Bacterial nucleic acid sequencing identification method based on DNA bar code
A technology of bacterial nucleic acid and identification method, which is applied in the field of bacterial nucleic acid sequencing and identification based on DNA barcoding, can solve the problems of unclear and clear DNA barcoding nucleic acid sequence fragments, non-standard and unified basis for judging sequencing results, and little attention to the accuracy of sequence information.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Example 1. Establishment of DNA barcodes and standard nucleic acid sequence databases for identification of common microbial pollutants in pharmaceutical production environments
[0052] 1. Log in to the NCBI Genebank database, search for the target bacterial genera under the Taxonomy item, such as Staphylococcus, Micrococcus, Pseudomonas, Bacillus, Escherichia coli, Salmonella, etc., and further filter "16SrRNAand refSeq and length 1000-2000bp", to obtain the qualified 16S rRNA nucleic acid sequence.
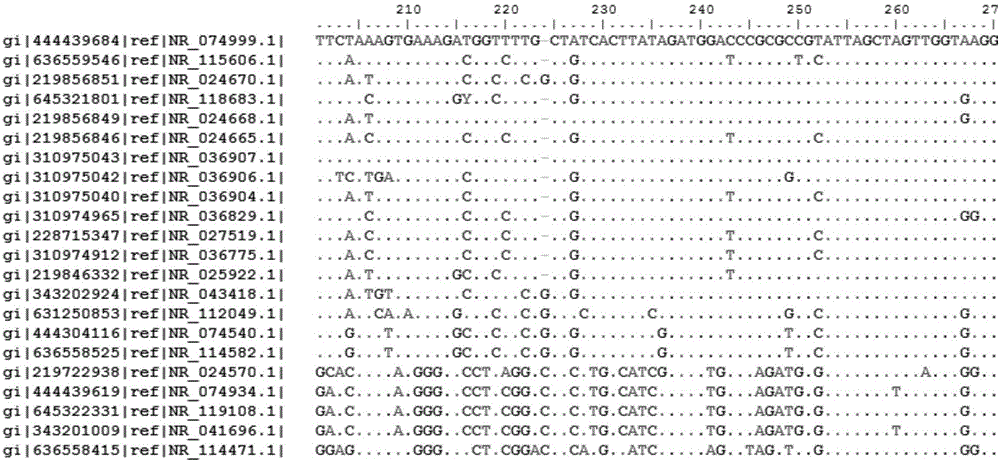
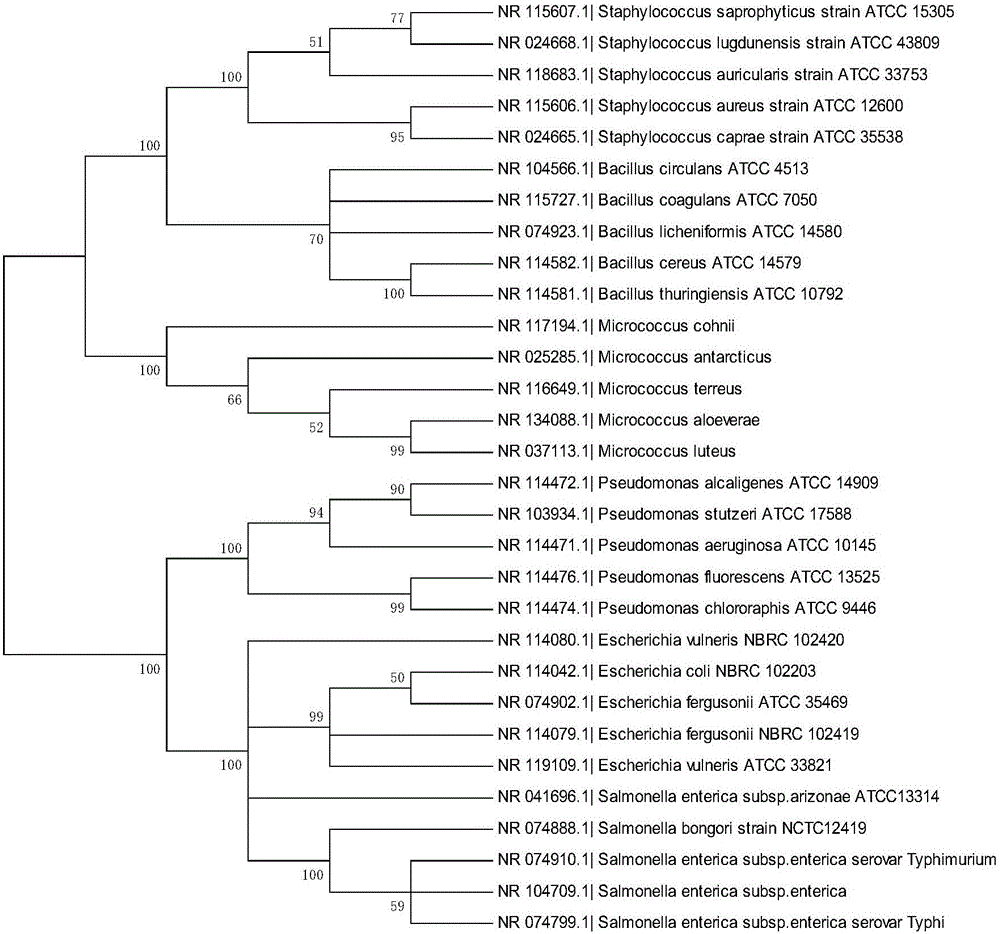
[0053] 2. Download the above sequence from the Genebank database in the Fasta file format, import it into the Bioedit sequence comparison software, perform ClustalW sequence comparison analysis with the ClustalW Multiple Alignment function, Full Multiple Alignment, Bootstrap NJTree (1000numbers) statistical methods, and select the sequence with identification and classification Significant nucleic acid sequence fragments, and design universal sequencing primers based on ...
