Patents
Literature
46 results about "Phantom power" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
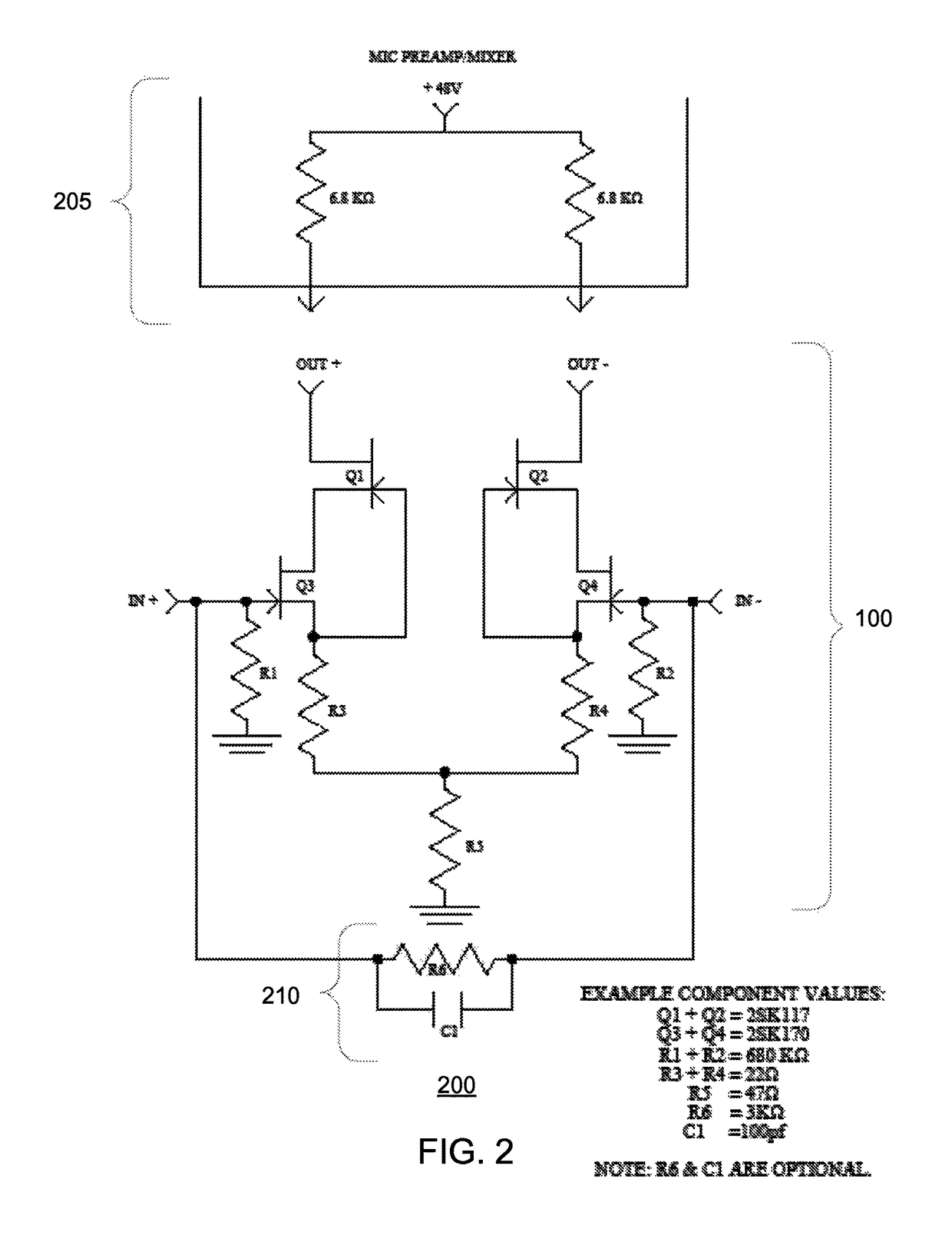
Phantom power, in the context of professional audio equipment, is DC electric power transmitted through microphone cables to operate microphones that contain active electronic circuitry. It is best known as a convenient power source for condenser microphones, though many active direct boxes also use it. The technique is also used in other applications where power supply and signal communication take place over the same wires.
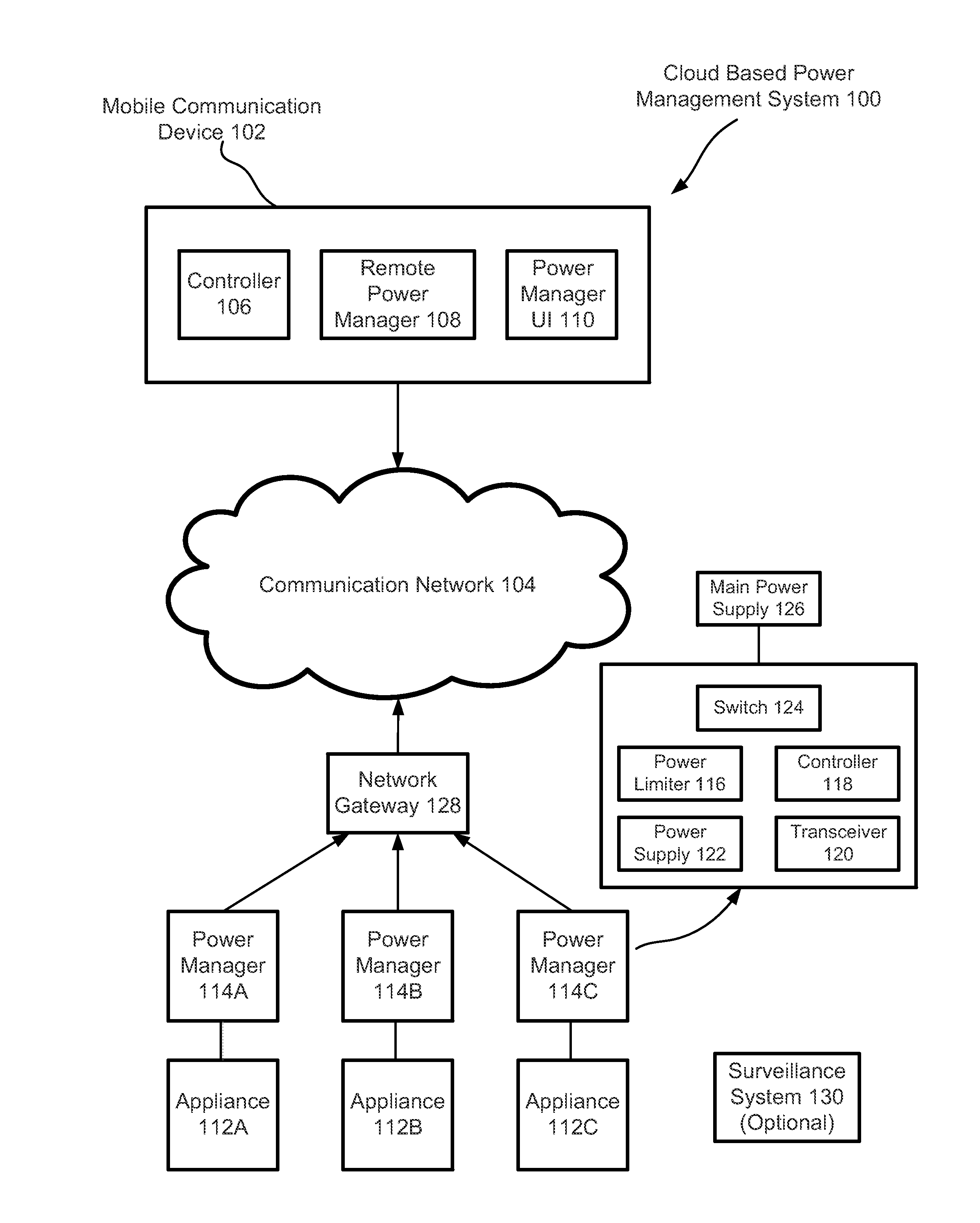
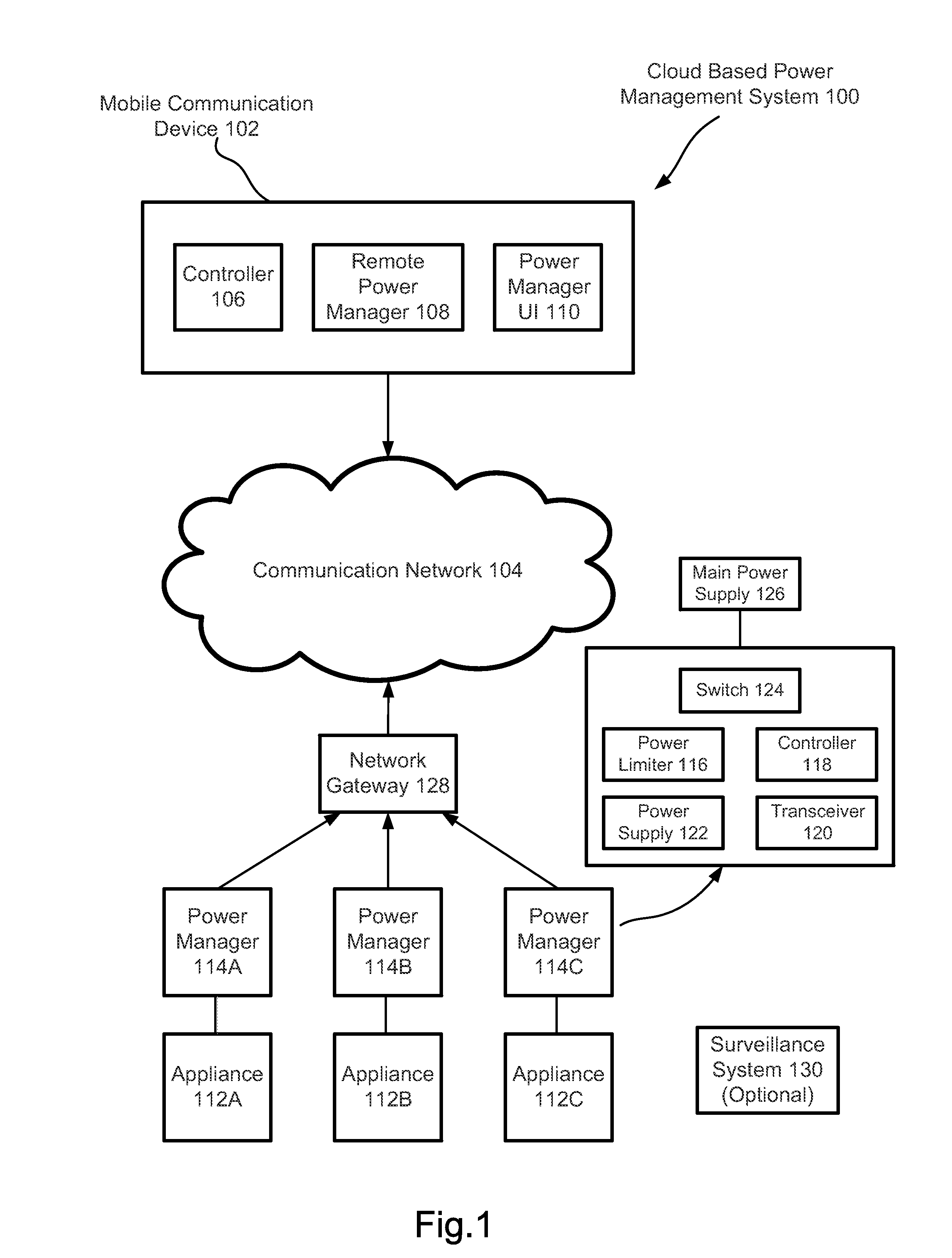
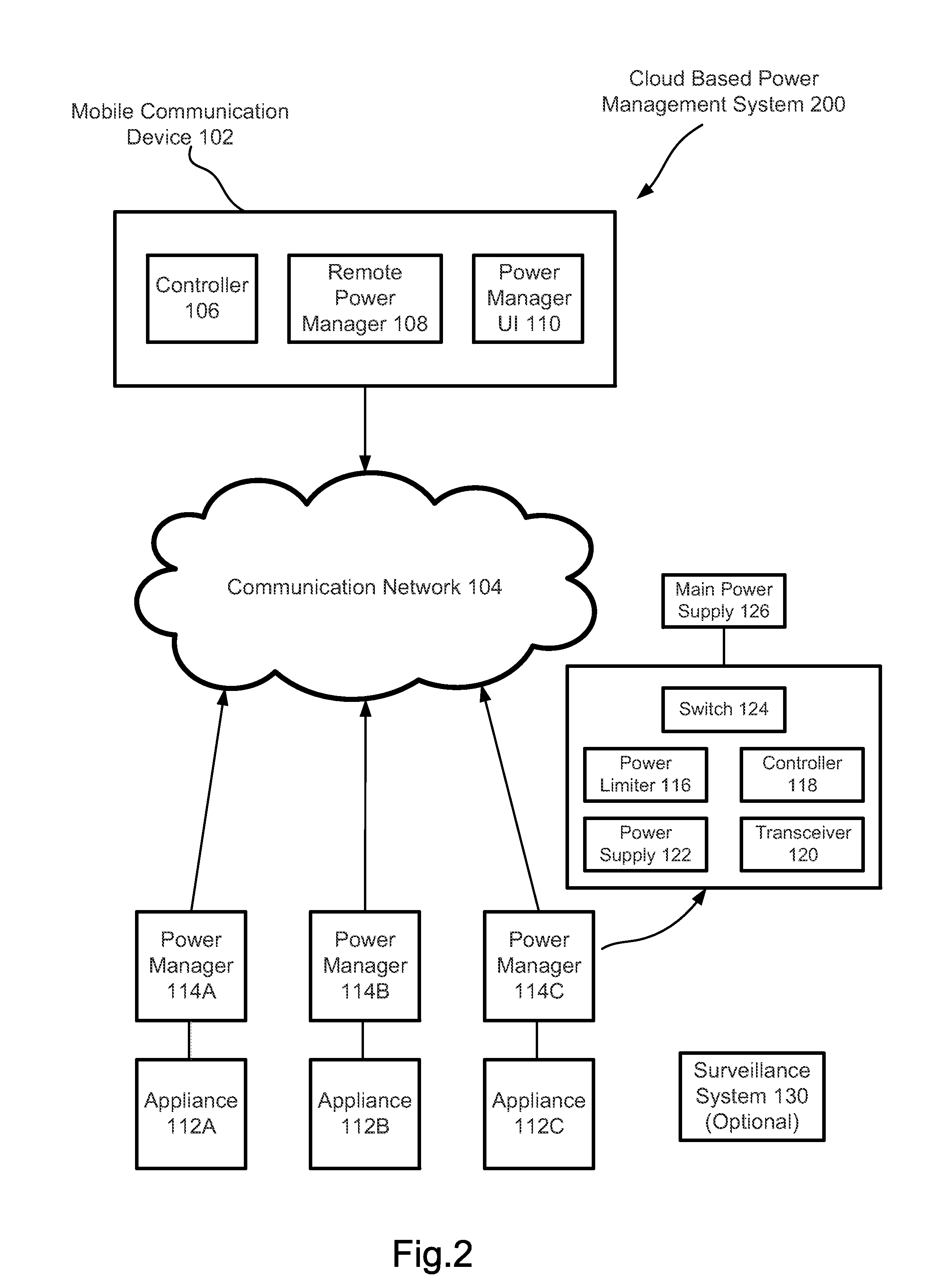
Cloud Based Power Management System
InactiveUS20150309521A1Eliminates phantom powerProgramme controlMechanical power/torque controlCloud basePhantom power
Cloud based power management system comprises a plurality of electrical appliances and a mobile communication device. Each of the electrical appliances is connected to a power manager connectable to the cloud. The power manager may limit the maximum power consumed by the appliance. The power manager may also eliminate phantom power consumed by the appliance. The power managers are controllable by the mobile communication device through the cloud.
