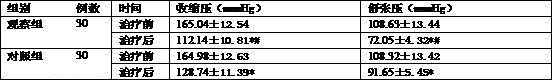Patents
Literature
65 results about "Taxus cuspidata" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
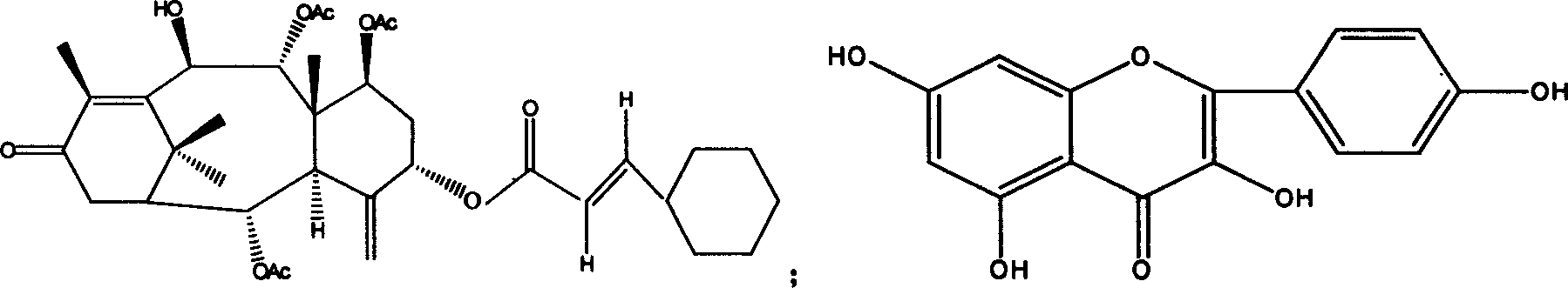
Taxus cuspidata, the Japanese yew or spreading yew, is a member of the genus Taxus, native to Japan, Korea, northeast China and the extreme southeast of Russia. It is an evergreen tree or large shrub growing to 10–18 m tall, with a trunk up to 60 cm diameter. The leaves are lanceolate, flat, dark green, 1–3 cm long and 2–3 mm broad, arranged spirally on the stem, but with the leaf bases twisted to align the leaves in two flattish rows either side of the stem except on erect leading shoots where the spiral arrangement is more obvious.
Method for asexually propagating taxus cuspidata
The invention provides a method for asexually propagating taxus cuspidata, relating to the method for propagating the taxus cuspidate. The invention solves the problems of low rooting rate and weak nursery stock in the existing cutting propagation method for the taxus cuspidate and low survival rate under natural condition when the taxus cuspidata is transplanted for afforestation on a mountain. The method comprises the following steps: ears are picked up in winter of the first year, and is buried by ice and snow; in spring of the second year, cutting is carried out on a disinfected cutting bed, a film is coated on the cutting bed in 2.5 to 3 months with humidity of between 85 and 88 percent at the temperature of between 26 and 29 DEG C and shading degree of between 70 and 75 percent after cutting is completed, and the cutting bet is subject to fertilizer application and sterilization; the coated film is removed, cold-proof water is irrigated before winter; and the bed is changed in spring of the third year, and culture is conducted for two years to obtain the taxus cuspidata for afforestation. The cultured sapling has 100 percent of lignification, 80 to 96 percent of cut rooting rate and 85 to 90 percent of planting percentage, thus the mature period of medical forest is shortened. The method can be used for large-scale afforestation.
Owner:HARBIN HONGDOUSHAN TECH DEV
Cuttage breeding method of taxus chinensis in northeast
InactiveCN101663946AGuaranteed humidityGuaranteed freshnessCultivating equipmentsPlant protectionDiseaseHigh survival rate
The invention relates to a cuttage breeding method of taxus chinensis in northeast, comprising the following steps: selecting a one-year-old branch as a branch for cuttage; concealing the branch at ashade place, and carrying the branch to a destination after the branch is packaged by a plastic bag; retaining 1-2 leaves on the upper end of each nursery stock stalk when shearing a seedling, shearing the parts longer than 3cm of the retained leaves, and also shearing leaves inserted into the stalk positioned in the middle of a seedling bed; disinfecting a