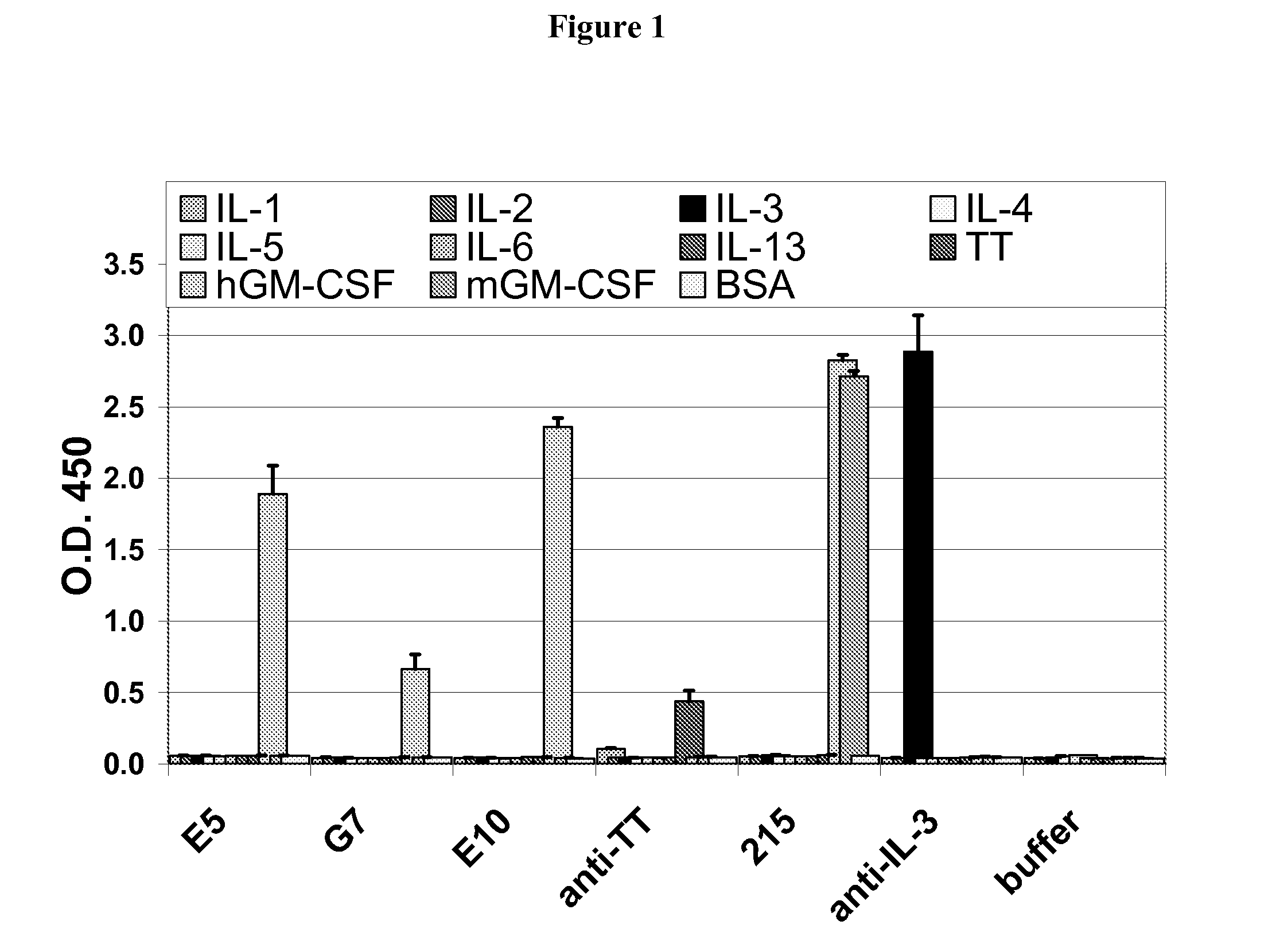
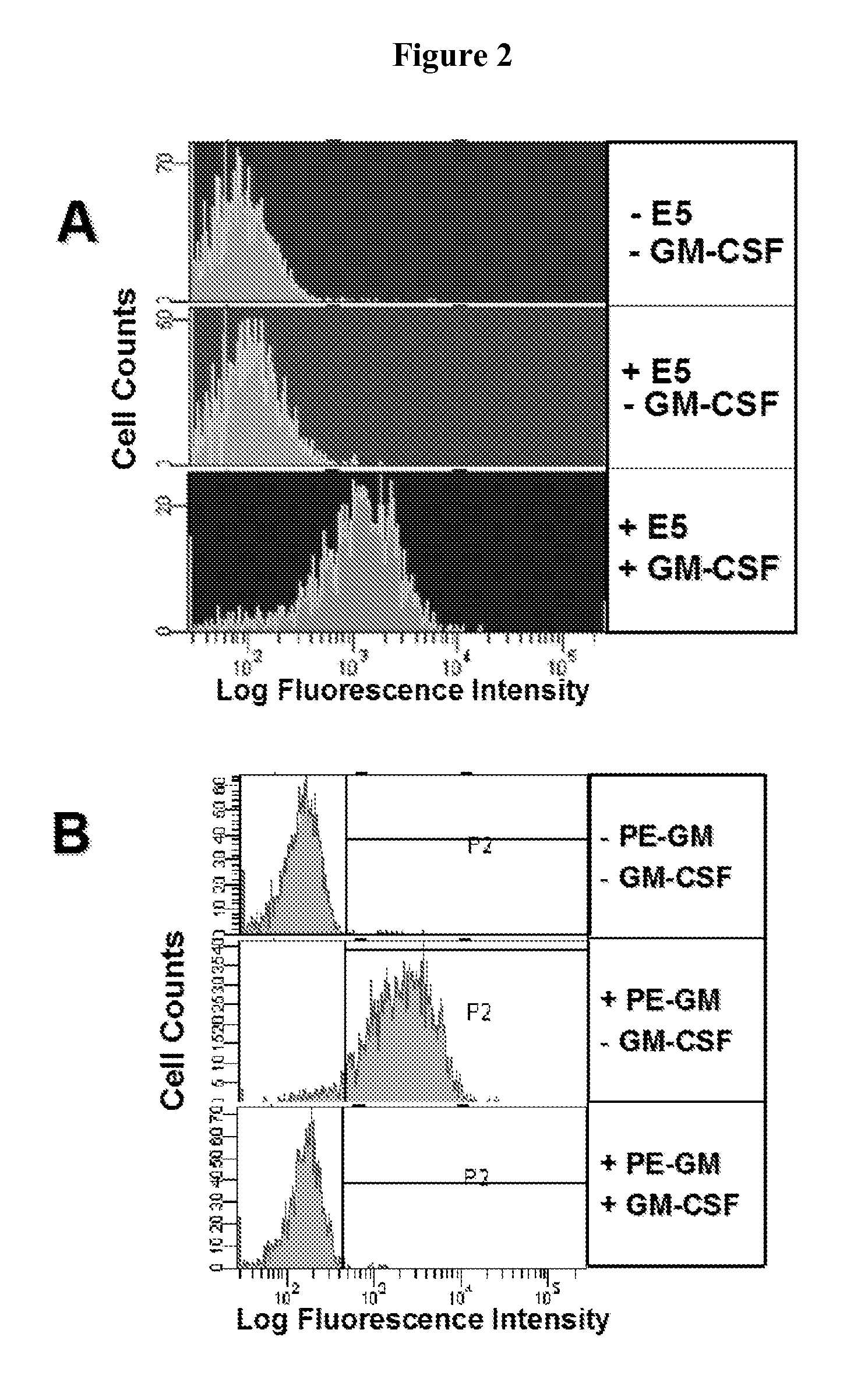
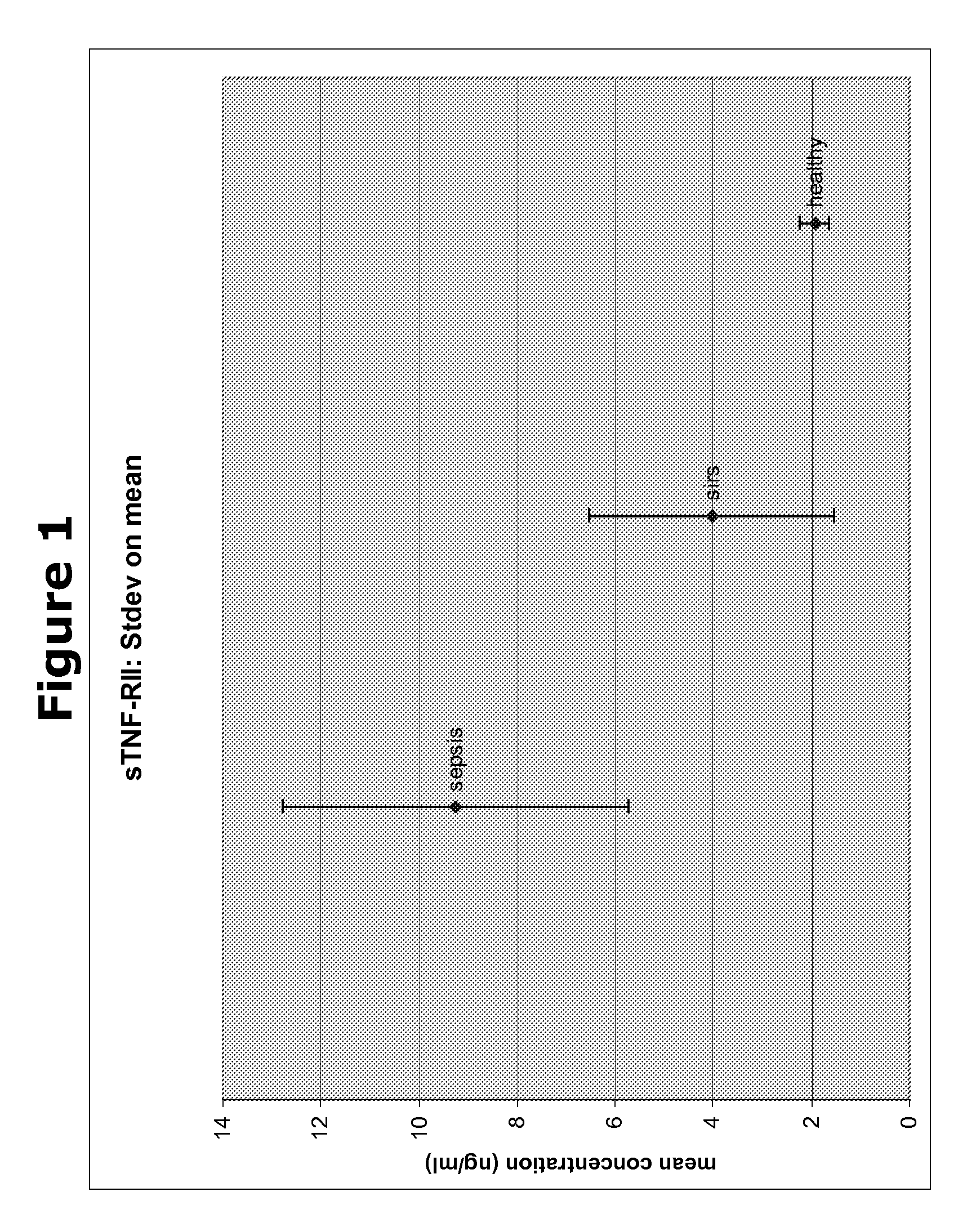
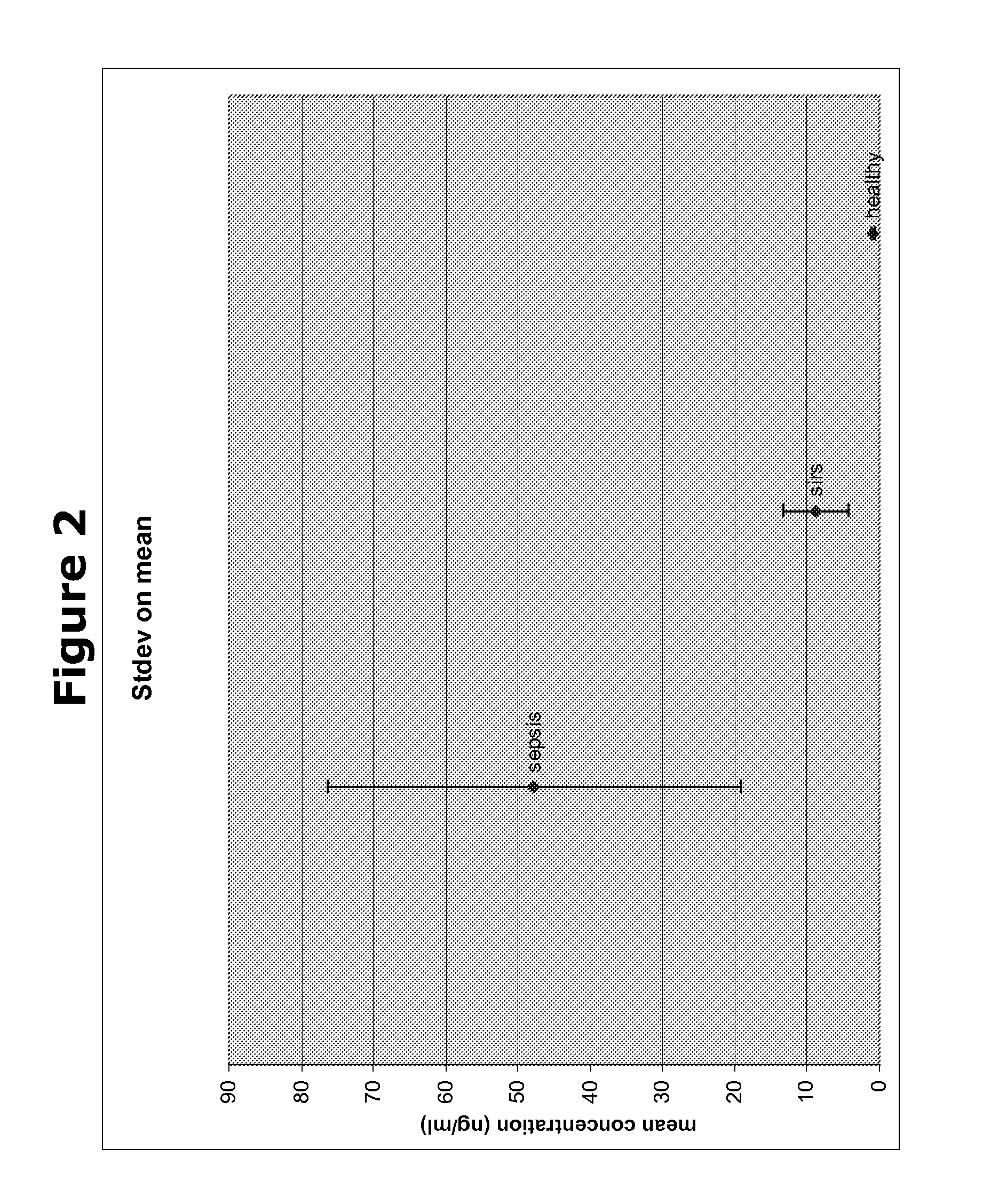
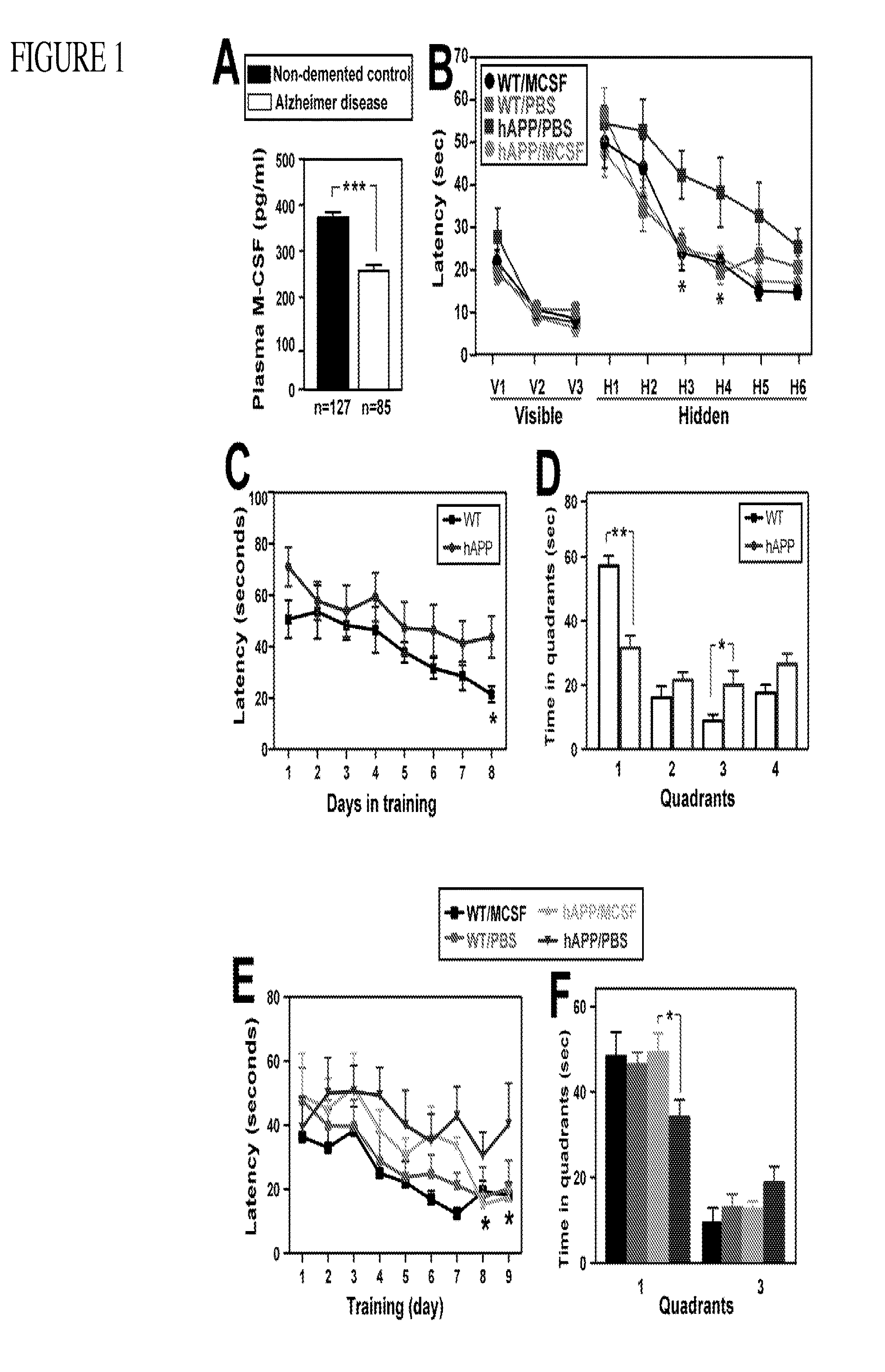
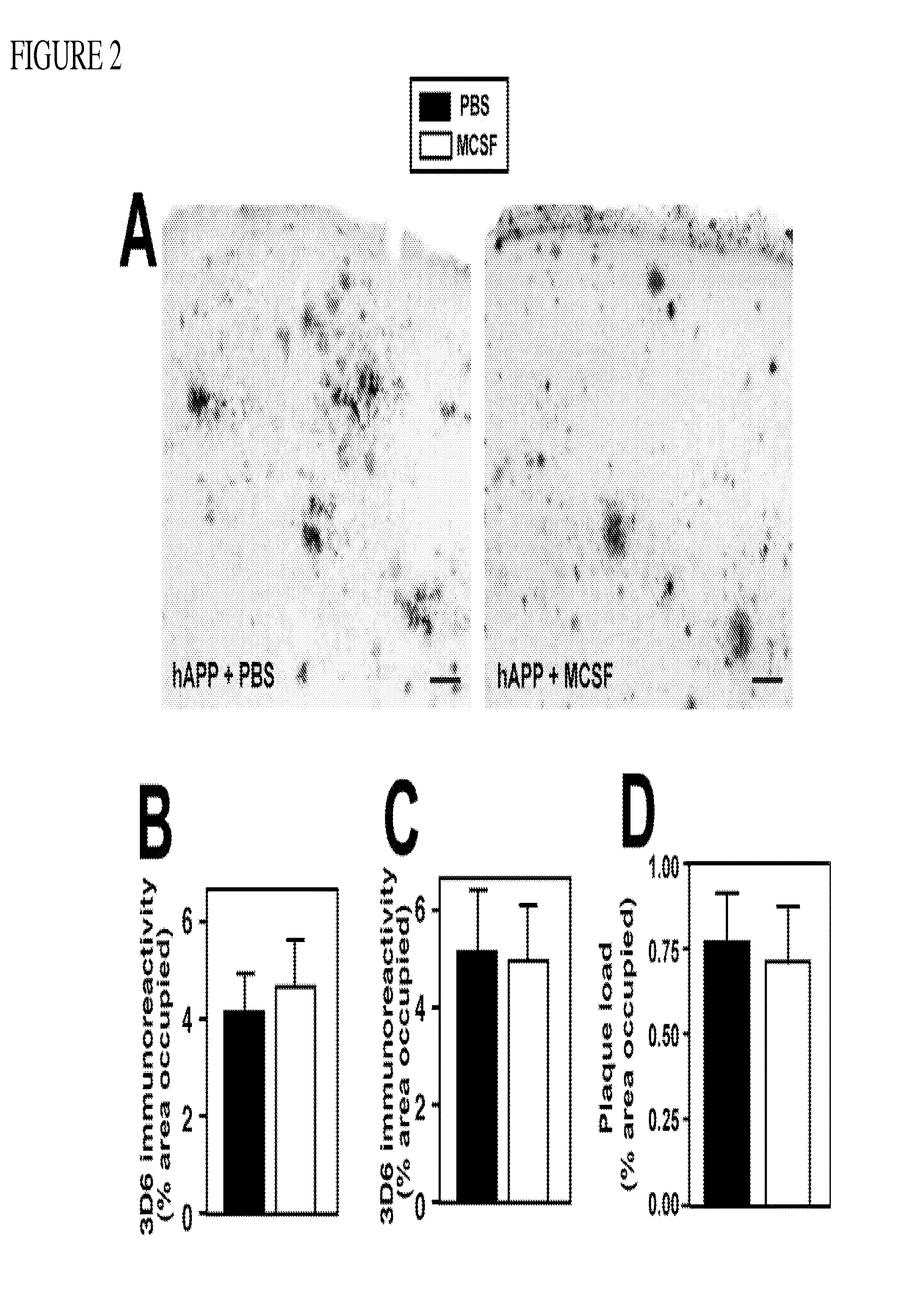
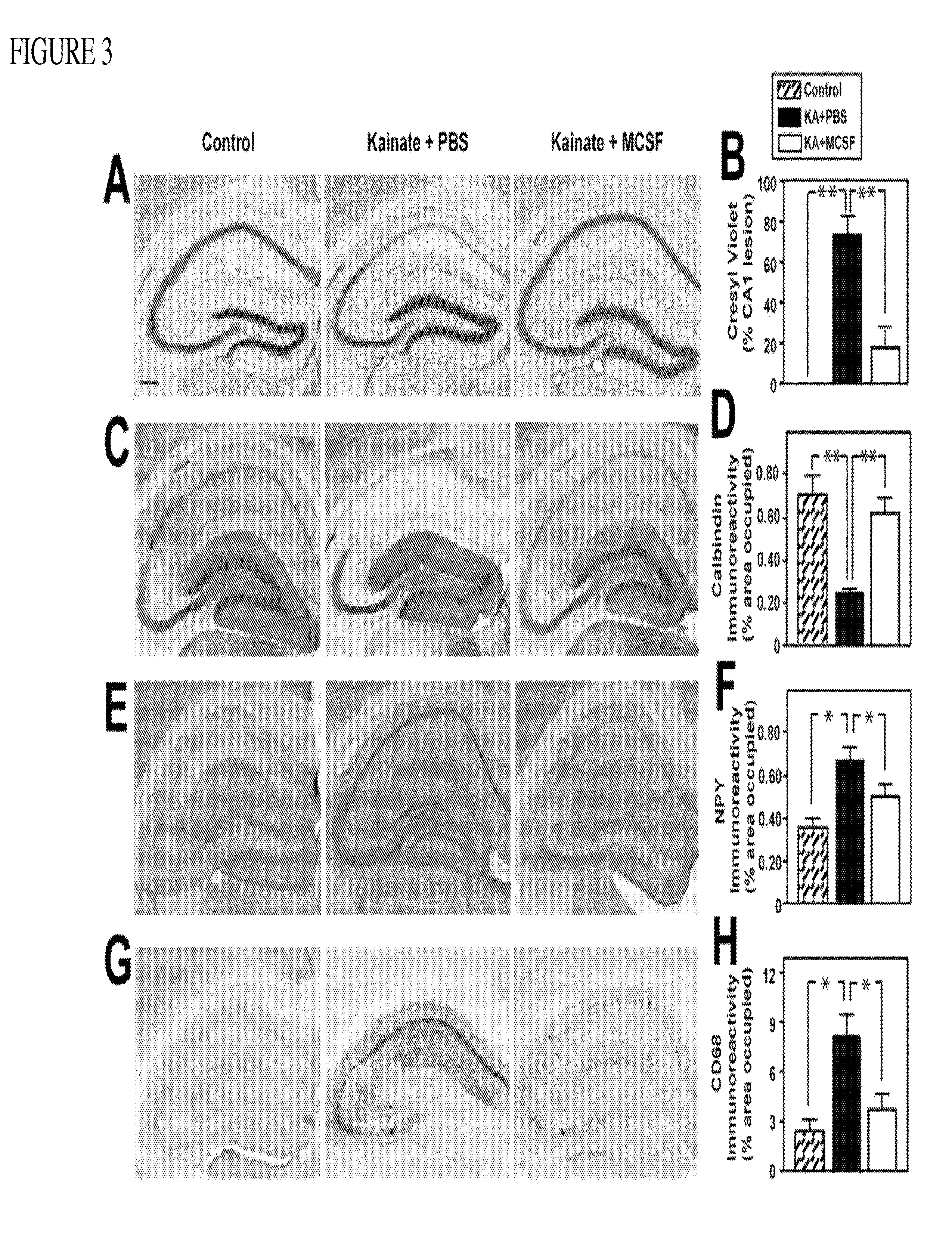
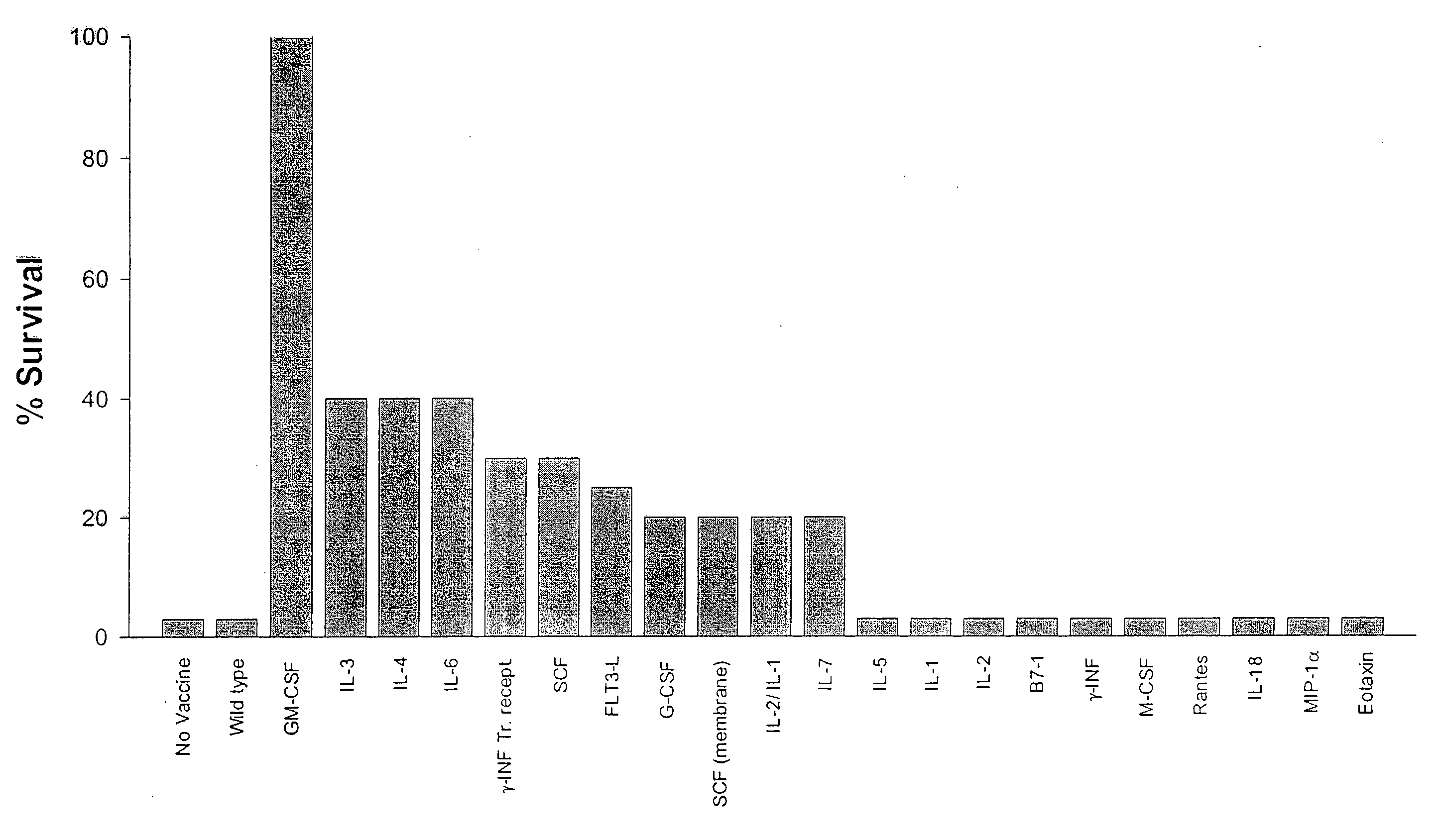
Patents
Literature
189 results about "Macrophage colony-stimulating factor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The colony stimulating factor 1 (CSF1), also known as macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), is a secreted cytokine which causes hematopoietic stem cells to differentiate into macrophages or other related cell types. Eukaryotic cells also produce M-CSF in order to combat intercellular viral infection. It is one of the three experimentally described colony-stimulating factors. M-CSF binds to the colony stimulating factor 1 receptor. It may also be involved in development of the placenta.
