Patents
Literature
515 results about "Aminolevulinic Acid Hydrochloride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
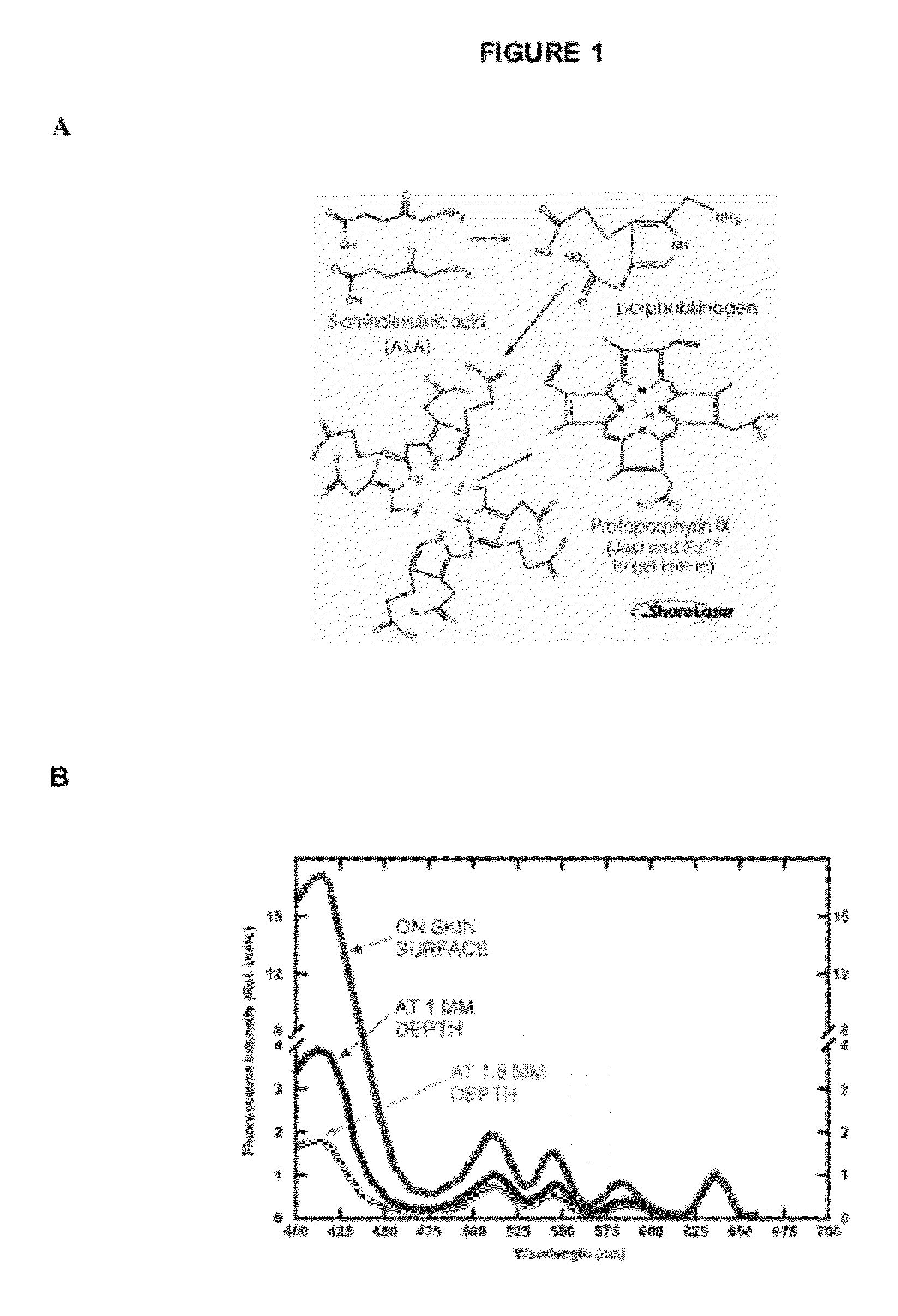
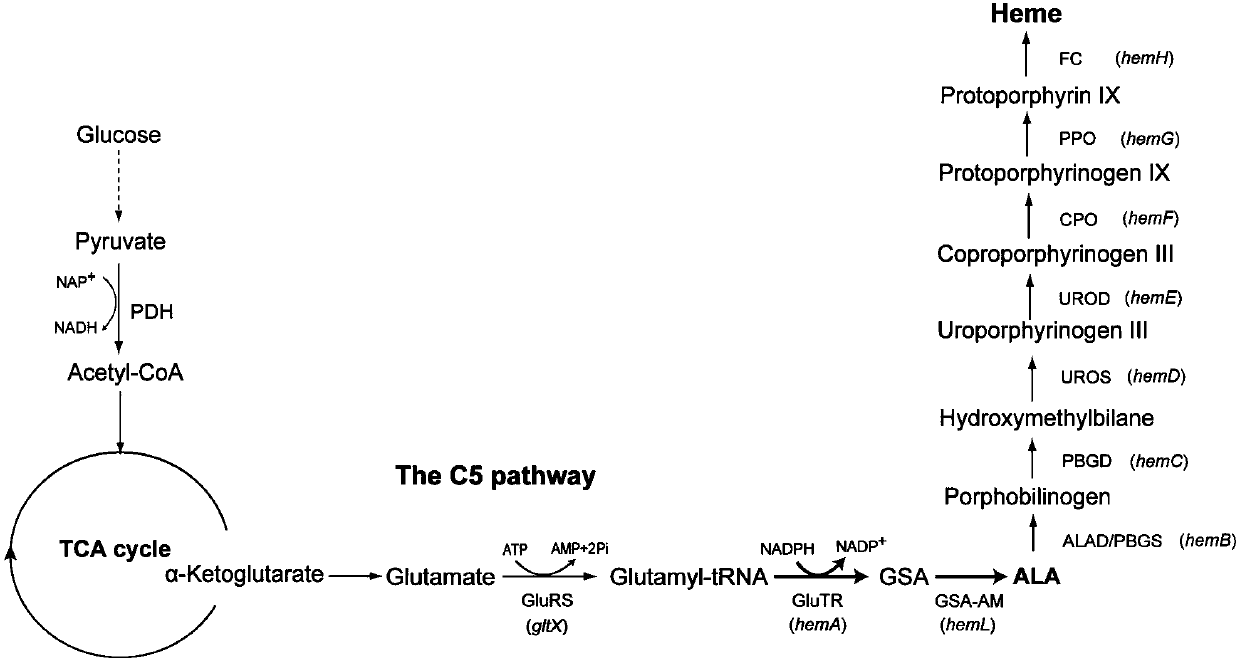
Δ-Aminolevulinic acid (also dALA, δ-ALA, 5ALA or 5-aminolevulinic acid), an endogenous non-proteinogenic amino acid, is the first compound in the porphyrin synthesis pathway, the pathway that leads to heme in mammals and chlorophyll in plants.
Topical aminolevulinic acid-photodynamic therapy for the treatment of acne vulgaris
InactiveUS6897238B2Reduce sebum productionSmall sizeBiocideOrganic active ingredientsBacteroidesDisease
Light treatments of sebaceous gland disorders with 5-aminolevulinic acid and photodynamic therapy are disclosed. A preferred treatment includes topical application of 5-aminolevulinic acid to the skin followed by light exposures with repeated treatment at various intervals. At low doses of ALA and photodynamic therapy (PDT) in single or multiple treatments, improvement in the sebaceous gland disorder, e.g., acne, provides the discovery that diminishment in sebum secretion and the eradication of bacteria occurs. At high doses of ALA and a single high energy PDT treatment, permanent changes to the sebaceous gland and sebum secretion have been discovered.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Use of 5-aminolevulinic acid or a derivate thereof for photodynamic diagnosis and/or photodynamic therapy