land before the cuttage so as to reducerhizoctonia solani kuhn, and carrying out the cuttage from the middle ten days of October to the first ten days of November or from February to March; using a light shielding net of 80 percent to shield light without directly shining with the sun during the daily management of the seedling; controlling the soil water content at 35-45 percent; and paying attention to the water drainage of the seedling in rainy days and intertillage weed control in ordinary days, and preventing and curing diseases of the seedling in time by chemical agents. By adopting the cuttage breeding method, the taxus chinensis in northeast has high survival rate, fast breeding cultivation and high disease resistance.
Owner:苏庆良
Extraction method of taxol from branches and leaves of artificially cultivated yew
InactiveCN101560197AProtect resourcesSimple processOrganic chemistryChromatographic separationNatural source
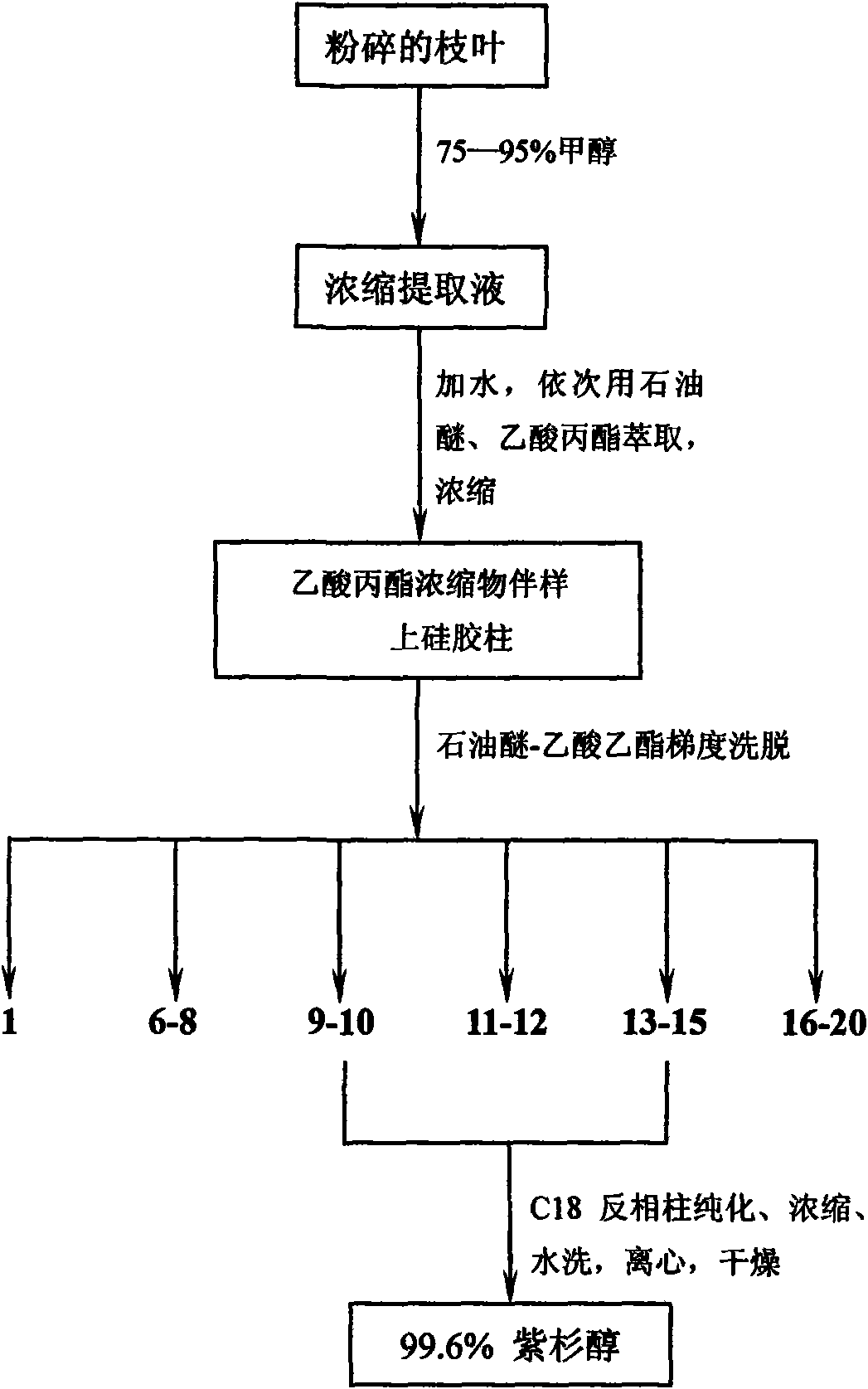
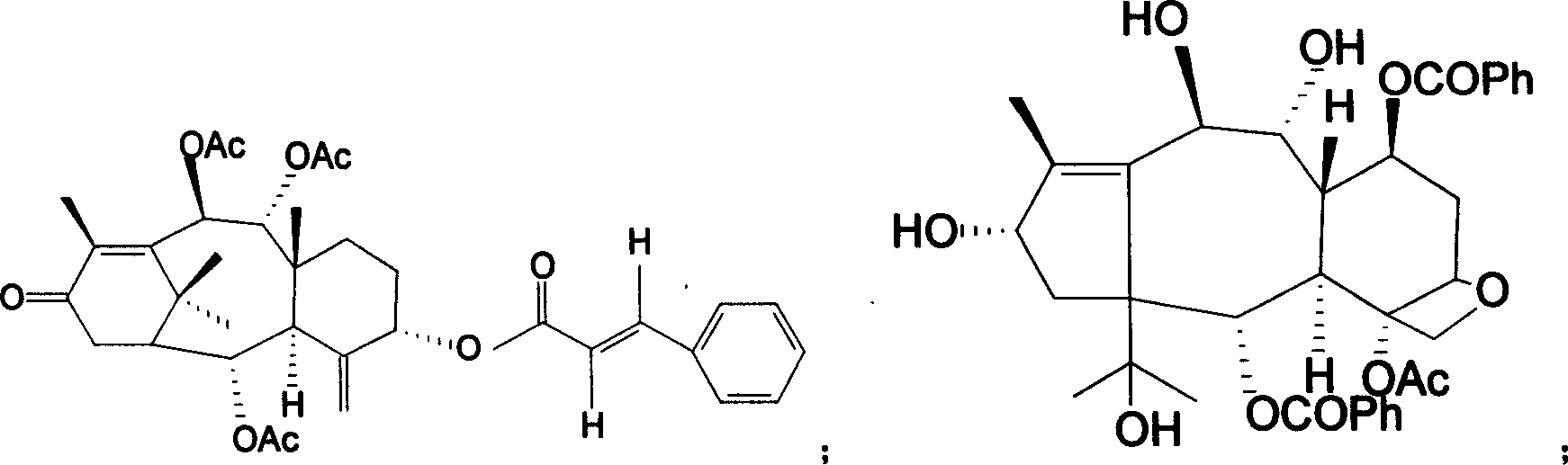
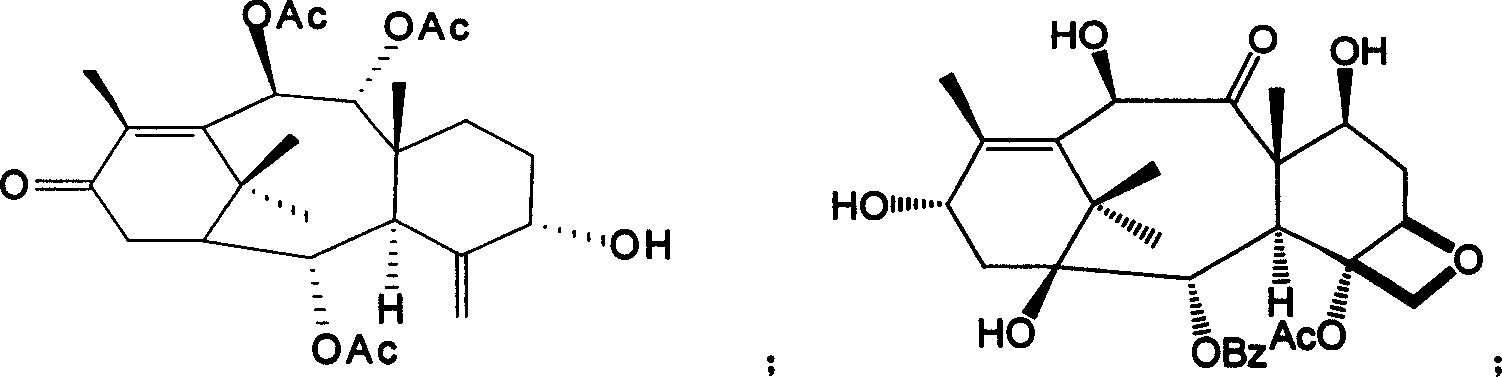
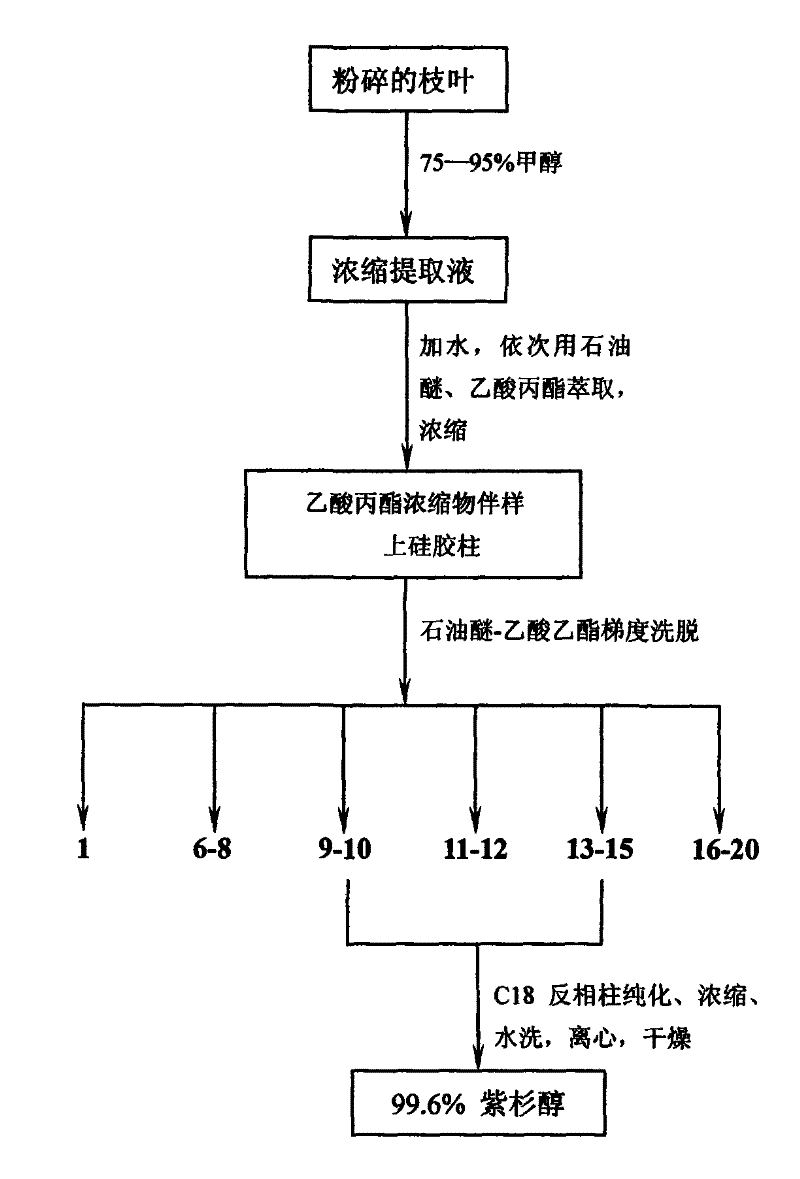
The invention relates to an extraction method of taxol from branches and leaves of artificially cultivated yew. A plurality of methods, such as planting of stocky yew, cultivating of tissue and semi-synthesis and total synthesis of taxol, have been developed home and abroad so as to obtain taxol raw material; however, the tissue cultivating method has low yield and high broth price; and the total synthesis has extremely low yield, worse therapeutic effect than natural-source taxol, and a high cost; thereby being difficult for commercial application. The invention uses branches and leaves of artificially cultivated taxus media, Yunnan taxus, southern taxus or northeastern taxus as raw materials; the raw materials are marinated by carbinol and extracted by petroleum oil and propyl acetate in sequence; and normal-pressure normal-phase silica gel column chromatography or reverse-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography is used to obtain high-purity taxol with a purity being higher than 99.6%. The preparation method has simple process, low cost, recyclable solvent and eluant; therefore, the method is applicable to industrial production and protects plant resource.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Yew genus plant extract and its extraction method and application
ActiveCN1594247ASolve the problem of sustainable useIncrease profitOrganic active ingredientsOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationLignanCurative effect
The invention relates to the Yew genus plant extract and its extraction method and application, wherein the extract is extracted from the stems and leaves of Northeastern yew and comprises taxone diterpenoid, total lignans, total flavone. The extract can be used as the effective composition for anti-cancer drugs.
