Patents
Literature
253results about How to "Light intensity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
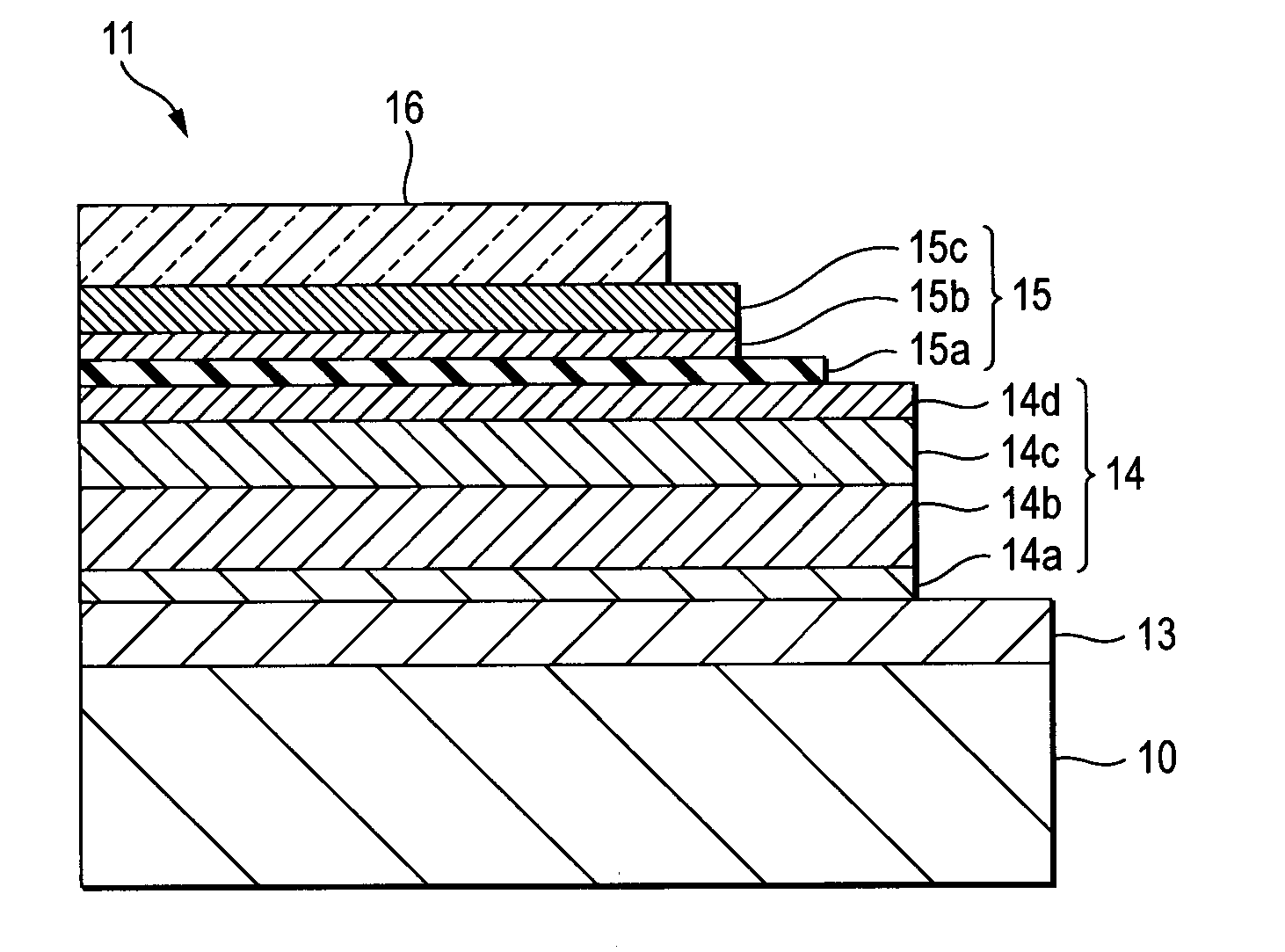
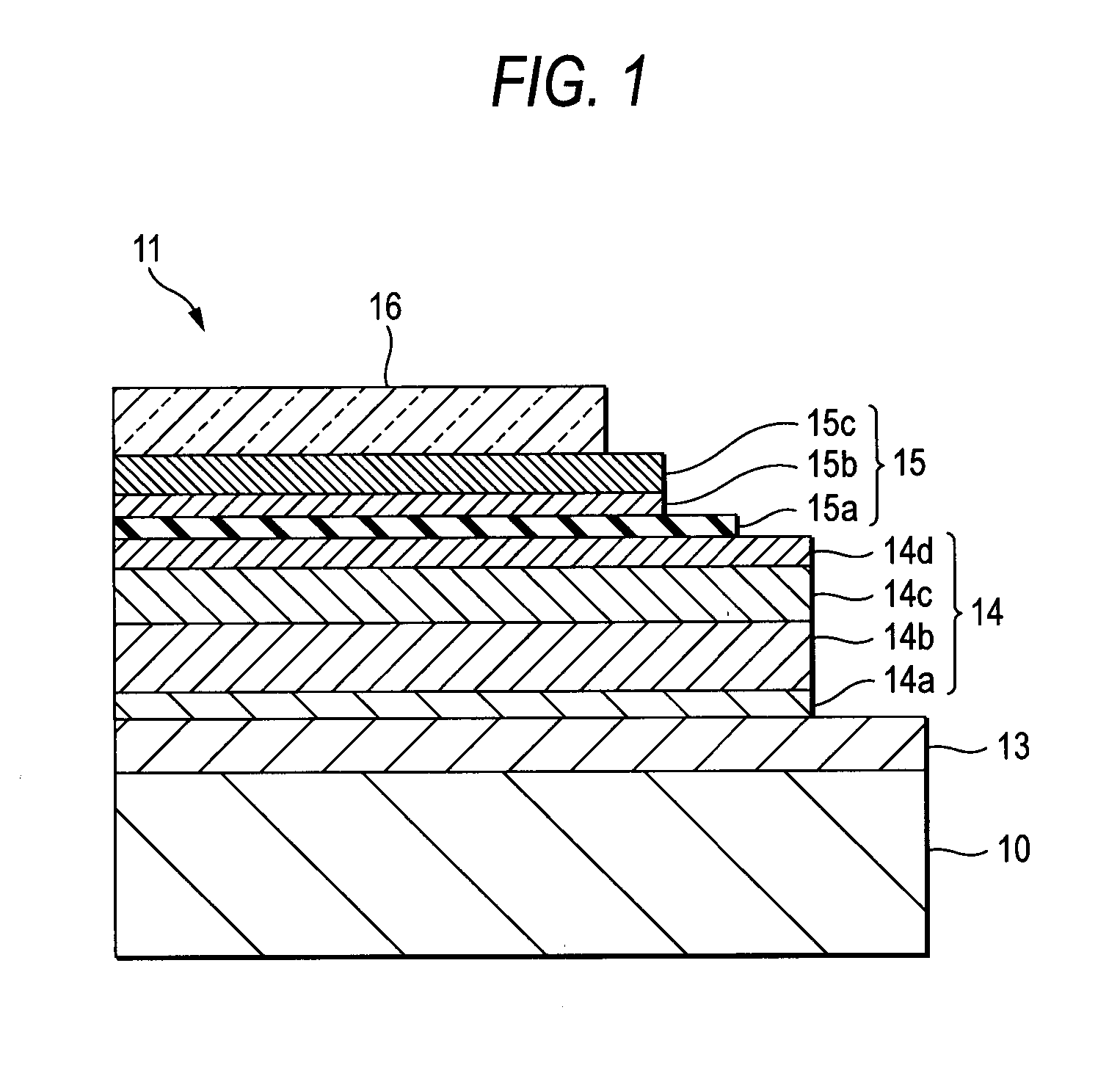
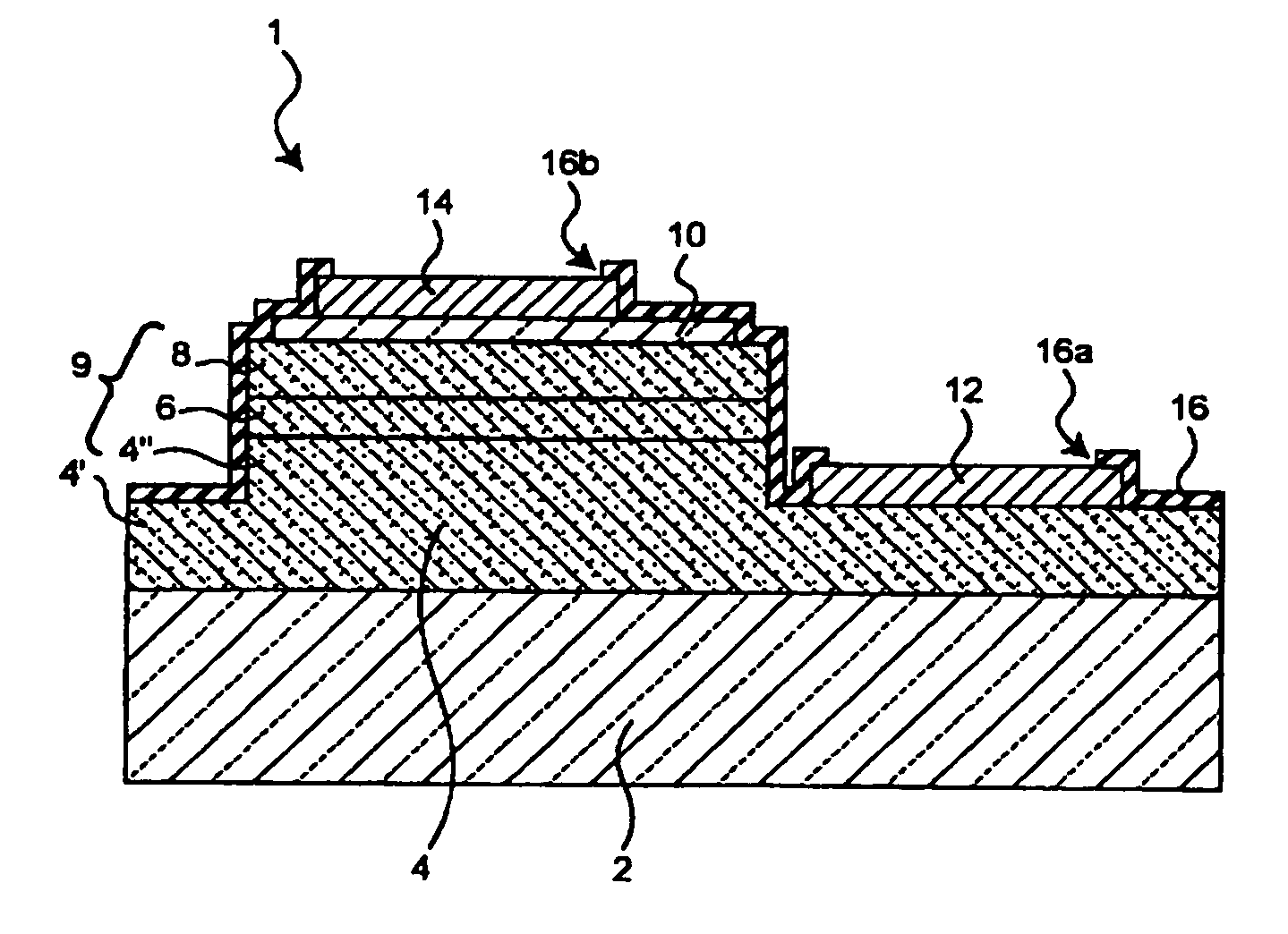
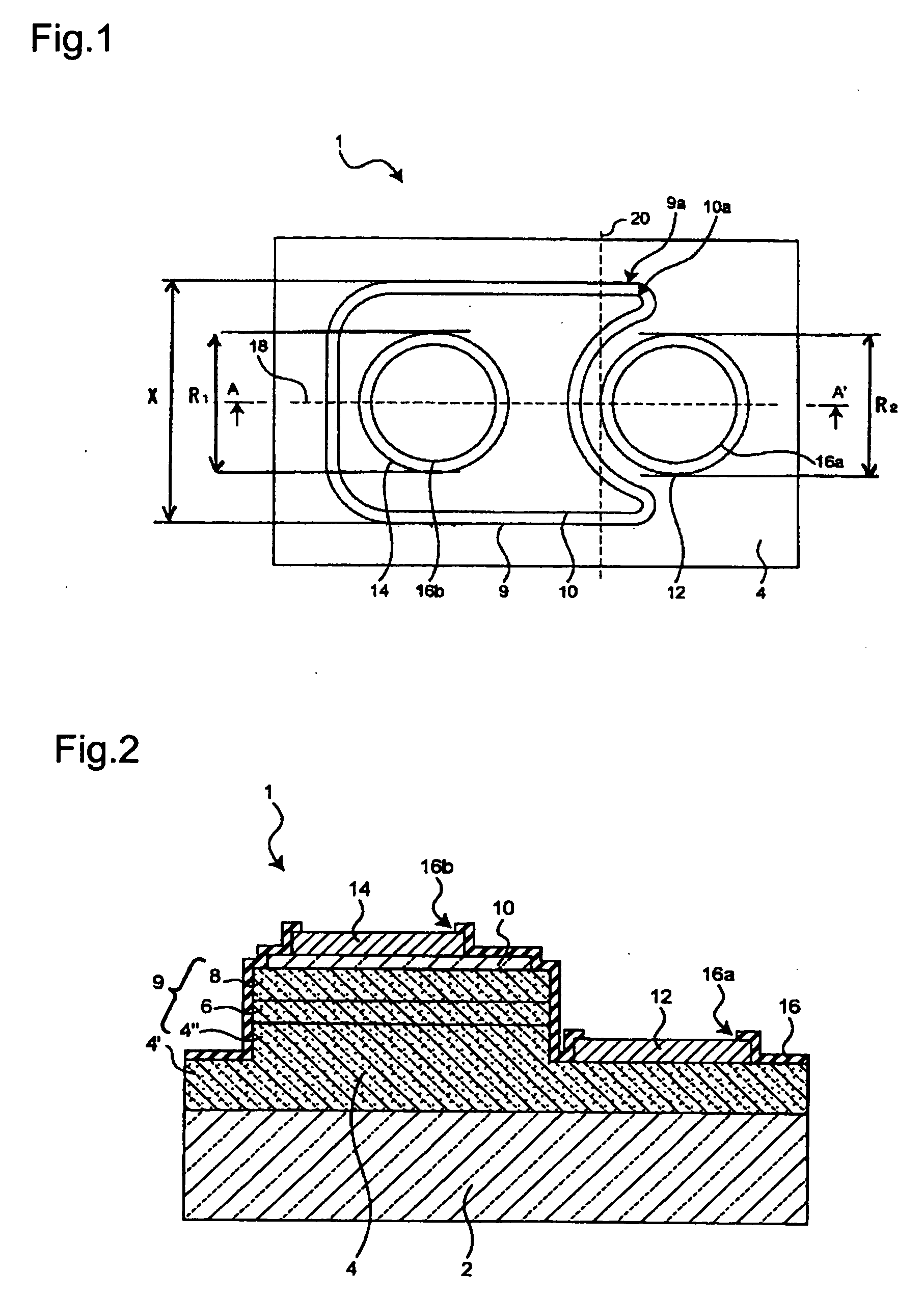
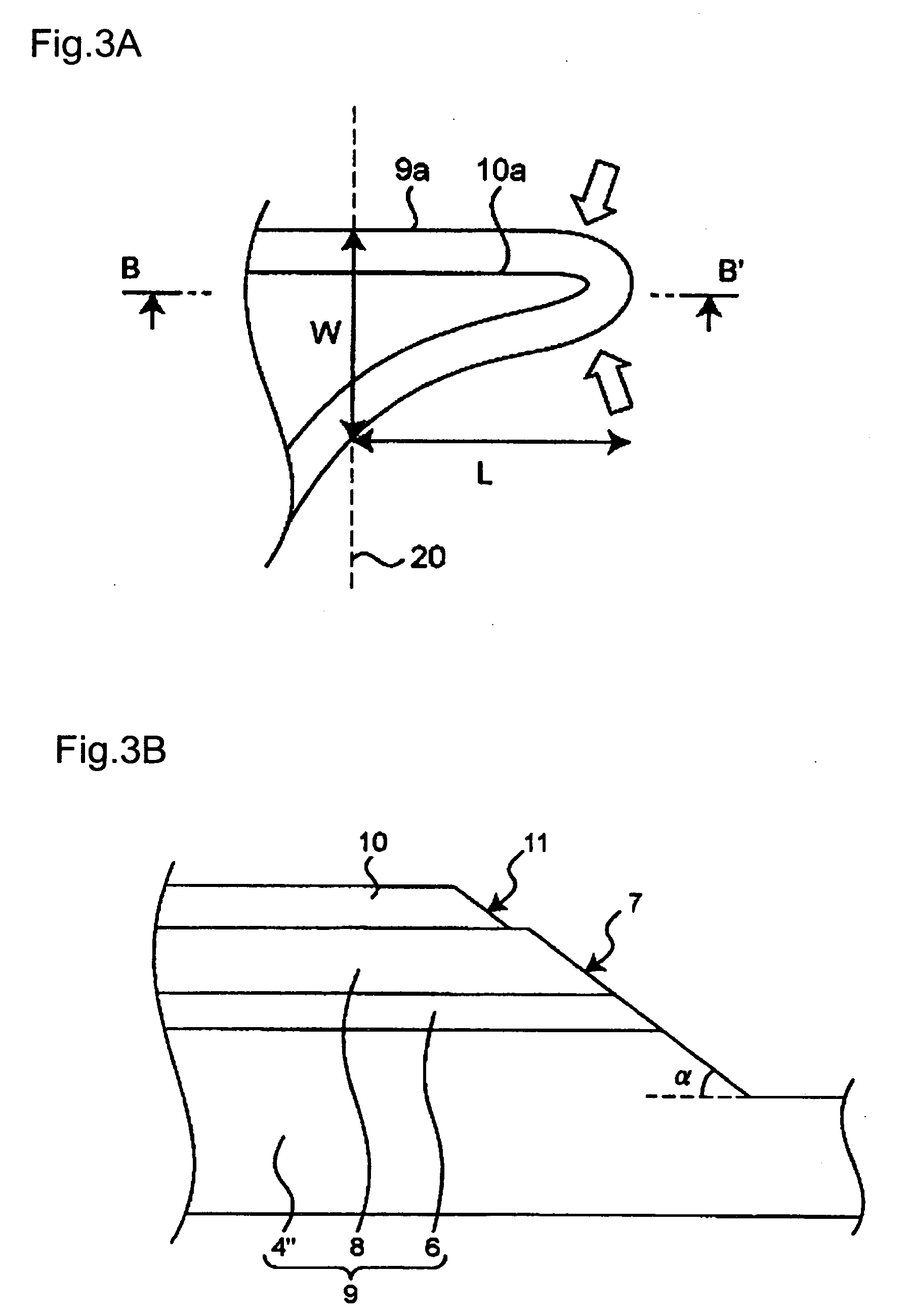
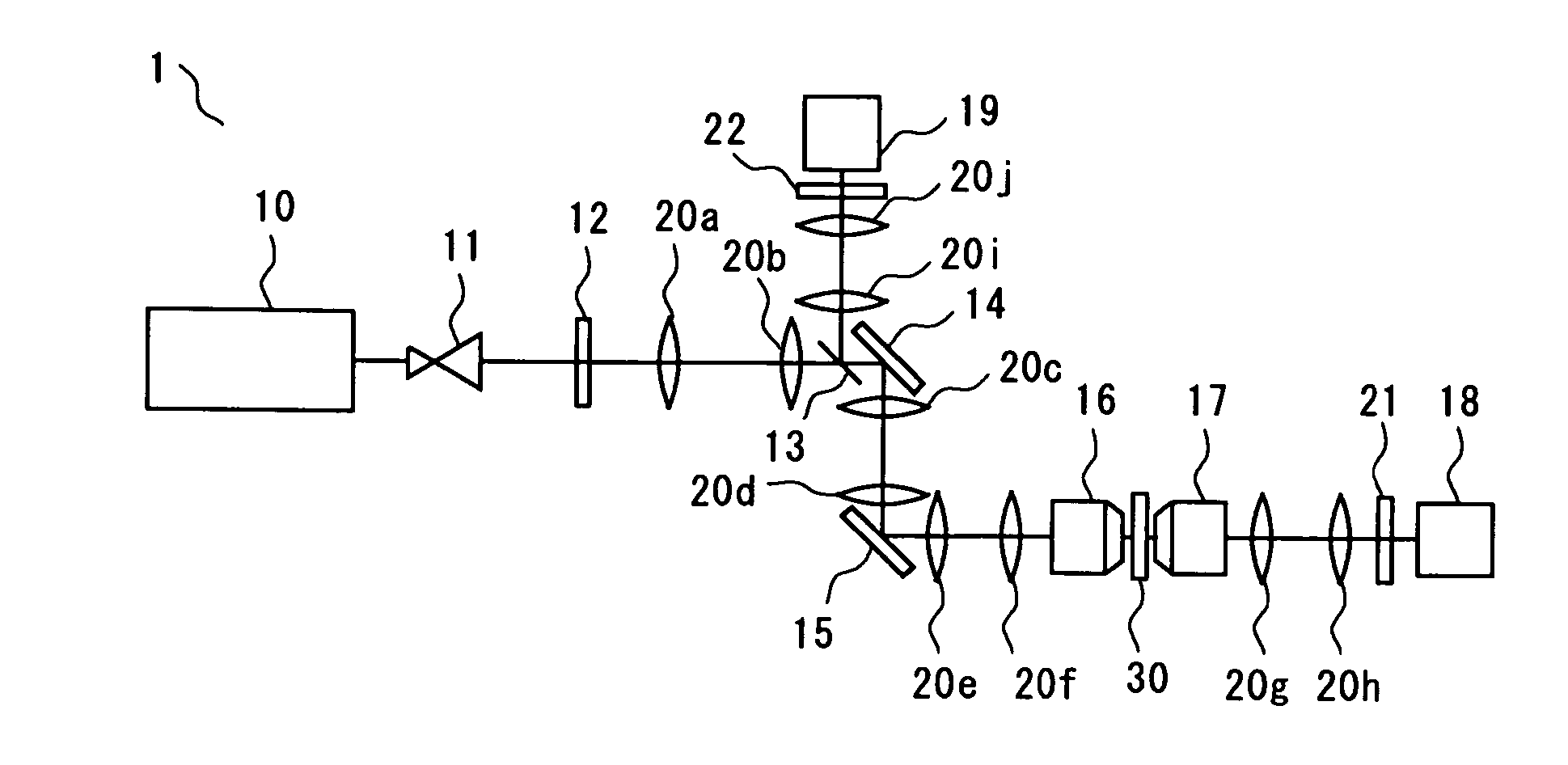
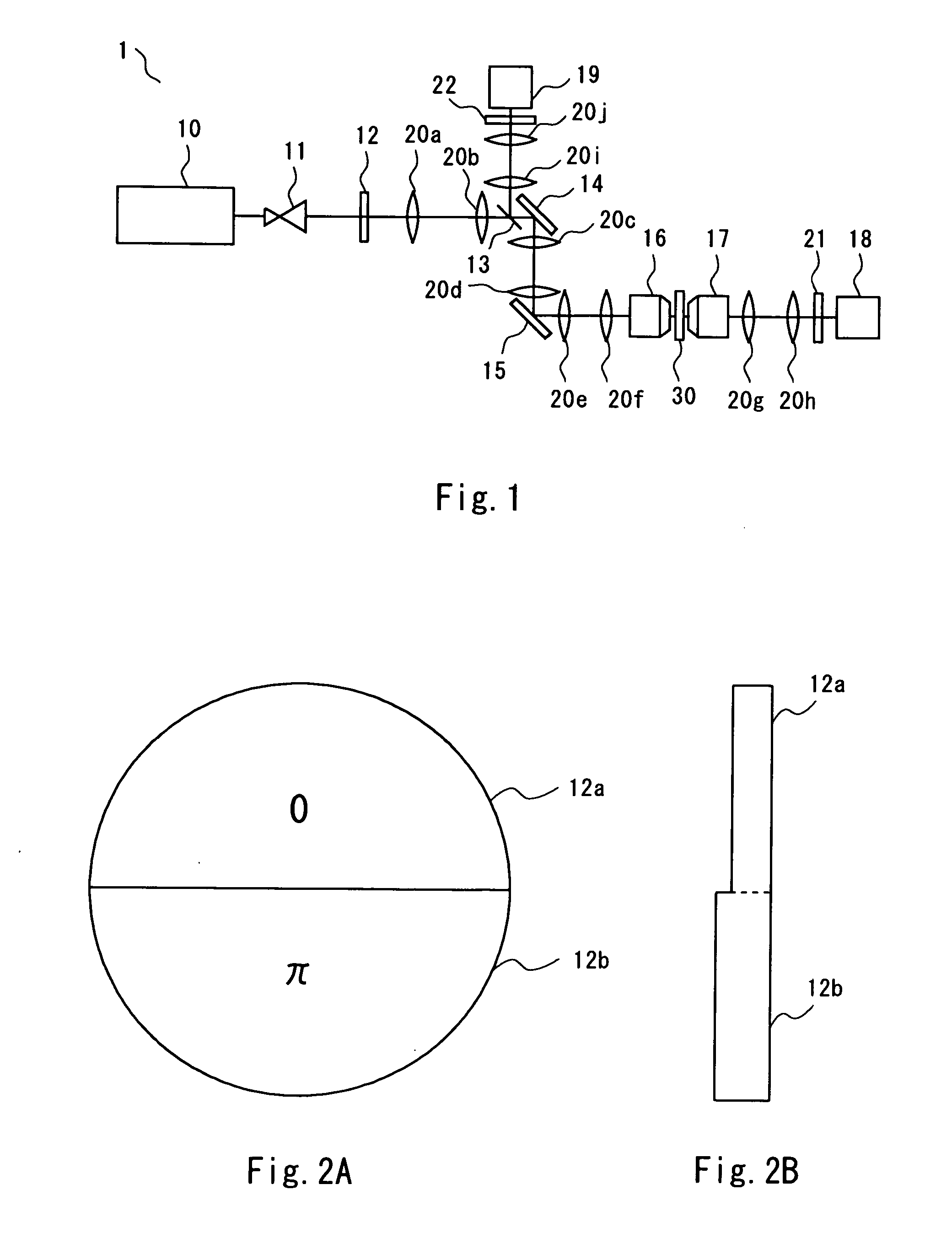
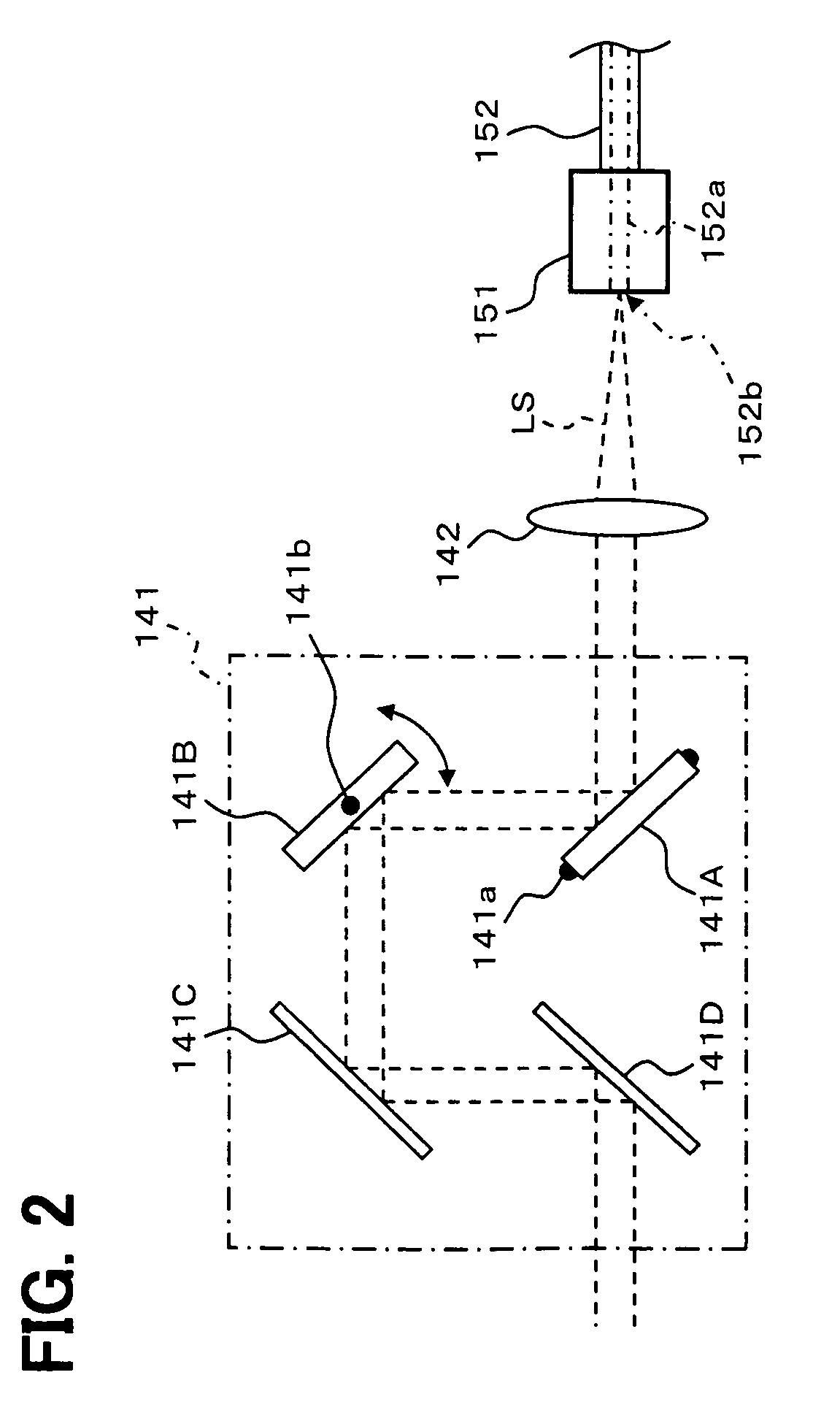
Display device with a cavity structure for resonating light
InactiveUS7102282B1Shifting amount is very smallIncreased peak intensityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesSpectral widthPhase shifted
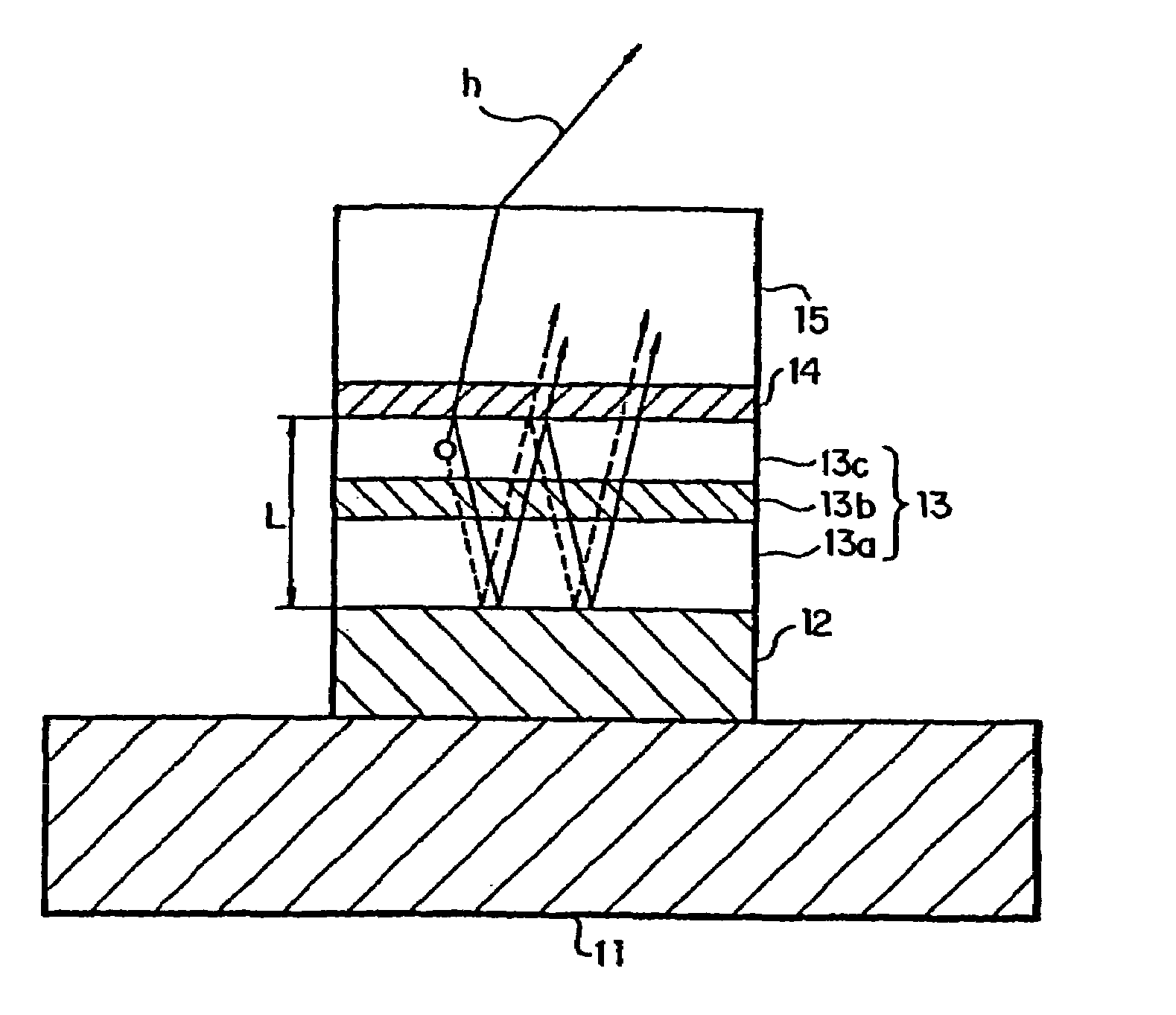
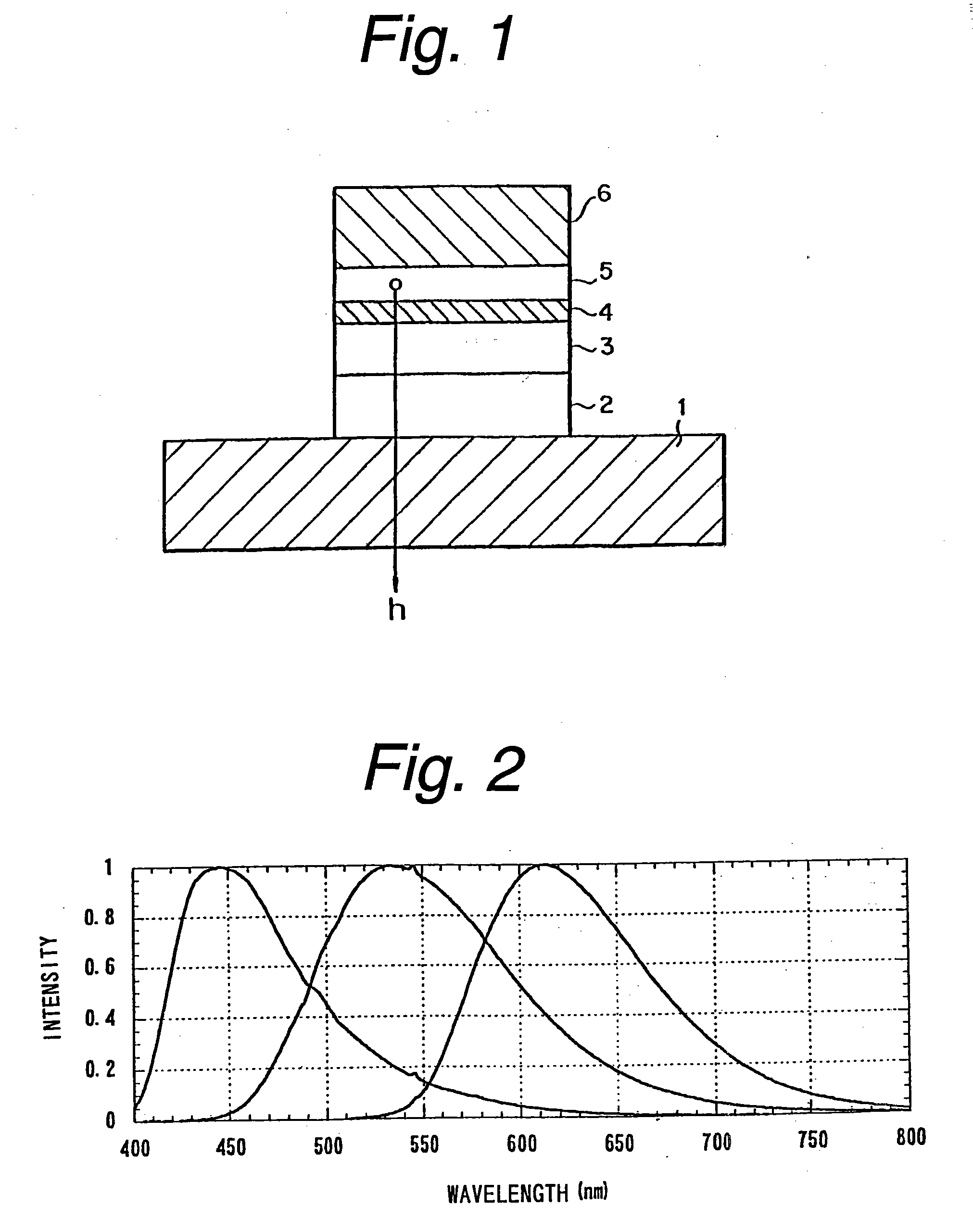
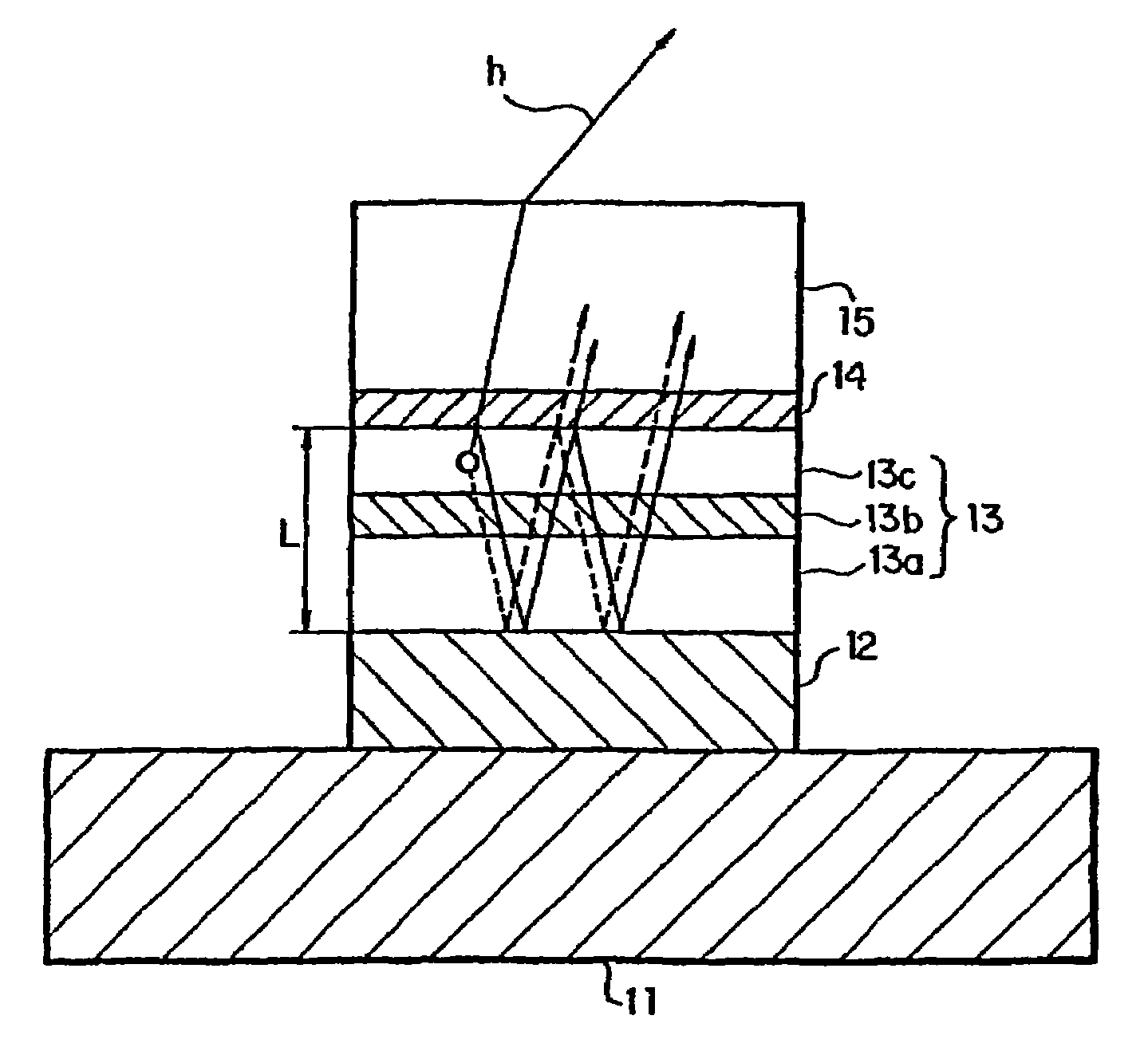
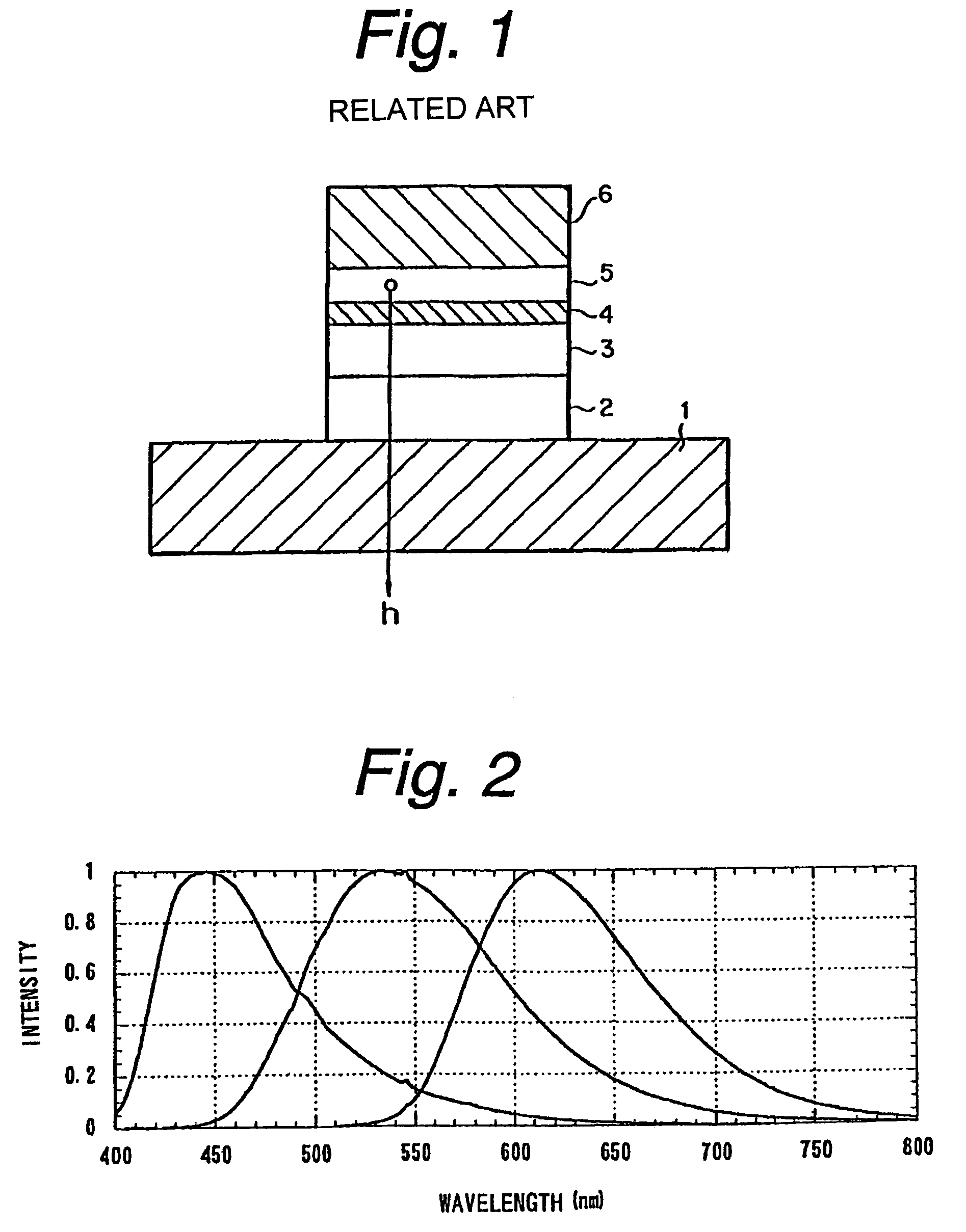
