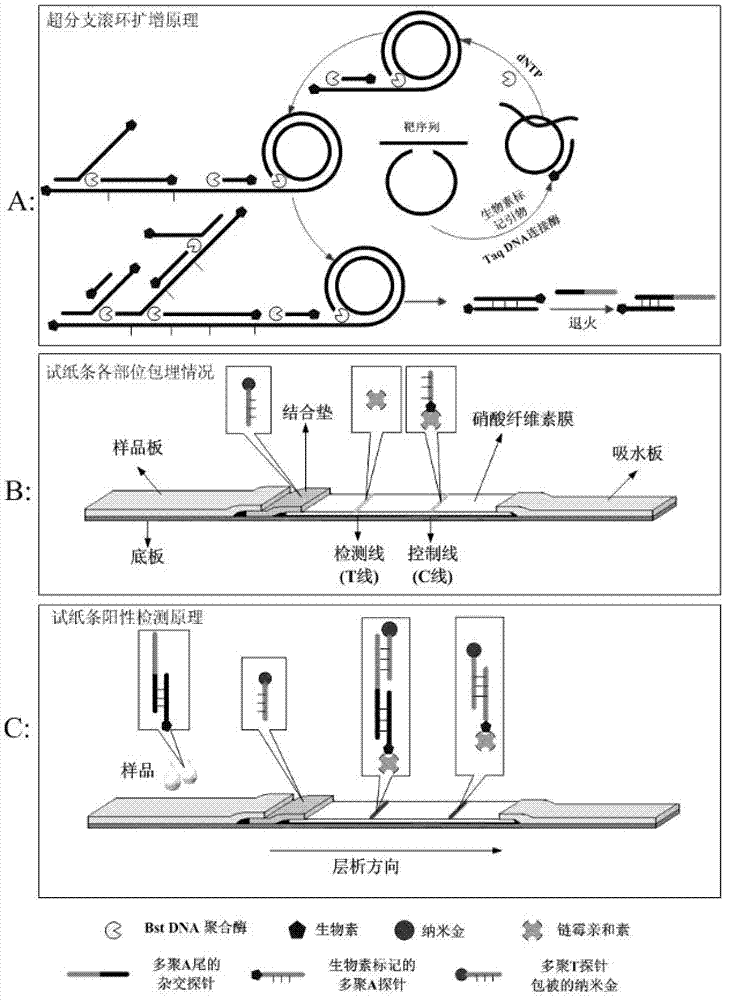
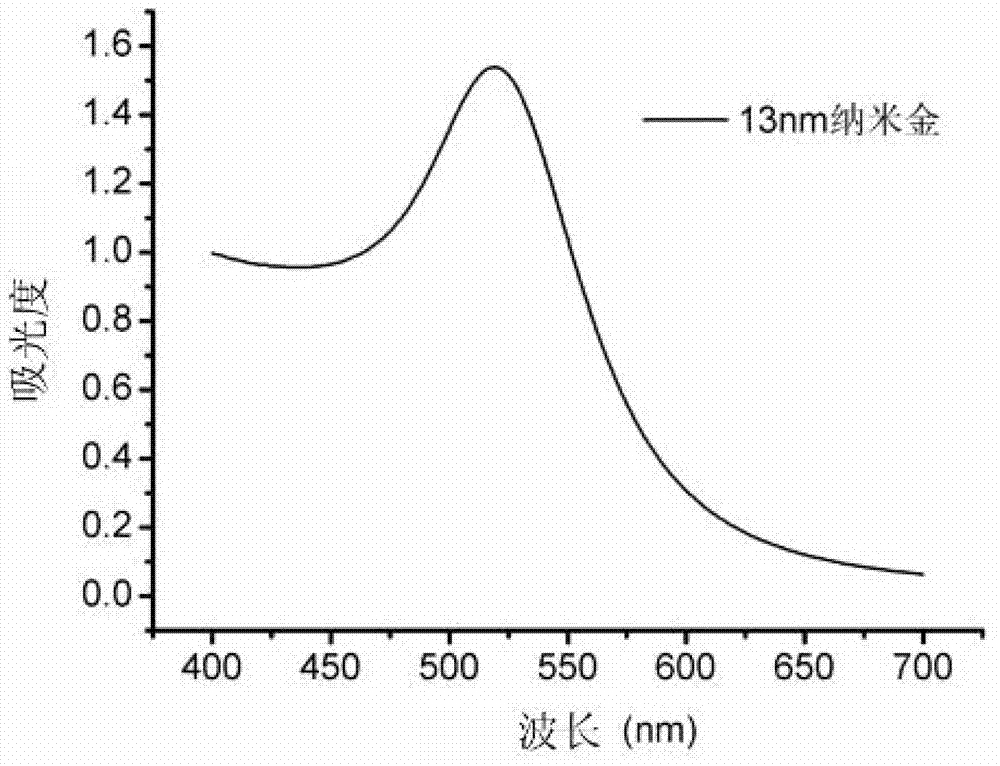
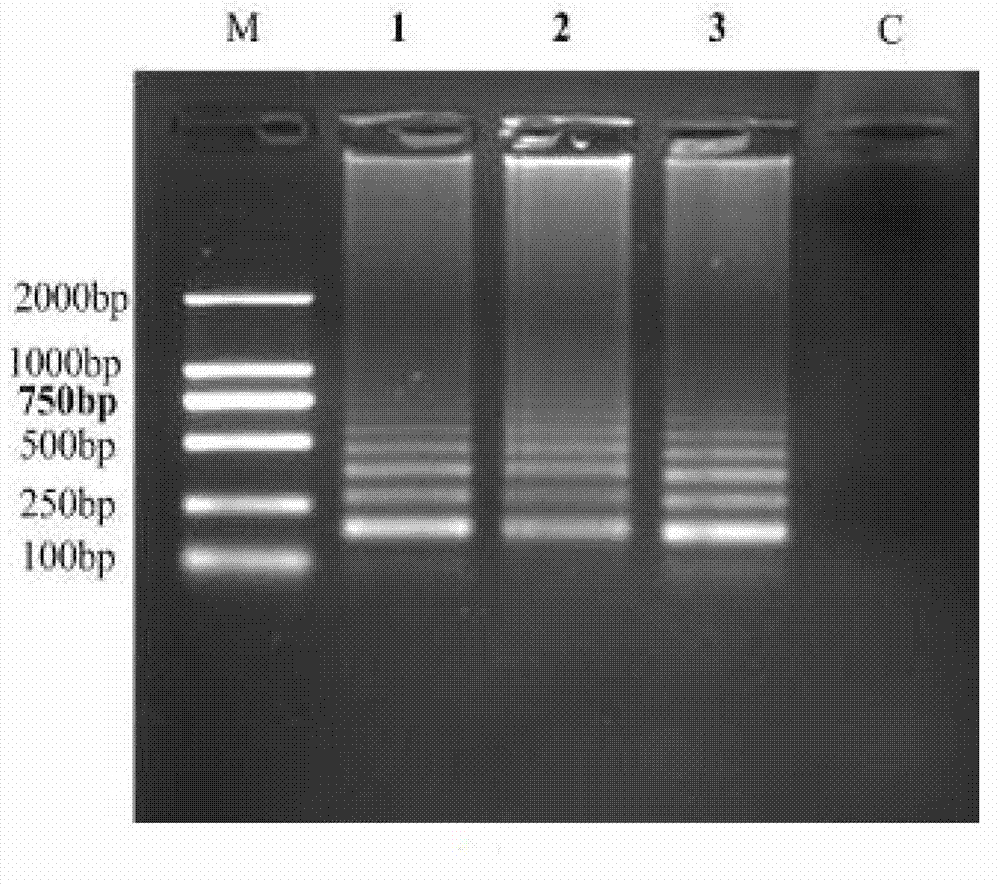
Method for detecting food-borne pathogenic bacteria by using nucleic acid test strip based on hyper-branched rolling cycle amplification and kit
A technology of nucleic acid test strips and rolling circle amplification, applied in the field of kits for the detection of Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella, which can solve the problems of complex probe design, time-consuming and laborious, and expensive monoclonal antibodies
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0102] 1. Extraction and digestion of DNA from Listeria monocytogenes
[0103] Genomic DNA of Listeria monocytogenes (strain number CMCC54007, purchased from Guangzhou Institute of Microbiology) was extracted using TIANamp Bacteria DNA kit. The conserved sequence of Listeria monocytogenes is the expression of lysin O gene (hlyA, NCBI number: AF253320), and the genomic DNA of Listeria monocytogenes is digested with EcoT14Ⅰ (StyⅠ) enzyme and Bsp1286Ⅰ (SduⅠ) enzyme.
[0104] 20μL Bsp1286Ⅰ digestion reaction system:
[0105]
[0106] Reaction conditions: 60°C for 1h→95°C for 10min;
[0107] 40μL EcoT14Ⅰ digestion reaction system:
[0108]
