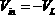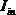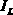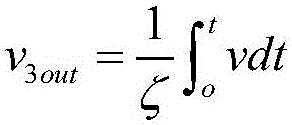Patents
Literature
52 results about "Negative impedance converter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
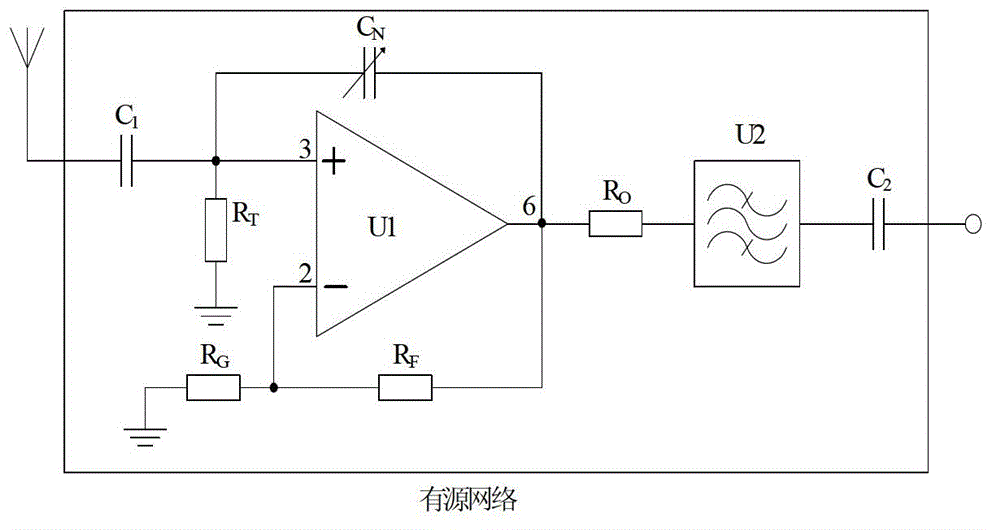
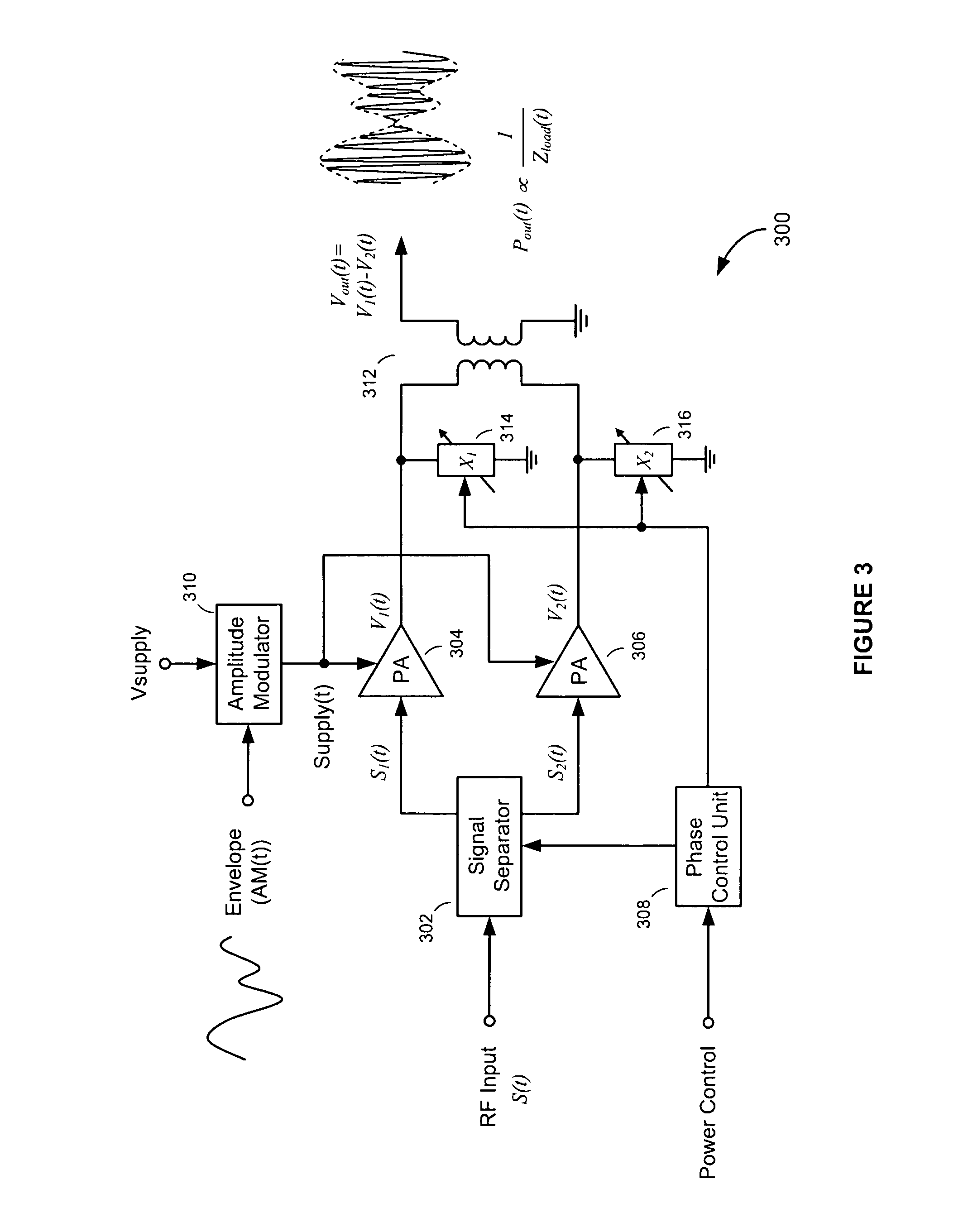
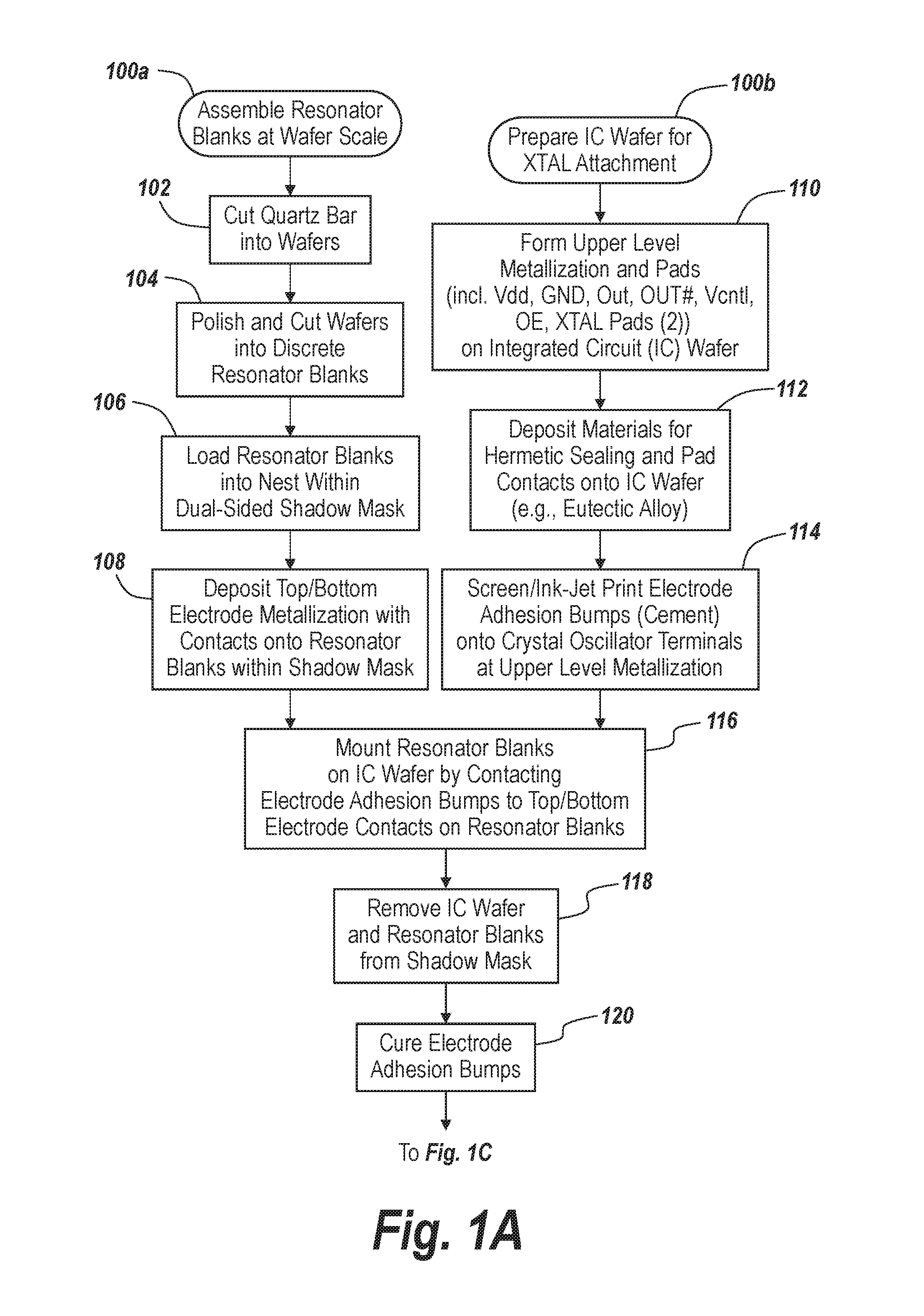
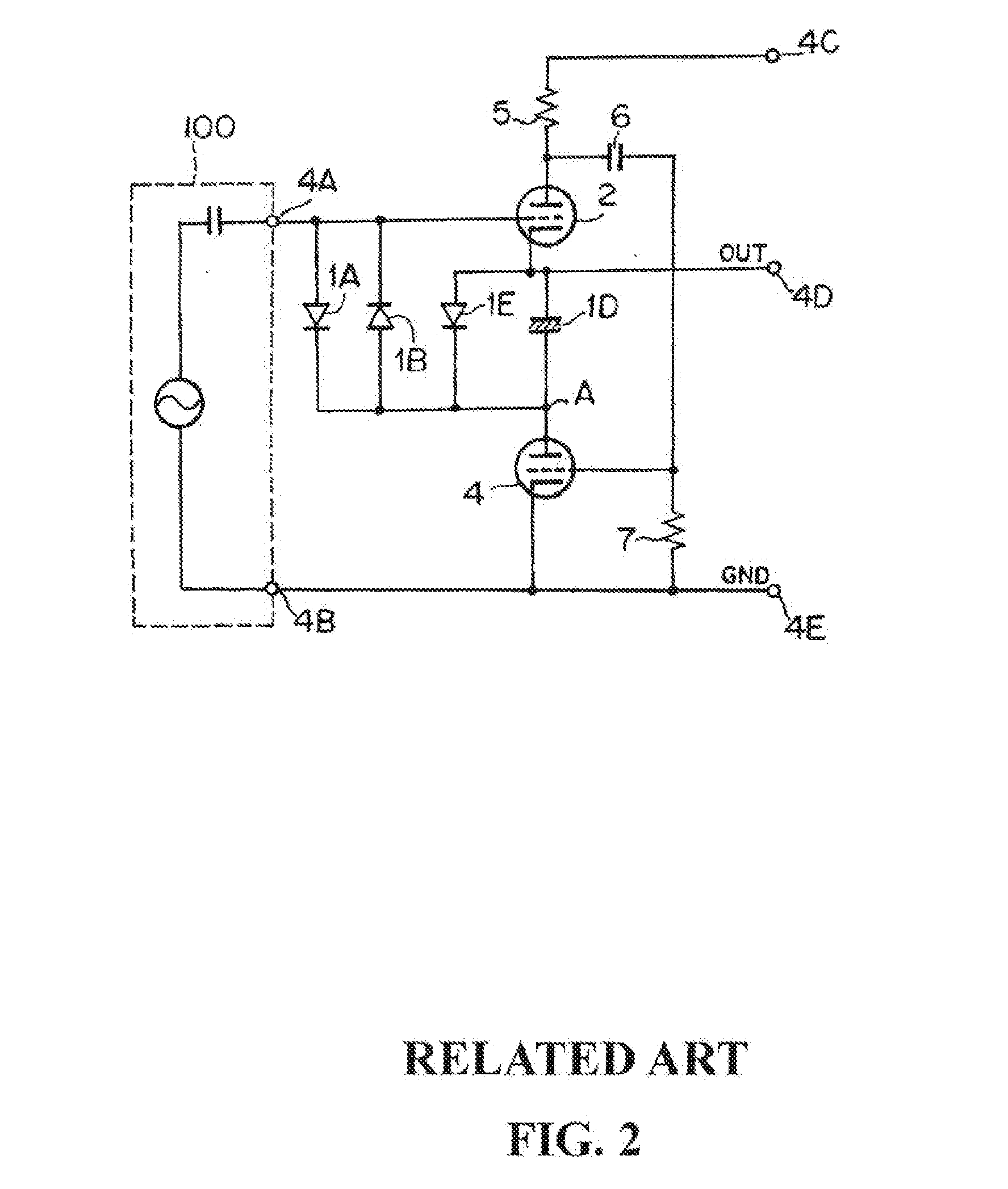
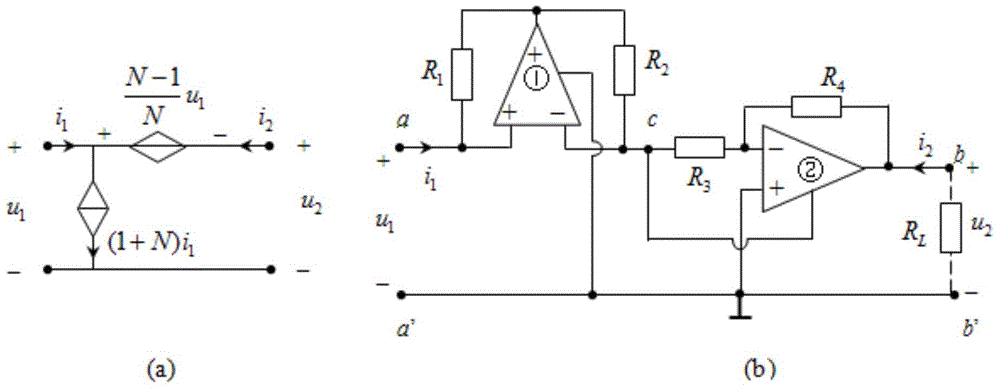
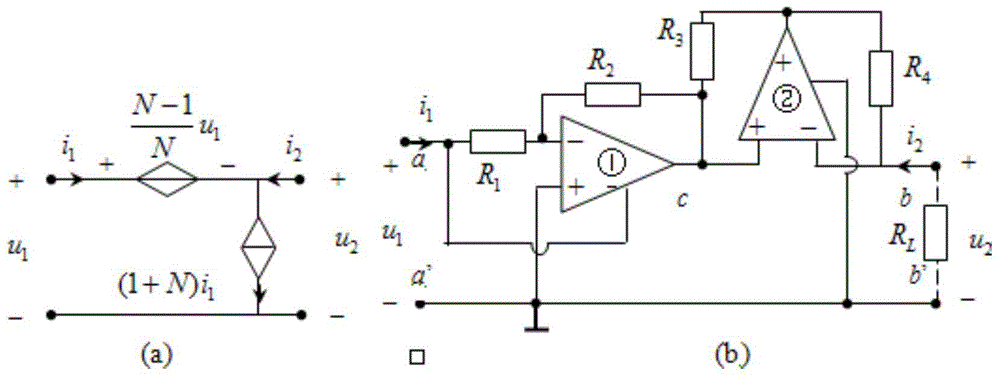
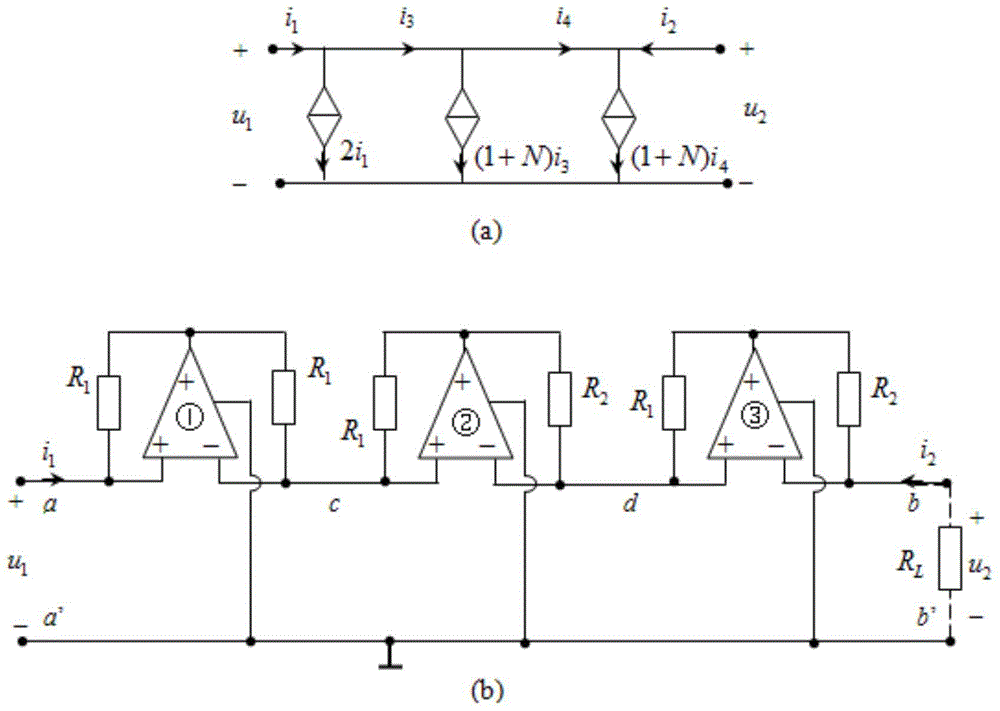
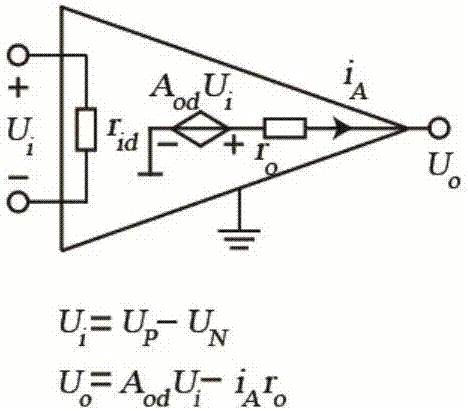
The negative impedance converter (NIC) is a one-port op-amp circuit acting as a negative load which injects energy into circuits in contrast to an ordinary load that consumes energy from them. This is achieved by adding or subtracting excessive varying voltage in series to the voltage drop across an equivalent positive impedance. This reverses the voltage polarity or the current direction of the port and introduces a phase shift of 180° (inversion) between the voltage and the current for any signal generator. The two versions obtained are accordingly a negative impedance converter with voltage inversion (VNIC) and a negative impedance converter with current inversion (INIC). The basic circuit of an INIC and its analysis is shown below.
