Patents
Literature
53 results about "Circuit Emulation Service" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
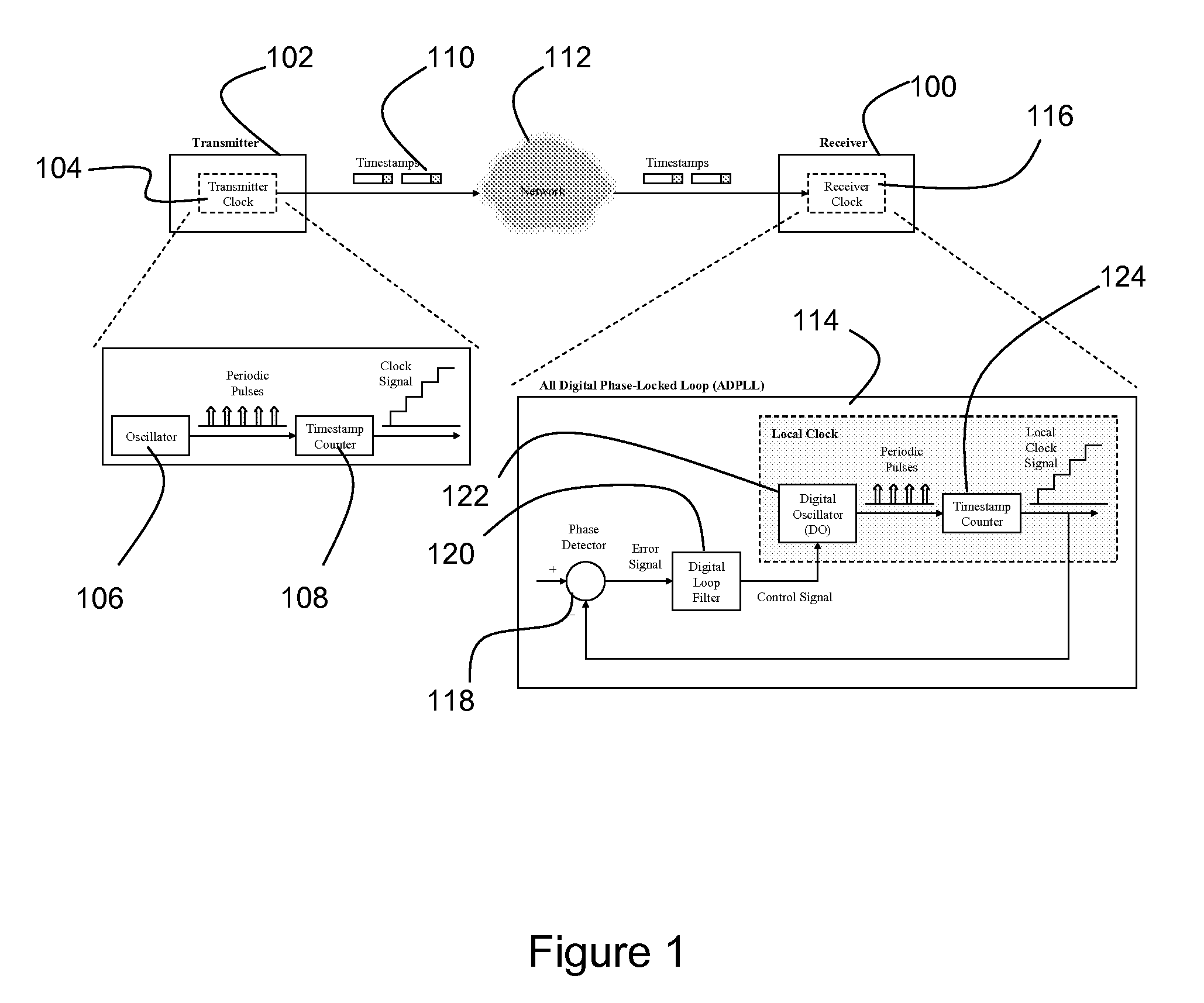
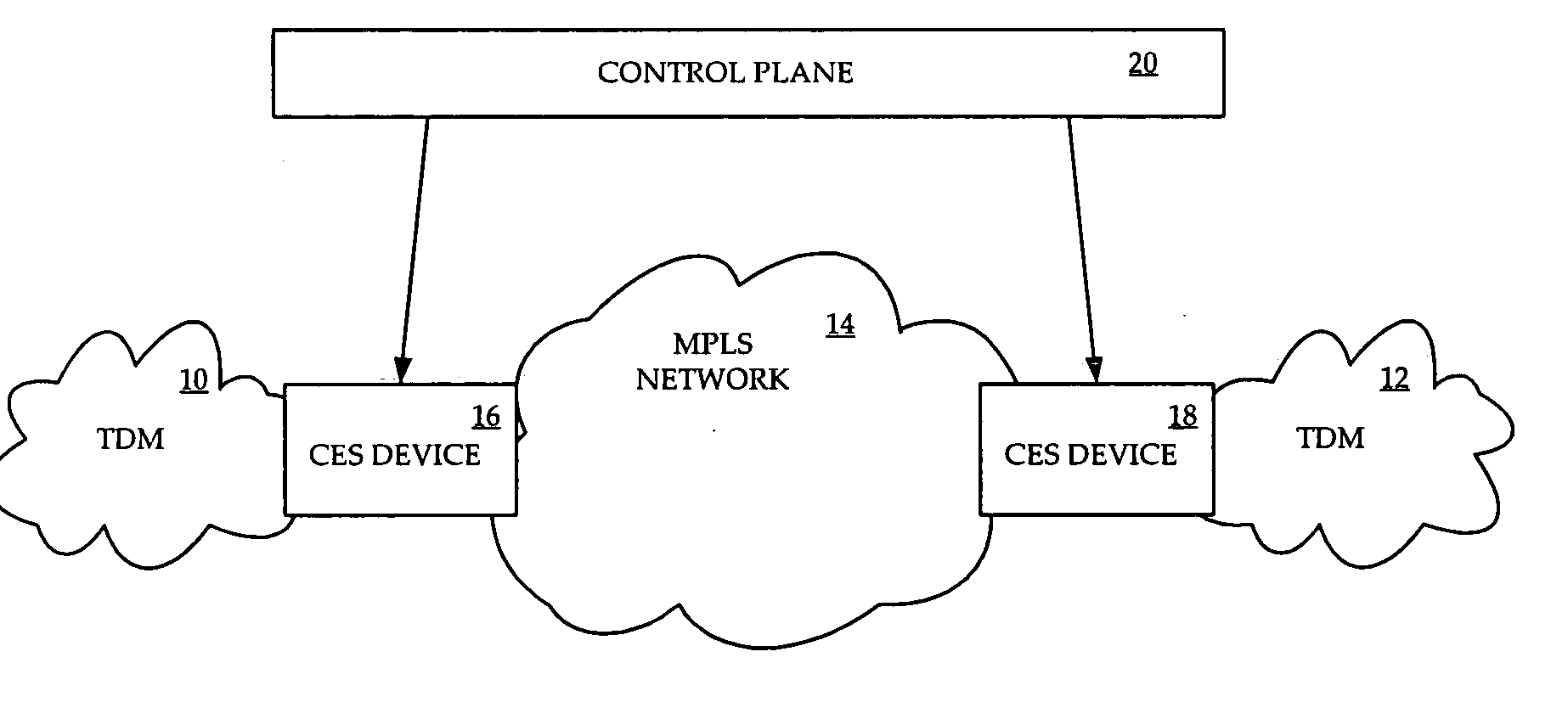
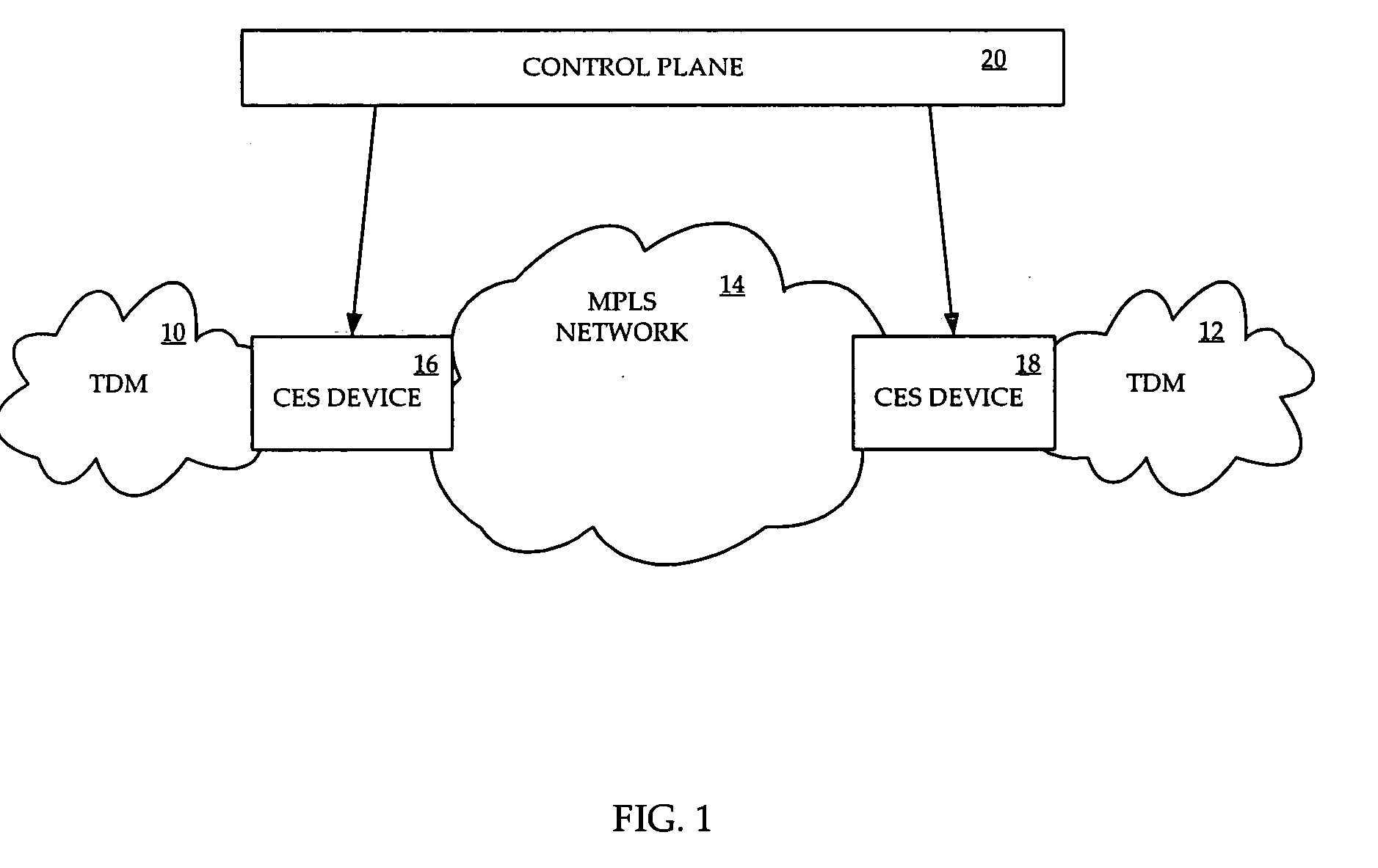
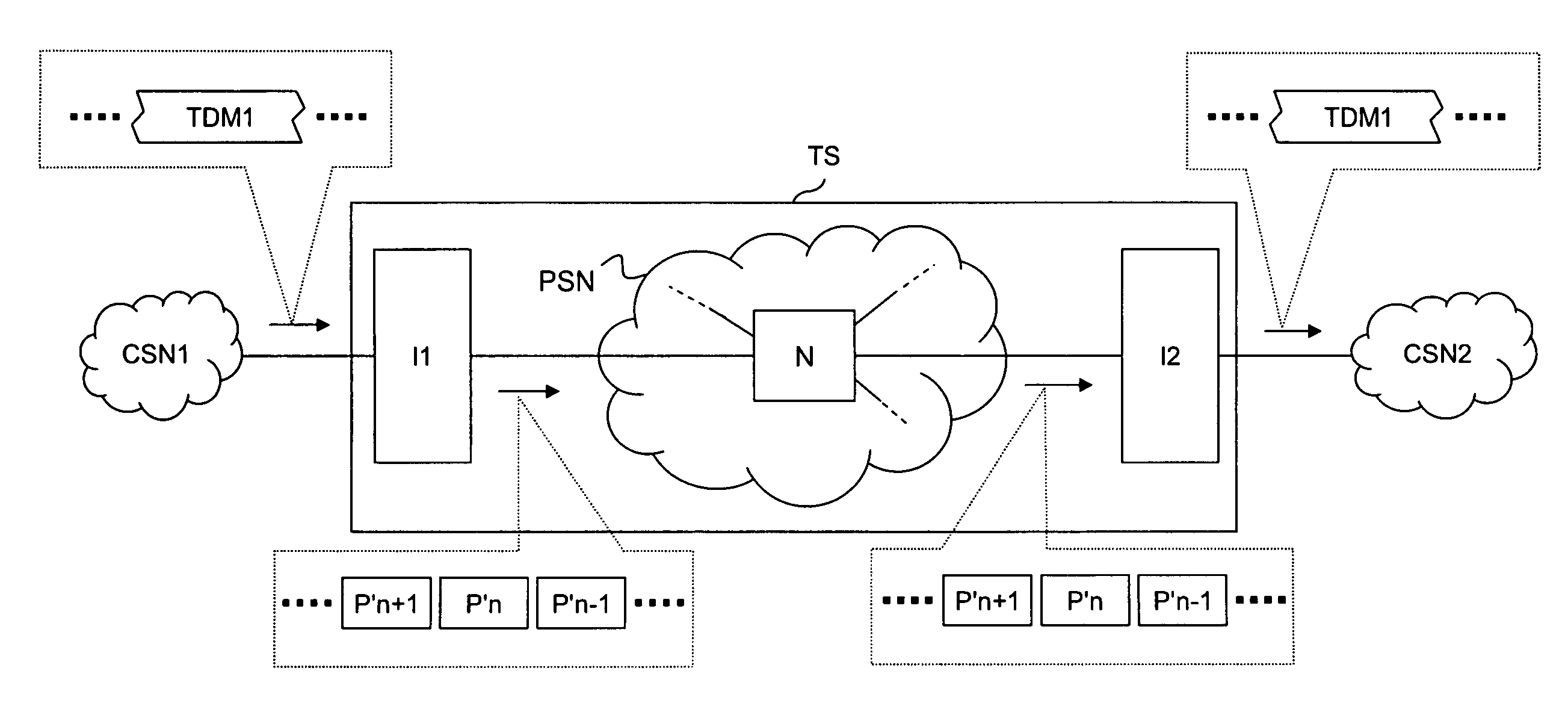
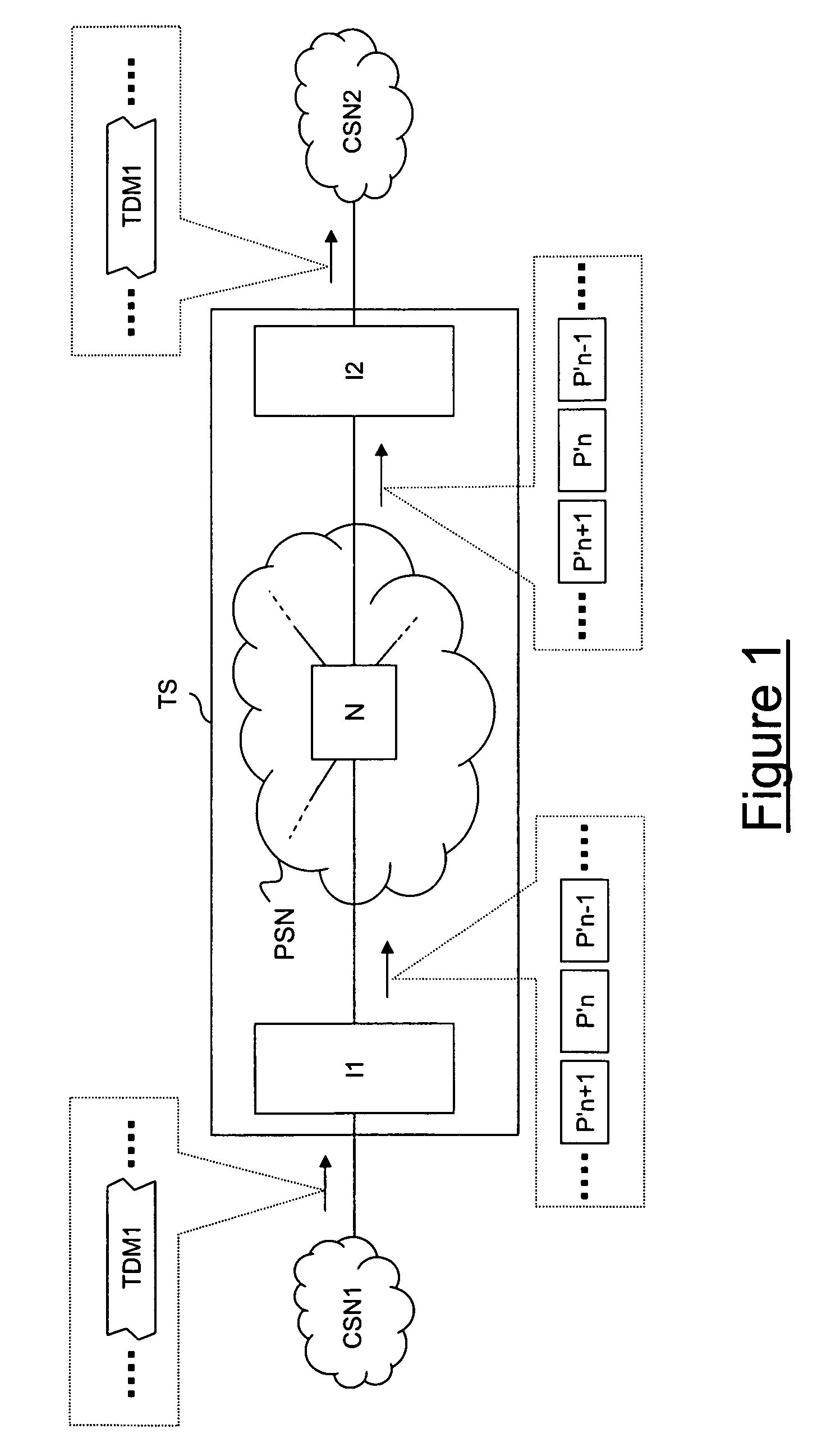
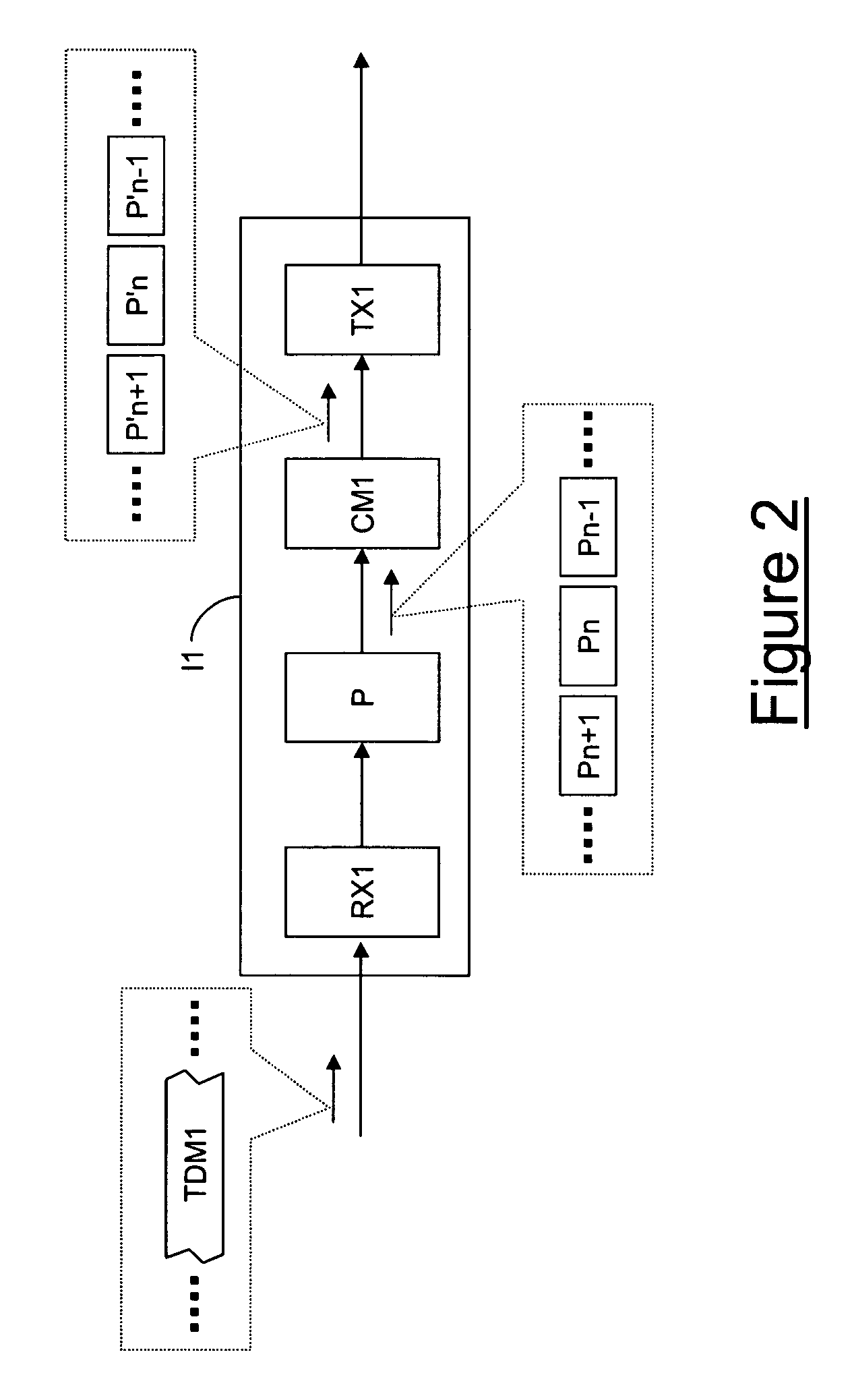
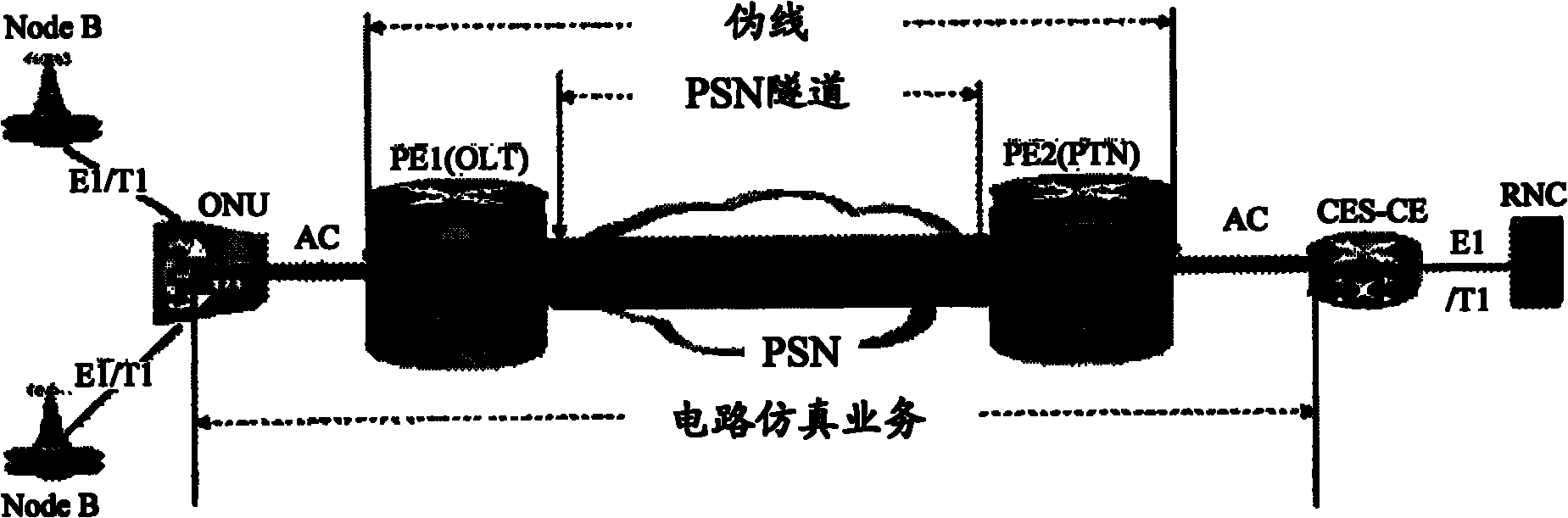
Circuit emulation service (CES) is a telecommunication technology used to send information over asynchronous data networks like ATM, ethernet or MPLS, so that it is received error-free with constant delay, similar to a leased line.
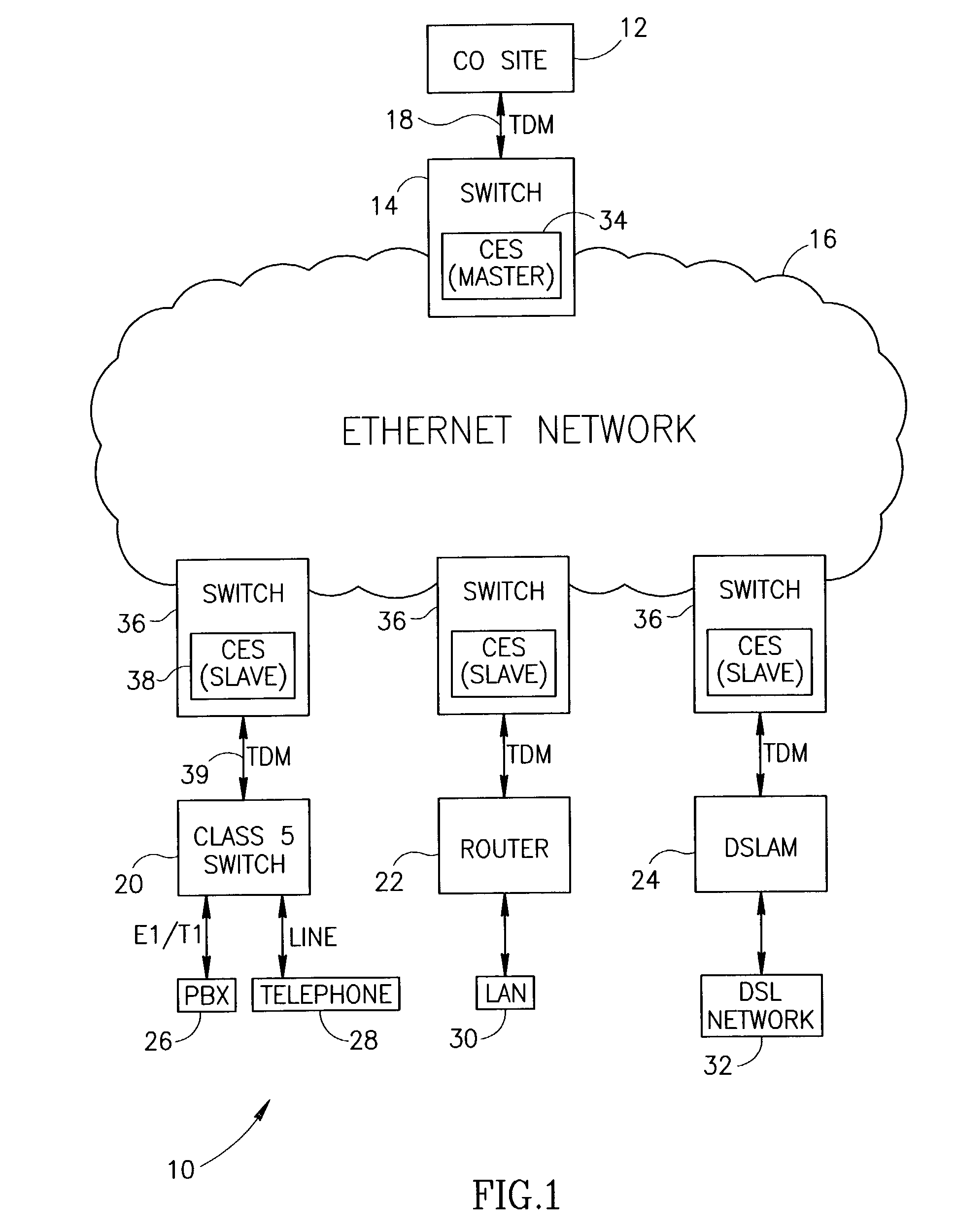
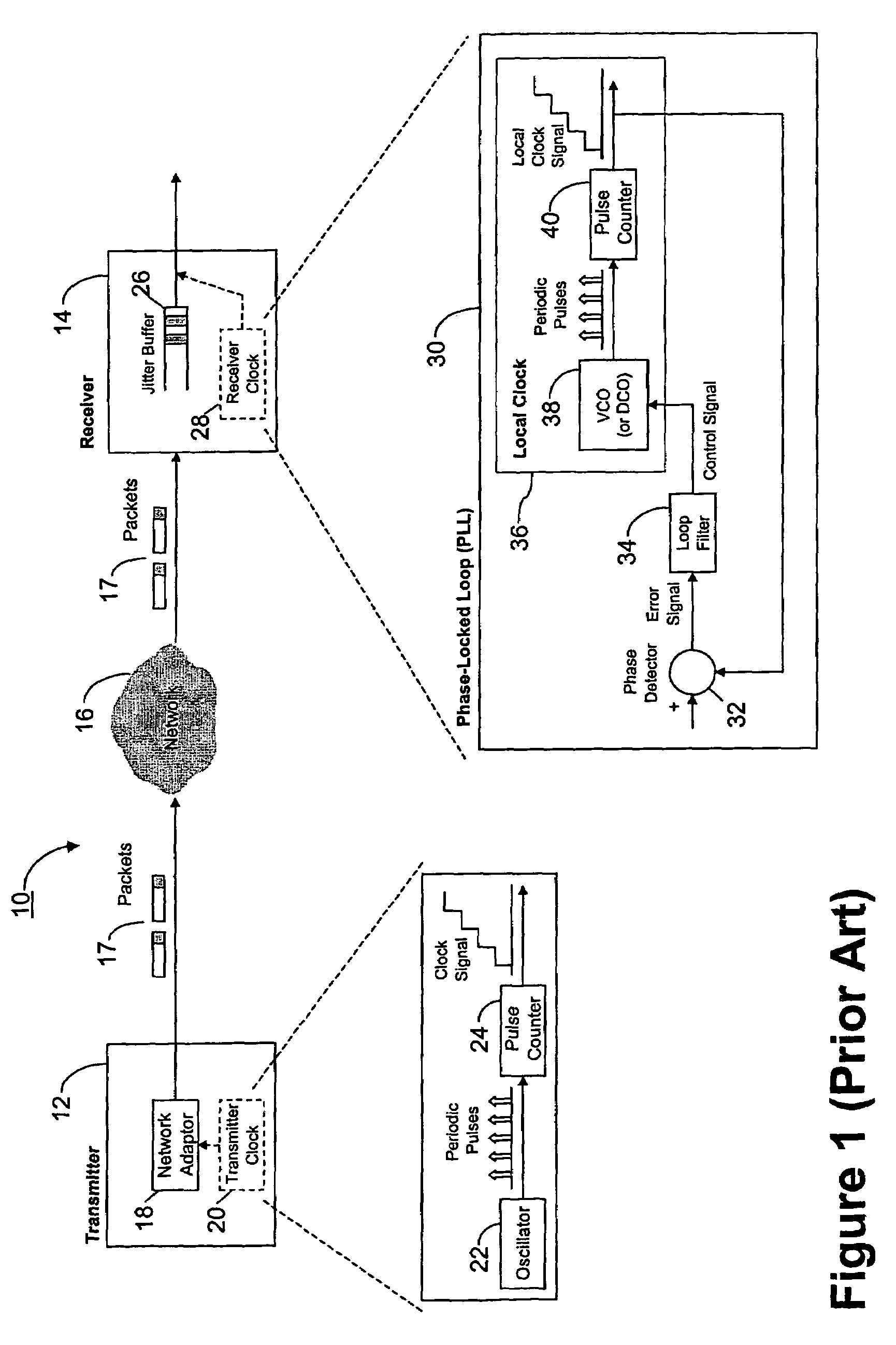
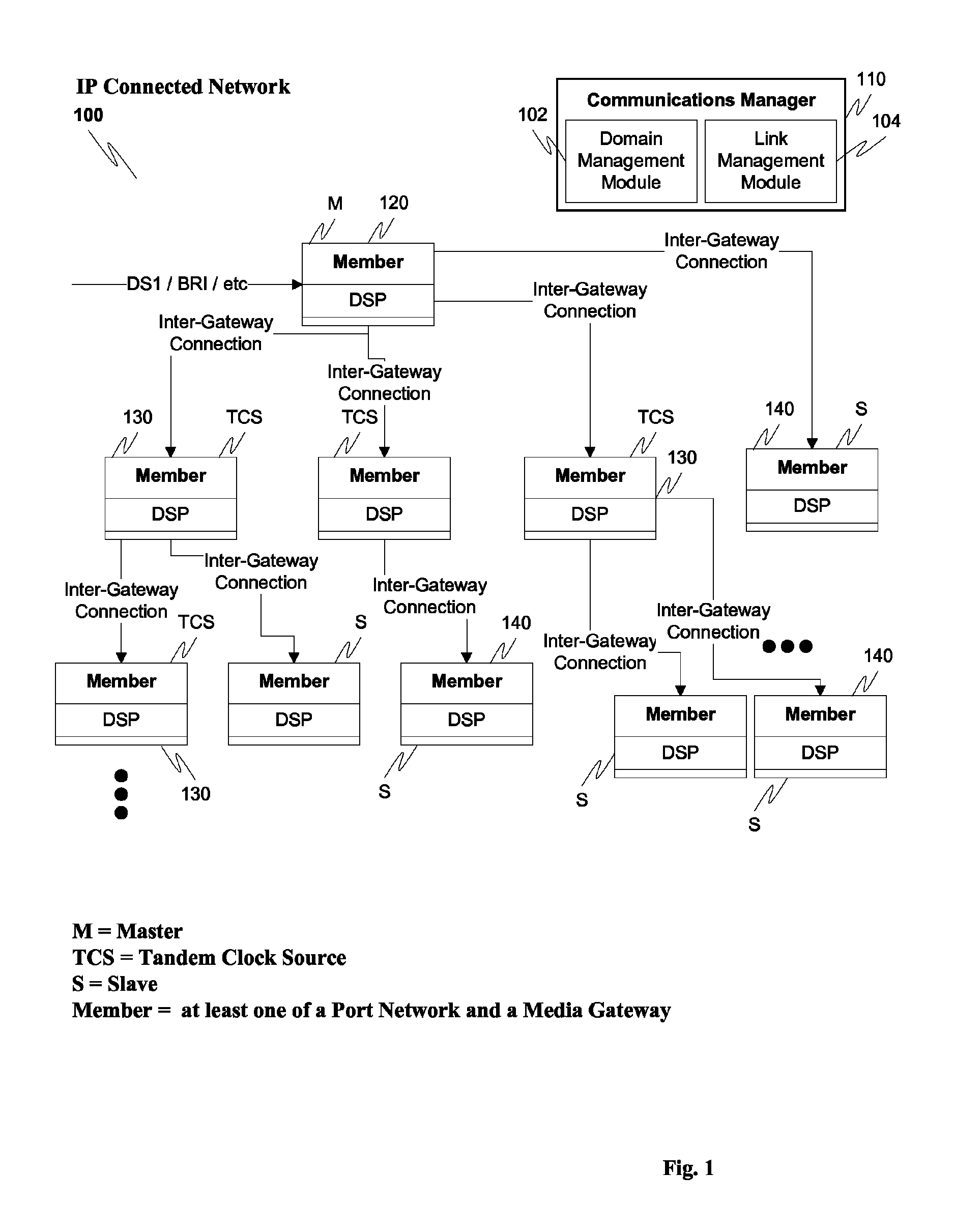
Centralized clock synchronization for time division multiplexed traffic transported over Ethernet networks
InactiveUS7613212B1Improve accuracyImprove clock reliabilityTime-division multiplexTransmissionTraffic capacityAsynchronous network
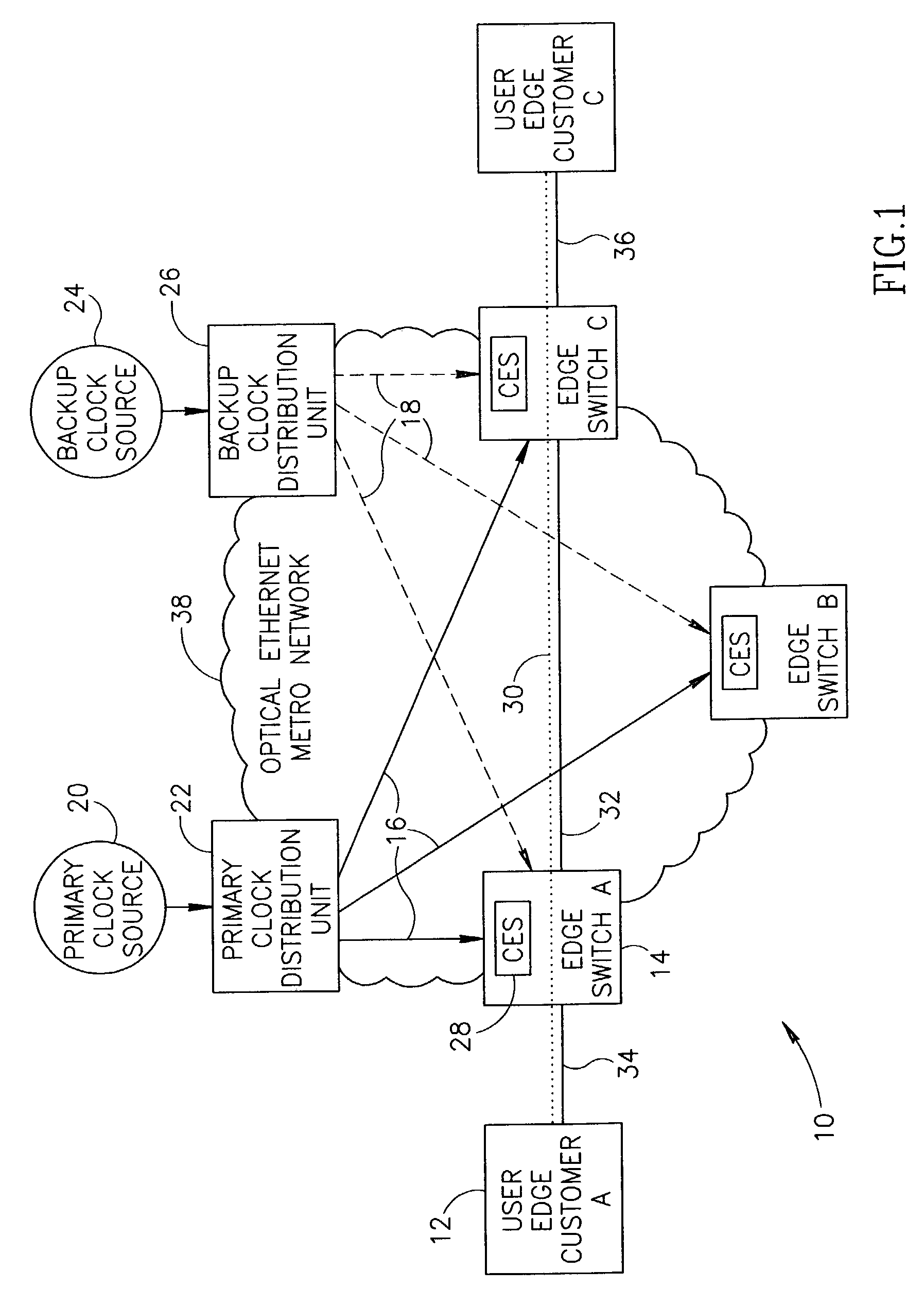
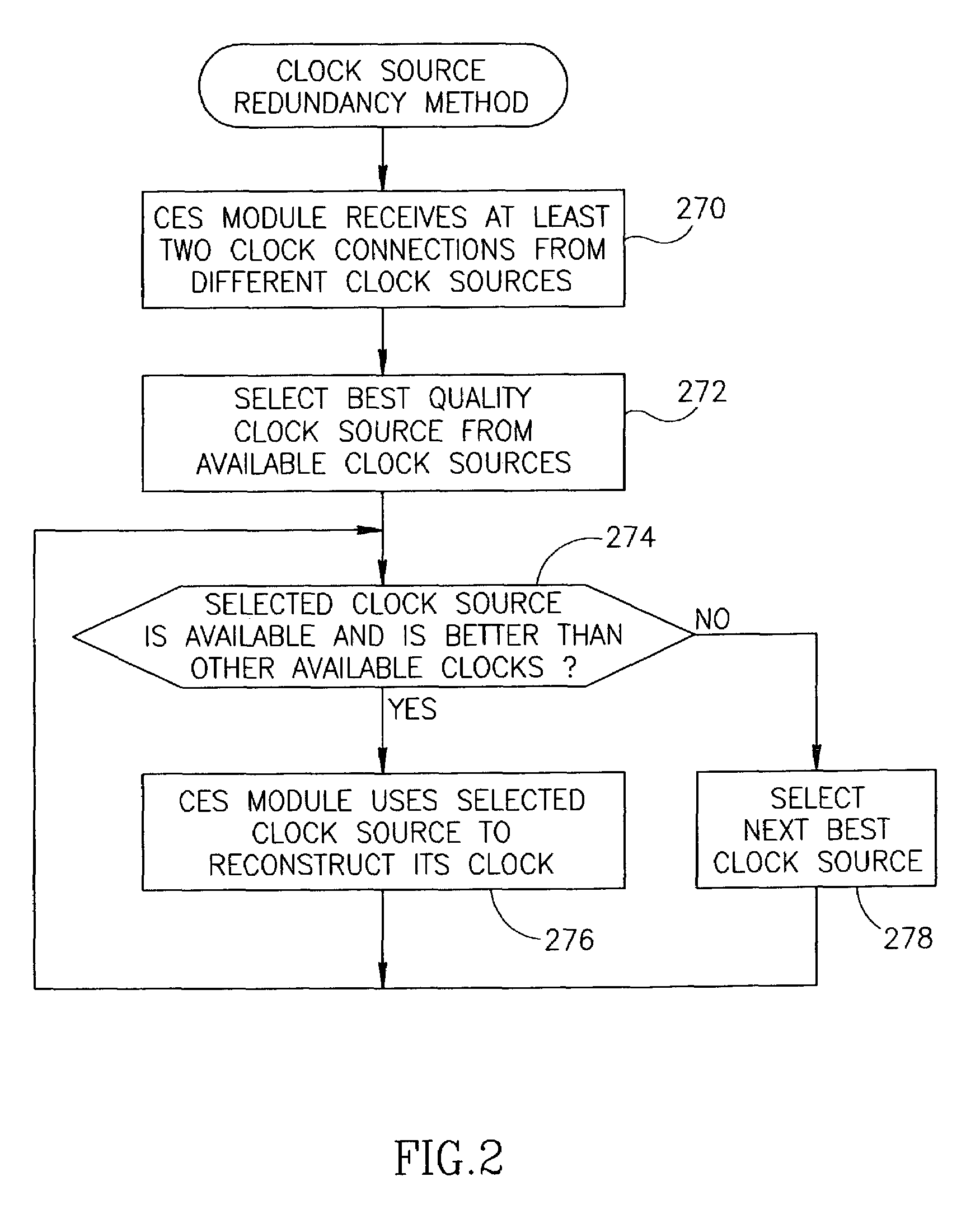
A centralized clock distribution mechanism for synchronous TDM communications traffic transported over asynchronous networks such as Ethernet networks. The centralized clocking mechanism of the present invention distributes a high accuracy central clock source to a plurality of CES modules over an Ethernet network. Clock synchronization information based on a high quality clock reference source is distributed to circuit emulation service (CES) modules in the network. CES modules receive the clock synchronization information and use it to reconstruct a local clock. A plurality of clock distributors provide clock redundancy whereby each CES module selects the best clock source to use in reconstructing the local clock.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
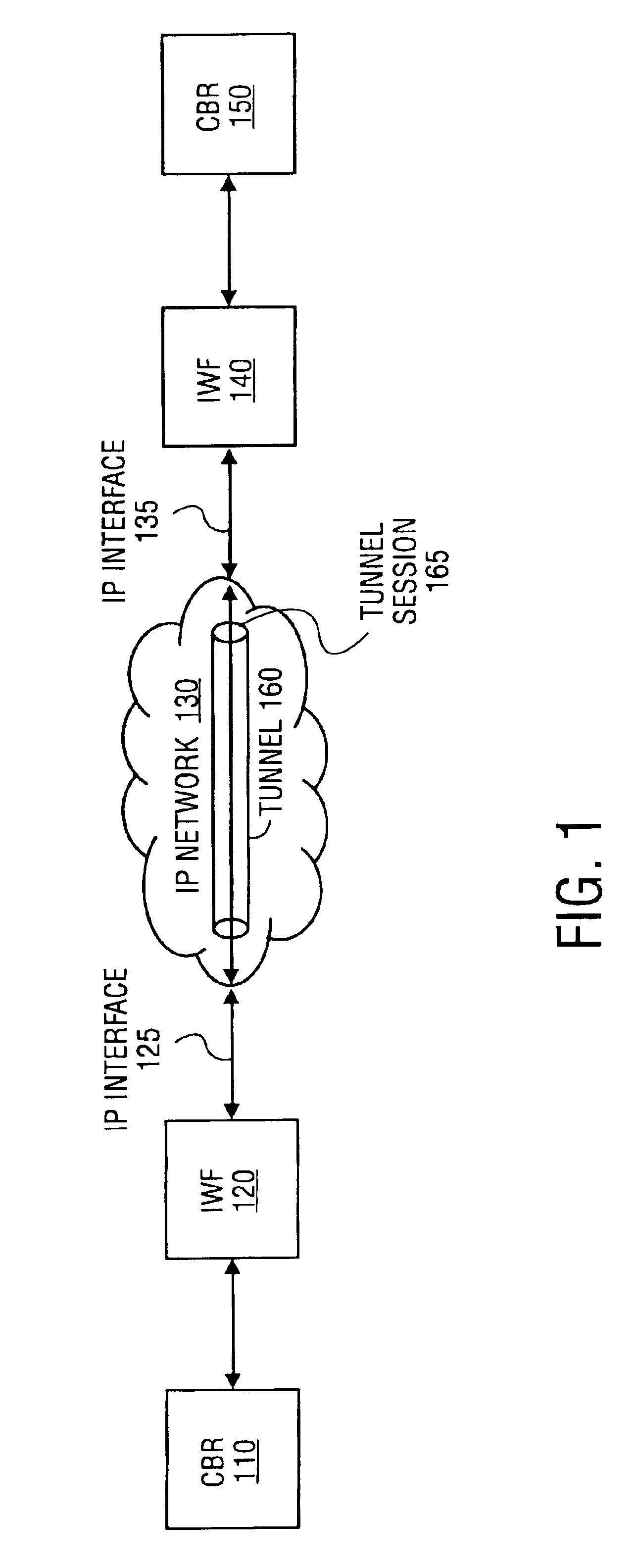
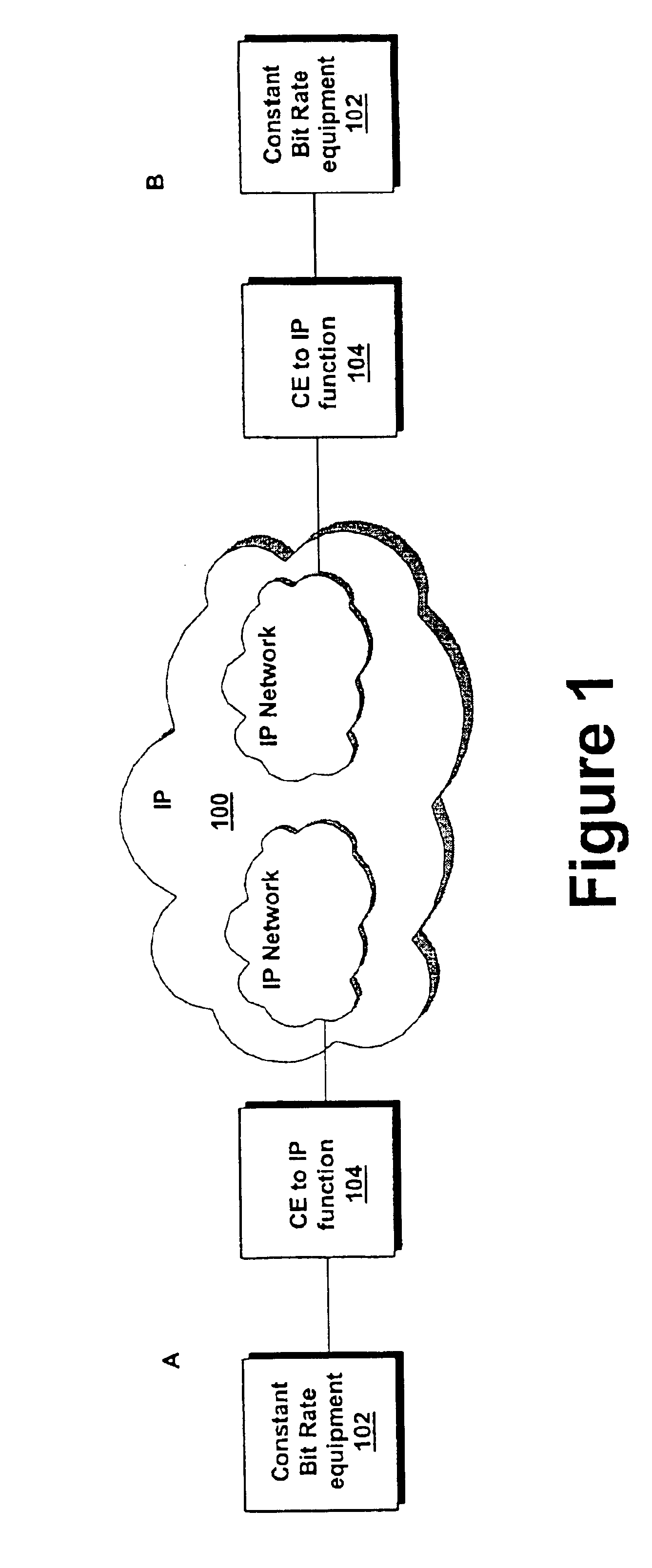
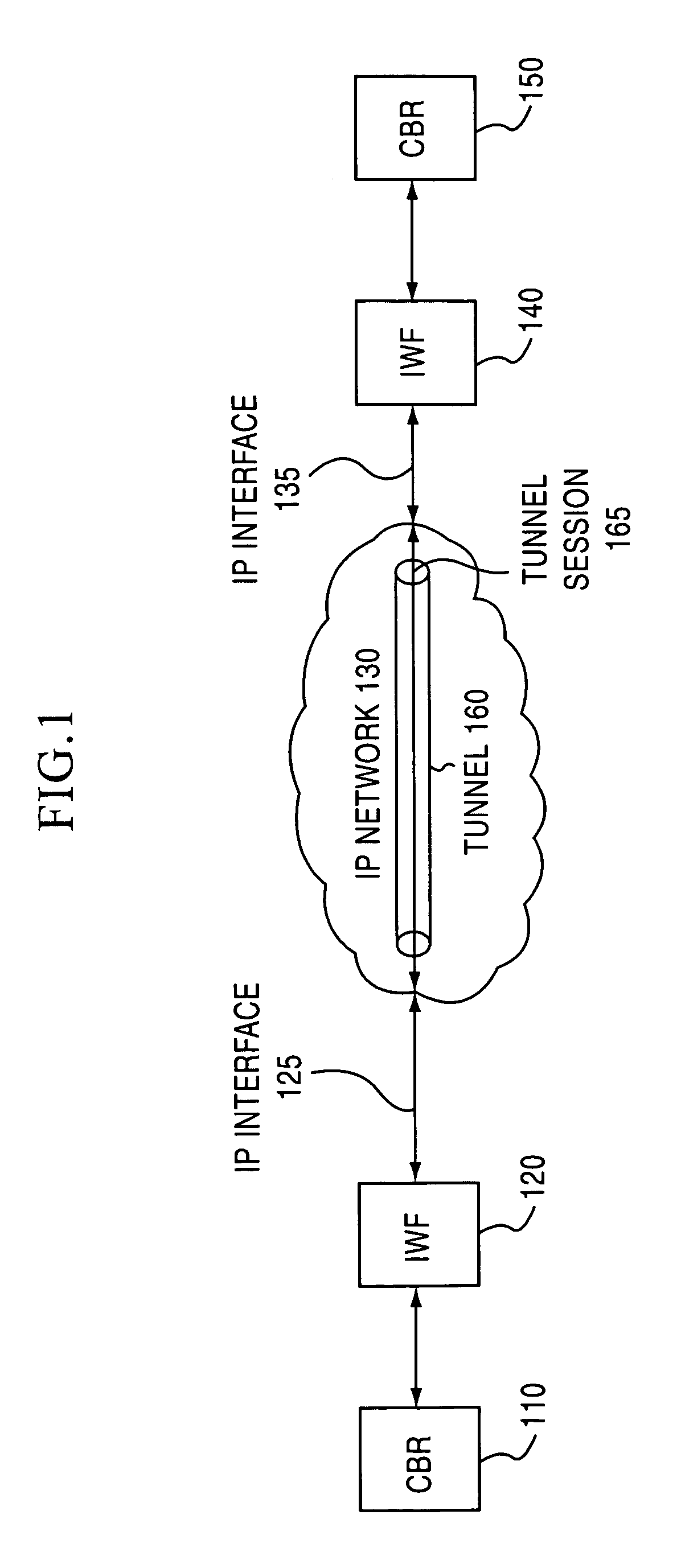
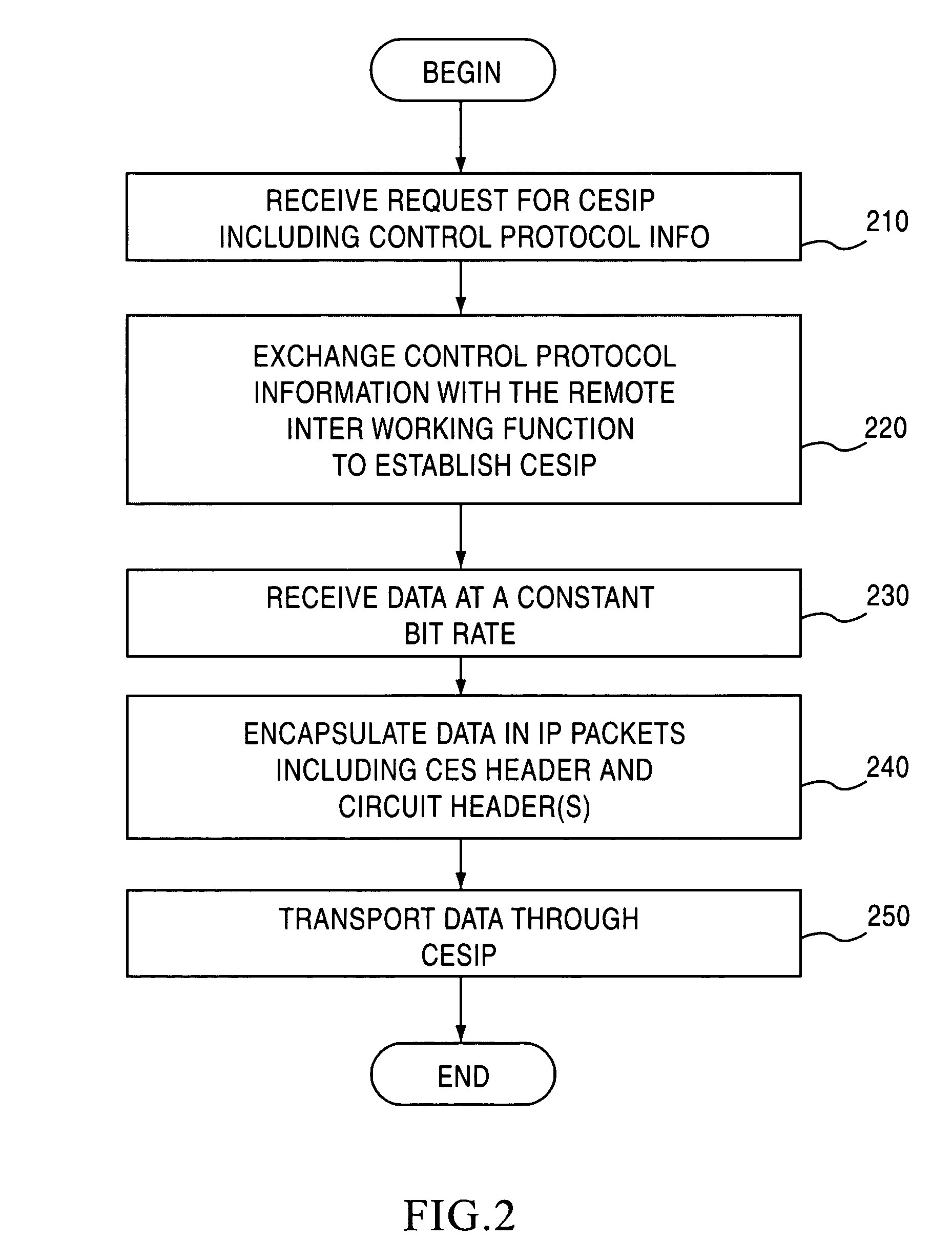
Circuit emulation service over an internet protocol network
InactiveUS6870837B2Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTTEthernetData segment
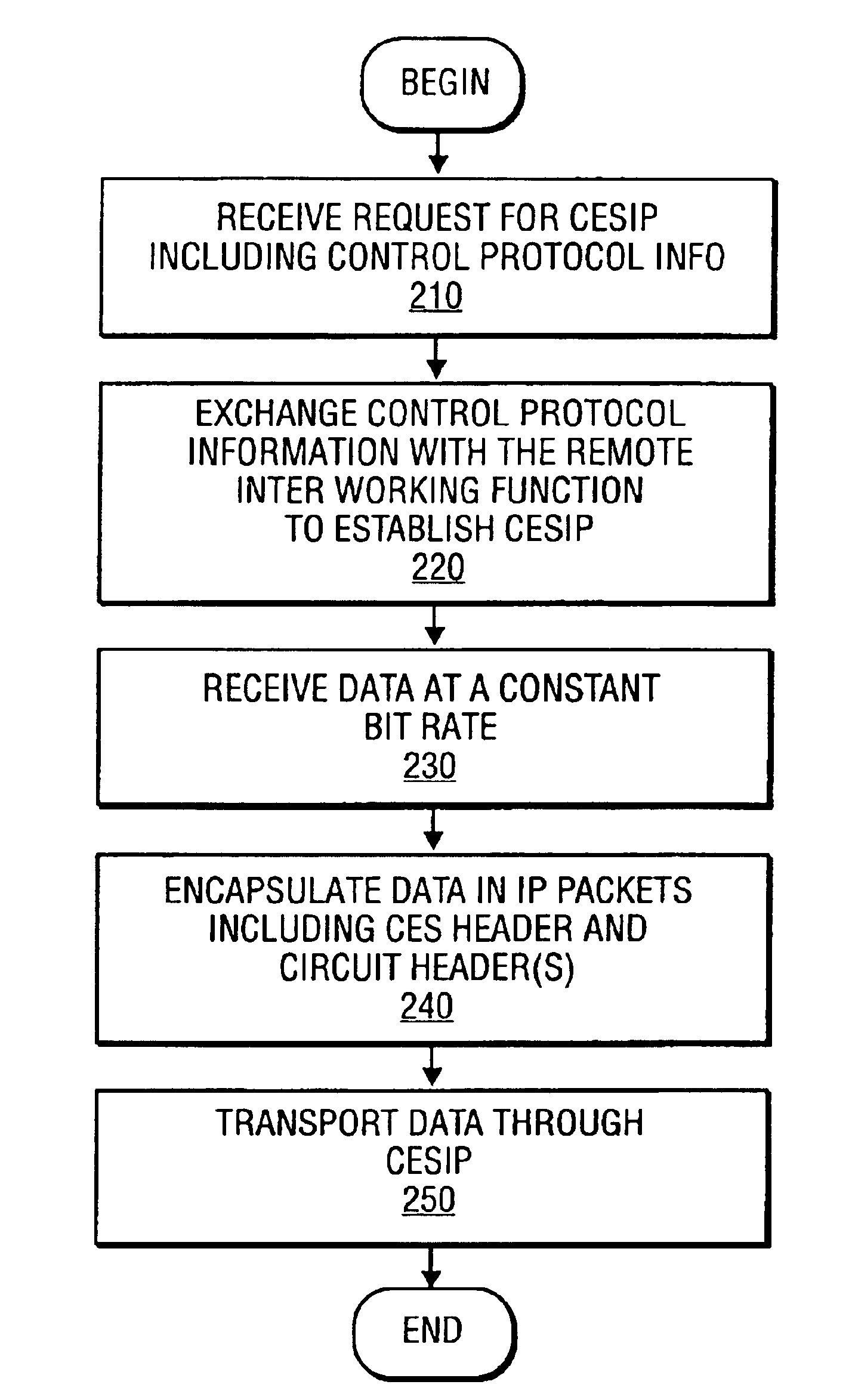
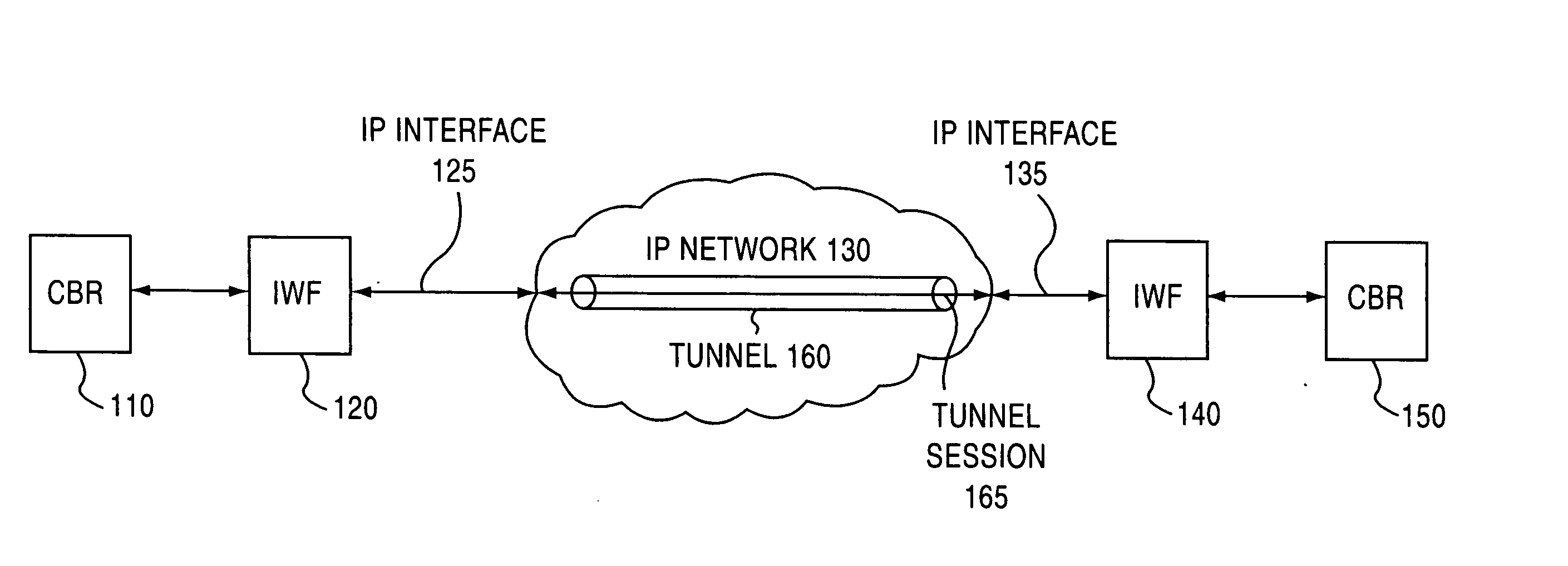
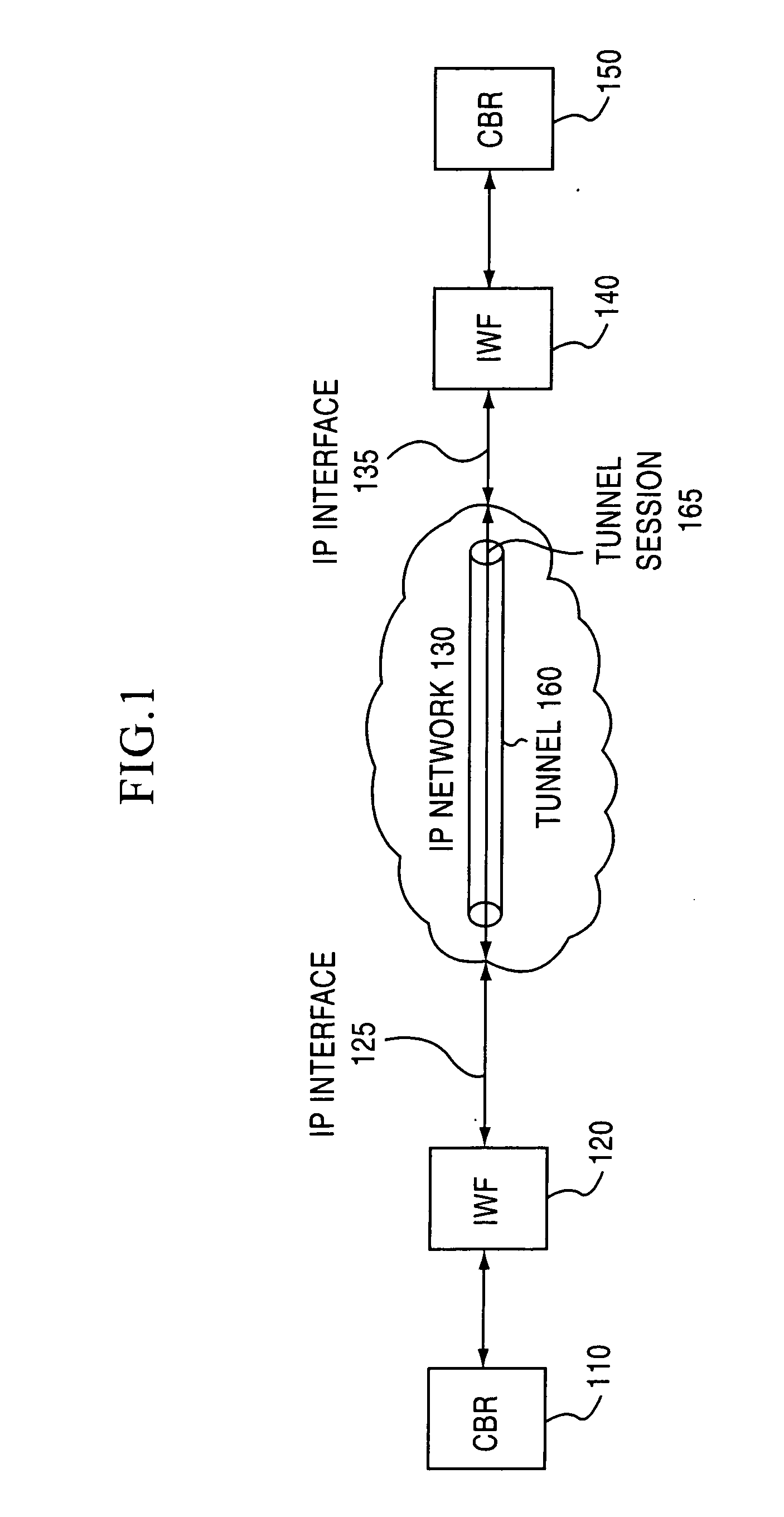
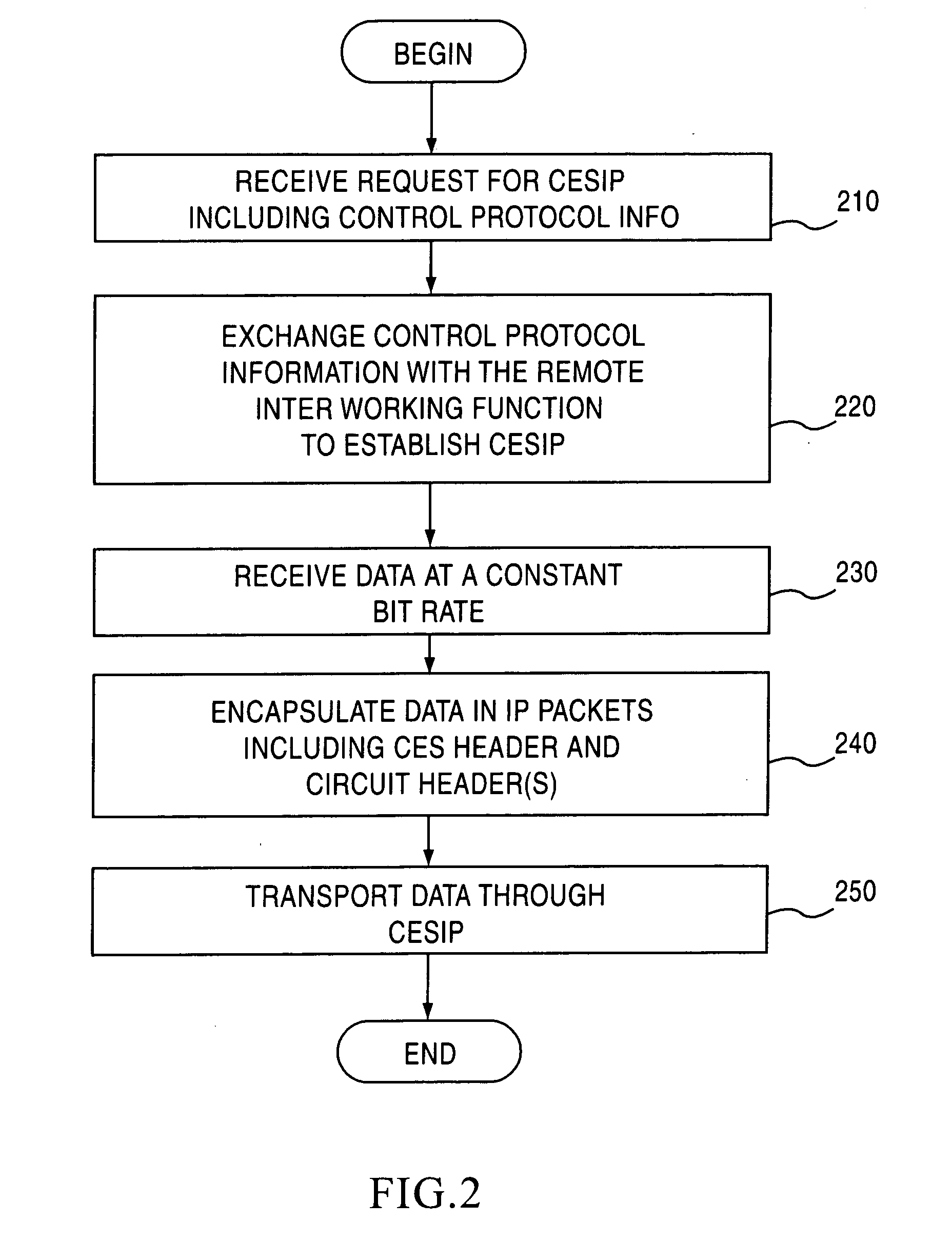
The present invention establishes a circuit emulation service (CES) over an internet protocol (IP) network based on properties of the IP network. The CES emulates a circuit from a local interworking function to a remote interworking function. Data that is received at a constant bit rate at the local interworking function is encapsulated into a number of IP packets configured according to the CES. The IP packets are transported from the local interworking function to the remote interworking function according to the CES. In one embodiment, each IP packet also includes data segments for simultaneously encapsulating multiple constant bit rate circuits. In another embodiment, each data segment includes a separate CES circuit header.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
