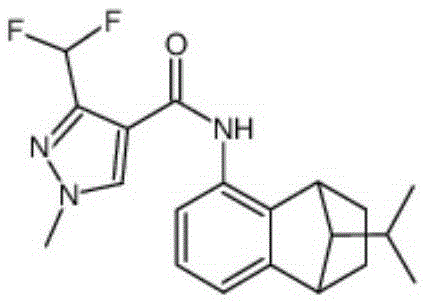
Patents
Literature
68 results about "Succinate dehydrogenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) or succinate-coenzyme Q reductase (SQR) or respiratory Complex II is an enzyme complex, found in many bacterial cells and in the inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotes. It is the only enzyme that participates in both the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain. Histochemical analysis showing high succinate dehydrogenase in muscle demonstrates high mitochondrial content and high oxidative potential.
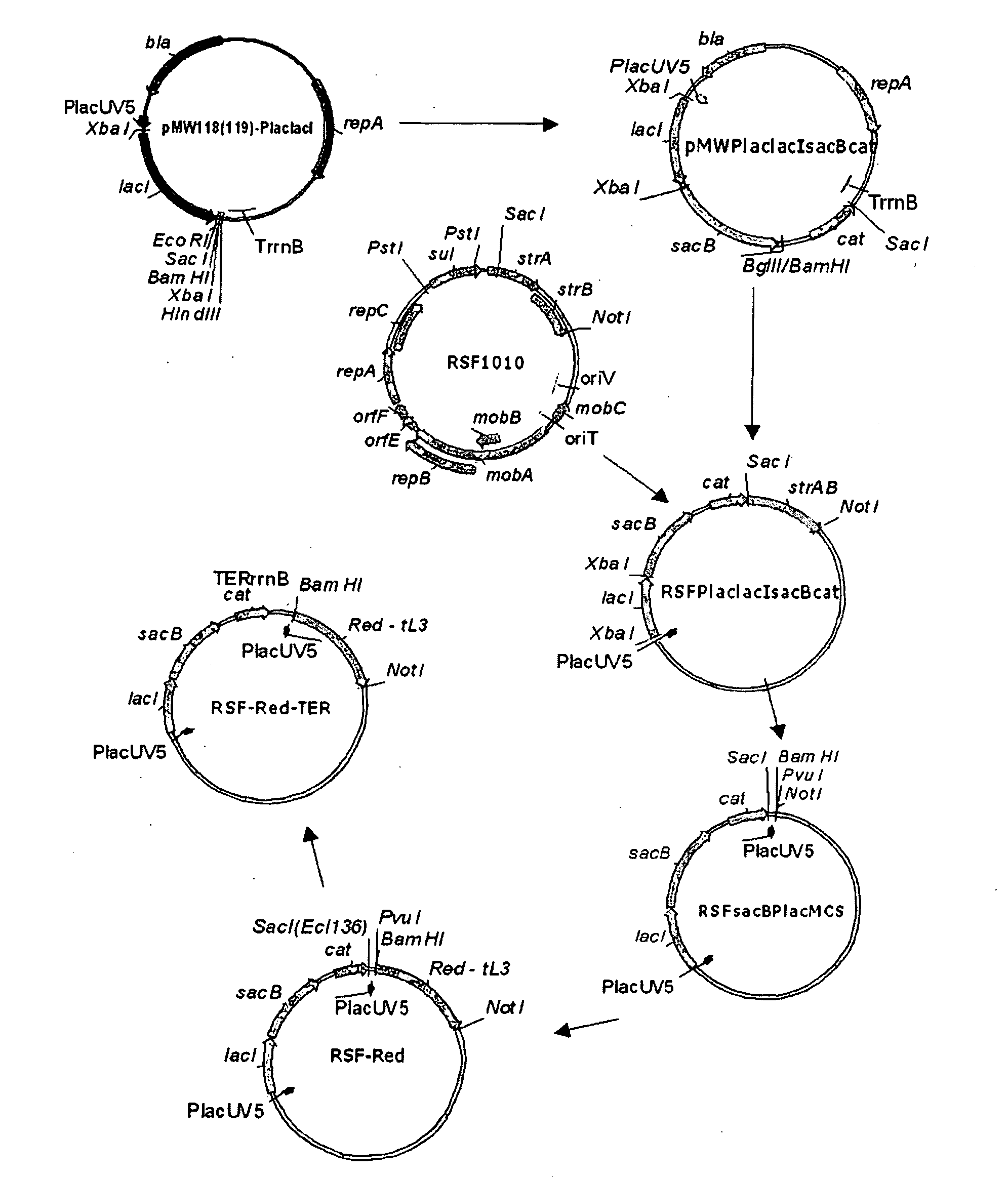
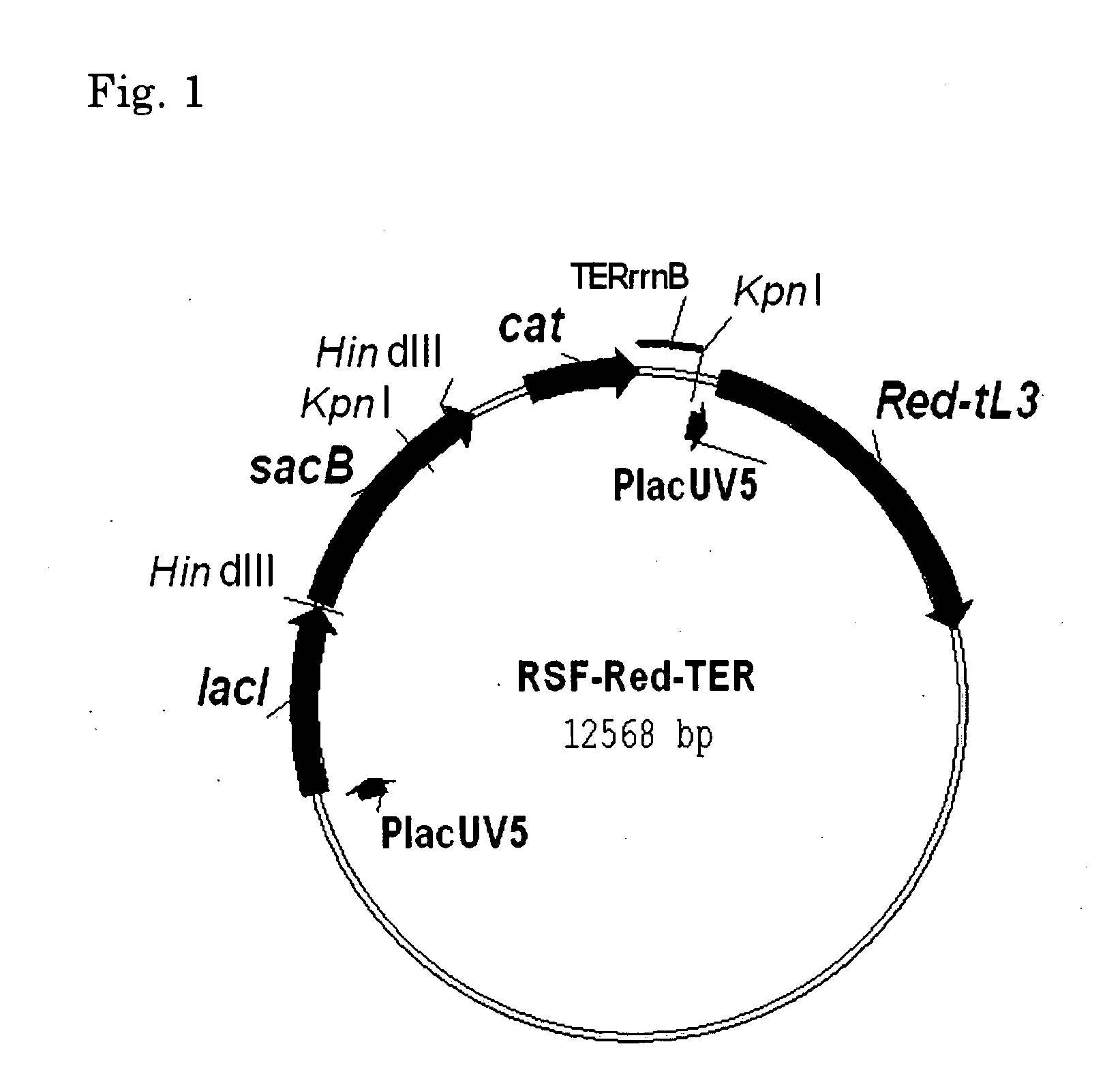
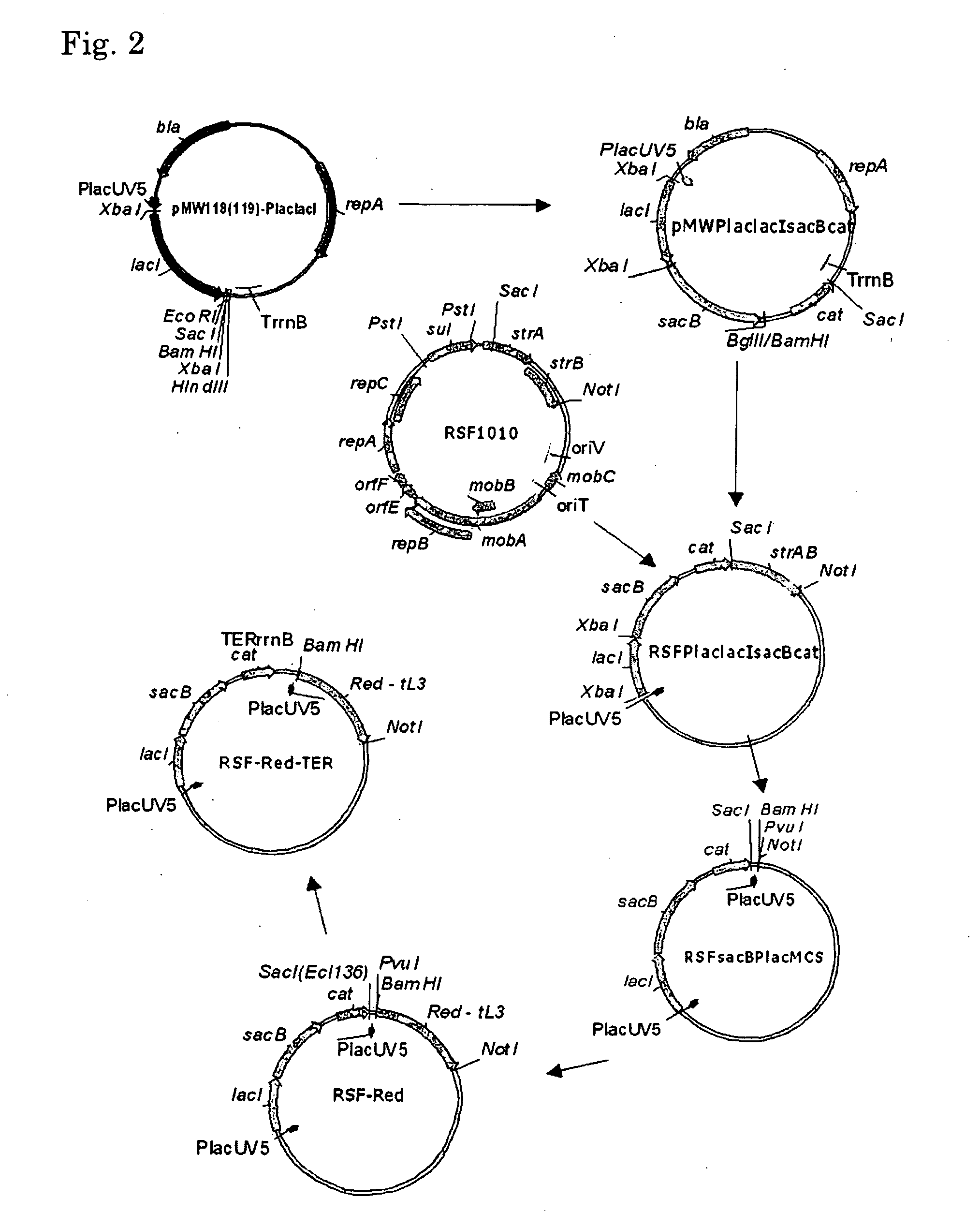
Method for producing an l-amino acid
ActiveUS20090286290A1Efficient productionEasy to useOxidoreductasesFermentationMicroorganismKetoglutarate dehydrogenase
A microorganism which has an L-amino acid producing ability and has been modified so that succinate dehydrogenase activity and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase activity are decreased is cultured in a medium to produce and accumulate an L-amino acid in the medium or cells of the microorganism, and the L-amino acid is collected from the medium or cells to produce the L-amino acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
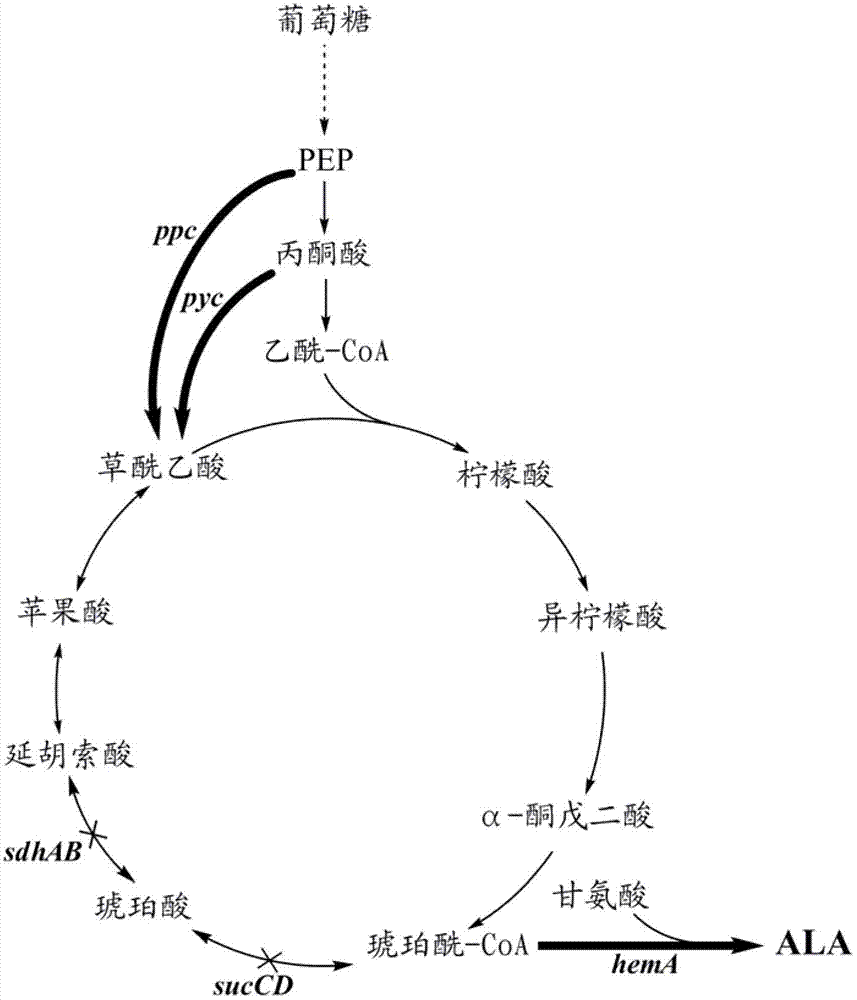
High-yield 5-aminolevulinic acid strain and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN103981203BImprove conversion rateIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphatePhosphoric acid
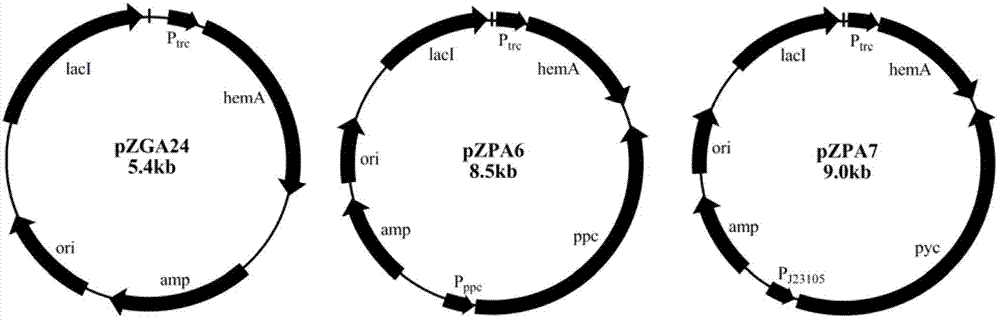
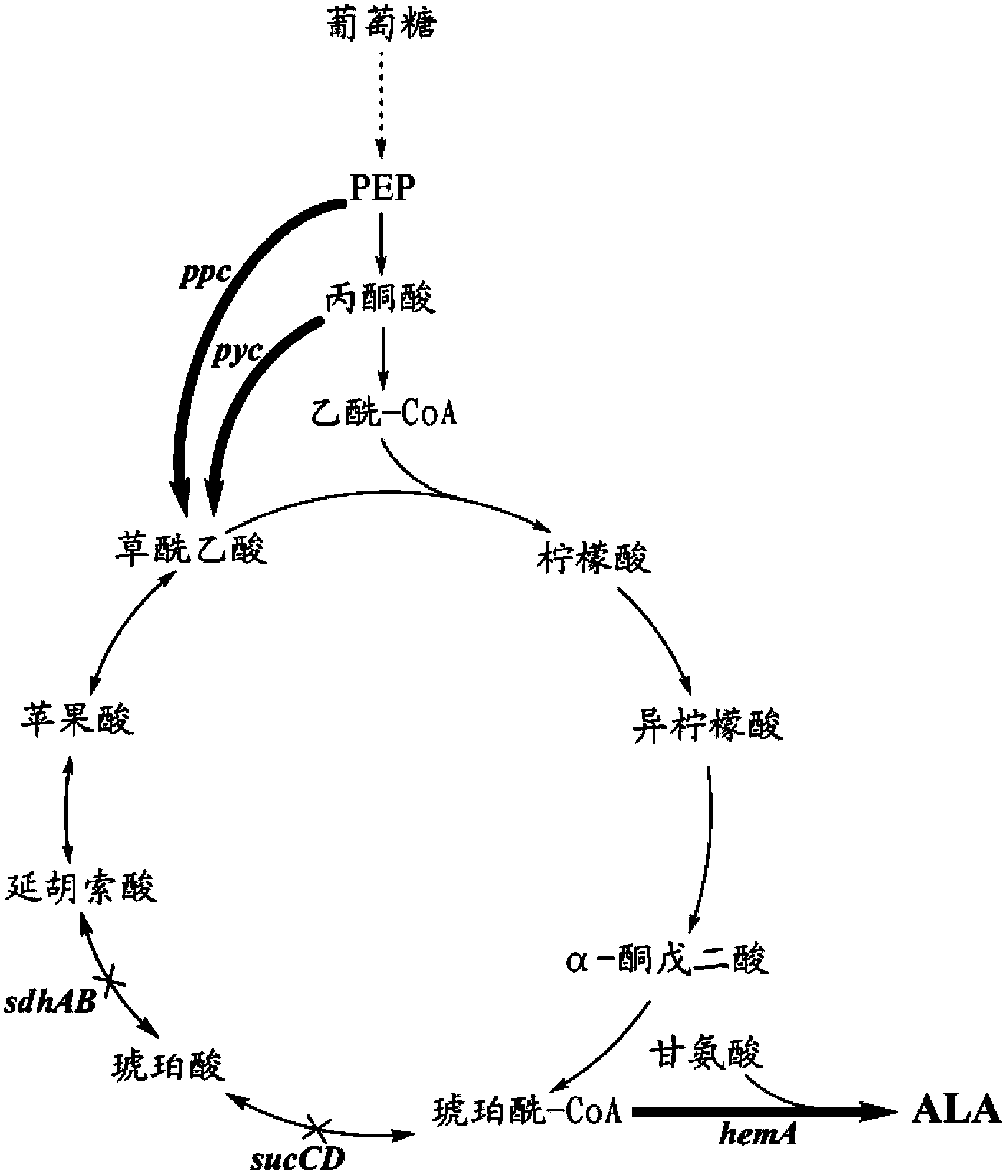
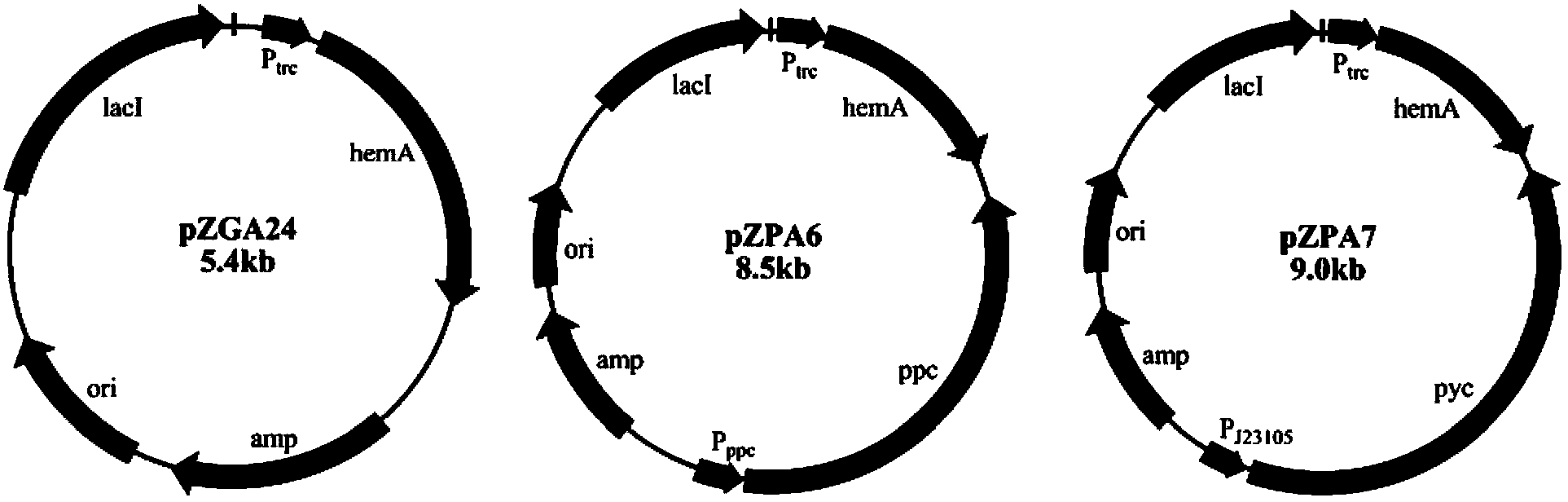
The invention discloses a method for constructing an ALA production strain, that is, enhancing the activity of related enzymes promoting the synthesis of oxaloacetate in the 5-aminolevulinic acid production strain or introducing exogenous related enzymes promoting the synthesis of oxaloacetate , such as phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase or pyruvate carboxylase, and / or weaken the succinyl-CoA downstream metabolic pathway-related enzymes in the strain, such as succinyl-CoA synthetase or succinate dehydrogenase active. The invention also discloses an ALA high-yield strain constructed by the method and a method for preparing ALA by using the strain. The bacterial strain of the invention can produce ALA efficiently, at low cost and with low pollution without adding exogenous succinic acid.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
5-amino levulinic acid (ALA) high-yield strain and preparation method and application thereof
A method for constructing an ALA production bacterial strain, the method enhances the activity of related enzymes promoting the synthesis of oxaloacetate and in the 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) production bacterial strain, or introducing exogenous related enzymes promoting the synthesis of oxaloacetate, such as phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase or pyruvate carboxylase, and / or reducing the activity of related enzymes in the downstream metabolic pathway of succinyl coenzyme A in the bacterial strain, such as succinyl coenzyme A synthetase or succinate dehydrogenase, and / or reducing the activity of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylated kinase and / or malic enzyme. An ALA high-yield bacterial strain constructed by utilizing the method, and method for utilizing the bacterial strain to prepare ALA.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
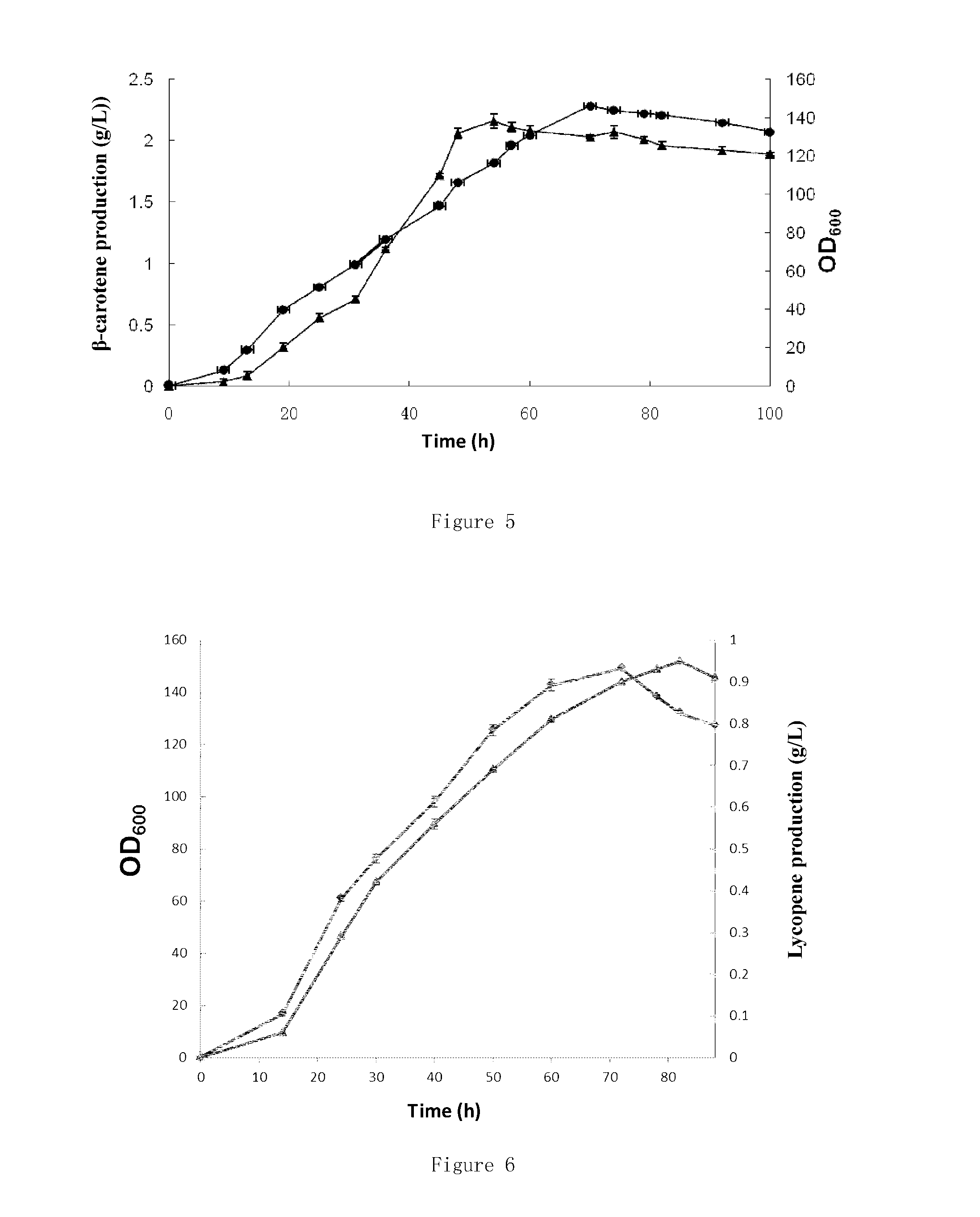
Recombinant microorganism for generating terpenoid and construction method thereof