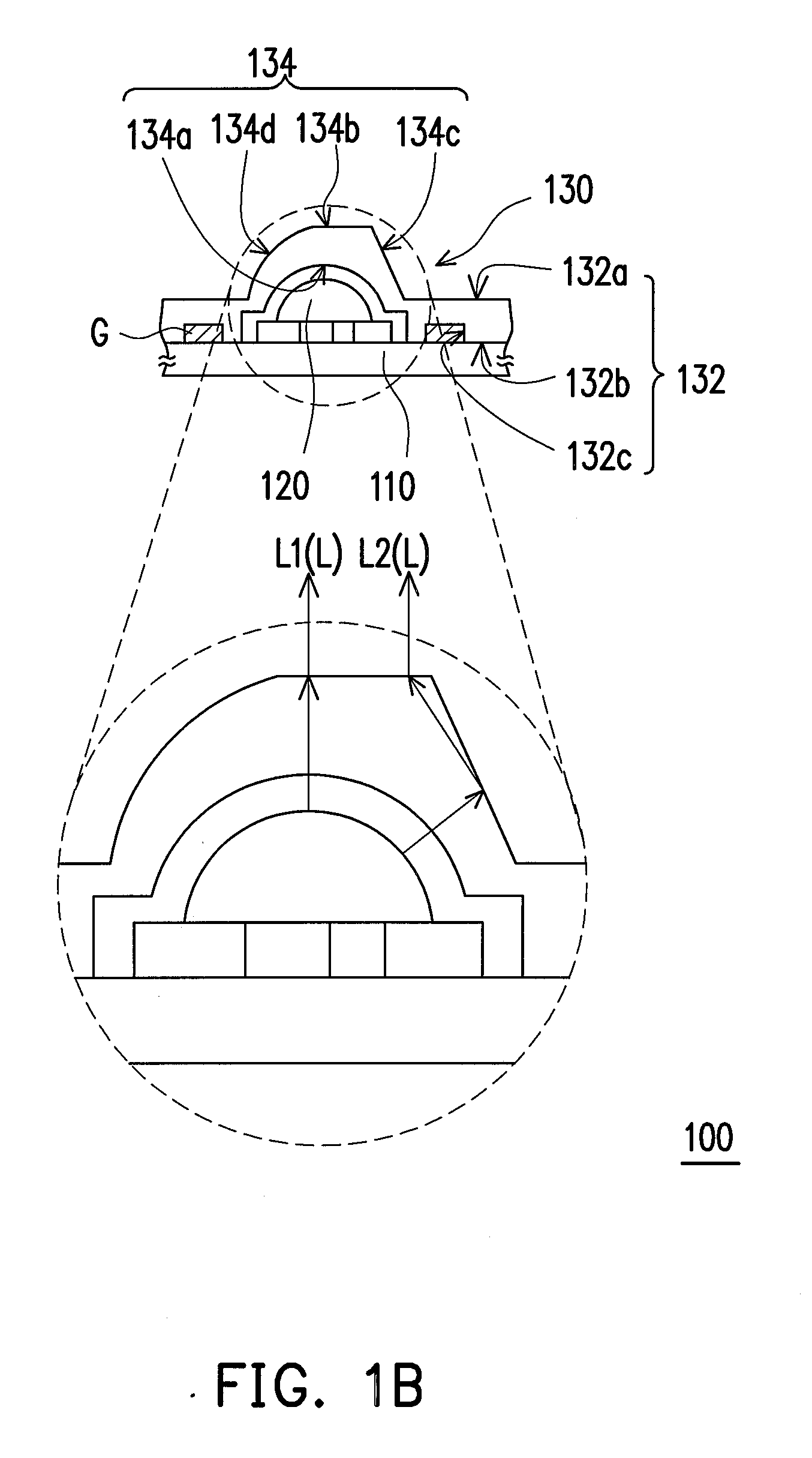
In an organic EL device having a first electrode of a light reflective material, organic layer including an organic light emitting layer, semitransparent reflection layer, and second electrode of a transparent material that are stacked sequentially, and so configured that the organic layer functions as a cavity portion of a cavity structure, light that resonates in a certain spectral width (wavelength λ) is extracted by so configuring that optical path length L becomes minimum in a range satisfying (2L) / λ+Φ(2Π)=m (m is an integer) where the phase shift produced in light generated in the organic light emitting layer when reflected by opposite ends of the cavity portion is Φ radians, L is optical path length of the cavity portion, and λ is the peak wavelength of the spectrum of part of light to be extracted.