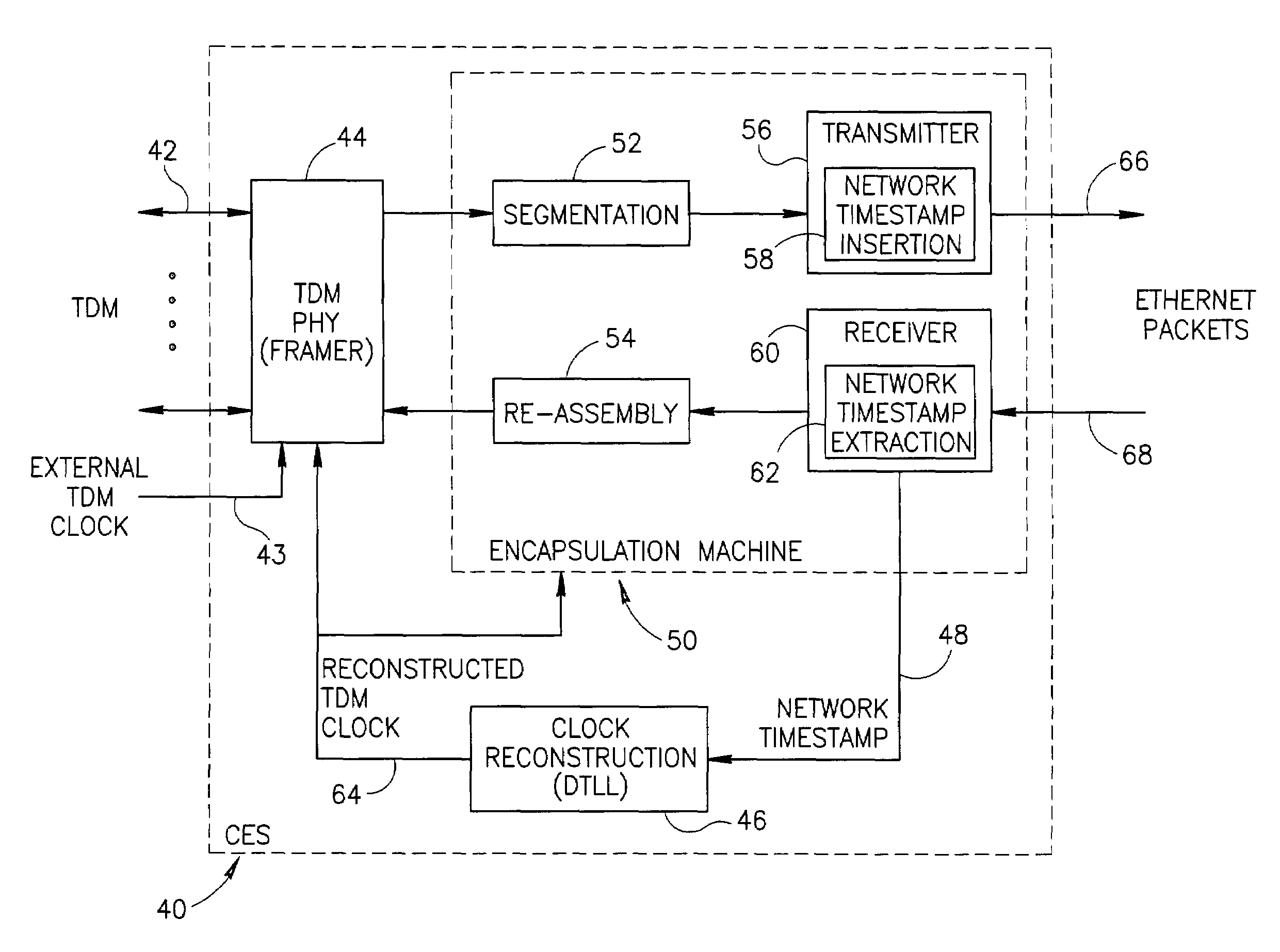
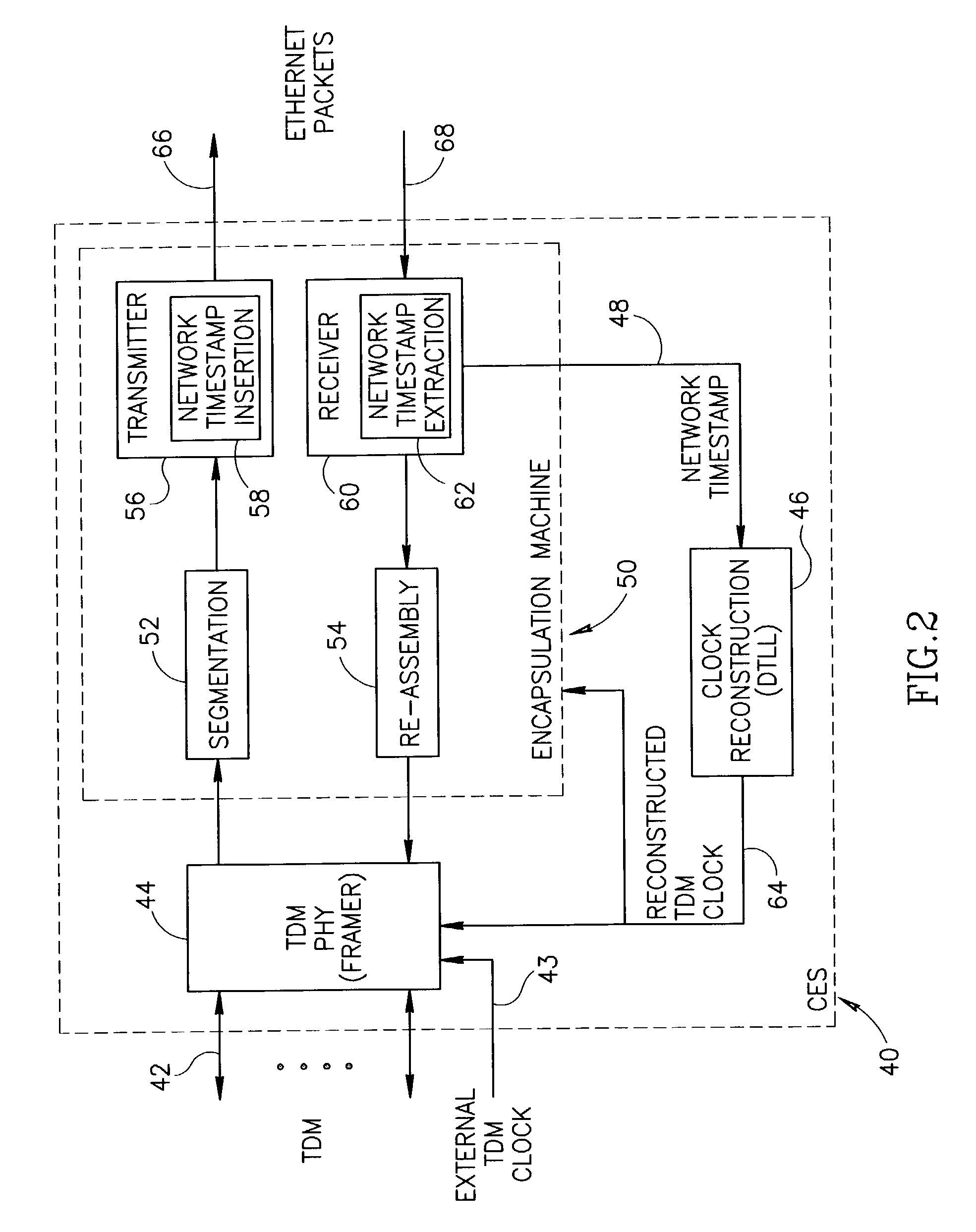
Clock reconstruction for time division multiplexed traffic transported over asynchronous ethernet networks
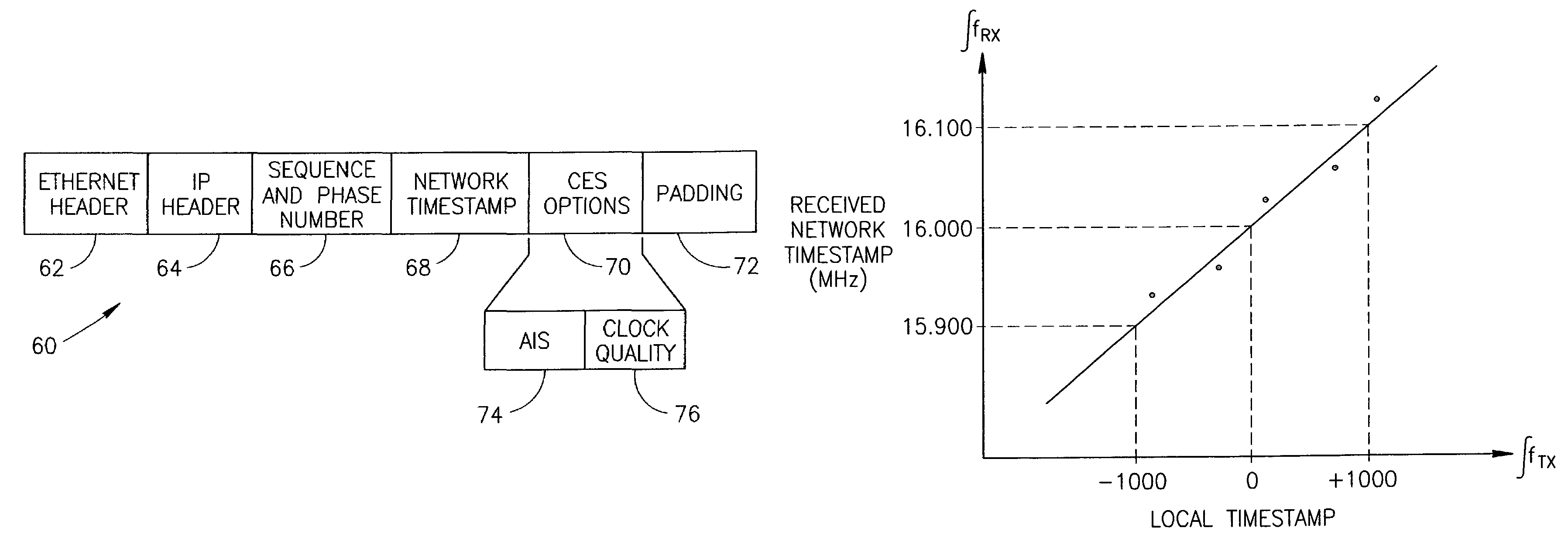
A clock reconstruction mechanism for synchronous TDM communications traffic transported over asynchronous networks such as Ethernet networks. The invention is applicable to edge switches in Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs) that transport legacy TDM traffic using a Circuit Emulation Services (CES) module whereby TDM traffic is encapsulated and transported across the Ethernet network where it is de-encapsulated and clocked out to the destination. The mechanism encapsulates the input TDM data stream into Ethernet packets and inserts a network timestamp within the packet. At the destination CES, a local timestamp is generated for each received packet as it is received. The network timestamp is extracted and input along with the local timestamp to a Digital Time Locked Loop (DTLL) which is operative to accurately reconstruct the original transmit TDM clock. The filter in the DTLL performs a Least Squares Regression (LSR) algorithm and Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) filter algorithm to generate a clock control signal for adjusting the clock generated.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING III +1
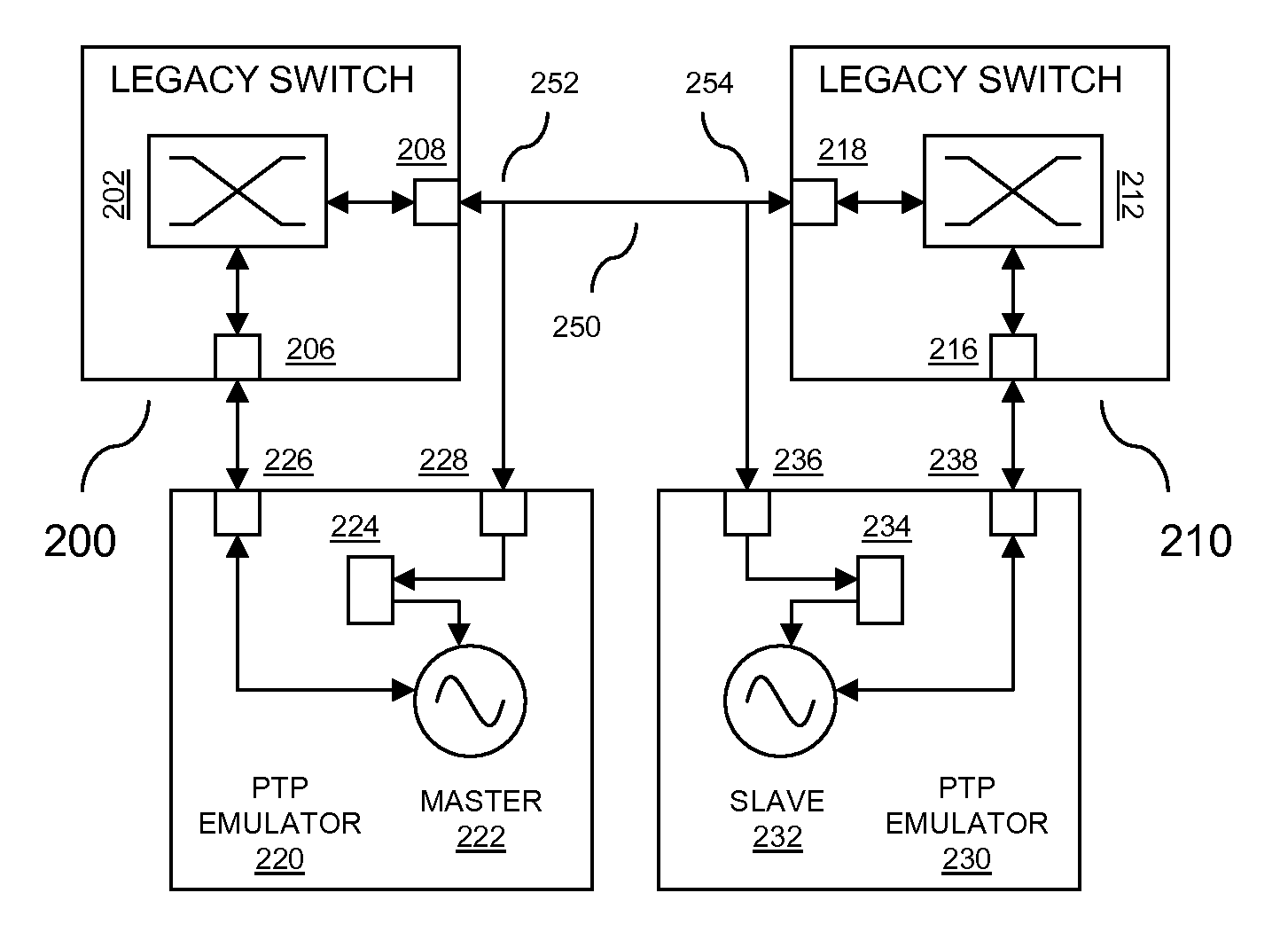
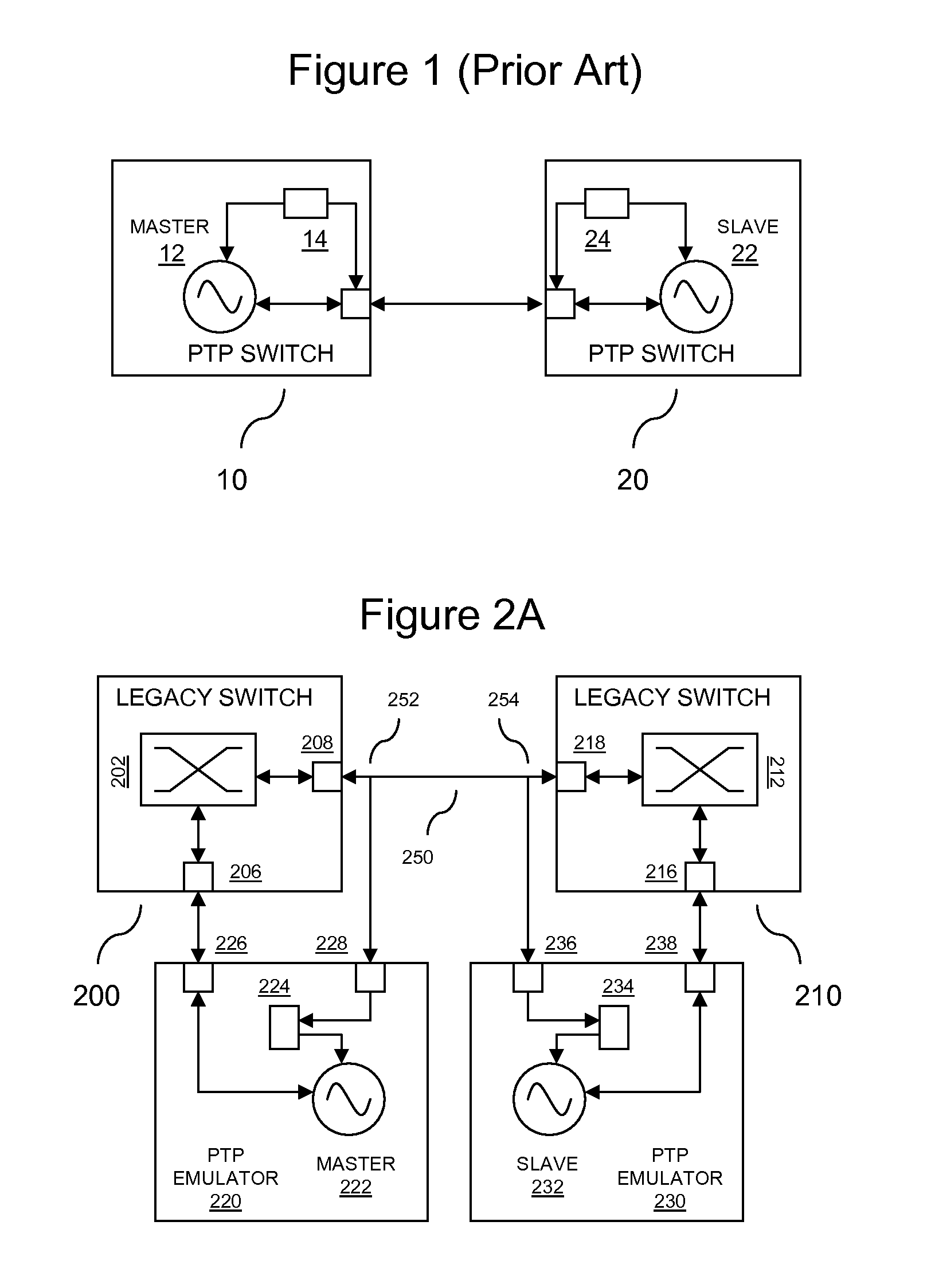
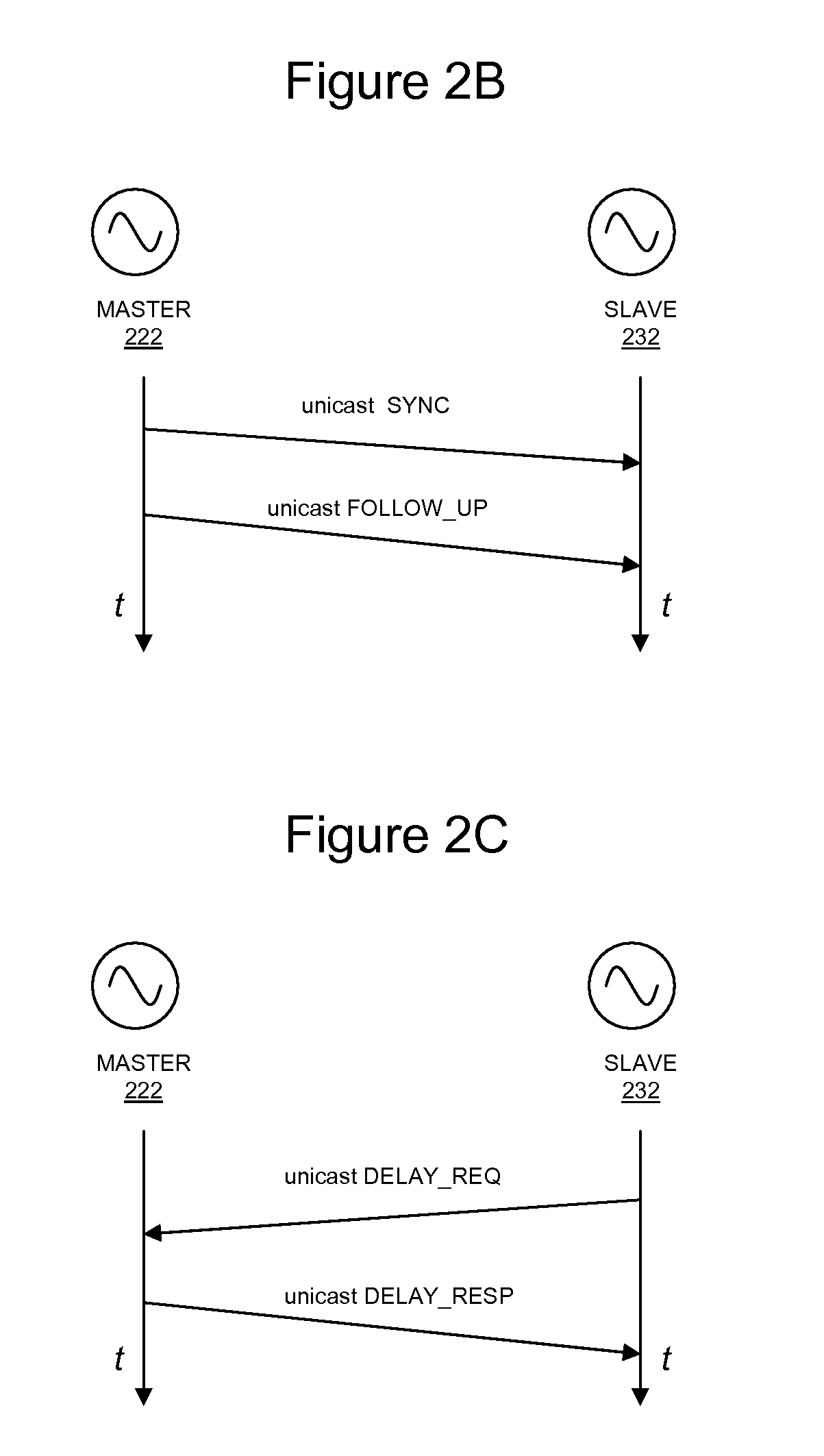
Precision Time Protocol Emulation for Network Supportive of Circuit Emulation Services
Precision Time Protocol (PTP) emulation service for a data communication network of a type that is adapted to support circuit emulation services (CES). The PTP emulation service enables seamless PTP-style clock synchronization over such a network using any combination of legacy switches, PTP boundary switches and PTP switches. The PTP emulation service is delivered through the expedient of external PTP emulation devices that are associated with legacy switches and PTP boundary switches.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
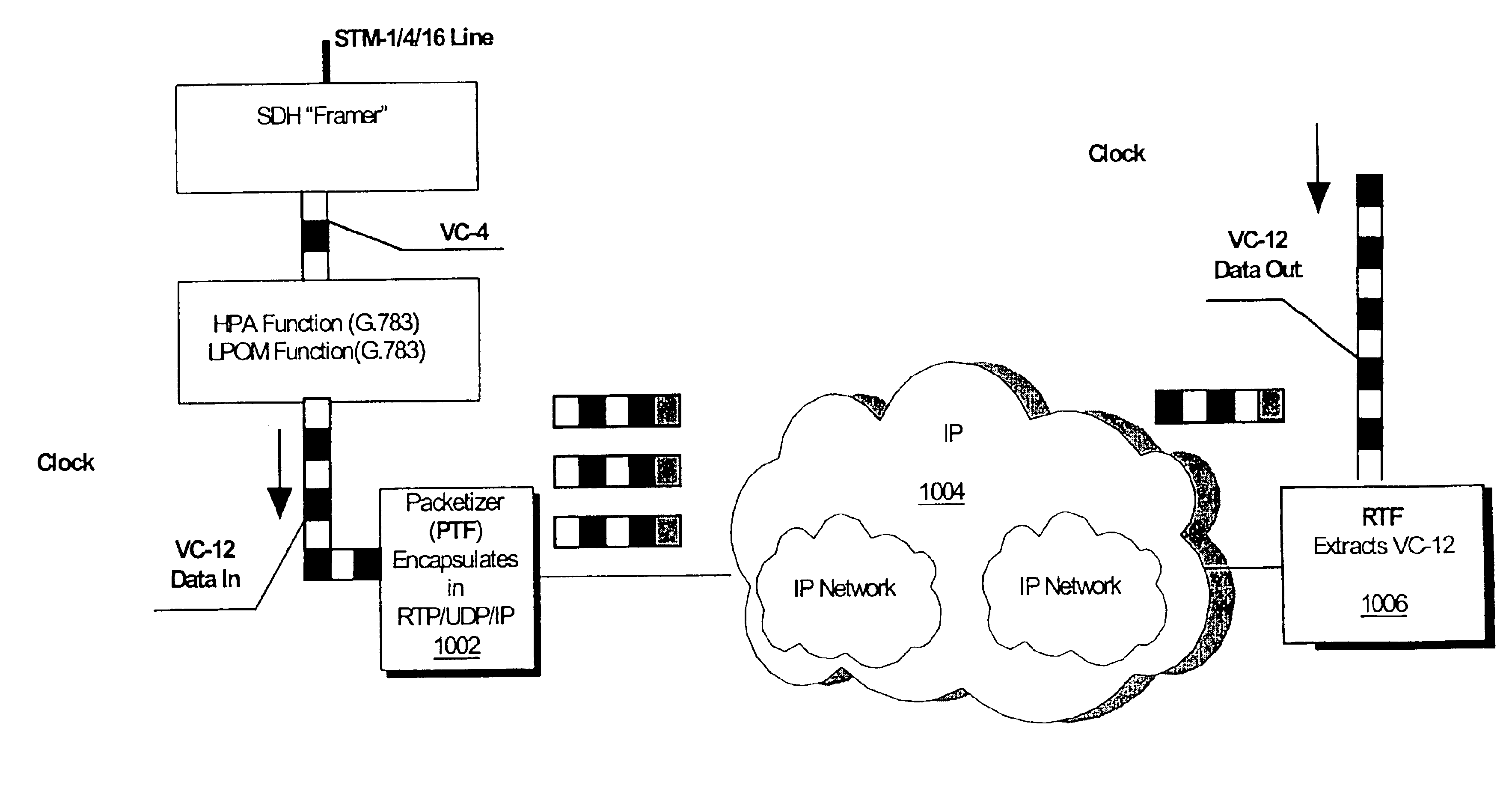
Circuit emulation service (CES) over IP
InactiveUS6898213B1Time-division multiplexTransmissionStructure of Management InformationClock recovery
Streams of data including explicit synchronization patterns (such as entire T1 / E1) are transmitted utilizing an unstructured data format, while streams not containing explicit synchronization patterns (such as fractional T1 / E1) are sent utilizing a structured data format, i.e., the data structure itself provides for circuit alignment at the receiving end. In addition, SDH VC-12 frames are transmitted over the IP network by encapsulating the entire frame (payload and overhead) into an RTP packet. Furthermore, the clock is reconstructed (clock recovery) from the packet stream at the receiver's side.