ActiveCN103087972AIncrease production capacityHigh strengthBacteriaOxidoreductasesEscherichia coliMicroorganism
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Picarbutrazox and succinate-dehydrogenase-inhibitor-bactericide composition and preparation thereof and applications of composition and preparation
InactiveCN106922708ADelay drug resistanceReduce the risk of resistanceBiocideDead animal preservationCross-resistanceSuccinate dehydrogenase
The invention belongs to the field of agriculture, and relates to a bactericidal activity compound composition, in particular to a composition containing picarbutrazox and a succinate-dehydrogenase-inhibitor (SDHIs) bactericide and a preparation thereof and applications of the composition and the preparation. The bactericidal composition comprises a bactericidal activity compound I and a bactericidal activity compound II, the bactericidal activity compound I is the picarbutrazox, and the bactericidal activity compound II is the succinate-dehydrogenase-inhibitor (SDHIs) bactericide. The bactericide composition has the advantages of being wide in control spectrum and free of cross resistance, the using quantity and the using number of the SDHI can be obviously decreased, and the resistance is delayed. The invention also provides the preparation of the bactericidal composition, a preparation method suitable for the composition is designed, the effect of a medicament can be developed to a maximum degree, and the using quantity of the medicament is decreased. The invention also provides the applications of the bactericidal composition and the preparation, so that medicine is guided to be correctly used, and misusing of the medicament is reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG XINNONG CHEM CO LTD
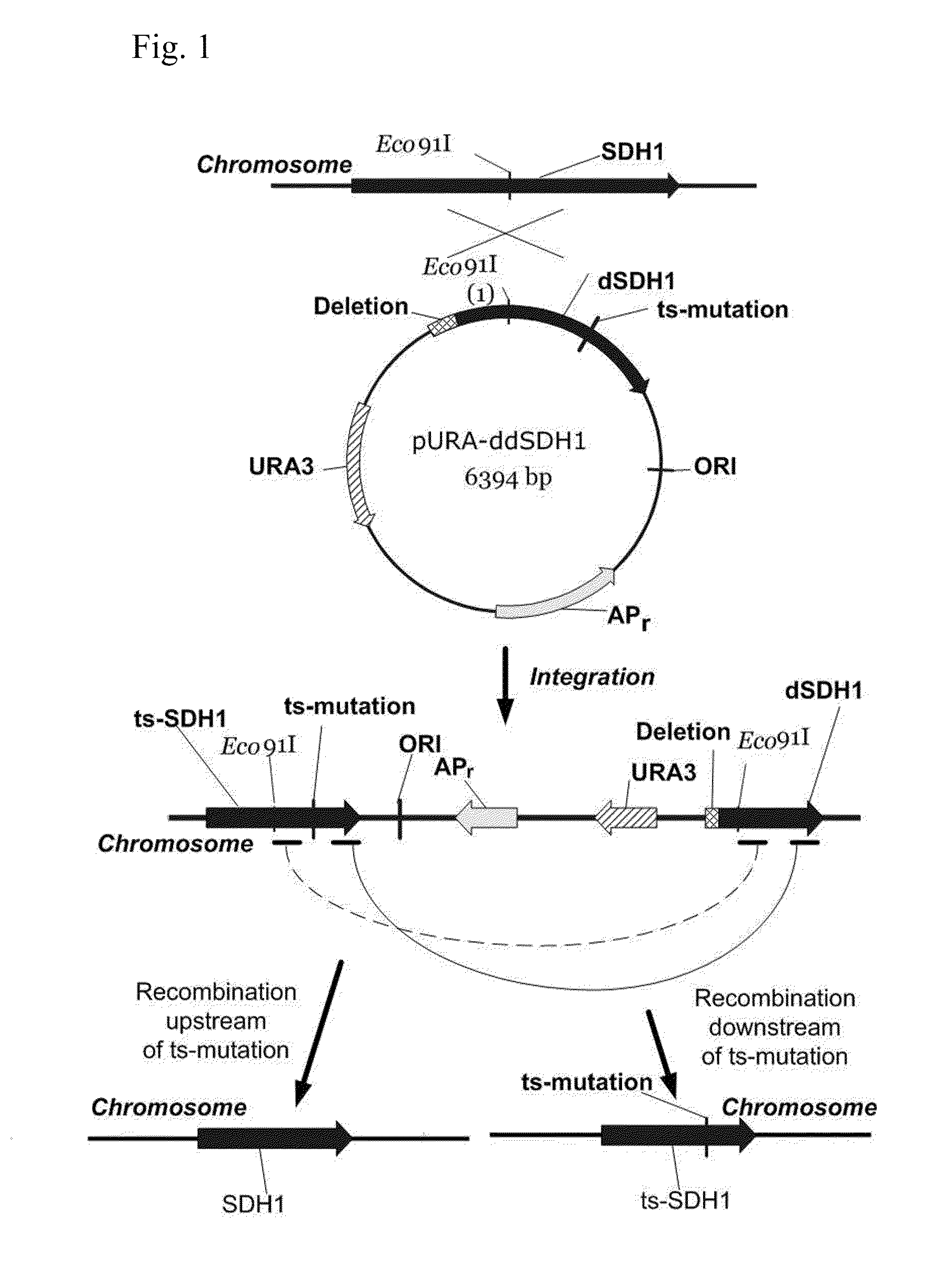
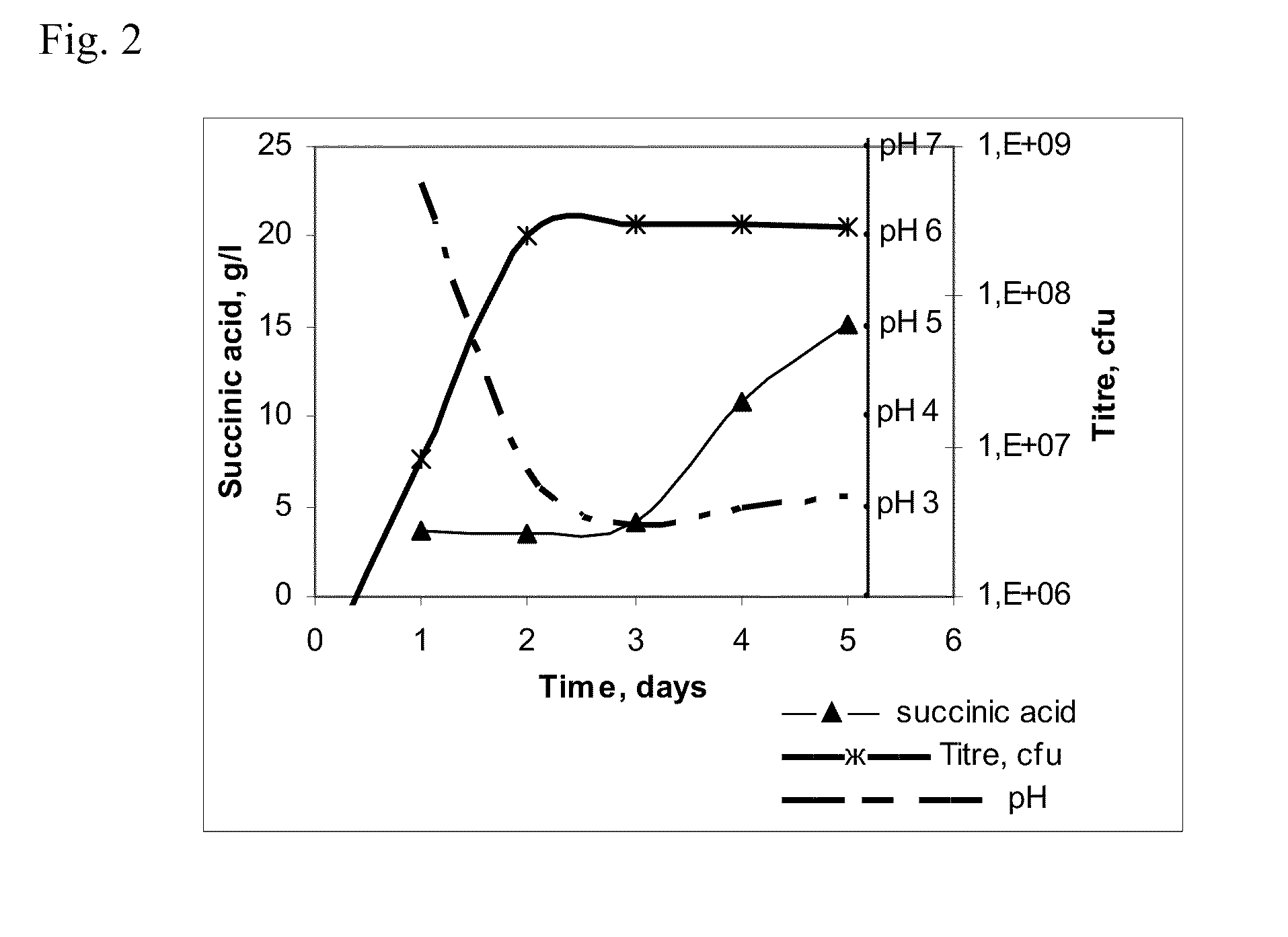
METHOD FOR PRODUCING SUCCINIC ACID USING A YEAST BELONGING TO THE GENUS Yarrowia
ActiveUS20120015415A1Improve productivityProducing succinic acidFungiOxidoreductasesSuccinic acidSuccinate dehydrogenase
The present invention provides a method for producing succinic acid using a yeast belonging to the genus Yarrowia, which has been modified to reduce activity of succinate dehydrogenase in said yeast.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
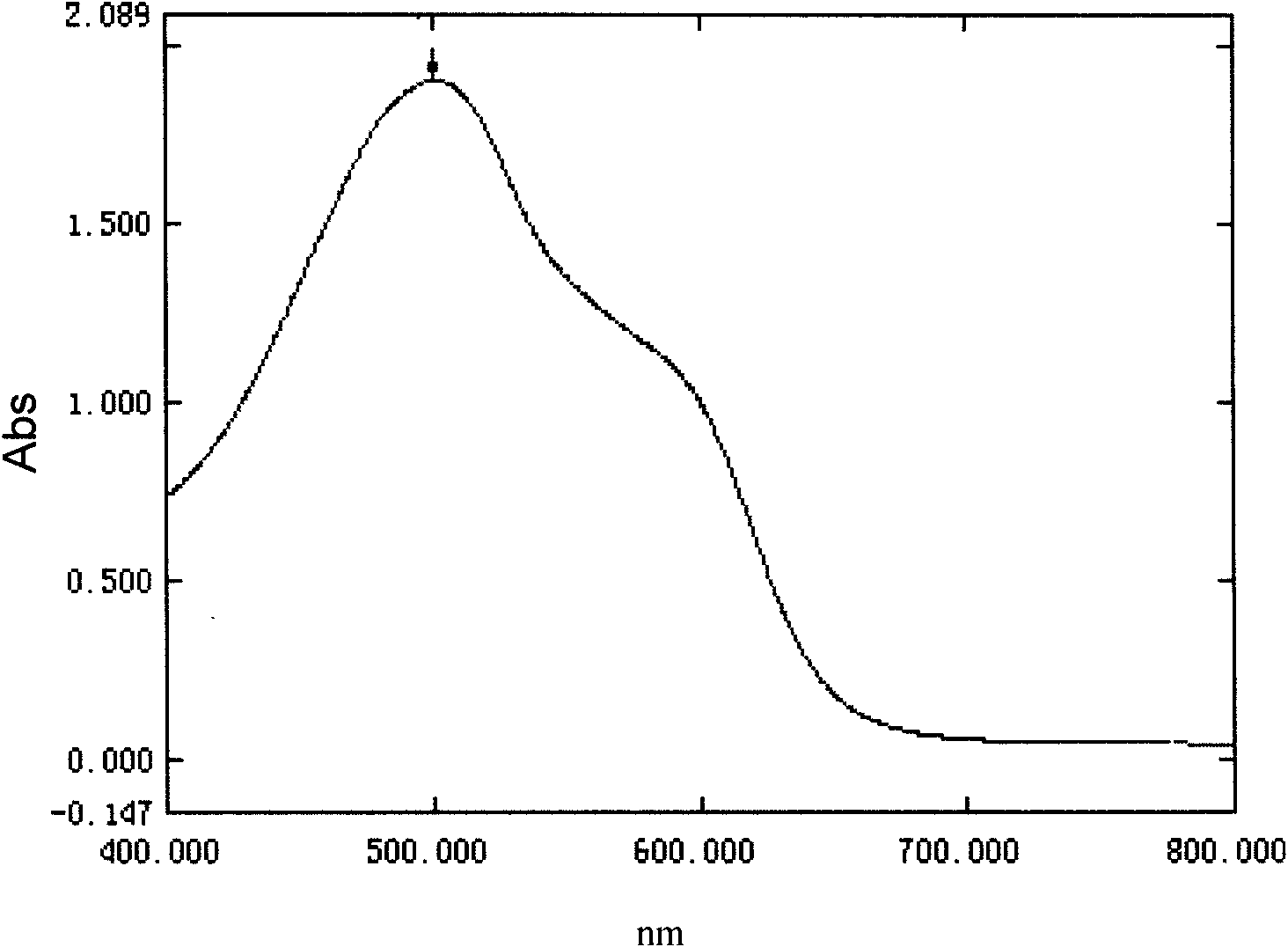
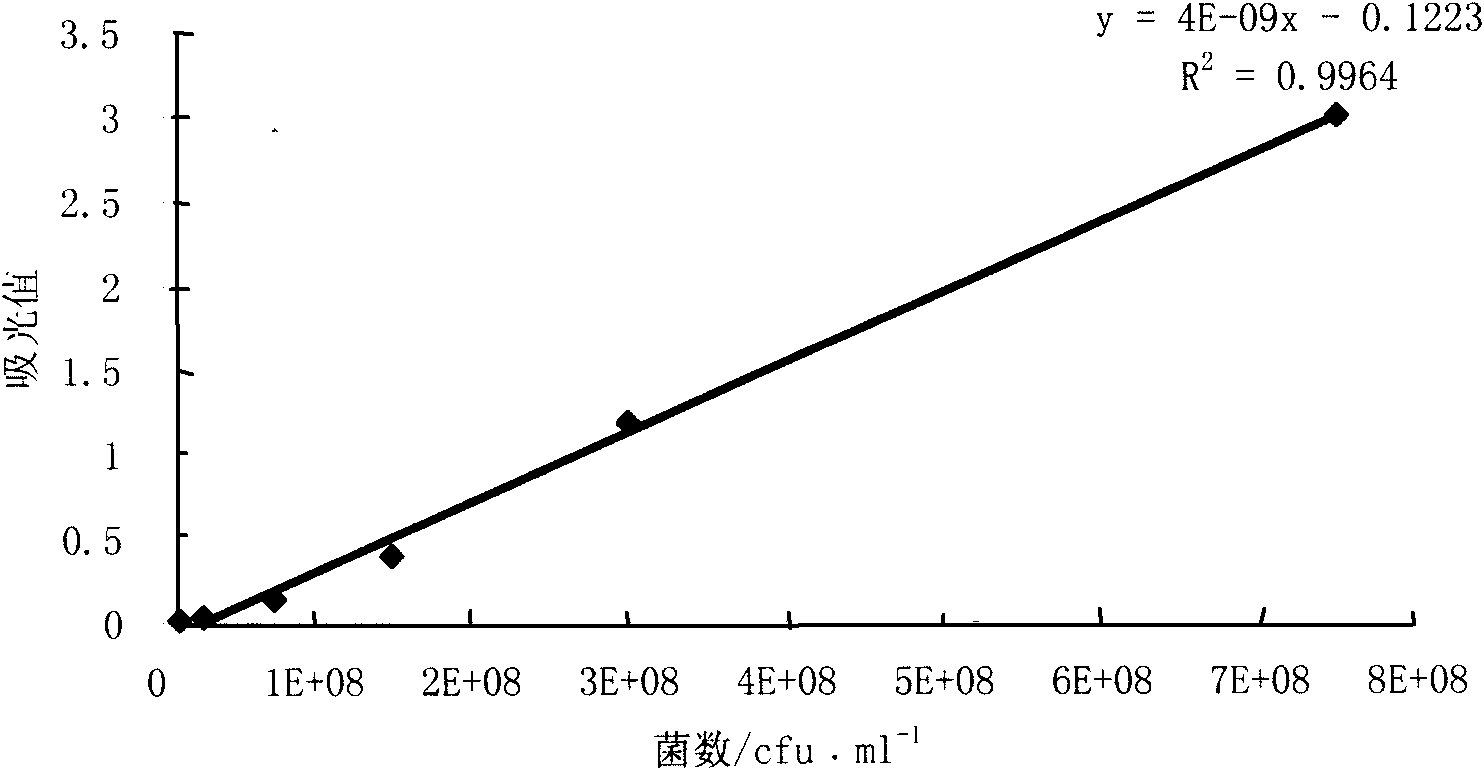
Method for quickly measuring total number of live bacteria of luminous bacteria by using MTT method
InactiveCN101620188ANovel detection principleThe detection method is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceReaction temperatureLength wave
The invention aims at establishing a method for quickly measuring total number of live bacteria of luminous bacteria, in particular to a method for counting the live bacteria based on the MTT coloration principle. The invention adopts MTT colorimetric method to measure the viable count of the luminous bacteria and carries out optimizing selection on the detection condition of the MTT colorimetric method. Therefore, the optimal method for measuring total number of the live bacteria of the luminous bacteria is determined. In the invention, first, the product of formazan generated from the reaction of succinate dehydrogenase in MTT and live thalli is dissolved in DMSO, light absorption value is determined within the range of 400nm-800nm, and the largest detected absorption wavelength is determined to be 500nm. By optimizing time and influencing the light absorption value by temperature, the optimal measurement condition is detected: the reaction time is 2h, and the reaction temperature is 25 DEG C. The invention has novel detection principle, simple