Owner:SONY CORP
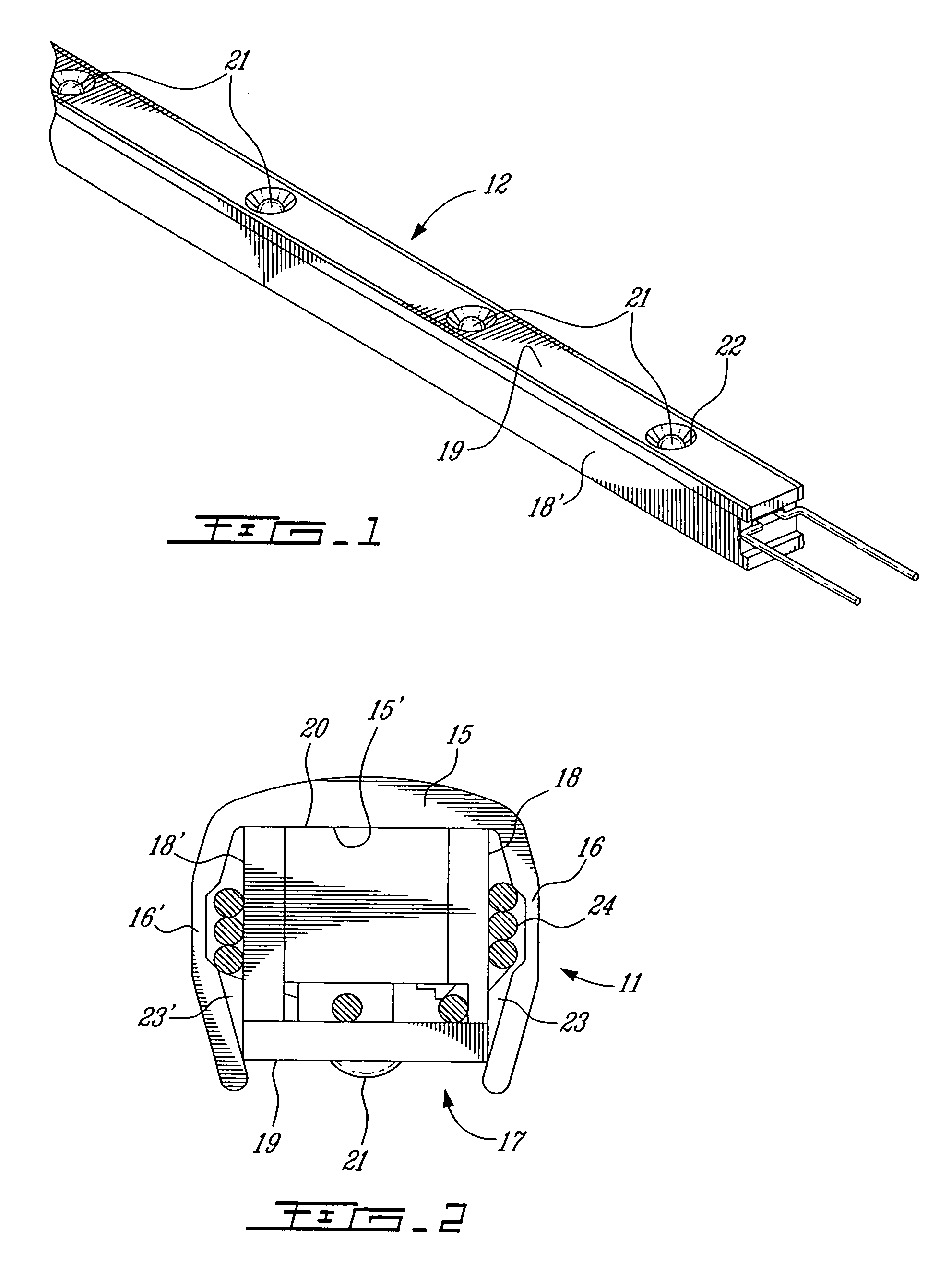
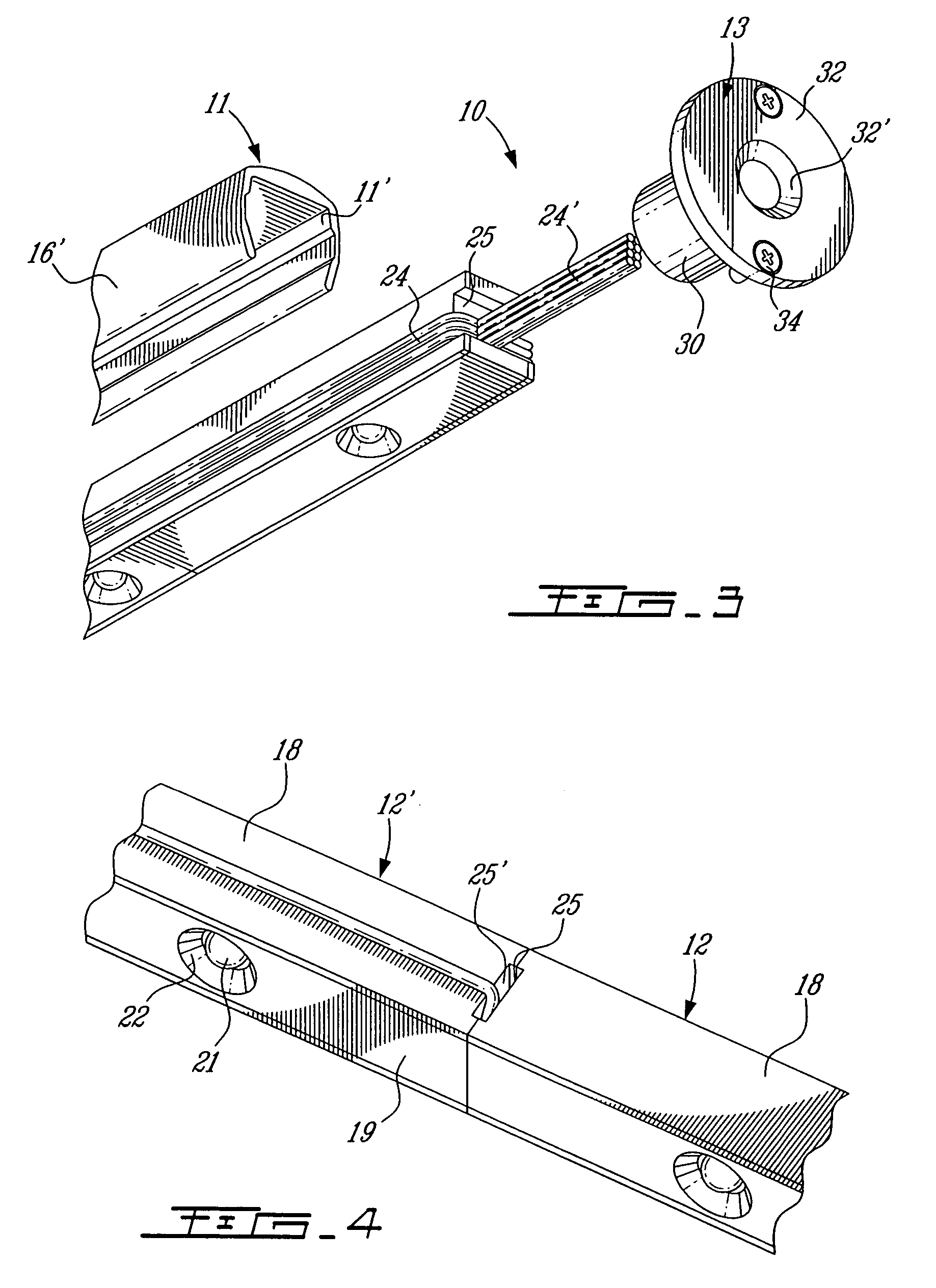
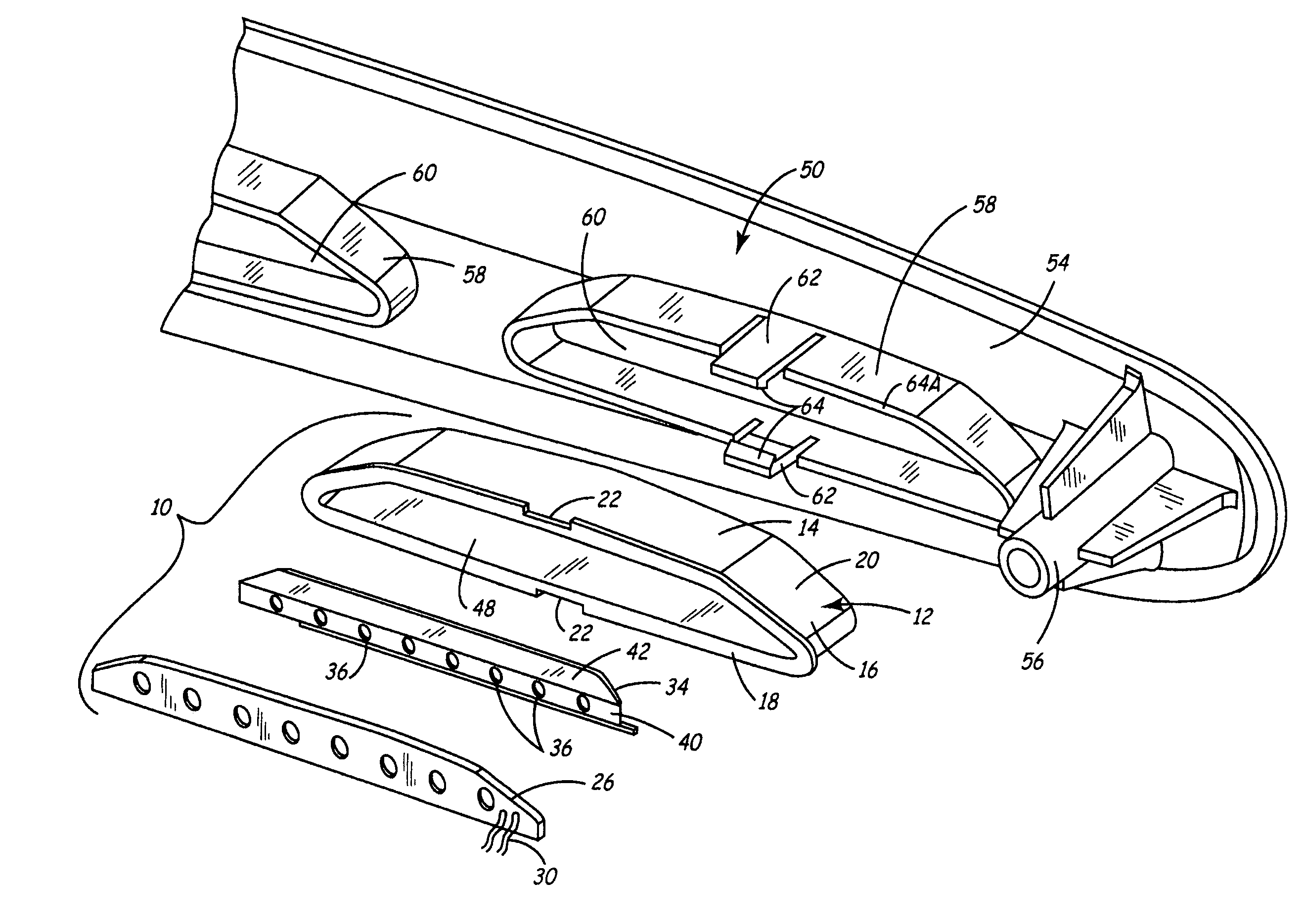
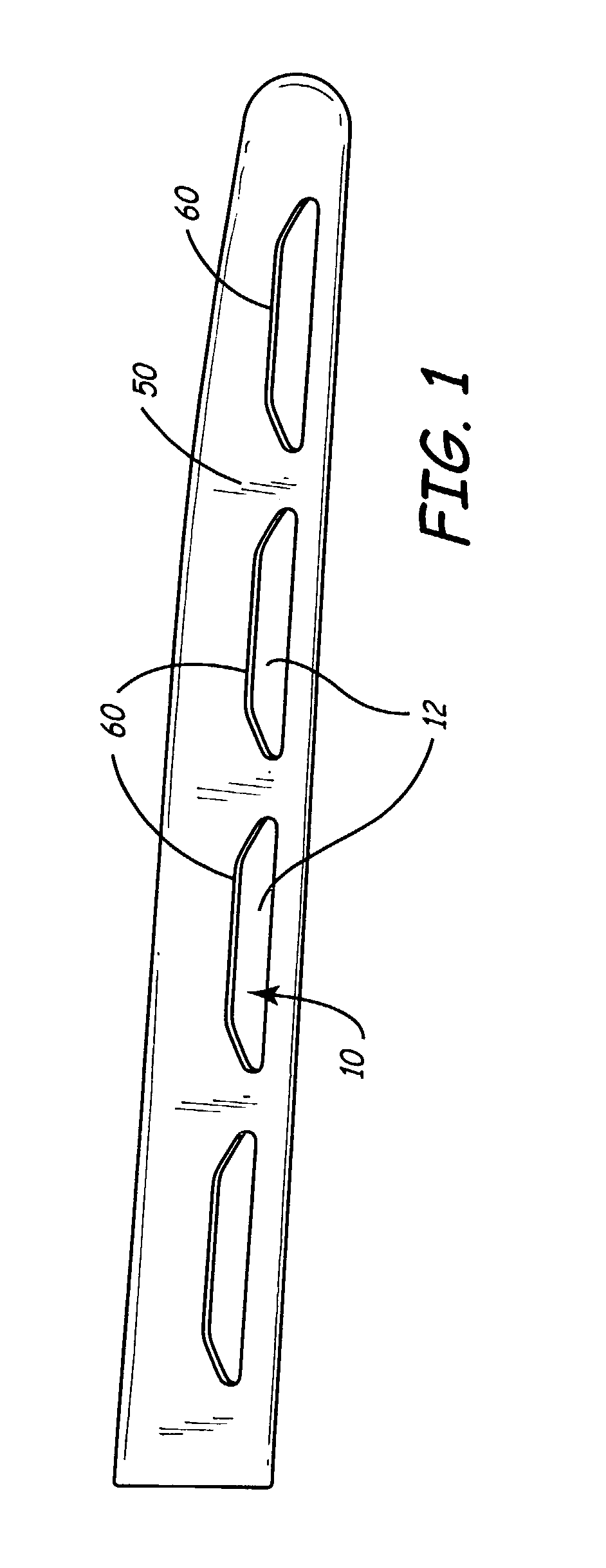
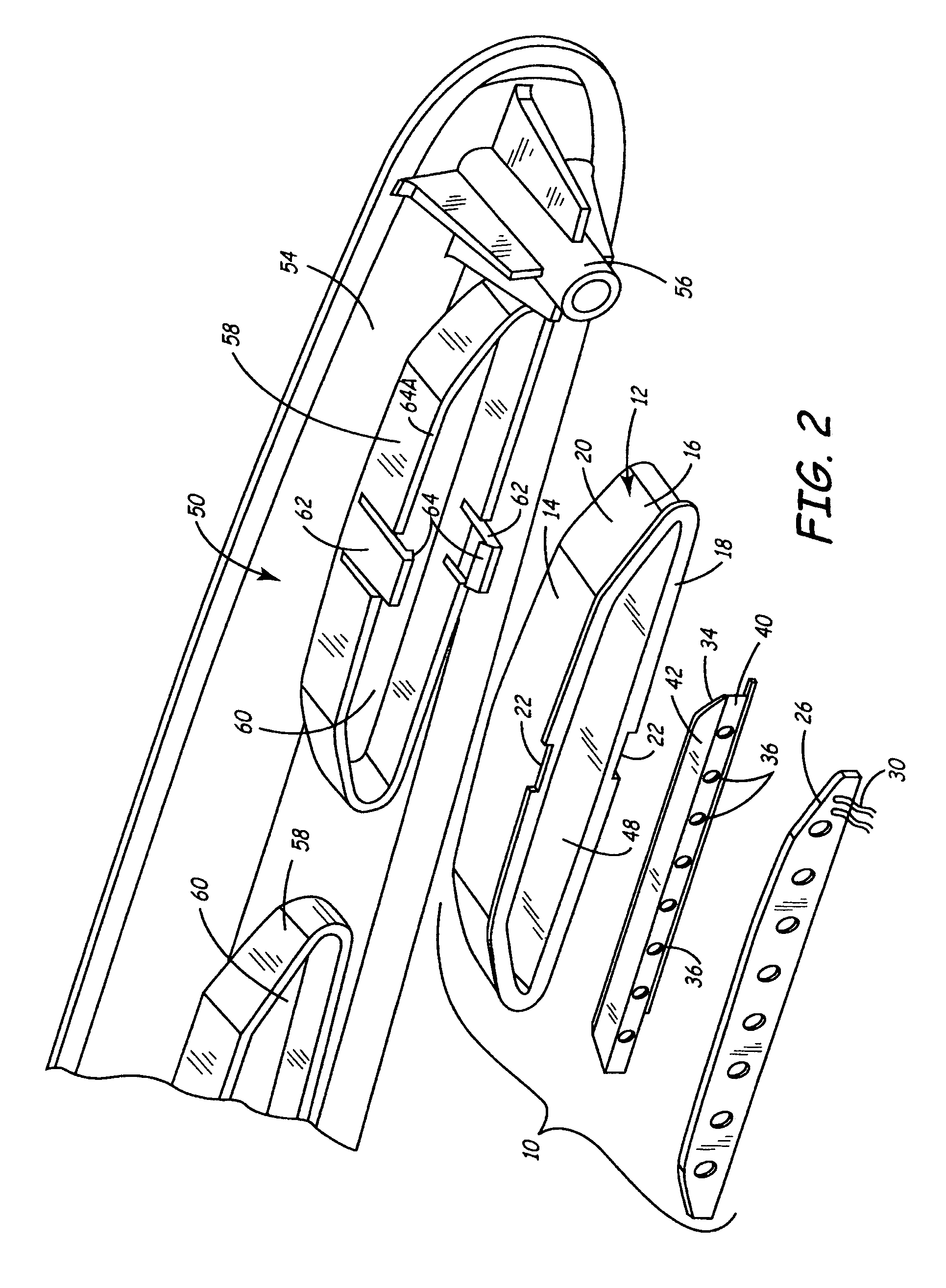
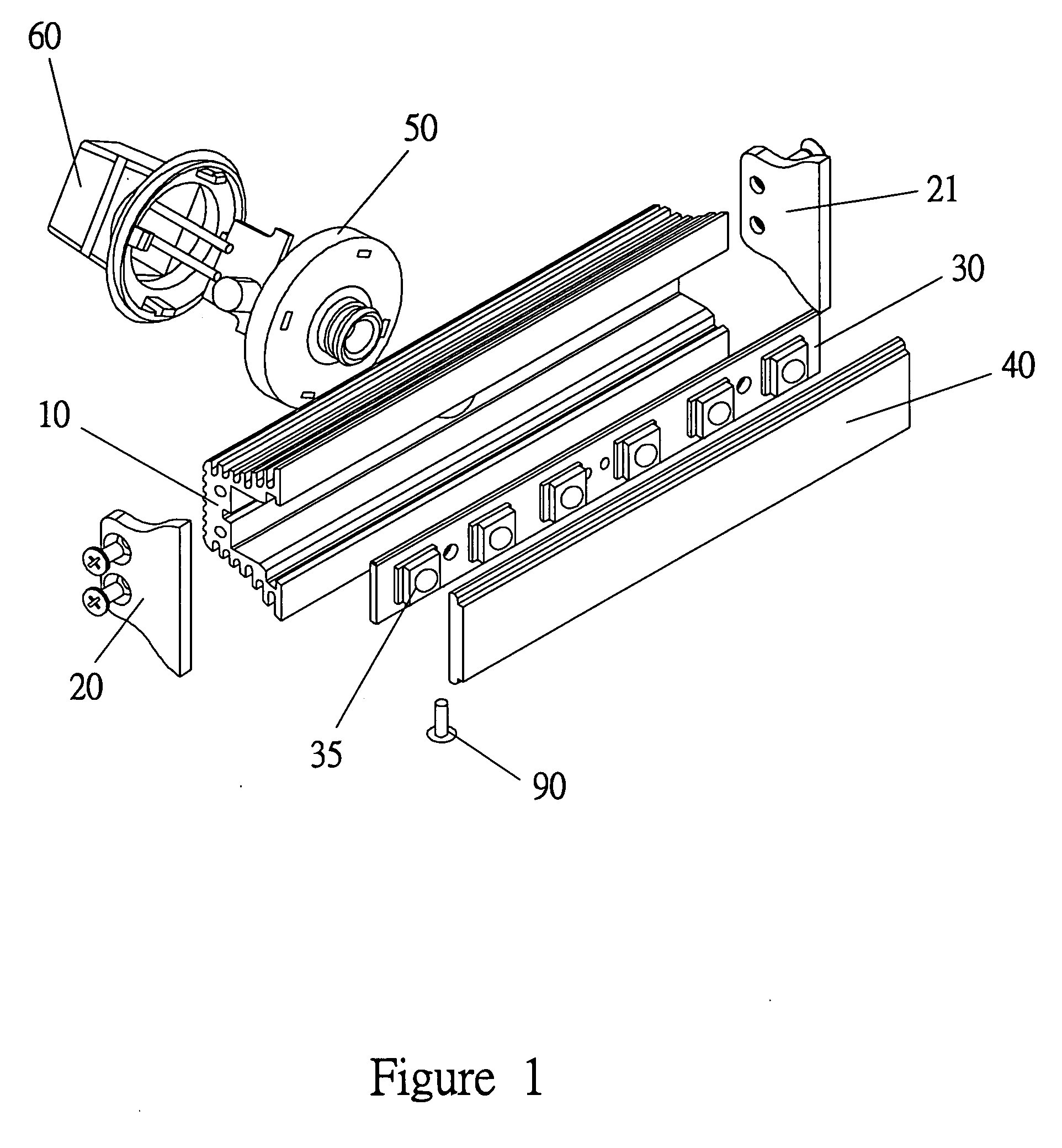
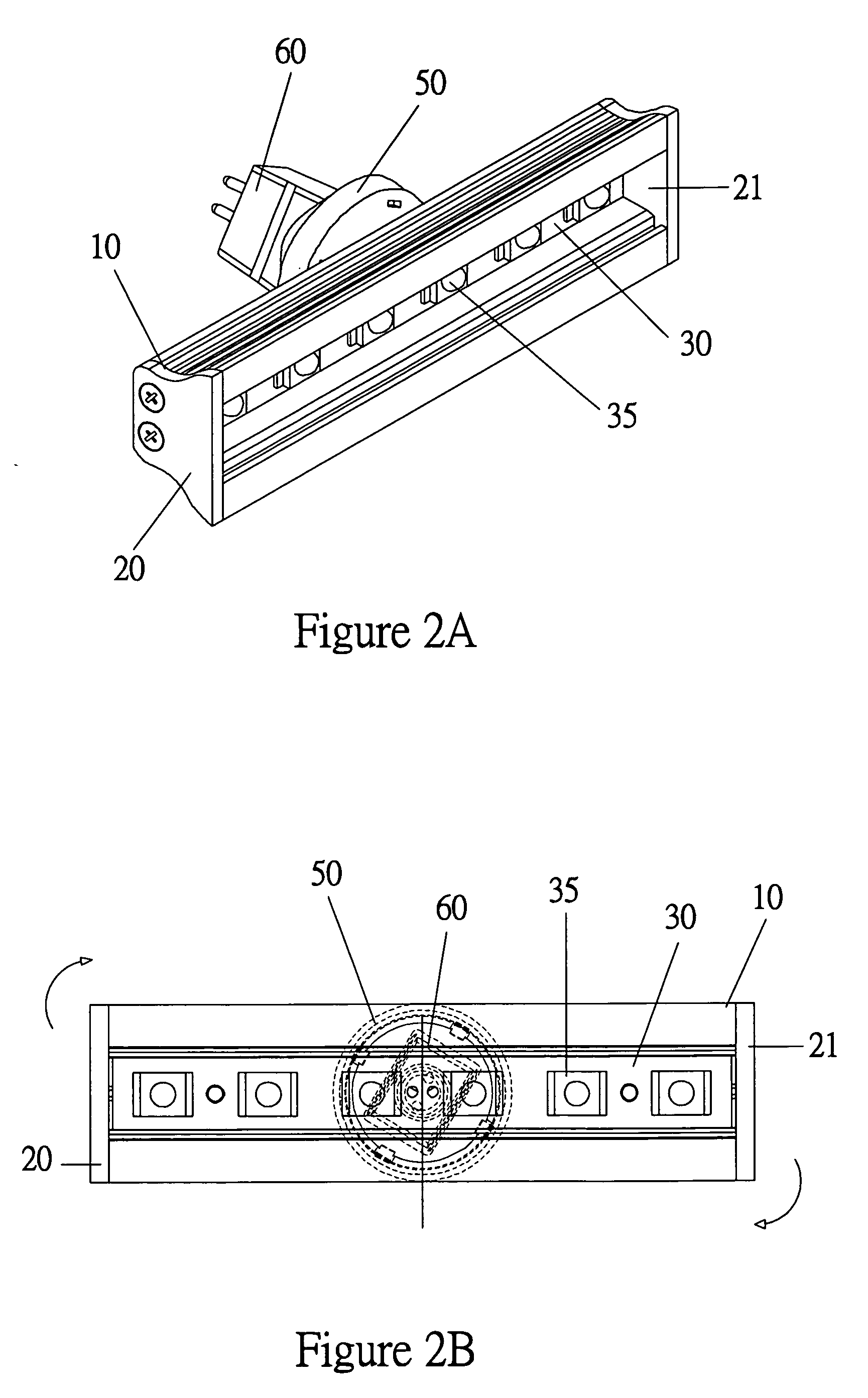
LED light bar assembly
InactiveUS7296912B2Increase intensityLight intensityShow cabinetsPoint-like light sourceEngineeringLED lamp
An LED (light emitting diode) light bar assembly is comprised of an elongated casing having an elongated cavity of substantially U-shape cross-section. The casing has a base wall, opposed side walls and an elongated open end between the side walls. One or more elongated heat sink LED modules each having two or more LEDs and electrical component parts thereof are retained in each of the modules. The LEDs are exposed in a spaced-apart relationship in a common wall of the modules. The casing is configured to removably receive and retain one or more of the modules therein in end-to-end relationship. The casing defines in combination with the one or more modules, at least one internal channel for the passage of wiring which is non-visible exteriorly of the module. At least one end connector is detachably securable to an end of the casing for securing the casing to a support structure. The connector has an internal passage for receiving wiring from the modules retained in the casing.
Owner:BEAUCHAMP PIERRE J
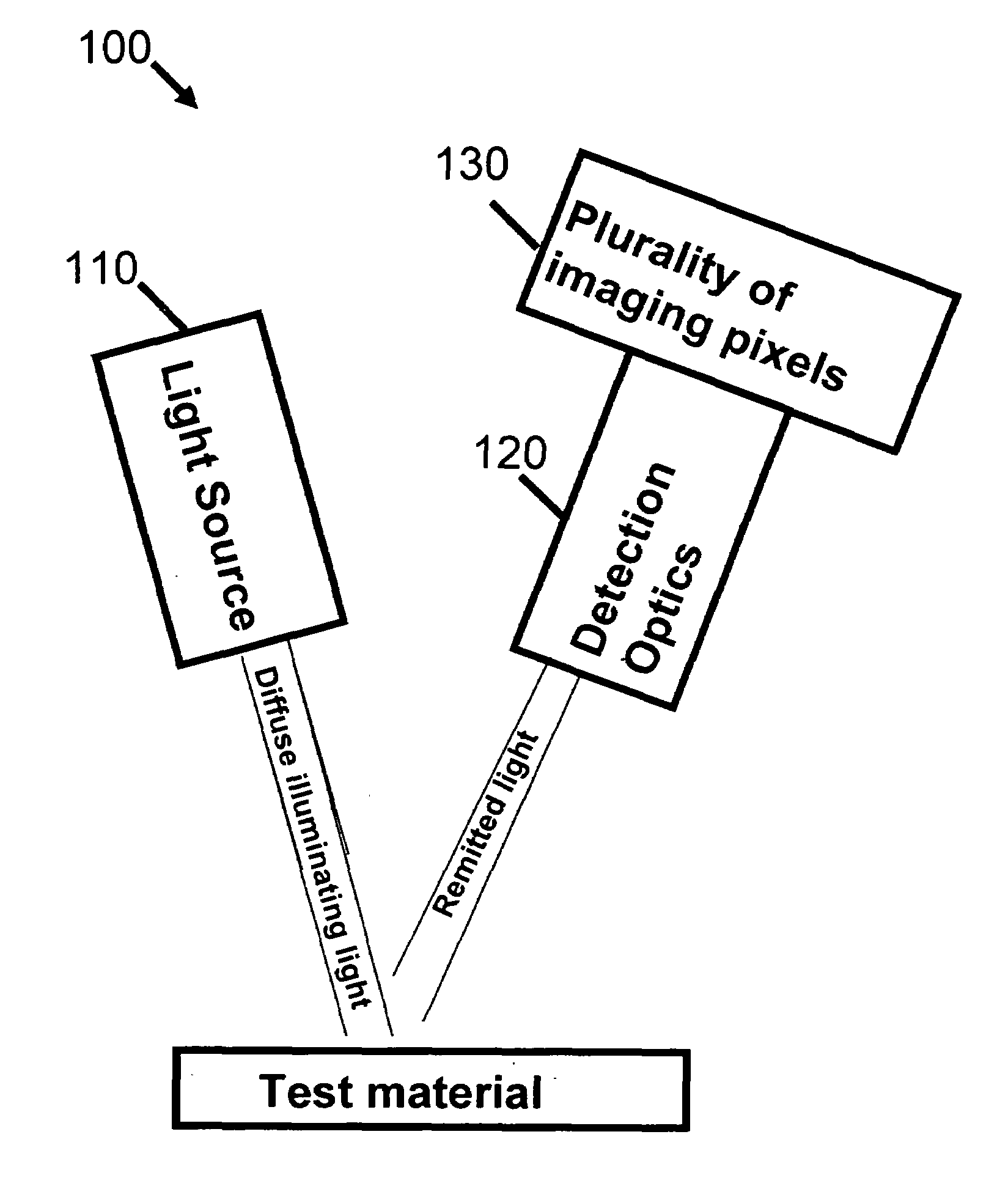
System and method for imaging sub-surface polarization-sensitive material structures
InactiveUS7289211B1Light intensityConvenient lightingPolarisation-affecting propertiesDiagnostic recording/measuringAngle of incidenceMedical imaging
A method of visually quantifying a test material along with an imaging apparatus for practicing the method is disclosed. The method comprises: (a) illuminating the test material at a known angle of incidence with diffuse light of a known and adjustable polarization state; (b) receiving light from the test material with a polarization state modified by the test material; (c) measuring an intensity of the polarization components of the received light for each illuminated pixel substantially simultaneously; (d) calculating the Stokes Vector in two dimensions for each illuminated pixel; and (e) creating an image map for the known polarization state. The method may also include adjusting the known polarization or the incident angle of the diffuse light to create additional image maps. The method and apparatus are intended for use in medical imaging including minimally invasive surgery.