Owner:AXERRA NETWORKS
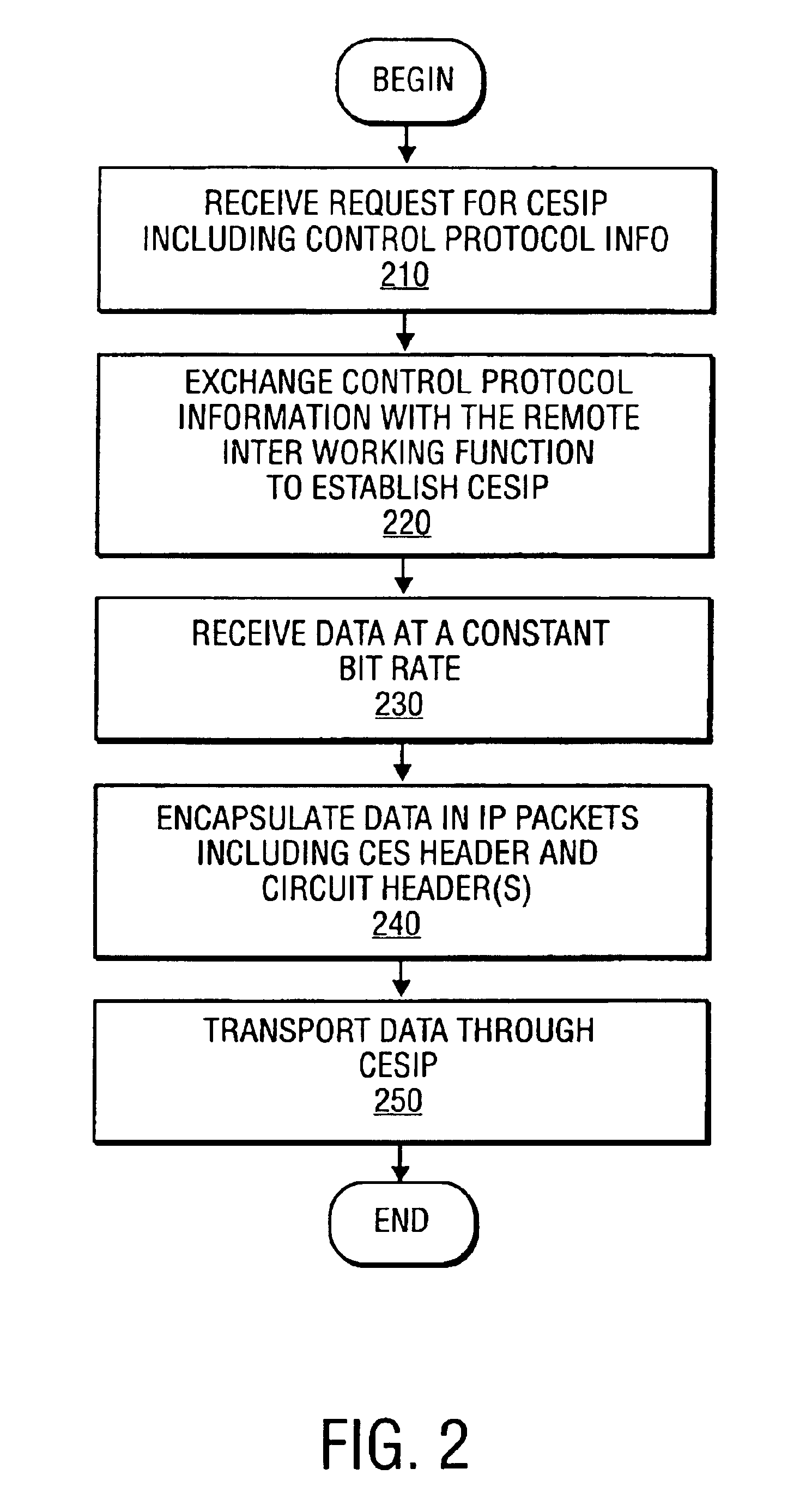
Jitter buffer for a circuit emulation service over an internet protocol network
A jitter buffer receives a plurality of data packets comprising a circuit emulation service over internet protocol (CESIP), buffers the plurality of data packets, and plays data from the plurality of data packets at a constant bit rate corresponding to the CESIP.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
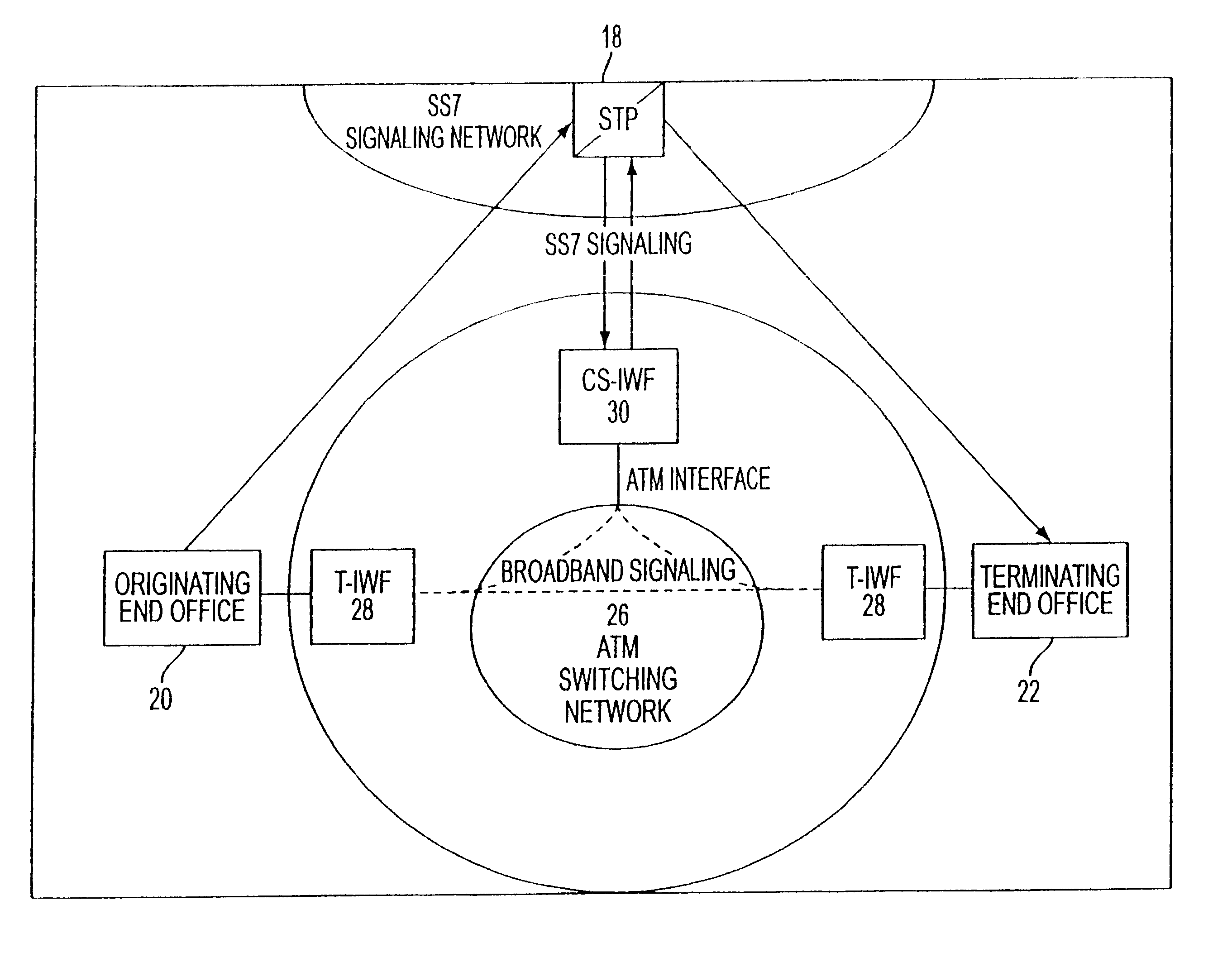
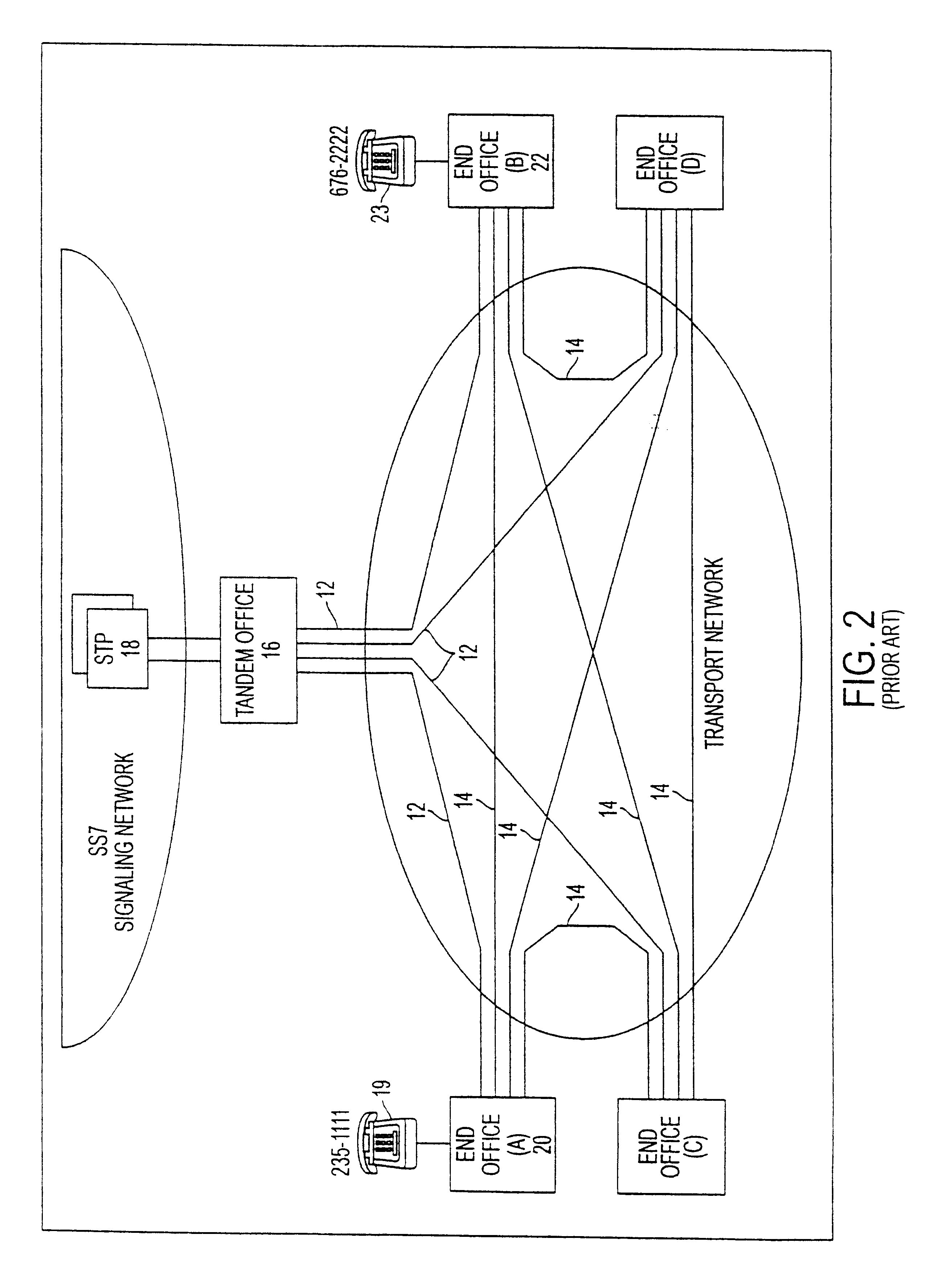
ATM-based distributed virtual tandem switching system
InactiveUS6389011B2Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationAtm switchingBroadband
An Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)-based distributed virtual tandem switching system is provided in which a network of ATM-based devices is combined to create a distributed virtual tandem switch. The system includes an ATM switching network that dynamically sets up individual switched virtual connections. The system also includes a trunk interworking function (T-IWF) device and a centralized control and signaling interworking function (CS-IWF) device. The trunk interworking function device converts end office voice trunks from TDM channels to ATM cells by employing a structured circuit emulation service. The centralized control and signaling interworking function device performs call control functions and interfaces narrowband signaling and broadband signaling for call processing and control within the ATM switching network. Consequently, the ATM based distributed virtual tandem switching system replaces a standard tandem switch in the PSTN.
Owner:SBC TECH RESOURCES
Clock synchronization backup mechanism for circuit emulation service
InactiveUS7191355B1Maintaining clock synchronizationRemoving errorTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationData synchronizationWrite buffer
A clock synchronization backup mechanism is disclosed for maintaining clock synchronization during periods of degraded synchronization. The clock synchronization backup mechanism includes a jitter buffer having a fill value at a given sample time which is compared with a threshold. When the jitter buffer fill value exceeds the threshold, a non-normal condition is registered and the local clock frequency is set to a combination of a long-term frequency setting plus a threshold sensitive frequency adjustment. The clock synchronization backup mechanism is particularly useful for overcoming residual errors accumulated due to temperature change, oscillator degradation, and a variety of other system perturbations problematical for clock synchronization mechanisms known in the art.
