Method for detecting food-derived pathogenic enterobacteria by composite fluorescence PCR technique
A composite fluorescence, technical detection technology, applied in the field of food-borne pathogenic Enterobacteriaceae, detection of pathogenic bacteria, can solve the problems of difficult biochemical identification of molecular biology detection methods, save detection cost and time, save time, Sensitive effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
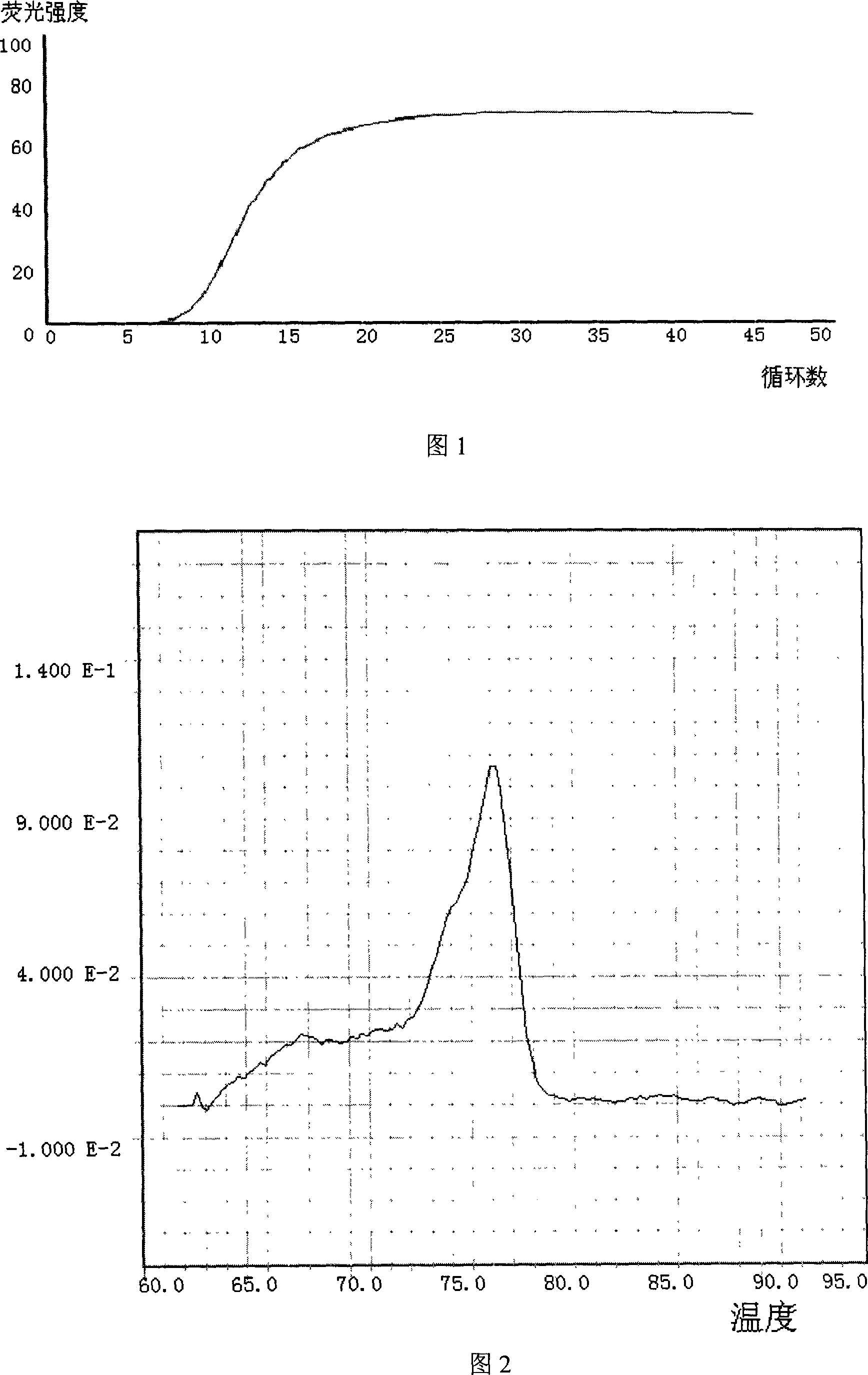
Embodiment 1
[0079] Sample: An export of fresh meat.
[0080] Use routine physiological and biochemical methods to detect suspected Shigella colonies, and then perform the following composite fluorescent PCR technology to detect foodborne pathogenic bacteria:
[0081] 1. Sample Processing
[0082] (1) Take 100 grams of the sample to be tested and pulverize it.
[0083] (2) Dissolve in 1 liter of nutrient broth and incubate at 37°C for 8 hours.
[0084] 2. DNA extraction
[0085] Take 1 mL of nutrient broth and let it stand in an ice bath for 5 minutes, then centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 5 minutes at room temperature, discard the supernatant, add 100 μL of lysozyme solution, incubate at 37°C for 10 minutes, and add 500 μL of TE buffer , shake to mix. Add the same volume of Tris saturated phenol (pH 8.0), shake vigorously, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 3 minutes, take the supernatant, and repeat the phenol extraction. Take the supernatant, add 0.1 times the volume of sodium acetate (2mol / ...
