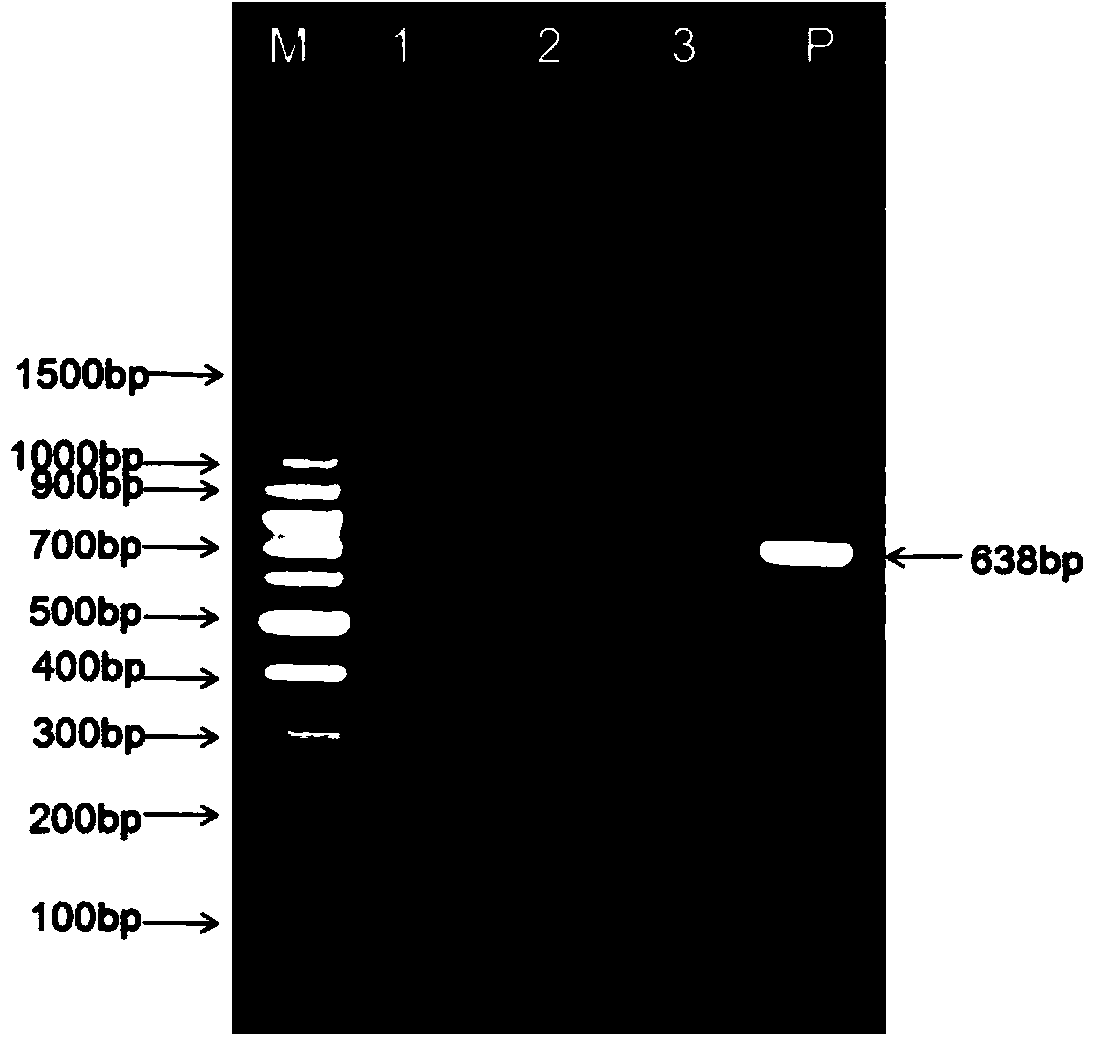
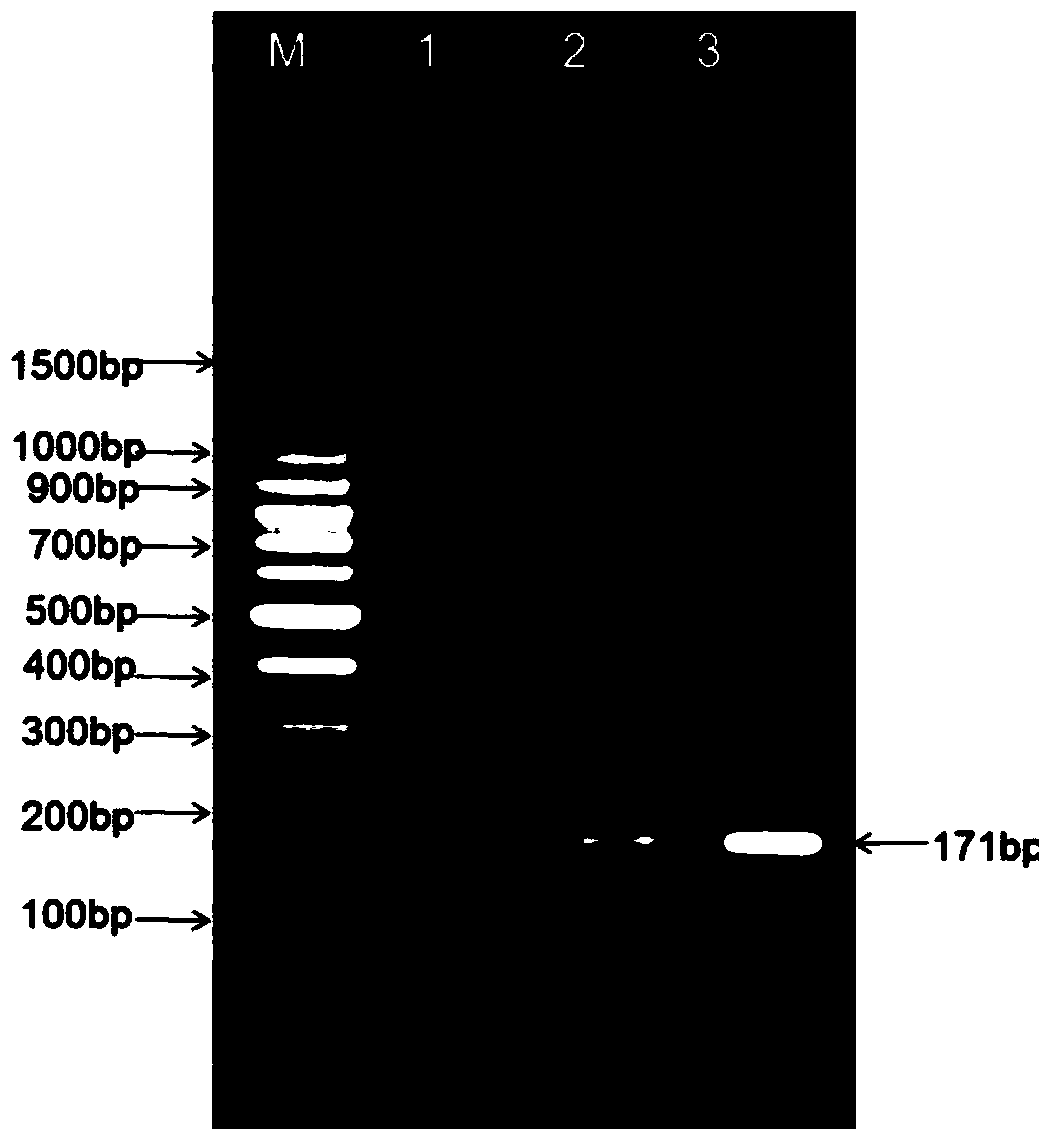
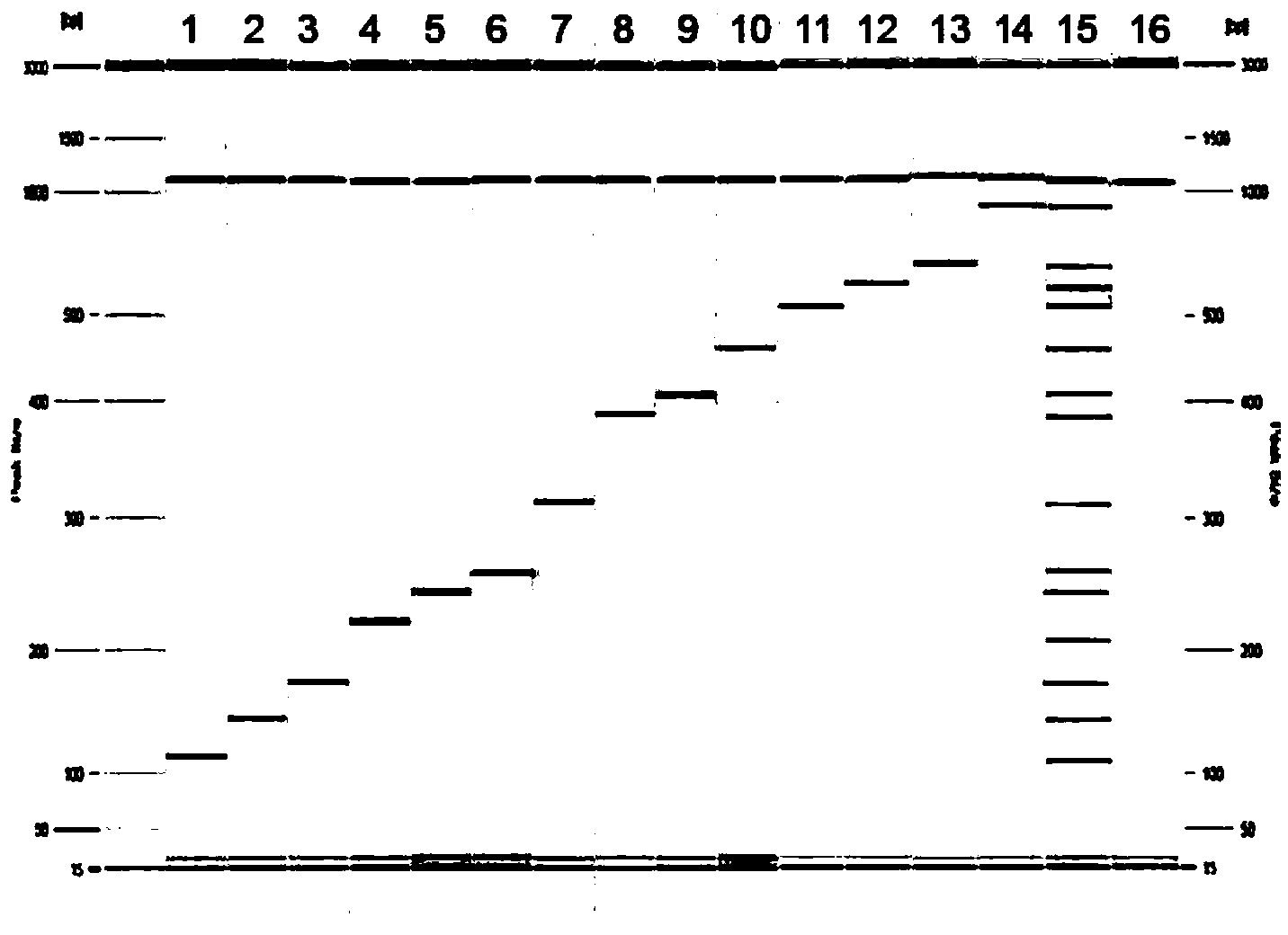
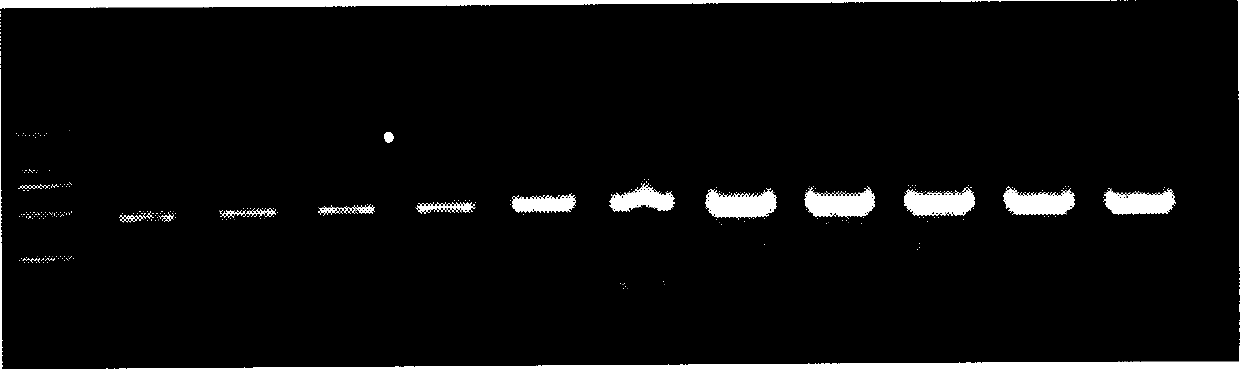
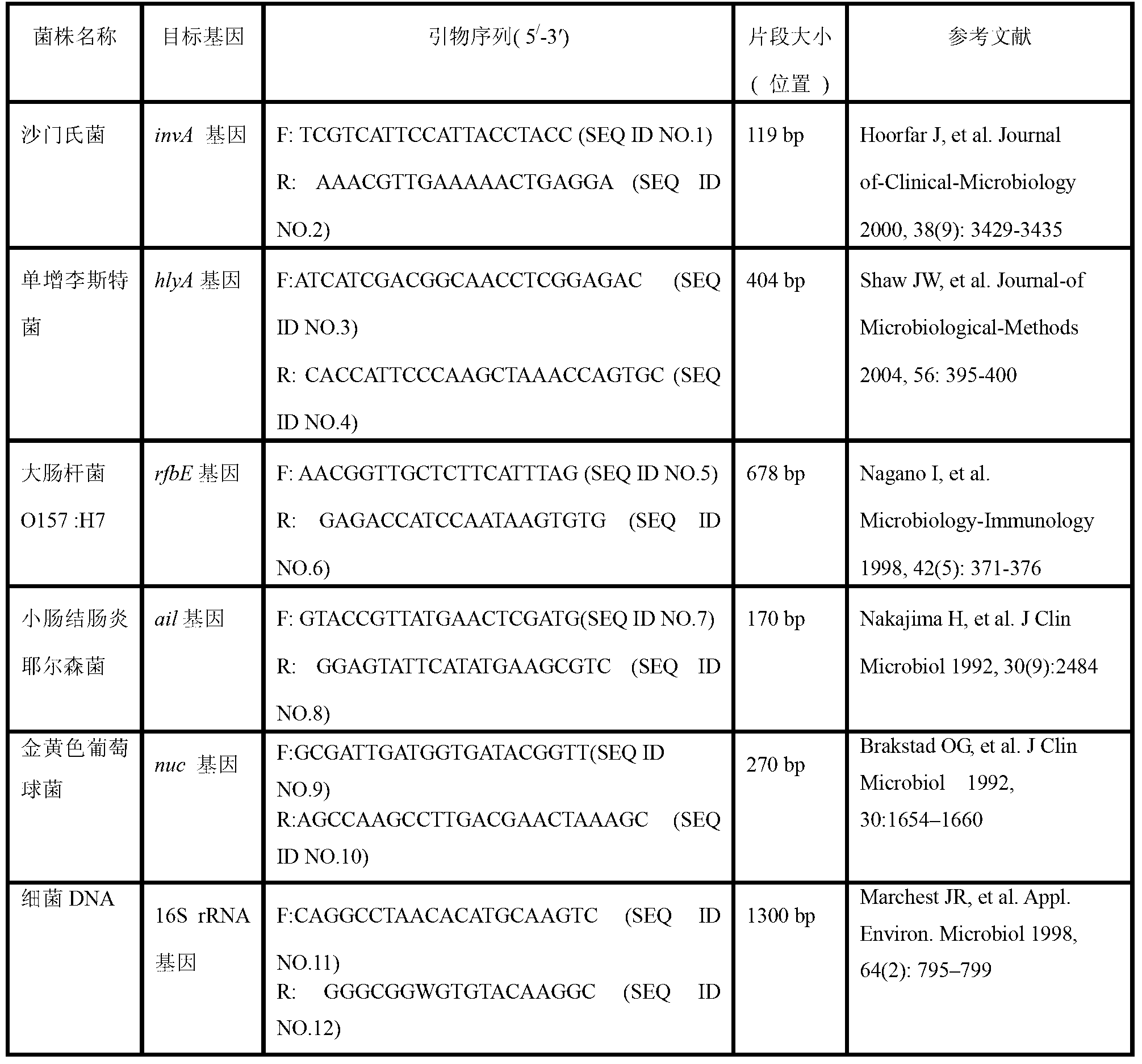
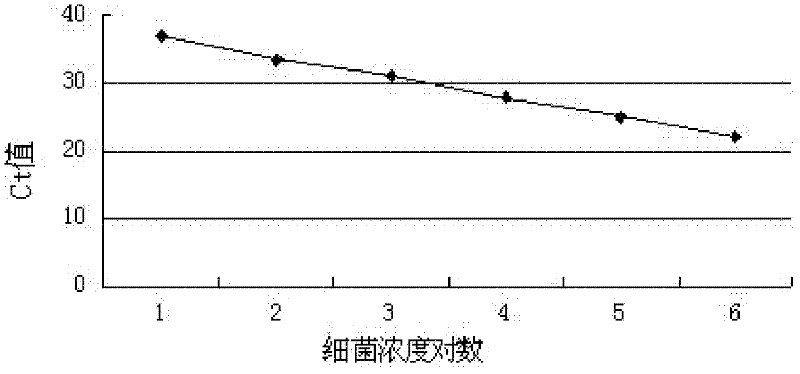
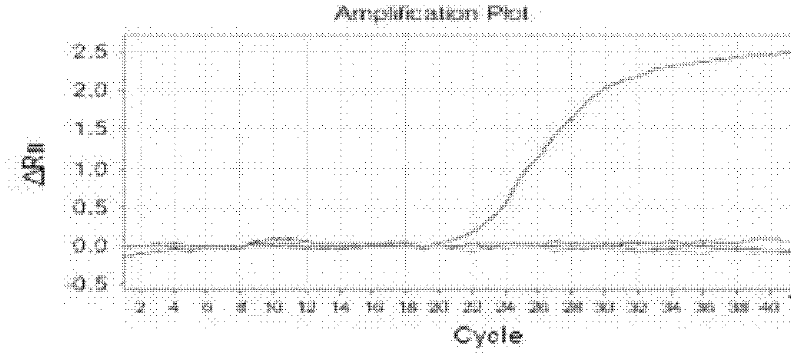
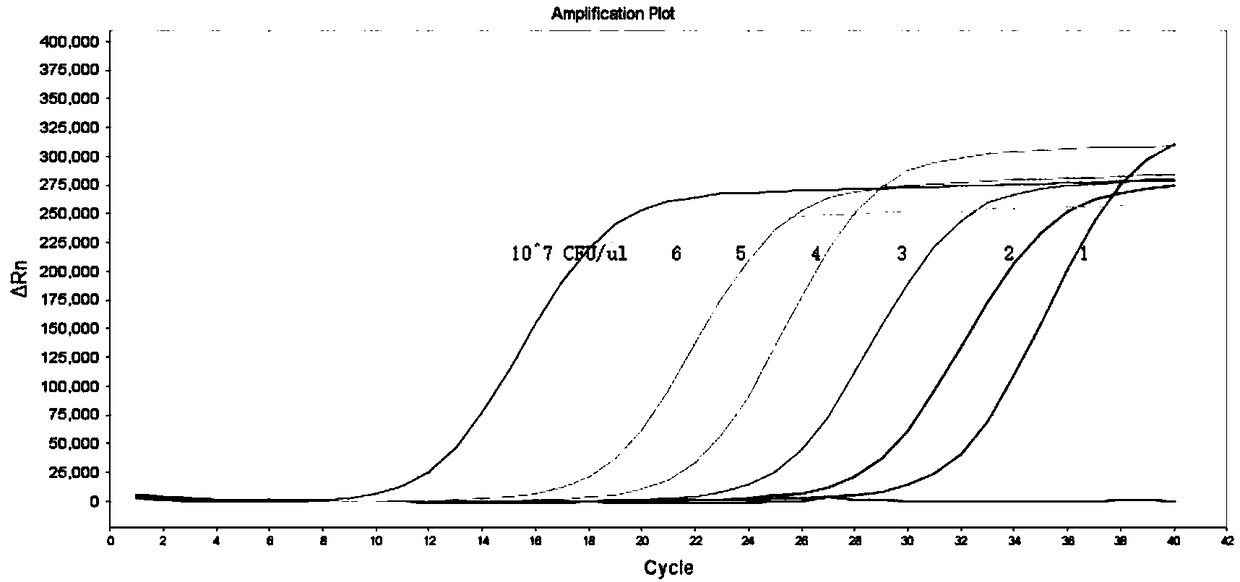
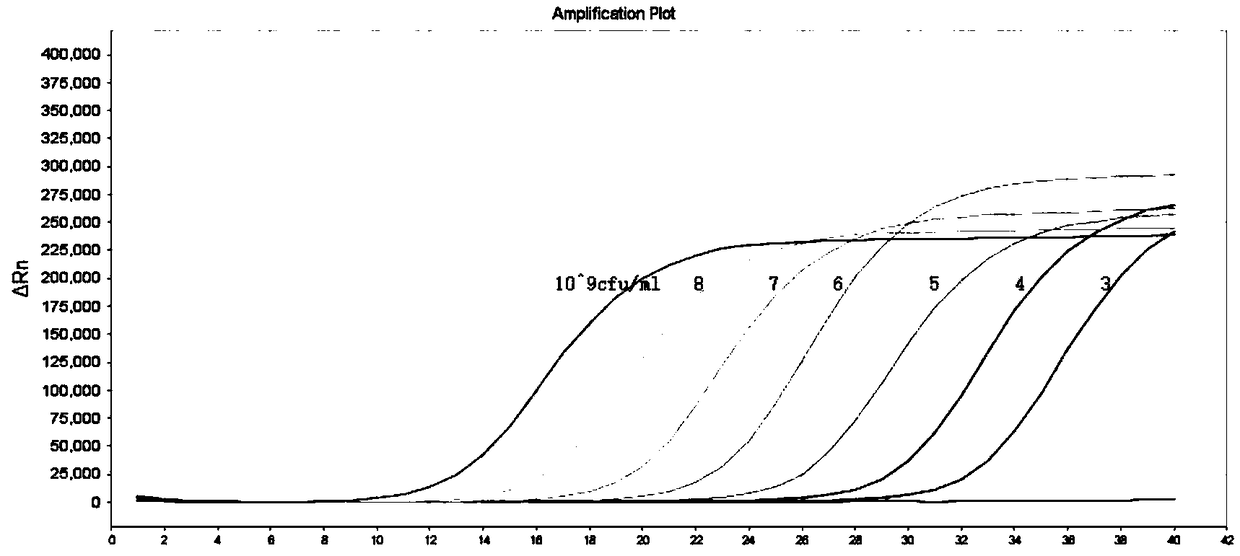
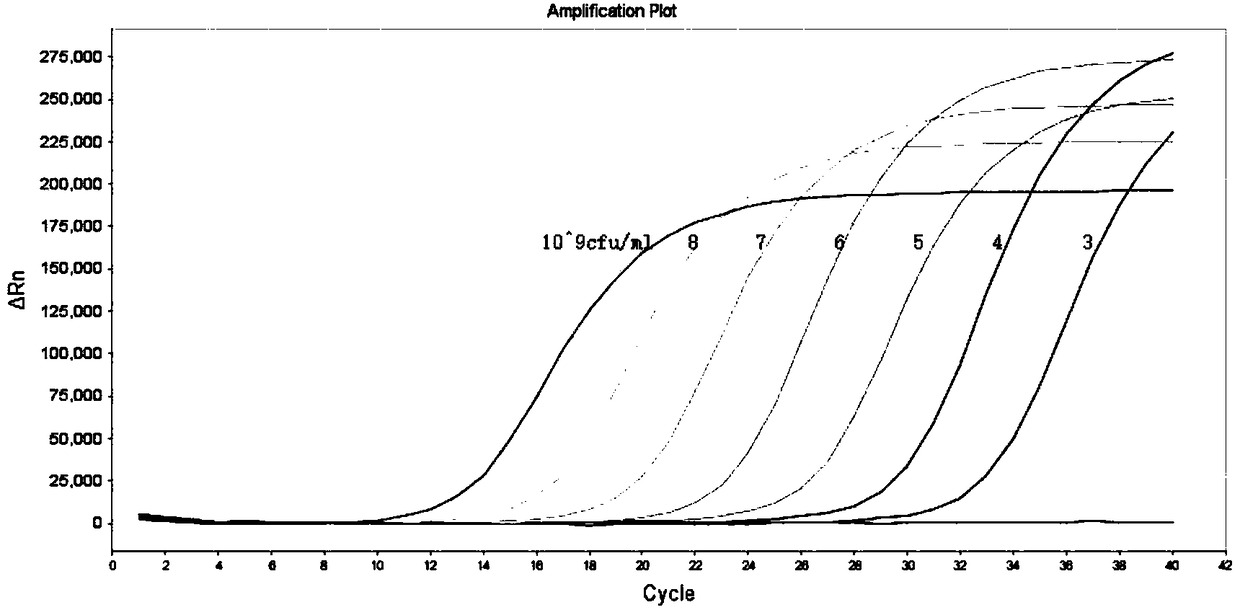
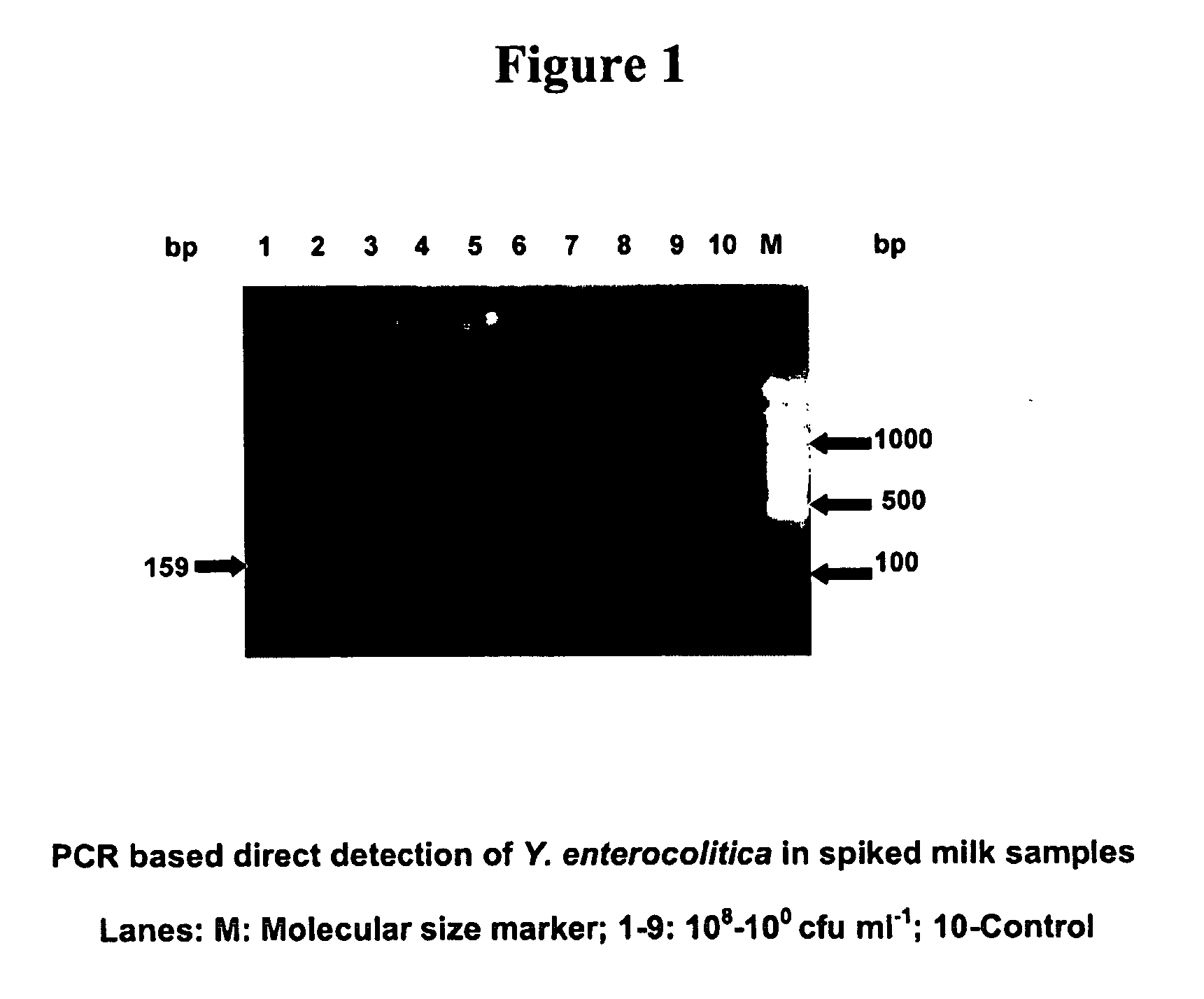
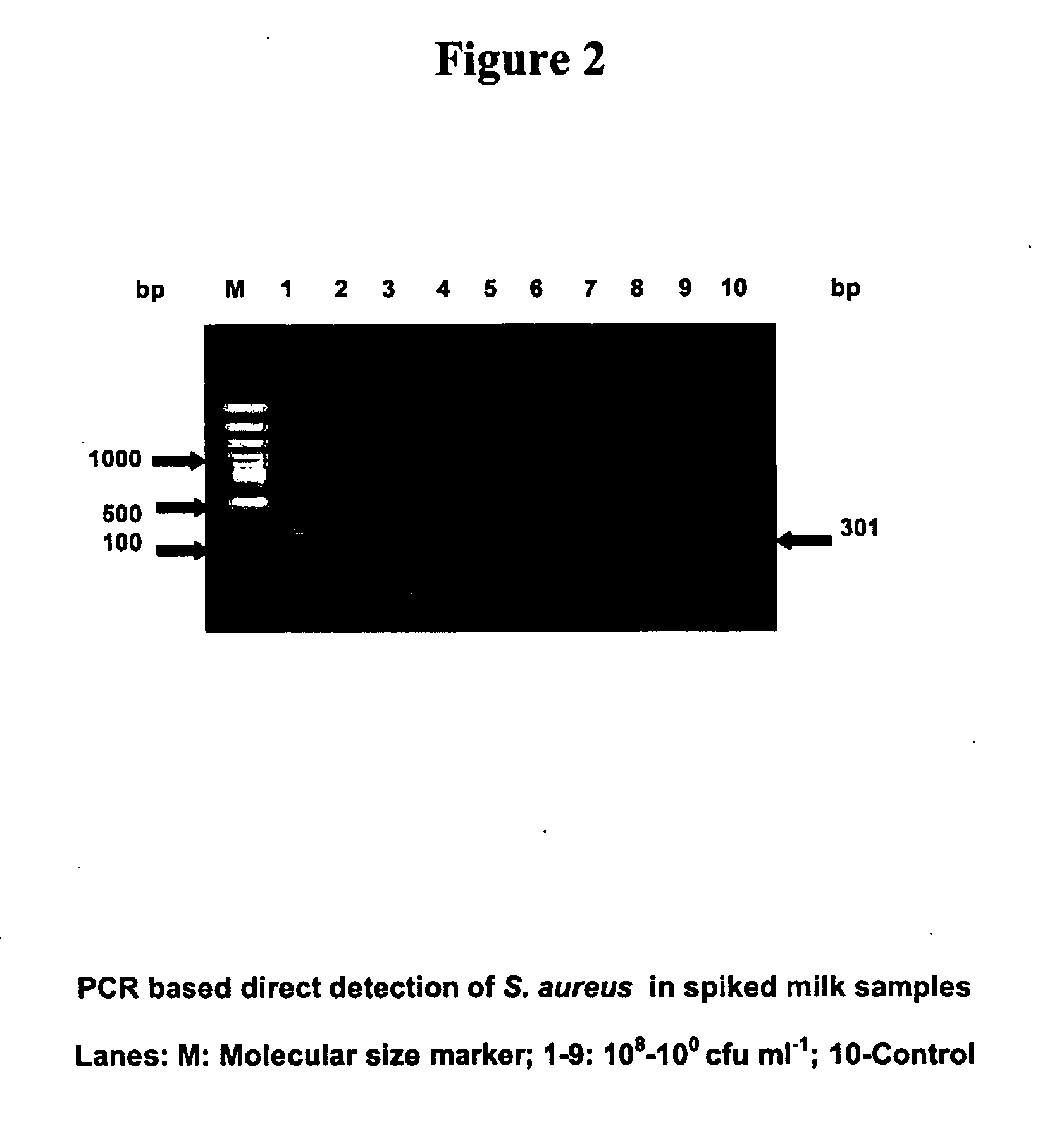
Patents
Literature
90 results about "Yersinia enterocolitica" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Yersinia enterocolitica is a Gram-negative bacillus-shaped bacterium, belonging to the family Yersiniaceae. It is motile at temperatures of 22–29° C (72-84°F), but becomes nonmotile at normal human body temperature. Y. enterocolitica infection causes the disease yersiniosis, which is an animal-borne disease occurring in humans, as well as in a wide array of animals such as cattle, deer, pigs, and birds. Many of these animals recover from the disease and become carriers; these are potential sources of contagion despite showing no signs of disease. The bacterium infects the host by sticking to its cells using trimeric autotransporter adhesins.
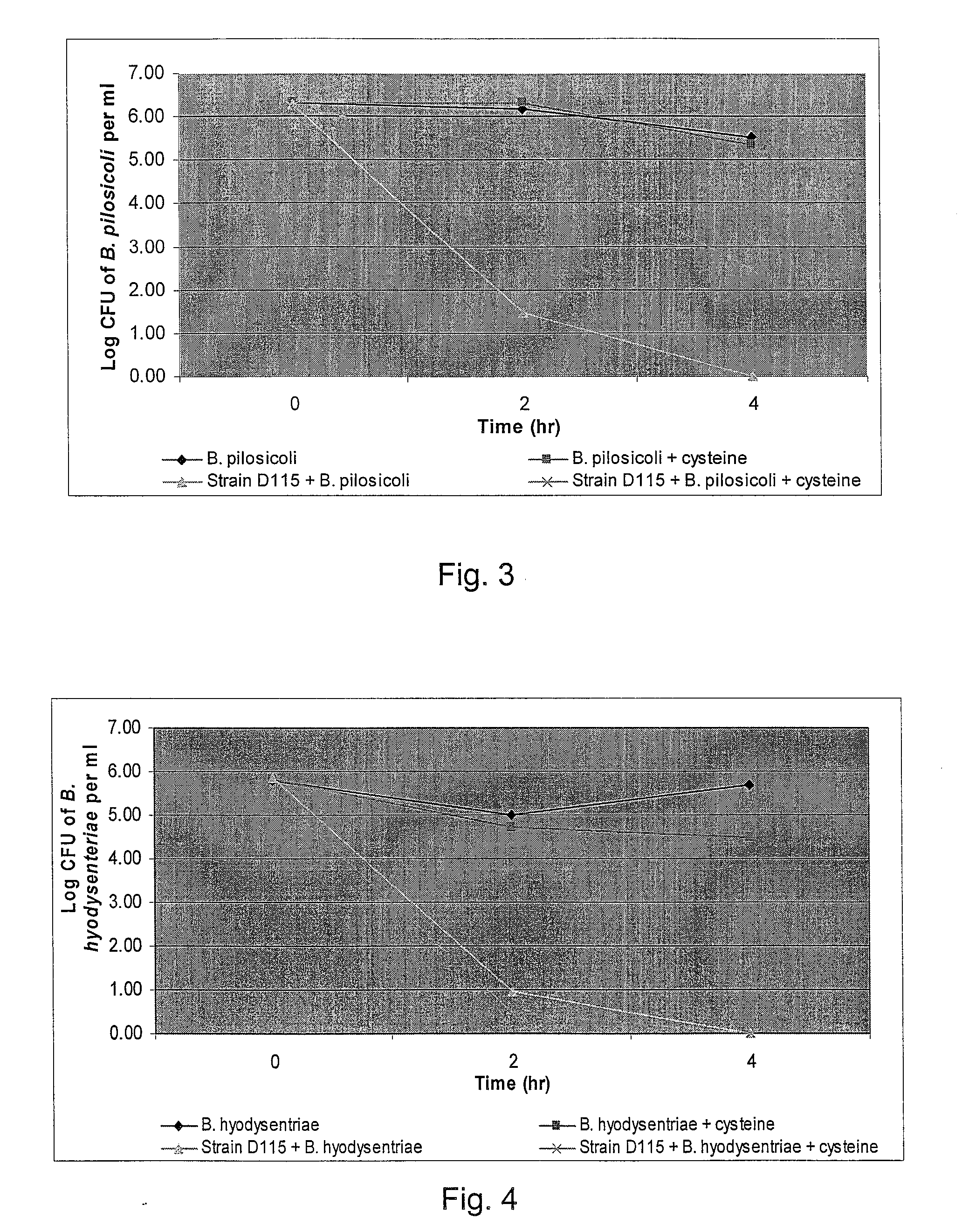
Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of Lactobacillus Johnsonii D115