Owner:PAN YANG
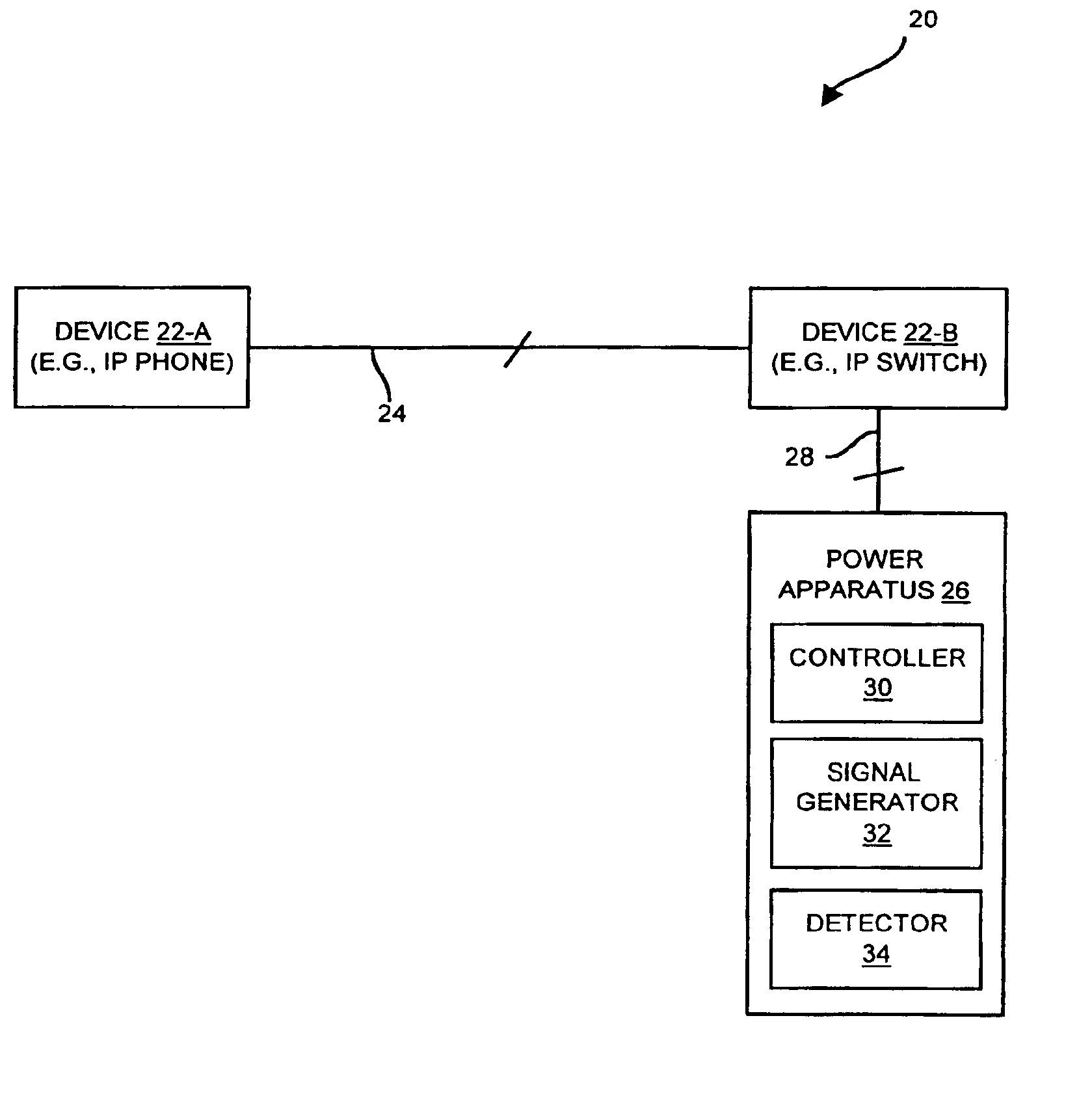
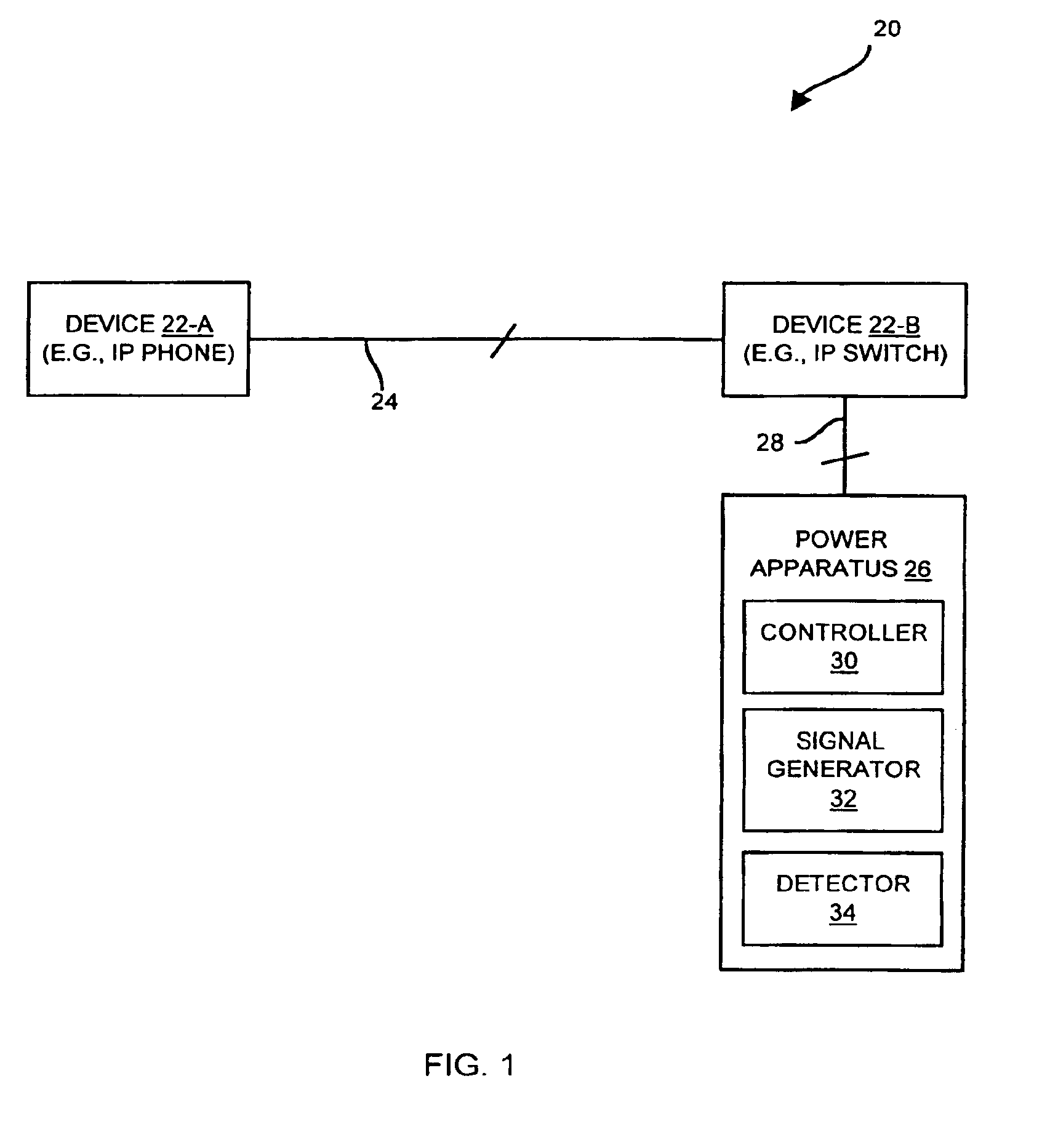
Remotely powerable device with powerability indicator for selectively indicating a backward wired device condition and a remotely powerable device condition
InactiveUS6874093B2Avoid damageElectric devicesVolume/mass flow measurementPhantom powerSignal generator
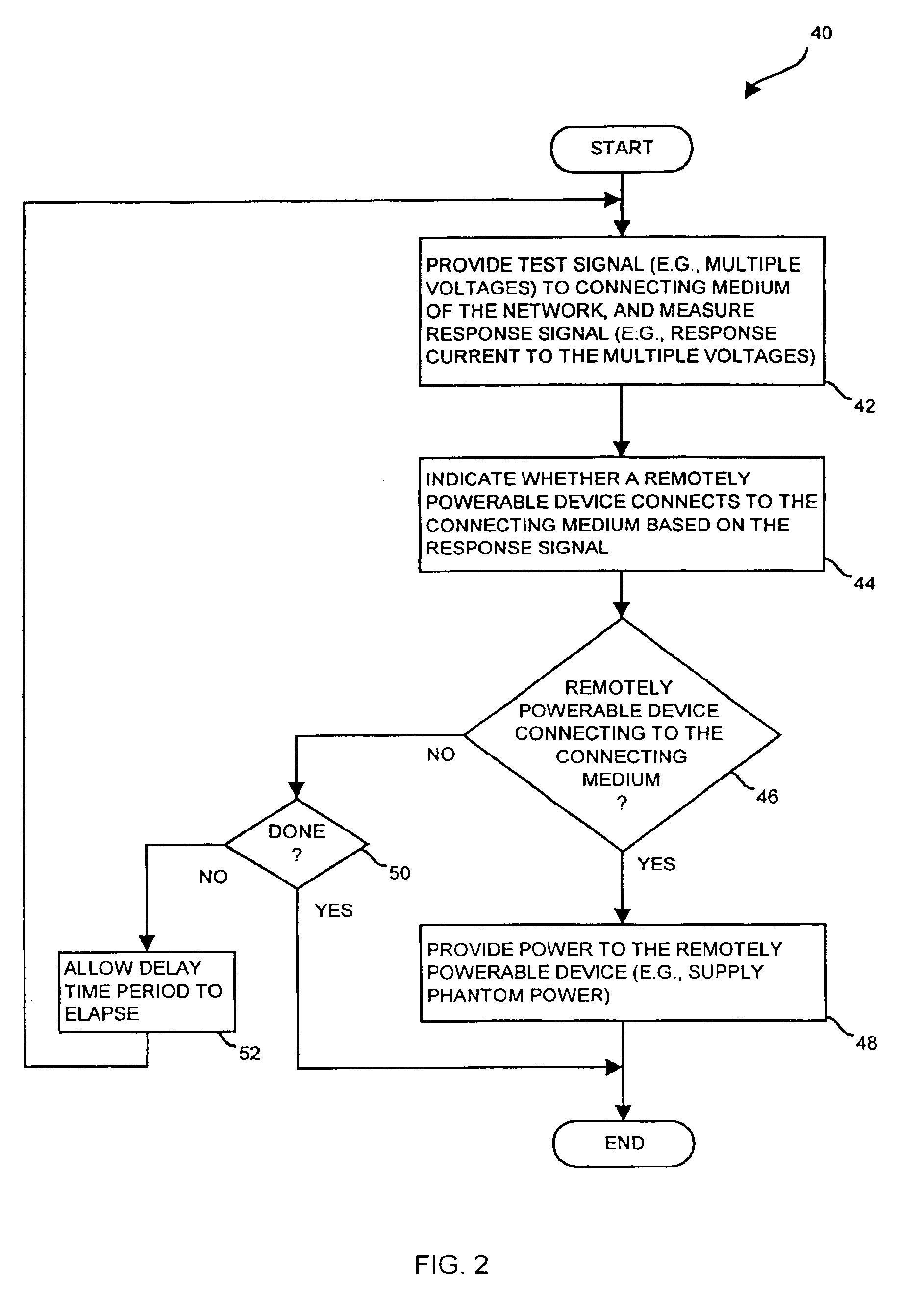
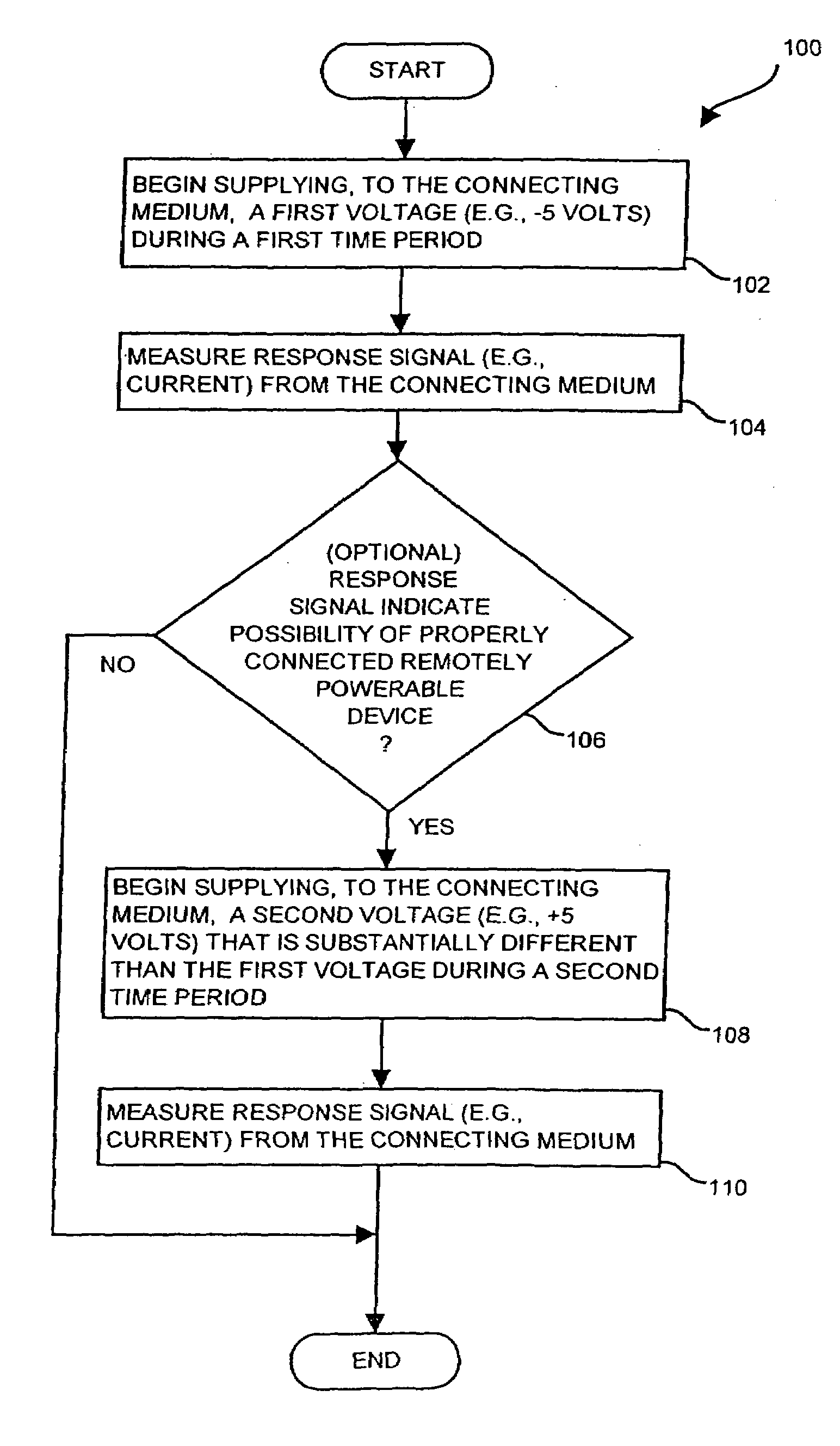
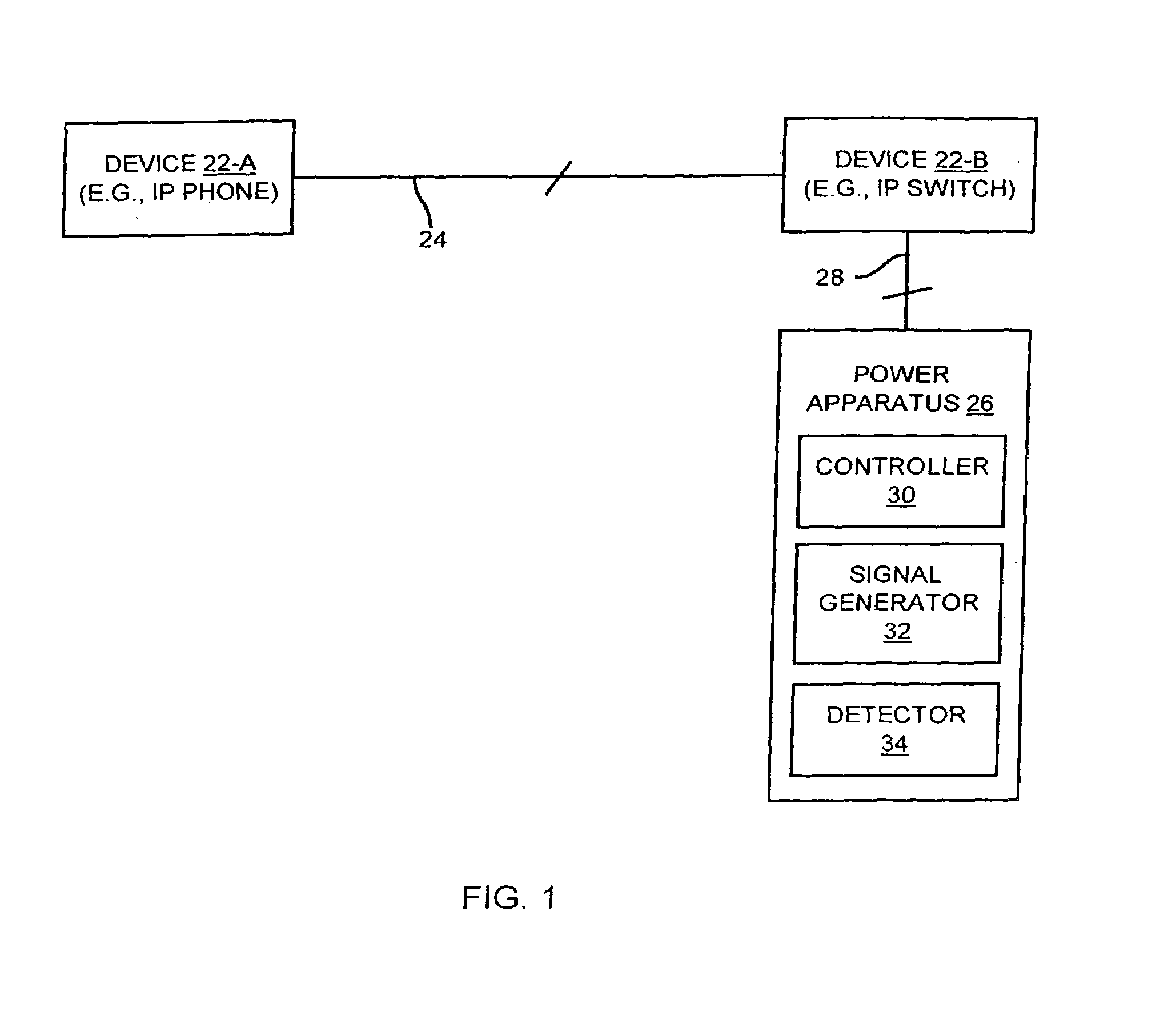
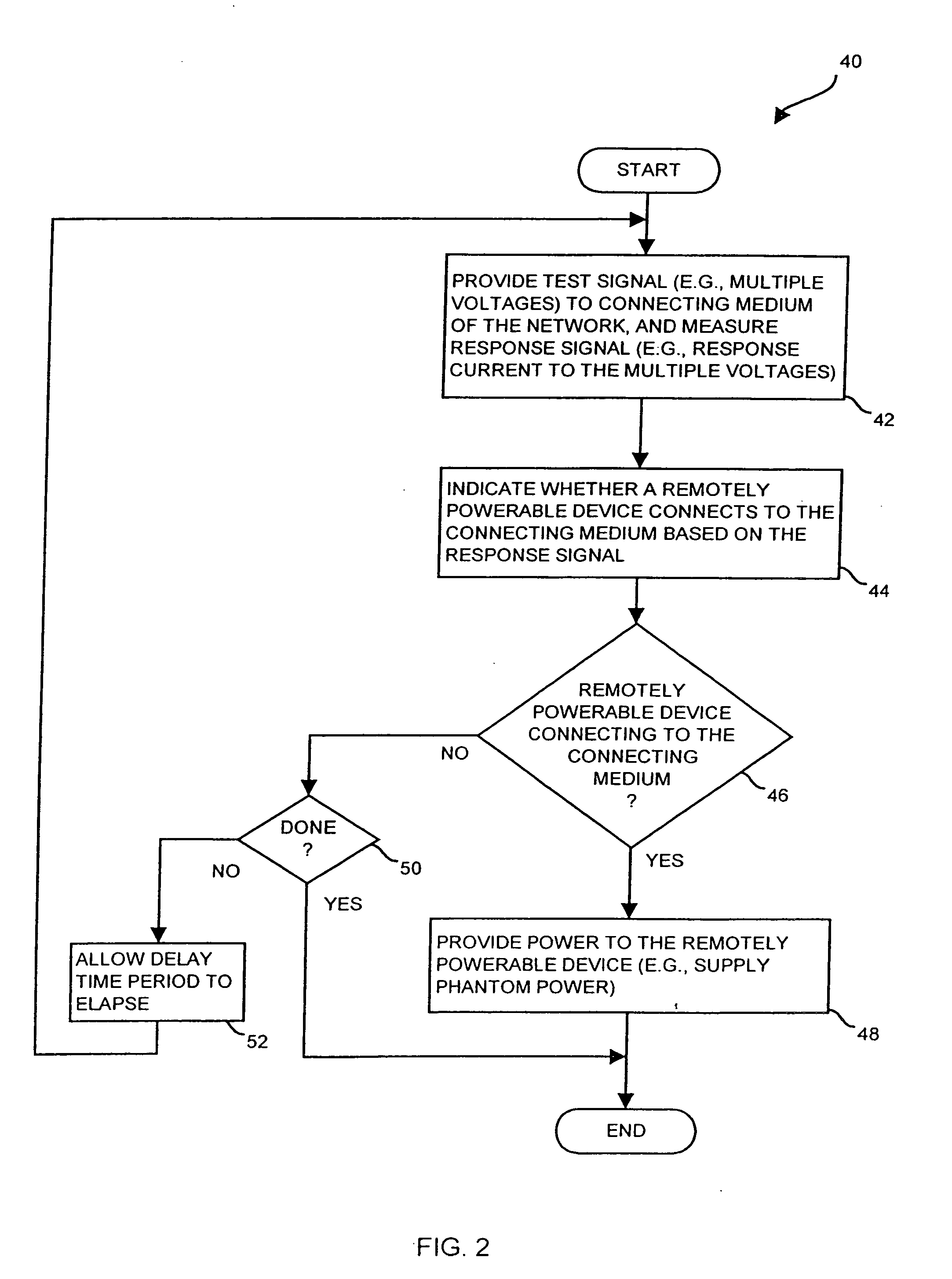
The invention is directed to techniques for discovering a powerability condition of a computer network such as the existence of a remotely powerable device attached to a connecting medium of the computer network. Such detection can then control whether a remote power source (e.g., a data communications device such as a switch) provides remote power (e.g., phantom power) to the computer network. One arrangement of the invention is directed to an apparatus for discovering a powerability condition of a computer network. The apparatus includes a signal generator, a detector and a controller which is coupled to the signal generator and the detector. The controller configures the signal generator to provide a test signal to a connecting medium of the computer network, and configures the detector to measure a response signal from the connecting medium of the computer network. The controller then indicates whether a remotely powerable device connects to the connecting medium of the computer network based on the response signal. Accordingly, if the