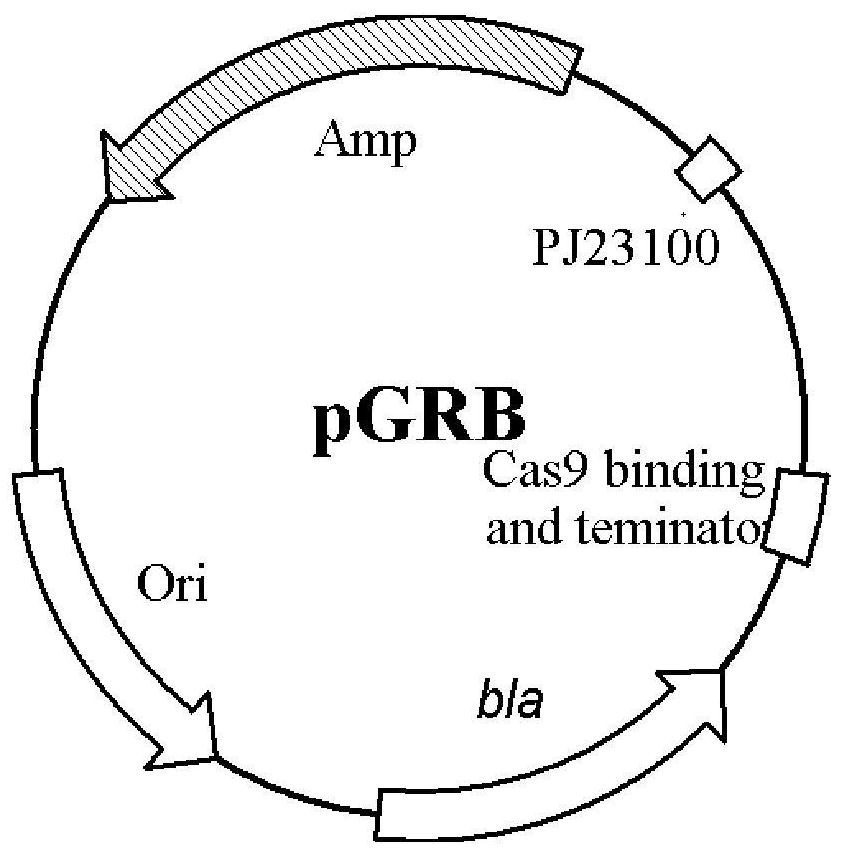
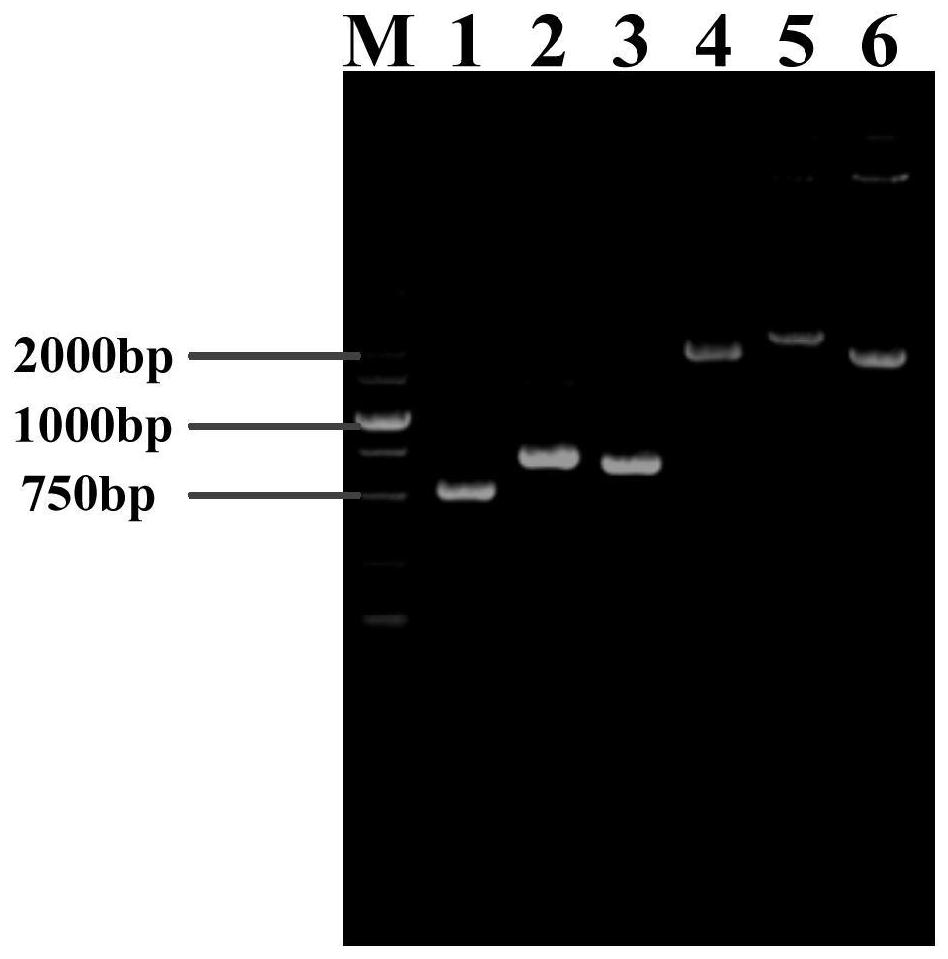
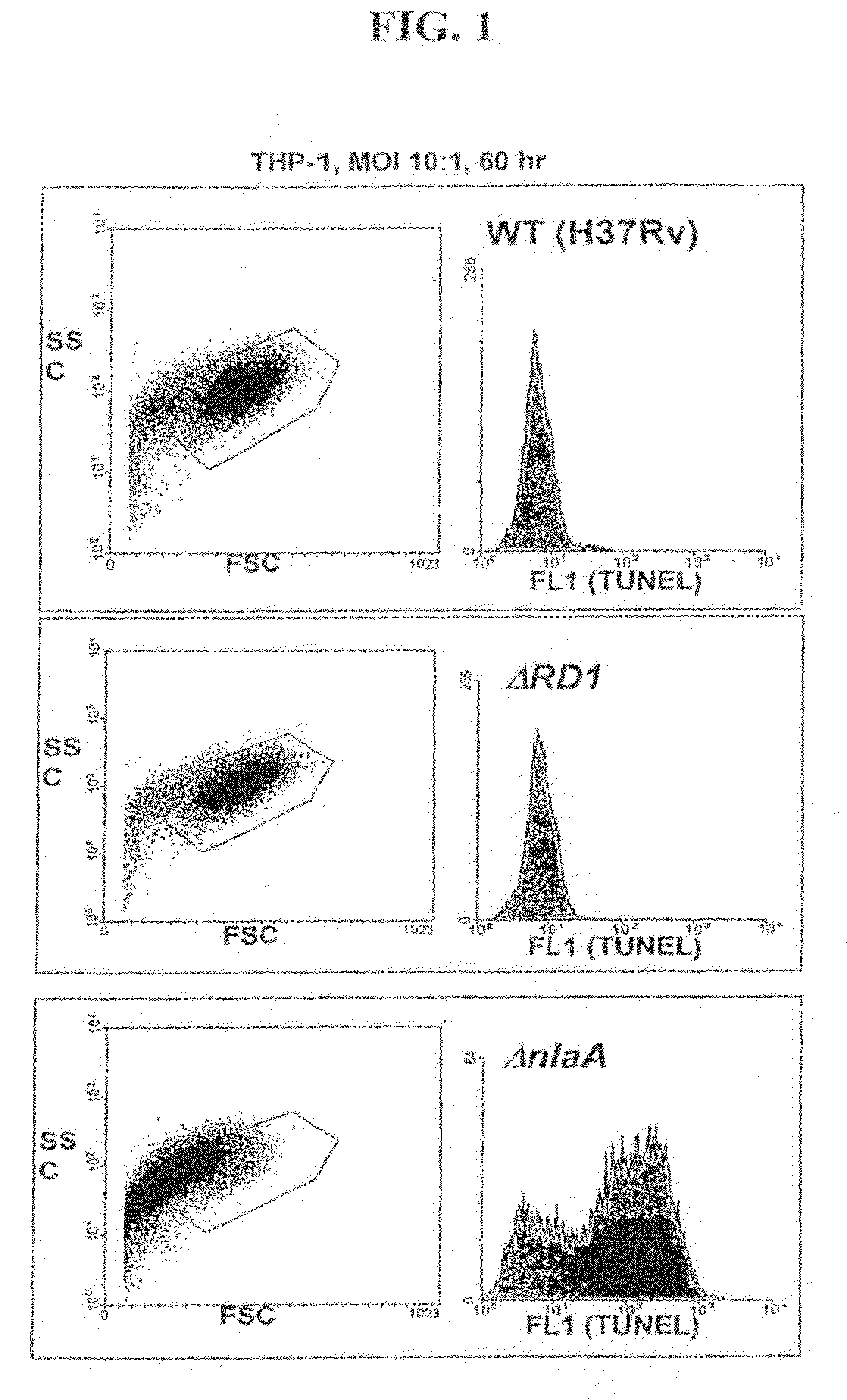
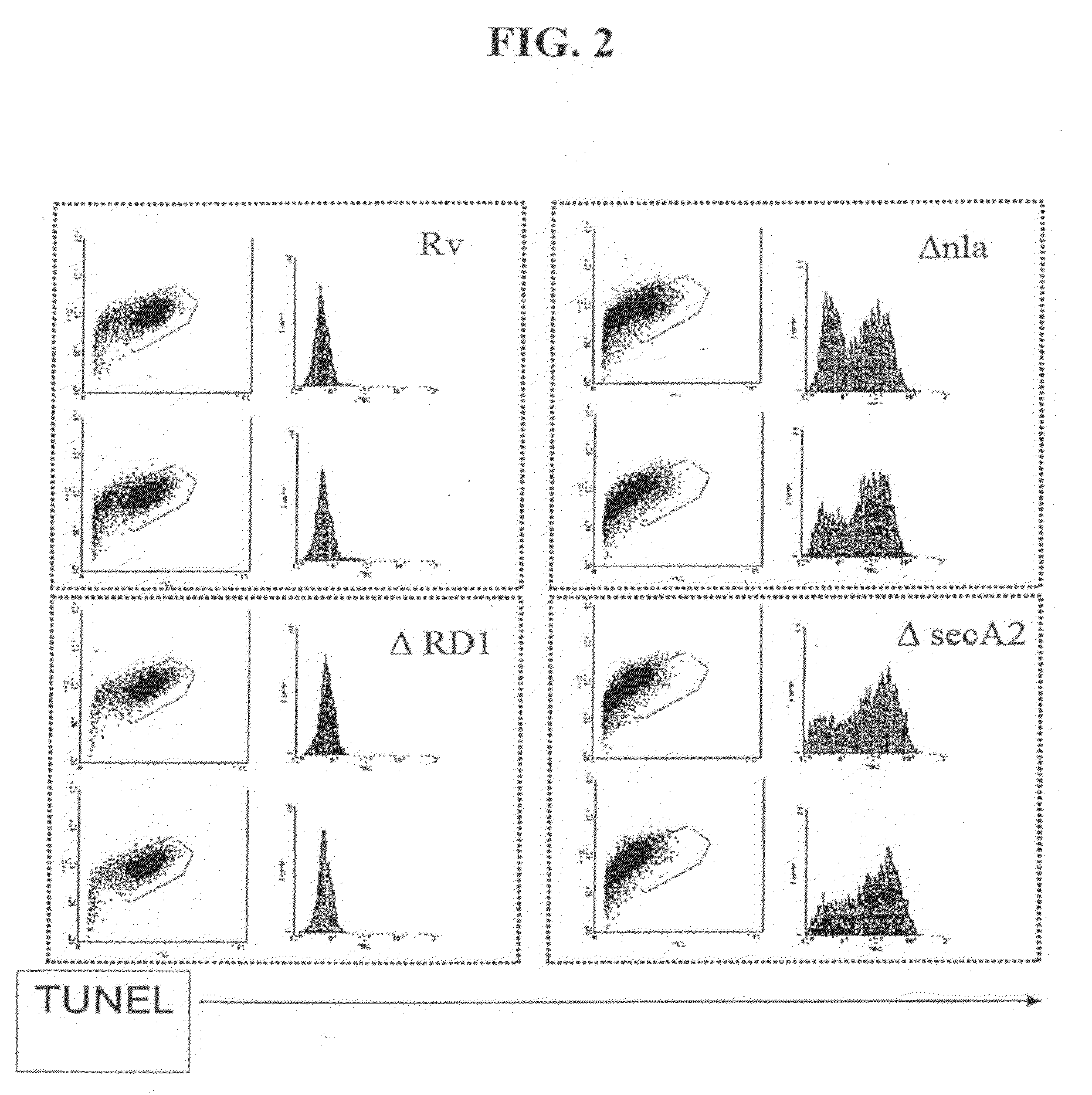
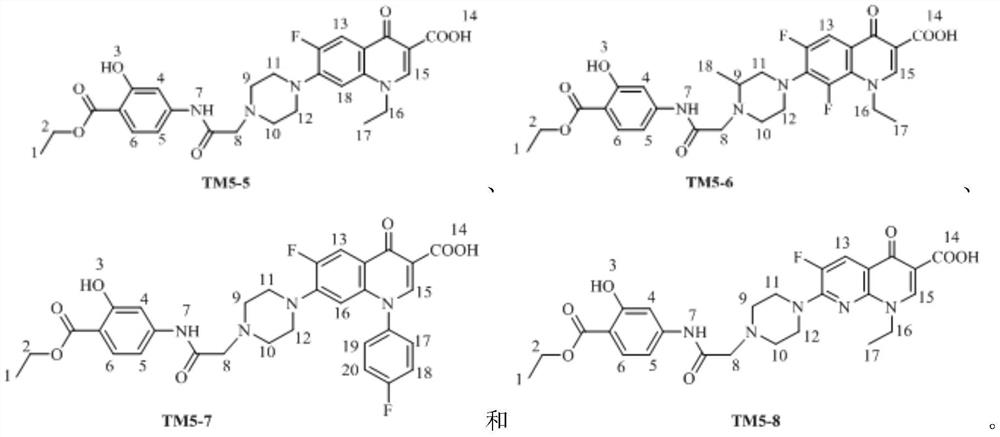
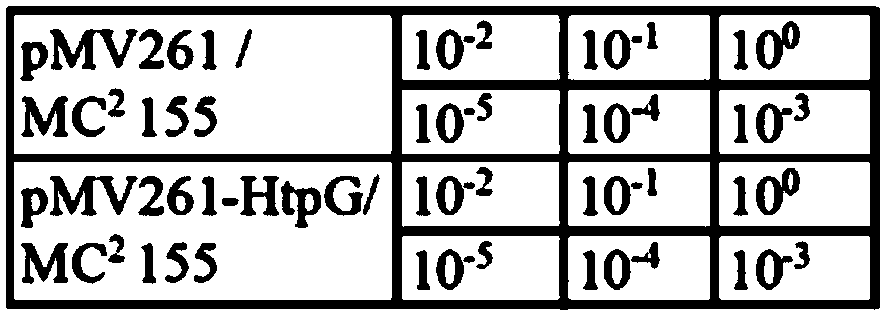Patents
Literature
82 results about "Bacillus smegmatis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mycobacterium smegmatis is an acid-fast bacterial species in the phylum Actinobacteria and the genus Mycobacterium. It is 3.0 to 5.0 µm long with a bacillus shape and can be stained by Ziehl-Neelsen method and the auramine-rhodamine fluorescent method.