The present invention demonstrated the potential use of Lactobacillus johnsonii D115 as a probiotic, as a prophylactic agent or as a surface treatment of materials against human and animal pathogens such as Brachyspira pilosicoli, Brachyspira hyodysenteriae, Shigella sonnei, Vibrio cholera, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Campylobacter jejuni, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium, Clostridium perfringens, Yersinia enterocolitica, Escherichia coli, Klebbsiella pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella spp., Bacillus cereus, Aspergillus niger and Fusarium chlamydosporum. The proteineous antimicrobial compound was partially characterized and found to be heat tolerant up to 121° C. for 15 min, and acid tolerant up to pH1 for 30 min at 40° C. The compound is also stable to enzymatic digestion, being able to retain more than 60% antimicrobial activity when treated with pepsin and trypsin.
Owner:KEMIN IND INC
Pathogenic microorganism DNA detecting chip and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101113476ASensitive hybridization detectionAccurate readingMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesESCHERICHIA COLI ANTIGENNucleic Acid Probes
The invention relates to a pathogenic microorganism DNA detection chip and the chip comprises a carrier and a nucleic acid probe on the carrier. The nucleic acid probe is provided with a target detection probe used for detecting target gene of pathogenic microorganism. The pathogenic microorganism comprises but not limits to vibrio cholerae, pathogenic escherichia coli, campylobacter jejuni, Yersinia enterocolitica, parahemolytic vibrio, salmonella, and shigella and Listeria monocytogenes. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the pathogenic microorganism DNA detection chip and provides applications of the pathogenic microorganism DNA detection chip in detection of pathogenic microorganism. Also a pathogenic microorganism DNA detection chip kit is provided.
Owner:ICDC CHINA CDC
Fourteen-food-borne pathogenic bacterium multiplex PCR detection primer set and kit
ActiveCN103484546ATo achieve the detection effectMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBacteroidesEscherichia coli
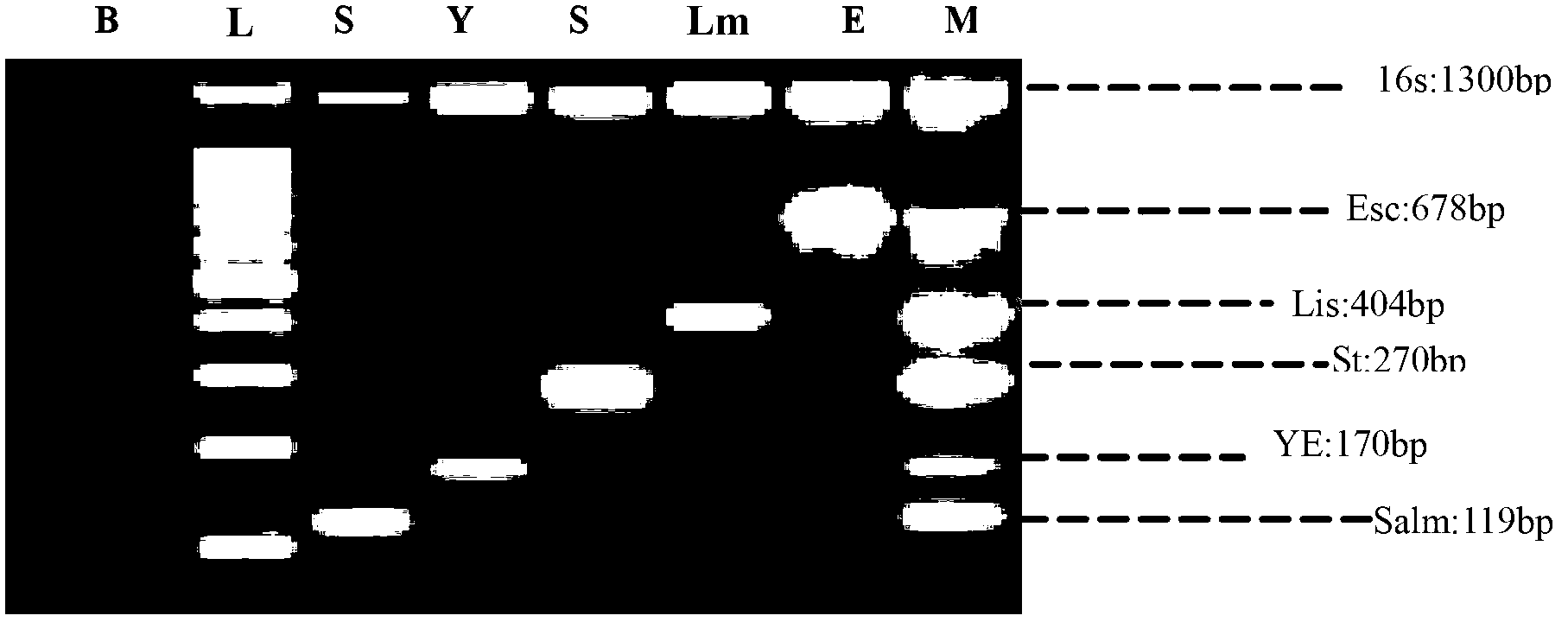
The invention discloses a fourteen-food-borne pathogenic bacterium multiplex PCR detection primer set and a kit. The detection primer set is composed of primer pairs for detecting salmonella, Shigella, Vibrio parahemolyticus, campylobacter jejuni, campylobacter coli, staphylococcus aureus, bacillus cereus, Listeria monocytogenes, yersinia enterocolitica, enterobacter sakazakii, Escherichia coli, vibrio cholerae, Escherichia coli O157, aeromonas hydrophila and internal positive control. A multiplex PCR detection method based on an ordinary PCR platform is built, multiplex PCR reactions are carried out on genomic DNA, extracted from a sample to be tested, of bacteria in the same reaction system through the primer pairs acquired through analysis and design, and whether the food-borne pathogenic bacteria are contained in the sample or not is judged through the electrophoretic analysis of reaction products.