Owner:WALSH JR JOSEPH T +1
Near field lens
ActiveUS20080310159A1Brighter light intensityLight intensityPoint-like light sourcePortable electric lightingCamera lensLight source
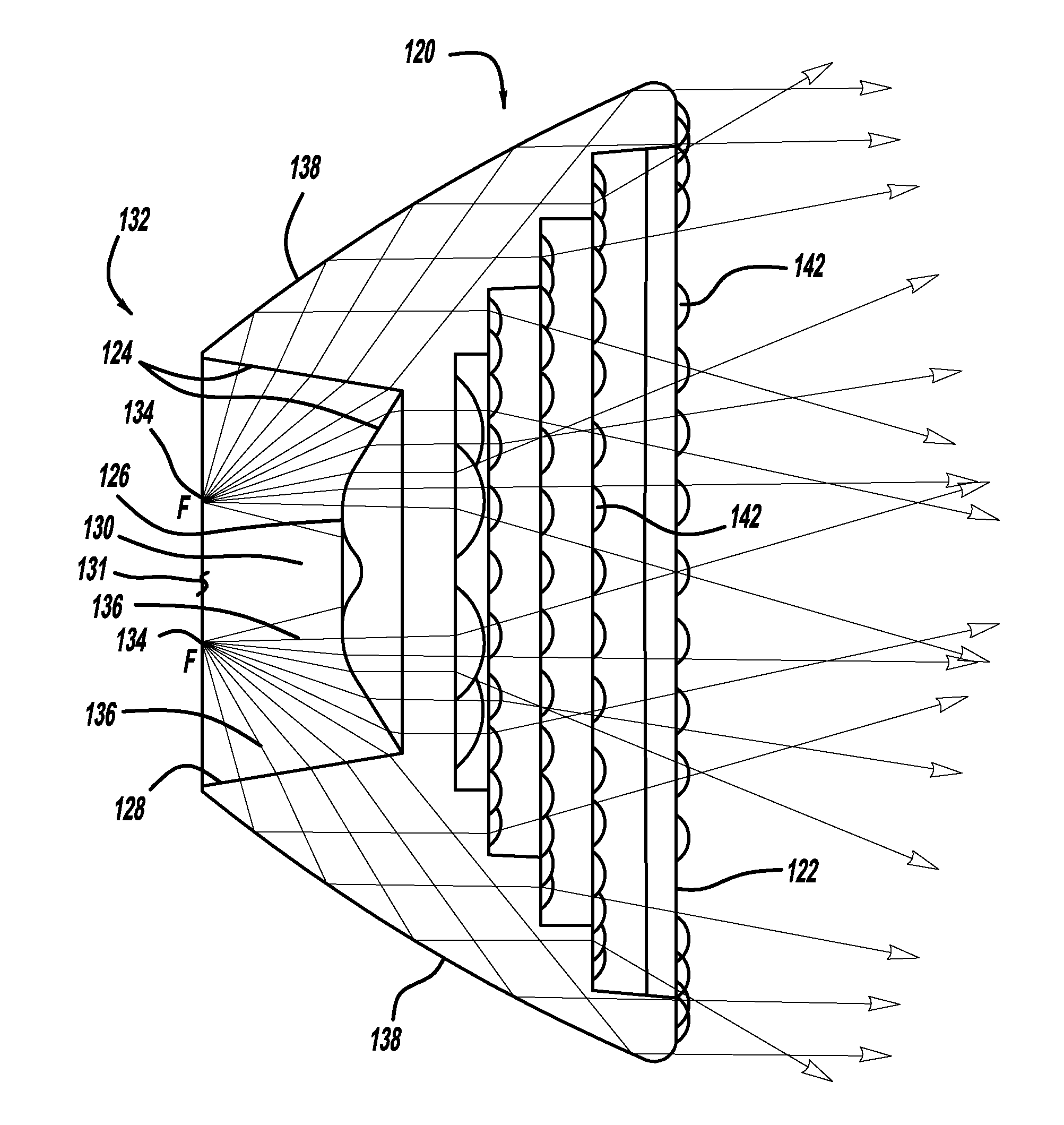
A lens has a main body for use with at least one light source. The main body has a light-emitting face, a light-collecting face disposed opposite the light-emitting face, and a plurality of focal points, the latter of which form a focal ring. A central axis extends through the light-collecting face and the light-emitting face. The main body is substantially radially symmetrical about the central axis and the focal ring extends around the central axis of the main body of the lens.
Owner:VARROC LIGHTING SYST SRO
Organic electroluminescence device
InactiveUS20060220534A1Reduce probabilityLight emission efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic electroluminescenceElectrically conductive
An organic electroluminescence device including a lower electrode disposed on a substrate, an organic layer having at least a light emission layer and disposed above the lower electrode, and upper electrode having a transparent conductive film and disposed above the organic layer, in which the device has an electron injecting layer between the organic layer and the upper electrode. The electron injecting layer has a buffer layer comprising an insulative material and a mixed layer comprising an organic material that has an electron transporting property and a metal material that has an electron injecting property.
Owner:SONY CORP
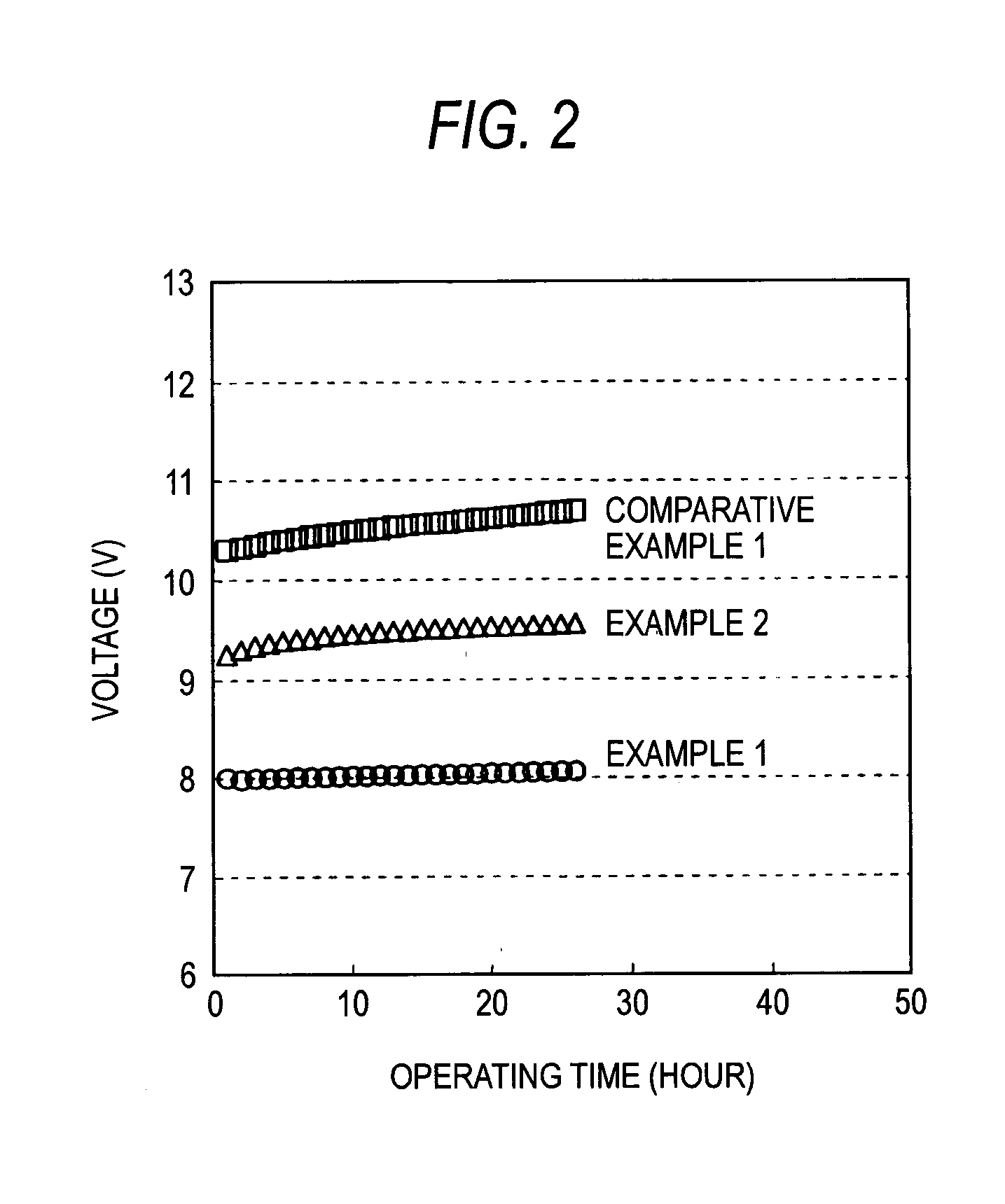
Display device
InactiveUS20060175966A1Reducing reflection of external lightIncrease contrastIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensSpectral widthPhase shifted
In an organic EL device having a first electrode of a light reflective material, organic layer including an organic light emitting layer, semitransparent reflection layer, and second electrode of a transparent material that are stacked sequentially, and so configured that the organic layer functions as a cavity portion of a cavity structure, light that resonates in a certain spectral width (wavelength λ) is extracted by so configuring that optical path length L becomes minimum in a range satisfying (2L) / λ+Φ((2π)=m (m is an integer) where the phase shift produced in light generated in the organic light emitting layer when reflected by opposite ends of the cavity portion is Φ radians, L is optical path length of the cavity portion, and λ is the peak wavelength of the spectrum of part of light to be extracted.
Owner:SONY CORP
Electrically driven hair removal device
InactiveUS6871402B2Convenient lightingImprove convenienceMetal working apparatusHair removalEngineering
An electrically operated hair removing device, comprising a housing, an operating system connected to the housing for clipping and / or plucking hair, the system having at least two operating elements which are movable relative to one another and at least one of which is driven, and an illumination device for illuminating the operating system, the illumination device being integrated in at least one of the operating elements.
Owner:BRAUN GMBH
Power control circuit and method
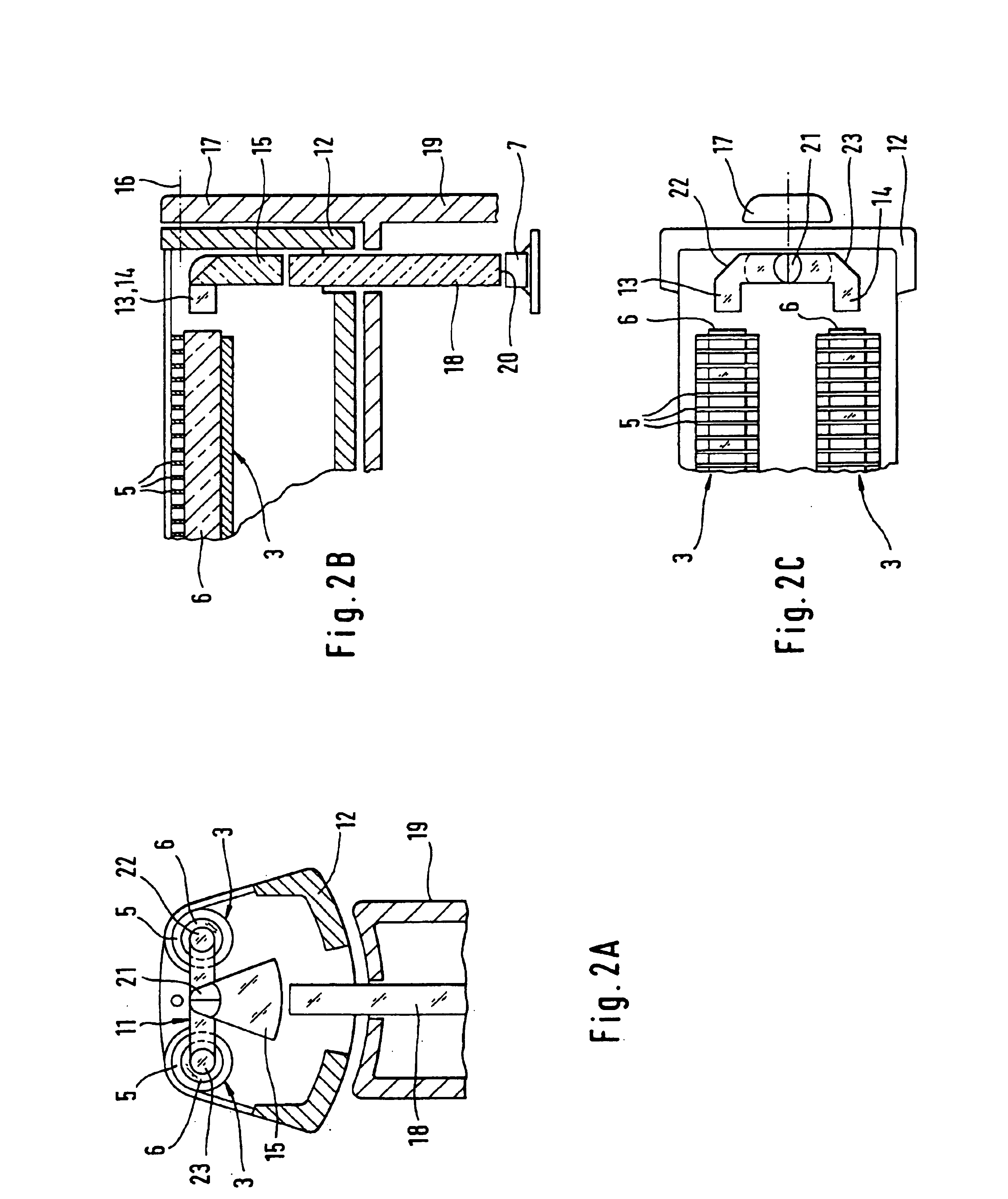
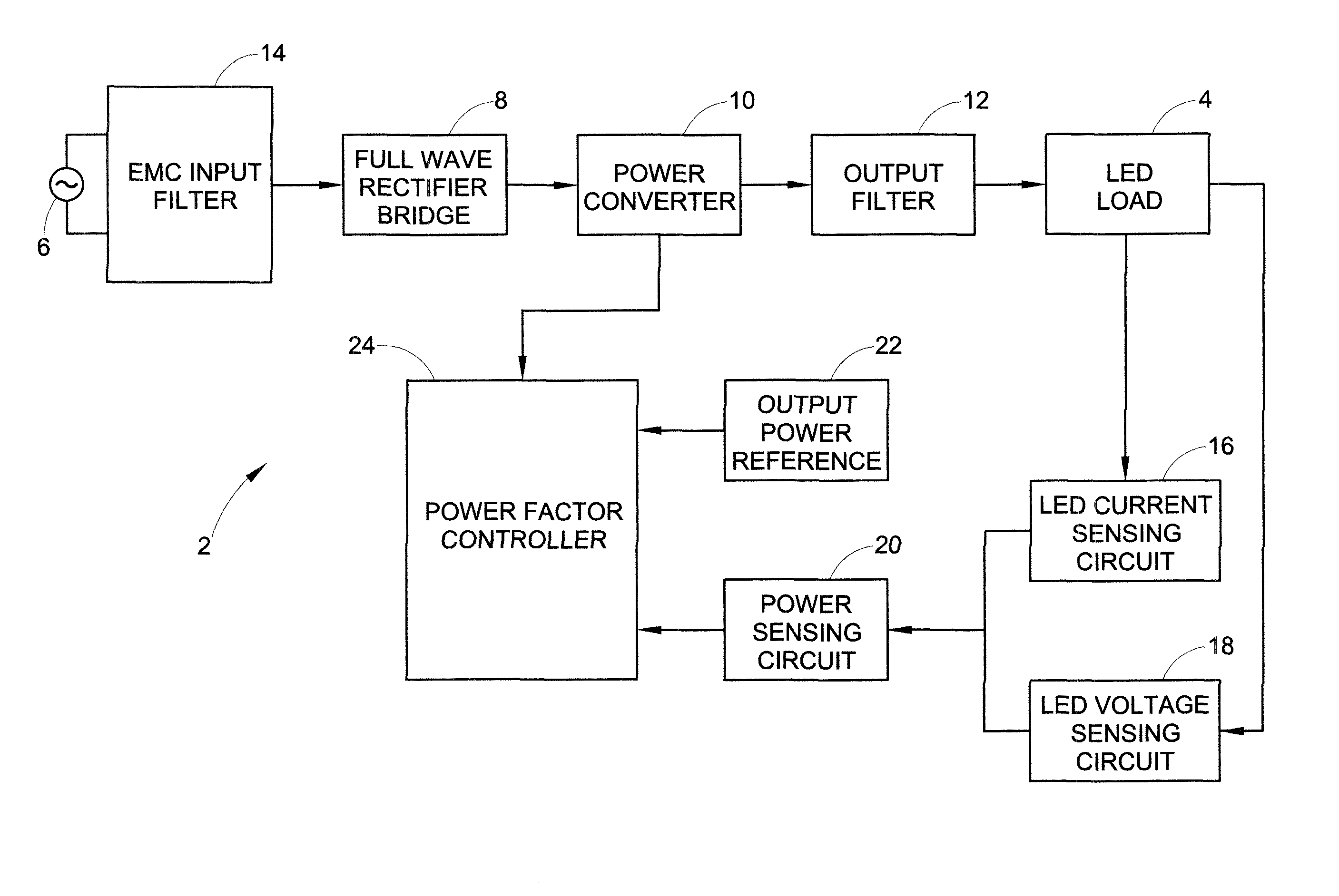
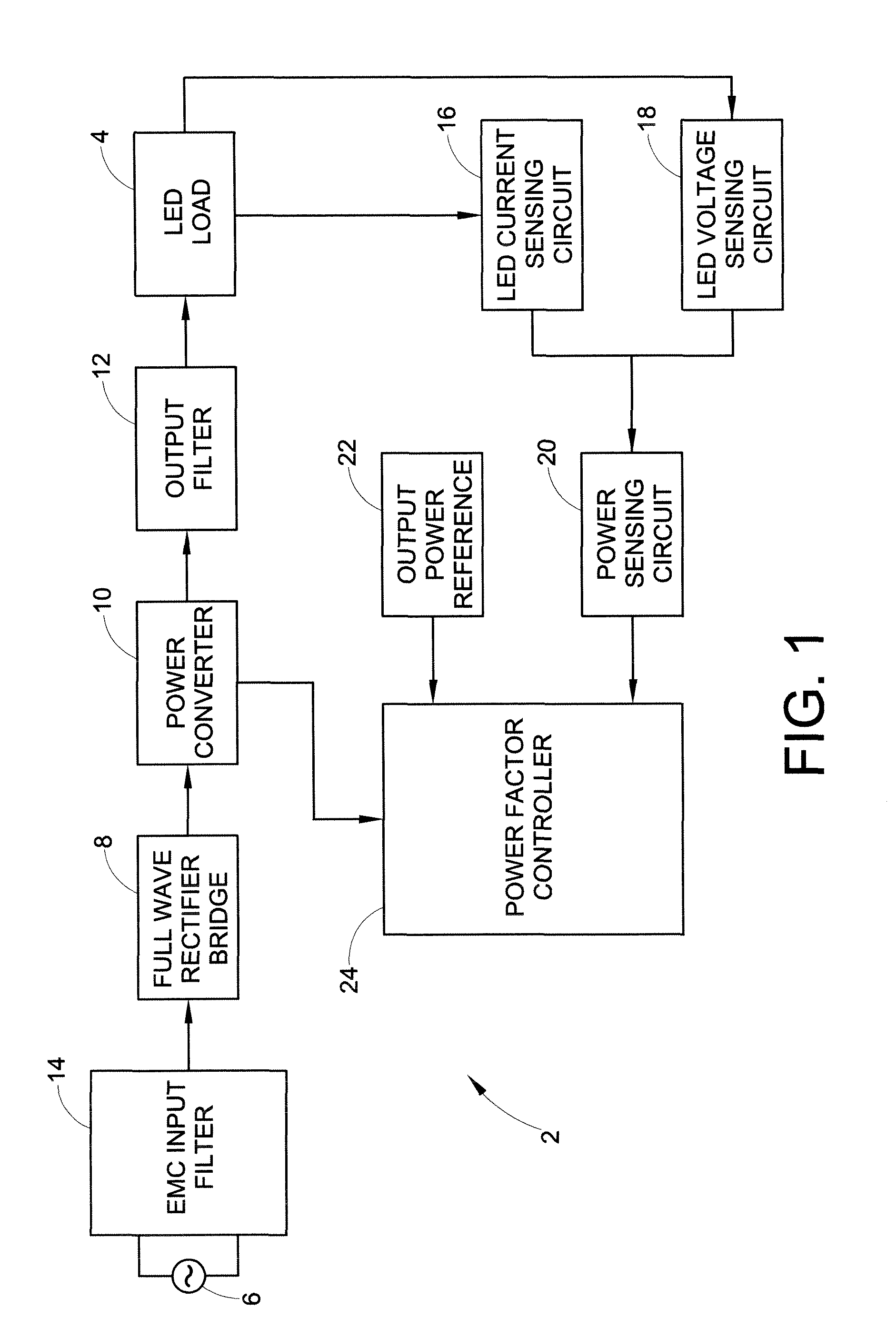
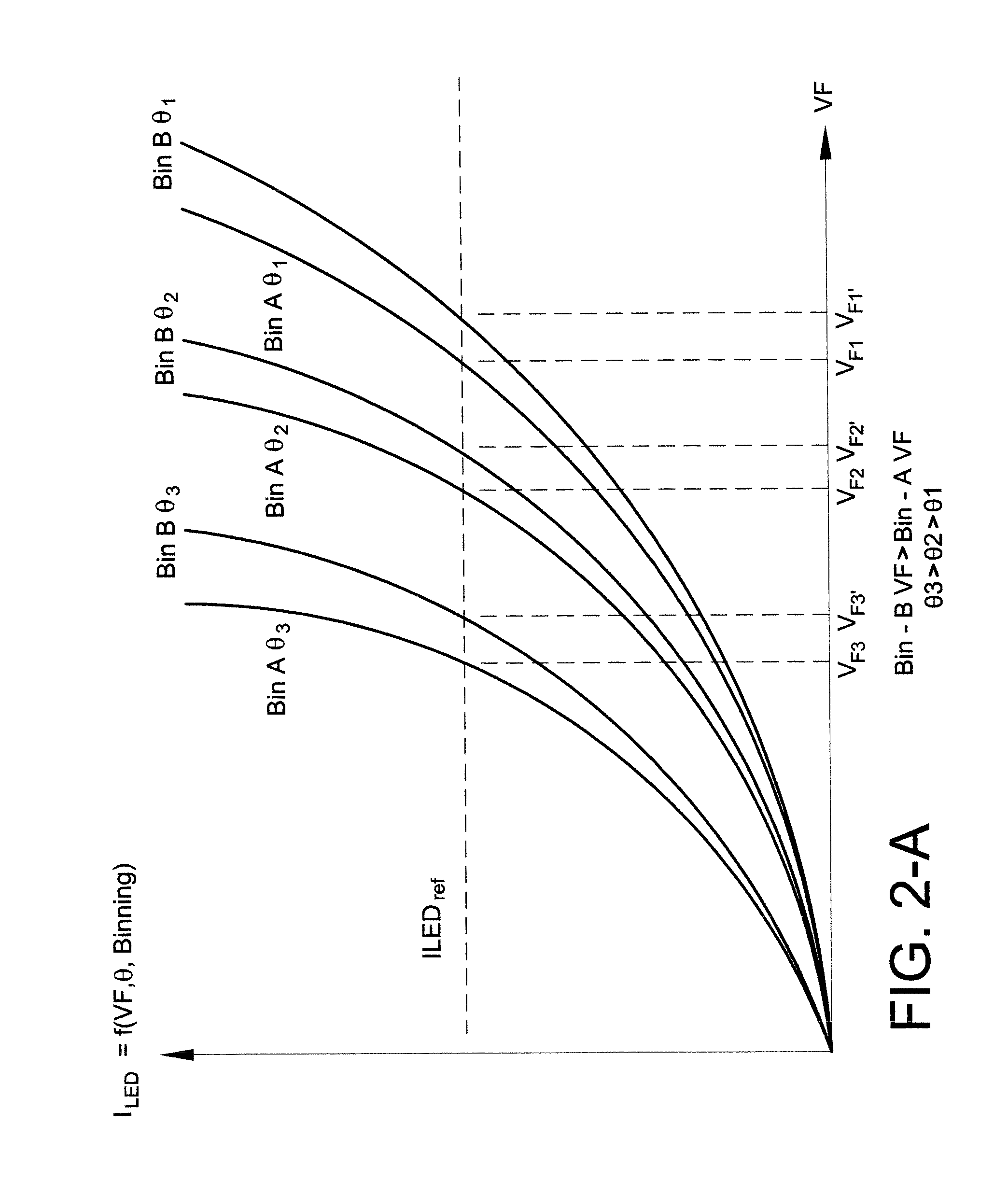
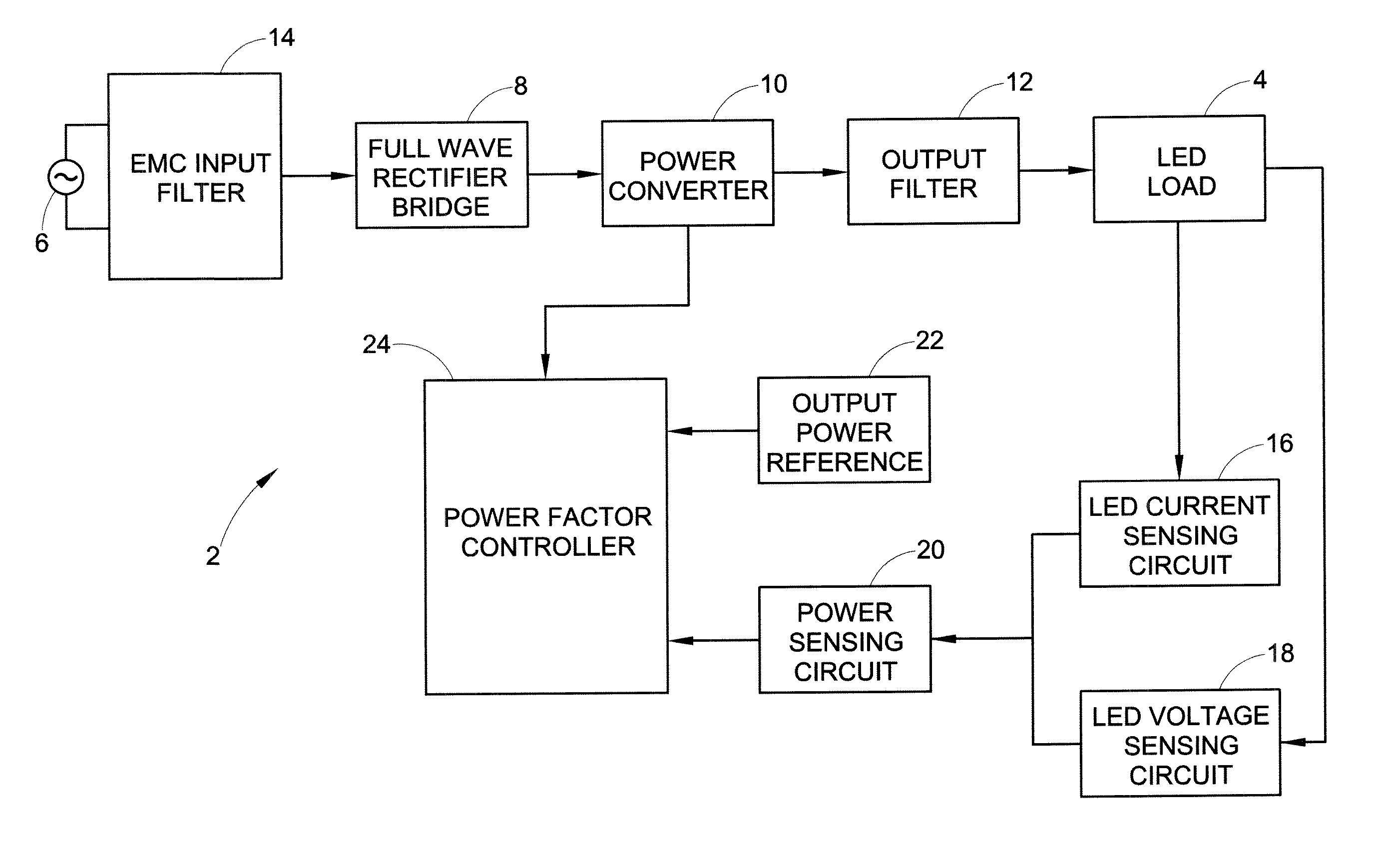
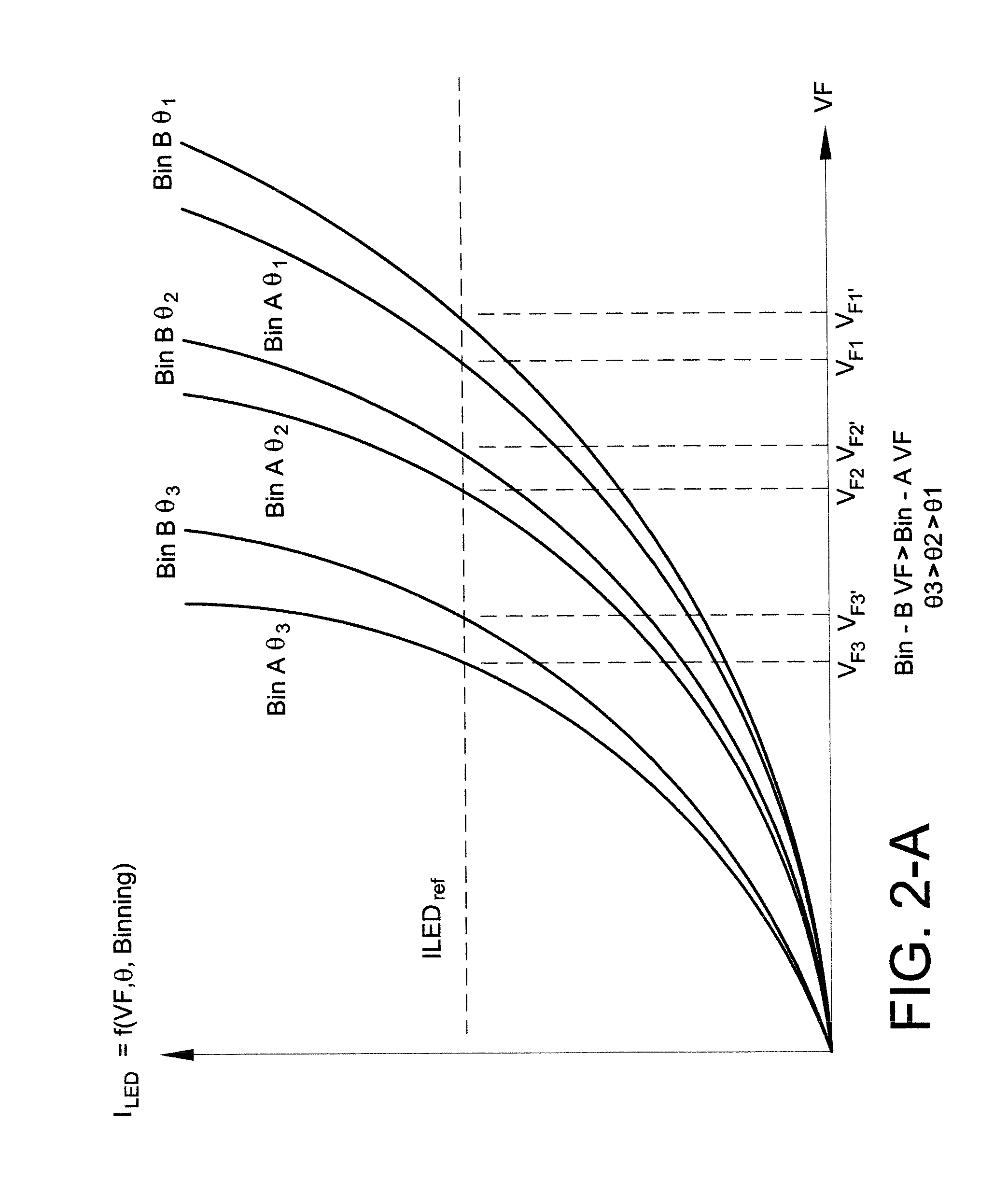
ActiveUS8174197B2Light intensityPower consumption of lightDischarge tube incandescent screensElectric discharge tubesFeedback circuitsControl circuit
A light source with substantially constant intensity and power consumption is provided. The light source includes a controllable dc voltage and current source; a non-linear light-emitting load supplied with dc voltage and current from the controllable dc voltage and current source; a current sense circuit connected in series with the non-linear light-emitting load; a variable LED forward voltage (varying with temperature, binning batch, aging) sensor circuit; a multiplier operative to measure a power-representative signal; and a power consumption control feedback circuit through which the dc voltage and current source is controlled in relation to the variable forward voltage representative signal to adjust the dc voltage and then a current to amplitudes that keep the light intensity and power consumption produced by the light source substantially constant.
Owner:GE LIGHTING SOLUTIONS LLC
Nitride semiconductor light emitting device