Circuit-loaded conformal metasurface cloak
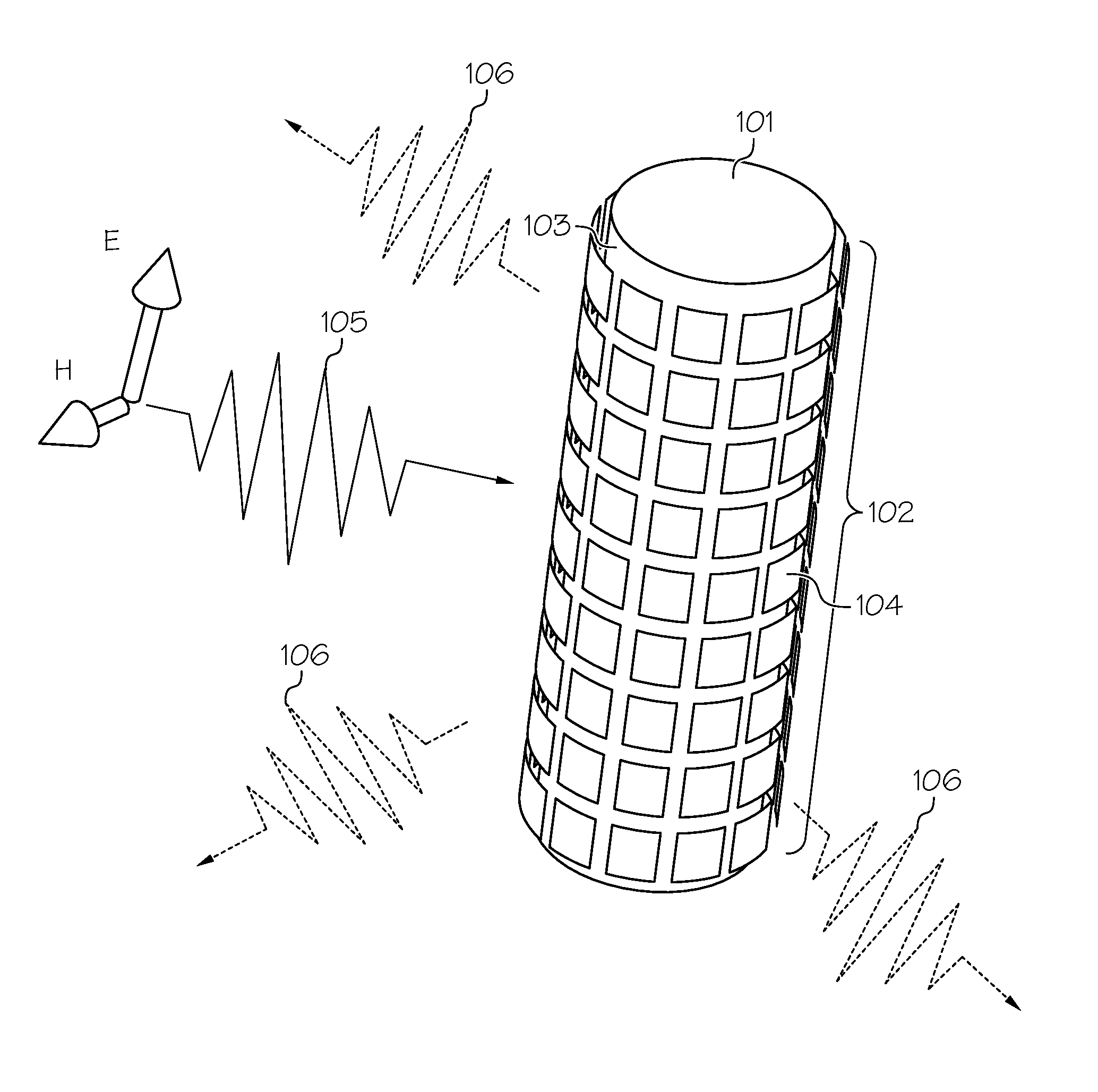
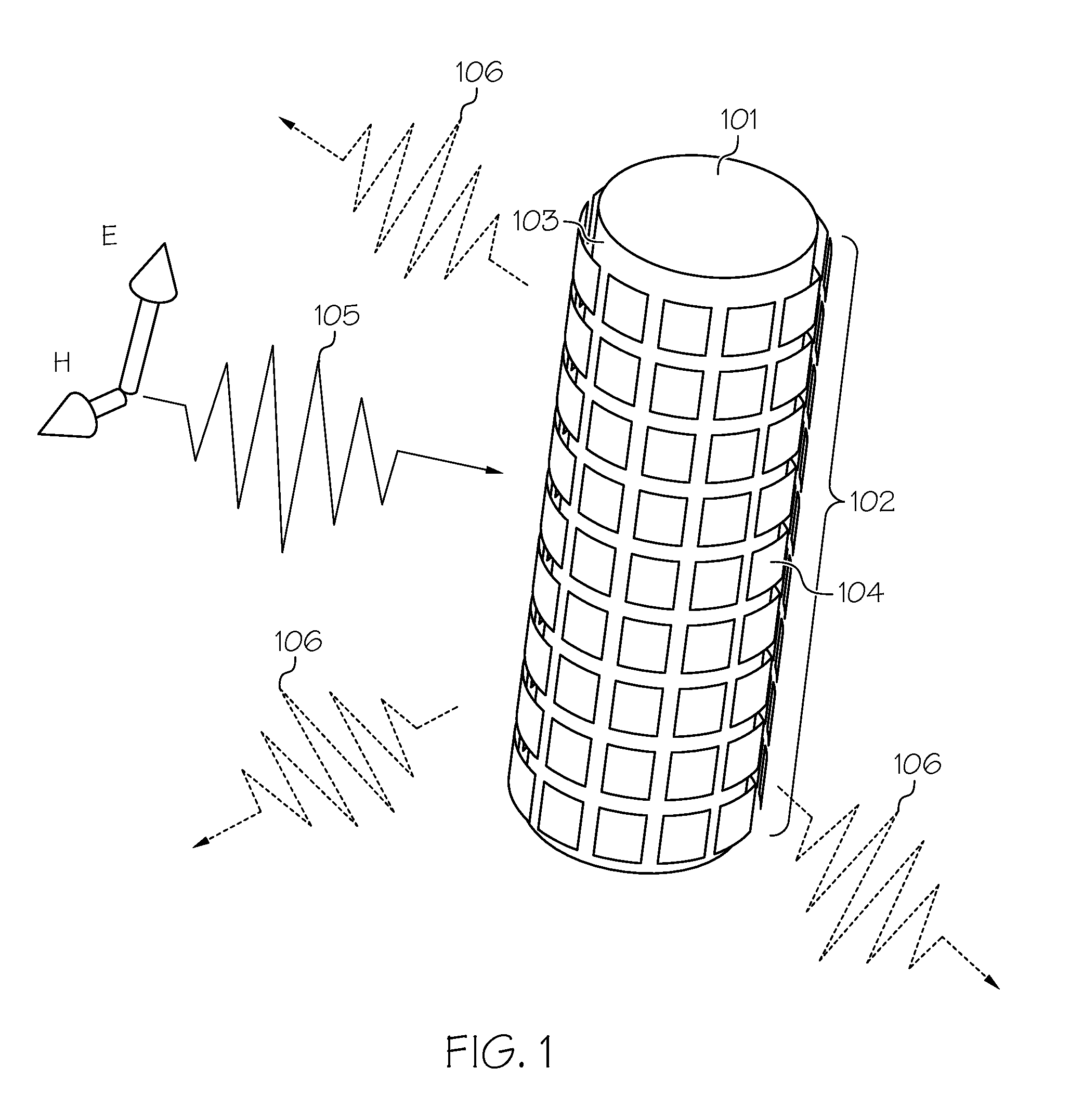
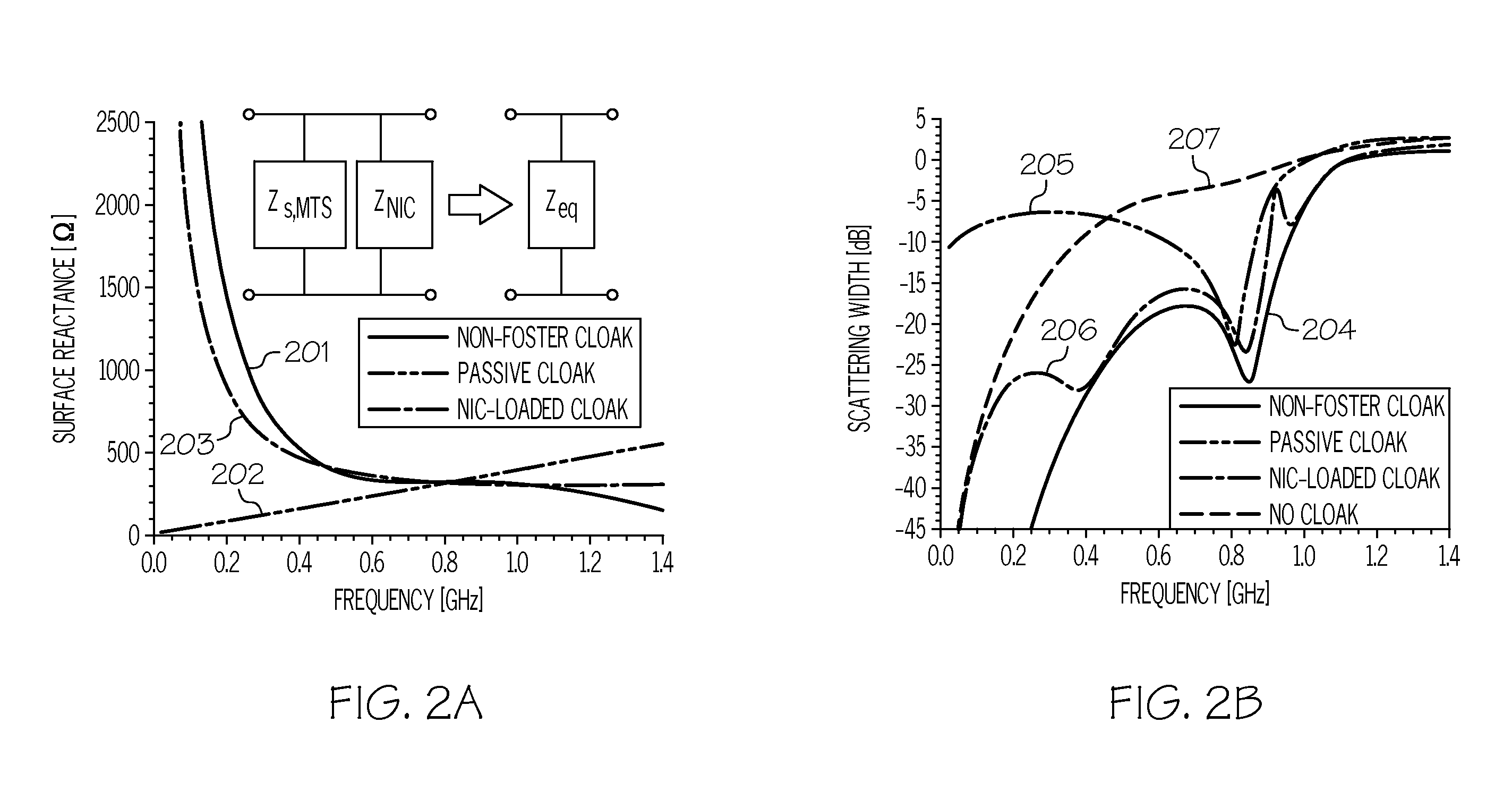
An electromagnetic invisibility cloaking device with a broadened cloaking bandwidth and / or a tunable frequency of operation. The cloaking device includes an object (e.g., antenna) and a metasurface (301) that conforms to the surface design of the object. The metasurface includes an array of metal cells (302A, . . . , 302Y), where each of the metal cells includes a circuit element (304) (e.g., active, passive, negative impedance converter element). The array of metal cells may be represented as an array of metal square patches, a mesh grid, horizontal or vertical conductive strips, or any arbitrary combination of unit cell patterns, where each opening, or a subset of them, in such an array includes an embedded circuit element. By incorporating the circuit elements in the conformal metasurface, the cloaking bandwidth is broadened and the frequency of operation is actively controlled and tuned.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Broadband piezoelectric shunts for structural vibration control
InactiveUS6075309APiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesNetwork simulating reactancesCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
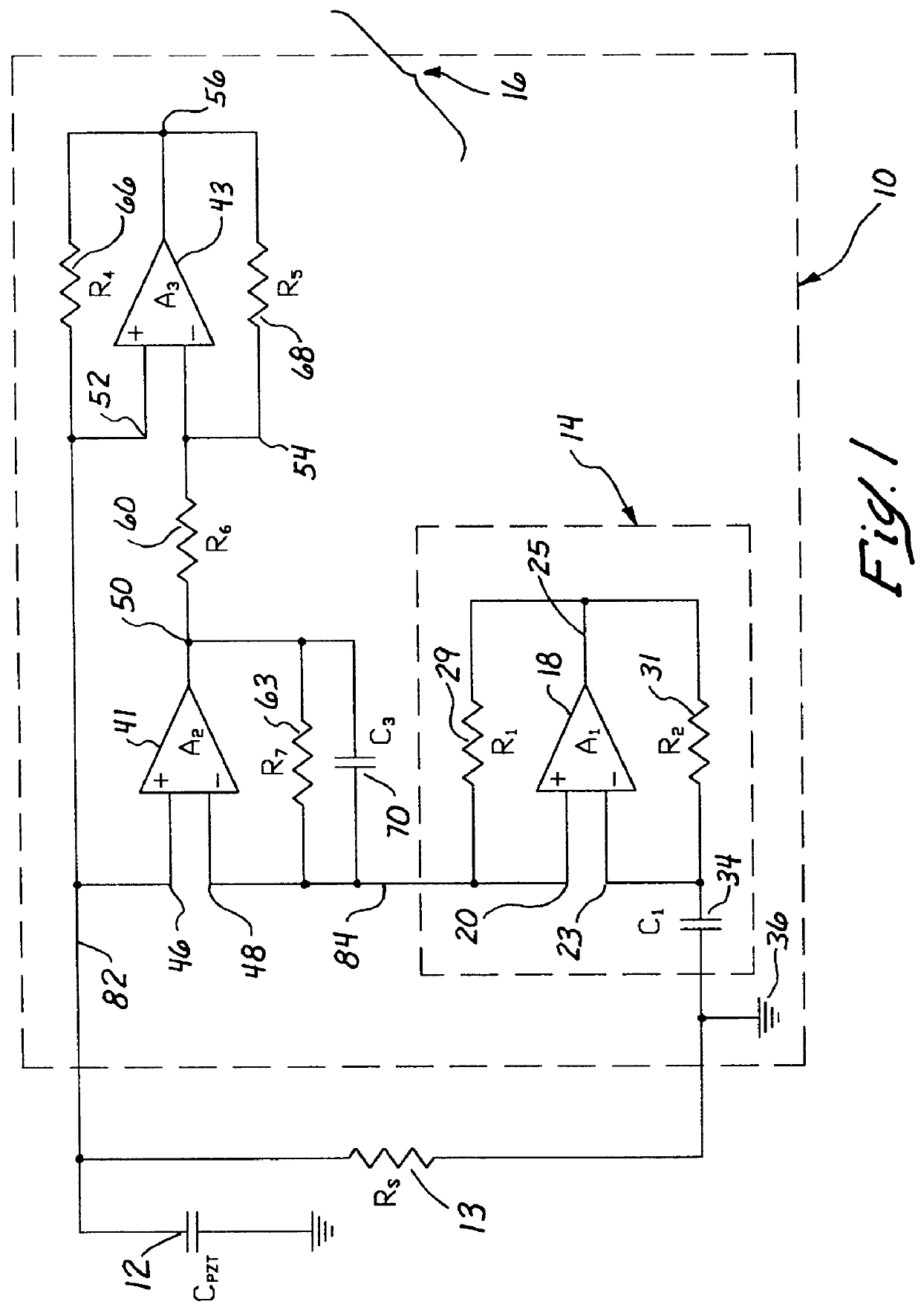
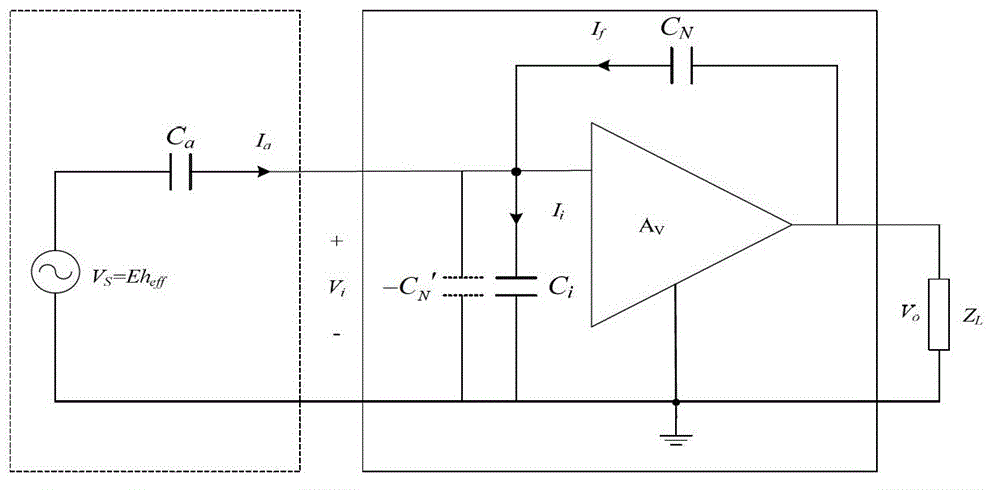
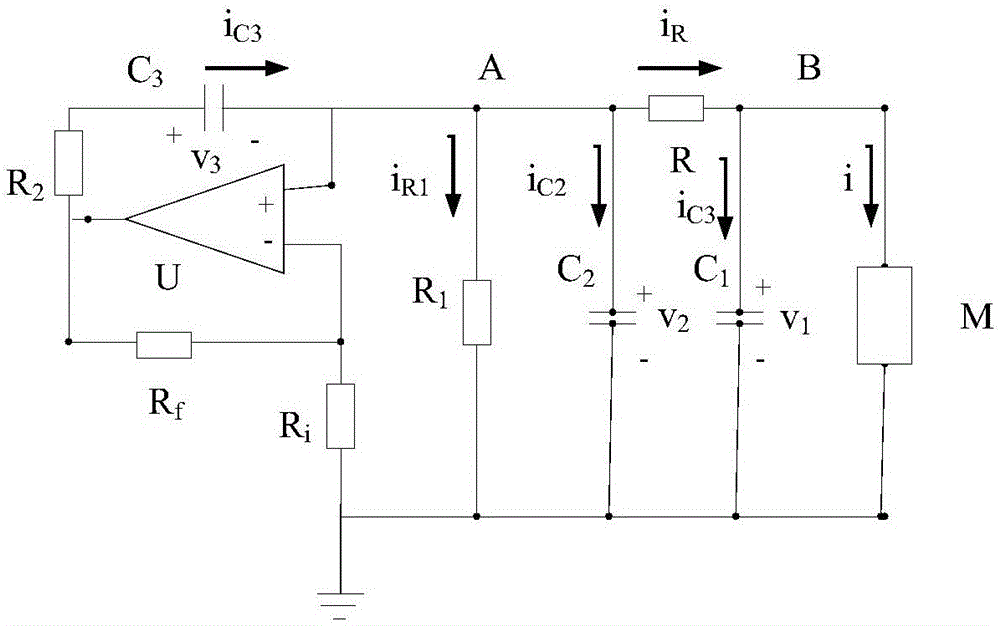
A negative capacitance converter is used in combination with a buffer circuit to form an electrical shunt circuit. The negative capacitance converter and the buffer circuit, together, minimize or eliminate oscillations of a negative impedance generated by the electrical shunt circuit. Additionally, a specific configuration of the negative capacitance converter is used to provide optimum stability. The buffer circuit includes a Riordan-type circuit, with the negative capacitance converter being substituted for one of the impedance elements of the Riordan-type circuit. Resistors are used to replace the other impedance elements of the Riordan-type circuit. An additional capacitor is placed across one of the operational amplifiers of the Riordan-type circuit, in order to provide additional stability.
