Method for identifying composition species of mixed traditional Chinese medicine powder by utilizing denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE)
A technology of traditional Chinese medicine powder and species, which is applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of high price, high technical threshold, and difficulty in popularization and use, so as to reduce experimental costs, lower technical thresholds, repeat sex high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1: Identification of Yupingfeng powder prescription mixed traditional Chinese medicine powder
[0031] 1 Select and prepare samples
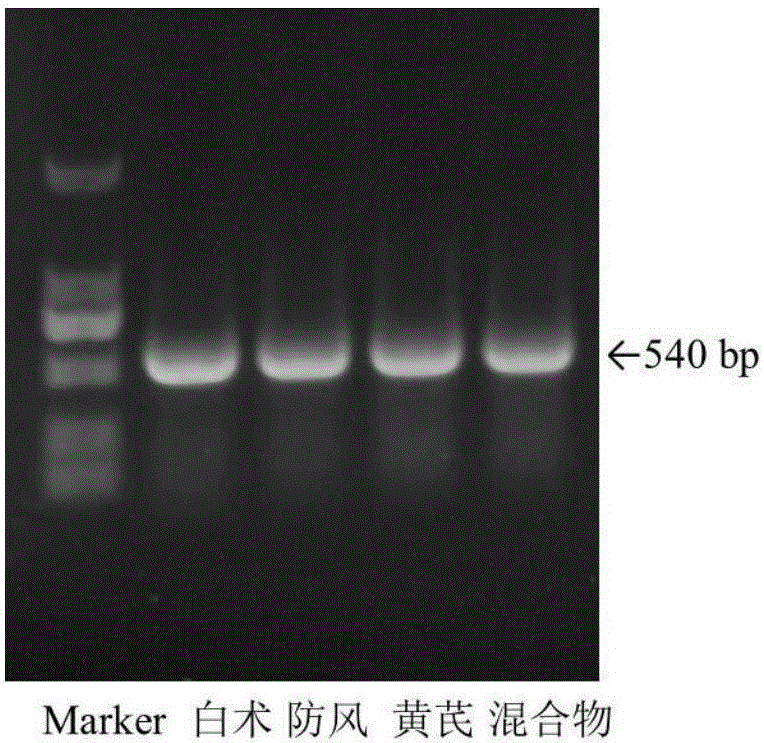
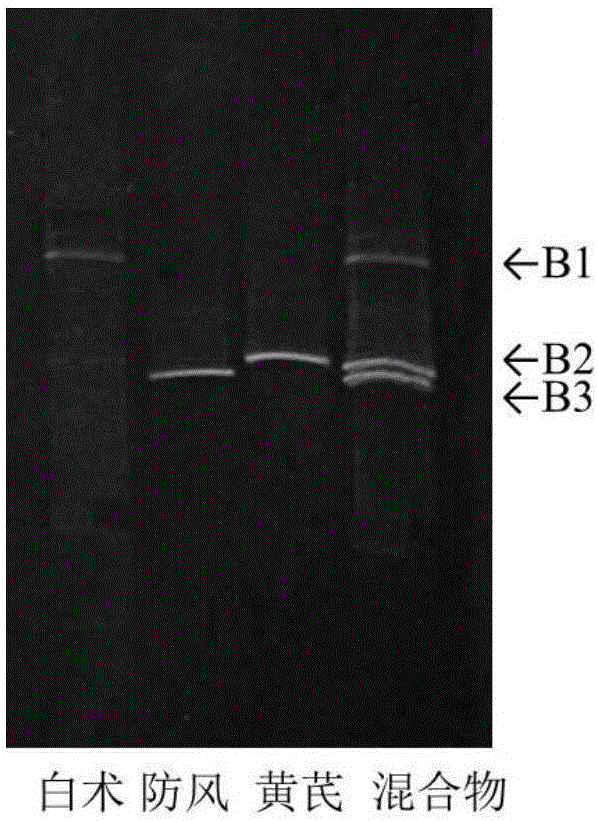
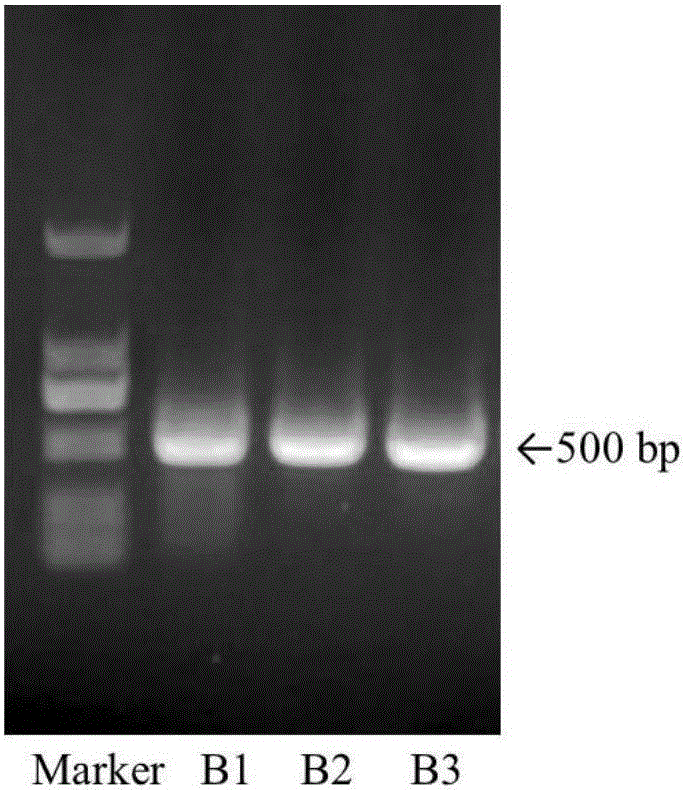
[0032] Taking Yupingfeng powder (drug composition: Astragalus, Fangfeng, Atractylodes macrocephala) as an example, each medicinal material is separately crushed into fine powder, mixed with equal weight and uniform, and used as an experimental sample.
[0033] 2 Genomic DNA extraction (modified CTAB method)
[0034] Weigh 100 mg of the sample, put it into a 2.0 mL centrifuge tube, add 2 Φ5 mm sterilized steel balls, shake it with a biological sample homogenizer at 6.0 m / s for 30 s, and repeat the shaking twice with an interval of 30 s. Add 1000 μL of CTAB free buffer (100 mM Tris-HCl, 20 mM EDTA, 1.4 M NaCl) to the centrifuge tube, shake vigorously, rotate and mix for 5 min, centrifuge at 1,3000 rpm for 3 min, discard the supernatant; repeat this step 1-2 times. Add 800 μL of CTAB buffer solution (3% CTAB, 100 mM Tris-HCl, 20 mM...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Example 2: Identification of Ginseng, Panax notoginseng, Radix Ginseng and Platycodon grandiflora mixed Chinese medicine powder (using ITS2 as a common primer)
[0052] 1. Select and prepare samples
