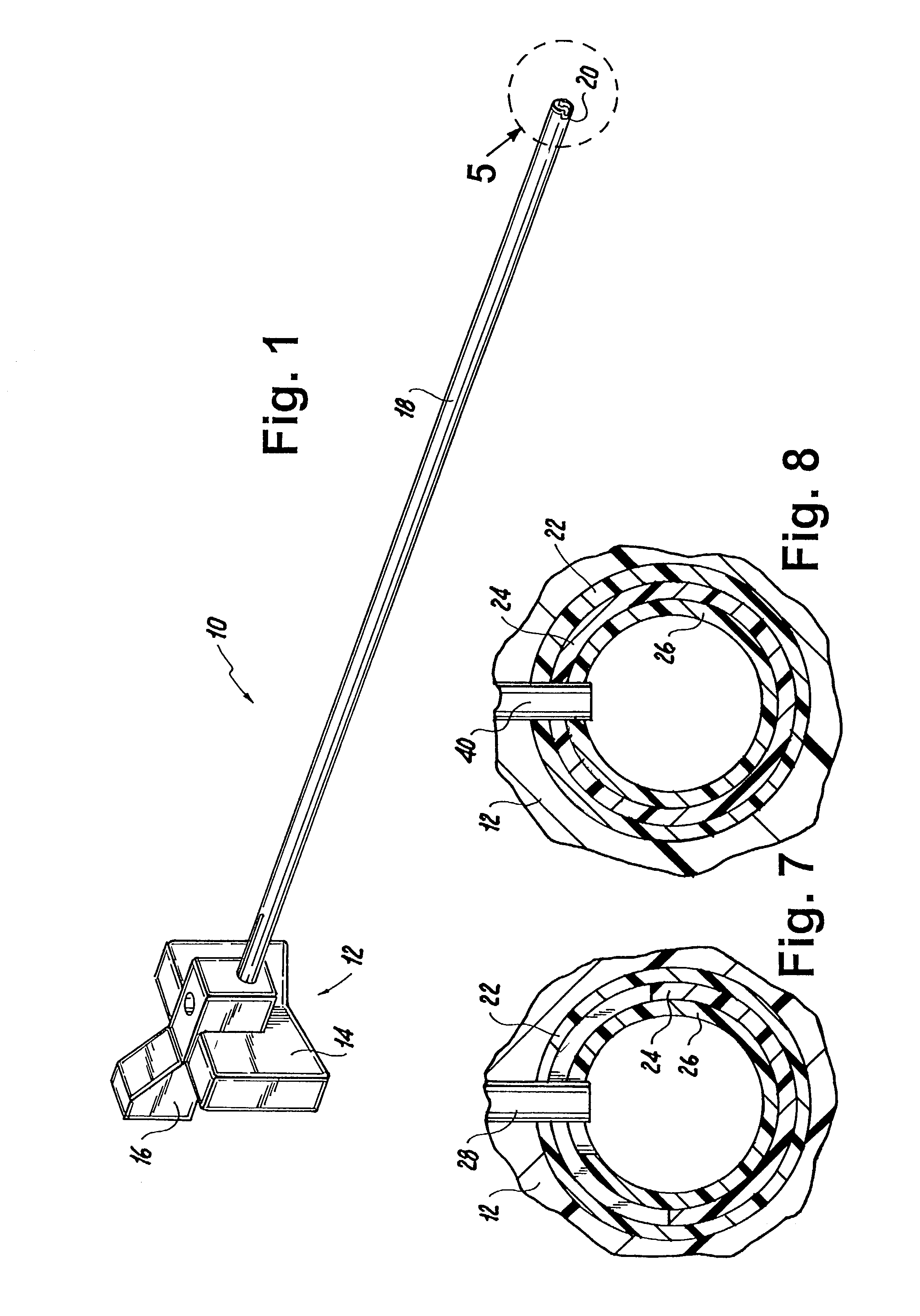
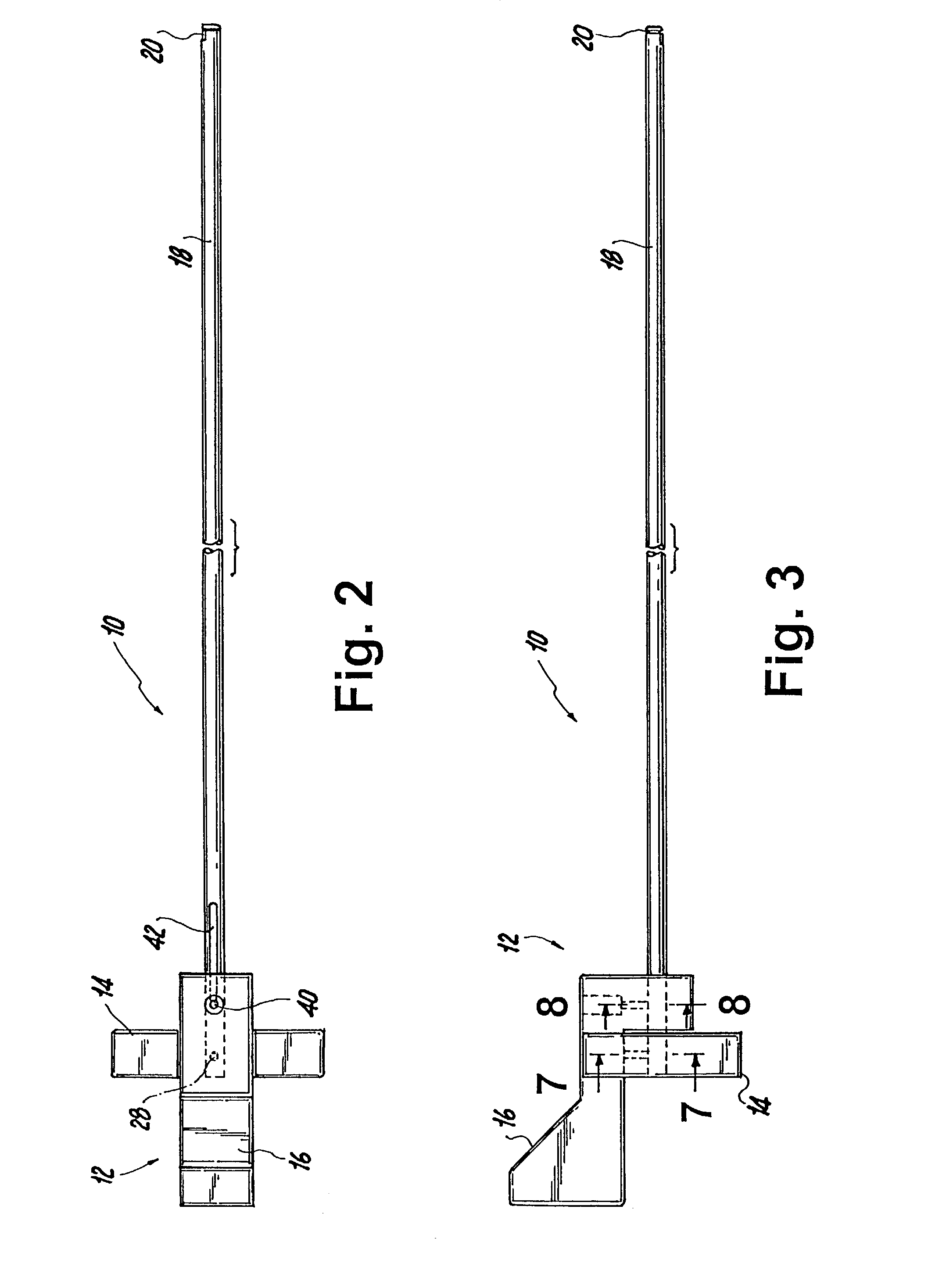
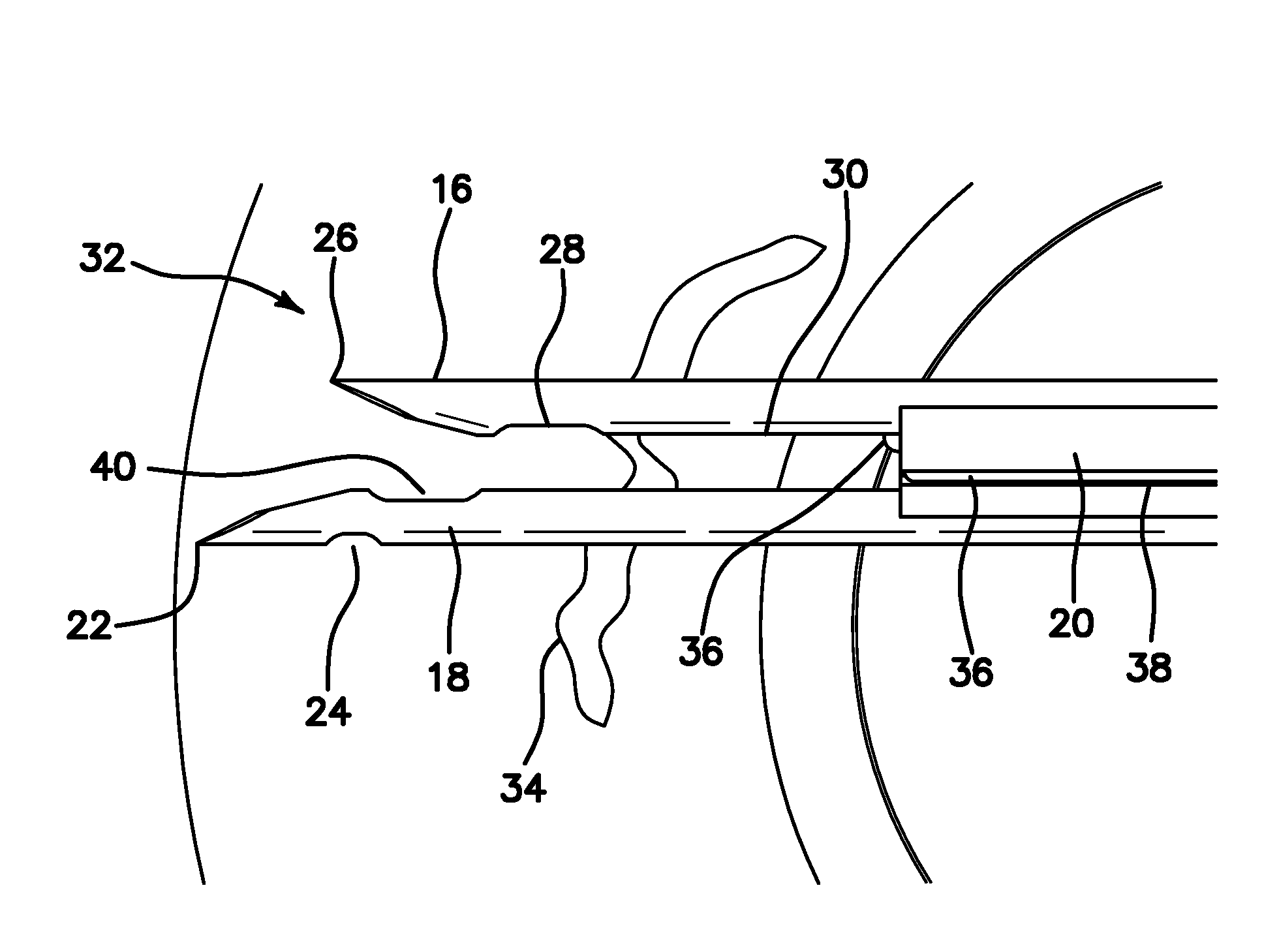
InactiveUS20080051833A1Reduce harmReduce riskSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsAnatomical structuresSuturing needle
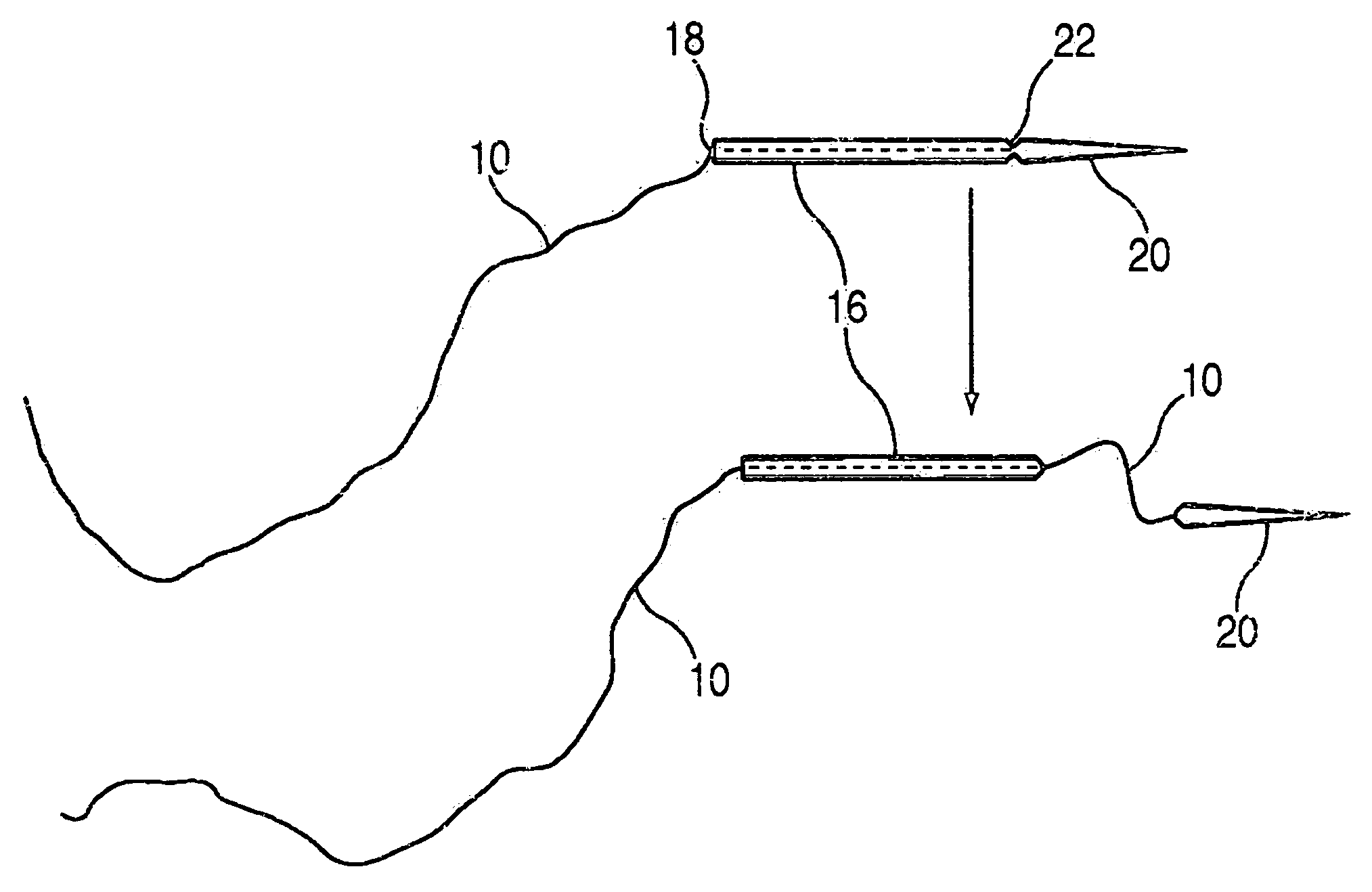
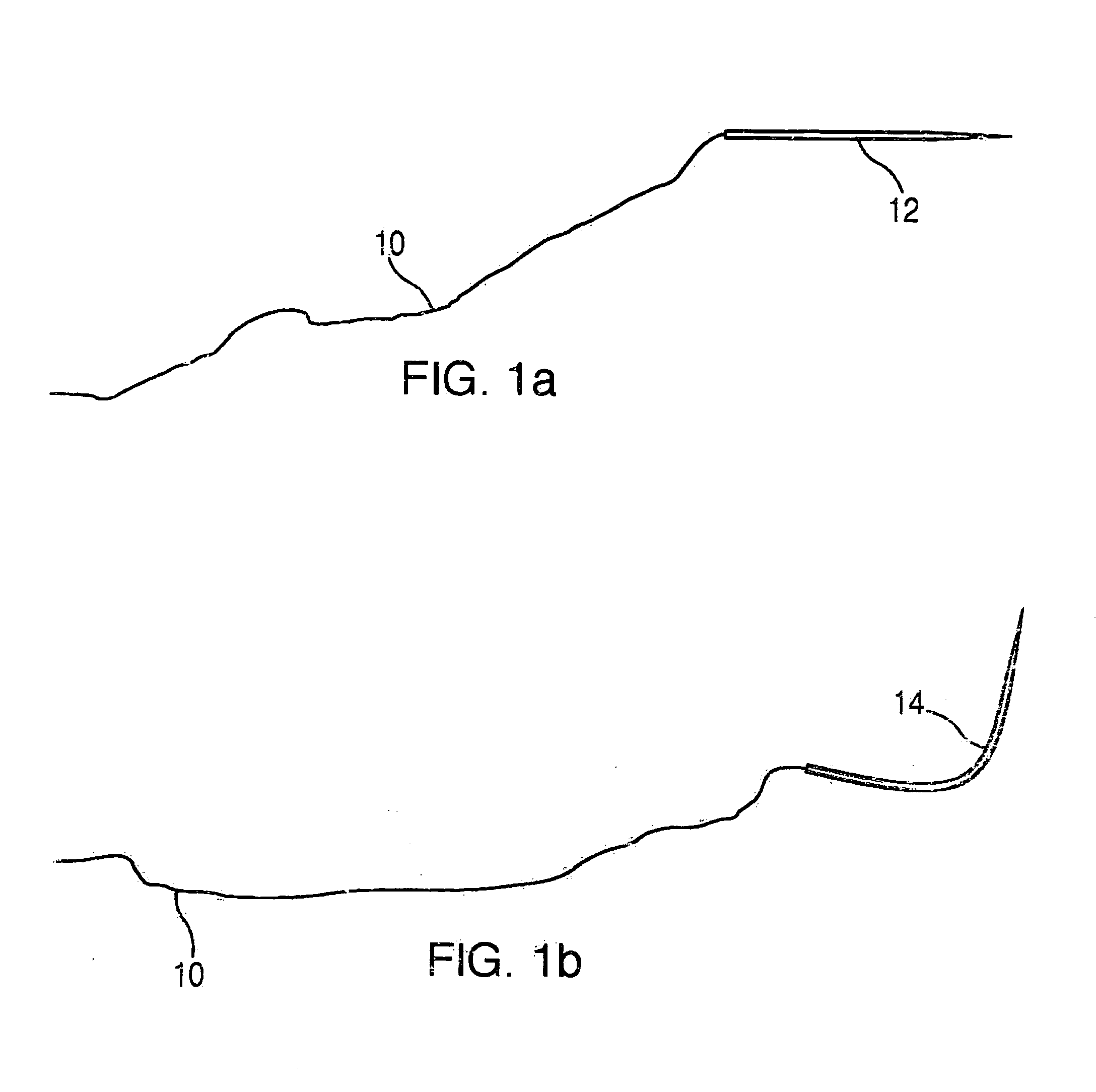
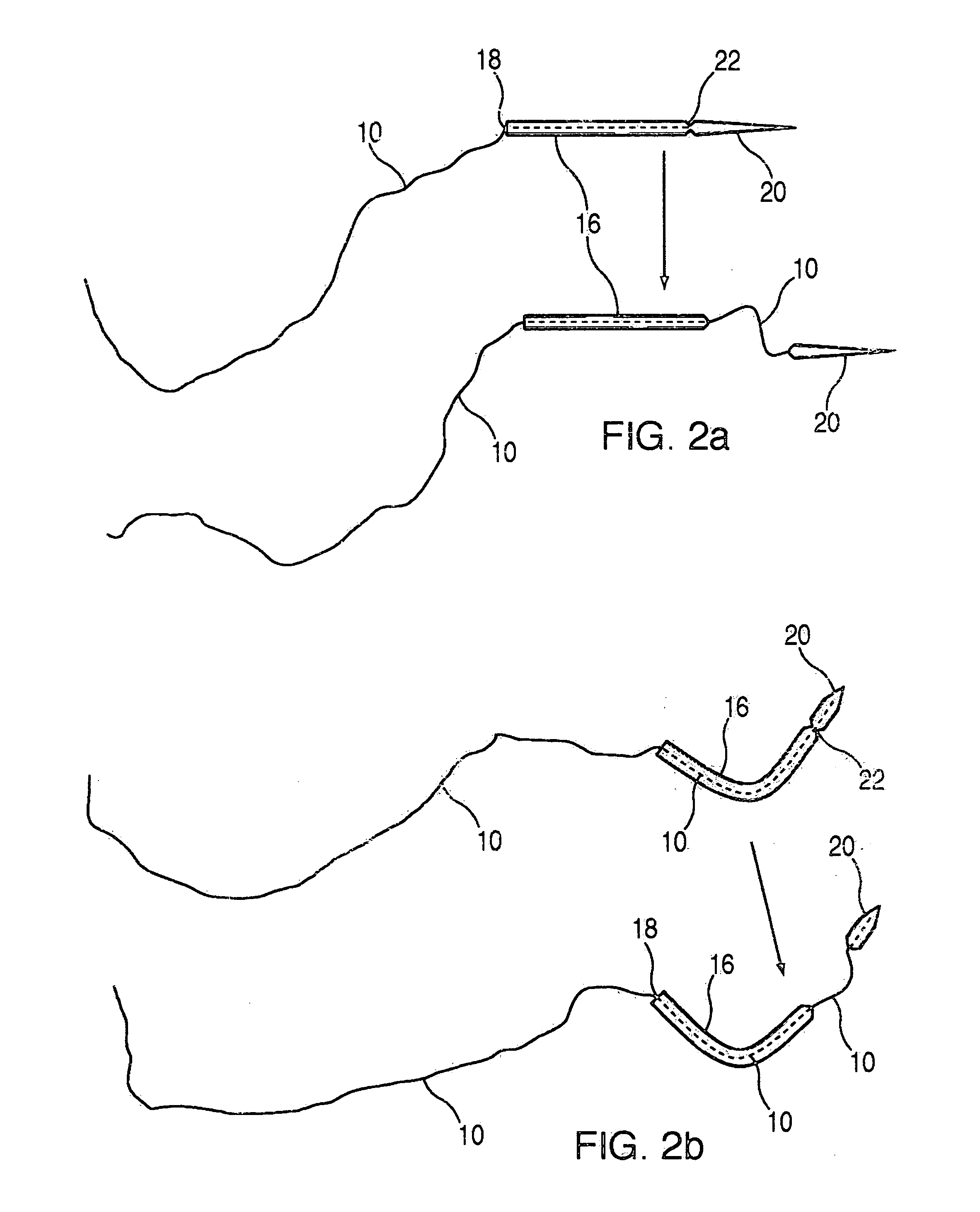
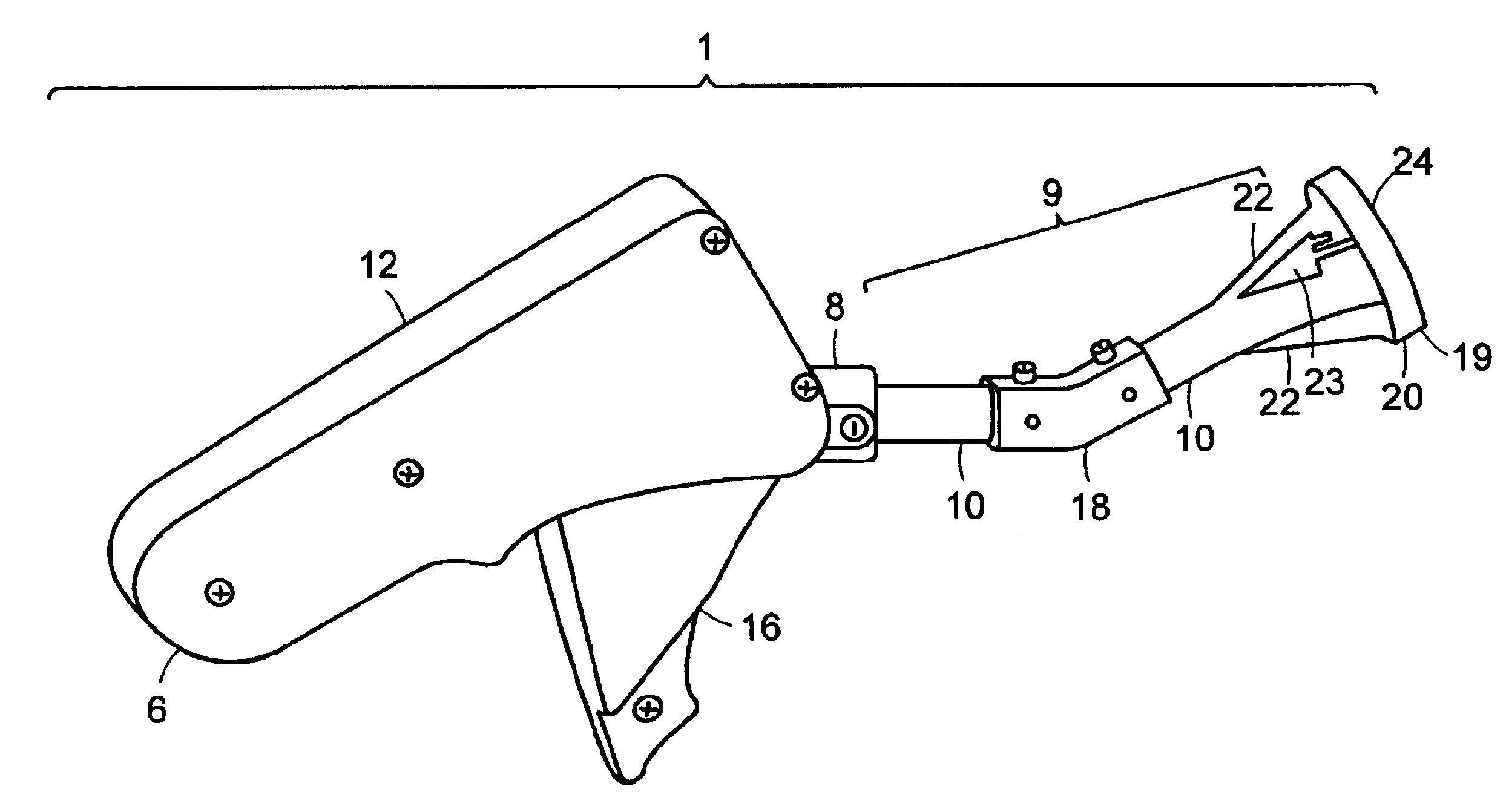
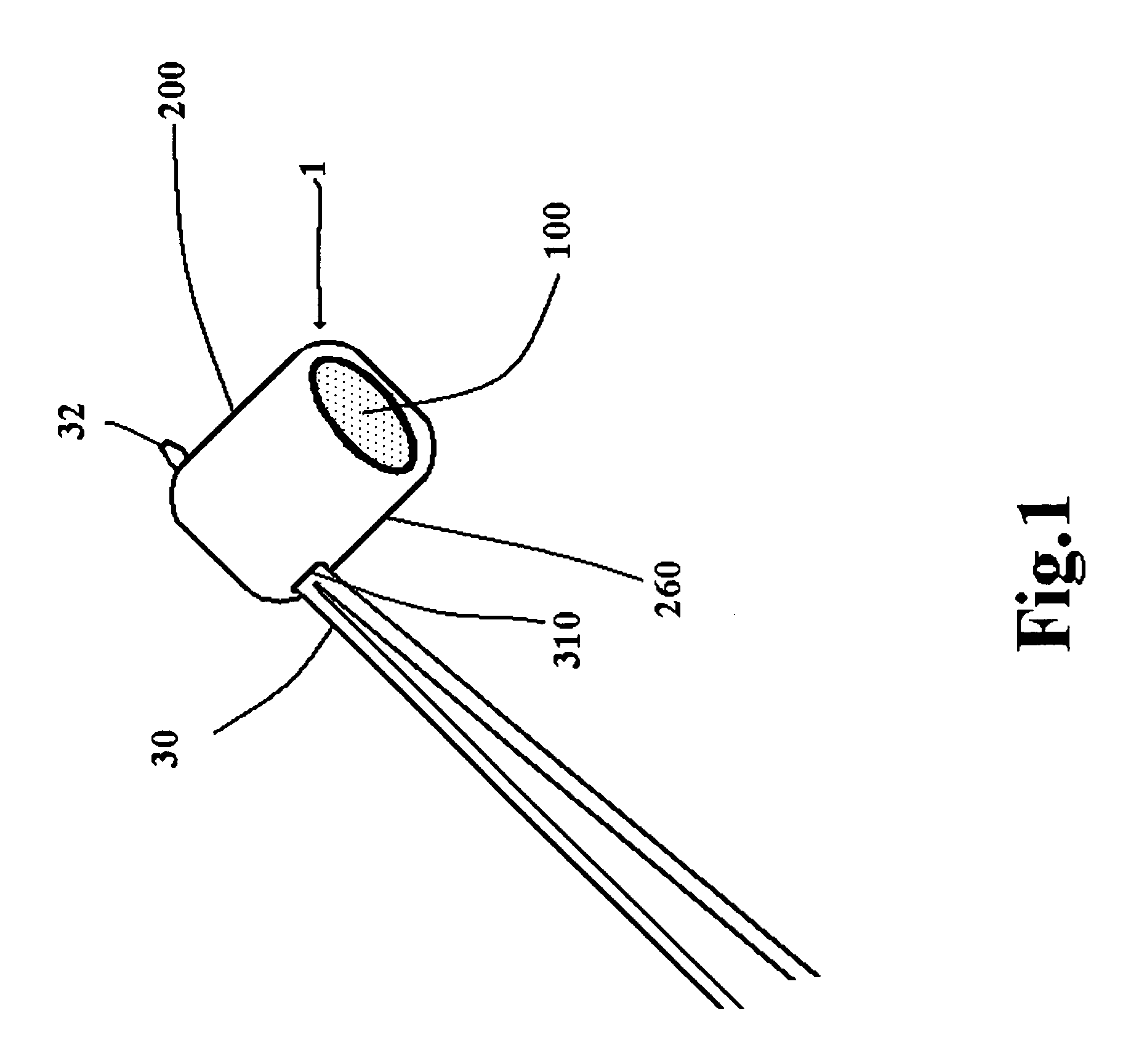
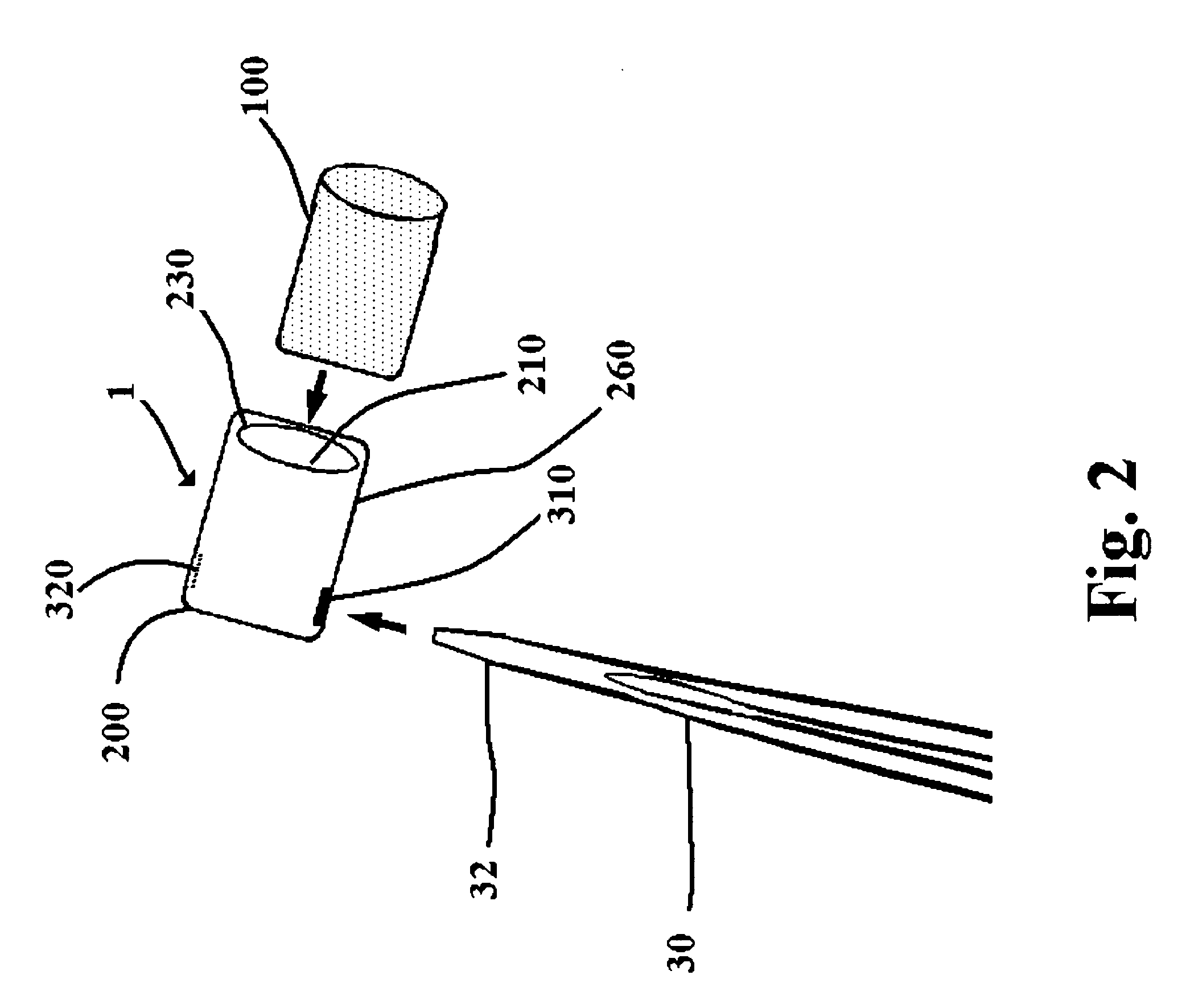
A suture and needle combination is disclosed for use during surgical and non-surgical procedures comprising a suture needle 16 with a breakaway tip 20, insertable tip 24 or reusable tip 32. Suture 10 passes freely through hollow needle 16 after a user removes needle tip (20,24, or 32) during use. This suture needle combination reduces the amount of room needed within a surgical site, reduces the length of needle 16 needed to exit tissue (for example) while suturing, and decreased trauma to at risk anatomical structures during a surgical procedure or other use.
Owner:GRAMUGLIA VINCENT +1
Apparatus and method for surgical suturing with thread management
InactiveUS6923819B2Efficient preparationExcellent ease of useSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsSuturing needleEngineering
An apparatus and a method for surgical suturing with thread management. An apparatus for tissue suturing comprising a cartridge having a suturing needle having a pointed end and a blunt end, the suturing needle capable of rotating about an axis; a pusher assembly comprising a cartridge holder having a needle rotation drive capable of releasably engaging the cartridge and rotating the suturing needle about the axis; and an actuator capable of releasably engaging the needle rotation drive to rotate the needle rotation drive. A method for suturing tissue comprising placing a suturing device having a cartridge containing a suturing needle to span separated tissue segments; activating an actuator to cause rotational movement of the suturing needle through the separated tissue segments; and deactivating the actuator to stop an advancing movement of the suturing needle to cause a suturing material to be pulled through the separated tissue segments forming a stitch.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Semi-robotic suturing device
