Extraction method of taxol from branches and leaves of artificially cultivated yew
A technique for artificial cultivation of branches and leaves of Taxus chinensis, which is applied in the field of biochemical product preparation, can solve the problems of pollution, difficulty in separation, and high toxicity of the eluent, and achieves the effects of simple process, protection of plant resources and low cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
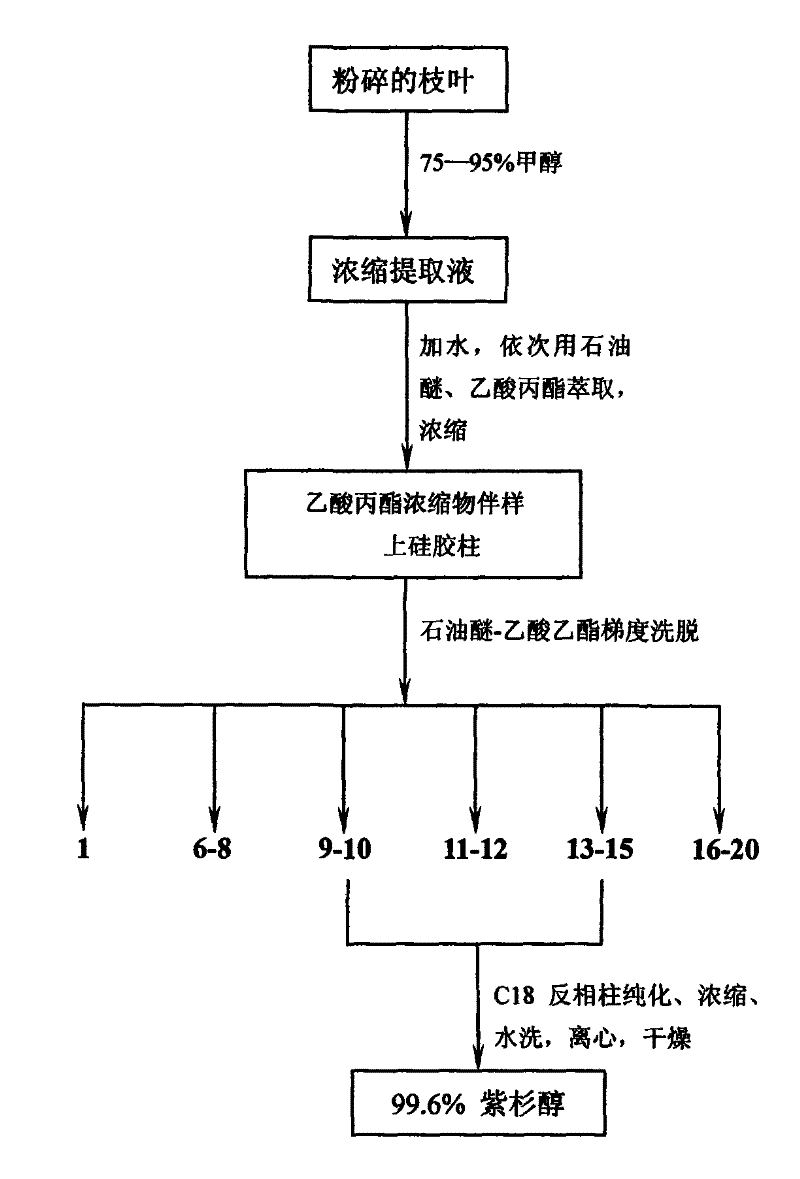
[0047] Such as figure 1 As shown, the method of extracting paclitaxel from artificially cultivated yew branches and leaves is:
[0048] (1) Take 1kg of artificially cultivated dried branches and leaves of Taxus Media, crush them with a crusher, add 3L of 90% methanol in a 5L round bottom flask, stir well, and soak them at 40~50℃ three times, each time 4~6 hour. Stir for 3 to 6 times during the placing process. After the soaking is completed, filter to remove waste residue, and concentrate the filtrate to a light green viscous liquid with a volume of about 50ml. Add 2L of petroleum ether to the solution, mix well, add 2L of water, stir for 30min, and leave for about 25min to form the upper light green clear liquid and the lower dark green gelatinous liquid. Separate the upper petroleum ether phase and extract 3 times continuously to remove the fat Impurities such as soluble pigments. Add 2L of propyl acetate to the separated lower aqueous phase, stir for 30 min, leave for about ...
Embodiment 2
[0056] (1) Take 100kg of fresh branches and leaves of artificially cultivated 3-year-old Medica yew, crush them with a crusher and place them in 2m 3 Then add 550L of 90% methanol to the extraction tank, stir evenly, and soak for 4 hours with intermittent stirring at 40-50°C. After the soaking is completed, let out the solution in the extraction tank, and then soak 3 times in the same way. The released methanol solutions are combined and concentrated in a concentration tank to a volume of about 25L. In the extraction tank, add about 250L of petroleum ether to the solution, mix well, add 250L of water and stir for 1 hour, leave it for about 30min to form two layers, and separate the lower layer. Add about 250L of propyl acetate to the lower layer solution, mix well, stir for 1 hour, and leave it for about 30 minutes to form two layers.
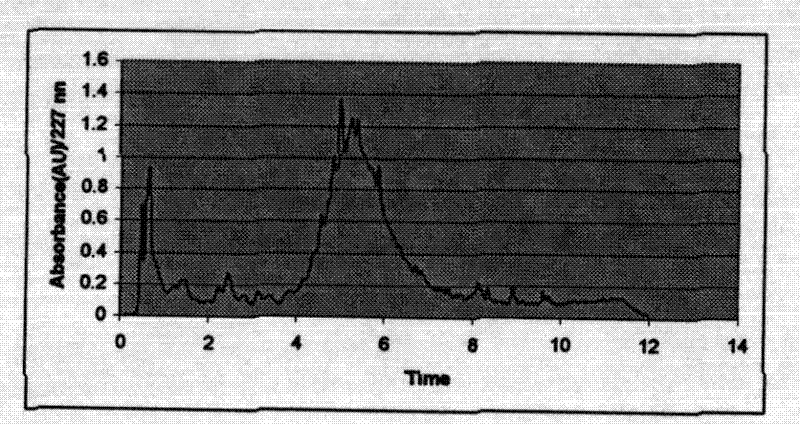
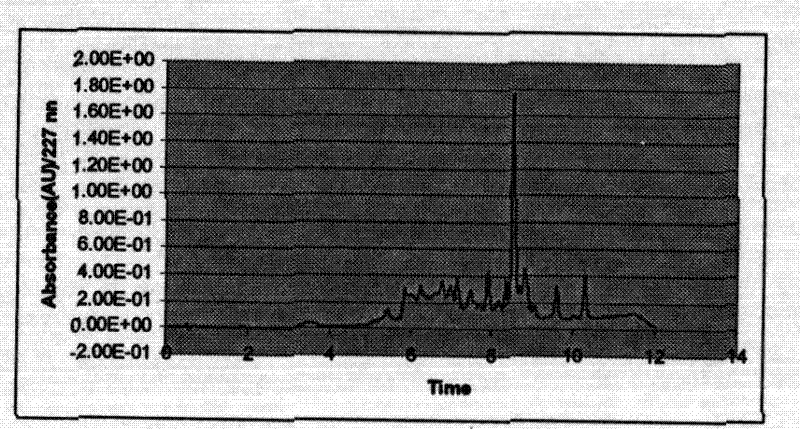
[0057] (2) The lower layer of propyl acetate extract was released and evaporated to dryness under reduced pressure to form 1032 grams of brown p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com