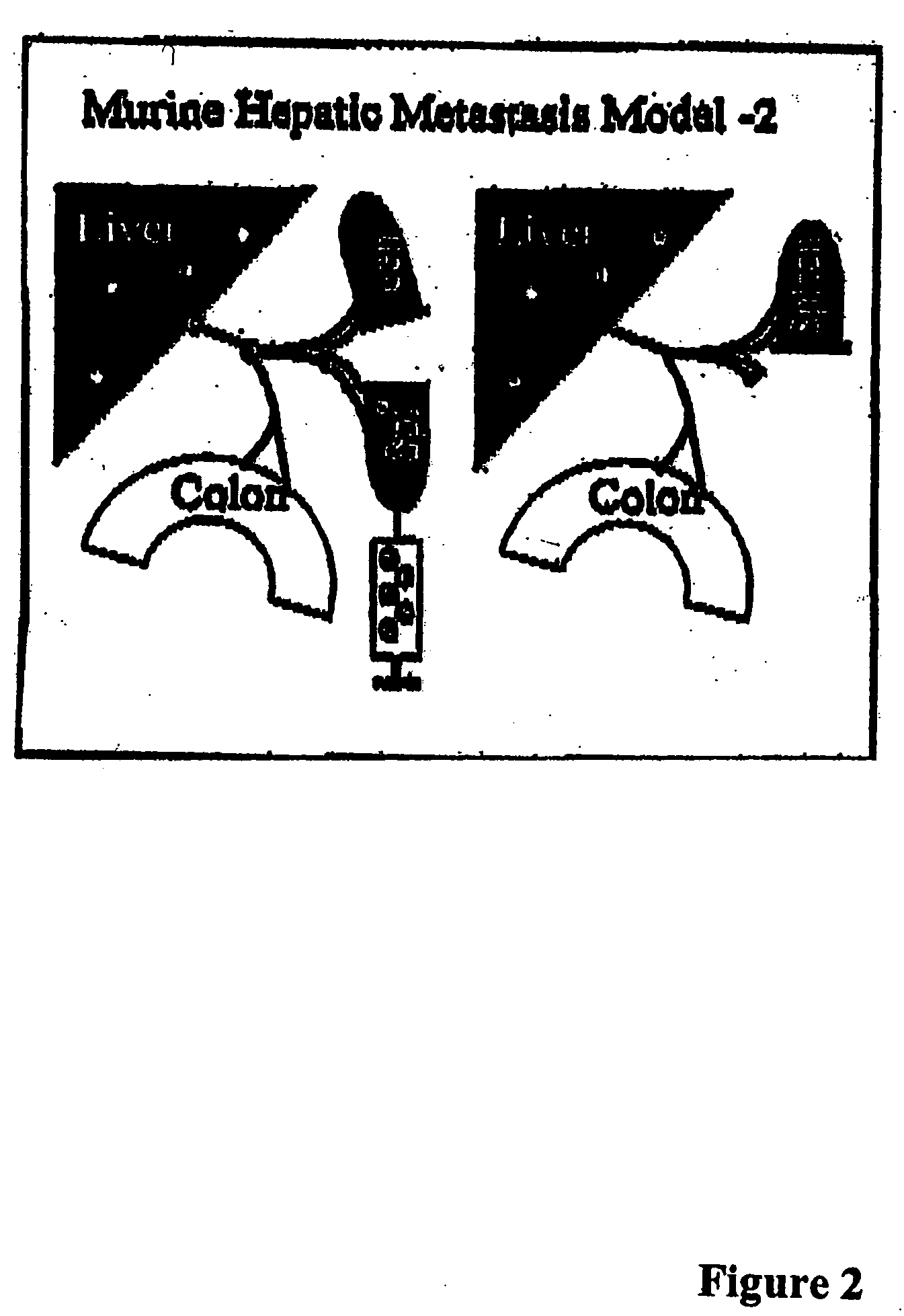
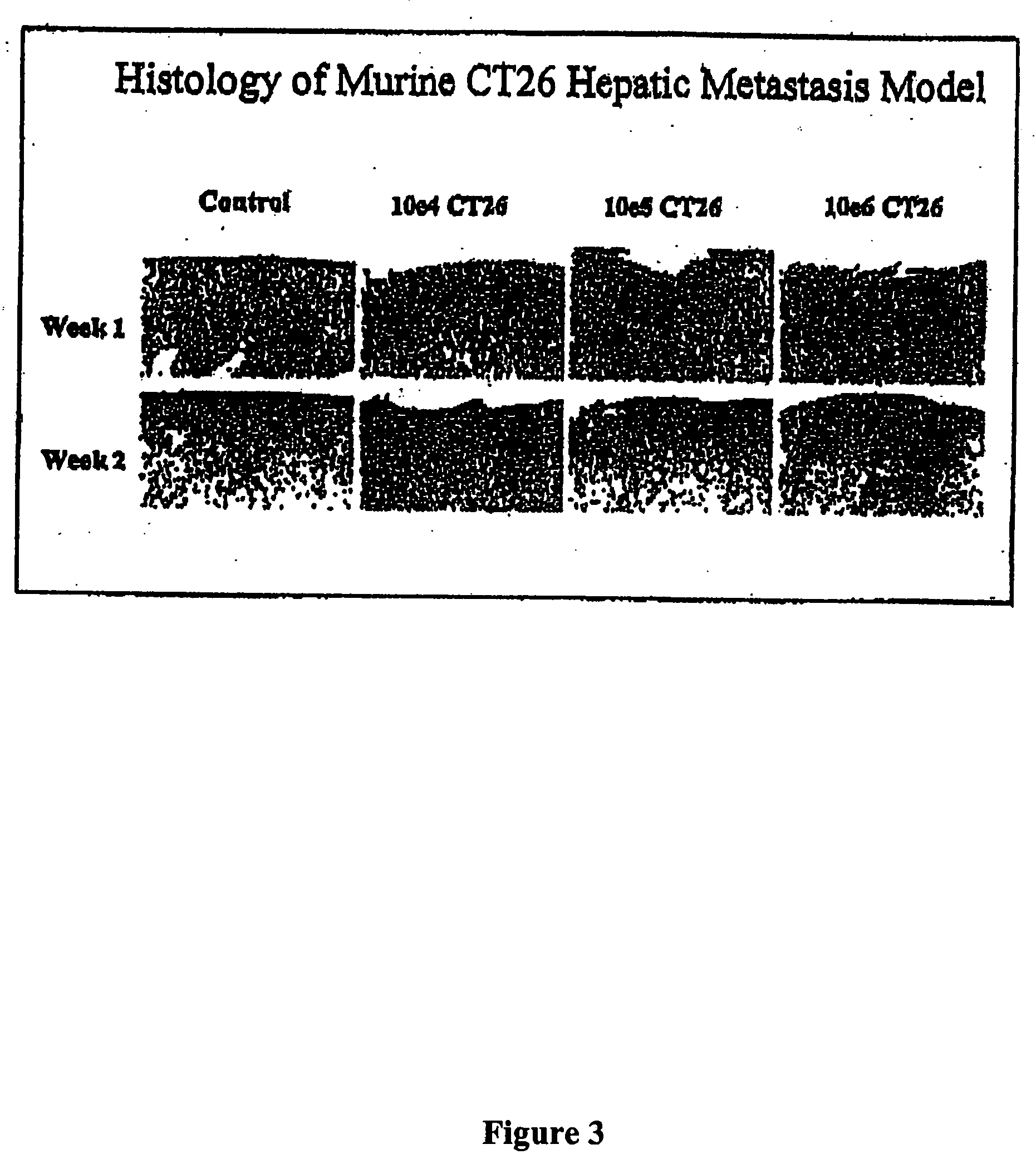
Methods and compositions for the targeting of a systemic immune response to specific organs or tissues
The invention provides methods and compositions for targeting a separately generated immune response to a specific organ or tissue, e.g. one affected by cancer, using one or more agents with a tropism for the organ or tissue or that can be specifically localized to the desired organ or tissue. For example, the invention provides methods ands compositions for treating liver metastases from colorectal cancer using a combination of a granulocyte / macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) augmented tumor cell vaccination and Listeria monocytogenes (LM) infection.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Diagnostic Methods Of Multiple Organ Amyloidosis
InactiveUS20080038192A1In-vivo radioactive preparationsMicrobiological testing/measurementElevated C-reactive proteinPredictive biomarker
Described are methods of assessing whether a subject has or is at risk of having multiple organ amyloidosis (MOA) The method includes detecting a diagnostically predictive collection of biomarkers of multiple organ amyloidosis, wherein the detection of a diagnostically predictive collection of biomarkers indicates the subject has or is at risk of having multiple organ amyloidosis Also described are methods of monitoring treatment of subjects with multiple organ amyloidosis and evaluating therapeutic compounds Representative biomarkers for use in the methods may be selected from variant serum amyloid A (SAA) allele, elevated SAA level, elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) level, depressed glycosammoglycan (GAG) level, elevated interleukin-18 (IL-18) level, elevated macrophage-colony stimulating factor (M-CSF) level, elevated hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) level, presence of an antibody against citrullmated vimentm (Sa), presence of a monoclonal immunoglobulin light chain, increased serum albumin, and increased creatinine clearance
Owner:NEUROCHEM INT
Method of isolating and culturing mesenchymal stem cell derived from umbilical cord blood
InactiveUS20070092967A1Increase success rateArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsInterleukin 6G-csf therapy
The present invention relates to a method of isolating and culturing mesenchymal stem cells using umbilical cord blood that is most ideal for cell therapy. The method comprises adding an anti-coagulant to umbilical cord blood having a volume of more than 45 ml per unit, which is obtained within 24 hours after parturition; diluting the resulting mixture of the anti-coagulant and umbilical cord blood with an αMEM (alpha-minimum essential medium), followed by centrifugation to harvest monocytes; and subjecting the obtained monocytes into suspension culture in the αMEM containing Stem Cell Factor, GM-CSF (granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor), G-CSF (granulocyte colony-stimulating factor), IL-3 (interleukin-3) and IL-6 (interleukin-6).
Owner:HAN HOON
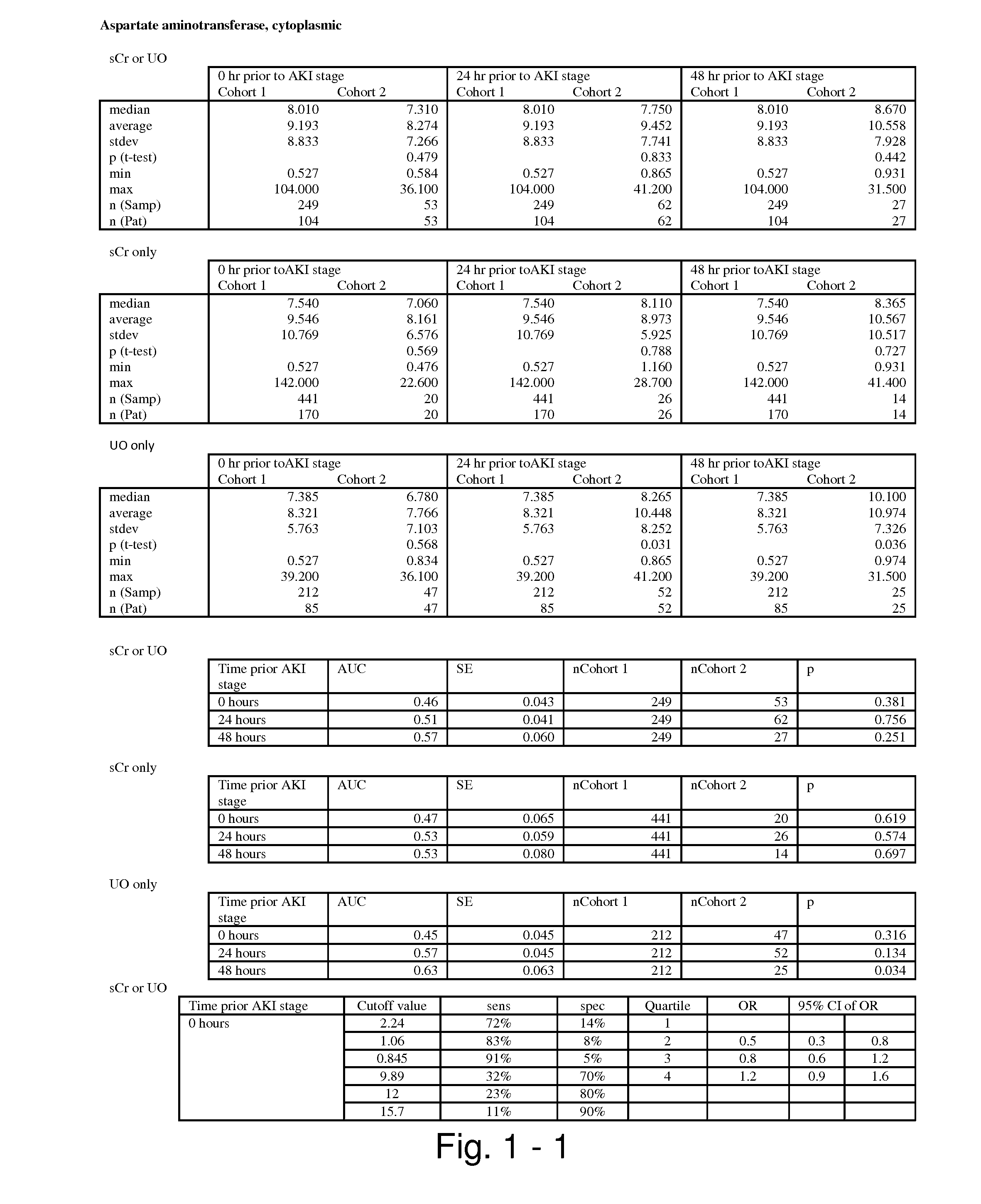
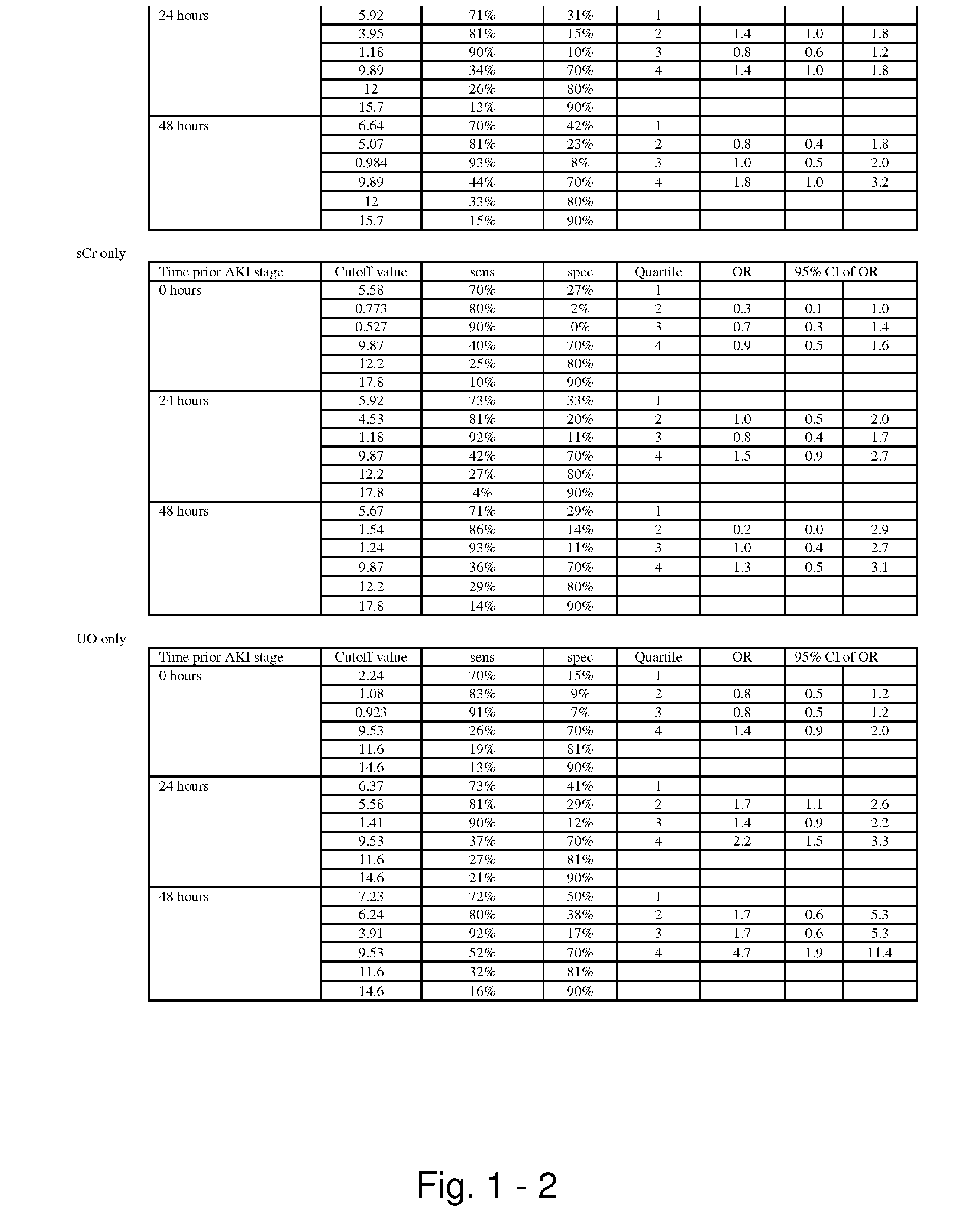
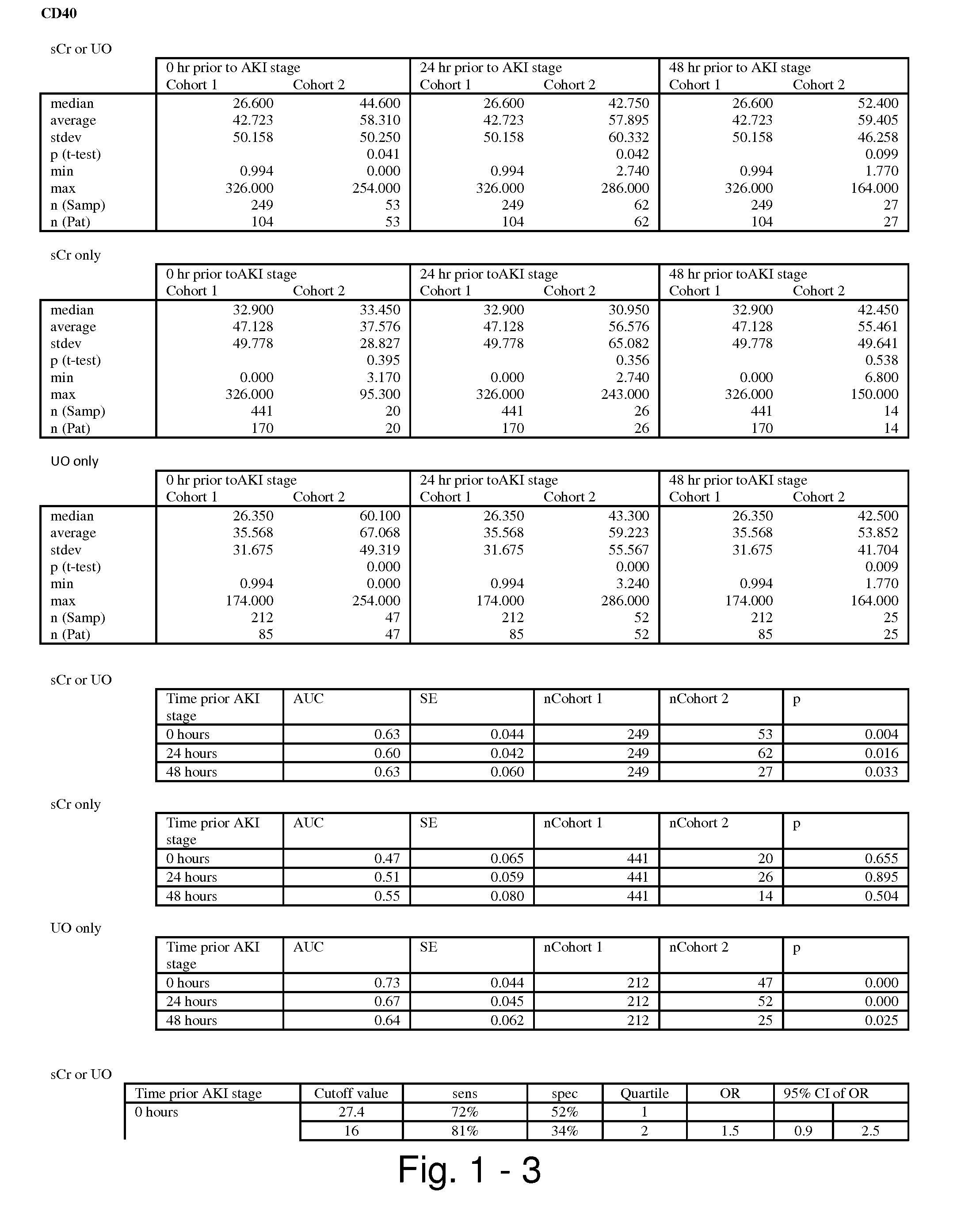
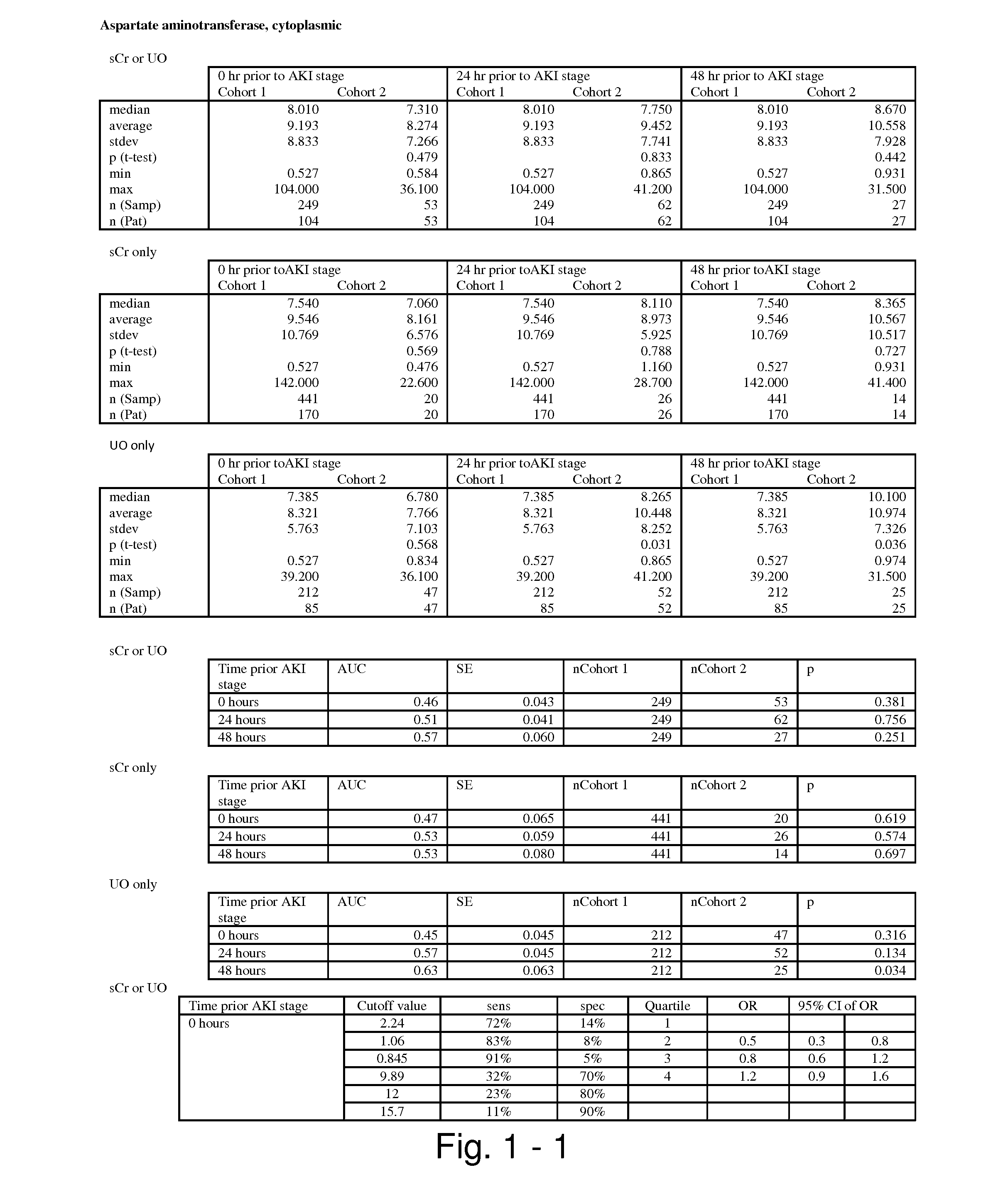
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and prognosis of renal injury and renal failure
ActiveUS20110201038A1Easy to adaptMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisInterleukin 10Soluble P-Selectin
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for monitoring, diagnosis, prognosis, and determination of treatment regimens in subjects suffering from or suspected of having a renal injury. In particular, the invention relates to using assays that detect one or more markers selected from the group consisting of Cytoplasmic aspartate aminotransferase, soluble Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 5, soluble CD40 Ligand, soluble C-X-C Motif chemokine 16, S100-A12, Eotaxin, soluble E-selectin, Fibronectin, Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, Heparin-binding growth factor 2, soluble Hepatocyte growth factor receptor, Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, Interleukin-1 beta, Interleukin-10, Interleukin-15, Interleukin-3, Myeloperoxidase, Nidogen-1, soluble Oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor 1, Pappalysin-1, soluble P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1, Antileukoproteinase, soluble Kit ligand, Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1, Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2, soluble Tumor necrosis factor, soluble Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, and Vascular endothelial growth factor A as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in renal injuries.