Owner:HARBIN HONGDOUSHAN TECH DEV
Paclitaxel oral anticancer preparation obtained by nontoxic extraction from complete stool of Chinese yew and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102552338ALow toxicityEffective activity does not destroyAlcoholic beverage preparationPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMedicineTherapeutic effect
The invention provides a paclitaxel oral anticancer preparation obtained by nontoxic extraction from a complete stool of Chinese yew and preparation method thereof, which uses Chinese yew in Northeast China as the main raw material, by a ethanol immersion 16-step method and a nontoxic extraction technology, to obtain a 30% paclitaxel crude product, which is used as main raw material of paclitaxel drug wine and paclitaxel oral liquid. Based on drug effect research, the prepared oral anticancer preparation has greatly visble treatment effect on late period caser patients of 20 kinds of different singularity and the late period and anaphase cancer patients which is failure on combined chemotherapy, and the preparation has advantages of good ease pain effect and non-poison.
Owner:林树芳
Cultivation and separation method for taxus stem cells
InactiveCN103087974AMeet actual needsHas the ability to split infinitelyPlant cellsCambiumEvery Two Weeks
The invention relates to a cultivation and separation method for taxus stem cells. The method comprises the steps of sterilizing annual epicormic branches of taxus cuspidate, with the diameter of 1 centimeter, for 10 minutes by using 0.1% mercury chloride; cutting off explants including periderm, phloem and cambium from the epicormic branches, cutting into slices; putting the slices on a B5 medium containing 0.2-2.0 mg.L<-1> picloram and 0.2-1.5 mg.L<-1> naphthalene acetic acid, culturing in the dark at a temperature of 25 DEG C; taking the explants with obvious cambium proliferation out after two weeks; separating cambium stem cells and transferring the stem cells to a subculture medium for culture, wherein the subculture medium is a B5 medium containing 0.2-2.0 mg.L<-1> picloram and 0.2-1.5 mg.L<-1> naphthalene acetic acid; and sub-culturing one time every two weeks. A mass of stem cells can be obtained in a short time. The stem cells cultured by the method are cells in an undifferentiated state which have the capacity of infinite division and can obtain a mass of the stem cells, so that a great amount of paclitaxel can be produced, thereby meeting the needs of patients.
Owner:鹭港生物药业有限公司
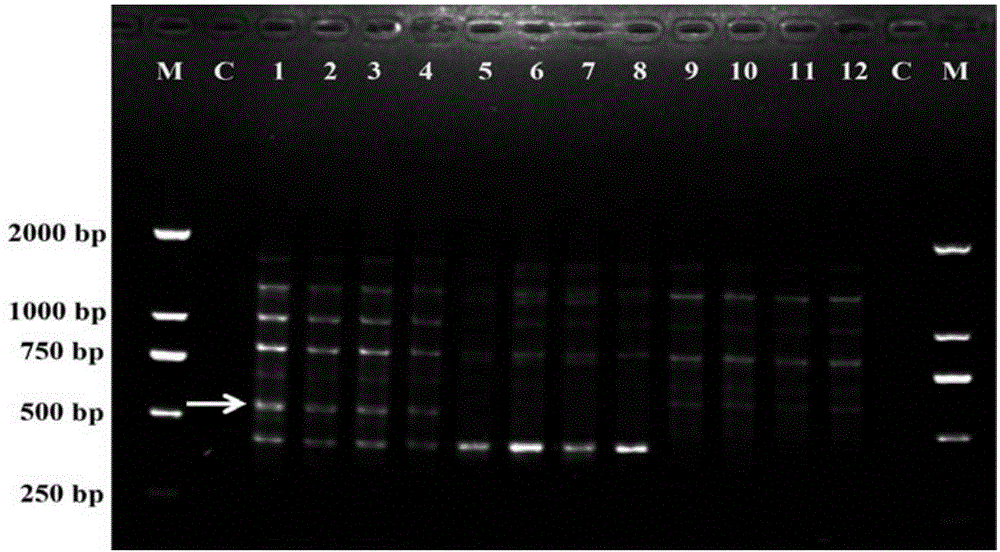
DNA bar code primer pair, kit and method for identifying Taxus chinensis species
InactiveCN105177151AEfficient identificationRich genetic variationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA barcodingA-DNA
The invention discloses a DNA bar code primer pair, kit and method for identifying Taxus chinensis species. The kit comprises the following DNA bar code primer pair including an upstream primer Taxus Indel-F(SEQ ID NO.1) and a downstream primer Taxus Indel-R(SEQ ID NO.2). DNA bar codes include the Taxus chinensis DNA bar code, the Taxus chinensis var.mairei DNA bar code, the Taxus cuspidata DNA bar code, and the Taxus baccata DNA bar code, wherein the sequence of the Taxus chinensis DNA bar code is shown as SEQ ID NO.3 to SEQ ID NO.6, the sequence of the Taxus chinensis var.mairei DNA bar code is shown as SEQ ID NO.7 to SEQ ID NO.8, the sequence of the Taxus cuspidata DNA bar code is shown as SEQ ID NO.9, and the sequence of the Taxus baccata DNA bar code is shown as SEQ ID NO.10. The kit and the identifying method are simple, easy to implement and capable of being effectively used for Taxus species identification, protection and related research, and results are accurate and reliable.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Test tube one-step seedling method of taxus cuspidata
ActiveCN103039365AReach the goal of rapid multiplication in one stepHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureAxillary budSucrose
The invention relates to a plant planting technology, namely a test tube one-step seedling method of taxus cuspidate. The test tube one-step seedling method comprises the following steps of: (1) taking a newly-sprouted main stem on a taxus cuspidate wild seedling trunk and cutting into segments as explants for further use; (2) when stem segments grow roots, utilizing an axillary bud germination growth culture medium including components and contents: a culture medium+indoleacetic acid IAA (0.03-0.04mg / L)+naphthylacetic acid NAA (0.02-0.03mg / L)+kinetin KT (0.11-0.12mg / L)+gibberellin GA3 (2.60-2.80mg / L); adding agar powder with the concentration of 8.0g / L and adding cane sugar with the concentration of 20.0g / L; adjusting the pH (Potential of Hydrogen) value to 5.6; and culturing tender stem segments under the conditions that the illumination period is 6 hours per day, the illumination intensity is 700lx and the temperature is 20+ / -2 DEG C. The invention further provides high-quality seedlings for artificially propagating and cultivating the taxus cuspidate in scales. The hardening-seedling and transplanting survival rate can reach more than 95.2%.
