Recombinant microorganism for generating terpenoid and construction method thereof
一种重组菌、合成基因的技术,应用在生物领域,能够解决MEP途径效率低等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
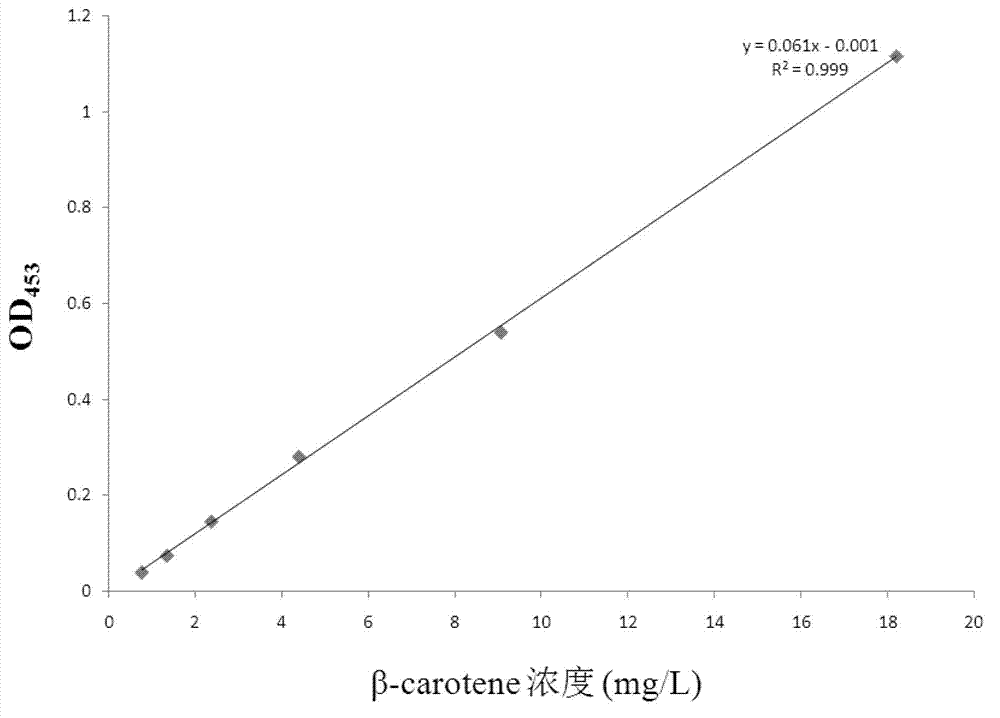
[0104] Embodiment 1, β-carotene synthesis gene is introduced into Escherichia coli to obtain recombinant Escherichia coli
[0105] 1. Construction of recombinant Escherichia coli ATCC8739 (pACYC184M-crt) by introducing β-carotene synthesis gene through plasmid
[0106]Escherichia coli itself can synthesize IPP, DMAPP and FPP through the MEP pathway and FPP synthetase. But Escherichia coli cannot synthesize β-carotene by itself. The β-carotene synthesis genes clustered under the same operon in Pantoea agglomerans, and the β-carotene synthesis gene cluster was composed of geranyl geranyl diphosphate (GGPP) synthase gene (crtE , SEQ ID NO: 1), β-carotene cyclase gene (crtX, SEQ ID NO: 2), lycopene β-cyclase gene (crtY, SEQ ID NO: 3), phytoene desaturase gene (crtI, SEQ ID NO: 4 ), phytoene synthase gene (crtB, sequence 5).
[0107] 1. Construction of recombinant Escherichia coli ATCC8739 (pACYC184-M-crt)
[0108] Introducing the β-carotene synthesis gene cluster into Escheric...
Embodiment 2
[0167] Example 2, construction and fermentation of recombinant Escherichia coli CAR001
[0168] The construction and fermentation of recombinant Escherichia coli CAR001 are divided into the following 8 steps:
[0169] 1. Improving the expression intensity of the β-carotene synthesis gene cluster in recombinant Escherichia coli QL002 and constructing recombinant Escherichia coli QL105
[0170]Recombinant Escherichia coli QL105 replaces the trc regulatory element (sequence 6 in the sequence listing) of the β-carotene synthesis gene cluster crtEXYIB in QL002 with the M1-12 artificial regulatory element (sequence 7 in the sequence listing) by two-step homologous recombination .
[0171] The artificial regulatory element is inserted in front of the gene to be regulated through two-step homologous recombination, and no resistance gene or FRT marker fragment is left after the operation. In the first step of homologous recombination, the original regulatory elements of the gene to b...