Owner:ASTUTE MEDICAL
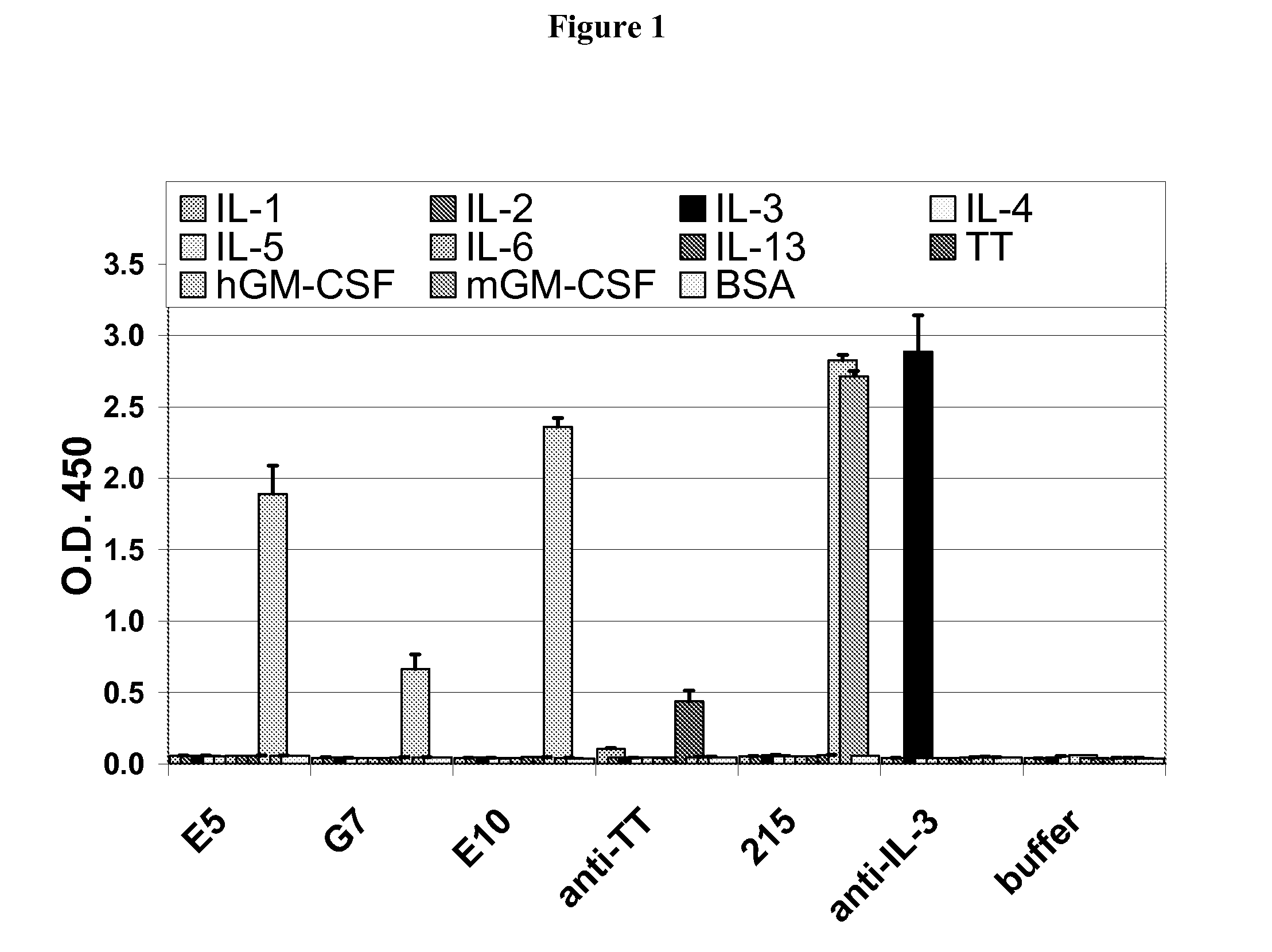
Antigenic GM-CSF peptides and antibodies to GM-CSF
Hybridoma lines that secrete human monoclonal antibodies with high binding specificity and biological activity, particularly neutralizing activity against granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor, and methods of generating the hybridoma lines are provided. Target antigens and epitopes are also provided. The antibodies may be used in therapeutic methods, for example in the treatment of cancer, infectious disease, or autoimmune disease.
Owner:EISAI INC
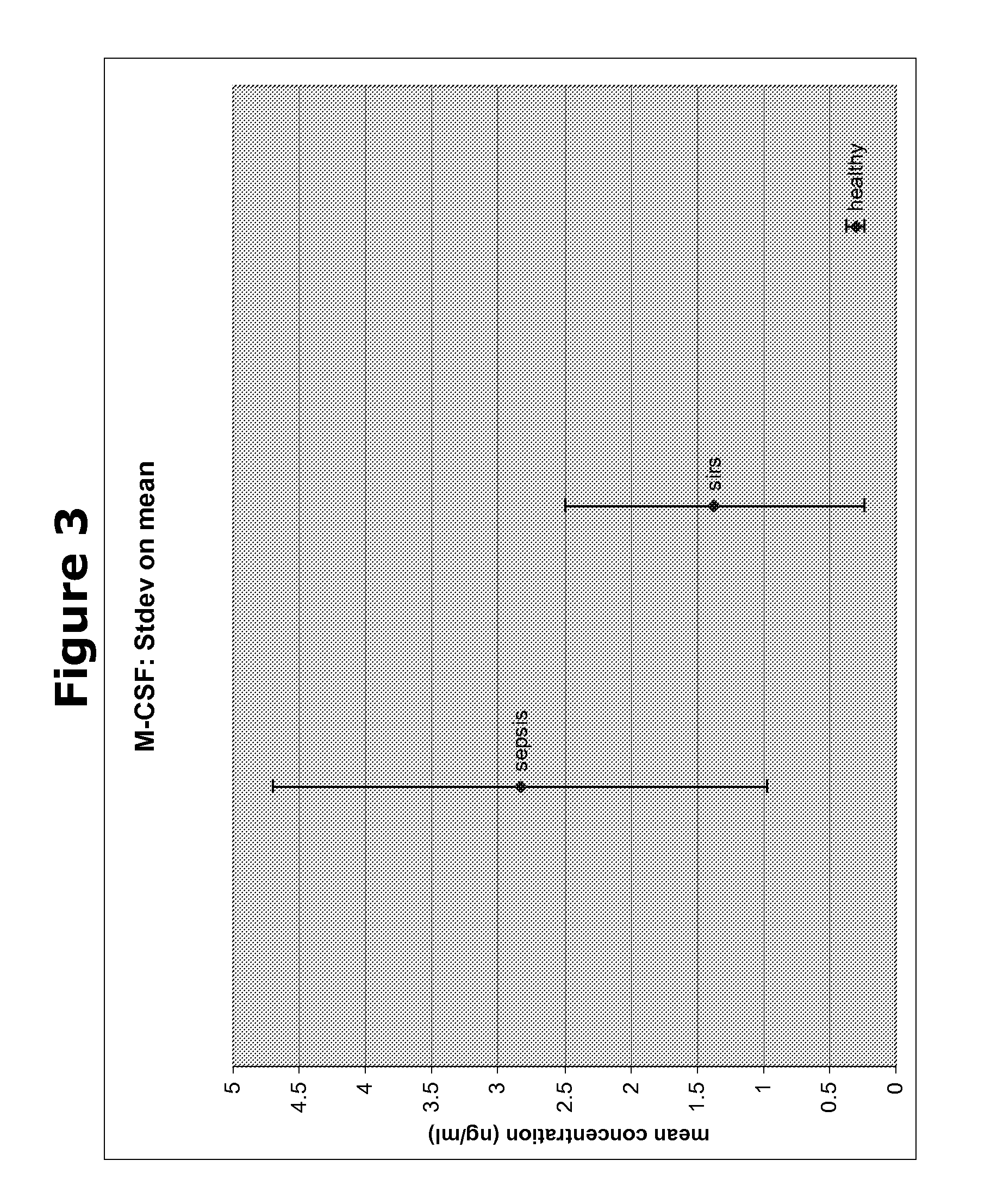
Biomarkers and methods for diagnosing, predicting and/or prognosing sepsis and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100292131A1Peptide librariesPeptide/protein ingredientsHealthy subjectsBiomarker (petroleum)
The present invention provides kits and methods for the diagnosis, prognosis and prediction of sepsis in a subject or for the differentiation between sepsis and SIRS in a subject, the method comprising(a) measuring the level of pro-hepcidin (pro-HEPC) in a biological sample taken from said subject, (b) measuring the level of at least one further biomarker selected from the group consisting of soluble TNF-receptor 2 (sTNFR2), Pentraxin-3 (PTX-3), Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor (MCSF), pro-Brain Natriuretic Protein (pro-BNP), one or more members of the Histone protein family, Procalcitonin (PCT) and c-Reactive Protein (CRP) in a biological sample from said subject, (c) using said measurements obtained in steps (a) and (b) to create a profile for said biomarkers and (d) comparing said profile with a reference biomarker profile obtained form a patient having SIRS or from a healthy subject.
Owner:BIOCARTIS NV
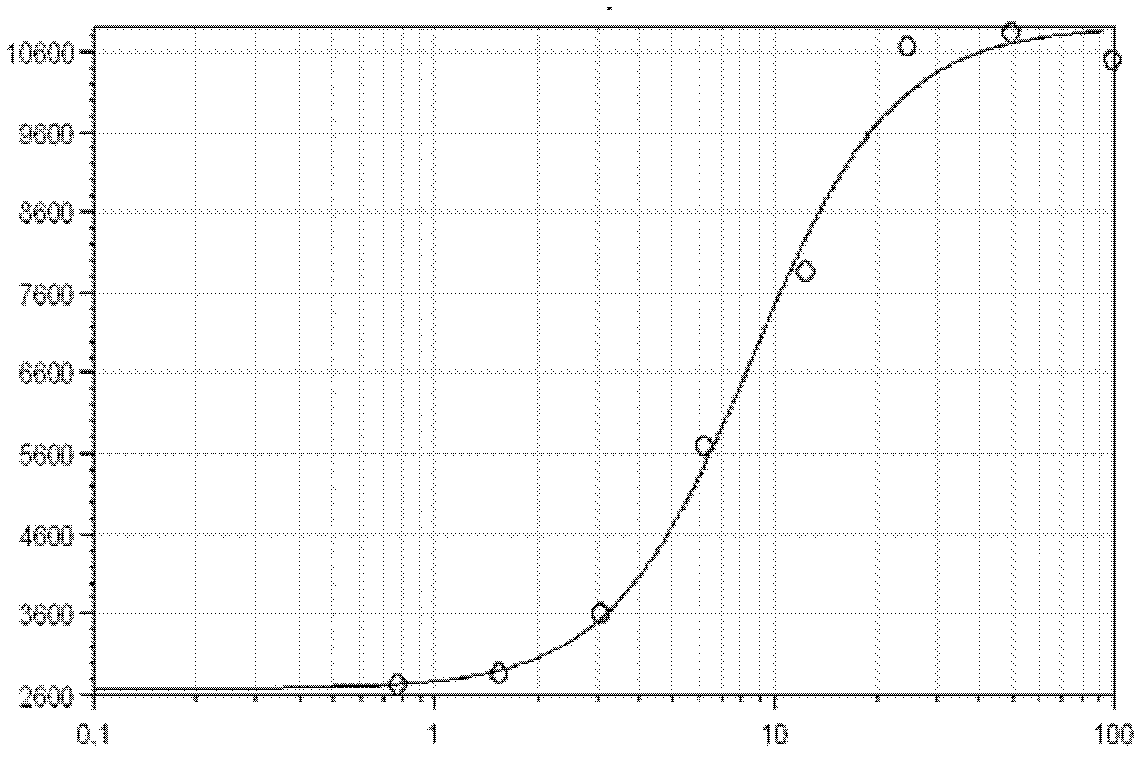
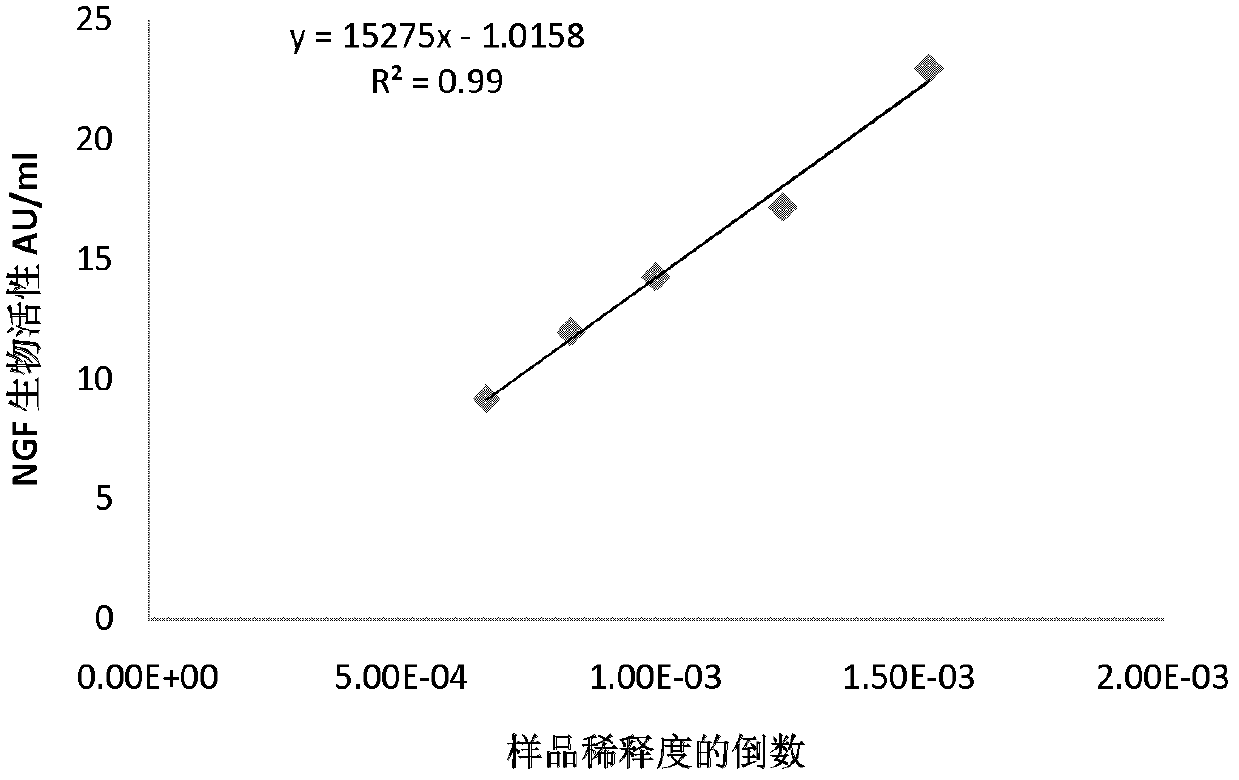
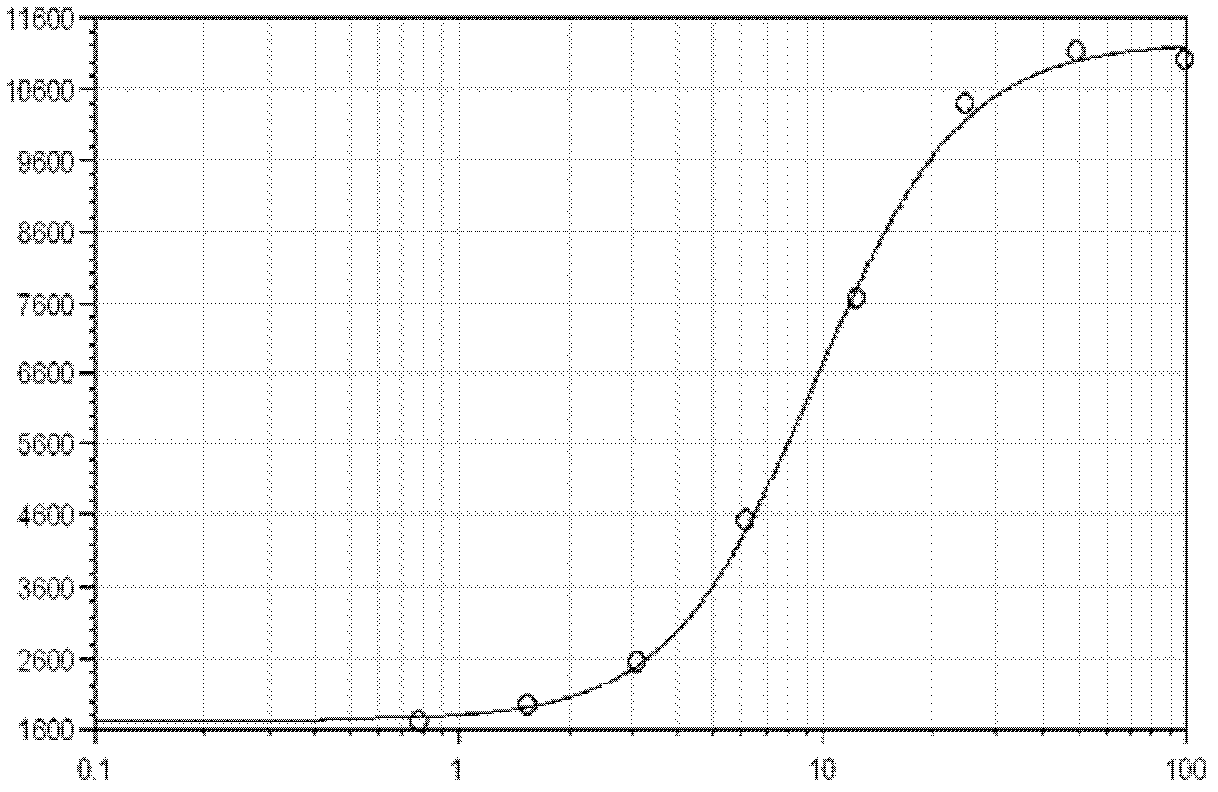
Quantitative determination method for activity of nerve growth factor
The invention discloses a quantitative determination method for activity of a nerve growth factor. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) washing TF-1 cells in a logarithmic phase by a basal culture medium that contains no serum and recombined human granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factors, and then resuspending the TF-1 cells to obtain TF-1cell suspension liquid; (2) respectively adding the TF-1cell suspension liquid into a gradient-diluted nerve growth factor standard sample and a sample to be tested, and incubating at 37 DEG C in presence of 5% of CO2; then respectively adding an indicating agent to detect the absorbance / fluorescence value and drawing a standard curve line; and (3) calculating the activity concentration of the nerve growth factor of the sample to be tested according to the standard curve line and the absorbance / fluorescence value of the sample. The quantitative determination method for activity of the nerve growth factor disclosed by the invention has good accuracy and precision.