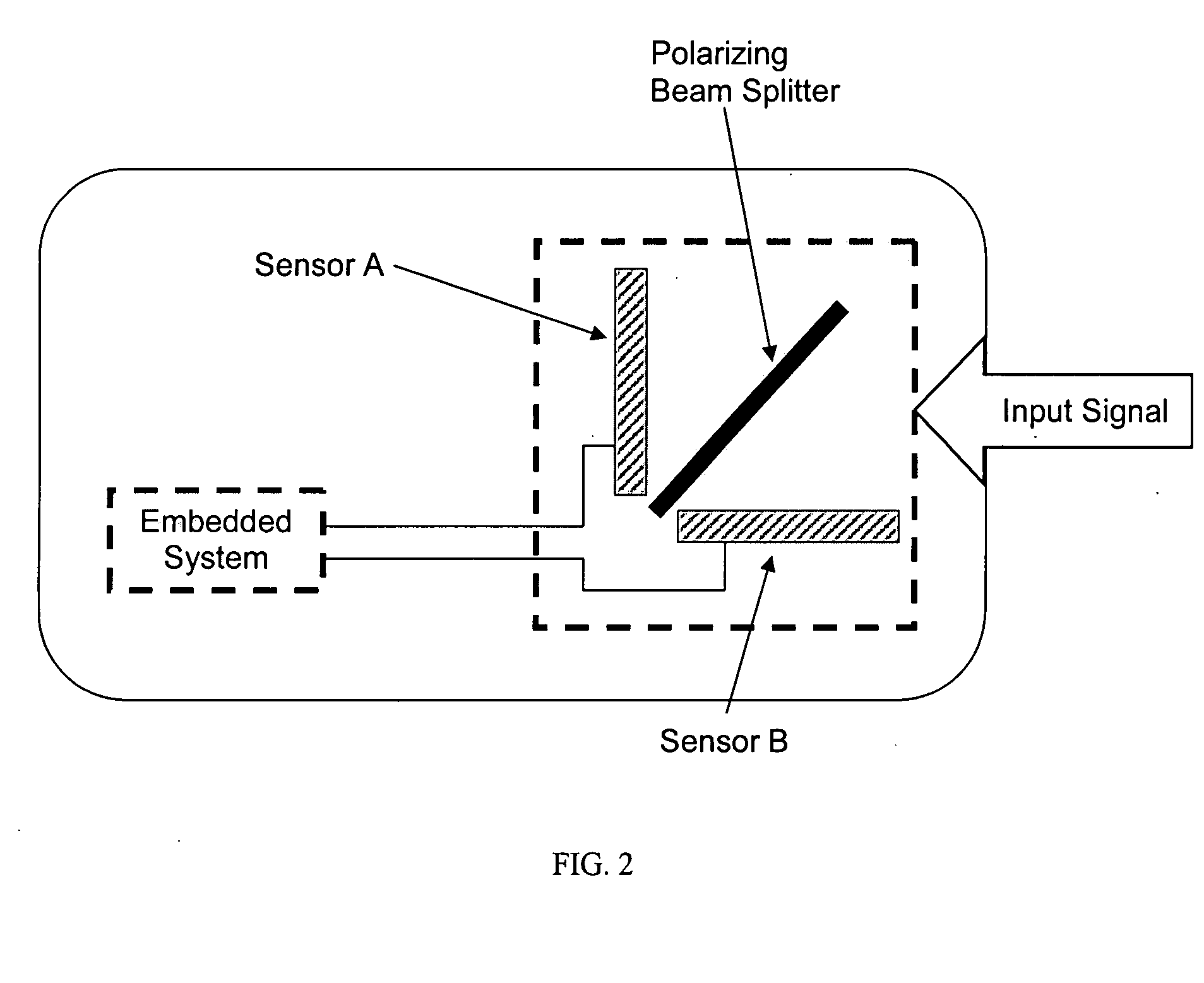
InactiveUS6860879B2Rapid dissociation reactionImprove permeabilityImpression capsTooth pluggers/hammersBiological bodyNon malignant
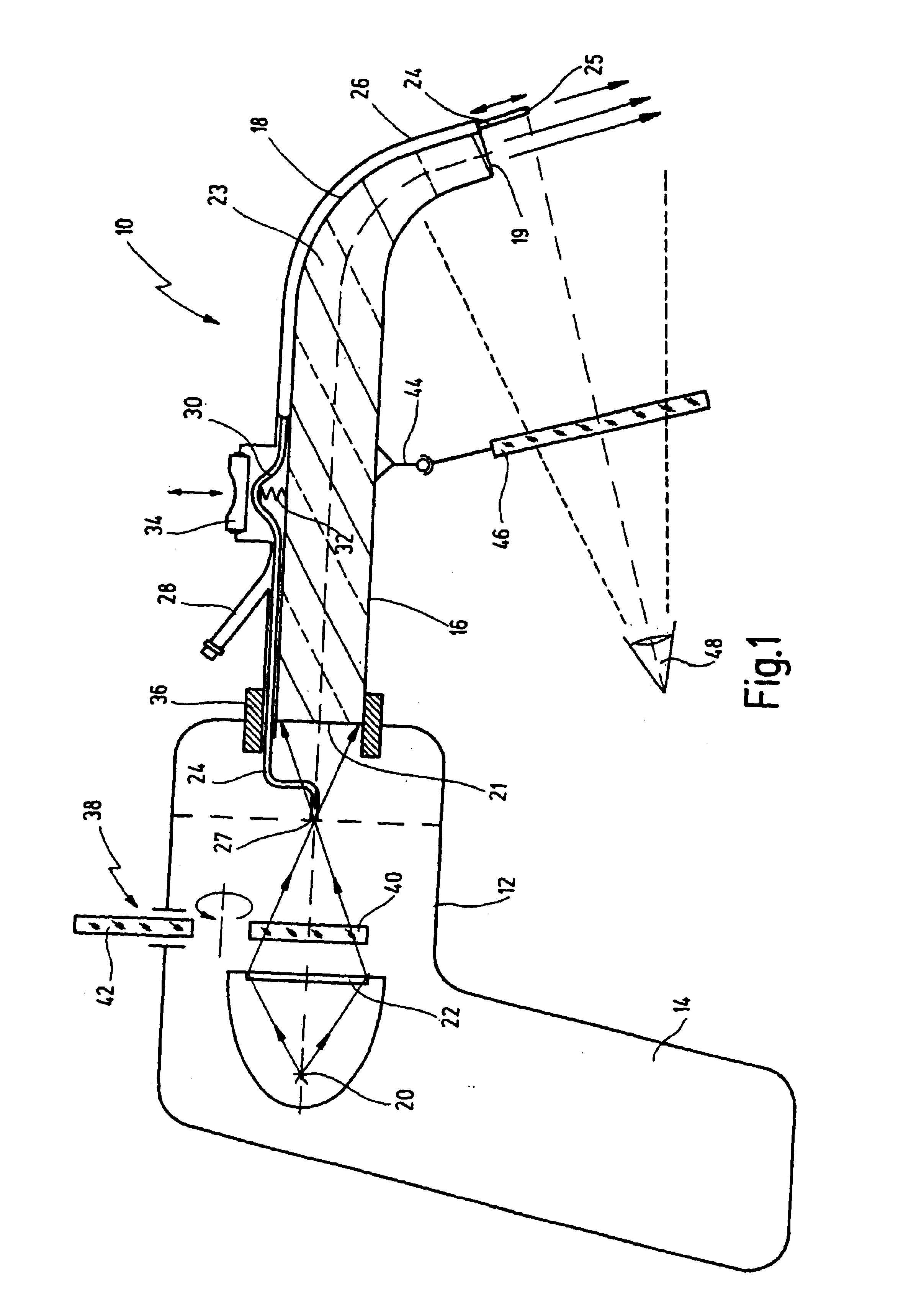
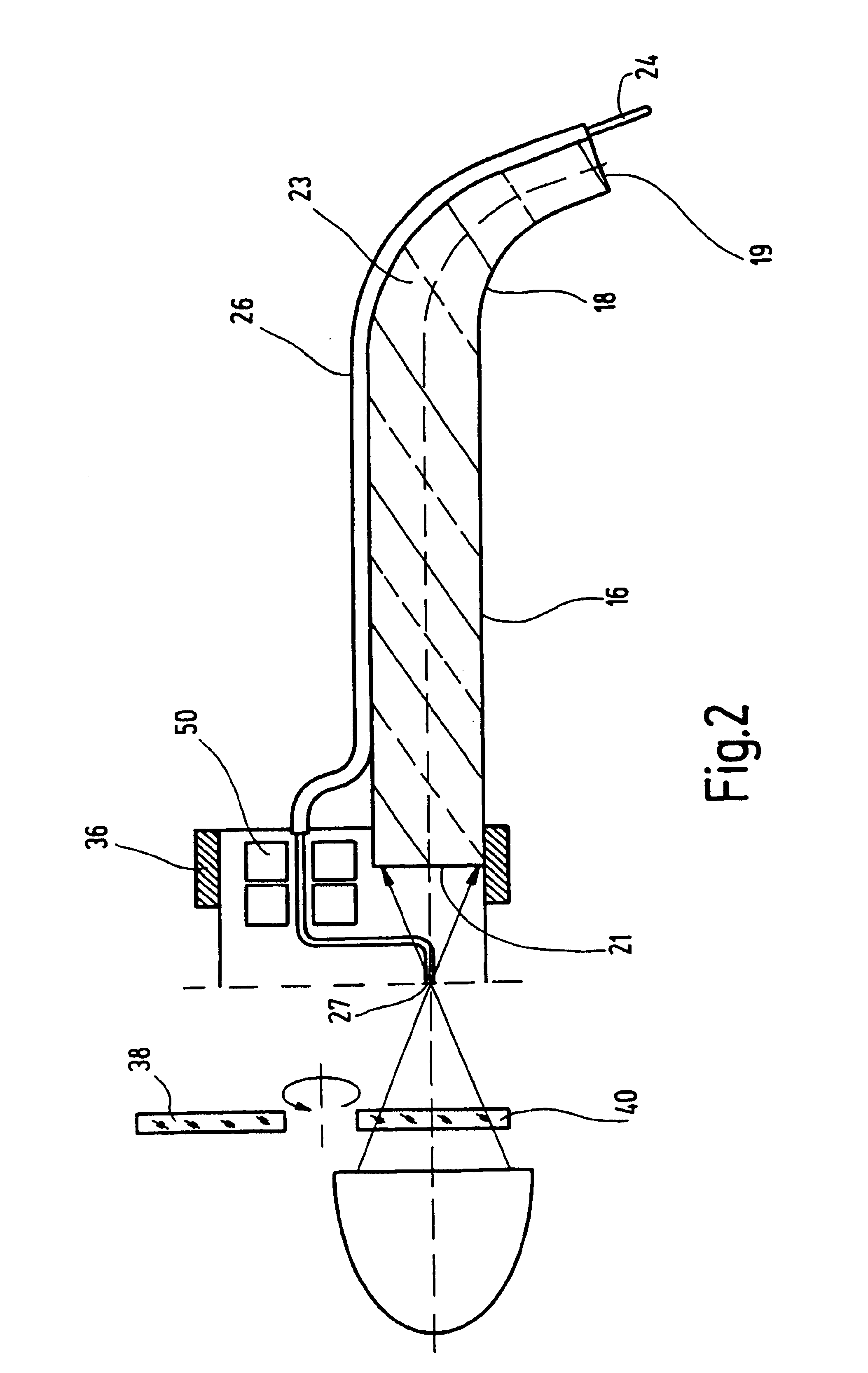
A light application unit for a combined photodynamic diagnosis and photodynamic therapy of non-malignant diseases of a parodontium and a tooth of a living being having administered a pharmaceutical preparation allowing the photodynamic diagnosis and the photodynamic therapy comprises a light source, a focusing unit for focusing light emitted by the light source, at least one element arrangeable in a light beam path of the light, and at least one wave guide for transmitting the light from the light source to a distal emitting end, the wave guide is configured rigidly in at least a distal handling end section thereof and being curved in a distal end section.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
Photosensitizer composition for treating skin disorders
A composition comprising an active ingredient selected from the group of 5-aminolevulinic acid or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or derivative thereof; and an aqueous carrier comprising at least one absorption enhancer, an anesthetic, hyaluronic acid and at least one acid selected from the group consisting of glycolic acid and lactic acid. The composition is useful in a photodynamic method of treating skin disorders.