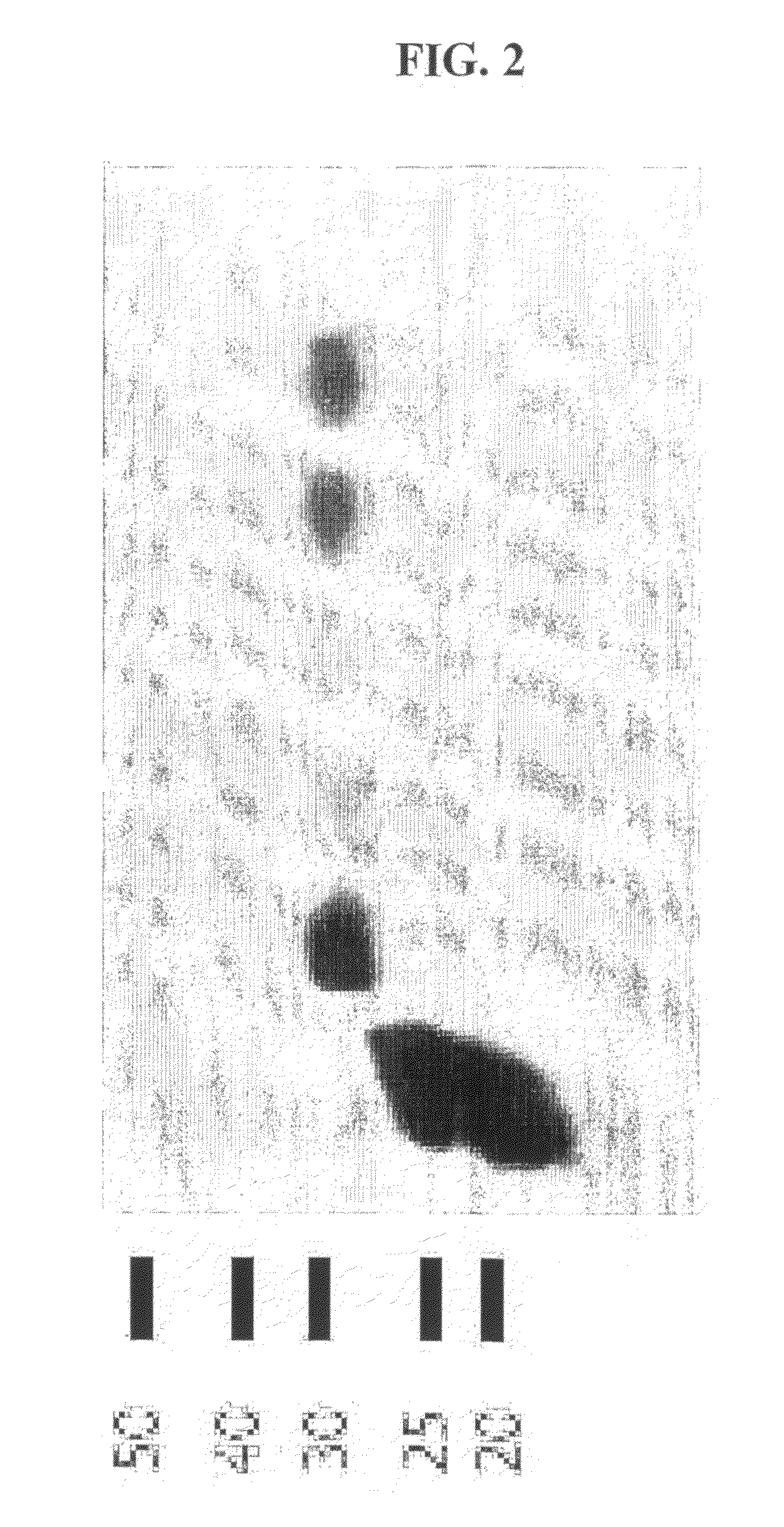
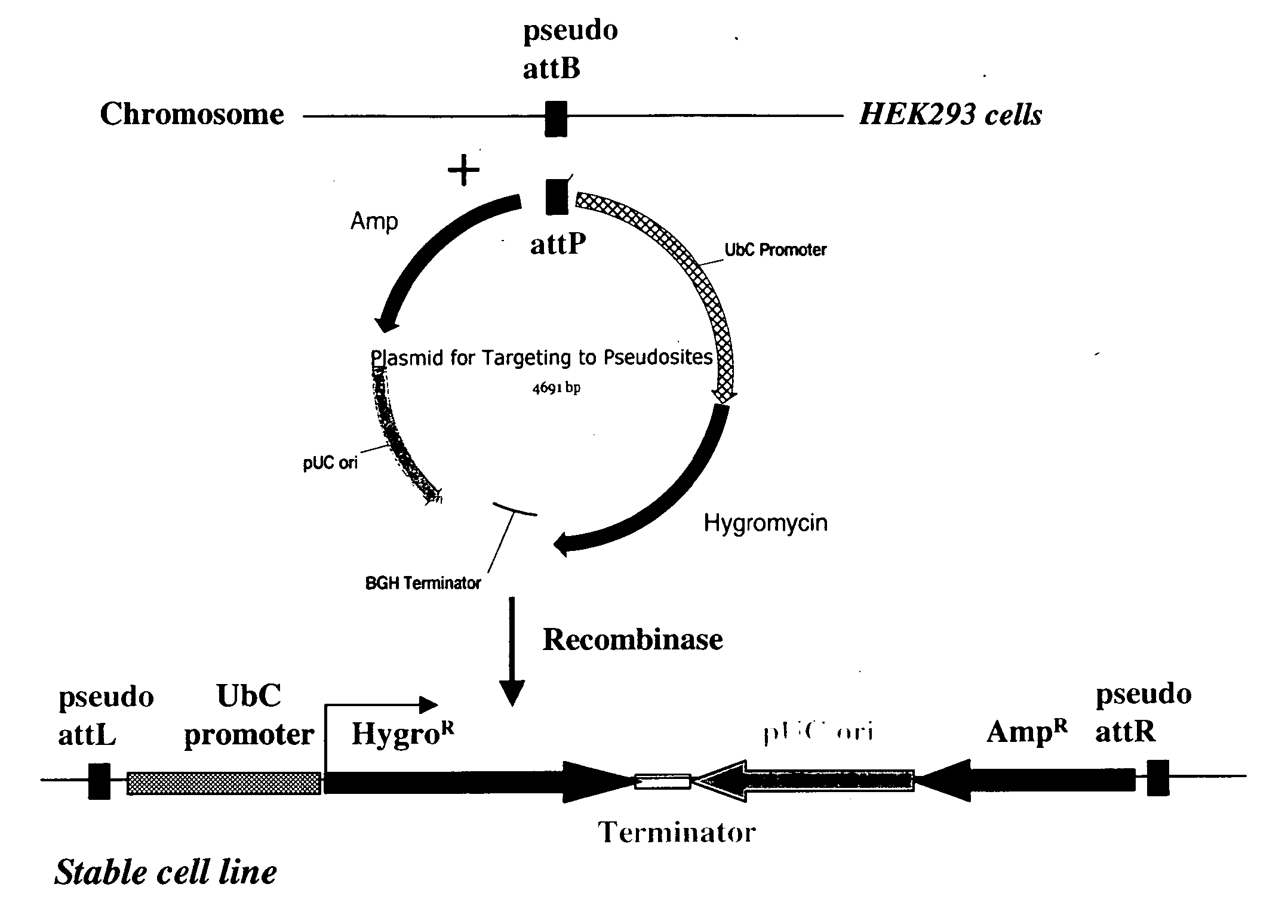
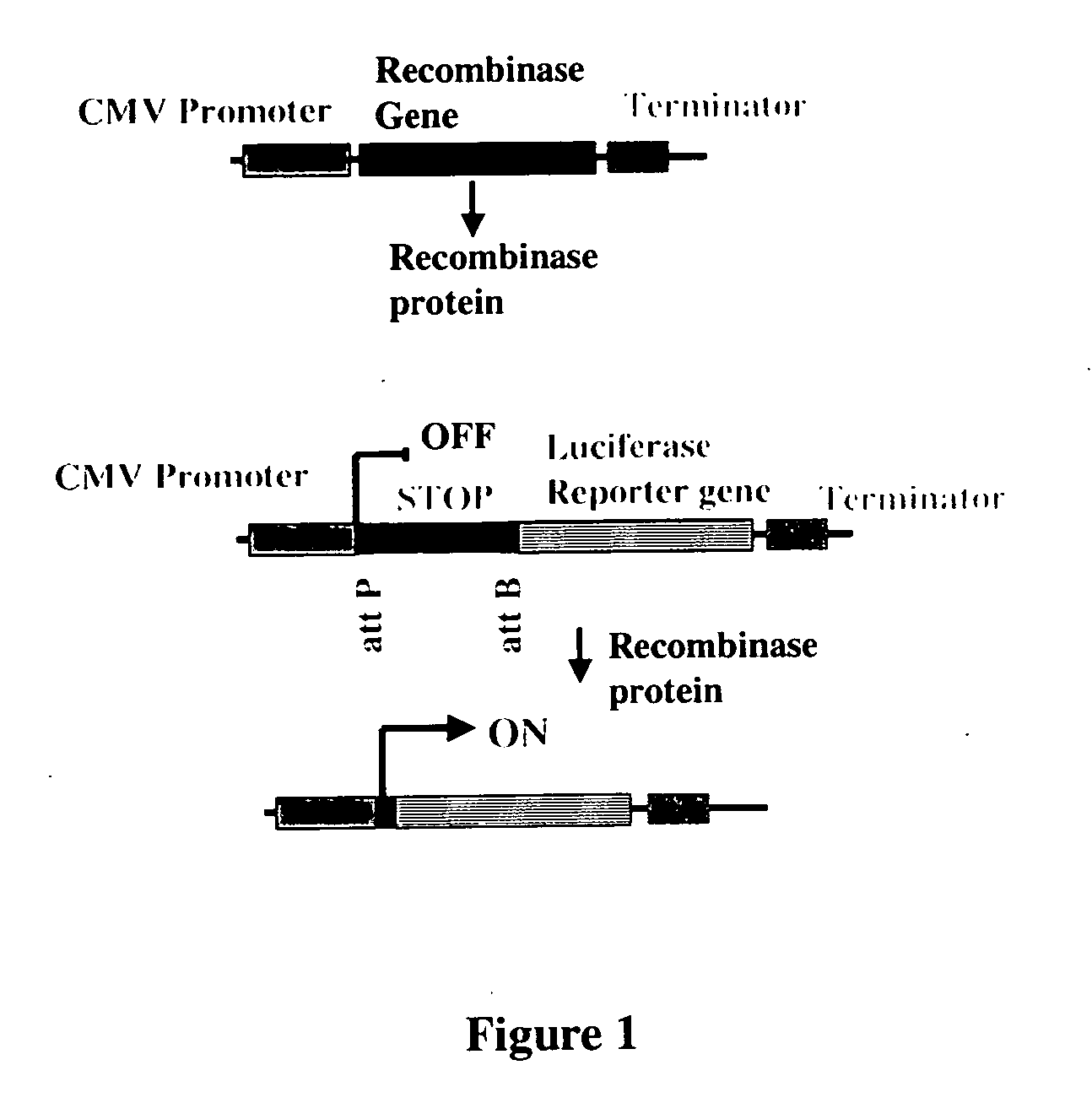
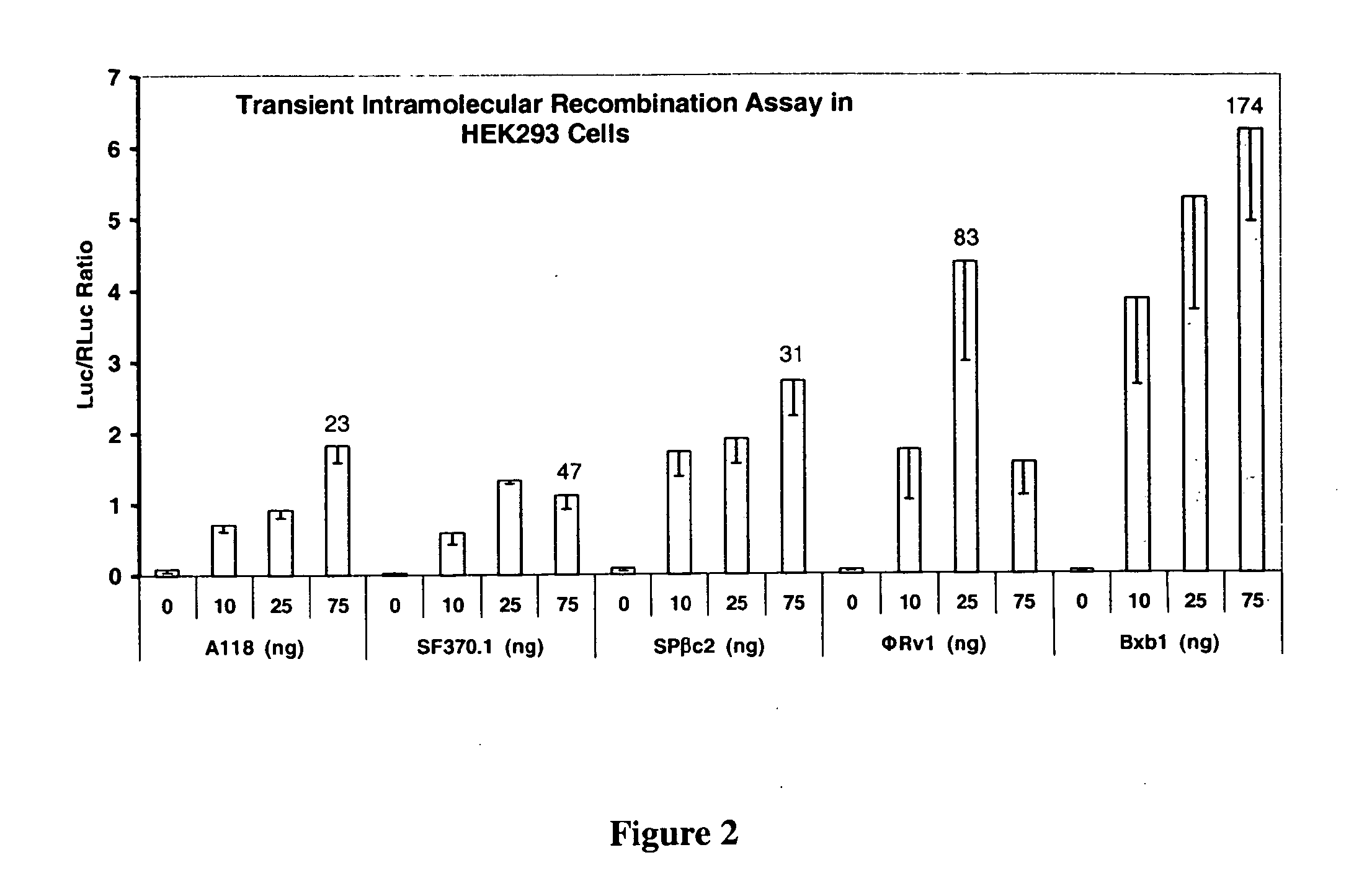
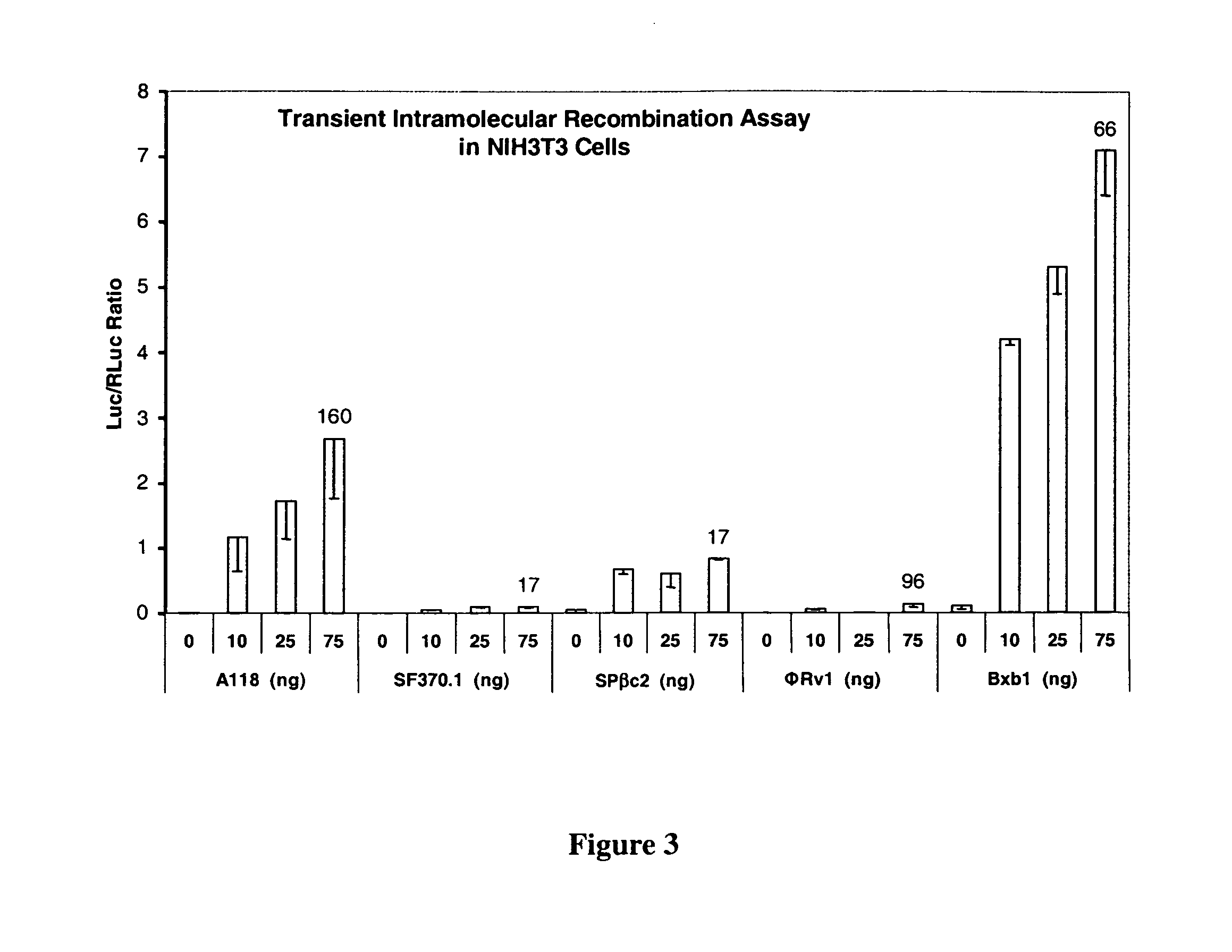
Site-specific serine recombinases and methods of their use
InactiveUS20080020465A1Antibacterial agentsHydrolasesStreptococcus pyogenesSite-specific recombination
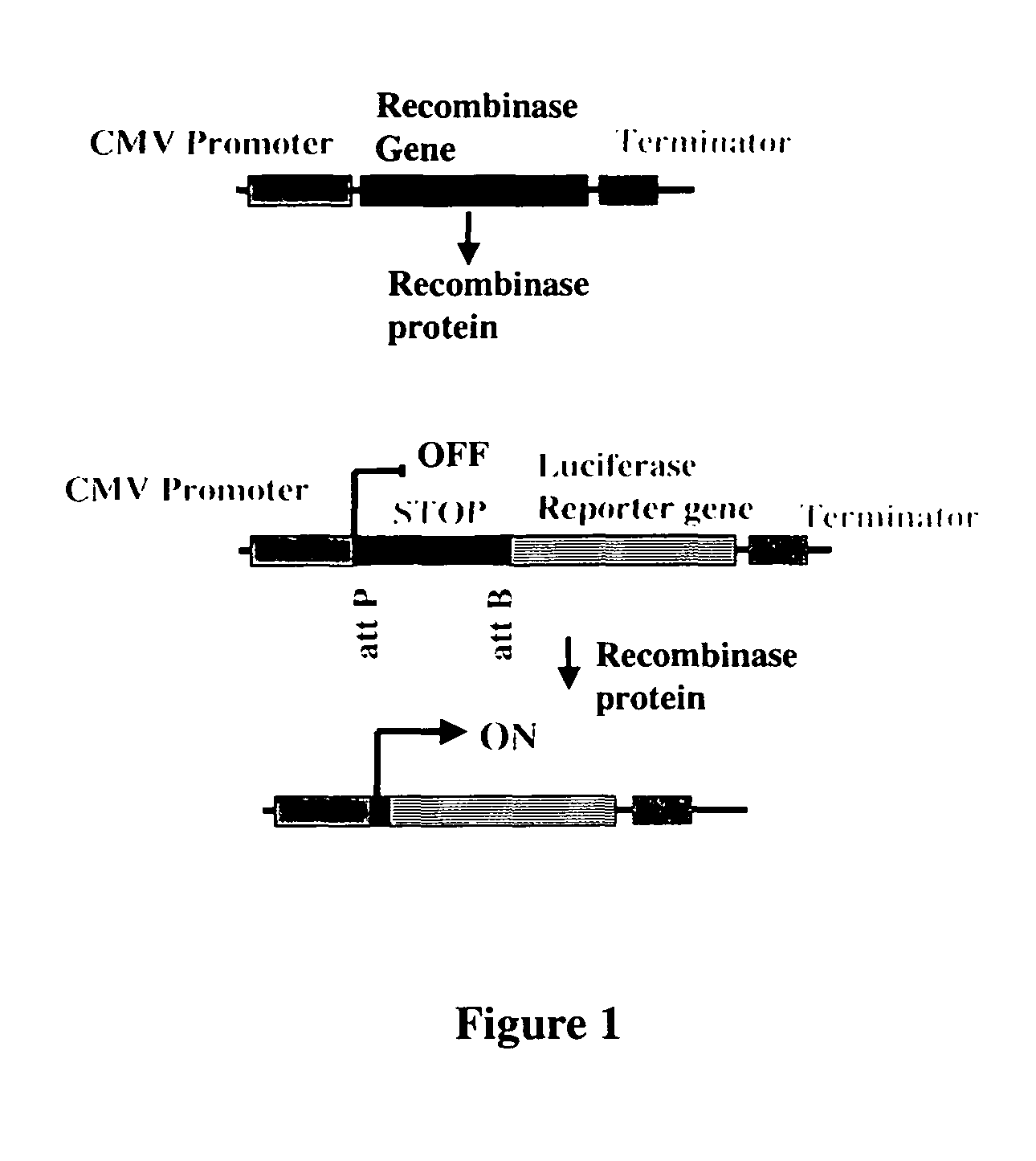
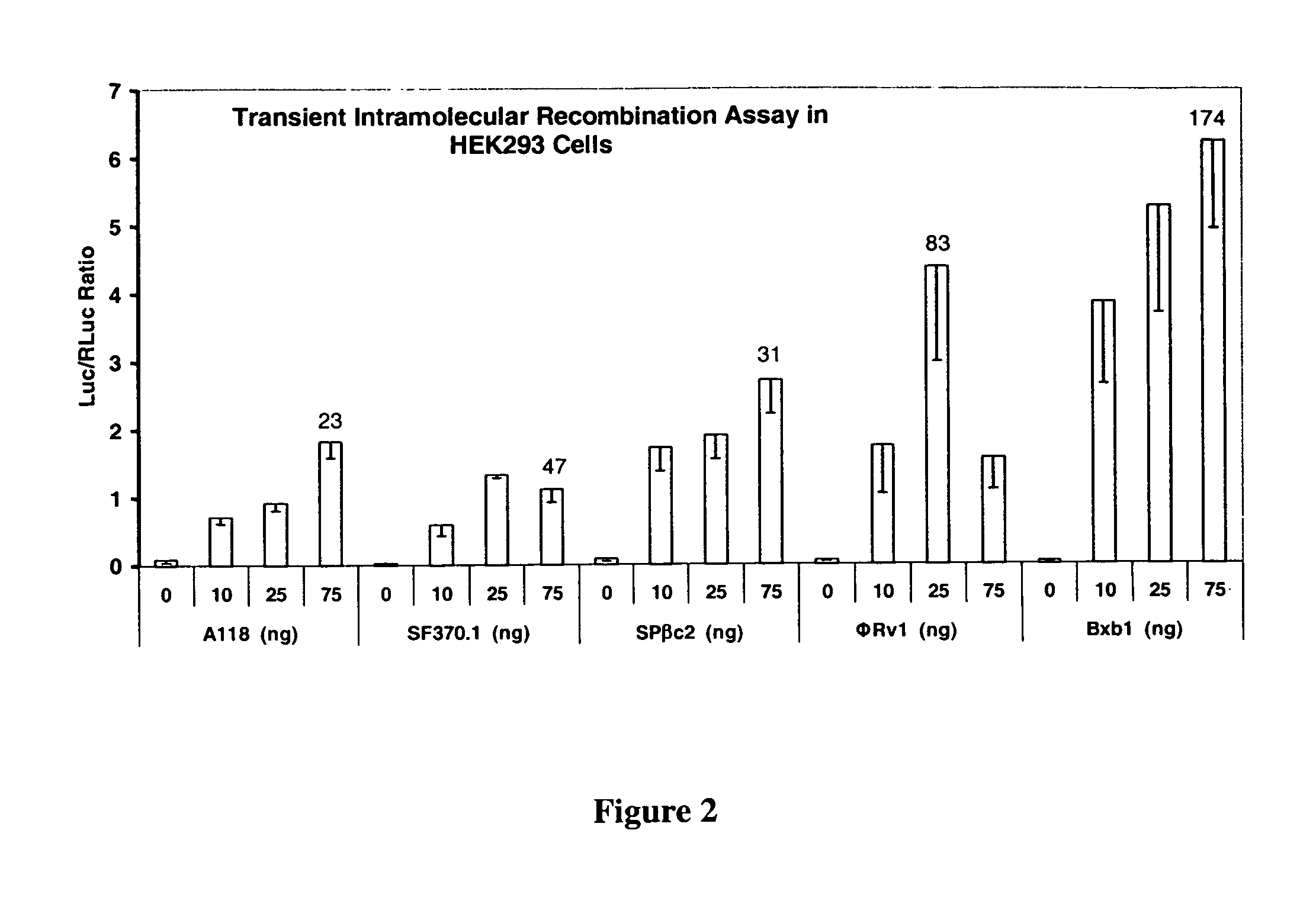
The present invention provides a method for obtaining site-specific recombination in a eukaryotic cell, the method comprising providing a eukaryotic cell that comprises a first recombination attachment site and a second recombination attachment site; contacting the first and second recombination attachment sites with a prokaryotic recombinase polypeptide, resulting in recombination between the recombination attachment sites, wherein the recombinase polypeptide can mediate recombination between the first and second recombination attachment sites, the first recombination attachment site is a phage genomic recombination attachment site (attP) or a bacterial genomic recombination attachment site (attB), the second recombination site is attB or attP, and the recombinase is selected from the group consisting of a Listeria monocytogenes phage recombinase, a Streptococcus pyogenes phage recombinase, a Bacillus subtilis phage recombinase, a Mycobacterium tuberculosis phage recombinase and a Mycobacterium smegmatis phage recombinase, provided that when the first recombination attachment site is attB, the second recombination attachment site is attP and when the first recombination attachment site is attP, the second recombination attachment site is attB. The invention also describes compositions, vectors, and methods of use thereof, for the generation of transgenic cells, tissues, plants, and animals. The compositions, vectors and methods of the present invention are also useful in gene therapy applications.
Owner:PADIDAM MALLA
Method and kit for quickly detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis
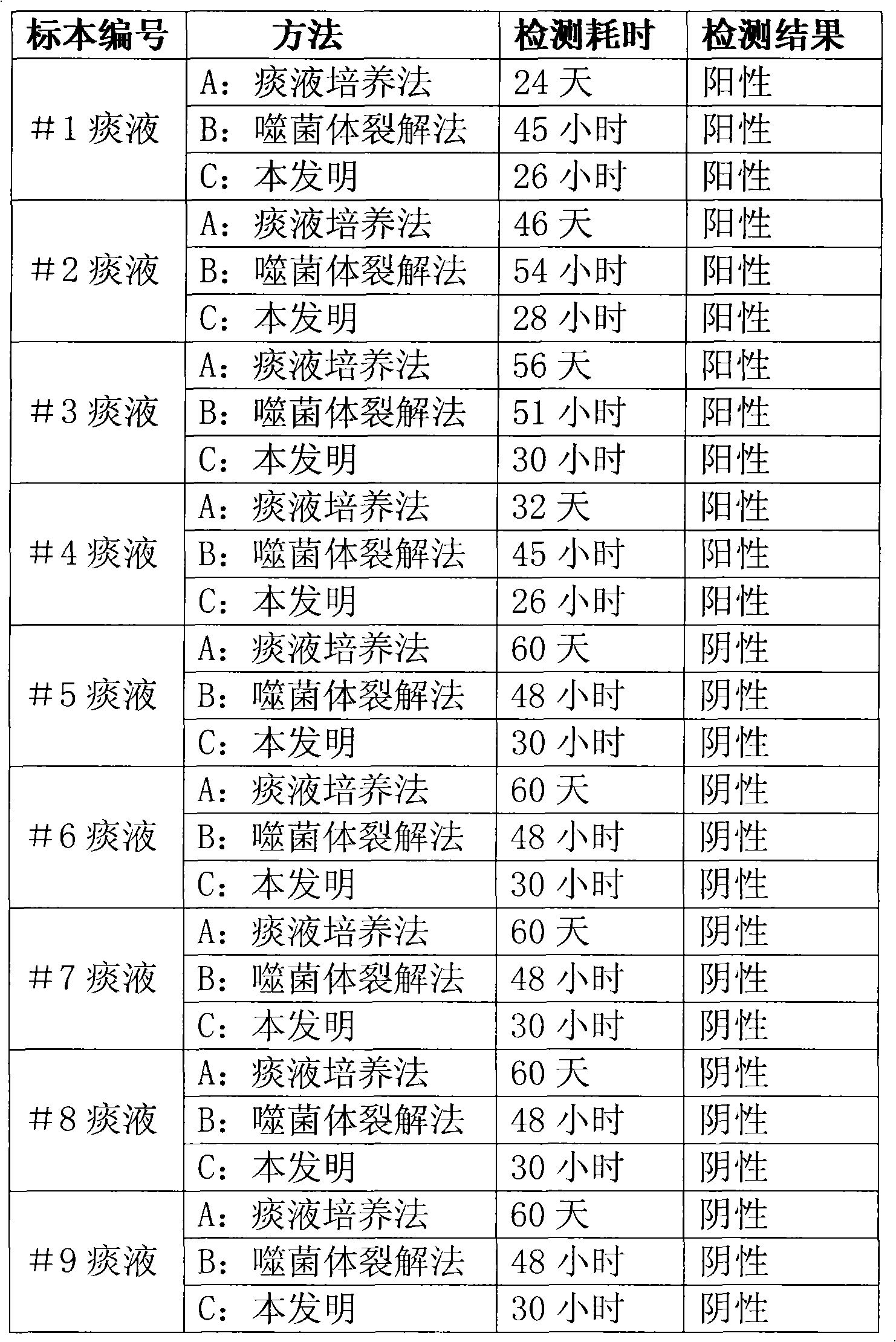
The invention discloses a method for quickly detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis, which comprises the following steps: 1, infecting phage with the mycobacterium tuberculosis; 2, killing the phage notinfecting outside the mycobacterium tuberculosis; 3, amplifying the infecting phage; and 4, after labeling gold with antiphage antibody, adopting quick immunochromatography to detect whether the phage exists or not so as to judge whether the mycobacterium tuberculosis exists in a sample. In addition, the invention also discloses a corresponding kit, which comprises sample treating fluid, proliferous liquid, a killing agent, mycobacterium smegmatis, mycobacteriophages and a phage colloidal gold method immunity-chromatography test pen. The method and the kit can quickly and accurately detect the mycobacterium tuberculosis so as to meet the requirement of quickly diagnosing pulmonary tuberculosis and timely medicate the patient.
Owner:ABBOTT DIAGNOSTICS (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Site-specific serine recombinases and methods of their use
The present invention provides a method for obtaining site-specific recombination in a eukaryotic cell, the method comprising providing a eukaryotic cell that comprises a first recombination attachment site and a second recombination attachment site; contacting the first and second recombination attachment sites with a prokaryotic recombinase polypeptide, resulting in recombination between the recombination attachment sites, wherein the recombinase polypeptide can mediate recombination between the first and second recombination attachment sites, the first recombination attachment site is a phage genomic recombination attachment site (attP) or a bacterial genomic recombination attachment site (attB), the second recombination site is attB or attP, and the recombinase is selected from the group consisting of a Listeria monocytogenes phage recombinase, a Streptococcus pyogenes phage recombinase, a Bacillus subtilis phage recombinase, a Mycobacterium tuberculosis phage recombinase and a Mycobacterium smegmatis phage recombinase, provided that when the first recombination attachment site is attB, the second recombination attachment site is attP and when the first recombination attachment site is attP, the second recombination attachment site is attB. The invention also describes compositions, vectors, and methods of use thereof, for the generation of transgenic cells, tissues, plants, and animals. The compositions, vectors and methods of the present invention are also useful in gene therapy applications.