Owner:STAIDSON (BEIJING) BIOPHARMACEUTICALS CO LTD
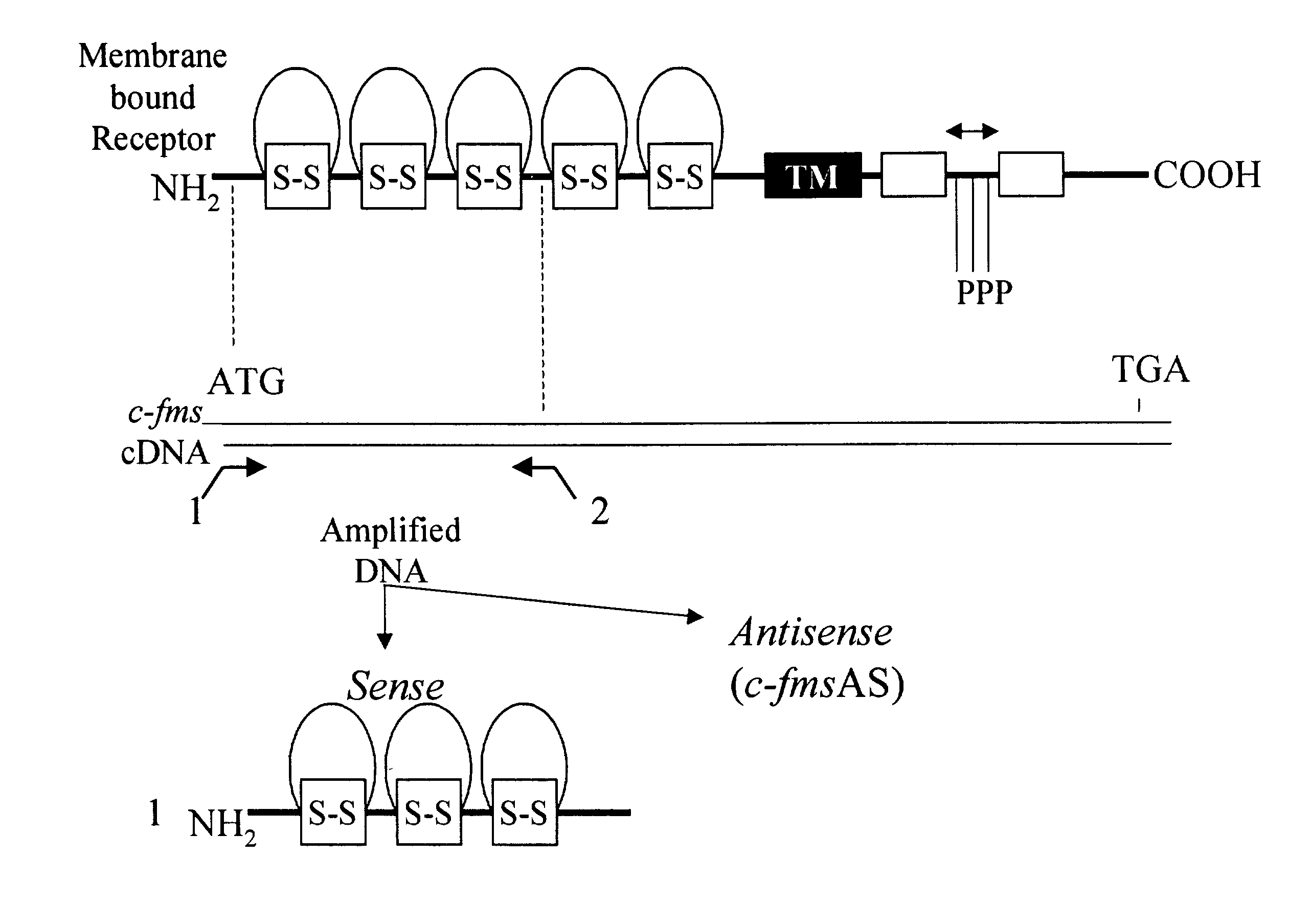
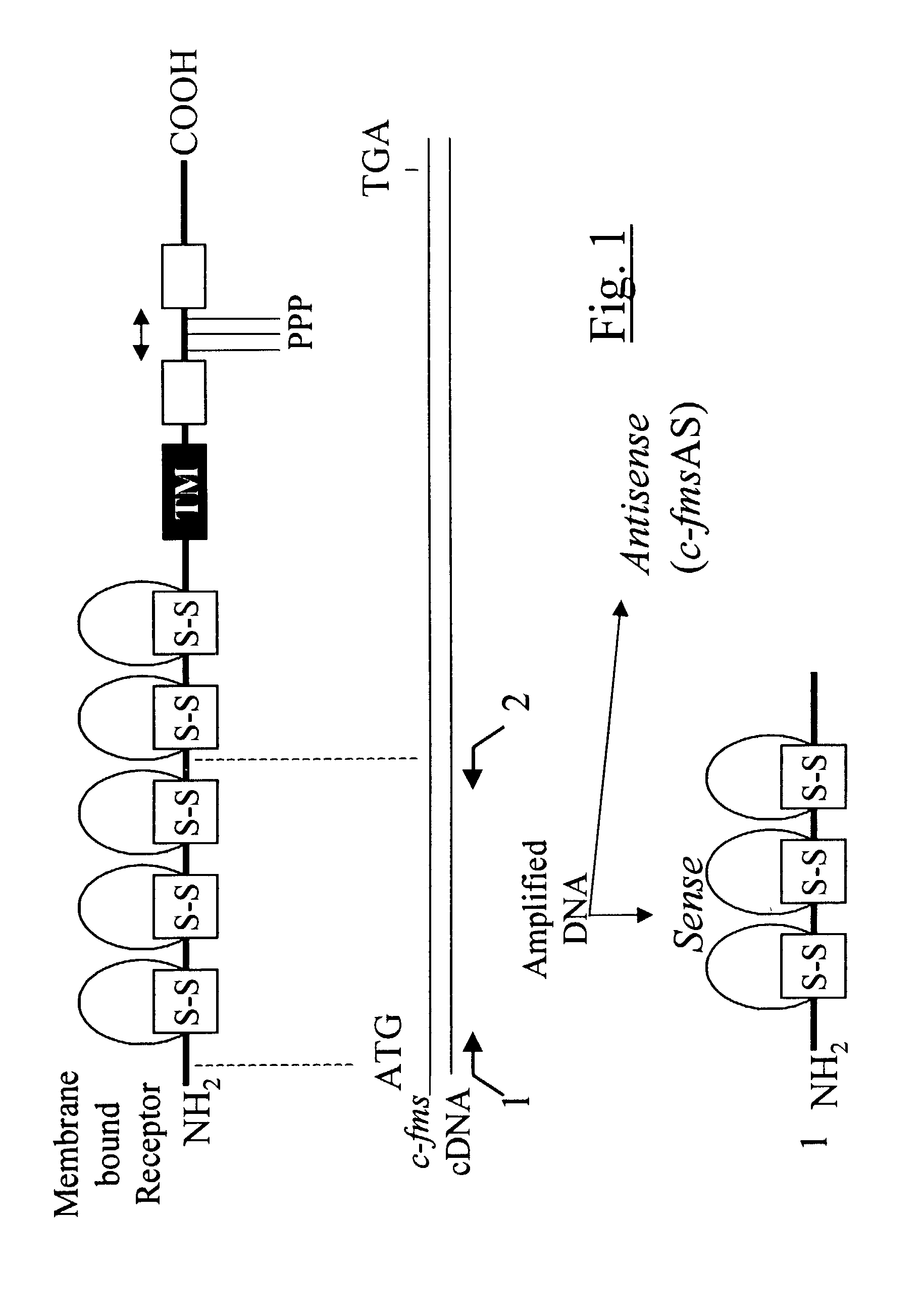
Methods for inhibiting macrophage colony stimulating factor and c-FMS-dependent cell signaling
Owner:RAJAVASHISTH TRIPATHI
Antibodies to GM-CSF
Owner:EISAI INC
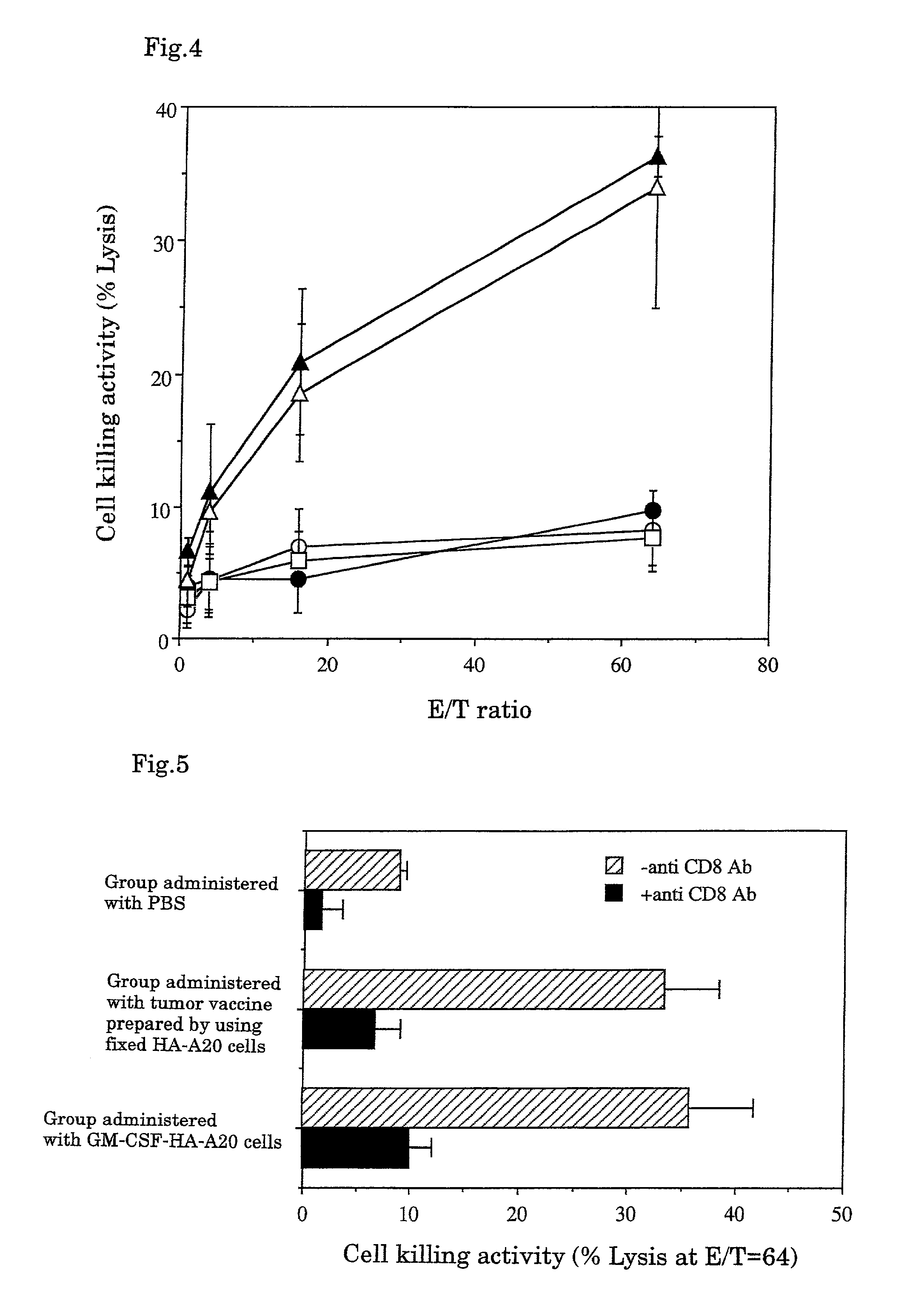
Tumor vaccines
InactiveUS7247310B1Easy to handleImprove anti-tumor effectPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthGranulocyte colony-stimulating factor
A tumor vaccine which comprises a microparticle or a lysate prepared from a solidified tumor material selected from the group consisting of a tumor tissue, a tumor cell, and a component thereof, and at least one cytokine and / or cytokine-inducing agent (e.g., a granulocyte-macrophage-colony stimulating factor and / or interleukin-2 and the like), and optionally an adjuvant. The vaccine can be easily prepared and widely applied for prevention of recurrence, inhibition of metastasis and therapeutic treatment regardless of a type of a tumor, and has excellent antitumor effect.
Owner:RIKEN +1
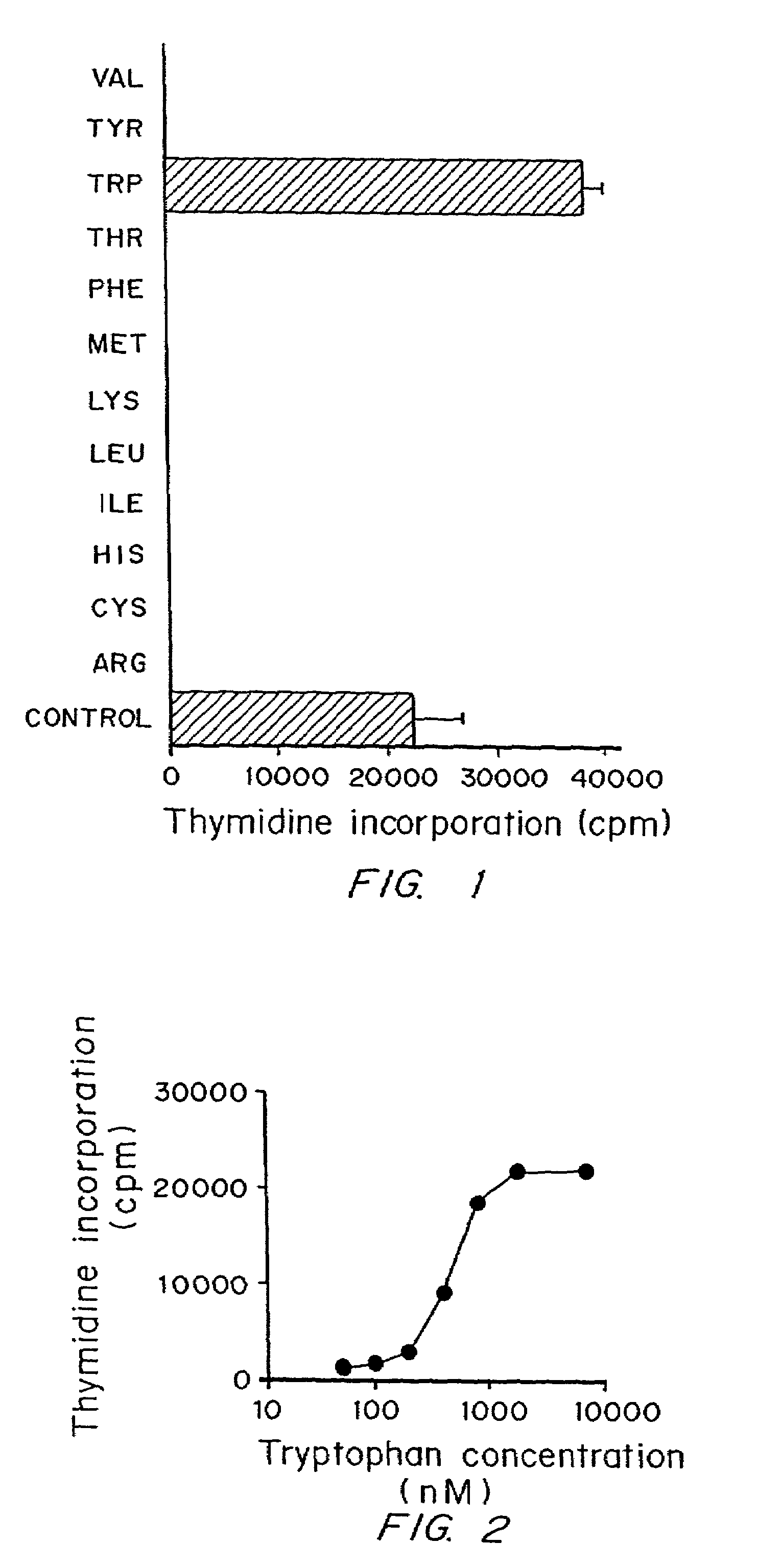
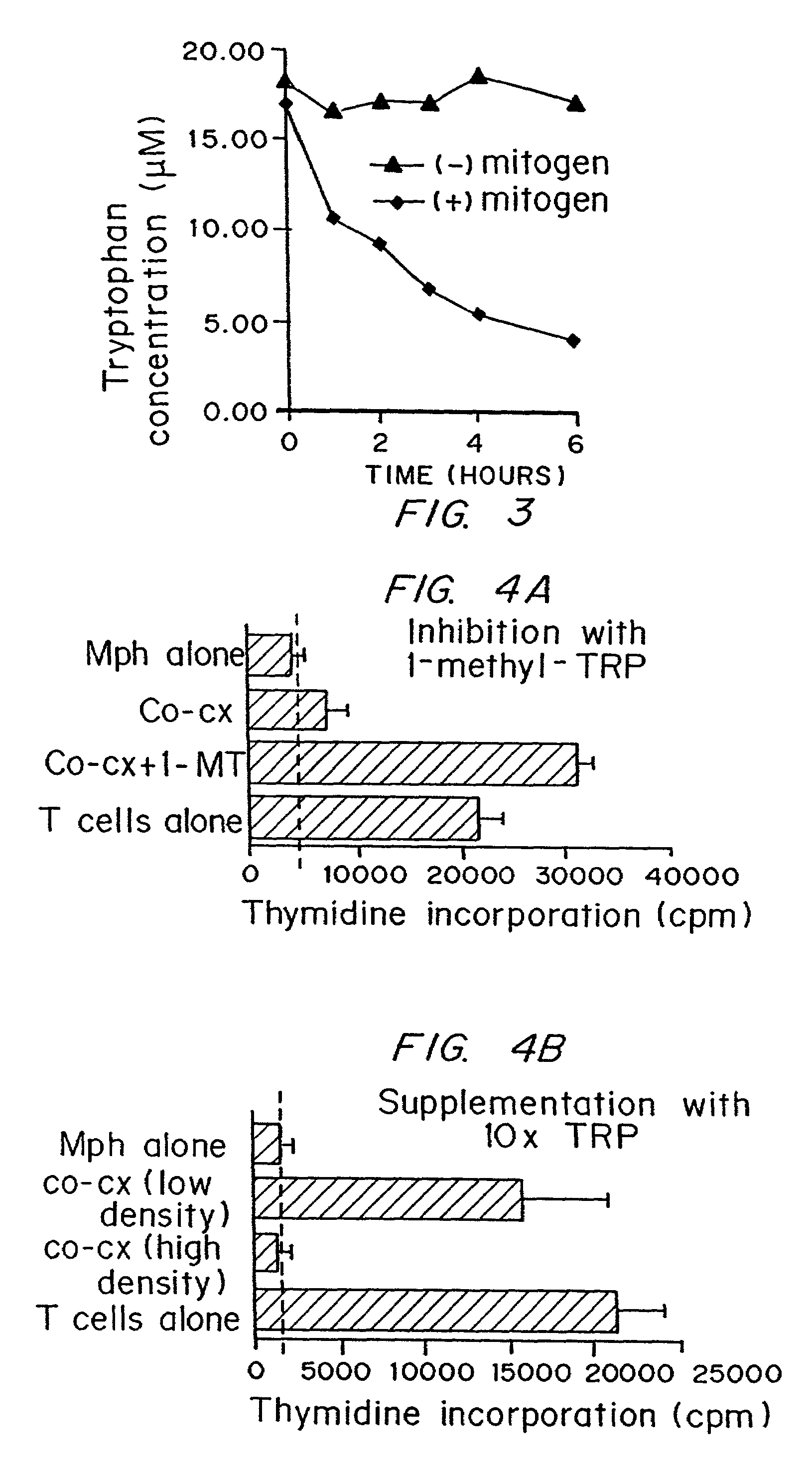
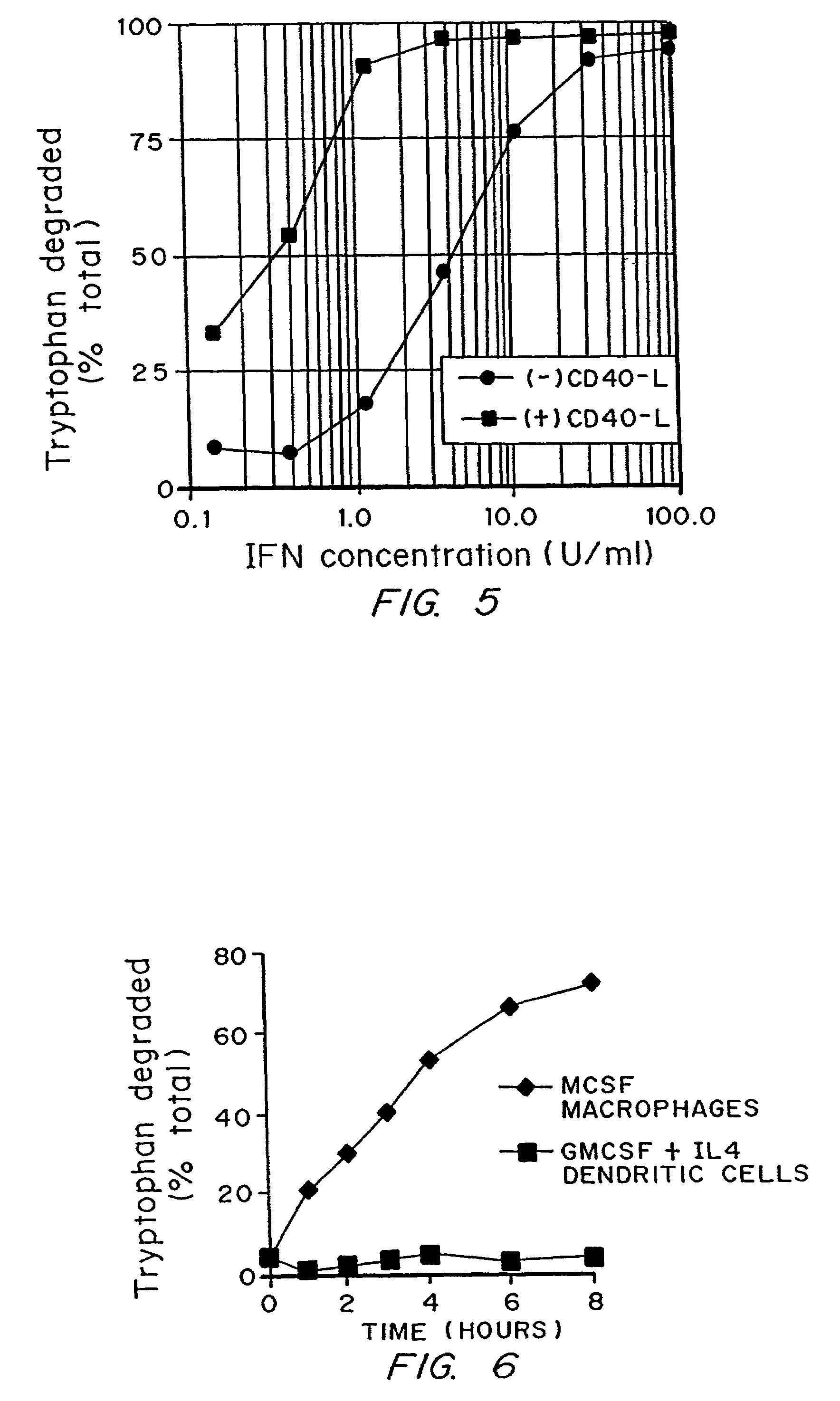
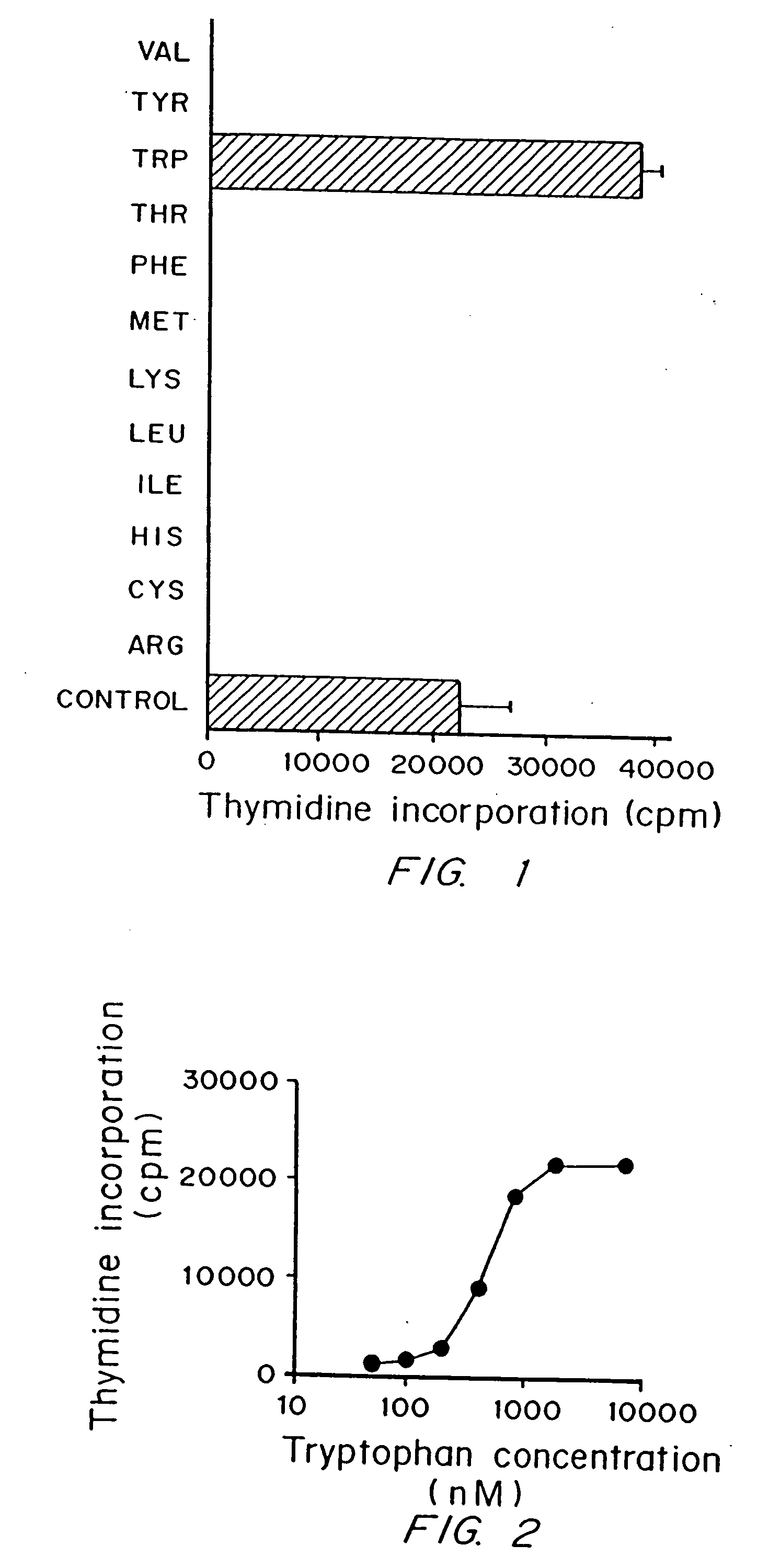
Regulation of T cell-mediated immunity by tryptophan
InactiveUS7160539B2Reduce viral loadAvoid destructionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenPregnancy
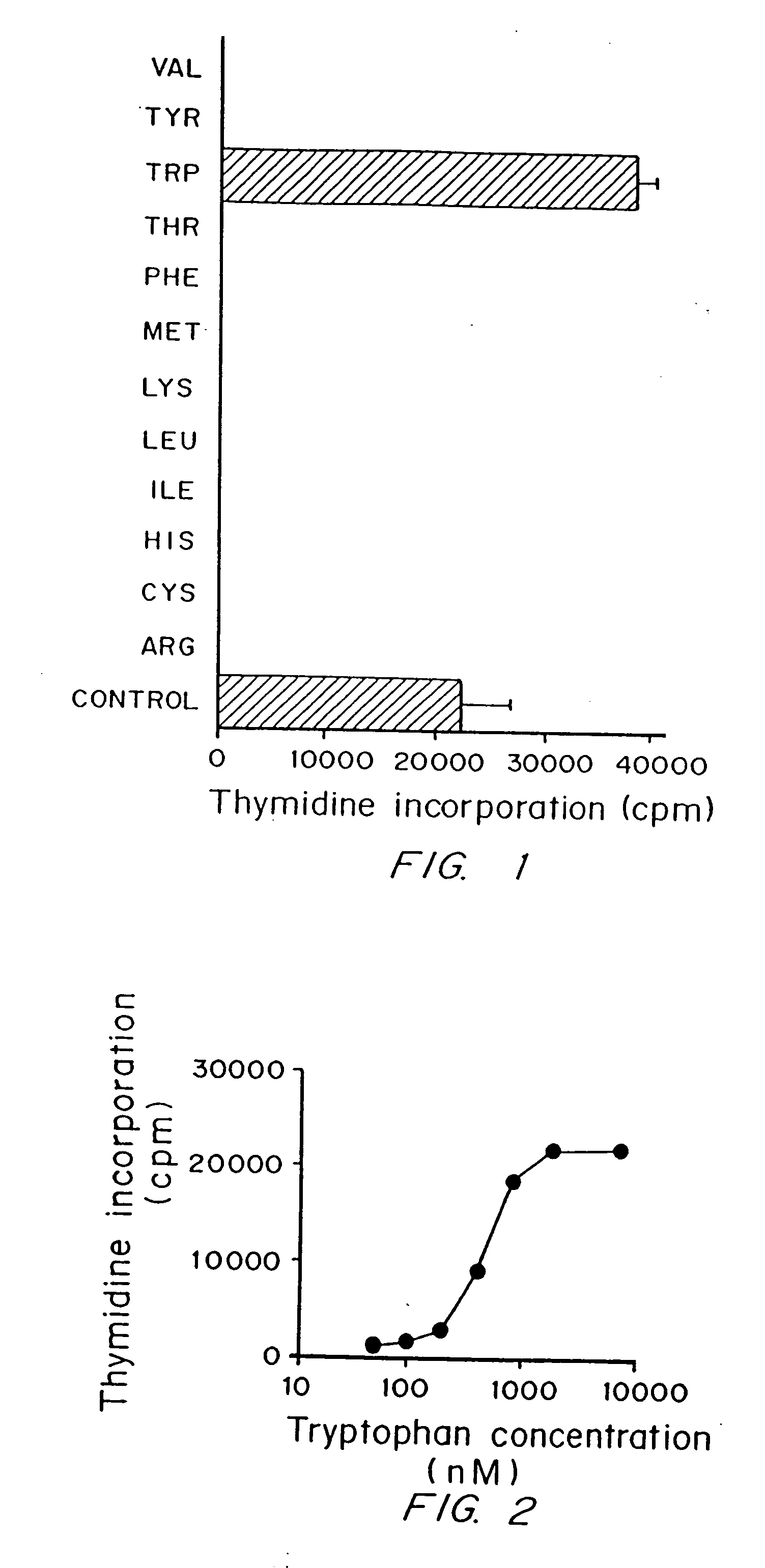
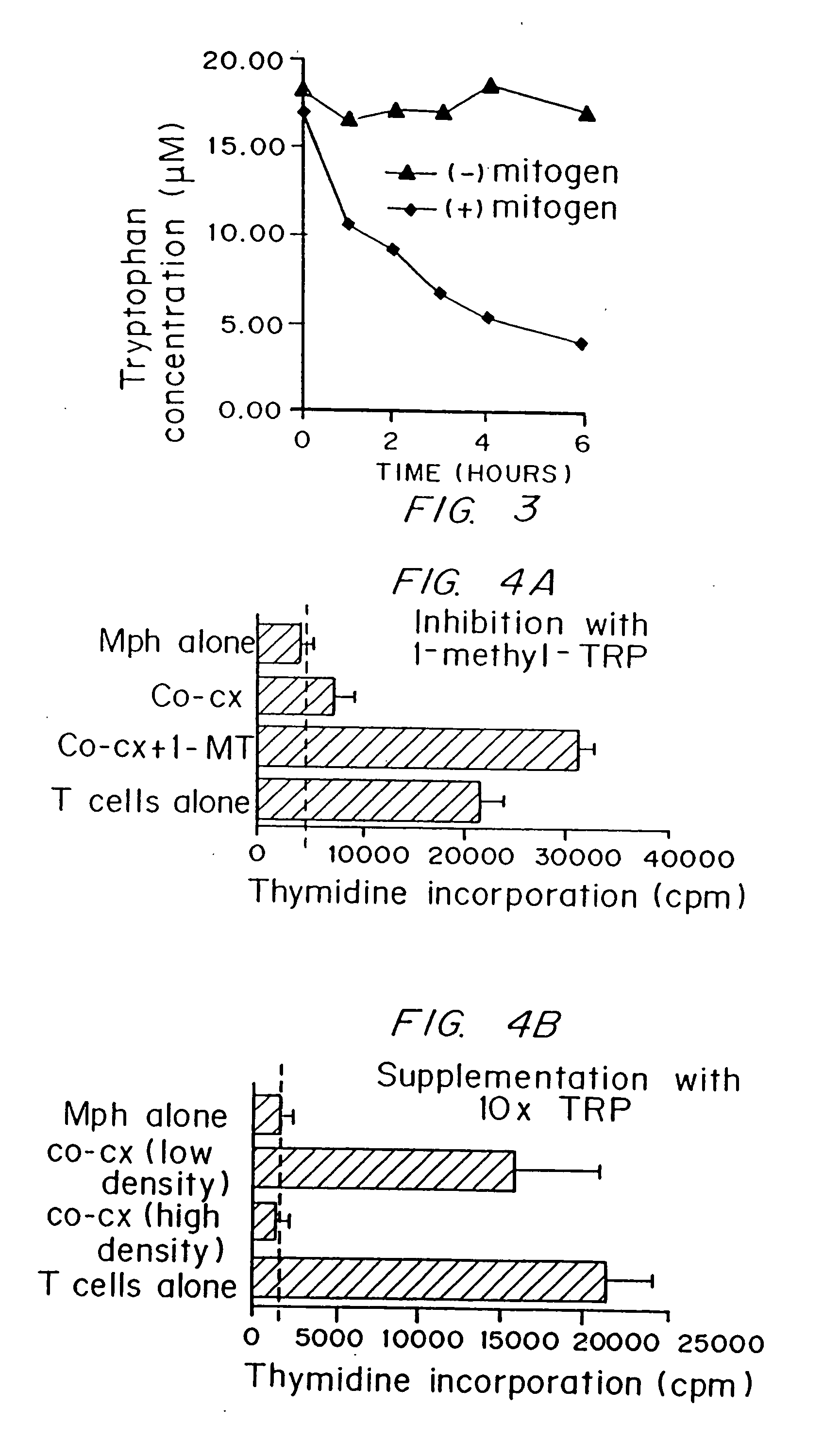
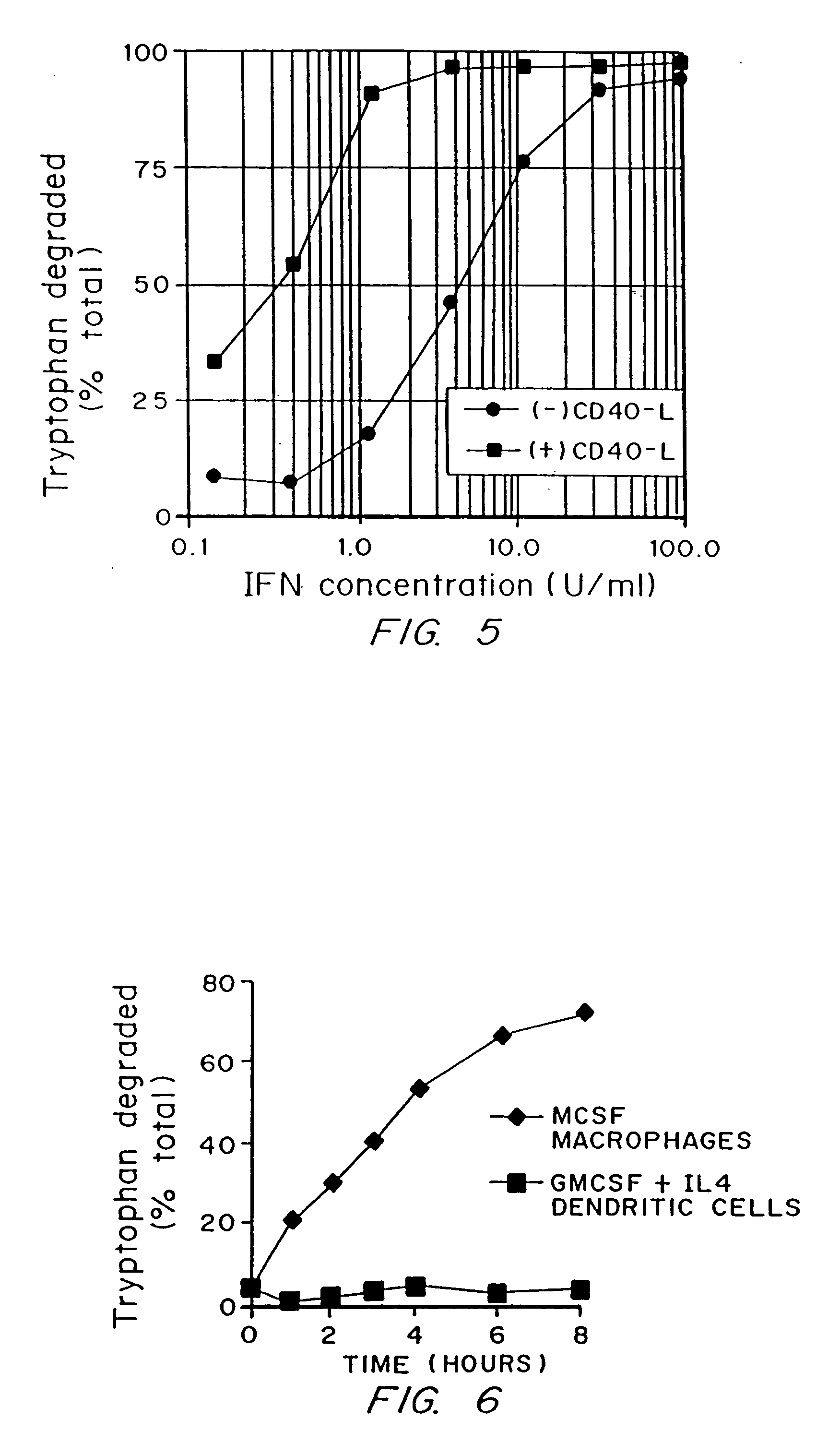
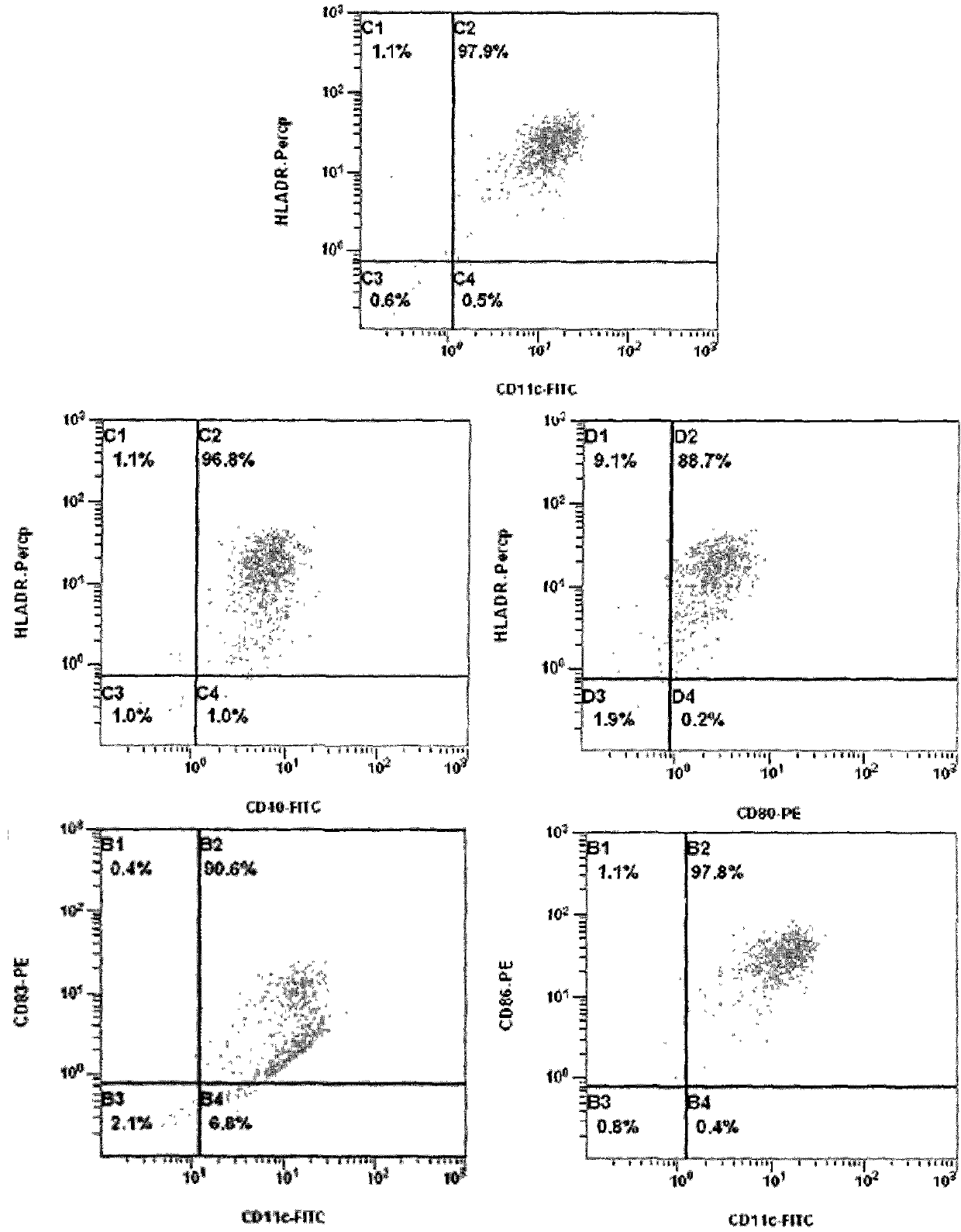