Embodiment 3
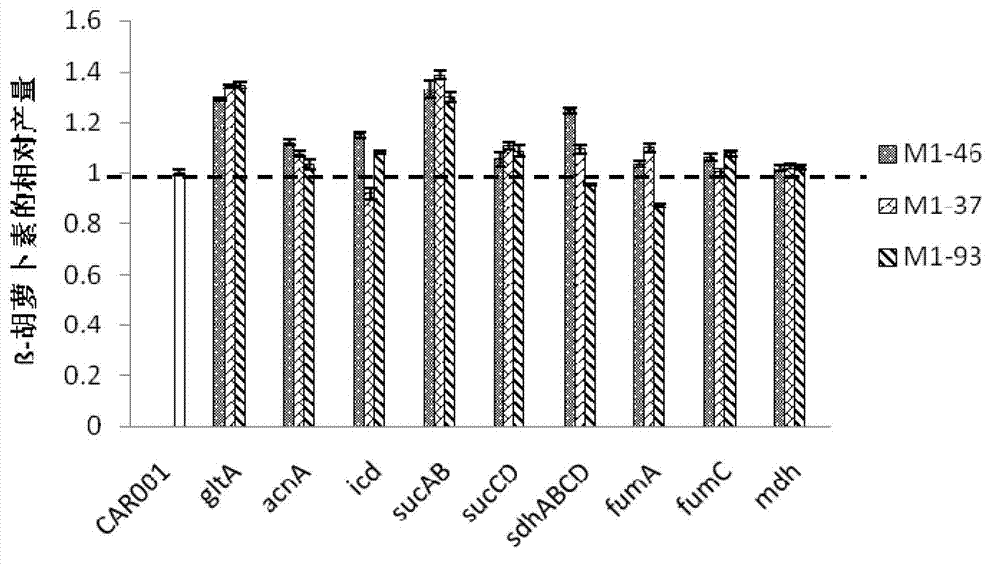
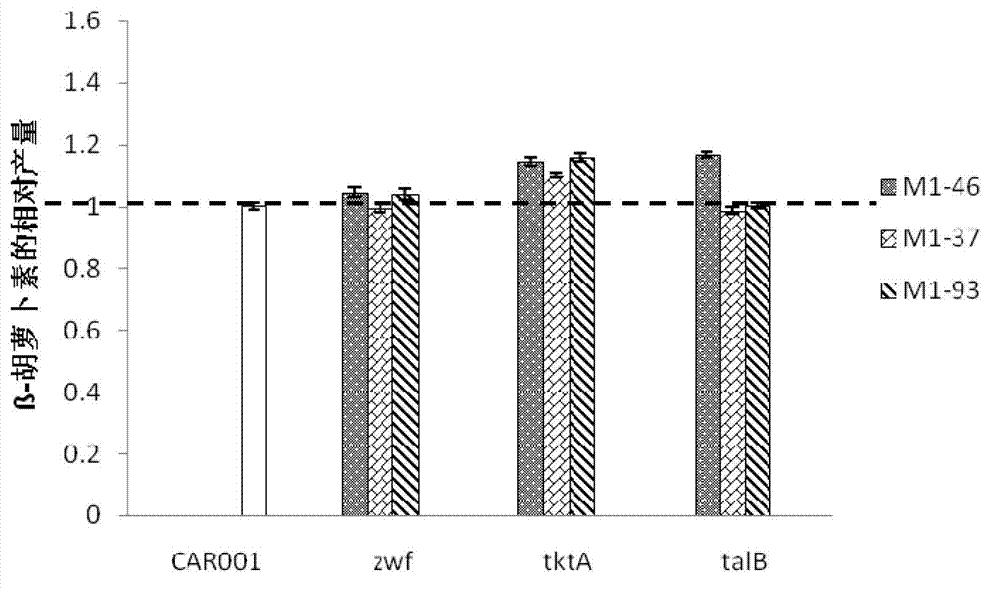
[0248] Example 3, Improving the expression intensity of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase gene of recombinant Escherichia coli CAR001
[0249] 1. Improve the expression intensity of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase gene of recombinant Escherichia coli CAR001 and construct recombinant bacteria SucAB46-FKF, SucAB37-FKF, SucAB93-FKF
[0250] Recombinant Escherichia coli SucAB46-FKF, SucAB37-FKF, and SucAB93-FKF are respectively replacing the original regulatory element (sequence 15) of the α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase gene (sucAB) of recombinant Escherichia coli CAR001 with artificial regulatory element M1 -46 (Sequence 14), M1-37 (Sequence 10), M1-93 (Sequence 11).
[0251] Through a pair of universal primers, the original regulatory regions of genes on the chromosome of Escherichia coli are replaced by artificial regulatory elements with various strengths by using a one-step homologous recombination method. The upstream primer is gene-up-FRT, including 50 bases outside the original ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com