Owner:TONGHUA NORMAL UNIV
Light supplement cultivation method for promoting fast growth of taxus cuspidata container seedlings
InactiveCN104429555AHuan Miao KuaiEasy to operateSaving energy measuresFertilising methodsCulture environmentSeedling
The invention relates to a cultivation method for taxus cuspidata in a cold region, in particular to a light supplement cultivation method for promoting fast growth of taxus cuspidata container seedlings. The purpose is to solve the problems that existing taxus cuspidata container seedlings grow too slowly, an existing light supplement method is unobvious in effect, and after light is supplemented, seedling bodies are weak and even die as whole plants. The light supplement cultivation method includes the steps of (1) collecting, (2) seedling planting, (3) light supplement treatment on the seedlings and (4) fertilization treatment on the seedlings. The light supplement cultivation method has the advantages that after being planted, the taxus cuspidata container seedlings can be recovered fast and adapt to the container seedling culture environment; the cultivation method is easy to implement, low in cost and remarkable in effect; the mode of applying fertilizer of small amount many times is adopted and is beneficial for improving the robustness of nursery stocks; the growth rate of the taxus cuspidata container nursery stocks is increased by over 70%. The cultivation method is mainly used for promoting fast growth of the taxus cuspidata container seedlings.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
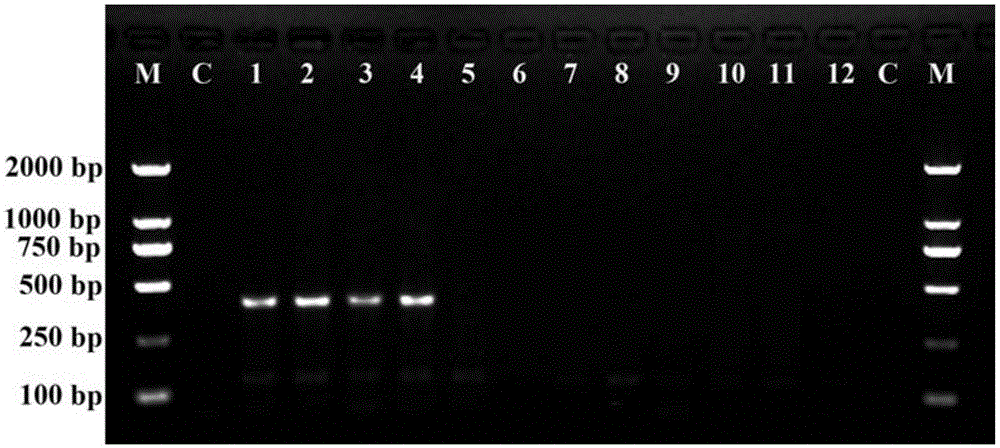
Nucleotide sequence, molecular probe and method for identifying taxus media seedling
ActiveCN104480210AHigh sensitivitySimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention relates to a nucleotide sequence, a molecular probe and a method for identifying a taxus media seedling. The nucleotide sequence for identifying the taxus media seedling is represented as SEQ ID NO.1; upstream MHSF of the nucleotide molecular probe for identifying the taxus media seedling is represented as SEQ ID NO.2, and downstream MHSR is represented as SEQ ID NO.3; and by means of the nucleotide molecular probe MHSF / MHSR, taxus media is identified with a conventional PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method. The sample consumption is small, and the overall operation can be completed only by a small quantity of samples; accuracy and sensitivity are high; MHSF / MHSR is a specific molecular probe for the taxus media, and negative reaction is caused if T. chinensis or T. cuspidata is detected; and the method is simple, the PCR technology is adopted for detection, time is short, and the detection can be finished by half day.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Taxus chinensis clone
InactiveCN101768567AMeet clinical needsDo not destroy wild resourcesMicroorganism based processesPlant cellsEcological environmentDry weight
The invention provides a Taxaceae clone of a stable and high-yield Taxol, in which the content of the Taxol can be 0.8-0.12% of the dry weight of the cultured materials, and is 4-6 times of wild Taxus chinensis. The invention also provides culture technique of the clone and a method for producing the clone culture in large scale rapidly. The method combines liquid and solid culture, produces seed through the liquid culture and obtains the culture materials through the solid culture, selects the culture with excellent comprehensive performance as seeds to be reserved for the liquid culture, and does the process repeatedly. The method can be used for large scale production, the production cycle is shorten greatly compared with the wild type, and has stable quality and high yield. Additionally, the culture process of the method doses not occupy cultivated land, does not damage the wild resource of the Taxus chinensis, protects the environment and solves the problem of shortage of Saussurea involucrate resource.
Owner:DALIAN PRACTICAL BIOTECH +2
Open type simplified culture medium for taxus cuspidata
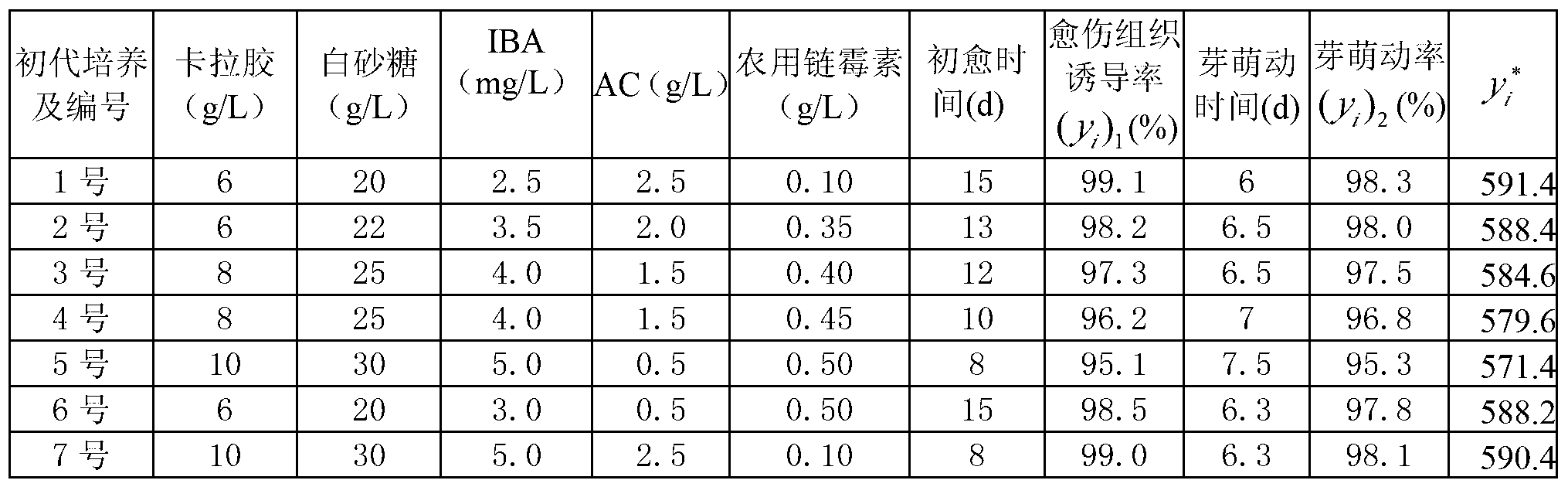