Owner:MCDONNELL DOUGLAS
Active broadband matching method of short-wave frequency-band electrically small antenna and matching circuit thereof
InactiveCN104202007AGood offsetting effectMultiple-port networksTransmissionCapacitanceTransmission line transformer
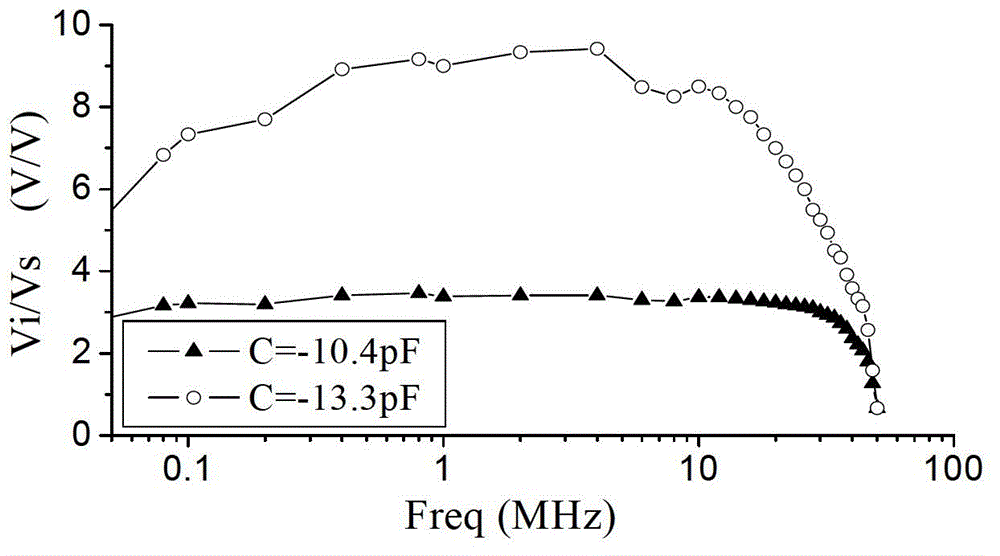
The invention discloses an active broadband matching method of a short-wave frequency-band electrically small antenna and a matching circuit thereof, the electrically small antenna is matched by a non-Forster reactive element and a passive broadband matching network, the non-Forster reactive element is realized by a negative impedance converter, the negative impedance converter and the passive broadband matching network are cascaded into an active broadband matching network with two ports, one port of the matching network is connected with the electrically small antenna, and said two ports are connected with an emitter / receiver. In the invention, the non-Forster reactive element and the passive broadband matching network are comprehensively considered, led loss is regulated in realization process of the non-Forster reactive element, single traditional negative capacitor can be replaced by in series connecting a negative capacitor and a negative inductor to better neutralize the impedance imaginary part, a transmission line transformer is led into the matching network, and the deviation between a testing value and a design value can be compensated by slightly adjusting the transformation ratio of the transmission line transformer.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
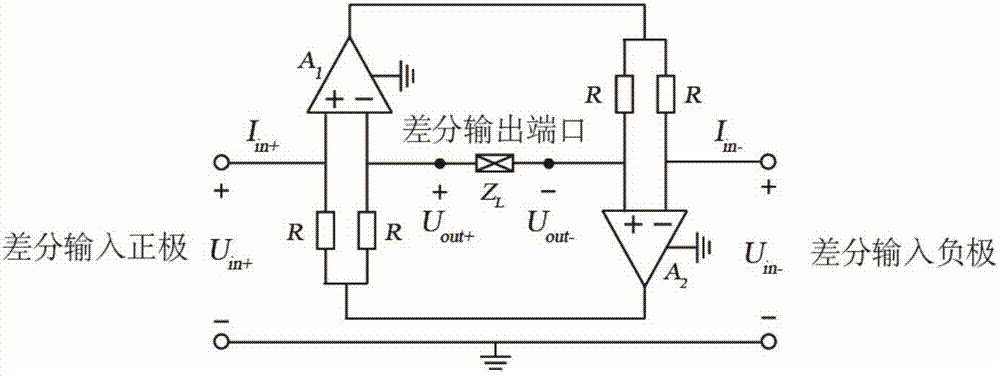
Differential negative impedance converters and inverters with variable or tunable conversion ratios
ActiveUS8988173B2Reduce parasitismImprove matchImpedence convertorsNetwork simulating reactancesCapacitanceEngineering
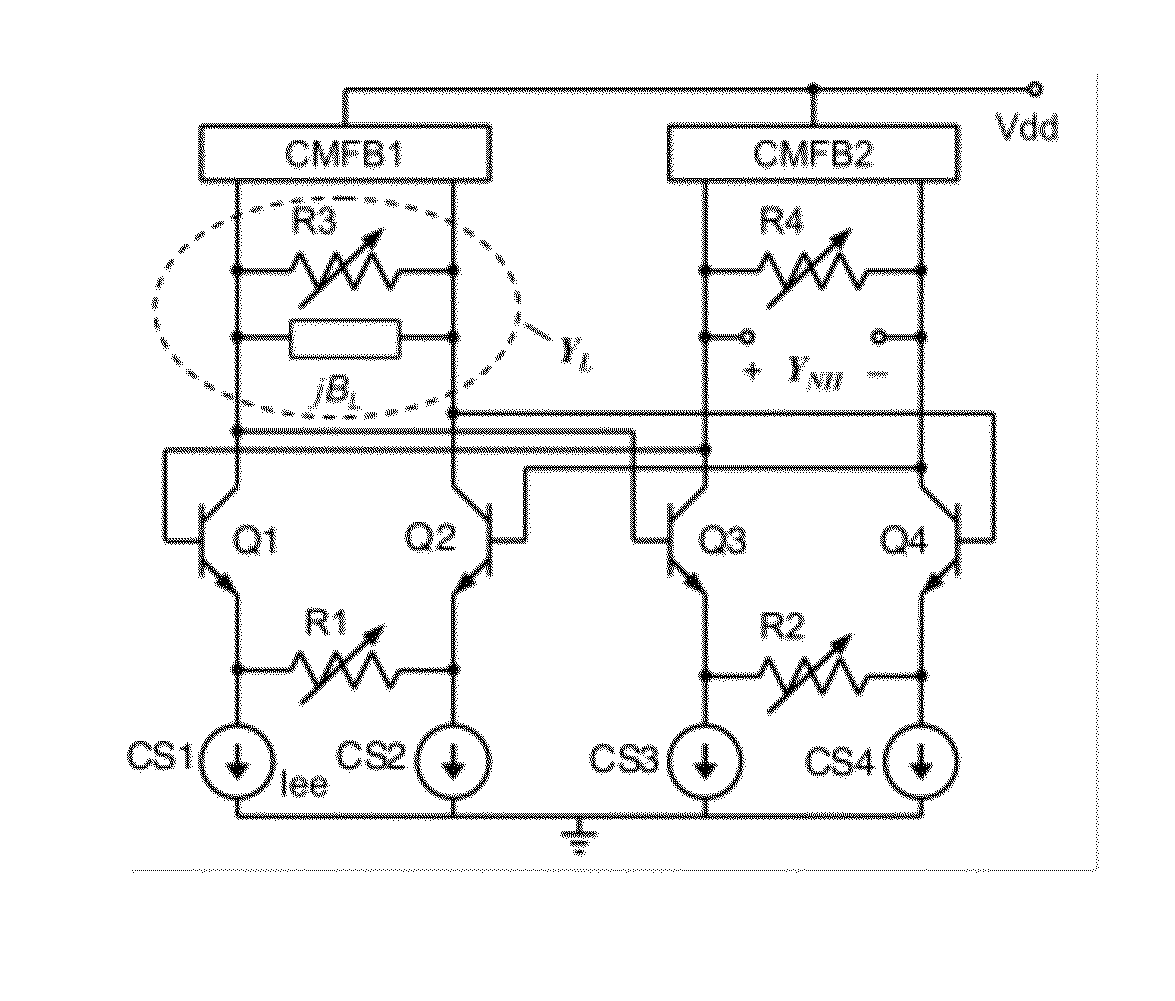
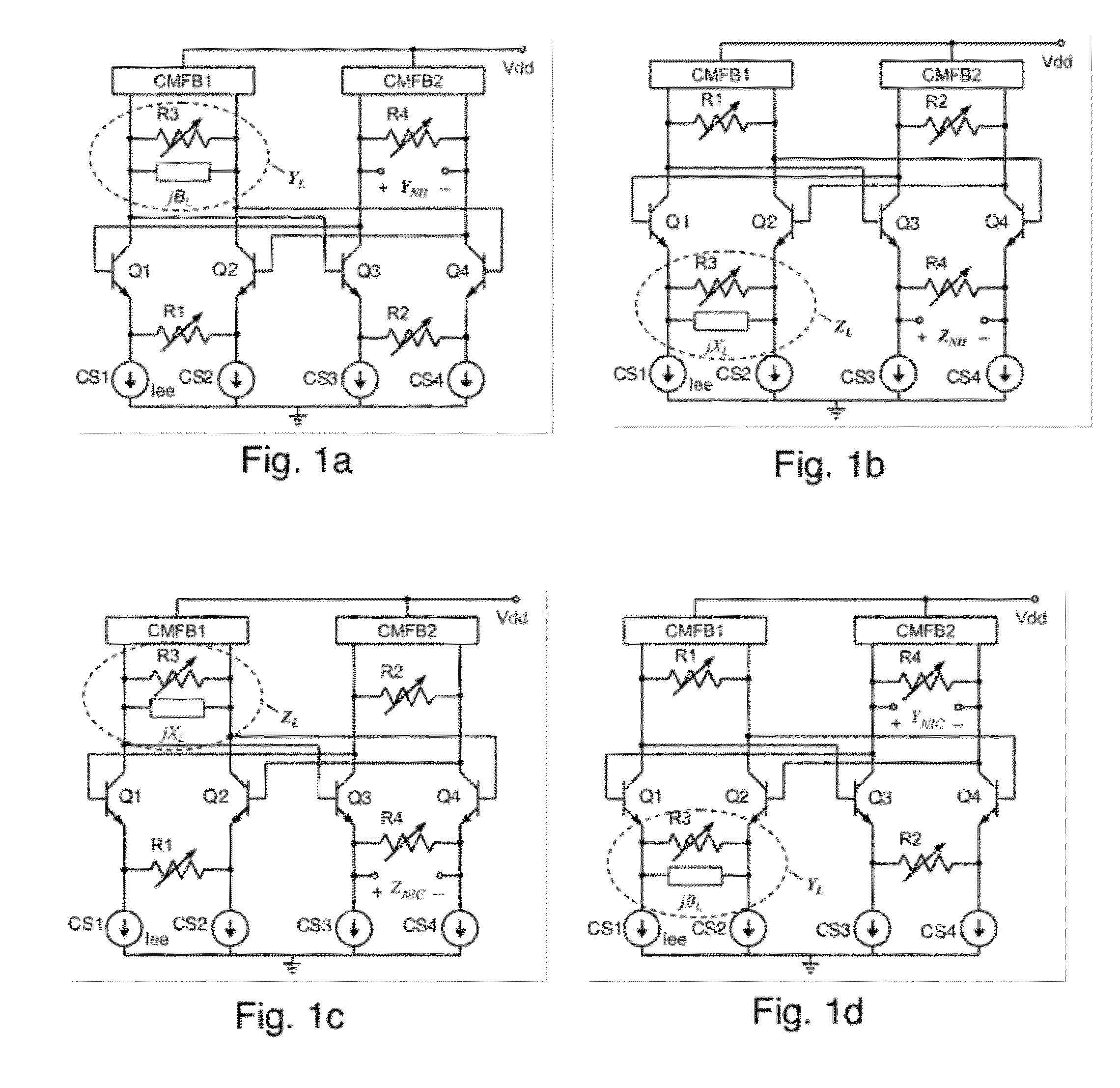
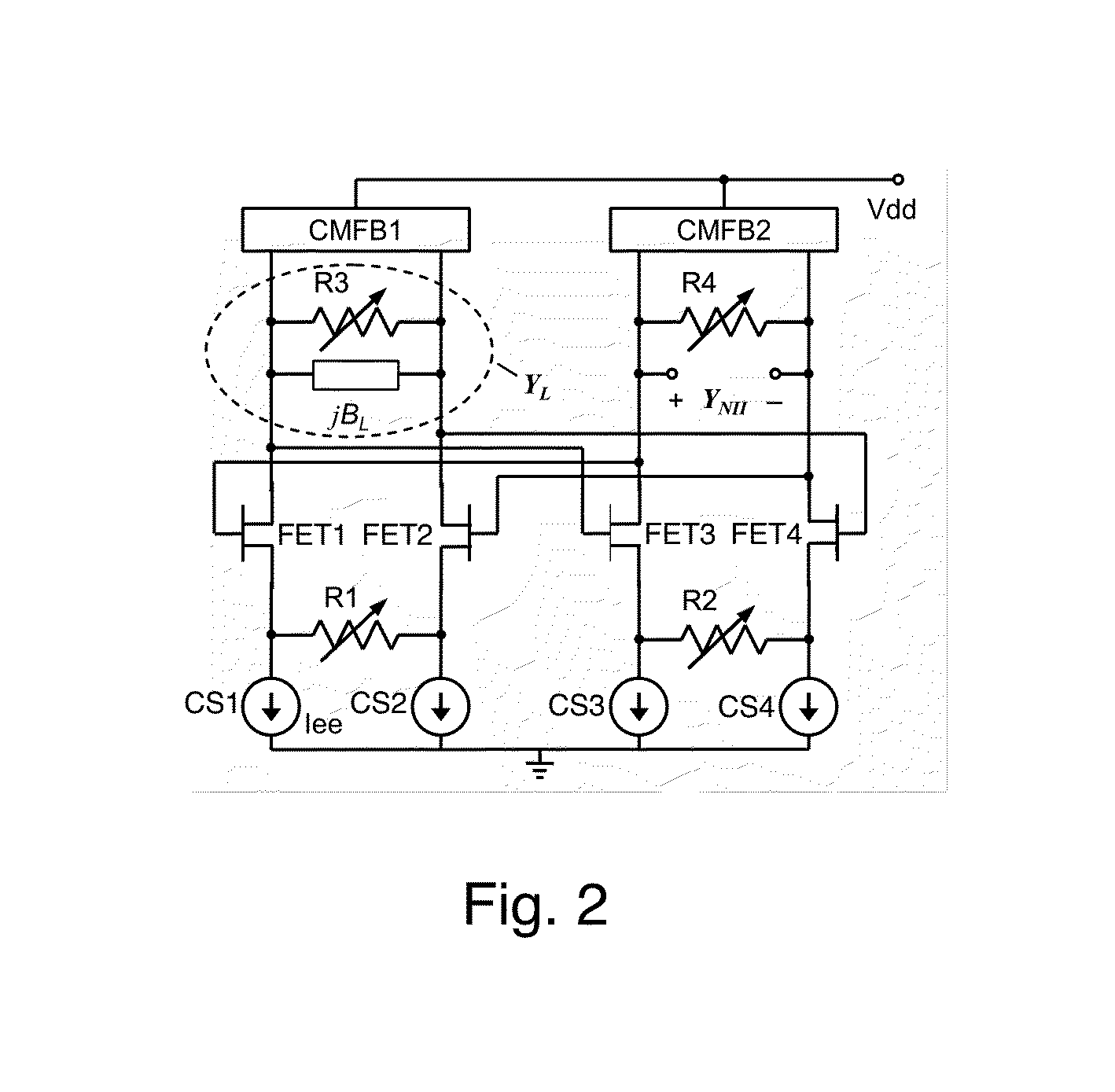
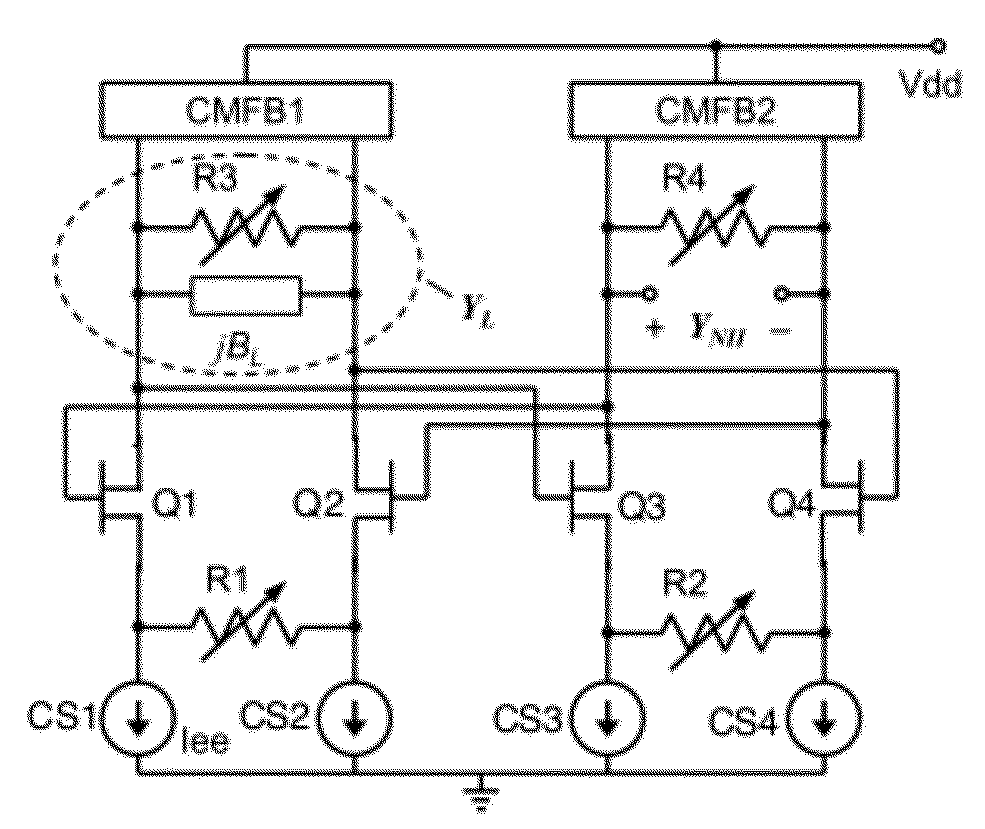
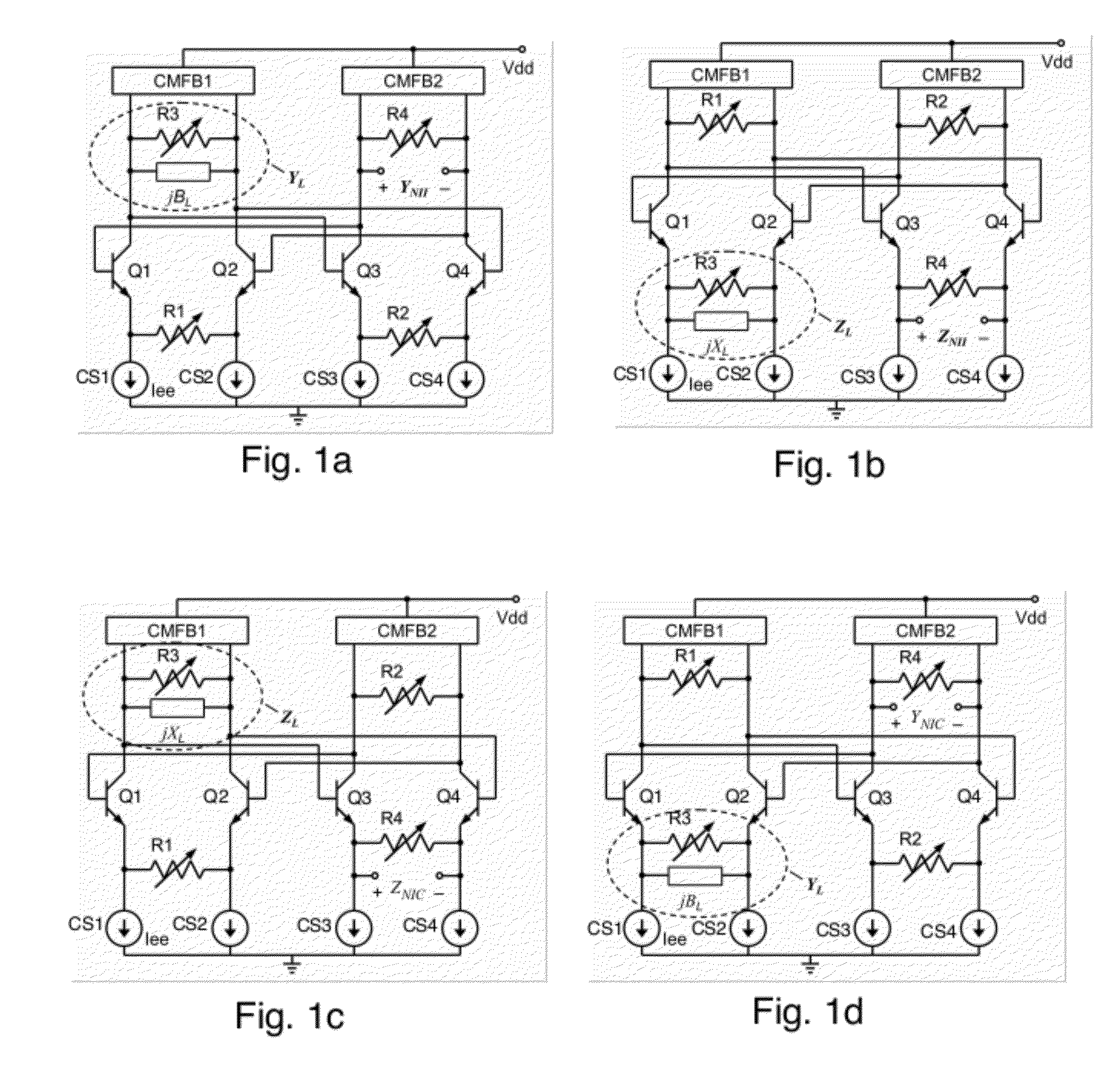
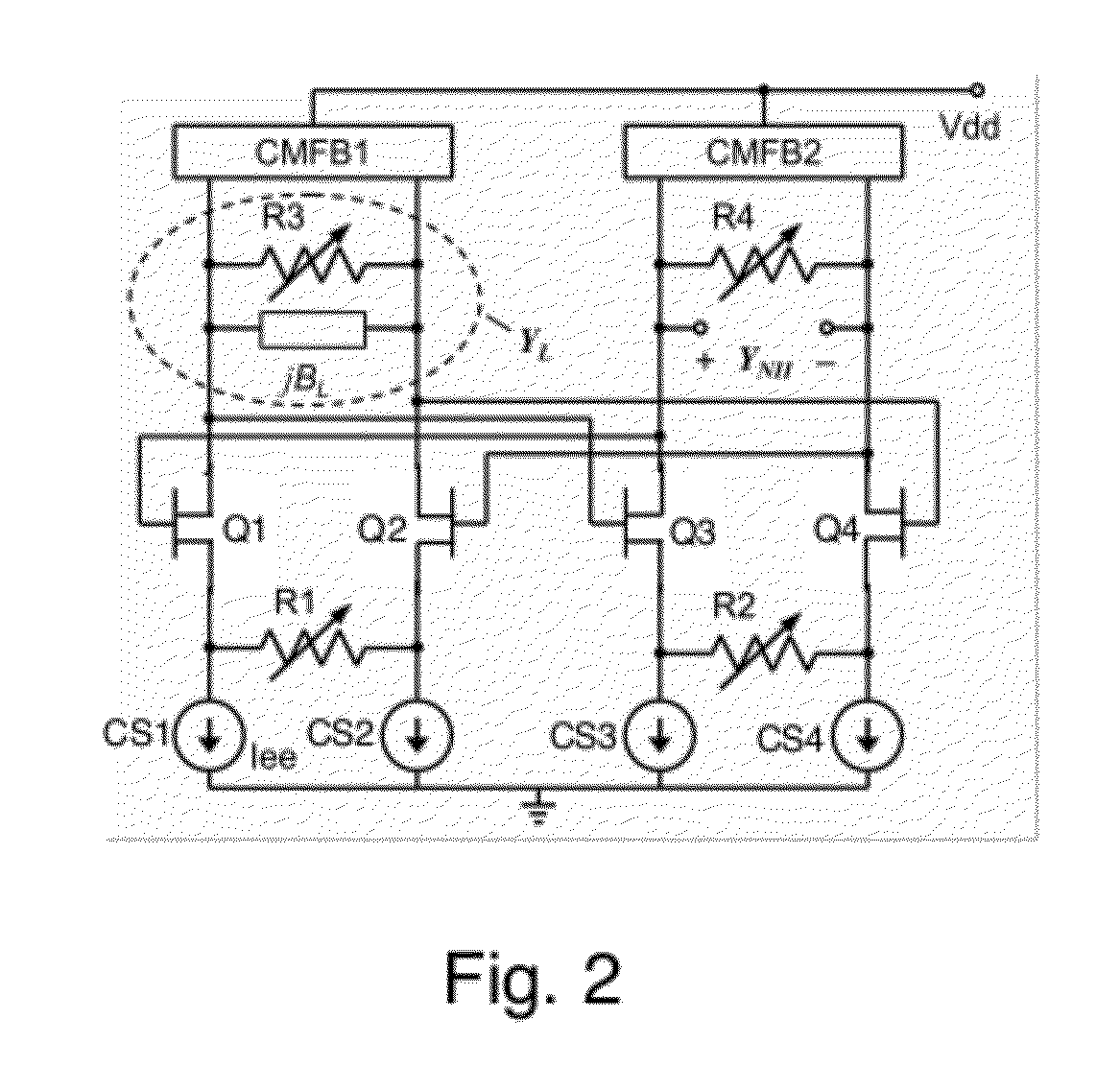
A differential circuit topology that produces a tunable floating negative inductance, negative capacitance, negative resistance / conductance, or a combination of the three. These circuits are commonly referred to as “non-Foster circuits.” The disclosed embodiments of the circuits comprises two differential pairs of transistors that are cross-coupled, a load immittance, multiple current sources, two Common-Mode FeedBack (CMFB) networks, at least one tunable (variable) resistance, and two terminals across which the desired immittance is present. The disclosed embodiments of the circuits may be configured as either a Negative Impedance Inverter (NII) or a Negative Impedance Converter (NIC) and as either Open-Circuit-Stable (OCS) and Short-Circuit-Stable (SCS).