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
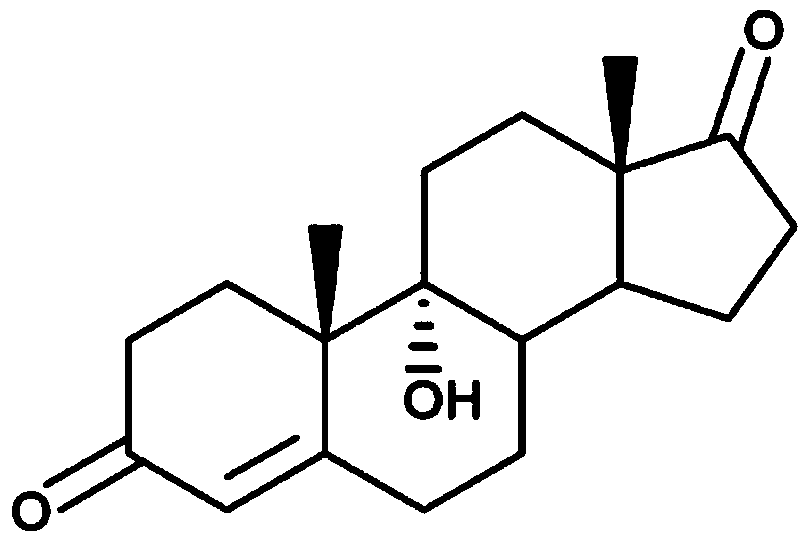
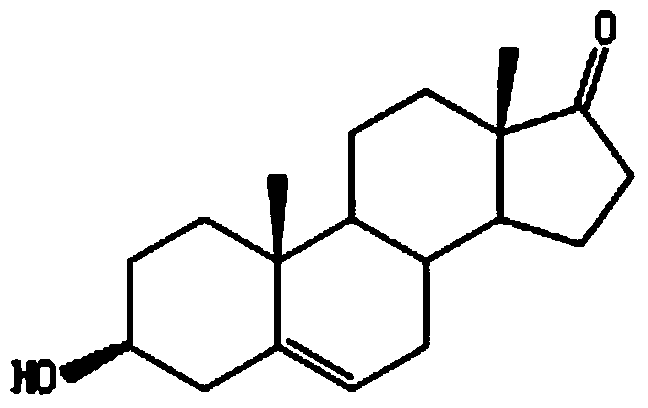
Method for producing 9-alpha-hydroxyandrostenedione by microbial fermentation
InactiveCN104232722AImprove conversion rateHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention provides a method for producing 9-alpha-hydroxyandrostenedione by microbial fermentation. Recombinant Mycobacterium smegmatis is fermented to convert phytosterin to produce the 9-alpha-hydroxyandrostenedione. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a recombinant expression vector pMV261-ksh; constructing a recombinant strain; and carrying out culture propagation and fermentation conversion. Gene engineering means are utilized to obtain the gene engineering strain for overexpressing 3-sterone-9-alpha-hydroxylase gene (ksh); after the strain is fermented for 120 hours, the conversion rate of the phytosterin is up to 95% above; and the method has the characteristics of high yield, fewer byproducts, short fermentation time simple extraction, small pollution, low pressure for environmental protection and the like, and has huge advantages in industrial production.
Owner:宋浩雷
Process and composition for inhibiting growth of microorganisms
ActiveUS7214392B2Prolong storage and shelf lifeAvoid pollutionCosmetic preparationsBiocideBacteroidesCinnamomum zeylanicum
A natural preservative composition obtained from plant materials provides antimicrobial activity for various compositions such as a food composition. The antimicrobial agent is effective in inhibiting the growth of gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus, gram-negative Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, acid-fast bacterium Mycobacterium smegmatis, the yeast Candida albicans. The antimicrobial agent has a MIC of 3.0 μl / ml capable of inhibiting these organisms. The antimicrobial agent includes mixtures of Origanum vulgare L., Thymus vulgaris L., Cinnamomum zeylanicum Nees, Rosmarinum officinalis L., Lavandula officinalis L., Hydrastis canadensis L. and olive leaf extract. The antimicrobial agent is an effective natural alternative to commonly used synthetic ingredients for product preservation.
Owner:BIO BOTANICA
Therapeutic vaccine for malignant tumors and composition thereof
The invention relates to a therapeutic vaccine for malignant tumors and a composition thereof. The therapeutic vaccine for malignant tumors is a tumor cell line which contains plasmid of antisense nucleic acid of human transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta2); the therapeutic vaccine composition for malignant tumors comprises the therapeutic vaccine for malignant tumors and an immunopotentiator, and the immunopotentiator is one selected from the group consisting of a Corynebacterium parvum preparation, a non-cell Corynebacterium parvum preparation, a BCG polysaccharide, a nucleic acid preparation, a Nocardia rubra-cell wall skeleton preparation, a group A Streptococcus preparation, a non-cell group A Streptococcus preparation, a Pseudomonas aeruginosa preparation, a non-cell Pseudomonas aeruginosa preparation, a Brucella preparation, a non-cell Brucella preparation, a non-cell Mycobacterium vaccae preparation and a non-cell Mycobacterium smegmatis preparation, preferably the non-cell Corynebacterium parvum preparation; and the malignant tumors include a lung cancer, a liver cancer, a pancreatic cancer, leukemia, lymphoma, an ovarian cancer, a colon cancer, a stomach cancer and a breast cancer.