apparatus discovers a remotely powerable device attached to the computer network (i.e., the power requirement condition of the network), the apparatus can provide power to the device remotely (e.g., through the connecting medium). However, if the apparatus does not discover a remotely powerable device attached to the computer network (e.g., another power requirement condition), the apparatus can avoid providing power remotely and thus avoid possibly damaging any non-remotely powerable device on the computer network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
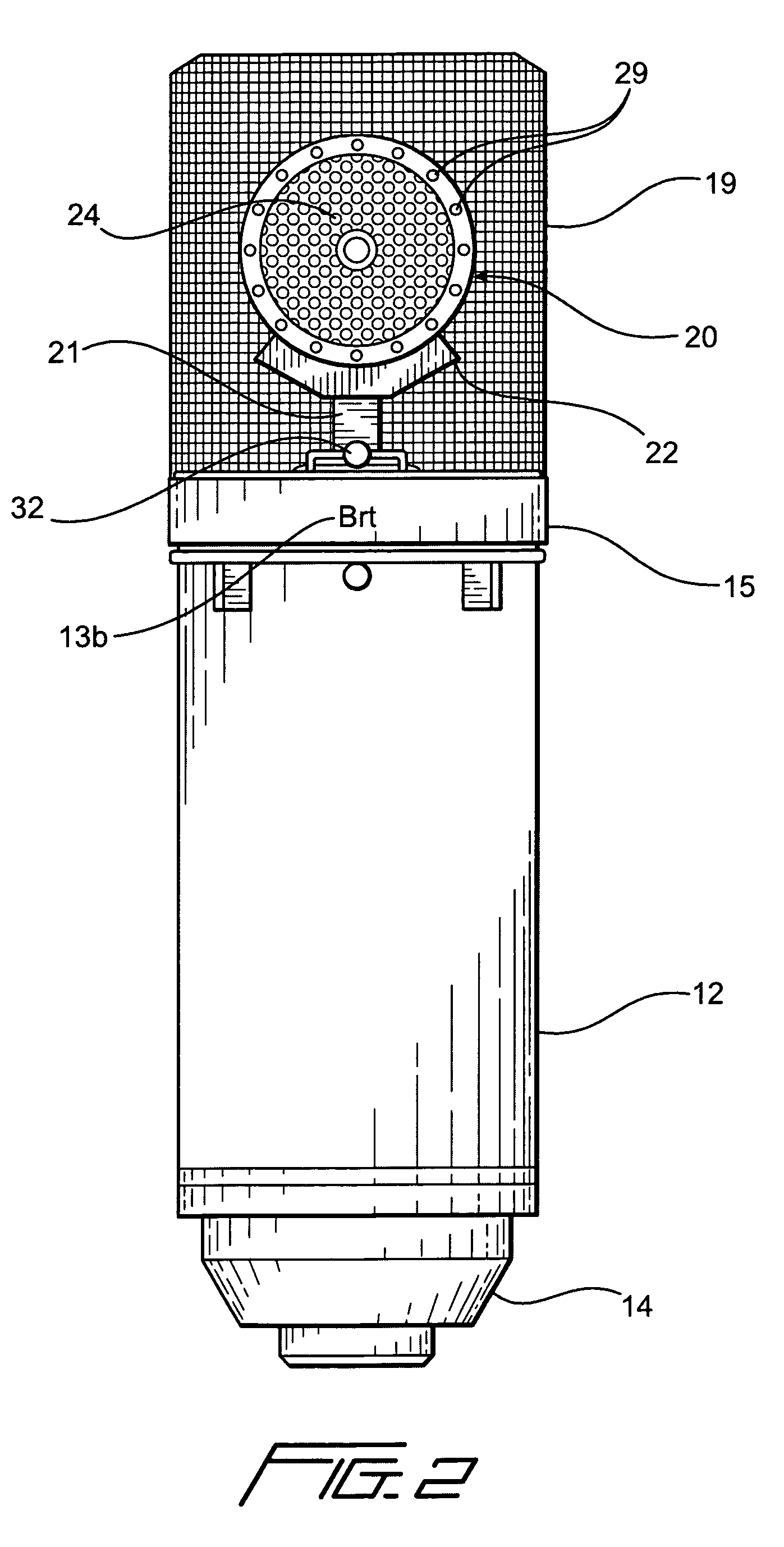
Selectable diaphragm condenser microphone
ActiveUS20080152174A1Piezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesElectrostatic transducer microphonesCapacitanceEngineering
A condenser microphone having a capsule with a cardioid pattern diaphragm on opposite sides of a back plate wherein each diaphragm is selectively activated via a switch to complete the audio circuit. The microphone employs two different diaphragm materials to produce two different sound reproduction characteristics. A first diaphragm produces a “warm and lush” sound output, while the second diaphragm produces a “bright and airy” sound output. The microphone includes the use of a pair of light emitting diodes located behind the grill indicating which capsule diaphragm is activated. The dual diaphragm arrangement is mounted on a standard microphone body and includes conventional electronics for connection to an associated piece of audio equipment producing phantom power.