Owner:HRL LAB
Active EMC filter for machine tools
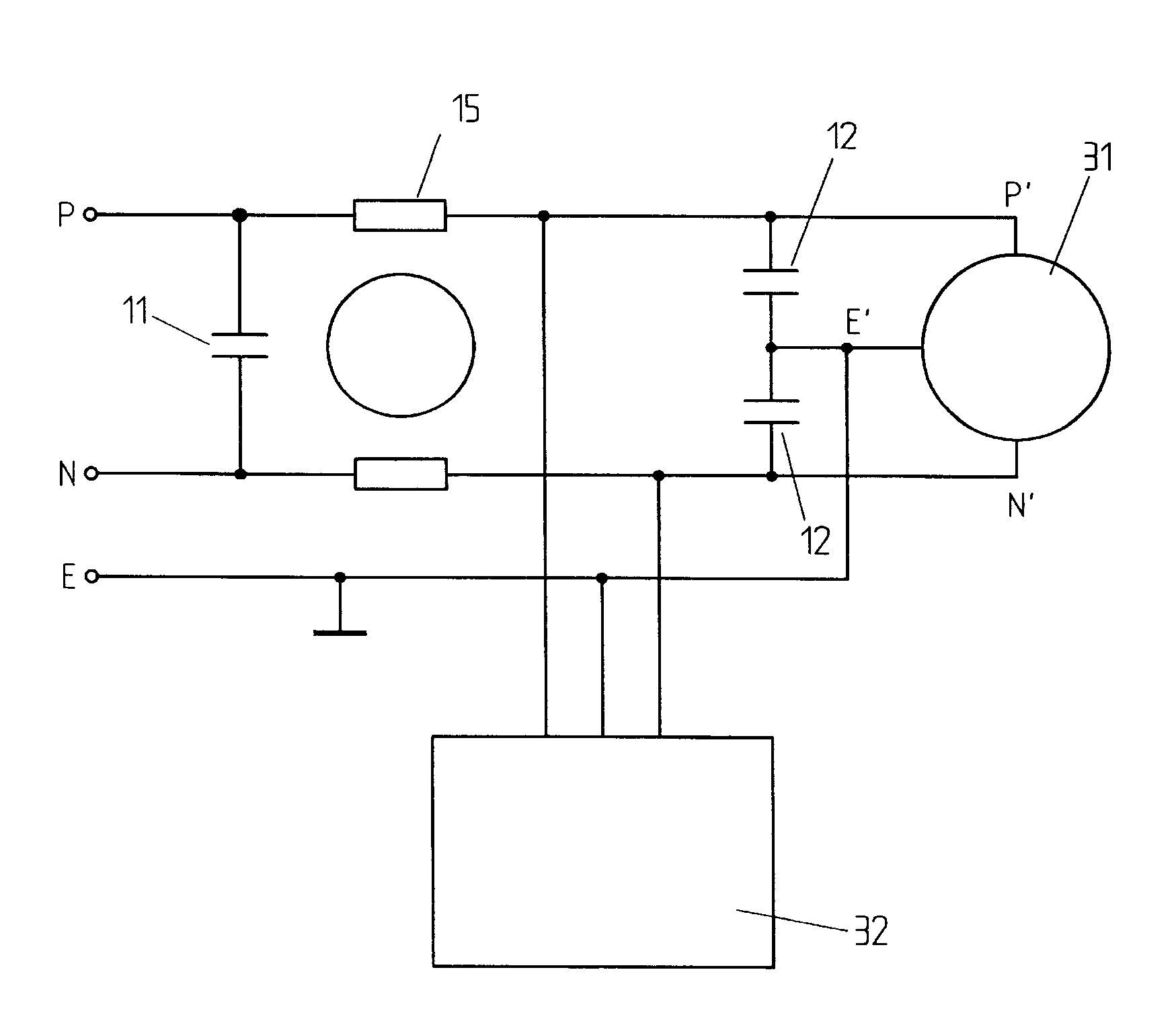
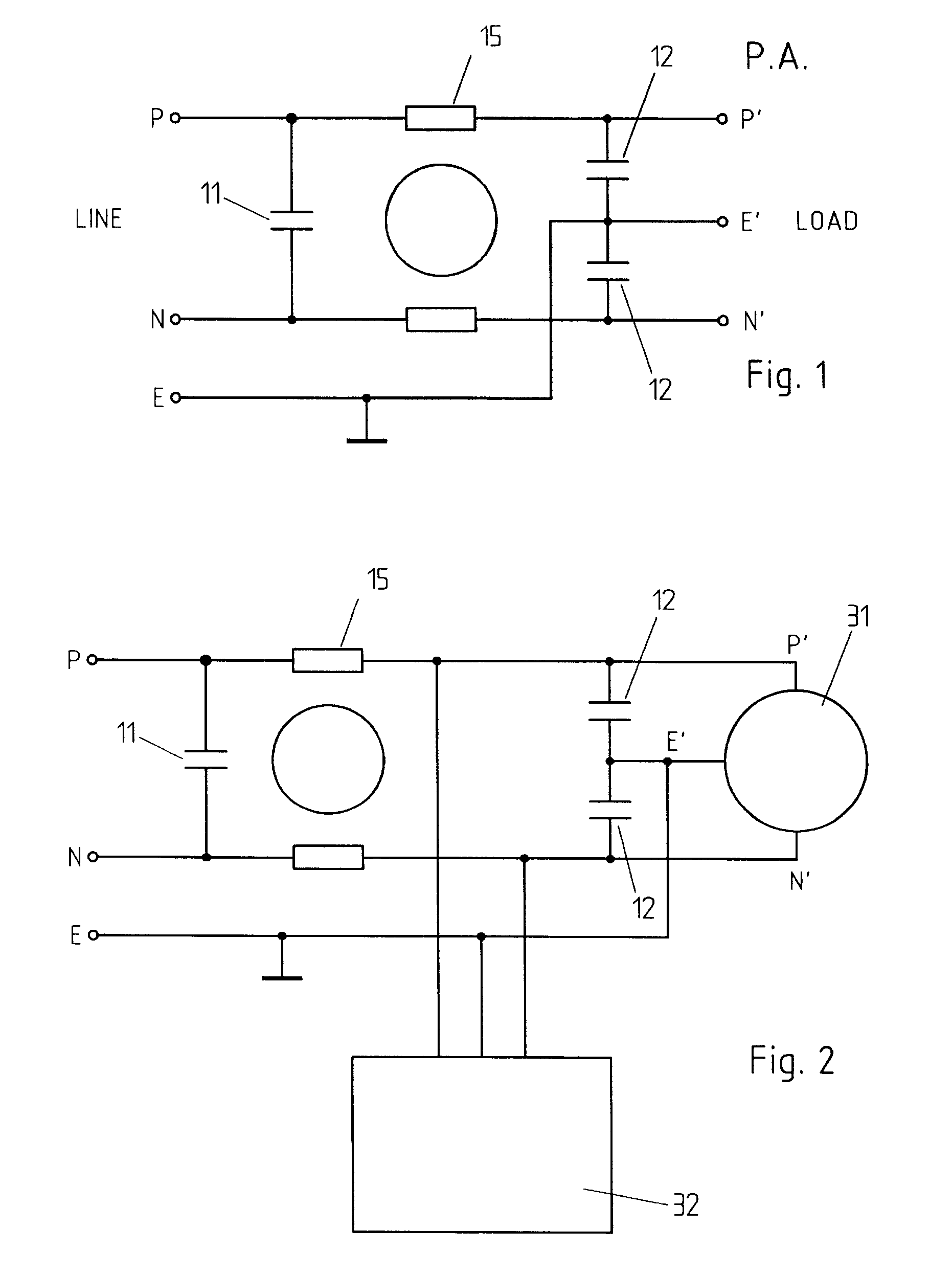
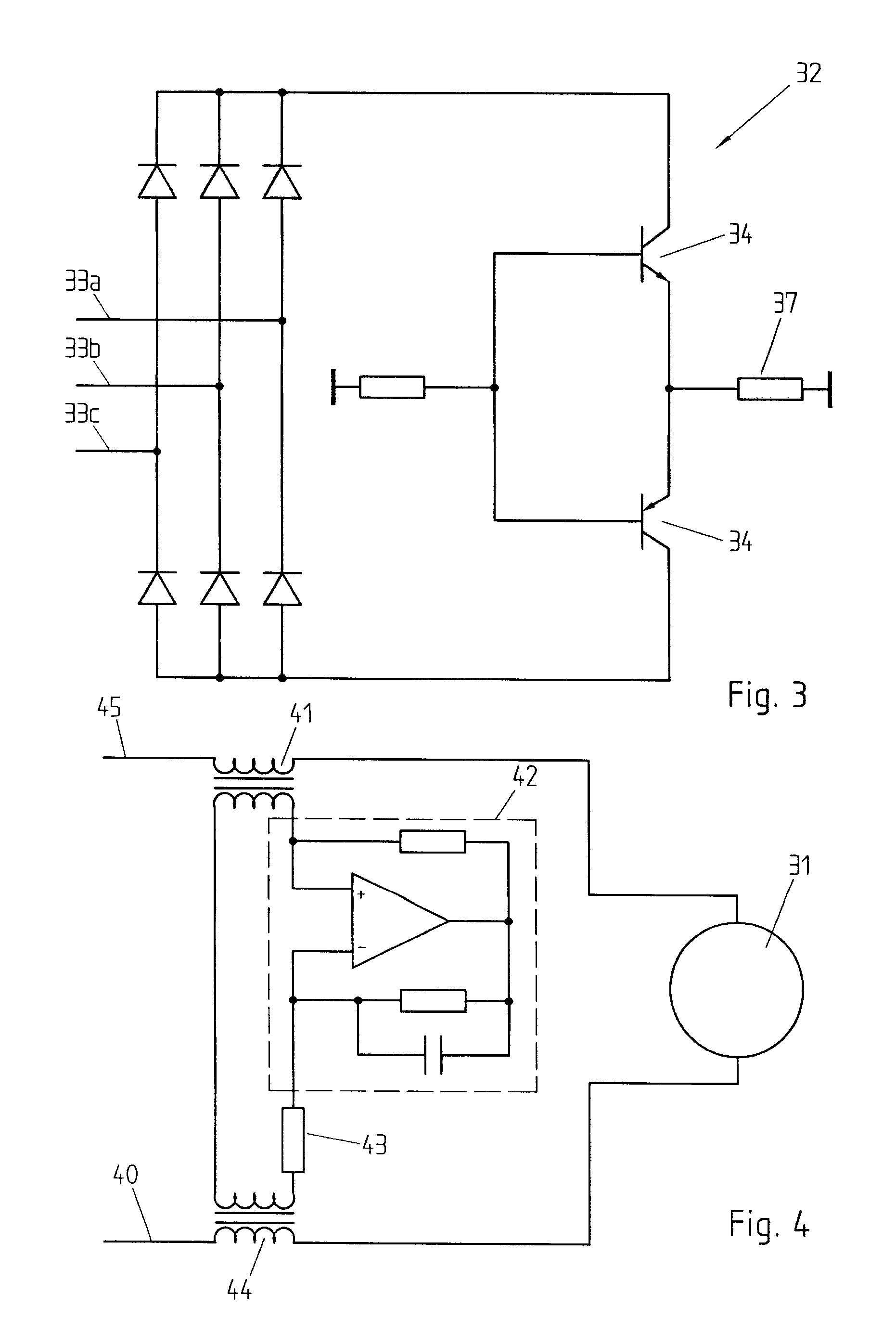
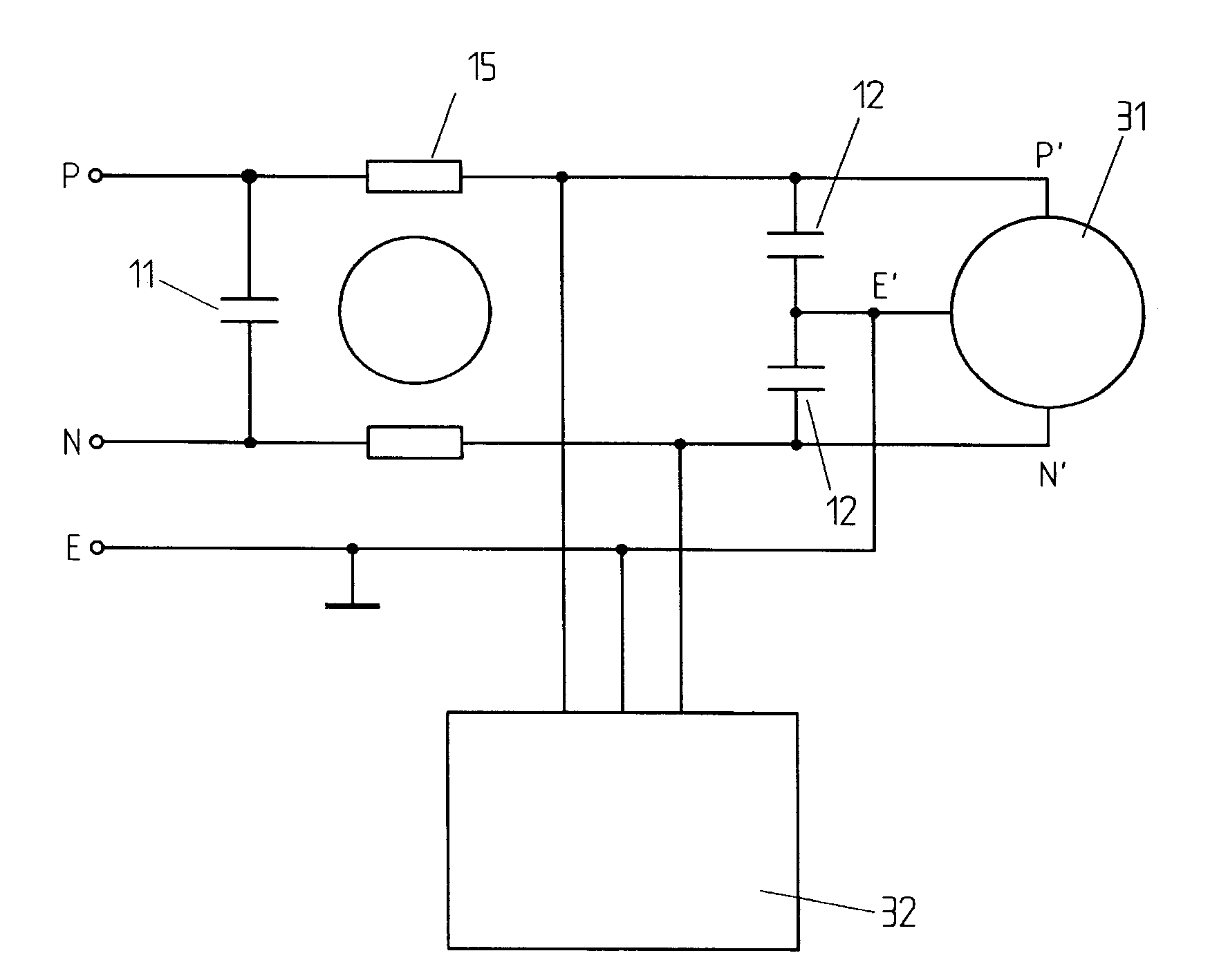
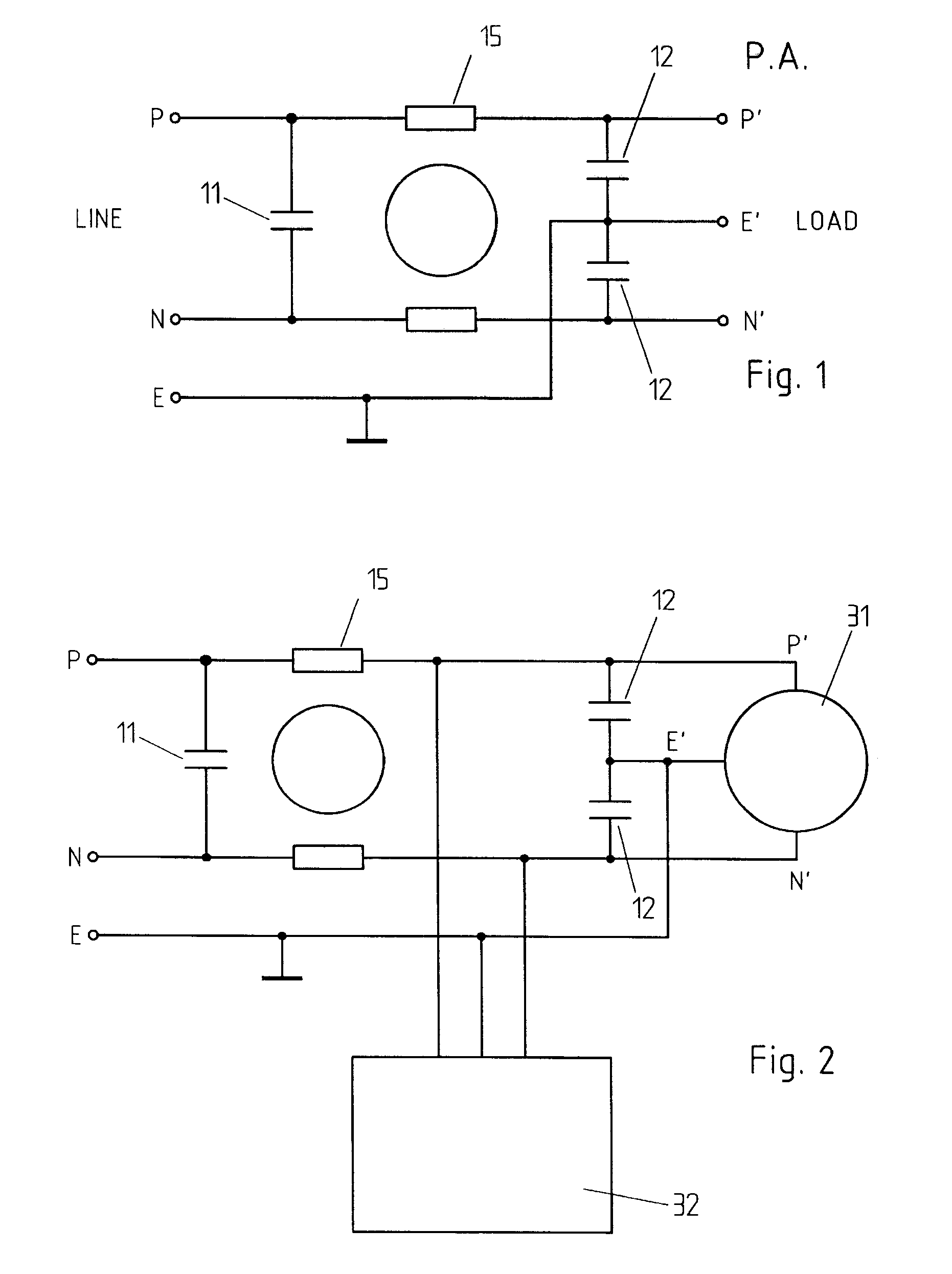
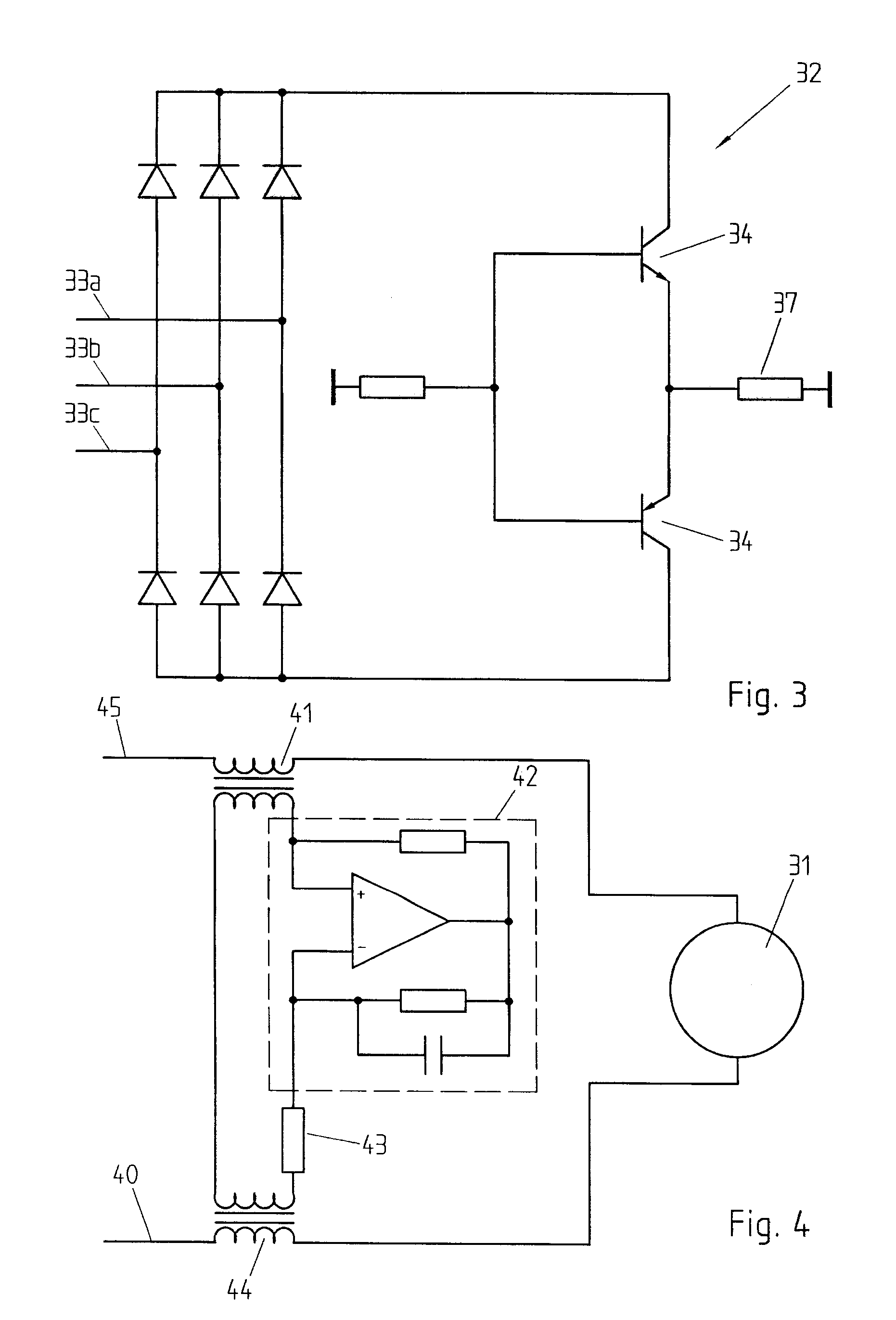
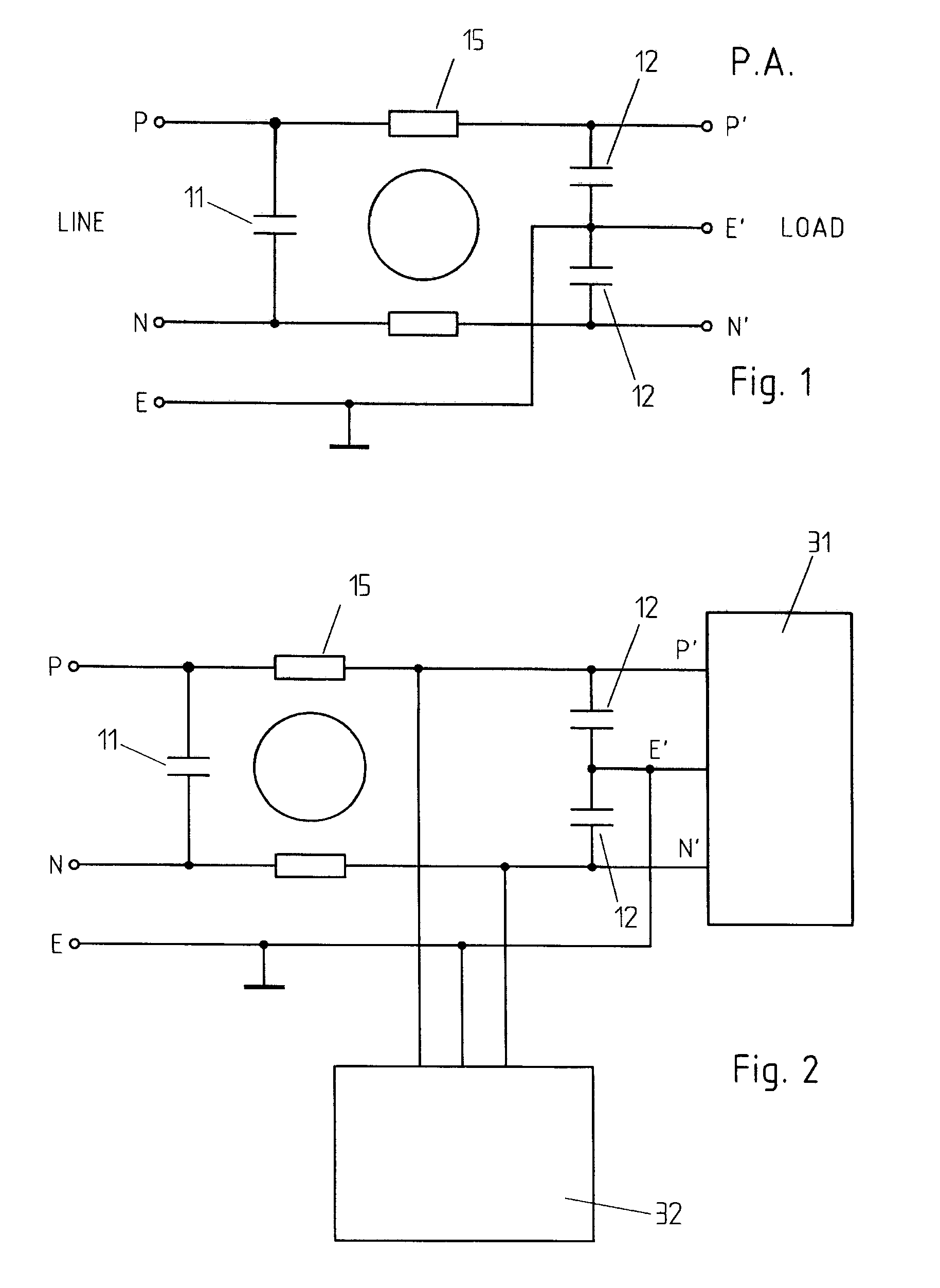
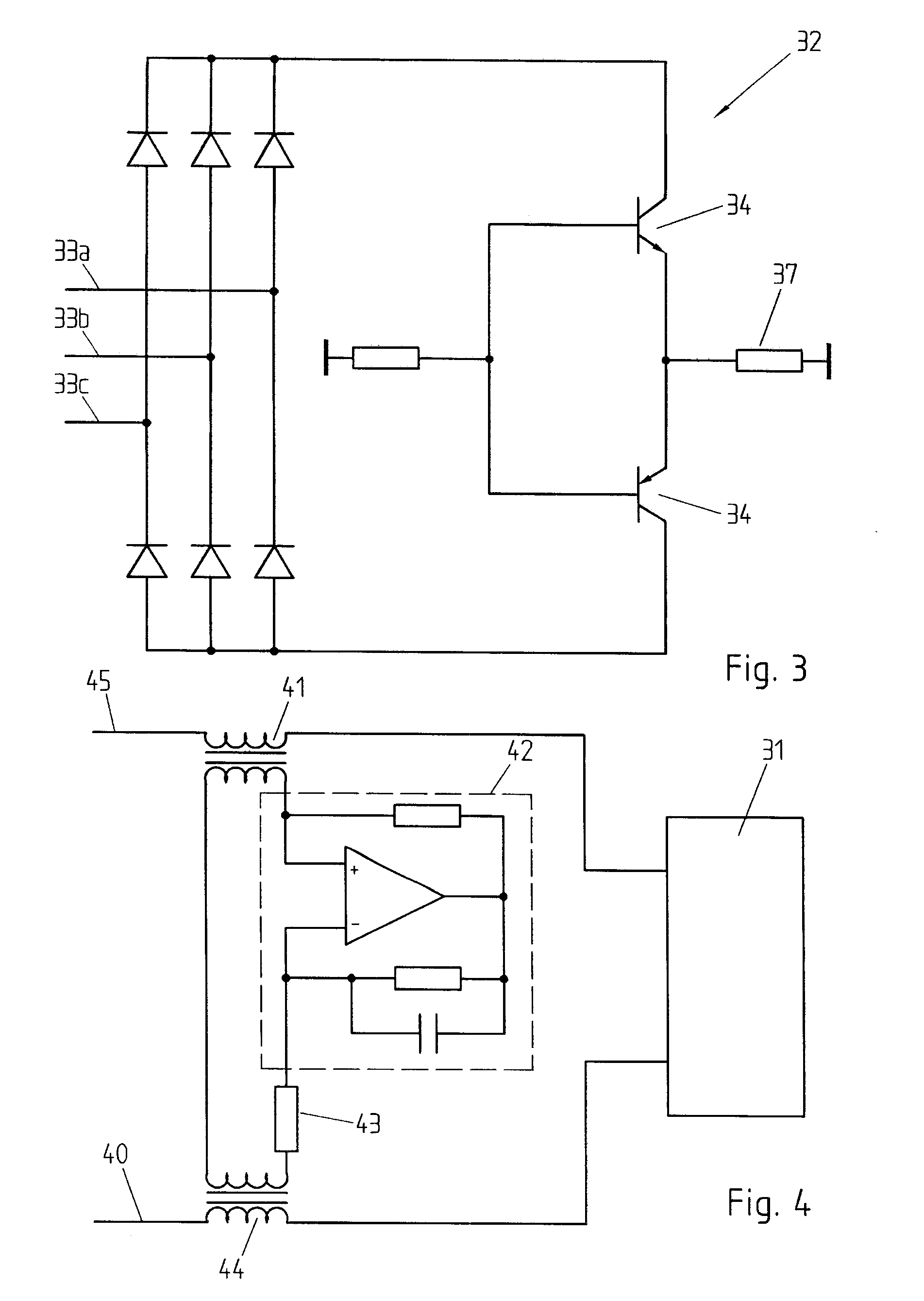
An active EMC filter for machine tools allows reducing the leakage current normally induced by large phase-to-ground capacitances. The filter may comprise an active shunt module or an impedance converter or a correction signal generator and is suitable both for three-phase and single-phase applications.