Owner:CIENA
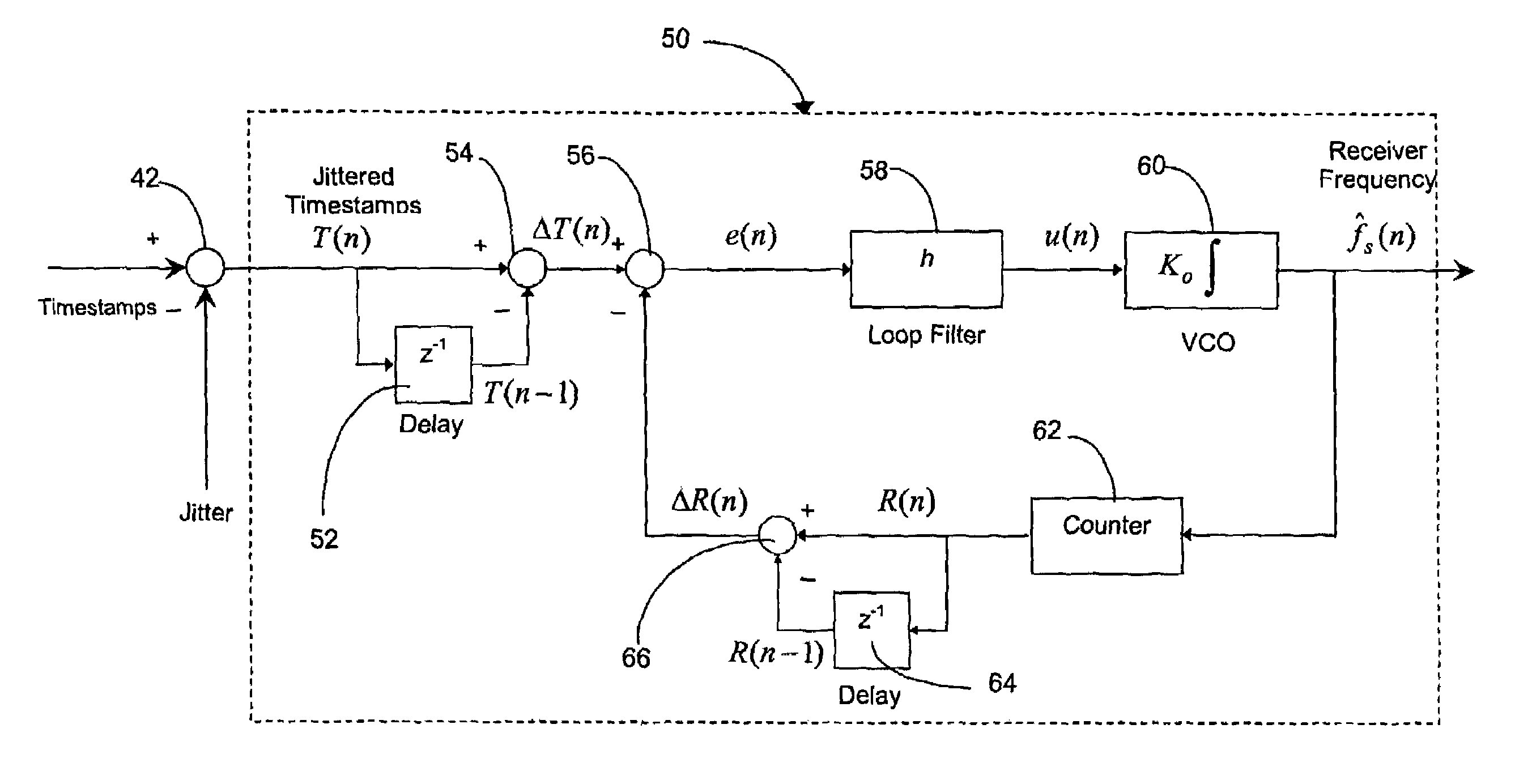
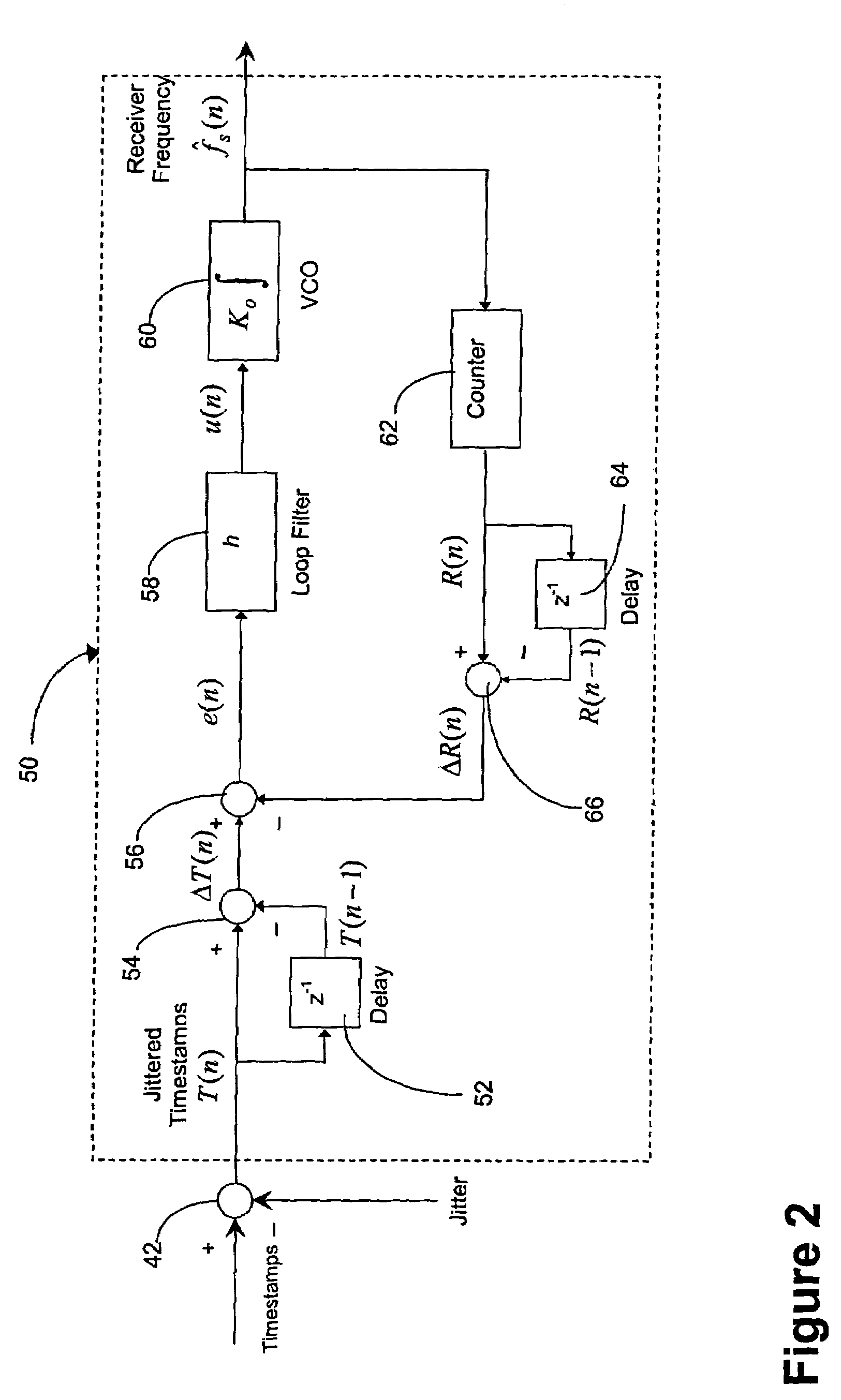
Timestamp-based all digital phase locked loop for clock synchronization over packet networks
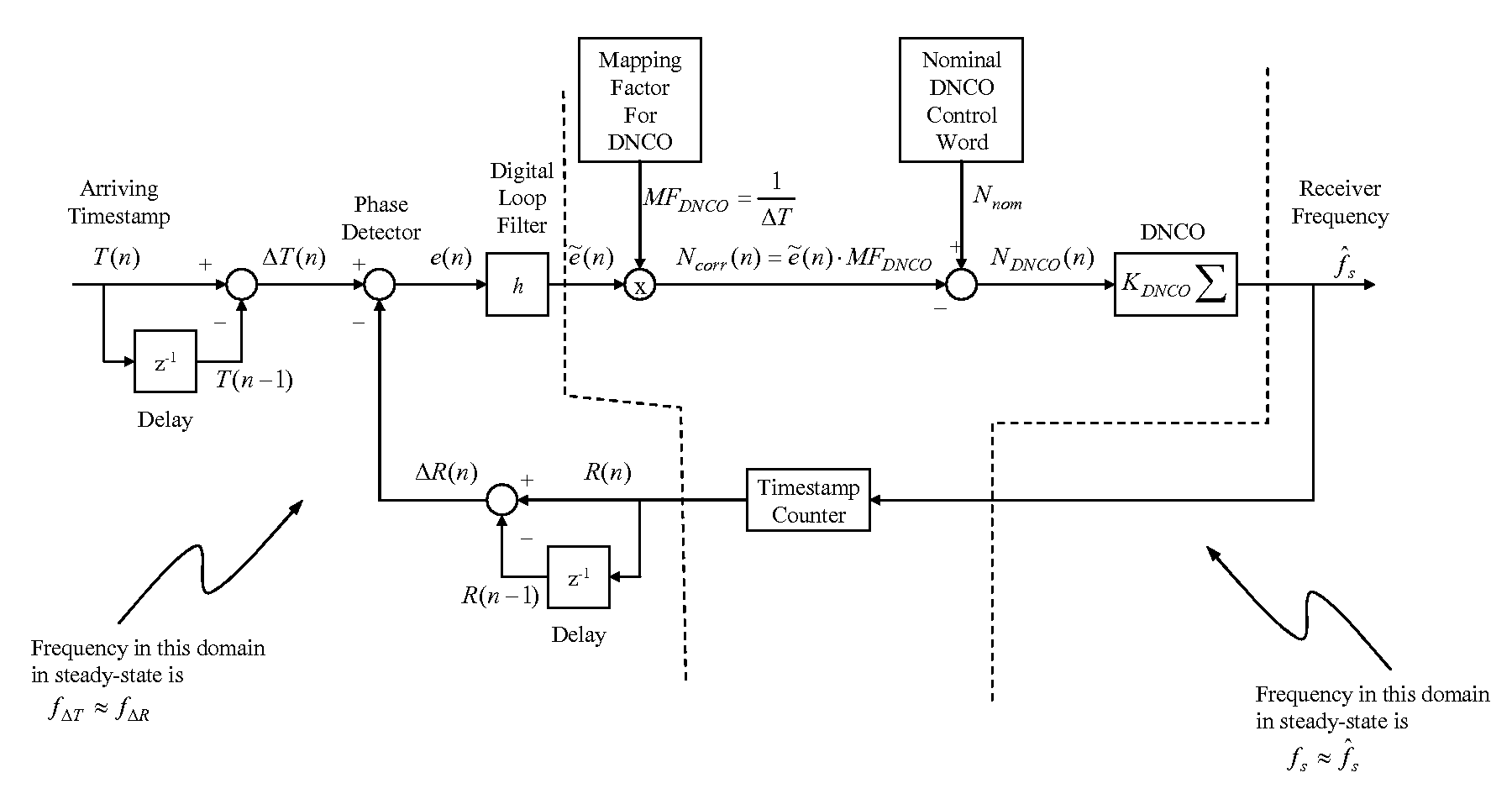
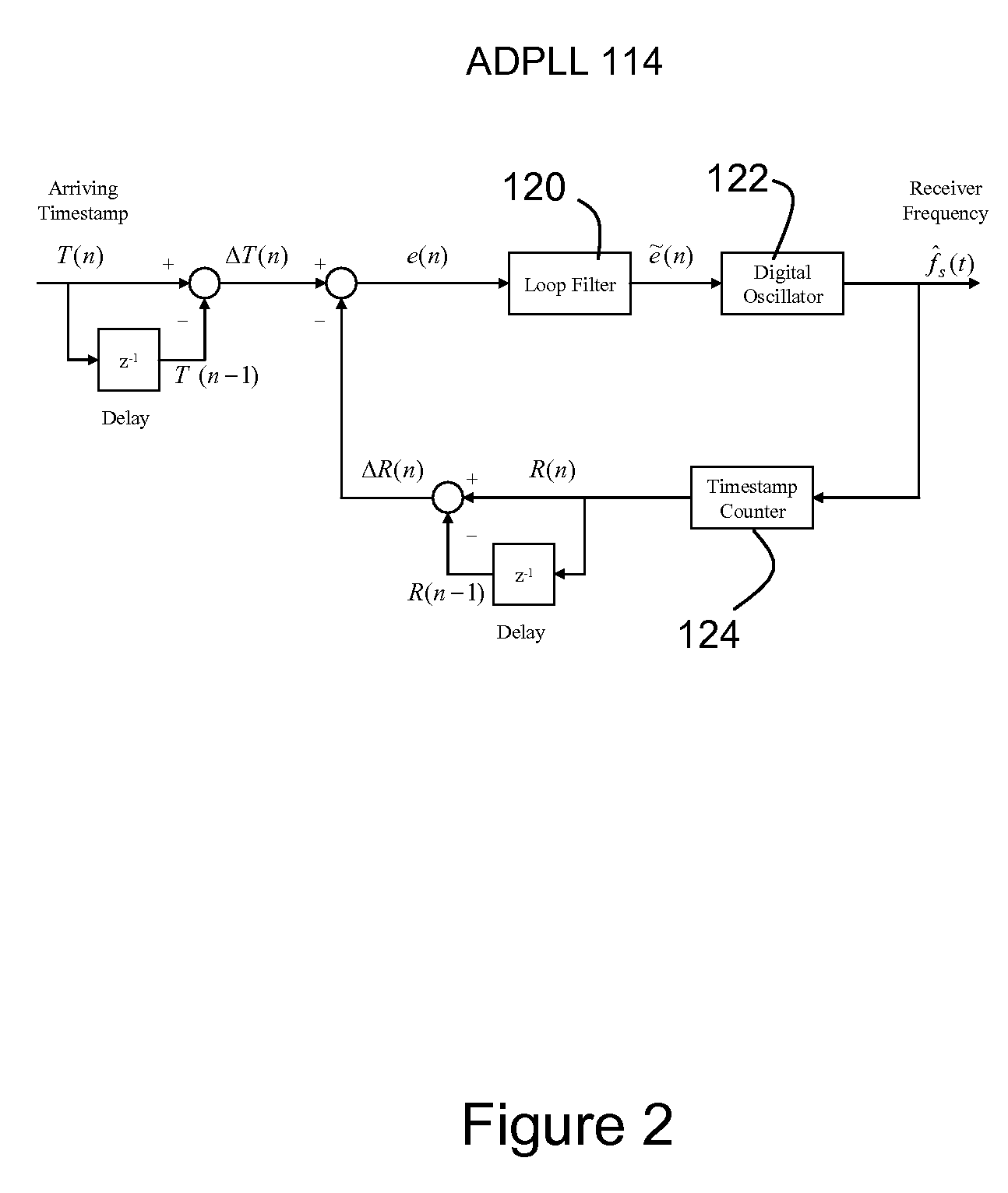
ActiveUS7656985B1Reduce jitterReduce noiseFrequency-division multiplex detailsModulated-carrier systemsPhase detectorLoop filter
A timestamp-based all digital phase locked loop is utilized for clock synchronization for Circuit Emulation Service (“CES”) over packet networks. The all digital phase locked loop at a CES receiver includes a phase detector, a loop filter, a digital oscillator and a timestamp counter. The all digital phase locked loop enables the CES receiver to synchronize a local clock at the receiver with a clock at a CES transmitter, where indications of transmitter clock signals are communicated to the receiver as timestamps. The phase detector is operable to compute an error signal indicative of differences between the timestamps and a local clock signal. The loop filter is operable to reduce jitter and noise in the error signal, and thereby produce a control signal. The digital oscillator is operable to oscillate at a frequency based at least in-part on the control signal, and thereby produce a digital oscillator output signal. The timestamp counter operable to count pulses in the digital oscillator output signal, and output the local clock signal.
Owner:CIENA
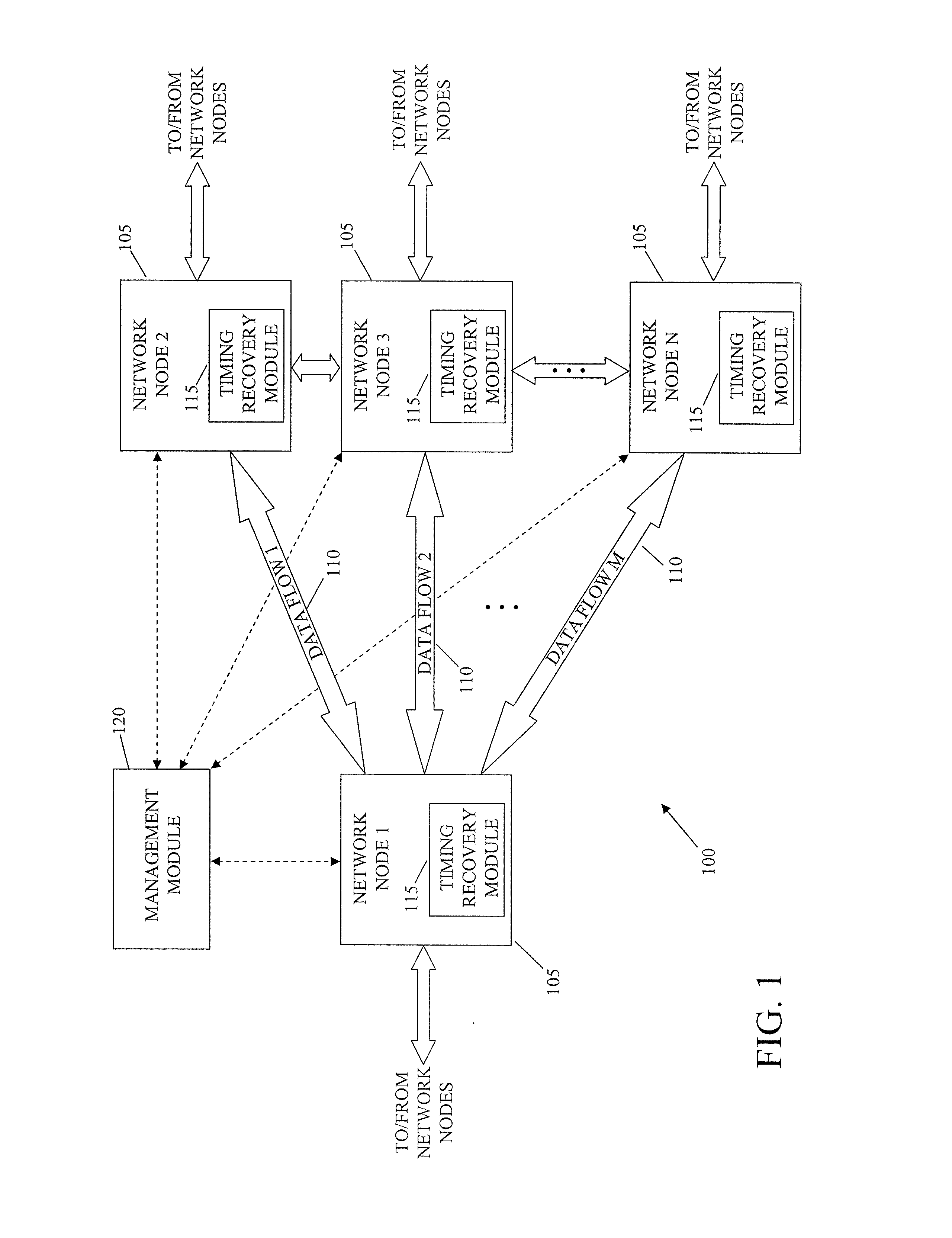
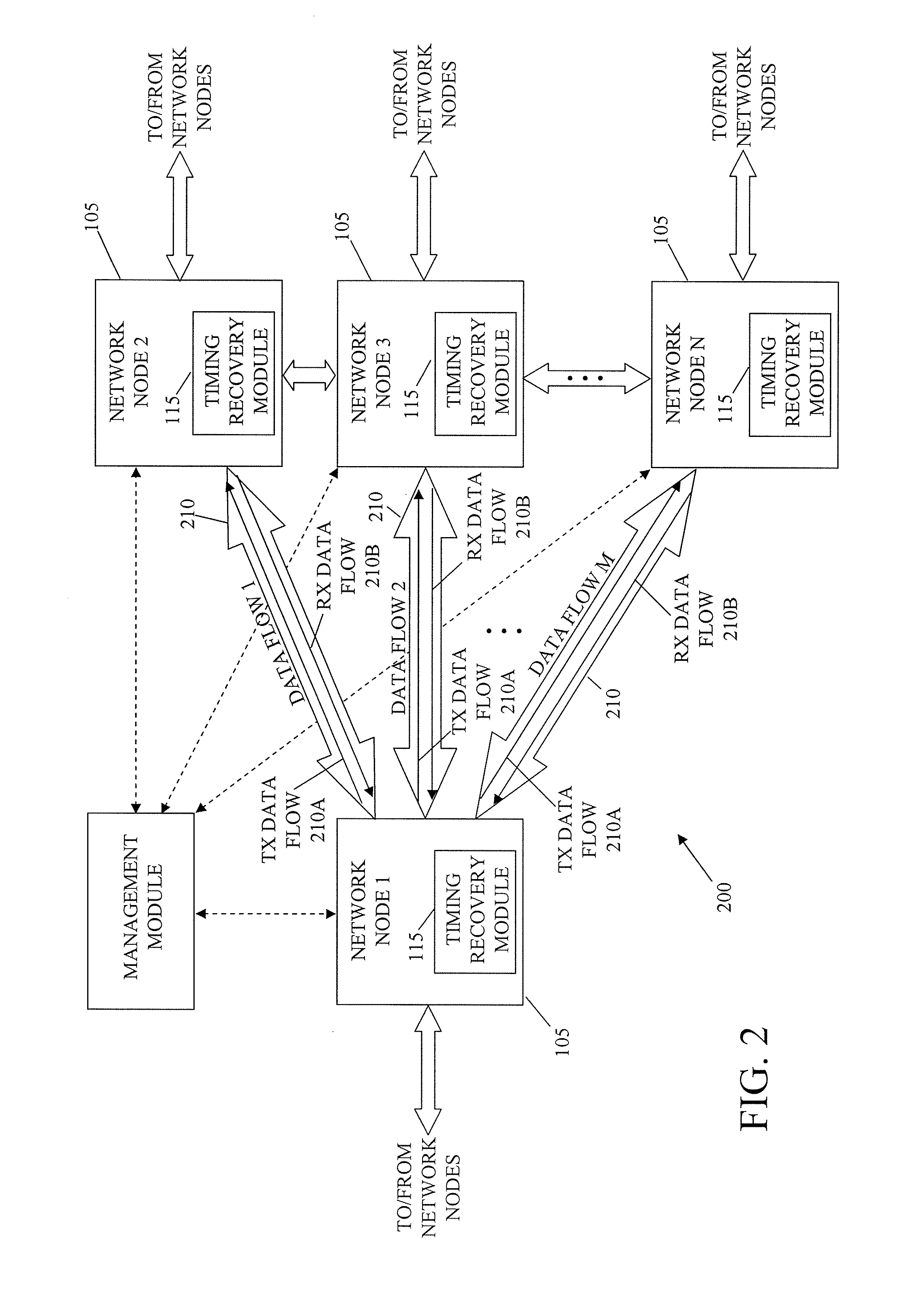
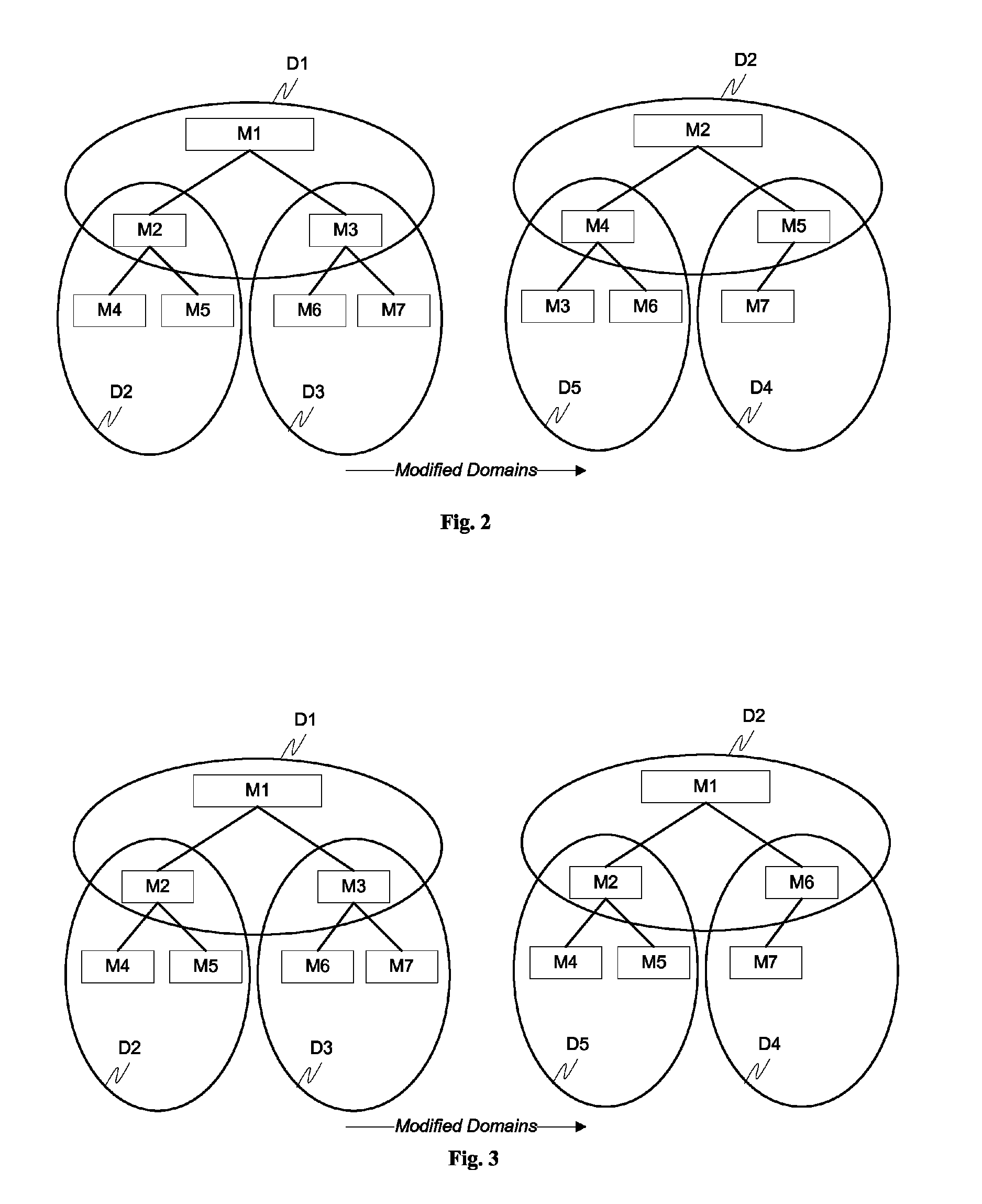
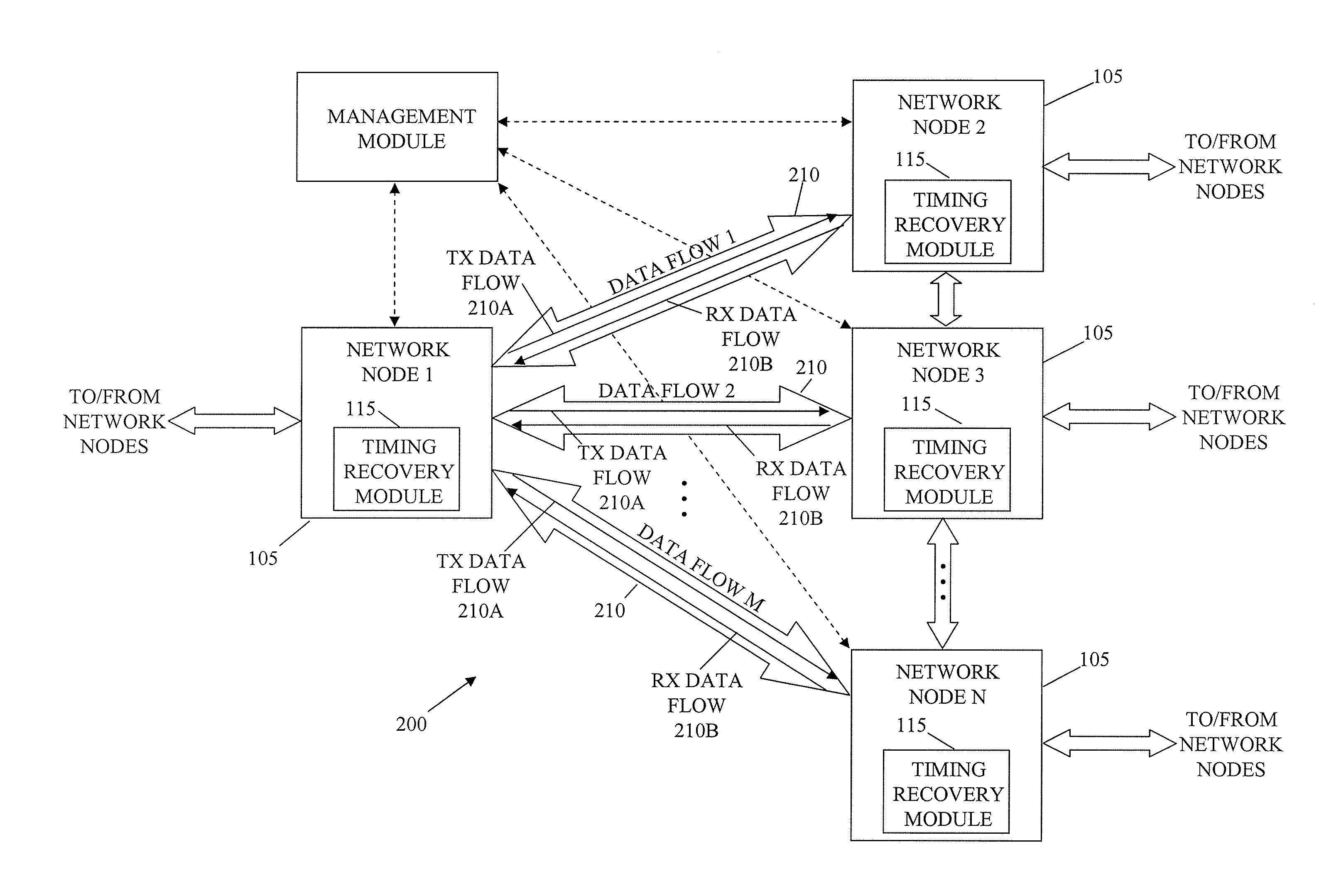
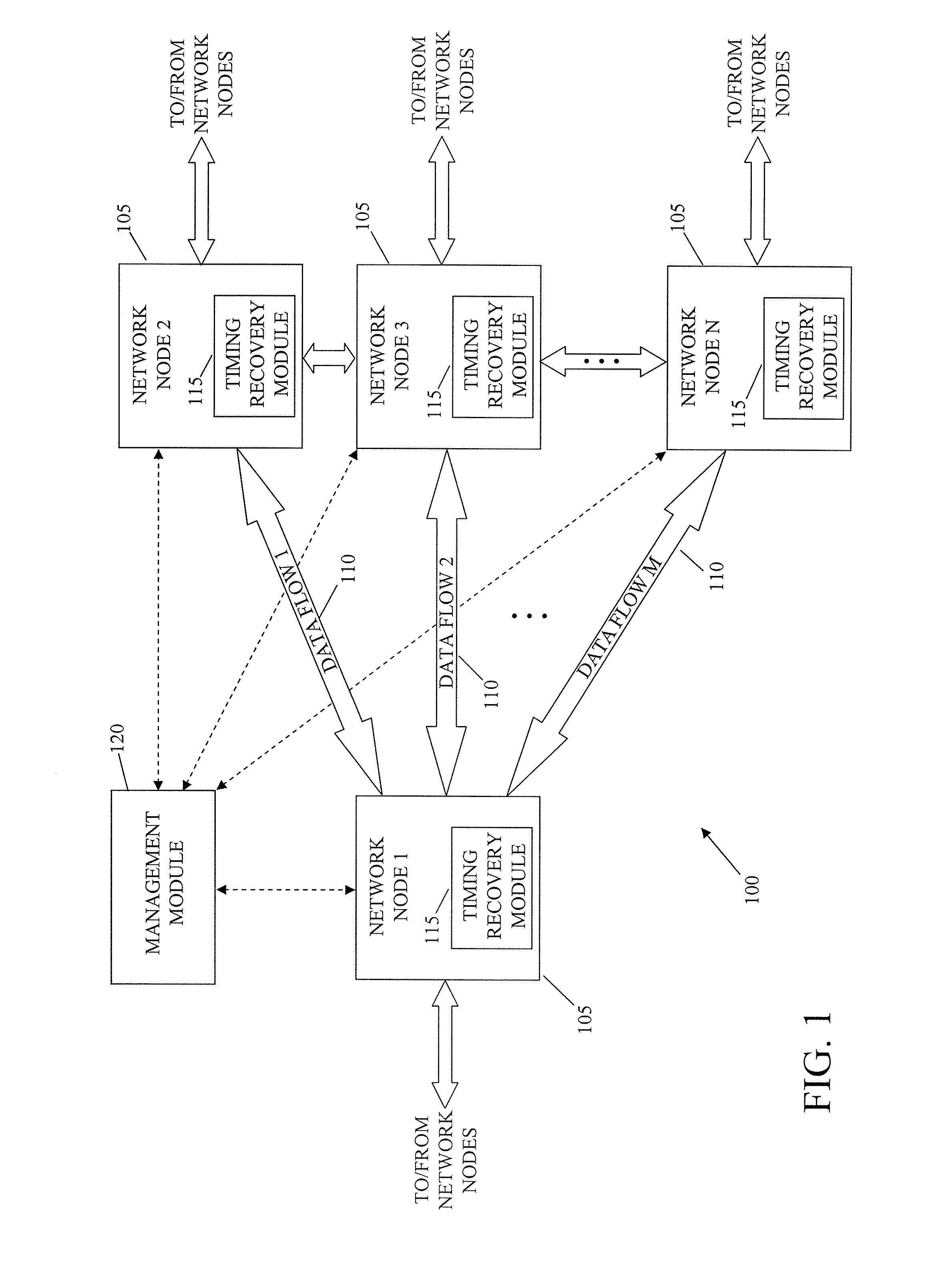
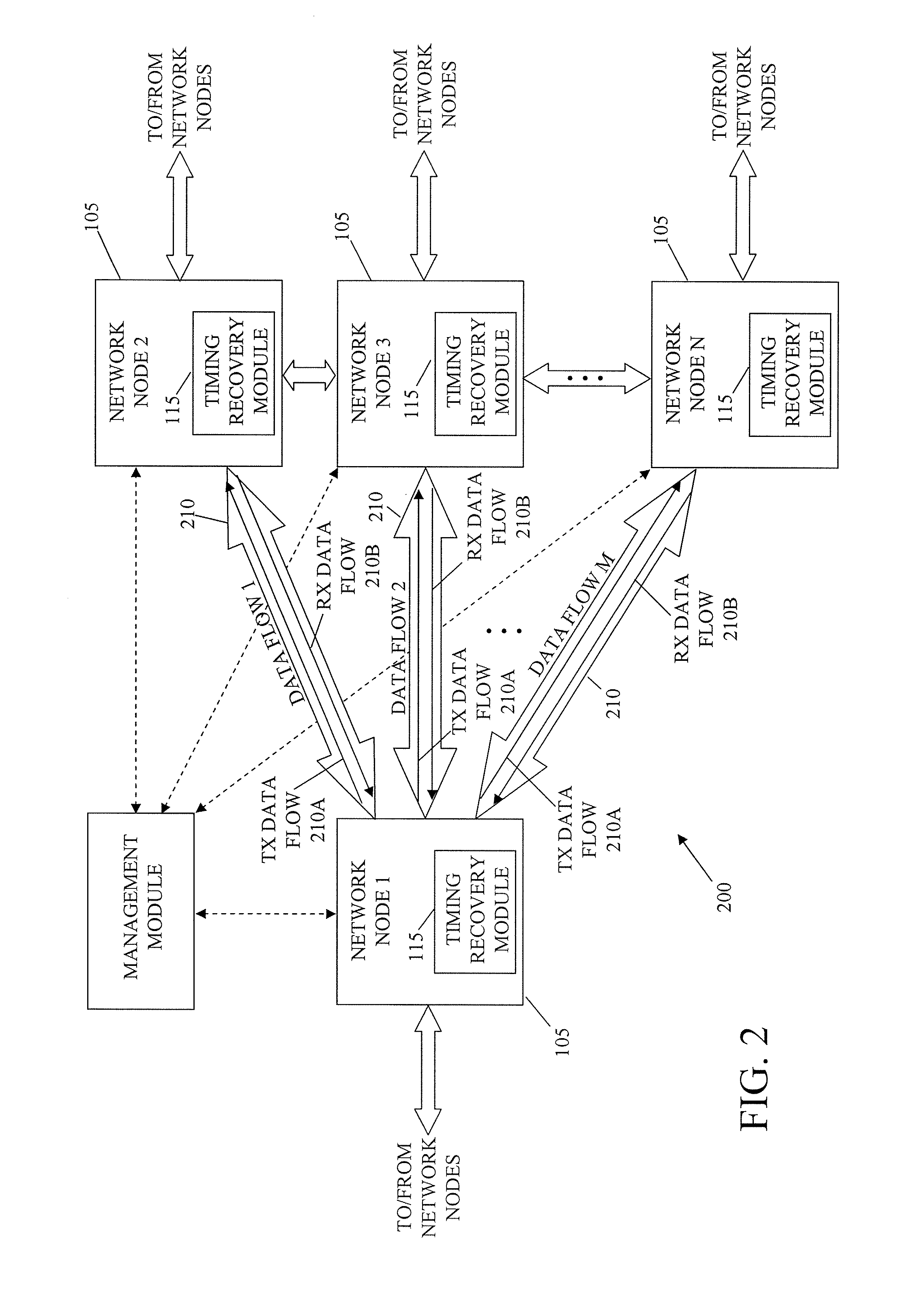
System and method for packet timing of circuit emulation services over networks
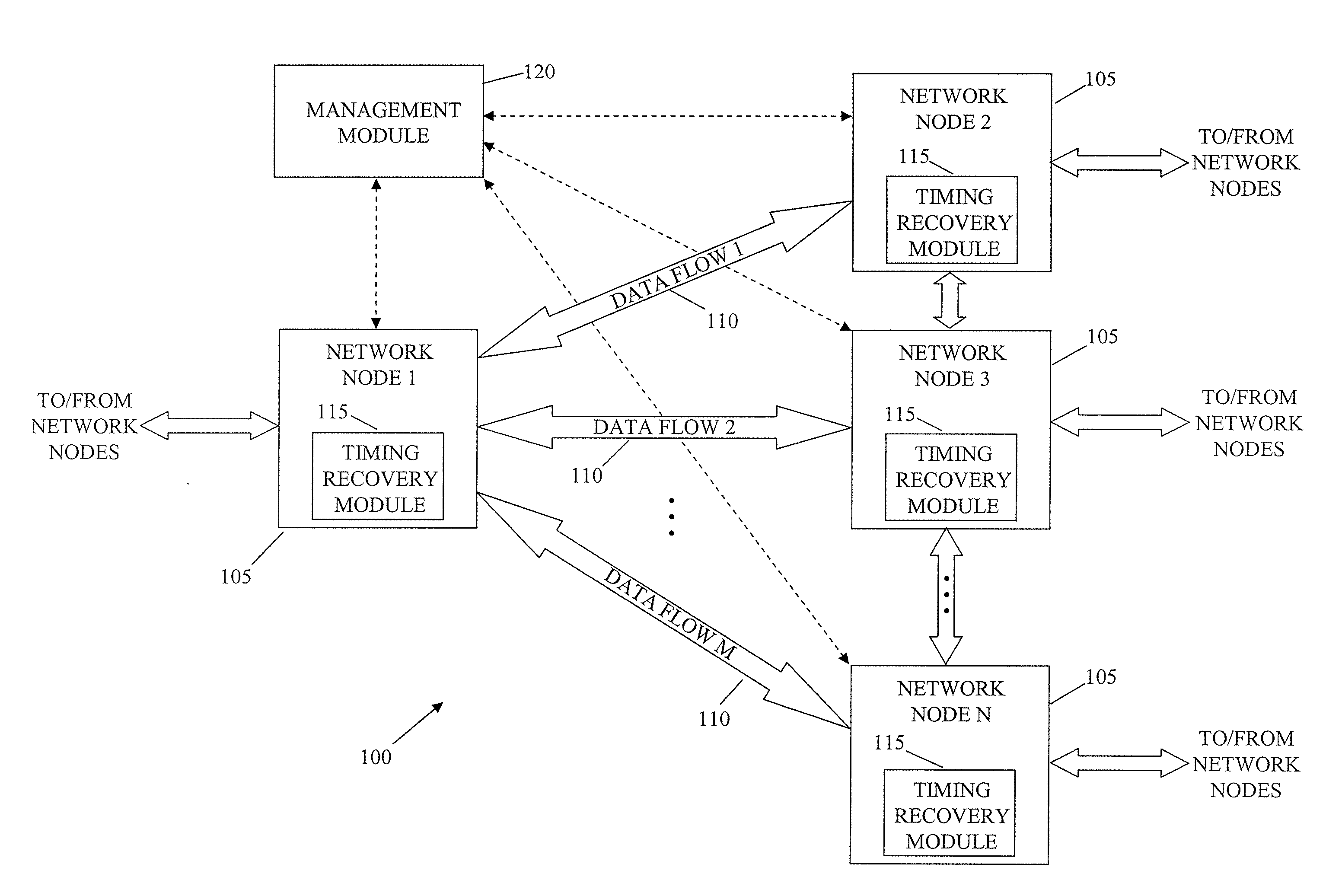
InactiveUS20070189164A1Reduce non-linearityError preventionTransmission systemsData streamData transmission
A system and method for managing information communication in a network includes a plurality of network nodes. A plurality of circuit emulation data flows are established between a first network node and at least a second network node. Different data transmission rates are assigned to each circuit emulation data flow such that the frequency of communicated packets is different at least for each circuit emulation data flow used for timing recovery to make the plurality of circuit emulation data flows substantially independent of each other. For example, different frame rates can be assigned to synchronous backhaul transmission links such that the frequency of the backhaul transmission rates is substantially independent of the circuit emulation flow rates.