Owner:MODI PANKAJ
Photochemotherapeutic method using 5-aminolevulinic acid and other precursors of endogenous porphyrins
InactiveUS6710066B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideAmino-Levulinic AcidProtoporphyrin IX
Methods of detecting and treating rapidly growing exogenous cells, such as Protista, or parasites, that preferentially accumulate a photoactivatable porphyrin in which 5-aminolevulinic acid or precursor thereof is administered to the patient, or contacted to the exogenous cells, in an amount sufficient to induce synthesis fluorescence and / or photosensitizing concentrations of a protoporphyrin IX in the exogenous cells, followed by exposure of the exogenous cells to light of photoactivating wavelengths.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF KINGSTON
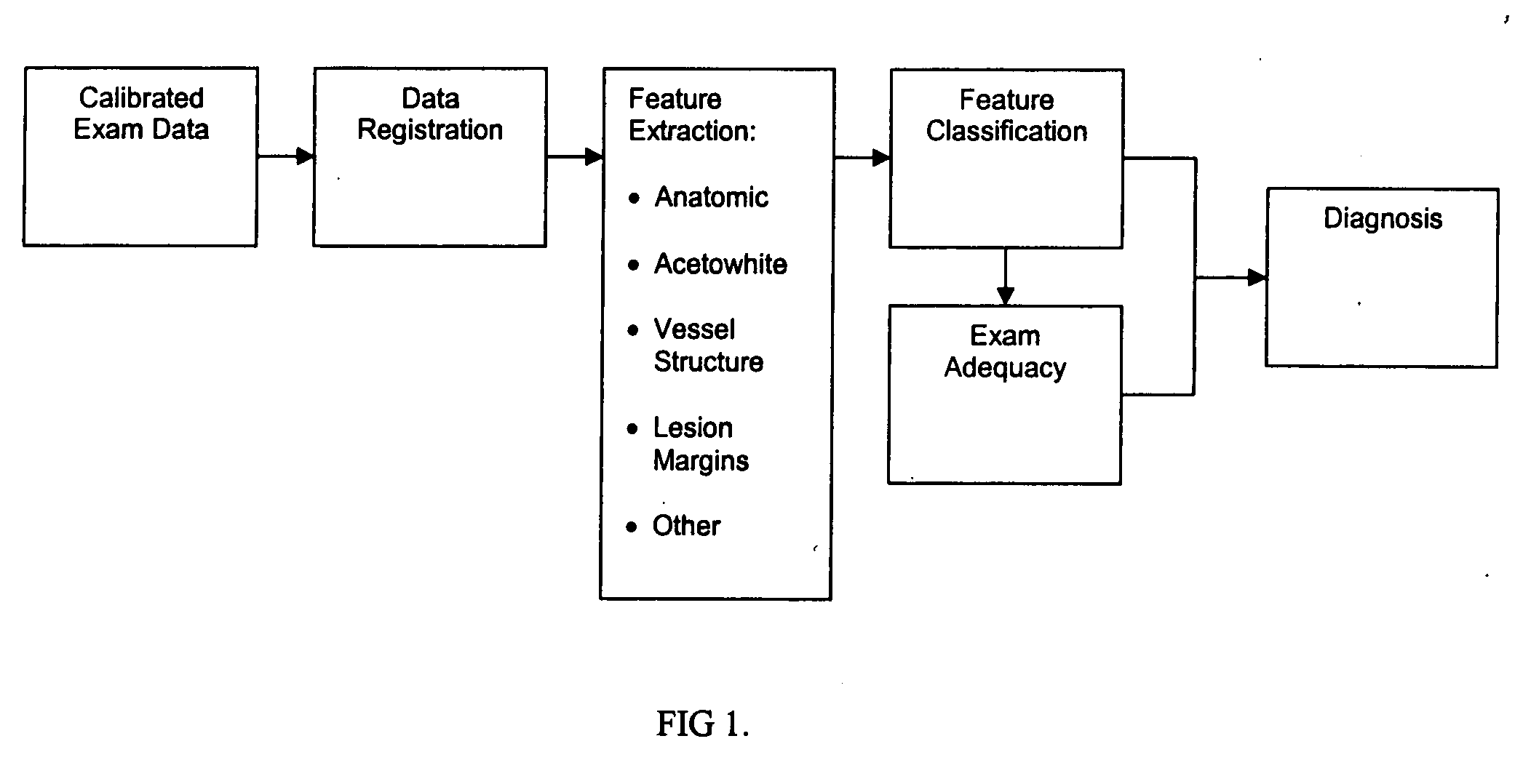
Uterine cervical cancer computer-aided-diagnosis (CAD)
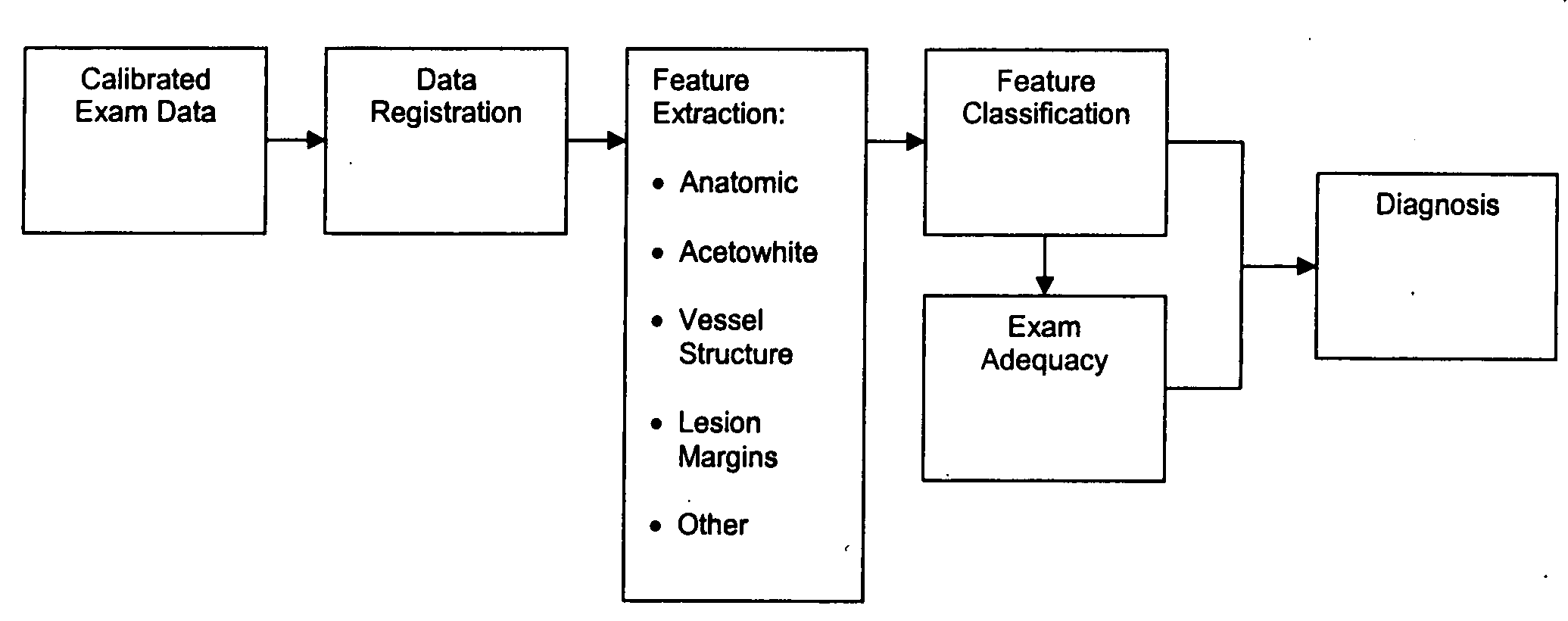
Uterine cervical cancer Computer-Aided-Diagnosis (CAD) according to this invention consists of a core processing system that automatically analyses data acquired from the uterine cervix and provides tissue and patient diagnosis, as well as adequacy of the examination. The data can include, but is not limited to, color still images or video, reflectance and fluorescence multi-spectral or hyper-spectral imagery, coherent optical tomography imagery, and impedance measurements, taken with and without the use of contrast agents like 3-5% acetic acid, Lugol's iodine, or 5-aminolevulinic acid. The core processing system is based on an open, modular, and feature-based architecture, designed for multi-data, multi-sensor, and multi-feature fusion. The core processing system can be embedded in different CAD system realizations. For example: A CAD system for cervical cancer screening could in a very simple version consist of a hand-held device that only acquires one digital RGB image of the uterine cervix after application of 3-5% acetic acid and provides automatically a patient diagnosis. A CAD system used as a colposcopy adjunct could provide all functions that are related to colposcopy and that can be provided by a computer, from automation of the clinical workflow to automated patient diagnosis and treatment recommendation.
Owner:STI MEDICAL SYST
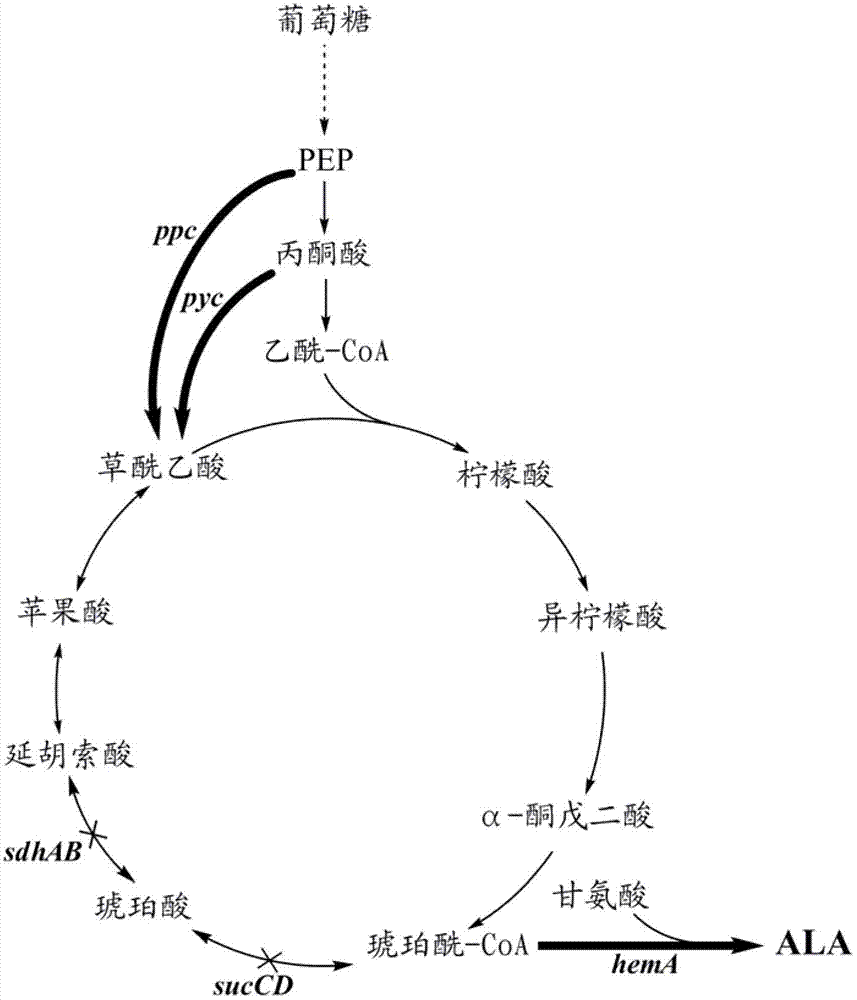
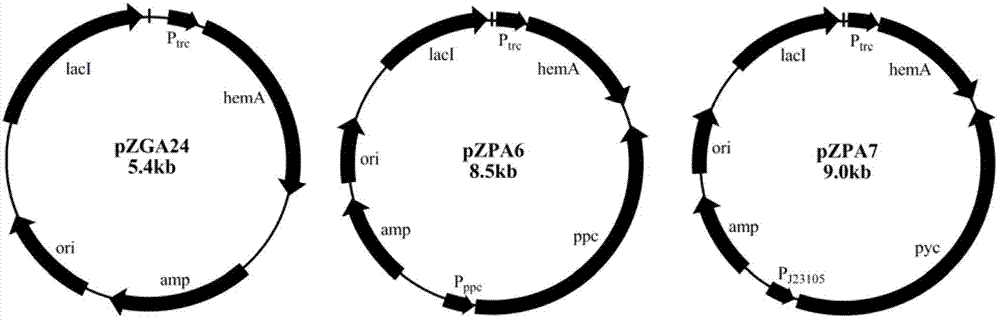
High-yield 5-aminolevulinic acid strain and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN103981203BImprove conversion rateIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphatePhosphoric acid
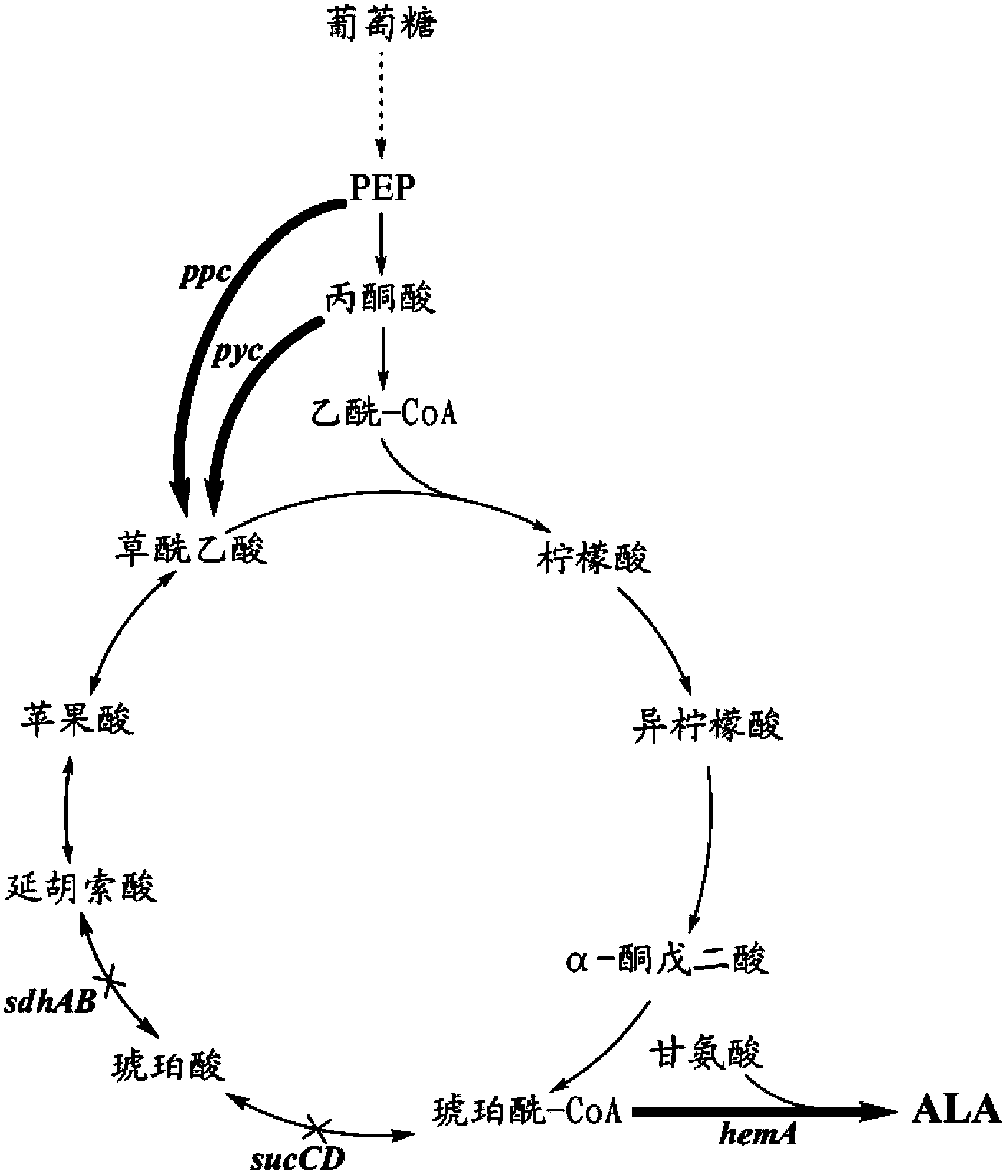
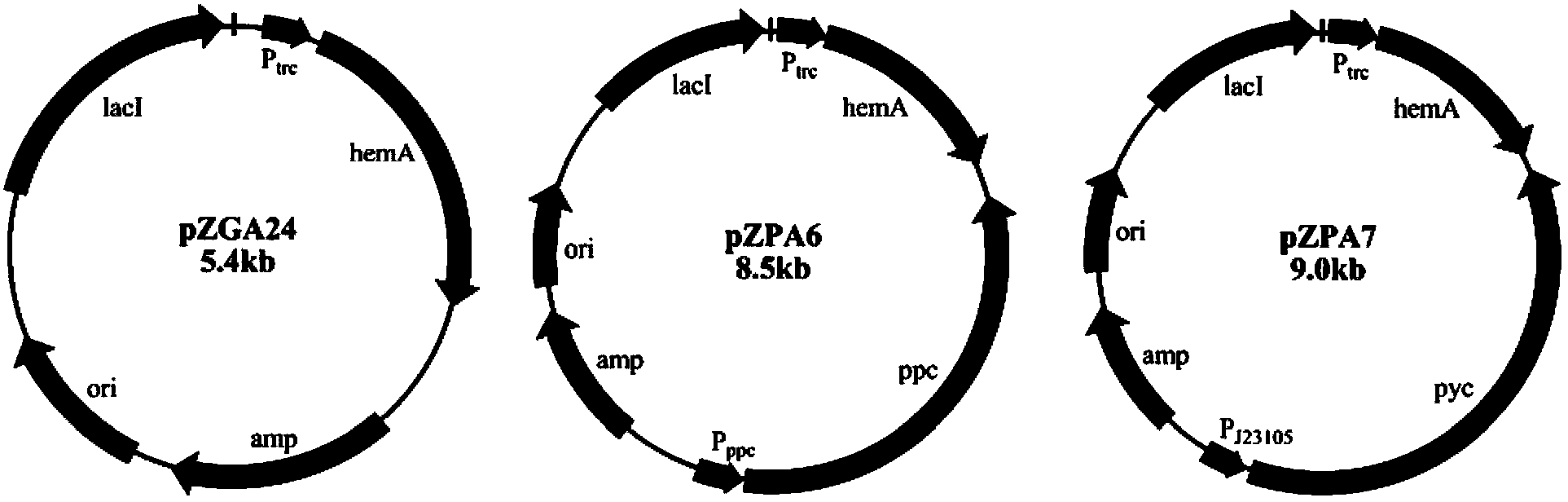