Owner:SCHAFFNER EMV AG
Broadband active matching method and matching circuit for electronically small receiving antenna based on negative impedance conversion
InactiveCN102751962AHigh gainImprove signal-to-noise ratioImpedence matching networksCapacitanceElectricity
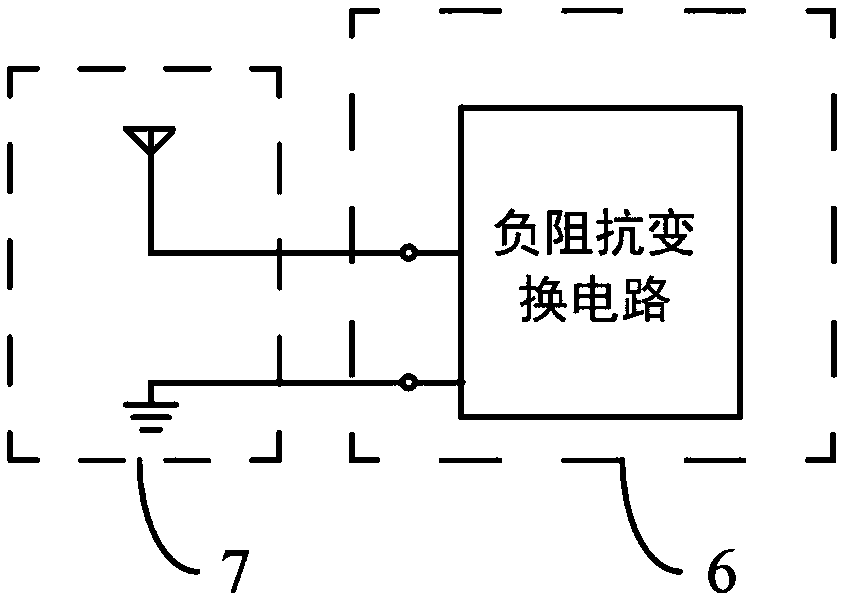
The invention provides broadband active matching method and matching circuit for an electronically small receiving antenna based on negative impedance conversion. An amplifier which is directly connected with a capacitive electronically small antennae is introduced into a negative impedance conversion so as to enable the amplifier to become a negative impedance conversion amplifier, and the negative impedance conversion obtains a negative capacitance on the input end of the amplifier; when an absolute value of the negative capacitance is greater than the input capacitance of the amplifier, the input end of the amplifier obtains equivalent negative capacitance, the equivalent positive capacitance (input by the electronically small antenna) of an electric reactor is counteracted by the negative electricity capacitance, and the input end of an active electric network is provided with an equivalent negative capacitor According to the method and the circuit, the active receiving antenna has a broadband character and has similar gain and similar signal-to-noise performance with an enhancement mode Non-Foster (negative impedance) matching method, but a circuit is relatively simple; and the combination property is good, the amplification and the negative impedance conversion can be realized in the same circuit, and only a positive feedback capacitor is added compared with the classical active receiving antenna.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
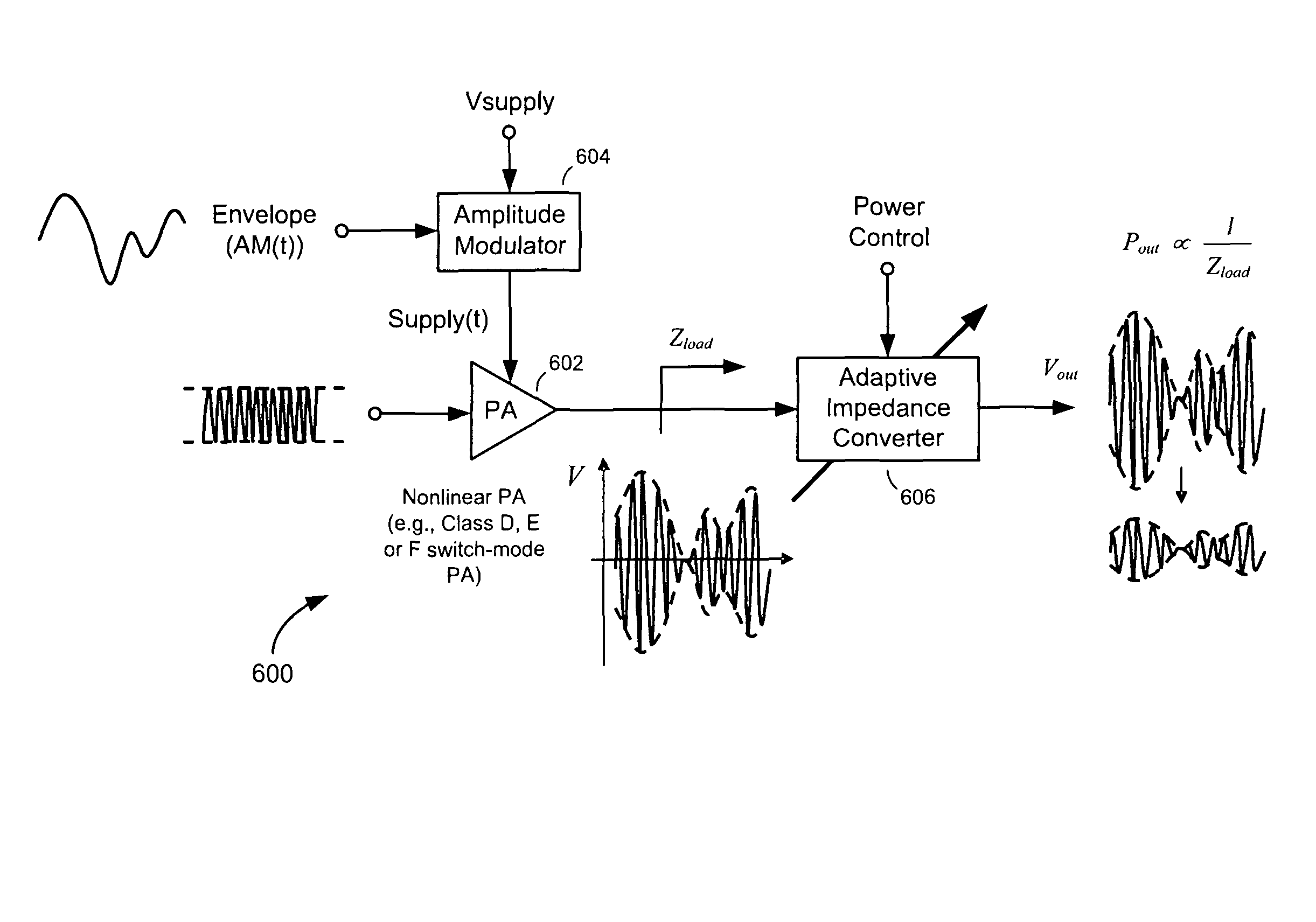
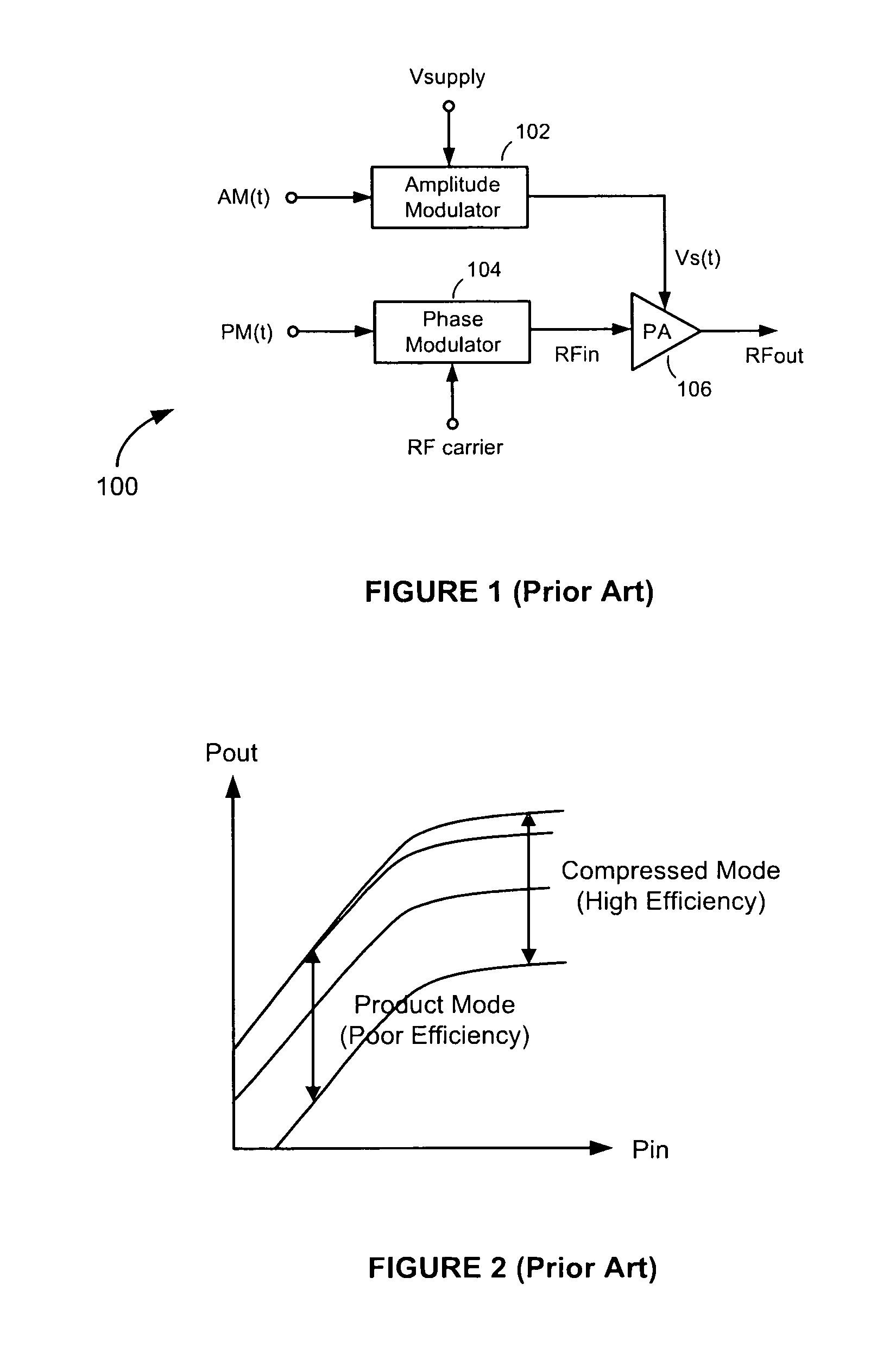
Adaptive impedance converter adaptively controls load impedance
ActiveUS8140030B2Difficulty to to changesDifficulty to respondResonant long antennasModulated-carrier systemsEngineeringRadio frequency
Owner:APPLE INC
Differential negative impedance converters and inverters with variable or tunable conversion ratios
ActiveUS20120256709A1Reduce parasitismGood device matchingImpedence convertorsNetwork simulating reactancesCapacitanceEngineering
A differential circuit topology that produces a tunable floating negative inductance, negative capacitance, negative resistance / conductance, or a combination of the three. These circuits are commonly referred to as “non-Foster circuits.” The disclosed embodiments of the circuits comprises two differential pairs of transistors that are cross-coupled, a load immittance, multiple current sources, two Common-Mode FeedBack (CMFB) networks, at least one tunable (variable) resistance, and two terminals across which the desired immittance is present. The disclosed embodiments of the circuits may be configured as either a Negative Impedance Inverter (NII) or a Negative Impedance Converter (NIC) and as either Open-Circuit-Stable (OCS) and Short-Circuit-Stable (SCS).
Owner:HRL LAB
Tunable broadband antenna matching circuits and devices using same
InactiveUS8836602B2Impedence matching networksAntennas earthing switches associationTransceiverRadio frequency signal
An improved wireless radio-frequency (RF) transmission system is disclosed. The wireless RF transmission system comprises: 1) a radio frequency (RF) transceiver configured to transmit and receive radio-frequency signals; ii) an electrically small antenna having a complex impedance comprising a real part and an imaginary part; and iii) a tunable negative impedance converter (NIC) circuit coupling the electrically small antenna to the RF transceiver. The tunable NIC circuit is configured to perform antenna matching by reducing the imaginary part of the complex impedance of the electrically small antenna. The tunable NIC circuit is tuned by adjusting a transconductance value associated with the tunable NIC circuit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Tunable broadband antenna matching circuits and devices using same
InactiveUS20130187826A1Easy to optimizeReducing imaginary partImpedence matching networksAntennas earthing switches associationTransceiverRadio frequency signal
An improved wireless radio-frequency (RF) transmission system is disclosed. The wireless RF transmission system comprises: 1) a radio frequency (RF) transceiver configured to transmit and receive radio-frequency signals; ii) an electrically small antenna having a complex impedance comprising a real part and an imaginary part; and iii) a tunable negative impedance converter (NIC) circuit coupling the electrically small antenna to the RF transceiver. The tunable NIC circuit is configured to perform antenna matching by reducing the imaginary part of the complex impedance of the electrically small antenna. The tunable NIC circuit is tuned by adjusting a transconductance value associated with the tunable NIC circuit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
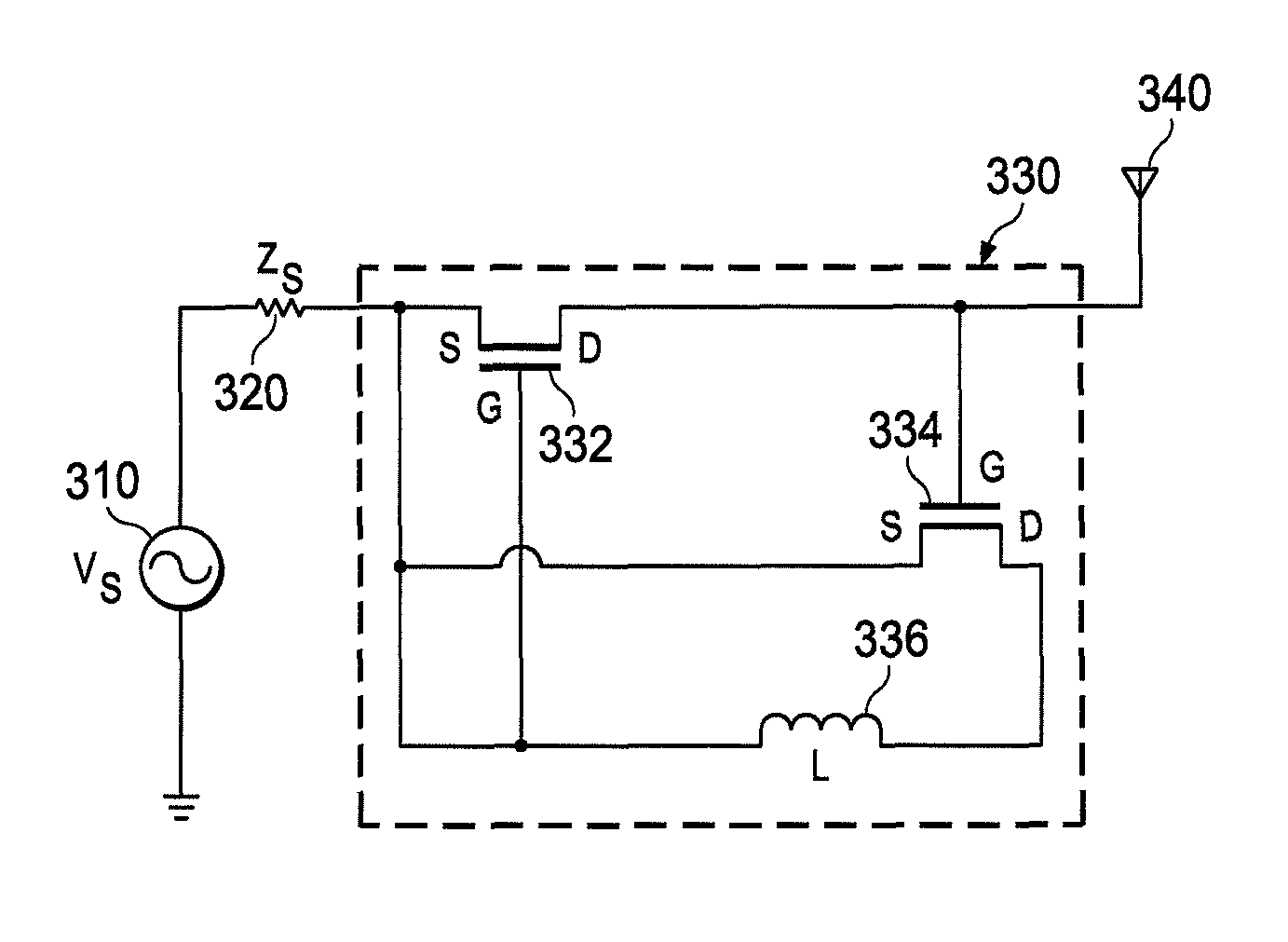
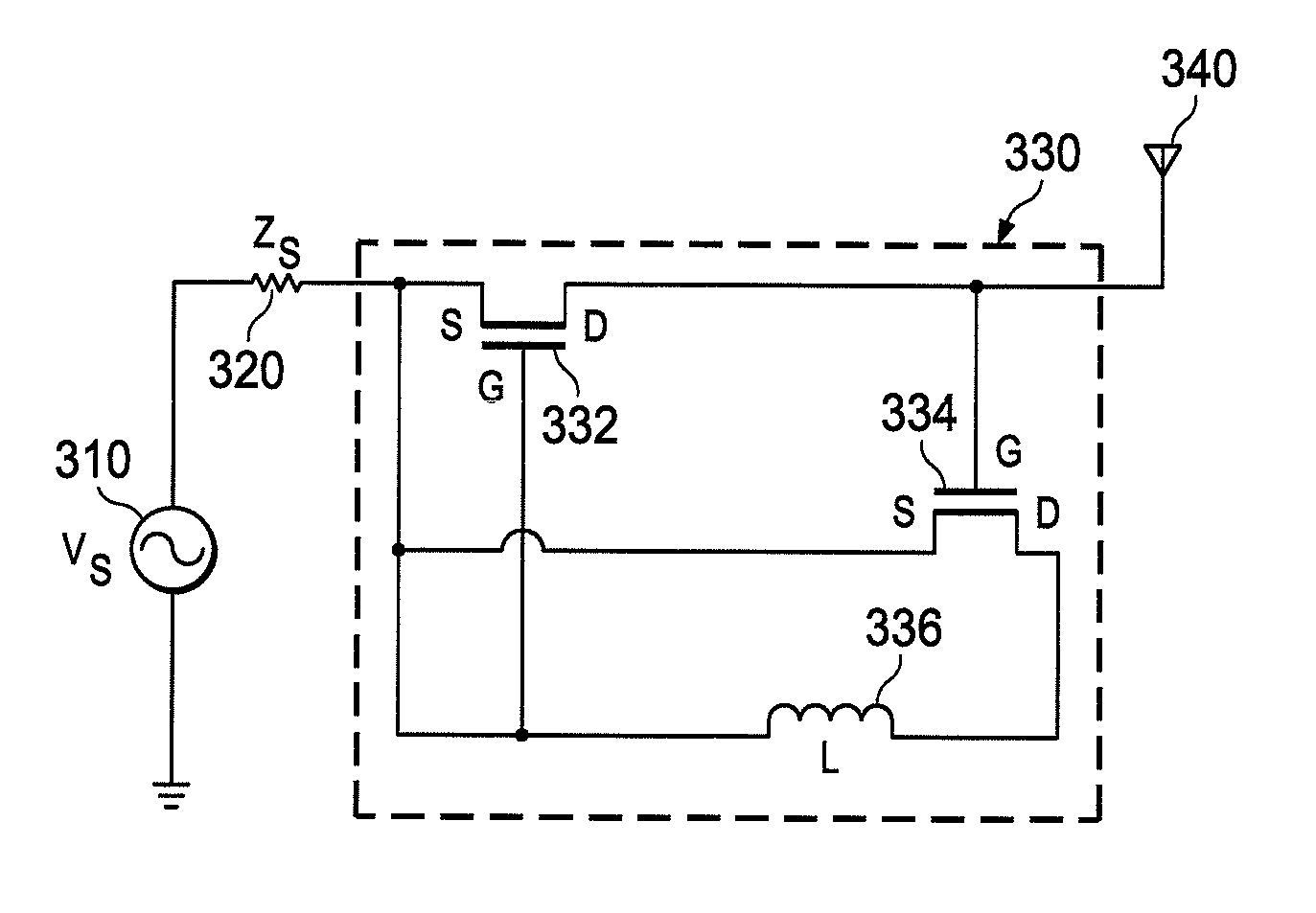
Linearized negative impedance converter matching circuits and impedance adjustment circuit for a negative impedance converter
InactiveUS20180123567A1Impedence matching networksImpedence convertorsNegative impedance converterElectrical impedance
There is disclosed a negative impedance converter for a matching circuit for matching an impedance of an antenna to an impedance of an RF source or load. The negative impedance converter comprises first and second transistors connected in a cross-over configuration. Each transistor has a source or emitter, a drain or collector and a gate or base, and each transistor further has a first biasing circuit connected to its gate or base. The first biasing circuit comprises a first DC biasing signal source and a first diode or a third transistor connected between the first DC biasing signal source and the gate or base. There is also disclosed a negative impedance converter for a matching circuit for matching an impedance of an antenna to an impedance of an RF source or load. The negative impedance converter comprises first and second transistors connected in a cross-over configuration, each transistor having a source or emitter, a drain or collector and a gate or base. The source or emitter of one transistor is configured as an RF input port and the source or emitter of the other transistor is configured as an RF output port. The drain or collector of the first transistor is connected to the gate or base of the second transistor and the drain or collector of the second transistor is connected to the gate or base of the first transistor. An impedance is connected between the drain or collector of the first transistor and the drain or collector of the second transistor. The negative impedance converter is further provided with a passive impedance adjustment network connected between the source or emitter of the first transistor and the source or emitter of the second transistor.