and fast detection method, good repeatability, can be used for the quantitative detection of the number of the live bacteria of the luminous bacteria in the fields of food hygiene and safety, environmental monitoring and the like. The invention can also be applied to the tests of microbiology, immunology and other disciplines and used for measurement of the activity and number of the live bacteria materials. The invention can also develop the method for measuring the total number of the bacteria which is used for replacing the traditional method for measuring the total number of the live bacteria.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Use of succinate dehydrogenase inhibitors for extending shelf life of fruits and vegetables
InactiveUS20120258989A1Prolong lifeImprove stabilityBiocideFruit and vegetables preservationSuccinate dehydrogenaseHorticulture
The present invention relates to the use of succinate dehydrogenase Inhibitors for extending shelf life and storage stability of fruits and vegetables, to a method for extending shelf life of fruits and vegetables by applying a succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor to the crops prior to the harvest of the fruits or vegetables and to a fruit or vegetable treated with a succinate dehydrogenase Inhibitor.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCIENCE AG
Allele of succinate dehydrogenase B subunit gene sdHB of Corynespora cassiicola and use thereof
ActiveCN107384884AHigh amide resistanceHigh fluopyram resistanceOxidoreductasesFermentationHigh resistanceSuccinate dehydrogenase
The invention discloses an allele of a succinate dehydrogenase B subunit gene sdHB of Corynespora cassiicola and a use thereof. The invention provides a protein. The protein is obtained through mutation of a succinate dehydrogenase B subunit amino acid I at 280th site in the amino acid sequence into V, wherein other amino acid residues are not changed. Novel unreported allele mutation is found in the Corynespora cassiicola group collected in the Liaoning province and can cause high resistance of the strain to fluopyram. The mutation has the important guiding significance for detection of SDHIs resistance in the field and the later drug resistance management.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Use of Succinate Dehydrogenase Inhibitors For Controlling Powdery Mildew Primary Infections
ActiveUS20100222397A1Reduce in quantityPrevent rapid infectionBiocideDead animal preservationSuccinate dehydrogenaseBiology
The present invention relates to the use of succinate dehydrogenase Inhibitors for controlling powdery mildew primary infections in crops and to a method for controlling those primary infections.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCIENCE AG
Recombinant microorganism for preparing terpenoid and method for constructing recombinant microorganism
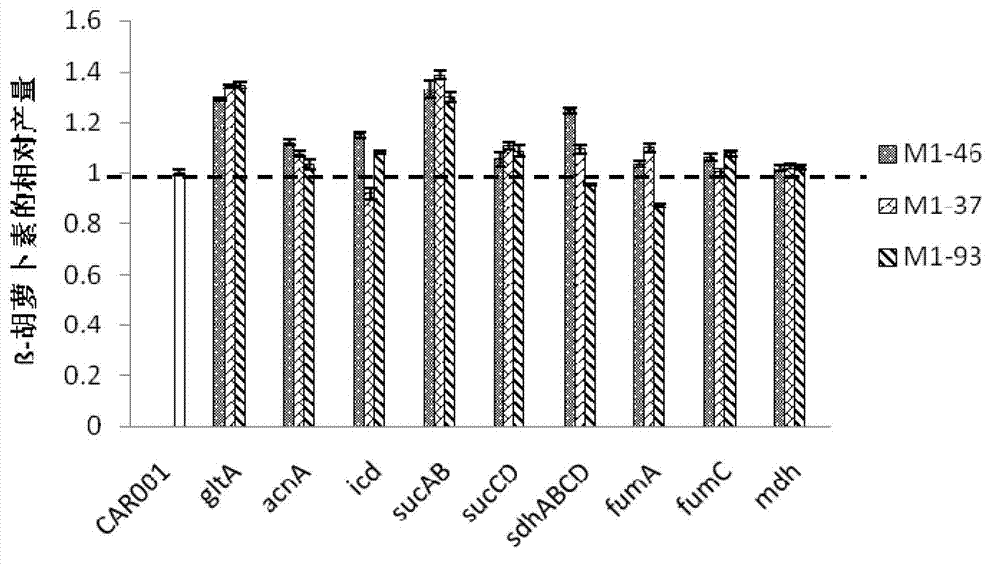
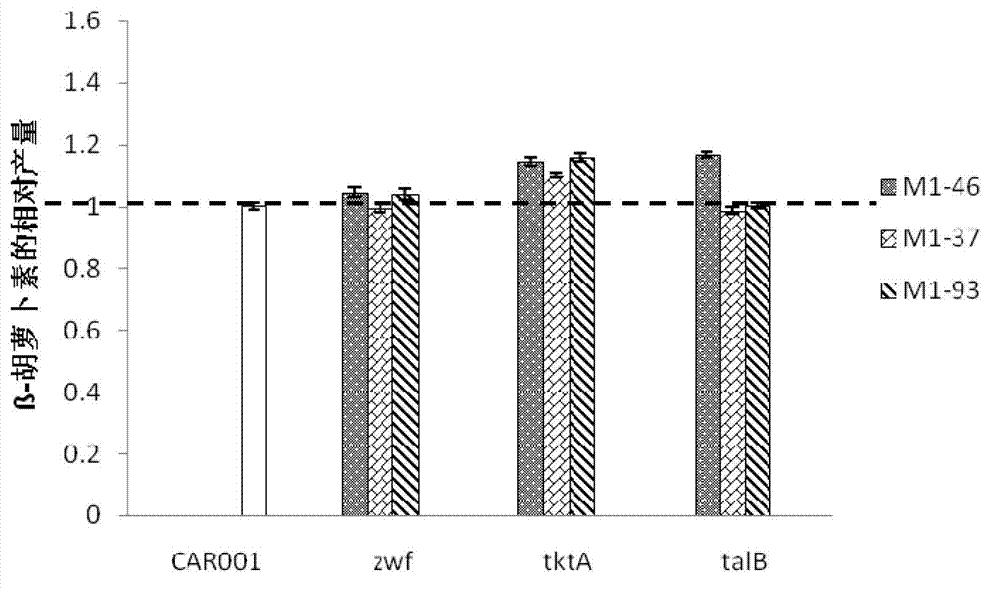
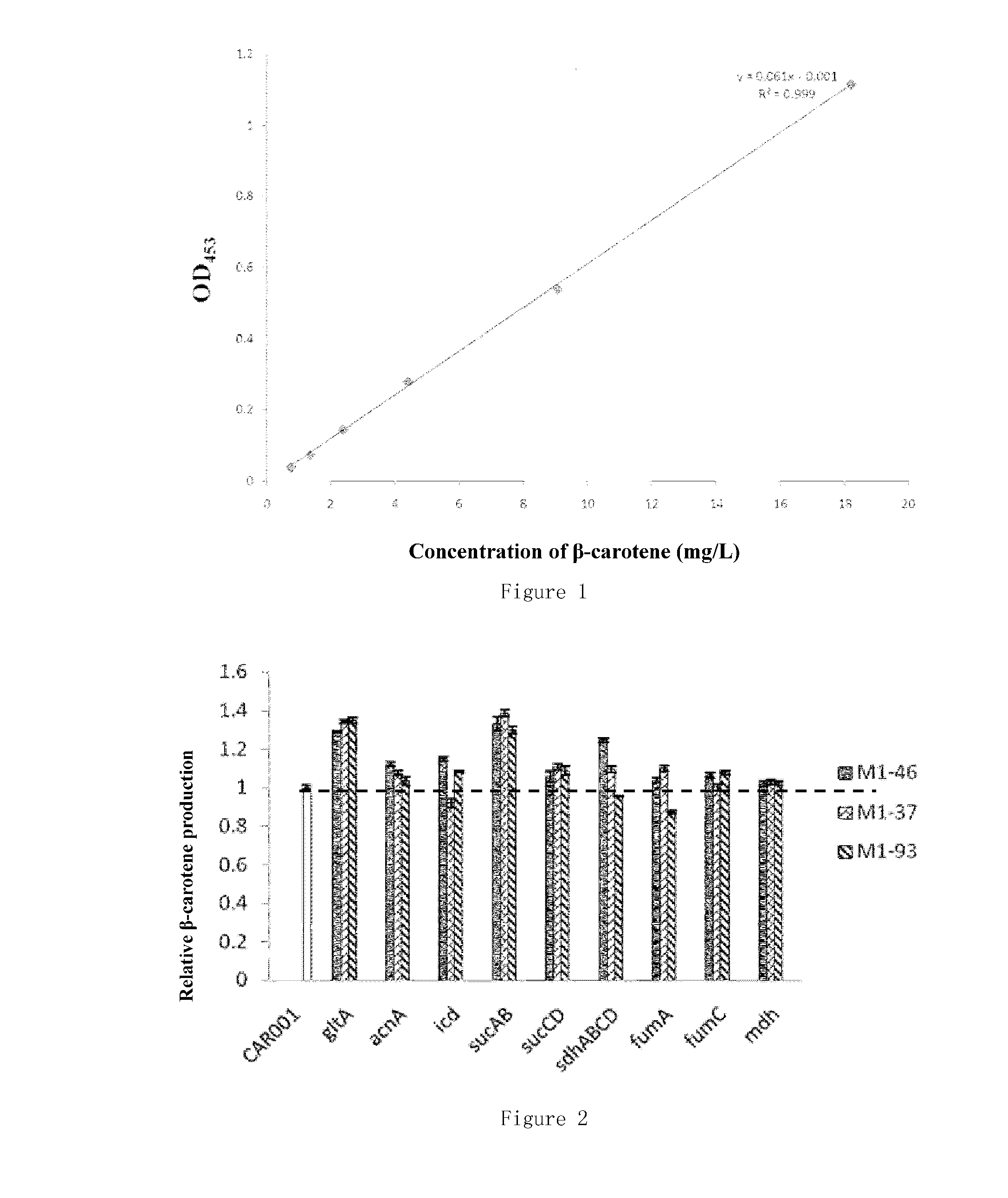
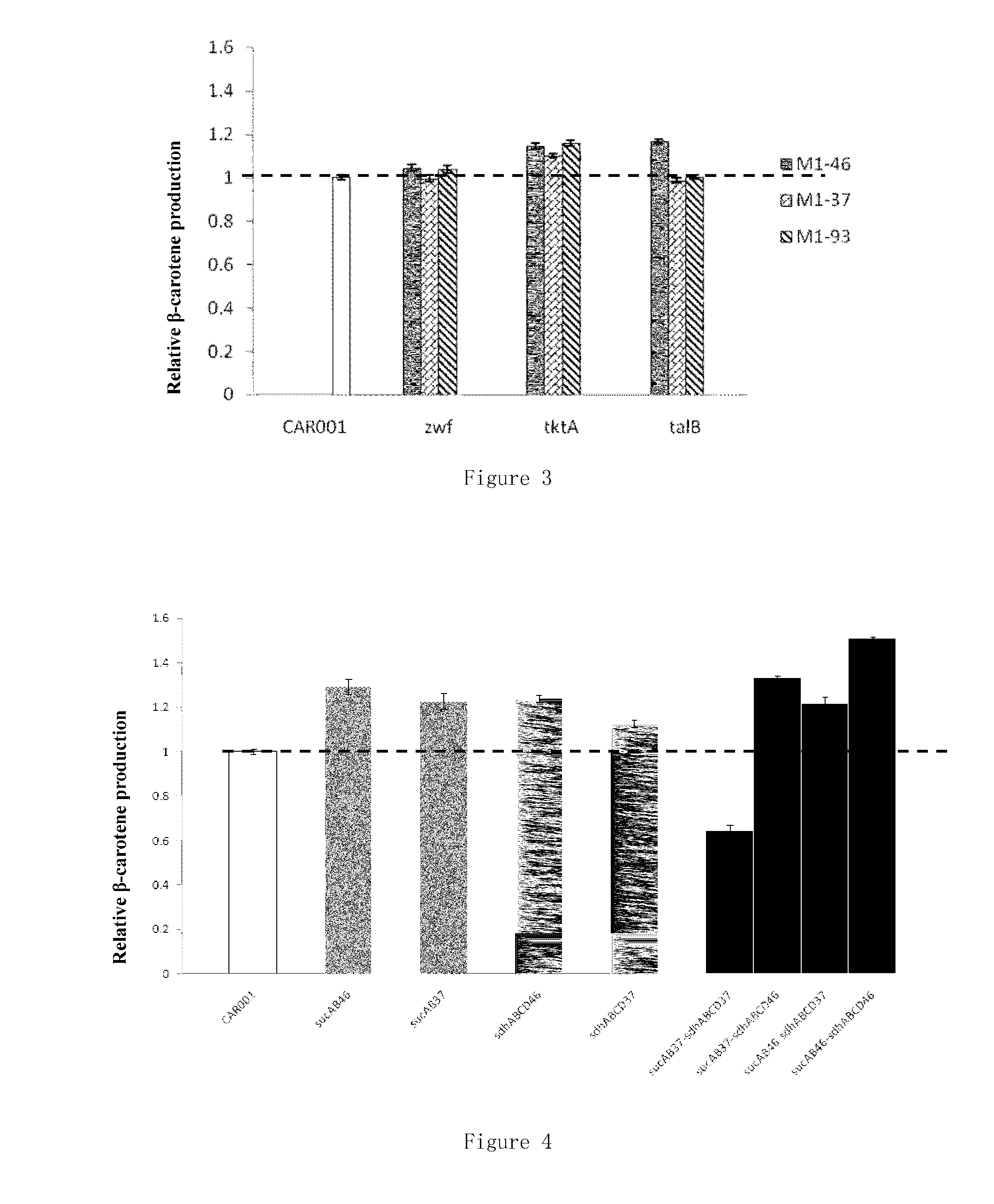
Provided are a recombinant strain for preparing a terpenoid, and method for constructing the recombinant strain. Also provided is a recombinant bacterium 1, the recombinant bacterium 1 being a recombinant bacterium obtained in order to improve the enzymatic activity of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase in escherichia coli or the mutant thereof. The method for improving the enzymatic activity of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase in escherichia coli or the mutant thereof is replacing the original regulating element of the ketoglutarate dehydrogenase gene (sucAB) in escherichia coli or the mutant thereof with any of the following regulating elements: artificial regulating element M1-46, M1-37, and M1-93. Also provided are a plurality of recombinant bacteria. By improving the enzymatic activity of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, succinic acid dehydrogenase and transaldolase therein and improving the ability of a cell to synthesize NADPH and ATP, the efficiency of the MEP pathway and the production capacity of terpenoid are improved.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor containing compositions