Owner:MARSHALL ELECTRONICS
High-power downhole electromagnetic pulse transmission device
InactiveCN102147484AHigh energy ratioLarge capacityElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyData acquisitionObservation system
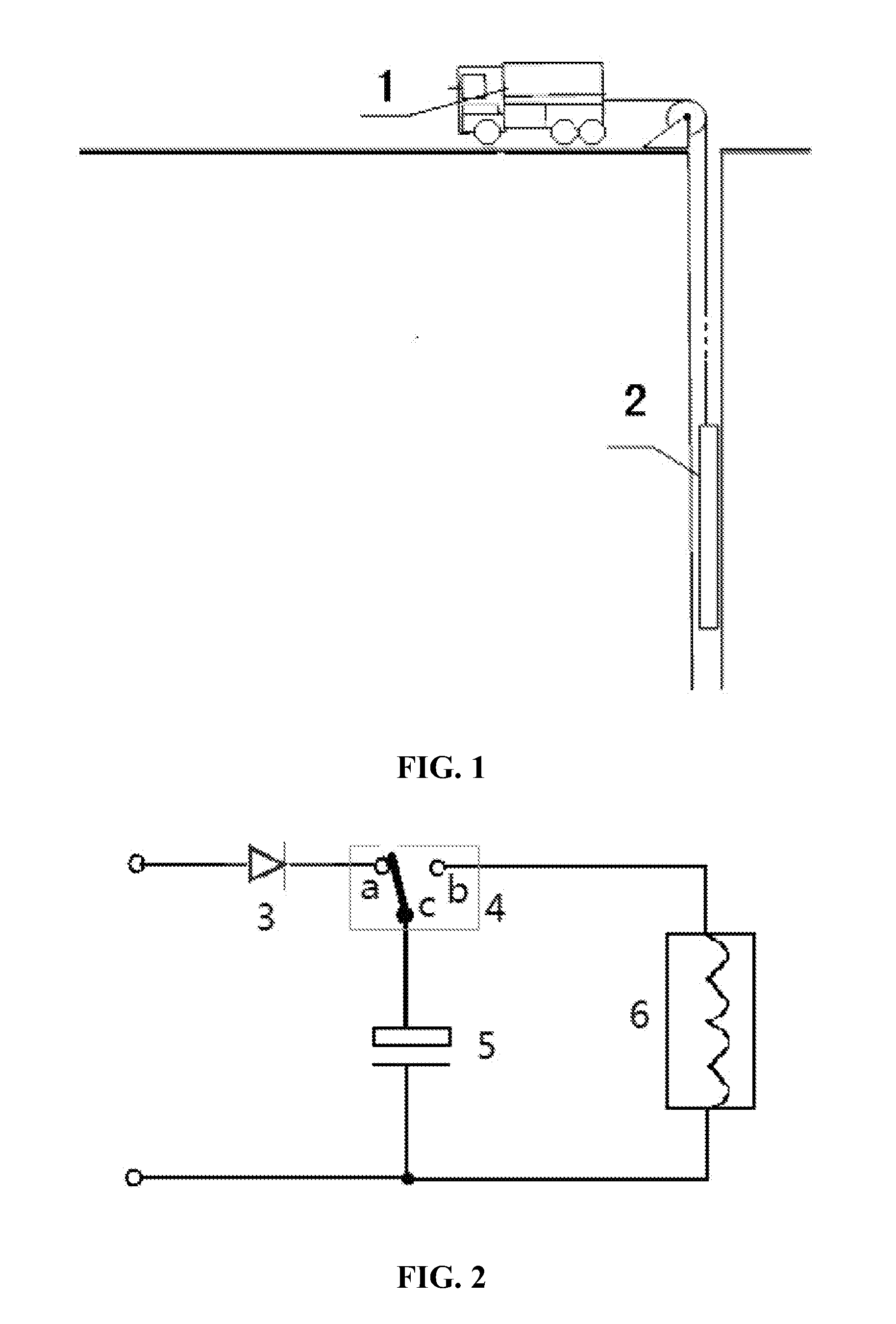
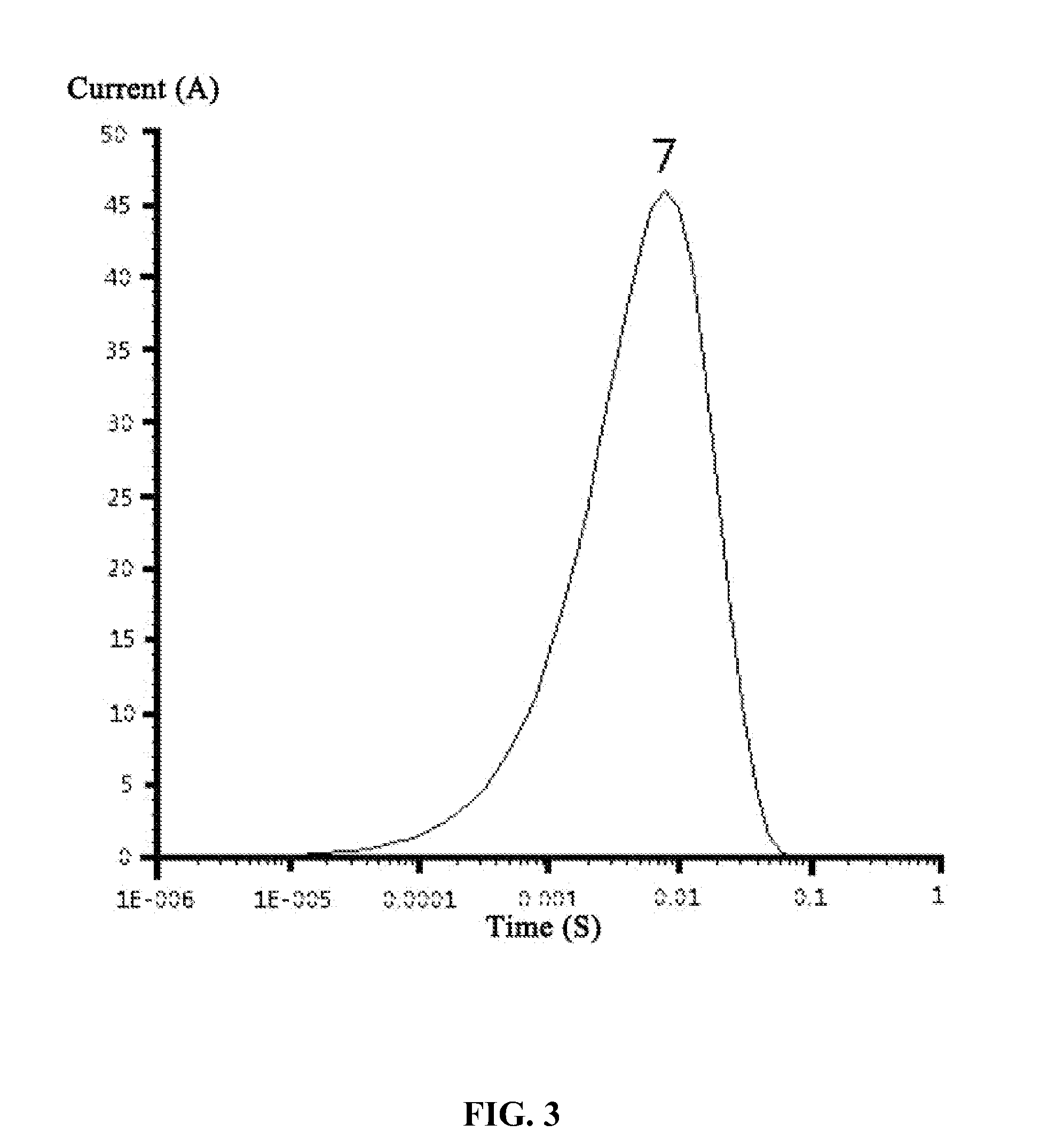
The invention discloses a high-power downhole electromagnetic pulse transmission device which comprises a ground instrument and a downhole instrument. The core of the ground instrument is an industrial personal computer and consists of a depth / magnetic mark / global position system (GPS) signal recording module, a Manchester coding and decoding module and a cable driving module; the depth / magnetic mark / GPS signal recording module and the Manchester coding and decoding module are connected with the industrial personal computer respectively through two serial ports; based on the principle of phantom power supply, the cable driving module is connected with the downhole instrument by a cable; the downhole instrument is sequentially provided with an alternating-current boost module, an energy-storage capacitor, a transmitting coil, a data acquisition module, a high-voltage discharging switch and a controller manipulated by a computer; and the ground instrument supplies power to the downhole instrument through the cable. By the high-power downhole electromagnetic pulse transmission device, magnetic field pulse excitation with instantaneous high power can be realized in a cased well, full time-interval data during transmitting wave forms and receiving signals in a well is recorded, and an observation system is provided for a downhole electromagnetic detection method which is used for evaluating and developing the distribution state of remaining oil in an oil storage layer.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Microphone suitable for professional live performance
InactiveUS20110135118A1Decreases bass boostIncreases bass boostPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesElectrostatic transducer microphonesDynamic range compressionAcoustic energy
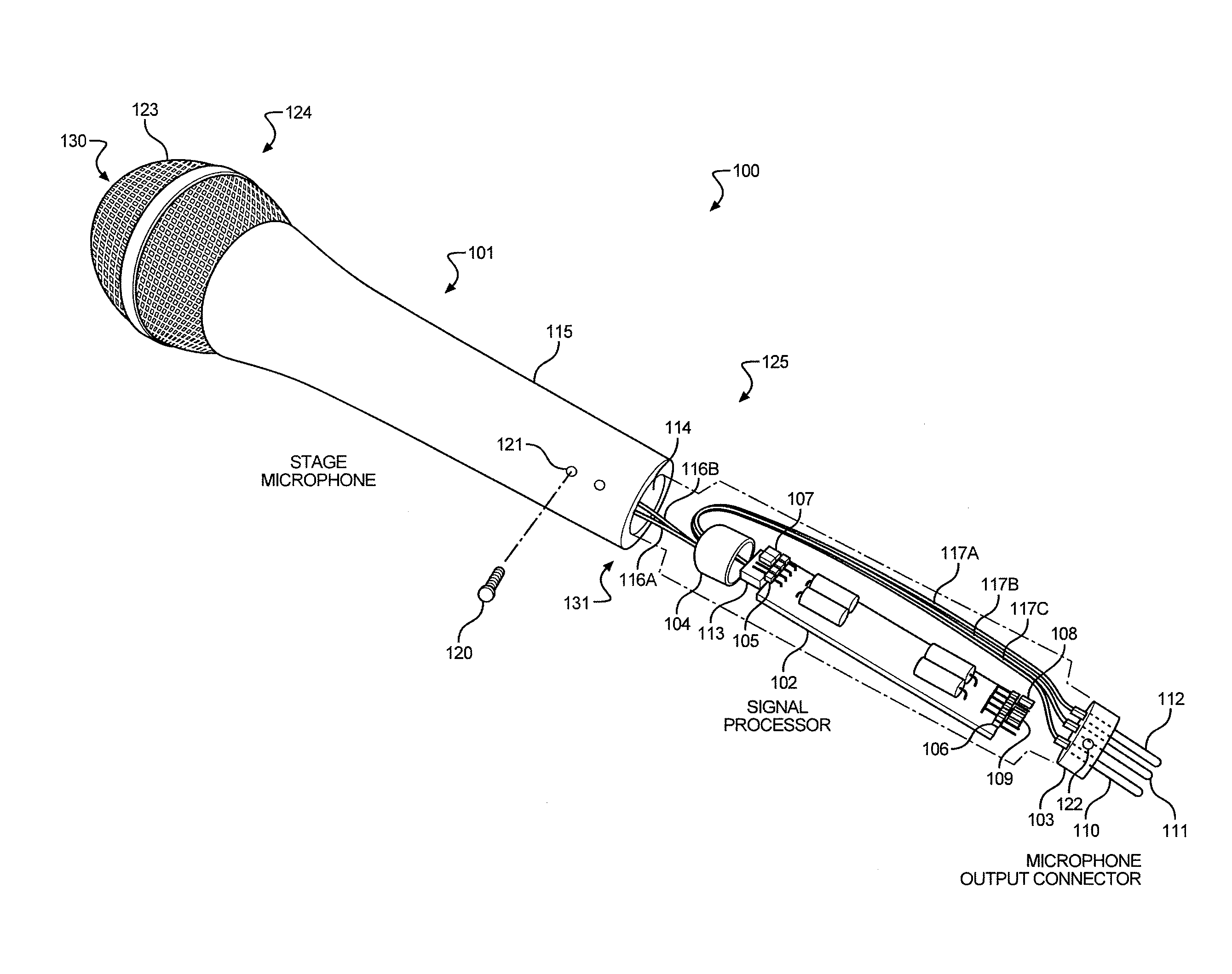
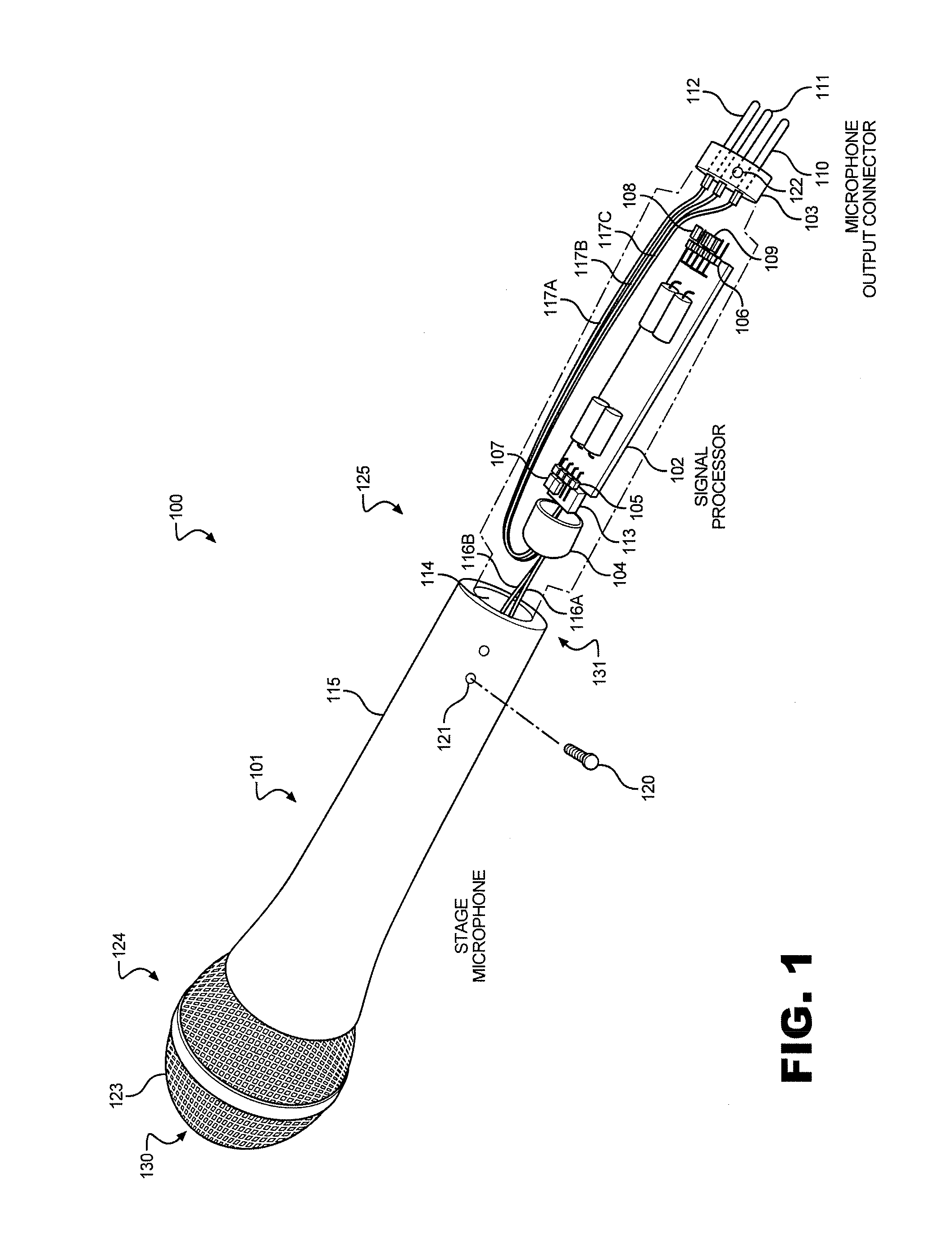
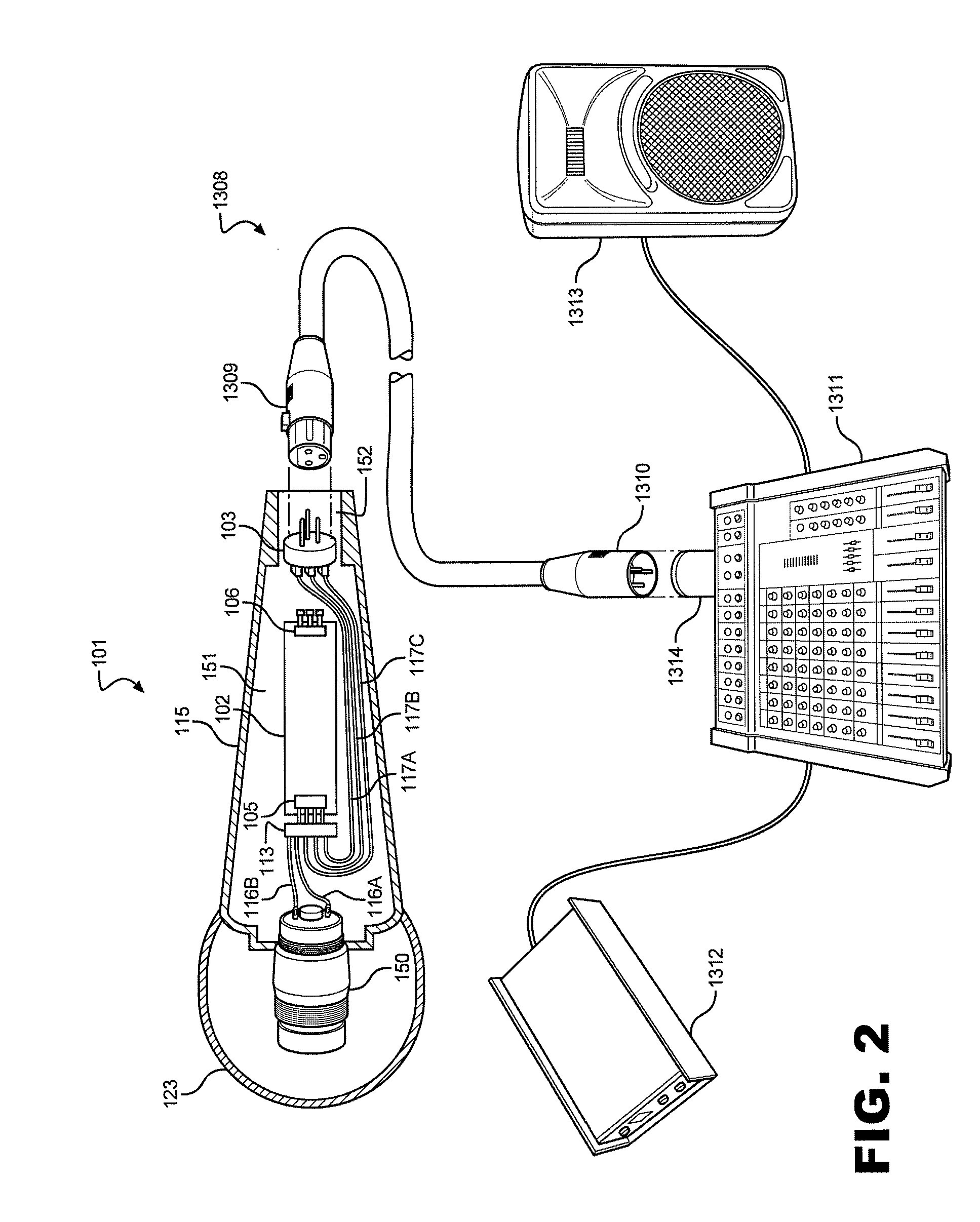
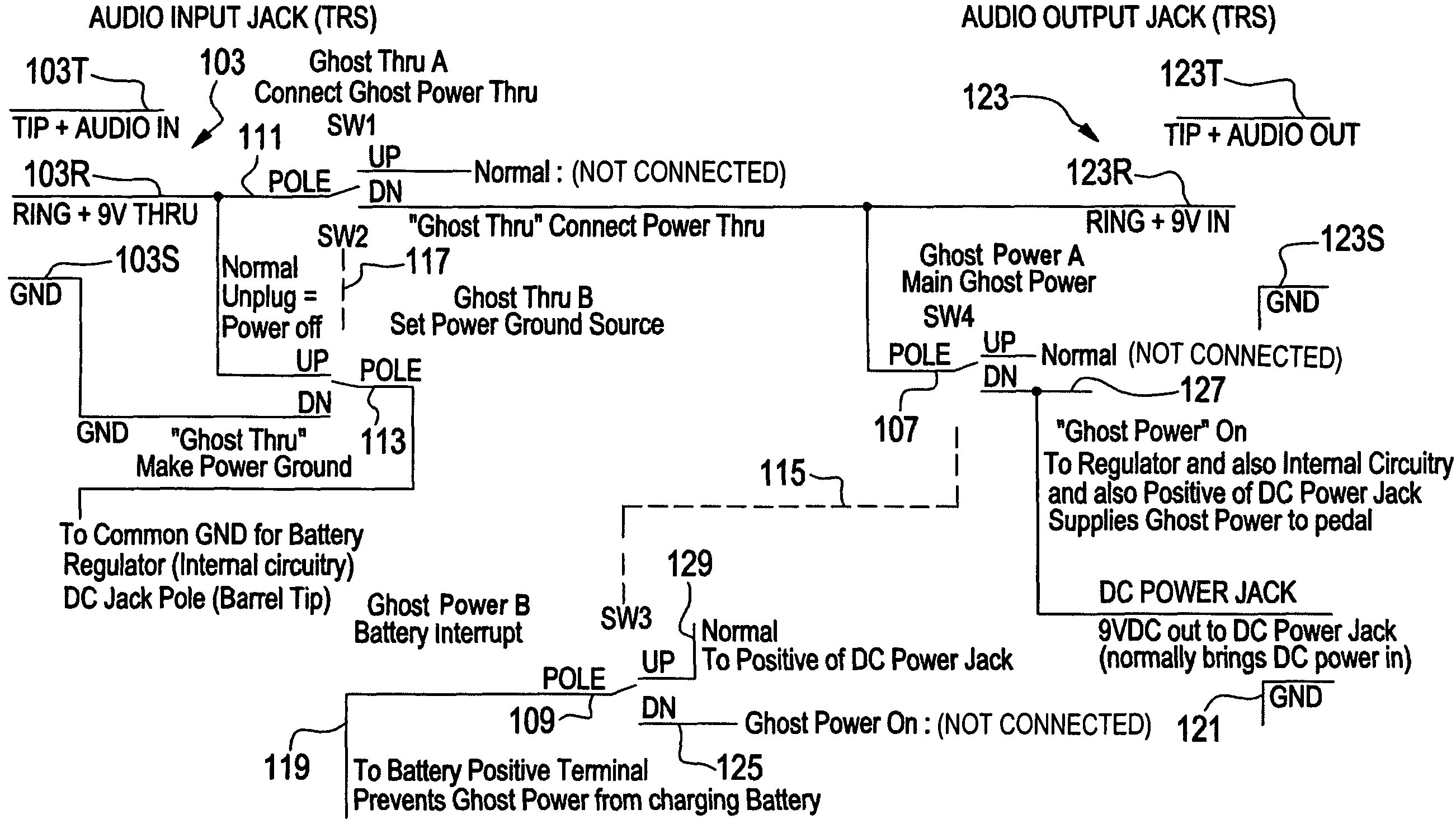
A personal microphone that includes a structure having a live-performance form factor, a capsule that converts acoustic energy into an input signal, a signal processor that converts the input signal into a processed output signal, and a microphone output connector. The signal processor has input terminals that receive the input signal and input / output terminals that receive a phantom DC voltage from the microphone output connector while sending the microphone output connector a processed output signal. The signal processor has a dynamic range compressor that compresses the processed output signal, and a programming or adjustment device that sets the signal processor operating parameters. The personal microphone can have a security device for avoiding unwanted changes to the operating parameters of the adjustable signal processor. The personal microphone can be powered by a phantom power supply coupled to the microphone output connector via a mixing console and / or other devices.