Owner:SMART ANTENNA TECH
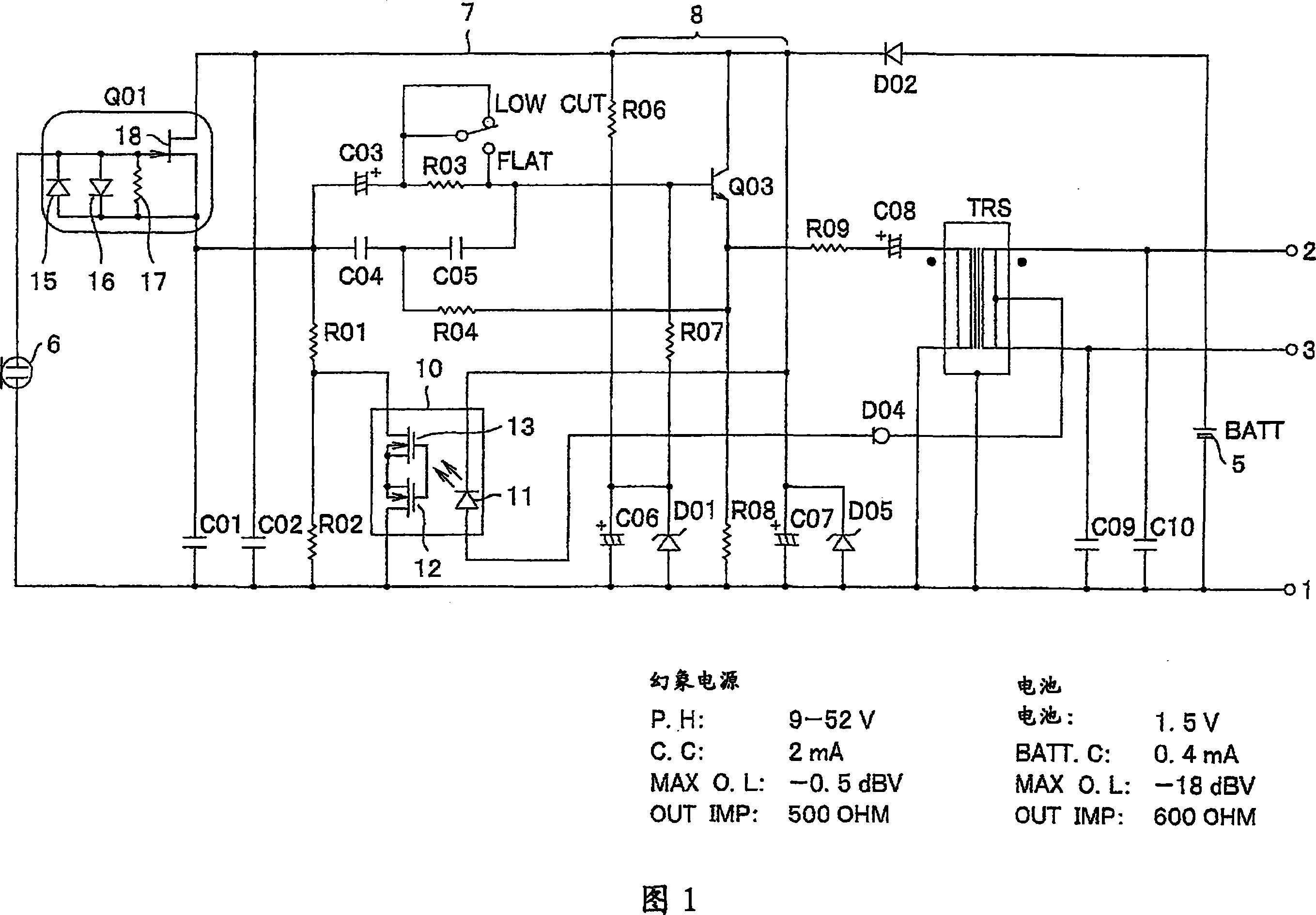
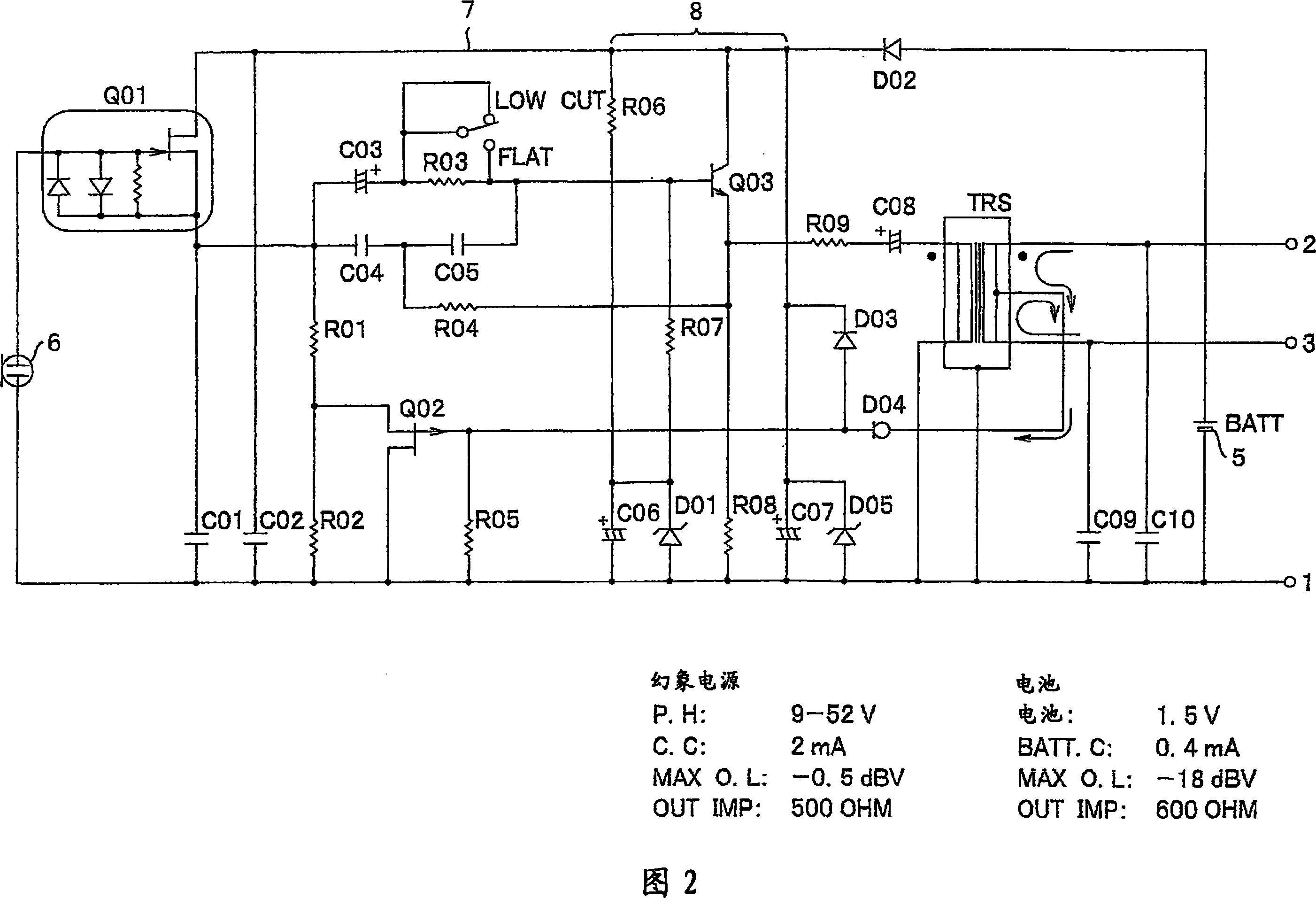
Condenser microphone circuit
InactiveCN101048015AElectrets selectrostatic transducerMouthpiece/microphone attachmentsCondenser microphoneTime of use
In a condenser microphone which selectively uses a phantom power supply and a built-in battery power supply, and which switches load resistance elements of an impedance converter corresponding to a selected power supply, a noise due to the high frequencies is prevented from occurring even if a cellular phone or the like is used in the vicinity. The condenser microphone includes: a condenser type electro-acoustic transducer element; an impedance converter that converts an output impedance of the electro-acoustic transducer element; load resistance elements of the impedance converter; a phantom power supply and a built-in battery power supply for operating the impedance converter; a switch that switches the values of the load resistance between at the time of using the phantom power supply and at the time of using the built-in battery power supply, wherein the switch is an optical switch that turns on / off optical coupling. The optical switch is switched so that the value of the load resistance is larger at the time of using the phantom power supply than at the time of using the built-in battery power supply.
Owner:AUDIO-TECHNICA
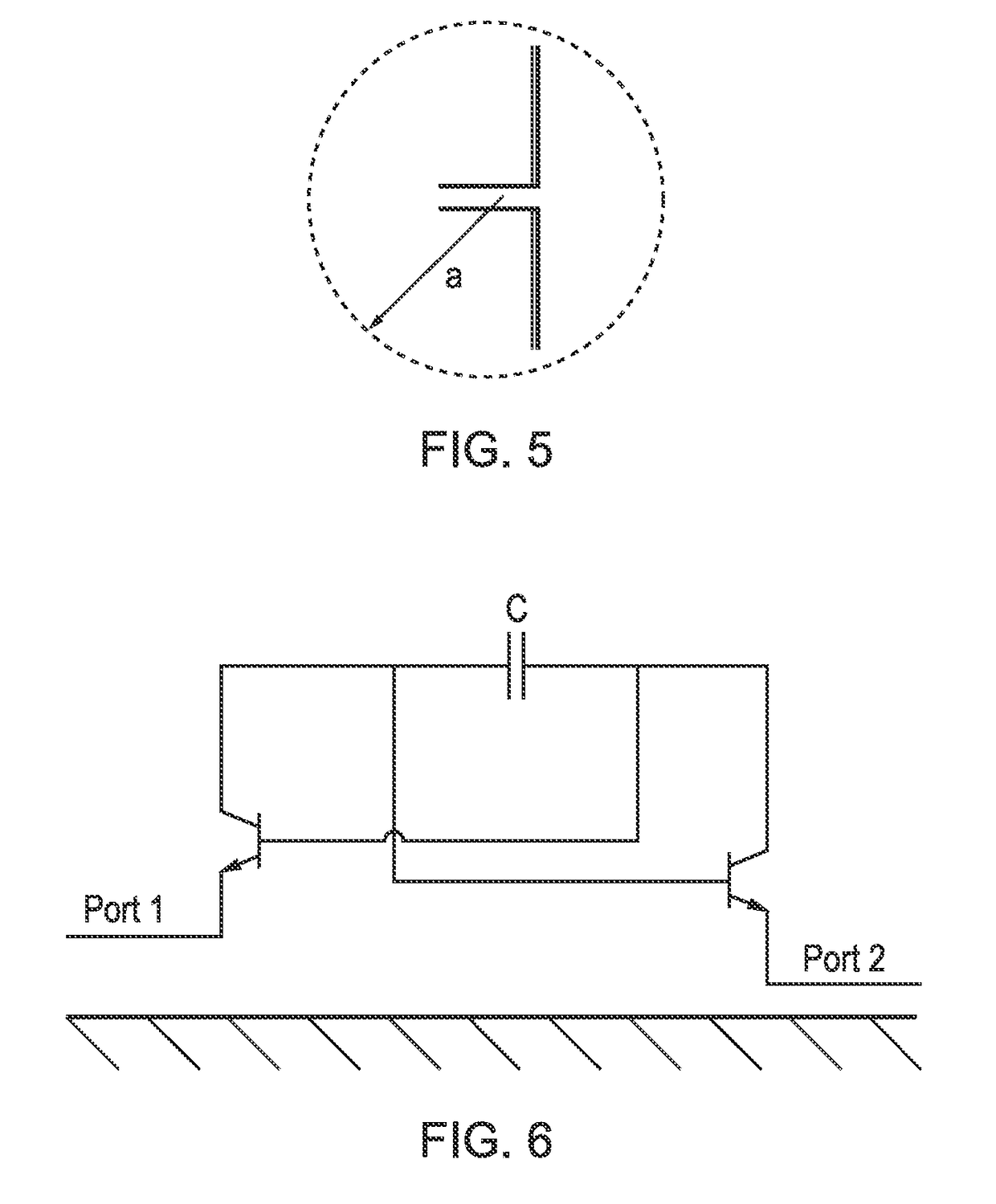
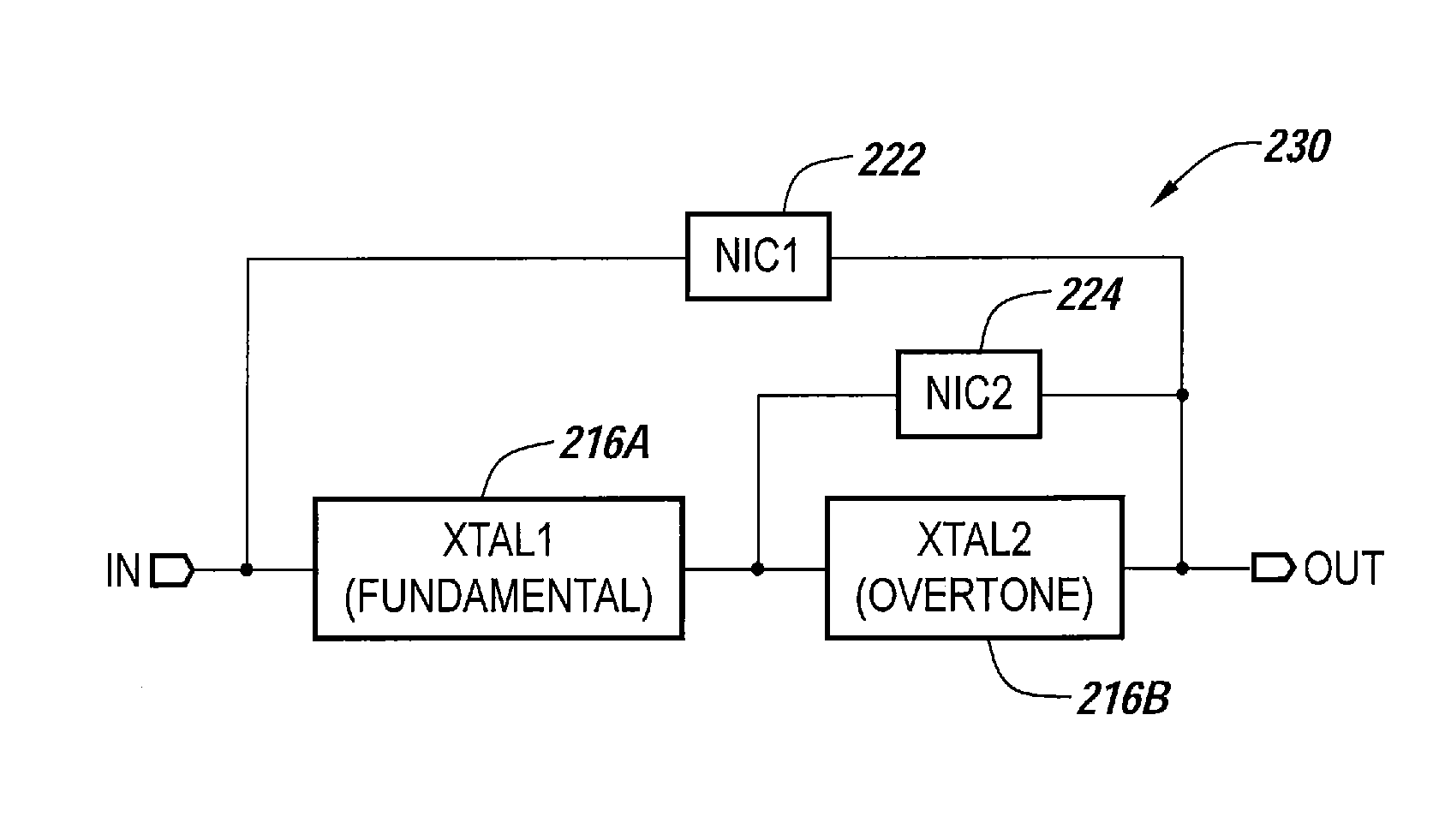
Monolithic composite resonator devices with reduced sensitivity to acceleration and vibration
An integrated circuit device includes a pair of serially-connected crystal resonators arranged as a first crystal resonator, which is configured to preferentially support a fundamental resonance mode in response to an input signal, and a second crystal resonator, which is configured to preferentially support a third or higher overtone resonance mode in response to a signal generated at an output terminal of the first crystal resonator. A negative impedance converter (NIC) is also provided, which has an input terminal electrically connected to an input terminal of the first crystal resonator and an output terminal electrically connected to one of the output terminal of the first crystal resonator and the output terminal of the second crystal resonator. The NIC may be a CMOS-based NIC that is devoid of inductive reactance from a passive inductor.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Active electromagnetic interference filter circuit for suppressing a line conducted interference signal
InactiveCN101010874AMultiple-port networksImpedence convertorsElectromagnetic interferenceConducted Interference
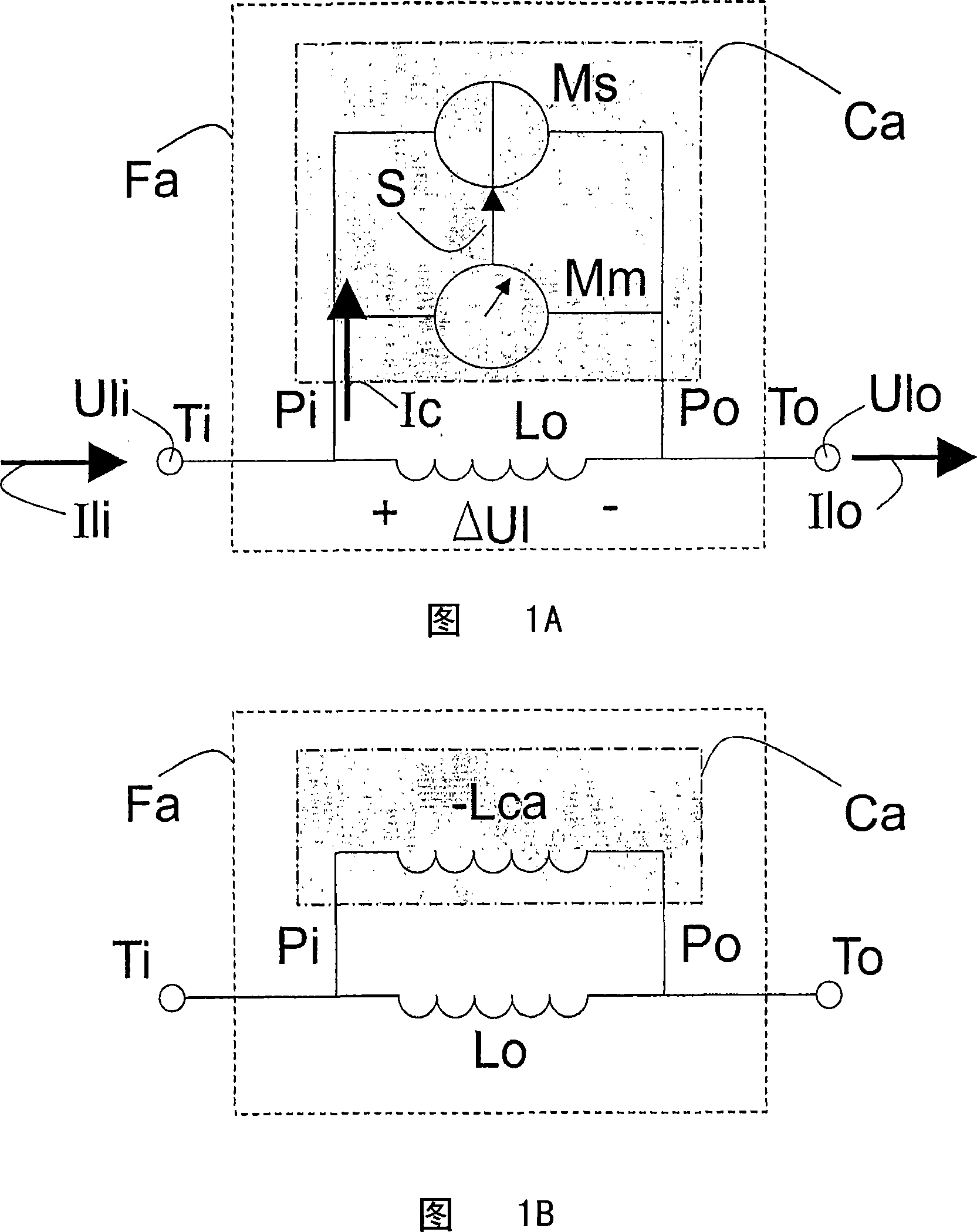
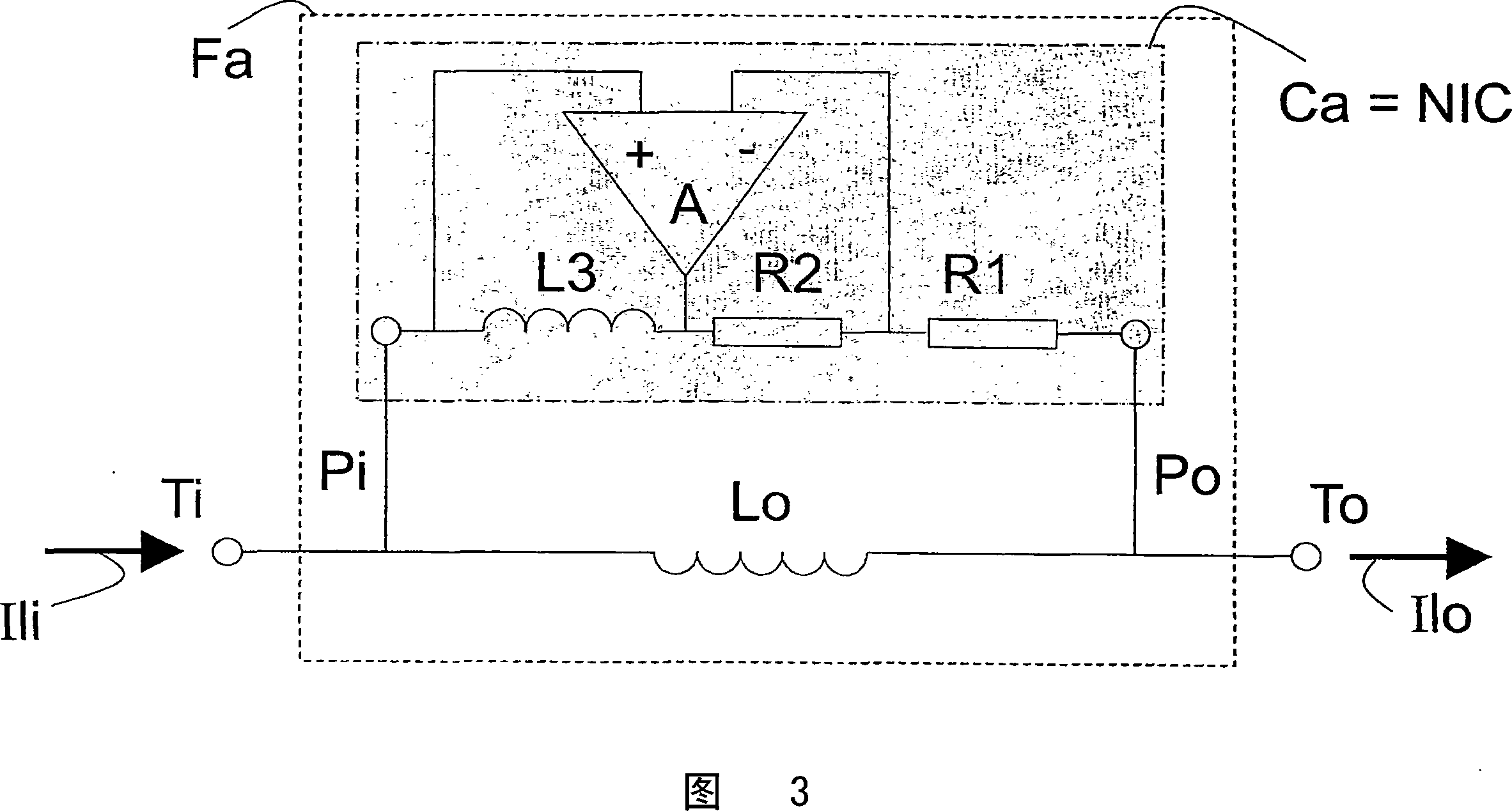
The invention relates to an Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) filter circuit (Fa) for suppressing a Line Conducted Interference (LCI) signal. The EMI filter circuit (Fa) comprises a filter inductance (Lo) to carry a supply current (Isup) between a supply voltage (Vsup) and a load (L). The EMI filter circuit (Fa) further comprises an active circuit (Ca), arranged in parallel with the filter inductance (Lo). The active circuit (Ca) comprises a sensing circuit (Mm) to sense the LCI signal and further comprises a suppressing circuit (Ms) to suppress the LCI signal. In an embodiment of the active EMI filter circuit (Fa), the active circuit (Ca) comprises a negative inductance generating circuit to create a negative inductance value. Selecting the negative inductance generating circuit to create an inductance value (Lca) larger than the inductance value of the filter inductance (Lo) creates a resulting inductance (Lr) which is higher compared to the inductance value of the filter inductance (Lo). In one embodiment, the negative inductance generating circuit comprises a negative impedance converter.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Methods and apparatus for a continuous time linear equalizer
ActiveUS20190305810A1High gainReduce area sizeTransmission control/equlisationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksNegative impedance converterPeak value
Various embodiments of the present technology comprise a method and apparatus for a continuous time linear equalizer (CTLE). In various embodiments, the CTLE comprises a cross-coupled transistor pair that operates as a negative impedance converter. The CTLE produces a transfer function that provides high gain peaking at a high frequency without increasing the size of the die area and / or the power supply level.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Coaxial high-power low-pass filtering-impedance converter
InactiveCN101056094ALow pass amplitude - good frequency characteristicsInhibition secondaryImpedence convertorsElectrical conductorImpedance Converter