InactiveUS20160286805A1Good curative effectReduce the amount requiredBiocideCosmetic preparationsMicroorganismMetal working fluid
A composition containing succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor and a potentiator has been discovered to enhance the activity of the succinate dehydrogenase such that the amount of the succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor need to effectively treat a microbial substance can be reduced substantially. The compositions may be used as additives for paints and coatings, and protecting crops, seeds, wallboard, metal working fluids, wood from mold, fungi and other microbes.
Owner:ARCH WOOD PROTECTION
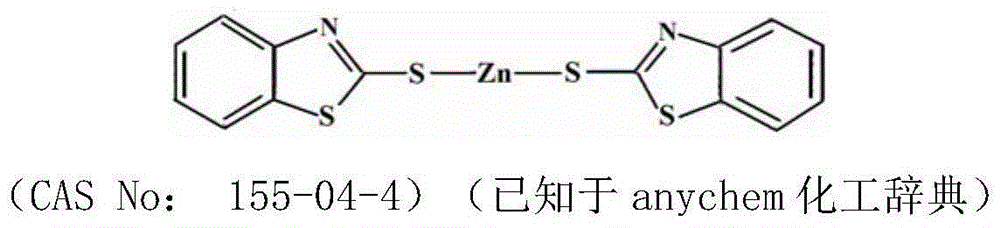
Zinc 2-mercaptobenzothiazole and succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor (SDHI) bactericide composition
ActiveCN105394050ADelay drug resistanceReduce the risk of resistanceBiocideFungicidesFluopicolideSuccinate dehydrogenase
The present invention belongs to the field of agriculture, and relates to a sterilization activity compound composition, particularly to a zinc 2-mercaptobenzothiazole and succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor (SDHI) bactericide composition, a preparation and applications thereof. The sterilization composition contains a sterilization activity compound I and a sterilization activity compound II, wherein the sterilization activity compound I is zinc 2-mercaptobenzothiazole, and the sterilization activity compound II is at least one selected from succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor bactericides such as flutolanil, boscalid, fluopicolide, isopyrazim, sedaxane, fluxapyroxad, trifluzamide, bixafen and fluopicolide. With the sterilization activity compound composition of the present invention, the generation of drug resistance of plant diseases can be effectively reduced, and the resistance risks caused by the single use of the SDHI bactericide and the zinc 2-mercaptobenzothiazole can be substantially reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG XINNONG CHEM CO LTD +1
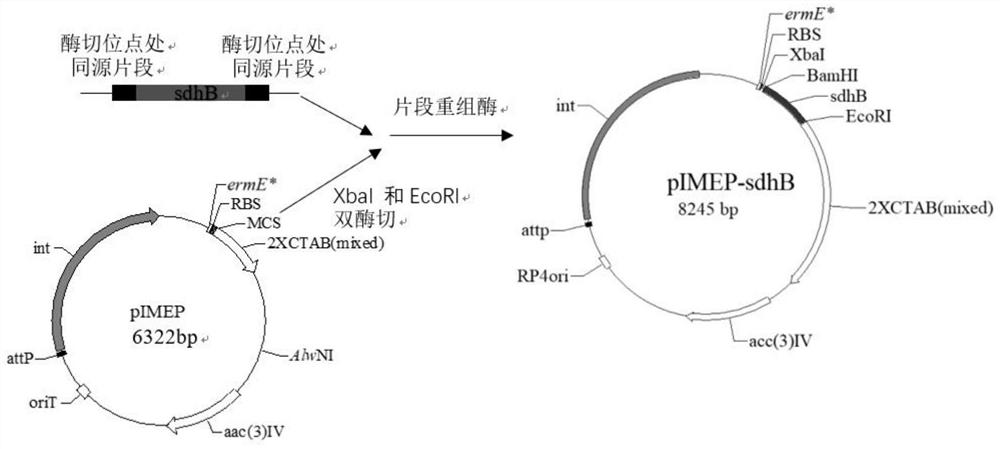
Genetically-engineered high-producing strain streptomyces diastatochromogenes, production method of epsilon-polylysine and application
ActiveCN111621454AIncreased ability to produce ε-polylysineRaise the level of fermentationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAmylaseSuccinic acid
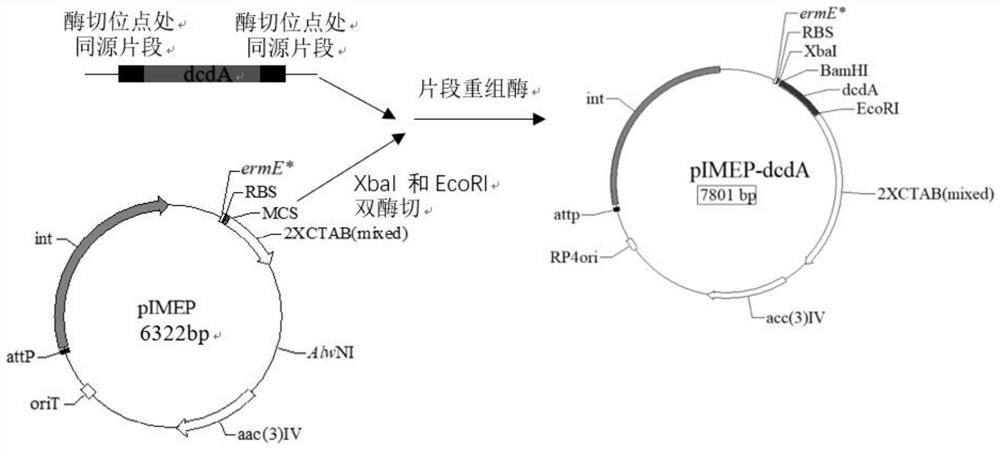
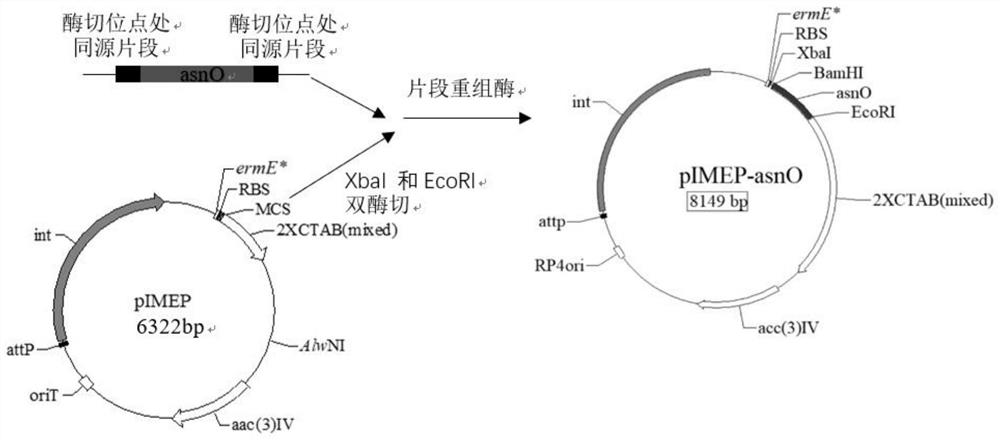
The invention relates to a genetically-engineered strain streptomyces diastatochromogenes with high production of epsilon-polylysine. The streptomyces diastatochromogenes is obtained by over-expressing three key genes, in different metabolic pathways, of a succinate dehydrogenase gene sdhB, a lysine / ornithine decarboxylase gene dcdA and an asparagine synthetase gene asnO in streptomyces diastatochromogenes TUST separately. According to the genetically-engineered strain streptomyces diastatochromogenes with high production of the epsilon-polylysine, by over-expressing the key genes in the different metabolic pathways, the genetically-engineered recombinant strain is obtained, and an experiment proves that the epsilon-polylysine-producing capability of the streptomyces genetically-engineeredstrain is improved compared with that of the original strain streptomyces diastatochromogenes TUST in the same situation, so that the excellent strain is provided for production of epsilon-polylysine.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