A semi-robotic apparatus and methods of use thereof for suturing body tissue, wherein the apparatus includes a housing; at least two distal arms connected to and extending distally from the housing, wherein the at least two distal arms are independently both extendable and retractable; a suture needle clasp connected to a distal end of each of the at least two distal arms, wherein the suture needle clasp is radially rotateable orthogonal to the longitudinal axis of the distal arm to which it is connected; and at least one controller operable for controlling at least a portion of the extension or retraction of the at least two distal arms, the rotation of the suture clasps and the opening and closing of the suture needle clasps.
Owner:SUTURE ROBOTICS
Rotational driver
ActiveUS9192376B2Enhances maneuvering and safetyEfficiently sutureSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsSuturing needleLinear motion
A rotational driver that comprises a interactive portion, wherein each interactive portion comprises a first extended member and a second extended member, a rotational system and a linear motion system, wherein the rotational driver permits a left or right handed surgeons to perform the surgical suturing procedure in a less complicated and more secure way by allowing more control over the suturing needle and the area to be stitched, even when the suturing area is small, deep, and / or restricted.
Owner:ERGOSURGICAL GRP CORP
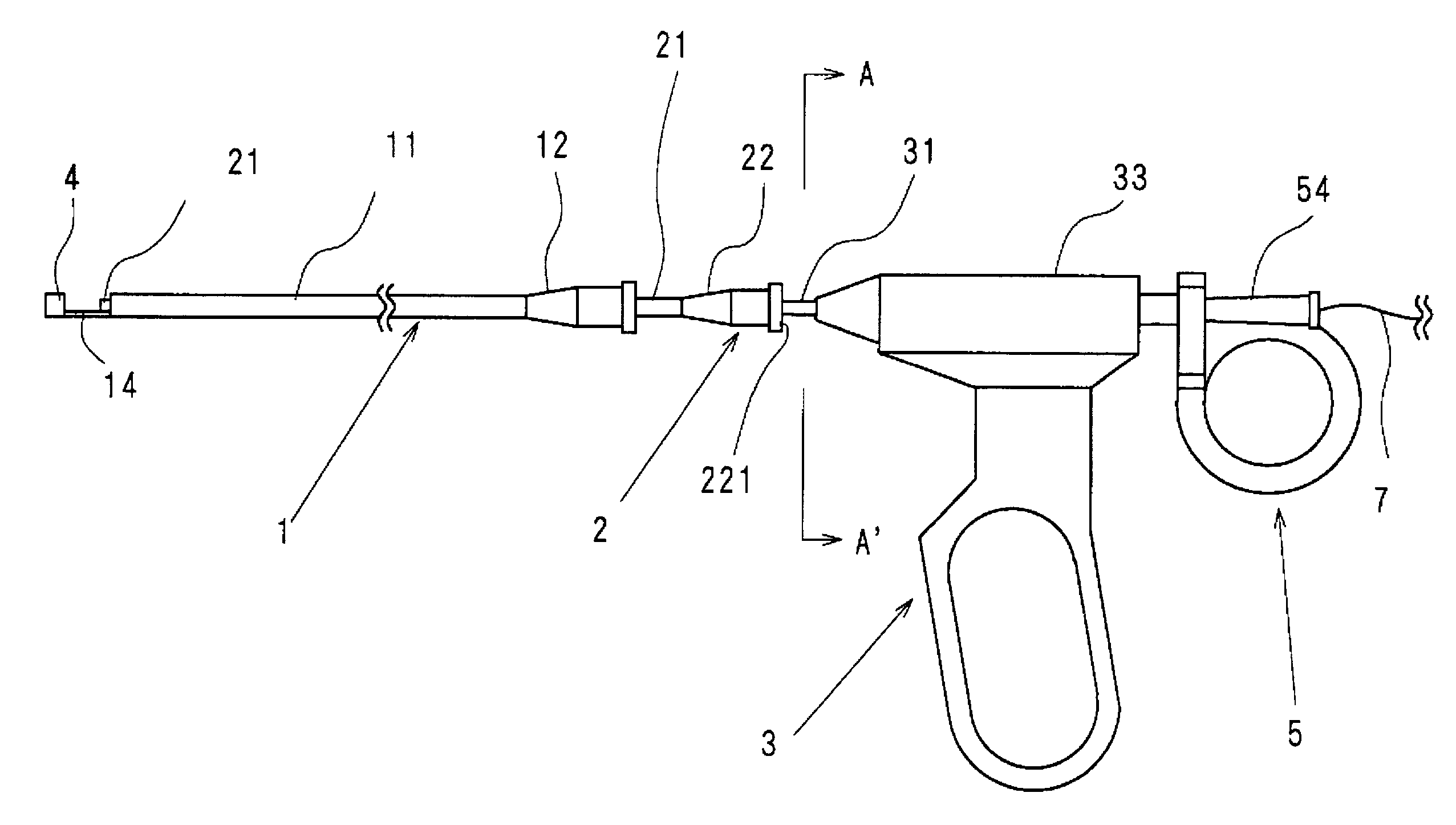
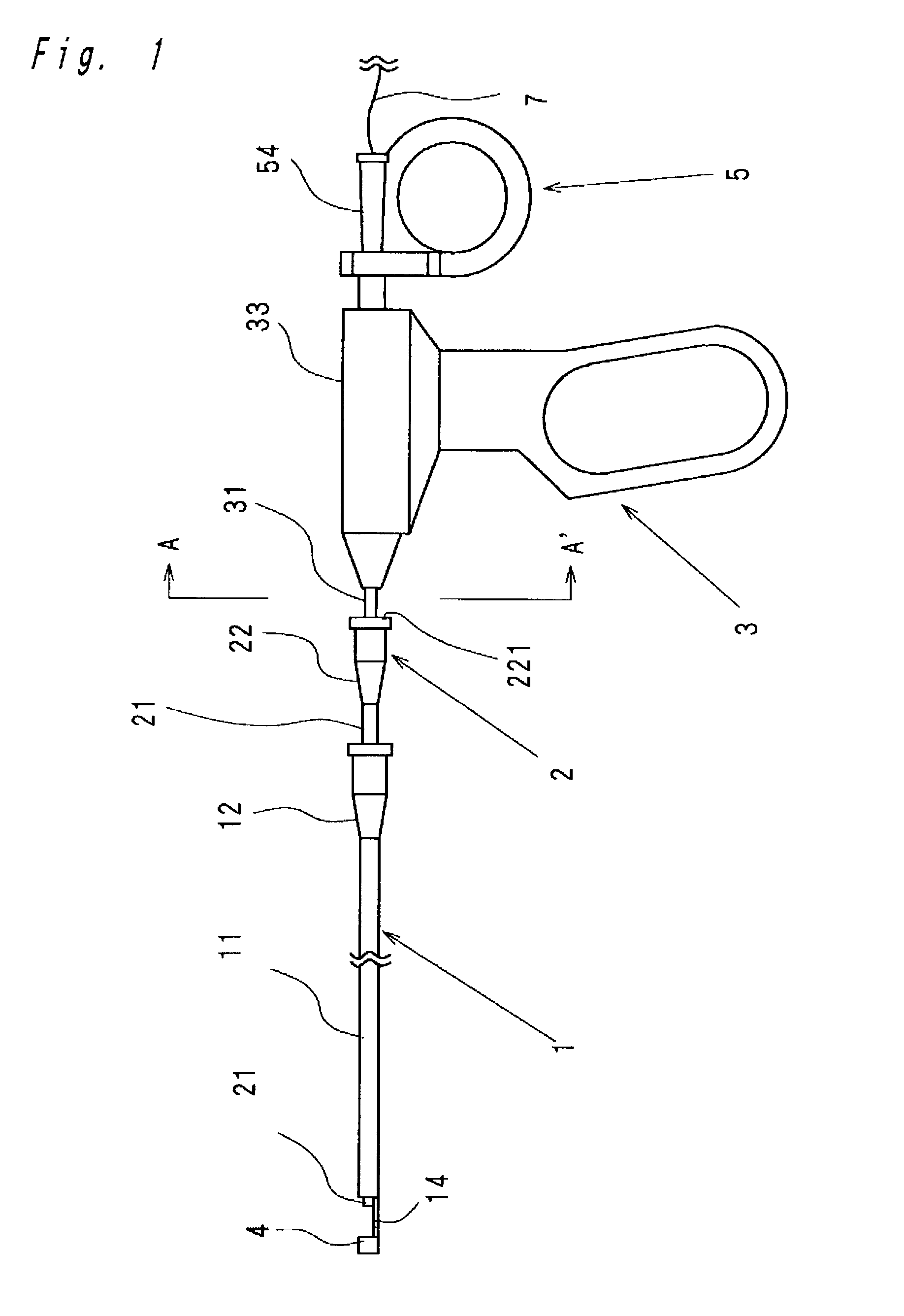
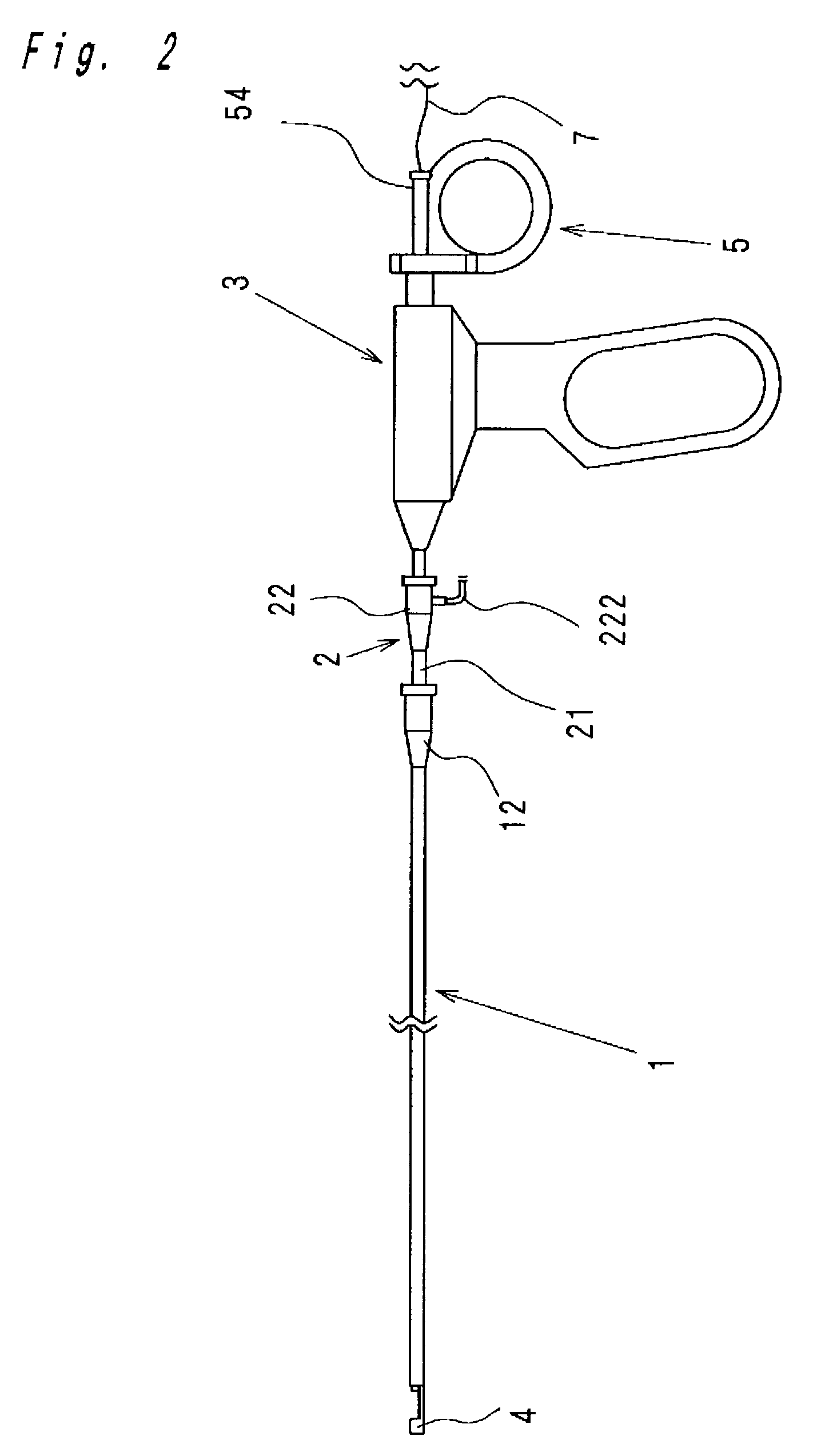
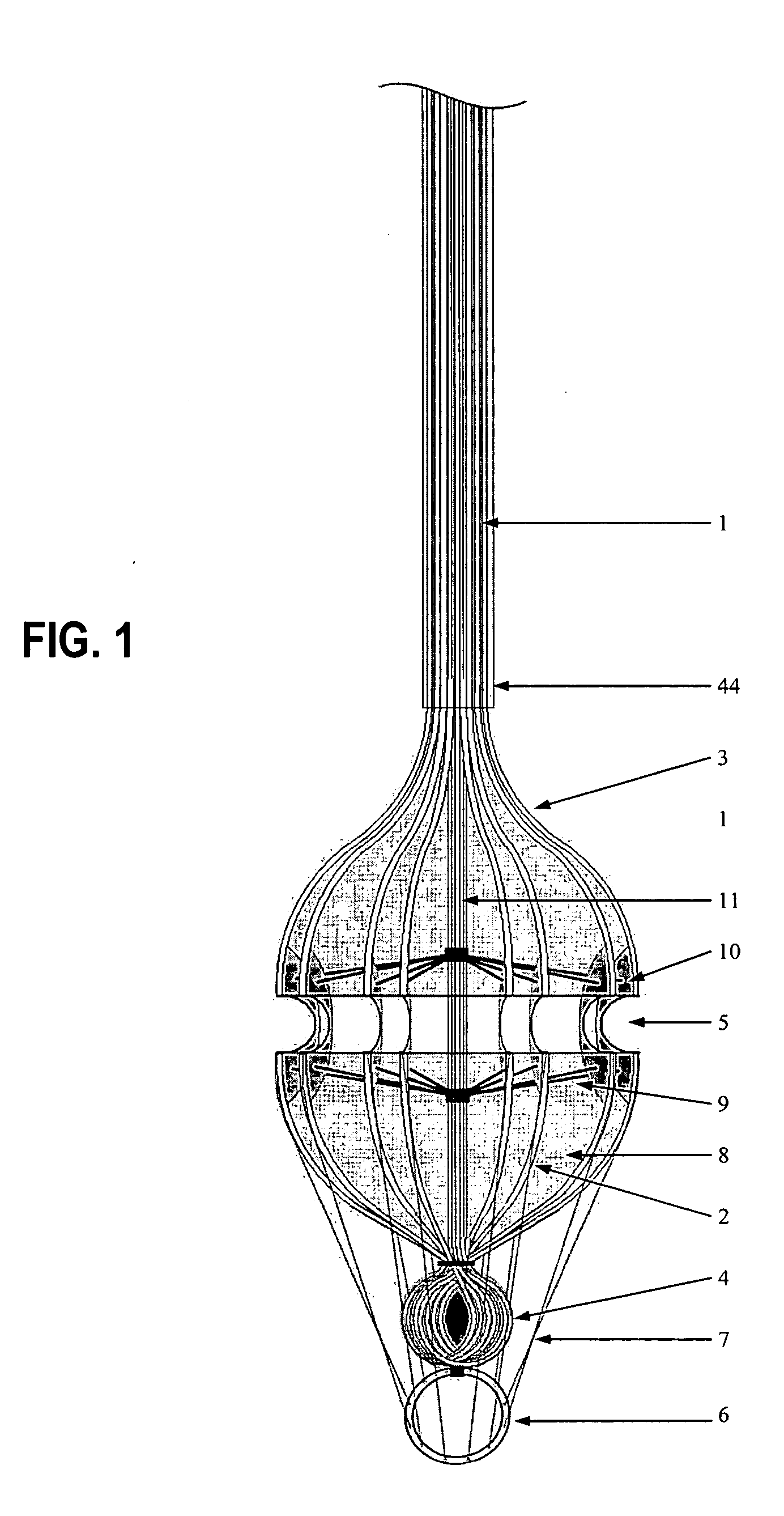
Intracardiac suture device
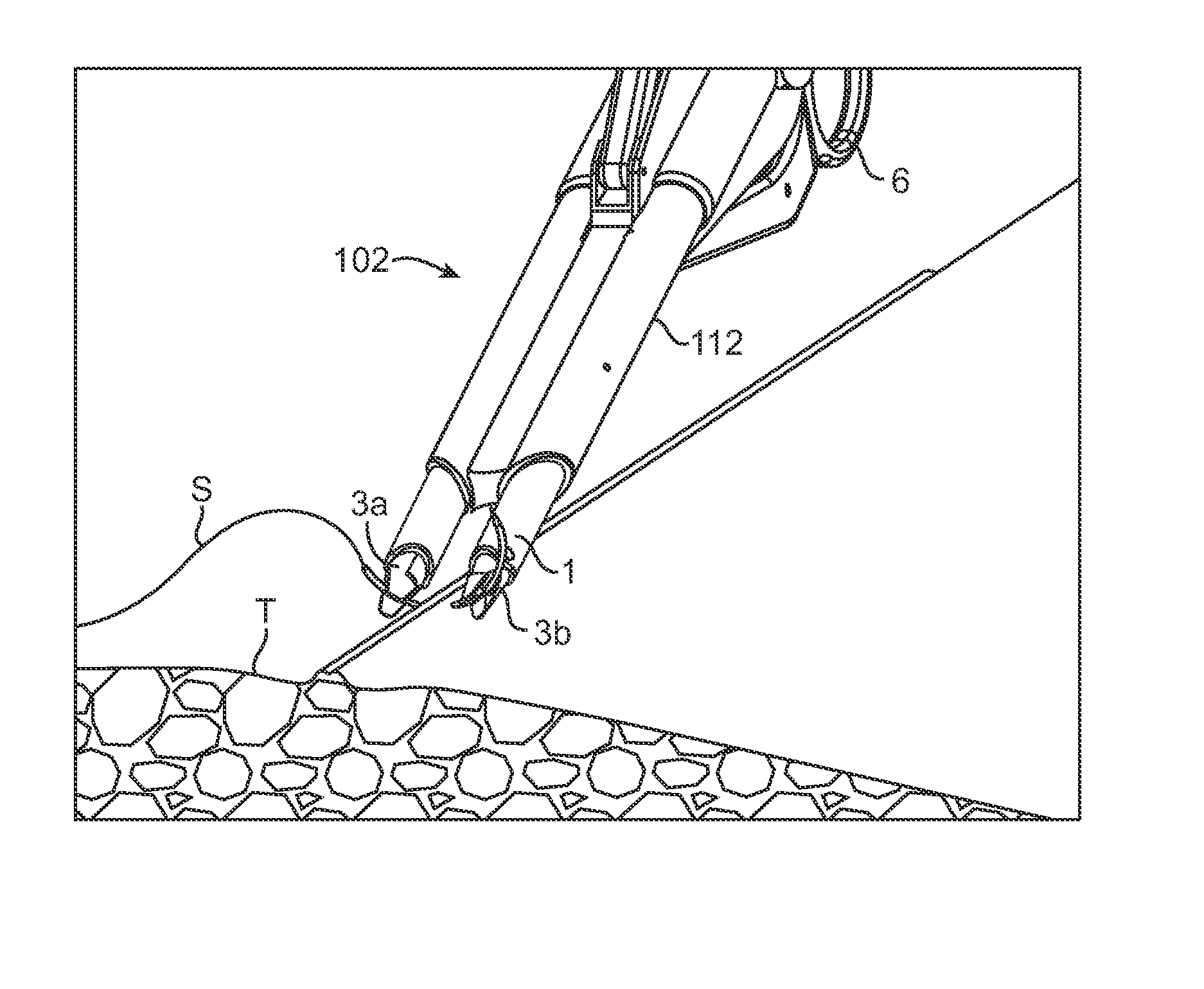
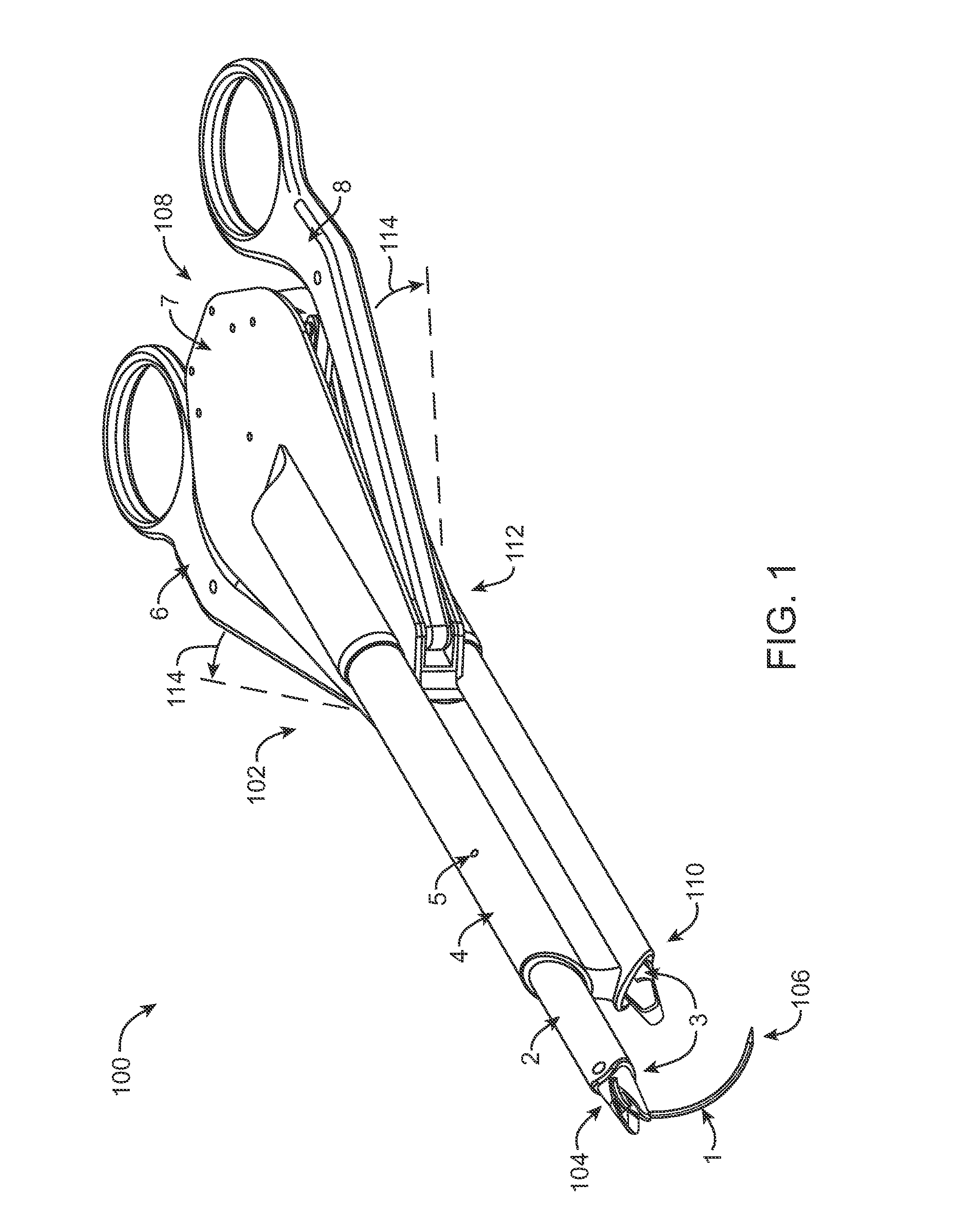
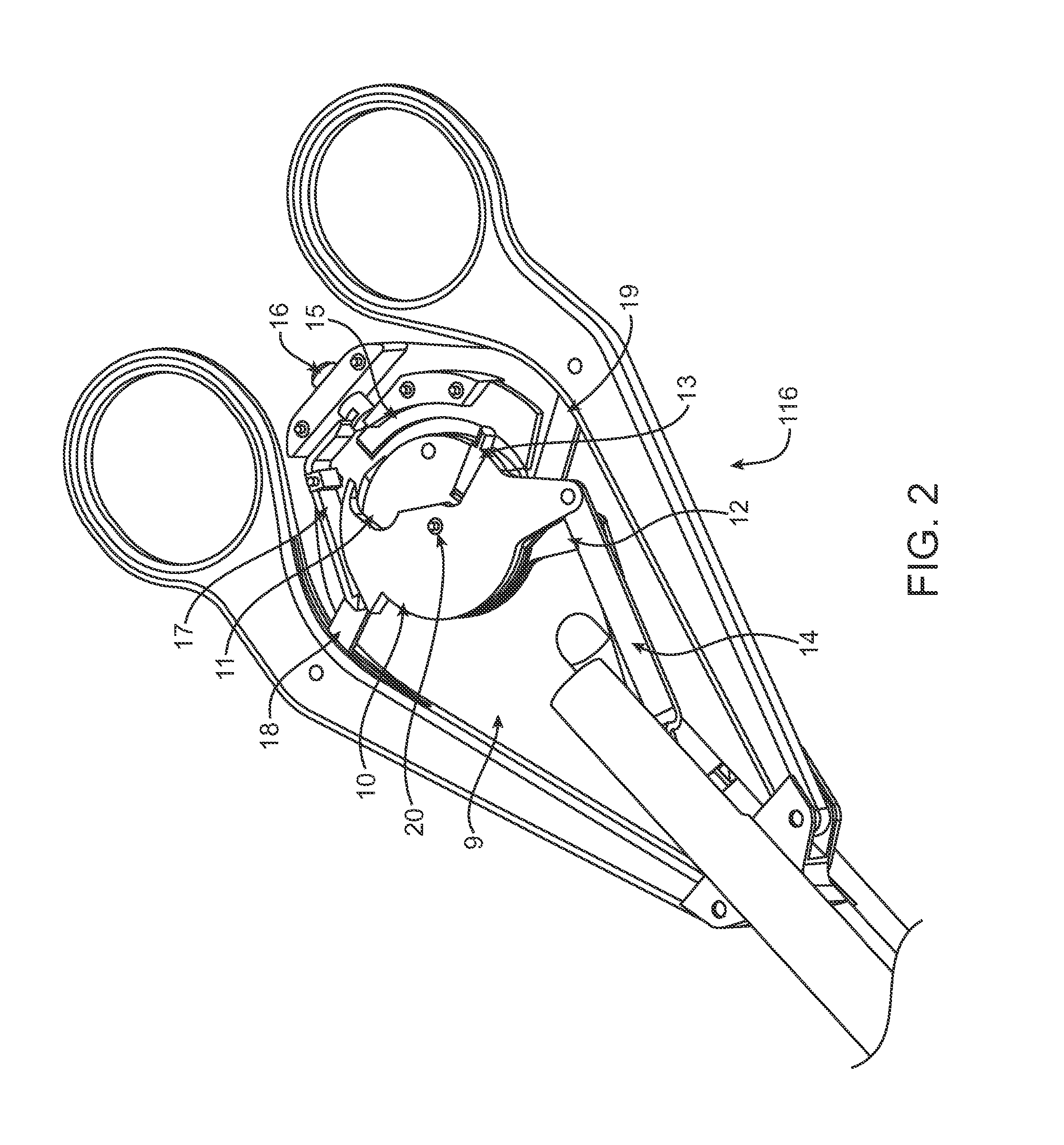
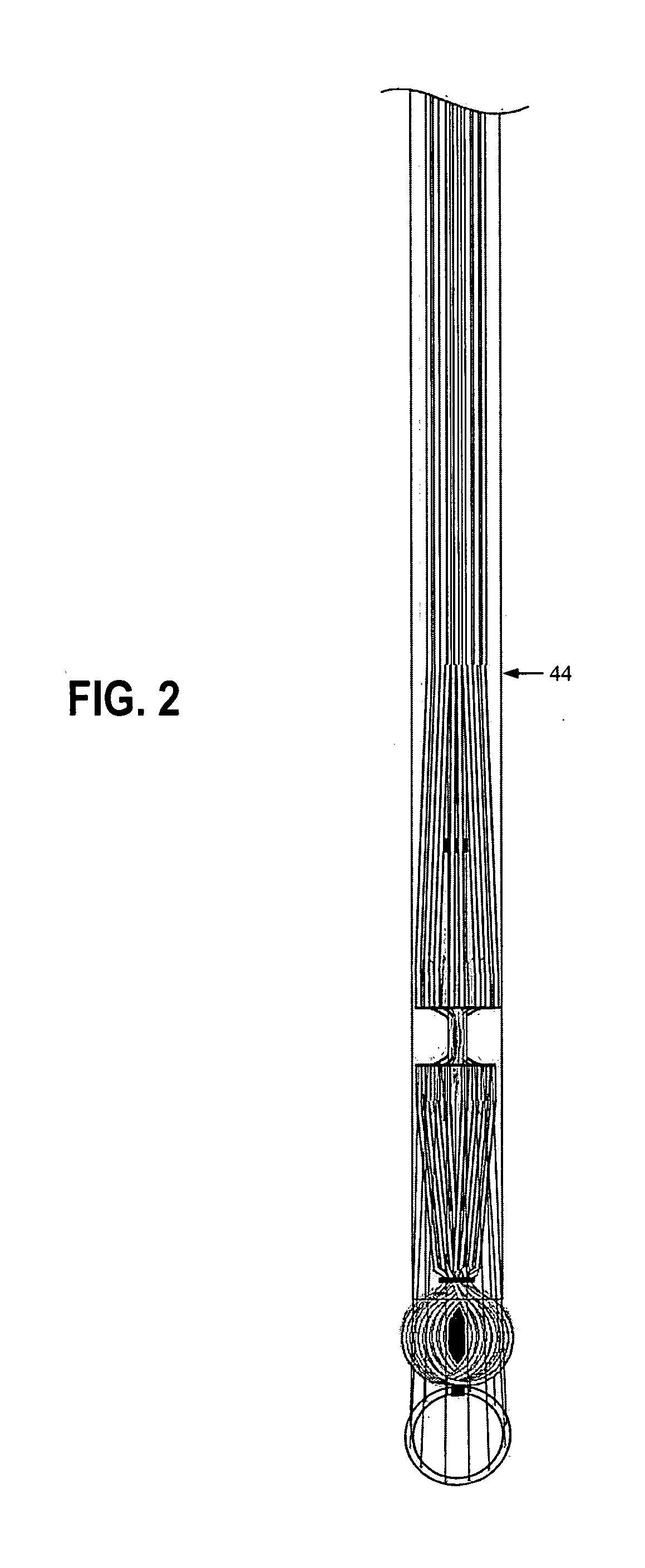
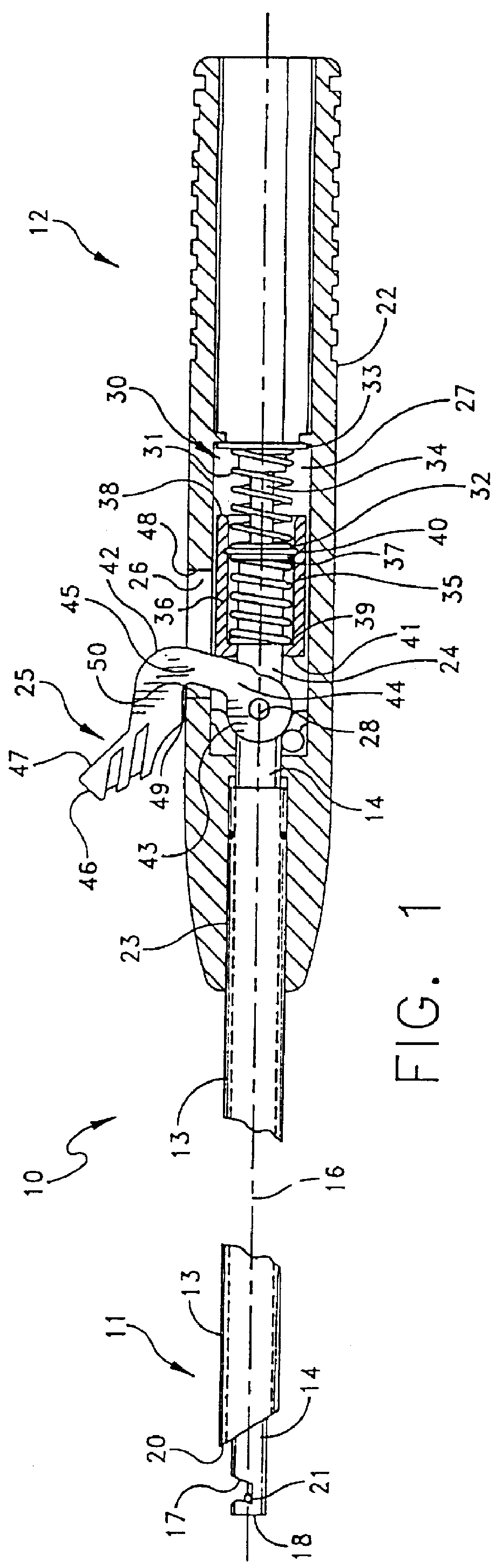
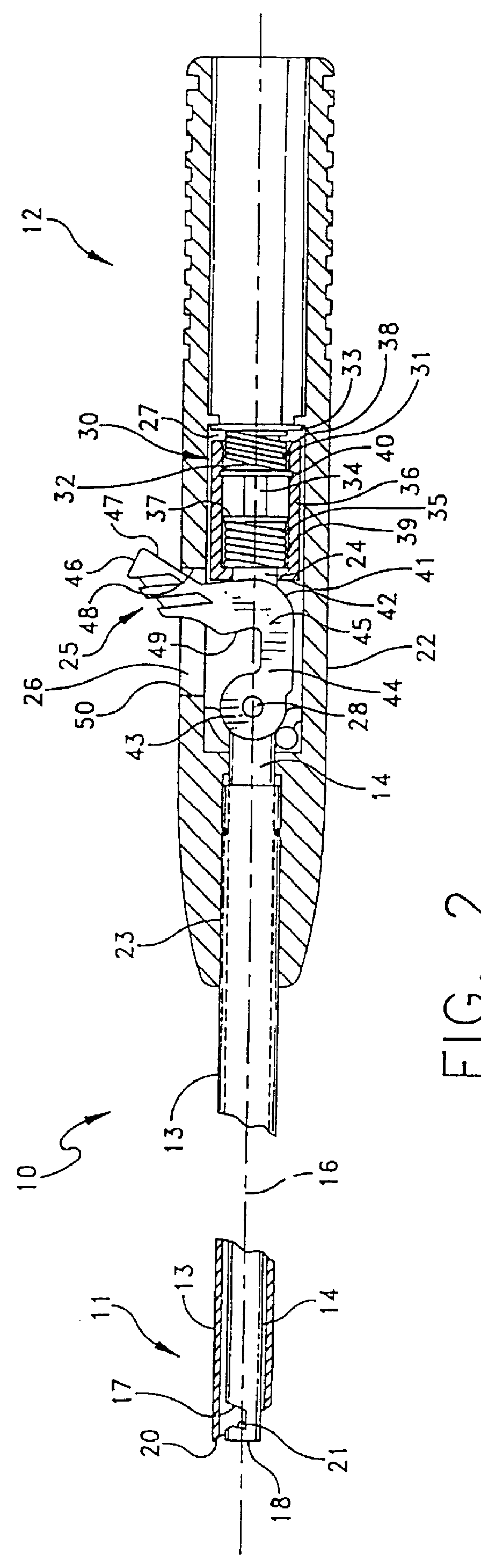
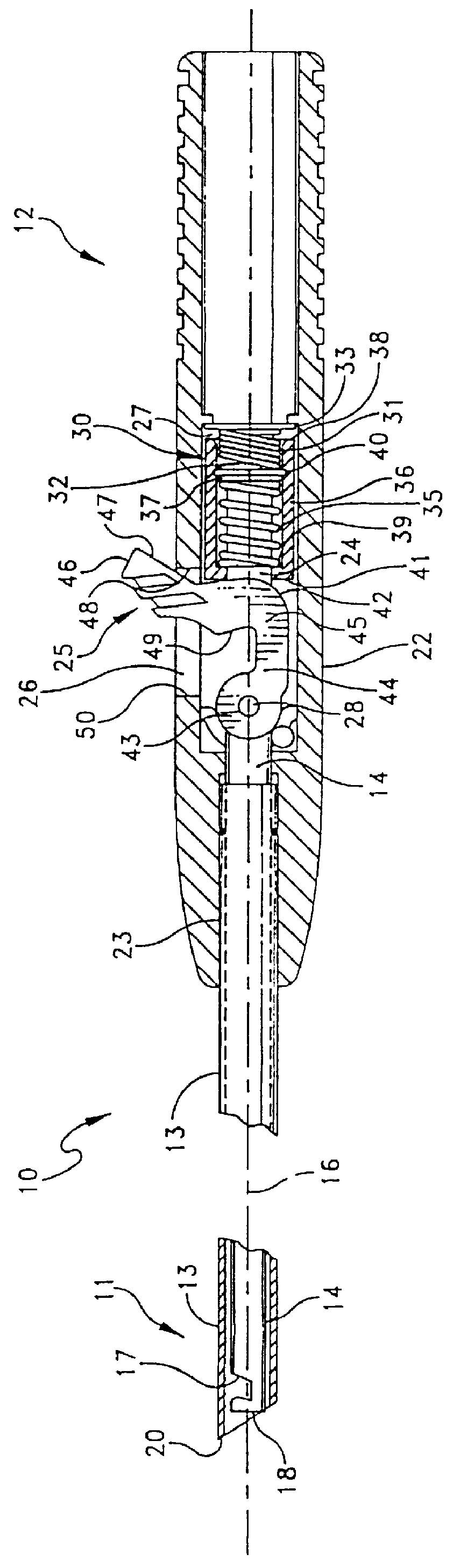
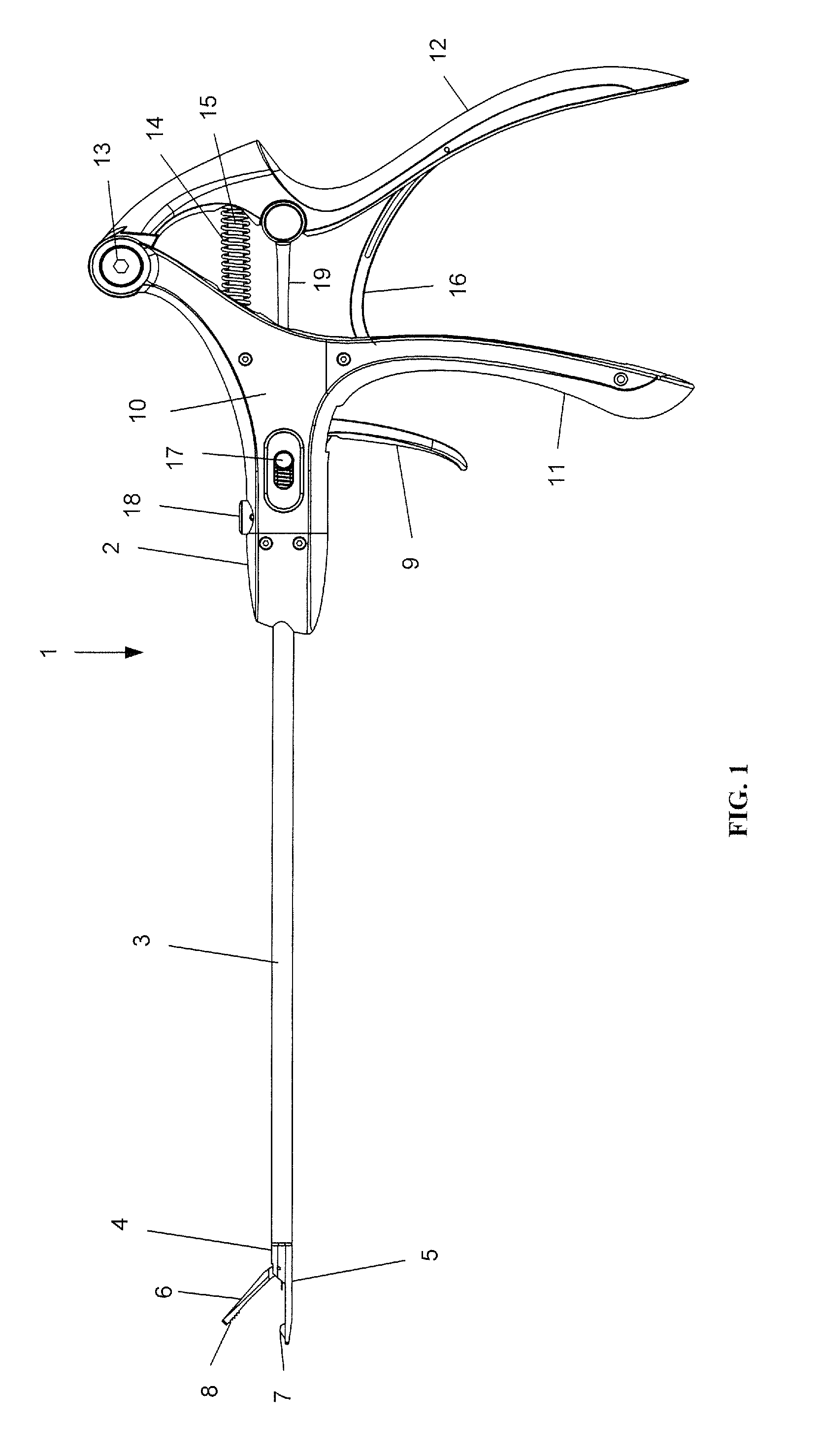
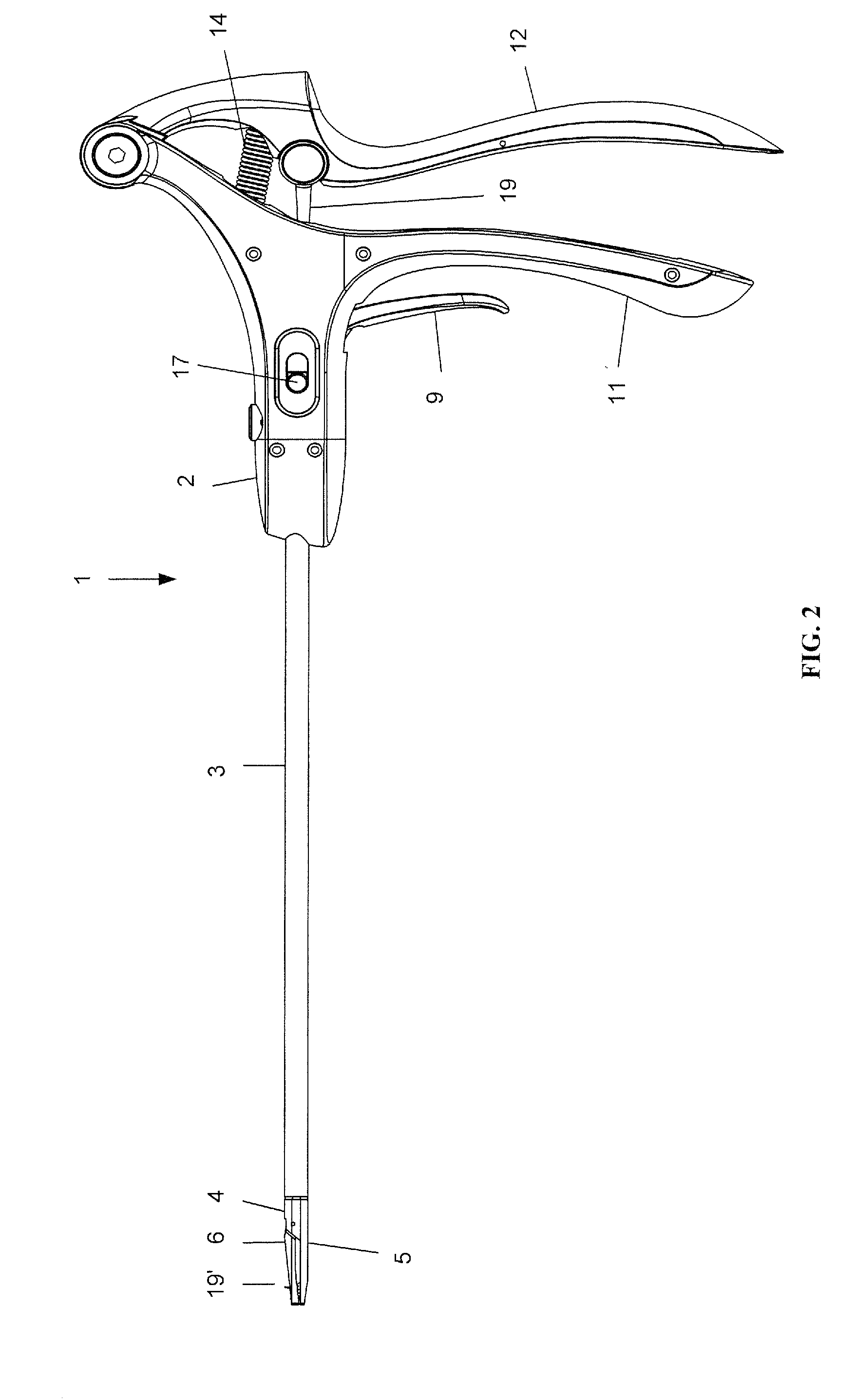
An intracardiac suture device comprises: a first shaft assembly 1 including a first shaft 11 and a first suture needle-holding means 4 provided at a distal end of the first shaft 11; a second shaft assembly 2 comprising a second shaft 21; a third shaft assembly 3 comprising a third shaft 31 and a handling portion 33; and a puncture assembly 5 provided at a proximal end thereof with a second suture needle-holding means 51. The second shaft 21 is protrusible by sliding-movement from the distal end of the first shaft 11 toward the first suture needle-holding means 4, and a suture needle 6 is transferable between the first suture needle-holding means 4 and the second suture needle-holding means 51 when the third shaft 31 is slid to the distal end of the second shaft 21 after sliding the second shaft 21 to a position where a suture site is held between the second shaft 21 and the first suture needle-holding means 4.