[0053] Taking ginseng, Panax notoginseng, Radix Ginseng and Platycodon grandiflora as examples, each herb was separately crushed into fine powder, mixed with equal weights and evenly used as experimental samples.
[0054] 2. Genomic DNA extraction (modified CTAB method)
[0055] Weigh 100 mg of the sample, put it into a 2.0 mL centrifuge tube, add 2 Φ5 mm sterilized steel balls, shake it with a biological sample homogenizer at 6.0 m / s for 30 s, and repeat the shaking twice with an interval of 30 s. Add 1000 μL of CTAB free buffer (100 mM Tris-HCl, 20 mM EDTA, 1.4 M NaCl) to the centrifuge tube, shake vigorously, rotate and mix for 5 min, centrifuge at 1,3000 rpm for 3 min, discard the supernatant; repeat this step 1-2 times. Add 800 μL of CTAB buffer solution (3% CTAB, 1...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Example 3: Identification of Ginseng, Panax notoginseng, Radix Ginseng and Platycodon grandiflora mixed Chinese medicine powder (using trnL as a common primer)
[0073]The primers in Example 2 were replaced by trnL, and the PCR amplification system was: 12.5 μL of Taq DNase master mix, primer GCtrnL_F (5`-CGCCCGCCGCGCGCGGCGGGCGGGGCGGGGGCACGGGGGGCGAAATCGGTAGACGCTACG-3`) and reverse primer: trnL_R (5`-CCATTGAGTCCTGCACCTATC-3` ) each 1.0 μL, genomic DNA obtained in step 2 2.0 μL, ddH 2 O to make up the volume to 25.0 μL. Reaction program: 95°C, 2min; 95°C, 30s, 50°C, 30s, 72°C, 50s, 40 cycles; 72°C, 5min. The resulting electrophoresis of the first round of PCR amplification products is as follows: Figure 7 Shown; DGGE analysis results are shown in Figure 8 Shown; The electrophoresis of the second round of PCR amplification products is shown in Figure 9 shown. The results were all 100% similarity by gene bank comparison.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com