Lipase, its gene, yalulipolytic geast for producing said enzyme and its application
A yarrow lipolytic yeast and lipase technology, applied in the application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement and other directions, to simplify separation and purification steps, improve stability and use batches, and facilitate continuous production.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Embodiment 1: the acquisition of Yarrow lipolytica strain
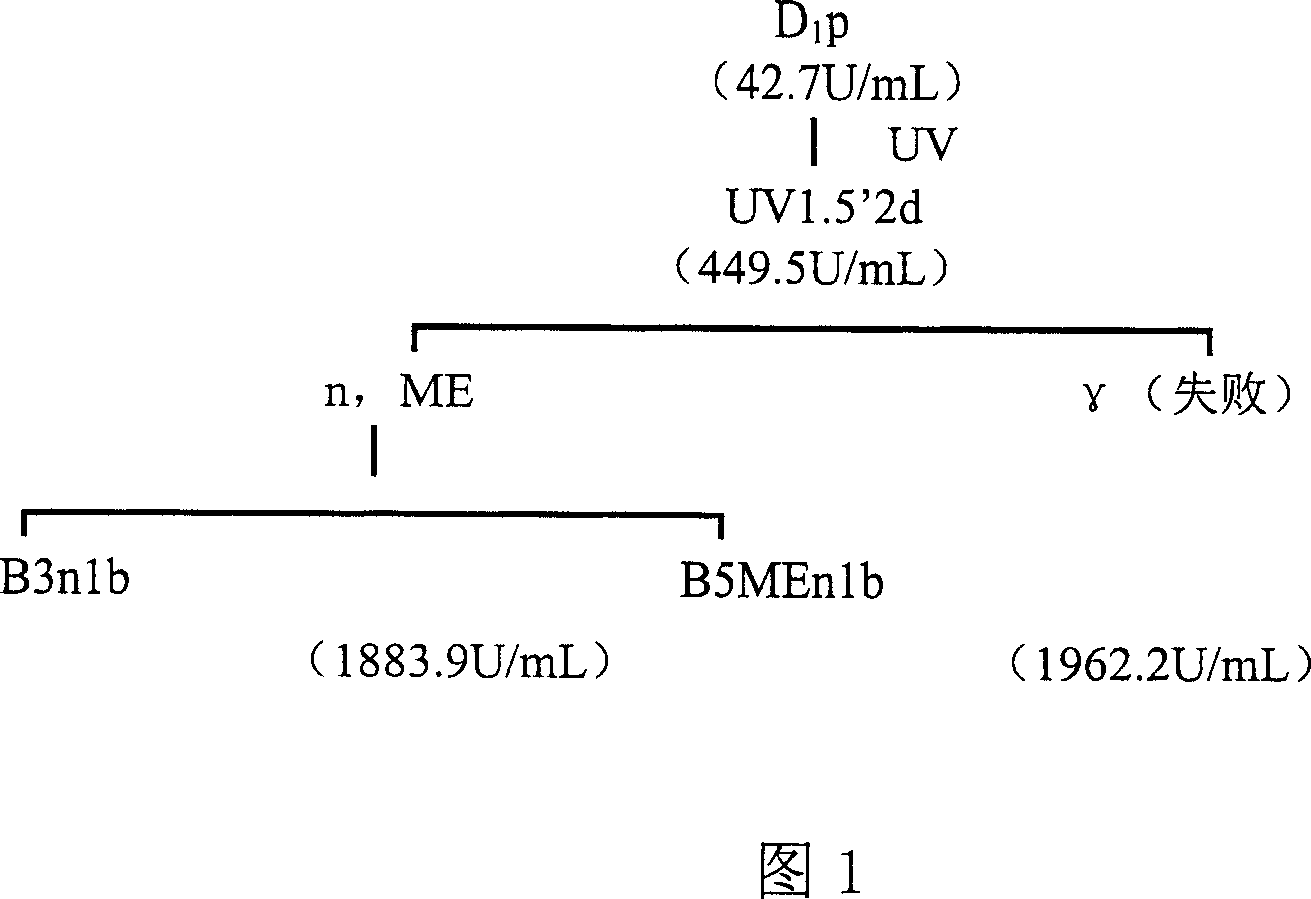
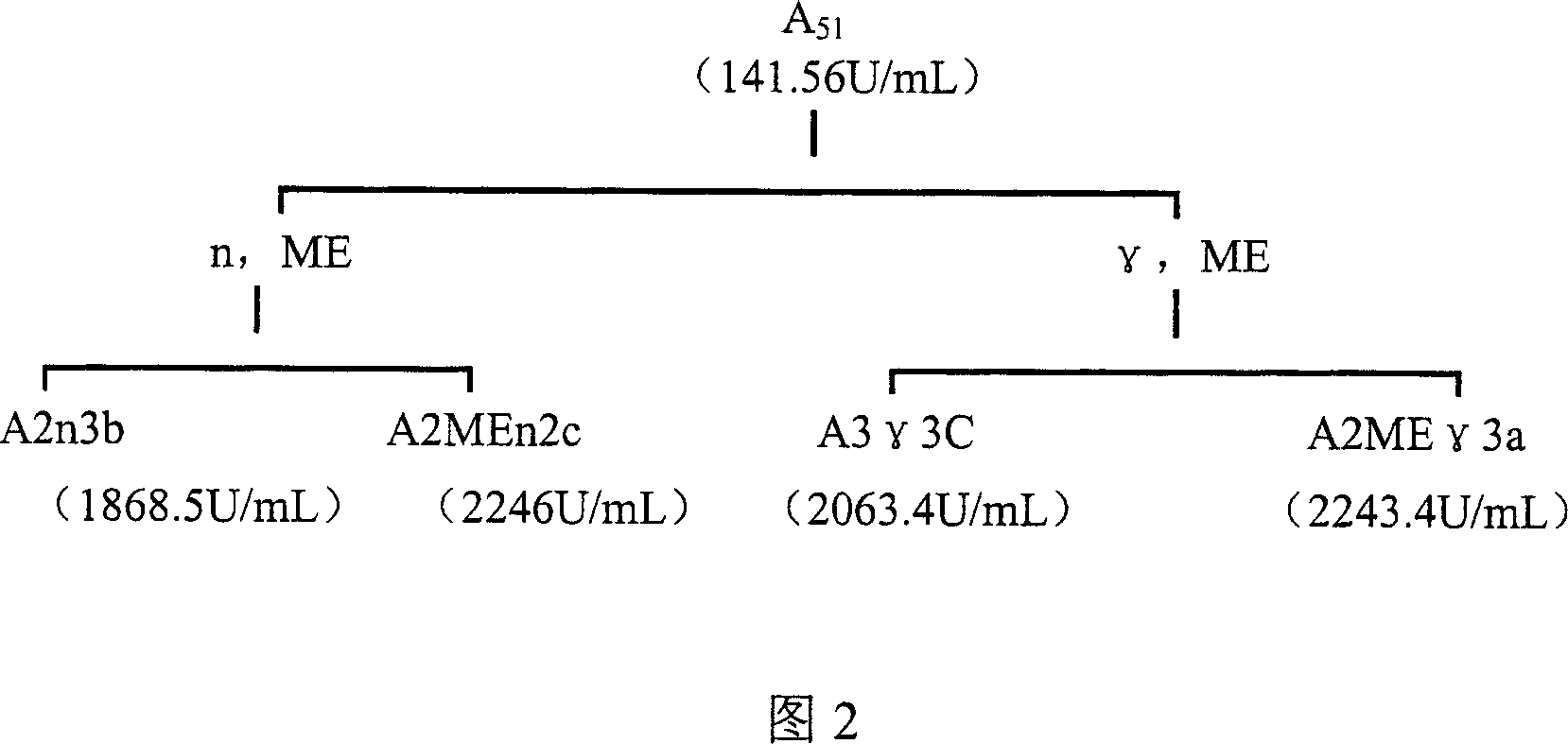
[0042] The strain is a lipase high-yield breeding obtained by combining fast neutron, gamma ray and magnetic field compound treatment after ultraviolet radiation and nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis. In short, the ultraviolet mutagenesis times were 1 minute, 1.5 minutes, and 2 minutes, the fast neutron mutagenesis doses were 5 kilolats, 10 kilolats, and 15 kilolats, and the gamma-ray mutagenesis doses were 5 kilolats, respectively. Ten thousand roentgens, 100,000 roentgens, and 150,000 roentgens, as shown in Figures 1 and 2. Fig. 1 illustrates compound mutagenesis lineage I, wherein UV is ultraviolet light, n is fast neutron, gamma is gamma ray, ME is magnetic