Owner:NIPRO CORP
Knotless bioabsorbable suture anchor system and method
InactiveUS7381213B2Secure attachmentEasy passSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSuturing needleSurgery
A knotless suture system for anchoring tissue to bone is provided. The system includes a suture anchor configured to radially expand into bone. The suture anchor has a proximal end and a distal end with a bore formed therein. The system further includes a first loop of suture thread attached to the distal end of the suture anchor, a suture needle, and a second loop of suture thread attached to the needle and interlocked with the first loop of suture thread. The system also includes an expander pin that is configured and sized for insertion into the bore of the suture anchor, causing the anchor to radially expand from a first outer diameter to a second outer diameter. A method is also provided by which a detached tissue may be securely attached to bone in an anatomically correct position without the need to tie a knot.
Owner:DEPUY MITEK INC
Vascular access port with integral attachment mechanism
An implantable port with an integral attachment mechanism. The implantable port includes one or more suture needles enclosed within a port body, the suture needle(s) coupled to a movable member such that movement of the movable member results in movement of the suture needle(s) out of the port body and into the tissue of a body into which it is implanted. The movable member can be a cam or tensioning member that rotates about a central port axis. The movable member can be coupled to a gear to permit movement of the movable member following implantation of the port within a subcutaneous pocket.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Blunt intercostal suture needle
InactiveUS20060259048A1Wire cutting can be preventedSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSuturing needleBlunt needle