Owner:ERICSSON WIFI
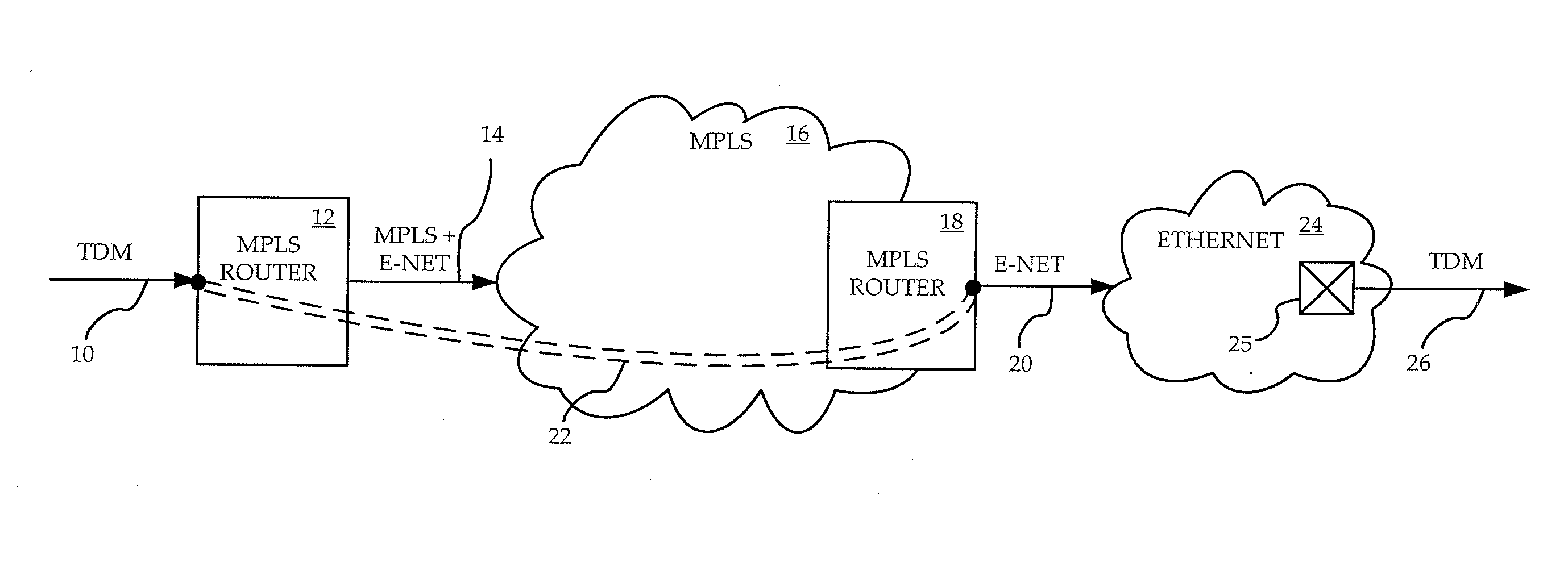
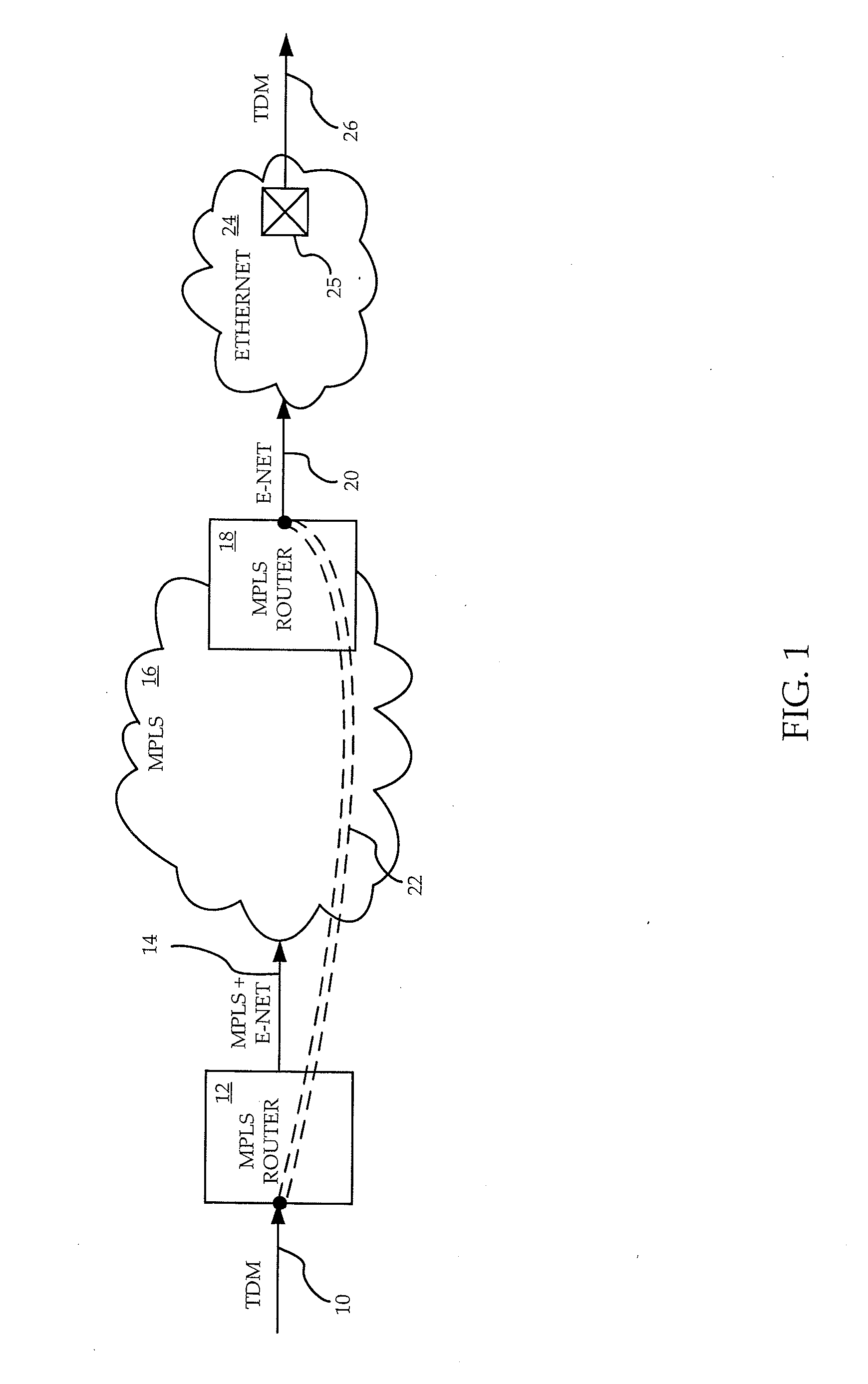
Ethernet over mpls circuit emulation service
InactiveUS20080304476A1High volume costGuaranteed reliabilityNetwork connectionsEthernet frameEmbedded system
A method and apparatus are provided for providing CES using both Ethernet and MPLS networks. TDM data is packetized and Ethernet encapsulated, and then MPLS encapsulated. Following insertion into an MPLS core network, the packet is routed to a destination MPLS router using MPLS routing. The MPLS encapsulation is then removed, and the resulting Ethernet frame inserted into a destination Ethernet network. The Ethernet frame is routed to a destination Ethernet port using Ethernet routing. The TDM data is extracted, and inserted into the appropriate TDM channel. The invention allows inexpensive Ethernet equipment to be used at the boundary with the TDM network, and a reliable MPLS network with its QoS functionality to be used for any long-haul part of the CES.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
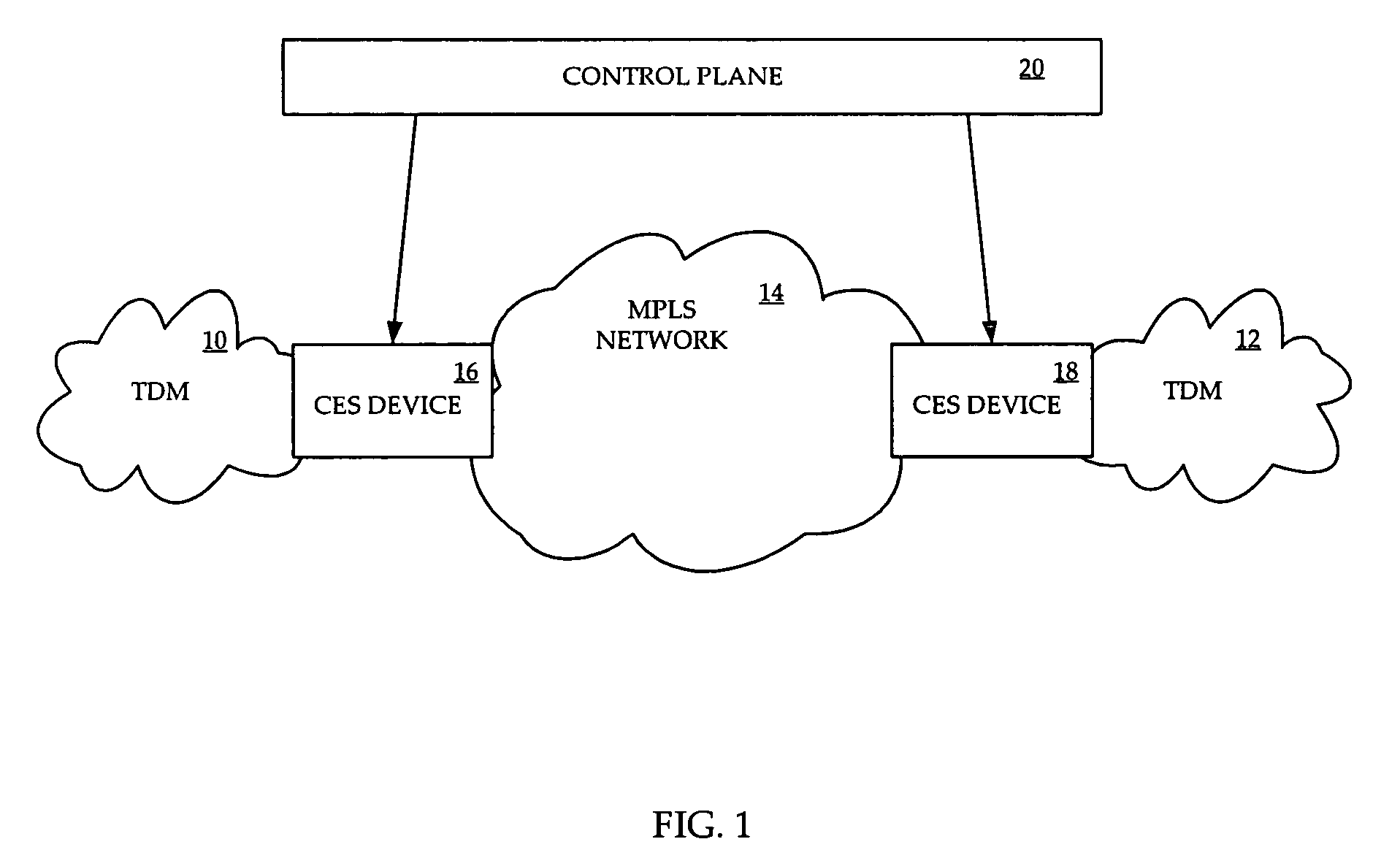
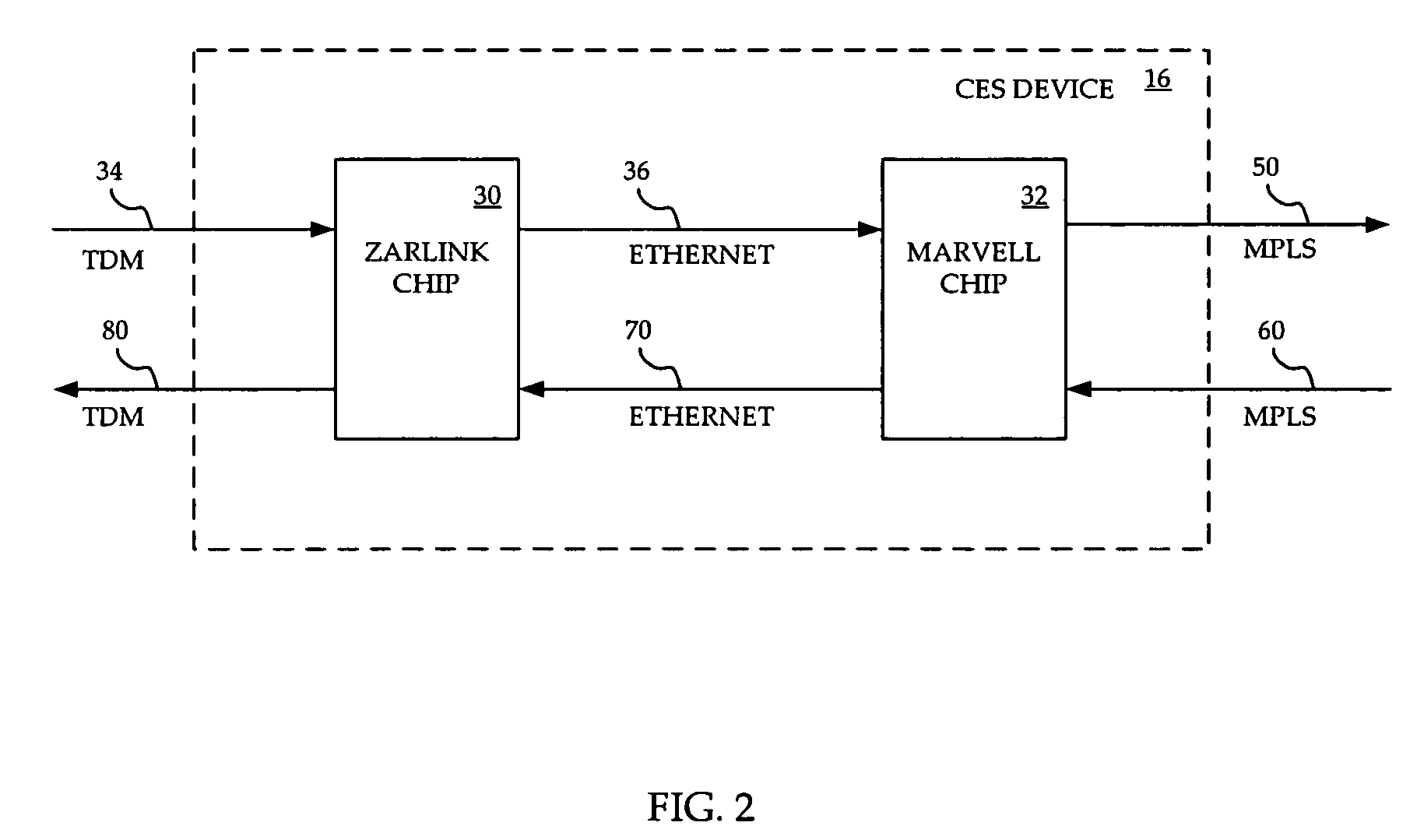
Interworking circuit emulation service over packet and IP/MPLS packet processing
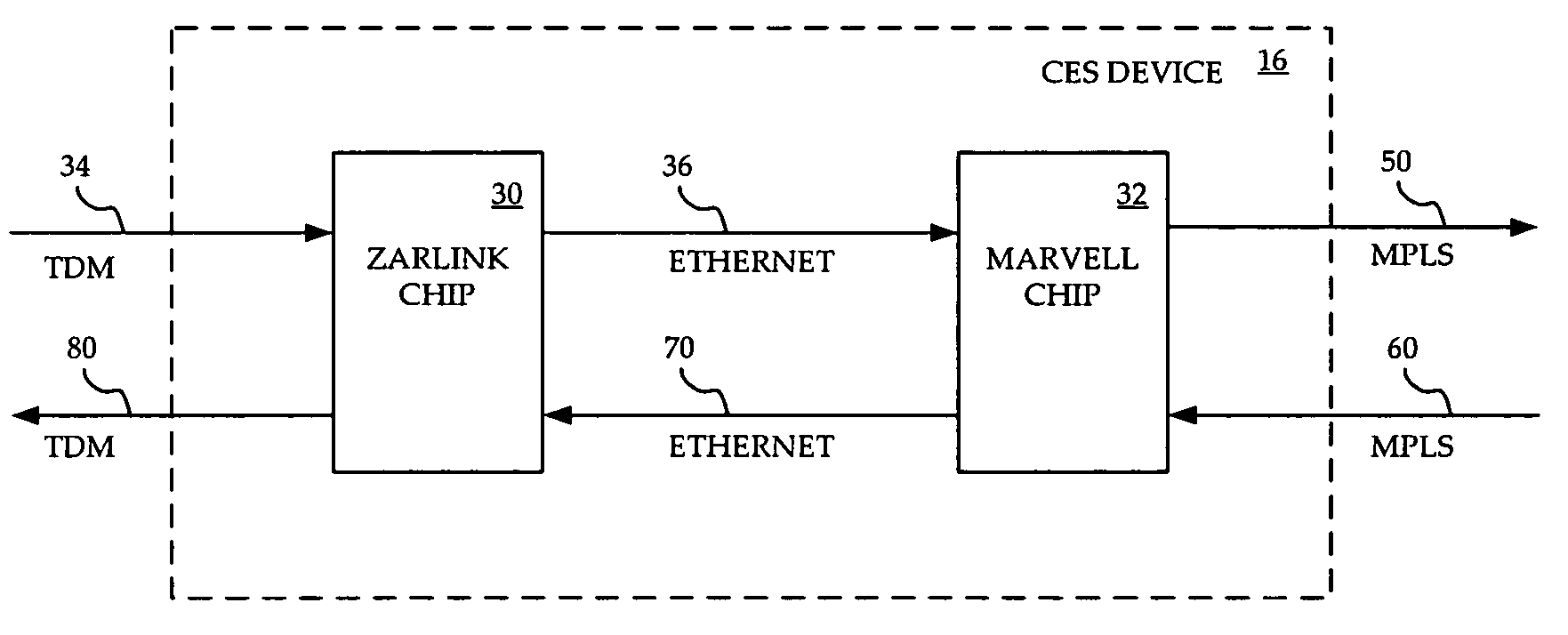
InactiveUS20070071029A1InexpensivelyEfficient implementationTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationEthernetVirtual circuit
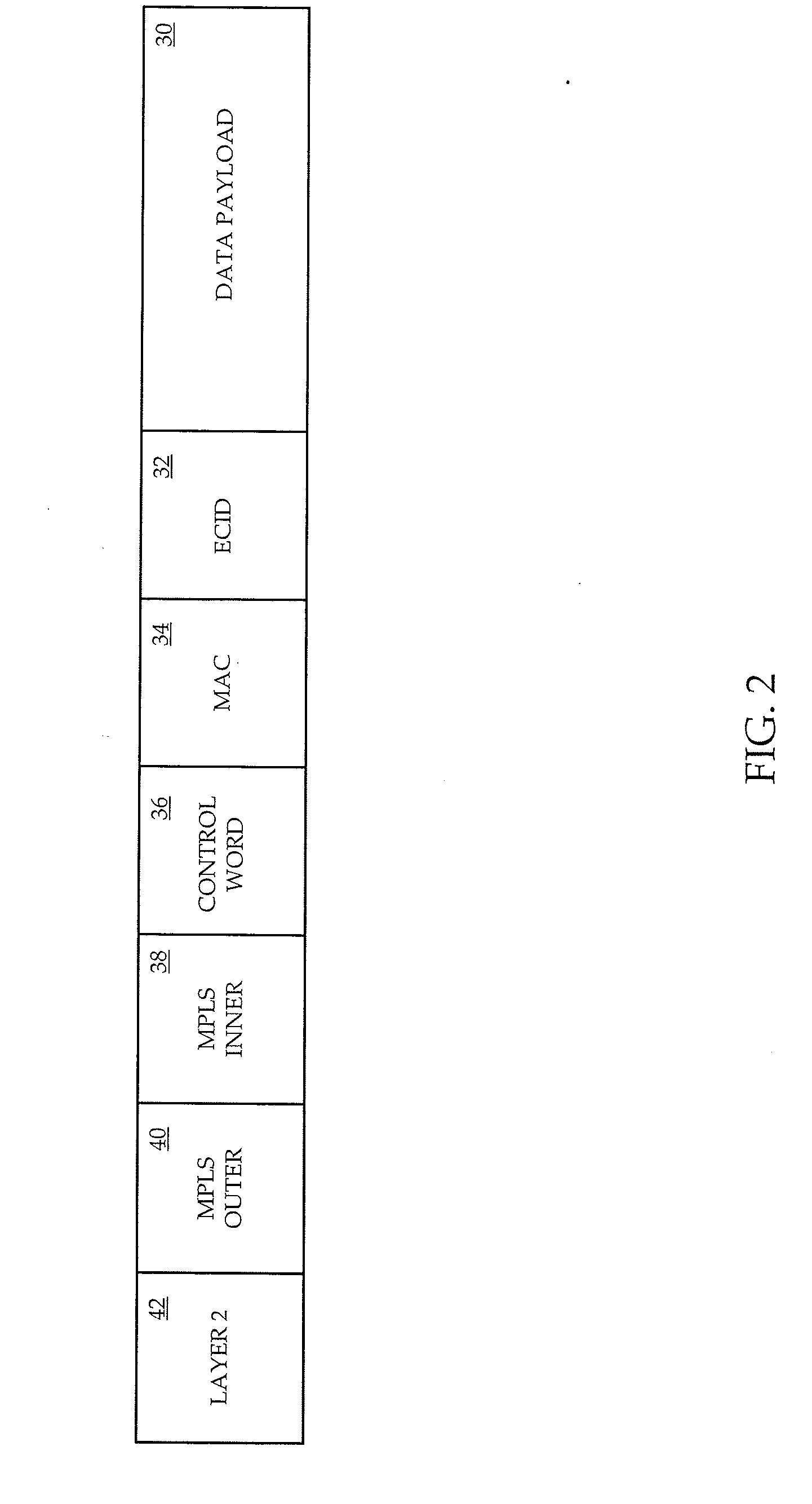
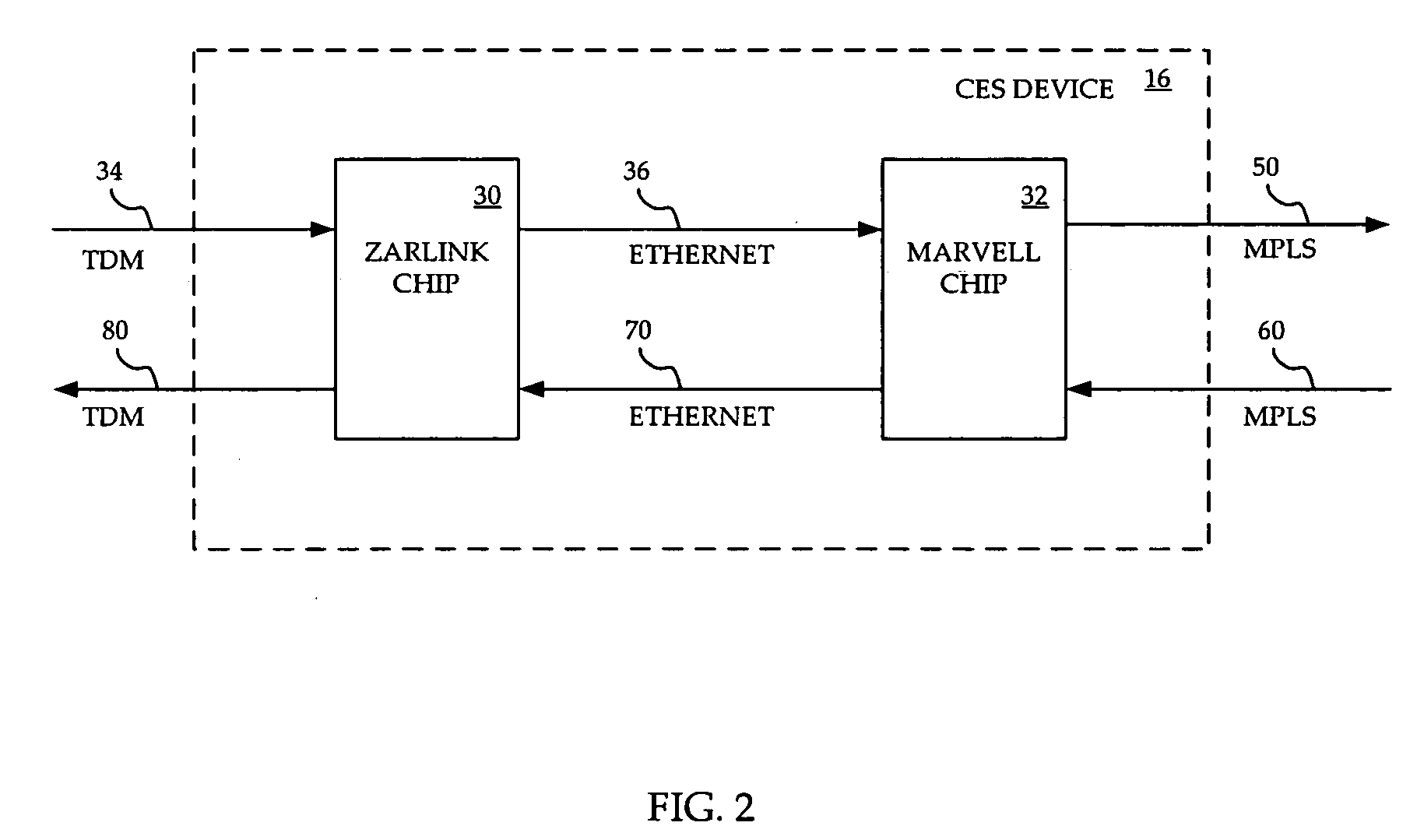
A system and method are provided for implementing CESOP inexpensively yet effectively implemented across an MPLS or an IP network. A Zarlink chip provides CESOP functionality, providing a TDM pseudowire by converting TDM streams into Ethernet packets. These Ethernet packets can be processed by a Marvell chip, which has the ability to perform QoS functions on the packets. The Marvell chip converts the Ethernet packets into MPLS or IP packets for transmission over a packet network. Use of a single virtual circuit label, invisible to the packet network for routing purposes, within the Ethernet packet allows Marvell chips at each end of the emulated circuit to tie traffic to a particular customer and to thereby apply appropriate QoS constraints.
Owner:RPX CORP
Jitter buffer for a circuit emulation service over an internal protocol network
A jitter buffer receives a plurality of data packets comprising a circuit emulation service over internet protocol (CESIP), buffers the plurality of data packets, and plays data from the plurality of data packets at a constant bit rate corresponding to the CESIP.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
Circuit emulation service method and telecommunication system for implementing the method
ActiveUS20090141629A1Efficient transportIncrease the number ofError preventionTransmission systemsExchange networkPacket switch
It is disclosed a method for implementing a circuit emulation service through a packet-switched network, wherein the packet-switched network cooperates with a first interface and a second interface suitable to connect a first user and a second user, respectively, to the packet-switched network. The method comprises: a) at the first interface, receiving a TDM flow from the first user; b) converting the TDM flow in packets formatted according to the circuit emulation service, wherein at least one of the packets comprises a header in turn comprising a redundant field; c) compressing the header into a compressed header by processing the redundant field, and forming a compressed packet comprising the compressed header; d) transmitting the compressed packet through the packet-switched network to the second interface.