InactiveCN103238522AGood inhibitory effectEasy to produceHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureCarrageenanHigh pressure
The invention relates to an open type simplified culture medium for taxus cuspidate. The culture medium comprises a primary culture medium and a subculture medium. The primary culture medium is prepared by adding and mixing carrageenan, white granulated sugar, indolebutyric acid IBA, active carbon AC and agricultural streptomycin into optimized B5 basic mother liquor. The subculture is prepared by adding and mixing carrageenan, white granulated sugar, indolebutyric acid IBA, 6-benzyl amino adenine BA, active carbon AC and agricultural streptomycin into optimized MS basic mother liquor. According to the culture medium provided by the invention, with the adoption of open type simplified tissue culture, the cost and the inoculating time of the culture medium are remarkably saved, the autoclaved sterilization program is cancelled, and the production flow is simplified by replacing autoclaved sterilization and strict enclosed environment operation by a bacteriostatic agent, so that the labor and equipment investment in industrialized seedling production can be reduced, and the fund is saved by 30-50%.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for extracting and purifying 7-xylose-10-deacetyl paclitaxel from taxus cuspidata
InactiveCN101575356AEfficient and reasonable useSimple methodSugar derivativesSolid sorbent liquid separationSeparation technologyHigh pressure
The invention relates to a method for extracting and purifying a functional element from a traditional Chinese herb and aims at providing a convenient, safe, economical and efficient method for extracting and purifying 7-xylose-10-deacetyl paclitaxel which is a monomeric compound from taxus cuspidata. The technical proposal adopted by the invention comprises the steps: fresh or dried leaves of taxus cuspidate are taken as raw materials, and macroporous adsorption resin enrichment technology, normal-pressure chromatography preparation technology and high-pressure liquid phase separation technology are combined to prepare the 7-xylose-10-deacetyl paclitaxel with the purity higher than 99.90 percent at an extraction rate of 0.05 percent. The raw materials used in the invention can be waste materials from the paclitaxel production, thus fully utilizing natural resources. Moreover, the method comprises extraction, primary impurity removal and repurification, thus being simple and easy; and the loss of the target compound is low.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +1
Composite essential oil prepared from taxus cuspidata and coniferous plants and application of composite essential oil
InactiveCN105087165AReduce ammonia contentImprove air qualityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsIndoor air qualityPreparing skin
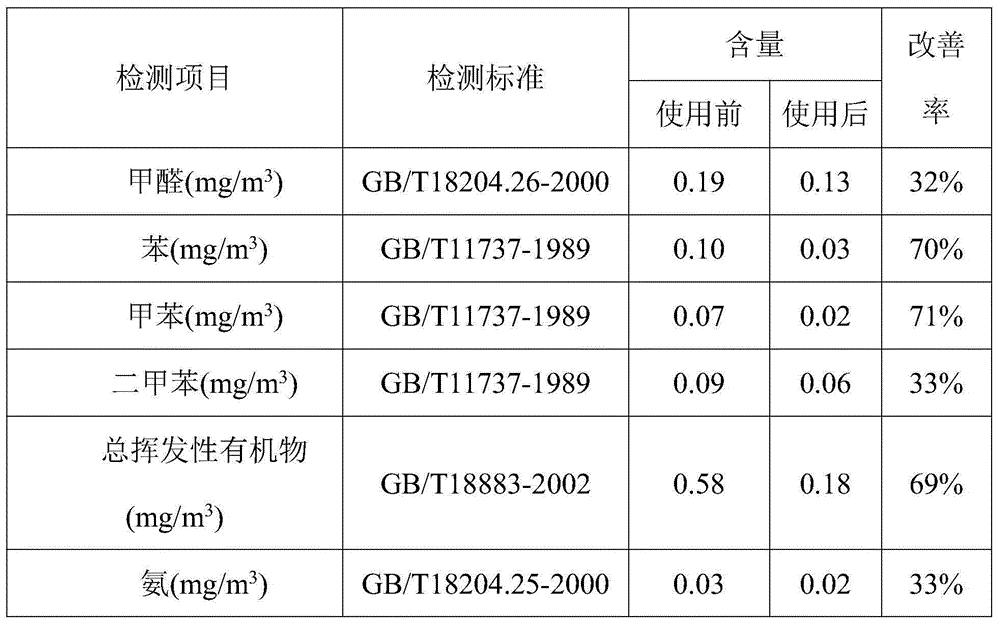
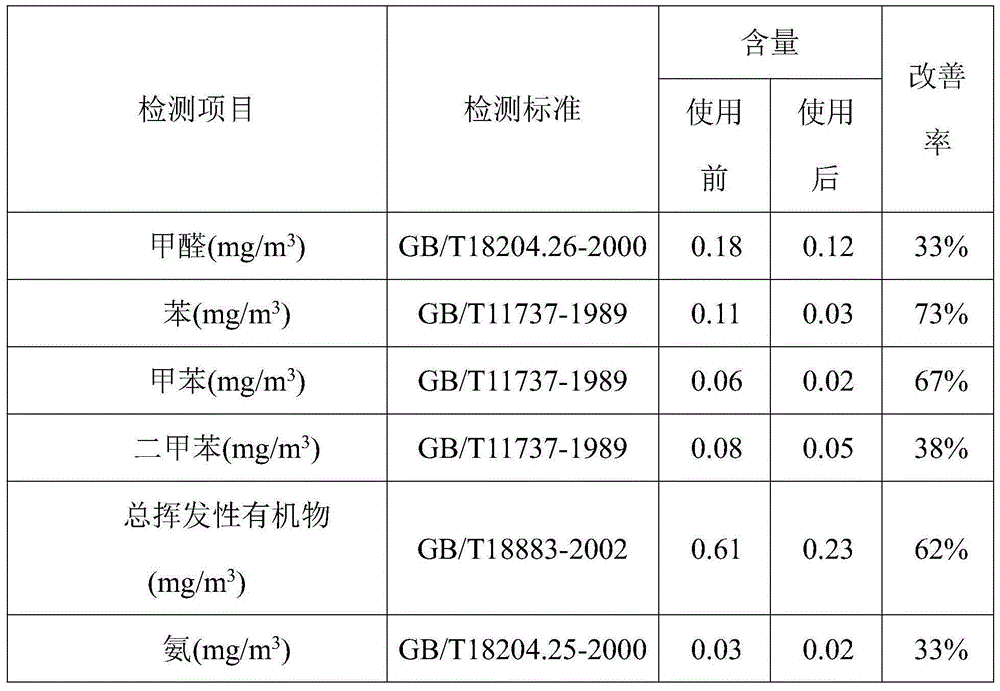
The invention discloses composite essential oil prepared from taxus cuspidata and coniferous plants and application of the composite essential oil. The composite essential oil prepared from taxus cuspidata and coniferous plants is prepared from taxus cuspidata and coniferous plants at the weight ratio of 1:1-1:3, and the composite essential oil can be used for preparing aroma essential oil, aroma candles and air fresheners for improving indoor air quality or preparing skin essential oil soap. The composite essential oil can effectively purify air, improve air quality and effectively reduce indoor methanal, benzene, methylbenzene, dimethylbenzene, total volatile organic compounds and ammonia content.
Owner:HARBIN HONGDOUSHAN TECH DEV +2
SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) molecular marker for identifying taxus cuspidata and application of SNP molecular marker
PendingCN109486982AImprove featuresHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceMolecular marker