The invention discloses a method for constructing an ALA production strain, that is, enhancing the activity of related enzymes promoting the synthesis of oxaloacetate in the 5-aminolevulinic acid production strain or introducing exogenous related enzymes promoting the synthesis of oxaloacetate , such as phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase or pyruvate carboxylase, and / or weaken the succinyl-CoA downstream metabolic pathway-related enzymes in the strain, such as succinyl-CoA synthetase or succinate dehydrogenase active. The invention also discloses an ALA high-yield strain constructed by the method and a method for preparing ALA by using the strain. The bacterial strain of the invention can produce ALA efficiently, at low cost and with low pollution without adding exogenous succinic acid.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
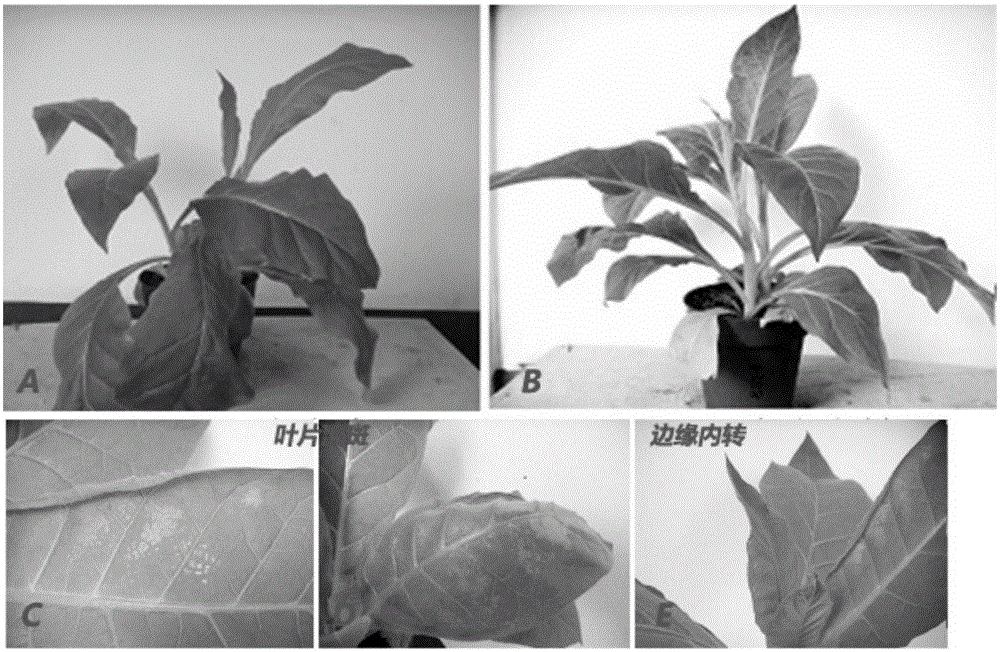
Method for improving fruit color
A method for promoting the colouring on fruit (apple, pear, peach, grape, etc) features that the 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA), or levulinic acid (LA)1 or glutamic acid (Glu) is applied to the fruit.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method of planting tea trees in forest
InactiveCN104472160APlanting Method AdvantagesReduce bitternessCalcareous fertilisersFertilising methodsBalance of natureShoot
The invention relates to a method of planting tea trees in a forest. The method comprises the steps: (1) selection of a tea tree planting base; (2) seed selection; (3) seeding; (4) management and protection of tea trees; (5) fertilization; (6) trimming and (7) timely plucking. In the method, 5-aminolevulinic acid and inoculant of photosynthetic bacteria are added to a leaf fertilizer, are cooperated to promote tea trees to efficiently utilize weak sunshine for photosynthesis and are beneficial to improve the color of tea leaves and the shoot tenderness-keeping ability of fresh tea leaves; and high-active nano-selenium is added to the leaf fertilizer, so that the produced tea leaves are rich in selenium and reduced in bitter taste. In addition, the tea leaves planted by the method has extremely high amino acid content and the produced tea leaves are green and pollution-free; ecological useful insects and birds in the forest construct an ecological chain prevention and control environment for controlling pests for natural plants; the method of planting tea trees in the forest overcomes the instability of the present tea garden ecosystem; the resource utilization rate is improved, the ecological balance is kept and the low-consumption, safety, good quality and high efficiency of the plantation of the tea trees are realized.