Owner:熊慧
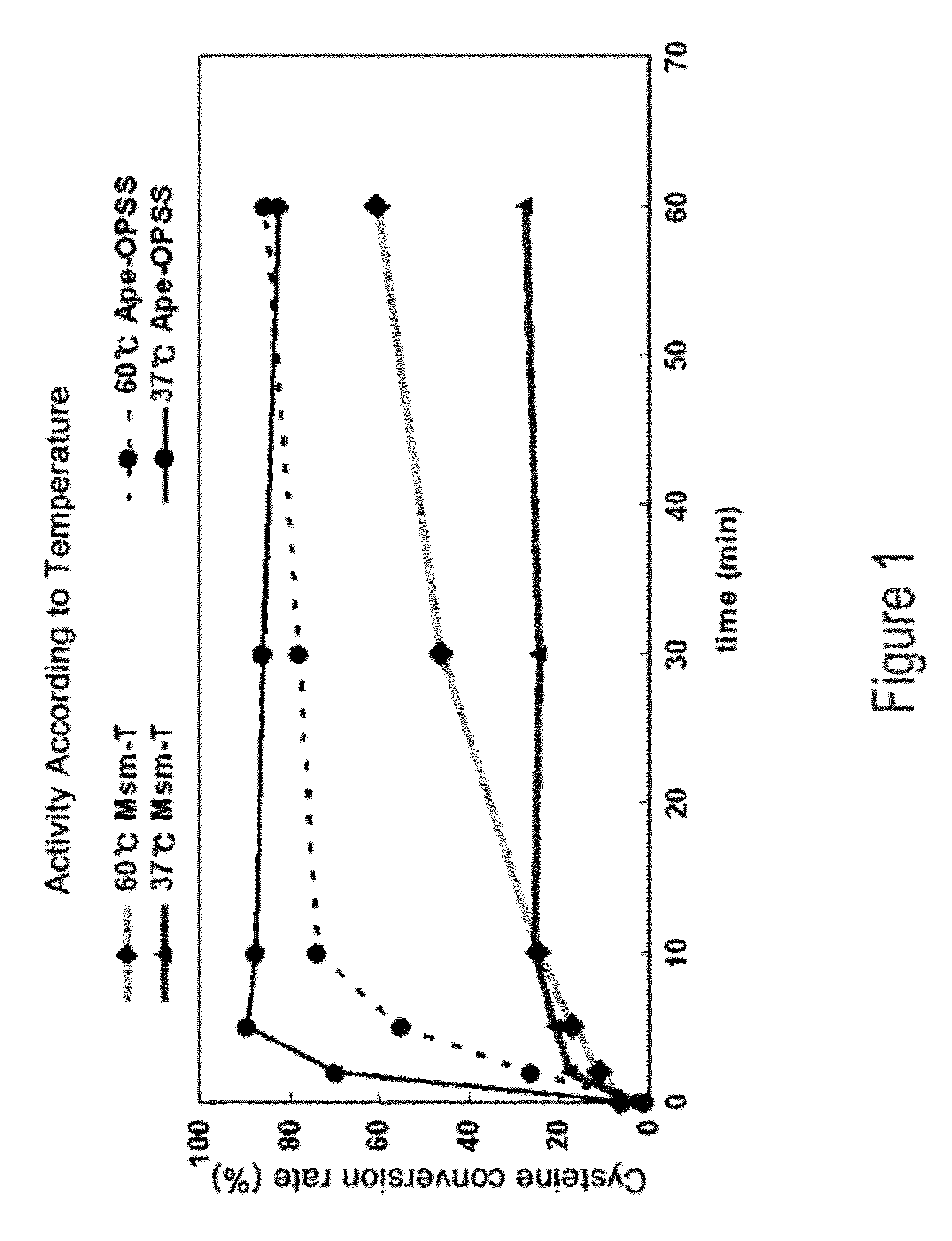
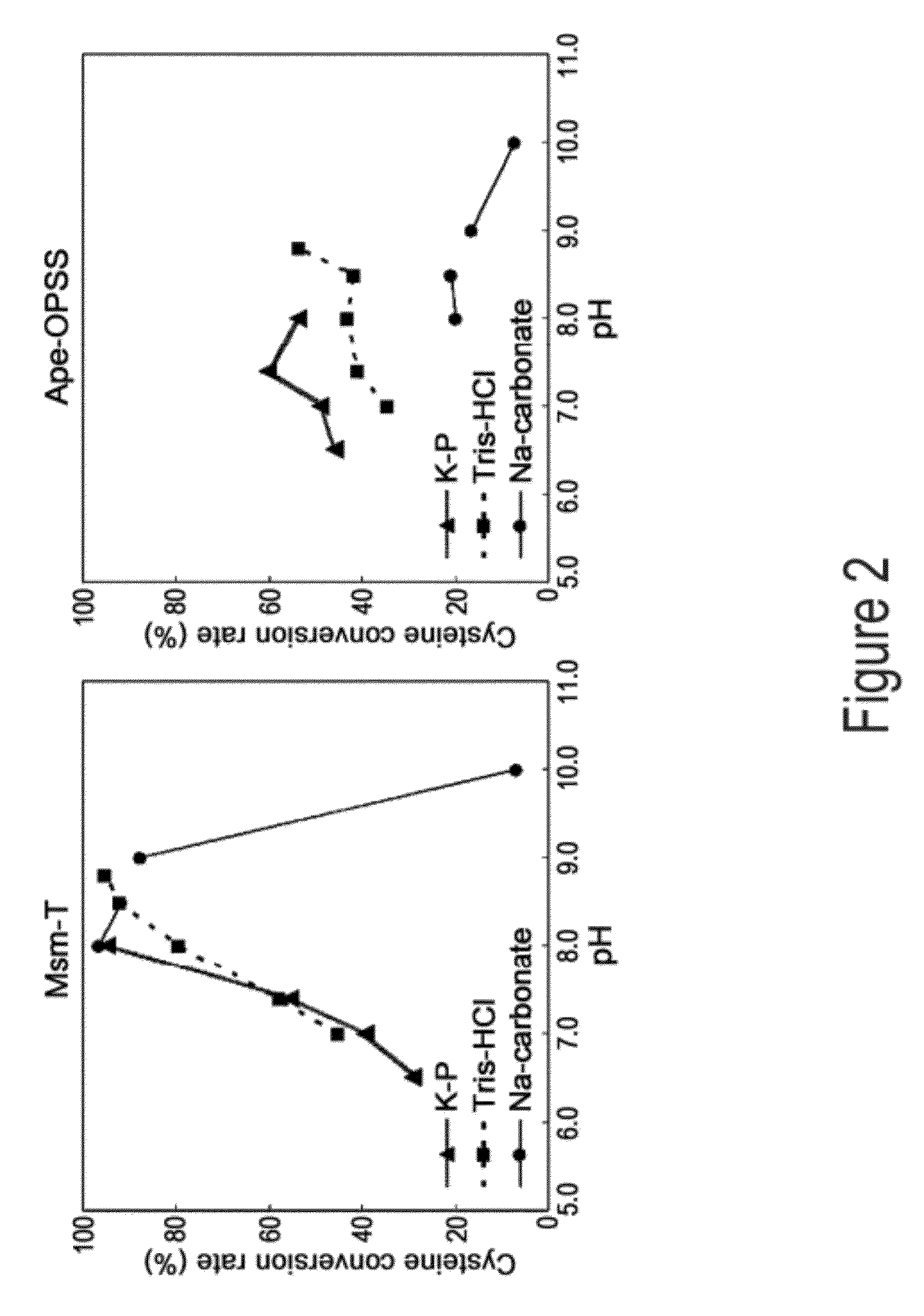
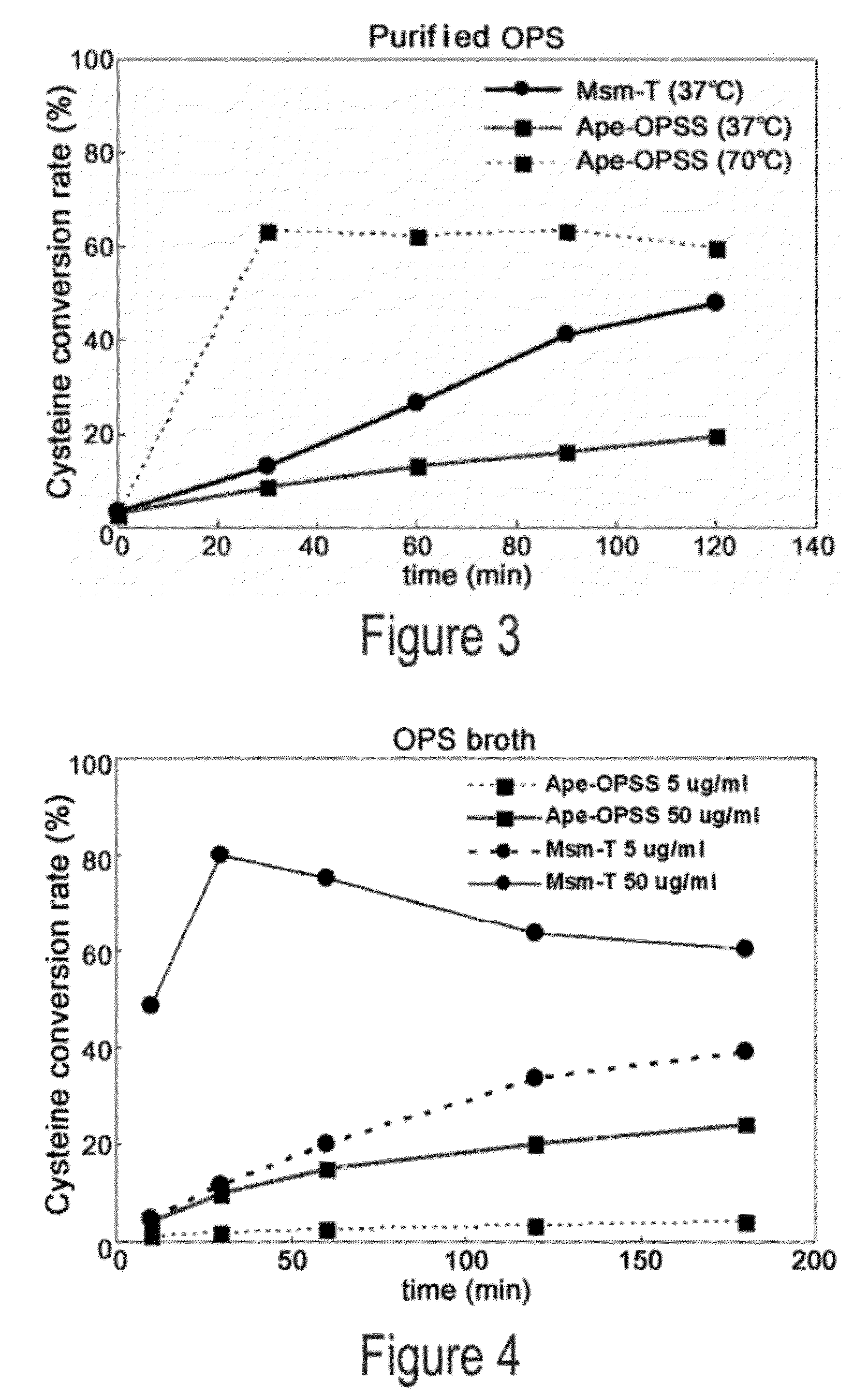
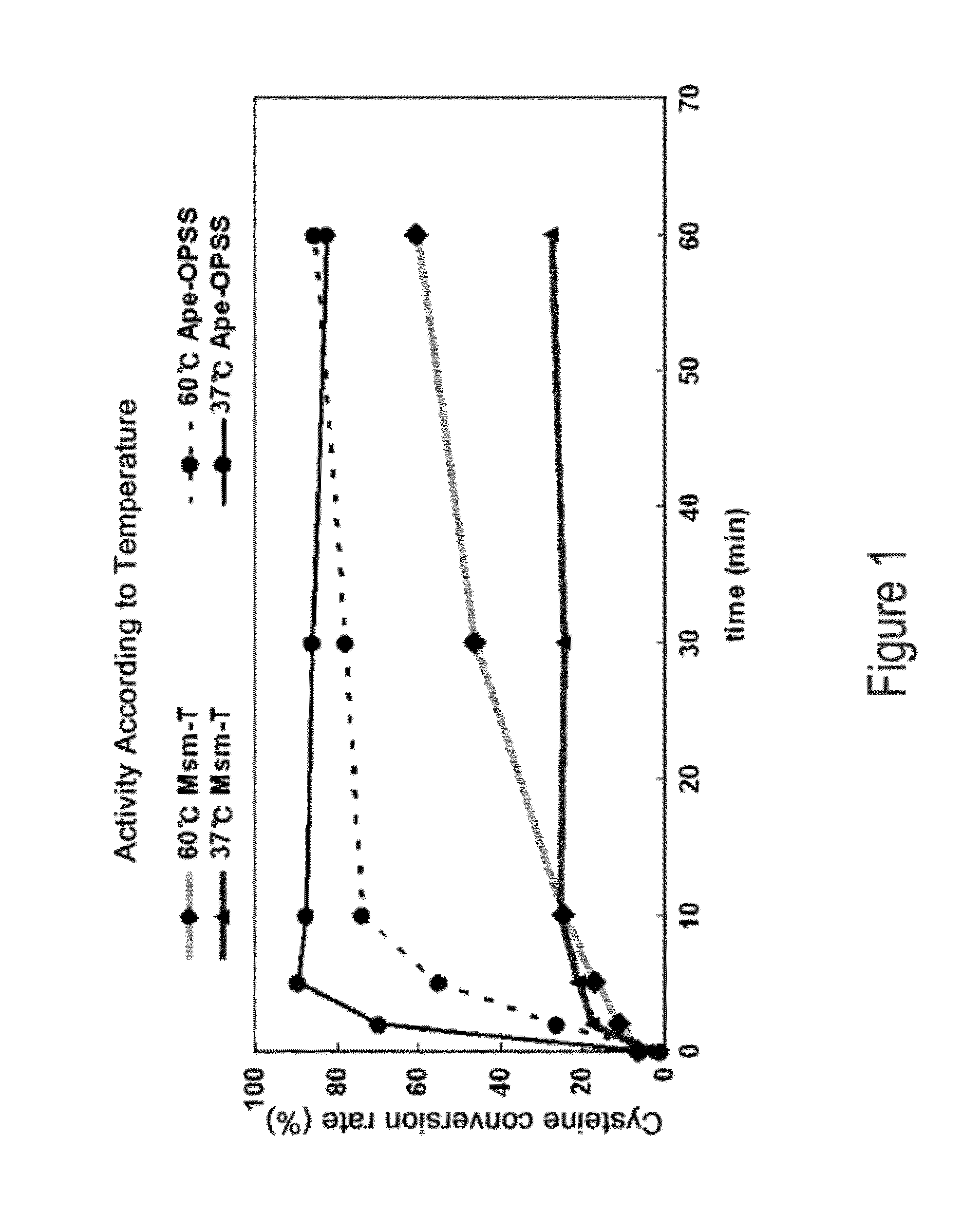
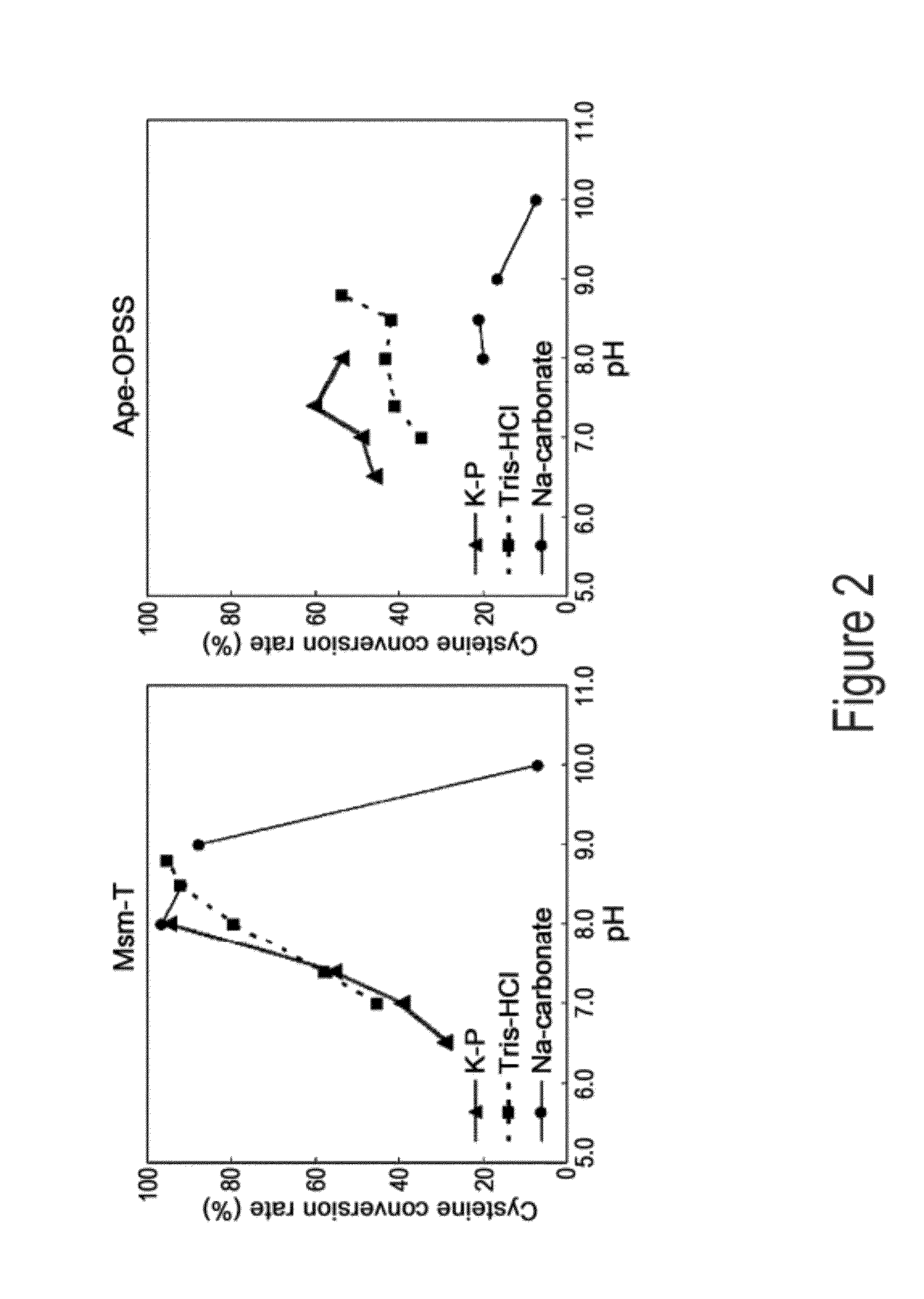
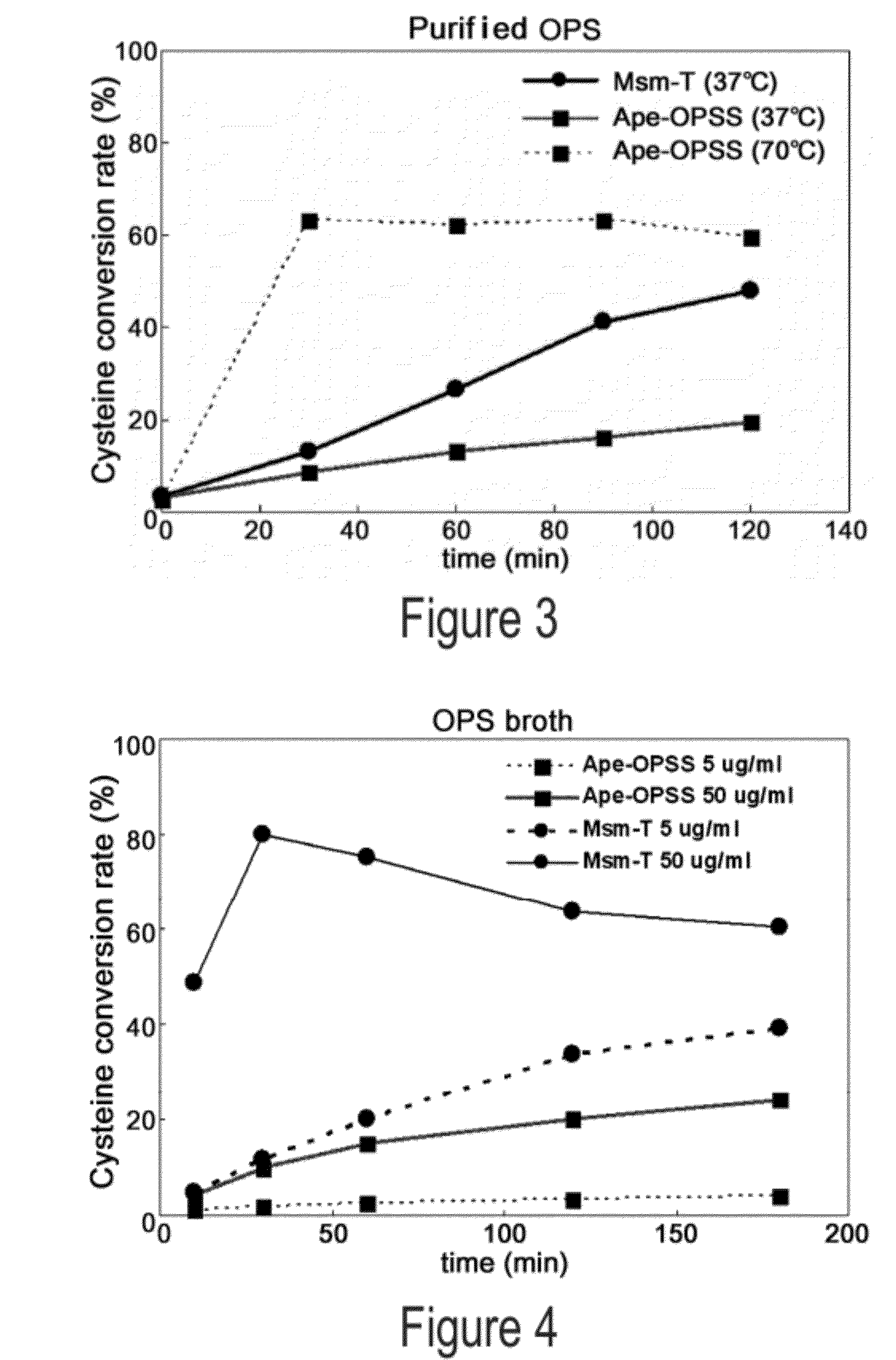
O-phosphoserine sulfhydrylase mutants and method for production of cysteine using the same
ActiveUS9127324B2Improve enzymatic activityHigh yieldSugar derivativesBacteriaMycobacterium smegmatisO-phosphoserine sulfhydrylase
Disclosed is an O-phosphoserine sulfhydrylase (OPSS) mutant which has a Mycobacterium smegmatis-derived amino acid sequence corresponding to that of SEQ ID NO: 1 which is devoid of three to seven C-terminal amino acid residues. Also, a nucleic acid molecule encoding the OPSS mutant, an expression vector carrying the nucleic acid molecule, and a transformant transformed with the expression vector are disclosed. In addition, a method is provided for producing cysteine in which O-phospho-L-serine (OPS) is reacted with a sulfide in the presence of the OPSS mutant. The OPSS mutant has improved enzymatic activity and can be applied to the environmentally friendly production of L-cysteine through a simple enzymatic conversion reaction.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Co-expression system and construction method of polyvalent bacteriophage lyase genes, live vaccine of carrying system and preparation and application of live vaccine
InactiveCN104673821AEnables cheap scalingNo autolysisAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsMycobacterium smegmatisLatent tuberculosis
The invention discloses a co-expression system and construction method of polyvalent bacteriophage lyase genes, a live vaccine of a carrying system and preparation and application of the live vaccine. Eukaryotic expression plasmids are used as an expression vector, and LysinA, LysinB and Holin gene segments are directionally inserted into the plasmids to simultaneously express the co-expression system of the bacteriophage lyase genes of three kinds of targeted mycobacterium tuberculosis. Mycobacterium smegmatis with good targeting property of macrophages or genetically-modified recombinant BCG is used as a live vector, the co-expression system simultaneously carrying three kinds of genes is electrically transformed into the mycobacterium smegmatis or the genetically-modified recombinant BCG, and then the recombinant therapeutic tuberculosis live vaccine is obtained through expansion in vitro. The live vaccine has a good effect on the field of curing active tuberculosis or latent tuberculosis infection caused by proliferative mycobacterium tuberculosis, dormant mycobacterium tuberculosis and drug-resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Owner:伊正君
Method for producing dehydroepiandrosterone through microbial fermentation
InactiveCN104232673AReduce manufacturing costImprove product quality yieldMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyMycobacterium smegmatis