Owner:RPX CORP
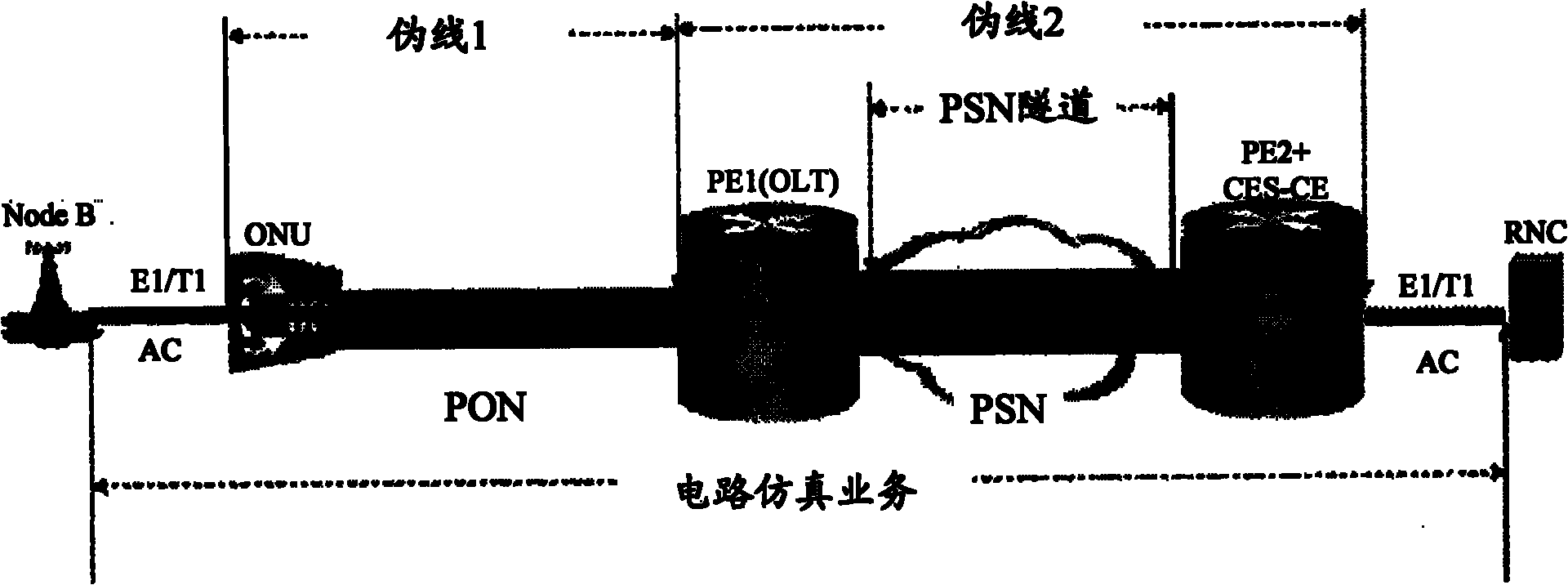
Configuration method and system of circuit emulation service in passive optical network
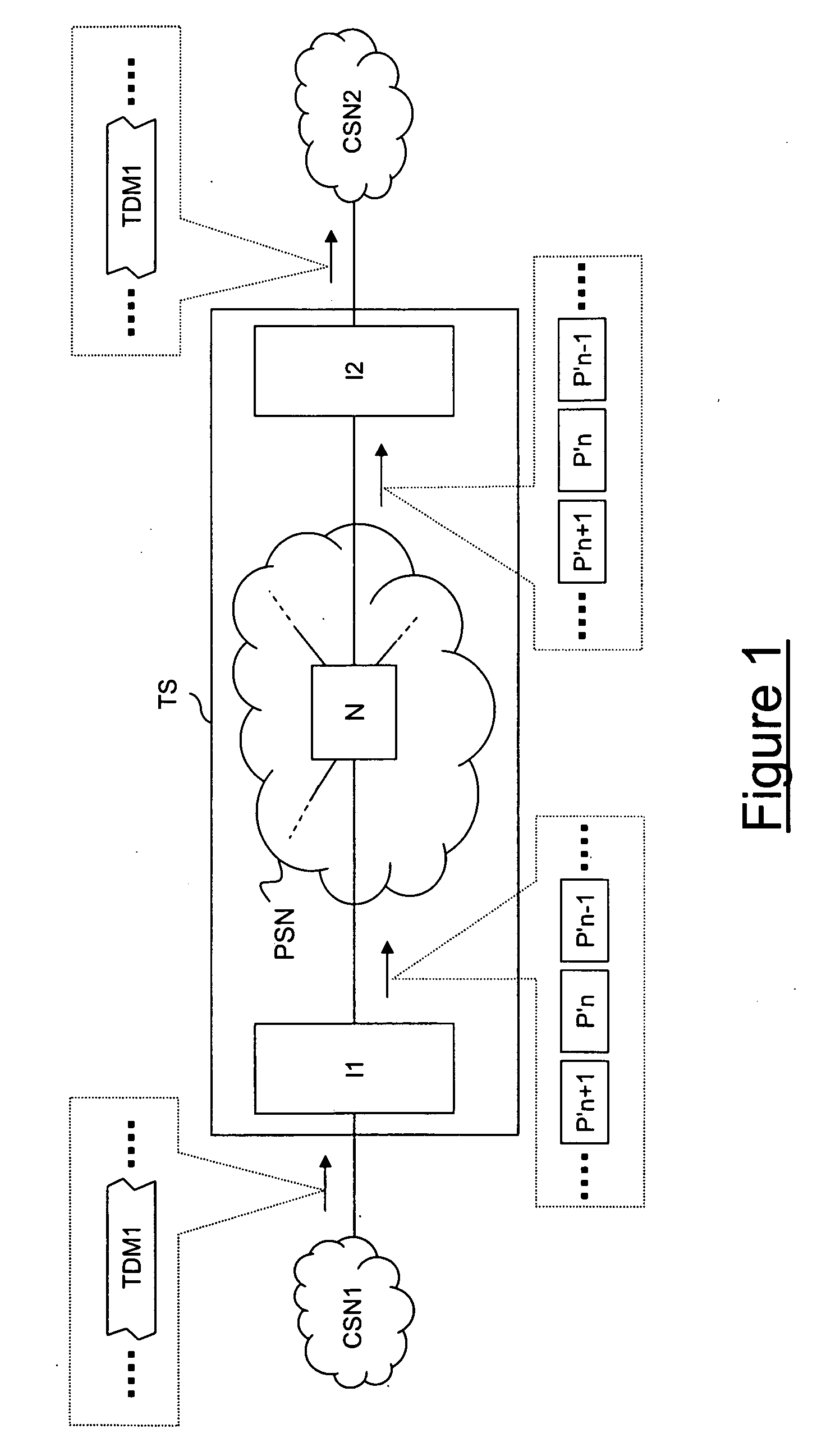
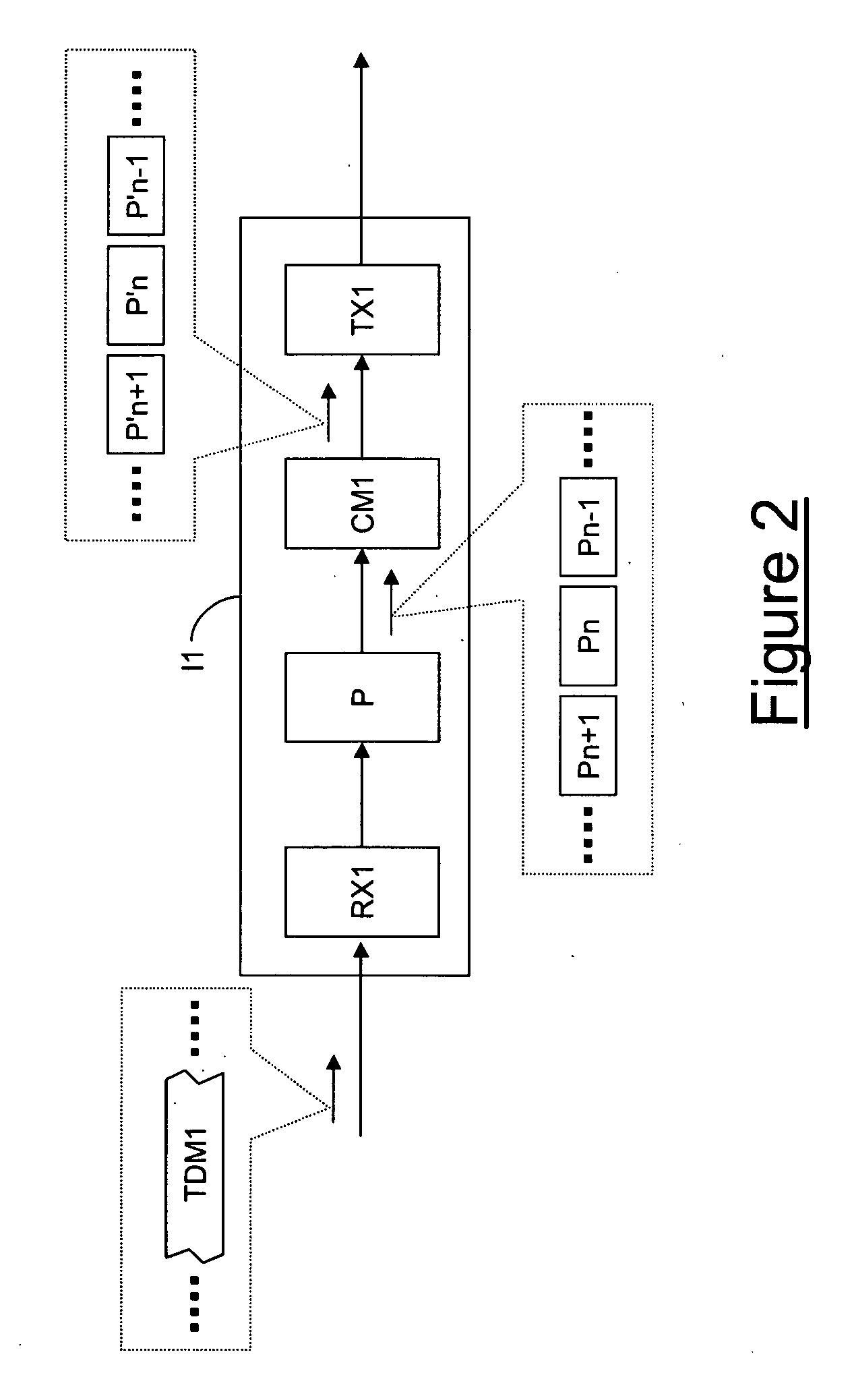
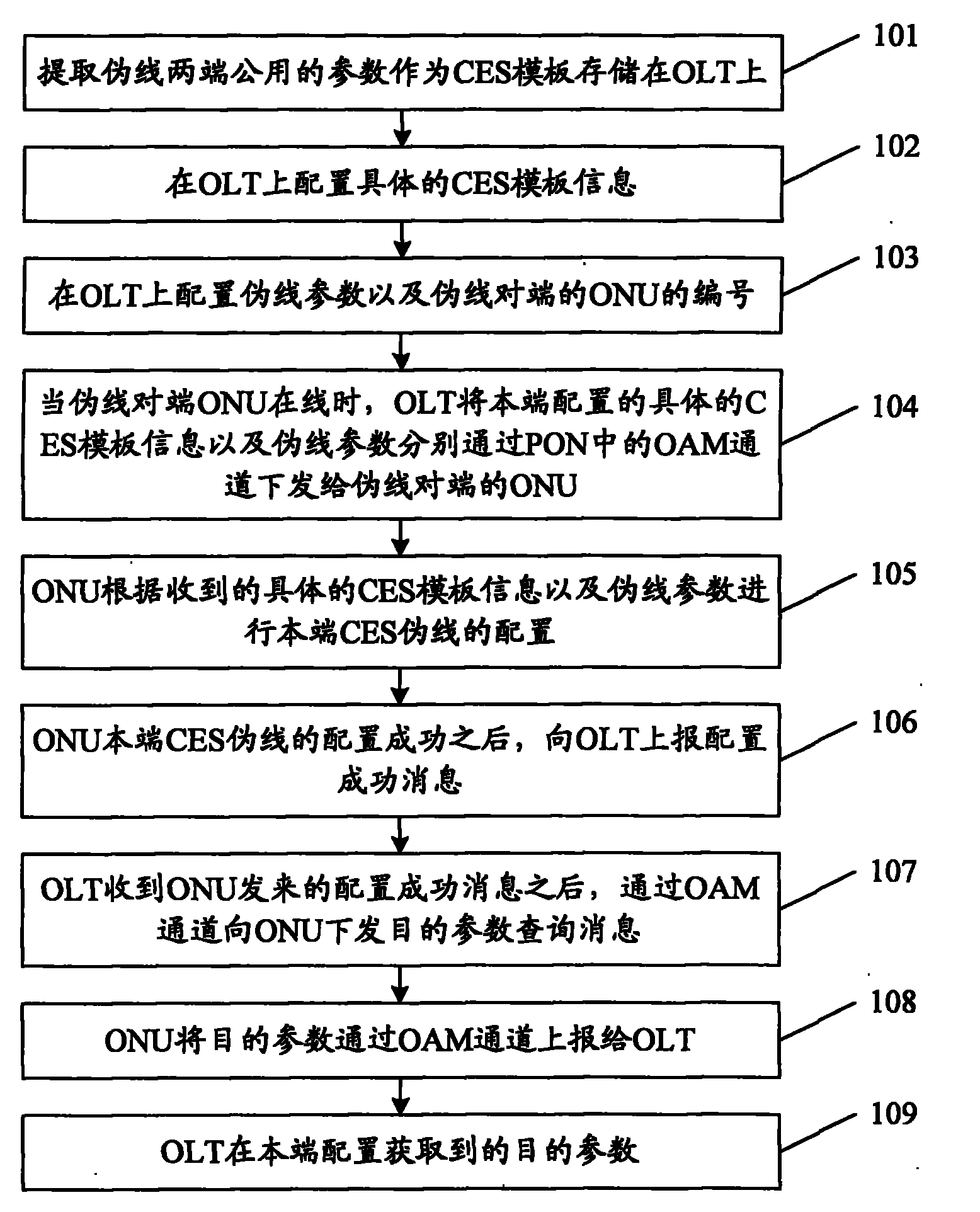
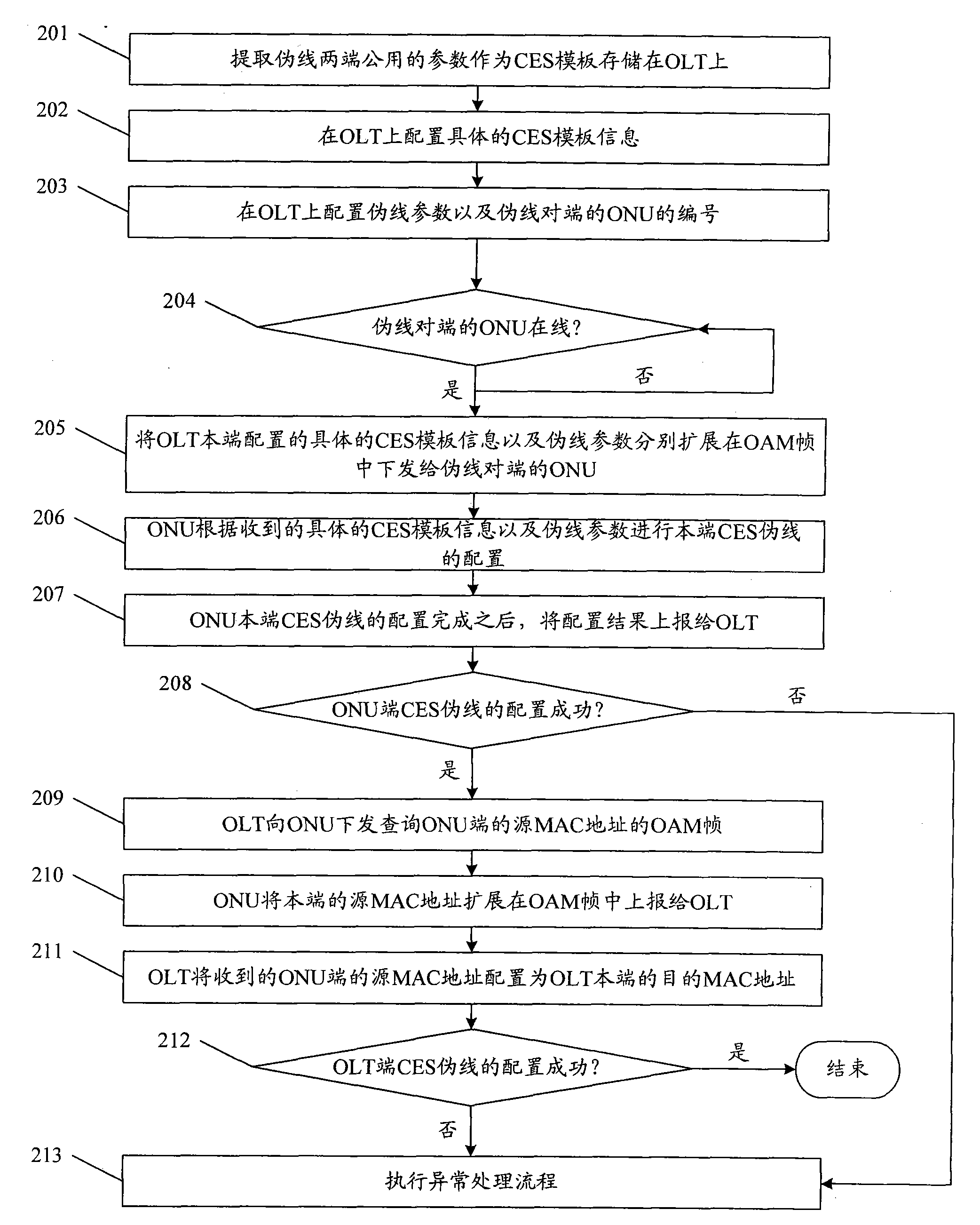
ActiveCN101902350AReduce complexityReduce error rateMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksPseudo-wireOptical network unit
The invention discloses a configuration method of circuit emulation service (CES) in a passive optical network (PON). The method comprises the following steps: according to a CES template prestored on an optical link terminal (OLT), CES template information is configured on the OLT; pseudo-wire parameter is configured on the OLT; when an optical network unit (ONU) on the opposite terminal of the pseudo-wire is on-line, the OLT issues the CES template information and pseudo-wire parameter configured on the terminal to the ONU; the ONU performs the local configuration of the CES pseudo-wire according to the received CES template information and pseudo-wire parameter; after the configuration succeeds, a successful configuration message is reported to the OLT; after the OLT receives the successful configuration message sent by the ONU, the OLT issues a target parameter query message to the ONU; the ONU reports the target parameter stored in the local terminal to the OLT; and the OLT obtains the target parameter in the local configuration. The invention also discloses a configuration system of the CES in the PON.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Data transmission method, device and system
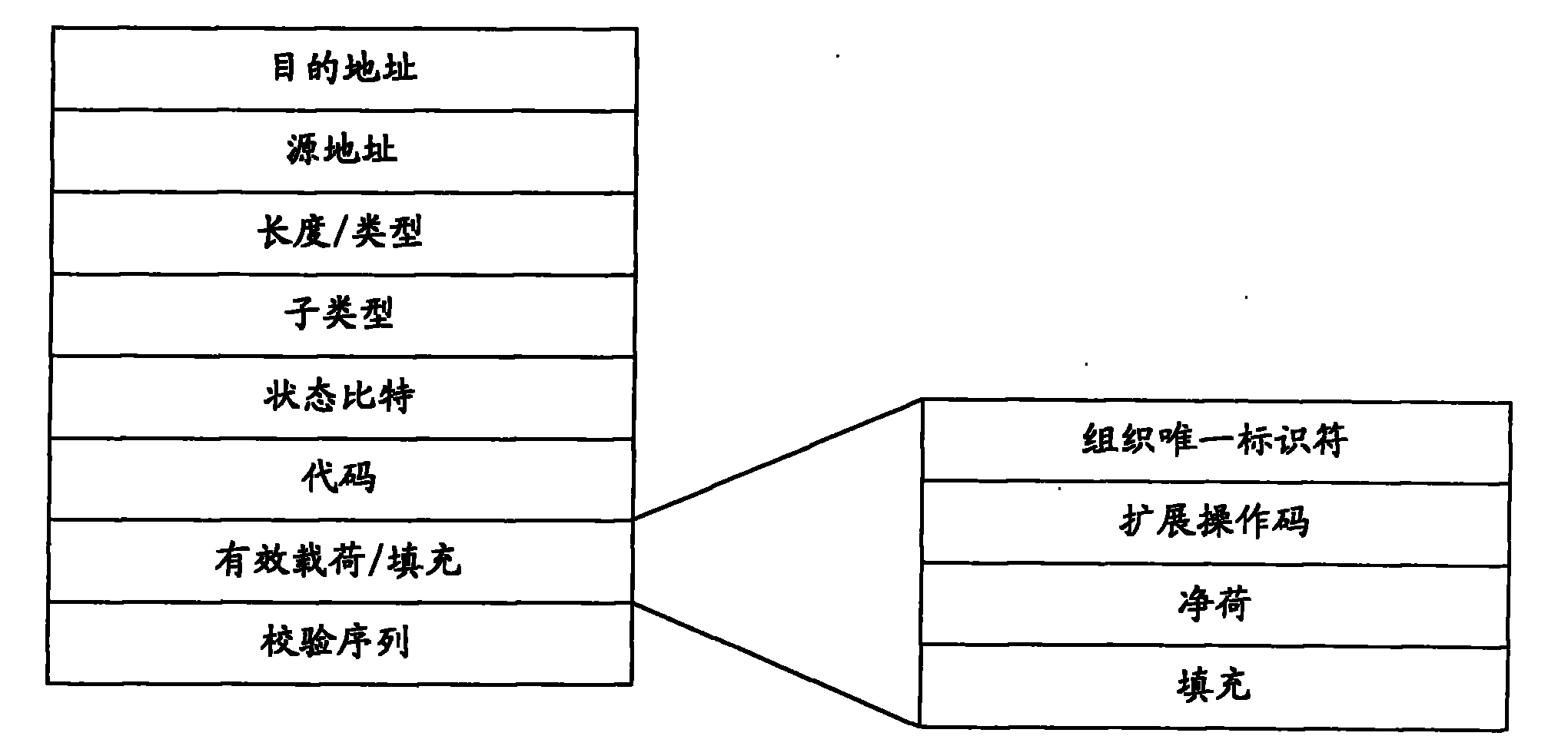
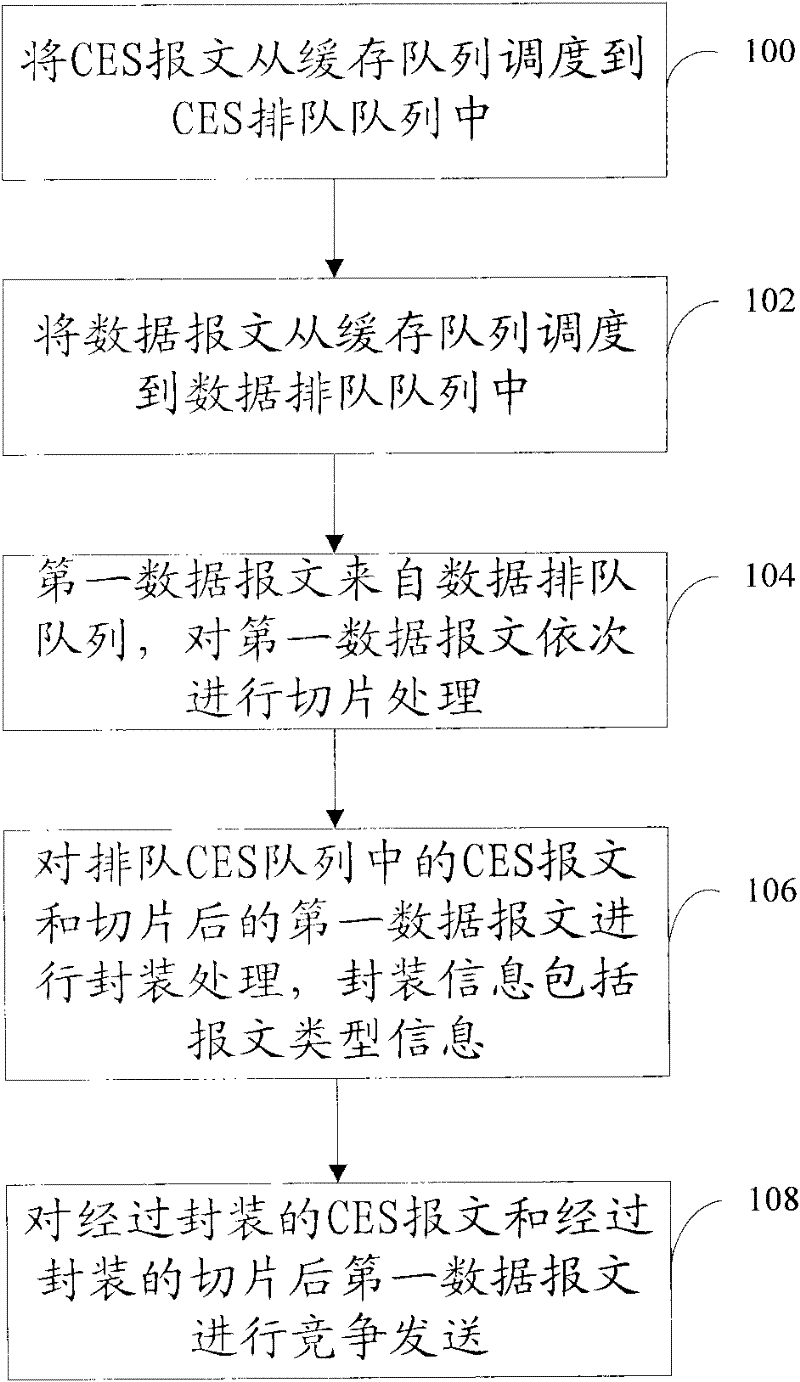
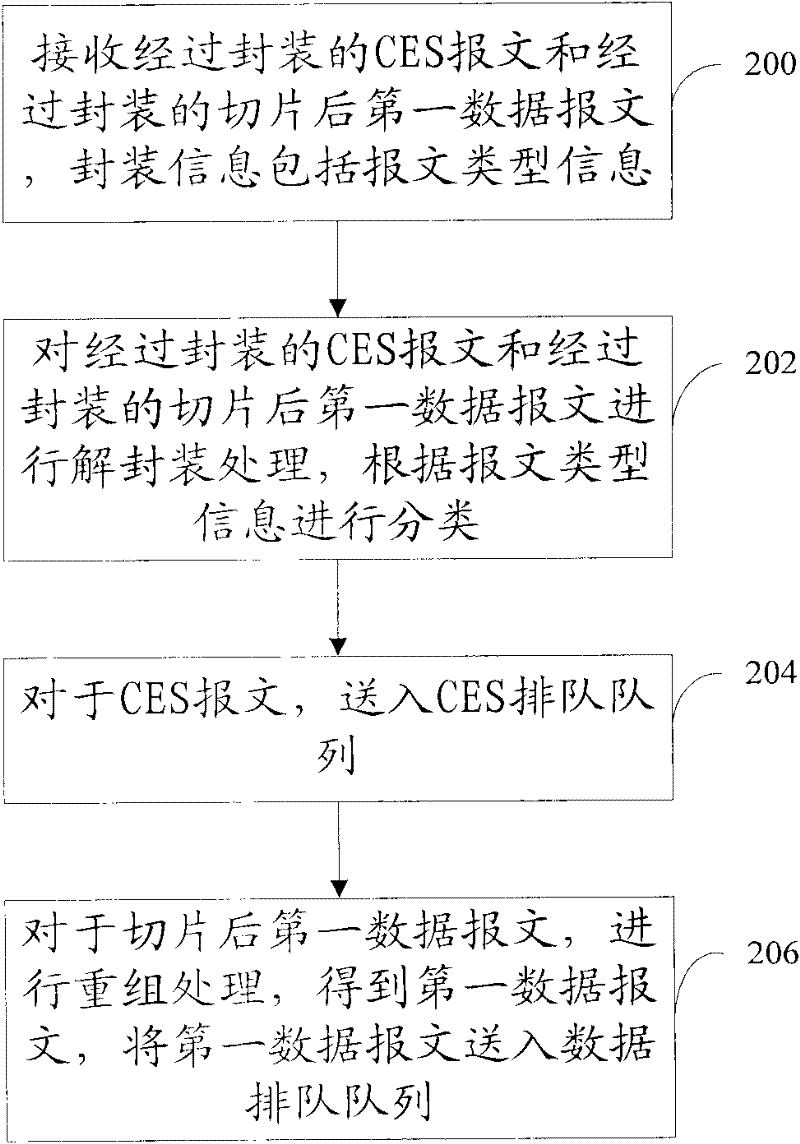
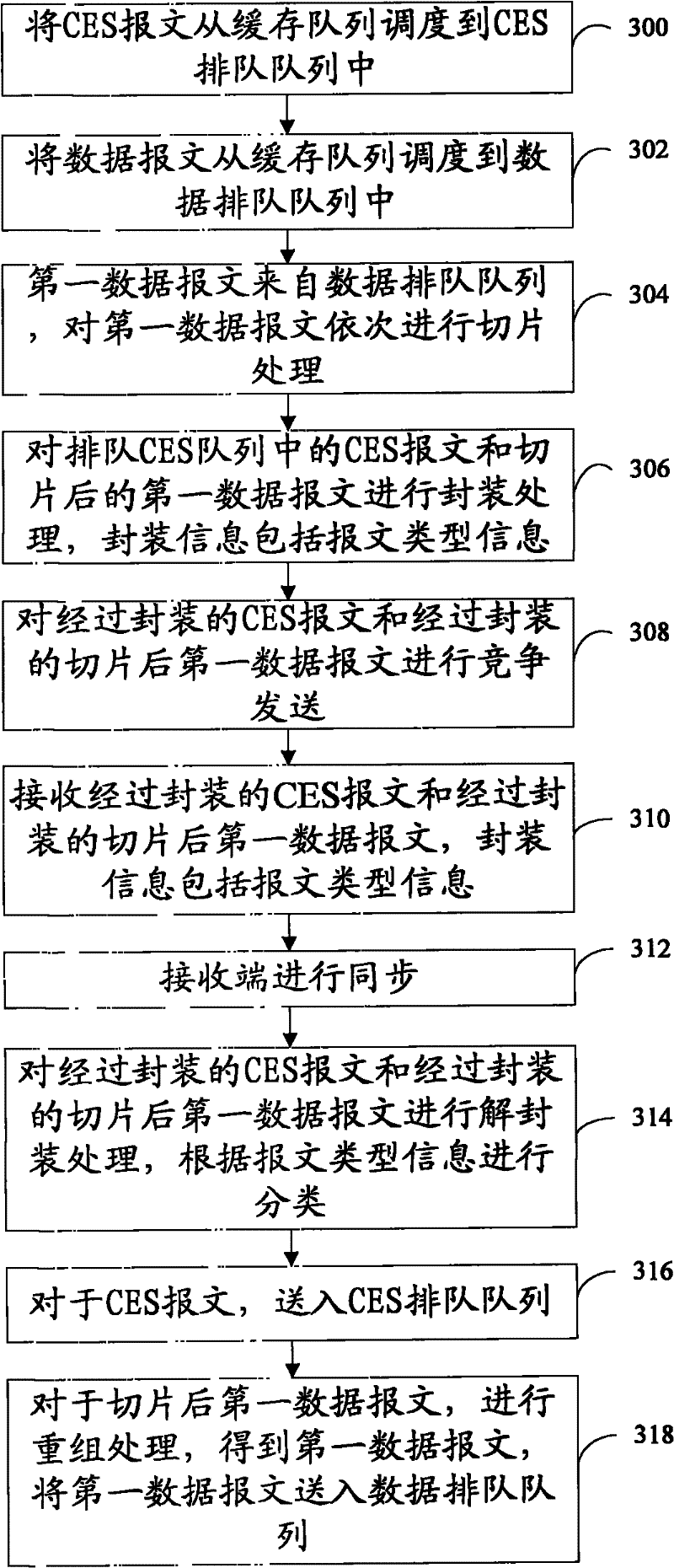
ActiveCN102238064AFix jitterSave on packaging overheadError preventionNetworks interconnectionMessage typeActive message
The embodiment of the invention discloses a data transmission method, which comprises the following steps of: scheduling a circuit emulation service (CES) message from a buffer queue to a CES queue; scheduling a data message from the buffer queue to a data queue; sequentially performing slicing processing on a first data message from the data queue; performing encapsulation processing on a CES message in the CES queue and the sliced first data message, wherein encapsulation information comprises message type information; and competitively transmitting the encapsulated CES message and the encapsulated sliced first data message. The embodiment of the invention also discloses the data transmission method, a data transmission device and a data transmission system. The first data message is sliced, and the CES message can be instantly transmitted only after the transmission of a slice is finished without waiting for the complete transmission of the whole data message, so the problem of jitter of CES can be well solved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Circuit emulation service method and telecommunication system for implementing the method
InactiveUS8023505B2Increase the number ofEasy to transportError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsExchange networkComputer science
It is disclosed a method for implementing a circuit emulation service through a packet-switched network, wherein the packet-switched network cooperates with a first interface and a second interface suitable to connect a first user and a second user, respectively, to the packet-switched network. The method comprises: a) at the first interface, receiving a TDM flow from the first user; b) converting the TDM flow in packets formatted according to the circuit emulation service, wherein at least one of the packets comprises a header in turn comprising a redundant field; c) compressing the header into a compressed header by processing the redundant field, and forming a compressed packet comprising the compressed header; d) transmitting the compressed packet through the packet-switched network to the second interface.
Owner:RPX CORP
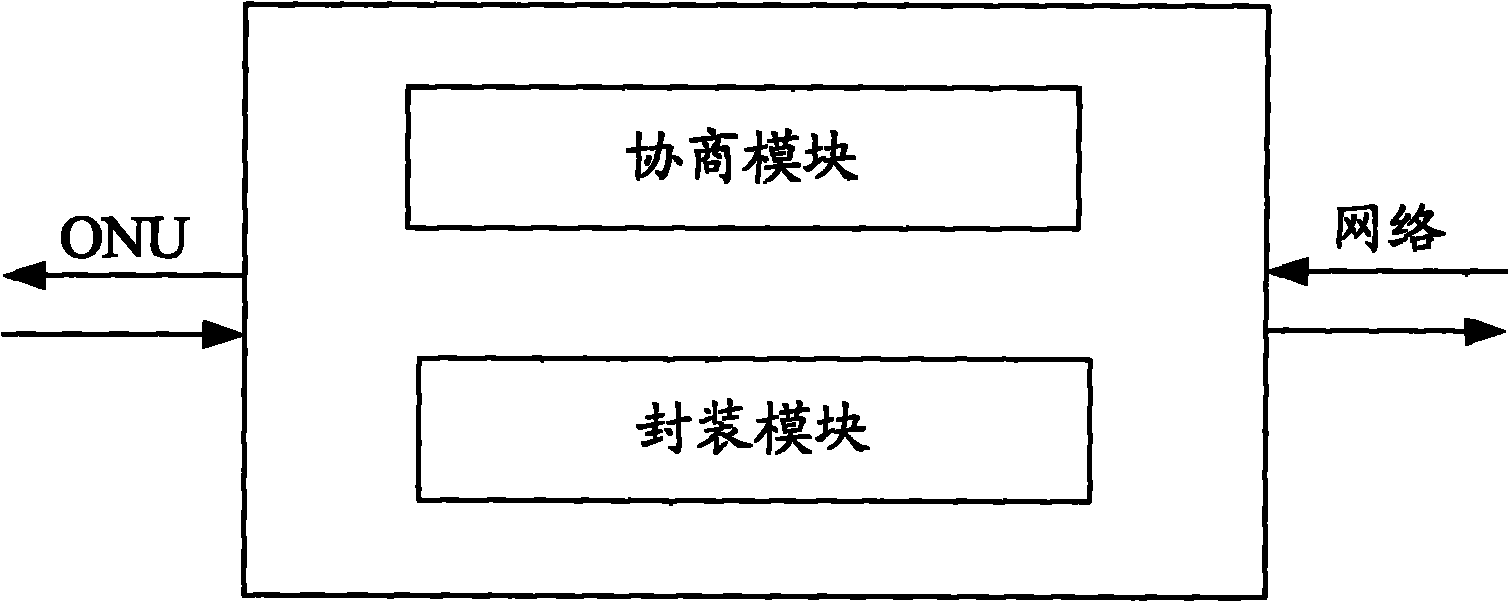
PTN (Packet Transport Network) equipment and CES (Circuit Emulation Service) equipment
The invention provides PTN (Packet Transport Network) equipment and CES (Circuit Emulation Service) equipment. The PTN equipment comprises a negotiation module and an encapsulating module, wherein the negotiation module is used for negotiating an inner pseudo-wire label and a tunnel label and sending the inner pseudo-wire label to the CES equipment, and the encapsulating module is used for encapsulating the tunnel label, a source MAC (Medium Access Control) address and a destination MAC address in an MPLS (Multi Protocol Label Switching) encapsulating format for an Ethernet message received from the CES equipment according to an outer VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) label in the Ethernet message, sending the encapsulated Ethernet message to the network, stripping the tunnel label, the source MAC address and the destination MAC address from the Ethernet message received from the network, encapsulating the outer VLAN label in the Ethernet message according to the tunnel label and sending the Ethernet message to the CES equipment. The invention can realize the end-to-end circuit simulation service.
Owner:ZTE CORP
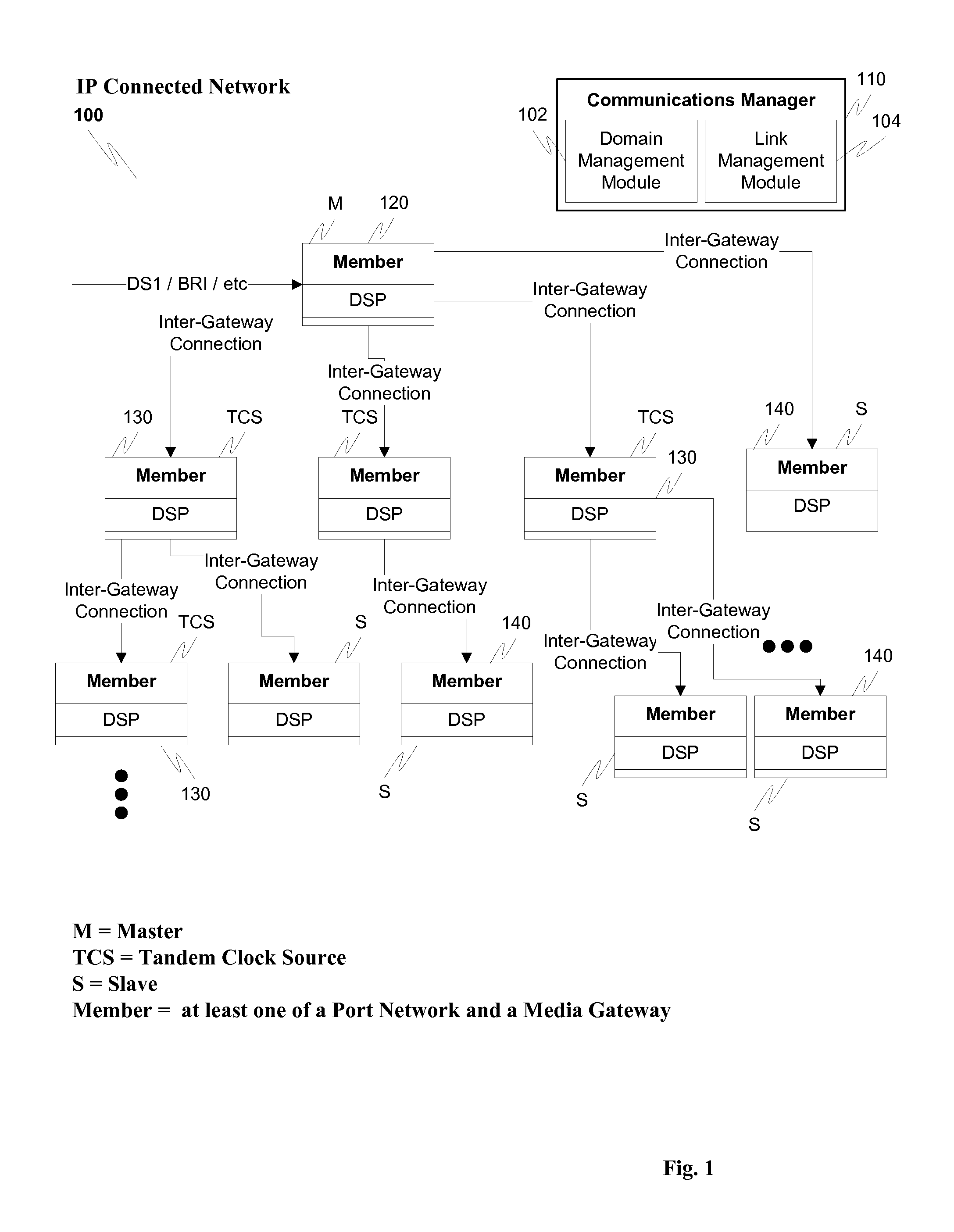
Network synchronization over IP networks
Owner:AVAYA INC
System and method for packet timing of circuit emulation services over networks
A system and method for managing information communication in a network includes a plurality of network nodes. A plurality of circuit emulation data flows are established between a first network node and at least a second network node. Different data transmission rates are assigned to each circuit emulation data flow such that the frequency of communicated packets is different at least for each circuit emulation data flow used for timing recovery to make the plurality of circuit emulation data flows substantially independent of each other. For example, different frame rates can be assigned to synchronous backhaul transmission links such that the frequency of the backhaul transmission rates is substantially independent of the circuit emulation flow rates.