When closing the sternum in cardiothoracic surgery, elderly people with a fragile sternum can experience bleeding from the suture sites because of loose knots. The knots are loose because of the danger of cutting into the sternum from the tension caused by the suture wire. In extreme cases, the sternum can be fractured. If the closure is attempted intercostally, there are internal thoracic arteries that run longitudinally underneath the sternum and they may be hurt if a sharp needle is used. Intercostal fixation on its own is inadequate, and additional wires that directly insert into the manubrium are required. Of the sternal closure wires currently available, there is discordance in the numbers provided and actually used, resulting in leftovers that need unnecessary sterilization and reuse. To solve the above problems, an intercostal specific blunt needle has been devised, and packaged together with a sharp needle that will directly insert into the sternum. The set may contain one of each needle or a required combination of both, and come in a pre-sterilized pack. The needle is blunt at the cutting edge, and has a hook, or a side hole. The opposite end has a handle attached. The needle is configured so the wire can be hooked on, or threaded through the hook and hole respectively, and the operative procedure involves lifting up the wires.
Owner:KOSEKI TOMOAKI
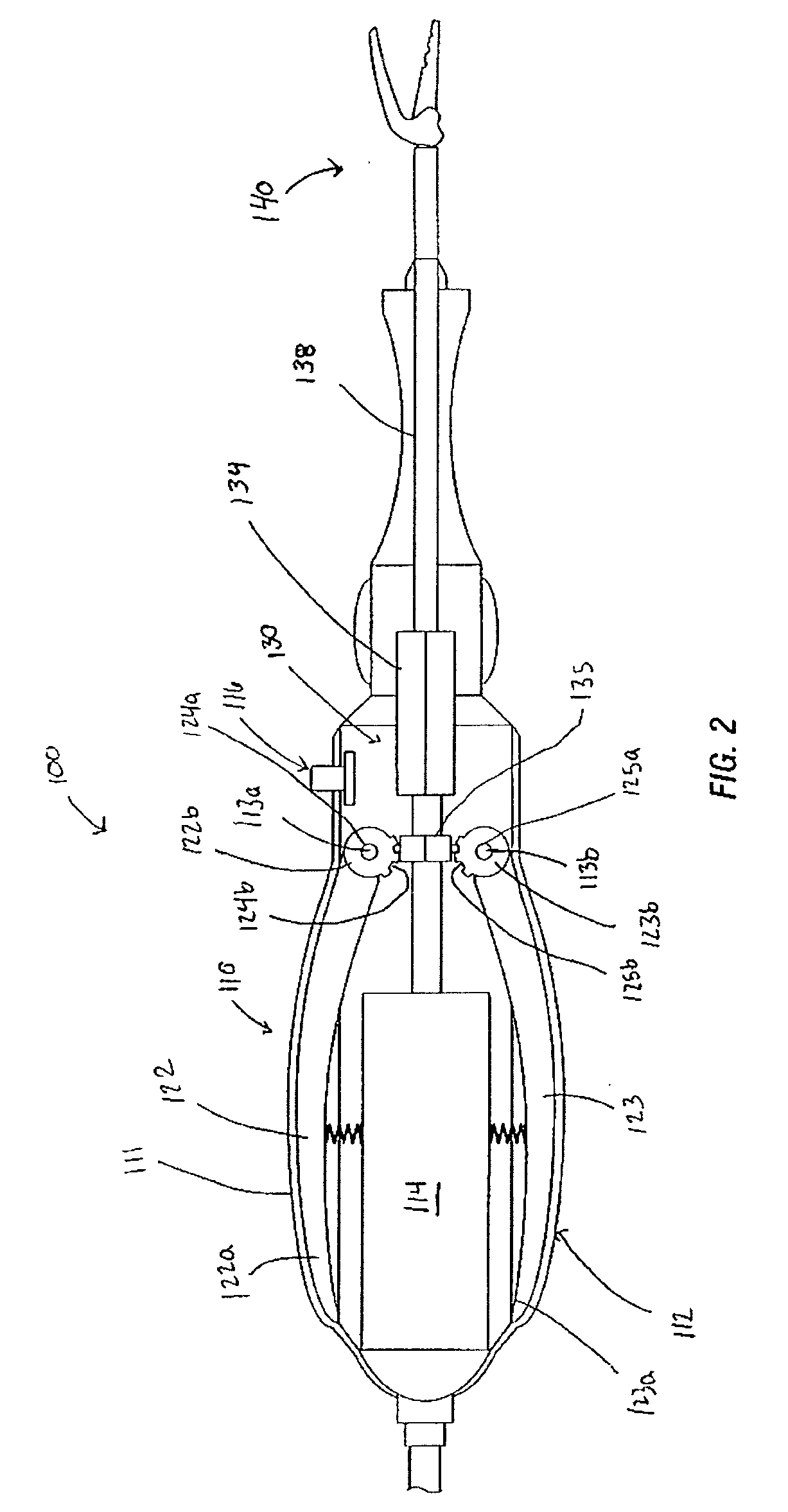
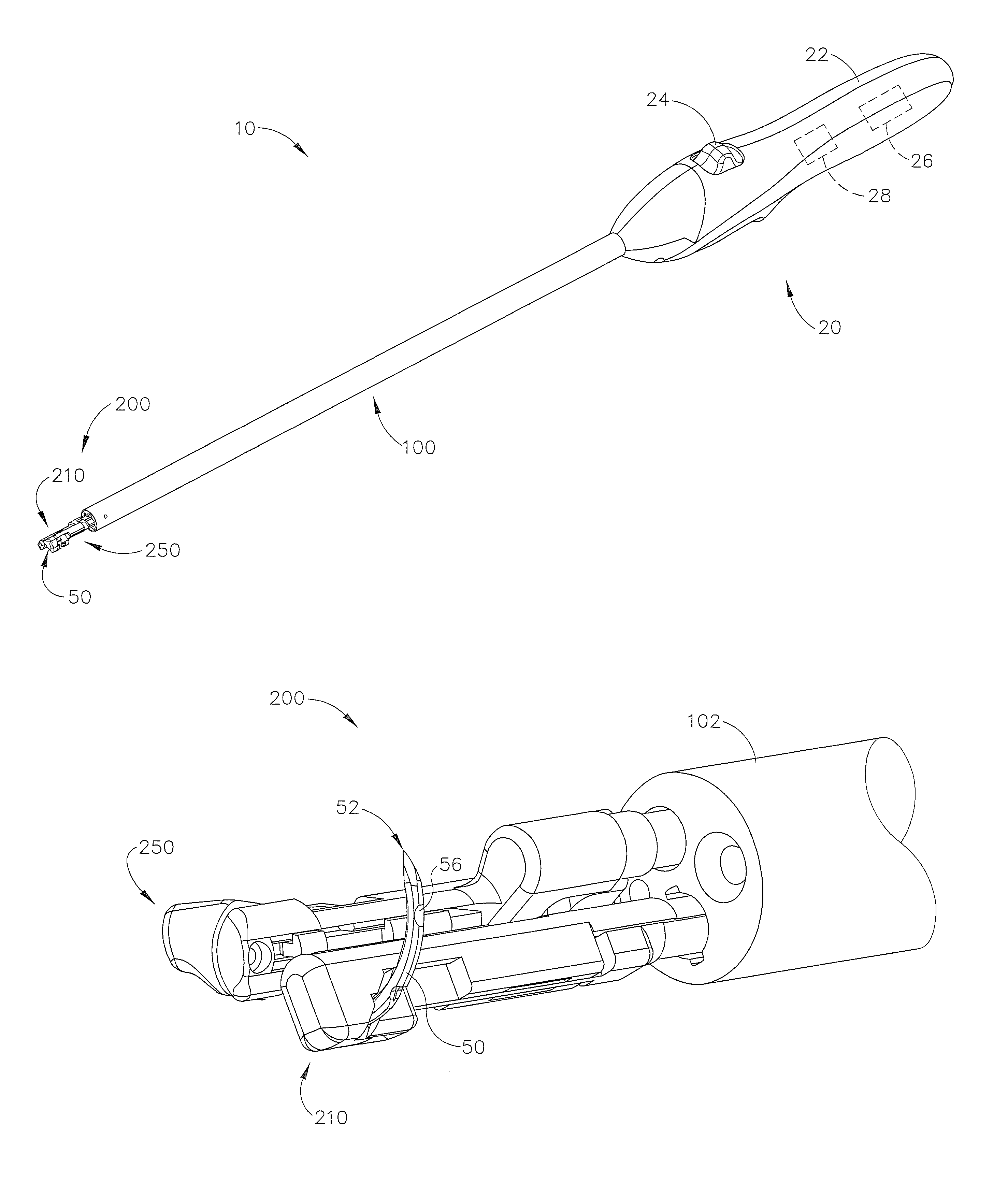
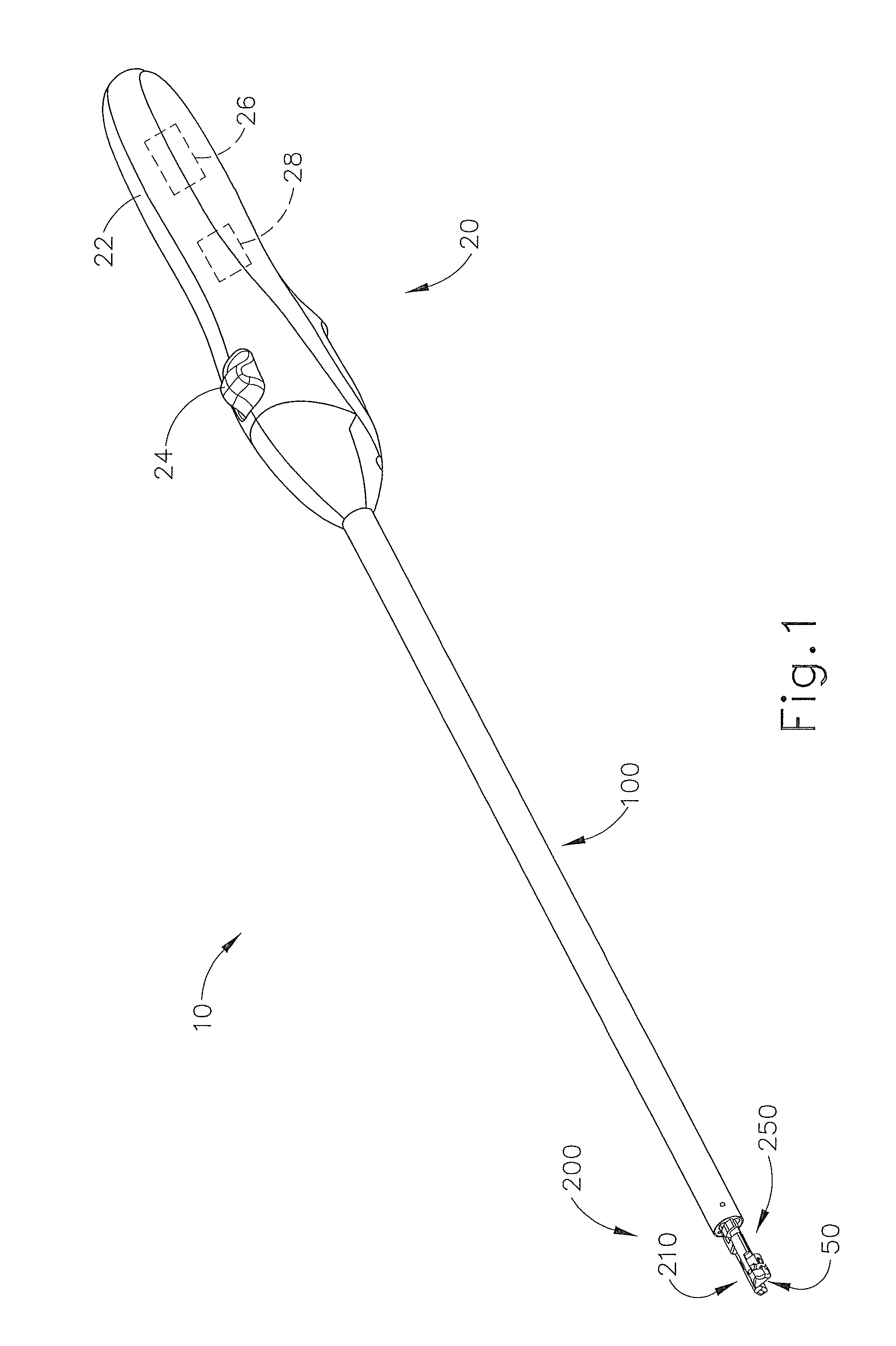
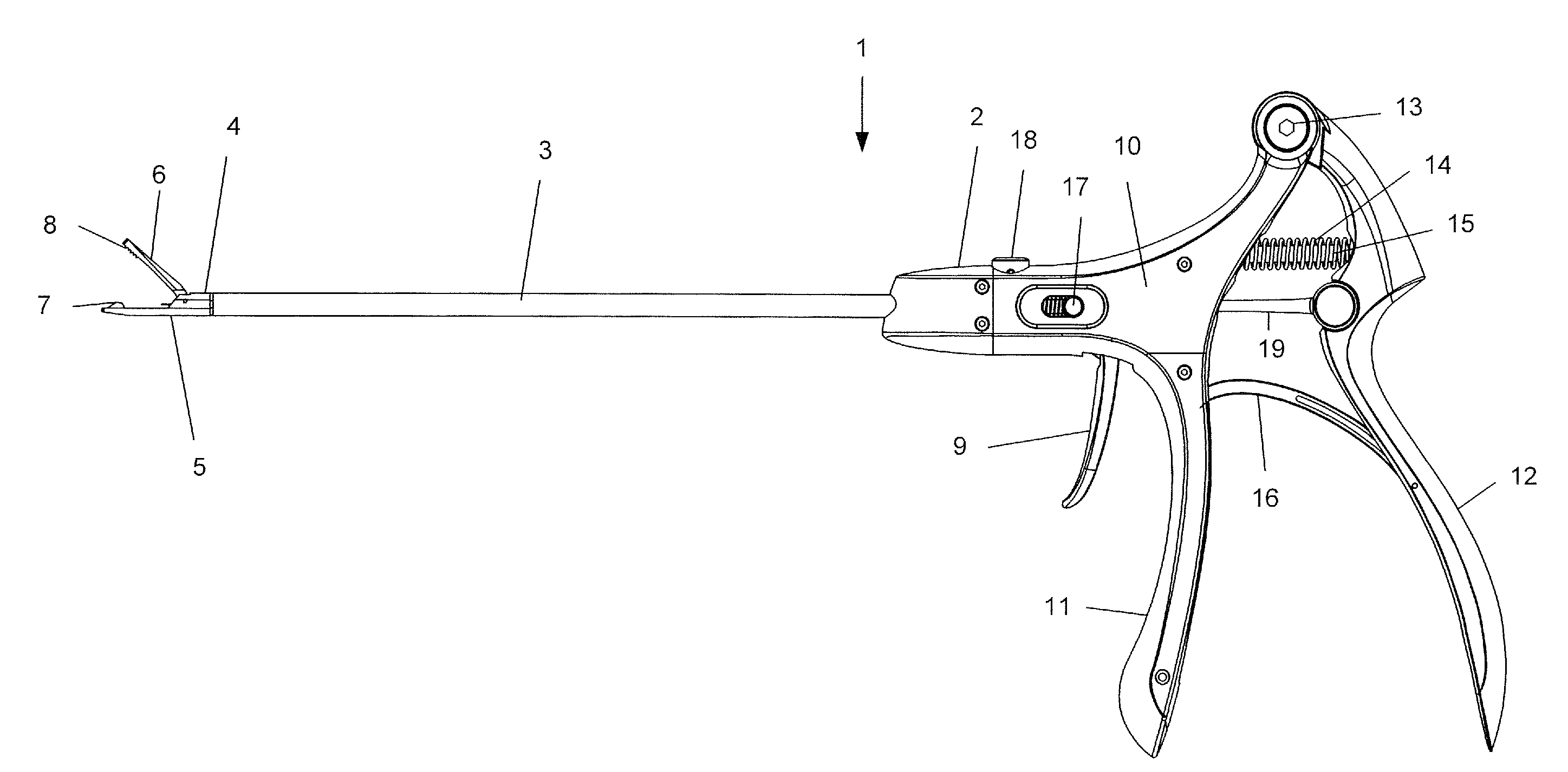
Suturing Device, System, and Method
ActiveUS20070060931A1Improve ease of useIncrease speedSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSuturing needleDistal portion
Improved medical suturing devices, systems, and methods may hold a suture needle at a fixed location relative to a handle of the device, allowing the surgeon to grasp and manipulate the handle of the suturing device to insert the needle through tissues in a manner analogous to use of a standard needle gripper. Cycling the handle from a closed position to an open position and back to the closed position may alternate the device between gripping the needle with a first clamp (for example, along a proximal portion of the needle) to gripping the needle with a second clamp (for example, along a distal portion of the needle) and optionally back to gripping with the first clamp, with the needle often staying at a substantially fixed location relative to the suturing device body. Related single-clamp needle grasping devices can be bent plastically by a surgeon, and / or have bodies that are grasped by a hand while a portion of the hand actuates a handle.