The invention provides a method for producing dehydroepiandrosterone through microbial fermentation. The method can be used for producing dehydroepiandrosterone by transforming phytosterol by utilizing the single water phase fermentation of recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis and comprises the following steps of: constructing knockout original 5228up-kan-5228down; constructing a recombinant strain; propagating the strain, and fermenting and transforming. According to the method provided by the invention, the recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis is obtained by knocking out a 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase encoding gene MSMEG_5228 by utilizing a molecular biology method and dehydroepiandrosterone is produced in a single water phase fermentation system by taking phytosterin as a raw material. The method reduces the production cost, achieves the mass yield of dehydroepiandrosterone more than 90%, simplifies the extraction process, reduces the extraction cost and has the advantages of little pollution, low environmental-friendly pressure and great industrial production superiority.
Owner:宋浩雷
Mycobacteria Expressing Hiv-1 and Malaria Antigens
Provided are recombinant mycobacteria expressing an HIV-1 antigen and a malarial antigen. Also provided are Mycobacterium smegmatis expressing an HIV-1 antigen. Further provided are vaccines capable of inducing an immune response in a mammal against HIV-1 and the malarial pathogen. Additionally provided are methods of inducing an immune response in a mammal against HIV-1 and a malarial pathogen. Also provided are methods of inducing an immune response in a mammal against HIV-1. The methods comprise infecting the mammal with any of the above-described mycobacteria.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +2
Vaccine for blocking transmission of echinococcosis pathogeny echinococcus granulosus from source
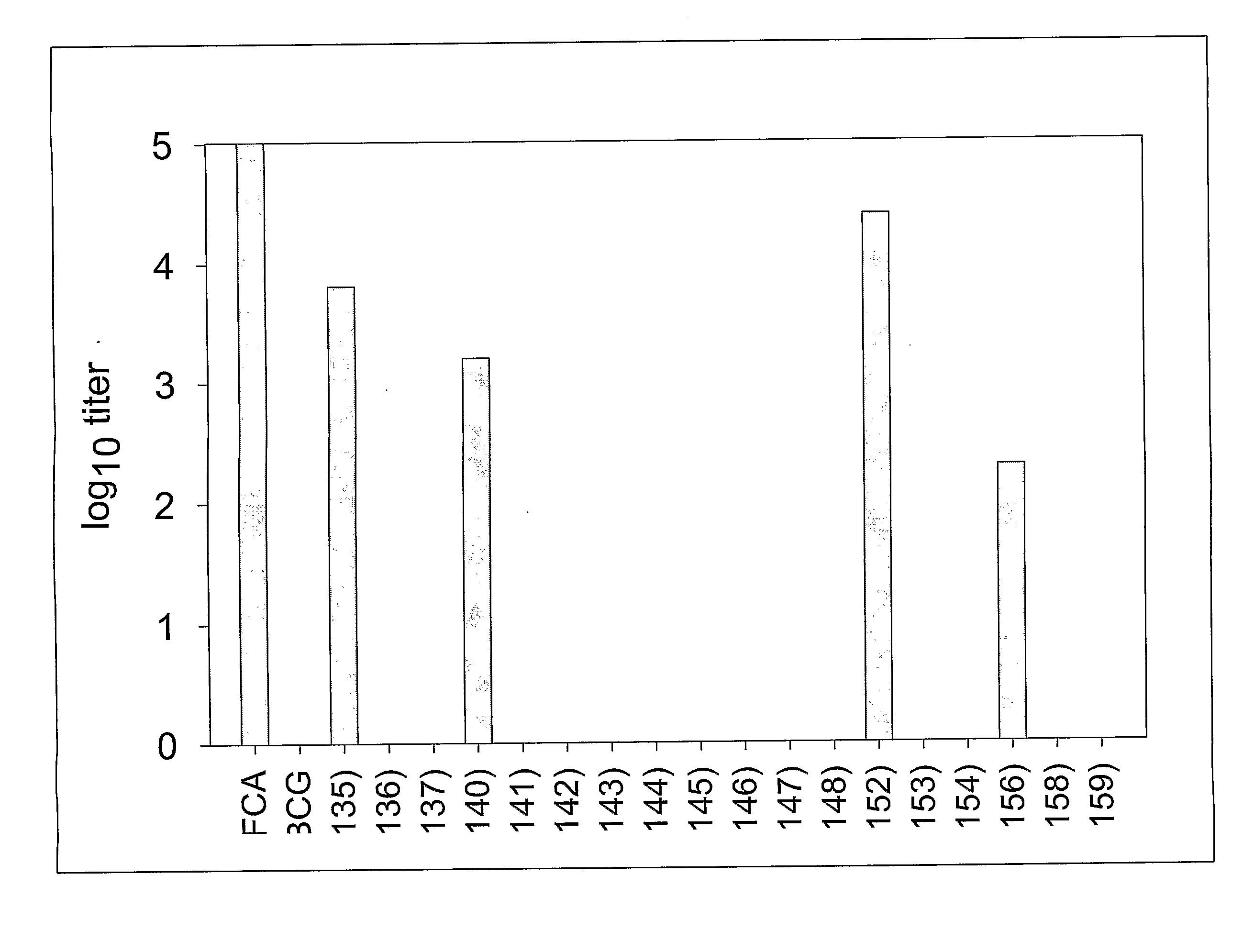
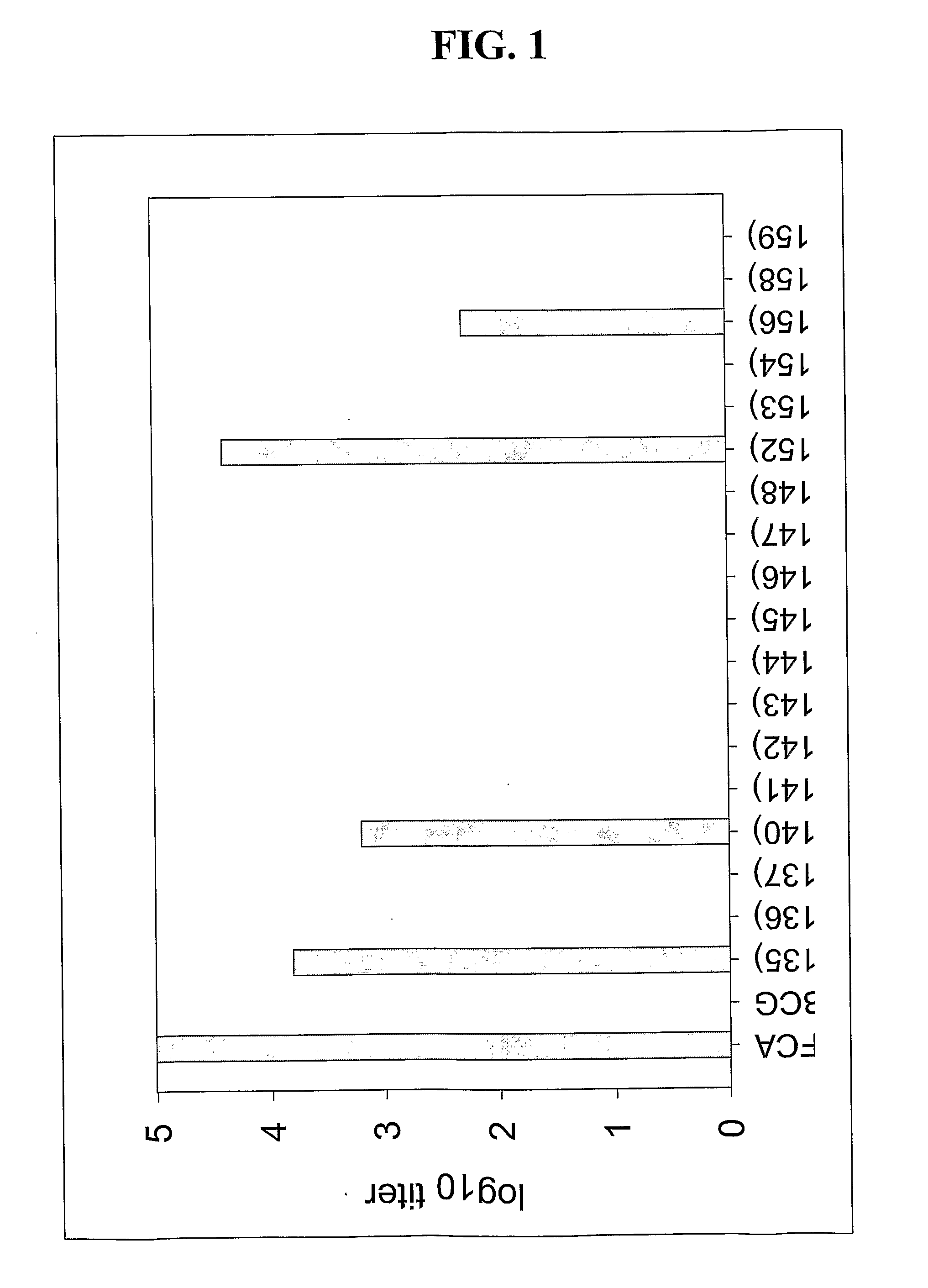
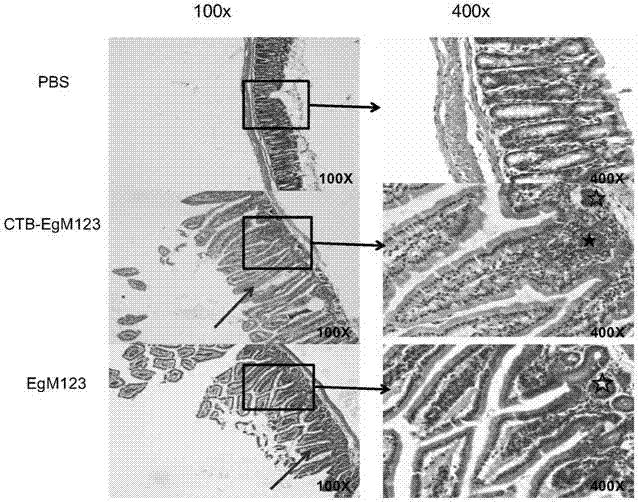
ActiveCN107510841AIncreased serum titerImprove immunityBacterial antigen ingredientsProtozoa antigen ingredientsMucosal Immune ResponsesMycobacterium smegmatis
The invention discloses a vaccine for blocking transmission of echinococcosis pathogeny echinococcus granulosus from a source. The vaccine provided by the invention is a CTB-EgM123 vaccine or a complete set of vaccine consisting of the CTB-EgM123 vaccine and a subunit vaccine of an EgM123 protein recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis vaccine. An active ingredient of the CTB-EgM123 vaccine is a fusion protein formed by fusion of a cholera toxin B subunit and an echinococcus granulosus EgM123 protein; the active ingredient of the EgM123 protein recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis vaccine can express the recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis of the echinococcus granulosus EgM123 protein. The vaccine provided by the invention can stimulate the immune response in a host, improves the immune level of the host, enhances the intestinal mucosal immune response, and plays an important protective role in resisting infection of echinococcosis.
