Random early detection over wireless links
a technology of random detection and wireless links, applied in data switching networks, frequency-division multiplexes, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of two phases of tcp being extremely inefficien
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017]A description of preferred embodiments of the invention follows.
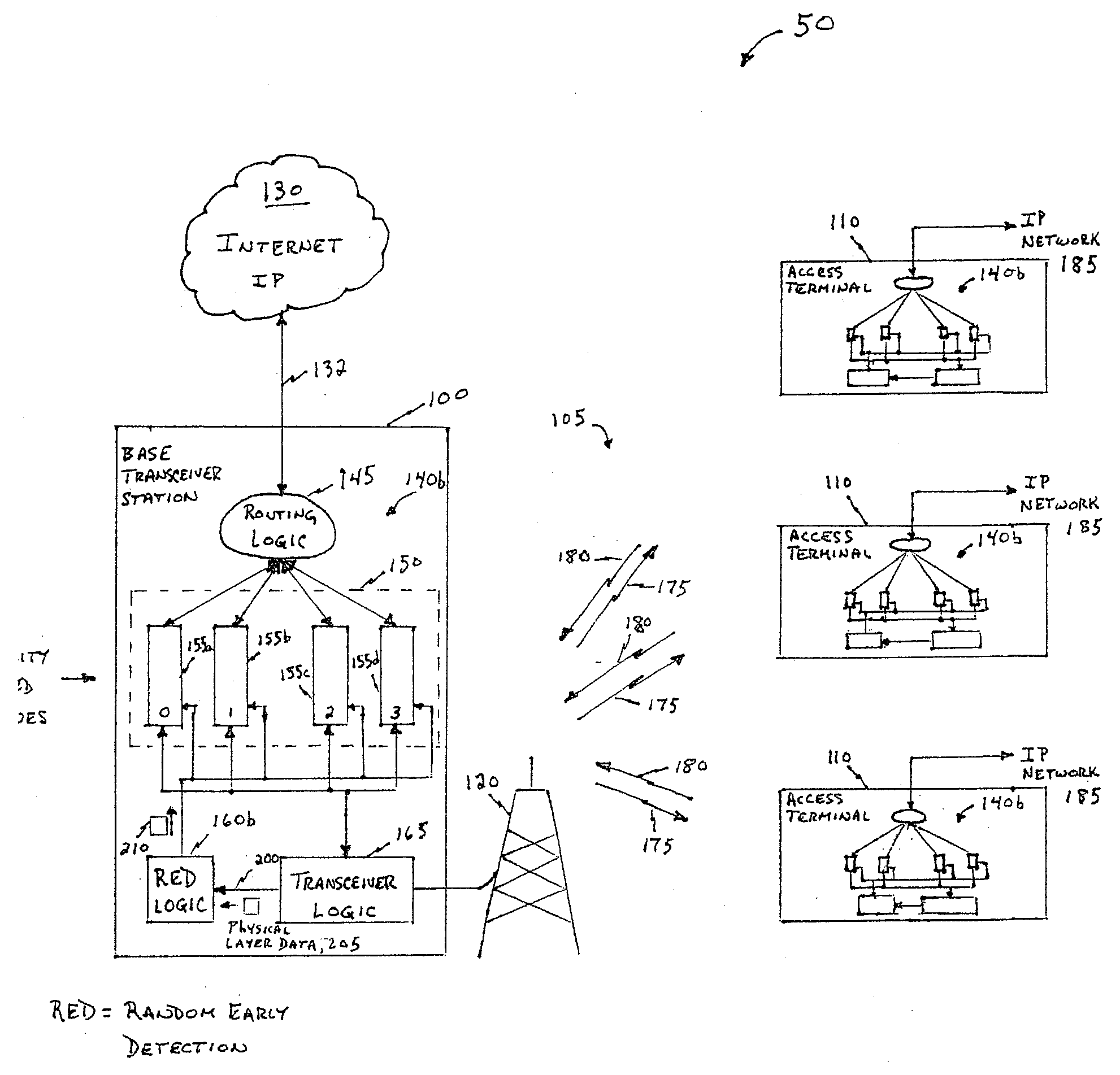
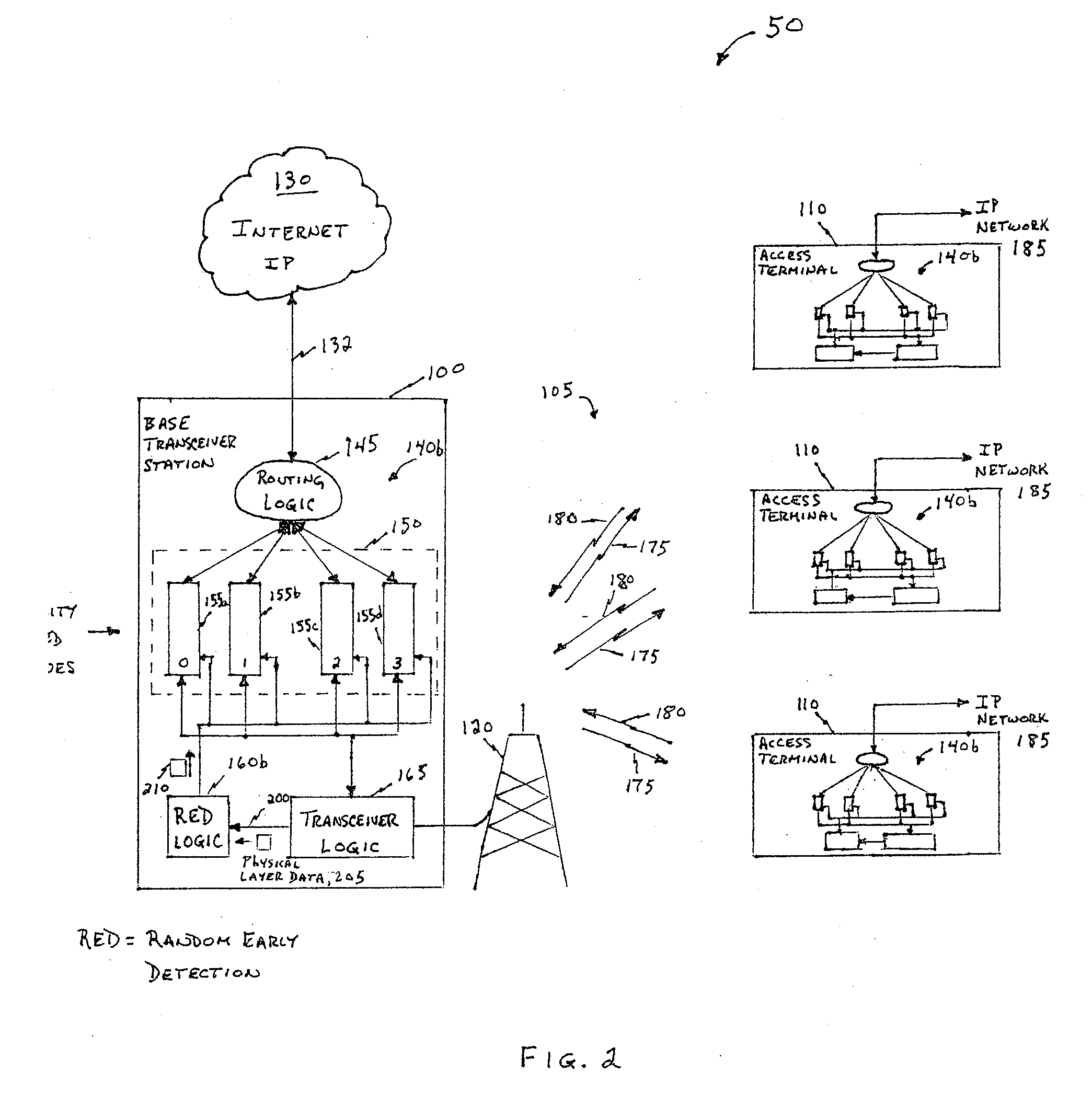
[0018]FIG. 2 is a block diagram of the wireless network 50 of FIG. 1, described above, in which an embodiment of the present invention is deployed. In this embodiment, the transceiver logic 165 is coupled to Random Early Detection (RED) logic 160b via a bus 200. Physical layer data 205 flows from the transceiver logic 165 to the RED logic 160b. The RED logic 160b determines whether to trigger random early detection controlled loss in one of the priority based queues 150. If the RED logic 160b determines to trigger the RED controlled loss based on a change in processing gain (due to any number of factors), then it sends a message or command 210 to at least one of the queues 155a-155d.
[0019]In contrast to the prior art configuration in the which the RED logic 160a (FIG. 1) monitors buffer levels of the priority based queues 150, the RED logic 160b of the present invention monitors the transceiver logic 165 or other...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com