ActiveUS20060017061A1Efficiently extract lightEfficient extractionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingExternal circuitElectrode
A nitride semiconductor light emitting device comprising an n-side nitride semiconductor layer and a p-side nitride semiconductor layer formed on a substrate, with a light transmitting electrode 10 formed on the p-side nitride semiconductor layer, and the p-side pad electrode 14 formed for the connection with an outside circuit, and the n-side pad electrode 12 formed on the n-side nitride semiconductor layer for the connection with the outside circuit, so as to extract light on the p-side nitride semiconductor layer side, wherein taper angles of end faces of the light transmitting electrode 10 and / or the p-side nitride semiconductor layer are made different depending on the position.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
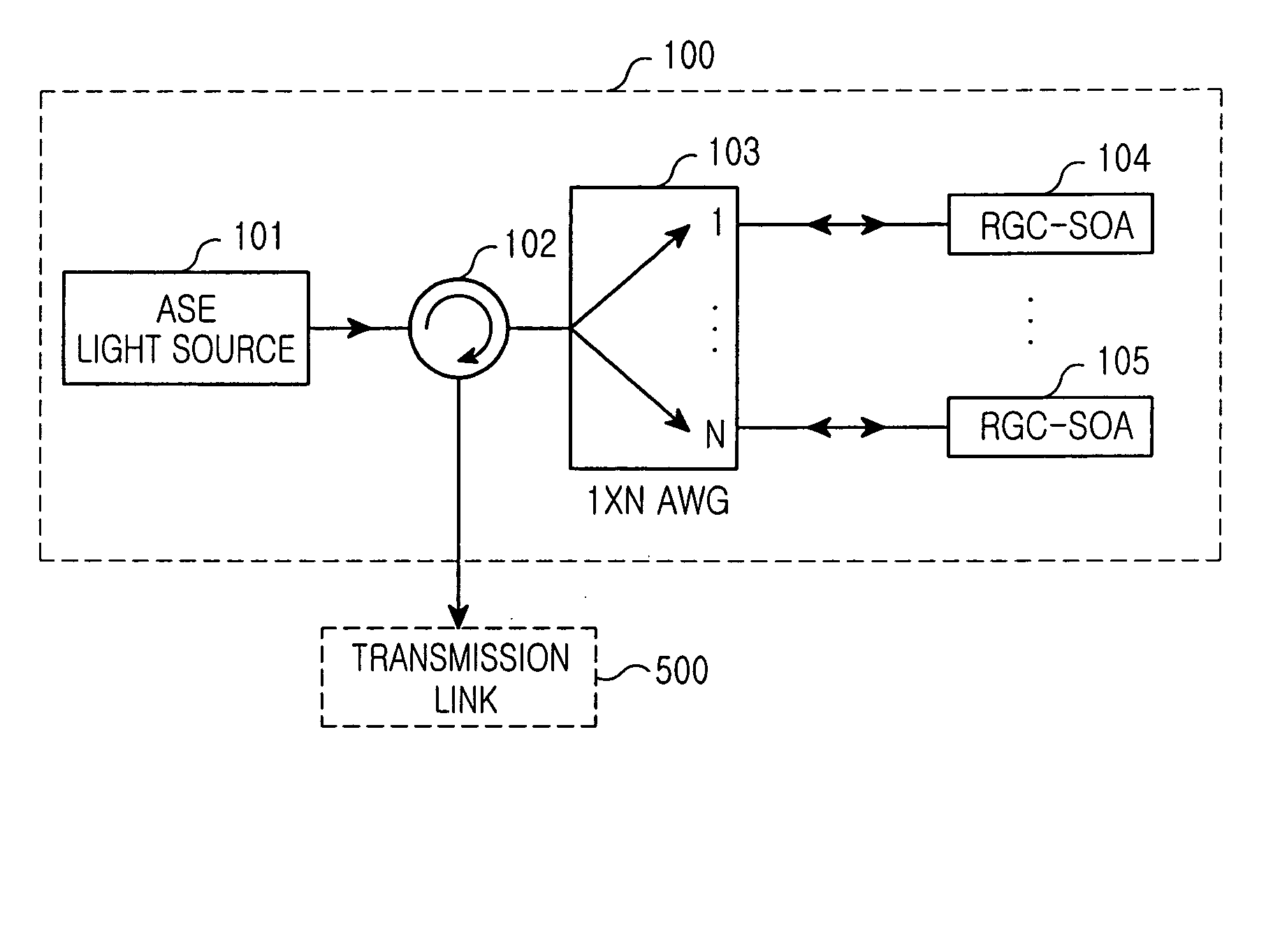
Optical signal transmission apparatus including reflective gain-clamped semiconductor optical amplifier
InactiveUS20050088724A1Improve modulation speedIncrease optical powerWavelength-division multiplex systemsSemiconductor laser optical deviceAudio power amplifierOptical power
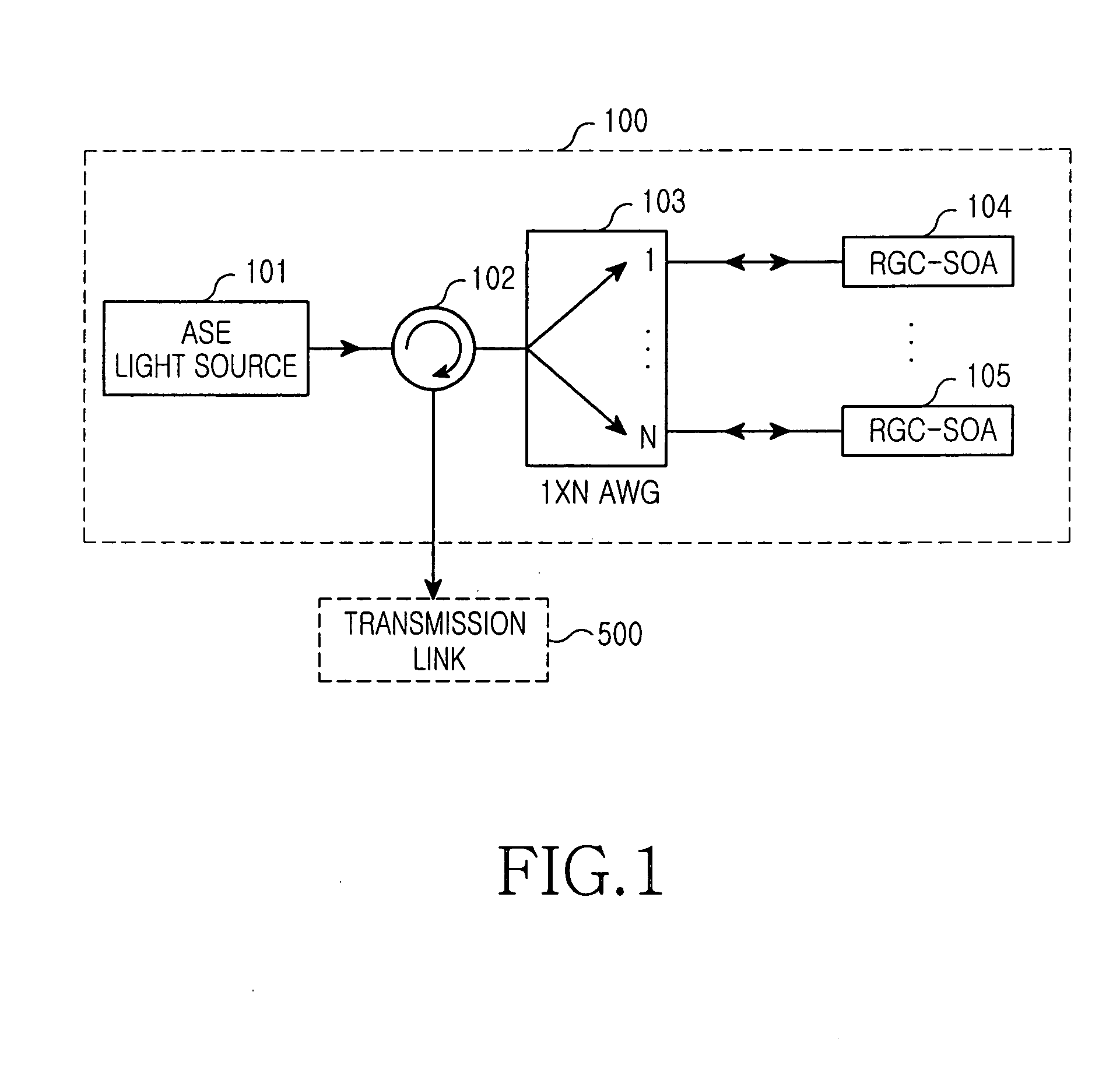
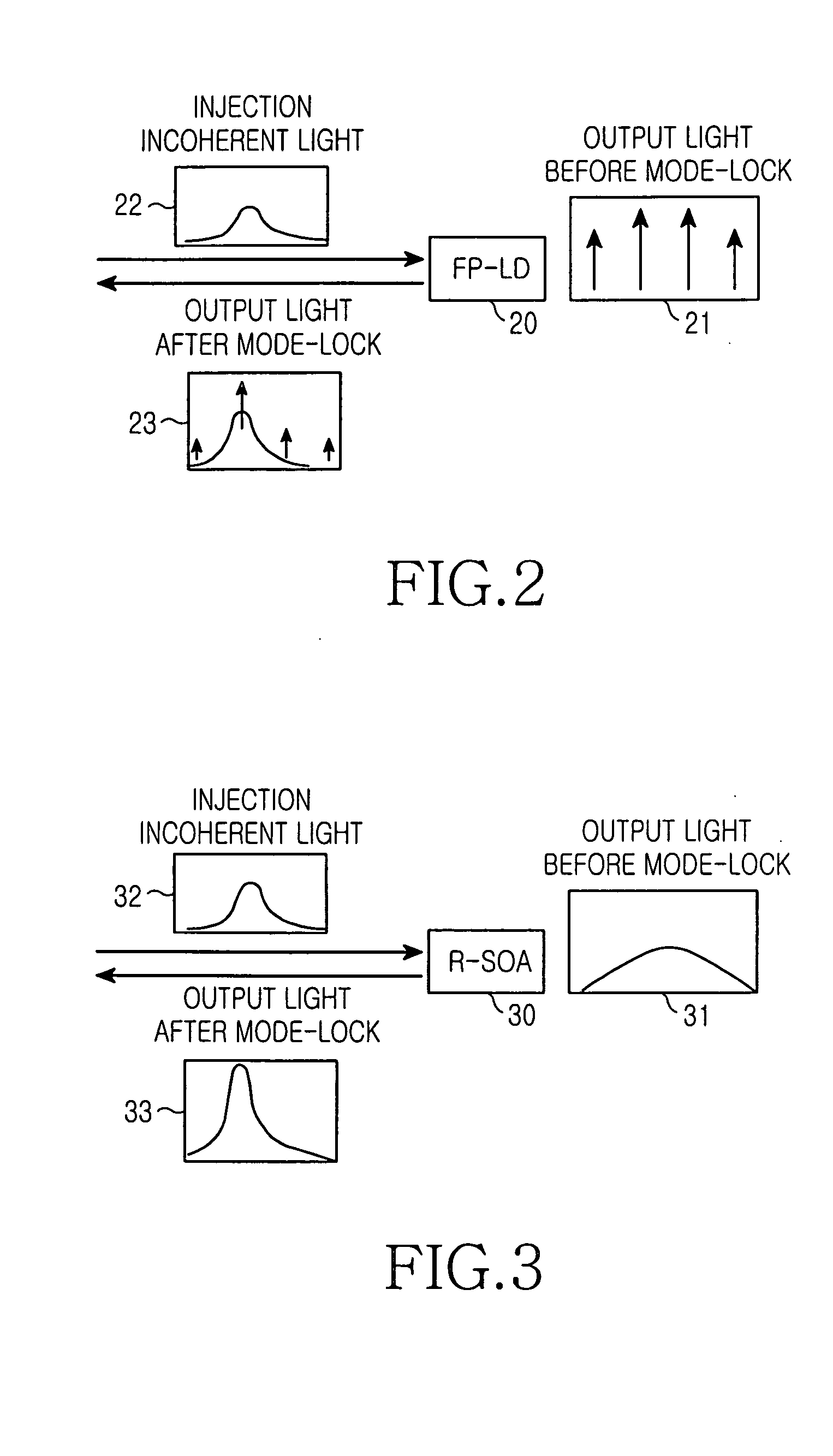
Disclosed are optical signal transmission apparatus including a reflective gain-clamped semiconductor optical amplifier and optical communication system using the optical signal transmission apparatus, which can improve modulation speed and optical power by effectively suppressing intensity noise of an incoherent light source. The optical signal transmission apparatus comprises a light source; a reflective gain-clamped semiconductor optical amplifier to generate gain-clamped optical signals having a substantially constant output intensity in a gain saturation region; a wavelength division multiplexing apparatus configured to spectrum-slice light from the light source, provide the spectrum-sliced light to the reflective gain-clamped semiconductor optical amplifier, and multiplex optical signals gain-clamped by the reflective gain-clamped optical amplifier. and a circulator for inputting the light generated by the light source to the wavelength division multiplexing apparatus, and outputting the optical signal multiplexed by the wavelength division multiplexing apparatus to a transmission link.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Muzzle flash suppressor
A flash suppressor of the open prong type having a twist in its structure formed of alternating grooves and flutes or prongs provides a highly effective flash suppression for small and medium caliber weapons and especially for automatic weapons and machine guns when placed on the end of their barrels. The orientation of the direction of the twist of the structure is in a direction opposite to the direction of the rifling in its firearm barrel. Various objective laboratory tests and subjective user evaluation on its performance prove out its effectiveness in terms of mitigating visible flash on shorten machine gun barrels as well as standard full length barrels used in critical helicopter black out operations using night vision equipment. In addition, precise aiming of a weapon equipped with the inventive flash suppressor exhibits lower dispersion of actual projectile impact compared to conventional flash suppressors.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Architecture for high efficiency polymer photovoltaic cells using an optical spacer
InactiveUS20060211272A1Improve equipment efficiencyExcessive chargingNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesHeterojunctionCharge carrier
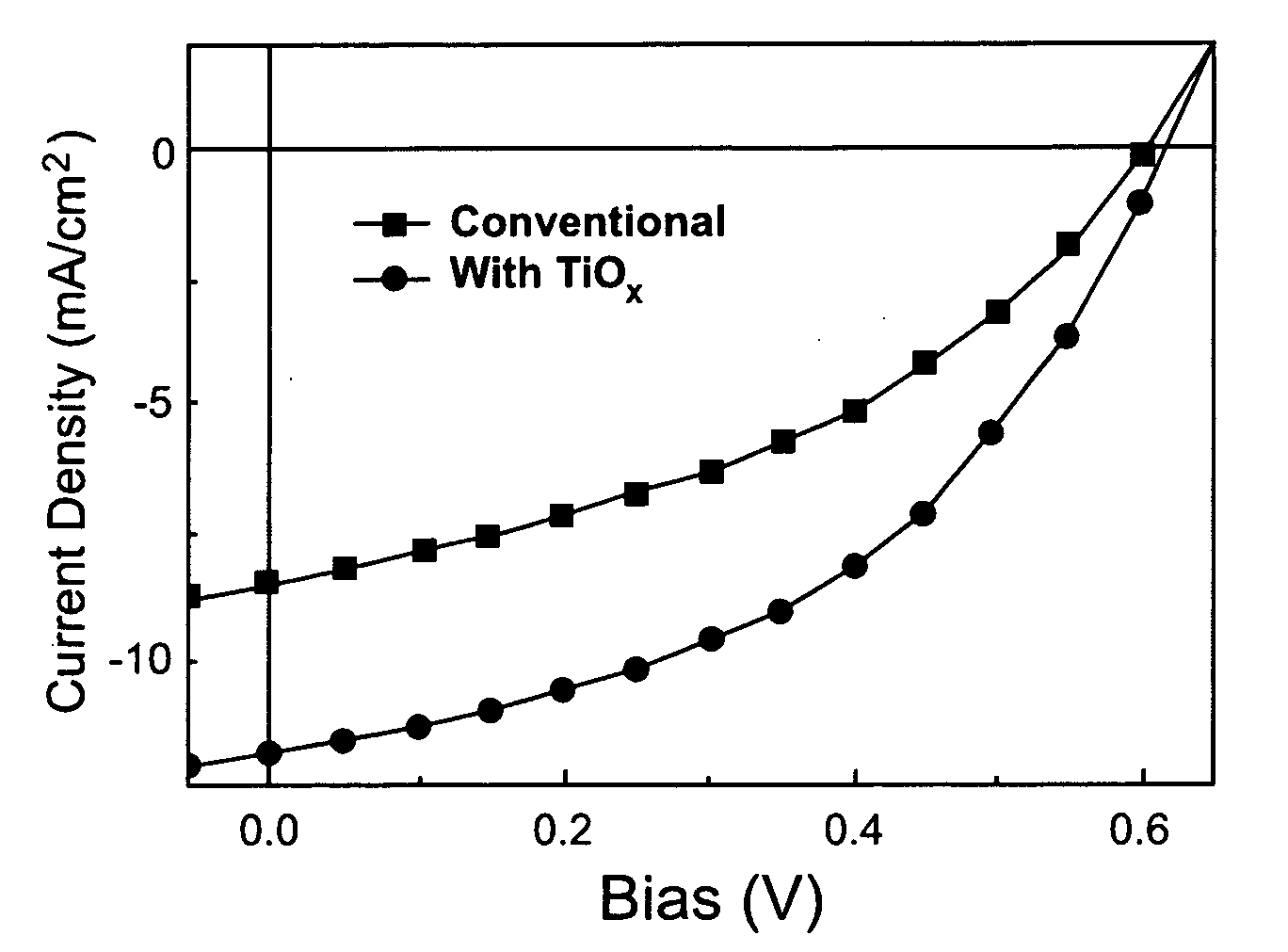
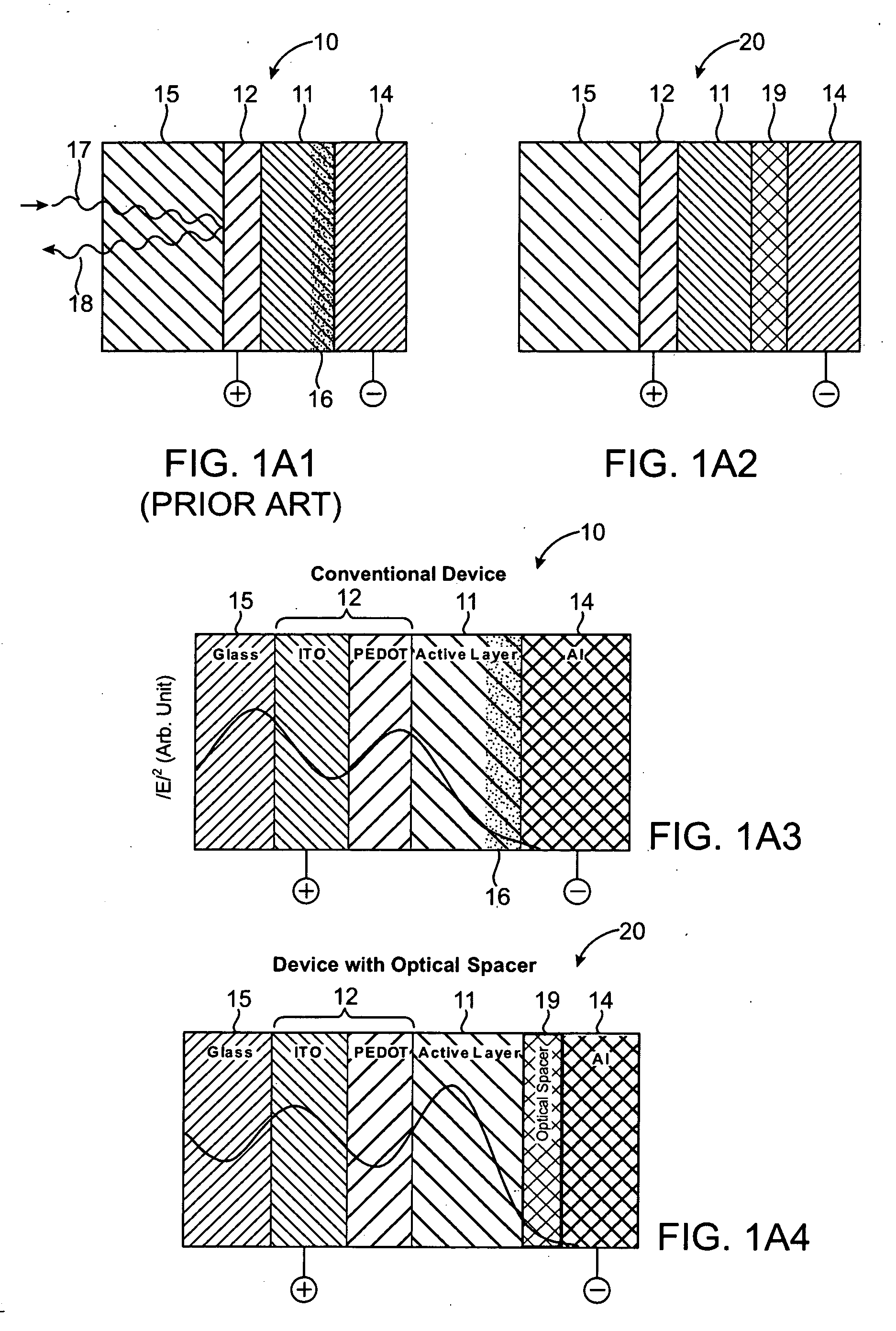
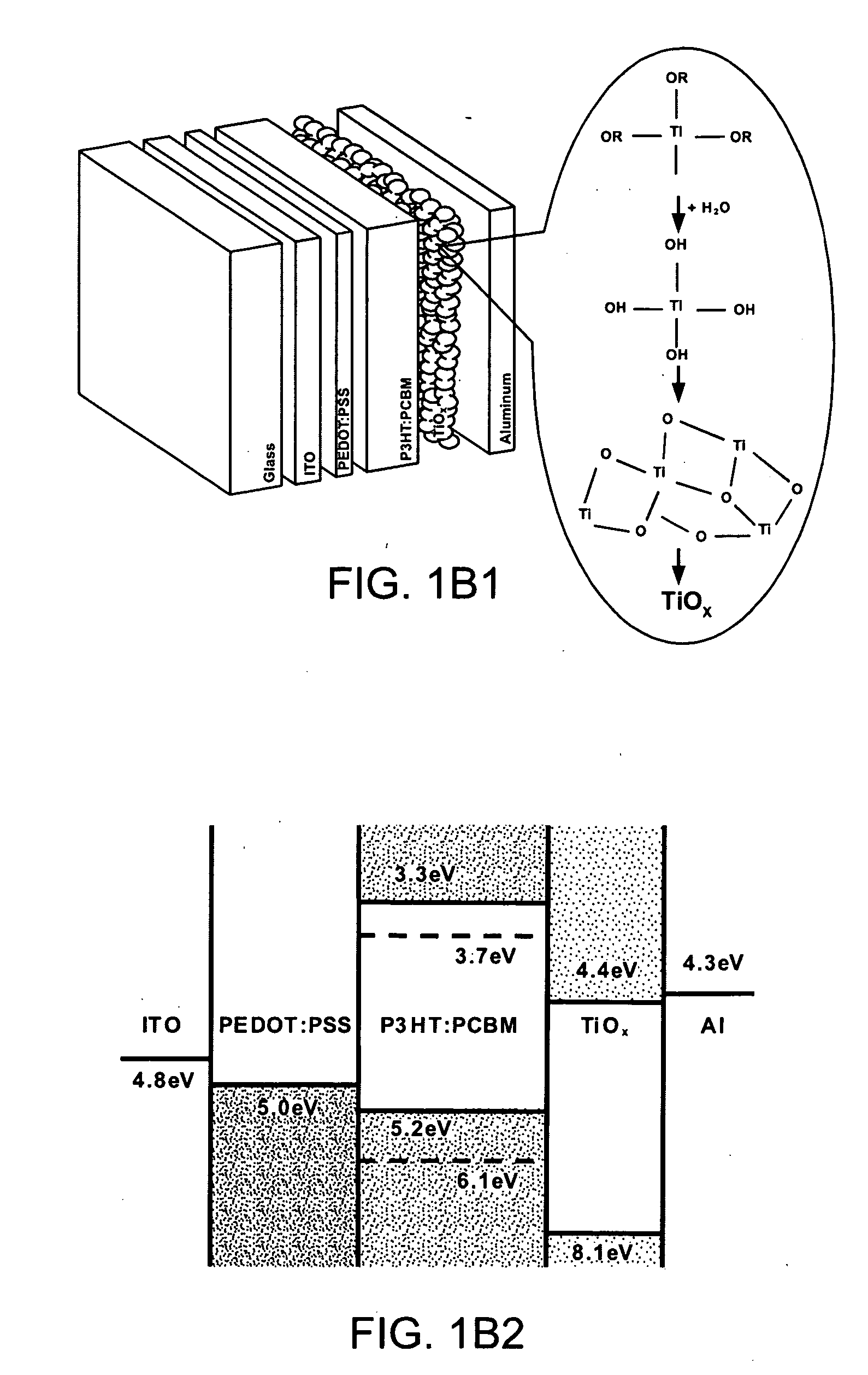
High efficiency polymer photovoltaic cells have been fabricated using an optical spacer between the active layer and the electron-collecting electrode. Such cells exhibit approximately 50% enhancement in power conversion efficiency. The spacer layer increases the efficiency by modifying the spatial distribution of the light intensity inside the device, thereby creating more photogenerated charge carriers in the bulk heterojunction layer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Modular light assembly for decorative lights
InactiveUS6939029B1Light intensityWell formedNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceModularityEngineering
A modular light for decorative use on light strips on motorcycles or similar vehicle has an outer lens or light transmitting housing that forms an interior chamber. The chamber has an open side, and a light transmitting wall is opposite from the open side through which light will be transmitted. A circuit board carrying a plurality of LEDs is shaped to close the open side of the chamber in the light transmitting housing. The circuit board supports a reflector that has openings through which the LEDs protrude. The circuit board is secured in place in the light transmitting housing to form a modular light that be used in a number of locations. The modular light fits into a support housing on a light support strip or similar structure that will mount the modular light in desired locations on a vehicle.
Owner:KURYAKYN HLDG
Bendable solid state planar light source structure, flexible substrate therefor, and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20070217200A1Desirable effectPreferred photoelectric characteristicPlanar light sourcesLighting elementsMetal coatingEngineering
A bendable LED planar light source structure, a flexible substrate therefore, and a manufacturing method thereof are provided. The flexible substrate has metal layers on both sides, where the metal layer on one side has a circuit layout, and the metal layer on the other side has a pattern structure or a whole metal coating with reflecting and scattering characteristics. Meanwhile, bonding pads are provided on the same side or opposite side as the metal layer with the circuit layout, and an array of LED dies is bonded with the bonding pads through wire bonding or flip chip bonding, such that the LED dies are conducted with current through the circuit layout on the flexible substrate, so as to form a planar light source.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
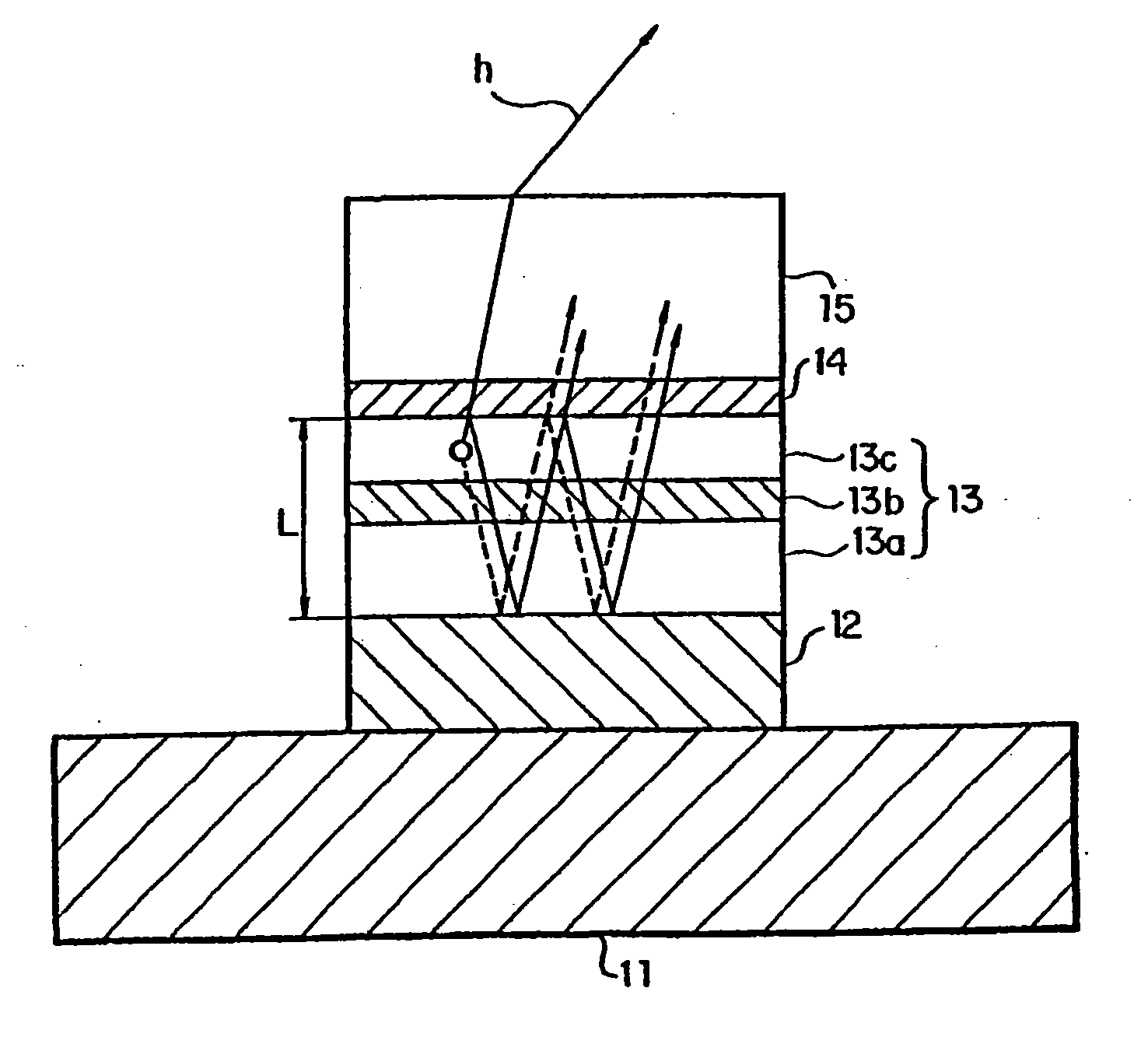
Display device
InactiveUS7218049B2Shifting amount is very smallIncreased peak intensityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesSpectral widthPhase shifted
In an organic EL device having a first electrode of a light reflective material, organic layer including an organic light emitting layer, semitransparent reflection layer, and second electrode of a transparent material that are stacked sequentially, and so configured that the organic layer functions as a cavity portion of a cavity structure, light that resonates in a certain spectral width (wavelength λ) is extracted by so configuring that optical path length L becomes minimum in a range satisfying (2L) / λ+Φ((2π)=m (m is an integer) where the phase shift produced in light generated in the organic light emitting layer when reflected by opposite ends of the cavity portion is Φ radians, L is optical path length of the cavity portion, and λ is the peak wavelength of the spectrum of part of light to be extracted.
Owner:SONY CORP
Bendable solid state planar light source structure
ActiveUS7626208B2Desirable effectPreferred photoelectric characteristicPlanar light sourcesLighting elementsMetal coatingEngineering
A bendable LED planar light source structure, a flexible substrate therefore, and a manufacturing method thereof are provided. The flexible substrate has metal layers on both sides, where the metal layer on one side has a circuit layout, and the metal layer on the other side has a pattern structure or a whole metal coating with reflecting and scattering characteristics. Meanwhile, bonding pads are provided on the same side or opposite side as the metal layer with the circuit layout, and an array of LED dies is bonded with the bonding pads through wire bonding or flip chip bonding, such that the LED dies are conducted with current through the circuit layout on the flexible substrate, so as to form a planar light source.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Light emitting device and method of producing the same
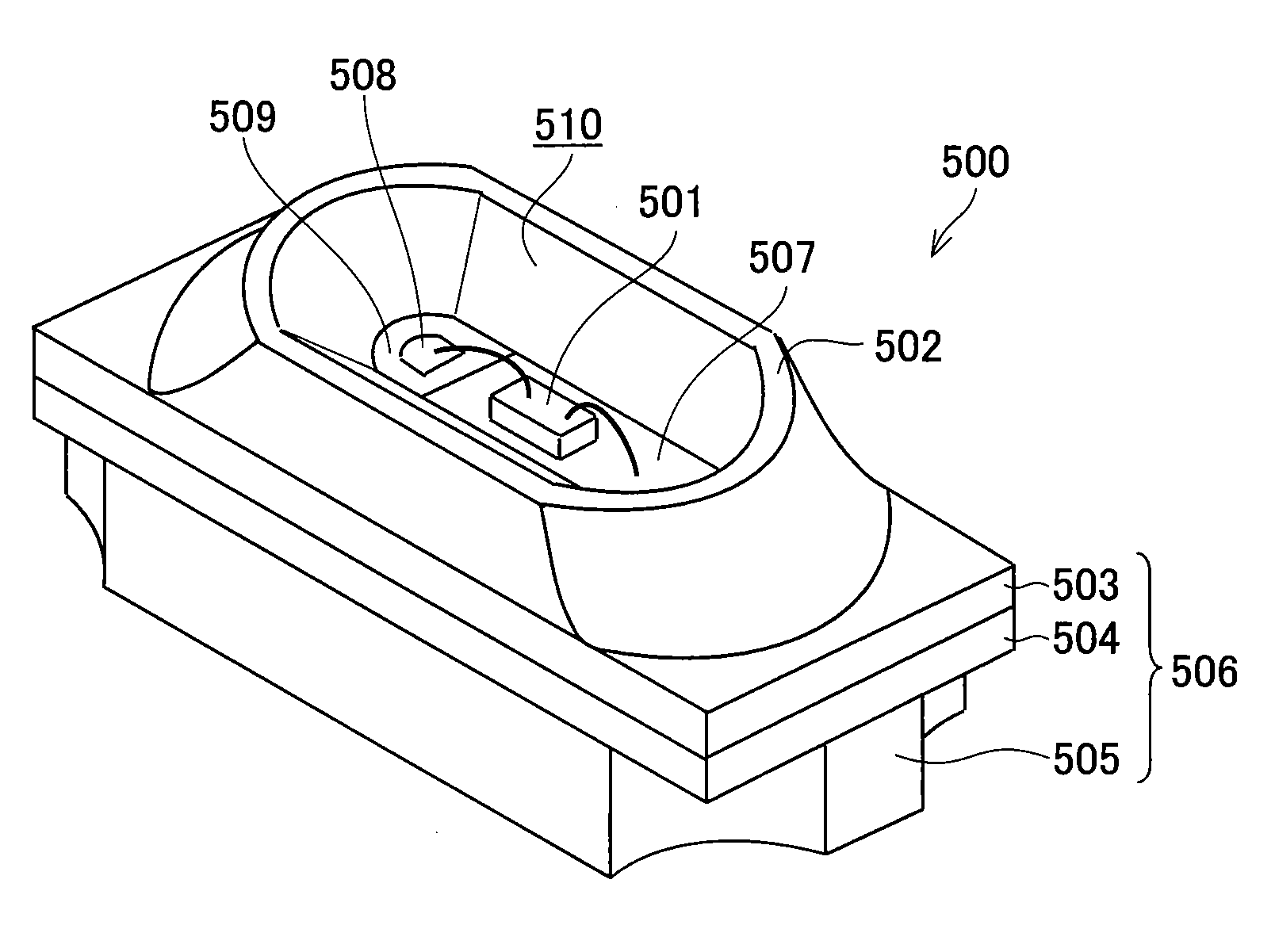
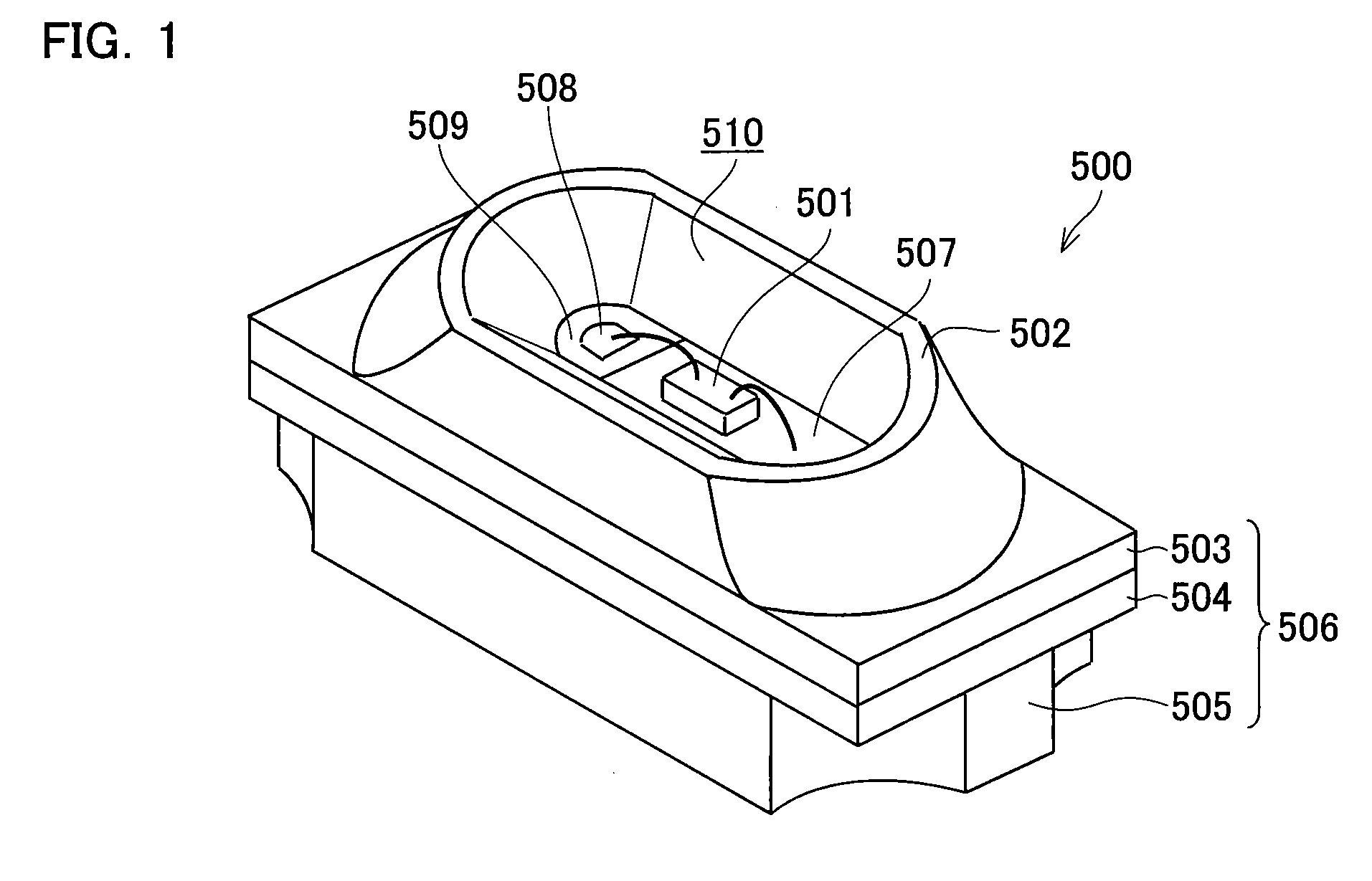
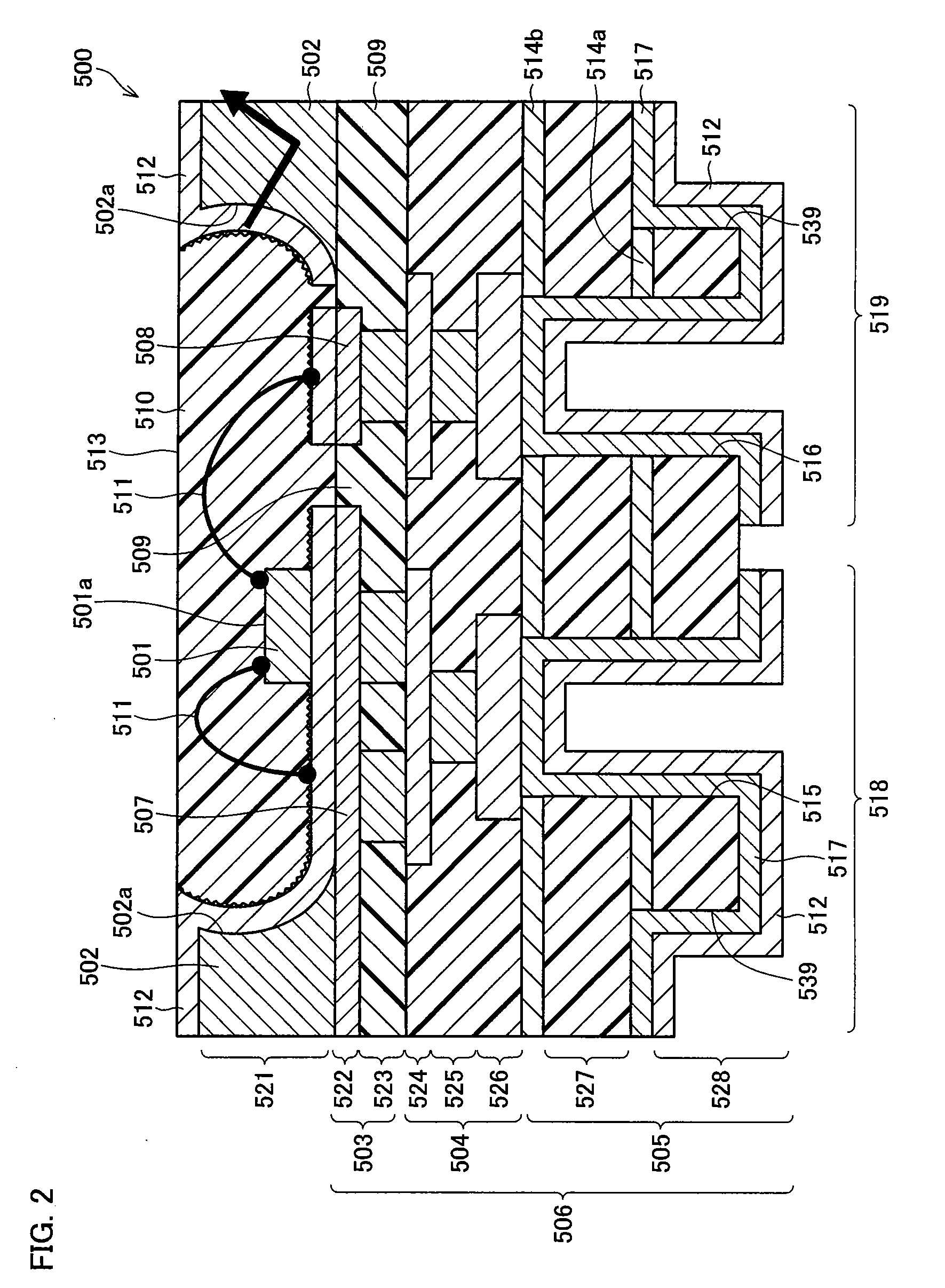
InactiveUS20080237621A1Reduce light leakageIncrease light intensitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight emitting deviceDioxide titanium
To provide a light emitting device that is improved in intensity of light emitted from a light outgoing surface and has excellent heat releasing property, the light emitting device according to the present invention includes an LED chip 501 mounted on a substrate and an insulating section 509 formed on a front surface of the substrate and made of light-transmitting resin. The insulating section 509 has a multilayer structure constituted of a titanium dioxide-added resin layer 509c to which titanium dioxide is added and a titanium dioxide-free resin layer 509b to which no titanium dioxide is added.