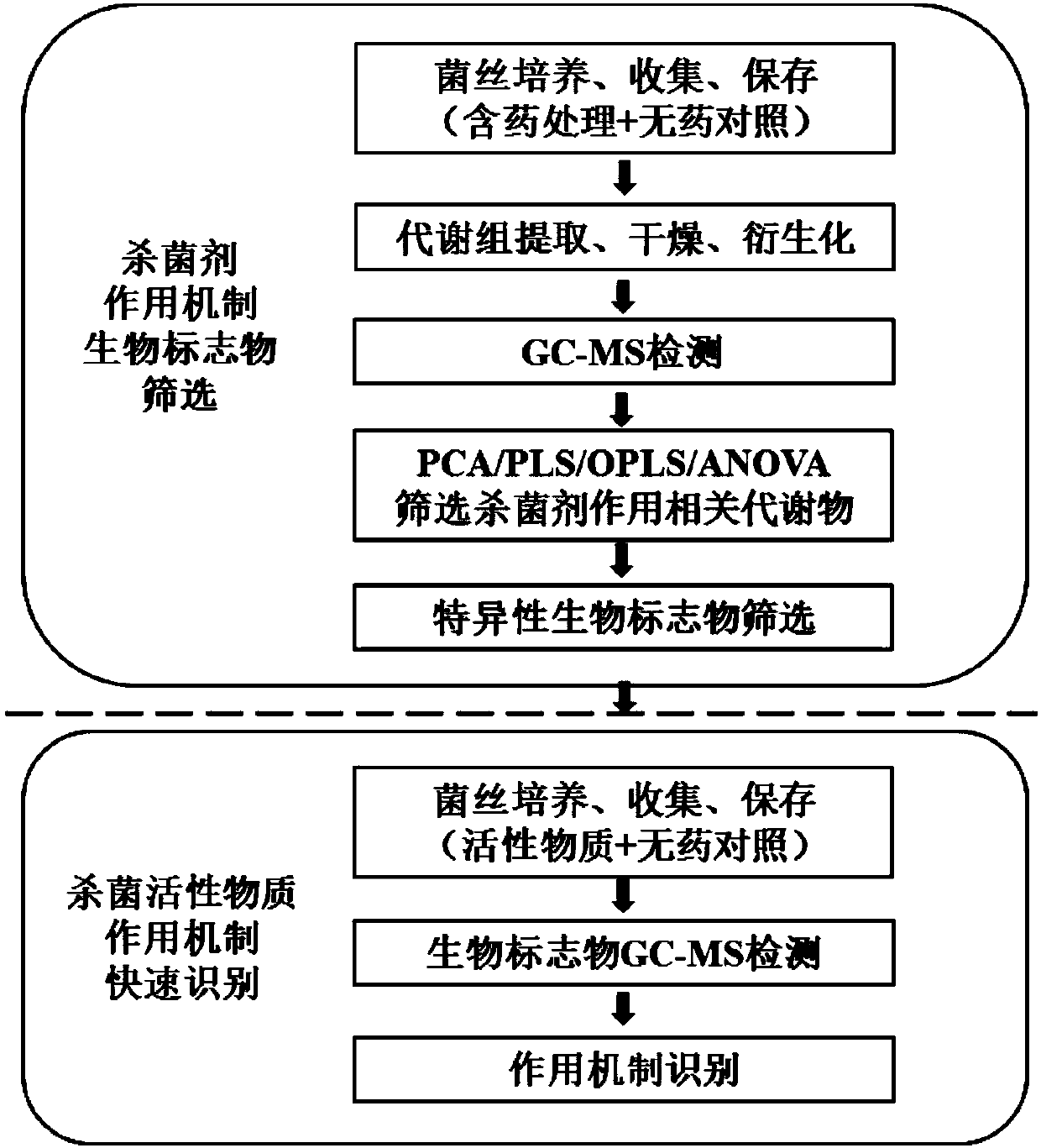
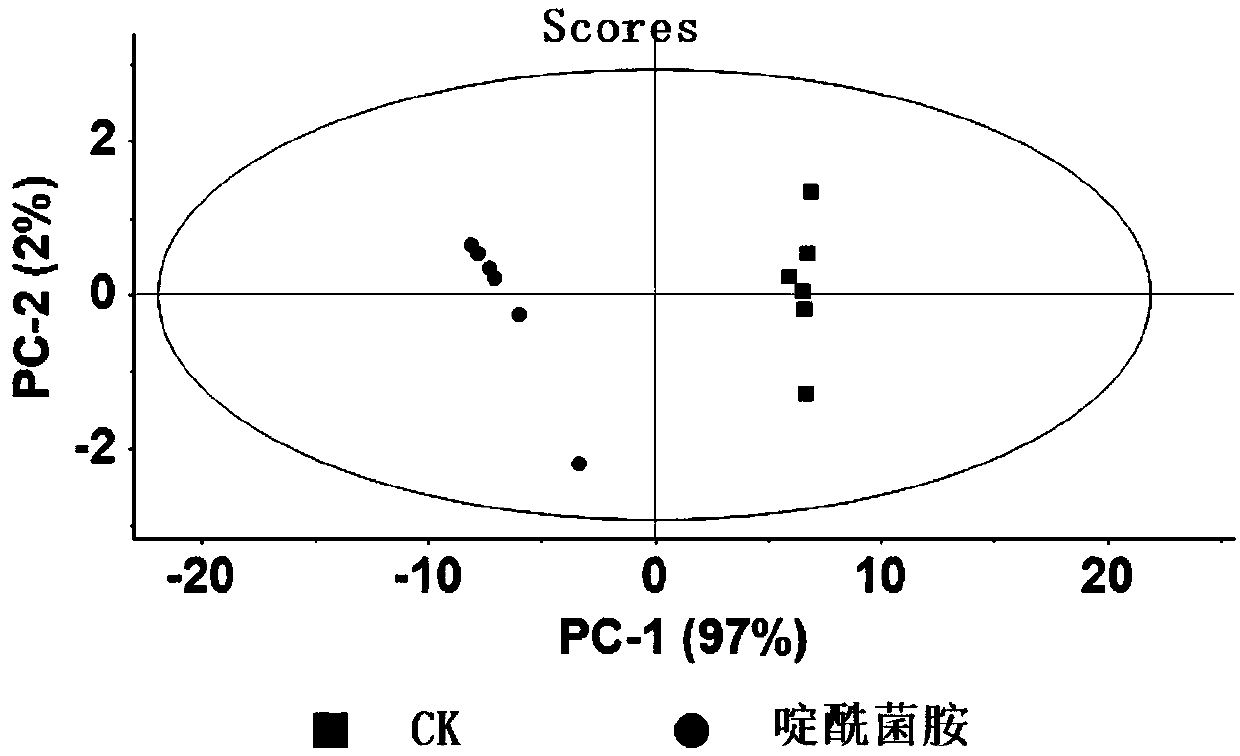
Method for researching action mechanism of bactericide based on metabolomics
InactiveCN107796884ASpecific fastStrong specificityComponent separationMetaboliteMechanism of action
The invention discloses a method for researching the action mechanism of a bactericide based on metabolomics. According to the method, pathogen hyphae respectively cultured by a bactericide-containingmedium and a bactericide-free control medium are subjected to metabolomics detection, differential metabolites are found through comparing the metabolomics research methods, common metabolites with different mechanisms of action are eliminated, a specific biomarker with a target bactericide action mechanism is acquired, and the bactericide action mechanism is identified and is subjected to high-throughput analysis through biomarker content change. The invention also discloses a use of succinic acid as a biomarker of a succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor. The method is fast and reliable and canproduce a biomarker with strong specificity. Through biomarker specificity change, the rapid identification and high-throughput analysis of the active substance action mechanism are realized.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
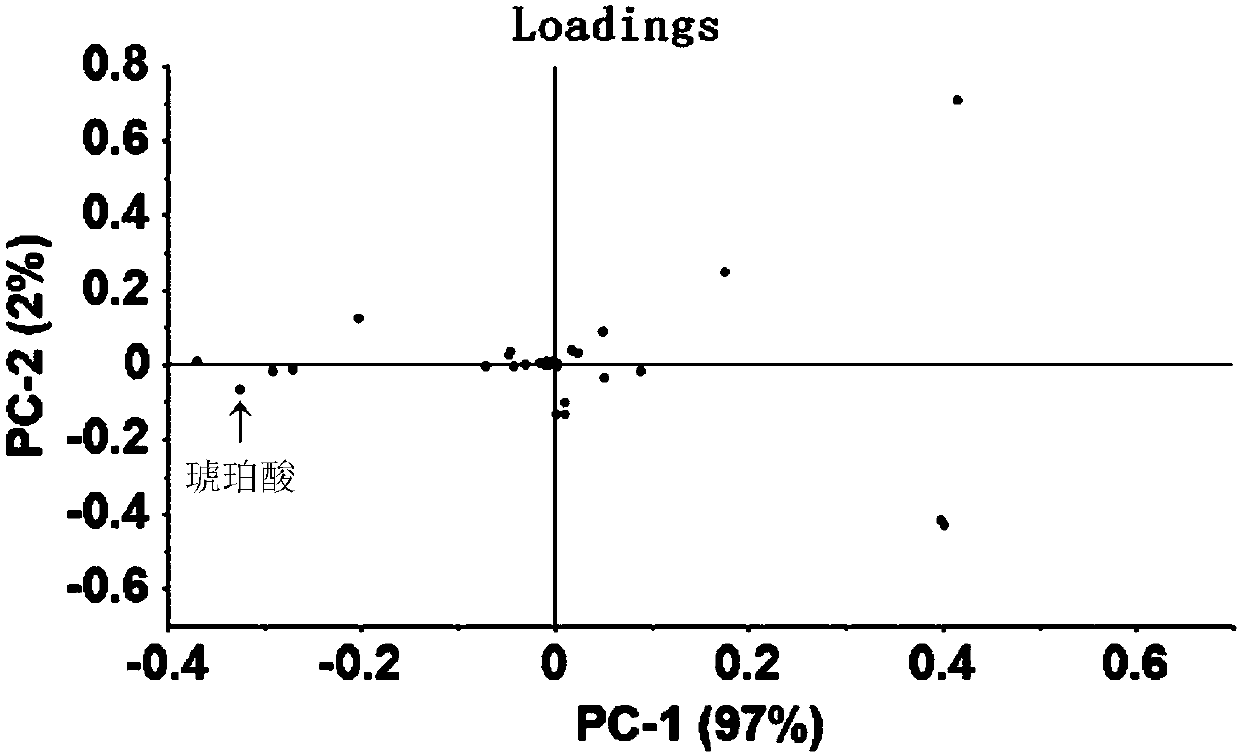
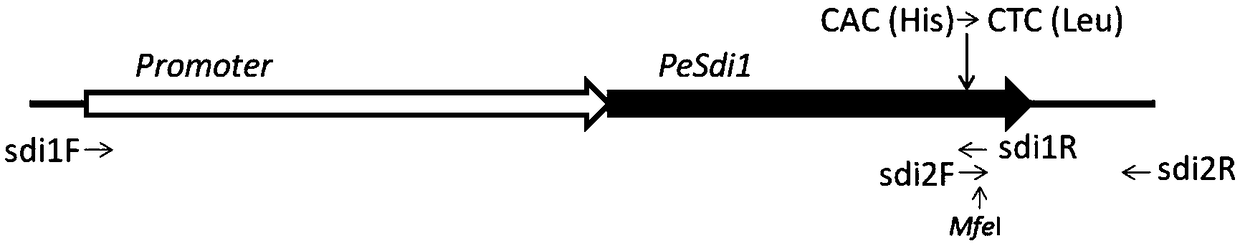
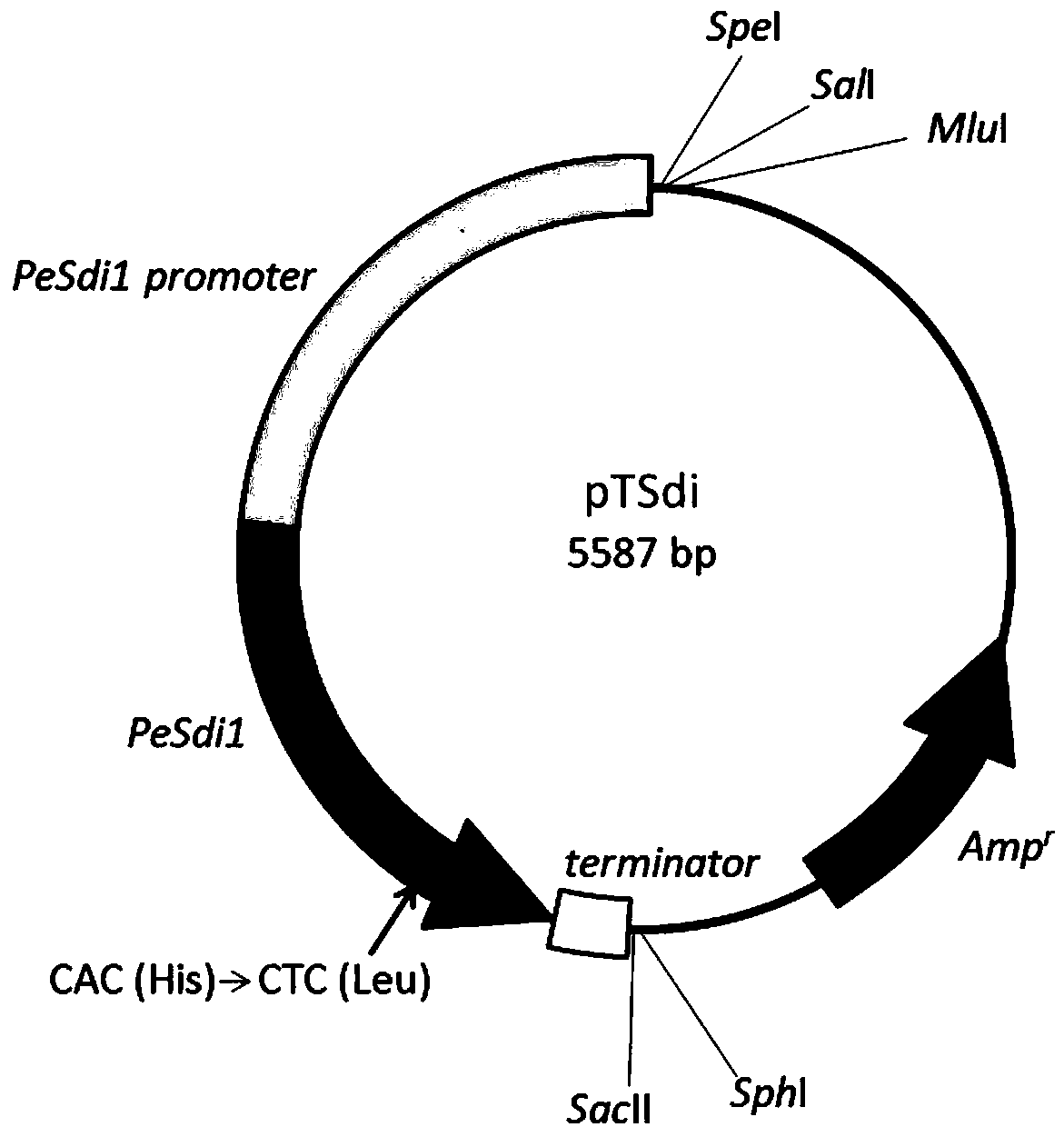
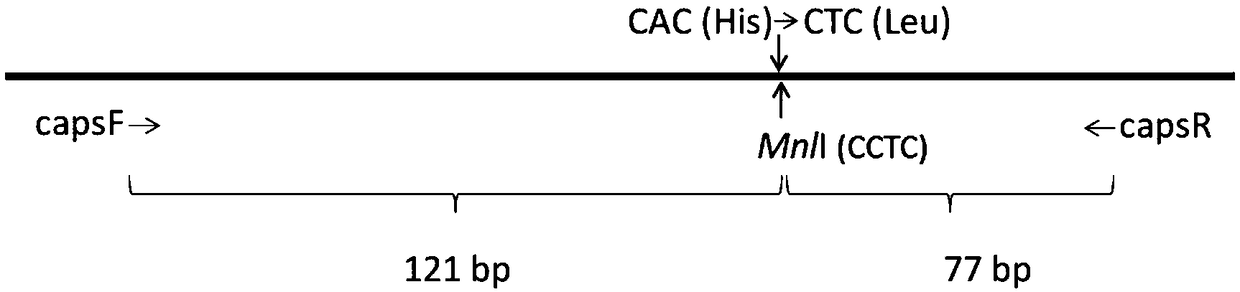
Pleurotus eryngii carboxin resistance screening and transforming vector as well as construction method and application thereof
The invention relates to a pleurotus eryngii carboxin resistance screening and transforming vector as well as a construction method and application thereof. A DNA fragment of succinate dehydrogenase iron sulfur subunit with point mutation is ligated into a plasmid vector, and is denoted as pTSdi. The transforming vector provided by the invention can be used for transforming pleurotus eryngii so asto enable the pleurotus eryngii to obtain the resistance to a fungicide-carboxin; in addition, an enzyme cleavage site for inserting an exogenous gene fragment is reserved in the constructed transforming vector, so that an interested exogenous gene can be conveniently inserted into the transforming vector and transformed into the pleurotus eryngii for performing genetic research; therefore, the pleurotus eryngii carboxin resistance screening and transforming vector has a good application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Use of succinate dehydrogenase inhibitors for extending shelf life of fruits and vegetables
ActiveUS20100292080A1Prolong lifeImprove stabilityBiocideFruit and vegetables preservationSuccinate dehydrogenaseHorticulture
The present invention relates to the use of succinate dehydrogenase Inhibitors for extending shelf life and storage stability of fruits and vegetables, to a method for extending shelf life of fruits and vegetables by applying a succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor to the crops prior to the harvest of the fruits or vegetables and to a fruit or vegetable treated with a succinate dehydrogenase Inhibitor.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCIENCE AG
Genetic transformation selection marker of Pleurotus eryngii