[0109] Reaction conditions: 60°C for 1 h→95°C for 10 min to obtain the hlyA target fragment, its sequence: 5'-TCTCCGCCTGCAAGTCCTAAGACGCCAATCGAAAAGAAACACGC-3'.
[0110] 2. Primer and probe design
[0111] Design a 5' phosphorylated padlock probe based on the hlyA target sequence, which is used to connect with the target sequence to for...
Embodiment 2
[0142] Genomic DNA of Salmonella (strain number CMCC50040, purchased from Guangzhou Institute of Microbiology) was extracted using TIANamp Bacteria DNA kit, according to the conserved sequence in the Salmonella invA gene sequence (GenBank EU348367) published by NCBI, and compared using blast in NCBI, Taq Ⅰ (restriction site is TCGA) and Alu Ⅰ (restriction site is AGCT) were used for enzyme digestion reaction to obtain invA target fragment, its sequence is: 5'-GTCTCTACAGAGACCGTACCGTTGACTTGTGCCGAAGAGCCGGC-3'.
[0143] Design a 5' phosphorylated padlock probe according to the invA target fragment sequence, the padlock probe sequence is: 5'-phosphate-TCAACGGTACGGTCTCTGTAGAGACGGGATTAGGTTACTGCGATTAGCACAAGCACCAAGAGCAACTACACGAATTCCGGCTCTTCGGCACAAG-3'; Part of it is complementary to the target sequence, and the middle two parts are the binding regions of primer 1 and primer 2 respectively. According to the principle of hyperbranched rolling circle amplification, padlock probes designed ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com