Owner:OSBORNE GARY T
Phantom powered pedals
ActiveUS7820904B1Electrophonic musical instrumentsLinear/angular speed measurementElectrical connectorPhantom power
Musical instrument effects pedals are powered from adjacent pedals by providing electrical connectors between adjacent pedals and by providing tip-ring-sleeve jacks in the pedals and three wire connectors with tip-ring-sleeve connectors, which carry sound signals from an instrument through sequential pedals and electrical power in an opposite direction to the pedals.
Owner:ROBLING JASON O +1
Selectable diaphragm condenser microphone
ActiveUS7889882B2Piezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesElectrostatic transducer microphonesCapacitanceEngineering
A condenser microphone having a capsule with a cardioid pattern diaphragm on opposite sides of a back plate wherein each diaphragm is selectively activated via a switch to complete the audio circuit. The microphone employs two different diaphragm materials to produce two different sound reproduction characteristics. A first diaphragm produces a “warm and lush” sound output, while the second diaphragm produces a “bright and airy” sound output. The microphone includes the use of a pair of light emitting diodes located behind the grill indicating which capsule diaphragm is activated. The dual diaphragm arrangement is mounted on a standard microphone body and includes conventional electronics for connection to an associated piece of audio equipment producing phantom power.
Owner:MARSHALL ELECTRONICS
Apparatus for discovering a powerability condition of a computer network
InactiveUS7111181B2Avoid damageLevel controlVolume/mass flow measurementPhantom powerSignal generator
The invention is directed to techniques for discovering a powerability condition of a computer network such as the existence of a remotely powerable device attached to a connecting medium of the computer network. Such detection can then control whether a remote power source (e.g., a data communications device such as a switch) provides remote power (e.g., phantom power) to the computer network. One arrangement of the invention is directed to an apparatus for discovering a powerability condition of a computer network. The apparatus includes a signal generator, a detector and a controller which is coupled to the signal generator and the detector. The controller configures the signal generator to provide a test signal to a