InactiveCN108950041AImprove conversion efficiencyImprove securityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTransformation efficiencySuccinate dehydrogenase
The invention relates to a genetic transformation selection marker of Pleurotus eryngii. The selection marker is obtained by a single base mutation of a succinate dehydrogenase iron sulfur subunit gene encoded by the genome of Pleurotus eryngii. The carboxin resistance selection marker obtained by the invention is derived from a single base mutation of a self-gene of Pleurotus eryngii with no introduction of foreign DNA of other species, and has high safety. Meanwhile, the selection marker has high transformation efficiency and can replace a hygromycin resistance screening marker commonly usedin the genetic transformation of Pleurotus eryngii. The selection marker obtained by the invention can be safely and efficiently applied to the genetic improvement of Pleurotus eryngii, lays a foundation for cultivating new varieties of Pleurotus eryngii which accords with the production demand and consumer preferences, and has a good market application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Sterilization composition and application thereof
InactiveCN105248424AGood synergyImprove the effect of prevention and controlBiocideDead animal preservationFluopyramSuccinate dehydrogenase
The invention discloses a sterilization composition and application thereof and relates to the technical field of pesticide mixtures. The sterilization composition is prepared from effectively ingredients including phenazino A and succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor bactericide B, wherein succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor bactericide B is one or more of fluopyram, bicycle-fluxapyroxad penflufen and the like. The weight ratio of phenazino A to succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor bactericide B is 1:100-100:1. The effective ingredients A and B are blended to achieve remarkable synergism, and the application amount of single agents can be effectively reduced. Good effects on enlarging the bacteriocidal spectrum and delaying plant drug resistance are achieved, the lasting period can be prolonged, and obvious popularization value is achieved. The composition can be added with other auxiliary ingredients allowing to be used in pesticide to be prepared into any dosage forms.
Owner:LIER CROPSCIENCE CO LTD
Detection method of gene mutation of mitochondrial succinate dehydrogenase and kit
InactiveCN101684486AStrong specificityHigh amplification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationPheochromocytomaSuccinate dehydrogenase
The invention discloses a reagent for detecting whether gene mutation of mitochondrial succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) exists in samples and a kit containing the reagent. The reagent or the kit can be used for susceptibility analysis of pheochromocytoma. The invention also discloses an optimized method by which SDH gene amplification products are obtained and a method for determining whether gene mutation of SDH exists in the nucleic acid samples to be tested.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Traditional Chinese medicine composite used for releasing fatigue as well as preparation method and application of traditional Chinese medicine composite
InactiveCN104587151AAvoid fatigueDevelopment of Resistance to FatigueAntinoxious agentsPlant ingredientsAdemetionineWeakness