Owner:北京卓诚惠生生物科技股份有限公司
Oligonucleotide probe kit for detecting common intestine trac kpathogenic bacteria and its use
InactiveCN1683565AQuick checkAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesAntigenBio engineering
The present invention belongs to the field of microbe detecting technology. The oligonucleotide probe for detecting common intestinal tract pathogenic bacteria is designed on 16S rRNA and 23S rRNA of bacteria, ipaH of dysentery bacillus giant plasmid, VipR of Salmonella typhi and other gene sequence, has length of 25-50 bp, and relatively high sensitivity and specificity. The oligonucleotide probe is suitable for detection based on nucleic acid hybridization principle, especially detection based on gene chip principle. Under certain use condition, it can detect Listeria, parahemolutic vibrio, Campylobacter, etc. It may be used in many aspects, such as disease diagnosis, environment detection, food poisoning detection, etc.
Owner:RADIOLOGY INST ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICINE SCI PLA
Immobilized microbial consortium useful for rapid and reliable BOD estimation
InactiveUS6511822B1Improve survivabilityLong stabilityTesting waterOn/in organic carrierBacteroidesSerratia
An immobilized microbial consortium is formulated which comprises of a synergistic mixture of isolated bacteria namely, Aeromonas hydrophila, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Yersinia enterocolitica, Serratia liquefaciens, Pseudomonas fluoresces, Enterobacter cloaca, Klebsiella oxytoca, Citrobacter amalonaticus and Enterobacter sakazaki. The formulated microbial consortium is immobilized on charged nylon membrane. The said immobilized microbial consortium is attached to dissolved oxygen probe for the preparation of electrode assembly. The prepared electrode assembly is used for rapid and reliable BOD estimation. The prepared electrode assembly is used for monitoring of BOD load of synthetic samples such as Glucose-Glutamic acid (GGA) used as a reference standard in BOD analysis and industrial effluents; covering a range from low to high biodegradable organic matter.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Type III bacterial strains for use in medicine
Owner:UNIVERSITE CATHOLIQUE DE LOUVAIN
Immobilized microbial consortium for the treatment of phenolic waste-water from petroleum refineries
InactiveUS6406882B1Wider surface areaEasy diffusion of oxygenWater contaminantsOn/in organic carrierBacteroidesFiber
An immobilized microbial consortium is formulated which comprises of a synergistic mixture of all the bacterial strains of Aeromonas hydrophila, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Bacillus circulans, Yersinia enterocolitica, Enterobacter cloaca and Bacillus brevis. The formulated microbial consortium is immobilized on a non-biodegradable and economically cheaper support. The said immobilized microbial consortium is used for the biodegradation of synthetic phenol as well as phenol present in petroleum refinery effluent. The results of biodegradation obtained with the microbial consortium immobilized on coconut fiber are compared with those obtained with microbial consortium immobilized on well known support. The coconut fiber used for immobilization proved to be a better support than a well known support such as calcium alginate.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Method for detecting fluorescent quantitative PCR of 12 pathogenic bacteria in real time at the same time
PendingCN109182567AStrong specificityReactiveMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesStaphylococcus aureus