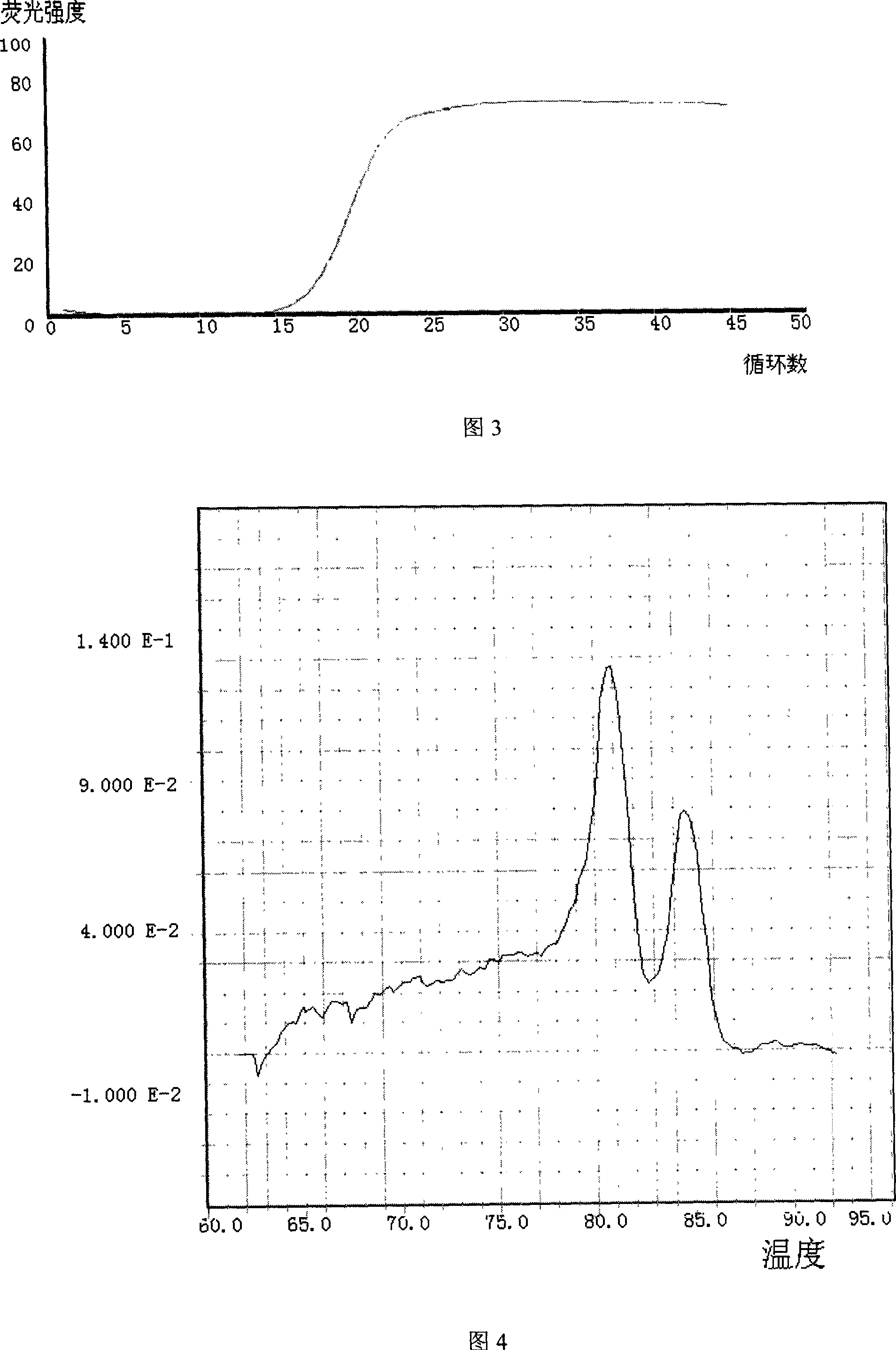
Embodiment 2
[0115] Sample: Somewhere exports cookies.
[0116] Use routine physiological and biochemical methods to detect suspected colonies of Salmonella, and then perform the following composite fluorescent PCR technology to detect foodborne pathogens:
[0117] 1. Sample Processing
[0118] (1) Take 100 grams of the sample to be tested and pulverize it.
[0119] (2) Dissolve in 1 liter of nutrient broth and incubate at 37°C for 8 hours.
[0120] 2. DNA extraction
[0121] Take 1 mL of nutrient broth and let it stand in an ice bath for 5 minutes, then centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 5 minutes at room temperature, discard the supernatant, add 100 μL of lysozyme solution, incubate at 37°C for 10 minutes, and add 500 μL of TE buffer , shake to mix. Add the same volume of Tris-saturated phenol (pH 8.0), shake vigorously, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 3 minutes, take the supernatant, and repeat the phenol extraction. Take the supernatant, add 0.1 times the volume of sodium acetate (2mol / L),...