Owner:THE FIRST TEACHING HOSPITAL OF XINJIANG MEDICAL UNIVERCITY +1
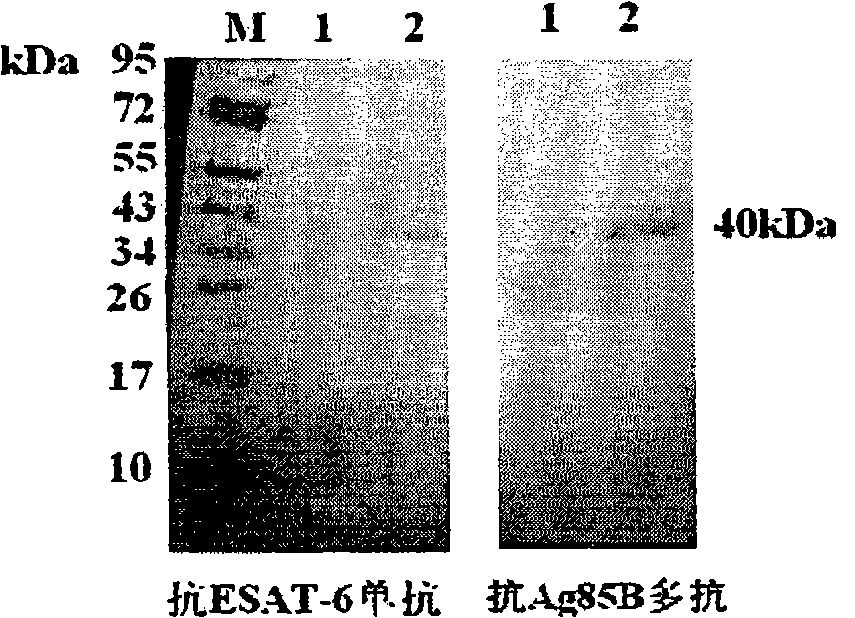
Recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis strain capable of expressing mycobacterium tuberculosis Ag 85B and ESAT-6 fusion protein and application thereof
InactiveCN101875913AStrong immune responseGood immune protectionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsMycobacterium smegmatisEukaryotic plasmids
The invention relates to a recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis strain capable of expressing mycobacterium tuberculosis Ag 85B and ESAT-6 fusion proteins and application thereof. Recombinant plasmids containing the Ag 85B and ESAT-6 fusion protein genes are turned into mycobacterium smegmatis (AE-MS for short) through electrotransformation, and the preservation serial number thereof is CCTCC M2010097. When used for immunizing mice, the recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis strain AE-MS obtained through screening can induce the immune response level which is stronger than that of the mycobacterium smegmatis. The invention also relates to the application of the structured mycobacterium smegmatis strain to the preparation of preparations or medicaments used for preventing and treating tuberculosis. The recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis expressing the Ag 85B and ESAT-6 fusion genes integrates the advantages of target antigens and live carriers; and after immunization, the recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis can increase the immune protection of an organism by simulating the stronger immune response of the organism, thereby having good prospect of application.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Mycobacteria expressing HIV-1 and malaria antigens
Provided are recombinant mycobacteria expressing an HIV-1 antigen and a malarial antigen. Also provided are Mycobacterium smegmatis expressing an HIV-1 antigen. Further provided are vaccines capable of inducing an immune response in a mammal against HIV-1 and the malarial pathogen. Additionally provided are methods of inducing an immune response in a mammal against HIV-1 and a malarial pathogen. Also provided are methods of inducing an immune response in a mammal against HIV-1. The methods comprise infecting the mammal with any of the above-described mycobacteria.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +2
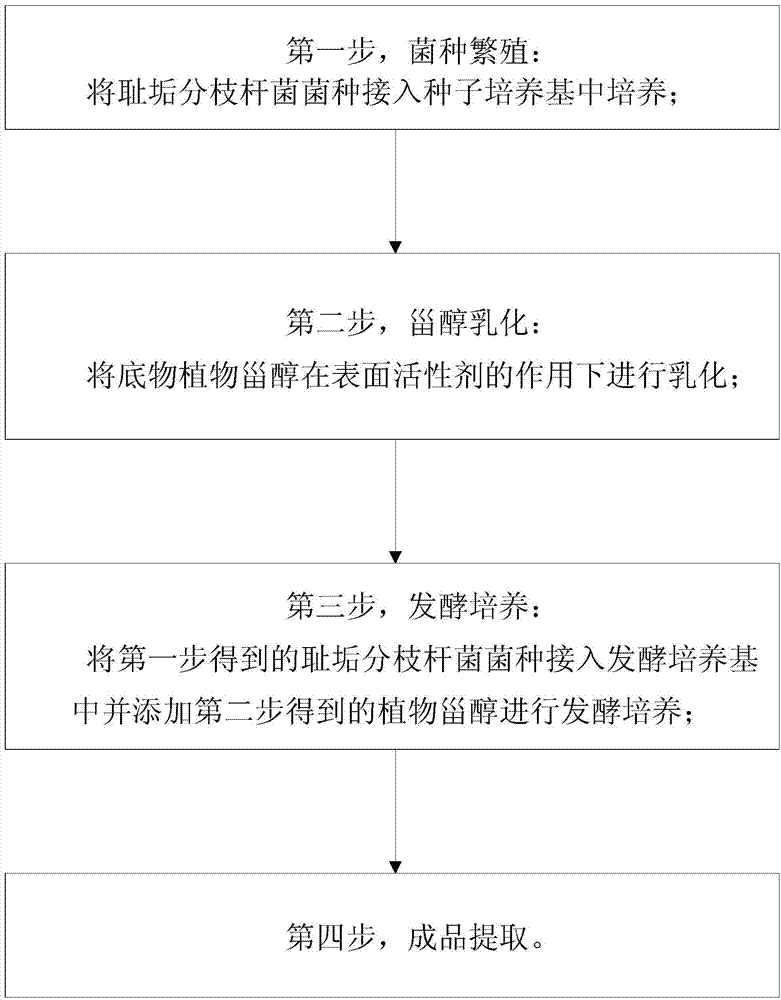
Method of preparing 4-androstenedione by fermentatively degrading phytosterol by virtue of single water phase system
InactiveCN103923966AIncrease profitReduce typesMicroorganism based processesFermentationSterolMycobacterium smegmatis
The invention provides a method of preparing 4-androstenedione by fermentatively degrading phytosterol by virtue of a single water phase system. The method comprises the following step: 1, strain cultivation, namely inoculating a mycobacterium smegmatis stain into a seed medium and cultivating; 2, sterol emulsification, namely emulsifying the phytosterol as a substrate under the action of a surfactant; 3, fermentation cultivation, namely inoculating the mycobacterium smegmatis stain obtained in the first step in a fermentation medium, adding the phytosterol obtained in the second step and carrying out fermentation cultivation; 4, finished product extraction. According to the method of preparing the 4-androstenedione by fermentatively degrading the phytosterol by virtue of the single water phase system, an emulsifier is added, so that the yield of 4-androstenedione is increased, and the extraction technology of the 4-androstenedione is also simplified; the cost is low, the pollution is little, and the environmental protection pressure is weak.
Owner:HEBEI ZHONGSHENG BIOTECH
New application of naphthoquine phosphate
The invention discloses a new application of naphthoquine phosphate and application of the naphthoquine phosphate in preparation of an antibacterial drug. The naphthoquine phosphate has the action of inhibiting hormodendrum compactum, hormodendrum dermatitidis, fonsecaea pedrosoi, microsporum gypseum, stellate thyton mentagrophytes, trichophyton verrucosum, microsporum canis, colon bacillus, staphylococcus albus, ataphylococcus aureus, mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.tuberculosis), mycobacterium smegmatis and staphylococcus epidermidis, has remarkable therapeutic effect on infection of the ataphylococcus aureus, the mycobacterium tuberculosis and trichophyton and is a very potential broad-spectrum antibacterial compound. With the antifungal action and the actions of a common pathogen of the naphthoquine phosphate, a novel broad-spectrum antibiotic drug with the action of resisting the common pathogen and the antifungal action is provided to people.
Owner:KPC PHARM INC
Genetically engineered strain for producing ergothioneine and application
ActiveCN112251392AShort fermentation cycleClear genetic backgroundBacteriaStable introduction of DNAEscherichia coliMycobacterium smegmatis
The invention provides a genetically engineered strain for high yield of ergothioneine and application. The stain takes escherichia coli as a host, and a coding gene hisG* of a corynebacterium glutamicum ATP phosphoribosyl transferase HisG mutant is integrated on a genome of the host; the copy number of a histidine operon gene hisDBCHAFI is further increased on the genome of the host; a mycobacterium smegmatis ergothioneine operon gene egtBCDE is further integrated on the genome of the host; an Escherichia coli glutamylcysteine ligase encoding gene gshA is integrated on the genome of the host,so that the synthesis of the ergothioneine is promoted; a neurospora crassa C-S lyase coding gene egtE<ncr> is further integrated on the genome of the host, so that the synthesis of ergothioneine isfurther promoted; and a gene egtB*<msm> of a sulfoxide synthase mutant is integrated on a genome of the host, so that synthesis of ergothioneine is further promoted.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
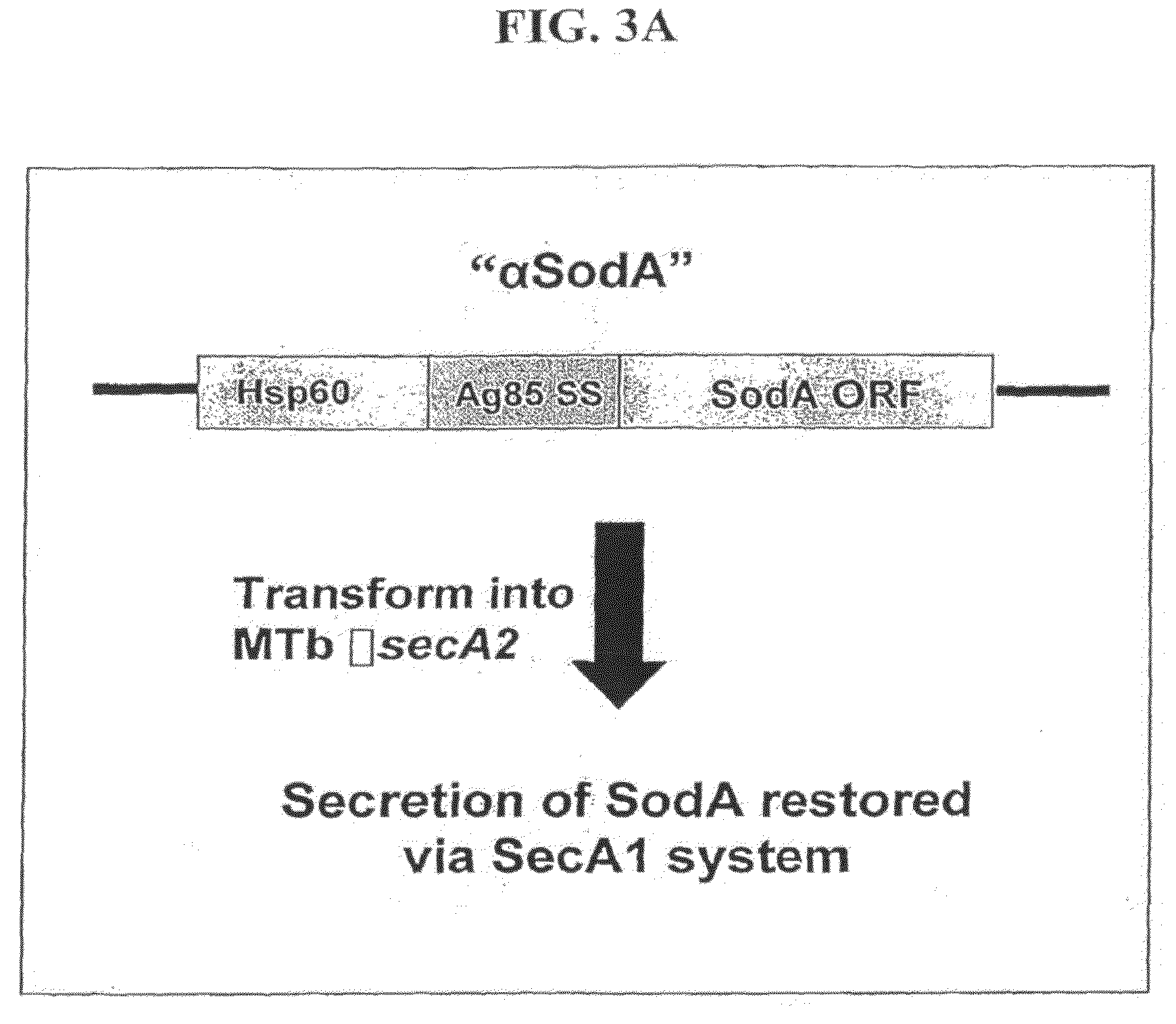
Mycobacterial SecA2 Mutants
ActiveUS20090110696A1Inhibit apoptosisImprove abilitiesAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsVirulent characteristicsMammal
Provided are mycobacteria comprising (a) a mutation that is not in a SecA2 gene that attenuates the virulence of the mycobacteria in a mammalian host, and (b) a mutation in a SecA2 gene that eliminates SecA2 activity. Also provided are mycobacteria that comprise a mutation in a SecA2 gene that eliminates SecA2 activity, where the mycobacteria are not Mycobacterium tuberculosis or Mycobacterium smegmatis. Additionally provided are methods of inducing an immune response in a mammal and methods of inducing an immune response to a pathogenic mycobacterium in a human using the above mycobacterial mutants.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV +2
Trehalose synthase mutant and gene thereof
ActiveCN106434586AIncrease enzyme activityGenetic engineeringFermentationMycobacterium smegmatisTrehalose synthase
The invention discloses a trehalose synthase mutant and a gene thereof. The enzyme is formed through mutation of mycobacterium smegmatis trehalose synthase. Particularly, amino acids at the 167th site, the 169th site, the 174th site, the 175th site and the 176th site of the emzyme are mutated into alanine, wherein the alanine mutated from the amino acids at the 169th site is freely selected to be combined with the alanine mutated from the amino acids at the 167th site, the 174th site, the 175th site and the 176th site. After mutation, compared with a wild type enzyme, enzyme activity is improved by 2.56 times at most.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH +1
glmm gene knock-out bacterial strain as well as preparation method and application in sieving mycobacterium tuberculosis phosphoglucomutase inhibitors
InactiveCN101928691AIntegrity breachImprove efficacyBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman bodyMycobacterium smegmatis
The invention discloses a glmM gene knock-out bacterial strain ML2009 (mycobacterium smegmatis), CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) 3418, which is constructed by using phosphoglucomutase participating in the biosynthesis of key components in a mycobacterium tuberculosis cell wall. The bacterial strain ML2009 can be used as a cell model for sieving phosphoglucomutase inhibitors with high flux, be used for sieving effective phosphoglucomutase inhibitors from a combined compound library, traditional Chinese medicine and natural products to prepare tuberculosis-resisting medicaments with high medicine effects; and in addition, in the cells of a human body, the synthesis approach of UDP (Uridine Diphosphate)-acetyl glucosamine is different from that of mycobacterium tuberculosis, no phosphoglucomutase exists in the UDP-acetyl glucosamine, therefore, the reaction catalyzed by the mycobacterium tuberculosis phosphoglucomutase does not exist in the cells of the human body so that the tuberculosis-resisting medicaments developed by using the phosphoglucomutase as a target enzyme are harmless to the human body, and the defect that the traditional antibacterial medicament also kill normal cells is overcome.
Owner:DALIAN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
P-aminosalicylic acid fluoroquinolone derivative as well as intermediate, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112159355ANovel structureHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsBiocidePichia pastorisAntifungal
The invention discloses a p-aminosalicylic acid fluoroquinolone derivative and an intermediate, a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of drug synthesis. Thestructural formula of the p-aminosalicylic acid fluoroquinolone derivative is shown in the specification. In-vitro activity determination results show that part of fluoroquinolone aminosalicylate derivatives (compounds for short) and intermediates have inhibition effects on mycobacterium smegmatis; the compounds and intermediates have good inhibition activity on common pathogenic bacteria as a whole; most compounds and intermediates have better antibacterial activity on pichia pastoris as a whole; part of the compounds have good inhibitory activity on citrus canker pathogens. The p-aminosalicylic acid fluoroquinolone derivative and the intermediate thereof have potential application prospects in the fields of tuberculosis resistance, bacteria resistance, fungus resistance and citrus pathogen resistance.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Recombinant expression vector of Hsp65-hIL-2 fusion expression and recombinant strain
InactiveCN102174555AEnhance killing activityStable secretionAntibacterial agentsBacteriaEscherichia coliAdjuvant
The invention discloses a recombinant expression vector of Hsp65-hIL-2 fusion expression. An Hsp65-hIL-2 fusion gene is inserted into an escherichia coli-mycobacterium shuttle secreting expression vector, and the Hsp65-hIL-2 fusion gene is formed by connecting an Hsp65 gene and hIL-2 through an enzyme cutting site and a linker. According to a recombinant strain of Hsp65-hIL-2 fusion expression, mycobacterium smegmatis is used as a host cell, and an exogenous expression vector for transforming the host cell is the escherichia coli-mycobacterium shuttle secreting expression vector containing the Hsp65-hIL-2 fusion gene. The mycobacterium smegmatis Hsp65-hIL-2-MS recombinant strain centralizes the advantages of a target antigen, a cytokine adjuvant and a live vector; and the immune inoculated recombinant strain can stimulate the body to produce immune response comprising body fluid immunity level and cellular immunity level and improve the immune protection of the body.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
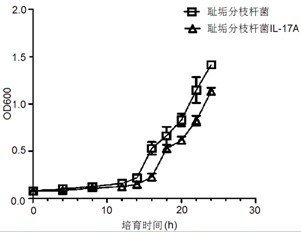
Mycobacterium smegmatis IL-17A and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102586161ADamage Prevention and ControlEnhanced effects of immune inflammatory injuryBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsEscherichia coliMycobacterium smegmatis
The invention relates to a mycobacterium smegmatis IL-17A and a preparation method thereof. An escherichia coli-mycobacteria shuttle expression vector for expressing an IL-17A gene is expressed in the mycobacterium smegmatis IL-17A; and a bacterial strain is preserved at Ordinary Microorganism Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 4446. The mycobacterium smegmatis IL-17A has the double effects of mycobacterium smegmatis and IL-17A, so that the effects of the recombined mycobacteria on promoting the nonspecific anti-infections immunity and restraining the allergen mediated airway immune inflammatory damage are remarkably enhanced, and particularly, the recombined mycobacteria can play important roles in preventing and controlling the asthma airway injury caused by allergic asthma or respiratory tract infection.
