Method for building high-yield 5-aminolevulinic acid escherichia coli engineering strains
A technology of aminolevulinic acid and Escherichia coli, applied in the fields of metabolic engineering and microbial fermentation, can solve the problem of high cost of ALA, and achieve the effect of shortening the fermentation period and reducing the production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Construction and identification of embodiment 1 recombinant plasmid
[0048] (1) Construction of recombinant plasmids pACYCDuet-1-hemLA, pCDFDuet-1-hemD, pCDFDuet-1-hemF, and pCDFDuet-1-hemD-hemF
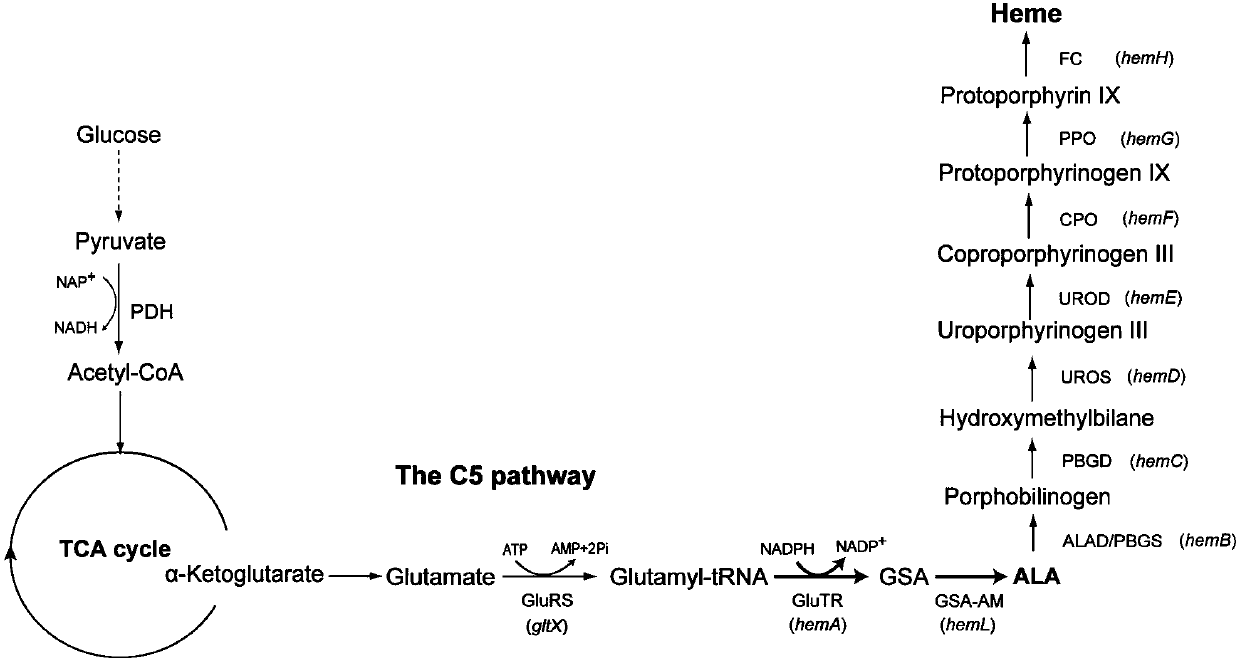
[0049] HemL, hemD, and hemF were obtained using the E. coli genome as a template, and hemA was derived from Salmonella typhi
[0050] The primers are as follows (the underlined part is the restriction site)
[0051] hemL-hemAF:CGC GGATCC ATAAAAGGAGGAAAATATATGAGTAAGTCTGAA
[0052] hemL-hemAR:TGCA CTGCAG CTACTCCAGCCGAGGCTG
[0053] hemD-F:CGC CATATG AGTATCCTTGTCACCCGCC
[0054] hemD-R:CCG CTCGAG TTATTGTAATGCCCGTAAAAGCG
[0055] hemF-F:CGC CATATG AAACCCGACGCACACC
[0056] hemF-R:CCG CTCGAG TTACACCCAATCCCTGACCTTAAT
[0057] hemD(2)-F:CGC GGATCC ATAAAAGGAGGAAAATATATGAGTATCCTTGTCACCCG
[0058] hemD(2)-R:TGCA CTGCAG TTATTGTAATGCCCGTAAAAGCG
[0059] The reaction conditions are: 94°C for 5min; 94°C for 30s, 58°C for 30s, 72°C for 150s (hemL-hemA) / 60s (hemD and ...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Embodiment 2 Recombinant bacteria shaking flask fermentation verification
