Method of producing L-alanyl-L-glutamine from recombinant escherichia coli
A technology for recombining Escherichia coli and glutamine, applied in the field of microbial genetic engineering, can solve the problems of low yield and high cost of L-alanyl-L-glutamine, and achieve the effects of enhanced system activity and important industrial application value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1: the design of amino acid ester acyltransferase gene sequence
[0031] According to the codon usage frequency of Escherichia coli to optimize gene codons, eliminate codons with low usage rate, and use the synonymous transformation method to eliminate the EcoRI restriction site, in order to facilitate the connection of the amino acid ester acyltransferase gene to other plasmid vectors , so a restriction site BamH Ⅰ (GGATCC) was inserted behind the terminator.
[0032] Considering the secondary structure of mRNA, it is first necessary to ensure that the codon translation pocket consisting of the AUG start codon and several bases after it is open, reducing the energy potential of ribosomes binding to mRNA, so that ribosomes can smoothly Translate backwards along the start codon.
[0033] For the original sequence of the amino acid ester acyltransferase gene sequence in this embodiment, see Genbank ACCESSIONAB610978, and for the optimized amino acid ester acyl...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2: Design of a phosphate promoter
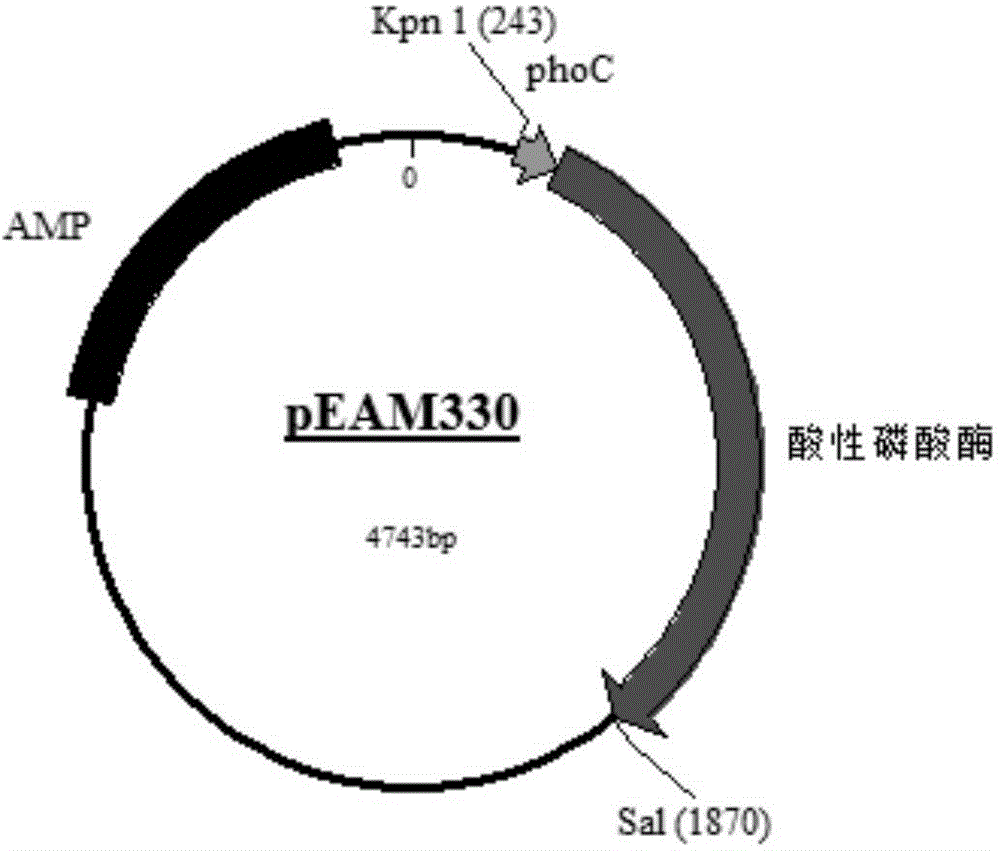
[0035] The phosphate promoter is derived from the pEAM330 plasmid, and the plasmid map is attached to the instruction manual figure 1, the phosphate promoter of the plasmid is derived from the phosphate operon of the E. coli K12 strain, which is a weak promoter suitable for a large amount of accumulation of microbial cells. In order to facilitate the connection of the phosphate promoter and amino acid ester acyltransferase to the plasmid vector An EcoR 1 restriction site (GAATTC) was inserted upstream of the promoter, and the phosphate promoter sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:2.