Owner:DAWU HUANGLONGBAIYUAN TEA CO LTD
5-amino levulinic acid (ALA) high-yield strain and preparation method and application thereof
A method for constructing an ALA production bacterial strain, the method enhances the activity of related enzymes promoting the synthesis of oxaloacetate and in the 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) production bacterial strain, or introducing exogenous related enzymes promoting the synthesis of oxaloacetate, such as phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase or pyruvate carboxylase, and / or reducing the activity of related enzymes in the downstream metabolic pathway of succinyl coenzyme A in the bacterial strain, such as succinyl coenzyme A synthetase or succinate dehydrogenase, and / or reducing the activity of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylated kinase and / or malic enzyme. An ALA high-yield bacterial strain constructed by utilizing the method, and method for utilizing the bacterial strain to prepare ALA.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Plant photosynthesis promoter and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101913951AImprove photosynthetic efficiencyIncrease productionFertilizer mixturesCyclodextrinNormal growth
The invention discloses a plant photosynthesis promoter, which comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.5 to 10 percent of 5-aminolevulinic acid and salts thereof, 0.05 to 1 percent of triacontanol, 70 to 95 percent of potash fertilizer, 1 to 10 percent of cyclodextrin, 0.5 to 5 percent of wetting spreader, and 0.1 to 5 percent of UV protective agent. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: A, adding triacontanol crystals and water in a weight ratio of 1:100-200 into a reactor, heating to the temperature of between 90 and 100 DEG C, adding the cyclodextrin with high-speed stirring, continuously stirring for 10 to 20 minutes, and performing spray drying on the mixed solution to obtain triacontanol emulsifiable powder; and B, crushing and grinding the triacontanol emulsifiable powder obtained by the step A, the 5-aminolevulinic acid and salts thereof, the potash fertilizer, the wetting spreader and the UV protective agent, sieving by using a 20-meshsieve, and mixing uniformly to obtain the finished product. The plant photosynthesis promoter can obviously improve the plant photosynthesis efficiency under the adverse conditions such as weak light, low temperature and dry heat, ensures the normal growth of the plants, and has the advantages of no pollution, no residue and no harm to human bodies and animals.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recombinant escherichia coli and application thereof in production of 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA)
ActiveCN102206606AImportant industrial application valueBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliAmino-Levulinic Acid
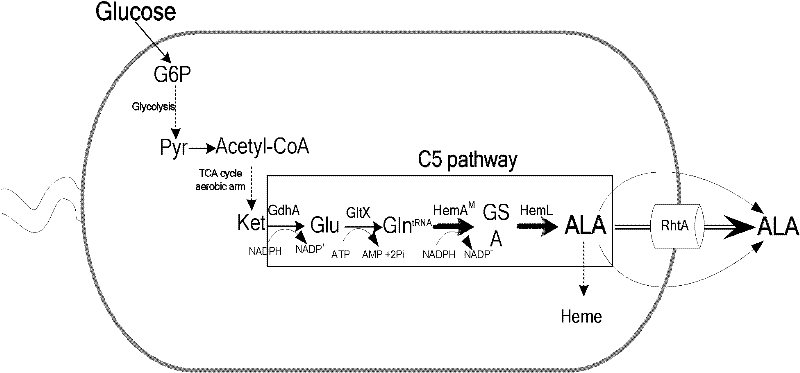
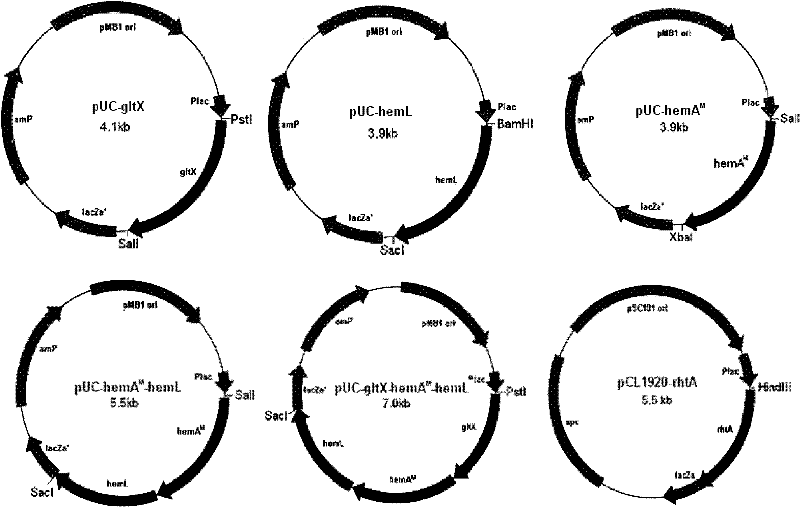
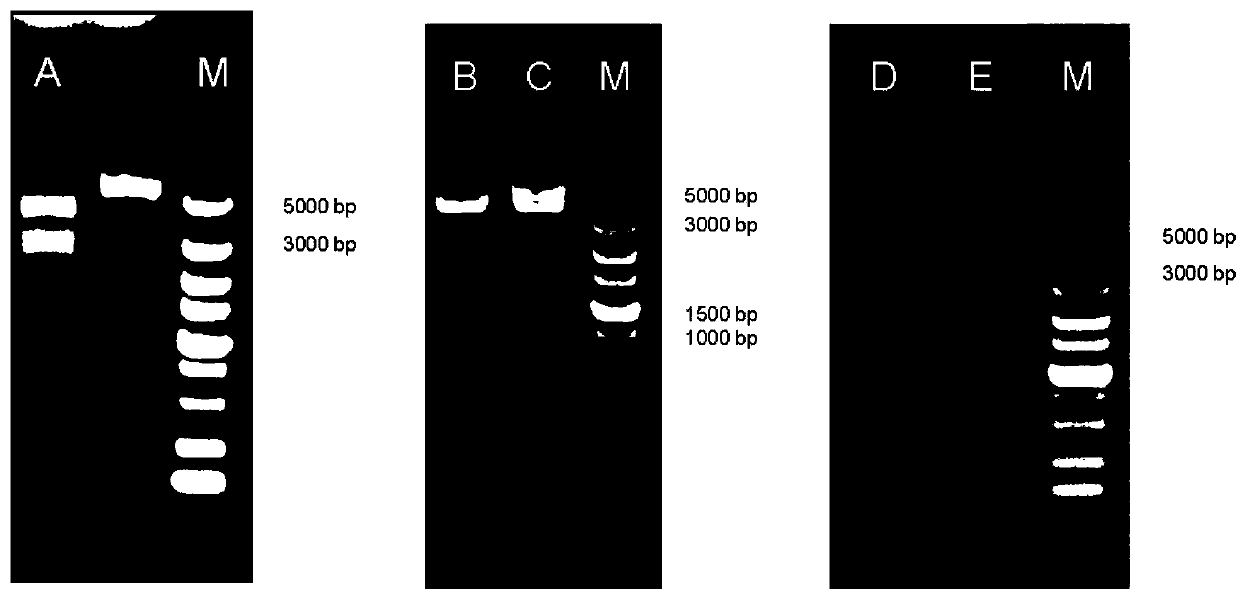
The invention discloses a recombinant escherichia coli which is called recombinant escherichia coli DALA. The recombinant escherichia coli DALA is prepared through the following steps: constructing a co-expression vector p-hemA<M>-hemL containing hemA<M> gene and hemL gene; constructing an expression vector p-rhtA containing rhtA gene; and converting constructed recombinant plasmids of p-hemA<M>-hemL and p-rhtA to the escherichia coli to obtain the recombinant escherichia coli DALA which can overexpress the hemA<M> gene, the hemL gene and the rhtA gene. The invention also discloses an application of the recombinant escherichia coli in production of the ALA. A fermentation result shows that the output of the ALA produced by the recombinant escherichia coli achieves 4.13 g / L, the conversionrate of the ALA to glucose is 0.168 g / g and the escherichia coli has good industrial development and application prospects.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
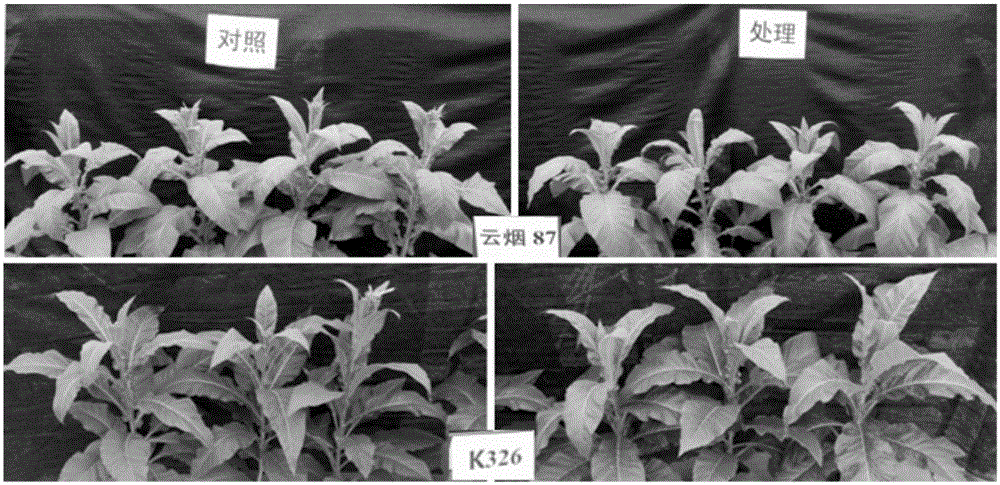
Cold-resisting agent for tobaccos as well as preparation and usage methods of cold-resisting agent
InactiveCN105191938AFertility status is normalImprove low temperature stress resistanceBiocidePlant growth regulatorsAmino-Levulinic AcidGlycine
The invention discloses a cold-resisting agent for improving cold resistance of seedlings of tobaccos as well as preparation and usage methods of the cold-resisting agent. The cold-resisting agent comprises main components as follows: 1.15-2.30 g / L of glycine betaine, 5.0-10.0 mg / L of salicylic acid, 3.0-5.0 mg / L of abscisic acid and 600-1,000 mg / L of 5-aminolevulinic acid. The agent is sprayed to leaf surfaces in the seedling recovering period and the root extending period before outplanting of the seedlings of the tobaccos or after land transplantation of the seedlings of the tobaccos, the agent is sprayed after the original agent is diluted by 3-5 times, and 25-30 L of the agent is sprayed per mu. The agent is a cold-resisting leaf surface spray agent prepared from physiological activity regulating substances, can effectively improve the resistance of shoots (the seedlings) of the tobaccos to low-temperature adverse situation, can better cope with low-temperature damage of birth blockage (and even early blossoming) of the seedlings of the tobaccos due to frequent late spring coldness in main southern tobacco producing areas, has no adverse effect on the quality of flue-cured tobaccos and has bright application prospect in tobacco production.