The invention provides a method for detecting fluorescent quantitative PCR of 12 pathogenic bacteria in real time at the same time, including the steps: collecting specific pathogenic gene or toxin gene of the target pathogen and using it as a target gene to design primers and probes so as to make the reaction conditions consistent; extracting a genome template of a sample to be detected; adding the template respectively into tubules equipped with different specific upstream and downstream primers and probes, and then adding the corresponding fluorescent quantitative PCR reagents; under the same cycle of fluorescent quantitative PCR, the corresponding primers and probes are used to detect the samples simultaneously, quickly and quantitatively in their respective reaction tubes. Easier, Quick and efficient, Twelve common pathogenic bacteria (Escherichia coli O157: H7, Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Streptococcus betae, Yersinia enterocolitica, Streptococcusfaecalis, Shigella, Proteus mirabilis, Vibrio fluvialis, Campylobacter jejuni, Staphylococcus aureus) can be detected simultaneously in drinking water and food economically.
Owner:INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE & OCCUPATIONAL MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY SCI
Detection genetic chip and detection kit for infectious diarrhea
InactiveCN102140507ALow costImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBacteroidesEscherichia coli
The invention provides a genetic chip and a detection kit related to major pathogenic microorganisms causing infectious diarrhea of human beings, which are mainly specific to 13 types of bacteria including lapactic bacillus coli / shigella, salmonella, comma bacillus, vibrio parahemolyticus, aeromona hydrophila, plesiomonas, virio hollisae, vibrio fluvialis, vibrio mimicus, Wauter's strains, vibriodamsela and vibrio furnissii. The genetic chip comprises a solid-phase carrier and an oligonucleotide probe fixed on the solid-phase carrier, wherein the oligonucleotide probe comprises DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) fragments selected from genes including a gyrB gene, an ITS gene, a dnaJ gene, a toxR gene and the like with remarkable biological evolution advantages or complementary DNA fragments. By adopting the genetic chip and the detection kit provided by the invention, major pathogenic microorganisms causing infectious diarrhea of human beings can be detected. The genetic chip and the detection kit have the characteristics of easiness and convenience for operation, high flux, high accuracy, high repeatability and the like, and can be applied to clinical detection of inspection departments in hospitals.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for detecting food-derived pathogenic enterobacteria by composite fluorescence PCR technique
InactiveCN101113471AStrong specificityAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingEscherichia coliBacteroides
Owner:ANIMAL & PLANT & FOOD INSPECTION CENT OF TIANJIN ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU +1
Primes for detecting food poisoning bacteria and a method thereof
InactiveUS20040248089A1Sensitive methodSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesFood poisoning
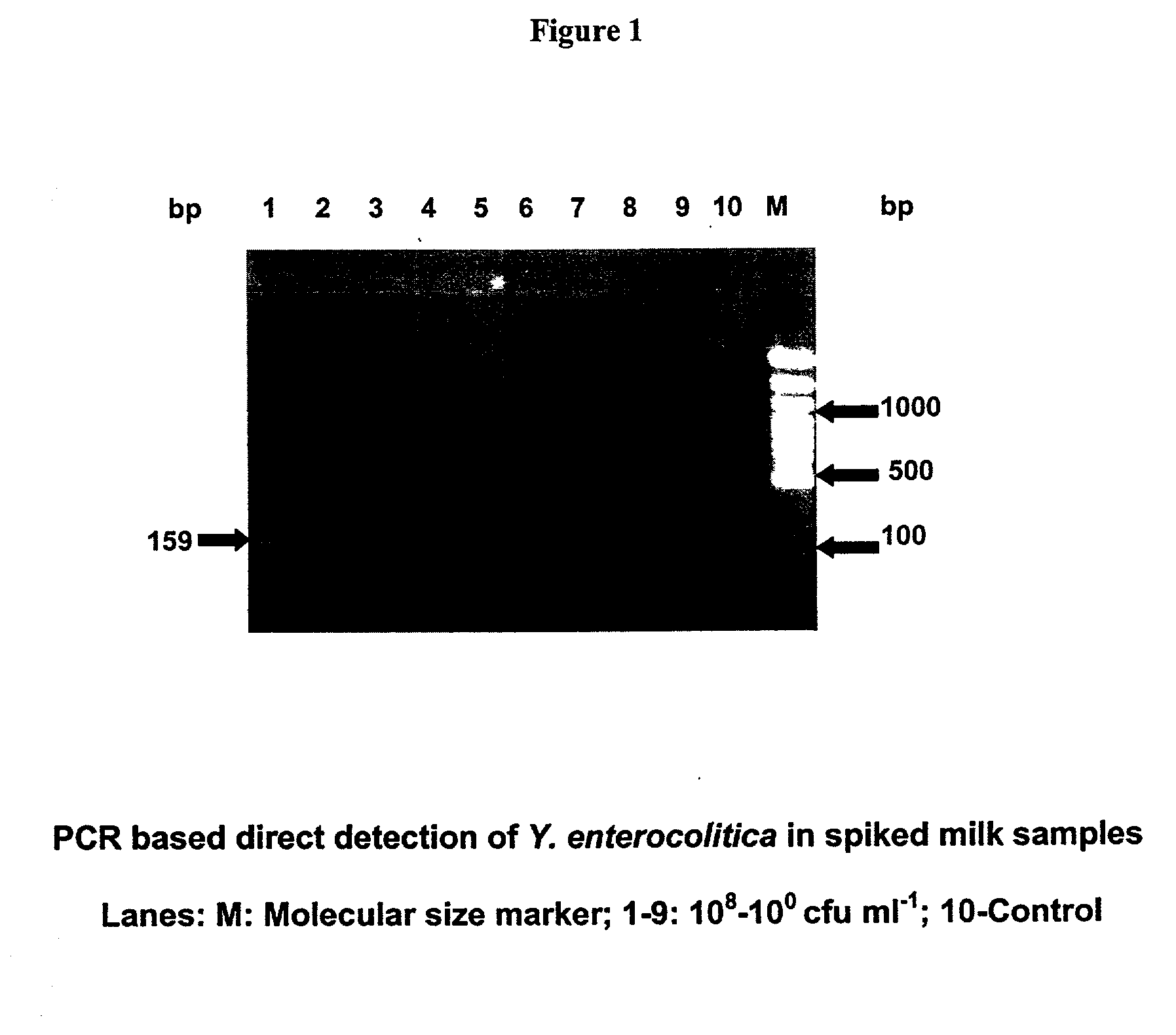
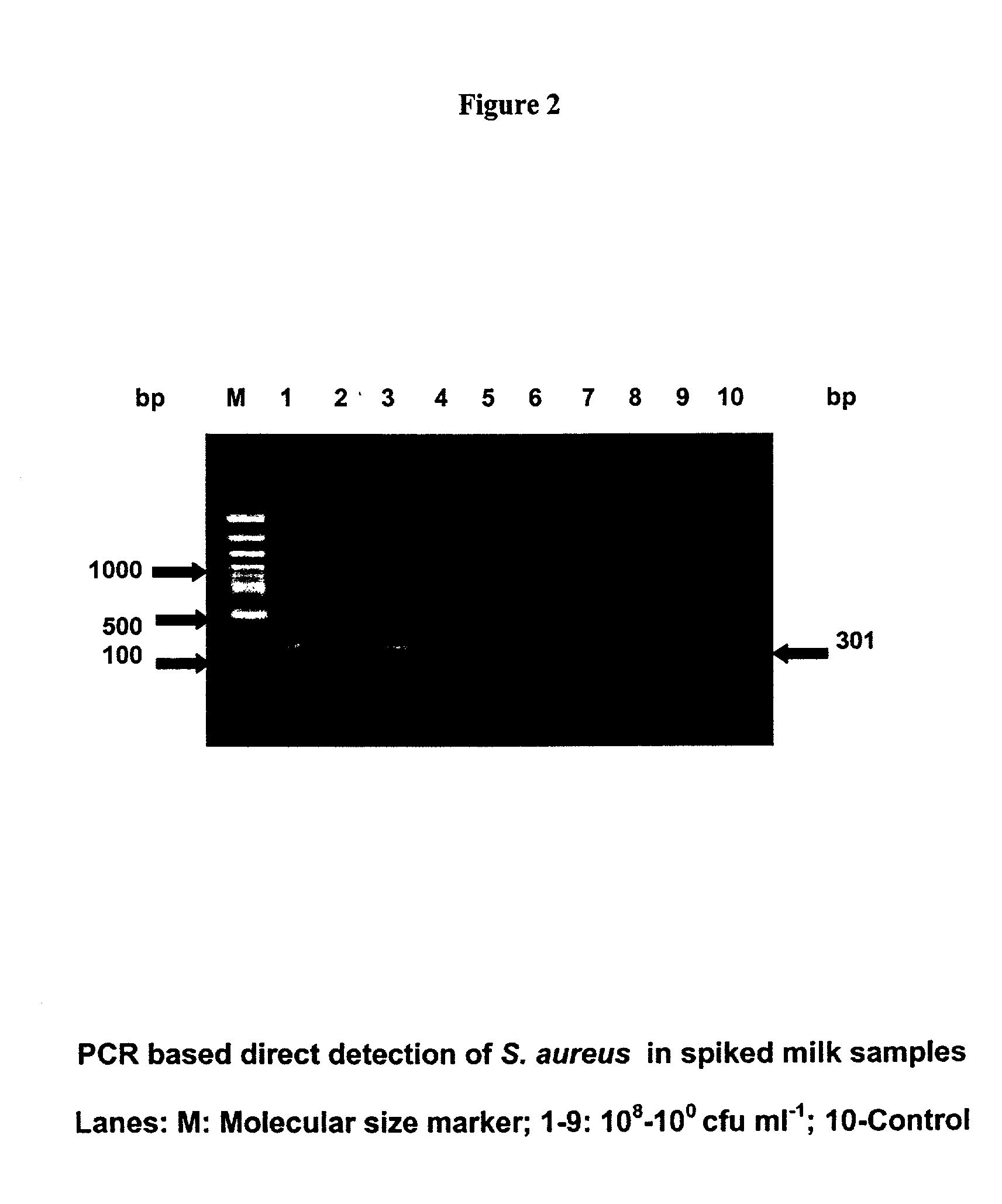
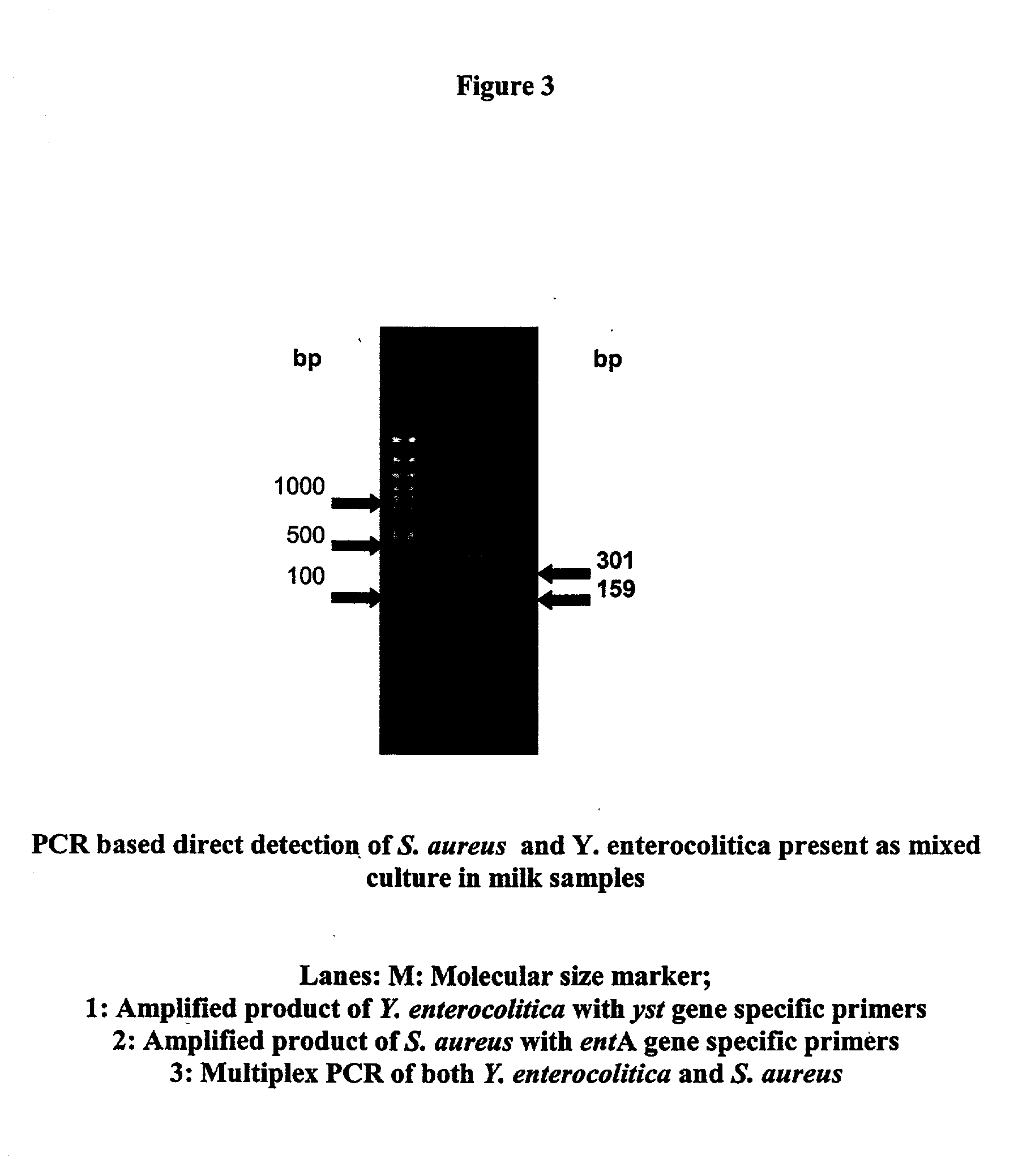
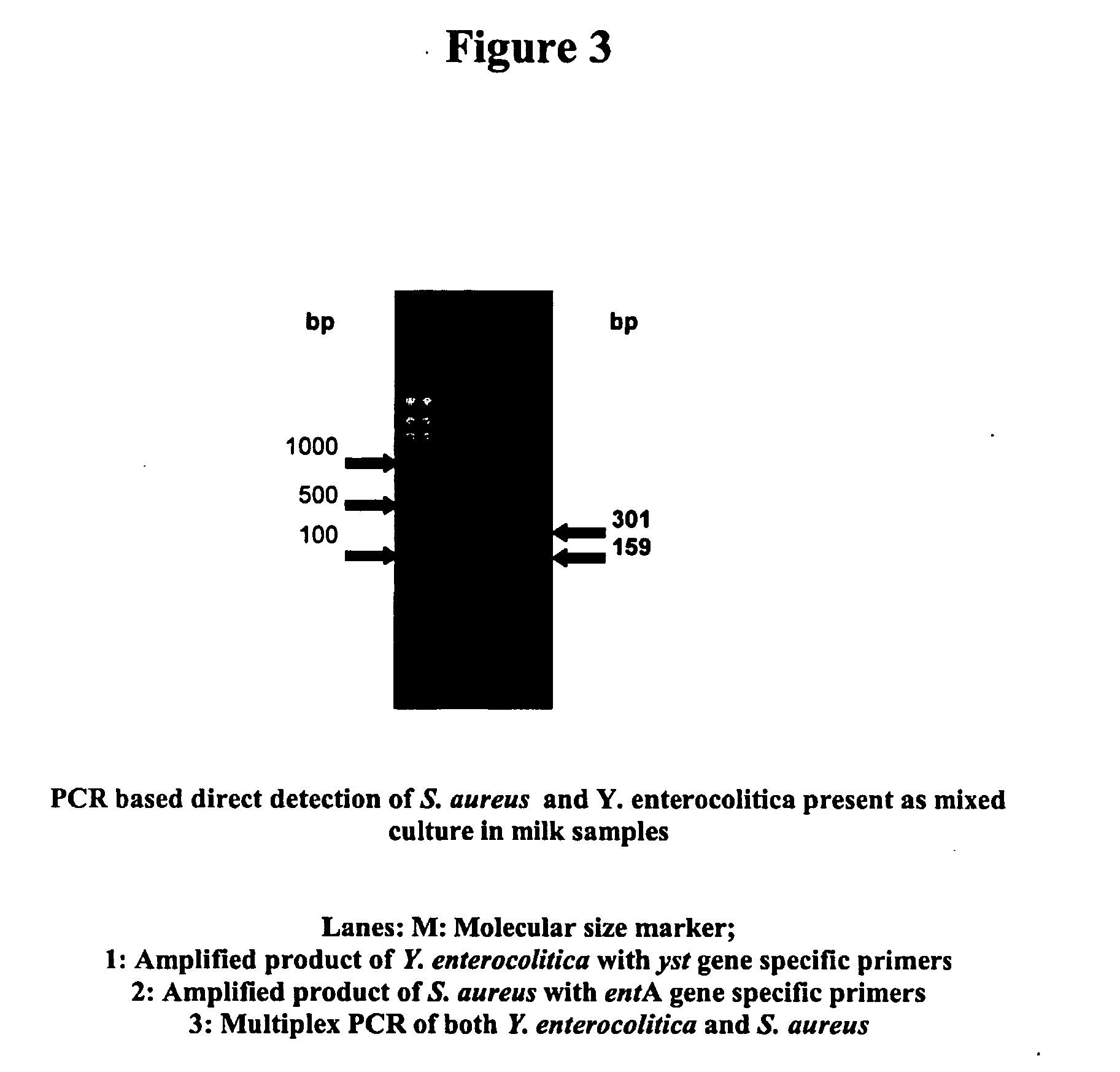
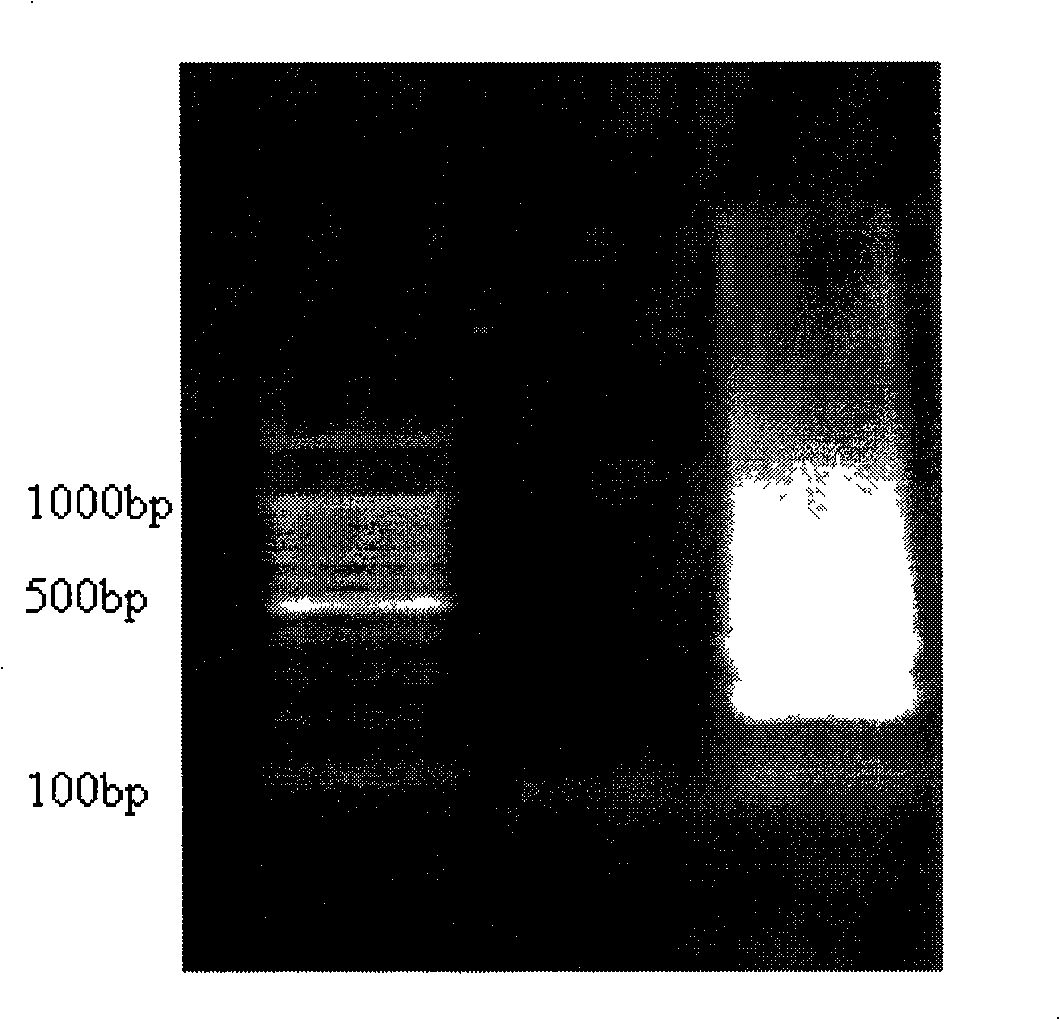
The present invention relates to novel primers of SEQ ID Nos. 1-4 useful for detecting poisoning in food articles wherein primers of SEQ ID Nos. 1 and 2 are directed against enterotoxin A gene (ent A) of bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and primers of SEQ ID Nos. 3 and 4 are directed against heat stable enterotoxin gene (yst) of bacteria yersinia enterocolitica, and a highly sensitive method of detecting said food poisoning bacterial species using said primers.