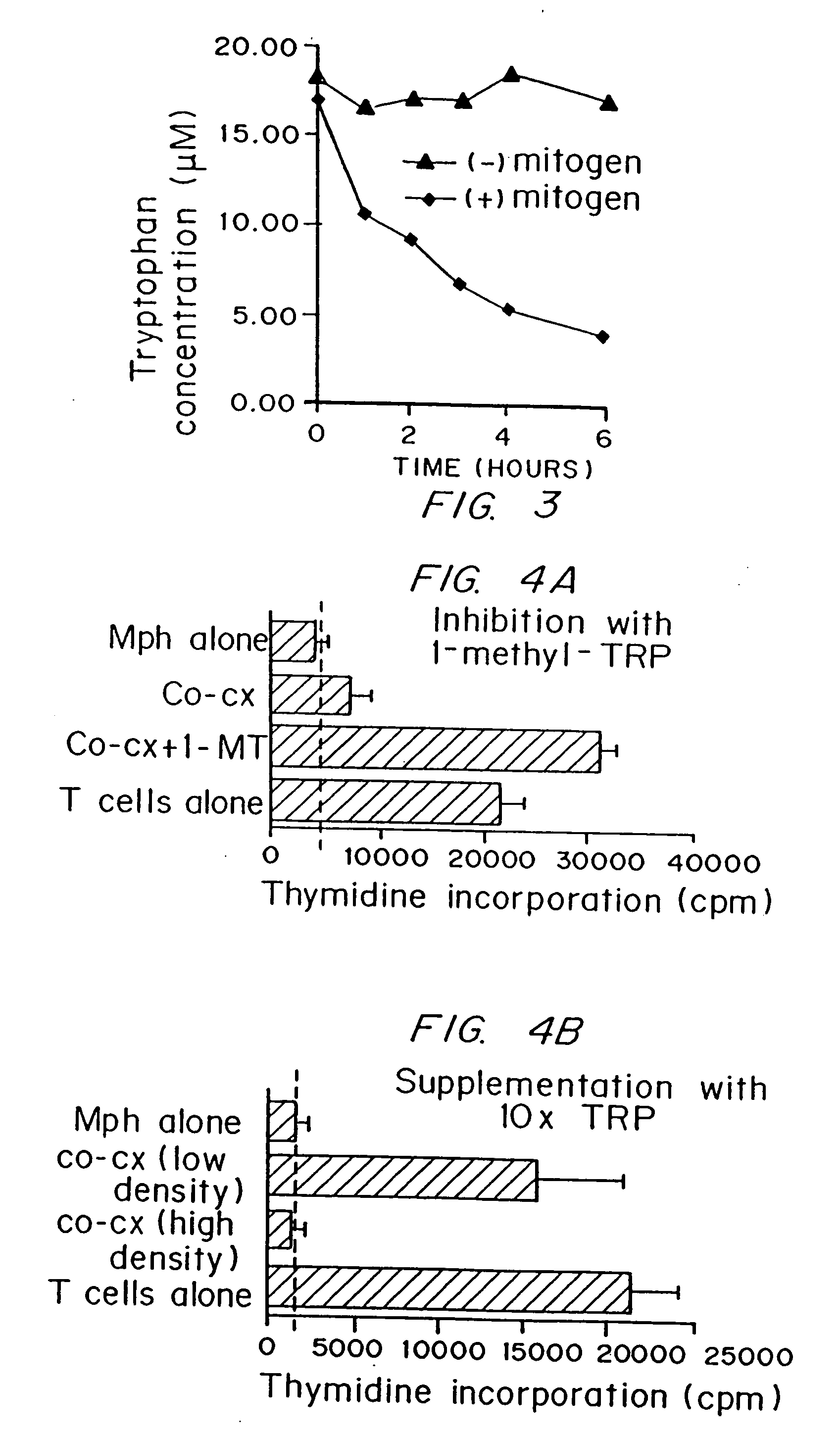
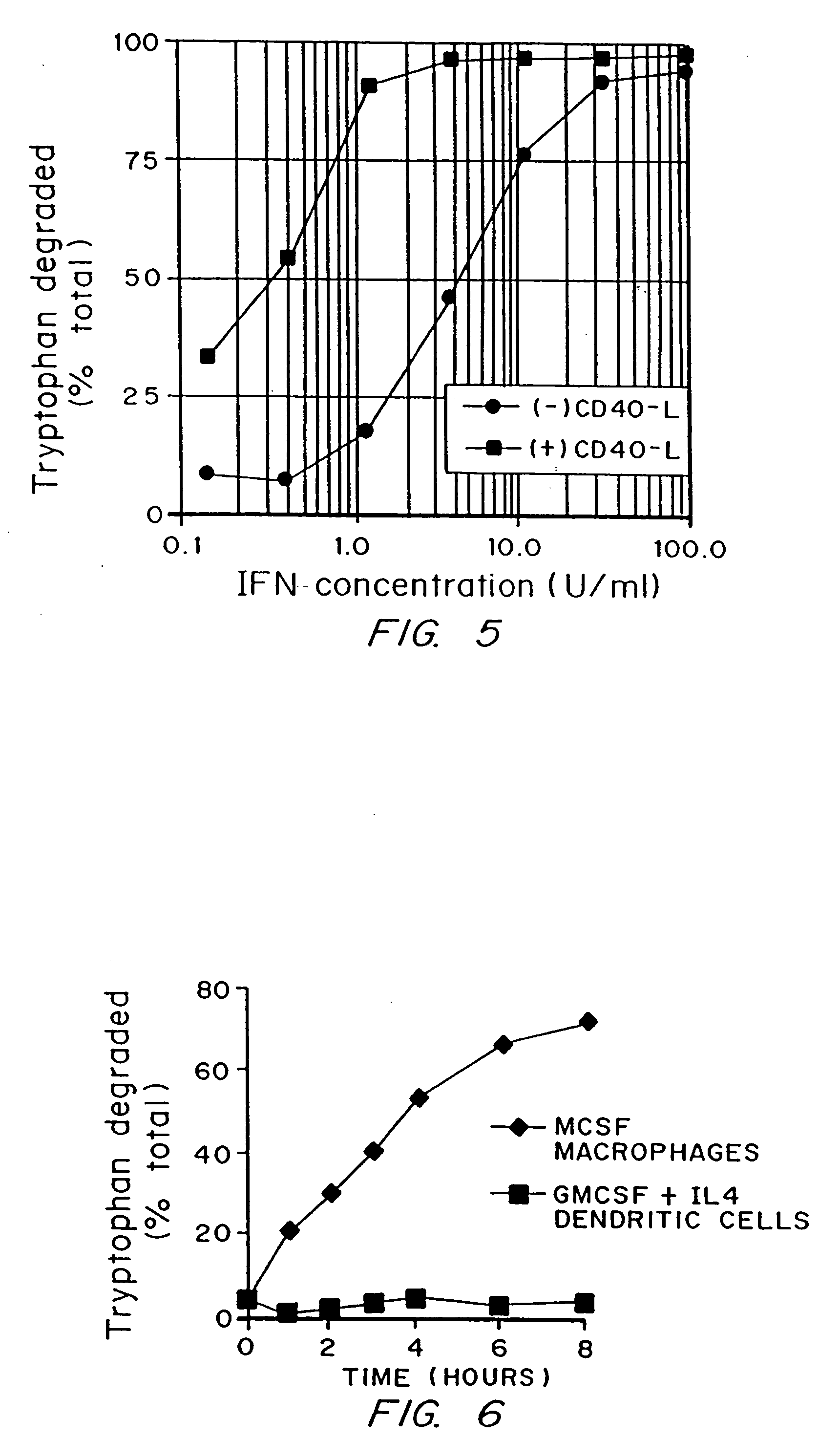
A mechanism of macrophage-induced T cell suppression is the selective elimination of tryptophan and / or increase in one or more tryptophan metabolites within the local macrophage microenvironment Studies demonstrate that expression of IDO can serve as a marker of suppression of T cell activation, and may play a significant role in allogeneic pregnancy and therefore other types of transplantation, and that inhibitors of IDO can be used to activate T cells and therefore enhance T cell activation when the T cells are suppressed by pregnancy, malignancy or a virus such as HIV. Inhibiting tryptophan degradation (and thereby increasing tryptophan concentration while decreasing tryptophan metabolite concentration), or supplementing tryptophan concentration, can therefore be used in addition to, or in place of, inhibitors of IDO. Similarly, increasing tryptophan degradation (thereby , decreasing tryptophan concentration and increasing tryptophan metabolite concentration), for example, by increasing IDO concentration or IDO activity, can suppress T cells. Although described particularly with reference to IDO regulation, one can instead manipulate local tryptophan concentrations, and / or modulate the activity of the high affinity tryptophan transporter, and / or administer other tryptophan degrading enzymes. Regulation can be further manipulated using cytokines such as macrophage colony stimulating factor, interferon gamma, alone or in combination with antigen or other cytokines.