Owner:SHANGHAI SIXTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
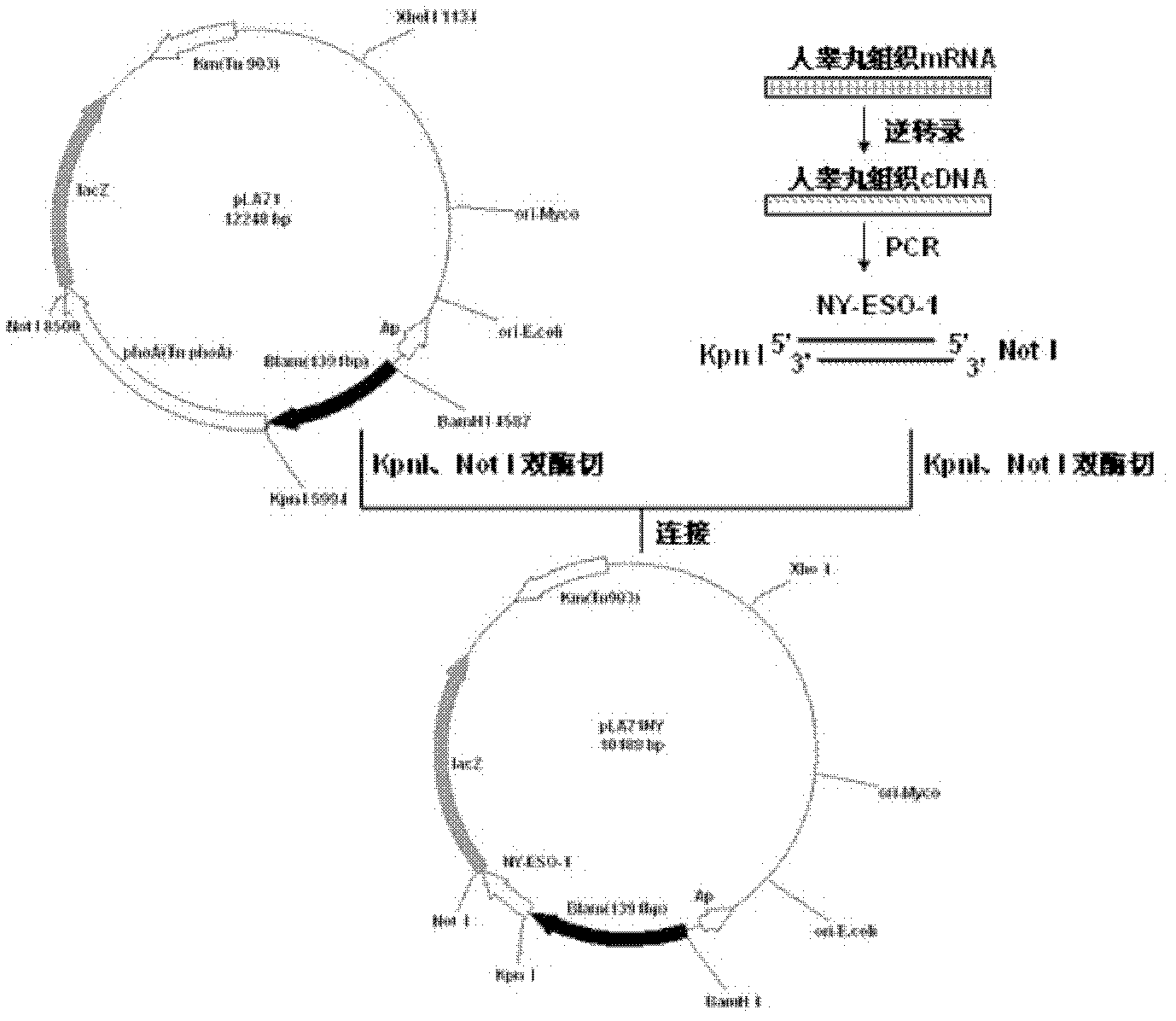
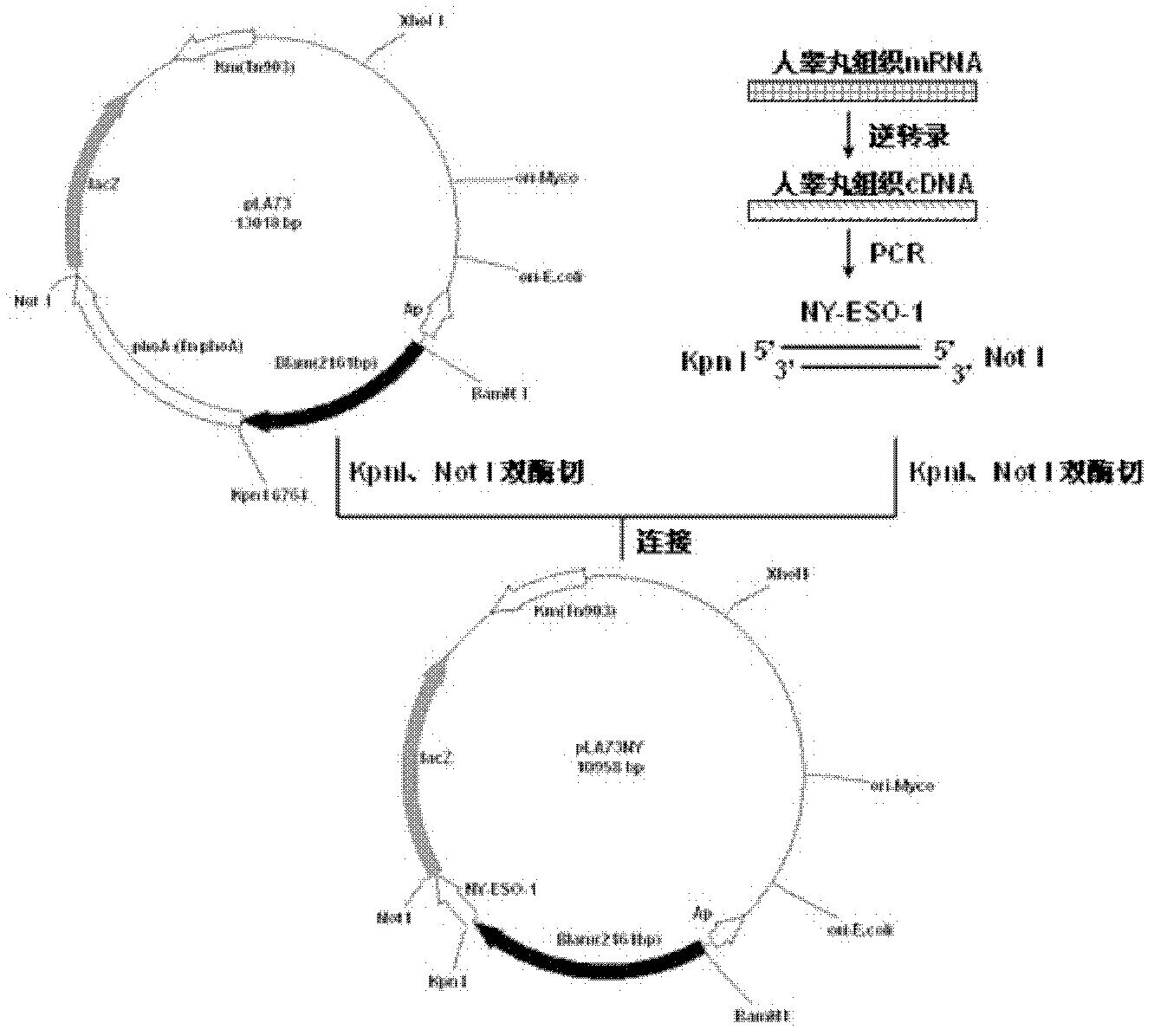
Preparation and application of recombinant Mycobacterium smegmatis expressing NY-ESO-1
InactiveCN102839186ASignificant lethal effectBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsMycobacterium smegmatisBeta-Galactosidases
The invention relates to preparation and application of recombinant Mycobacterium smegmatis expressing NY-ESO-1. Specifically, the invention provides a plasmid for expressing a recombinant cancer-testis antigen NY-ESO-1 protein; and the plasmid comprises a beta-galactosidase signal peptide coding sequence or a beta- galactosidase coding sequence, and an NY-ESO-1 coding sequence. The invention also provides a recombinant Mycobacterium smegmatis containing the plasmid provided by the invention and its composition, and application thereof. The recombinant Mycobacterium smegmatis provided by the invention has significant killing effect on tumor cells expressing NY-ESO-1; therefore the recombinant Mycobacterium smegmatis can be used in effective prevention and / or treatment of the tumors.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL PROD CO LTD
AIDS vaccine and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108823232AImprove immunityStimulate maturityBacteriaViral antigen ingredientsFeline immunodeficiency virusAntigen
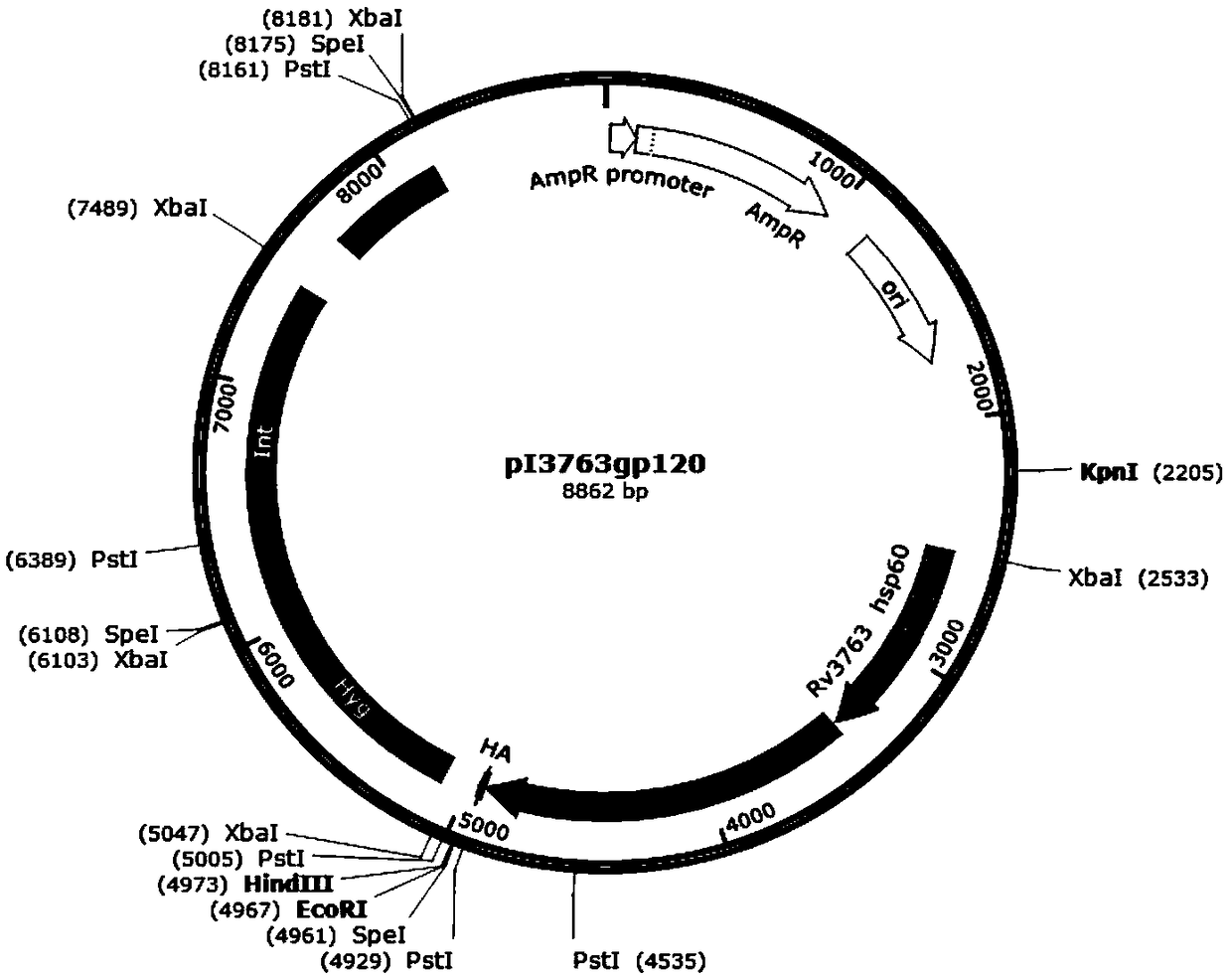
The invention discloses a recombinant plasmid. The recombinant plasmid contains a gp120 gene of the monkey immunodeficiency virus and at least one cell wall carrier protein gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The invention also discloses recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis which can stably express the gp120 gene of the monkey immunodeficiency virus and at least one cell wall carrier protein gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The invention also discloses an AIDS vaccine and a preparation method thereof. The AIDS vaccine contains the recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis, is easy to culture, grows fast and saves time, labor, material resources and financial resources. The vaccine comprising three strains of the recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis ZWY2 exhibiting the SIV gp120 antigen proteinon the surface can stably exhibit the SIV gp120 antigen protein on the surface of the mycobacterium smegmatis ZWY2 and has the immunological effect in C57 mice far superior to that of intracellular expression of the antigen protein gp120 and that of the already published AIDS vaccine exhibiting gp120 on the surface based on adenovirus vector construction.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Integrated recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis producing nicotinic acid and construction method thereof
ActiveCN108384739ASimple production conditionsNo pollution in the processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChemical synthesisMycobacterium smegmatis
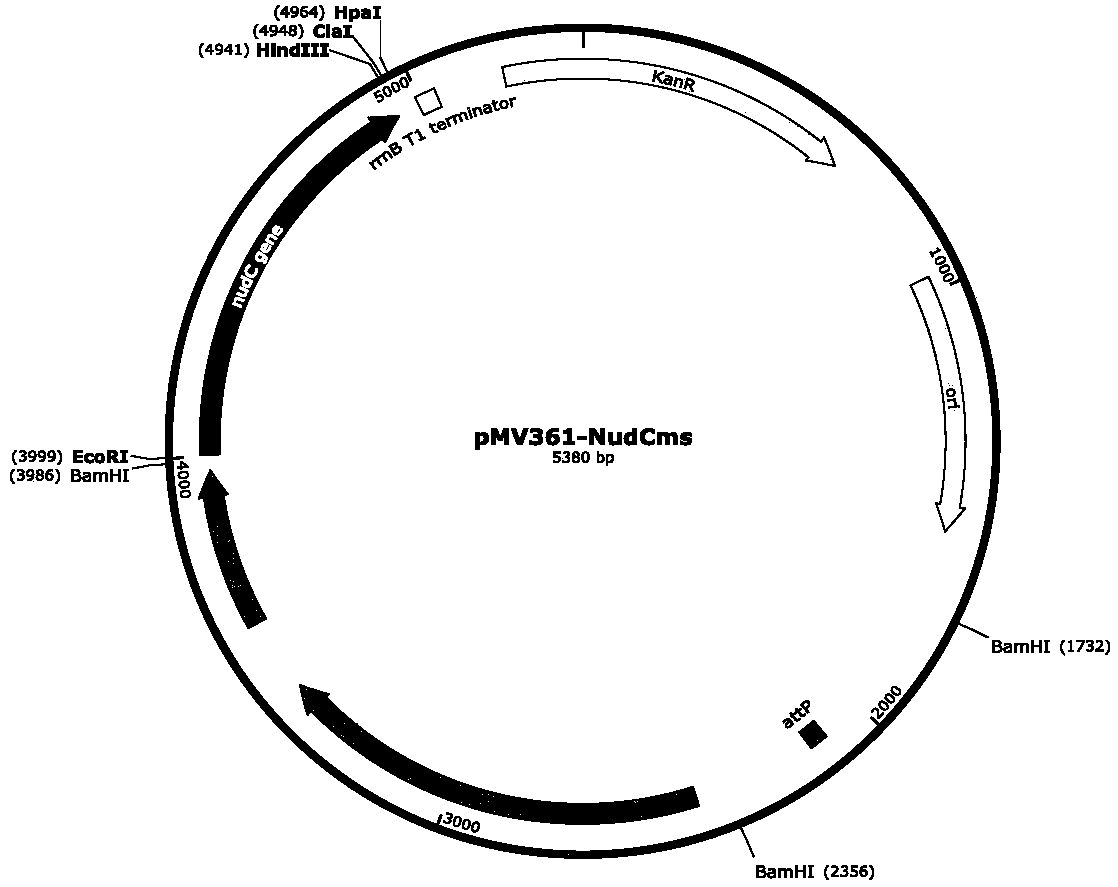
The invention discloses an integrated recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis producing nicotinic acid and a construction method thereof. The invention requires the protection of a recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis producing nicotinic acid, the recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis producing nicotinic acid is characterized in that the recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis contains recombinant integrative plasmid, which contains nudC gene, and the nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. Nicotinic acid can be directly obtained by one step through the engineering strain prepared by the invention without adding 3-cyanopyridine, therefore various shortcomings in the existing chemical synthesis process of nicotinic acid can be avoided, and also the method has the characteristics of simple production condition, no pollution, simplicity and feasibility, easy enlargement and low cost, is suitable for large-scale industrial production and application, and has great popularization and applicationvalue.
Owner:上海晶诺生物科技有限公司
O-phosphoserine sulfhydrylase mutants and method for production of cysteine using the same
ActiveUS20120190080A1Improve enzymatic activityHigh yieldBacteriaSugar derivativesMycobacterium smegmatisO-phosphoserine sulfhydrylase
Disclosed is an O-phosphoserine sulfhydrylase (OPSS) mutant which has a Mycobacterium smegmatis-derived amino acid sequence corresponding to that of SEQ ID NO: 1 which is devoid of three to seven C-terminal amino acid residues. Also, a nucleic acid molecule encoding the OPSS mutant, an expression vector carrying the nucleic acid molecule, and a transformant transformed with the expression vector are disclosed. In addition, a method is provided for producing cysteine in which O-phospho-L-serine (OPS) is reacted with a sulfide in the presence of the OPSS mutant. The OPSS mutant has improved enzymatic activity and can be applied to the environmentally friendly production of L-cysteine through a simple enzymatic conversion reaction.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Method for constructing high temperature stress-resistant recombinant Mycobacterium smegmatis
PendingCN109022337ASolving activitySolve the problem that high temperature is not conducive to the growth of Mycobacterium smegmatisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTemperature stressMicroorganism
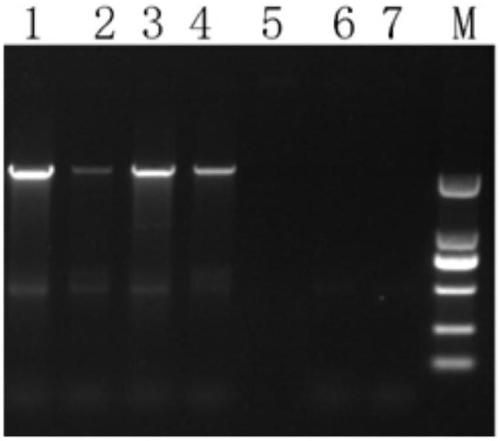
The invention discloses a method for constructing high temperature stress-resistant recombinant Mycobacterium smegmatis. The method is characterized in that an HtpG gene fragment is introduced to makethe recombinant Mycobacterium smegmatis have the function of expressing an HtpG protein. The HtpG gene fragment is introduced to Mycobacterium smegmatis to obtain the high temperature stress-resistant recombinant Mycobacterium smegmatis, so a problem that an hsp60 promoter in the Mycobacterium smegmatis expression system needs a high temperature to increase the expression activity and the high temperature is not conducive to the growth of the Mycobacterium smegmatis is solved. The method has great reference values in the biology research of mycobacteria for expressing specific genes with theMycobacterium smegmatis as a host strain and the development of new anti-tuberculosis vaccinse and microbial reactors. The invention also discloses the high temperature stress-resistant recombinant Mycobacterium smegmatis obtained by the construction method, and a primer pair for the PCR amplification of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis HtpG gene fragment.