Owner:BANADA PADMANABHA PADMAPRIYA +3
Universal primers and probe for on-site rapid detection of Brucella and kit
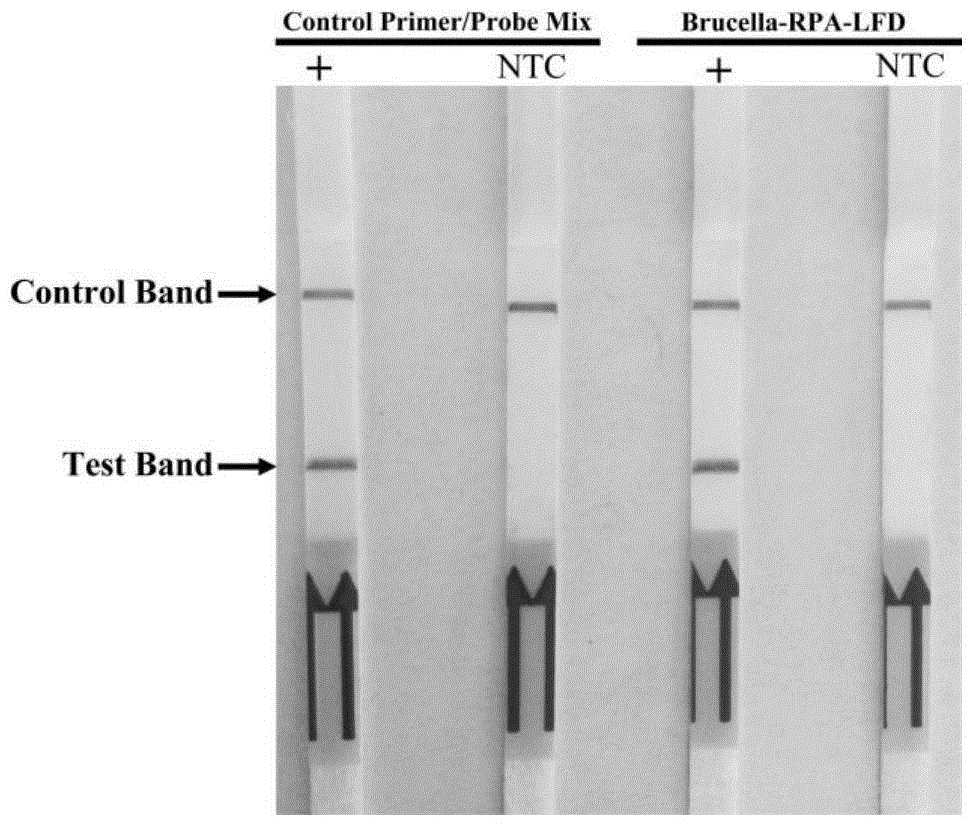
ActiveCN104946749AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesForward primerEscherichia coli
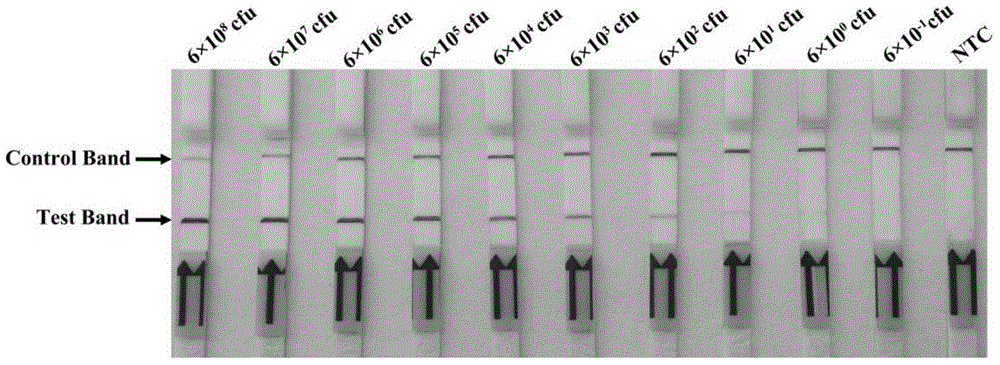
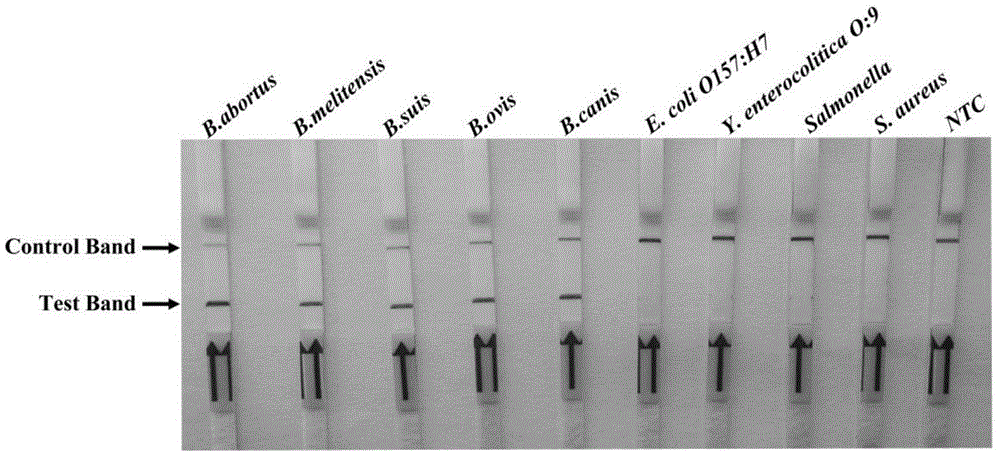
The invention discloses universal primers and a probe for on-site rapid detection of Brucella and a kit. The forward primer sequence is shown as SEQIDNo.1, the reverse primer sequence is shown as SEQIDNo.2, and the probe sequence is shown as SEQIDNo.3. The universal primers, the probe and the kit provided by the invention for detection of Brucella have high sensitivity and strong specificity, minimumly can detect 6.0*10<0>cfu Brucella, and have no cross reaction with Escherichia coli O157:H7, yersinia enterocolitica O:9, Salmonella, Staphylococcus aureus and other bacteria. The universal primers, the probe and the kit provided by the invention not only can be used for detection of Brucella strains, but also can be used for detection of clinical samples, which mainly include blood, milk samples, aerosol samples, and tissue samples, etc. The kit provided by the invention is convenient to use, has no need for special equipment, can carry out sensitive, specific and rapid detection of Brucella on the crude split product of a to-be-detected sample in 25min just at 38DEG C, and is suitable for field or grassroots brucellosis quarantine work.
Owner:DAIRY CATTLE RES CENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Quintuple PCR (polymerase chain reaction) rapid detection method for main pathogenic bacteria in pork
InactiveCN103290119AThe detection process is fastLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliFood borne
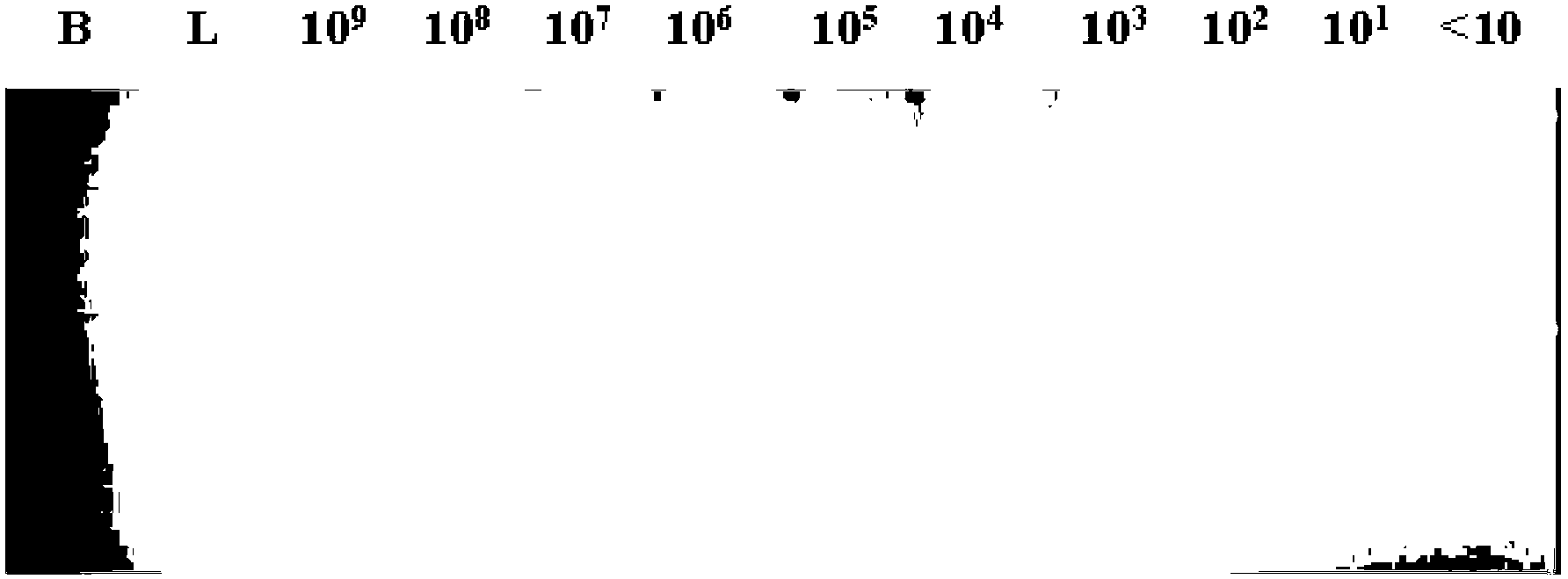
The invention discloses a quintuple PCR (polymerase chain reaction) rapid detection method for main pathogenic bacteria in pork. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting total bacteria DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid), synthesizing the primers represented by the sequences from SEQ ID NO.1 to SEQ ID NO.12; carrying out the quintuple PCR, performing electrophoresis analysis to(on) the PCR product by using 2% agarose, and then judging according to the electrophoresis result. When detecting five food-borne pathogenic bacteria (salmonella, staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes, Yersinia enterocolitica and escherichia coli O157:H7) by the method disclosed by the invention, the lowest detectable limits are respectively 142cfu / mL, 51cfu / mL, 9cfu / mL, 33cfu / mL and 670cfu / mL; compared with the traditional bacteria culture and single PCR, the rapid detection method provided by the invention has the characteristics of high detection speed, low cost, high sensitivity and high specificity; and furthermore, the rapid detection method is suitable for the routine safety monitoring of pathogenic bacteria in mass pork and pork products of the food industry during the sales process.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
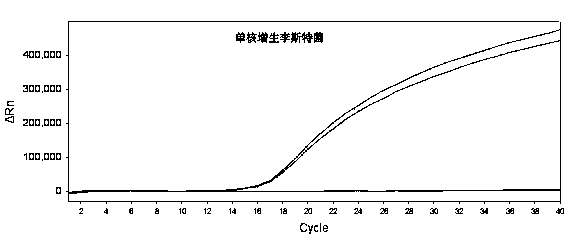
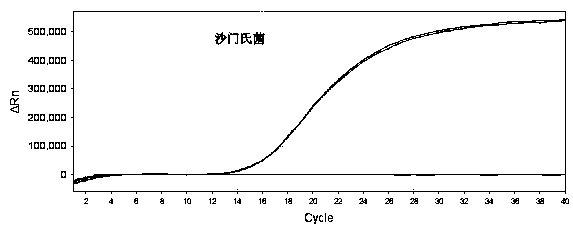
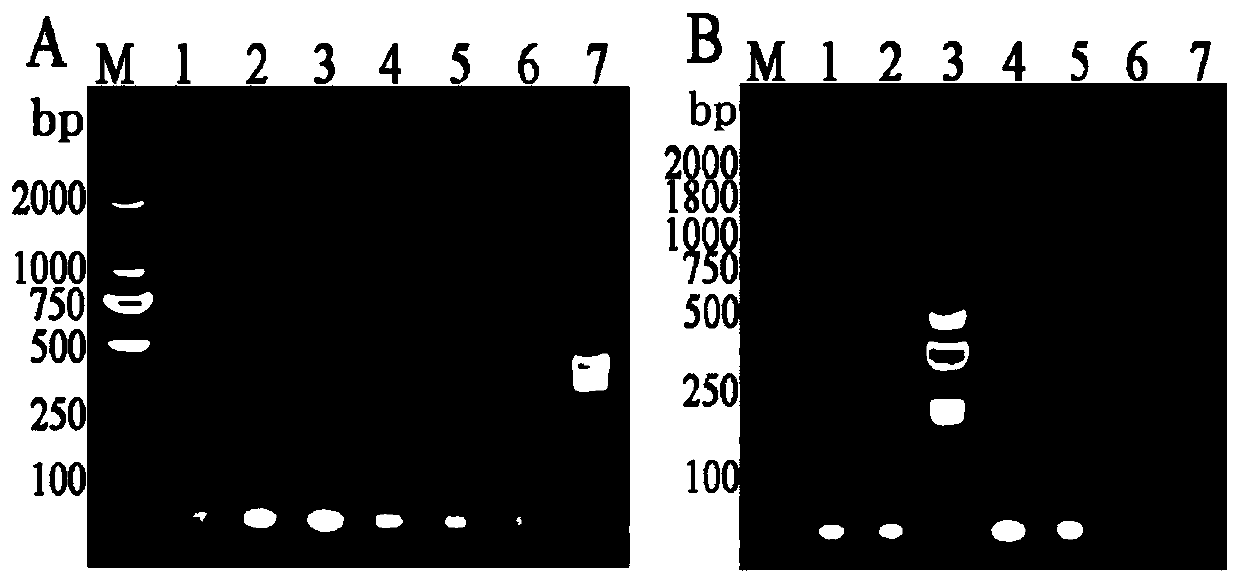
Fluorescence PCR (polymerase chain reaction) kit for detecting yersinia enterocolitica
InactiveCN102329864ADetection is simple and fastSolve the cumbersome operationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceRoxithromycinFluorescence
The invention relates to a fluorescence PCR (polymerase chain reaction) kit for detecting yersinia enterocolitica, reagents in the kit comprise a front primer, a rear primer, a TaqMan probe, a fluorescence PCR premixed solution, an ROX (roxithromycin) solution, pure water and a positive standard solution, wherein the front primer, the rear primer and the TaqMan probe are DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fragments of 20-21 bases, which are synthesized according to a specific and conserved gene nucleotide sequence of the yersinia enterocolitica and can be specifically combined with the yersinia enterocolitica. The invention further provides a method for detecting the yersinia enterocolitica, and the method comprises the following steps: performing pretreatment on samples; using the reagents of the kit for detection; and analyzing the detection result. The kit is simple, fast, sensitive, accurate and suitable for detecting a large number of samples.
Owner:南宁海关技术中心
Detection kit of 16 food born pathogenic bacteria
InactiveCN108220464ANo pollution in the processAvoid pollutionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliFood borne
The invention discloses a detection kit of 16 food born pathogenic bacteria. The detection kit comprises a PCR amplification reagent and reference reagents; the PCR amplification reagent is composed of PCR buffer solution A, enzyme system B, and a primer probe mixed solution of the 16 food-borne pathogenic bacteria; the reference reagents are mainly composed of a negative control and a positive control; the PCR buffer solution A contains 5*Buffer, 25mM dN(U)TPs; the enzyme system B is mainly composed of HotStart Hi Taq DNA polymerase and UNG anti-pollution enzyme; the primer probe mixed solution of the 16 food-borne pathogenic bacteria contains a mixed solution of detection primer probes of salmonella, Shigella, enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, enterotoxigenic E. coli, enteroinvasive escherichia coli, adherent escherichia coli, Escherichia coli O157, Staphylococcus aureus, listeria monocytogenes, Bacillus Cereus, campylobacter jejuni, vibrio parahaemolyticus, Vibrio cholerae group O1, Vibrio cholerae group O139, Yersinia enterocolitica, and enterobacter sakazakii. The detection kit is high in detection sensitivity, is simple, and is convenient.
Owner:HANGZHOU ZHUNXIN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Primers for detecting food poisoning bacteria and a use thereof
InactiveUS20050233345A1Sensitive to useHighly sensitive and quick useSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementE coli heat stable toxinStaphylococcus aureus
Provided are novel primers directed against enterotoxin A gene (ent A) of bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and primers directed against heat stable enterotoxin gene (yst) of bacteria Yersinia enterocolitica, for detecting poisoning in food articles. Also provided is a highly sensitive method for detecting bacterial food poisoning using the primers.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Target sequence for detection of yersinia enterocolitica and kit
InactiveCN101748197AEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecific detectionNucleotide
The invention provides a genetic marker and a method for detection of yersinia enterocolitica, in particular a nucleotide sequence for detection of the ail gene of the yersinia enterocolitica, oligonucleotide primers and a probe. The oligonucleotide primers and the probe are designed based on the nucleotide sequence. The invention also provides a method for rapid and specific detection of the yersinia enterocolitica with the primers. Moreover, the invention can detect the yersinia enterocolitica conveniently, rapidly, accurately, qualitatively and quantitatively.