Owner:MEDICAL COLLEGE OF GEORGIA FOUND
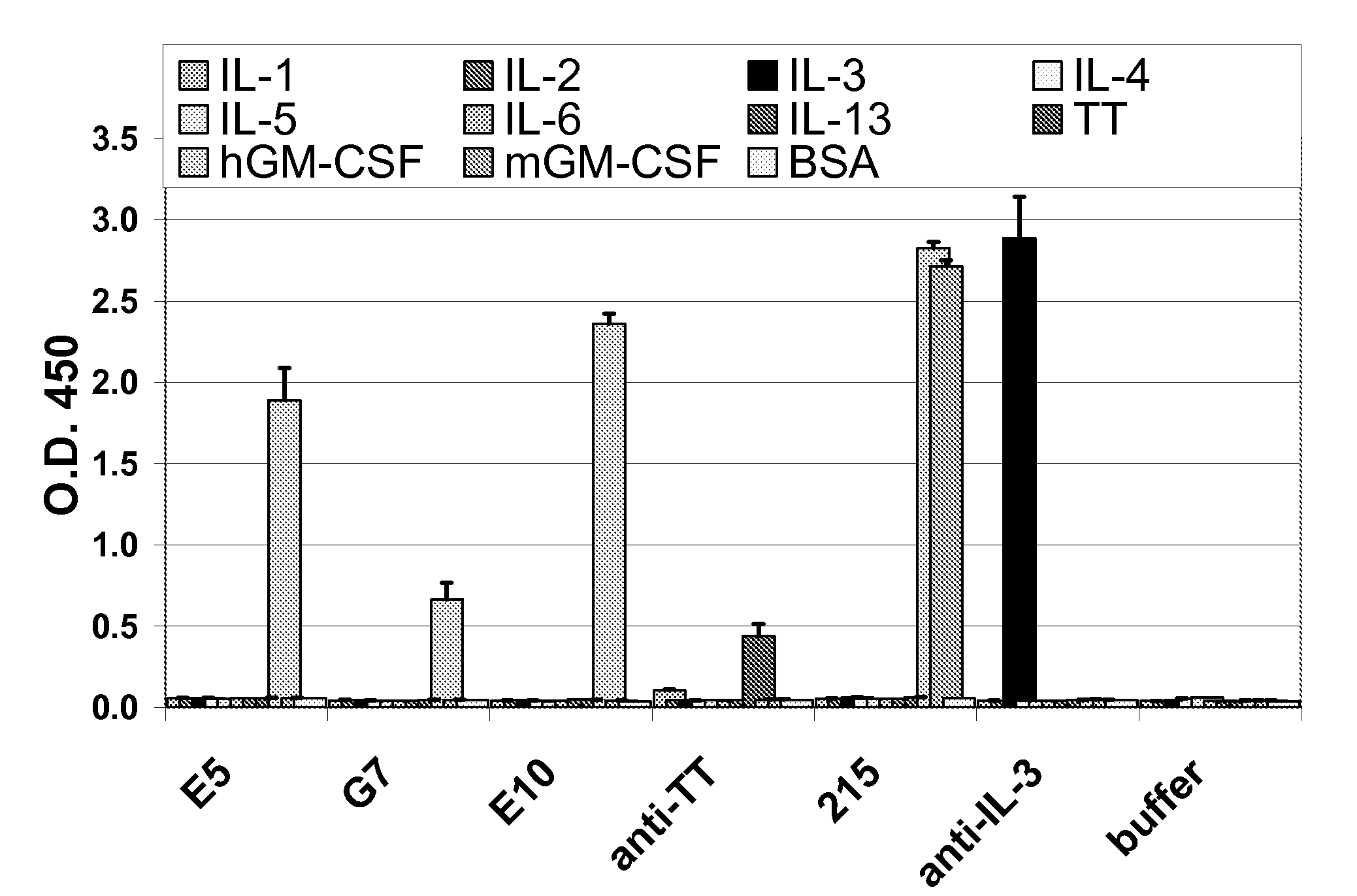
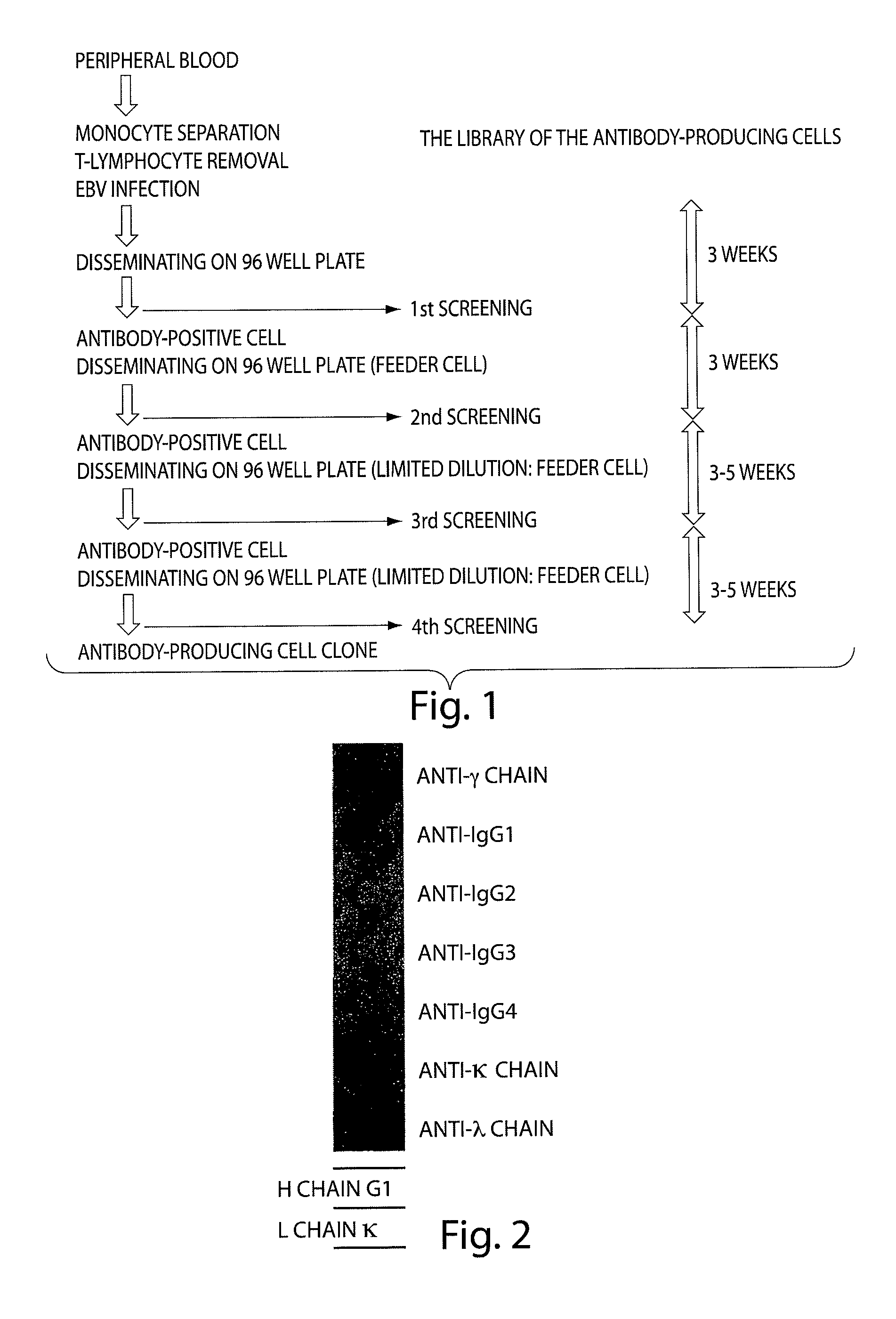
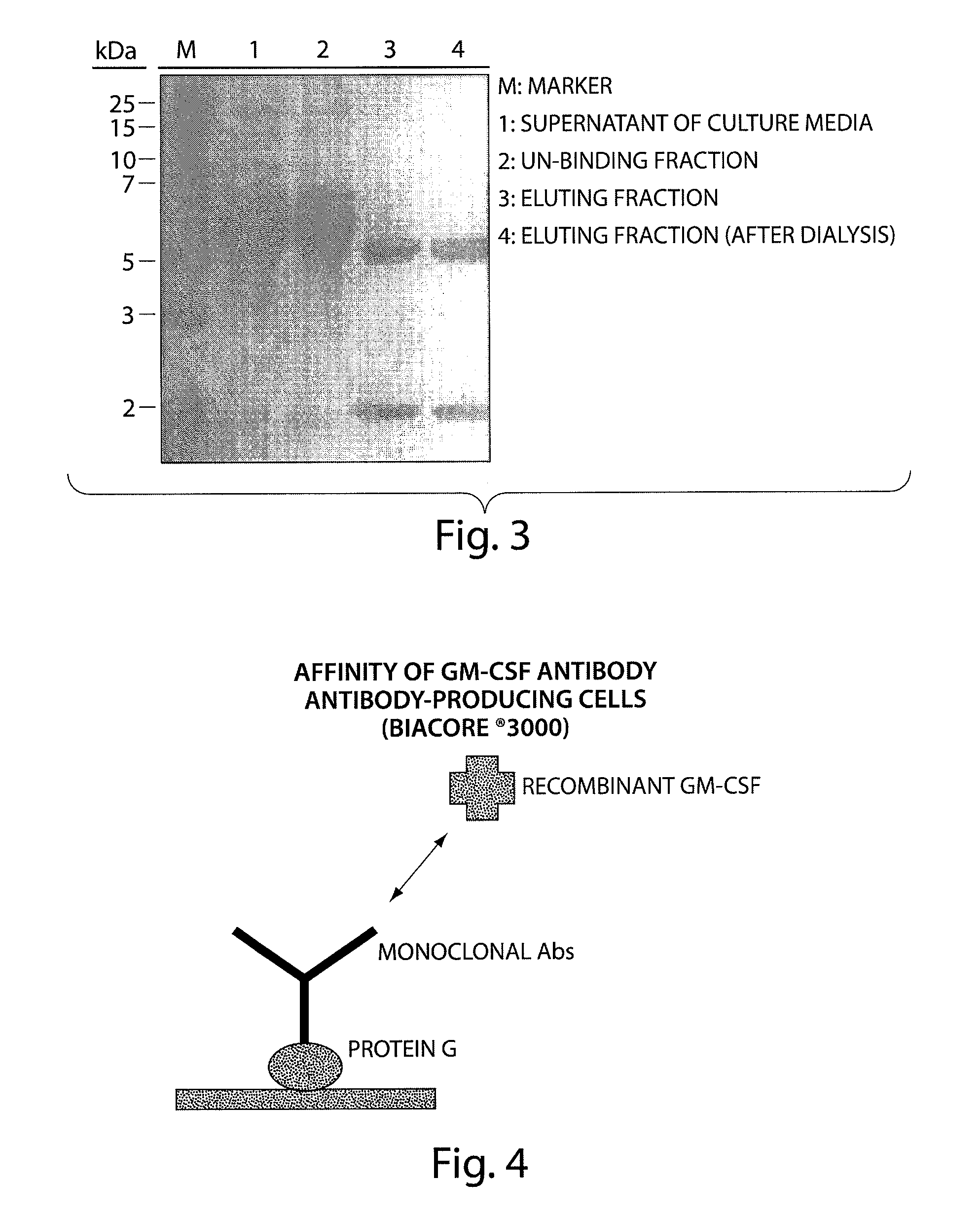
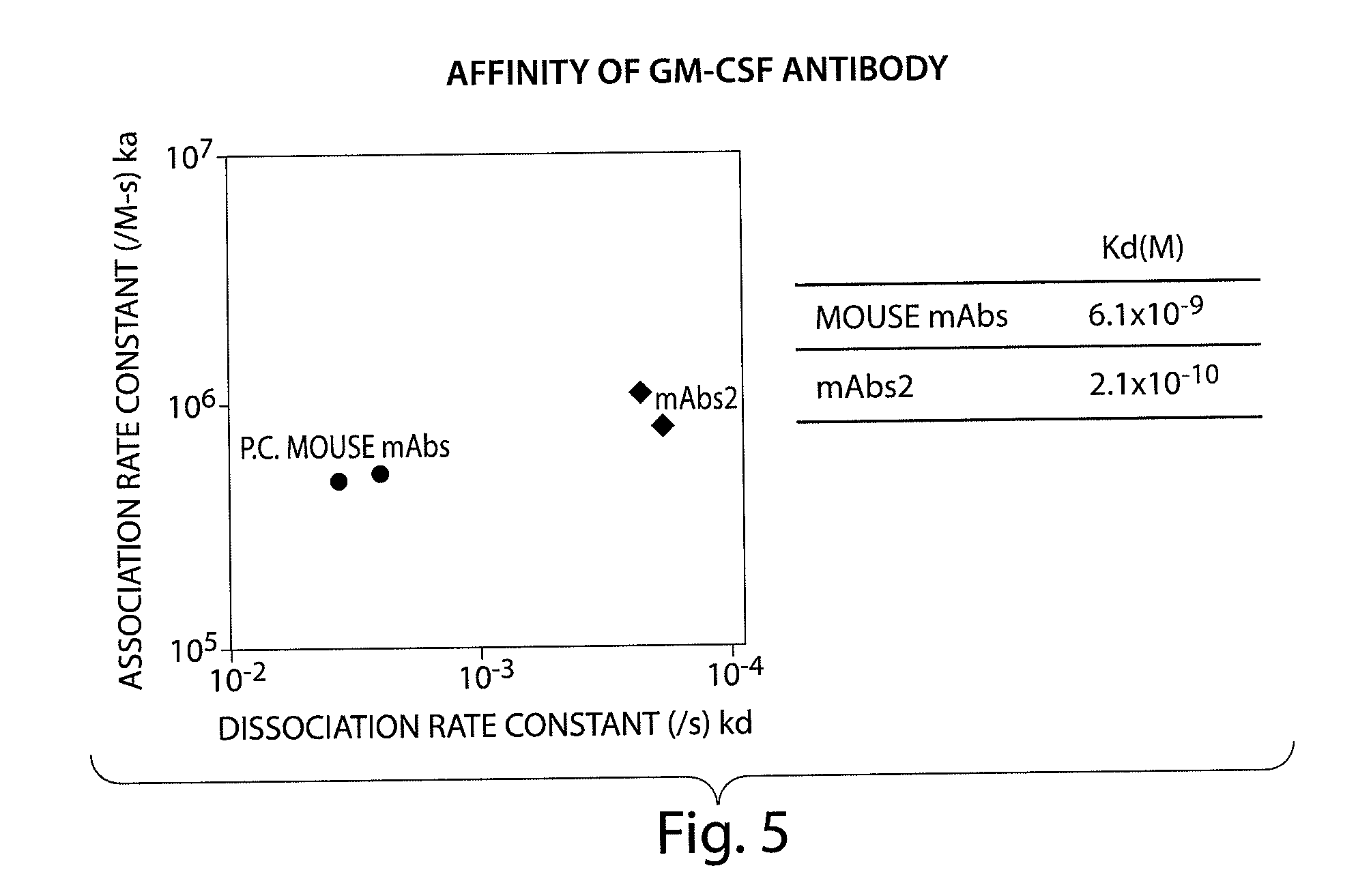
Human monoclonal antibody binding to hGM-CSF and its antigen binding portion
ActiveUS7935795B2High affinityPrevent proliferationSenses disorderAntipyreticComplementarity determining regionAutoimmune disease
The present invention provides a human monoclonal antibody, and antigen-binding portions thereof, capable of binding to human granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (hGM-CSF) and neutralizing the bioactivity of the hGM-CSF, wherein the anti-hGM-CSF monoclonal antibody has a light chain (L chain) including an amino acid sequence SEQ ID NO:1 and a heavy chain (H chain) including an amino acid sequence SEQ ID NO: 2. Also provided are human monoclonal anti-hGM-CSF antibodies, and antigen-binding portions thereof, characterized by complementarity determining regions (CDRs) or H chain and L chain variable regions related to SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2. Antibodies, and antigen-binding portions thereof, of the invention are useful in the treatment of diseases associated with overproduction of hGM-CSF, including allergic disease, graft rejection and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:EVEC
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and prognosis of renal injury and renal failure
ActiveUS8778615B2Easy to adaptMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibody ingredientsInterleukin 10Soluble P-Selectin
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for monitoring, diagnosis, prognosis, and determination of treatment regimens in subjects suffering from or suspected of having a renal injury. In particular, the invention relates to using assays that detect one or more markers selected from the group consisting of Cytoplasmic aspartate aminotransferase, soluble Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 5, soluble CD40 Ligand, soluble C-X-C Motif chemokine 16, S100-A12, Eotaxin, soluble E-selectin, Fibronectin, Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, Heparin-binding growth factor 2, soluble Hepatocyte growth factor receptor, Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, Interleukin-1 beta, Interleukin-10, Interleukin-15, Interleukin-3, Myeloperoxidase, Nidogen-1, soluble Oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor 1, Pappalysin-1, soluble P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1, Antileukoproteinase, soluble Kit ligand, Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1, Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2, soluble Tumor necrosis factor, soluble Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, and Vascular endothelial growth factor A as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in renal injuries.
Owner:ASTUTE MEDICAL
Methods of neuroprotection involving macrophage colony stimulating factor receptor agonists
ActiveUS20120258075A1Preventing and attenuating neuronal damageNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNeuronal damageMedicine
The present invention provides methods for preventing, attenuating neuronal damage or stimulating neuronal repair prior or following central nervous system injury.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Antibodies to magmas and uses thereof
InactiveUS7358041B2Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMitochondrial diseaseGranulocyte
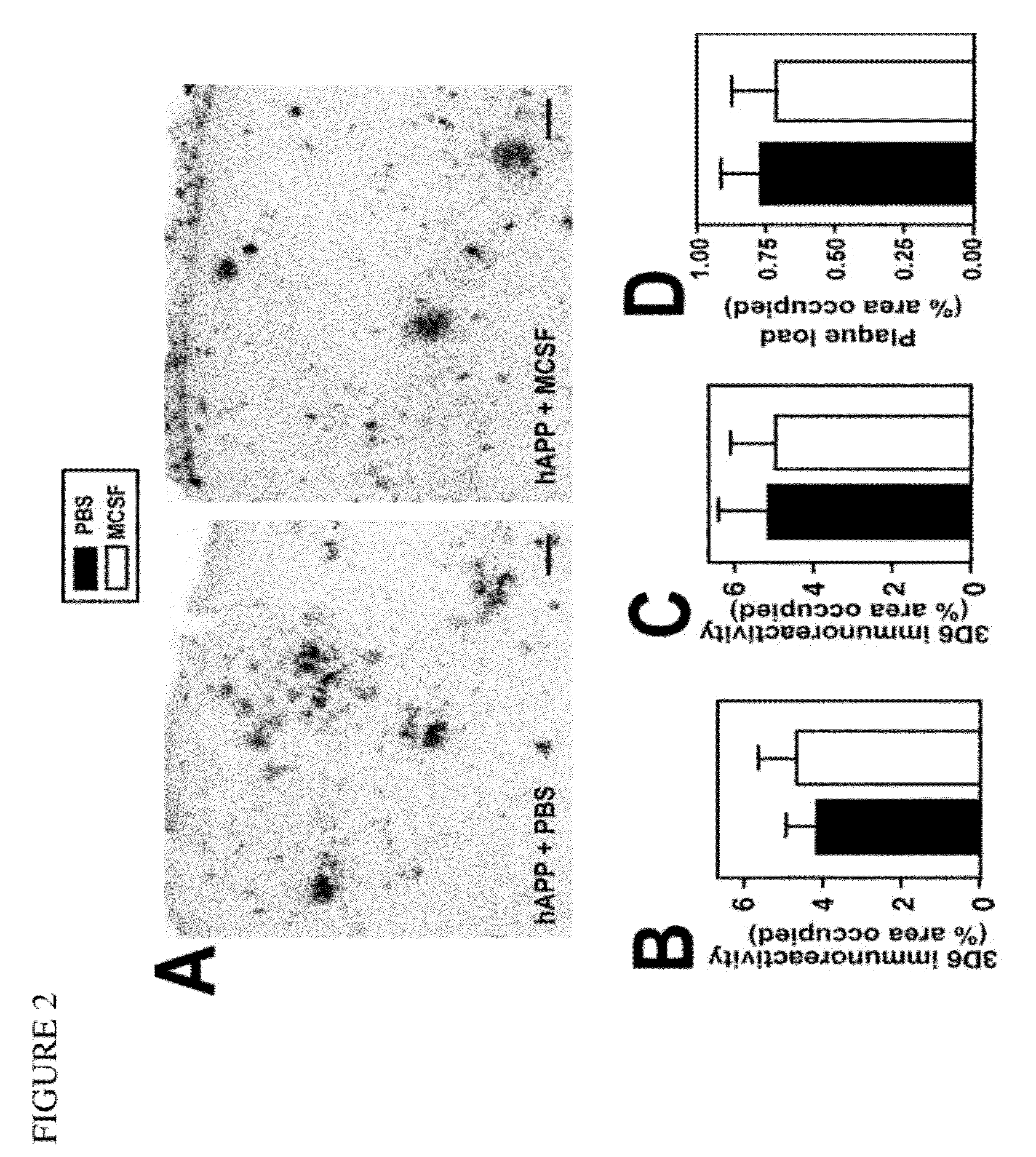
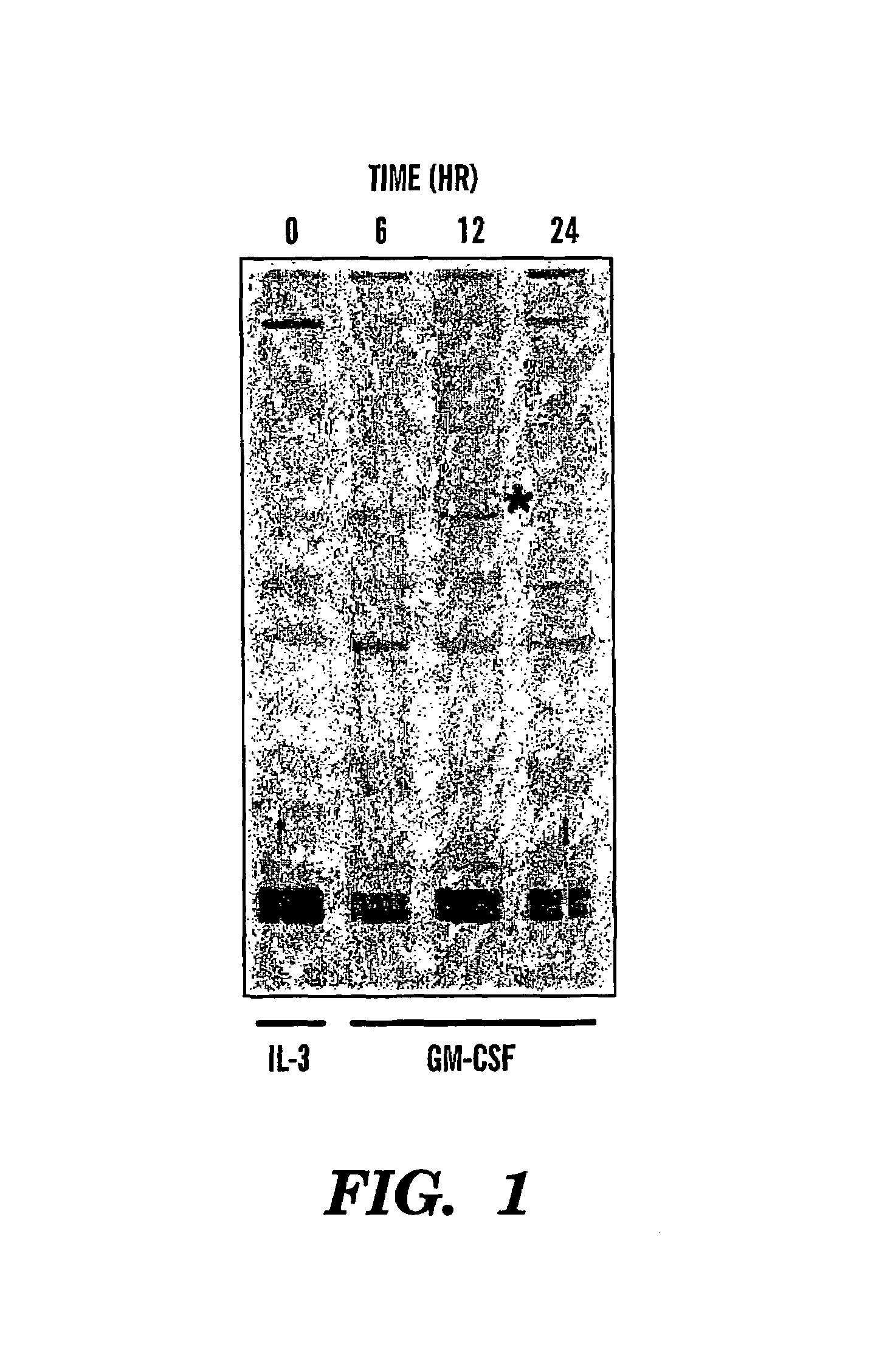
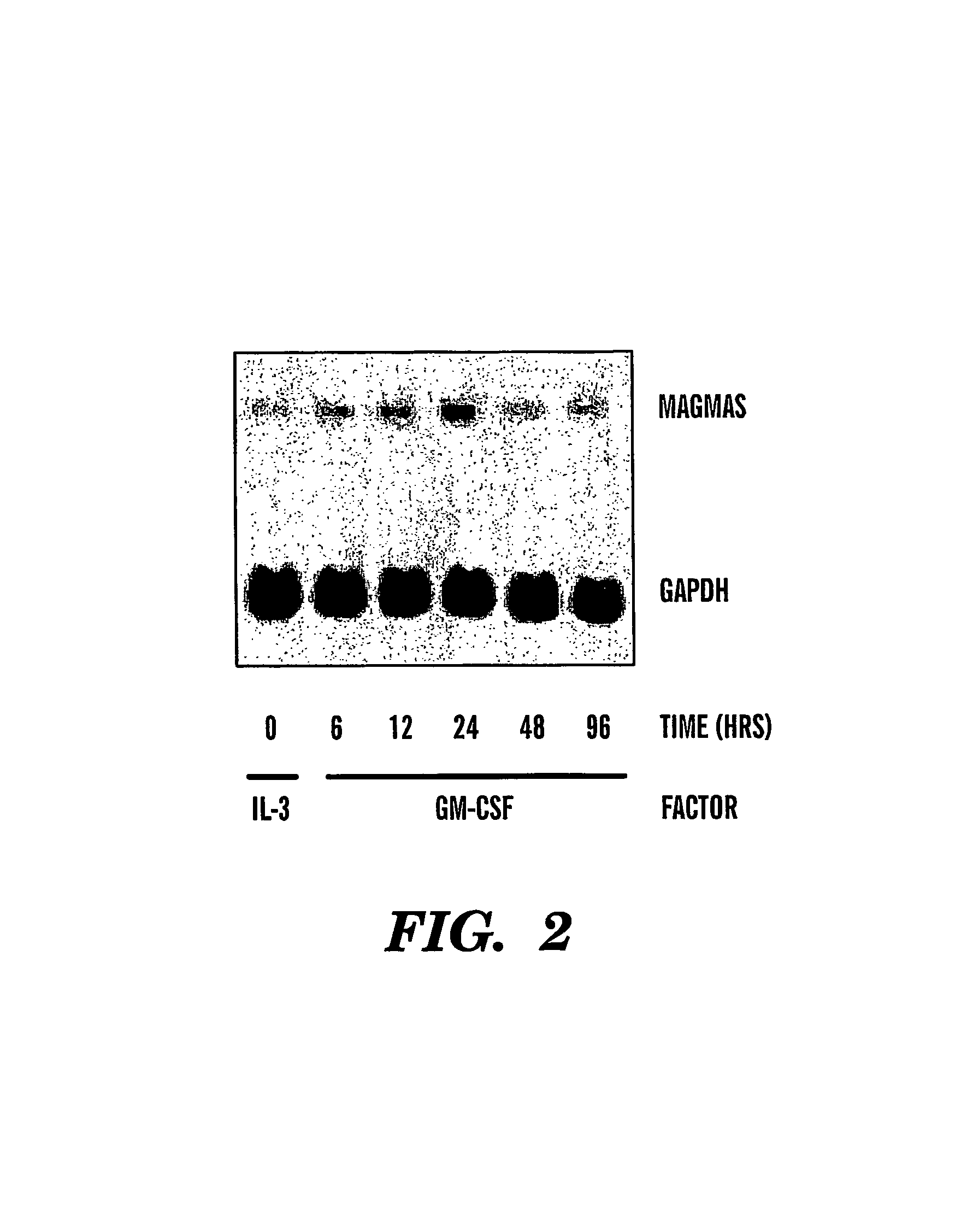
The present invention relates to isolated and purified Magmas protein, isolated and purified nucleic acids encoding Magmas protein, and antibodies to Magmas protein, which interacts with granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF). More specifically, the invention relates to uses of such anti-Magmas antibodies. The invention further relates to a method for diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of diseases, particularly, cancer, Alzheimer's disease and mitochondrial diseases using Magmas sequences and antibodies directed against the Magmas protein or fragments thereof.