Owner:BOSS INSTR
Ultrasonic needle driver
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
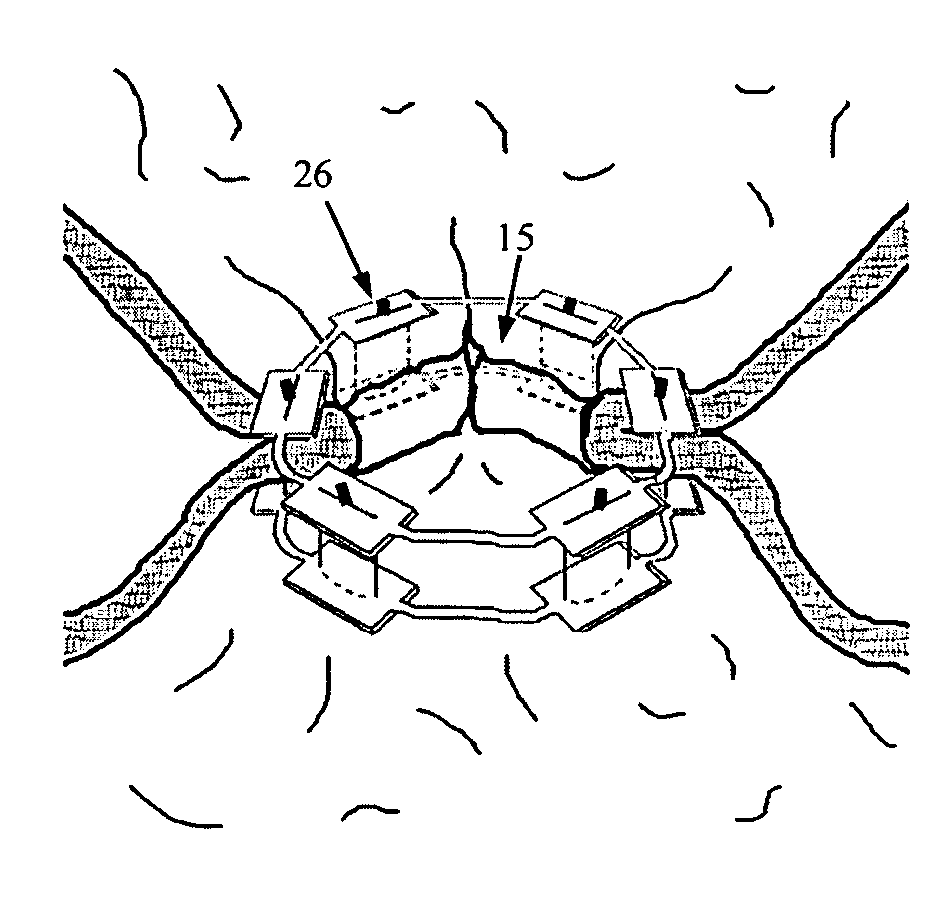
Endoluminal gastric ring and method
A ring or rings adapted for endoluminal placement within the stomach, other hollow organ or vessel, and a method for deploying the rings is described. The rings create a small pouch with a reinforced stoma in the stomach for the treatment and control of obesity. An endoluminal suturing device for deploying a circumferential line of interrupted mattress suture bites is inserted into the patient's stomach via the patient's mouth. The distal gastric ring is preloaded on the distal end of the suturing device and is incorporated with suture loops from the double-armed sutures contained within the device. The suturing device can have an expandable area at its distal end that can expand its diameter to between approximately 10 mm and 150 mm. The circumference of this expanded area has a suction opening that is used to draw in tissue when a vacuum is applied to the device. Flexible cannulas containing long flexible suture needles are positioned radially around the circumference of the suction opening. The long needles are are adapted to be advanced through the drawn in tissue incorporating their attached suture material. The expandable area of the device is collapsed, and the device is withdrawn from the patient. With the distal ring anchoring the sutures beneath the incorporated tissue folds, a column of sutures exits the device's suction port as the device is withdrawn. A second, proximal ring is then incorporated with the sutures and may then be endoscopically lowered into the patient's stomach and positioned proximal to the distal ring. The sutures are endoscopically secured and cut, thereby fixing the two rings together with tissue incorporated between them.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Vascular access port with integral attachment mechanism
An implantable port with an integral attachment mechanism. The implantable port includes one or more suture needles enclosed within a port body, the suture needle(s) coupled to a movable member such that movement of the movable member results in movement of the suture needle(s) out of the port body and into the tissue of a body into which it is implanted. The movable member can be a cam or tensioning member that rotates about a central port axis. The movable member can be coupled to a gear to permit movement of the movable member following implantation of the port within a subcutaneous pocket.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Needle grasping apparatus
Apparatus for needle grasping and performing a second modality comprising a sheath axially extending between distal and proximal ends thereof. The device includes an inner hollow tube with a slot formed therein for receiving a needle at the distal end. Retraction and extension of the inner tubular member relative to the sheath enable the grasping and releasing of a suture needle received in the slot. A handle is provided at the proximal end of the apparatus for selectively extending and retracting the inner tube relative to the sheath and for retaining the inner tube in its extended and retracted positions. A second switch can be provided in the handle to actuate a catheter slidably inserted through the inner tube to perform a second therapeutic modality. The catheter preferably includes a distal bight that forms a loop when extended from the distal end of the sheath for facilitating intracorporeal knot tying thereat. The catheter includes a lumen therethrough for receiving suture thread for use at the distal end of the sheath.
Owner:BOSTON SCI CORP
Suturing device, system and method
ActiveUS7588583B2Easy to controlIncrease speedSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSuturing needleDistal portion
Improved medical suturing devices, systems, and methods may hold a suture needle at a fixed location relative to a handle of the device, allowing the surgeon to grasp and manipulate the handle of the suturing device to insert the needle through tissues in a manner analogous to use of a standard needle gripper. Cycling the handle from a closed position to an open position and back to the closed position may alternate the device between gripping the needle with a first clamp (for example, along a proximal portion of the needle) to gripping the needle with a second clamp (for example, along a distal portion of the needle) and optionally back to gripping with the first clamp, with the needle often staying at a substantially fixed location relative to the suturing device body.
Owner:BOSS INSTR
Apparatus and method for minimally invasive suturing
The invention includes a needle loader that may be used with a suturing device. The needle loader includes a generally planar needle supporting surface, a hub configured and adapted for receiving a generally toroidally shaped suturing needle around the hub, and means for retaining a suturing needle in a fixed toroidal rotational position with respect to the hub about a center axis of needle rotation. Generally, a needle mounted around the hub is selectively disposable on and removable from the hub. In accordance with a further aspect, the loader may further include an opening for retaining suture material attached to a suturing needle. The opening may include a groove defined through the needle supporting surface. The needle loader may further include a guard for preventing access to the point of a suturing needle to protect the needle and / or to prevent accidental needle sticks.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
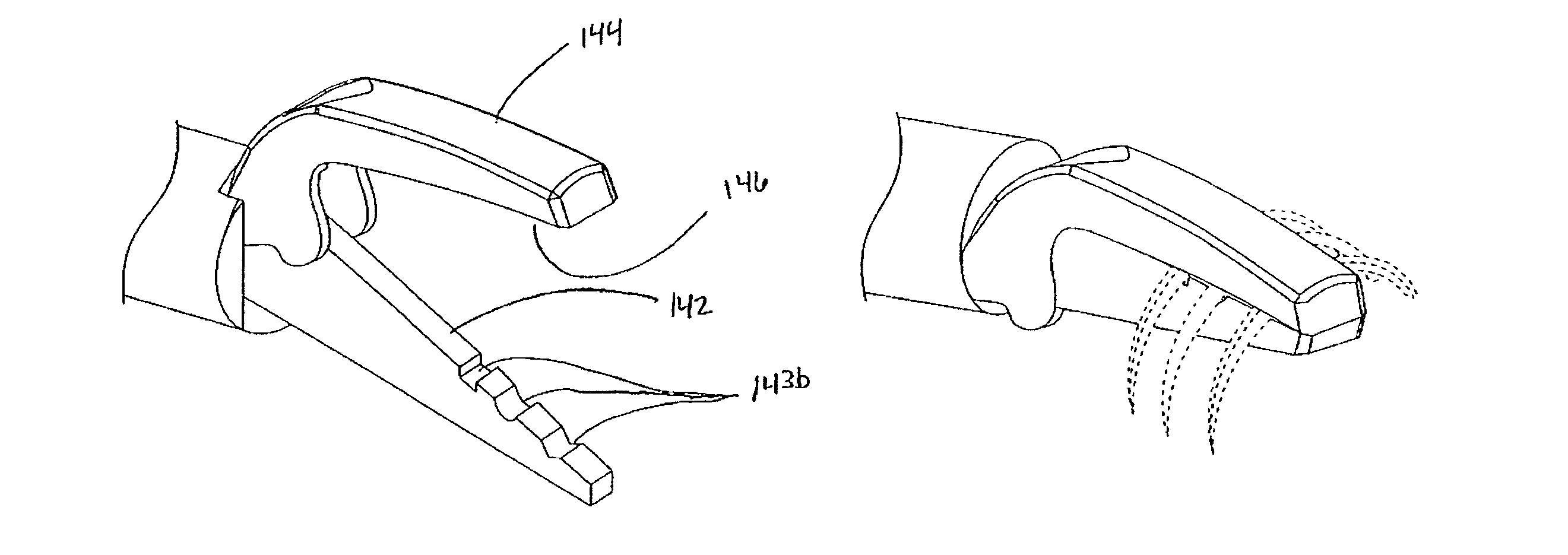
Fluid emitting suture needle
The invention provides a multifunctional suture needle that may be used to draw a suture through tissue surrounding a wound while simultaneously delivering a bioactive fluid through the needle tip. The suture needle possesses an internal cavity capable of containing a fluid, and a fine aperture adjacent to the point of the needle through which the fluid may egress. The fluid may be driven from the needle through the needle tip with a compressed gas that is sealed within the cavity adjacent to the fluid. Alternatively a fluid conducting suture may be employed to deliver fluid through the internal passage of the suture needle and out the aperture adjacent to the tip of the needle. The rate at which the fluid is emitted from the suture needle may be controlled by carefully selecting the fluid viscosity, design of the needle or suture passages, and pressure applied to the fluid.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Transfer tray for surgical sharps
The present invention is a dual function transfer tray that can be used for either a scalpel or a suturing needle holder with suturing needle. A scalpel slot is formed in the bottom of a relatively deep set of sloped walls. A suture needle cavity is formed above the first slot. However, at a mid-section of the scalpel slot and the half-cylindrical suture needle cavity are opposing and deep V-shaped cutaway sections in the sidewalls with a flat floor section between them. A user need never have to focus their attention for more than a split second to discern the location of the mid-section of the transfer tray. The user's thumb and forefinger are aimed at the V-shaped sidewall openings to grasp a midsection of a supported surgical sharps. The scalpel slot and half-cylindrical suture needle cavity are set relatively deep with respect to top edges of the transfer tray and the to form an open tray to prevent a user from being inadvertently injured by a scalpel blade or a suture needle. In addition, the scalpel cannot be placed in the scalpel slot unless it rests on one of its longitudinal edges, preferably the same one as that of its blade edge. Thus, a user grasping the mid-section of the scalpel handle in the cutaway and flat floor section picks up the scalpel in a ready-to-use position.