The invention discloses an SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) molecular marker for identifying taxus cuspidata. The SNP molecular marker is positioned at a 444th-site basic group of a sequence shownas SEQ ID NO.1. The taxus cuspidata is identified if the 444th-site basic group is T. The SNP molecular marker has the advantages that systems for quickly identifying the taxus cuspidata can be quickly established on the basis of the SNP molecular marker, accordingly, the purpose of quickly and accurately detecting the taxus cuspidata can be achieved, and the SNP molecular marker has important significance in port species inspection work and the like.
Owner:HANGZHOU KMB BIOTECH
Northeast Chinese yew transplanting method in coast saline-alkaline region
InactiveCN105900763AImprove the level of greeningImprove the landscape effectCultivating equipmentsForestryGreeningAqueous solution
The invention relates to a northeast Chinese yew transplanting method in a coast saline-alkaline region. The method comprises the steps of 1) selecting a place that has a shade and a high physical feature where hydrocele is difficult from the middle ten days of March to the middle ten days of April; 2) digging a tree aperture according to the soil ball size of a transplanted nursery stock; 3) mixing well raw soil dug from the tree aperture with turfy soil and river sand in volume ratio of 1:1:1 to obtain plantation soil; 4) filling part backfilling soil, putting the soil ball of the transplanted nursery stock to guarantee that the rhizome junction of the plant is 10cm higher than the ground, then filling the backfilling soil, stamping and compressing; 5) using an aqueous solution that containing 0.3mmp Naphthalene acetic acid, 0.5ppm indole butyric acid and 300ppm calcium nitrate as a root water. <{EN2}>According to the invention, the Chinese yew can be possibly planted in a coast saline-alkaline region, which means a lot for lifting city greening level and landscape effect.
Owner:TIANJIN TEDA GREEN GRP CO LTD
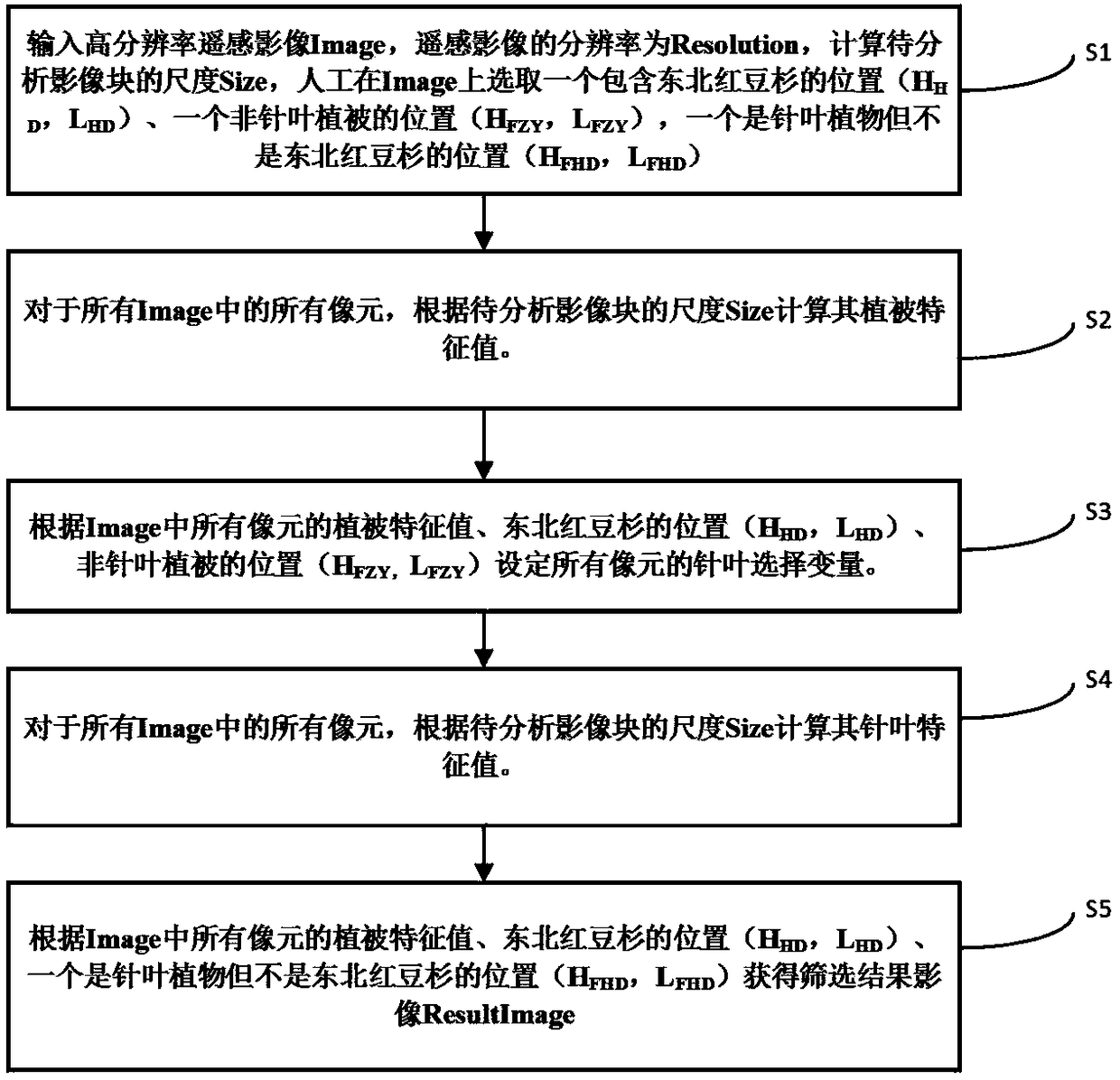
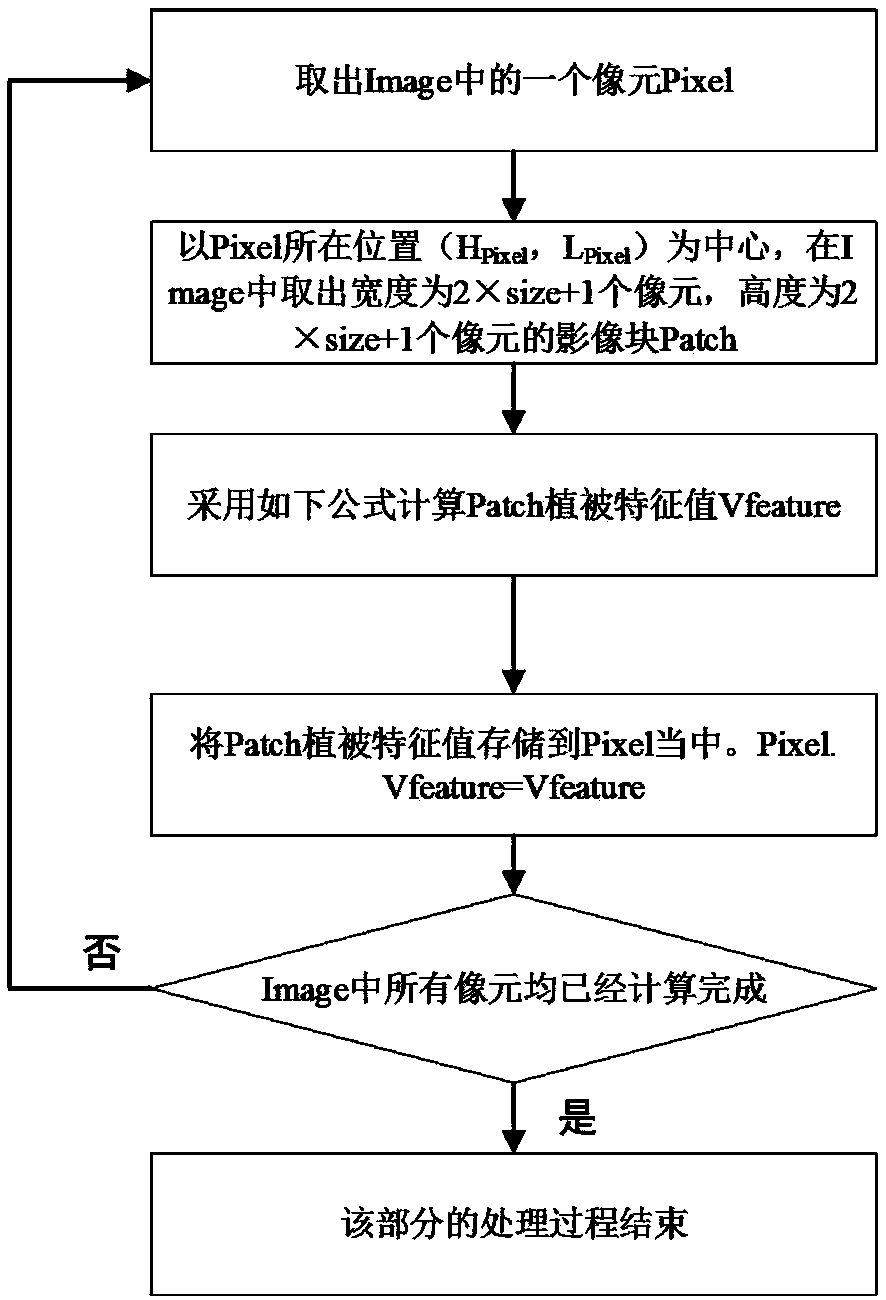
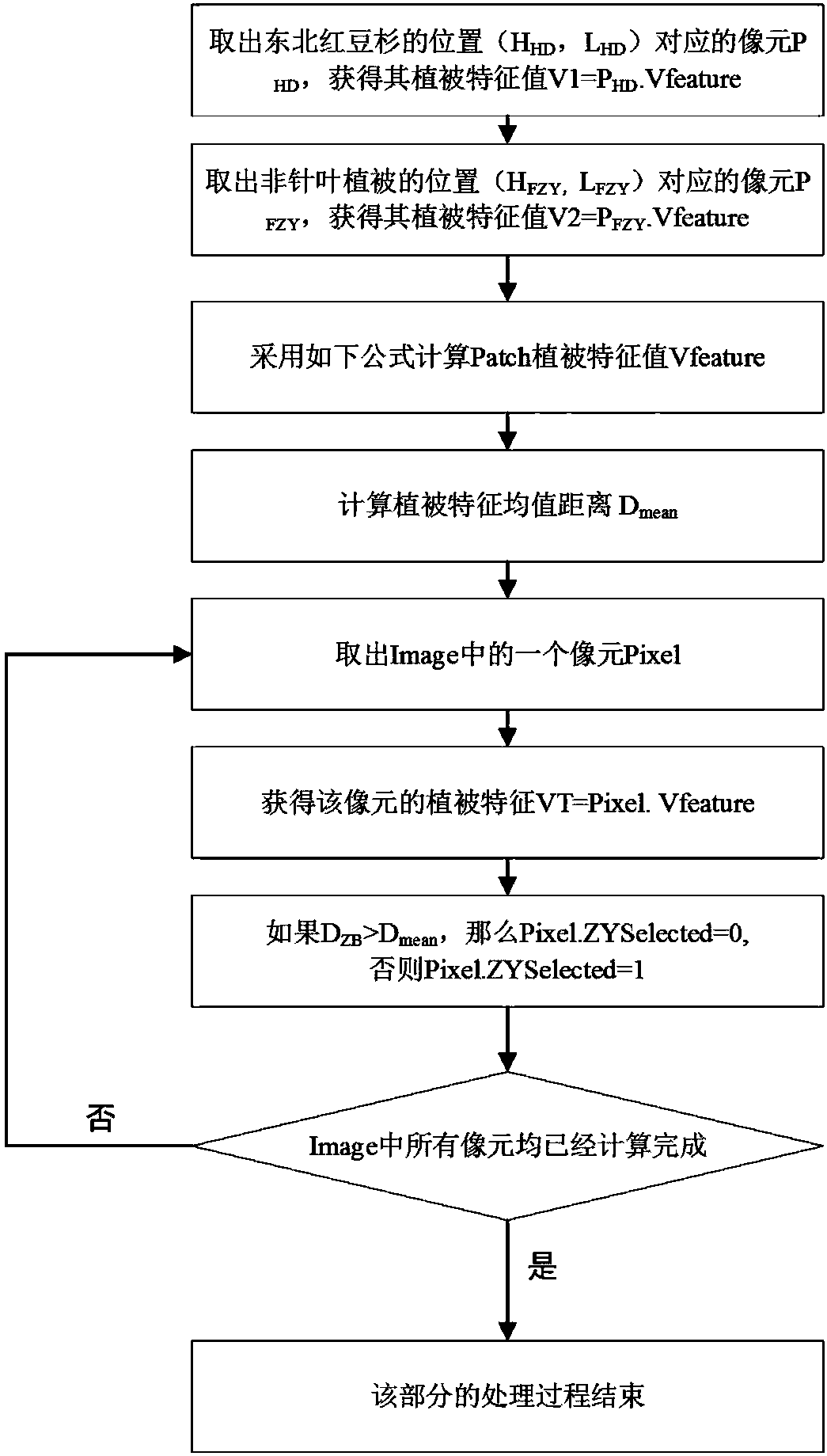
Method for automatically recognizing taxus cuspidata in high-resolution remote sensing images
ActiveCN108154138AImprove recognition qualityCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer scienceHigh resolution
The invention provides a method for automatically recognizing taxus cuspidata in high-resolution remote sensing images. The method has the advantages that only few ground samples are needed for high-accuracy recognition of the taxus cuspidata in the high-resolution remote sensing images, the advantages of low cost and wide coverage of the remote sensing images are fully utilized, the taxus cuspidata can be recognized from the remote sensing images on the basis of the few samples according to its unique features, high recognition quality is acquired, and accordingly, high social and economic value is achieved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF TECH
Method for producing cigarette filter sticks by adding Taxus cuspidata particles
ActiveCN106666825AImprove taste qualityImprove suction qualityTobacco smoke filtersNatural stateEngineering
A consumption habit with flue-cured tobacco cigarettes as a main part is formed in long time in our country, cut tobacco of this kind of flue-cured tobacco cigarettes has is rich in tar and is high in fragrance concentration, smell of cigarettes is thin and insufficient in fragrance due to the fact that the tar content of the cigarettes is sharply lowered, and consumers are difficult to accept it. In the method, Taxus cuspidate plant micropore particles or Taxus cuspidate plant ultra-micropore compound powder are added into cigarette filter tow in proportion, natural states and components of plant components such as Taxus cuspidate, vetiver roots, Houttuynia cordata, couchgrass root, and Reed Rhizome are fully utilized, these plants play a role in a positive effect of adjusting the flavor of the cigarettes, the smoke quality of the cigarettes is improved, harmful gas in smoke can be filtered out, and the tar and nicotine content of main smoke of the cigarettes can be reduced by 5.0-10.0%; and the Taxus cuspidate plant compound particles are added in a large proportion, and then the comprehensive use rate of tobacco raw materials can be greatly improved, and the tobacco leaves consumption can be effectively reduced.