Owner:SHORT MARY K +1
Regulation of T cell-mediated immunity by tryptophan
InactiveUS20070077234A1Reduce loadAvoid destructionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenMetabolite
Owner:GEORGIA HEALTH SCI UNIV RES INST
Preparation method of large-scale culture dendritic cell vaccine and application thereof
InactiveCN103301449ABlood/immune system cellsAntibody medical ingredientsWhite blood cellTumor necrosis factor alpha
The invention provides a preparation method of a large-scale culture dendritic cell vaccine. The preparation method comprises the following process steps of: performing in-vitro separation and purification on collected white blood cells in human peripheral blood by adopting a blood cell separation machine to obtain a large number of mononuclear cells, wherein the order of magnitude can be above 10<9>; using a human granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor and interleukin 4 to induce the culture to obtain a large number of immature dendritic cells, wherein the order of magnitude can be above 10<8>; and loading a tumor specific antigen in the immature dendritic cells, and then obtaining the mature dendritic cell vaccine with an anti-tumor effect under the induction culture conditions of a tumor necrosis factor alpha and lipopolysaccharides. The invention further provides a multi-time and multi-treatment course clinical application of the dendritic cell vaccine obtained through the method.
Owner:泰州市数康生物科技有限公司
Methods of neuroprotection involving macrophage colony stimulating factor receptor agonists
ActiveUS20160143996A1Preventing and attenuating neuronal damageNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNeuronal damageMedicine
The present invention provides methods for preventing, attenuating neuronal damage or stimulating neuronal repair prior or following central nervous system injury.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Vaccination with immuno-isolated cells producing an immunomodulator
The present invention relates to immuno-protected encapsulated cells producing an immunomodulator, for example GM-CSF (granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor). The cells of the invention are particularly well adapted for providing an active adjuvant or immunomodulator, for example in the context of immunisation in humans and animals. These cells can be used for vaccination where they provide the immunomodulator in an active form, in a continuous, non-immunogenic manner in the immediate vicinity of the vaccine antigen(s). The invention also relates to a vaccine composition comprising immuno-protected encapsulated cells producing an immunomodulator and an antigenic component. The invention also relates to a kit comprising a cell as described and an antigenic component. The strategy of the invention is perfectly suited for both cancer immunotherapy and vaccination against infectious agents.
Owner:MAXIVAX SA
Methods of neuroprotection involving macrophage colony stimulating factor receptor agonists
ActiveUS9161968B2Preventing and attenuating neuronal damageNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNeuronal damageMedicine
The present invention provides methods for preventing, attenuating neuronal damage or stimulating neuronal repair prior or following central nervous system injury.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Method for culturing osteoclast with mesenchyma stem cell combined with cell factor
InactiveCN101173247AIncrease the number ofSolve the difficulty of mass productionSkeletal/connective tissue cellsMesenchymal stem cellOsteoclast maturation
The invention discloses a culturing method of osteoclasts utilizing mesenchymal stem cells and cytikines, mainly utilizing the mesenchymal stem cells from mouse bone substance and the mouse splenic mononuclear cells and then adding nuclear factor kB receptor activator ligand and macrophage-colony to stimulate the factors. The invention has the advantages: the invention has the advantages of simpleoperation, convenience and practicality, capability of getting osteoclasts at the earliest time, and saving the culture time; the invention gets a large quantity of osteoclasts, solves the problem that osteoclasts are difficult to prepare in large scale, and can meet the need of a general cell biology experiment; the osteoclasts gotten through the invention has high maturity and strong bone substance absorptive capability, which is favorable for the function study; the cell factors needed by the invention is few, which saves expenditure.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Method of isolating and culturing mesenchymal stem cell derived from umbilical cord blood
InactiveCN1878860AImprove the success rate of cultivationMicroorganismsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsInterleukin 6G-csf therapy
The present invention relates to a method of isolating and culturing mesenchymal stem cells using umbilical cord blood that is most ideal for cell therapy. The method comprises adding an anti-coagulant to umbilical cord blood having a volume of more than 45 ml per unit, which is obtained within 24 hours after parturition; diluting the resulting mixture of the anti-coagulant and umbilical cord blood with an alphaMEM (alpha-minimum essential medium), followed by centrifugation to harvest monocytes; and subjecting the obtained monocytes into suspension culture in the alphaMEM containing Stem Cell Factor, GM-CSF (granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor), G-CSF (granulocyte colony-stimulating factor), IL-3 (interleukin-3) and IL-6 (interleukin-6).
Owner:韩薰
In Vitro Generation of Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells
InactiveUS20120082688A1Genetically modified cellsSnake antigen ingredientsMyeloid-derived Suppressor CellBone marrow
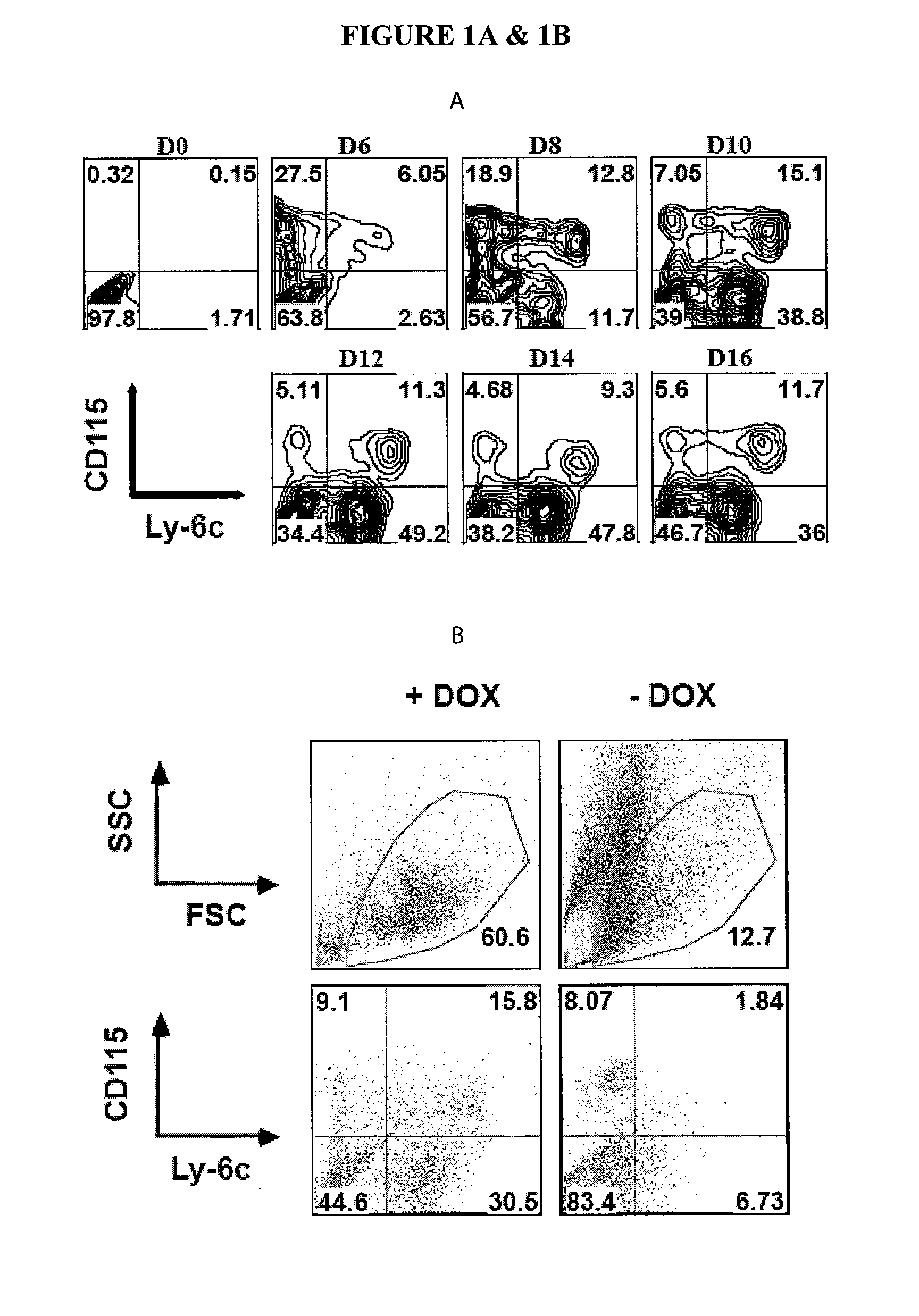
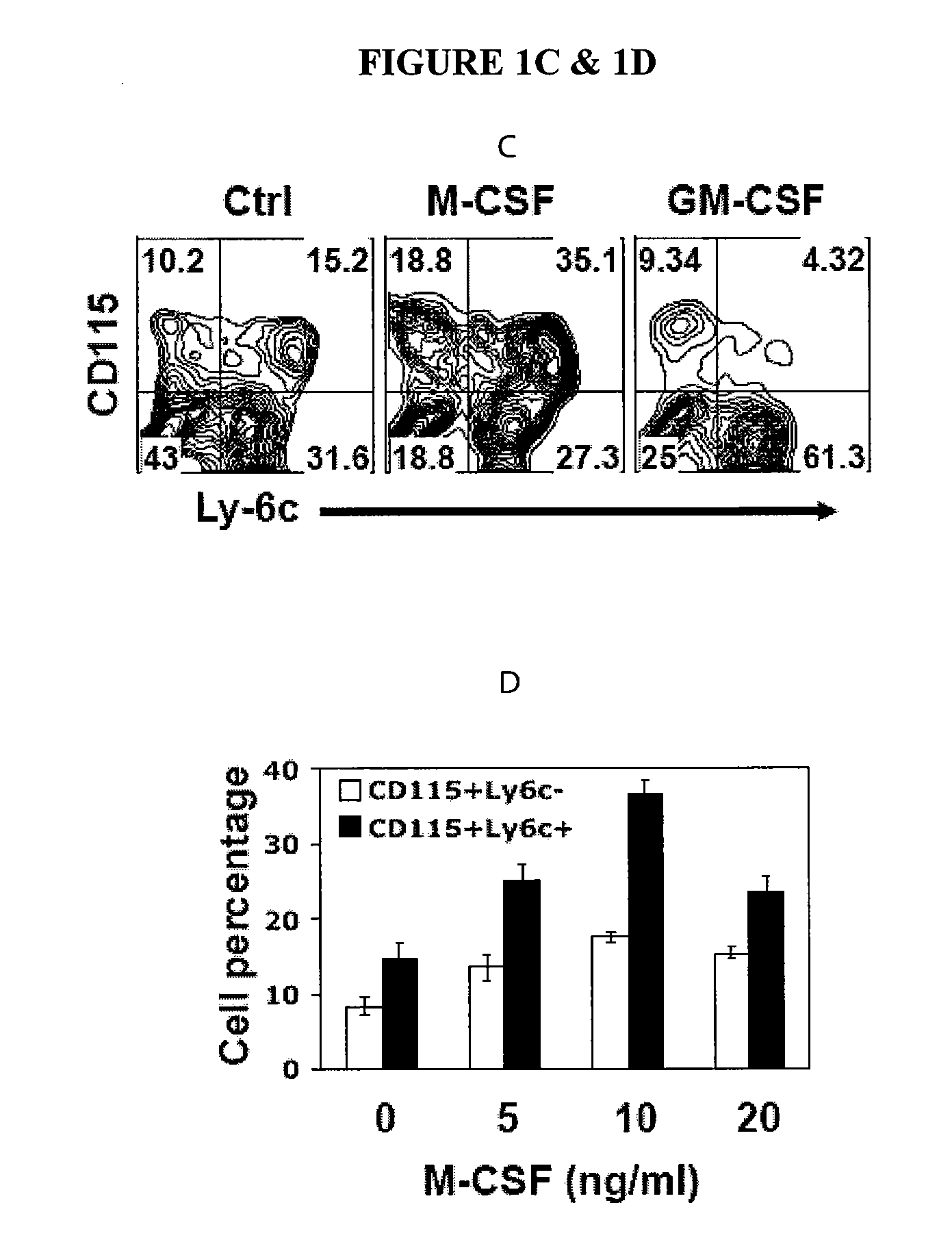
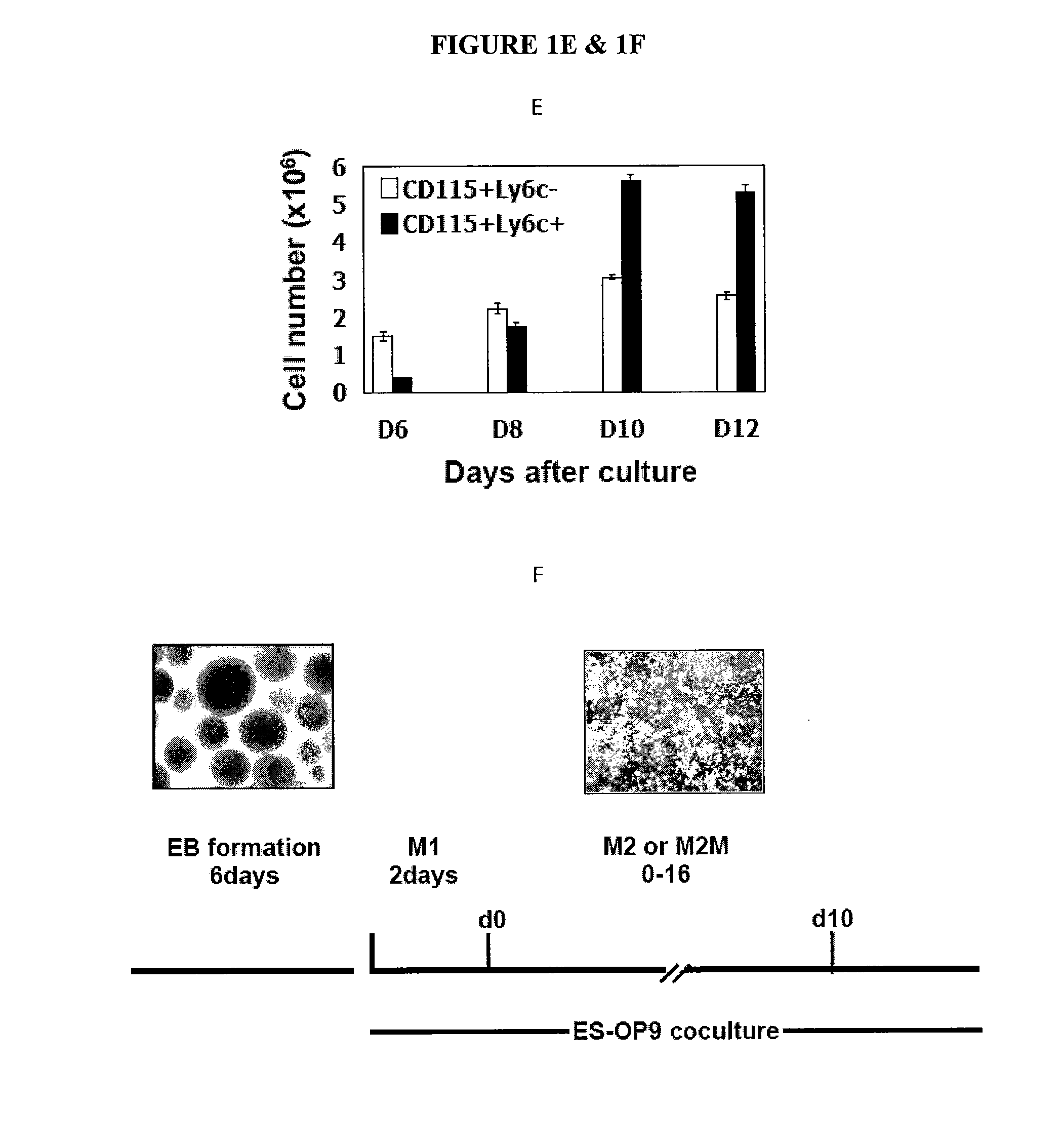
The invention relates to methods of isolating, culturing, and differentiating myeloid derived suppressor cells (MD-SCs) from embryonic stem (ES) cells and hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). In certain embodiments, the invention relates to methods and compositions for producing MDSCs from ES cells and HSCs using a combination of factors including macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF).
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Cosmetic Compositions
Disclosed is a method for preventing and / or soothing dry or sensitive skin against external stresses, comprising contacting the skin with a composition including an agent that decreases the release of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GMCSF) from keratinocytes in the skin, wherein under conditions of external stress, dry or sensitive skin is soothed and / or prevented. Agents that decrease the release of GMCSF include silybin, piperine, tetrahydropiperine, nortrachelogenine, rhapontin, arctiin, artigenin and mixtures thereof. Also disclosed is a method of identifying an agent that decreases the level of GMCSF released from keratinocytes.
Owner:COGNIS IP MANAGEMENT GMBH
Synthetic gene coding for human granulocyte-colony stimulating factor for the expression in E. coli
InactiveUS7655437B2Improved expression level (accumulation)Antibacterial agentsBacteriaEscherichia coliColony-stimulating factor
Owner:LEK PHARMA D D
Compositions to promote the healing of skin ulcers and wounds
InactiveUS20160346354A1Promote defense mechanismPromote wound healingPeptide/protein ingredientsHydroxy compound active ingredientsSkin ulcerationsGranulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor
The present invention provides compositions comprising as an essential feature granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) together with fosfomycin for the treatment of wounds, ulcers, sores, burns and other injuries to the skin or mucous membranes of the body.
Owner:REPONEX PHARMA APS
Regulation of T cell-mediated immunity by tryptophan
InactiveUS20070077224A1Reduce loadAvoid destructionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenMetabolite
A mechanism of macrophage-induced T cell suppression is the selective elimination of tryptophan and / or increase in one or more tryptophan metabolites within the local macrophage microenvironment. Studies demonstrate that expression of IDO can serve as a marker of suppression of T cell activation, and may play a significant role in allogeneic pregnancy and therefore other types of transplantation, and that inhibitors of IDO can be used to activate T cells and therefore enhance T cell activation when the T cells are suppressed by pregnancy, malignancy or a virus such as HIV. Inhibiting tryptophan degradation (and thereby increasing tryptophan concentration while decreasing tryptophan metabolite concentration), or supplementing tryptophan concentration, can therefore be used in addition to, or in place of, inhibitors of IDO. Similarly, increasing tryptophan degradation (thereby, decreasing tryptophan concentration and increasing tryptophan metabolite concentration), for example, by increasing IDO concentration or IDO activity, can suppress T cells. Although described particularly with reference to IDO regulation, one can instead manipulate local tryptophan concentrations, and / or modulate the activity of the high affinity tryptophan transporter, and / or administer other tryptophan degrading enzymes. Regulation can be further manipulated using cytokines such as macrophage colony stimulating factor, interferon gamma, alone or in combination with antigen or other cytokines.
Owner:MEDICAL COLLEGE OF GEORGIA RES INST
Purification method of recombinant yeast strain and rhGM-CSF to express human granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor
InactiveCN1487086AHigh specific activityReduce separation and purification stepsFungiPeptide preparation methodsEscherichia coliBiotechnology
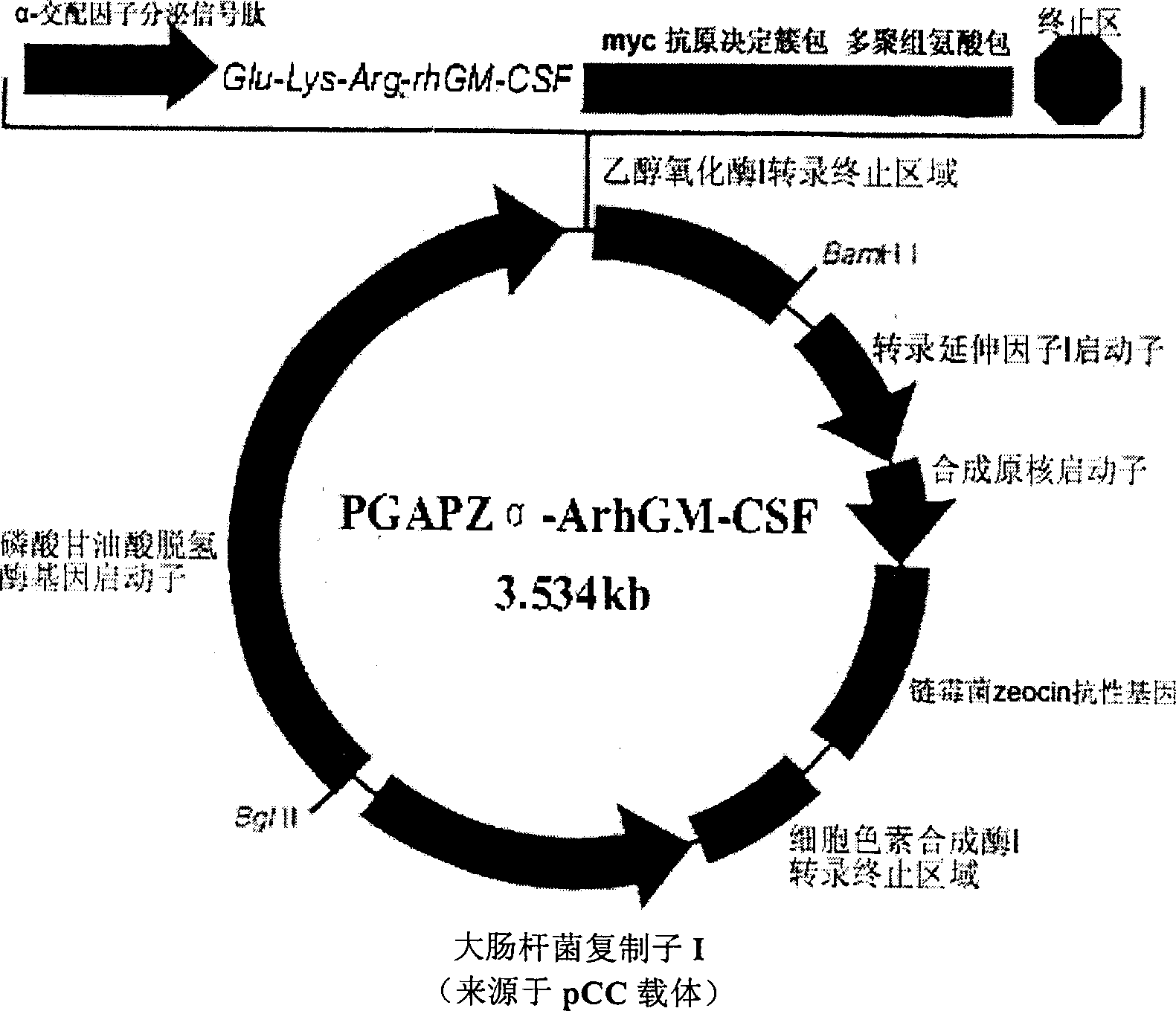
The present invention discloses one kind of secretion vector of recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (rhGM-CSF) and its simple purification method, host cell transformed with the secretion vector, as well as the method of fermentation with the recombinant pichia yeast engineering strain of the said expression vector to express rhGM-CSF. The present inention replaces colibacillus occlusion body expression system with yeast secreting expression sytem and has no need of renaturation of target protein rhGM-CSF, biological specific activity up to 3.4E7 unit / mg protein and less toxic side effect. Therefore, the rhGM-CSF of the present invention has high yield, simple purification process, low cost and less toxic side effect.