connecting medium of the computer network, and configures the detector to measure a response signal from the connecting medium of the computer network. The controller then indicates whether a remotely powerable device connects to the connecting medium of the computer network based on the response signal. Accordingly, if the apparatus discovers a remotely powerable device attached to the computer network (i.e., the power requirement condition of the network), the apparatus can provide power to the device remotely (e.g., through the connecting medium). However, if the apparatus does not discover a remotely powerable device attached to the computer network (e.g., another power requirement condition), the apparatus can avoid providing power remotely and thus avoid possibly damaging any non-remotely powerable device on the computer network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Self-identifying microphone
ActiveUS20050147255A1Transducer casings/cabinets/supportsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringPhantom power
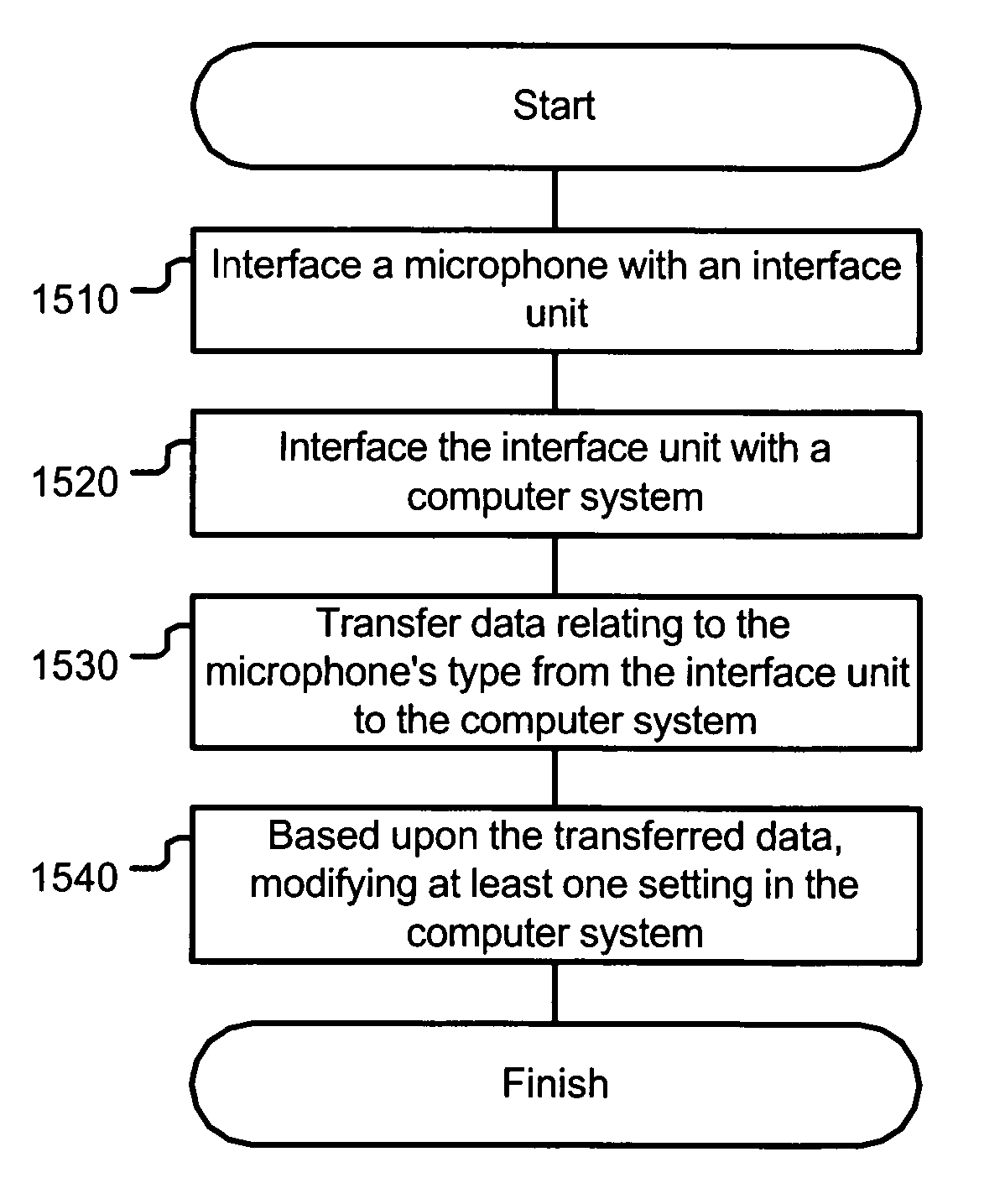
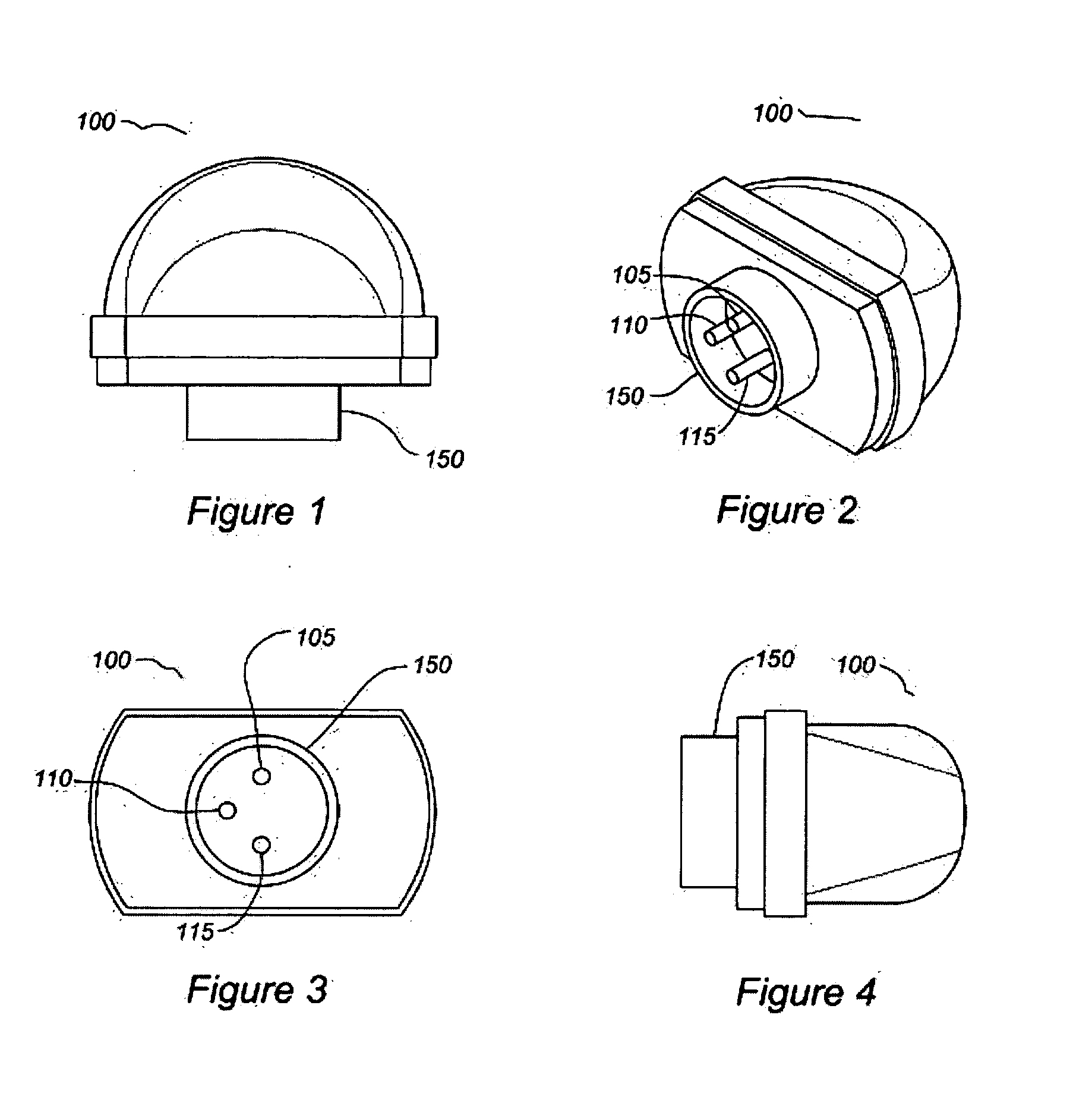
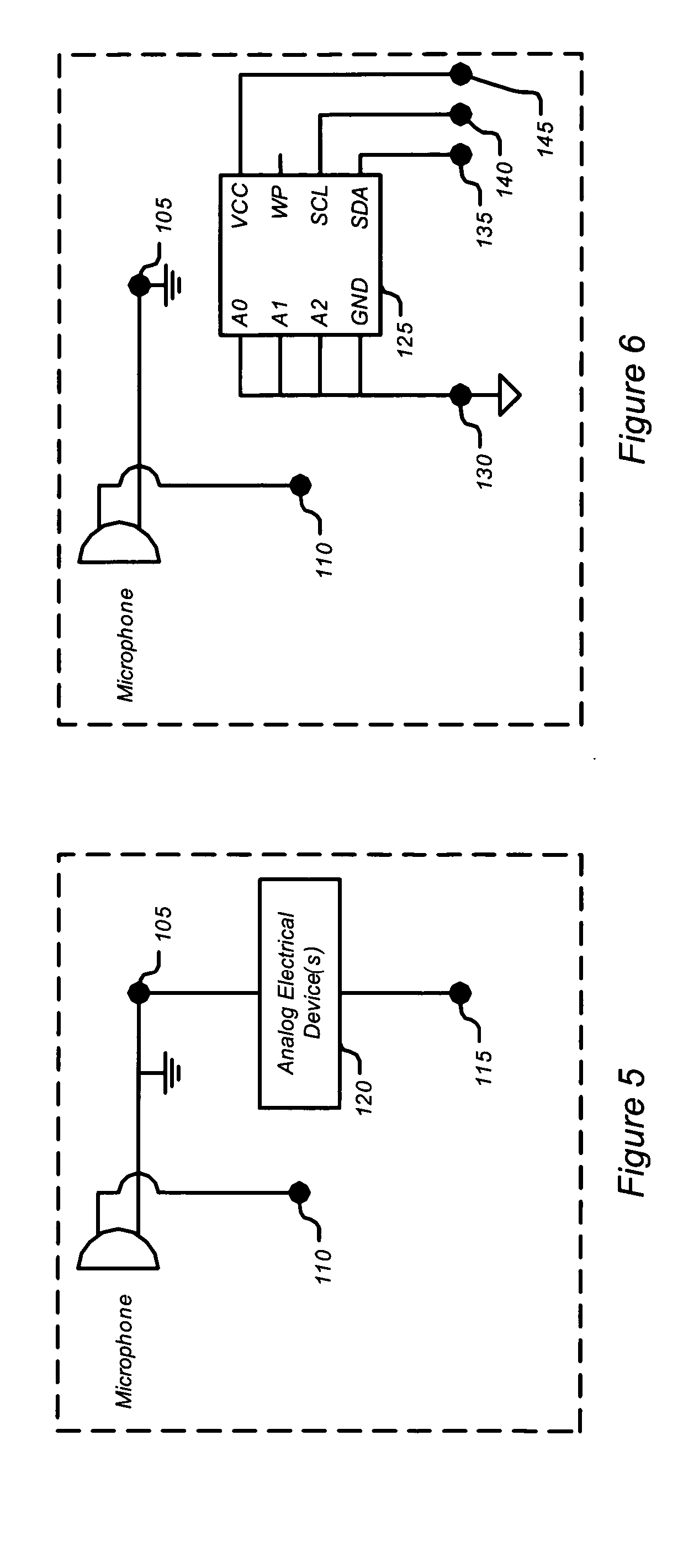
A microphone including a connector with a plurality of electrical contacts. The microphone interfaces with a computer system via a digital bus. The microphone can transmit data to the computer system via the connector that is related to at least one of the following: the microphone manufacturer, the microphone manufacture date, the microphone model number, the microphone serial number, the microphone frequency response, whether the microphone uses phantom power, the desired pre-amplifier gain, and the microphone dynamic response.
Owner:APPLE INC
Microphone
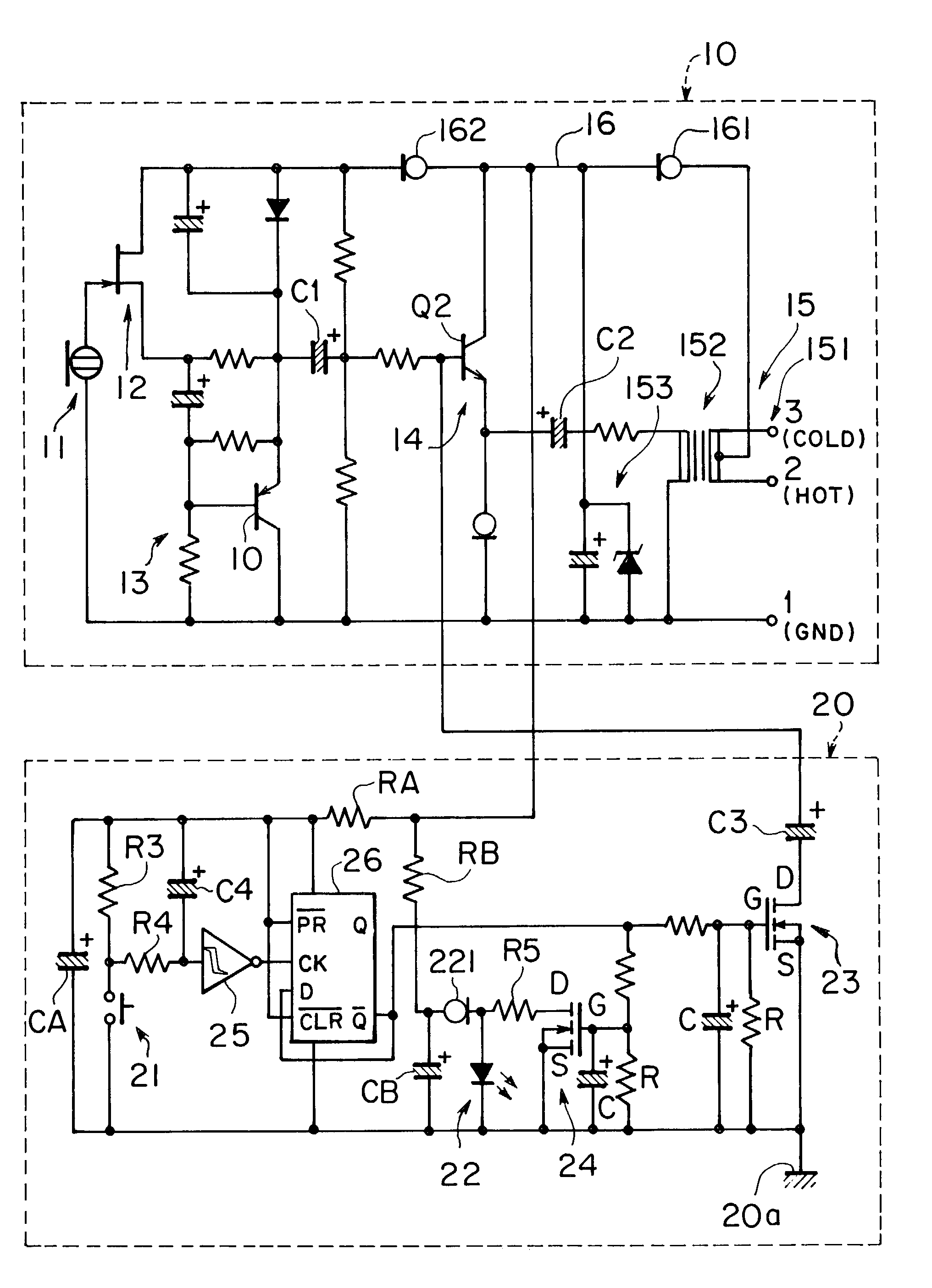
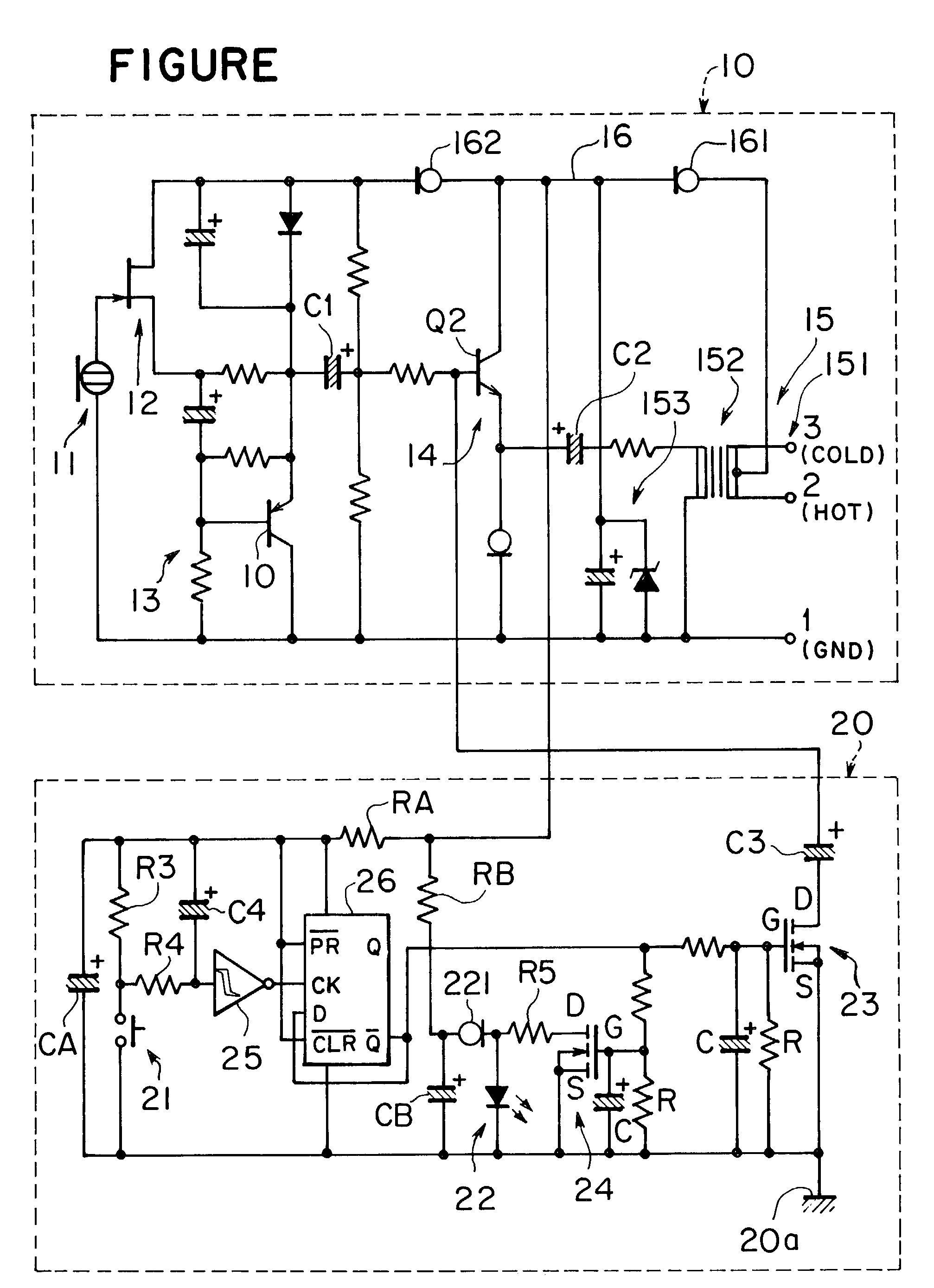
InactiveUS7046815B2Eliminate the problemMicrophone structural associationTransducer circuitsEngineeringPhantom power
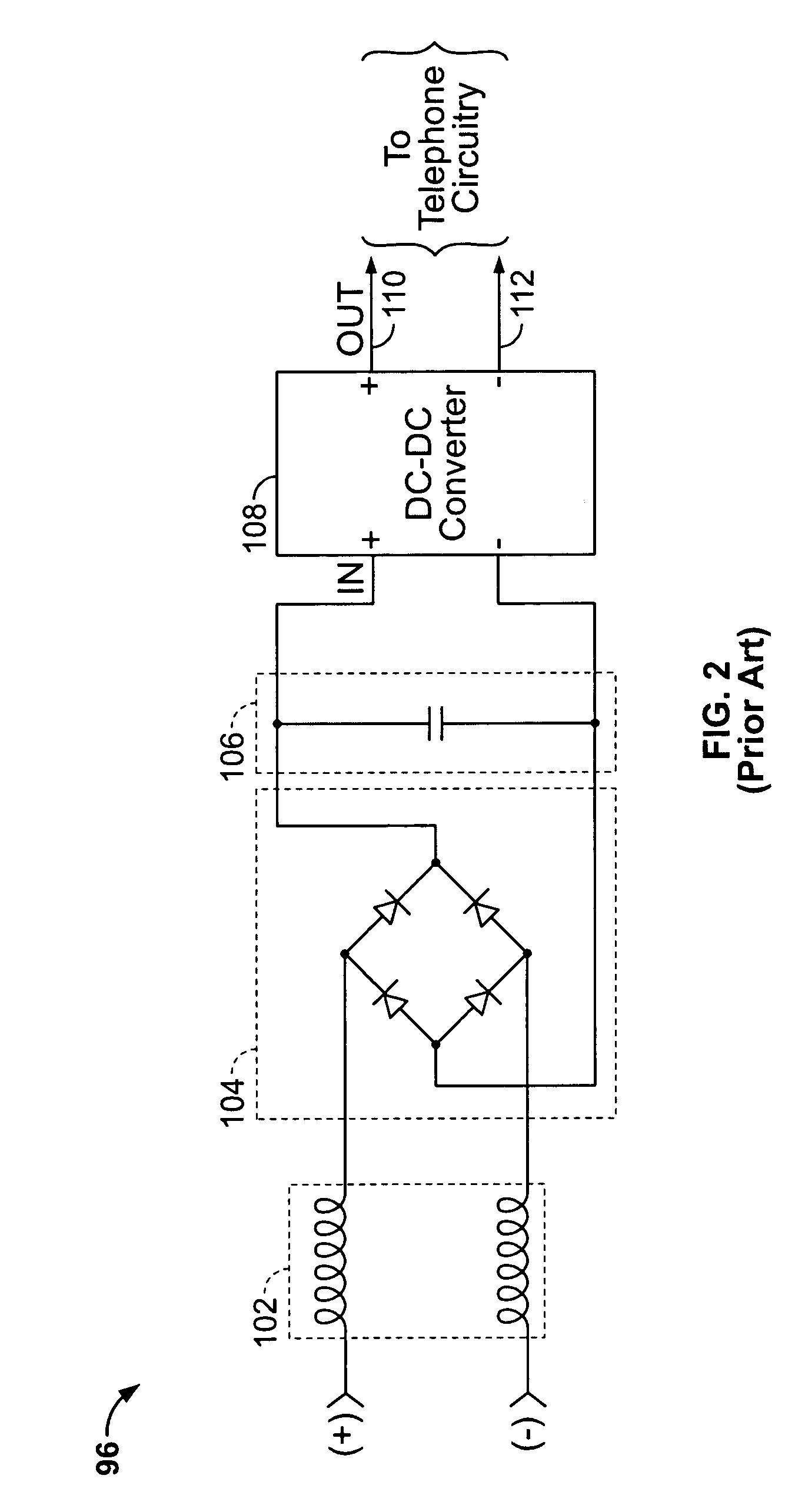
The improved microphone with the removable connection to the phantom power supply facilitates the setting and provides elimination of the forgetful operation of switch-off, in e.g. convention center. The microphone provides both of manual and automatic operations of its indicator lamp having indication of the power supply, and has a manual switch which provides a common mode for operation of, and an automatic operation of both of its audio signal output and the indicator lamp. It also has a first circuit by which the indicator lamp automatically lights up, separately from the manual switch, in response to the connection to the power supply; and a second circuit by which the indicator lights out and the audio signal output is turned to off after the elapse of a predetermined time from the connection. The first and second circuits comprise respective integration circuits.