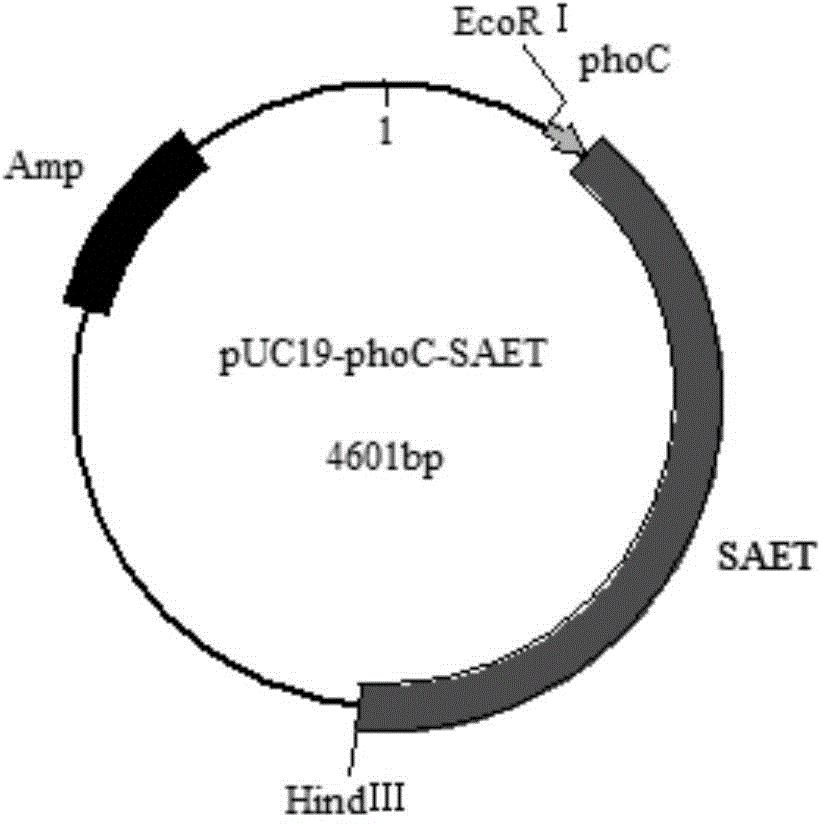
[0036] The amino acid ester acyltransferase gene sequence optimized in Example 1 and the phosphate promoter in Example 2 were directly connected together and submitted to Shanghai Xuguan Company for artificial synthesis and connected to the vector pUC19 to obtain the plasmid pUC19-phoC- SAET, the plasmid map is attached to the instructions figure 2...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Embodiment 3: Construction of amino acid ester acyltransferase gene expression vector
[0038] Using the plasmid pUC19-phoC-SAET as a template, using primers
[0039] CAGAAGCTTATGAAAAACACTATAAGCT and
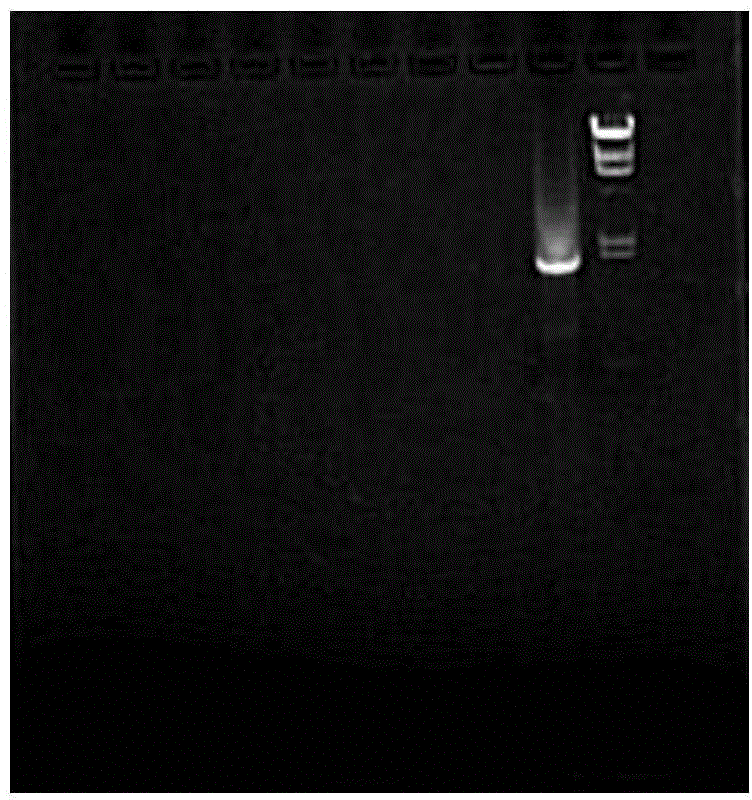
[0040] CGAGGATCCTTAGTCTTTCAGAACAGAA, for PCR amplification. A DNA fragment with a length of about 1800bp was obtained, and the electrophoresis of the PCR product was as follows image 3 shown.
[0041] (1) Construction of JM109 / pUC19-phoC-SAET
[0042] The plasmid pUC19-phoC-SAET synthesized in Example 1 and 2 was transformed into Escherichia coli JM109 competent cells. The transformation process is as follows: add 3 μL of connection solution to 50 μL of JM109 competent cells, then add 10 μL of 5×KCM buffer, mix well, place on ice for 30 minutes, heat shock at 42°C for 90 seconds, and then place on ice After standing for 5 minutes, add 500 μL of LB medium, incubate at 37°C, 220 rpm for 60 minutes, spread it on the Amp resistance plate, and incubate for 12 hours, pick...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com