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine composite used for releasing fatigue as well as preparation method of the traditional Chinese medicine composite. The traditional Chinese medicine composite disclosed by the invention takes Maca which has various functions of improving fertility, resisting fatigue, improving sexual performance, antioxidation, inhibiting hyperplasia of prostate, alleviating menopausal syndrome, strengthening immunity combined with American ginseng extract, rhizome chuanxiong extract, morinda officinalis extract, tuber onion seed extract and tangerine peel extract. The traditional Chinese medicine compound has the functions of antioxidation and antifatigue, can lower the levels of lactate dehydrogenase and serum urea, improve succinate dehydrogenase activity of muscles, effectively relief uncomfortable feeling after exercise, such as limb weakness, tiredness and muscle soreness. The invention also provides a traditional Chinese medicine preparation containing the traditional Chinese medicine composite and a preparation method of the traditional Chinese medicine preparation.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV +1
Screening and application of biomarker related to AD cell model constructed by A beta induction
The invention belongs to the field of biomarkers, and particularly relates to screening and application of a biomarker related to an AD cell model constructed by A beta induction. The biomarker comprises one or a combination of more of the following components: Cysteine Desulfurase, mistoral, the code is NFS1, NADH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) dehydrogenase [ubiquitin] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 9, mitochondrial, the code is NDUFA 9; 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase type-2, and the code is HSD17B10; Cytochrome c oxidase subunit NDUFA4, and the code is NDUFA4; NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase 75 kDa subunit, mitochondrial, the code is NDUFS1; Succinate dehydrogenase[ubiquinone]iron-sulfur subunit, mitochondrial, the code is SDHB; NADH dehydrogenase[ubiquinone]iron-sulfur protein 4, mitochondrial, the code is NDUFS4; Lipoprotein lipase, the code is LPL; NADH dehydrogenase[ubiquinone]1 alpha subcomplex subunit 5, the code is NDUFA5. A proteomics method is adopted, a group of biomarkers are found in an A beta-induced AD cell model, and the biomarkers are found to be mutually matched in the A beta-induced AD cell model and jointly play an important role. The method for detecting the AD cell model constructed through A beta induction is enriched, and a new target is provided for clinical research.
Owner:LIAONING UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Genetically modified microorganism and method for producing target substance using same
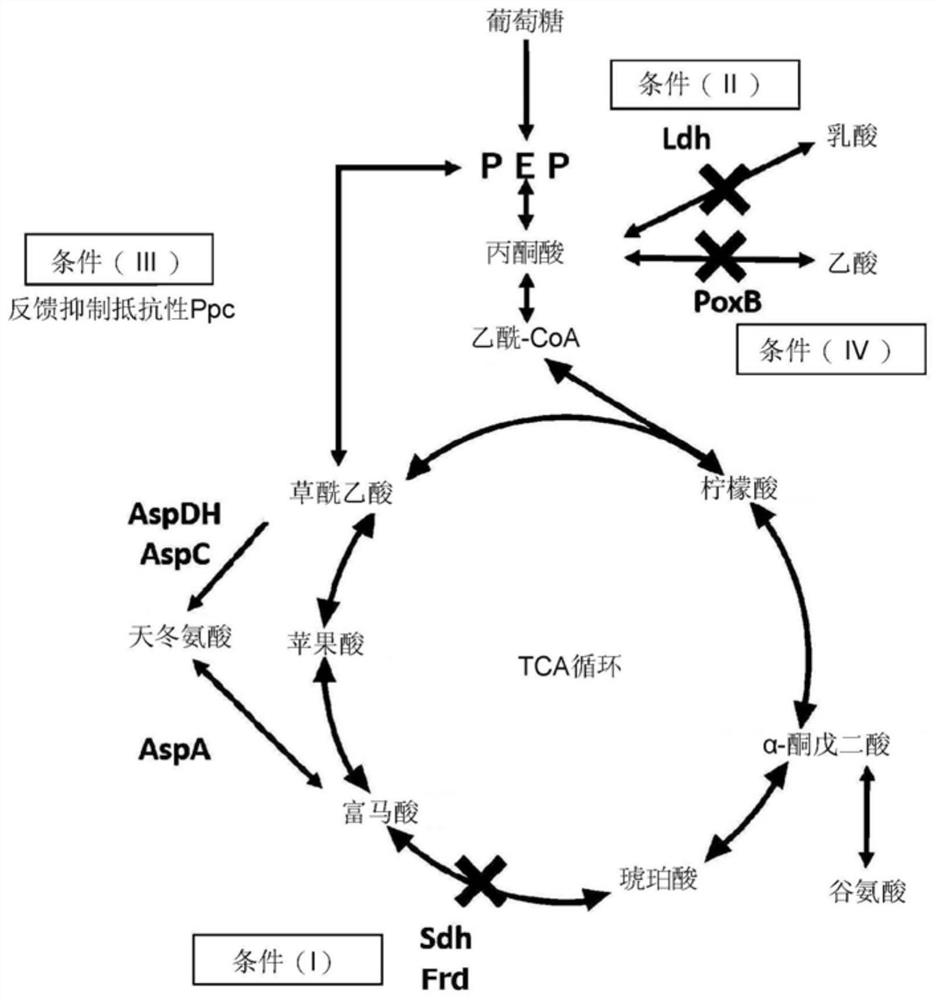
The present disclosure pertains to a genetically modified microorganism that satisfies some of specific requirements. The specific requirements include: (I) compared to a wild type microorganism, having reduced or inactivated succinate dehydrogenase activity or fumarate reductase activity; (II) compared to a wild type microorganism, having reduced or inactivated lactate dehydrogenase activity; (III) having a modified phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase activity and thus showing resistance against the feedback inhibition by aspartic acid in wild type phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase activity, or having an exogenous phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase activity and thus showing higher resistance against the feedback inhibition by aspartic acid than wild type phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase activity shown by a wild type microorganism; and (IV) compared to a wild type microorganism, having reduced or inactivated pyruvate : quinone oxidoreductase.