Owner:海南国栋药物研究所有限公司
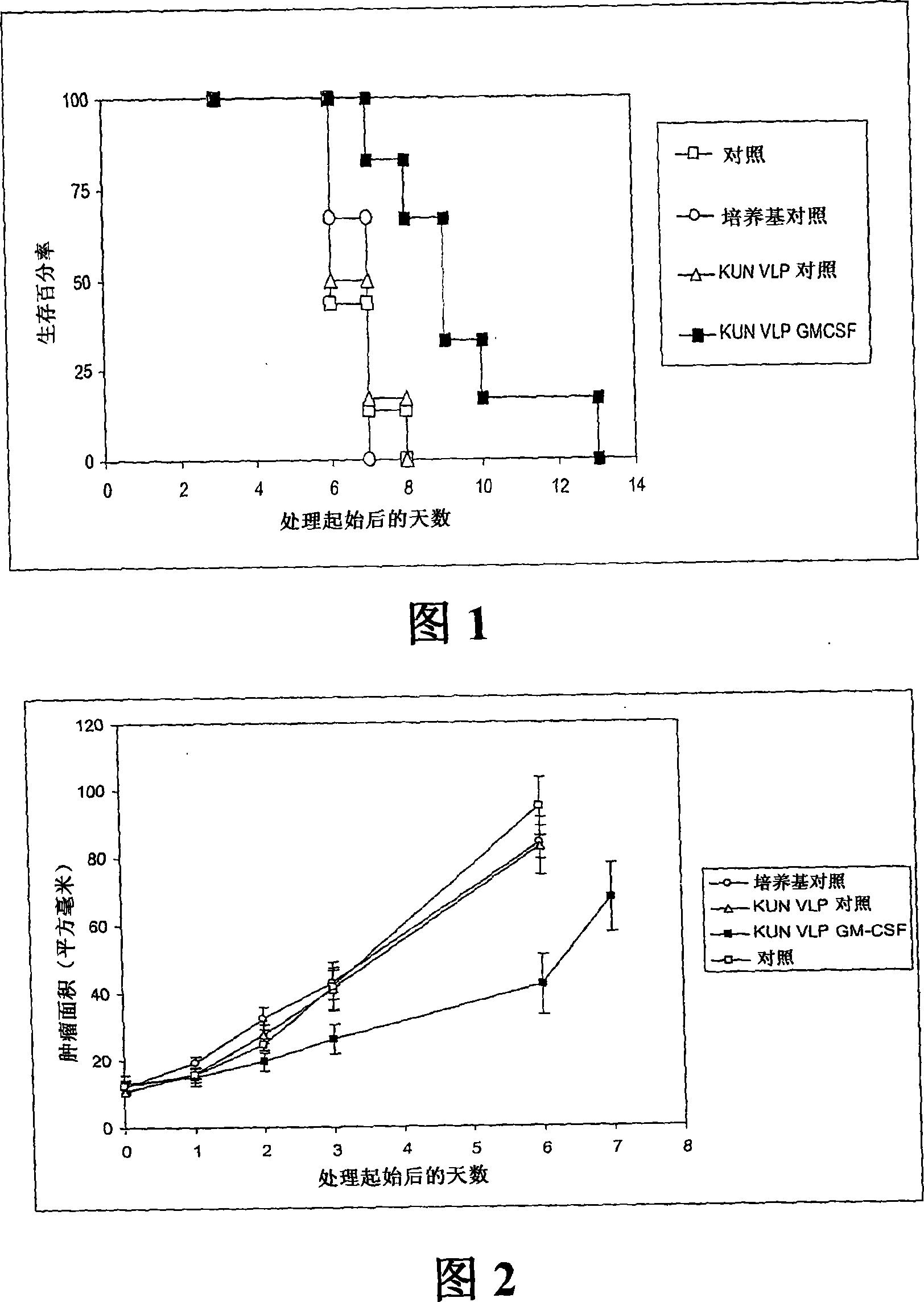
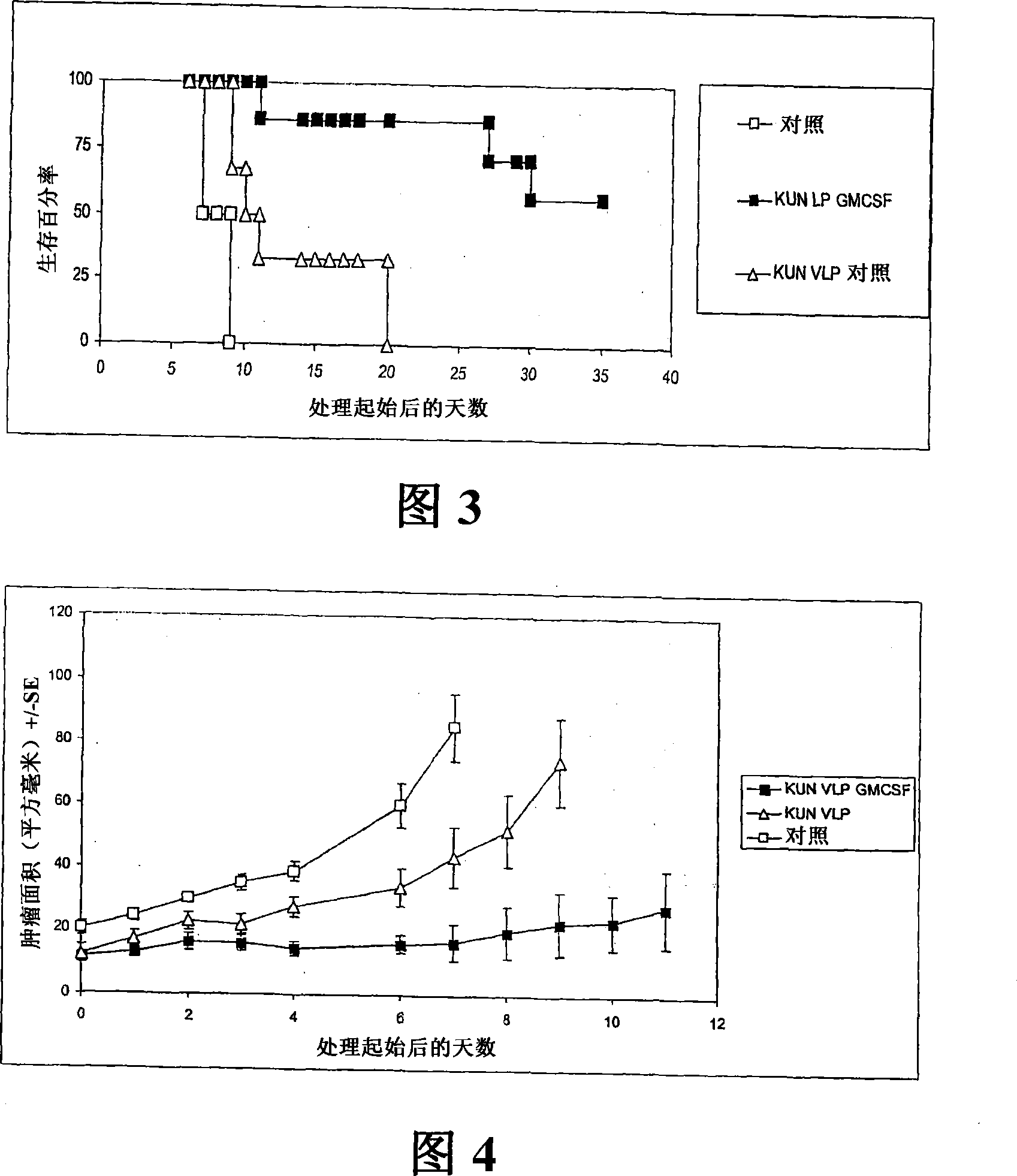
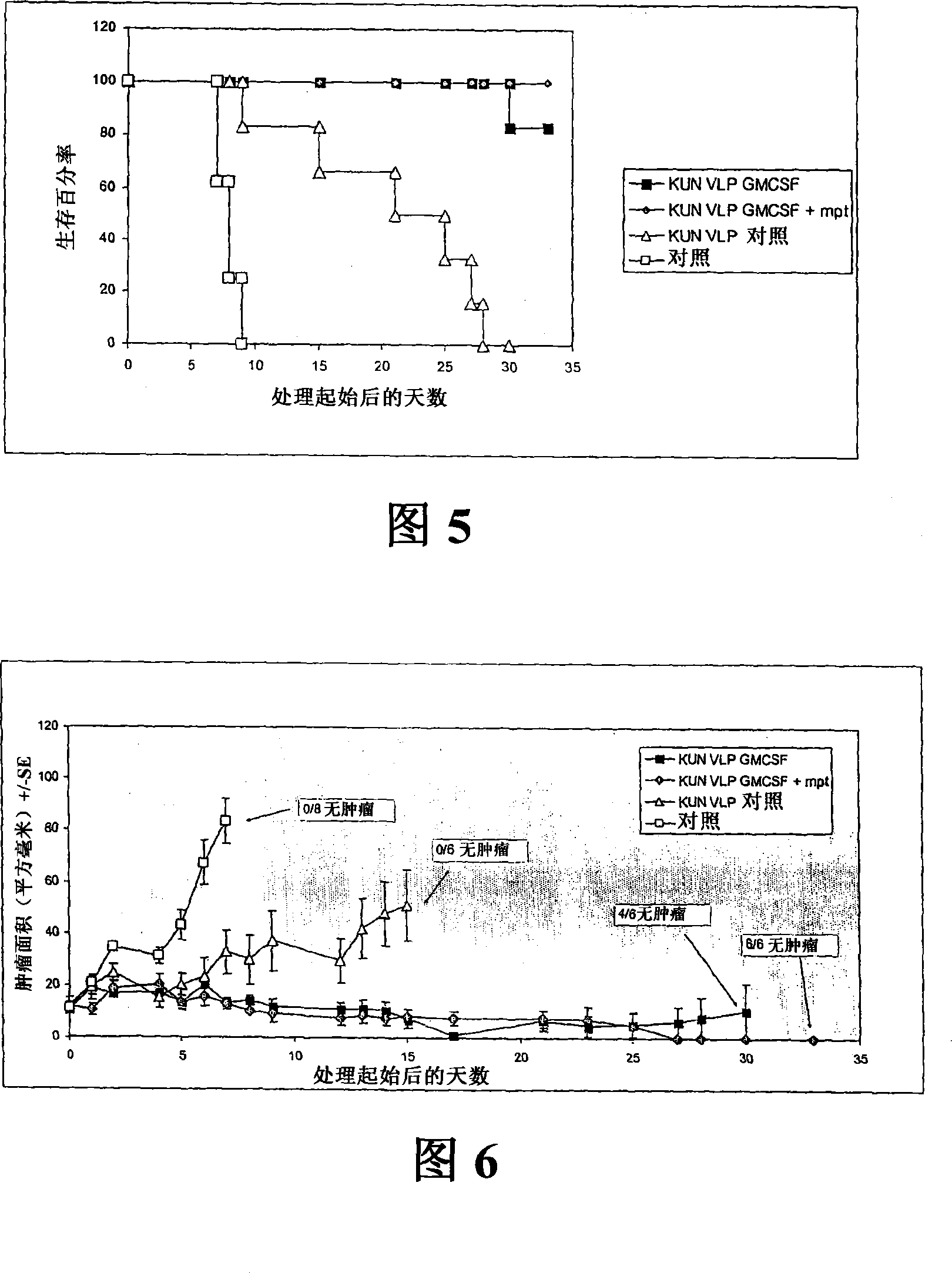
Flavivirus replicon constructs for tumour therapy
InactiveCN101120086AOrganic active ingredientsSsRNA viruses positive-senseParanasal Sinus CarcinomaMelanoma
Owner:レプリカン バイオテク プロプライエタリー リミテッド
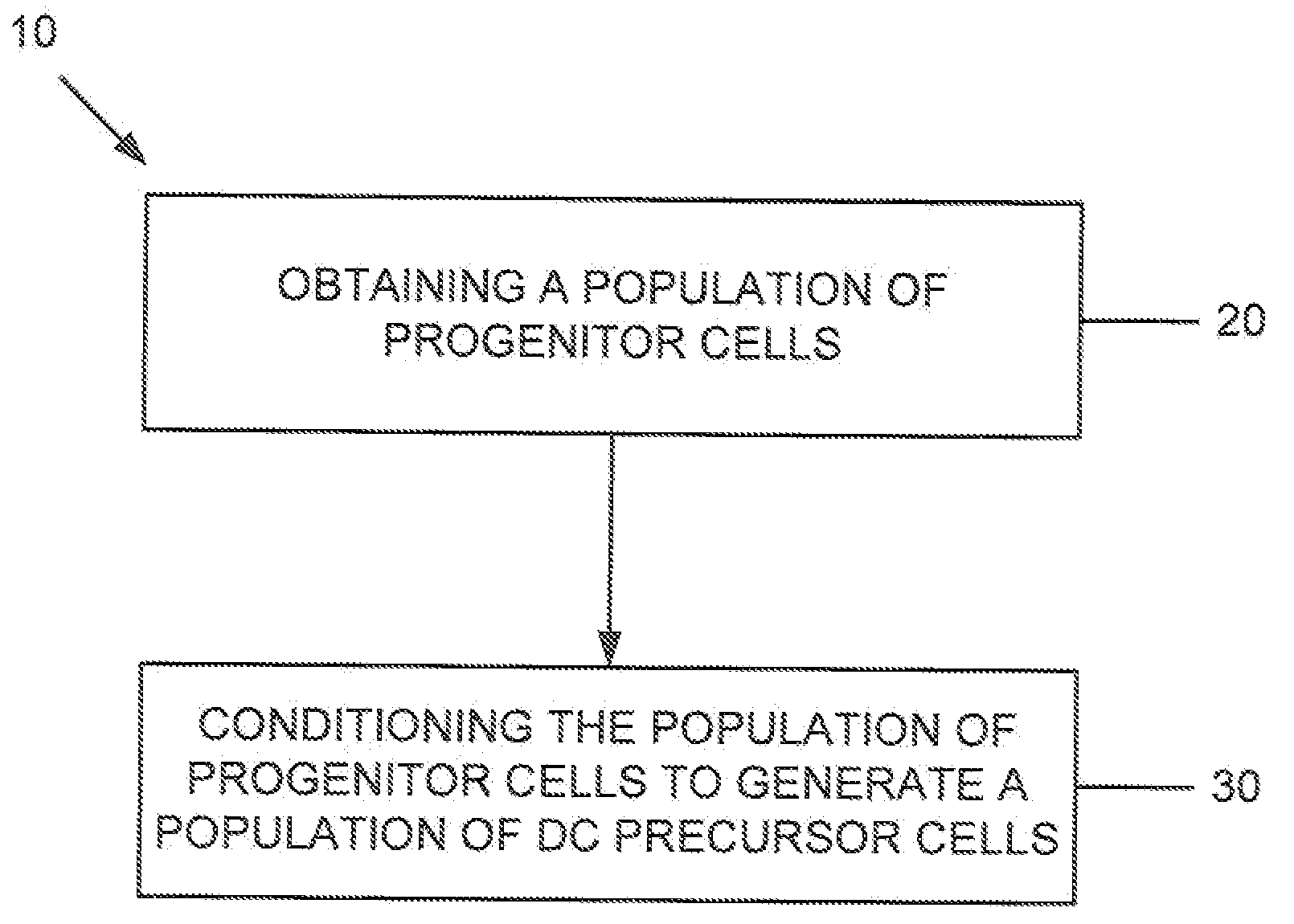
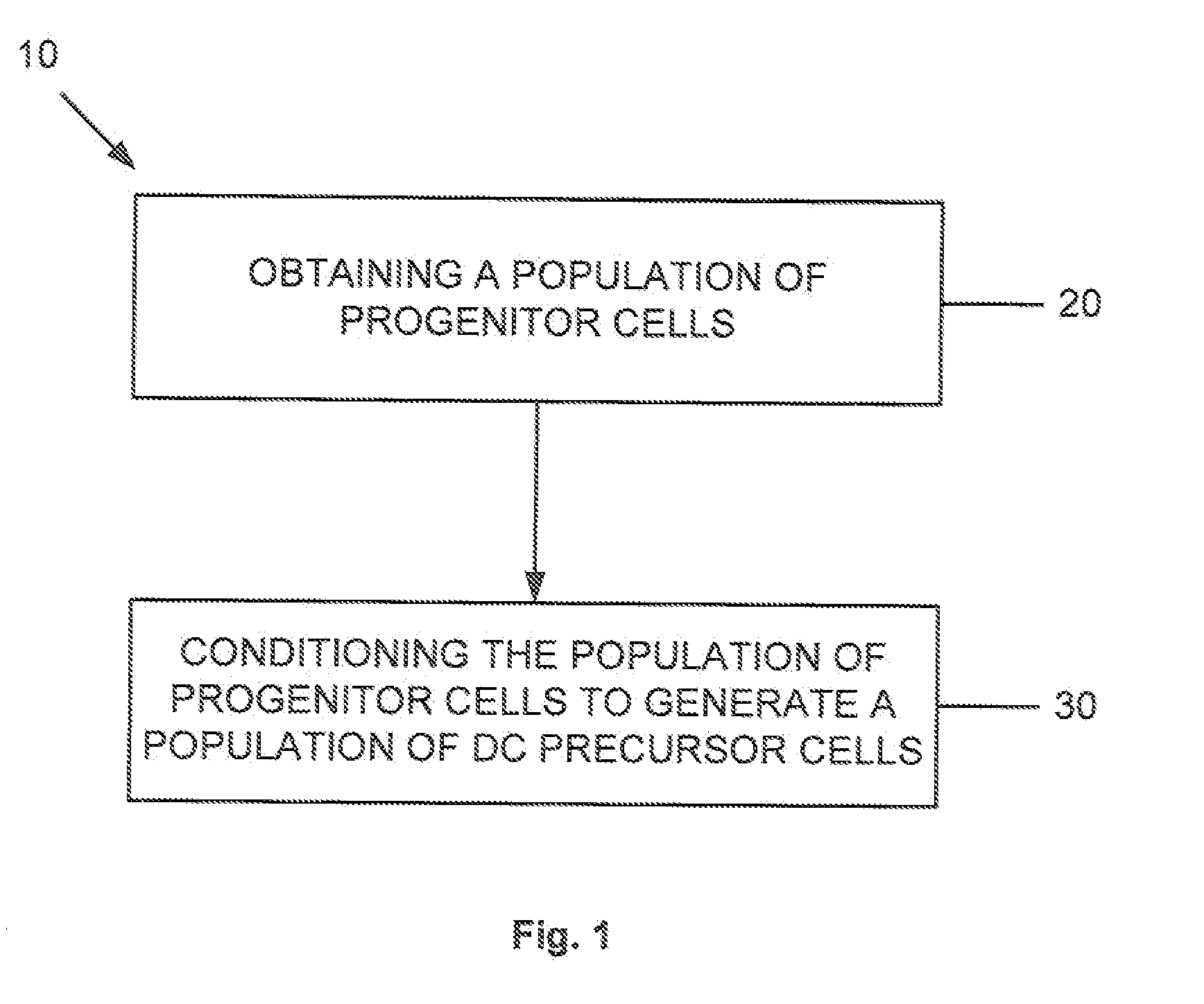
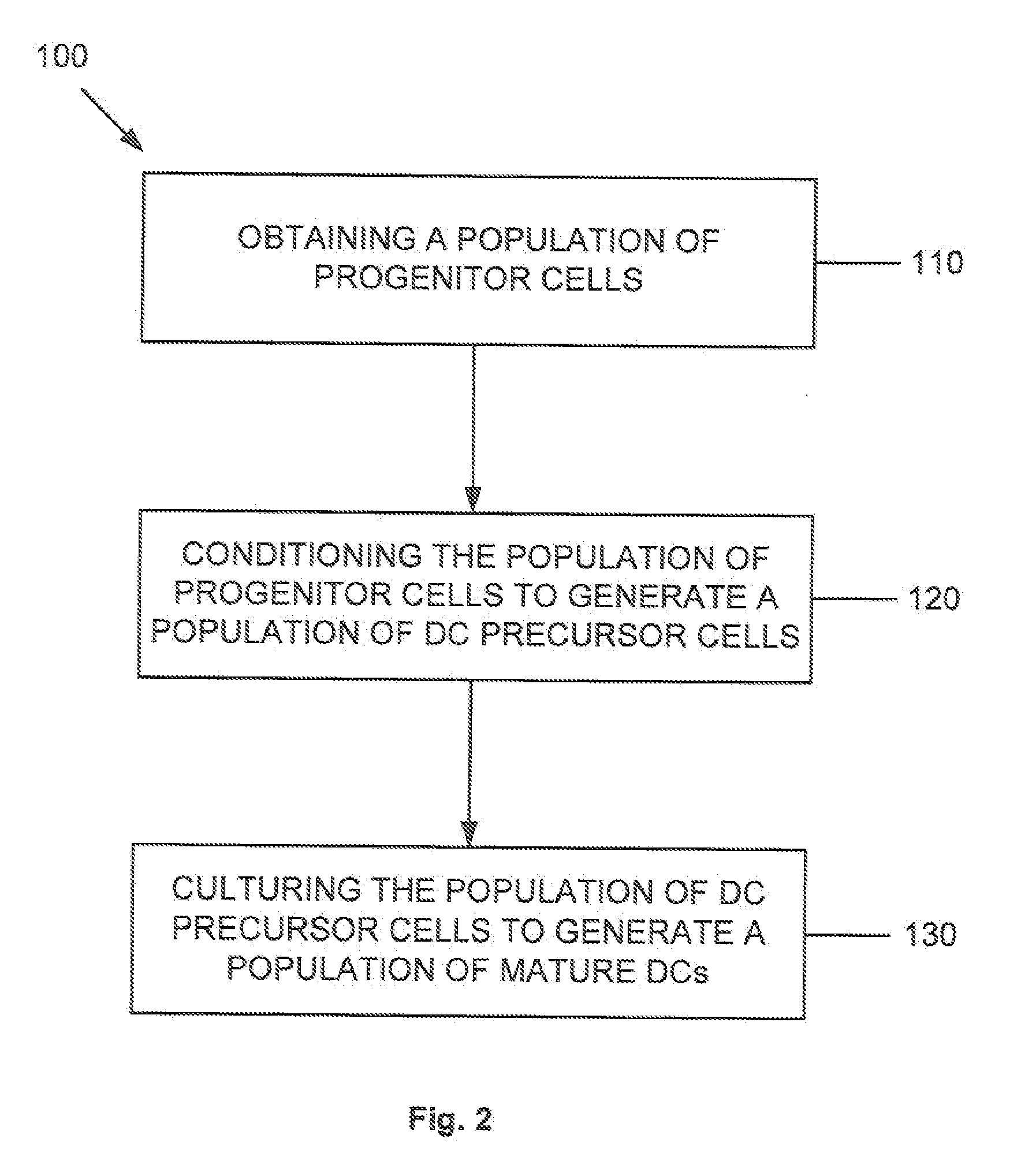
Dendritic cell precursors
A method of generating a population of dendritic cell (DC) precursors includes obtaining a population of progenitor cells from a subject and culturing the progenitor cells in a culture medium. The culture medium can include Flt3 ligand and interleukin-6 and be free of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com