The present invention relates to a coaxial big-power low-pass filtering- impedance converter which is characterized in that: the device has a coaxial structure formed by the inner and outer conductor and the insulated supporting plate, and the inner and outer conductor and the medium between then form the high and low impedance transmitting line; the high and low impedance transmitting lines are arranged at intervals, and the an insulated supporting plate is positioned between the inner and outer conductor of the low impedance transmitting line; the adjacent conductors are connected by screws. The advantages of the present invention reside in: a wider working frequency band and a bandwidth>=30% are provided; the device has a performance of lowpass amplitude-frequency and the secondary or more harmonic wave can be restrained effectively in the system; the output lowpass wave of the transmitter can be saved by using the device in the present invention to replace the impedance convertor in the multiway synthesizer and the inserted consumption of the RF output system is reduced, thus, the output system of the transmitter RF is simplified and the cost is also reduced.
Owner:鞍山同方吉兆广播电视设备有限公司
Segmented linear magnetic control memristor simulating equivalent circuit
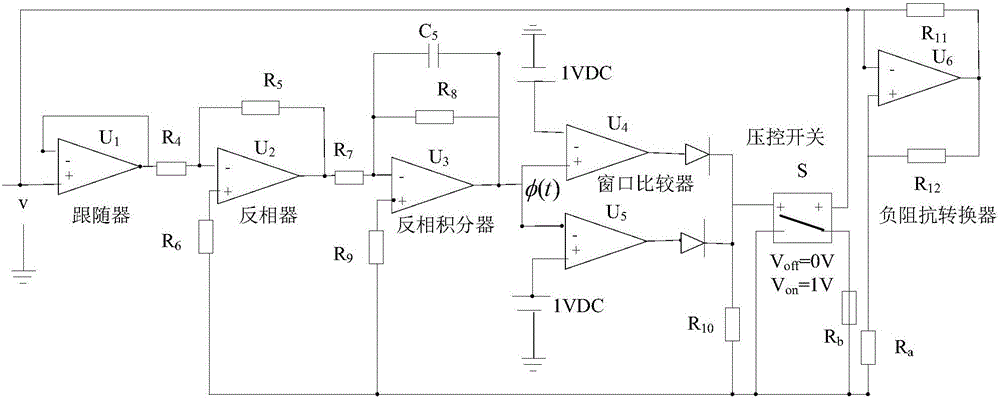
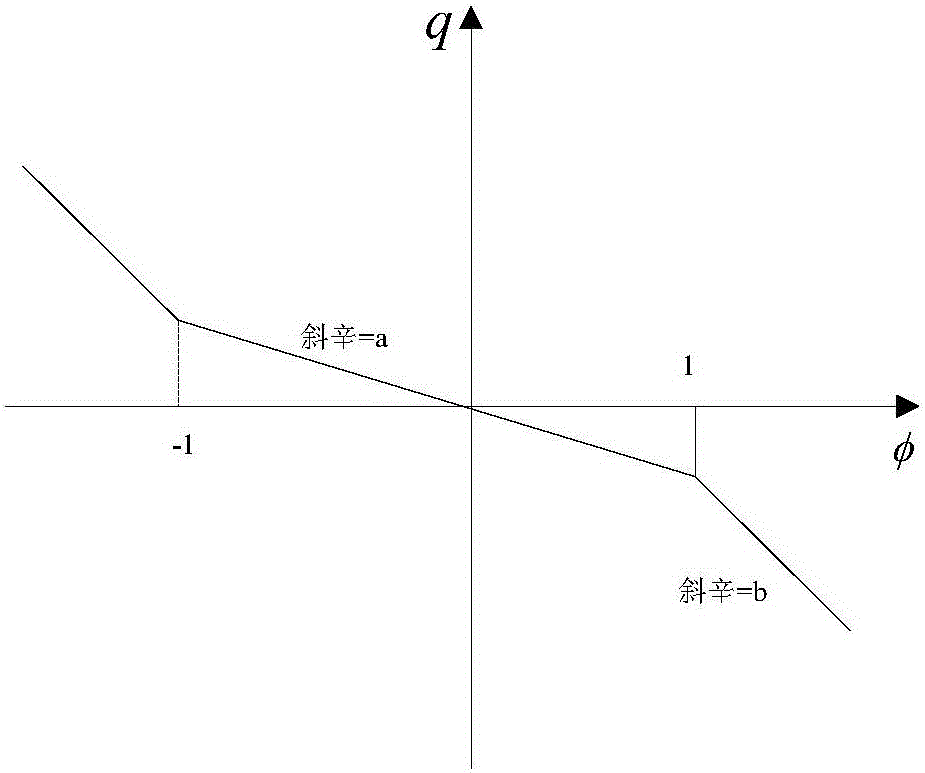
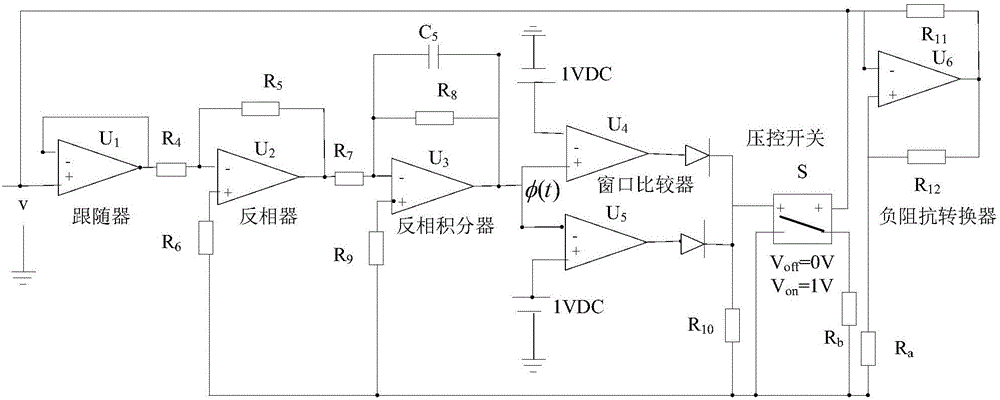
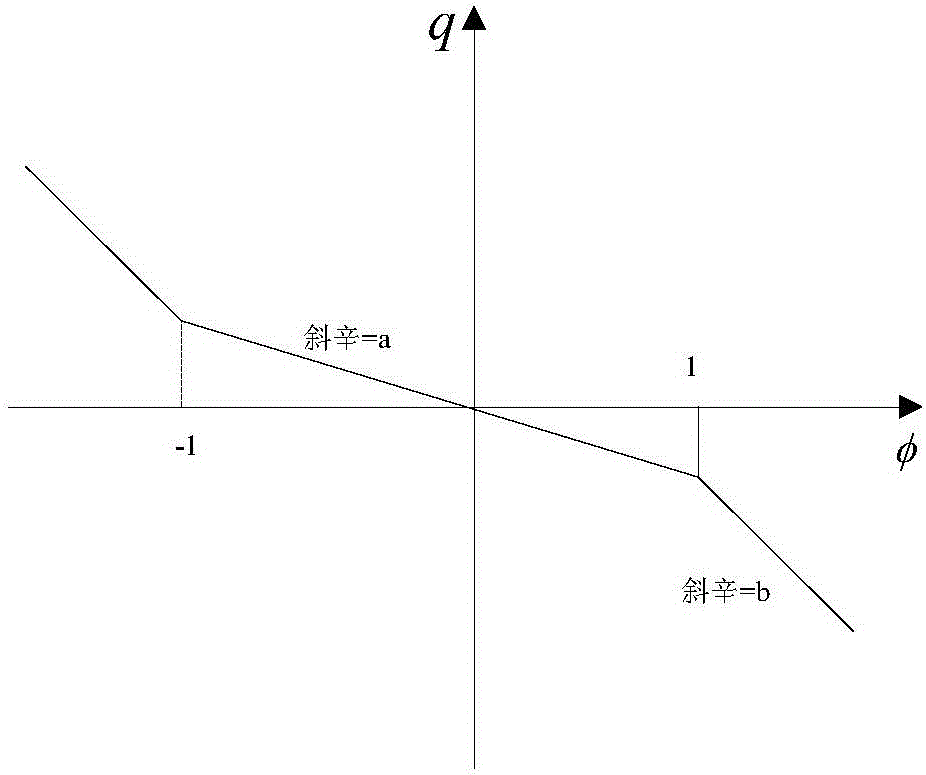
The invention discloses a segmented linear magnetic control memristor simulating equivalent circuit. The circuit comprises a follower, a phase inverter, a phase-reversing integrator, a window comparator, a voltage control switch S and a negative impedance converter and the above parts are connected in series. The follower is an operational amplifier U1 and is mainly used for isolation. The phase inverter is an operational amplifier U2. The phase-reversing integrator is an operational amplifier U3 and realizes integration of memristor port voltages. Output v3out of the operational amplifier U3 is corresponding to an inner state control variate phi (t) of a memristor. The window comparator comprises an operational amplifier U4 and an operational amplifier U5. An output level of the window comparator controls switching of the voltage control switch S. An operational amplifier U6 and a peripheral resistor form the negative impedance converter. When v3out is less than or equal to 1, the window comparator outputs a low electrical level, the voltage control switch S is switched off and conductance of the memristor is -1 / Ra, and when v3out is greater than 1, the window comparator outputs a high electrical level, the voltage control switch S is switched on and conductance of the memristor is (-1 / Ra+1 / Rb). The circuit has the characteristics of simple line and good effects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
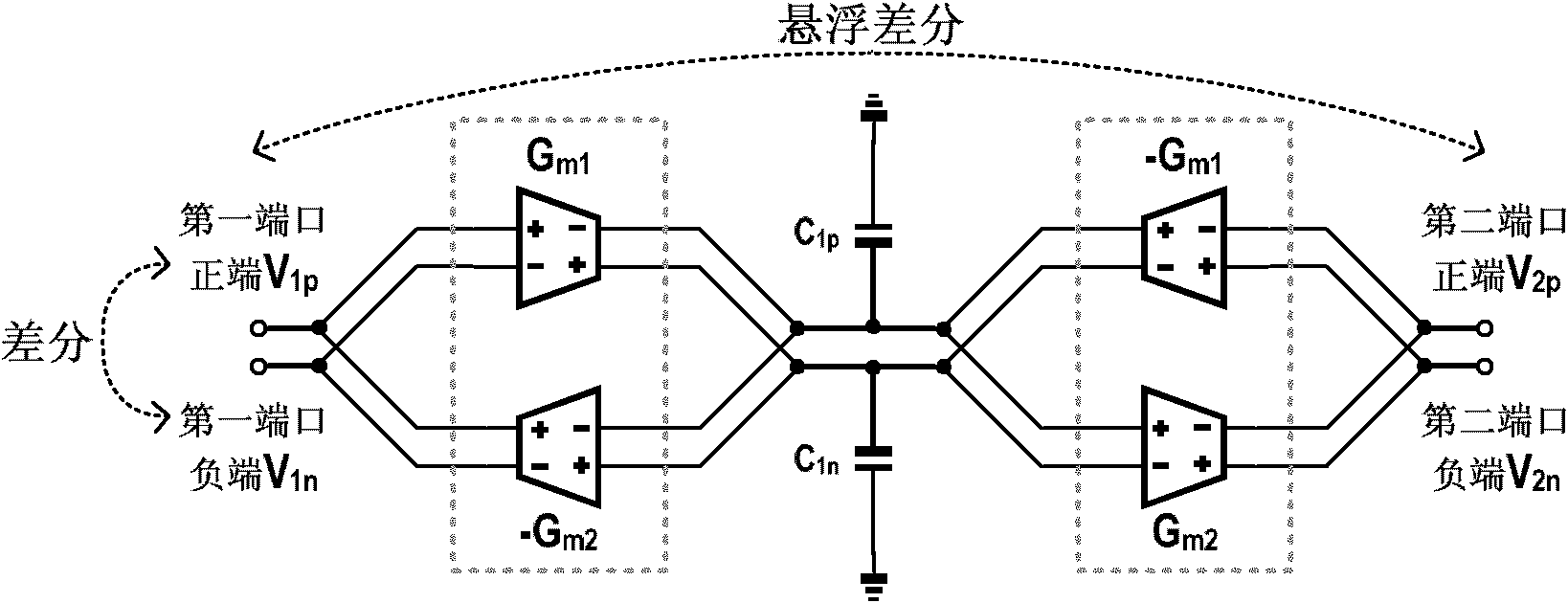
Suspension difference active inducer based on positive feedback
InactiveCN102111123ASimple structureSimple change designFrequency selective two-port networksCapacitanceTransconductance
The invention relates to a suspension difference active inducer based on positive feedback, belonging to the technical field of active inducer design, comprising a difference impedance converter, a positive transconductance stabilizer and a negative transconductance canceller, wherein the difference impedance converter comprises two pairs of difference impedance converters composed of two pairs of interconnected PMOS (positive channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor) transistors based on the positive feedback and two capacitors, wherein the two capacitors are converted into the suspension difference active inducers by the two pairs of difference impedance converters; the positive transconductance stabilize comprises two PMOS transistors for compensating the negative impedance of the impedance converters and solving the stability problem of the active inducer; and the negative transconductance canceller comprises two pairs of interconnected PMOS transistors for canceling the parallel impedance of the active inducer. The suspension difference active inducer uses the current multiplexing technology and only comprises the PMPS transistors, so the structure is symmetrical and simple; and thevariation of the high-low quality factor (Q) is simple. The inducer provided by the invention is used for replacing the suspension difference inactive inducer, and specifically for designing the active filter by an induction replacing method.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Electrical amplifier
ActiveUS20210184639A1Relatively large bandwidthReduced stabilityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationConvertersImpedance Converter
An exemplary embodiment of the invention relates to an electrical amplifier comprising a differential preamplifier having a first output port and a second output port; and a downstream amplifier stage having a first output unit and a second output unit; wherein the first output unit is connected to the first output port of the differential preamplifier and the second output unit is connected to the second output port of the differential preamplifier; and wherein a negative impedance converter is electrically located in at least one of said differential preamplifier and said downstream amplifier stage.