Owner:LILING BRANCH ZHUZHOU CO HUNAN TOBACCO CO LTD +1
Formulation for dermal application
InactiveUS20080227757A1Short reaction timeDelayed reaction timeBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDrugAminolevulinic Acid Hydrochloride
The present invention relates to formulations on an aqueous basis with polyetherpolyol, dimethyl isosorbide, lipid and alcohol content suitable for penetration reinforcement of pharmaceutical active ingredients in the dermal application. The pharmaceutical active ingredients can be amphiphilic, zwitterionic, strongly polar or lipophilic. A preferred active ingredient is 5-aminolevulinic acid.
Owner:BRAUNSCHWEIG UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for building high-yield 5-aminolevulinic acid escherichia coli engineering strains
ActiveCN104004701AEasy to synthesizeShorten the fermentation cycleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method for building high-yield 5-aminolevulinic acid Escherichia coli engineering strains, and belongs to the field of metabolic engineering and micro-biological fermentation. On the basis that key enzyme glutamy tRNA reduction enzyme and glutamyl aminotransferase which are 5-aminolevulinic acid C5 synthesis paths are overexpressed through carriers pACYCDuet-1, uroporphyrinogen III synthase (UROS) hemD codes and coproporphyrinogen III oxidase (CPO) hemF codes from an escherichia coli heme biosynthetic pathway are independently expressed with pCDFDuet-1 or are expressed together, and recombination strains are constructed. By means of fermentation verification, hemD or hemF is expressed separated, hemD and hemF are expressed together, and the ALA yield is obviously improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Nanoemulsion
The present invention relates to a nanoemulsion comprising at least one aqueous component and a carrier, wherein the carrier comprises at least one lipophilic component, at least one surfactant and at least one alcohol. The present invention further relates to a composition comprising the nanoemulsion and an active agent. In particular, the composition is present as a gel and the active agent is 5-aminolevulinic acid, a derivative, precursor and / or metabolite thereof. The invention further relates to the preparation of the nanoemulsion and / or composition and to their use for the treatment of dermatological diseases, virus-associated diseases as well as diseases associated with cell proliferation, in particular, tumor diseases and / or psoriasis. The present invention is further directed to the use of the nanoemulsion in cosmetics.
Owner:BIOFRONTERA BIOSCIENCE GMBH
Prophylactic/ameliorating agent for adult diseases comprising 5-aminolevulinic acid, derivative of 5-aminolevulinic acid, or salt of 5-aminolevulinic acid or the derivative or 5-aminolevulinic acid as active ingredient
ActiveUS20110196033A1Ameliorate and prevent adult diseaseImprove basal metabolismHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideImpaired liver functionDisease
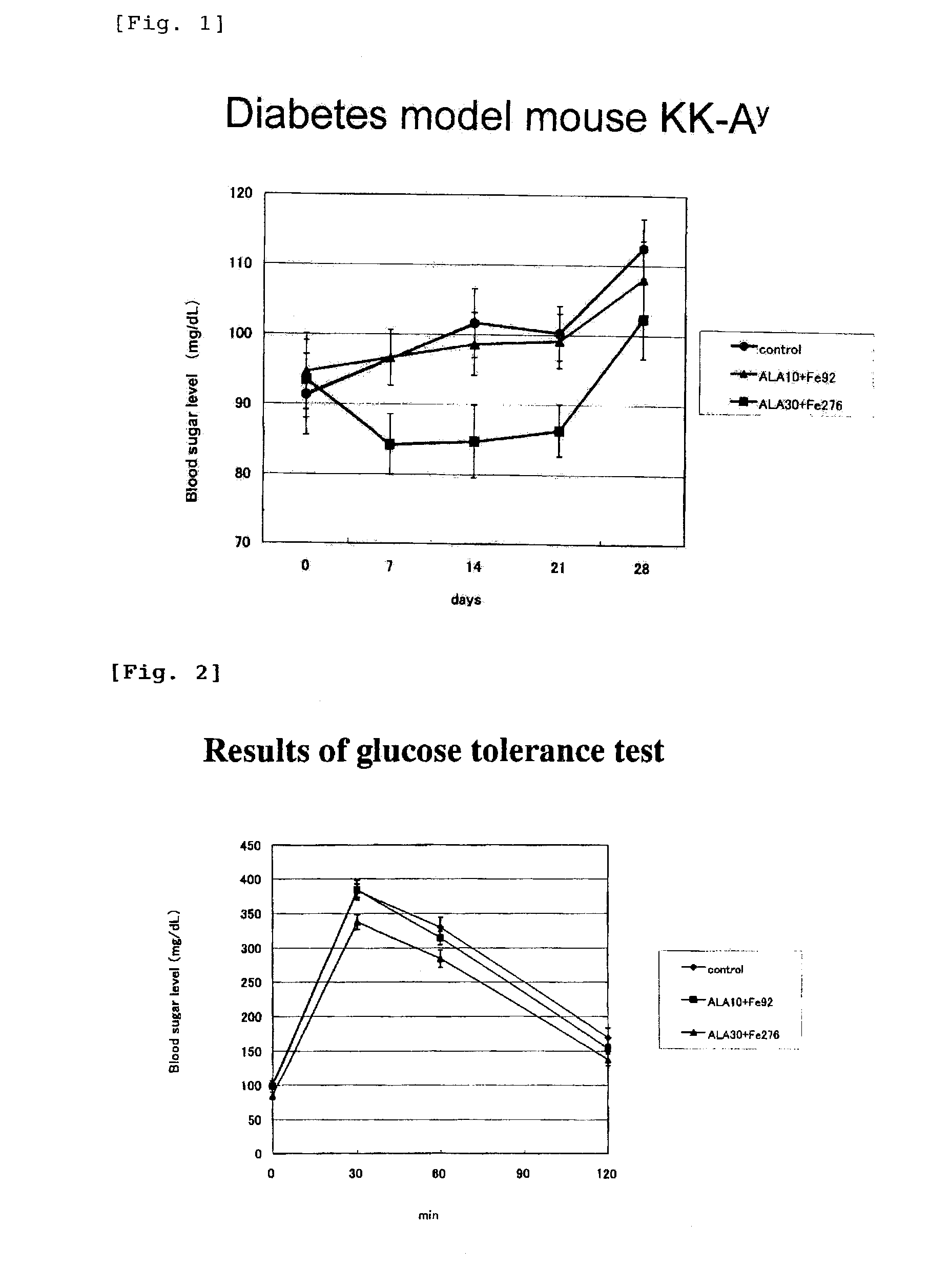
It is to provide a pharmaceutical composition which is different from an existing therapeutic agent of an adult disease, of a biochemical reaction-inhibiting type, and which action mechanism is to improve the basal metabolism, wherein the composition has no side effects, and does not generate drug resistance against adult disease; and a method for preventing / treating an adult disease by using the same. It is to provide a composition for preventing / ameliorating an adult disease such as metabolic syndrome, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, impaired liver function, renal failure, adiposity, erectile dysfunction, menopausal disorder, shoulder discomfort, and low back pain, comprising 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA), its derivative, or salt thereof, preferably comprising ALA, its derivative, or salt thereof, and an iron compound such as sodium ferrous citrate, iron sodium citrate and iron ammonium citrate; a food or food material for preventing / ameliorating an adult disease comprising the composition; and a method for using the composition for preparing an agent for preventing / ameliorating an adult disease.
Owner:SBI PHARMA CO LTD
Swine growth promoters and method of promoting swine growth
InactiveCN1538839AHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsBiotechnologyAmino-Levulinic Acid
A pig growth enhancer, which comprises, as an active ingredient, at least one compound selected from 5-aminolevulinic acid, a derivative thereof and a salt thereof, and a method for enhancing pig growth, which comprises administering the growth enhancer to a pig.
Owner:COSMO ALA CO LTD
Methods and compositions for dose-dependent photodynamic therapy of disorders
InactiveUS20090259167A1Potent vascular PDT reactionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseAmino-Levulinic Acid
The invention provides methods and compositions for treating a tissue disorder in a subject by parenterally administering a solution of aminolevulinic acid (ALA) or a derivative thereof that is not greater than 1.0 percent by weight into a local subcutaneous or dermal region of the subject; and administering high fluence light to said bodily area to produce a phototoxic species in said local region, thereby treating a tissue disorder in the subject.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
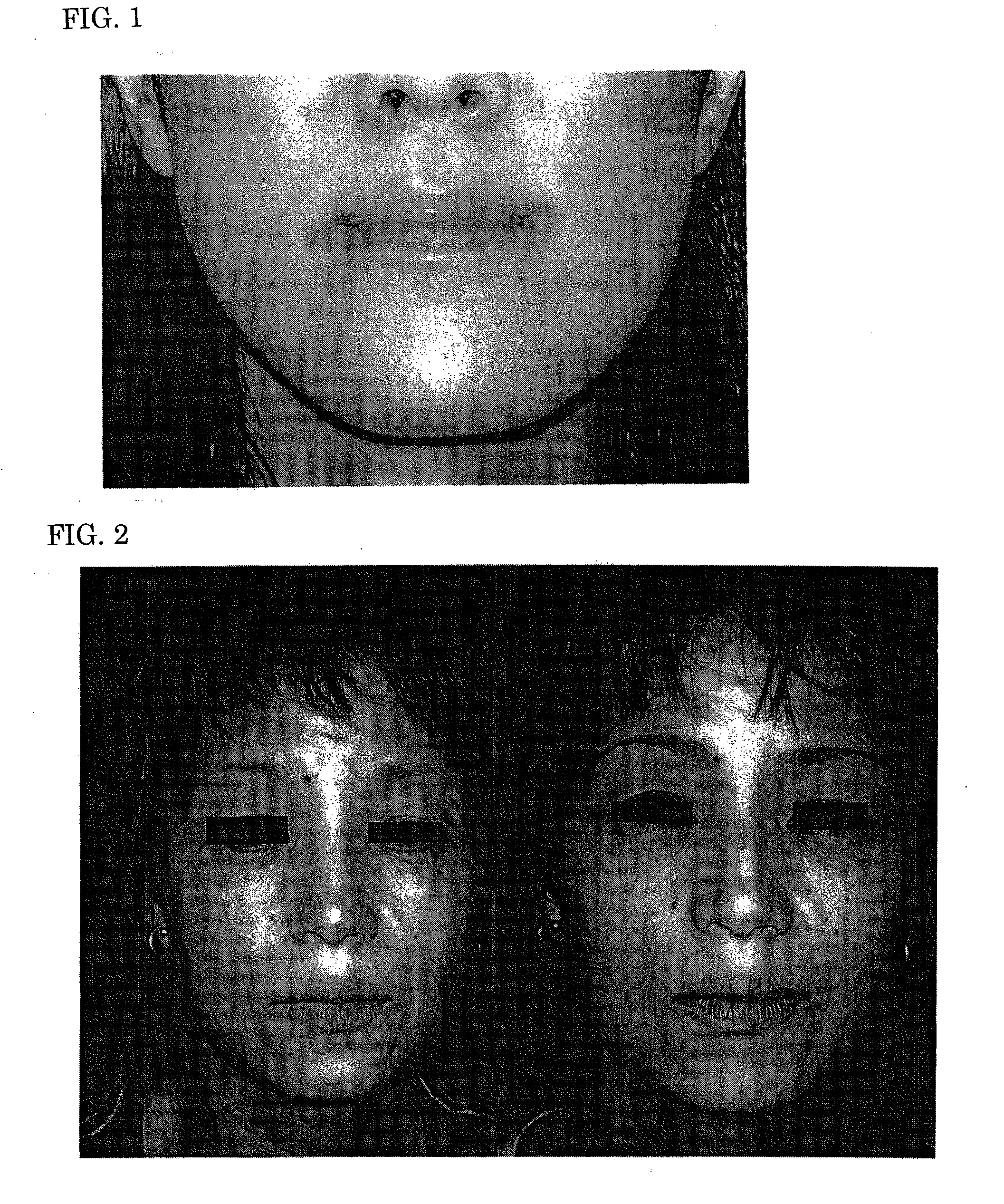
External preparation for skin
The present invention provides an external preparation for skin which contains 5-aminolevulinic acids as active components and which is excellent in skin-beautifying effects such as prevention / amelioration of skin roughness, dry skin, wrinkles, sagging and flecks of skin, and improvement of turnover of corneum; and in an ameliorating effect on skin diseases such as atopic dermatitis. An external preparation for skin which contains one or more compounds selected from the group consisting of 5-aminolevulinic acid, its salt and a derivative of them; and an iron compound; as active components, is used.