Owner:YUNNAN RELIKANG BIOTECH
Extraction method of taxol from branches and leaves of artificially cultivated yew
InactiveCN101560197BProtect resourcesSimple processOrganic chemistryChromatographic separationNatural source
The invention relates to an extraction method of taxol from branches and leaves of artificially cultivated yew. A plurality of methods, such as planting of stocky yew, cultivating of tissue and semi-synthesis and total synthesis of taxol, have been developed home and abroad so as to obtain taxol raw material; however, the tissue cultivating method has low yield and high broth price; and the totalsynthesis has extremely low yield, worse therapeutic effect than natural-source taxol, and a high cost; thereby being difficult for commercial application. The invention uses branches and leaves of artificially cultivated taxus media, Yunnan taxus, southern taxus or northeastern taxus as raw materials; the raw materials are marinated by carbinol and extracted by petroleum oil and propyl acetate insequence; and normal-pressure normal-phase silica gel column chromatography or reverse-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography is used to obtain high-purity taxol with a purity being higher than 99.6%. The preparation method has simple process, low cost, recyclable solvent and eluant; therefore, the method is applicable to industrial production and protects plant resource.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Batch transplanting method for taxus cuspidata seedlings
InactiveCN105165530AImprove survival rateCultivating equipmentsExperimental methodsObserved Survival
The invention discloses a batch transplanting method for taxus cuspidata seedlings, relates to a transplanting method for taxus chinenesis seedlings in cold regions and belongs to the field of taxus cuspidata seedling transplanting. The technical problems that in the prior art, the taxus cuspidata seedlings are low in survival rate of transplanting and poor in growth in the field are solved. The method includes the steps that 1, chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of transplanted seedling quality are estimated; 2, the environmental suitability of seedling transplanting land is investigated and evaluated; 3, the seedlings are transplanted. By the adoption of the experimental method, after three months of transplanting the taxus cuspidata seedlings, the survival rate is 95%, after five months of transplanting, the survival rate is 90%, and compared with other methods, the survival rate of transplanting is increased by 30-50%.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Tissue culture method of taxus cuspidata
InactiveCN106135002AImprove survival rateImprove proliferative abilityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureIntermediate cellSeedling
The invention discloses a tissue culture method of taxus cuspidata. The method includes the following steps that 1, intermediate cells of a newborn branch of taxus cuspidata are selected and treated into a 2 cm tissue slice, the tissue slice is disinfected and then cultured for 15-20 days in a B5 culture medium to form 10-12 cm tissue, and the 5-6 cm part in the middle is selected for the next step of culture; 2, the callus is transplanted into a rooting culture medium for rooting culture, a dark environment is kept in the first three days, and the illumination time of 12-14 h / d is kept three days later till 3 cm main roots emerge. According to the tissue culture method of taxus cuspidata, the intermediate cells of the newborn branch of taxus cuspidata are selected, contain rich taxol and have high proliferation capability, so that the tissue culture period of taxus cuspidata is short, and the survival rate is high; the selected culture medium is simple, easy to obtain and suitable for large-scale culture of taxus cuspidata seedlings.
Owner:夏学云
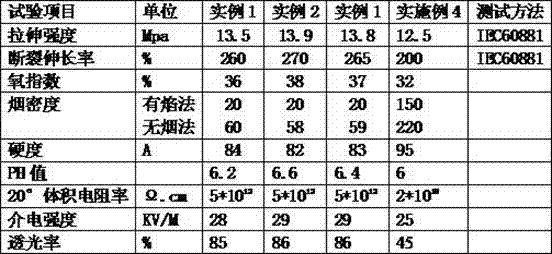
Low-smoke, halogen-free and flame-retardant thermoplastic elastomer cable material with ultralow smoke amount
InactiveCN107474373ALow smoke densityImprove flexibilityPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsElastomerCarvacryl acetate
The invention relates to a low-smoke, halogen-free and flame-retardant thermoplastic elastomer cable material with an ultralow smoke amount. An ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer, a polyolefin elastomer, an EPDM (ethylene-propylene-diene monomer), hydrogenated base oil, siloxane and a flame retardant are added to a high-speed mixer, organic silicon resin, sodium silicate, maleic anhydride grafted polyolefin elastomers, diammonium hydrogen phosphate, bark of taxus, pine bark, taxus cuspidate, chitosan, a citrus extract, a fresh ginger extract, chlorinated polyethylene resin, polytetrafluoroethylene and polyimide are added and put in an internal mixer, all components are mixed uniformly, and soft jelly is formed; the soft jelly is put in a single screw for mixing, plasticization and melt extrusion, water and volatile substances are extracted, cooling, granulation and drying are performed, and the cable material can be obtained. The low-smoke, halogen-free and flame-retardant cable material with the ultralow smoke amount is produced and releases less smoke during large-area burning.
Owner:JIANGSU SHENYUAN MATERIAL SCI CO LTD
Dihydrochlorothiazide (DCT) containing pharmaceutical composition for treating hypertension and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105687874AAvoid adverse reactionsGood treatment effectOrganic active ingredientsGranular deliveryHydrochlorothiazideTreatment effect
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines and particularly relates to a dihydrochlorothiazide (DCT) containing pharmaceutical composition for treating hypertension and a preparation method thereof. The DCT containing pharmaceutical composition for treating the hypertension, provided by the invention, is prepared from the following raw pharmaceutical materials in parts by weight: 15-30 parts of DCT, 2,000-4,000 parts of Eucommia ulmoides, 2,000-4,000 parts of Taxus cuspidata, 2,000-4,000 parts of Pogonatherum paniceum and 2,000-4,000 parts of Poa pratensis. According to the DCT containing pharmaceutical composition for treating the hypertension and the preparation method thereof, the traditional Chinese medicines and the DCT are combined, so that common adverse reactions of the DCT can be avoided, and the treatment effect on the hypertension is improved.