Owner:SHANGHAI FOSUN PHARMA (GROUP) CO LTD +1
Method for detecting food-borne enterocolitisyersinia genus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification
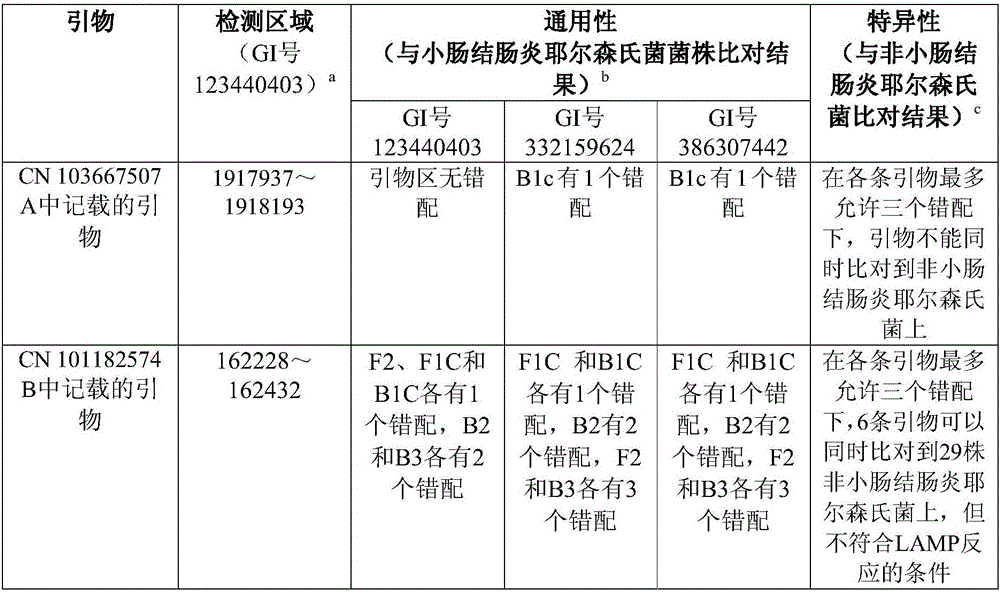
InactiveCN101182574BAccurate identificationRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementFood borneElectrophoresis
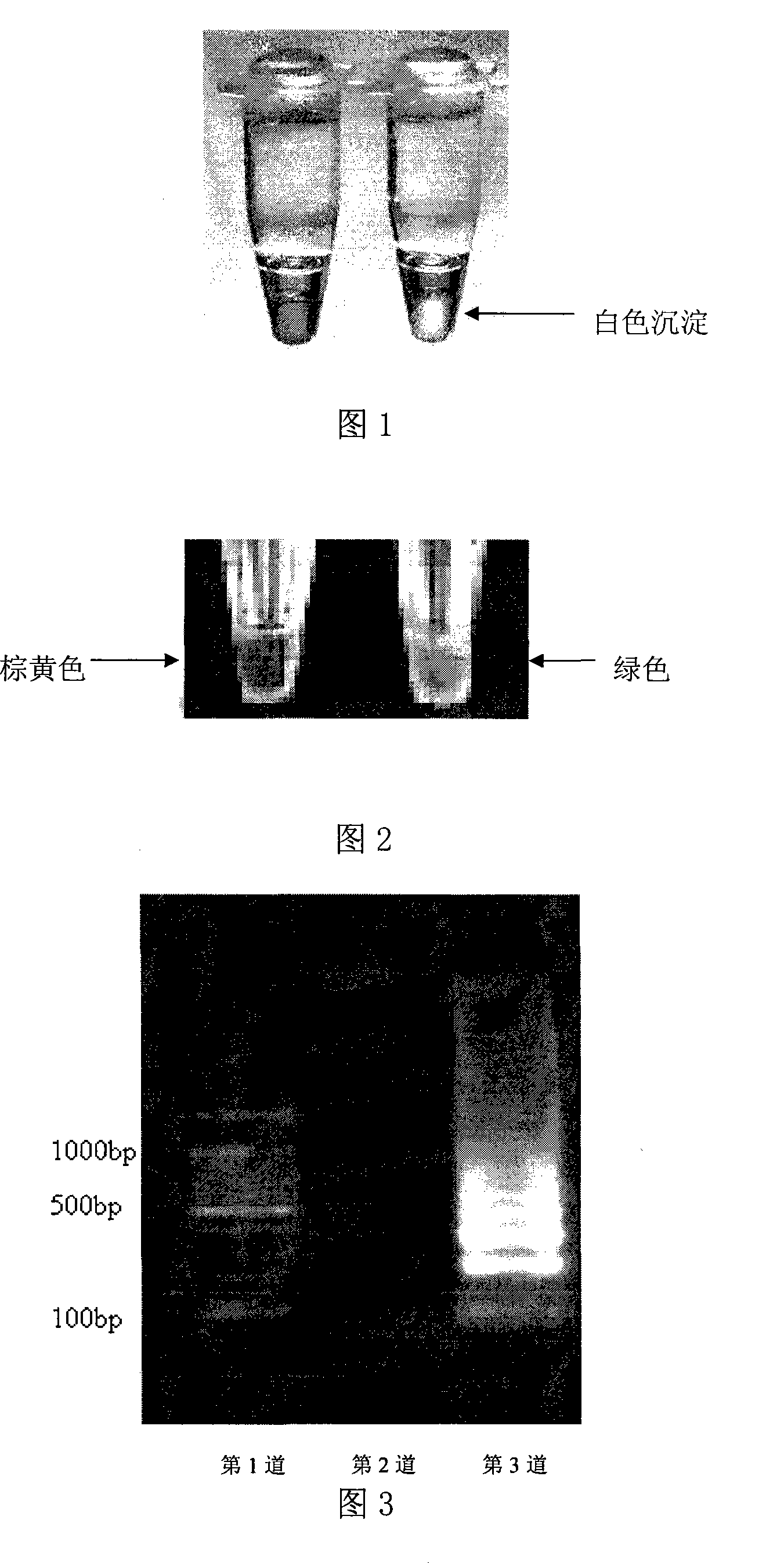
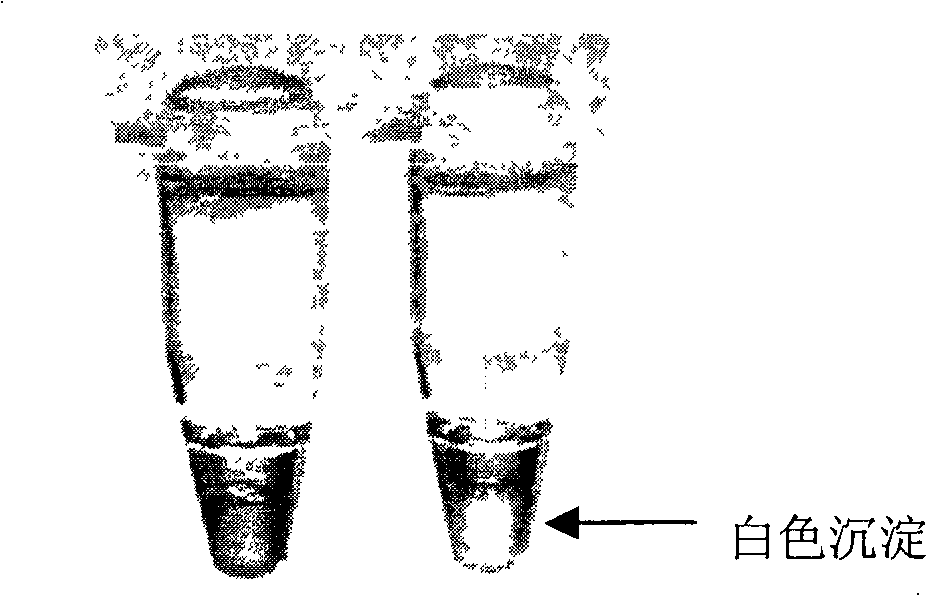
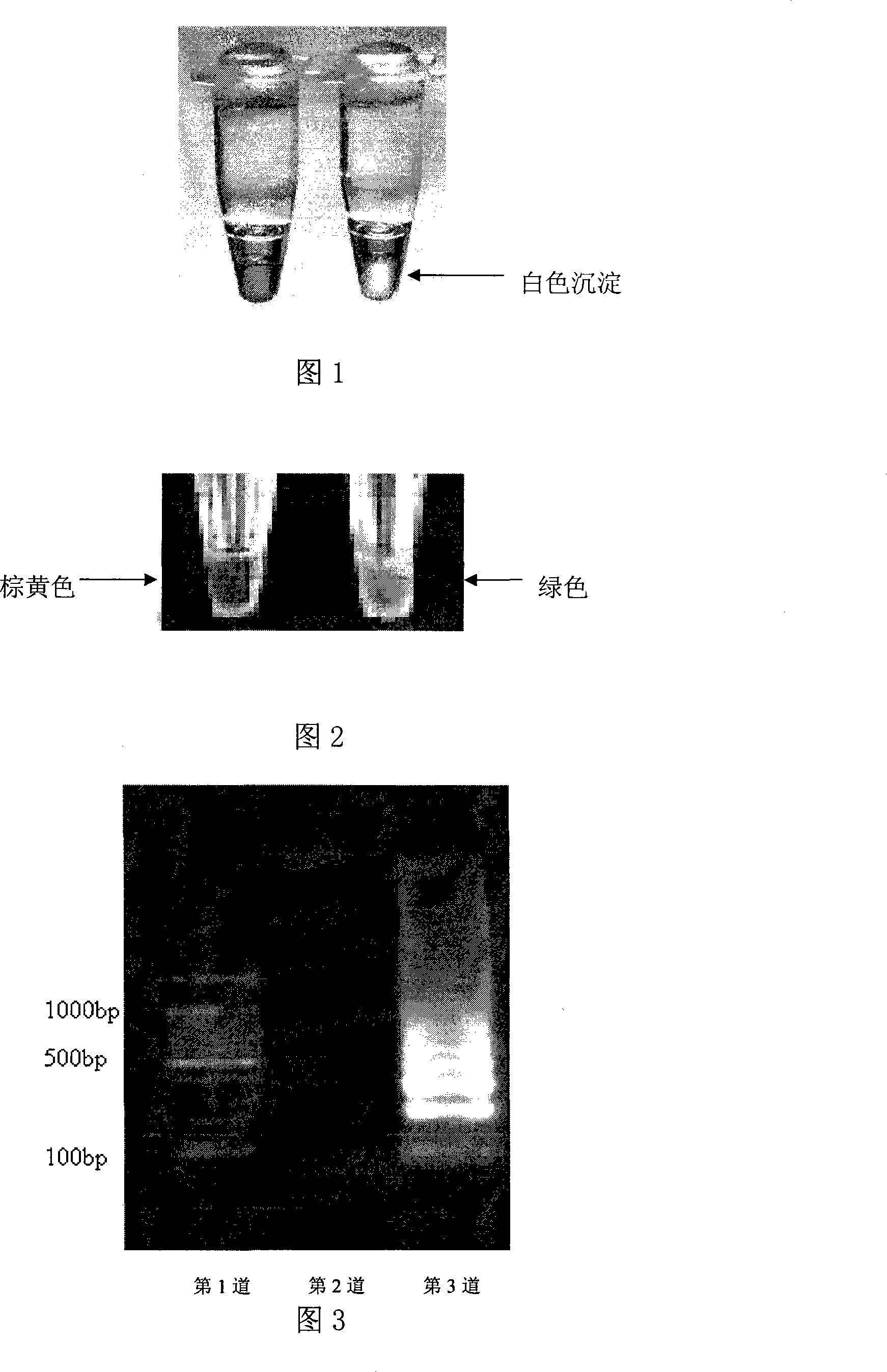
The invention discloses a method which is used for detecting the bacterium Yersini of food-borne coloenteritis with the loop-mediated constant-temperature magnification technology; the method belongs to the bacillus detection technology field and the main technical proposal is that a primer group sequence is designed and the loop-mediated constant-temperature magnification technology is adopted for detection; the loop-mediated constant-temperature magnified product detection methods comprise that 10,000 multiplied g, 5 minutes and room temperature; white sedimentation can be seen at the bottom of the tube in a positive way; visualization reagent is added and the positive result turns green; the process of 1.5 percent agarose gel electrophoresis is implemented and the step-shaped electrophoresis strip is formed; any one of the three loop-mediated constant-temperature magnified product detection methods can be chosen for detection. The method is characterized by accurate detection, strong special and high sensibility and with the method, special object bacillus can be identified fast and accurately and the identification efficiency is increased and the time is saved; in this way, the state that the traditional detection system can not meet the requirements of the ever increasing imports and exports.
Owner:ANIMAL & PLANT & FOOD INSPECTION CENT OF TIANJIN ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Reagent kit and method for detection of enterocolitis yersinia genus with ring mediated isothermality amplification method
InactiveCN101492732AAccurate identificationRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEnterocolitisYersinia enterocolitica
The invention discloses a method for detecting food origin enterocolitis Yersinia by using loop-mediated constant temperature PCR technology, belonging to the food sanitation field. The technical proposal is as follows: enterocolitis Yersinia 16S-23S regions are used as target detection sequences, and four specific primers containing the whole region sequences are designed. The invention comprises extraction of four specific primers of enterocolitis Yersinia 16S-23S regions and food origin enterocolitis Yersinia, detection method for loop-mediated constant temperature PCR amplification and interpretation of results. The method fills the gap of a method for detecting food origin enterocolitis Yersinia by using loop-mediated constant temperature PCR amplification technology, and is used for checking enterocolitis Yersinia in import and export foods. The method has the characteristics of low cost, high efficiency, simple operation and convenience.