Owner:ERICSSON WIFI
Method, device and system of data transmission
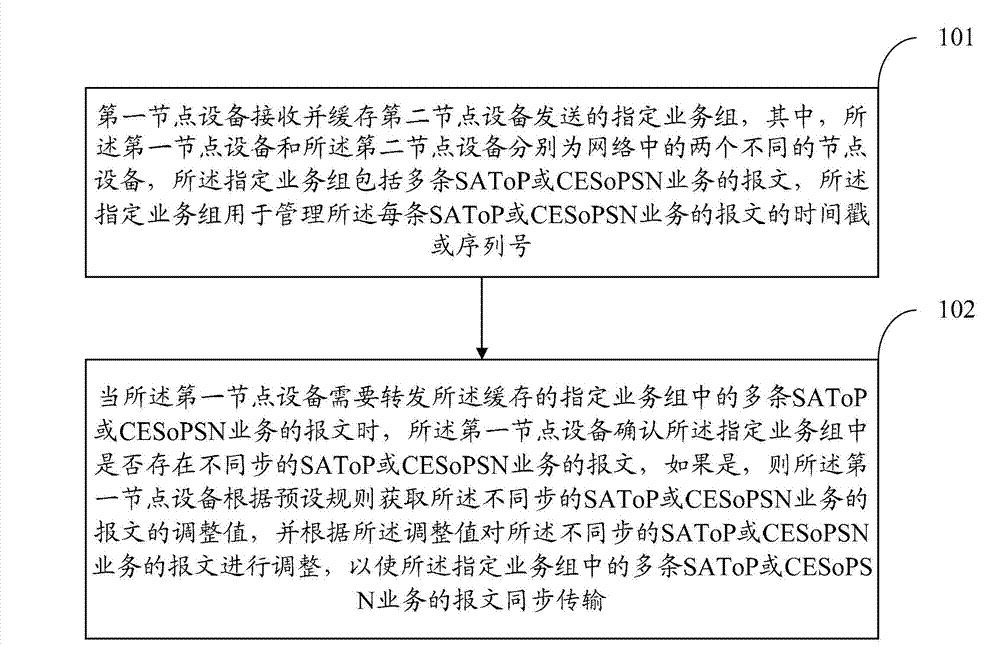
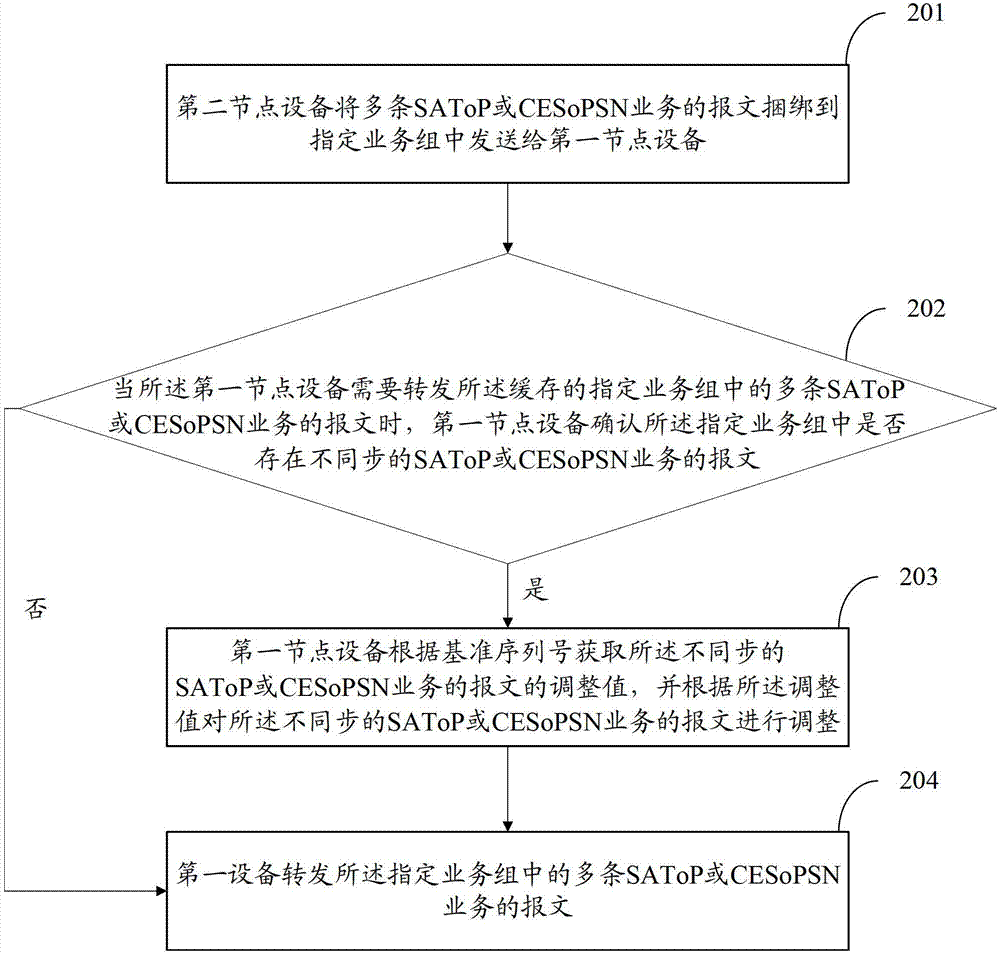
ActiveCN103117846ASolve the delay problemTime-division multiplexHybrid transportData transmissionComputer science
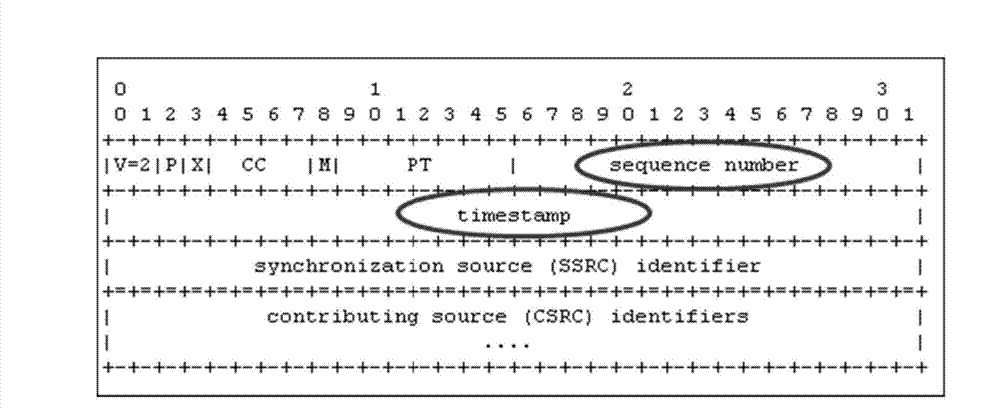
The invention discloses a method, a device and a system of data transmission, and belongs to the technical field of communication. The method comprises that a first node device receives and caches a specified business group sent by a second node device, when the first node device needs to transmit messages of multiple structure-agnostic transport over packet (SAToP) or circuit emulation service over packet switched network (CESoPSN) businesses in the cached specified business group, the first node device confirms that whether messages of the out-of-step SAToP or CESoPSN businesses exist in the specified business group, if yes, the first node device obtains adjustment values of the messages of the out-of-step SAToP or CESoPSN businesses according to a preset rule, and adjusts the out-of-step SAToP or CESoPSN businesses according to the adjustment value, so that the messages of the multiple SAToP or CESoPSN businesses in the specified business group can be enabled to be transmitted synchronously.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
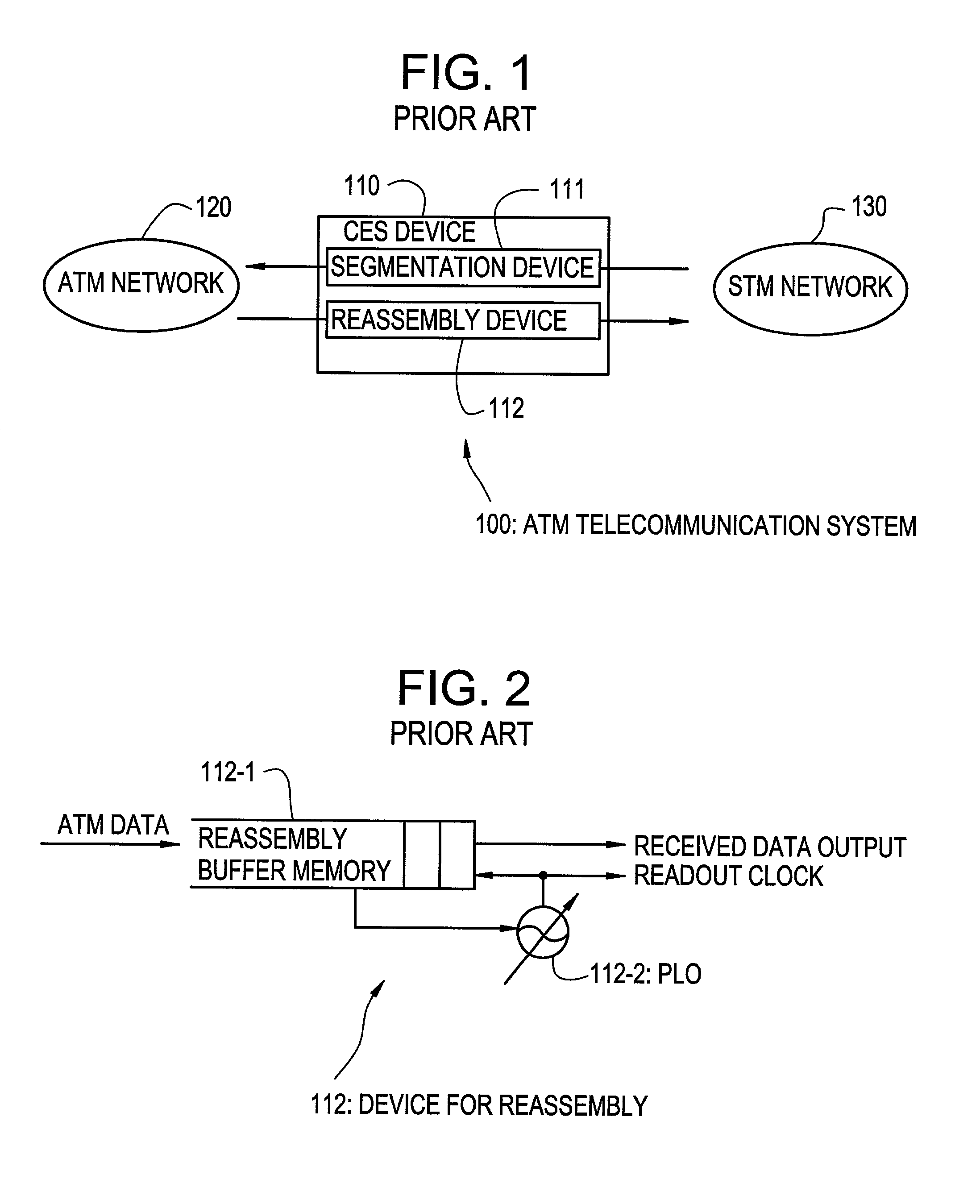
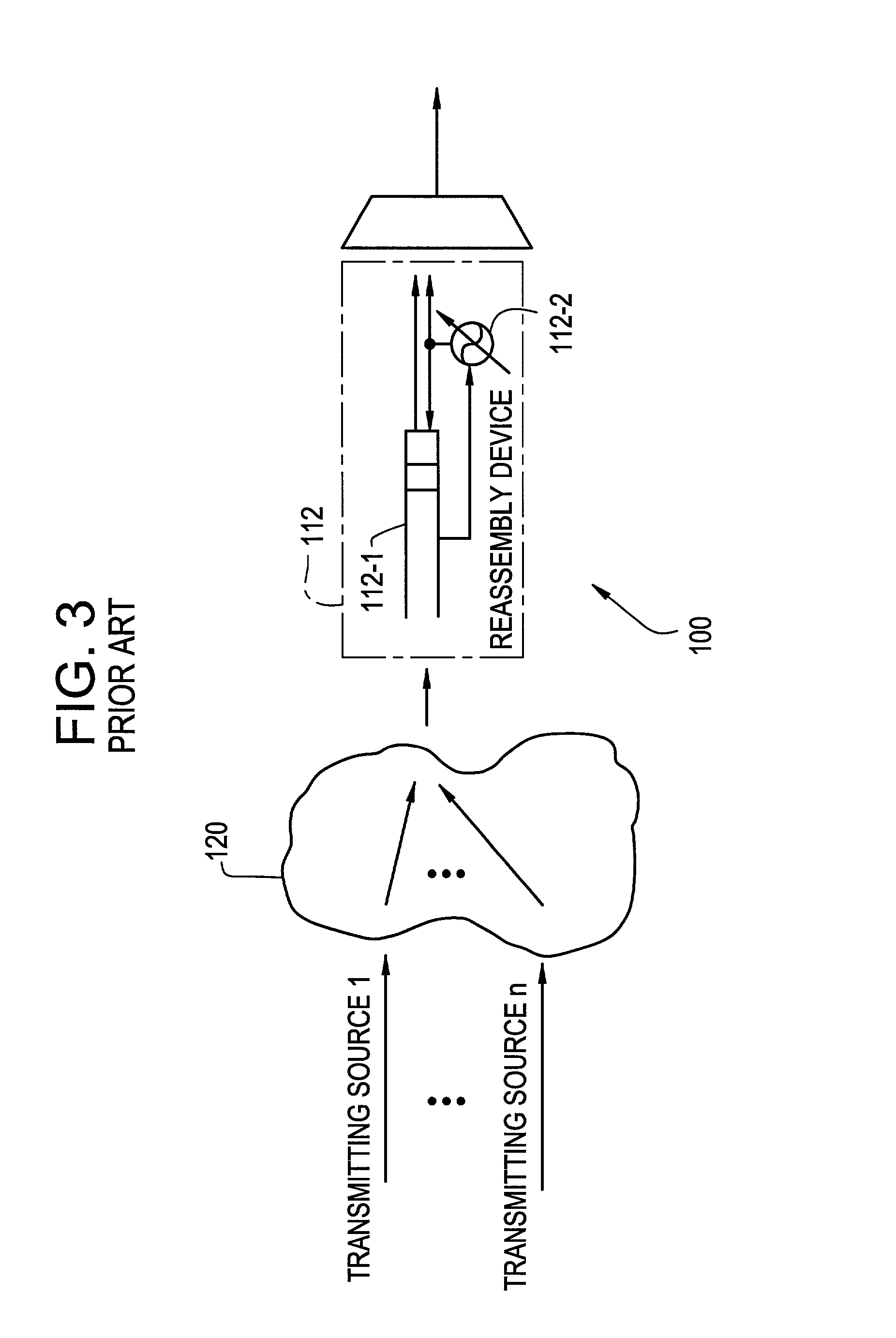
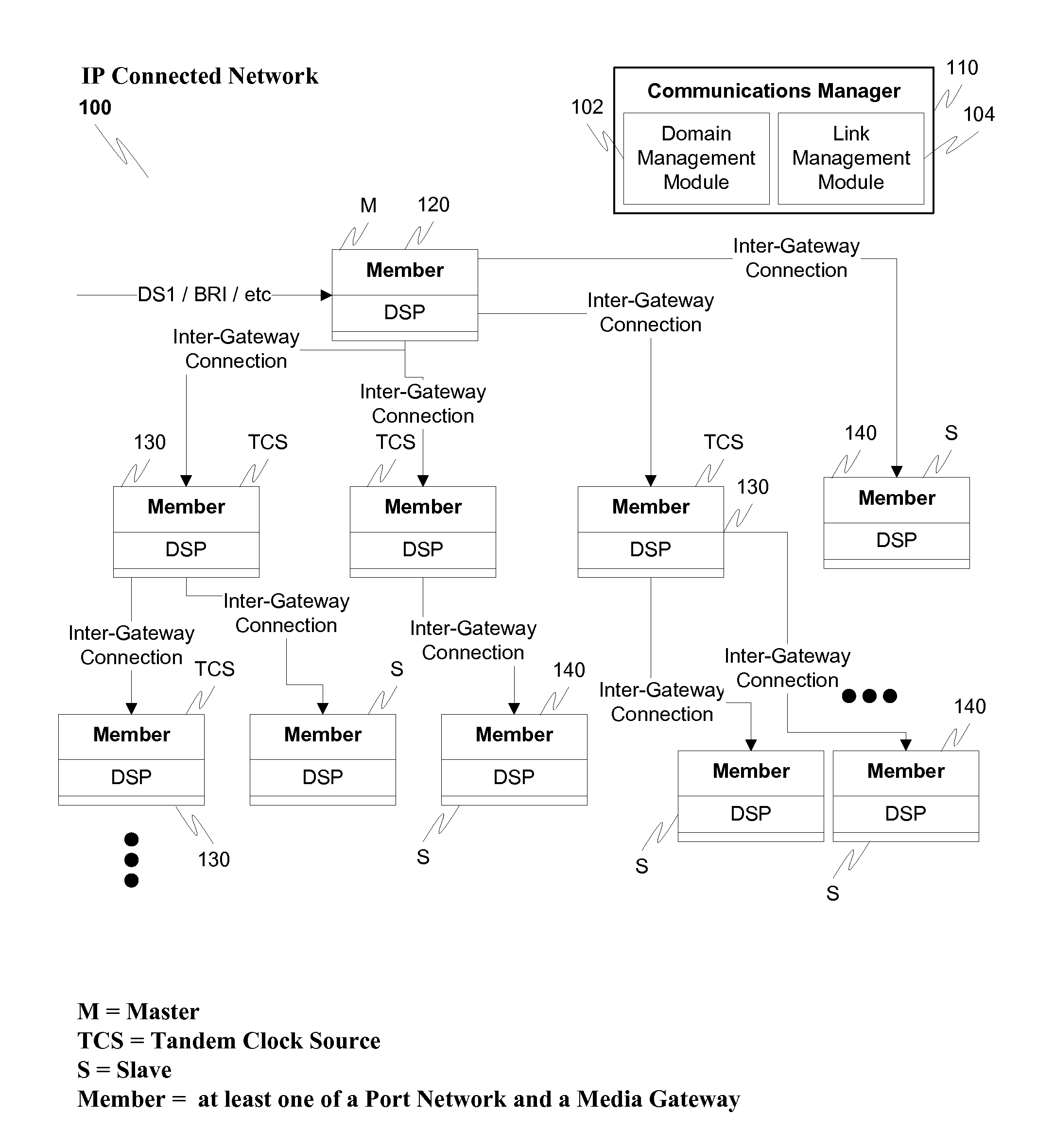
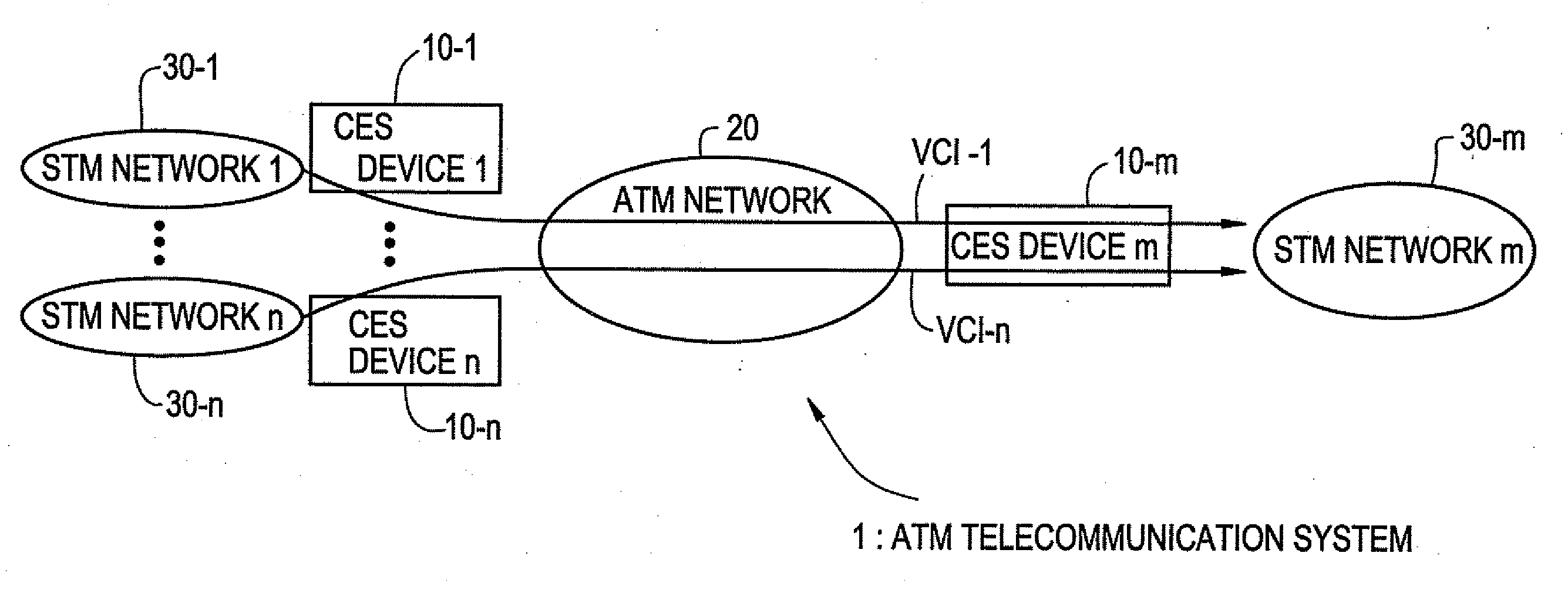
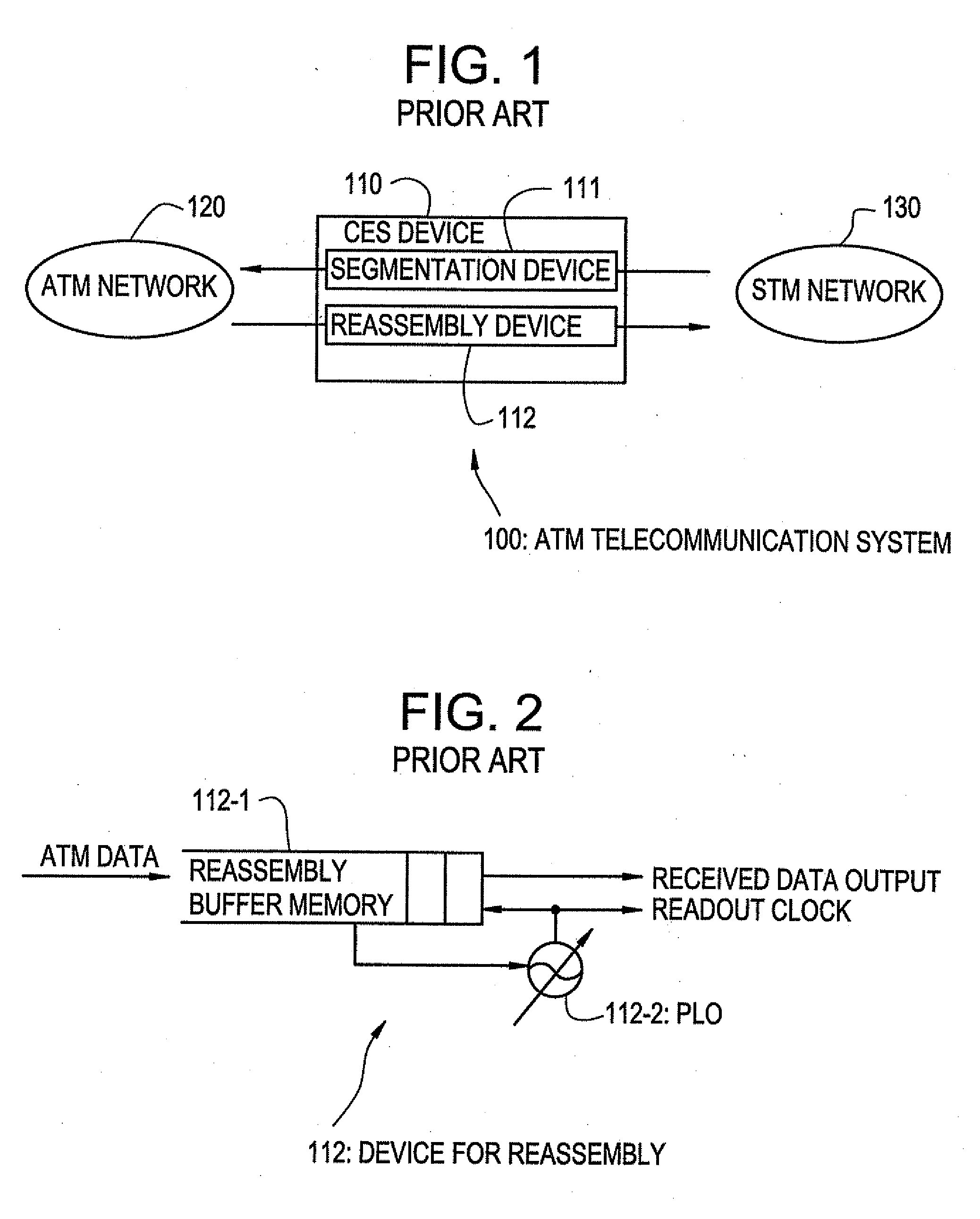
Device for reassembling cell data device for circuit emulation service and method of ATM synchronization control
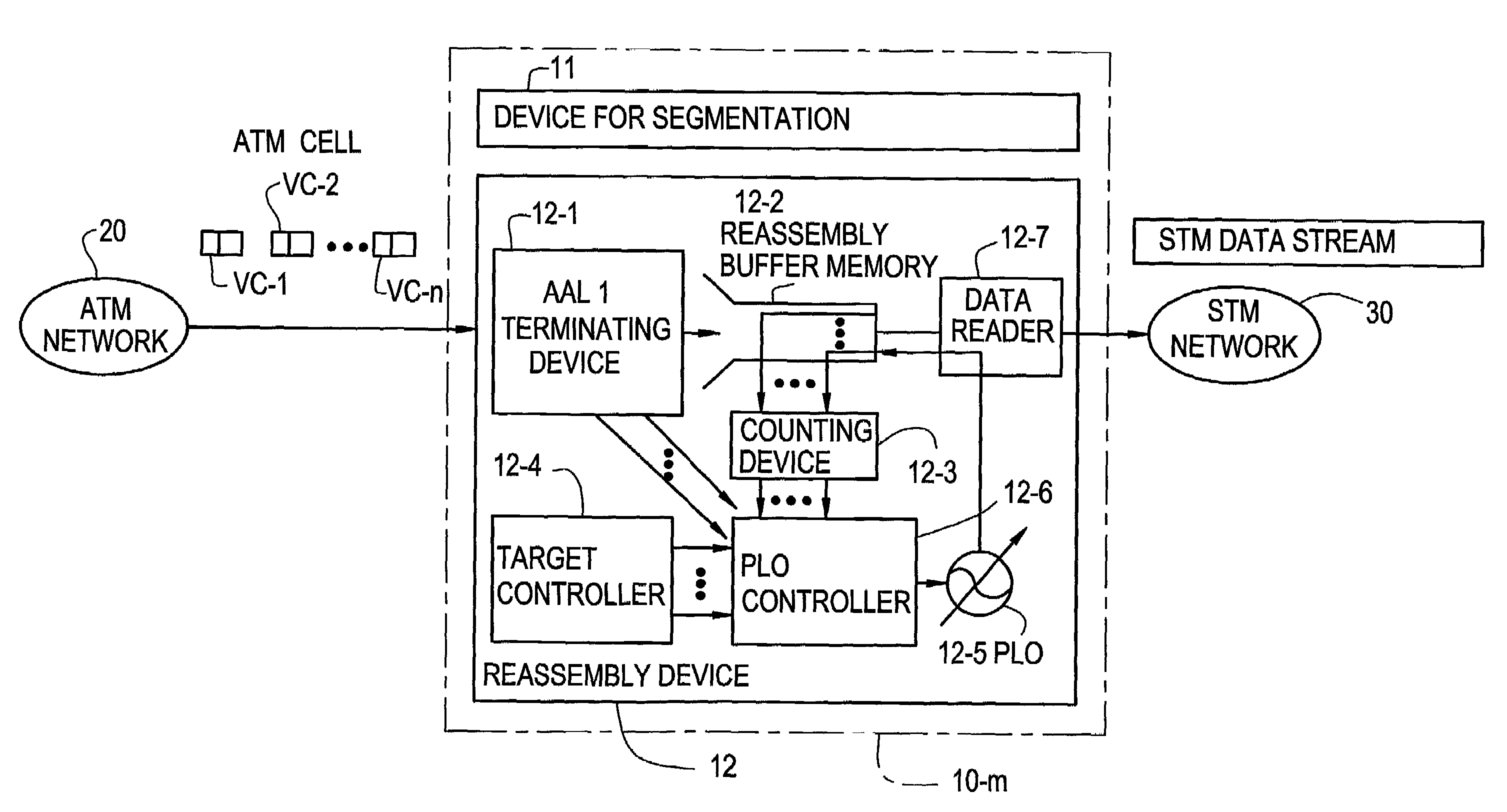
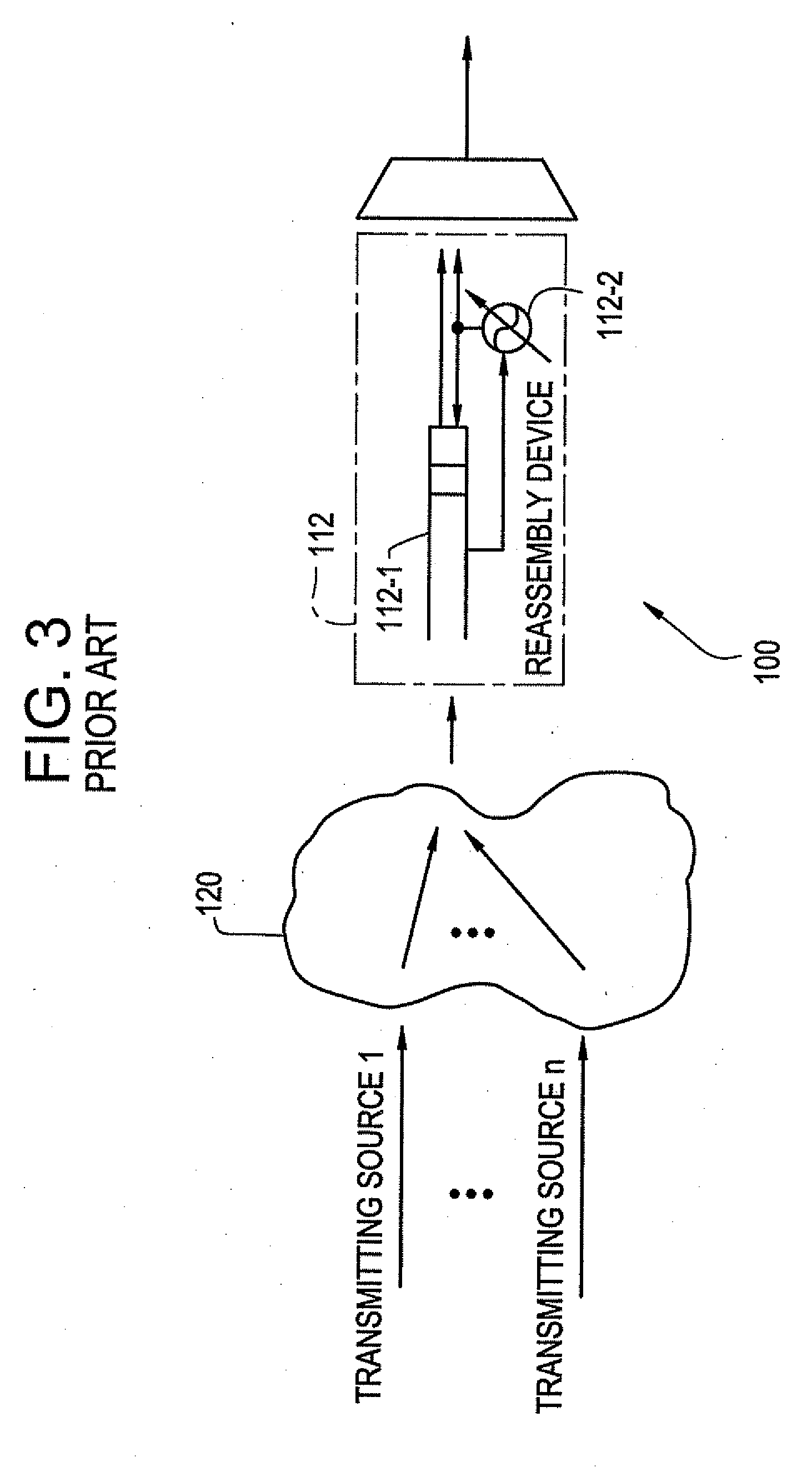
InactiveUS7103052B2Precise deliveryError preventionTransmission systemsData streamCommunications system
A device and method are disclosed for correctly restoring a read clock when there are a plurality of STM data stream transmission sources. In a CES device of an ATM communication system, ATM cells from respective connections, which are to be delivered to the same outgoing line, are accumulated in a reassembly buffer memory and a PLO control unit aggregates the amount of ATM cells accumulated in the reassembly buffer memory for each connection. Subsequently, the PLO control unit calculates the frequency of a read clock based on the amount of accumulated ATM cells for each connection. A PLO restores the read clock which is applied to read data from the reassembly buffer memory for delivery to an STM network.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
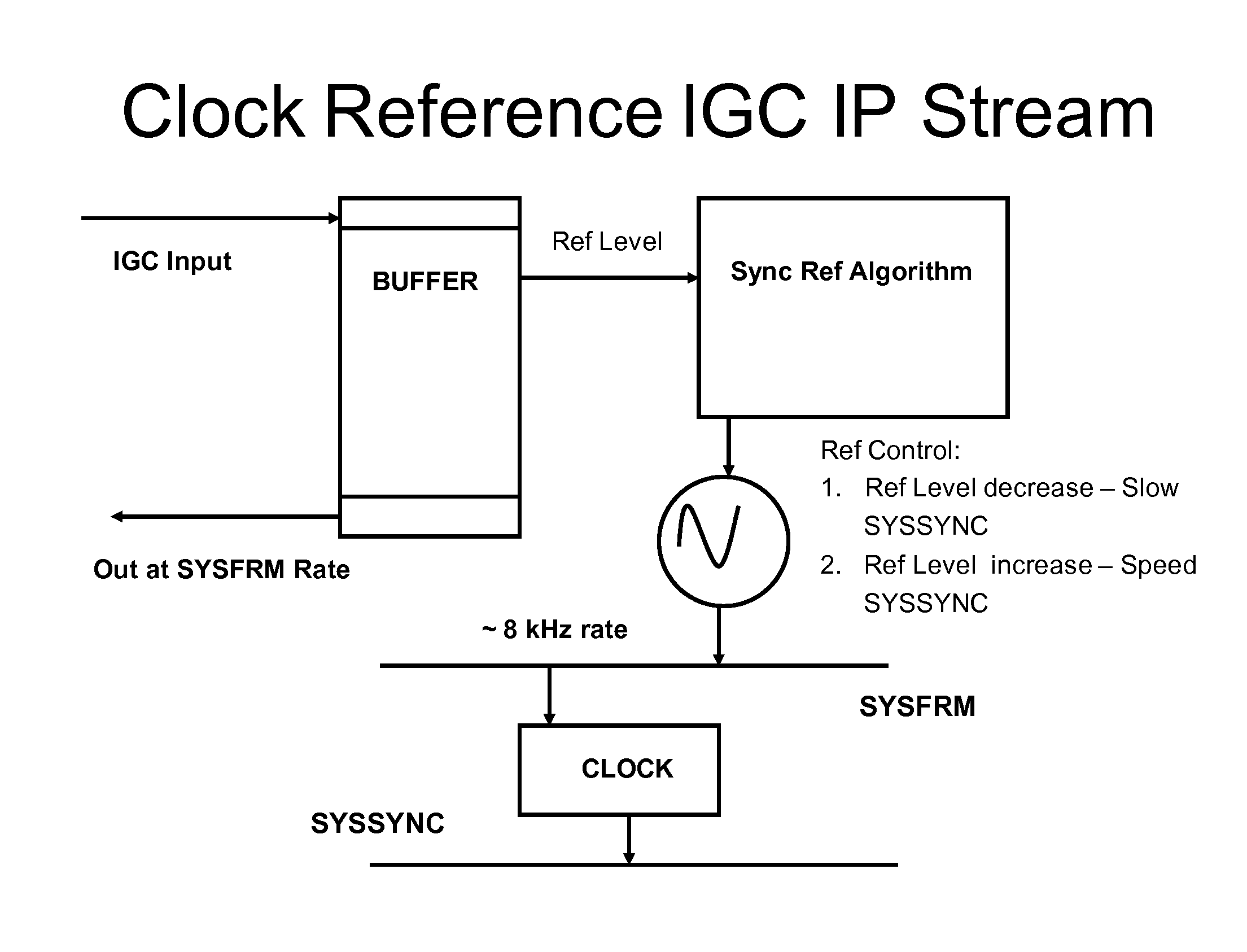
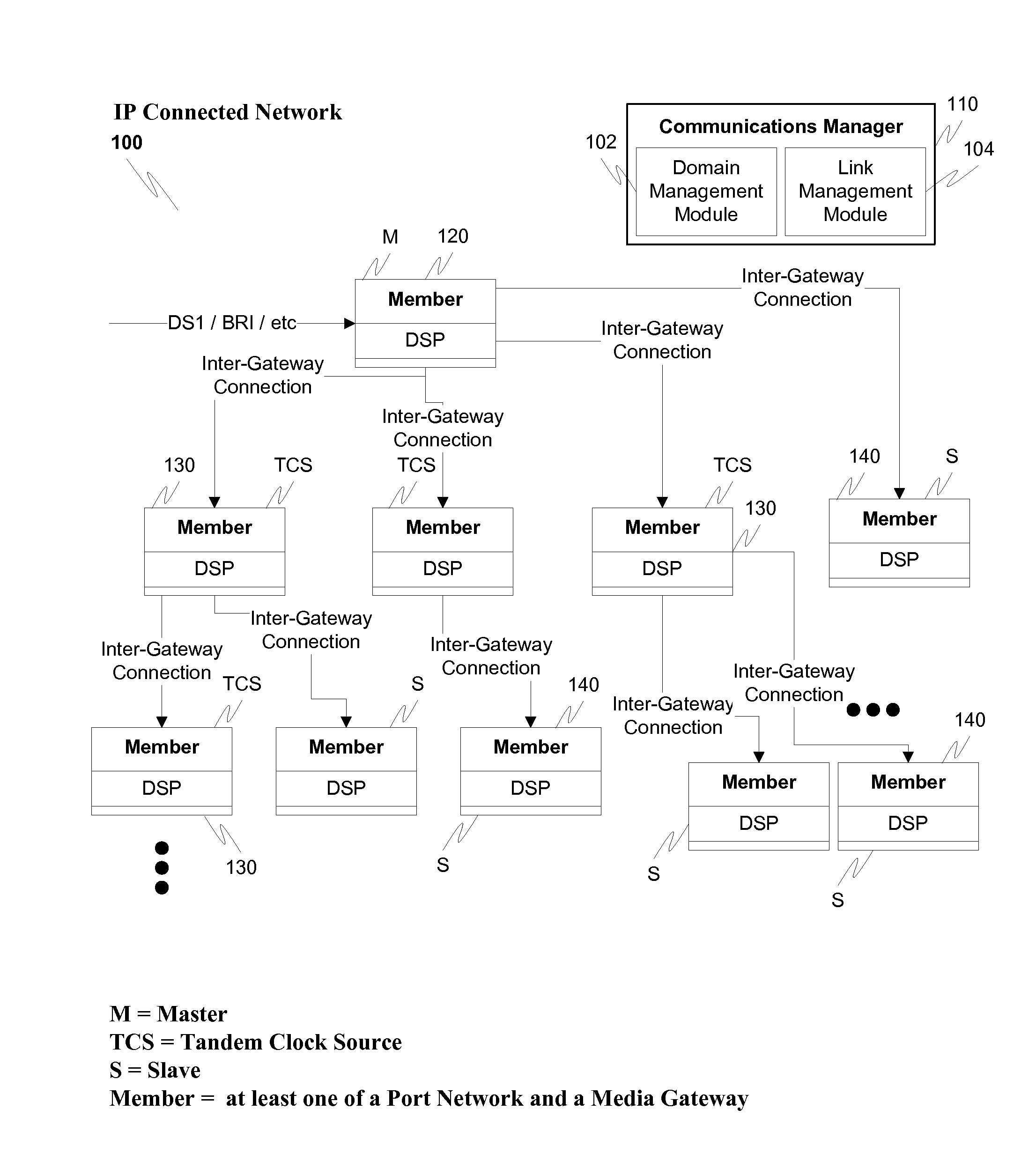
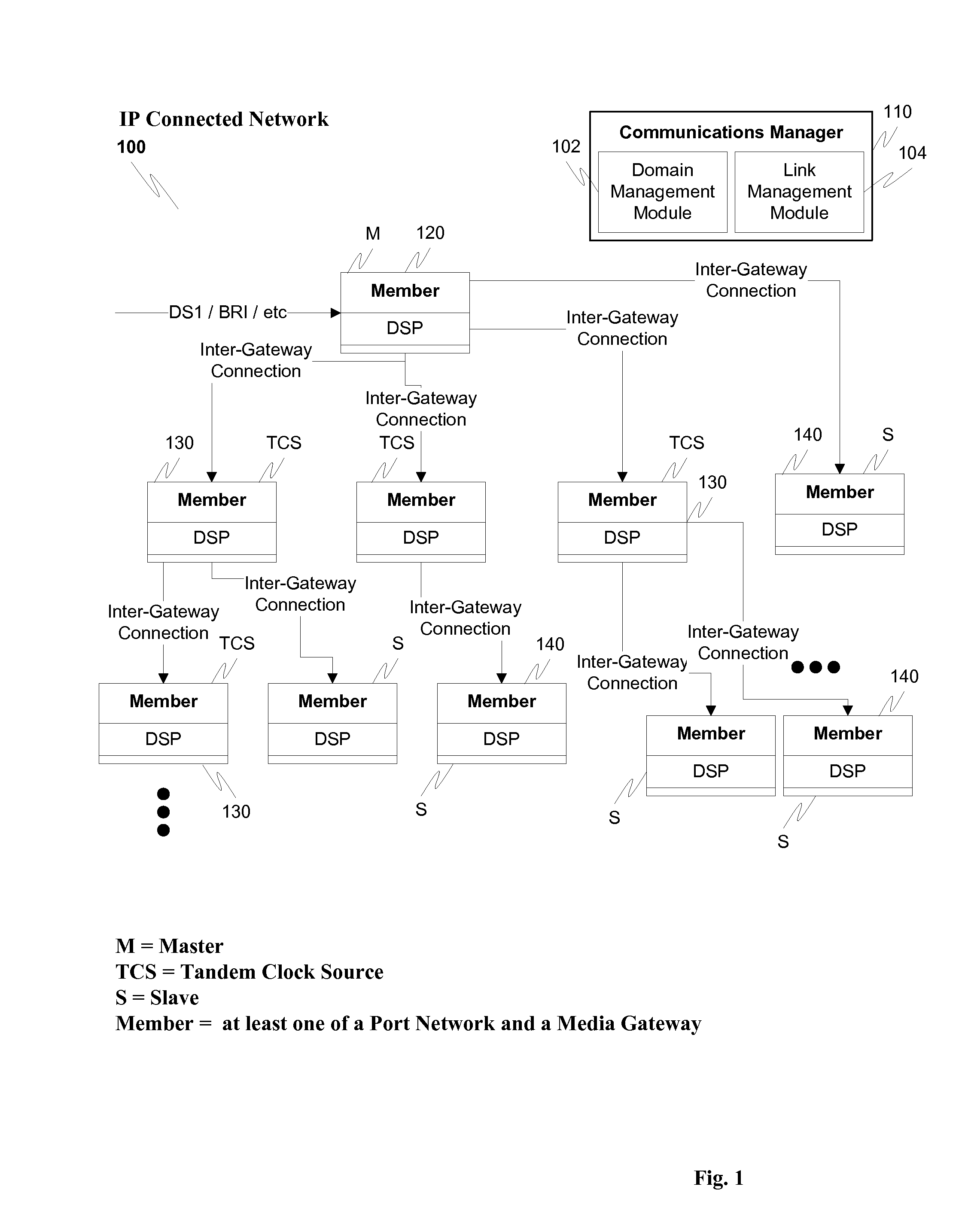
Network synchronization over IP networks
ActiveUS20100254499A1Digital computer detailsTime-division multiplexSpeech soundDigital signal processor
Network timing is derived from the PSTN and distributed through the network to gateways capable of deriving timing from the incoming UDP stream. The derived timing has the correct frequency for voice telephony without using external timing sources or extraneous hardware components. For example, a digital signal processor (DSP) can derive the timing from a timed TDM bus and distribute messages, such as IP messages, to other gateways or port networks. The other gateways and port networks use the incoming stream to extract the timing which is then used to time their TDM bus. The port networks and gateways can also distribute other streams to other gateways in a fan-out type of arrangement. This internally generated timing can be used, for example, for Circuit Emulated Services (CES).