Owner:SHARP KK
LED illuminating device
InactiveUS20070268698A1Highly versatileReduce power consumptionLighting applicationsMechanical apparatusEngineeringFront cover
A LED illuminating device with rotating capability for showcases or the like is disclosed in the present invention comprising an enclosure with a rectangular shape in front view and side covers attached to both ends of the enclosure. A substrate is attached within the enclosure and a plurality of light emitting diode (LED) is formed on and along the substrate. A transparent front cover is attached to the front side of the enclosure and a rotator is connected to the enclosure to allow the enclosure being rotated via an axis to a desired angle.
Owner:COLOR STARS
Light emitting device
InactiveUS20100295071A1Improve uniformity of light emissionLight intensityPlanar light sourcesPoint-like light sourceLight beamLight emitting device
A light emitting device includes a carrier, a light emitting element electrically connected to the carrier, a transparent plate having at least one through hole formed therein and including a flat-portion and a lens-portion and a permeable membrane structure disposed on a surface of the transparent plate. The lens-portion covers the light emitting element and has a light incident surface, a light emitting surface, a first and a second side surfaces. A first partial beam of the light beam passes through the light incident surface and leaves from the light emitting surface. A second partial beam of the light beam passes through the light incident surface and is transmitted to the first or the second side surface. The first or the second side surface reflects at least a part of the second partial beam of the light beam to be passed through the light emitting surface.
Owner:EVERLIGHT ELECTRONICS
Near field lens
ActiveUS7837349B2Light intensityPoint-like light sourcePortable electric lightingCamera lensLight source
A lens has a main body for use with at least one light source. The main body has a light-emitting face, a light-collecting face disposed opposite the light-emitting face, and a plurality of focal points, the latter of which form a focal ring. A central axis extends through the light-collecting face and the light-emitting face. The main body is substantially radially symmetrical about the central axis and the focal ring extends around the central axis of the main body of the lens.
Owner:VARROC LIGHTING SYST SRO
Shutter device for exposure subsystem of photoetching machine
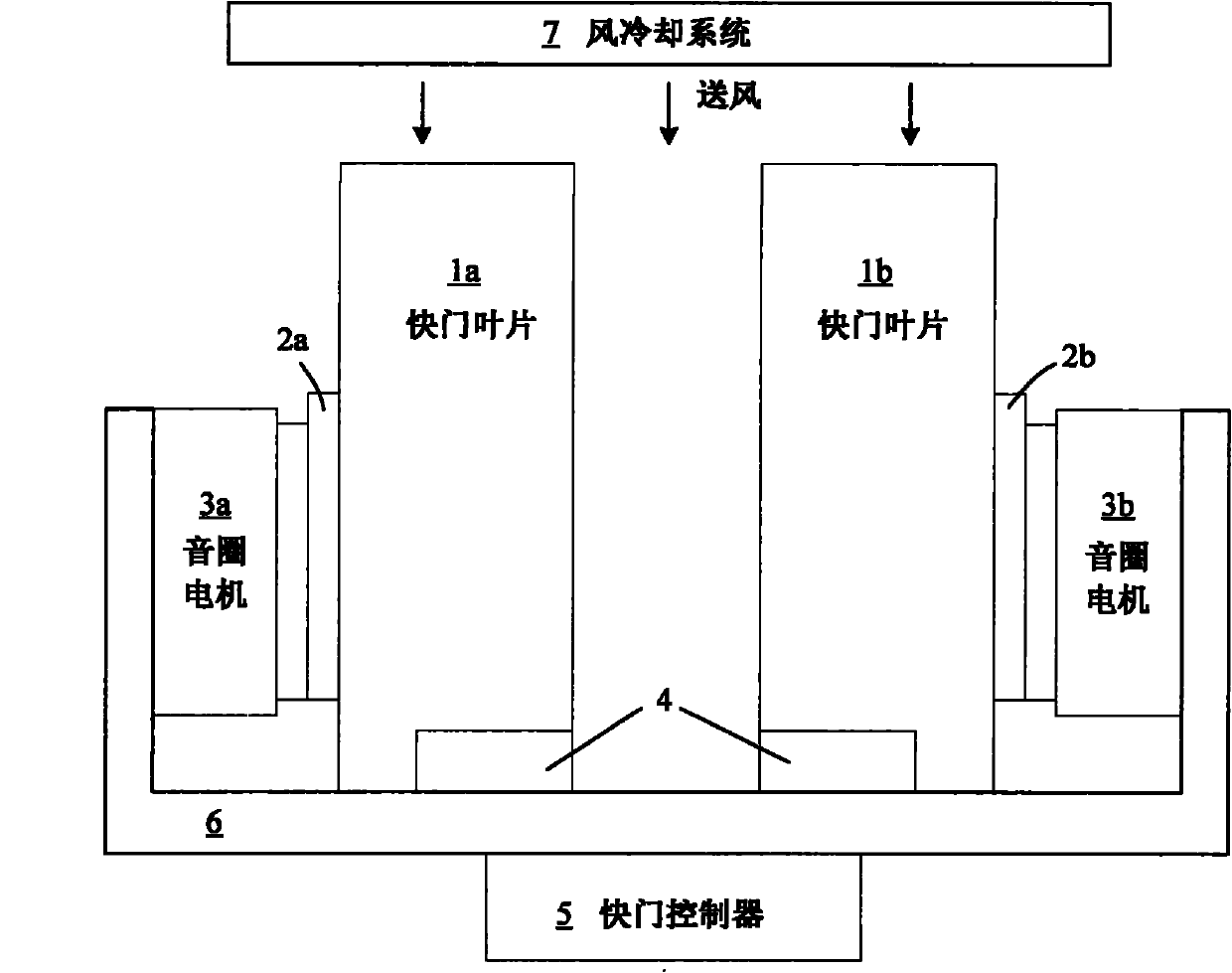
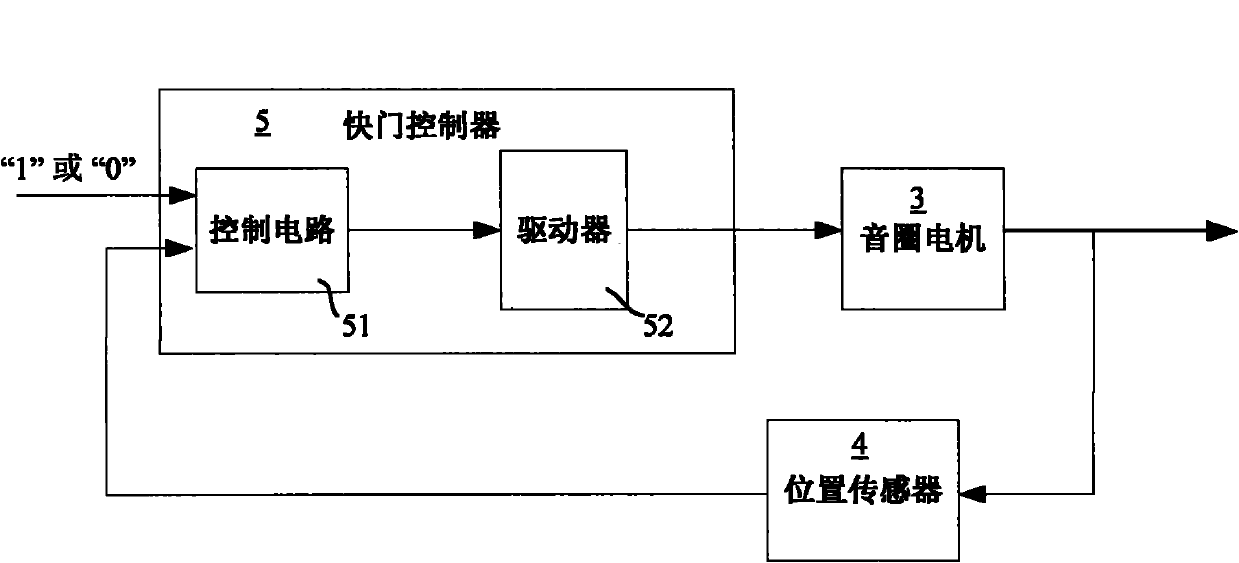
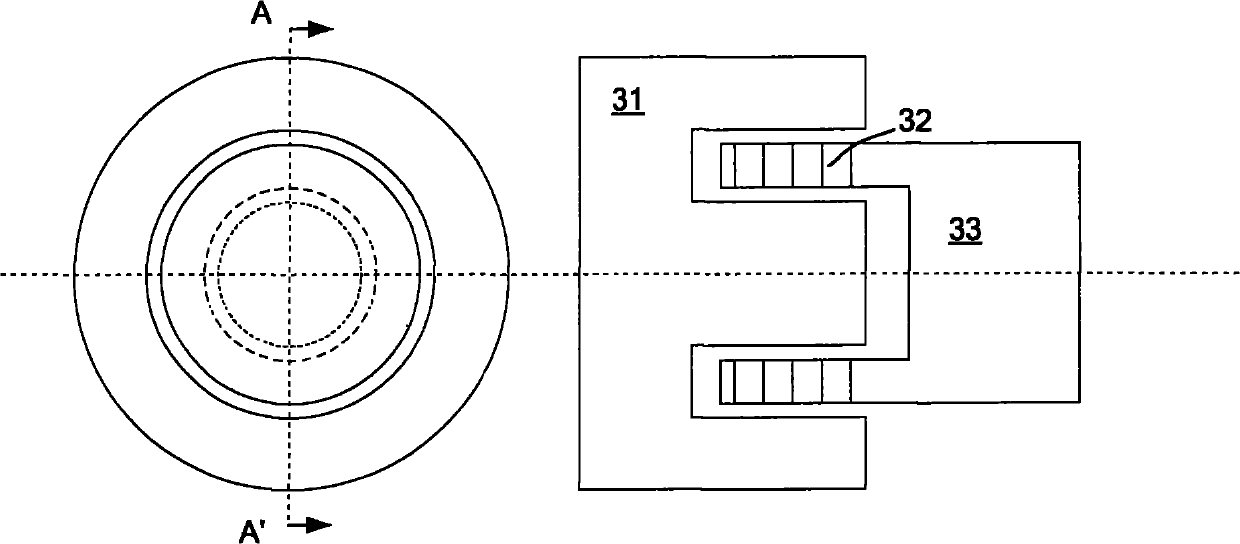
InactiveCN102087476ARealize the photolithography processFast shutter speedPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusMotor driveControl theory
The technical problem to be solved by the invention is to provide a shutter device for an exposure subsystem of a photoetching machine. The shutter device comprises at least one shutter blade, a shutter controller, a position sensor, a bracket and a voice coil motor, wherein the shutter controller is used for controlling opening and closing of the shutter blade; the positioning sensor is coupled with the shutter controller and the shutter blade and provides movement position information of the shutter blade for the shutter controller; the bracket is positioned below the shutter controller and the position sensor and is used for supporting the voice coil motor and the position sensor; the voice coil motor is controlled by the shutter controller to move; the voice coil motor is positioned on the bracket, is coupled with the shutter controller and is controlled by the shutter controller to move; the voice coil motor drives the shutter blade to move so as to form the operation of opening and closing the shutter blade; and the thickness of the shutter blade is 0.5 to 2mm. The shutter device is suitable for a large-dose exposure device. Due to the adoption of the shutter device, a thin photoresist process and a thick photoresist process can be realized simultaneously and on the premise of guaranteeing the speed of a shutter, the service life of the shutter in the high temperature environment is prolonged.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
Inkjet recording apparatus
InactiveUS20080079795A1Easy to handleEasy to measureOther printing apparatusEnergy intensityEngineering
An inkjet recording apparatus includes: an inkjet head that ejects an active energy-curable ink to form an image on a recording medium; an irradiating unit that includes a light source, and that irradiates an active energy ray from the light source to cure the active energy-curable ink ejected by the inkjet head; an energy intensity measuring unit that measures an intensity value of the active energy ray irradiated on the recording medium; and an irradiation condition control unit that controls an irradiation condition of the active energy ray on the recording medium on the basis of the intensity value measured by the energy intensity measuring unit after a passing of time to the extent of allowing the temperature of the irradiating unit to be stabilized at the start-up from lighting or rest of the irradiating unit.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
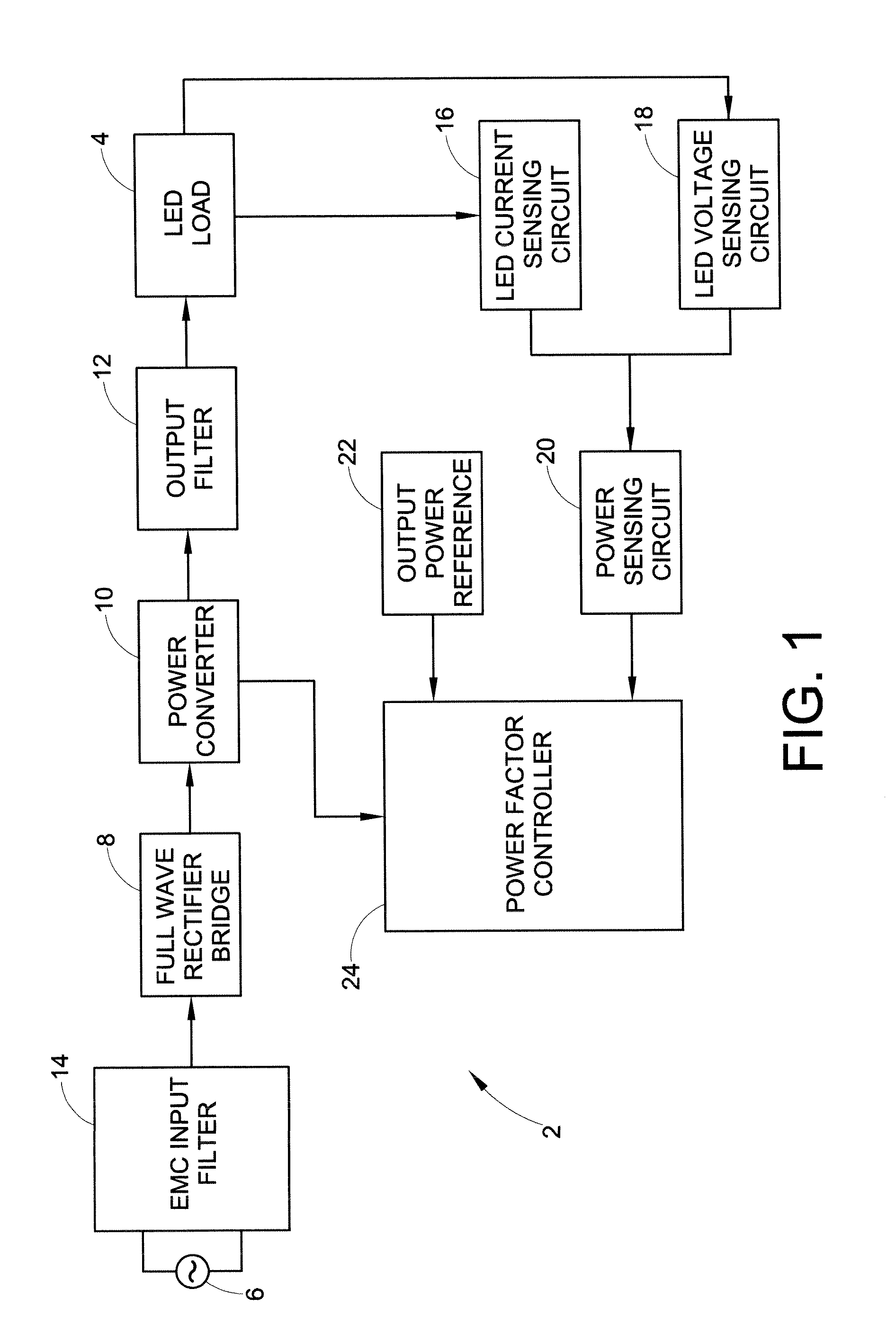
Power control circuit and method
ActiveUS20100259191A1Constant power consumptionMaintaining power consumptionDischarge tube incandescent screensElectric discharge tubesPower controlLight source
A light source with substantially constant intensity and power consumption is provided. The light source includes a controllable dc voltage and current source; a non-linear light-emitting load supplied with dc voltage and current from the controllable dc voltage and current source; a current sense circuit connected in series with the non-linear light-emitting load; a variable LED forward voltage (varying with temperature, binning batch, aging) sensor circuit; a multiplier operative to measure a power-representative signal; and a power consumption control feedback circuit through which the dc voltage and current source is controlled in relation to the variable forward voltage representative signal to adjust the dc voltage and then a current to amplitudes that keep the light intensity and power consumption produced by the light source substantially constant.
Owner:GE LIGHTING SOLUTIONS LLC
Nitride semiconductor light emitting device
ActiveUS7358544B2Effective lightingEfficient extractionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight emitting deviceExternal circuit
A nitride semiconductor light emitting device comprising an n-side nitride semiconductor layer and a p-side nitride semiconductor layer formed on a substrate, with a light transmitting electrode 10 formed on the p-side nitride semiconductor layer, and the p-side pad electrode 14 formed for the connection with an outside circuit, and the n-side pad electrode 12 formed on the n-side nitride semiconductor layer for the connection with the outside circuit, so as to extract light on the p-side nitride semiconductor layer side, wherein taper angles of end faces of the light transmitting electrode 10 and / or the p-side nitride semiconductor layer are made different depending on the position.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
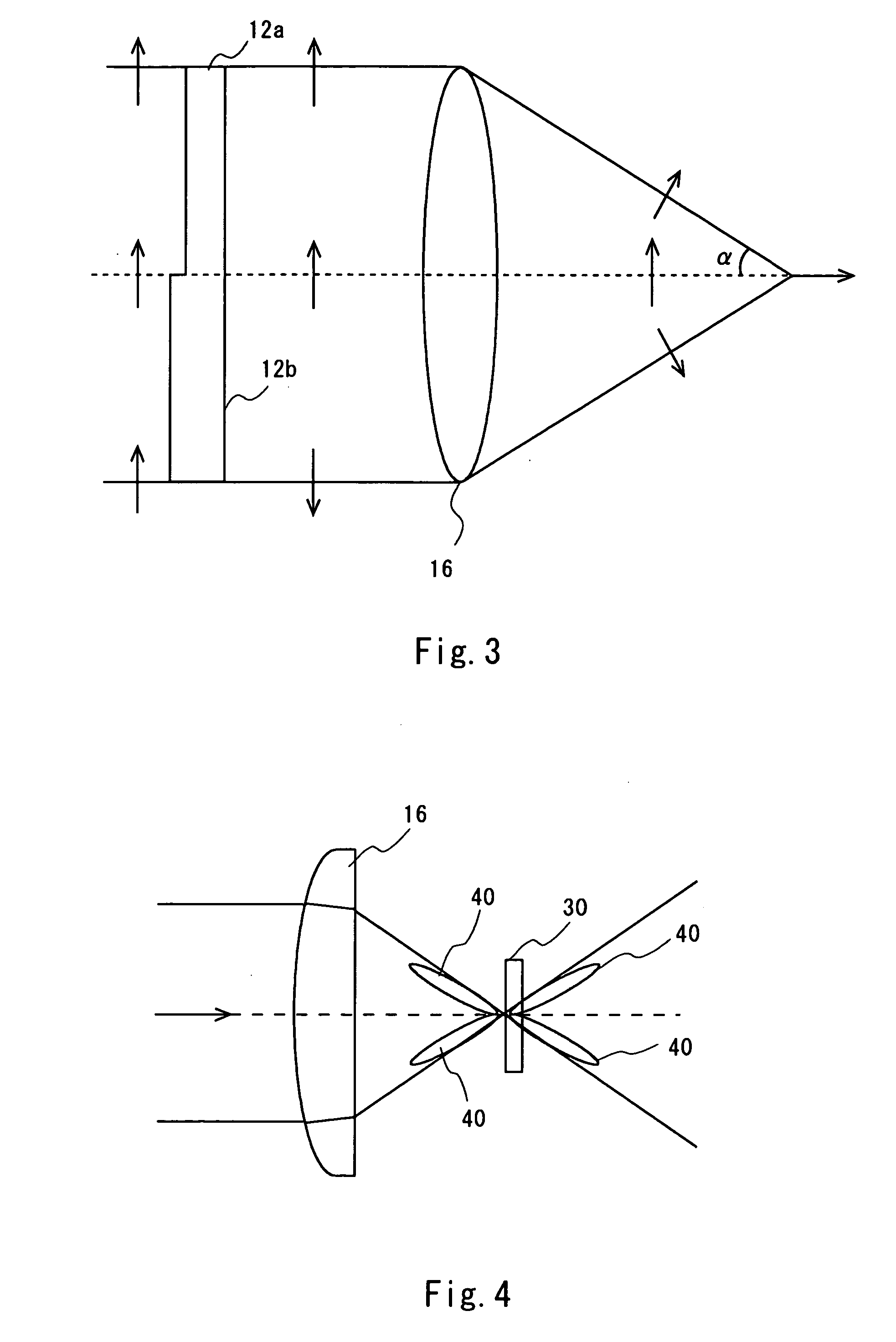
Laser microscope
InactiveUS20070076199A1Amount of second harmonic light emitted backward can be increasedIncrease volumeRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyPhotovoltaic detectorsPhase difference
A laser microscope according to an embodiment of the invention includes: a laser beam source; a phase plate providing a phase difference for laser beam from the laser beam source in accordance with an incident position; an objective lens focusing light transmitted through the phase plate onto a sample; a first separating unit separating second harmonic light emitted from the sample in a direction opposite to a traveling direction of the laser beams from a fundamental light reflected by the sample; and a photodetector detecting the second harmonic light separated from the fundamental light by the first separating unit.
Owner:NANOPHOTON
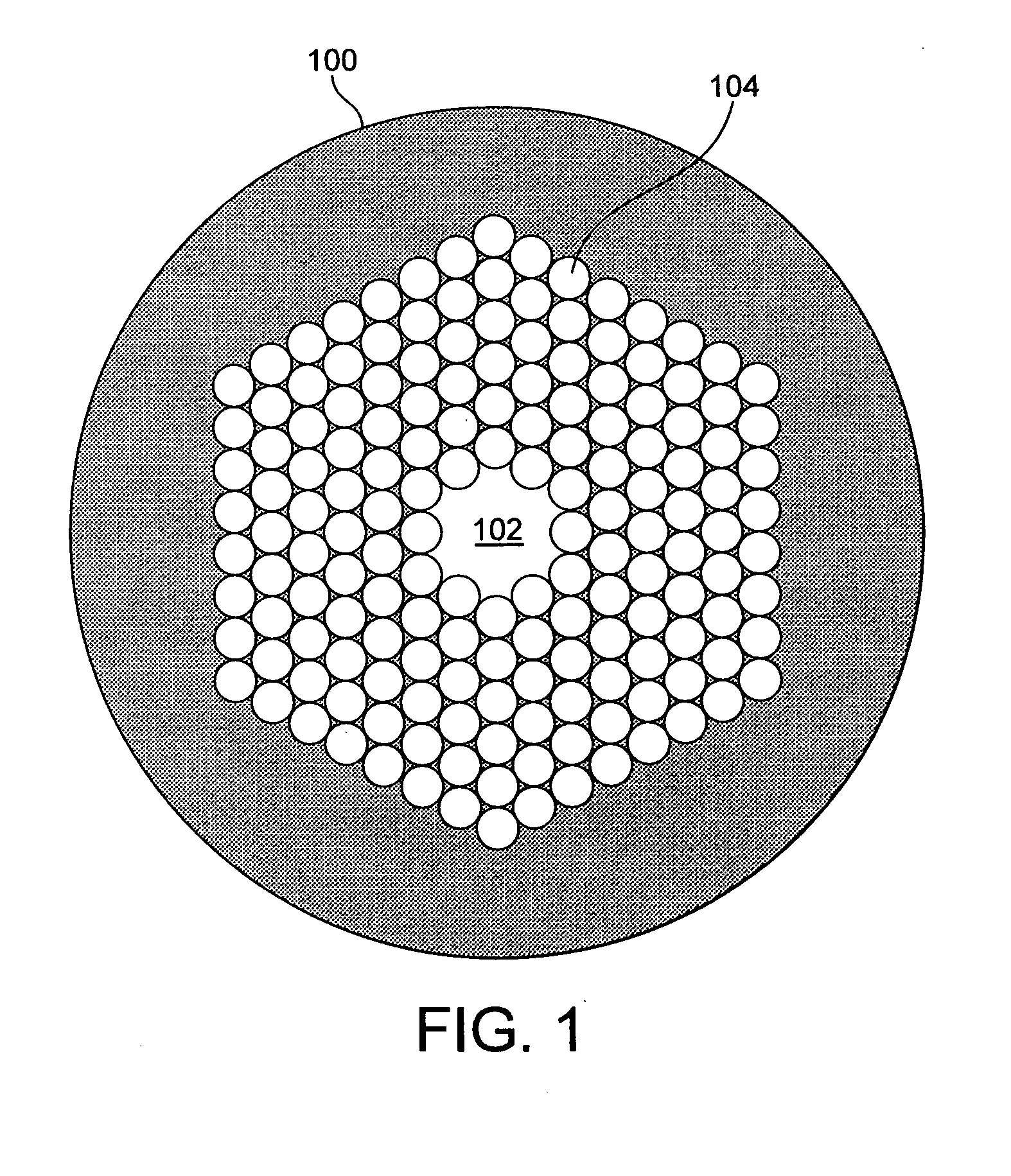
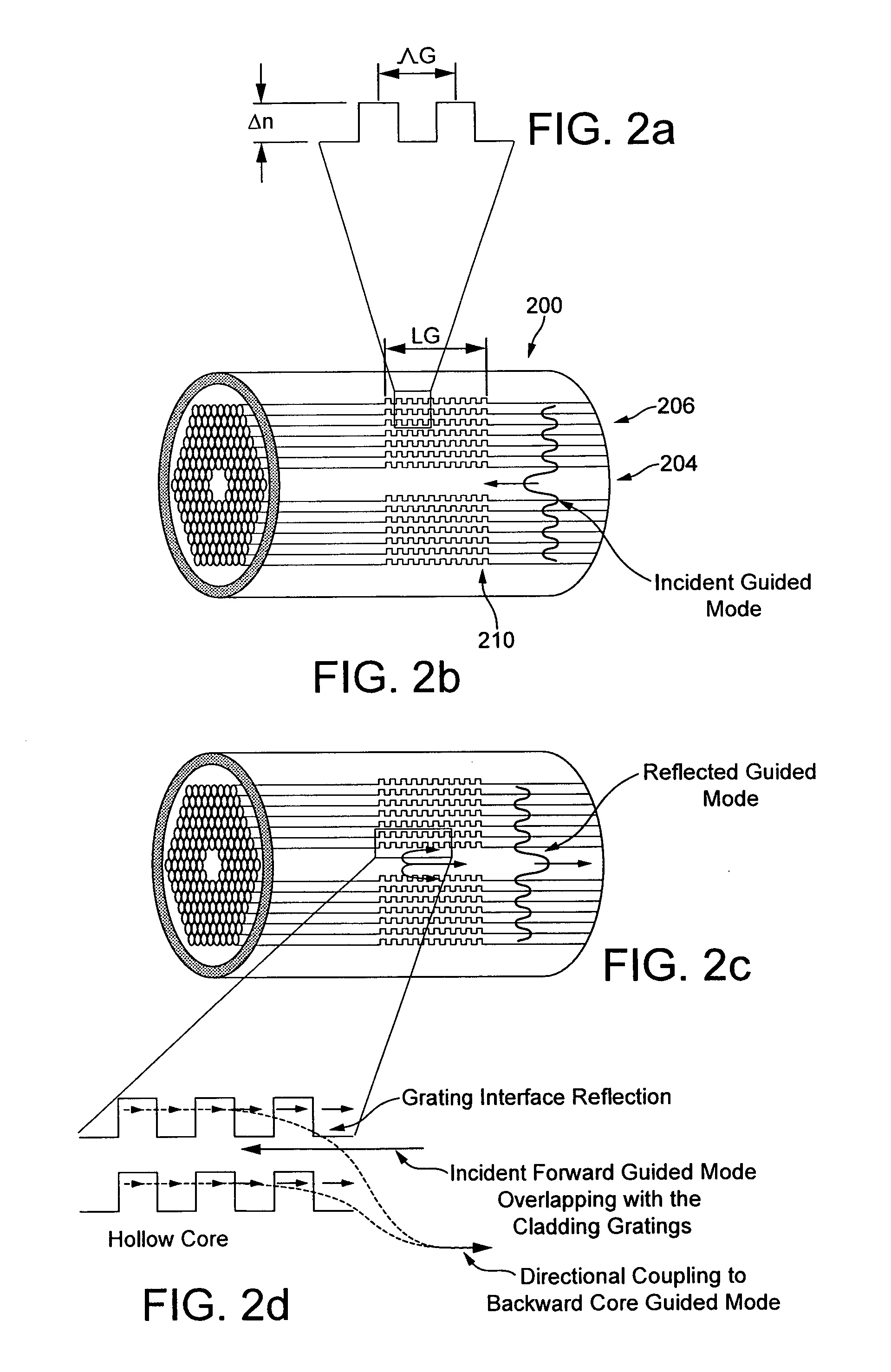
Hollow Core Photonic Crystal Fibre Comprising a Fibre Grating in the Cladding and Its Applications
InactiveUS20110267612A1Improve reflectivityLarge finesseRadiation pyrometryOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical propagationFiber
An optical fibre is provided having a fibre cladding around a longitudinally extending optical propagation core. The cladding has a reflection region of a varying refractive index in the longitudinal direction.