Embodiment 2
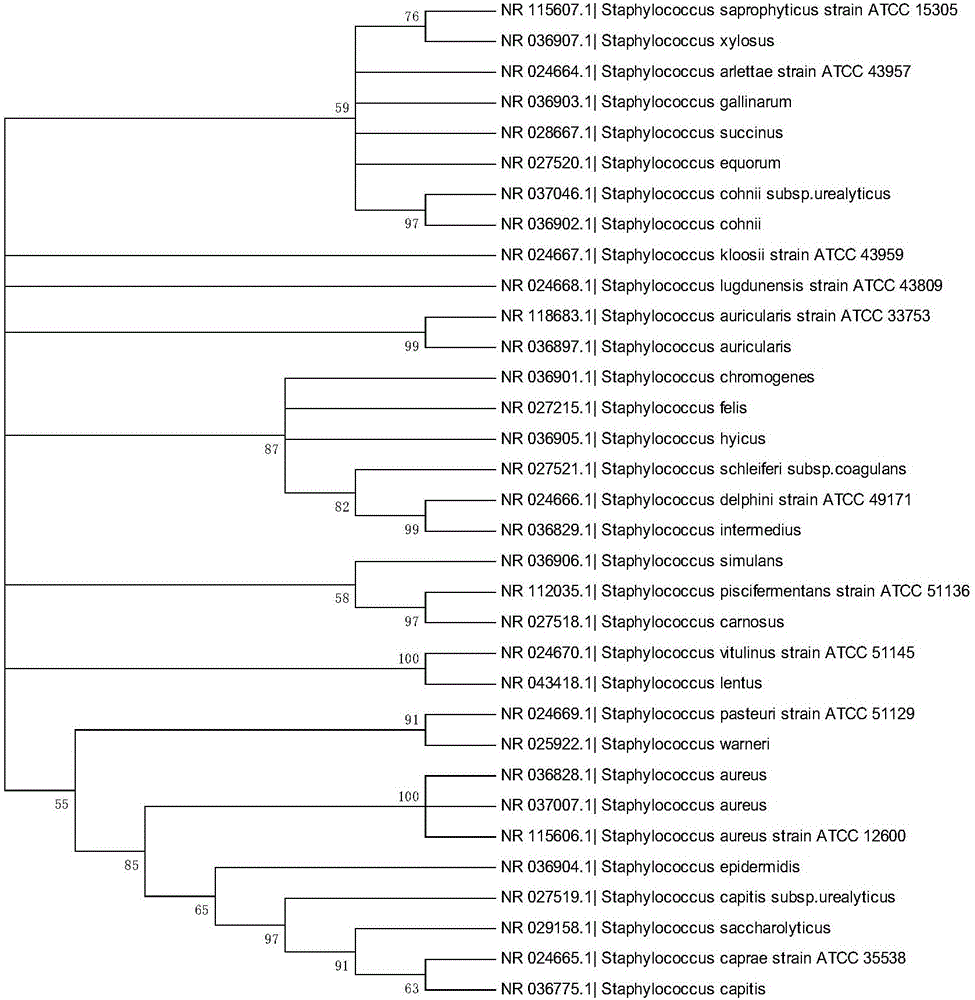
[0067] Example 2. Establishment of DNA barcodes and databases for identifying staphylococcal pollutants in pharmaceutical production environments
[0068] 1. Test method and operation steps
[0069] 1. Log in to the NCBI Genebank database, search for Staphylococcus under the Taxonomy item, and further screen "16S rRNAand refSeq and length 1000-2000bp" through the filter function to obtain the qualified 16S rRNA nucleic acid sequence.
[0070] 2. Download the above sequence from the Genebank database in the Fasta file format, import it into the Bioedit sequence comparison software, perform the ClustalW sequence comparison with the ClustalW Multiple Alignment function, Full Multiple Alignment, Bootstrap NJTree (1000numbers) statistical methods, and use the general sequencing primer V1forward( 27F) and V3reverse (548R) are positioned at both ends, and the nucleic acid sequence fragments of the same length are intercepted;
[0071] 3. Delete the sequence that the nucleic acid seq...
Embodiment 3
[0075] Example 3. Establishment of DNA barcode and database for identification of Pseudomonas pollutants in drug production environment
[0076] 1. Test method and operation steps
[0077] 1. Log in to the NCBI Genebank database, search for Pseudomonas under Taxonomy, and further screen "16S rRNA and refSeq and length 1000-2000bp" through the filter function to obtain the qualified 16S rRNA nucleic acid sequence.
[0078]2. Download the above sequence from the Genebank database in the Fasta file format, import it into the Bioedit sequence comparison software, perform the ClustalW sequence comparison with the ClustalW Multiple Alignment function, Full Multiple Alignment, Bootstrap NJTree (1000numbers) statistical methods, and use the general sequencing primer V1forward( 27F) and V3reverse (548R) are positioned at both ends, and the nucleic acid sequence fragments of the same length are intercepted;
[0079] 3. Delete the sequence that the nucleic acid sequence is not completel...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com