Owner:AUDIO-TECHNICA
Microphone system
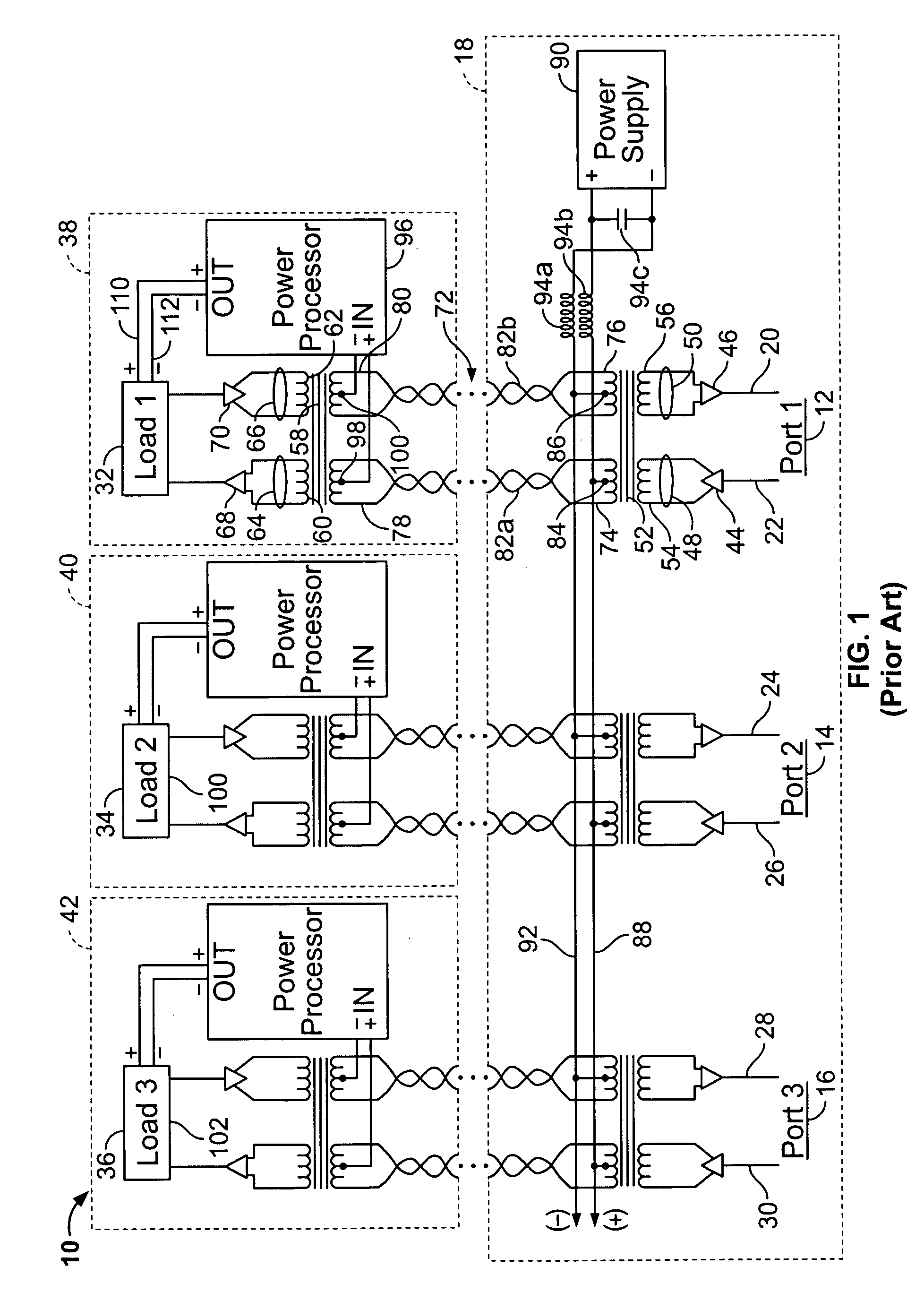
A microphone system includes a microphone capsule, an audio amplifier and microphone electronics. A phantom power supply provides power to the audio amplifier and the microphone electronics through cable conductors. The microphone system includes a power supply that provides a supply voltage to the microphone electronics, a polarization voltage to the microphone capsule and a supply voltage to the audio amplifier. The power supply includes a constant current generator. The constant current generator operates as a constant current sink for the phantom power supply.
Owner:AKG ACOUSTICS
Audio level compressor
InactiveUS20090136061A1Firmly connectedExcellent in harmonyGain controlSpeech analysisDynamic range compressionLoad resistance
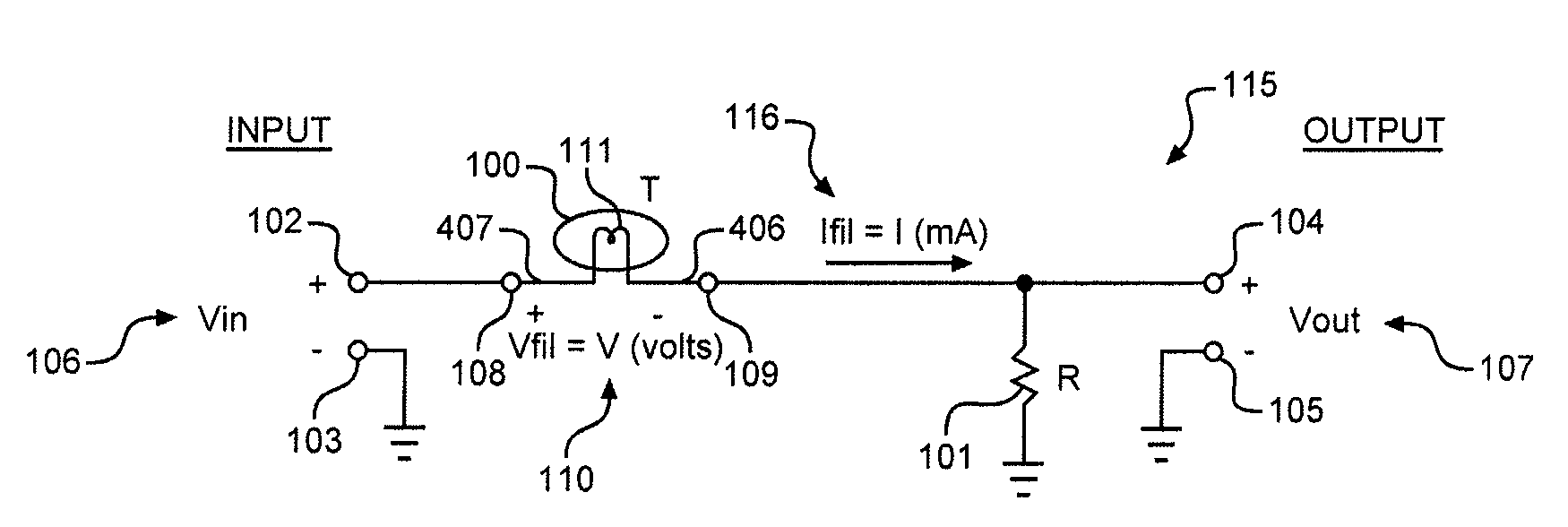
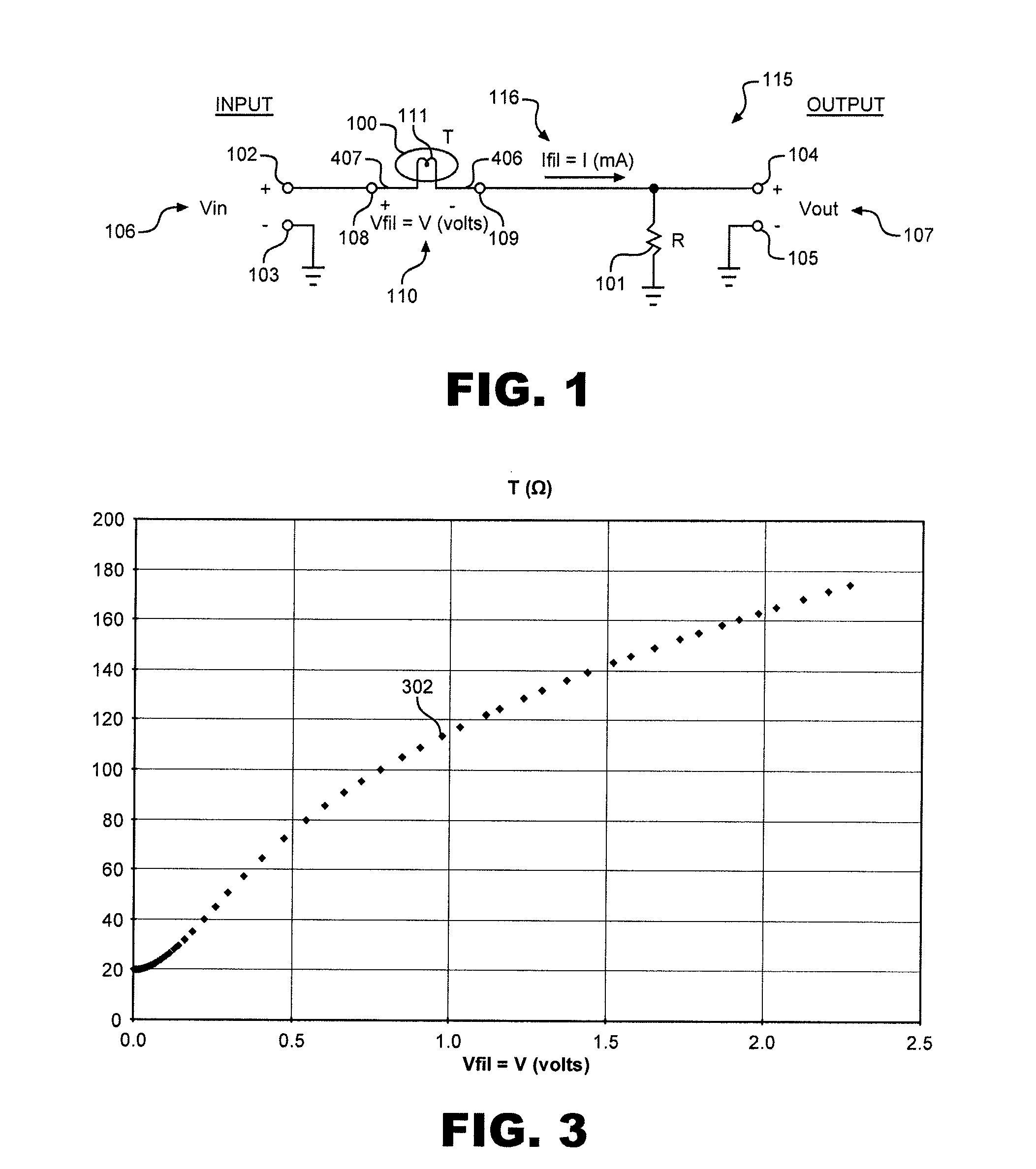
An audio level compressor for compressing the dynamic range of an input audio signal. The audio level compressor can be part of a microphone, or a separate component. The audio level compressor includes input terminals for receiving the input audio signal, a lamp having a filament resistance that is a function of the input audio signal; a load resistance; a signal gain controller that includes a means for increasing dynamic range compression of the input audio signal, and output terminals for providing an output audio signal that is a function of the input audio signal and the signal gain. The signal gain controller provides a signal gain that is a function of the filament resistance and the load resistance. The audio level compressor can also include an expander circuit or a power conditioning circuit. Power can be provided by an internal source or a phantom power supply.