Owner:SICOYA GMBH
Capacitor microphone and impedance converter therefor
ActiveUS20100272291A1Stable currentAvoid noiseTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsDeaf-aid setsImpedance ConverterNegative impedance converter
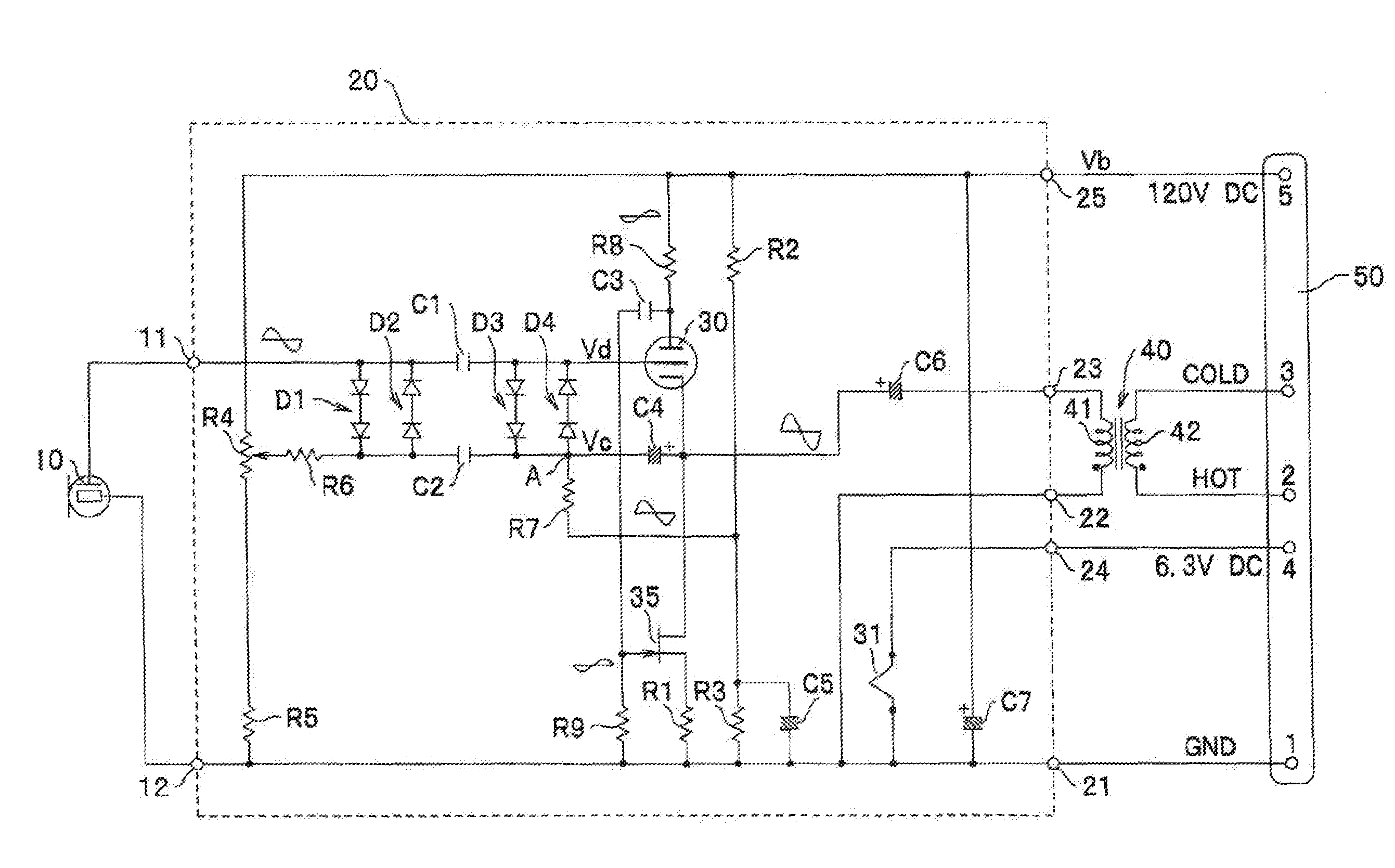
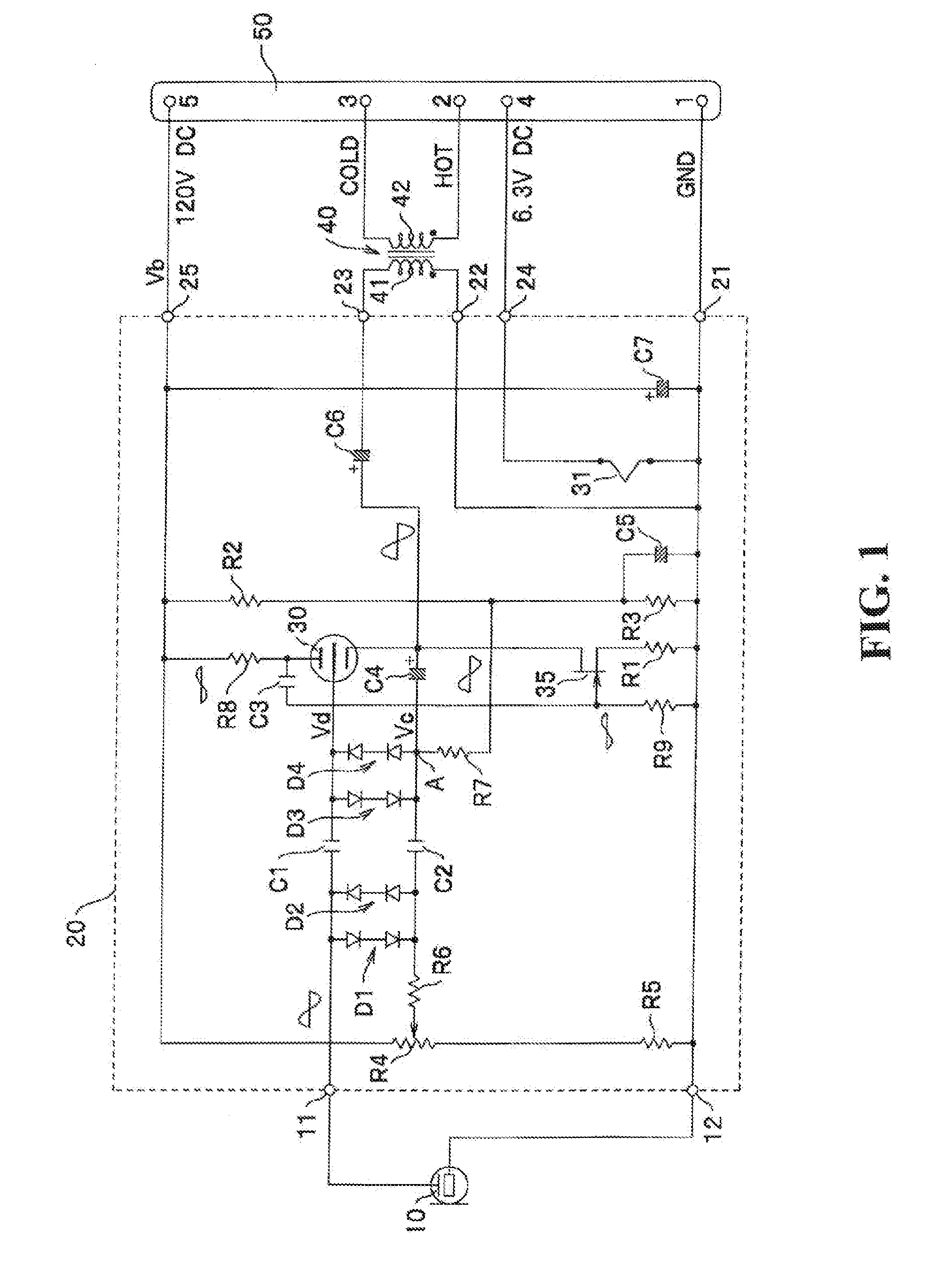
An impedance converter for a capacitor microphone includes: a vacuum tube that receives an output signal from a capacitor microphone unit through a grid and with which the signal is output as an output from a cathode follower; an FET in cascade connection with the vacuum tube and that defines a current flowing in the vacuum tube; and a bias circuit that applies a bias voltage to the grid of the vacuum tube. The bias circuit includes: a first diode and a second diode that apply the bias voltage to the grid of the vacuum tube; the first diode and the second diode being connected in inverse parallel; and a bias resistor for applying the bias voltage at a constant level to the grid of the vacuum tube via the first diode or the second diode.
Owner:AUDIO-TECHNICA
Chaotic circuit based on Wien bridge oscillator and piecewise linear memristor
InactiveCN106027223AImprove robustnessSecuring communication by chaotic signalsCapacitanceConverters
The invention discloses a chaotic circuit based on a Wien bridge oscillator and a piecewise linear memristor. The circuit is composed of the Wien bridge oscillator and the piecewise linear memristor M. The Wien bridge oscillator is composed of an operational amplifier, peripheral elements and a phase-shift network. The memristor M is an analog equivalent circuit of the piecewise linear memristor and is composed of a follower, a phase inverter, an inverting integrator, a window comparer, a voltage-controlled switch and a negative impedance converter which are connected in series. The Wien bridge oscillator forms an oscillating circuit. The phase-shift network is composed of a linear resistor and a linear capacitor. The memristor M acts in a non-linear device which enables the voltage or current in the circuit to generate sudden change; under the non-linear effect of the memristor, the circuit enters chaos and hyperchaos states from period doubling bifurcation. The circuit is simple in circuit and good in effect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Condenser microphone and its impedance converter
An condenser microphone is provided herein having an impedance converter directly coupled to the transducer of the condenser microphone. The impedance converter includes an active element for impedance conversion and a control circuit for filtering an AF output signal outputted from the active element in order to retrieve a bias direct voltage as a set value, the bias direct voltage being supplied to the other terminal of the bias resistor. A coupling capacitor between the condenser transducer and the active element is eliminated so that a bias resistor acting as a source of noise can be eliminated as well and the remaining bias resistor can be increased.
Owner:GUANGDONG TAKSTAR ELECTRONIC CO LTD
Active emc filter for machine tools
An active EMC filter for machine tools allows reducing the leakage current normally induced by large phase-to-ground capacitances. The filter may comprise an active shunt module or an impedance converter or a correction signal generator and is suitable both for three-phase and single-phase applications.
Owner:SCHAFFNER EMV
Negative N square impedance converter
InactiveCN106160698AImprove performanceIncrease useImpedence convertorsElectrical resistance and conductanceAudio power amplifier
The invention provides a negative N square impedance converter. The negative N square impedance converter comprises multiple operational amplifiers and multiple resistors. Each operational amplifier is matched with two resistors so that multiple current control current sources are formed or multiple voltage control voltage sources are formed or the current control current sources and the voltage control voltage sources of the same number are formed. The current control current sources and the voltage control voltage sources realize the negative N square impedance converter through cascading. The negative N square impedance converter is suitable for a DC circuit and also suitable for a sinusoidal current circuit so that the higher level of negative impedance conversion can be realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Compensation method for electric small antenna by operational amplifier
The invention discloses a compensation method for an electric small antenna by an operational amplifier. A negative impedance conversion circuit which consists of the operational amplifier is adoptedfor performing dispersion compensation on the electric small antenna; the negative impedance conversion circuit is connected to the electric small antenna in parallel; in the negative impedance conversion circuit, the positive input end of the operational amplifier U1 is connected to the self output end through a resistor R1; the reverse input end of the operational amplifier U1 is connected to the self output end through a resistor R2; and the reverse input end of the operational amplifier U1 is connected with one end of an inductor L while the other end of the inductor L and the positive input end of the operational amplifier U1 are used as the output two ends of the negative impedance conversion circuit. By virtue of the compensation method, broadband matching of the electric small antenna at high frequency is realized, and bandwidth broadening is realized; and dispersion compensation can be performed on an electric small antenna equal-altitude reactance device, so that the shortcoming that relatively high working frequency cannot be obtained in broadband matching of the conventional negative impedance conversion circuit is overcome.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
OP-AMP Sharing Technique to Remove Memory Effect in Pipelined Circuit
ActiveUS20140097897A1Cancellation effectAnalogue/digital conversionDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierMemory effect
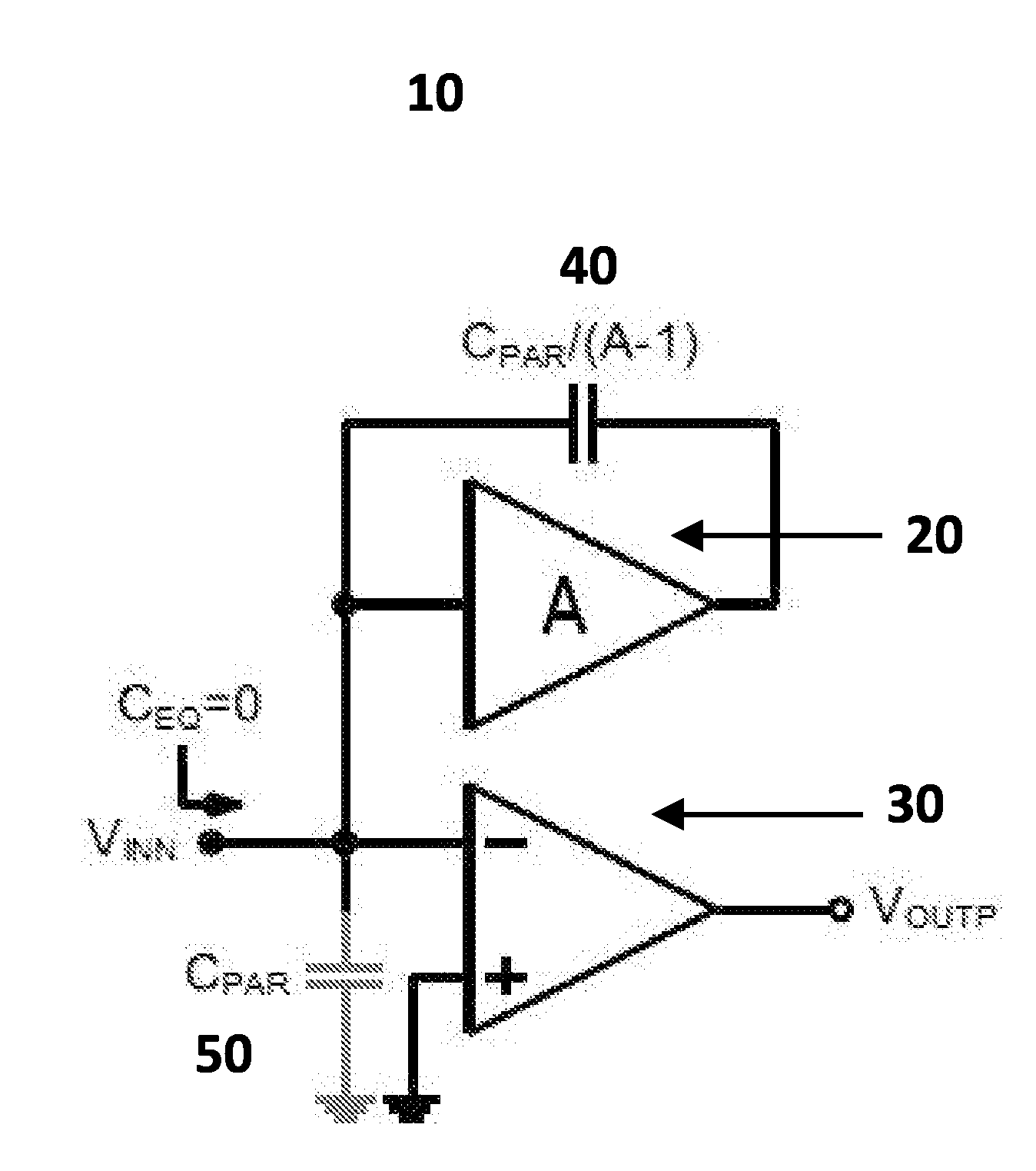
This document describes a new op-amp sharing technique for pipeline ADC without memory effect. The key features of this technique are: the usage of negative impedance converter and scaled replica of the op-amp input device to achieve zero error voltage, which in turns achieve low power dissipation due to the removal of the tradeoff between op-amp sharing and memory effect. With this technique much lower operation of pipeline ADC can be achieved for applications of data communications and image signal processing.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Electric energy quality regulator and control method
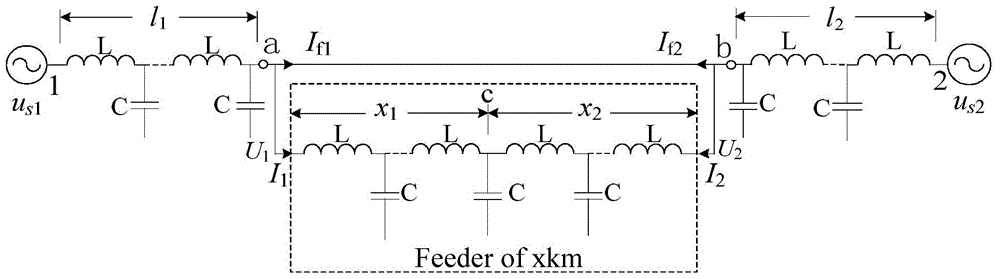
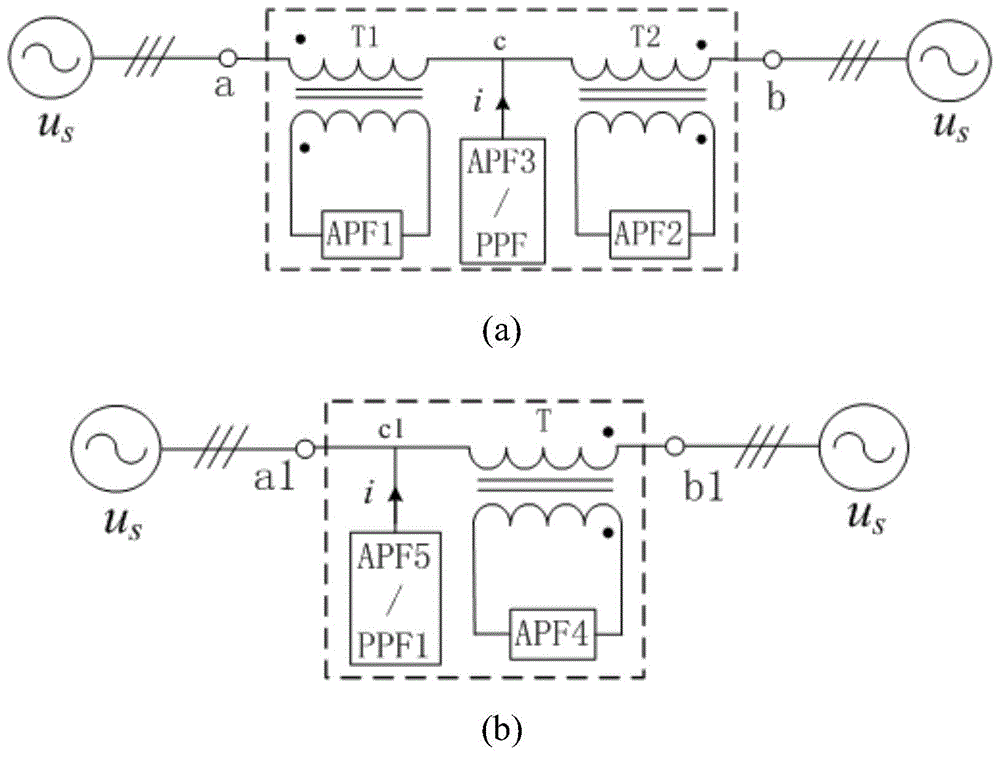
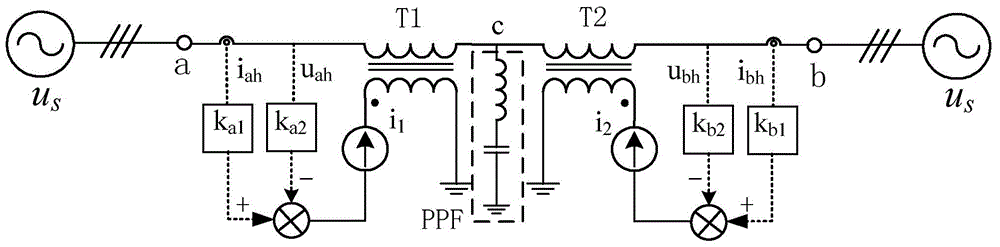
ActiveCN104009476AGrowth inhibitionReduce or even eliminate reflected wavesActive power filteringHarmonic reduction arrangementPower qualityElectricity
The invention discloses an electric energy quality regulator and a control method. The regulator is formed by active power filters connected in series, active power filters or passive power filters connected in parallel and transformers and can be formed in two manners of a double-transformer type impedance converter and a single-transformer type impedance converter. The impedance converter can be mounted at any position of an annular power grid, electric parameters of the power grid at the output end of the impedance converter are detected, and directive currents of phases a, phases b and phases c of all the active power filters are obtained according to the electric parameters; then subtraction is carried out on the directive currents and practical output currents of the active power filters, PI control is conducted on the difference value of the directive currents and the practical output currents, then PWM is carried out on the difference value, driving signals of the active power filters are obtained accordingly, and the converter is controlled according to the driving signals. The regulator has the advantages of avoiding harmonic oscillation, effectively suppressing harmonic amplification at each time and the like.
Owner:秦皇岛信能能源设备有限公司
Active emc filter for medical applications
An active EMC filter for medical applications allows reducing the leakage current normally induced by large phase-to-ground capacitances. The filter may comprise an active shunt module or an impedance converter or a correction signal generator and is suitable both for three-phase and single-phase applications.
Owner:SCHAFFNER EMV
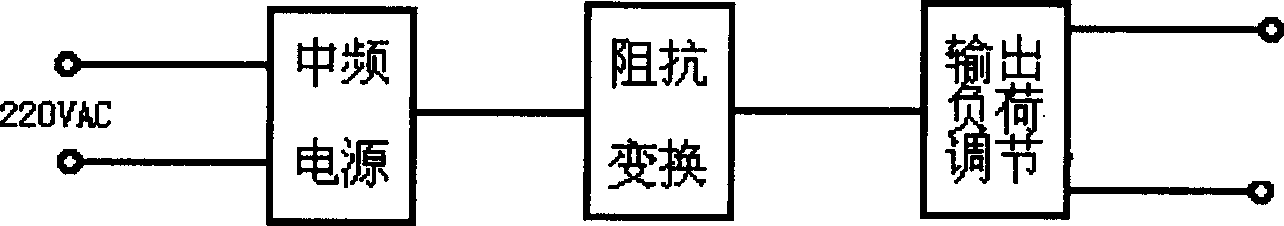
Failure tester for electric power cable
InactiveCN1123779CEasy to use on siteFault locationDetection using electromagnetic wavesPower cableIntermediate frequency
A failure test of electric power cable is composed of signal transmitter and signal receiver. Said signal transmitter consists of a MF power supply (220 V AC), impedance converter for converting 220 V at 800 Hz to 36V AC at 800 Hz, and load regulator for outputting. Said signal receiver is a low-frequency one. Its advantages include simple structure, convenient application, and small size.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
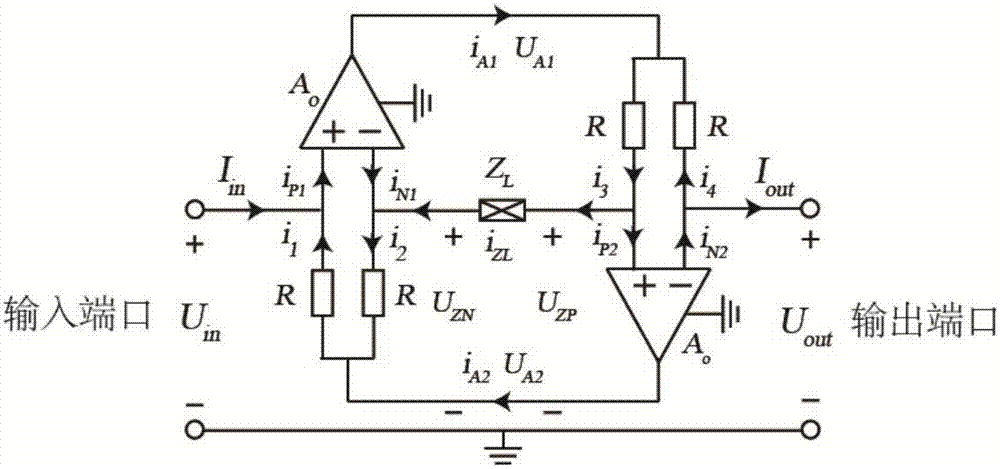
Series dual-port negative impedance converter for signal enveloping distortion compensation
ActiveCN107465398ATo overcome the shortcomings of only parallel connectionSmall sizeImpedence matching networksFrequency selective two-port networksTransceiverEngineering
The invention discloses a series dual-port negative impedance converter for signal enveloping distortion compensation. The converter is characterized in that the converter is based on improvements of a floating negative impedance converter with a differential structure; a three-port network structure is improved into a dual-port network structure, that is, a differential input anode is improved into an input port, a differential input cathode is improved into an output port, and an original differential output port is removed, so that the dual-port negative impedance converter with the series feature is achieved; and non-Foster features of a transmission coefficient of an overall circuit of the impedance converter are adjusted through resistors connected with anode input ports and cathode input ports of operational amplifiers and an impedor connected between the operational amplifiers, so that the enveloping dispersion compensation for square wave signals subjected to distortion by a high-pass filter can be achieved. The converter provided by the invention overcomes the defect that the traditional negative impedance converter can only be connected in parallel, has the characteristics of small size, high simplicity in structure, high adjustment precision and the like, and achieves circuit transmission coefficient adjustments and application prospects in dispersion compensation for circuits of a radio frequency transceiver and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com