Owner:HOFTMAN MIKE
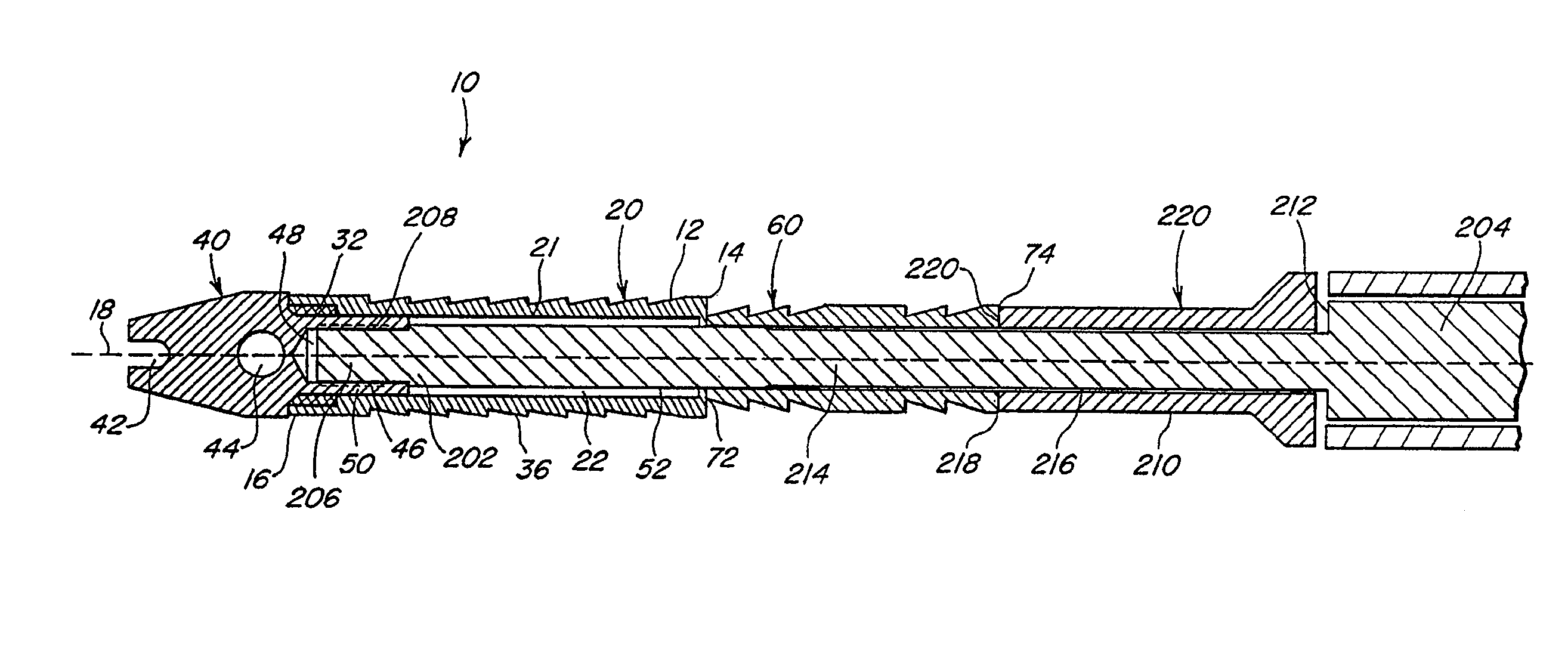
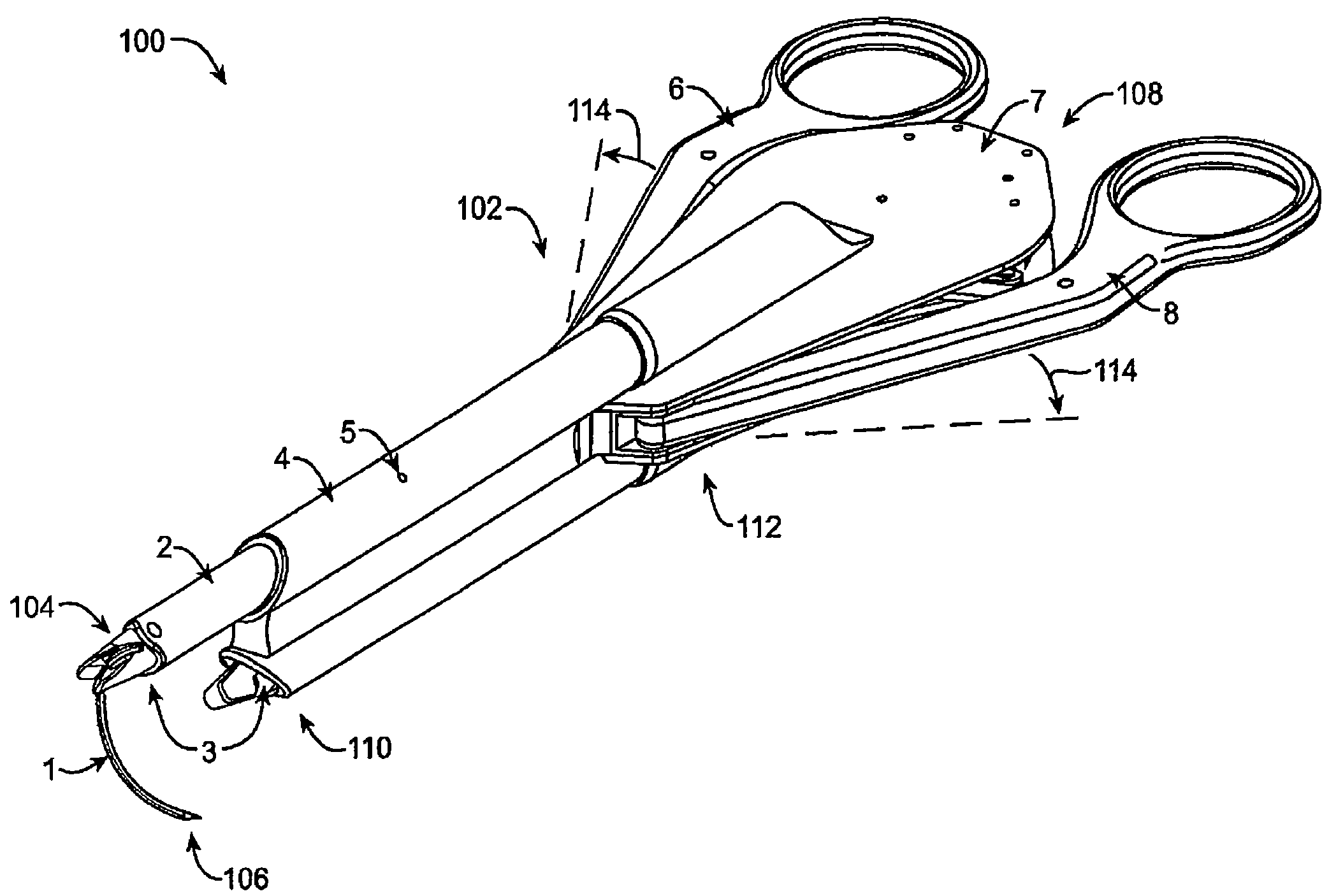
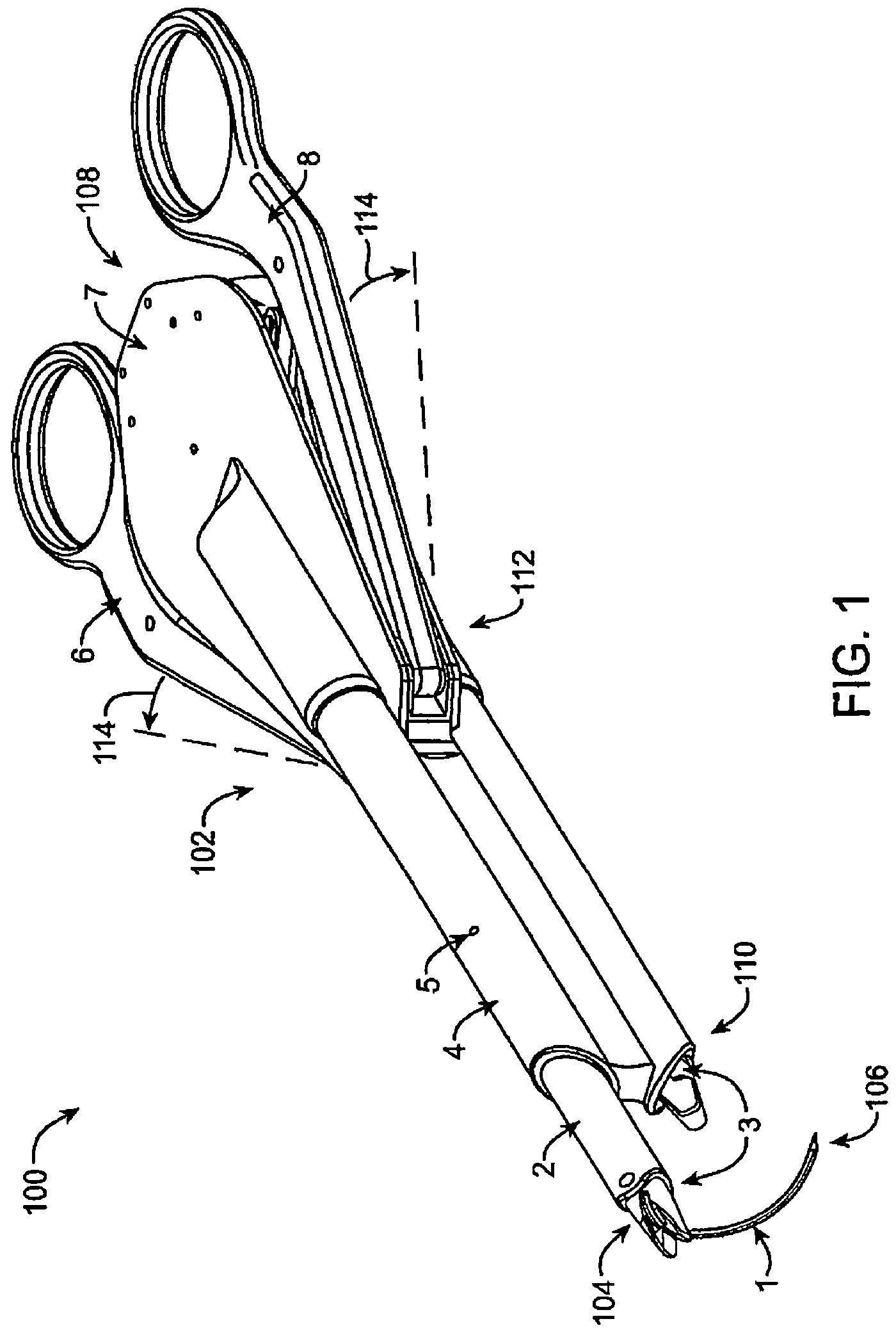
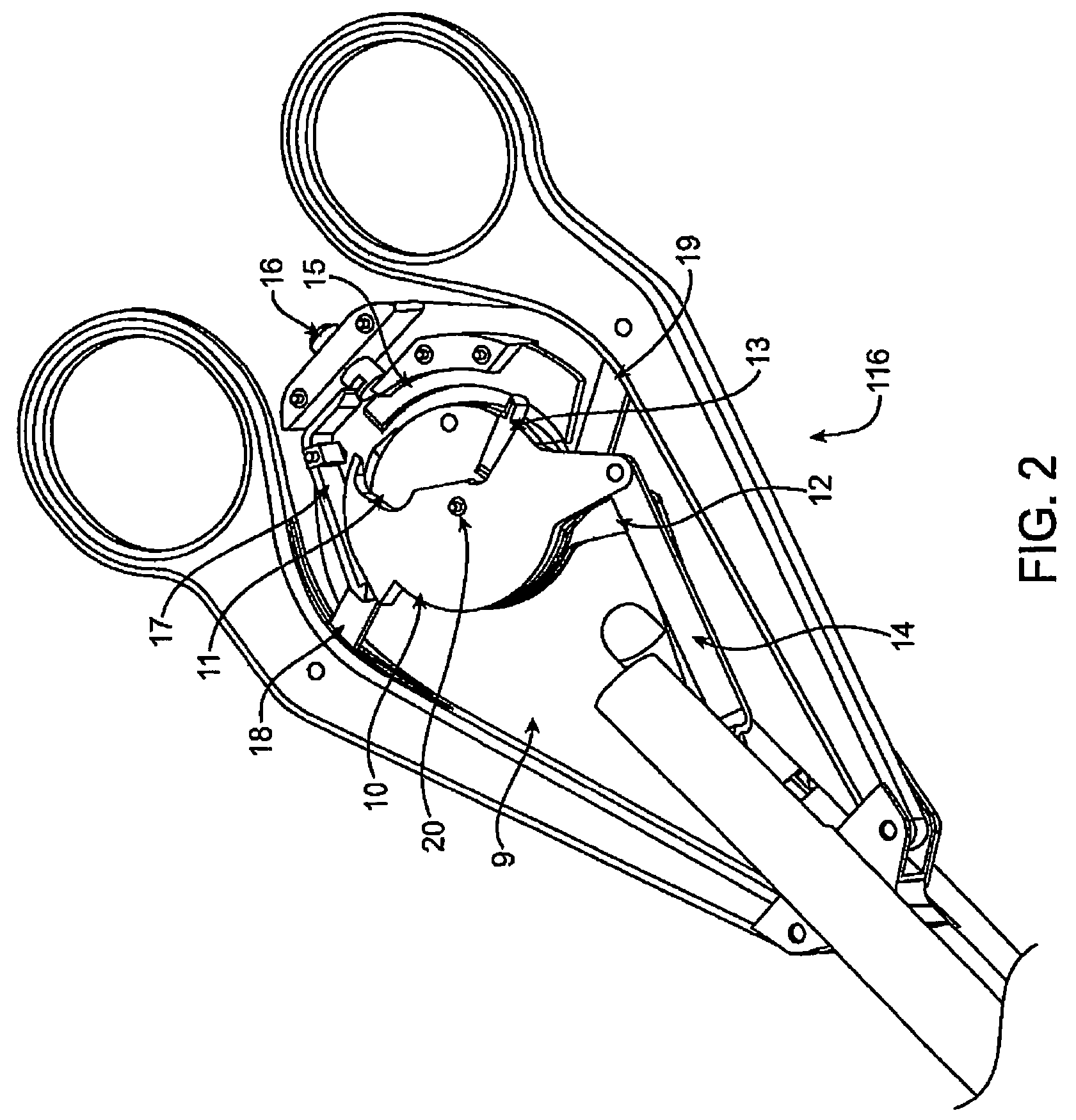
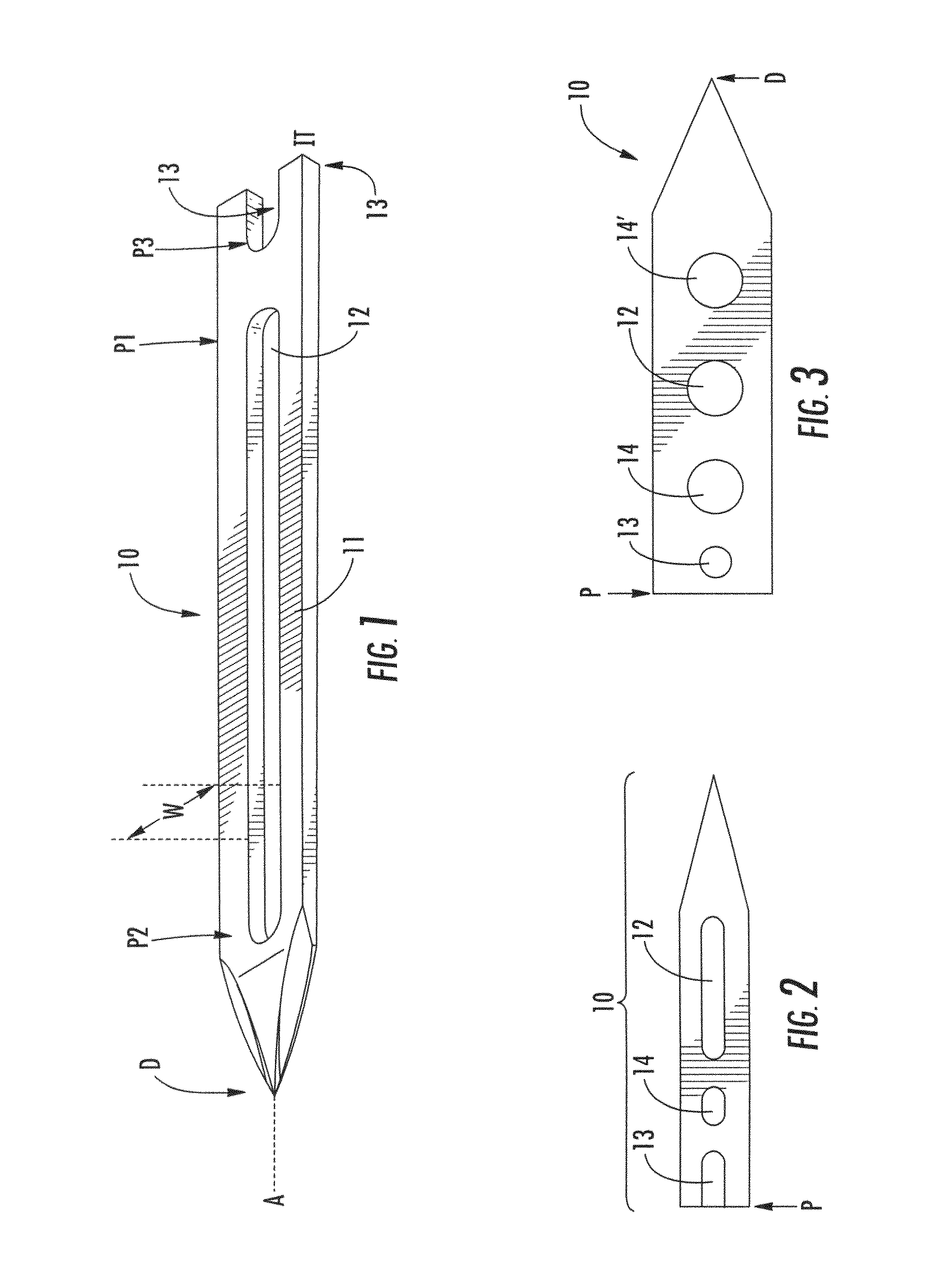
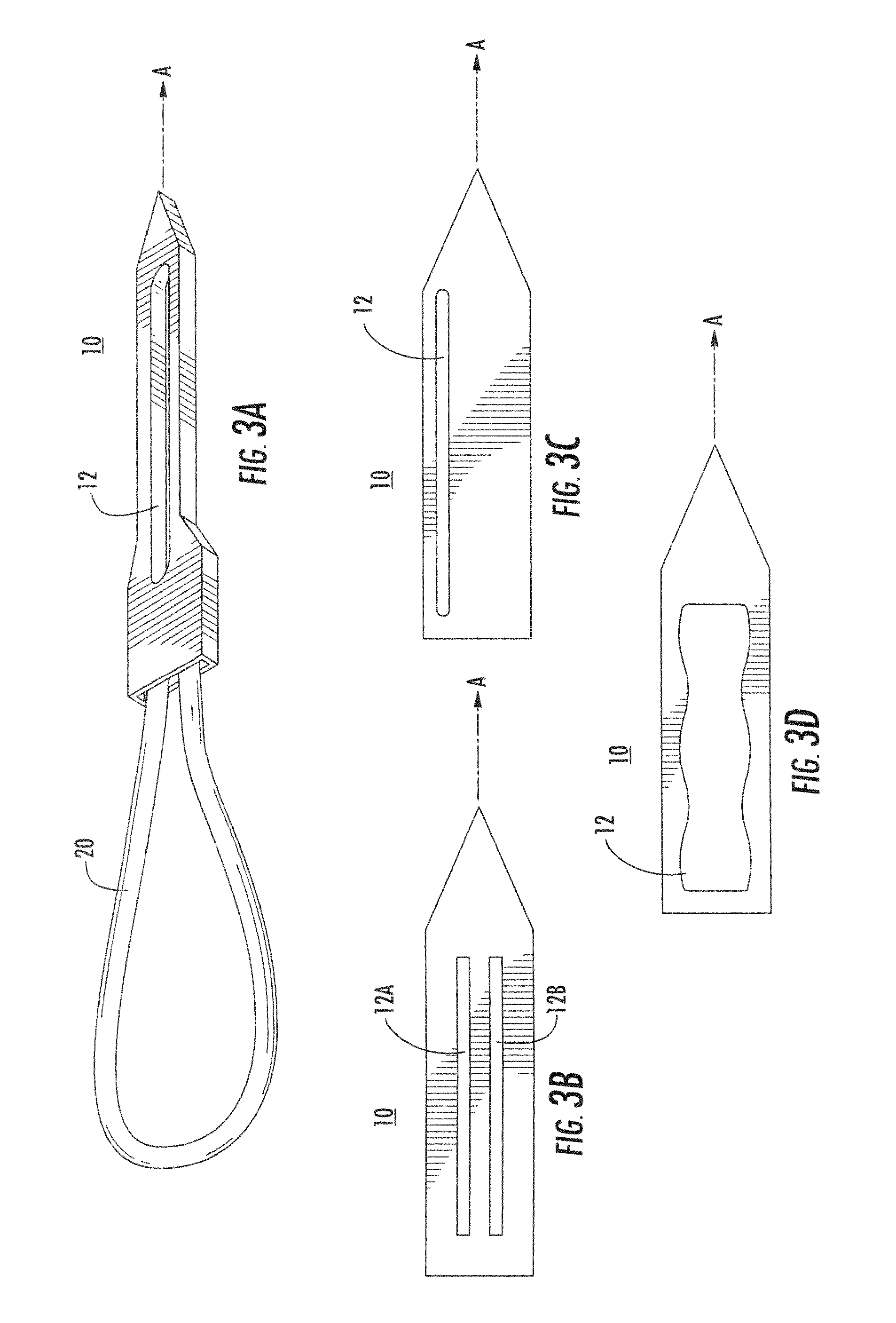
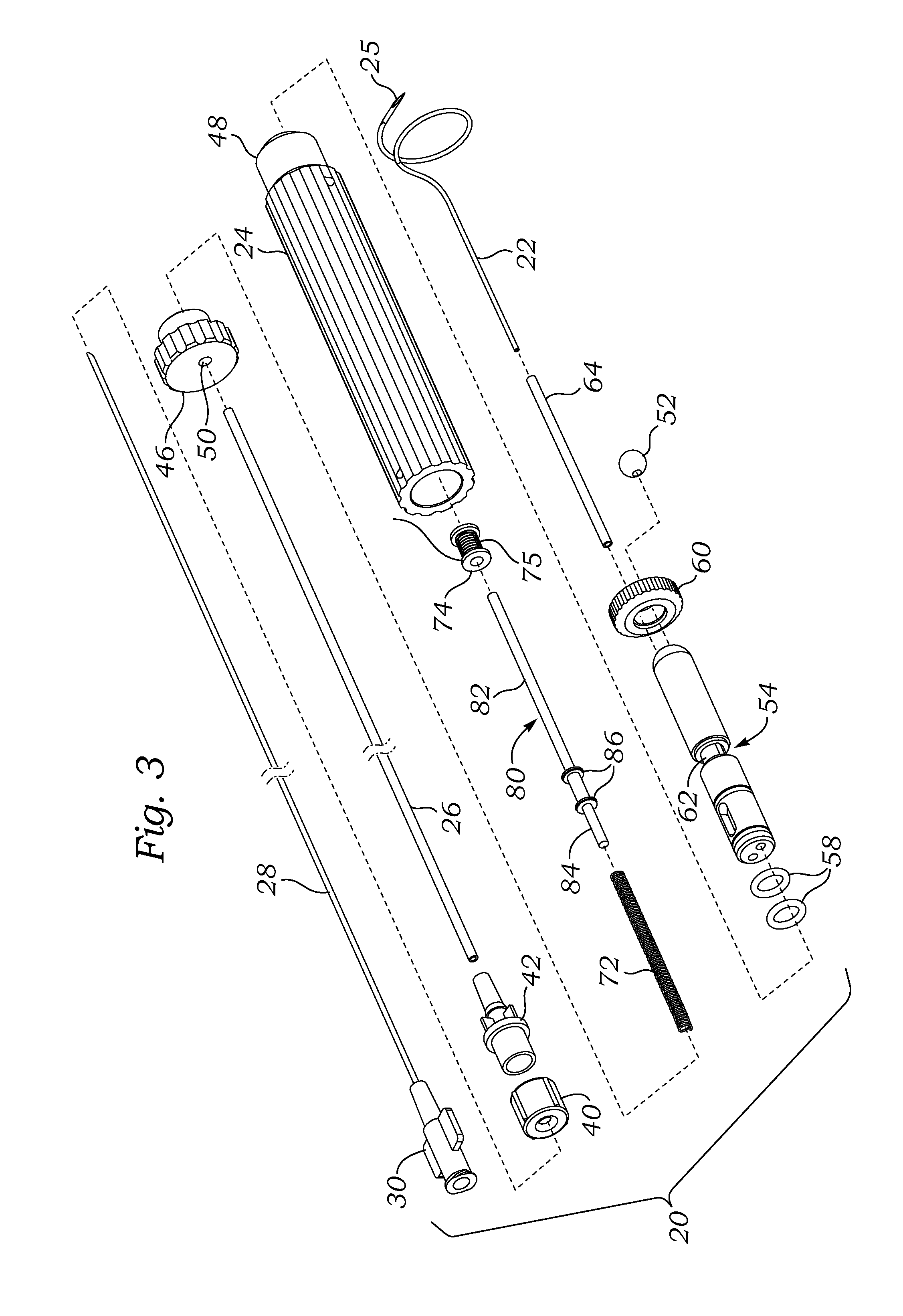
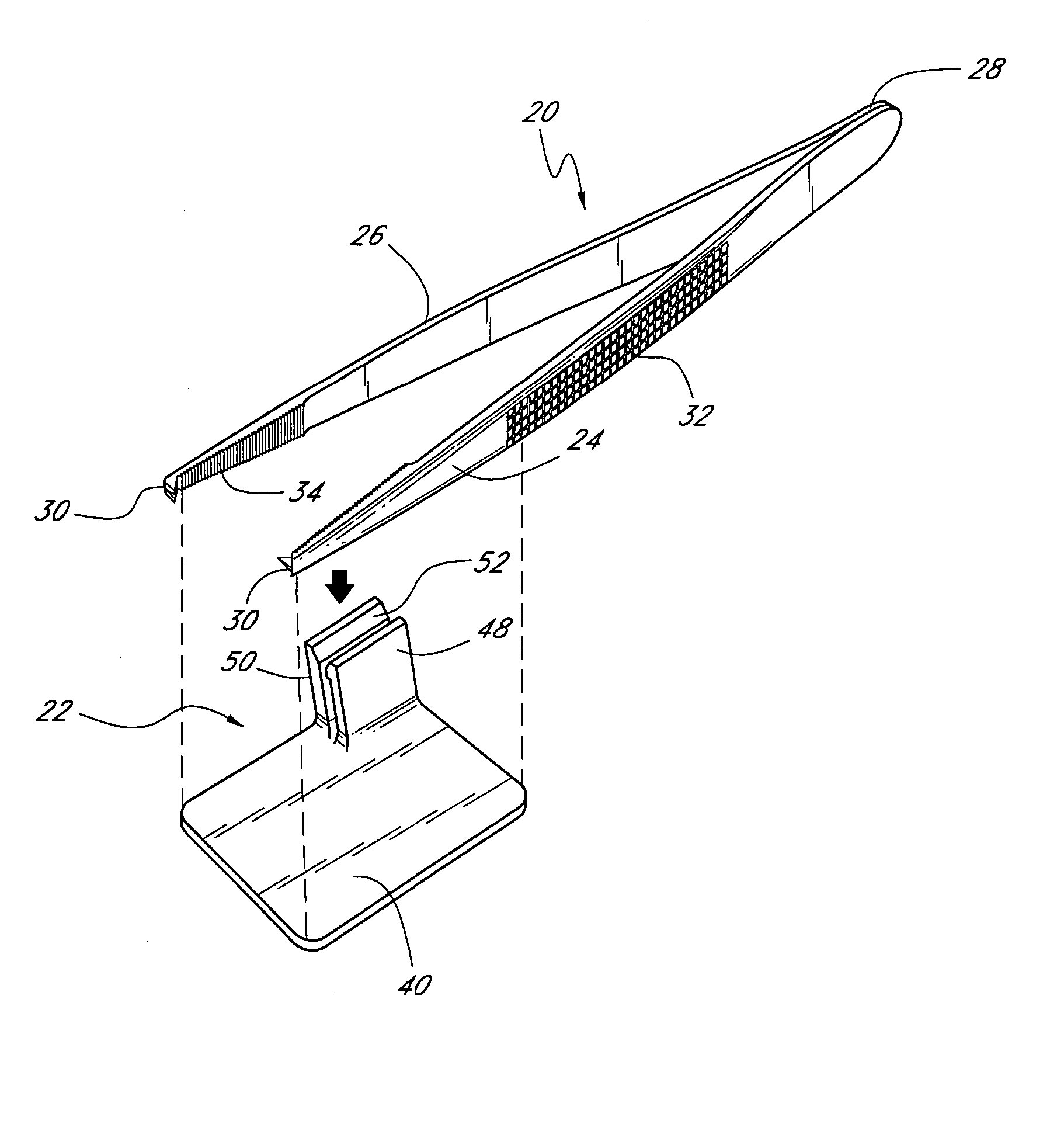
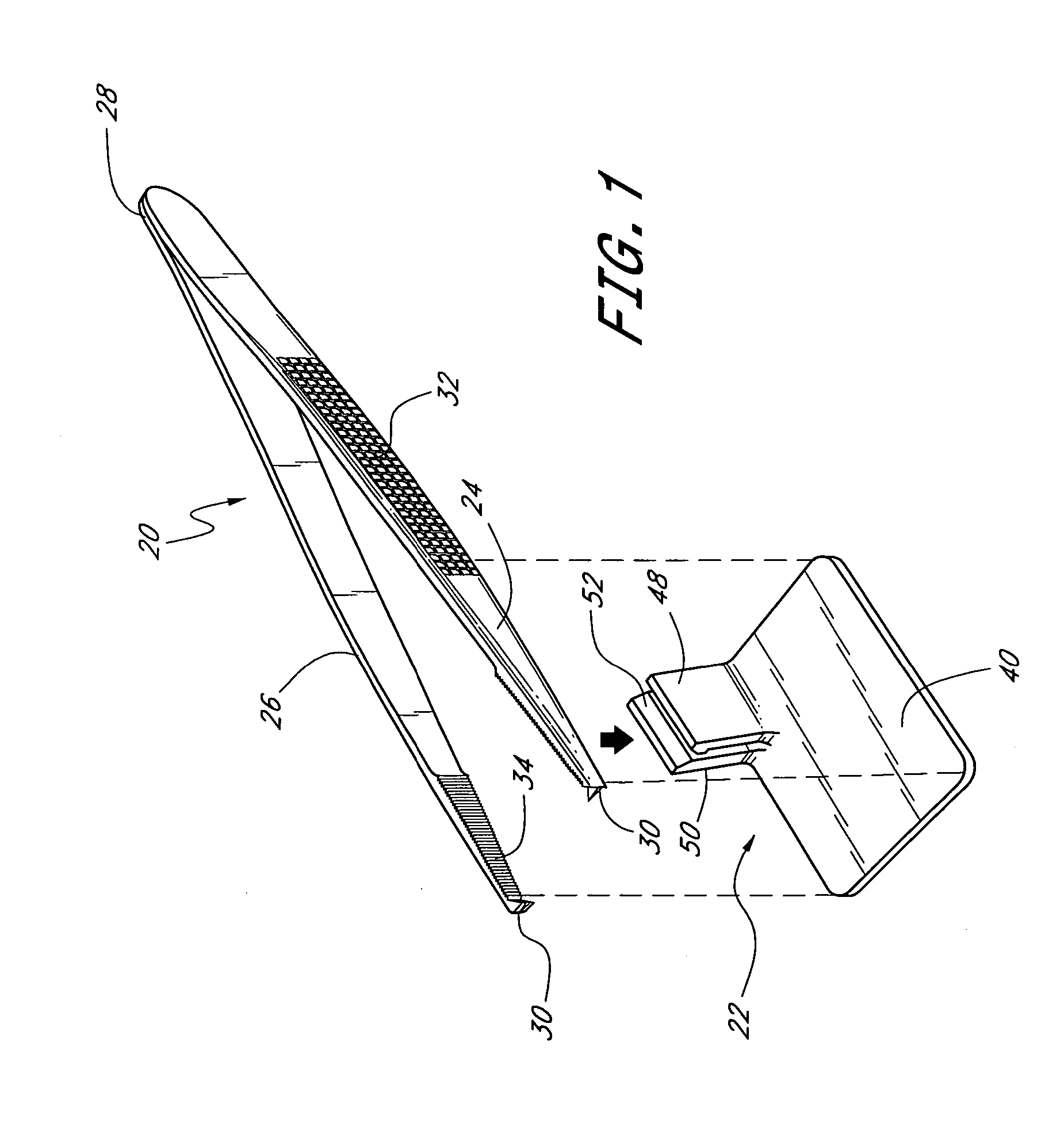
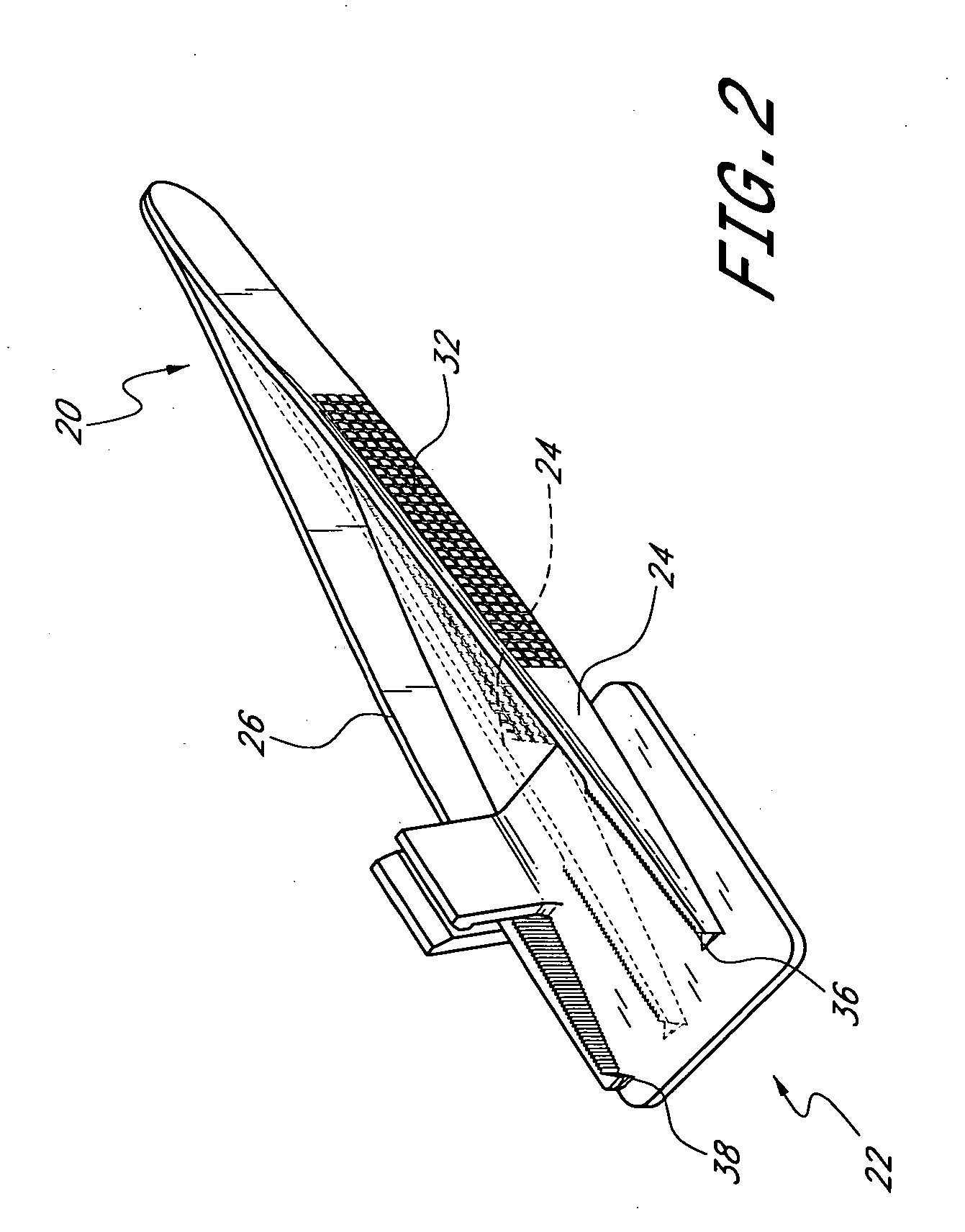
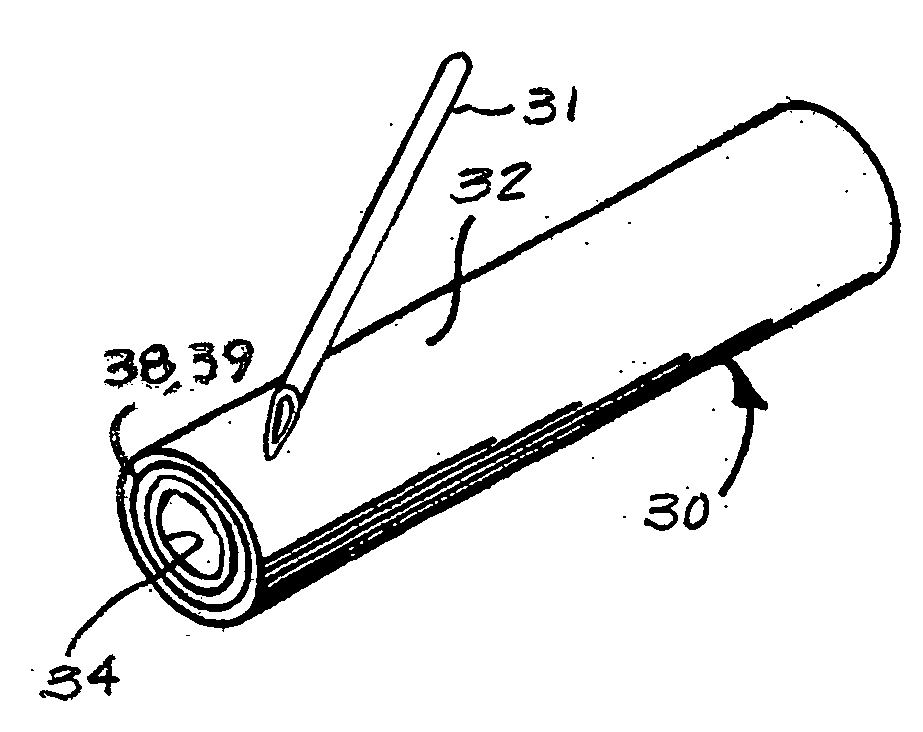
Suture needle, suture needle/suture assembly and suture passer device
A blade suture needle is adapted for use in a suture needle assembly, and with a suture passer device, for passing a suture needle assembly through tissue. The suture needle includes an elongated resilient sheet body member bounded by opposite principal surfaces. The body member includes at least one central aperture extending between the principal surfaces, having dimensions to permit of a capturing flange to pass therethrough. The suture needle may be part of a needle assembly further including an elongated suture passing through an aperture in the needle. A suture passer device includes an elongated pusher guide with pair of opposed jaw members disposed at its distal end, which may be opened or closed in response to a user action at its proximal end. The guide allows passage of an elongated pusher element through a pusher channel therein. One of the jaw members includes a suture assembly channel aligned with the pusher channel. The other jaw member has an aperture passing therethrough, which is aligned with the suture assembly channel when the jaw members are closed. This other jaw member includes an elongated resilient flange fixedly or retractably attached to the jaw member at the periphery of the aperture, and extending across the aperture to an opposite point on the periphery of the aperture.
Owner:AXYA MEDICAL INC
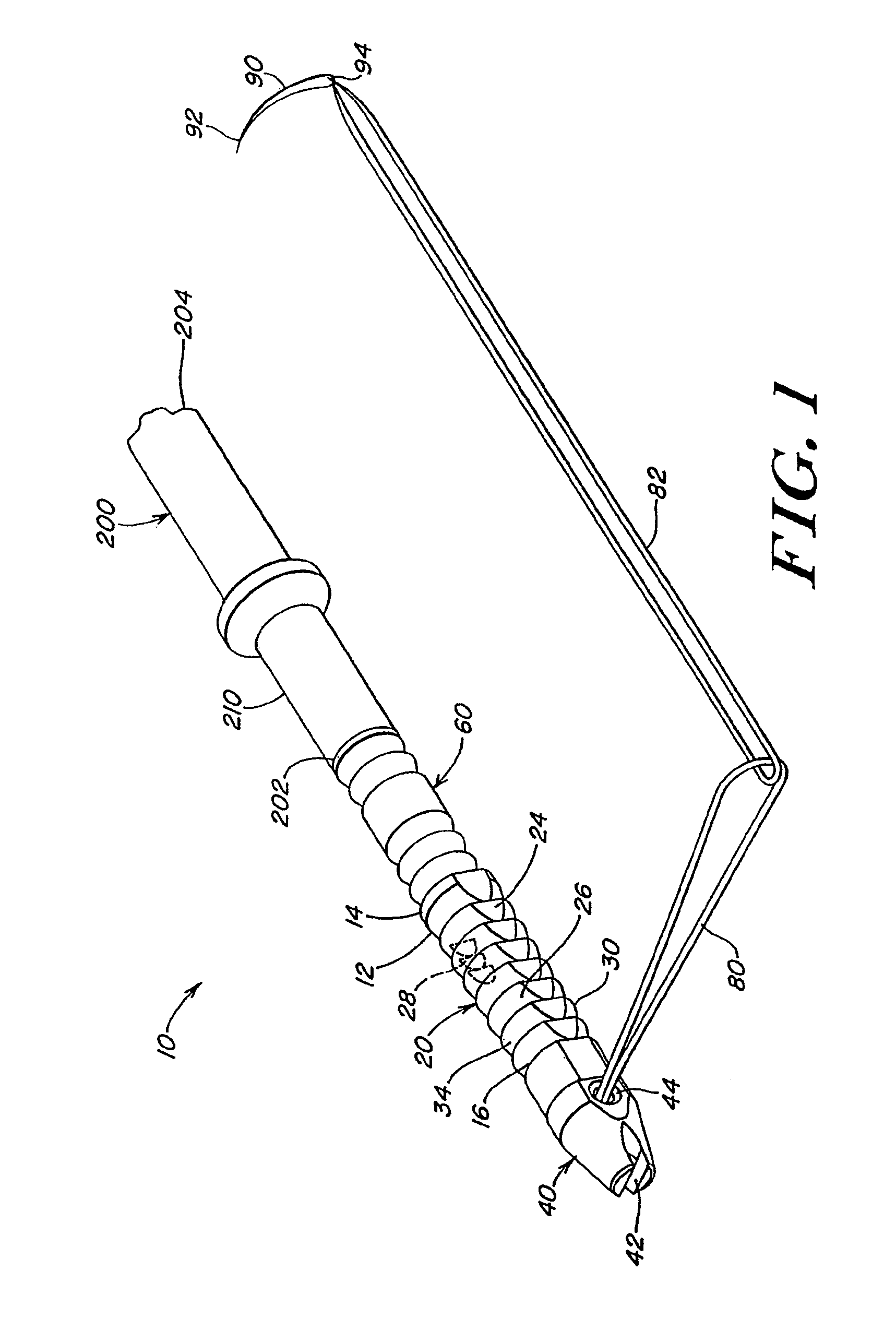
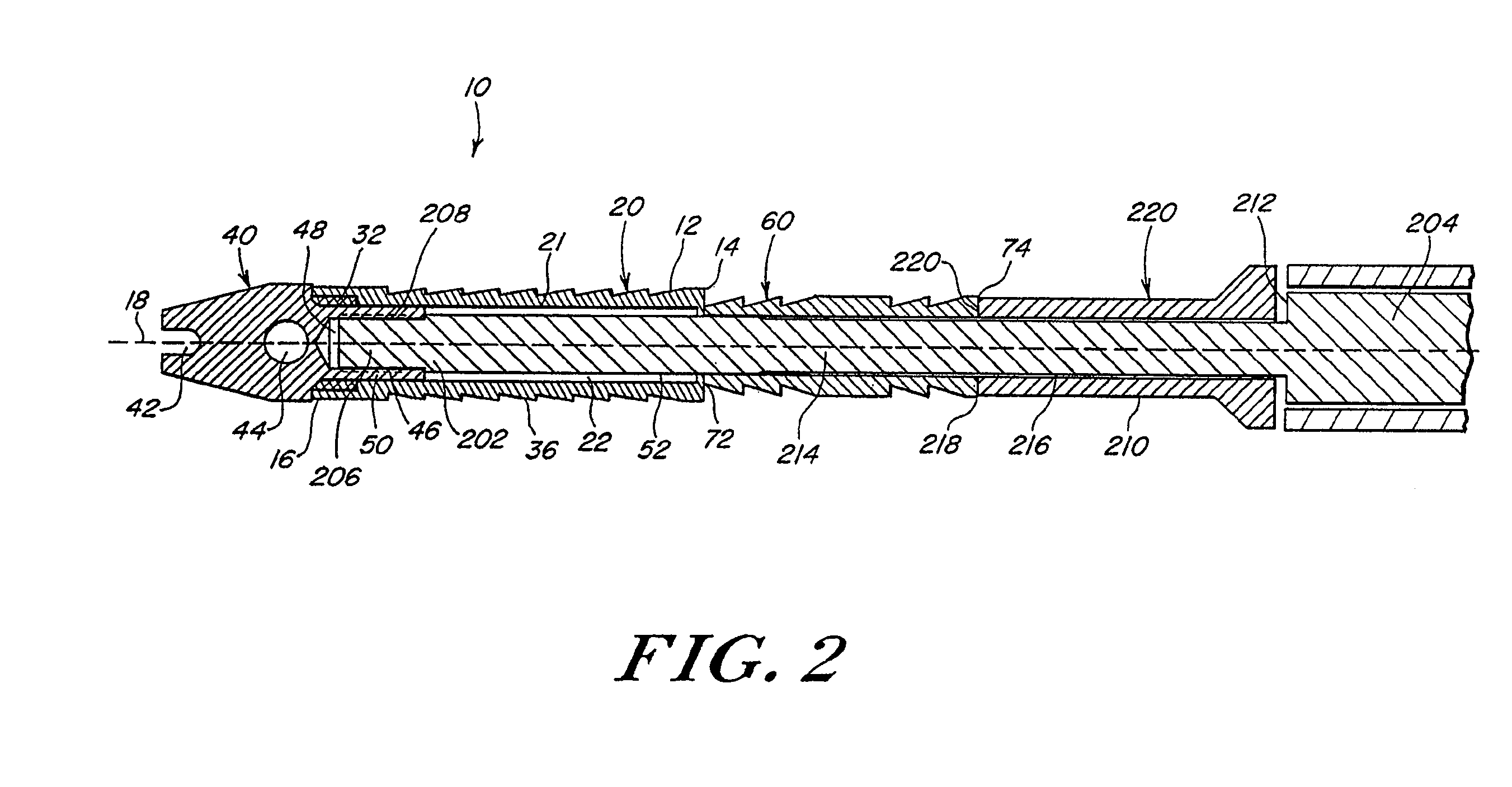
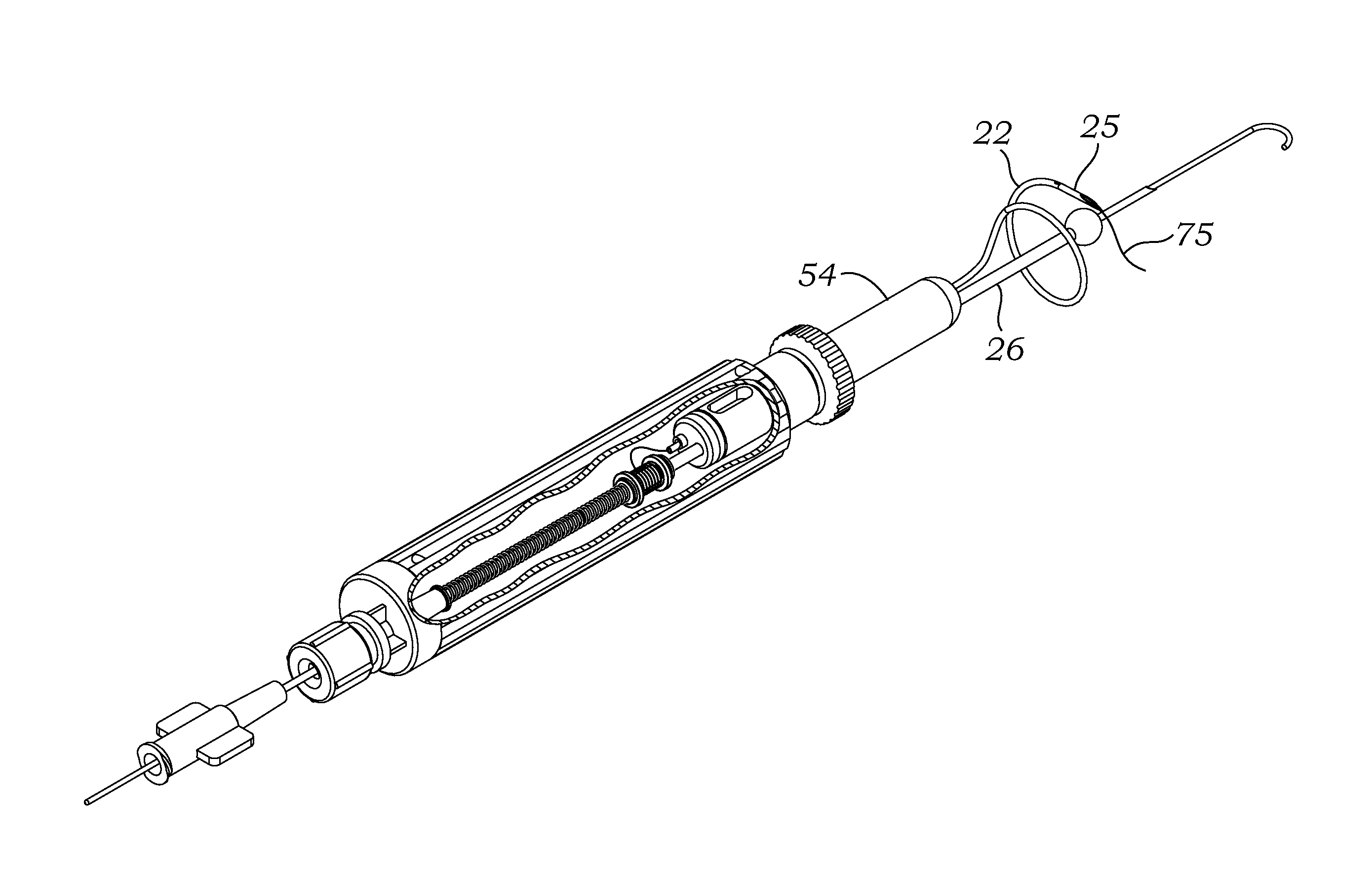