Owner:JINAN BANGWEN MEDICAL TECH
Fertilization method of taxus cuspidata container seedlings
InactiveCN104782457AHigh transplant survival rateFully absorbedFertilising methodsCultivating equipmentsNutrient leachingTaxus species
The invention discloses a fertilization method of taxus cuspidata container seedlings and relates to a fertilization method of taxus cuspidata container seedlings in cold regions. The fertilization method of the taxus cuspidata container seedlings solves the technical problems that by means of an existing fertilization method, nutrient leaching of taxus cuspidata seedlings, weak growing vigor of seedlings and withered and yellow needle leaves are prone to being caused as the nutrient utilization efficiency is low. The fertilization method comprises the first step of collection, the second step of planting of seedlings and the third step of fertilization treatment of seedlings. The method has the advantages that operation is easy, cost is low, and the effect is obvious on the aspect of improving the nutrient absorbing efficiency of seedlings; seedlings are recovered rapidly and adapt to the fertilization operation rapidly after taxus cuspidata seedlings are planted; the nutrient absorbing efficiency is as high as 80% and is improved by nearly two times compared with a traditional fertilization method. The method is mainly used for cultivation of taxus cuspidata container seedlings.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
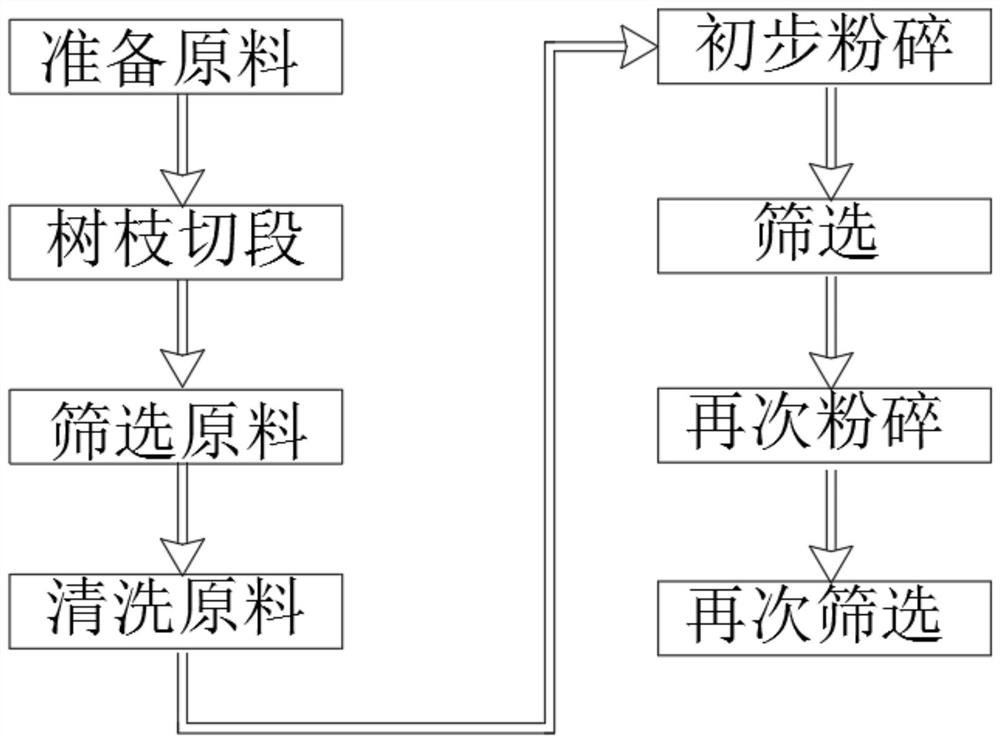
Raw material screening method for paclitaxel production
ActiveCN111760669AAvoid affecting the efficacy of the drugPrevent affecting extraction workOrganic chemistryDrying machines with local agitationBiologyMaterials science
The invention relates to the technical field of paclitaxel production and discloses a raw material screening method for paclitaxel production. The raw material screening method includes the followingsteps that S1, raw materials are prepared, wherein a whole taxus cuspidata tree is prepared, then peeling treatment is conducted, and taxus cuspidata bark, branches and leaves are distinguished; S2, branch segmentation is conducted, wherein the peeled bark and branches are segmented; S3, raw material screening is conducted, wherein the bark and branches which are not qualified due to worm damage or corrosion are removed through a tool; and S4, raw material cleaning is conducted. By means of the raw material screening method for paclitaxel production, impurities such as weed, bird dung and hives on raw materials can be separated out during raw material treatment, normal extracting work is prevented from being affected by the impurities, in addition, when large-diameter branches are completely subjected to peeling treatment, influences of xylem on the extracting work is prevented, the raw materials can be sufficiently smashed through two times of smashing, then a screen is used for screening, and it is ensured that the smashed raw materials meet the paclitaxel extracting requirement.
Owner:无锡紫杉药业股份有限公司
Cuttage breeding method of taxus chinensis in northeast
InactiveCN101663946BGuaranteed humidityGuaranteed freshnessCultivating equipmentsPlant protectionDiseaseHigh survival rate
Owner:苏庆良
Method for asexually propagating taxus cuspidata
The invention provides a method for asexually propagating taxus cuspidata, relating to the method for propagating the taxus cuspidate. The invention solves the problems of low rooting rate and weak nursery stock in the existing cutting propagation method for the taxus cuspidate and low survival rate under natural condition when the taxus cuspidata is transplanted for afforestation on a mountain. The method comprises the following steps: ears are picked up in winter of the first year, and is buried by ice and snow; in spring of the second year, cutting is carried out on a disinfected cutting bed, a film is coated on the cutting bed in 2.5 to 3 months with humidity of between 85 and 88 percent at the temperature of between 26 and 29 DEG C and shading degree of between 70 and 75 percent after cutting is completed, and the cutting bet is subject to fertilizer application and sterilization; the coated film is removed, cold-proof water is irrigated before winter; and the bed is changed in spring of the third year, and culture is conducted for two years to obtain the taxus cuspidata for afforestation. The cultured sapling has 100 percent of lignification, 80 to 96 percent of cut rooting rate and 85 to 90 percent of planting percentage, thus the mature period of medical forest is shortened. The method can be used for large-scale afforestation.
Owner:HARBIN HONGDOUSHAN TECH DEV
Method of returning Taxus cuspidata to wild
PendingCN110140577AReturn to the wildImprove survival rateCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsObserved SurvivalTaxus species
The invention provides a method of returning Taxus cuspidata to the wild. The method comprises the steps of S1, selecting seedlings, to be specific, selecting return seedlings 1-2 years or 4-5 years old; S2, lifting the seedlings, to be specific, lifting the return seedlings screened in the step S1, wherein the return seedlings 1-2 years old are lifted by means of nutrient bagging, and the returnseedlings 4-5 years old are lifted by means of bared root lifting; S3, transporting, to be specific, transporting the return seedlings lifted in the step S2 to a forest farm; S4, transplanting, to bespecific, transplanting the return seedlings of step S3 in May; and S5, providing protection, to be specific, applying a plant anti-biting agent to trunks of the return seedlings transplanted in the step S4. The method herein allows Taxus cuspidata to be returned to the wild; seedlings of Taxus cuspidata in nursery are returned to the natural growth environment, and survival rate of Taxus cuspidata to the wild returned to the wild can be increased.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Traditional Chinese medicine composition capable of cooperating with chemotherapy to treat non-small cell lung cancer
The invention belongs to the field of traditional Chinese medicine, and discloses a traditional Chinese medicine composition capable of cooperating with chemotherapy to treat non-small cell lung cancer and a preparation method thereof. The traditional Chinese medicine composition is prepared from milkvetch roots, taxus cuspidate, salvia miltiorrhiza, curcuma zedoaria, herba epimedii, hairyvein agrimony, lalang grass rhizome, cortex mori radicis, cordate houttuynia and liquorice. The traditional Chinese medicine composition is simple in prescription and scientific and rigorous in compatibility and has the significant effects of reinforcing qi, nourishing the blood, tonifying the spleen, strengthening the kidney, removing the blood stasis, removing toxin, clearing the lung and eliminating the phlegm; when the traditional Chinese medicine composition cooperates with the chemotherapy to treat the non-small cell lung cancer, the effects of enhancing the effect, reducing the toxin, enhancing the patient immunity and improving the survival quality can be achieved, and therefore the traditional Chinese medicine composition is worthy of clinical application and popularization.
Owner:QINGDAO MERRITT MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Meat fresh keeping agent prepared from taxus cuspidata extract
InactiveCN108812855AGood antibacterial and sterilization effectGood antibacterial effectMeat/fish preservation by coatingPolyphenolSodium polymetaphosphate
The invention relates to the technical field of low-temperature fresh keeping, in particular to a meat fresh keeping agent prepared from a taxus cuspidata extract. The meat fresh keeping agent comprises the following components in parts by mass of 15-20 parts of sodium hexametaphosphate, 7-10 parts of chitosan, 1-3 parts of tea polyphenols, 1-1.5 parts of lysozyme, 1-2 parts of nisin and 3-5 partsof a taxus cuspidata extract, wherein the taxus cuspidata extract is subjected to dissolving for many times, extraction and purification to obtain extractum; and the total yield of active substancesin the extractum of the taxus cuspidata extract is 2-4%. Lysozymes in the raw materials are egg white lysozymes, and the activity is 25000-30000U / mg. The fresh keeping agent is good in fresh keeping effects, is safe and harmless to human bodies, has certain health-care effects, and is healthy.
Owner:HEFEI JINTONGWEI LOW TEMPERATURE TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com