Owner:FOSHAN UNIVERSITY
Novel small molecule compound, preparation method and application thereof in preparation of mycobacterium drugs for resisting drug-resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis and like
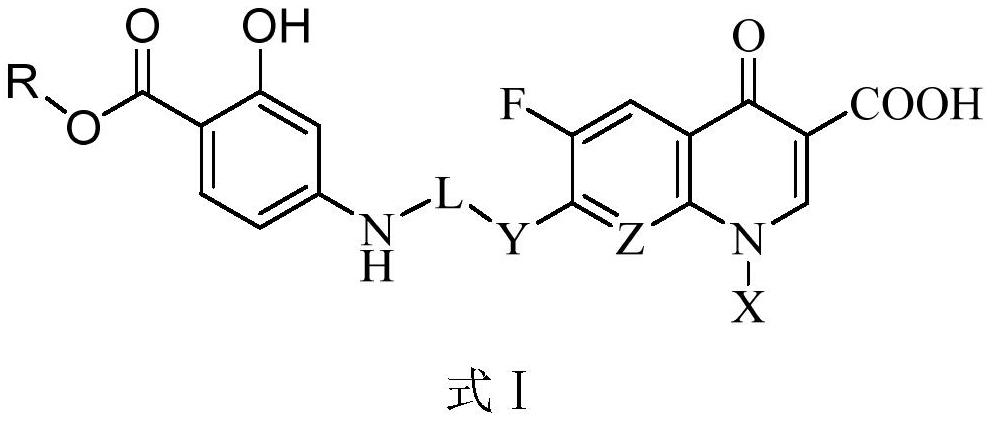
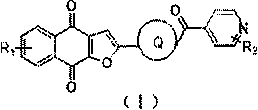
ActiveCN109988157AGood growth inhibitory activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMycobacterium smegmatisMedicine
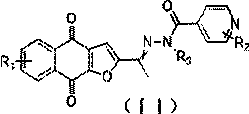
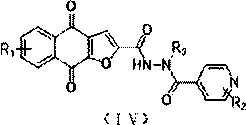
The invention discloses a novel small molecule compound and a preparation method and application thereof in preparation of mycobacterium drugs for resisting drug-resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis and like. The novel mycobacterium-resistant small molecule has a structural general formula (I), and the small molecule compound disclosed by the invention has a relatively good inhibition effect on mycobacteria. The antibacterial activity of mycobacterium smegmatis, mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv, H37Ra and drug-resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis are determined, and results show that the smallmolecule compound has good antibacterial activity on mycobacterium smegmatis, mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv, H37Ra and drug-resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis, and has an application prospect inpreparation of mycobacterium tuberculosis-resistant drugs.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
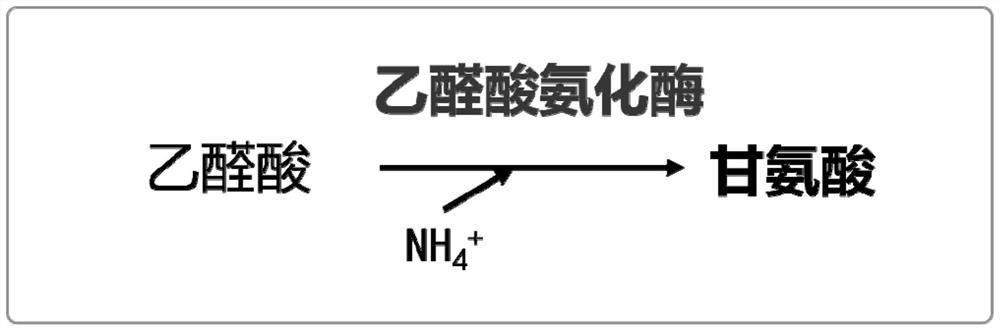
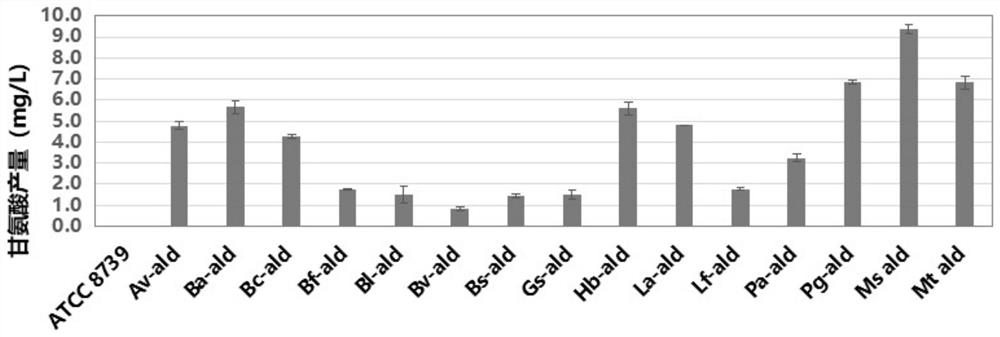
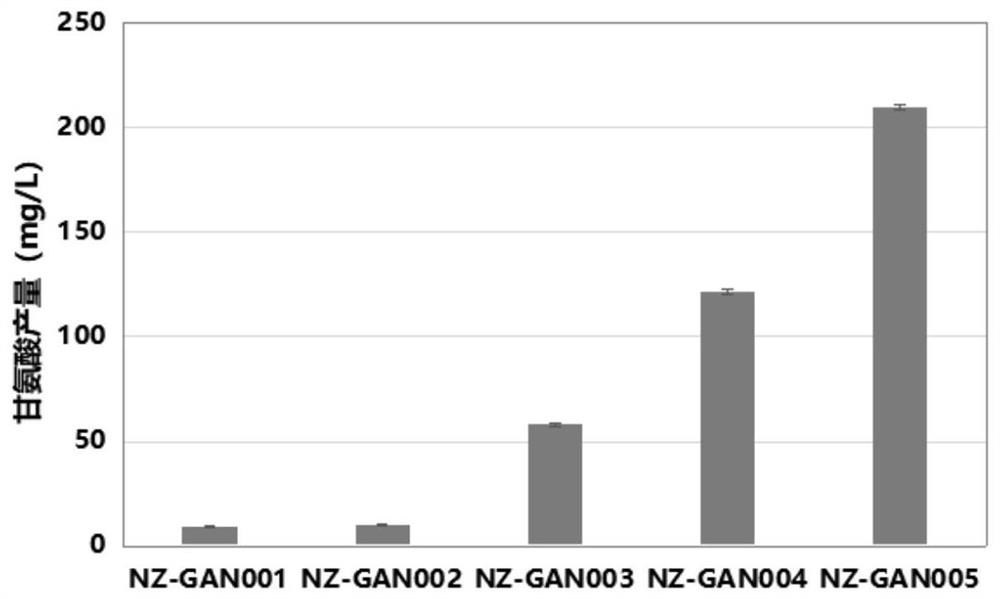
Production method of glycine
The invention discloses a production method of glycine. The invention provides a method for constructing an engineering strain capable of producing glycine, and the method comprises the following steps of: expressing glyoxylic acid ammoniation enzyme from mycobacterium smegmatis, paucisalibacillus globuius, mycobacterium tuberculosis, bacillus aquimaris, halomonas boliviensis, aeromonas veronii or labrenzia aggregata by recipient bacteria, thus obtaining a strain named as an engineering bacterium 1; the engineering bacterium 1 is an engineering strain capable of producing glycine. The invention opens up the precedent of synthesizing glycine by using a biological method.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Anti-drug-resistance antibacterial amidine oligomer as well as preparation method and application thereof
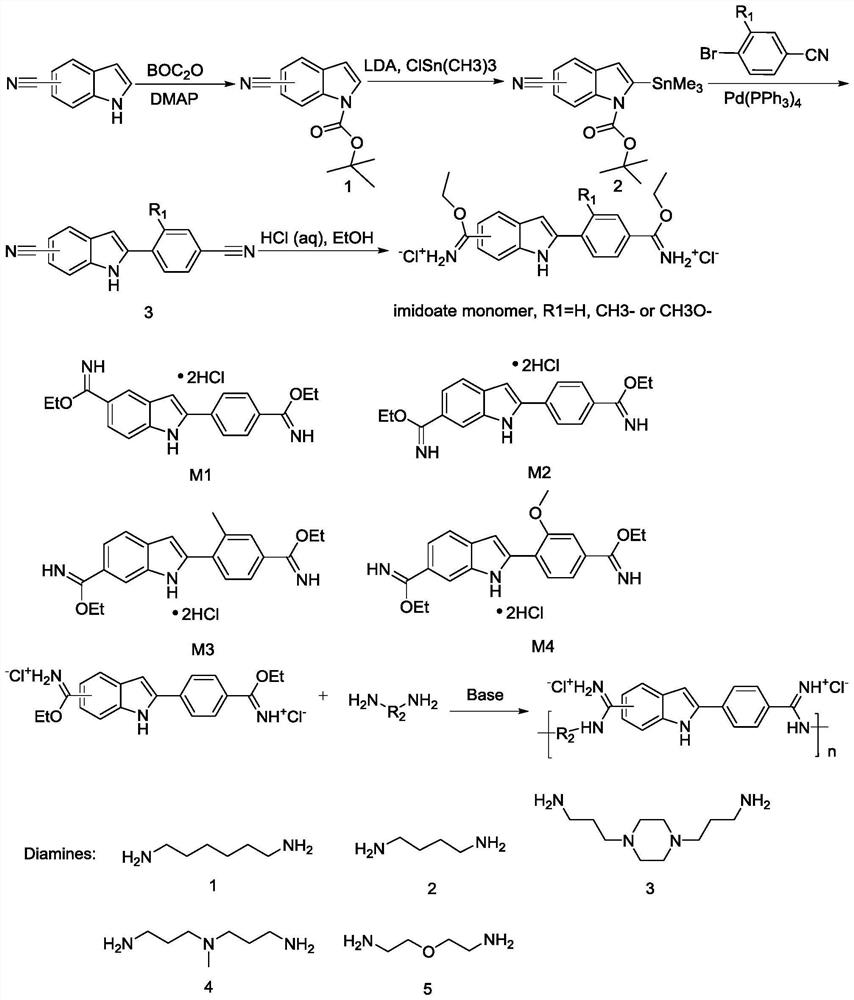
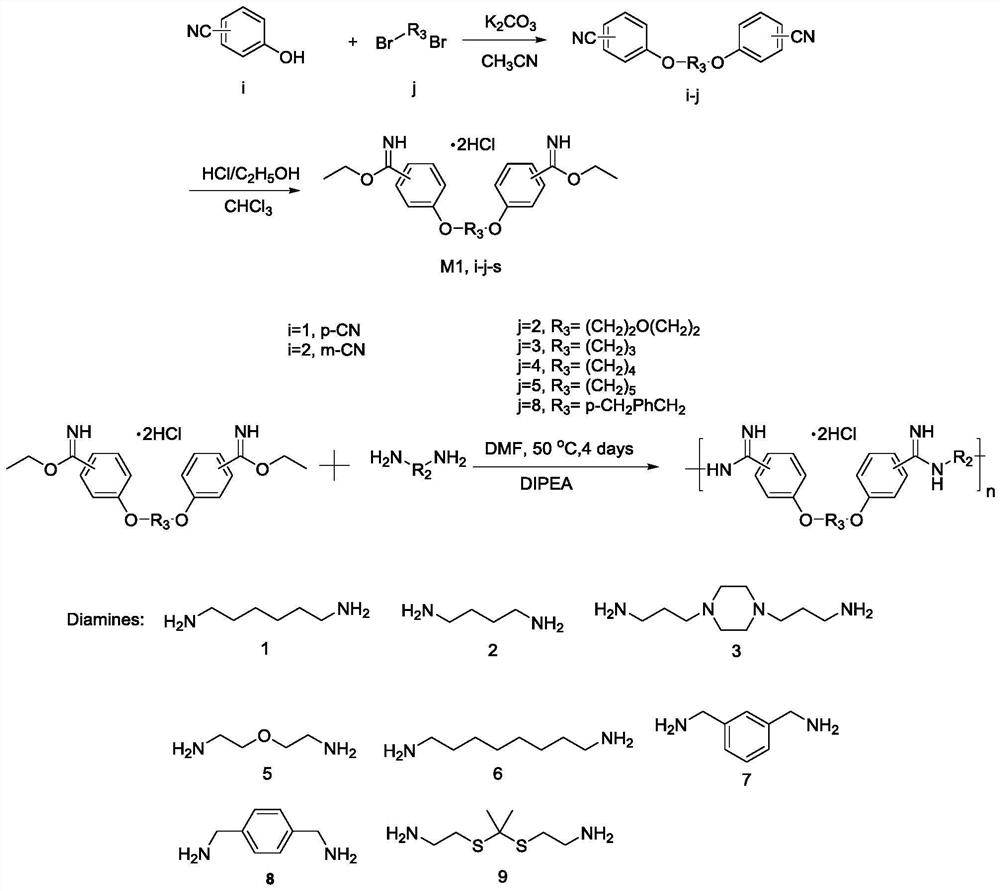
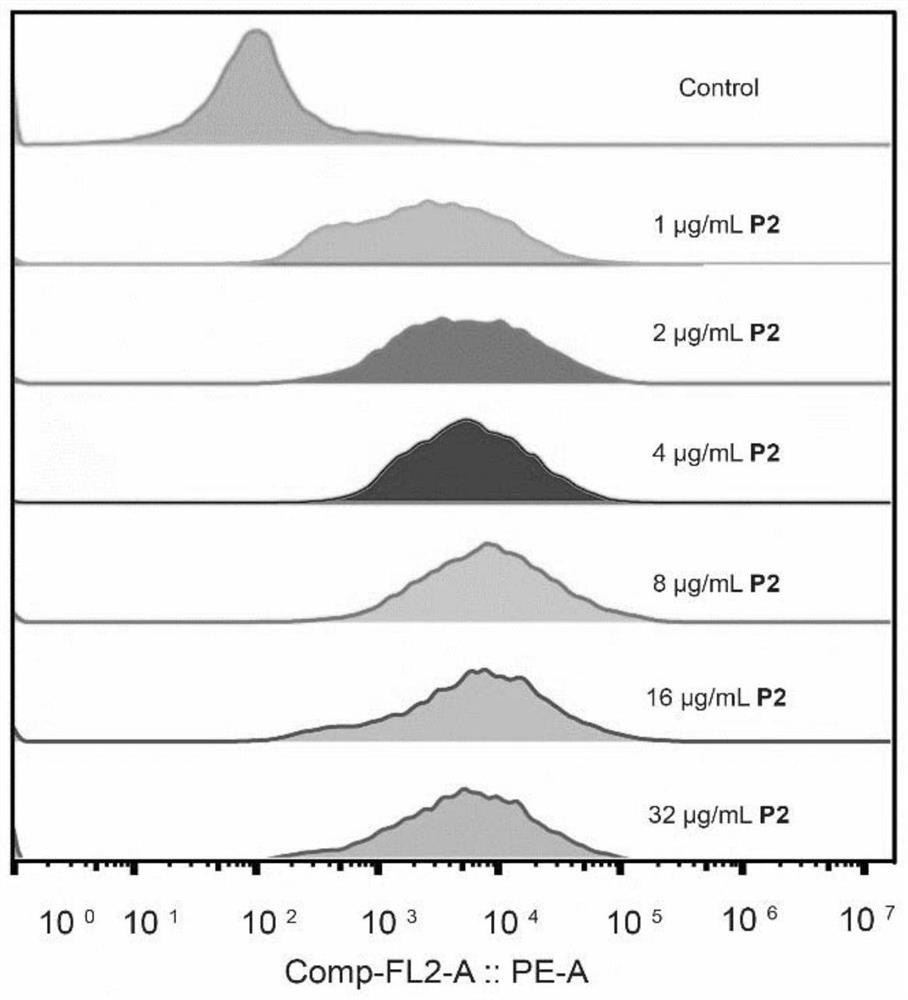
ActiveCN113754564ALow toxicityEfficient killingAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryMycobacterium smegmatisPseudomonas
The invention discloses an anti-drug-resistance antibacterial amidine oligomer, a preparation method, application and an antibacterial mechanism of the antibacterial amidine oligomer, and an application of the antibacterial amidine oligomer in sterilization in an intracellular infection model and a zebra fish model infected by mycobacterium fortuitum. The antibacterial types of the amidine oligomer comprise escherichia coli, enterococcus faecalis, staphylococcus aureus, klebsiella pneumoniae, acinetobacter baumannii, pseudomonas aeruginosa, mycobacterium smegmatis, mycobacterium fortuitum and the like. The structure disclosed by the invention has double antibacterial mechanisms of destroying bacterial cell membranes and combining chromosome DNA, has the characteristics of rapid sterilization and drug resistance, and shows antibacterial broad spectrum. In addition, the structure has low toxicity to blood cells, and has high safety in blood. Meanwhile, the structure can be applied to a Raw264.7 cell model infected by mycobacterium smegmatis and mycobacterium fortuitum, and the structure also has a good treatment effect on the zebra fish model infected by MRSA and mycobacterium fortuitum.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com