Owner:SBI PHARMA CO LTD
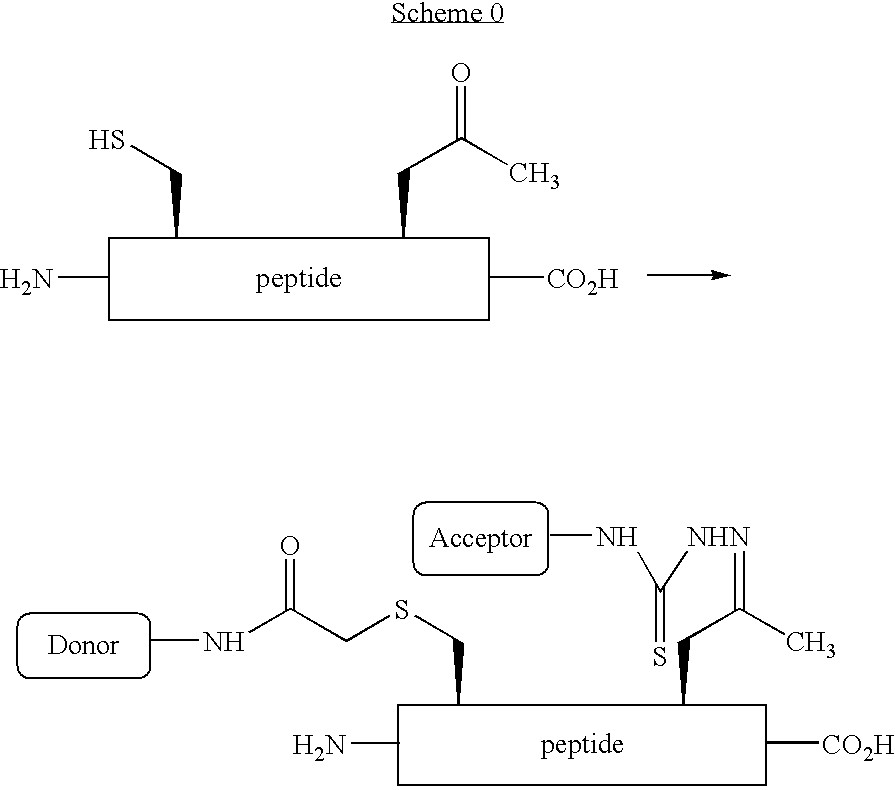
Synthetic peptides, conjugation reagents and methods
InactiveUS20060035305A1Sugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsCrystallographyAmino-Levulinic Acid
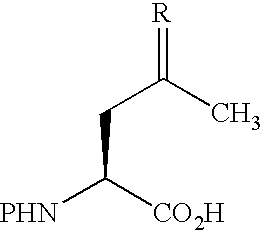
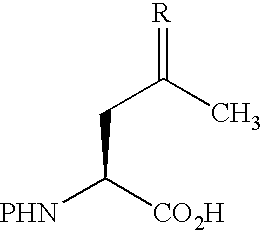
The invention provides methods and compositions useful for making synthetic peptide conjugates. In one embodiment, the invention provides compositions comprising the structure: wherein R is selected from lower substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, O, NH and S and P is an amine protection group. In more particular embodiments, the compositions comprise α-amine protected 4,5-dehydroleucine or α-amine protected (2S)-aminolevulinic acid and / or P is F-moc. These compounds may be incorporated into peptides, for example, peptides comprising a substituted or unsubstituted (2S)-aminolevulinic acid residue, such as (2S)-aminolevulinic acid residue is substituted with an O- or N-linked glycoconjugate, or a detectable label.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Lodging and senility resisting, high photosynthetic efficiency and yield increasing regulator for corn, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105594734AImprove stress resistanceImprove lodging resistanceBiocidePlant growth regulatorsAmino-Levulinic AcidGrain weight
The invention relates to a lodging and senility resisting, high photosynthetic efficiency and yield increasing regulator for corn, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The regulator contains 5-aminolevulinic acid, 2-(3,4-dichlorophenoxy)triethylamine and ethephon, and preferably contains an activator and a spreader, and the activator and the spreader are selected from one or more of tween20 and tween60. The regulator can substantially enhance the low temperature cold injury, high temperature, drought and low light stress resistance of corn, increases the effective spike number, the number of grains per spike and the thousand-grain weight of the corn, and increases the output of the corn by 20% or above. The regulator has the characteristics of low cost, use convenience and less field residual, is easy to promote and apply, and has an active promotion effect on Chinese corn production.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Hair Restorer
ActiveUS20070249721A1Easy to useSafe and stable hair restoring effectCosmetic preparationsBiocideAcetic acidAmino-Levulinic Acid
The object of the present invention is to provide a hair restorer which exhibits a stimulatory effect on hair restoration against hair loss, hair thinning, split ends, hair graying, etc., with higher stability and safety than those of known hair restorers containing 5-aminolevulinic acids as active components. By using 5-aminolevulinic acid or its salt or its derivative, and a composition containing iron sodium diethylenetriaminepentaacetate or iron ammonium diethylenetriaminepentaacetate as active components, a hair restorer and a method for restoring hair which are excellent in hair growth promotion, and stability and safety, are provided.
Owner:COSMO ALA CO LTD
High-efficiency fertilizer used for succulent flowers and having automatic water adjusting function and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN105503387APromote absorptionPromote growthAnimal corpse fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserBetaineOyster
The invention discloses high-efficiency fertilizer used for succulent flowers and having an automatic water adjusting function. The high-efficiency fertilizer is prepared from, by weight, sodium alginate, calcium peroxide, hydrogenated tea oil, nano carbon aerogel, active ash, rape seed cakes, purple perilla cakes, calcined oyster shell powder, composite microbial zymophyte, monopotassium phosphate, ammonium phosphate, tryptophan, zinc glycinate, boron glycinate, fulvic acid, dodecyl dimethyl betaine, aminolevulinic acid, beta-cyclodextrin, modified viscous starch, sodium polyacrylate, nano zeolite powder and an appropriate amount of water. Fermented granulated fertilizer is coated with envelope liquid to prepare the succulent fertilizer, and the high-efficiency fertilizer used for the succulent flowers is rich in organic matter and nutrition, can be absorbed and used by succulents conveniently and promotes growth of the succulents. Adopted sodium polyacrylate can improve the water absorption and retention performance and cold endurance of the non-hydrophytic succulents, the fertilizer can facilitate convenient and high-efficiency cultivation of the succulent flowers, and the ornamental effect of the succulent flowers is enhanced.