[0064] Strains:
[0065] LA: E.coli BL21(DE3)pACYCDuet-hemLA pCDFDuet-1
[0066] LAD:E.coli BL21(DE3)pACYCDuet-hemLA pCDFDuet-hemD
[0067] LAF:E.coli BL21(DE3)pACYCDuet-hemLA pCDFDuet-hemF
[0068] LADF:E.coli BL21(DE3)pACYCDuet-hemLA pCDFDuet-hemD-hemF
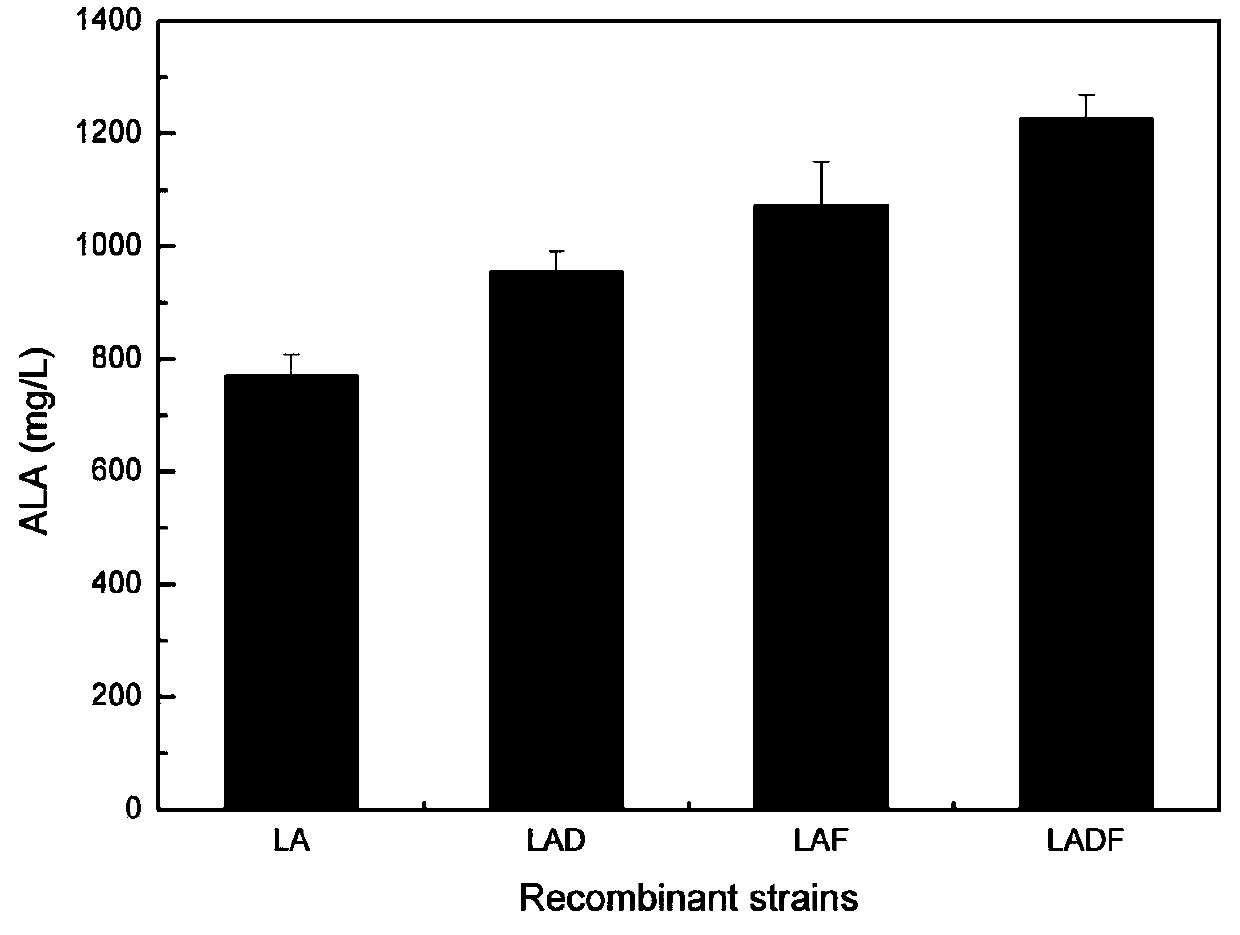
[0069] Different recombinant Escherichia coli and control bacteria were compared in fermentation experiments. Recombinant bacteria LAD, LAF and LADF were fermented to determine the ALA production as image 3 Shown: by expressing hemD and hemF alone and together, compared with the control strain LA, the ALA production is improved, and the ALA production is the highest under the situation of expressing the two enzyme genes at the same time, which is 1200mg / L ( image 3 ).
Embodiment 3
[0070] Embodiment 3 Recombinant bacteria LADF3L fermentation tank fermentation verification
[0071] Strains: LADF:E.coli BL21(DE3)pACYCDuet-hemLA pCDFDuet-hemD-hemF.
[0072] Recombinant Escherichia coli LADF was fermented and produced in a 3L fermenter with an inoculum size of 2%, an initial glucose concentration of 33g / L, and 0.1-0.5mMIPTG induction and corresponding antibiotics were added at 0h. As time changed, ALA began to accumulate in large quantities after 10h. At 30h, the ALA yield was the highest, which was 1800mg / L, and the fermentation period was significantly shortened ( Figure 4 ).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com