field; Fig. 2 illustrates compound mutagenesis lineage II, wherein n is fast neutron, gamma is gamma ray, ME is the magnetic field. Through the above series of mutagenesis processes, a lipase-producing strain with an enzyme activity of 2246 U / mL was finally...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2: Optimization of fermentation conditions
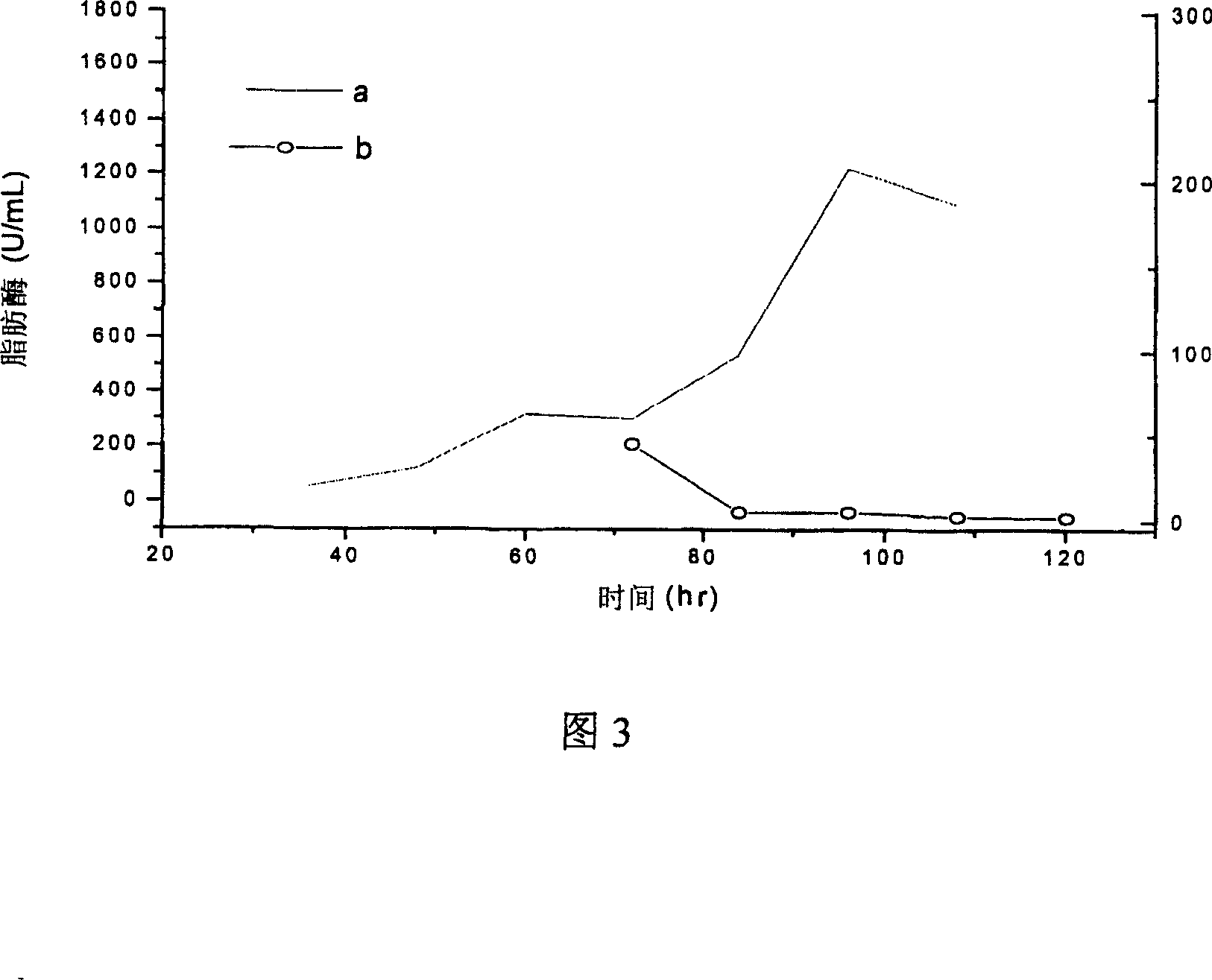
[0045] The effects of different nitrogen sources a and b (a is defatted soybean meal, b is full-fat soybean meal) (4%) on lipase production were compared, and the results are shown in Figure 3. It can be seen from the curve in Figure 3 that the lipase production in the medium with b as the nitrogen source is very low, far less than that with a as the nitrogen source.
[0046] Oils c, d, and e (c is soybean oil, d is rapeseed oil, and e is olive oil) that are beneficial to the production of lipase are selected as carbon sources (2.5%) for research, and the results are compared in Table 1 below:
[0047] Culture time (HR)
[0048] It can be seen from the table that among the three carbon sources compared, c has the highest lipase production.
[0049] In a constant temperature shaker, cultured at different temperatures for 96 hours, the results are shown in Figure 4. It can be seen from Figure 4 that the t...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3: Extraction of fermentation and lipase
[0053] Subsequently, a pilot scale-up experiment was carried out in a 500L fermenter, and the medium components were 4% soybean meal, 2.5% soybean oil, 0.1% K 2 HPO 4 , 0.1% SPAN 60, 03% foam enemy; the fermentation temperature is 26°C, the stirring speed is 200rpm, the pH is 5.7, and the ventilation rate is 0.35vvm. The fermentation enzyme activity reached 8000U / mL, the results are shown in Figure 6.
[0054] Extraction of lipase is performed by a method known to those skilled in the art. In short, the fermentation broth was centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 10 min, the supernatant was taken, flocculated and concentrated by adding 4% polyethylene glycol 6000, the layers were naturally settled, and the lower layer was taken. Add 3 times the volume of acetone to the lower layer to obtain a precipitate, which is dried to obtain a crude enzyme product. The enzyme activity of the crude enzyme product obtained after the above...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| acid value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com