Owner:HEFEI RICEFOOD CO LTD
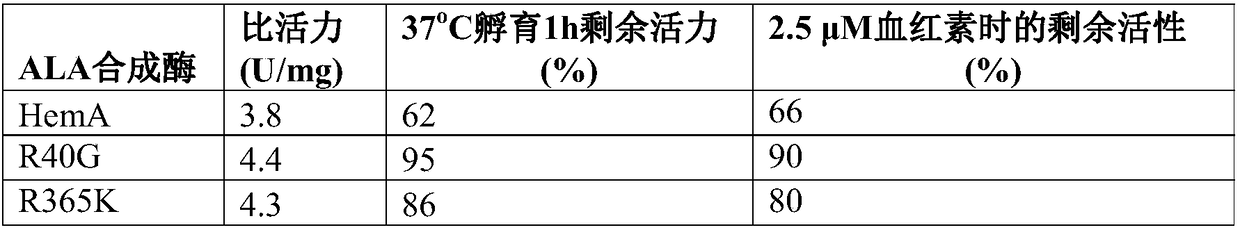
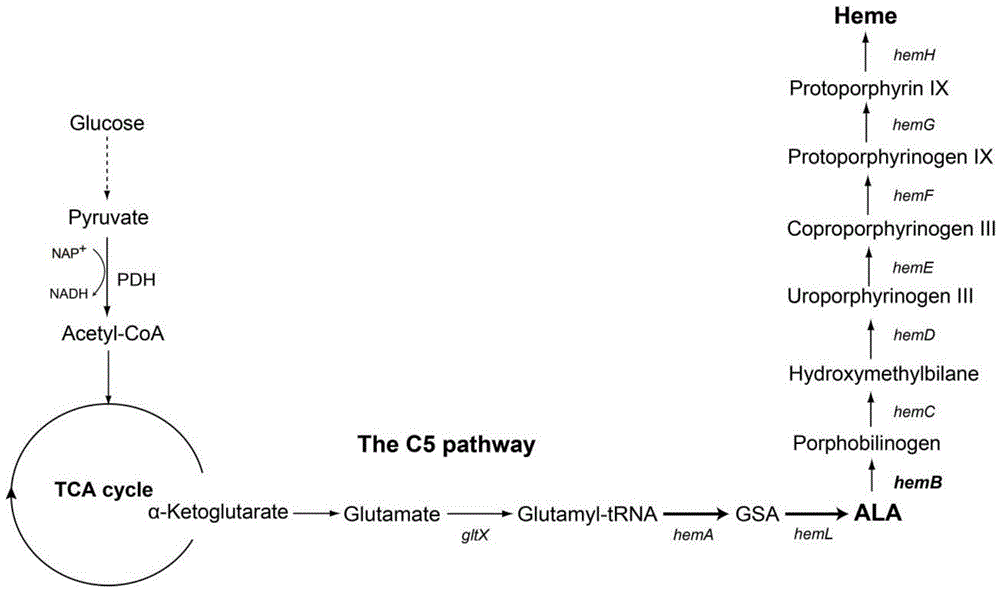
5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) synthetase mutant and host cells and application thereof
The invention provides a 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) synthetase. The amino acid sequence of the ALA synthetase has mutation at the amino acid residues of the 40th site, the 365th site, the 75th site,the 29th site and the 44th site corresponding to the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The ALA synthetase provided by the invention obviously improves the activity and also partially relieves the feedback inhibition of hemachrome. Furthermore, the invention also provides methods for preparing and modifying the ALA synthetase, an expression vector containing the ALA synthetase, host cells containing the ALA synthetase, and application of the ALA synthetase in ALA production.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Combination therapy for coronavirus infections including the novel corona virus (COVID-19)
ActiveUS10987329B1Reduce serious complicationsShorten the timeOrganic active ingredientsInorganic active ingredientsVitamin CDietary supplement
The present invention provides therapeutic combinations of 5-aminolevulinic acid, with at least one of: Vitamin C, curcumin, zinc, and methylene blue for the treatment of coronavirus infections, including the SARS-CoV-2 virus, and / or rhinoviruses. Optionally such compositions may comprise other dietary supplements and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients and also process for preparing it. The composition can also include other antiviral agents.
Owner:RAJU NADIMPALLY SATYAVARAHALA +4
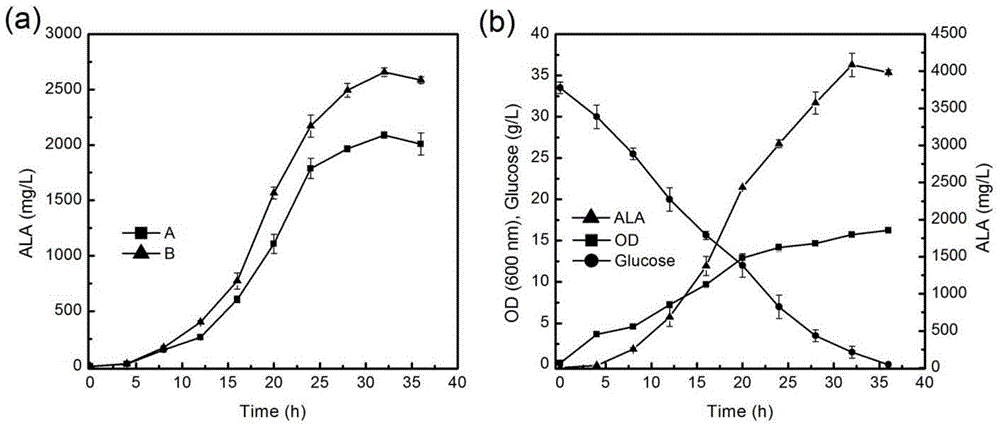
Method for weakening hemB gene expression to increase yield of 5-aminolevulinic acid synthesized by escherichia coli
ActiveCN104830748AIncrease productionEasy to synthesizeBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliCoproporphyrinogen III oxidase
The invention discloses a method for weakening hemB gene expression to increase yield of 5-aminolevulinic acid synthesized by escherichia coli and belongs to the field of and microorganism fermentation. On the basis of using carrier pRSFDuet-1 overexpression glutamy-tRNA reductase, pancreatic aldehyde amino transferase, coproporphyrinogen III oxidase and carrier pETDuet-1 overexpression urinary porphyrins III synthase, a promoter of hemB genes is horizontally transformed in a gene group so as to control expression of the hemB genes and surveying influence, on ALA accumulation, of the hemB genes. Shake-flask fermentation verifies that yield of a target product ALA is increased remarkably, and the ALA yield at 30h is 2680mg / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Photochemotherapeutic method using 5-aminolevulinic acid and other precursors of endogenous porphyrins
InactiveUS20040157905A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideAmino-Levulinic AcidProtoporphyrin IX
Methods of detecting and treating rapidly growing exogenous cells, such as Protista, or parasites, that preferentially accumulate a photoactivatable porphyrin in which 5-aminolevulinic acid or precursor thereof is administered to the patient, or contacted to the exogenous cells, in an amount sufficient to induce synthesis fluorescence and / or photosensitizing concentrations of a protoporphyrin IX in the exogenous cells, followed by exposure of the exogenous cells to light of photoactivating wavelengths.
Owner:DUSA PHARMA INC +1
5-Aminolevulinic acid salts and their use
The invention provides salts of 5-Aminolevulinic acid (ALA) of formula (I): wherein RY is an organic acid moiety; Y is selected from the group consisting of a sulfonic acid residue, mono- or di-phosphoric acid residue, mono- or di-carboxylic acid residue and R is selected from the group consisting of saturated, unsaturated, straight or branched C2-C20 chains, aryl, aralkyl or naphthyl. In preferred embodiments, RY is selected from benzenesulfonic acid (besylate), 2-naphthalene sulfonic acid (napsyate), p-toluenesulfonic acid (tosylate), diethyl phosphate, dibenzyl phosphate, di-(2-ethylhexyl) phosphate, caproic or stearic acids. The invention also provides methods for preparing the ALA salts of the invention, pharmaceutical compositions containing the ALA salts of the invention, and use of the ALA salts of the invention in photodynamic therapy (PDT).
Owner:BAR ILAN UNIV +1
Solution for diagnosing or treating tissue pathologies
InactiveUS20030158258A1Increase synthesisFast concentrationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideAmino-Levulinic AcidDelta aminolevulinate
The invention concerns a 5-aminolevulinic acid ester (E-ALA) solution for producing a pharmaceutical preparation useful for diagnosing and / or treating tissue and / or cell pathologies by local radiation exposure using radiation emitted by a light source energy followed, in the case diagnosis, by detection of fluorescent protoporphyrin IX (Pp1X). The E-ALA concentration in the solution is less than 1% and ranges between 0.01% and 0.5%. The low E-ALA concentration in the solution increases Pp1X synthesis and homogenises its distribution in the cell layers while highly reducing the secondary toxicity for the treated cells.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL) +1
Corynebacterium glutamicum strain for production of 5-aminolevulinic acid and construction and application of corynebacterium glutamicum strain
InactiveCN106047916AIncrease productionHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylasePhosphoric acid
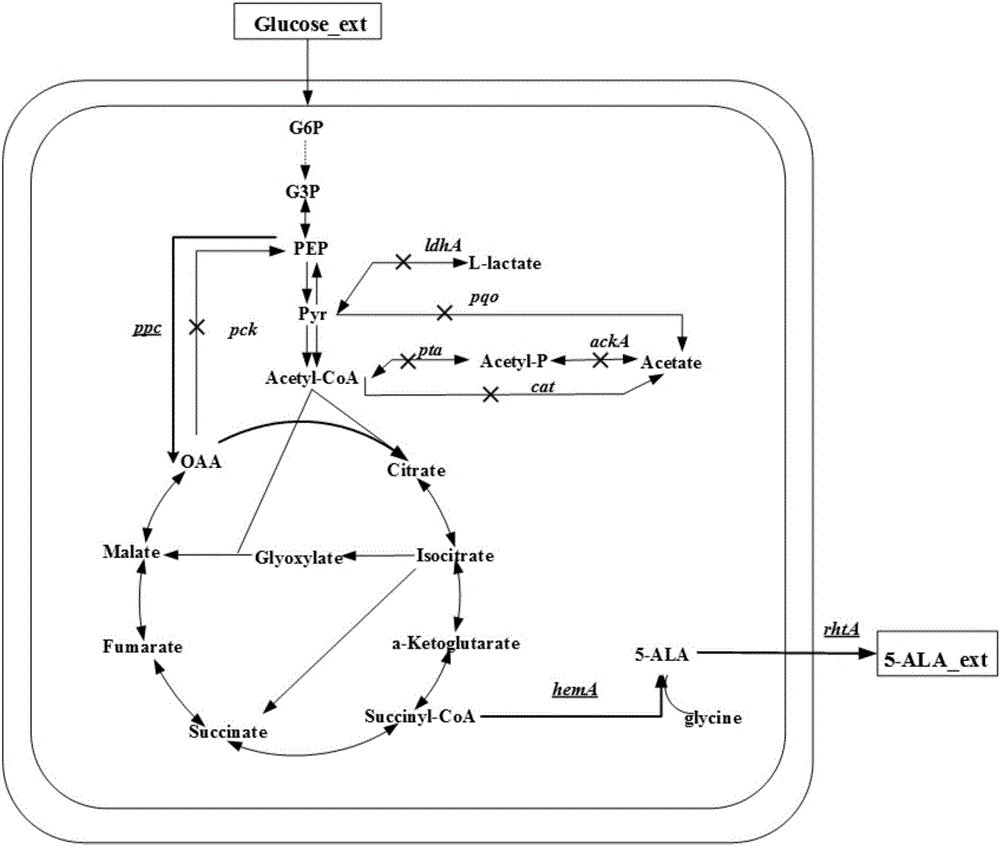
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum strain for production of 5-aminolevulinic acid and construction and application of corynebacterium glutamicum strain. A construction method includes: (1) deleting a lactic dehydrogenase coding gene 1dhA and acetic acid generation genes pta-ackA, pqo and cat in corynebacterium glutamicum to obtain a strain named CB4; inserting a strong sod promoter in front of a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase coding gene ppc in the strain CB4 to obtain a strain CB5; deleting a gene pck in the strain CB5 to obtain a strain CB6; (2) transferring plasmid pXA and plasmid pEP2<tuf>-rhtA into the strain CB6. The strain constructed according to the method is capable of generating 2.78g / L 5-aminolevulinic acid in a culture medium with 10g / L glucose serving as a carbon source, which lays a foundation for subsequent continuous feeding of a fermentation tank to increase yield of the 5-aminolevulinic acid.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com