Owner:GREEN EARTH INST CO LTD
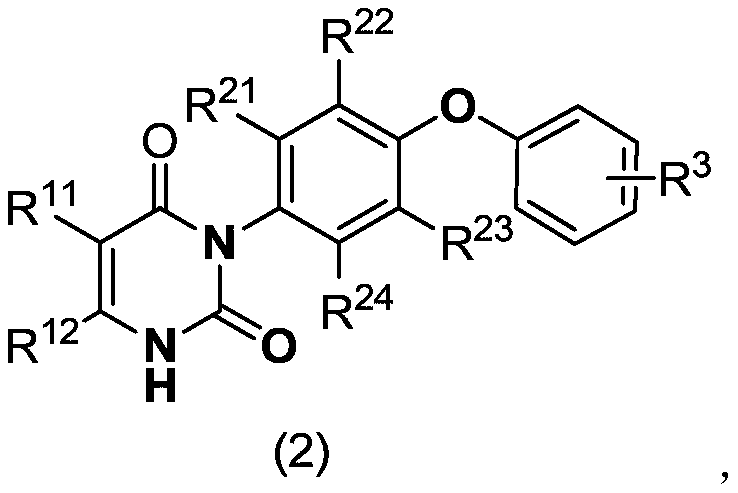
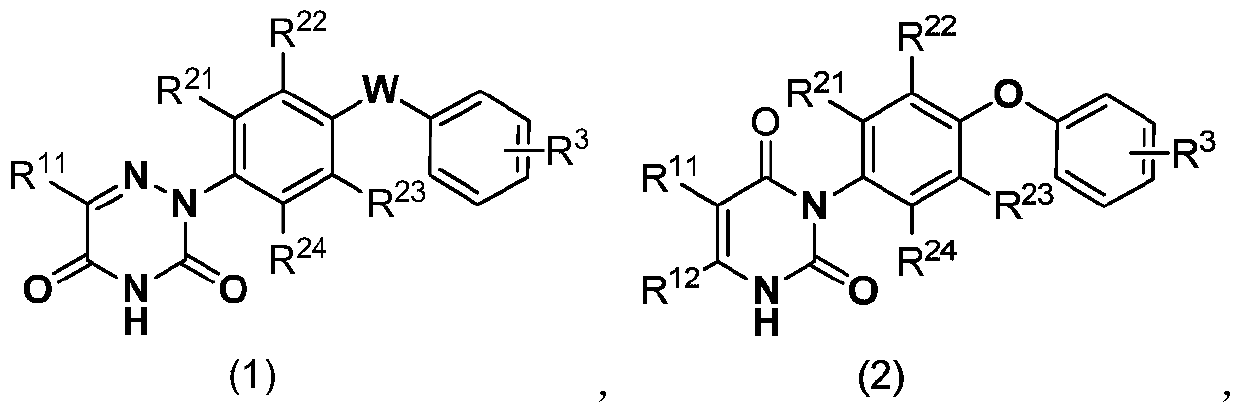
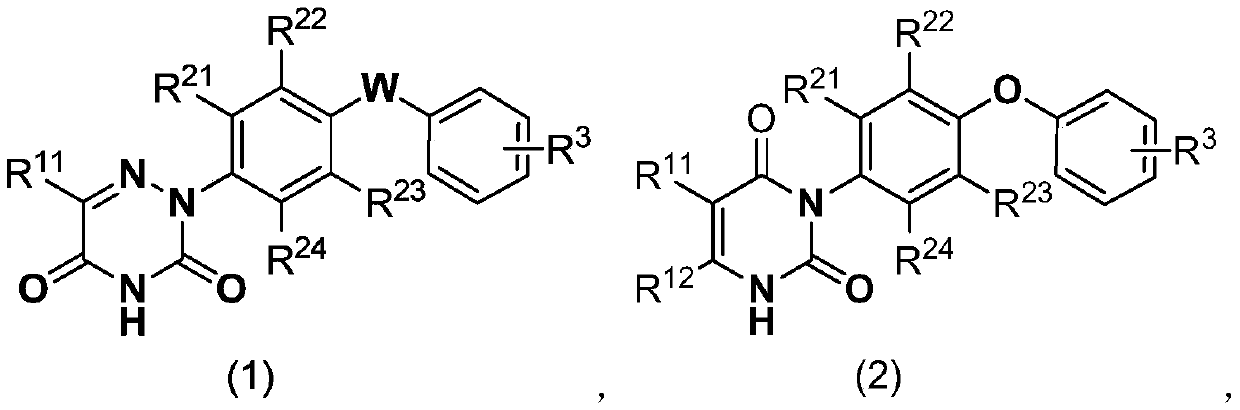
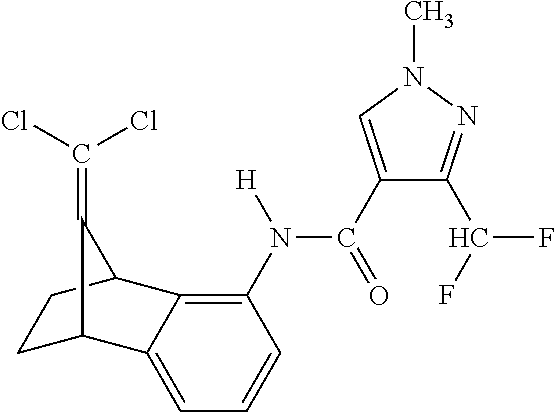
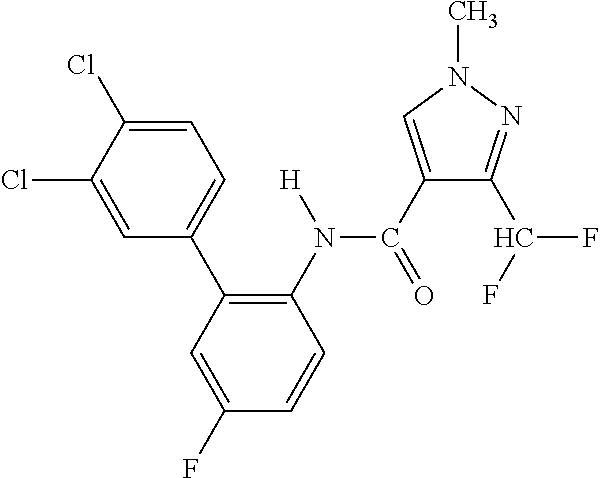
Diclazuril derivative and application thereof and fungicide containing derivative
The invention relates to the field of pesticides, and discloses a diclazuril derivative and an application thereof and a fungicide containing the derivative. The derivative has a structure representedby a formula (1) or formula (2). The provided diclazuril derivative can be applied as a mitochondrial succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor, and has an action against plant fungal diseases, and more specifically, the diclazuril derivative can be used for prevention and treatment of rice sheath blight, cucumber gray mold, cucumber downy mildew, cucumber powdery mildew and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
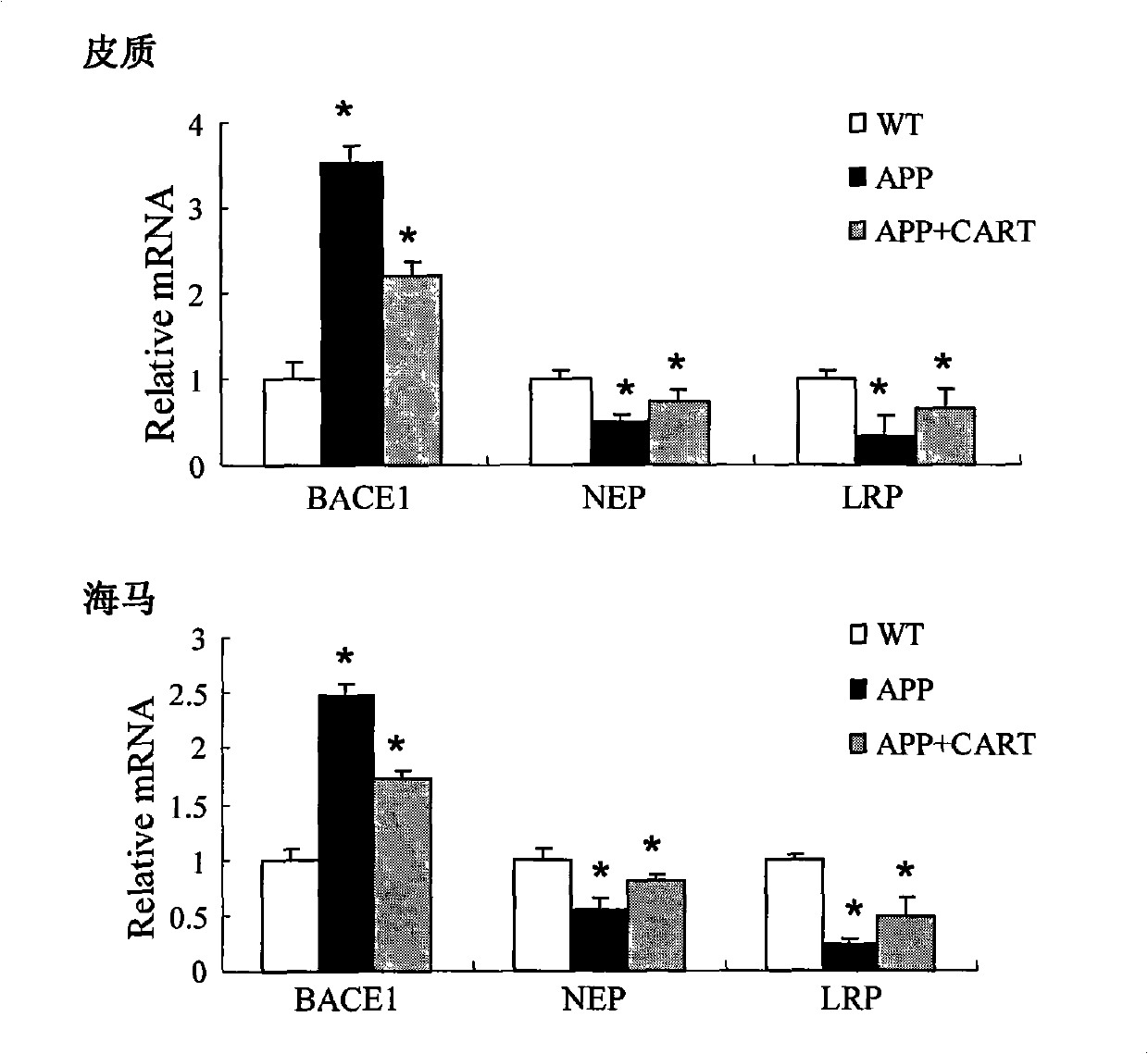
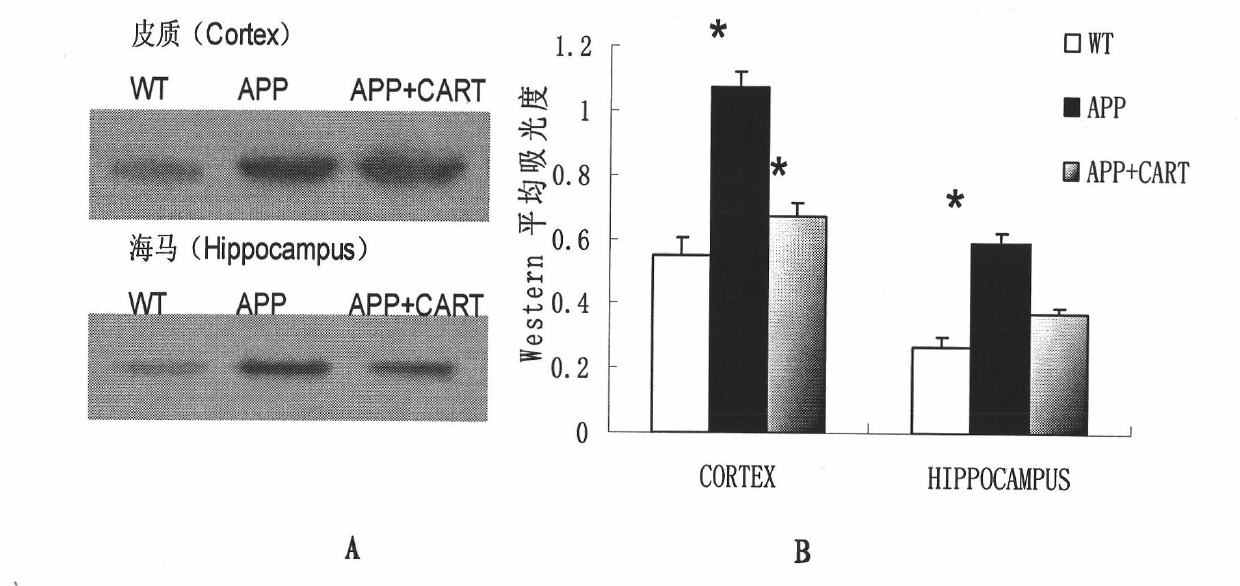
Application of CART (Cocaine Amphetamine Regulated Transcript) in preparing medicaments for treating alzheimers diseases
InactiveCN101874895AReduce formationHigh expressionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMembrane potentialSuccinate dehydrogenase
The invention relates to application of CART (Cocaine Amphetamine Regulated Transcript) in preparing medicaments for treating alzheimers diseases. In the invention, CART is prepared into injection preparations for treating alzheimers diseases, and the defects of the traditional medicaments for enhancing cholinergic action and N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) receptor antagonists are overcome. The novel medicament has multiple target point actions on the generation and the degradation of A beta as well as the influence of the neurotoxicity and the molecular mechanism of the A beta. The invention has effects on effectively treating dementia with estrogen and up-regulating intracephalic CART; more CARTs are distributed in intracephalic hippocampus; CART exists in intracephalic acetylcholine neurons and can promote the release of acetylcholine; and mitochondrial dysfunction induced by A beta neurotoxicity is the main pathway for the A beta to cause neuronal apoptosis. The CART has a directaction on mitochondrial succinodehydrogenase subunit B and can maintain the respiration of mitochondria and the generation of energy, alleviate oxidative stress, stabilize mitochondrial membrane potential and prevent the mitochondria from being damaged, thereby inhibiting apoptosis.
Owner:THE AFFILIATED DRUM TOWER HOSPITAL MEDICAL SCHOOL OF NANJING UNIV
Fungicidal bark sprays for trees
The present invention generally relates to methods for controlling tree and vine fungal pathogens comprising spraying the bark of trees and vines with an effective amount of at least one inhibitor of succinate-dehydrogenase (“SDHI”) fungicide with an adjuvant
Owner:VALENT USA CORP
Fungicidal combinations
A combination including a dithiocarbamate fungicide, a succinate dehydrogenase fungicide and at least one of ergosterol biosynthesis inhibitor fungicide or a quinone outside inhibitor fungicide.
Owner:UNITED PHOSPHORUS LTD
Method for producing an L-amino acid
ActiveUS8058035B2Efficient productionEasy to useOxidoreductasesFermentationKetoglutarate dehydrogenaseSuccinate dehydrogenase
A microorganism which has an L-amino acid producing ability and has been modified so that succinate dehydrogenase activity and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase activity are decreased is cultured in a medium to produce and accumulate an L-amino acid in the medium or cells of the microorganism, and the L-amino acid is collected from the medium or cells to produce the L-amino acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Fungicidal combinations
The invention discloses a combination comprising a multi-site contact fungicide, a succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor fungicide and a second systemic fungicide; and a method using the same.
Owner:UNITED PHOSPHORUS LTD
Succinate dehydrogenase inhibitor containing compositions
ActiveUS20170107380A1Good curative effectReduce the amount requiredCosmetic preparationsBiocideMicroorganismMetal working fluid
Owner:ARCH WOOD PROTECTION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com