Owner:ANIMAL & PLANT & FOOD INSPECTION CENT OF TIANJIN ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Immobilized microbial consortium useful for rapid and reliable BOD estimation
InactiveUS6531293B1Improve survivabilityLong stabilityTesting waterOn/in organic carrierBacteroidesSerratia
An immobilized microbial consortium is formulated which comprises of a synergistic mixture of isolated bacteria namely, Aeromonas hydrophila, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Yersinia enterocolitica, Serratia liquefaciens, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Enterobacter cloaca, Klebsiella oxytoca, Citrobacter amalonaticus and Enterobacter sakazaki. The formulated microbial consortium is immobilized on charged nylon membrane. The said immobilized microbial consortium is attached to dissolved oxygen probe for the preparation of electrode assembly. The prepared electrode assembly is used for rapid and reliable BOD estimation. The prepared electrode assembly is used for monitoring of BOD load of synthetic samples such as Glucose-Glutamic acid (GGA) used as a reference standard in BOD analysis and industrial effluents; covering a range from low to high biodegradable organic matter.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
LAMP detection reagent kit of food-borne yersinia enterocolitica and application of LAMP detection reagent kit
InactiveCN110734992AEasy to operateIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyFood safety
The invention discloses an LAMP detection reagent kit of food-borne yersinia enterocolitica. The reagent kit comprises a primer designed special for a food-borne yersinia enterocolitica ail gene and the primer comprises SEQID NO.2, SEQID NO.3, SEQID NO.4 and SEQID NO.5. The invention further discloses an application of the LAMP detection reagent kit to detection of food-borne yersinia enterocolitica of foods. For the LAMP detection reagent kit of the food-borne yersinia enterocolitica, the detection sensitivity can achieve 2.8 *10<2>CFU / mL, is 1000 times higher than common PCR, has the advantages of being good in specificity, visual in results and the like, and is suitable for real-time quick and accurate detection of the yersinia enterocolitica for food safety monitoring sites by grass-roots units.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for detecting food-borne enterocolitisyersinia genus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification
InactiveCN101182574AImprove efficiencyShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementLoop-mediated isothermal amplificationTesting tubes
The invention discloses a method for detecting foodborne Yersinia enterocolitica by using loop-mediated constant temperature amplification technology, which belongs to the technical field of bacterial detection. The constant temperature amplification technology is used for detection, and the detection method of the loop-mediated constant temperature amplification product includes: (1) 10,000 × g, 5 minutes, room temperature, positive visible white precipitate at the bottom of the test tube; (2) adding a chromogenic reagent, positive The result is green; (3) 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis, the result is a ladder-like electrophoresis band; any one of the above three loop-mediated constant temperature amplification product detection methods can be selected for detection. This method has the characteristics of accurate detection, strong specificity and high sensitivity, can quickly and accurately identify specific target bacteria, improves detection efficiency, saves time, and thus solves the current situation that traditional detection methods cannot meet the increasing import and export goods.
Owner:ANIMAL & PLANT & FOOD INSPECTION CENT OF TIANJIN ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Preparation method for pathogenic yersinia enterocolitica test strips
The invention relates to a preparation method for pathogenic yersinia enterocolitica test strips, effectively solving the problems of high time consumption, complexity and poor specificity of existing detection methods. The preparation method includes adding n-caprylic acid to mouse ascites and acetate buffer solution, mixing evenly and centrifuging the mixture, regulating the pH (potential of hydrogen) value of supernatant, adding ammonium sulfate, performing centrifugation, dissolving sediments by PBS solution, and performing dialysis to obtain monoclonal antibodies; activating red, blue and yellow latex particles with carboxyl groups by carbodiimide respectively to obtain suspended activated latex particles; dialyzing to-be-marked antibodies, adding the monoclonal antibodies, dropping the mixture into the activated latex particles, rinsing with NaH2PO4 to enable sediments to be suspended in bovine serum albumin buffer solution, adsorbing markers by glass fibers, drying the markers, and curing anti-mouse IgG (immunoglobulin G) antibodies on fiber films to form quality control areas. The preparation method has the advantages that the advantages of immunoreaction specificity, chromatography rapidity and intuition of the colored latex particles serving as tracers are combined, and accordingly, simplicity, convenience, specificity and sensitiveness are achieved.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF SCI INST OF BIOLOGY LIABILITY
Process for the preparation of cell beads BOD sensor useful for instant BOD estimation
InactiveUS20030036186A1Least chemical damageLeast physical damageBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesSerratia
Immobilized cell beads incorporating formulated microbial consortium comprising a synergistic mixture of the following bacterial strains namely, Enterobacter sakazaki, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Aeromonas sobria selected from the following isolated bacterial strains namely, Yersinia enterocolitica, Aeromonas sobria, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Serratia liquefaciens, Enterobacter sakazaki, Citrobacter amalonaticus, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacter cloaca, Acinetobacter calcoaceticus are prepared, the formulated microbial consortium is immobilized in an appropriate immobilizing agent resulting in the formation of beads and the beads are used for instant BOD estimation using an electronic device and the formulated cell beads are reusable and are capable of assimilating most of the organic matter present in varied industrial effluents.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
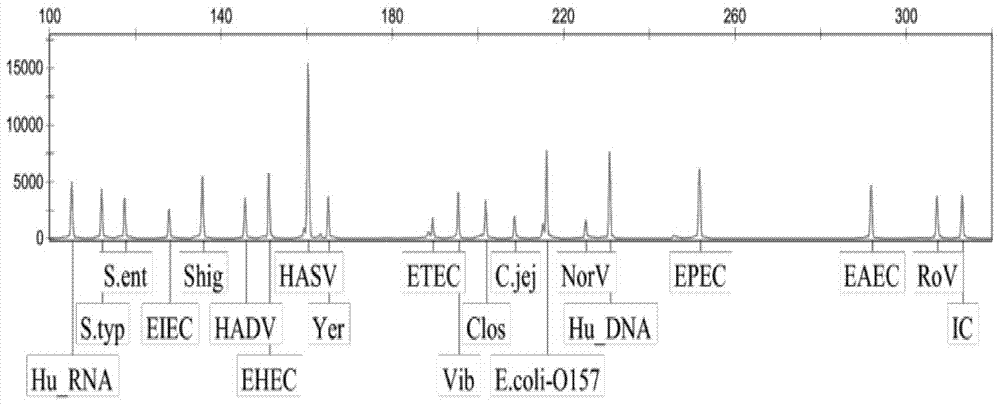
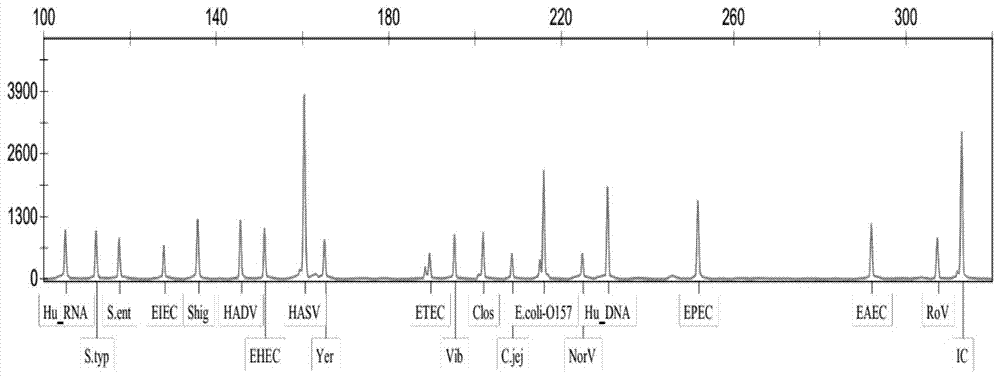
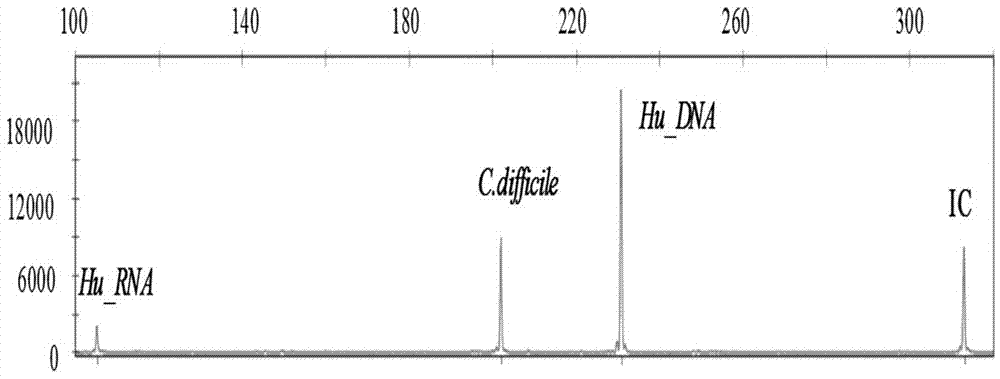
Diarrhea pathogenic bacteria multi-gene detection system and its kit and application
ActiveCN107083446AEliminate pollutionOptimize the reaction systemMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesEscherichia coliHuman DNA sequencing
The invention relates to a diarrhea pathogenic bacteria multi-gene detection system and its kit and application. The detection system has 15 pairs of primers, wherein 13 pairs of diarrhea pathogens primers, one pair of human genome beta-actin primers and one pair of system quality controlled beta-actin primers are included. Diarrhea pathogens refer to campylobacter jejuni, shigella, clostridium difficile, salmonella enteritidis, salmonella typhimurium, enterotoxigenic escherichia coli, escherichia coli O157, vibriones, yersinia enterocolitica and the like. The diarrhea pathogenic bacteria multi-gene detection system and its kit do not require routine culture and other steps, synchronous detection and analysis of the various diarrhea pathogens can be directly conducted on a stool sample in the same reaction system, the shortcomings that a routine detection method is low in flux and low in detection rate and takes much time are made up for, a comprehensive, accurate and low-cost pathogen diagnosis is provided for clinical use for the first time, and an important reference is provided for individualized medication and accurate medical treatment.
Owner:HUADONG HOSPITAL +1
RCA (rolling circle amplification) rapid detection primer and kit for Yersinia enterocolitica
InactiveCN102534023AGuaranteed specificityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMicrobiologyYersinia enterocolitica
The invention relates to a RCA (rolling circle amplification) rapid detection primer and kit for Yersinia enterocolitica, wherein the sequence of a primer combined with the specificity of a probe is SEQ ID NO: 1; the sequence of a primer combined with a fragment amplified through taking the probe as a template is SEQ ID NO: 2; and the sequence of the probe is SEQ ID NO: 3. The kit provided by the invention is characterized in that a padlock probe is designed according to the conserved gene sequence of a to-be-detected bacterial strain so as to ensure the specificity of a detection method. According to the invention, an improved rolling circle amplification (RCA) technique is adopted, and the technique is strong in specificity, and has higher sensitivity than that of a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method; meanwhile, the technique is simple, rapid, safe, pollution-free, and especially applicable to food detection mechanisms.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT SHANDONG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Preparation method of nucleic acid lateral flow test strip for detecting yersinia enterocolitica and application thereof
InactiveCN103789404ASimplify testing proceduresEasy interpretation of resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementPathogenic microorganismNucleic acid detection
The invention discloses a preparation method of a quick nucleic acid test strip detection kit for food-borne pathogenic microorganism-yersinia enterocolitica and an application thereof, and also discloses a design method of a primer for specific nucleic acid PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification for yersinia enterocolitica, and a method for detecting a PCR amplification product with the nucleic acid test strip for nucleic acid lateral flow and an application. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for detecting the amplification product of the target nucleotide sequence of pathogenic microorganisms from other sources by use of the specific nucleotide sequence amplification product, wherein the specificity is guaranteed by the amplification primer.
Owner:ANIMAL & PLANT & FOOD INSPECTION CENT OF TIANJIN ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Primers capable of simultaneously detecting various diarrhea pathogenic bacteria and application of primers
InactiveCN106868160AHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesEscherichia coliBacillus perfringens
The invention discloses primers capable of simultaneously detecting various diarrhea pathogenic bacteria and an application of the primers, and belongs to the field of nucleic acid detection of pathogenic bacteria. The invention discloses primers and probes as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1-39; and the primers and the probes can be used for rapidly and accurately detecting staphylococcus aureus, shigella, vibrio parahaemolyticus, yersinia enterocolitica, clostridium difficile, plesiomonas sp, listeria monocytogenes, escherichia coli O157:H7, aeromonas, salmonella, clostridium perfringens, bacillus cereus and campylobacter jejuni; therefore, great convenience is brought to clinical microorganism detection.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIAN BIOTECH CO LTD +1
Multiplex PCR kit for detecting 11 common food-borne pathogenic bacteria and application thereof
ActiveCN110512008AReduce interactionHigh detection throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFood borneShigella flexneri
The invention discloses a common primer-mediated PCR kit for detecting 11 food-borne pathogenic bacteria and an application of the common primer-mediated PCR kit. A common primer-mediated multiplex PCR technology is utilized; specific genes of 11 common food-borne pathogenic bacteria (salmonella, listeria monocytogenes, shigella flexneri, enterohemorrhagic escherichia coli O157, vibrio parahaemolyticus, staphylococcus aureus, vibrio cholerae, clostridium botulinum A, bacillus cereus, clostridium perfringens and yersinia enterocolitica) are used as detection markers; an efficient, high-specificity and high-flux multiplex PCR detection system is established, and a nucleic acid detection kit suitable for detecting the common food-borne pathogenic bacteria is researched and developed. The sensitivity of the common primers reaches 10<3> copies / mu L, a UP-M-PCR system for simultaneously detecting the 11 food-borne pathogenic bacteria is constructed, single-template and two-template experiments prove that the UP-M-PCR system has good specificity, and the sensitivity of a bacterial genome DNA detection system is as high as 0.01 ng / mu L.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method, primers and kit for quickly detecting yersinia enterocolitica in constant-temperature manner
ActiveCN106434890AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationYersinia enterocoliticaBiology
The invention discloses a method, a primer group and a kit for quickly detecting yersinia enterocolitica in a constant-temperature manner. The method comprises the following steps of extracting DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of a genome from a to-be-detected sample; using the DNA of the genome as a template, using a primer group capable of amplifying the specific sequence of the yersinia enterocolitica as primers, and carrying out constant-temperature amplification reaction under an enzyme reaction system; through judging whether a reaction result is positive or not, determining whether the yersinia enterocolitica exists in the to-be-detected sample or not. The detection method provided by the invention has high sensitivity and high specificity, is short in detection time, is simple in result decision, is convenient and quick to operate, is low in cost, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:上海市生物医药技术研究院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com