Owner:AVAYA INC
Multiplex section protection (MSP) system and protection method based on multicast way
ActiveCN104683078AConvenient business switchingImprove reliabilityError preventionData switching networksService configurationProtection system
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD +1
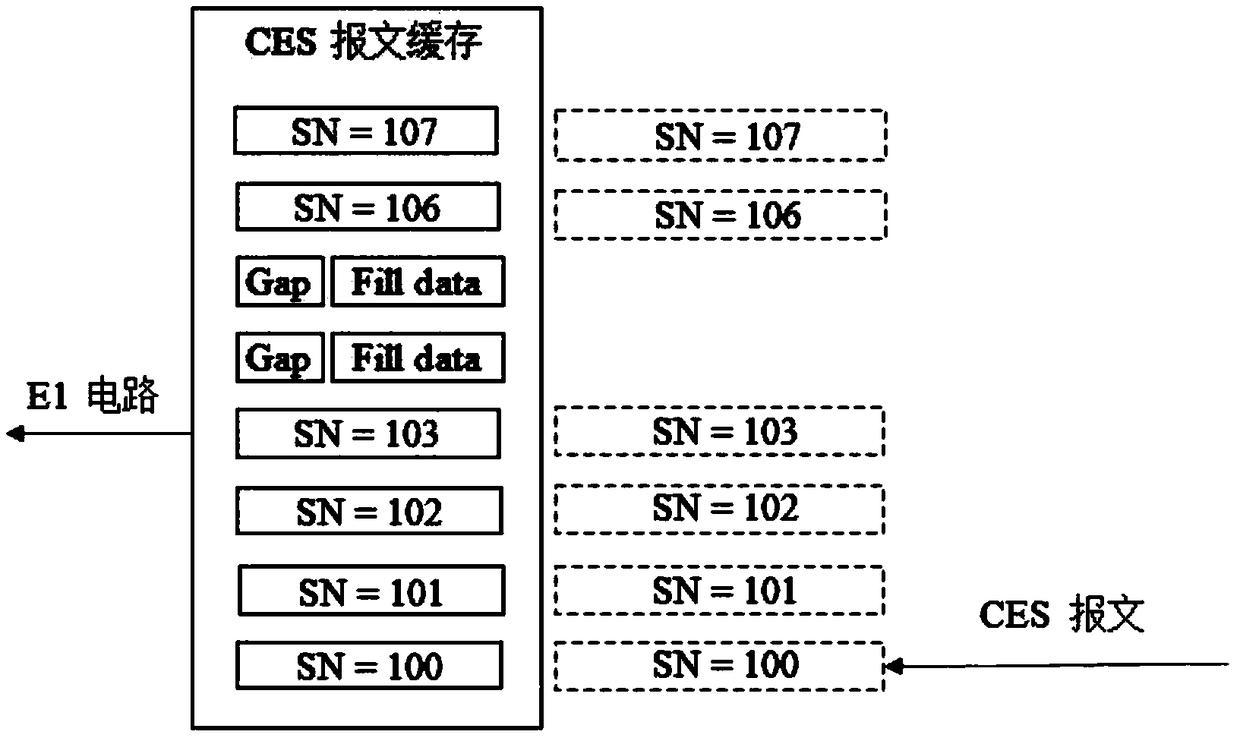
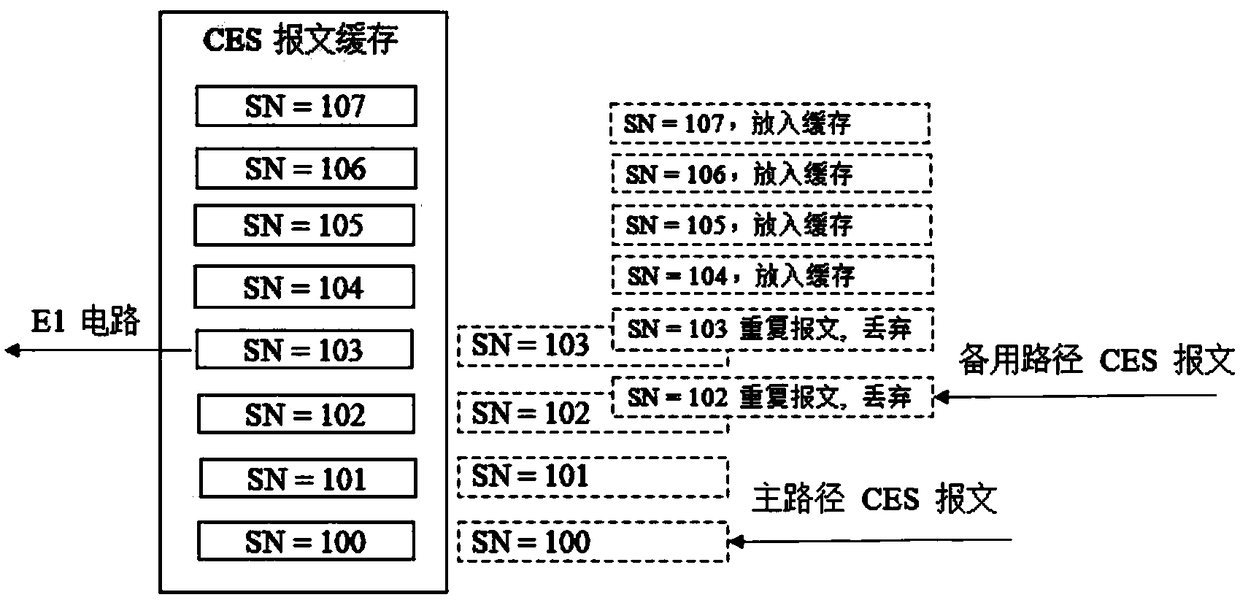
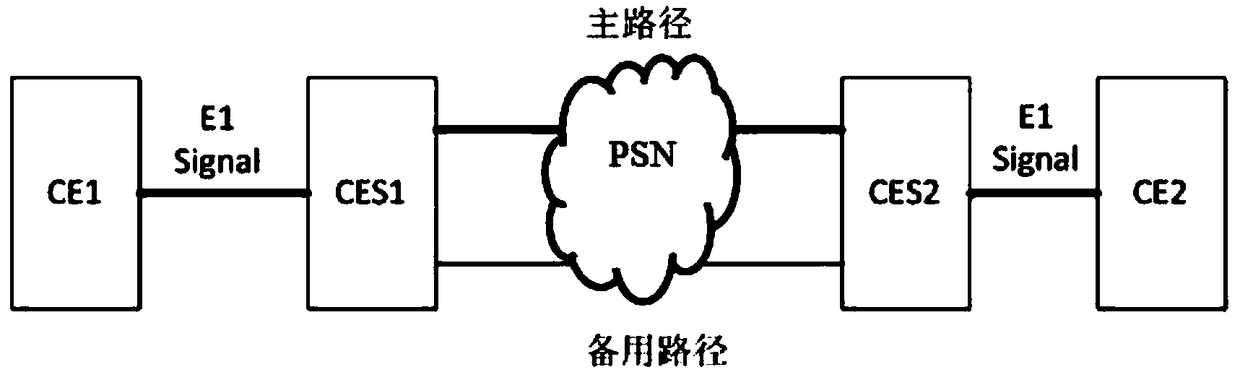
Lossless transmission method of CES (Circuit Emulation Service)
InactiveCN108965027ADoes not affect receptionLossless transfer implementationData switching networksComputer hardwareUser equipment
The invention provides a lossless transmission method of a CES (Circuit Emulation Service). The lossless transmission method mainly comprises the following steps: 1) enabling a CES packet to be simultaneously sent to main and standby paths for transmission; 2) enabling a receiving side to simultaneously receive the CES packet from the main and standby paths; 3) enabling a packet buffer of the receiving side to process the received CES packet, wherein a processing method includes an SN (Sequence Number) detection mechanism: receiving a CES packet having an expected SN from any path, putting theCES packet into the packet buffer, and then if a CES packet having a same SN is received from another path again, abandoning the CES packet received later; and 4) sending the CES packet in the packetbuffer to a user device, thereby implementing lossless transmission of the CES packet.
Owner:杭州依赛通信有限公司
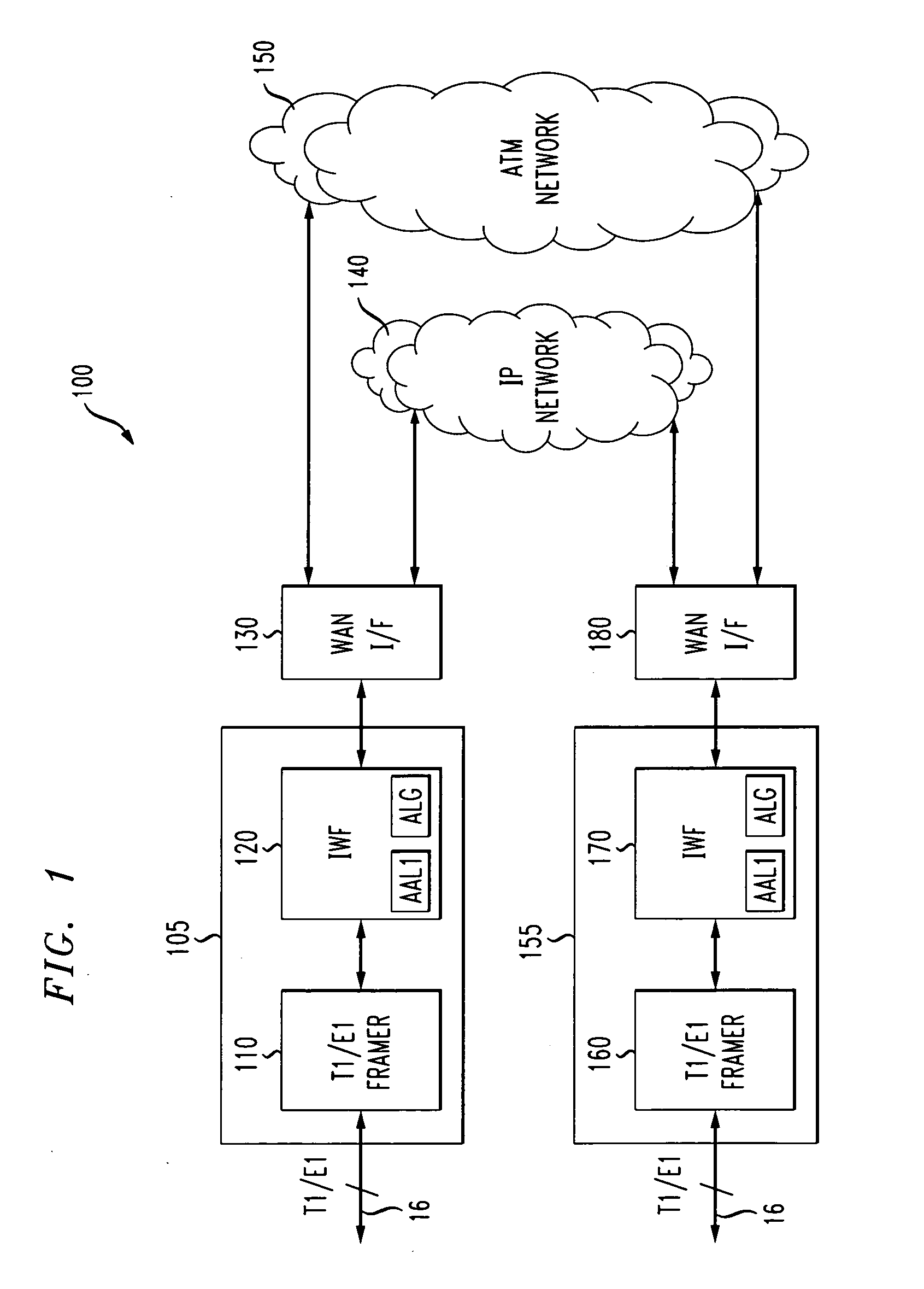
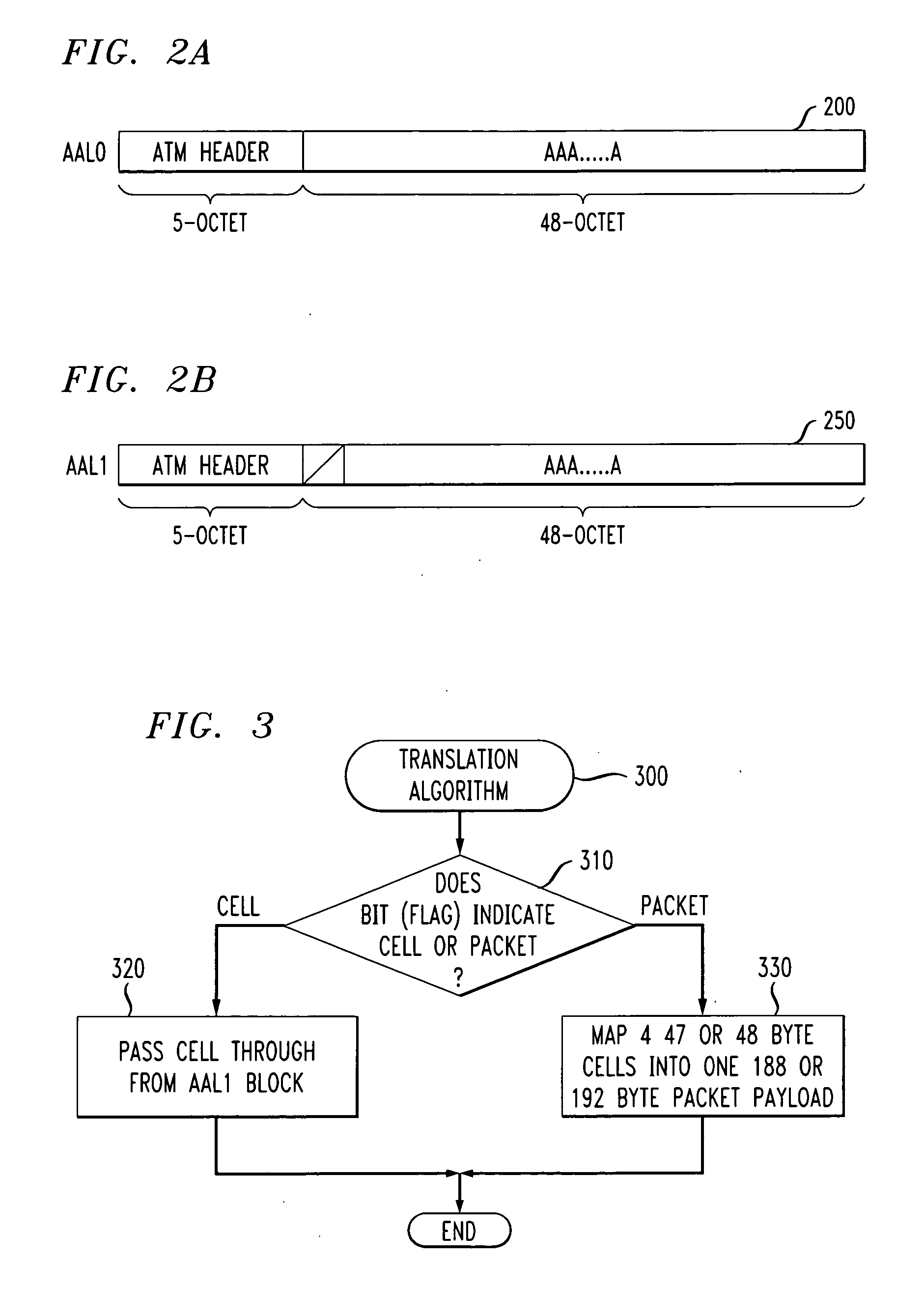
Method and apparatus for circuit emulation services over cell and packet networks
ActiveUS20080002738A1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationComputer scienceNetwork method
Methods and apparatus are provided for circuit emulation services over cell and packet networks. A constant bit rate traffic stream is mapped to one of a cell and packet structure. The constant bit rate traffic stream is mapped to one or more cells and the one or more cells are selectively translated to one or more packets if a packet stream is selected. In addition, one of a received cell and packet stream are mapped to a constant bit rate traffic stream. The packet stream is selectively translated to one or more cells and the one or more cells are translated to the constant bit rate traffic stream. A clock can optionally be recovered from the received cell or packet stream.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Device for reassembling cell data device for circuit emulation service and method of ATM synchronization control
InactiveUS20070002872A1Precise deliveryError preventionTransmission systemsData streamCommunications system
A device and method are disclosed for correctly restoring a read clock when there are a plurality of STM data stream transmission sources. In a CES device of an ATM communication system, ATM cells from respective connections, which are to be delivered to the same outgoing line, are accumulated in a reassembly buffer memory and a PLO control unit aggregates the amount of ATM cells accumulated in the reassembly buffer memory for each connection. Subsequently, the PLO control unit calculates the frequency of a read clock based on the amount of accumulated ATM cells for each connection. A PLO restores the read clock which is applied to read data from the reassembly buffer memory for delivery to an STM network.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
System and method for realizing network synchronization by packet network
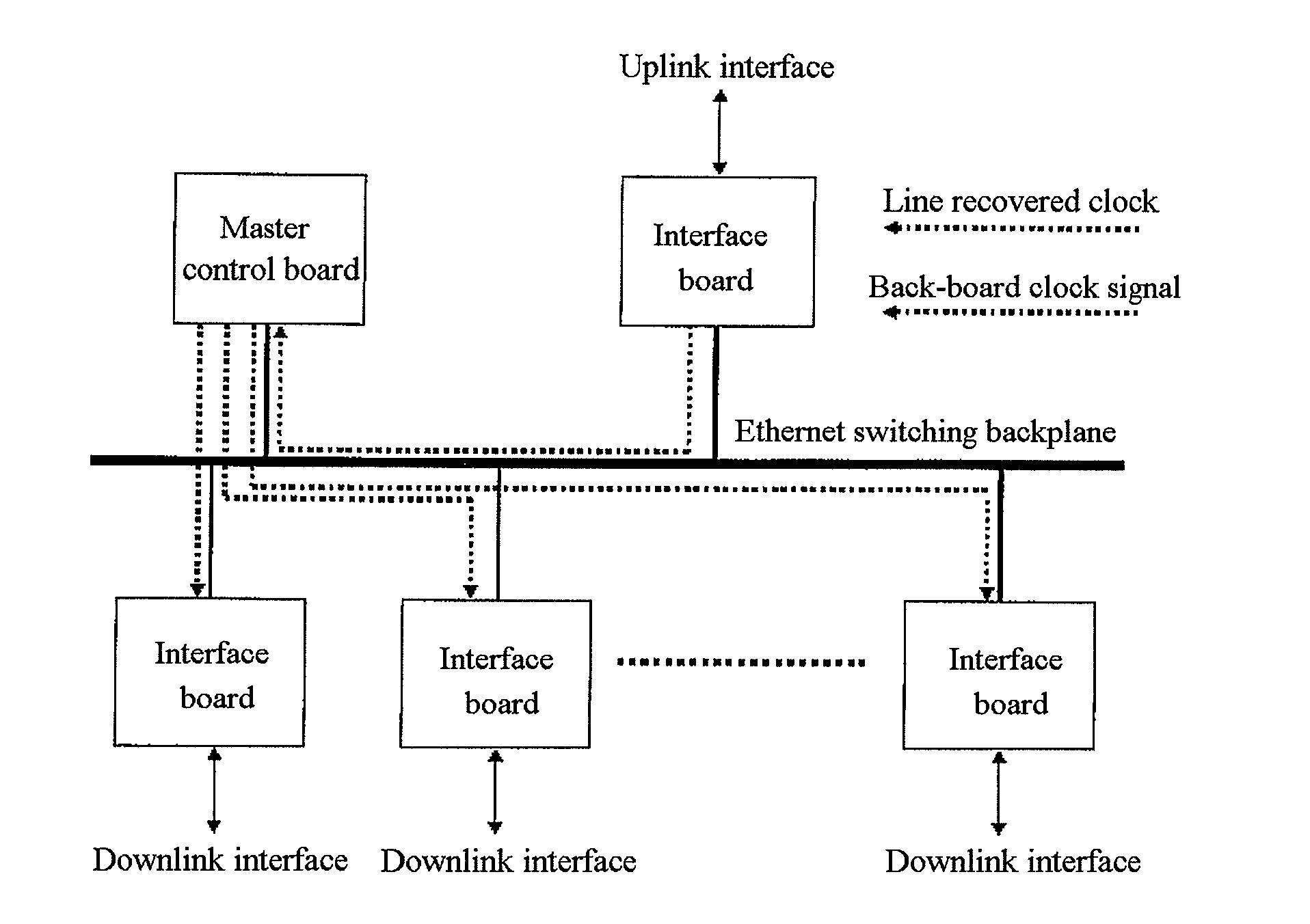
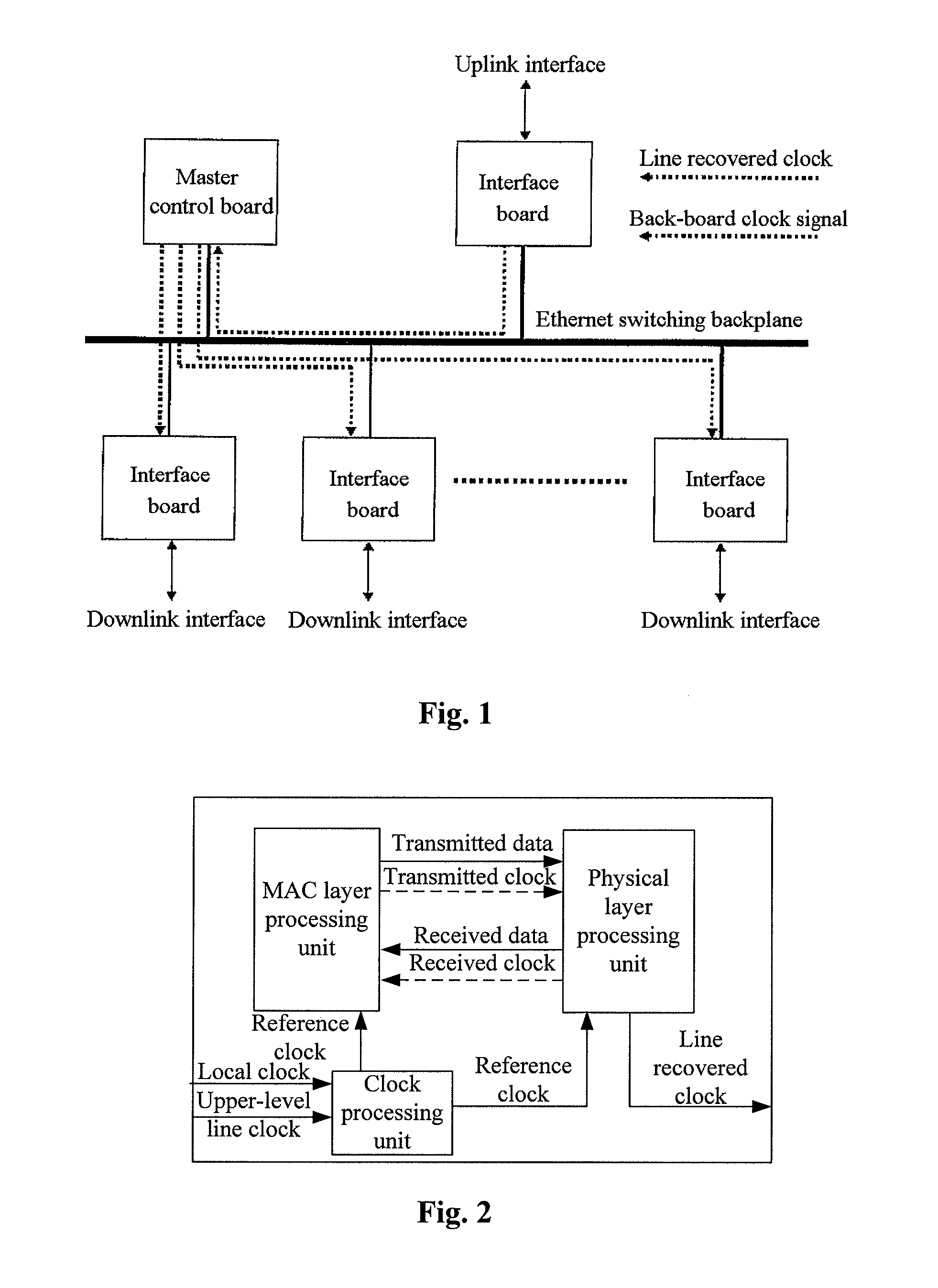
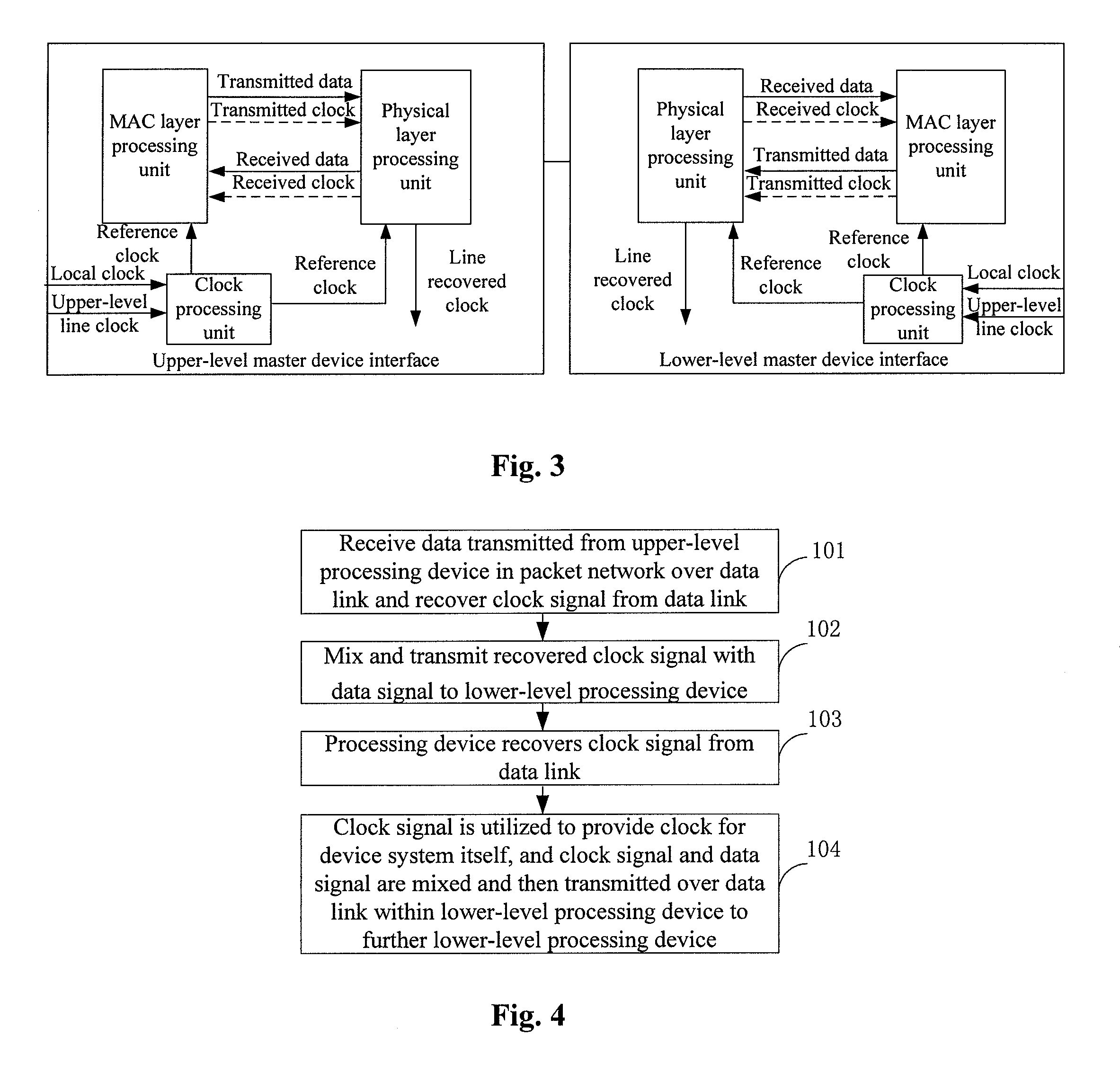
InactiveUS20080170594A1High bandwidthUniform timingTime-division multiplexHigh bandwidthSynchronous network
A system and method for realizing network synchronization by packet network mainly includes: restoring the clock signal from the superior processing equipment data link of the packet network, and sending it to the subordinate processing equipment; realizing the synchronization of said processing equipment based on said clock signal. It can realize the uniform timing of the whole network and change the IP network without the timing into the synchronous network, which is similarly with the circuit network, with high bandwidth. It can not only provide a circuit simulation service, but also a multi-service with high bandwidth.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Network synchronization over IP networks
Network timing is derived from the PSTN and distributed through the network to gateways capable of deriving timing from the incoming UDP stream. The derived timing has the correct frequency for voice telephony without using external timing sources or extraneous hardware components. For example, a digital signal processor (DSP) can derive the timing from a timed TDM bus and distribute messages, such as IP messages, to other gateways or port networks. The other gateways and port networks use the incoming stream to extract the timing which is then used to time their TDM bus. The port networks and gateways can also distribute other streams to other gateways in a fan-out type of arrangement. This internally generated timing can be used, for example, for Circuit Emulated Services (CES).
Owner:AVAYA INC
Interworking circuit emulation service over packet and IP/MPLS packet processing
InactiveUS7974308B2InexpensivelyEfficient implementationTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationEthernetVirtual circuit
A system and method are provided for implementing CESOP inexpensively yet effectively implemented across an MPLS or an IP network. A Zarlink chip provides CESOP functionality, providing a TDM pseudowire by converting TDM streams into Ethernet packets. These Ethernet packets can be processed by a Marvell chip, which has the ability to perform QoS functions on the packets. The Marvell chip converts the Ethernet packets into MPLS or IP packets for transmission over a packet network. Use of a single virtual circuit label, invisible to the packet network for routing purposes, within the Ethernet packet allows Marvell chips at each end of the emulated circuit to tie traffic to a particular customer and to thereby apply appropriate QoS constraints.
Owner:RPX CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com