Owner:GLOPHOTONICS
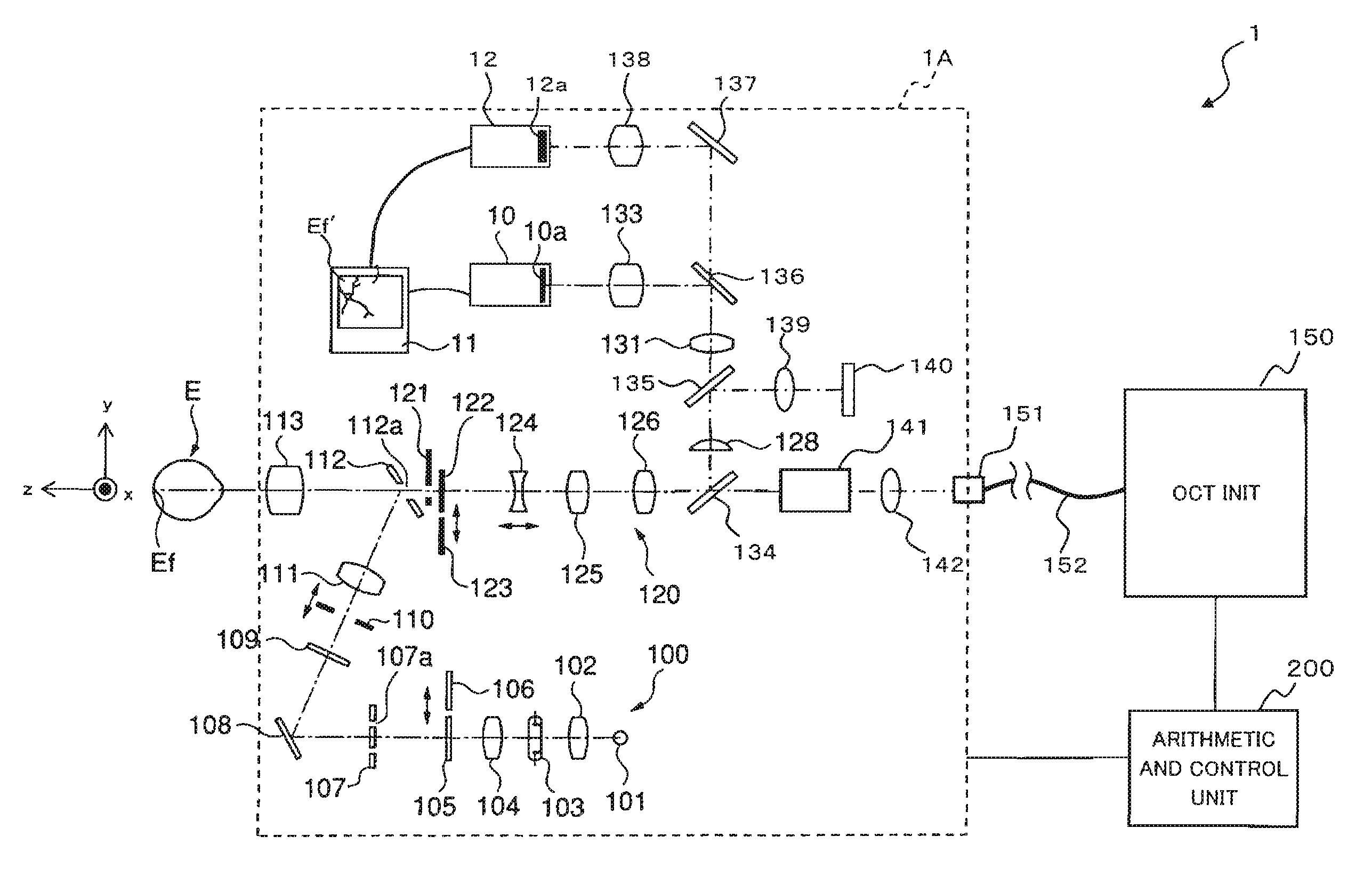
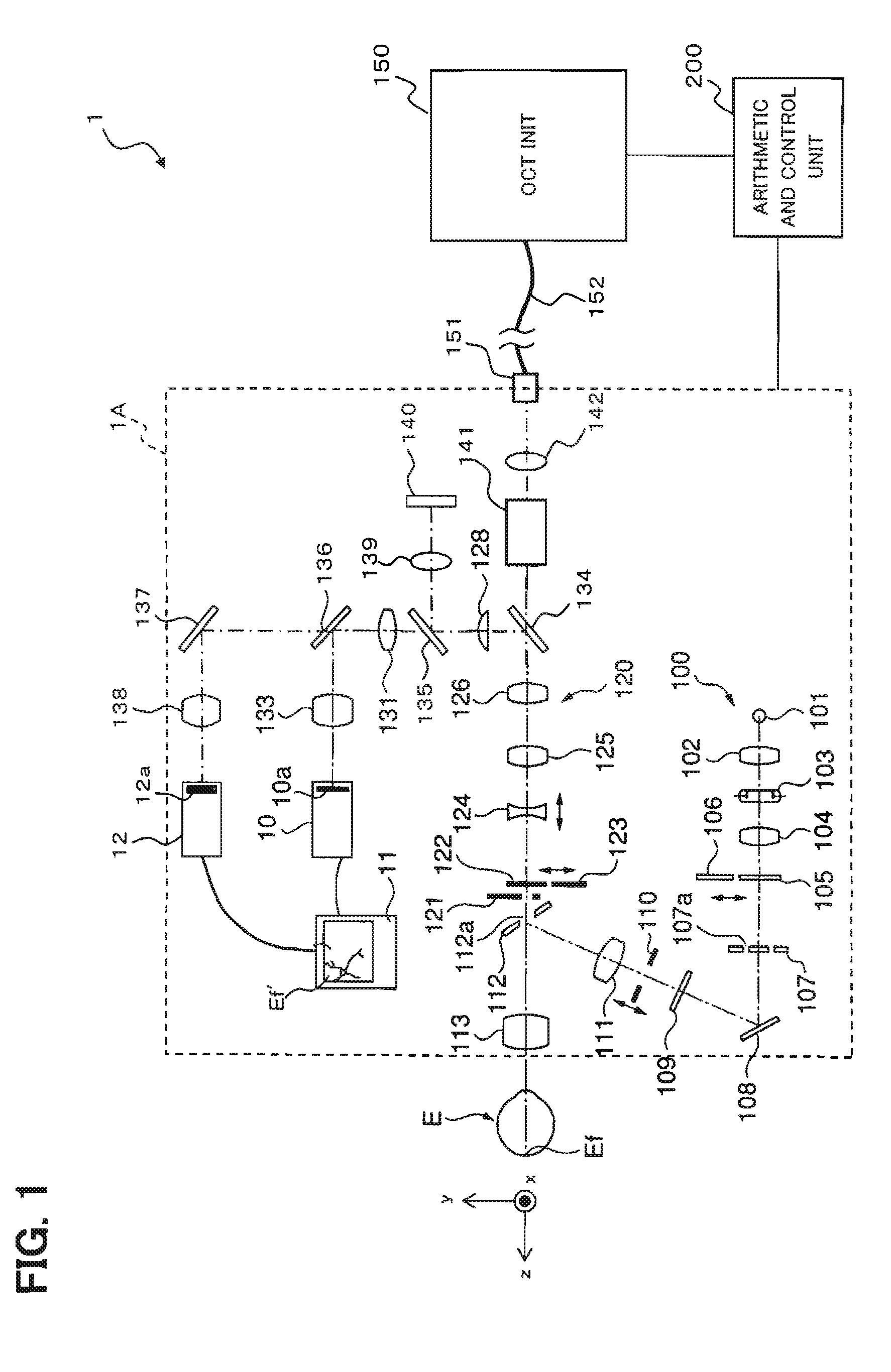
Optical image measurement device and optical image measurement method
ActiveUS7604351B2Easy to getLight intensityInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansMeasurement deviceImage formation
An optical image measurement device comprises: an interference-light generator configured to generate an interference light by splitting a low-coherence light into a signal light and a reference light and superimposing the signal light having passed through an eye and the reference light having passed through a reference object; a detector configured to detect the generated interference light; a calculator configured to obtain intensity distribution of the interference light in the eye, based on a result of the detection by the detector; a determining part configured to determine a projection position of the signal light to the eye, based on the obtained intensity distribution; and an image forming part configured to form an image of the eye, based on a result of detection of a new interference light based on a new signal light projected toward the determined projection position and a new reference light having passed through the reference object.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Electronic flare
InactiveUS7182479B1Avoid eye injuryLight intensityLighting applicationsLight source combinationsLight beamHand held
A portable, hand-held, electrically powered, high intensity directed light beam generating device for use as a replacement for a pyrotechnic flare for search and rescue, especially in a marine environment. The light intensity is generated by a xenon strobe flash tube in a covered, mirror reflective housing that allows for a directional beam of light of less than 6 steradians. The limited radiation light direction provides a safe optical solution for the user to prevent eye damage while increasing the beam intensity and range. The light and illumination section surrounding the strobe flash tube includes thermally conductive paths for the heat generated by the flash tube to be transmitted to the outside of the housing.
Owner:ACR ELECTRONICS INC
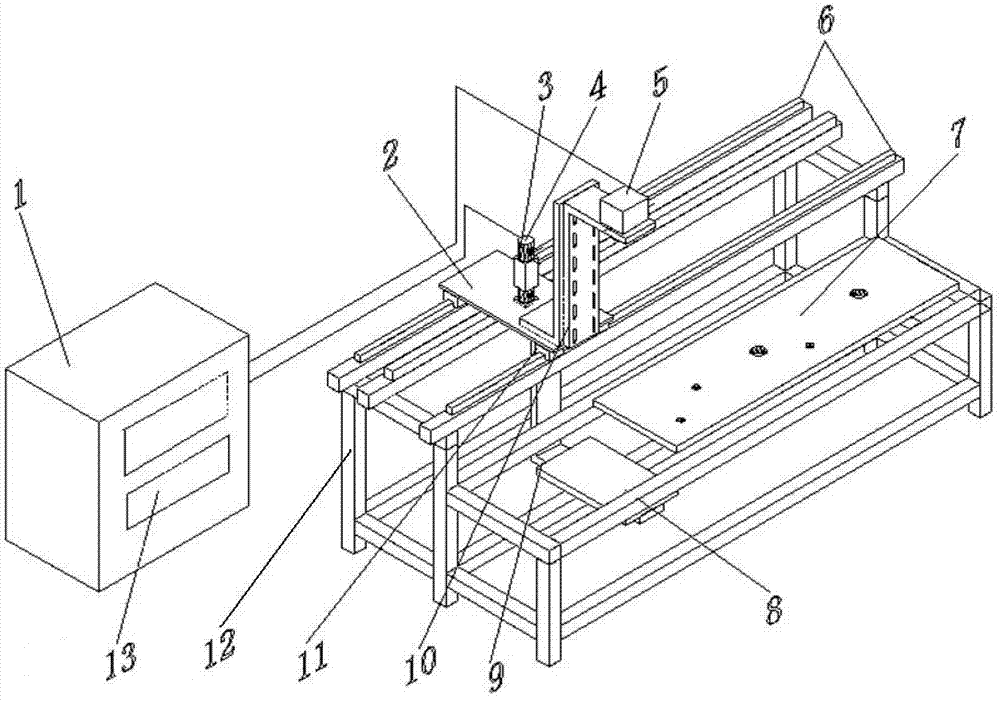
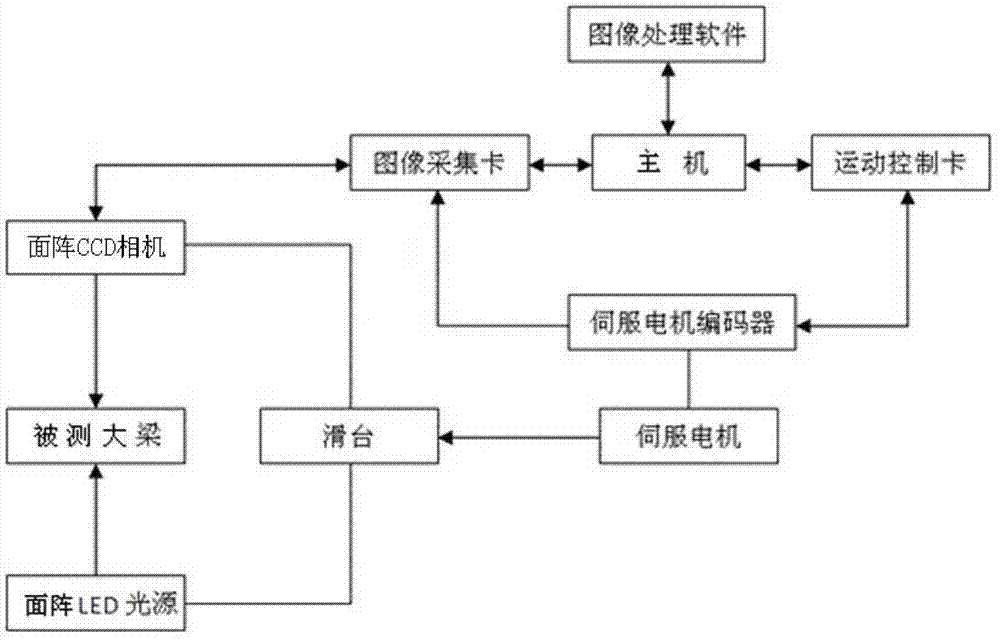
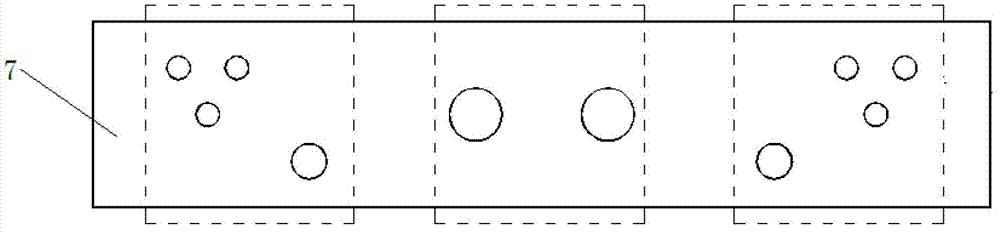
Automobile crossbeam assembly hole visual on-line measurement system and method thereof
The invention provides an automobile crossbeam assembly hole visual on-line measurement system and a method thereof. The system comprises a main control platform, a servo motor, a servo motor encoder, a slide platform, a slide block, a horizontal slide rail, a fixed high and low frame, a camera and a measured crossbeam. A host is arranged on the main control platform. A motion control card and an image acquisition card are respectively inserted in PCI insertion slots of the host. The host is connected with the servo motor through the motion control card. The servo motor encoder is coaxially connected with the servo motor. The servo motor is fixed on the slide platform. The slide platform is matched and connected with the horizontal slide rail through the slide block. The horizontal slide rail is arranged on the high side of the fixed high and low frame. The host is connected with the camera through the image acquisition card. The camera is arranged on the slide platform through a Z type height adjustable bracket. The measured crossbeam is arranged on the low side of the fixed high and low frame. According to the invention, non-contact and full-automatic high speed on-line measurement is carried out on the hole diameter and the hole site size of an automobile crossbeam assembly hole; and the system and the method are especially suitable for the measurement of the crossbeam with nonuniform assembly hole distribution and without assembly holes in certain areas.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Non-Reflective Optical Connections in Laser-Based Photoplethysmography
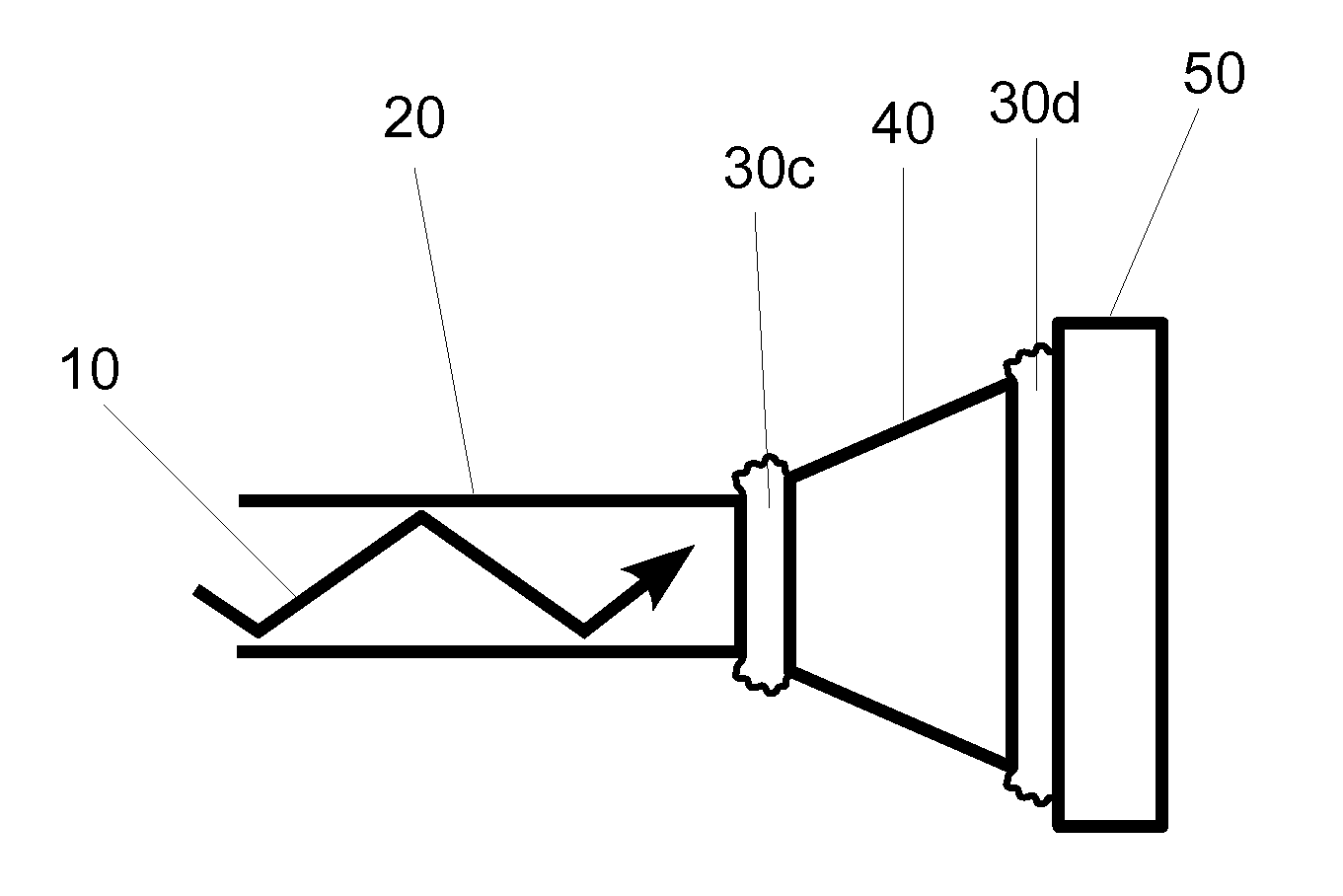
InactiveUS20120288230A1Minimize stabilityMaximize light availableMaterial analysis by optical meansCoupling light guidesCatoptricsLight delivery
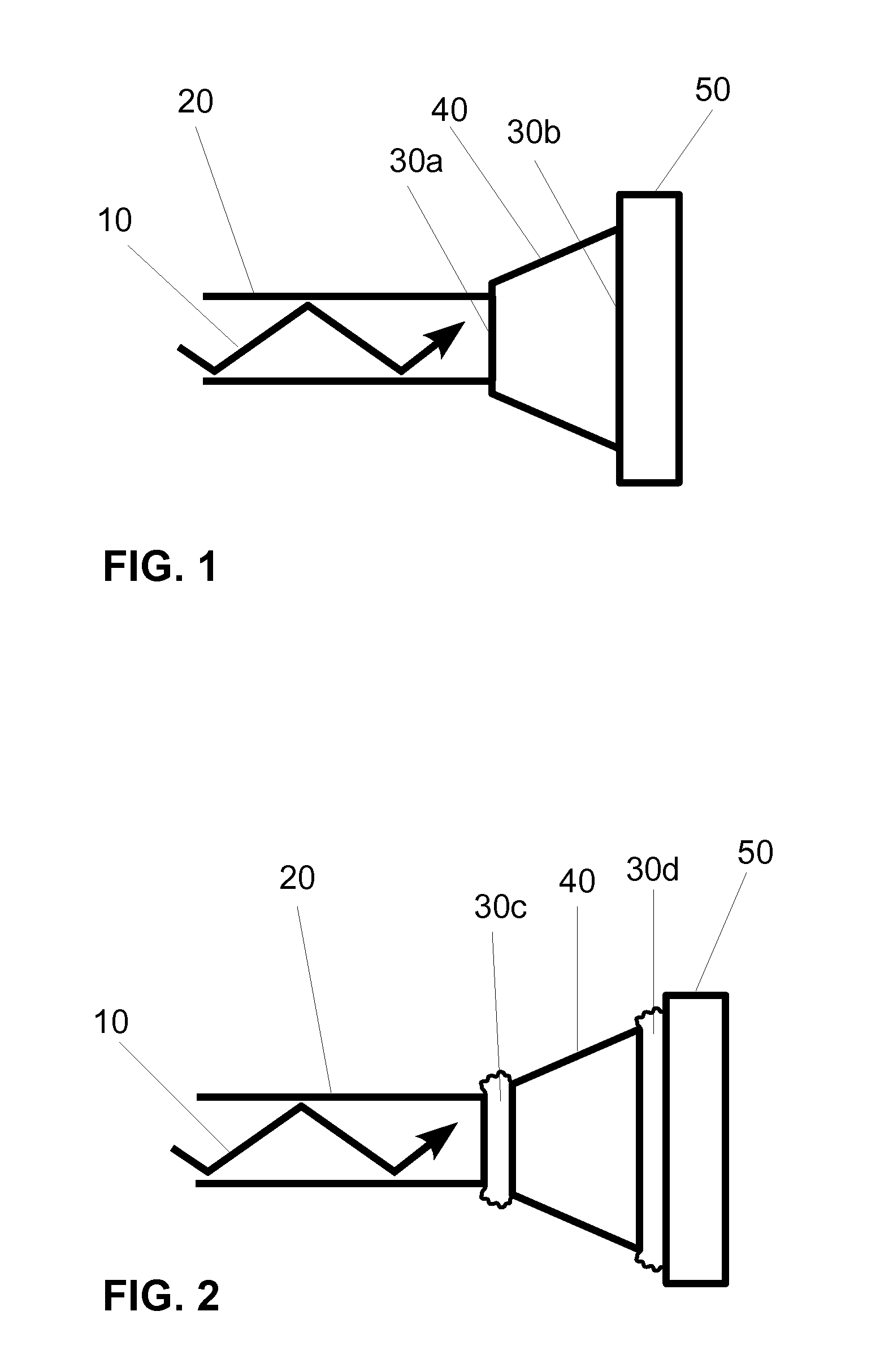
An embodiment of a light delivery portion of a photoplethysmographic device having a series of two or more optical elements. The series of two or more optical elements (20, 40, 50) are arranged to conduct light (10) from a laser and at least two consecutive elements of the series of two or more optical elements are coupled together by a non-reflective coupling (30a, 30b). This minimizes the extent to which back reflected light can re-enter the laser and adversely alter the optical output properties of the laser and additionally minimizes the light loss associated with back reflection thus helping to maximize the optical throughput. Other embodiments are described and shown.
Owner:KESTREL LABS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com