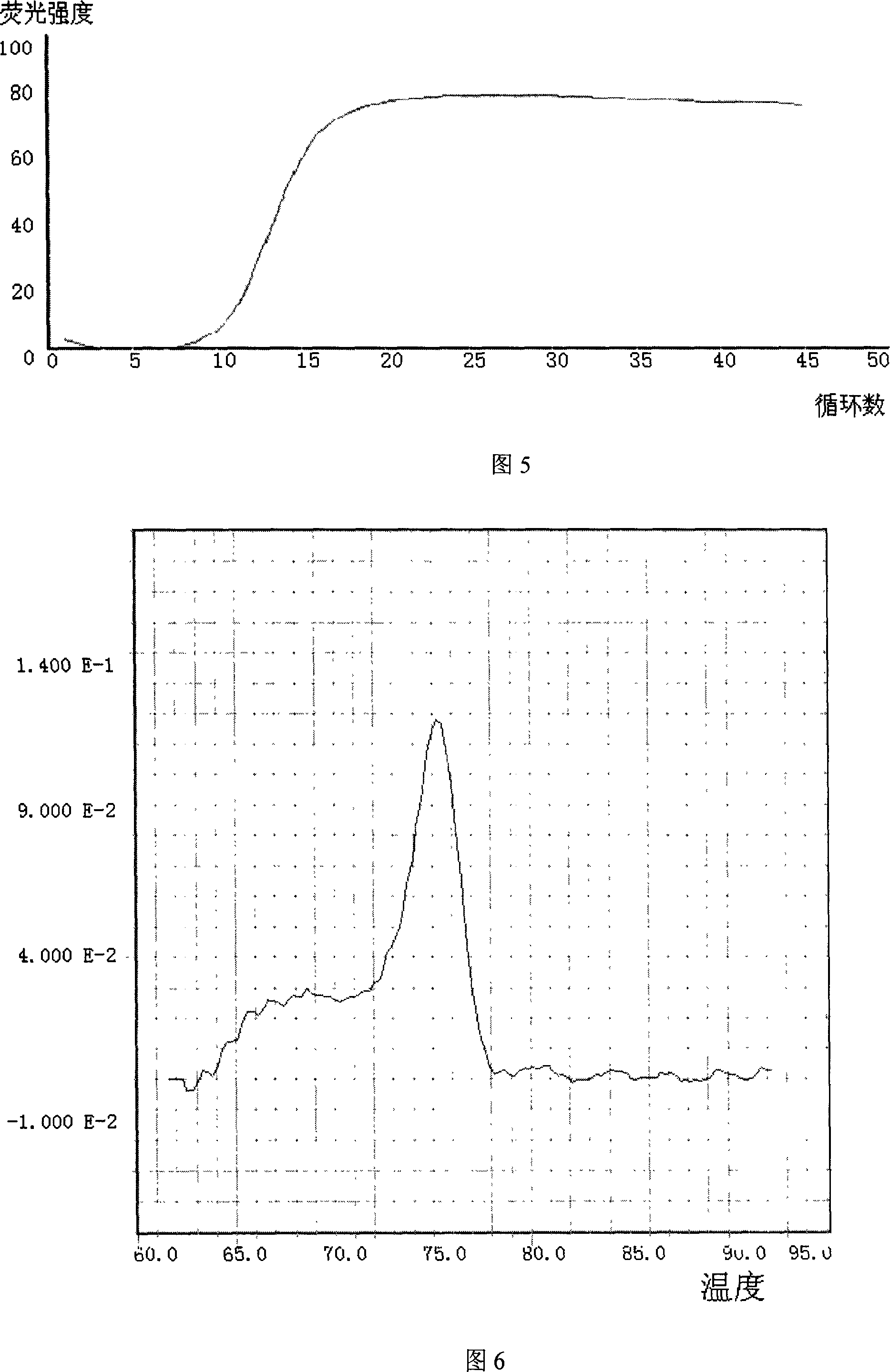
Embodiment 3
[0151] Sample: Raw milk sent for inspection somewhere.
[0152] Use conventional physiological and biochemical methods to detect suspected Yersinia enterica colonies, and then perform the following composite fluorescent PCR technology to detect foodborne pathogenic bacteria:
[0153] 1. Sample Processing
[0154] (1) Take 100 grams and centrifuge.
[0155] (2) The precipitate was redissolved in 1 liter of nutrient broth and incubated at 37°C for 8 hours.
[0156] 2. DNA extraction
[0157] Take 1 mL of nutrient broth and let it stand in an ice bath for 5 minutes, then centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 5 minutes at room temperature, discard the supernatant, add 100 μL of lysozyme solution, incubate at 37°C for 10 minutes, and add 500 μL of TE buffer , shake to mix. Add the same volume of Tris-saturated phenol (pH 8.0), shake vigorously, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 3 minutes, take the supernatant, and repeat the phenol extraction. Take the supernatant, add 0.1 times the volume ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com