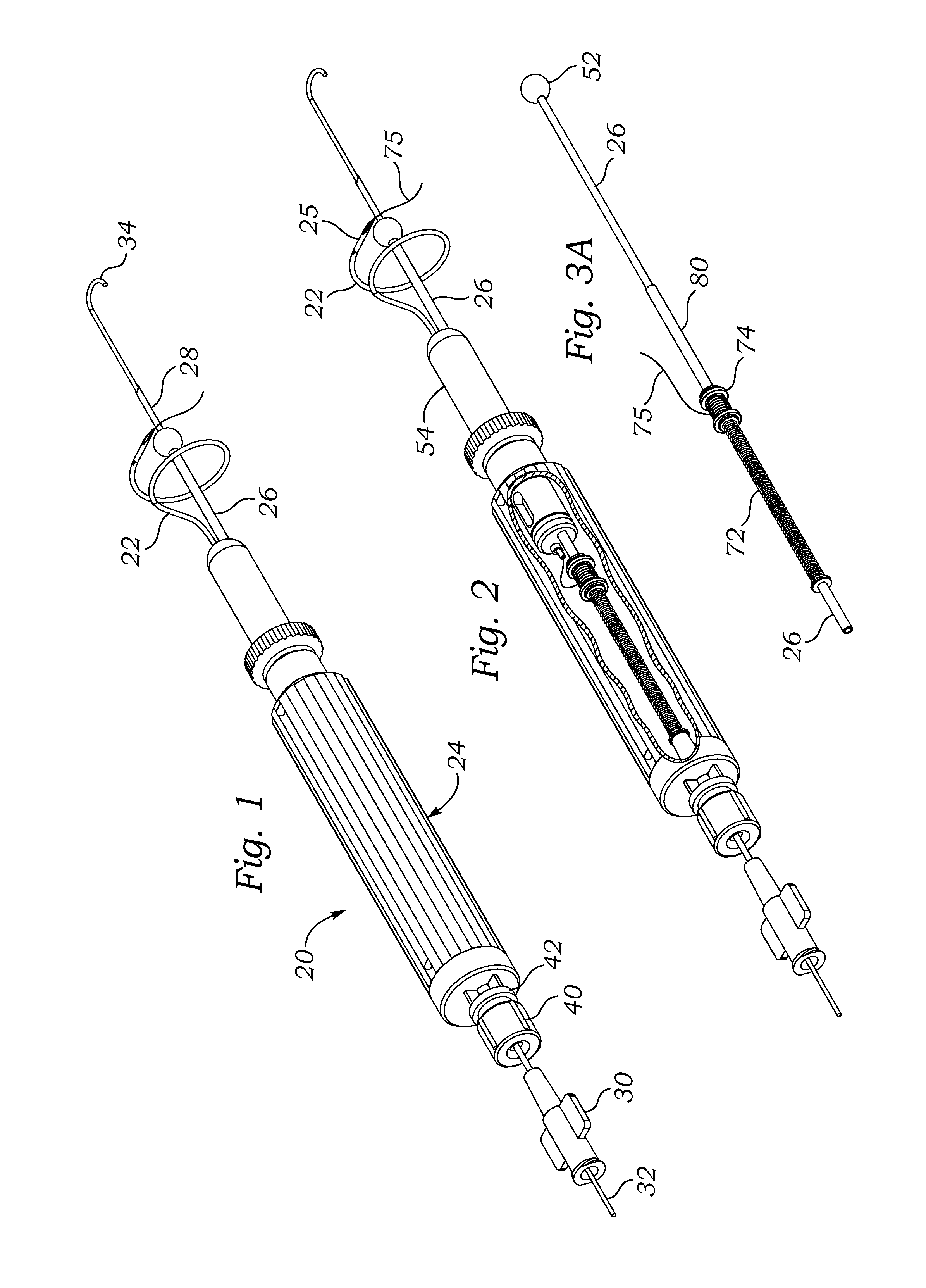
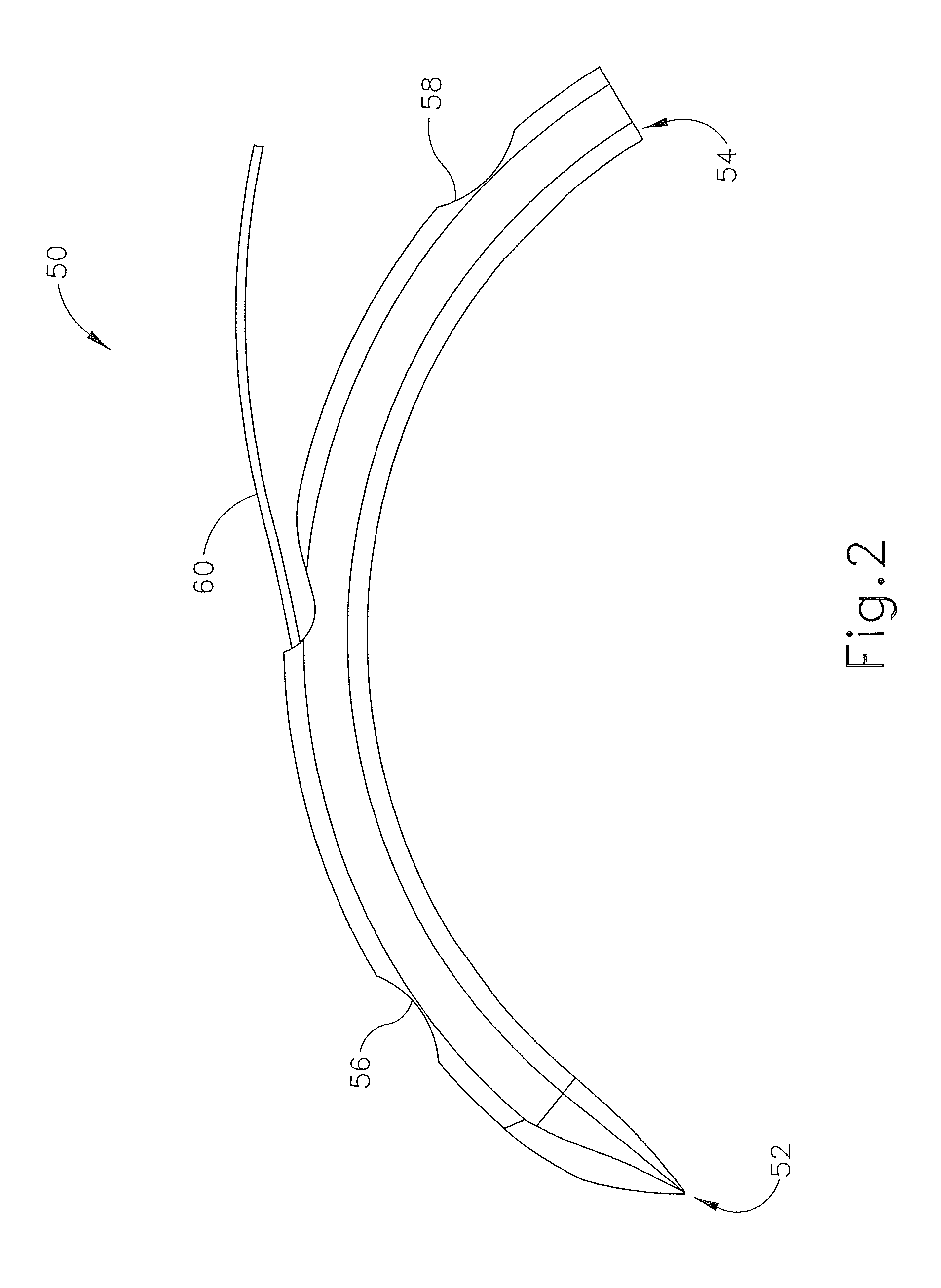
Surgical Puncture Cinch and Closure System
A system for forming a purse string suture, including a suture applicator having a proximal handle having a suture spool mounted thereon or in an internal chamber. A length of suture is partly wound on the spool, and a hollow suture needle extends from a distal end of the handle and contains a free end of the length of suture. The suture needle projects distally from the handle in a helical shape and terminates in a sharp distal tip with an opening in one side close to the distal tip. The free end of the length of suture may extend out of the distal tip and back into the hollow suture needle through the opening. The suture needle may have a deflection segment adjacent the distal tip that is more flexible than the rest of the helical distal portion of the suture needle. A linear hollow pivot shaft extends from a distal end of the handle substantially along an axis of the helical distal portion of the suture needle. The pivot shaft has a blunt tip with a substantially larger radial profile than the shaft to prevent puncturing tissue.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Surgical tissue guard
A guard attachable to a forceps is provided. In one embodiment, the guard is releasably securable to one arm of the forceps. In another embodiment, the guard is permanently secured to or integral with one arm of the forceps. In another embodiment, the guard is rotatable with respect to the forceps. A barrier portion of the guard extends between the forceps' arms, or along an outside of the forceps' arms. The barrier prevents tissue from getting between the forceps' arms. A physician can thus use the barrier to displace tissue from a surgical site. The barrier also provides protection to surrounding tissue, preventing suturing needles from pricking the tissue behind the barrier or pricking the physician. The guard may be slidable along at least a portion of the length of the forceps.
Owner:DEXTEUS
Apparatus for suturing a blood vessel
InactiveUS7041119B2Accurate operationShort amount of timeSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSuturing needleDistal portion
A vascular suturing device is disclosed which includes an elongated tubular body defining opposed proximal and distal end portions and having a longitudinal axis extending therethrough, the body including an inner tubular member, an outer tubular member and a central tubular member disposed between the inner and outer tubular members. The inner tubular member and the central tubular member are mounted for movement relative to the outer tubular member about the longitudinal axis of the body for sequentially driving a pair of suture needles through the wall of a blood vessel to close an incision formed therein. A vascular dilator having a tapered distal tip portion is supported within the inner tubular member and is dimensioned to extend beyond the distal end of the inner tubular member for positioning the suturing device at the incision in the wall of the blood vessel. The dilator is configured to direct blood flow from the distal portion of the dilator to a location remote from the blood vessel for observation to confirm the location of the device.
Owner:GREEN DAVID T
Arthroscopic meniscal repair systems and methods
ActiveUS20090228041A1Improve clinical outcomesPassage increaseSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesMeniscal repairSuturing needle
An arthroscopic meniscal tear repair device comprises a catch needle and a transfer needle. which are pierced into a torn meniscus and advanced past the tear. Suture is transferred by a suture needle from the transfer needle through the meniscus and into the catch needle. The catch needle has an internal mechanism that retains the suture. The suture needle is then retracted back to its home position inside the transfer needle, leaving the free end of the suture across the meniscus and in the catch needle. The device is then retracted out of the meniscus, leaving behind a stitch across the meniscal tear inside the meniscus. A pre-tied knot of suture is then slid down the device and cinched up using a knot pusher having a dilation tip, thus completing the repair.
Owner:CAYENNE MEDICAL INC
Laparoscopic suturing instrument with perpendicular eccentric needle motion
A suture needle driving instrument comprises a shaft and an end effector. The end effector is located at the distal end of the shaft and includes a pair of needle grasping arms. Each grasping arm extends along a respective arm axis. The grasping arms are operable to drive a suture needle along a rotational path about an axis, such as one of the arm axes, that is offset from the central longitudinal axis of the shaft. The rotational path may be perpendicular to the axis of the shaft. A needle driven by the end effector may have an arc radius that is greater than the radius of the shaft. At least one of the needle grasping arms may include a dogleg feature positioning a distal portion of the grasping arm outside the radius of the shaft. The instrument may be used through a trocar during minimally invasive surgery.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Implantable devices with reduced needle puncture site leakage
ActiveUS20060118236A1Reduce leakageGood biocompatibilitySynthetic resin layered productsLaminationElastomerFiber
A prosthetic implantable device that offers a reduction in fluid loss when the device is punctured, such as by a dialysis needle or suture needle, and the needle is subsequently removed. The device may be made to be thin and flexible, and with longitudinal stretch, in order that it also offers good handling and kink resistance to a surgeon. While the device is preferably of tubular form, flat sheets or other forms may also be made. The device includes inner and outer layers of a porous material having a microstructure of nodes interconnected by bent fibrils, and having void spaces between adjacent bent fibrils. The inner and outer layers are joined by an elastomeric adhesive that may interpenetrate the void spaces of the adjacent surfaces of the inner and outer layers, that is, the inner surface of the outer layer and the outer surface of the inner layer. Optionally, a middle layer of an elastomeric material may also be provided, joined to the inner and outer porous layers by the interpenetrating elastomeric adhesive. The device is preferably a vascular graft and more preferably a vascular graft for kidney dialysis.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Suture passer device and suture needle
A suture passer device includes a shaft, a handle, an end effector, and a suture capturing member. The shaft has a shaft proximal end and a shaft distal end. The handle assembly is coupled to the shaft proximal end. The end effector is coupled to the shaft distal end. The suture capturing member is within the end effector, is coupled to the handle assembly independently of the shaft, and is configured to capture a suture within the end effector.
Owner:COST CONTAINMENT
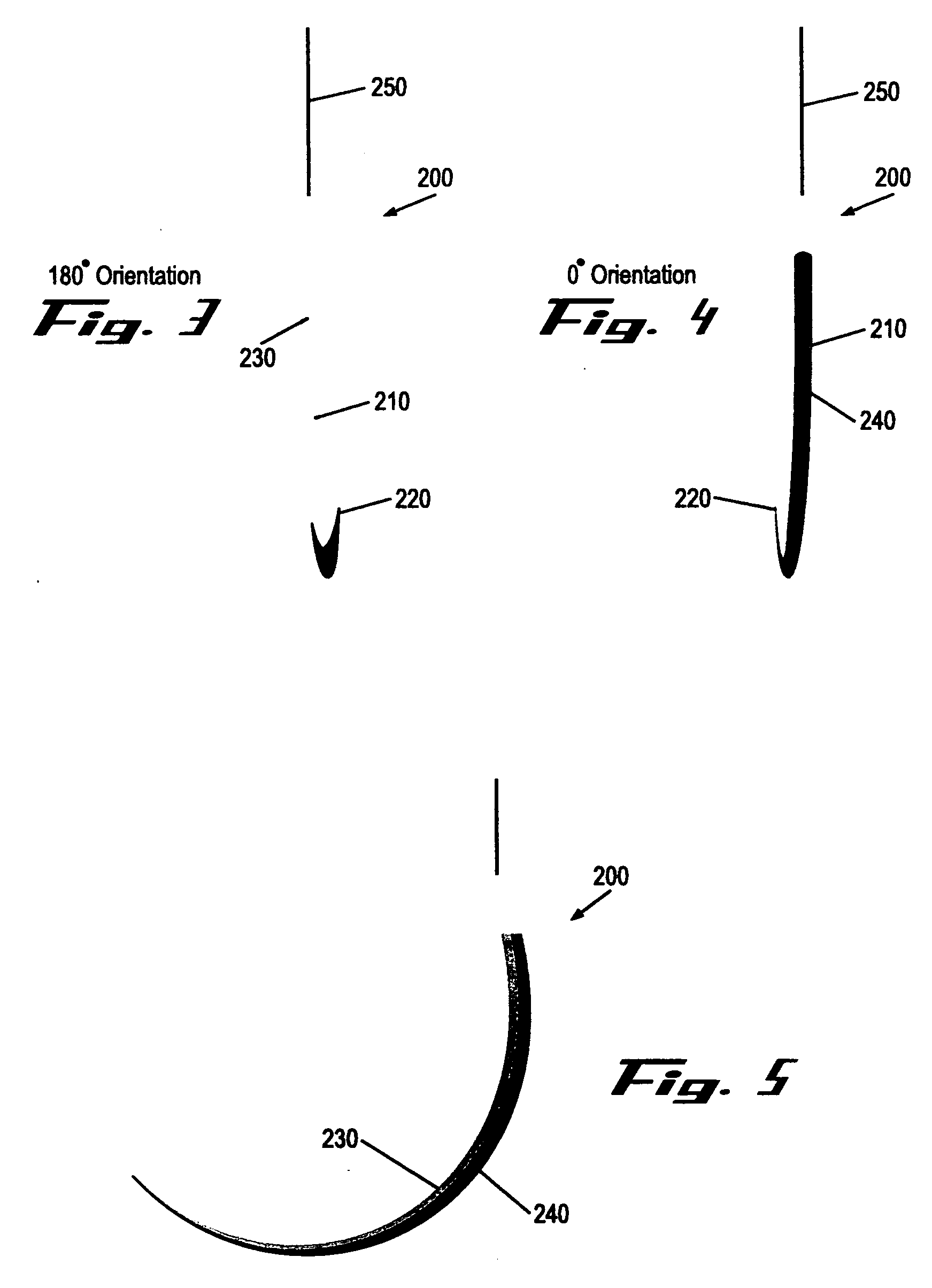
Suture needles and methods of use
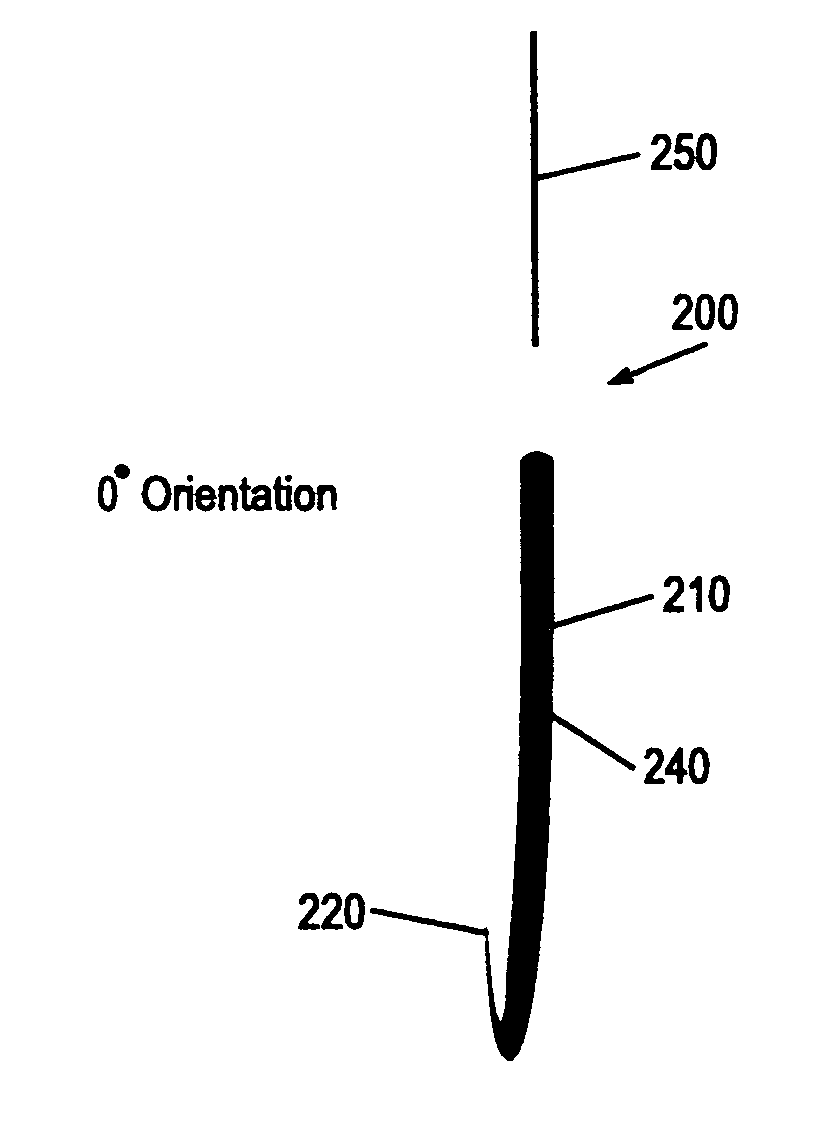
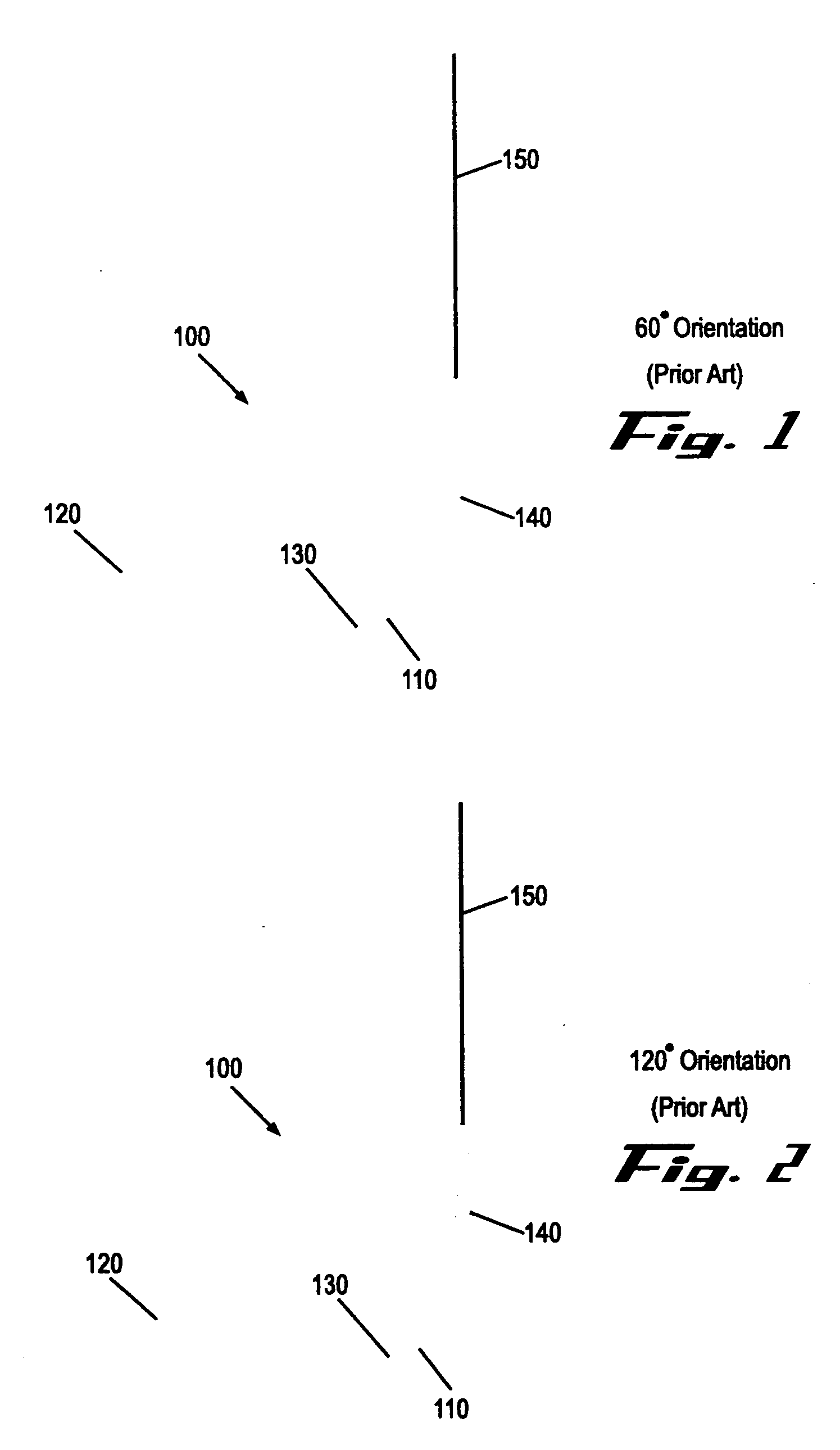
A suture needle is disclosed that includes a shaft, the shaft being marked at least partially with a visual indicator; and a puncture tip at one end of the shaft. The shaft of the needle includes a front surface and a rear surface. The front and / or rear surface of the needle includes the visual indicator. The visual indicator may be a color, but if both the front and rear surfaces include a color, then the colors of front and rear surfaces are different. Also disclosed are methods of using a suture needles, one such method including: inserting the suture needle into a mammal; viewing the suture needle; and immediately ascertaining the exact orientation of the suture needle with no manipulation of the suture needle.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Endoscopic Suturing Device, System and Method
InactiveUS20120165837A1Improve ease of useIncrease speedSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSuturing needleThroat
Improved medical suturing devices, systems, and methods may hold a suture needle at a fixed location relative to a handle of the device, allowing a surgeon to grasp and manipulate the handle of the suturing device to insert the needle through tissues. The exemplary device includes two needle grasping clamps extending from an elongate distal portion for endoscopic surgeries, including ear, nose and throat procedures. The two clamps alternate holding the suture needle, as the surgeon sutures the tissues, each clamp having a proximal and distal gripping jaw for grasping the needle. Preferably, the gripping surfaces of the proximal and distal gripping jaws are substantially parallel to the needle's plane of curvature and exert a holding force on the needle substantially along an axis of the device.
Owner:BOSS INSTR
Safety suture needle assemblies and methods
InactiveUS20070135838A1Save power consumptionMechanism is preventedSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSuturing needleNeedle puncture
Suture needles are a significant safety hazard for medical workers, mainly because of accidental needlestick injuries. Disclosed herein are safety suture needle assemblies and related methods. In particular, variations of a safety suture needle having an activatable sheath or flexible extension member are disclosed. The implementation of certain embodiments of the disclosed invention can result in a desired improvement in safety, including the prevention of unwanted needle punctures, while achieving efficient suturing.
Owner:MEYER MATTHEW EARL
Suture needle retention device
InactiveUS7763038B2Easy to placeQuick exchangeSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSuturing needleProximate
An improved suture needle retention device suitably adapted to be removably attached to the end of a surgical instrument for convenient placement proximate to the surgical field yet out of the way of the surgeon, said device having a needle pervious retention member to accept the sharp end of a suture needle, with said retention member encased by a needle impervious protective sheathing to prevent inadvertent pass-through of the suture needle.
Owner:OBRIEN TODD
Suture Straightening Device and Method
InactiveUS20120004672A1Easily employedEasy to engageSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsSuturing needleSuture needles
A device for straightening sutures or pre-packaged suture-needle combinations. The device has a body formed of substantially resilient material flexible enough to be penetrated by a pointed end of a needle along with a suture inserted into it or to obtain a substantial gap when a slit is cut or molded into it. The device may be held securely in a position for subsequent grasping by a user for drawing a suture through it or attached to an OEM suture packaging. A means of engagement such as adhesive provides means for temporary or permanent attachment to the suture packaging.
Owner:GIAP BRANDON +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com