Owner:OSBORNE GARY T
Condenser microphone
ActiveUS20060291672A1Suitable for operationElectrostatic transducer microphonesTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsCapacitanceOutput transformer
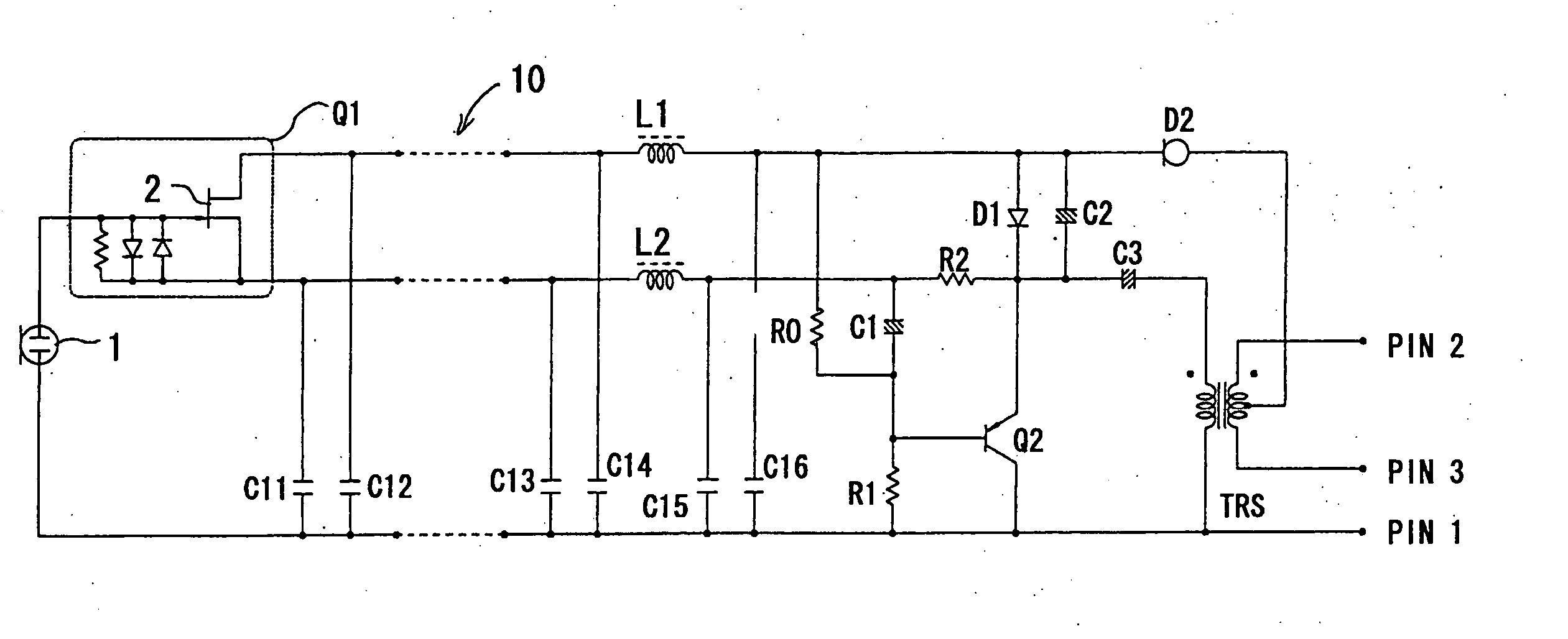
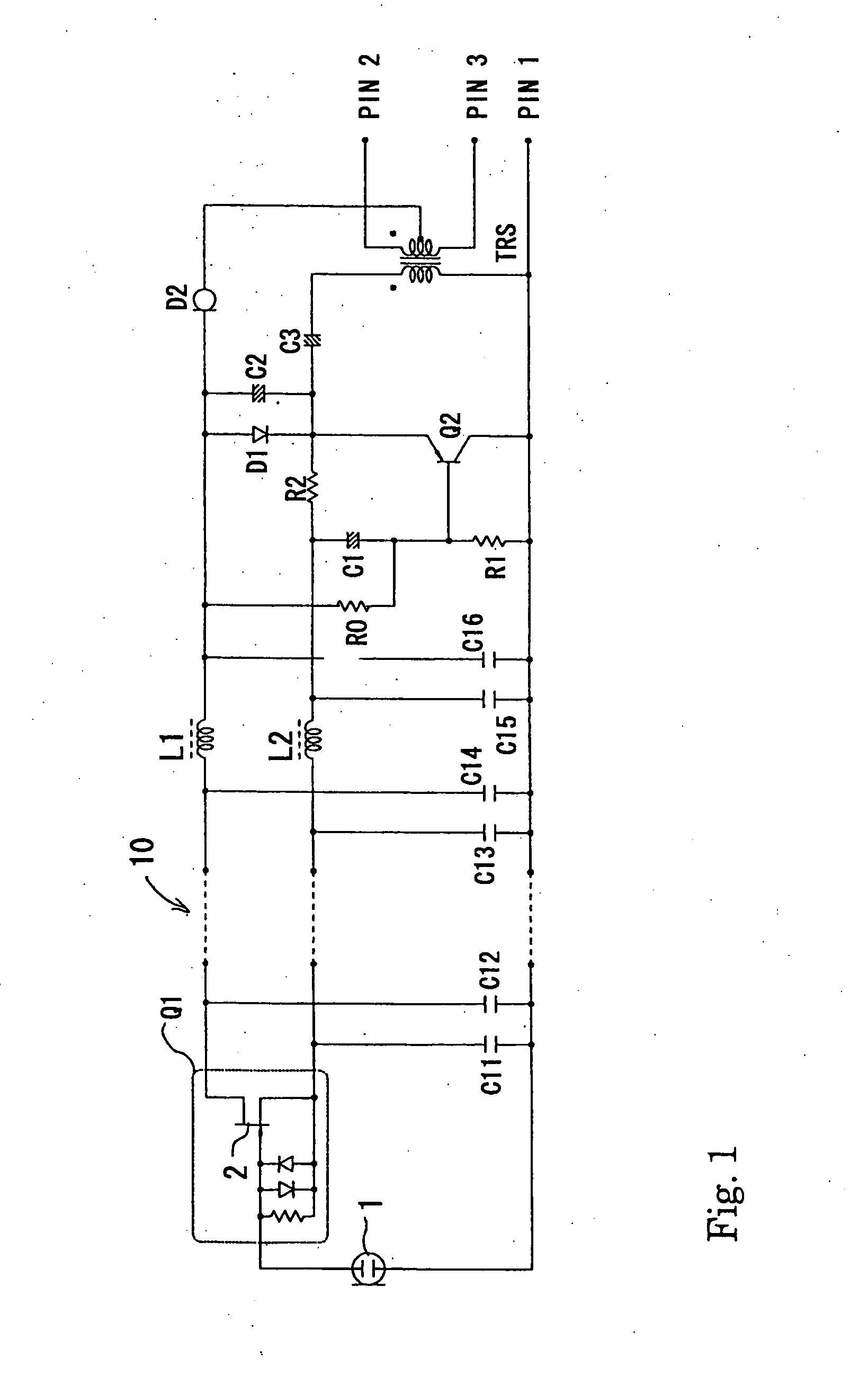
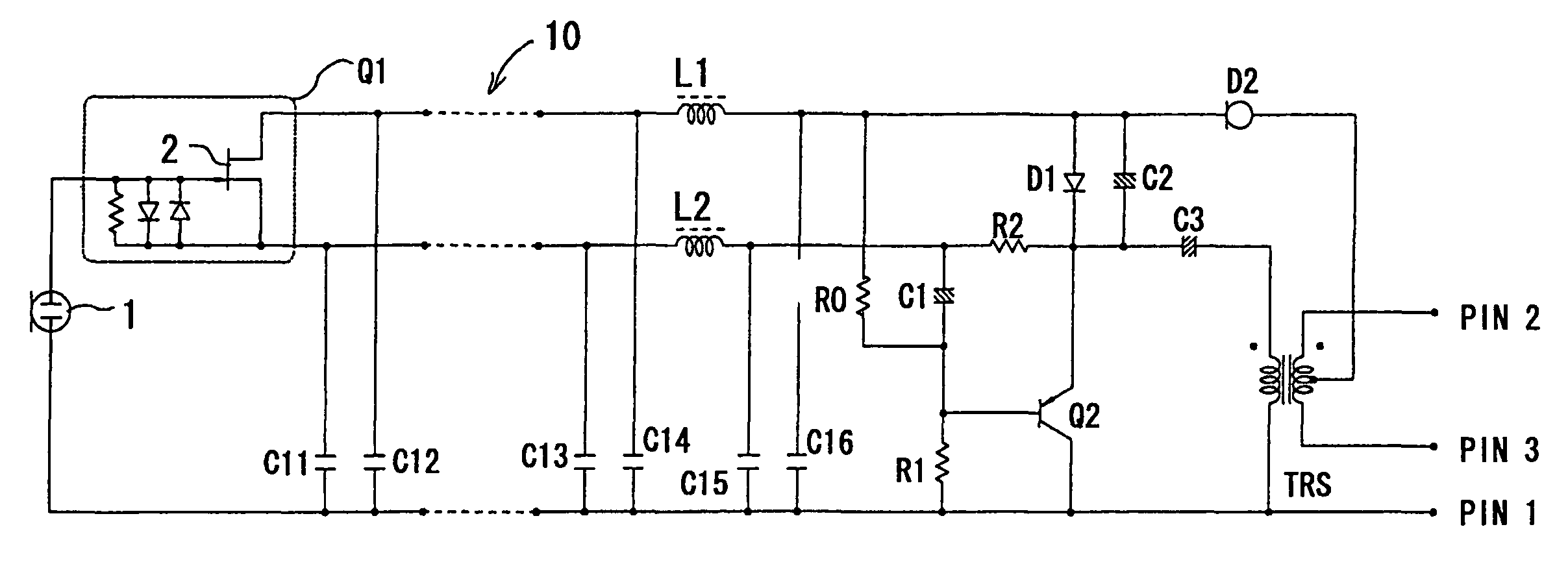
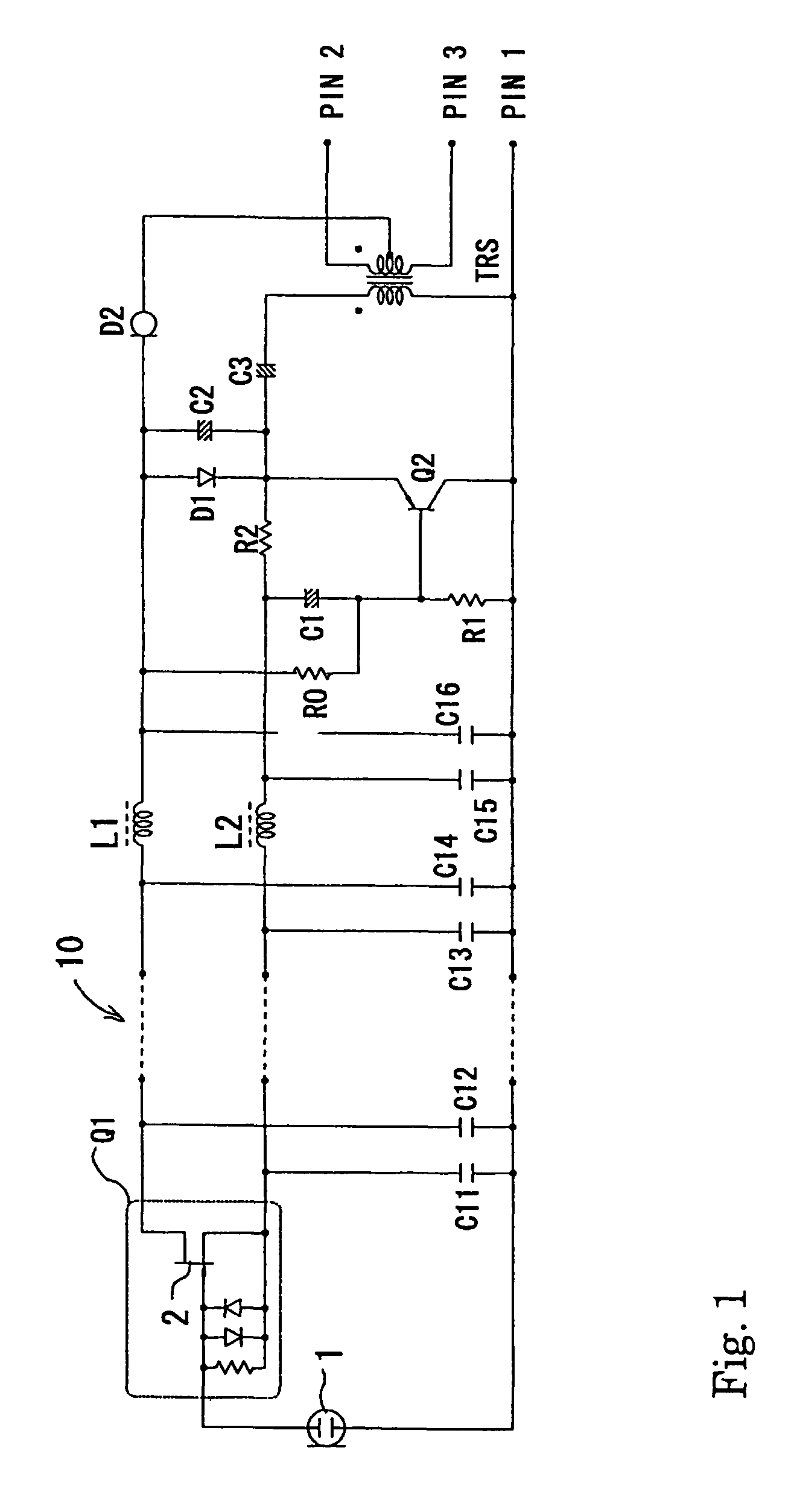
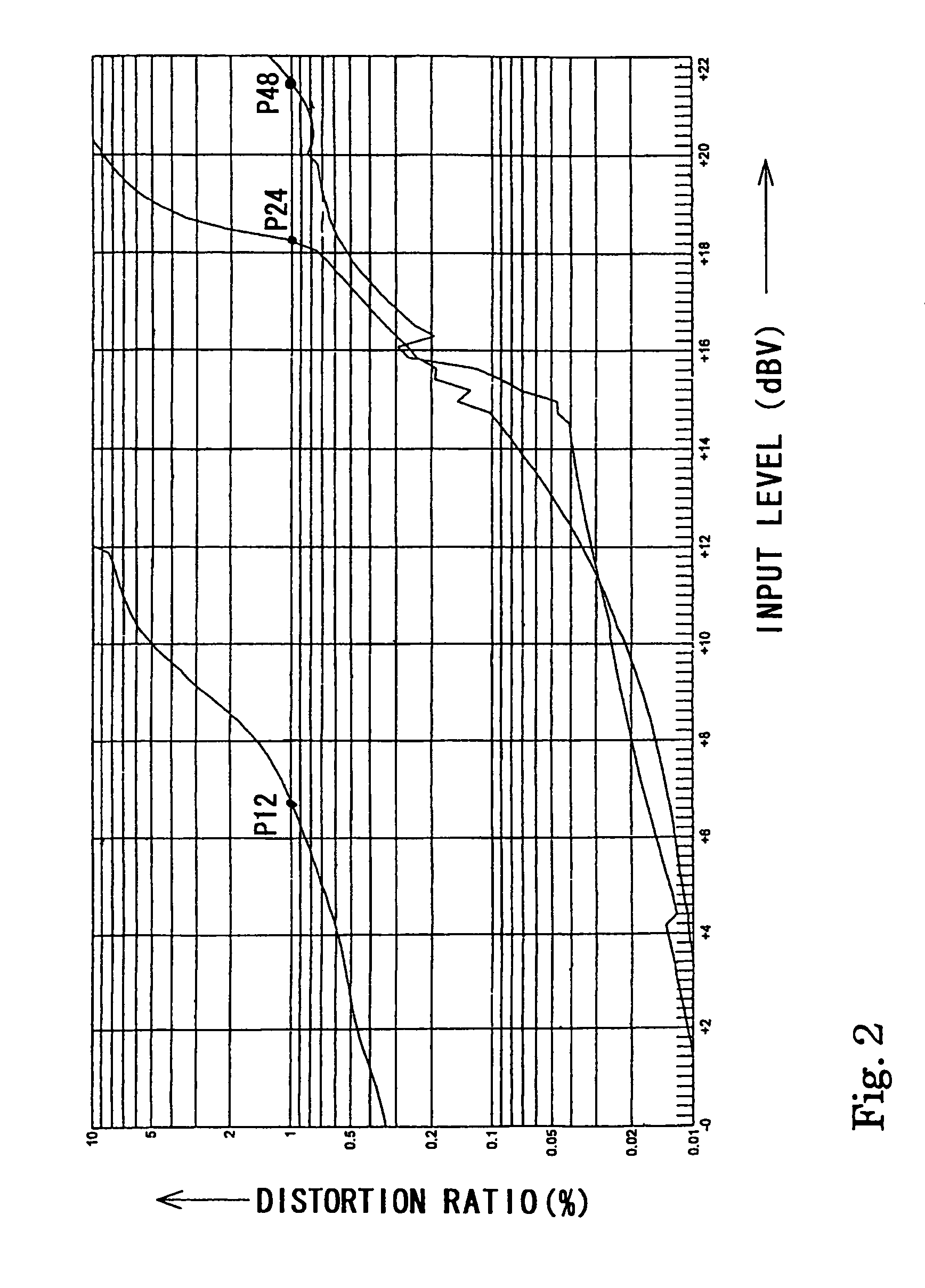
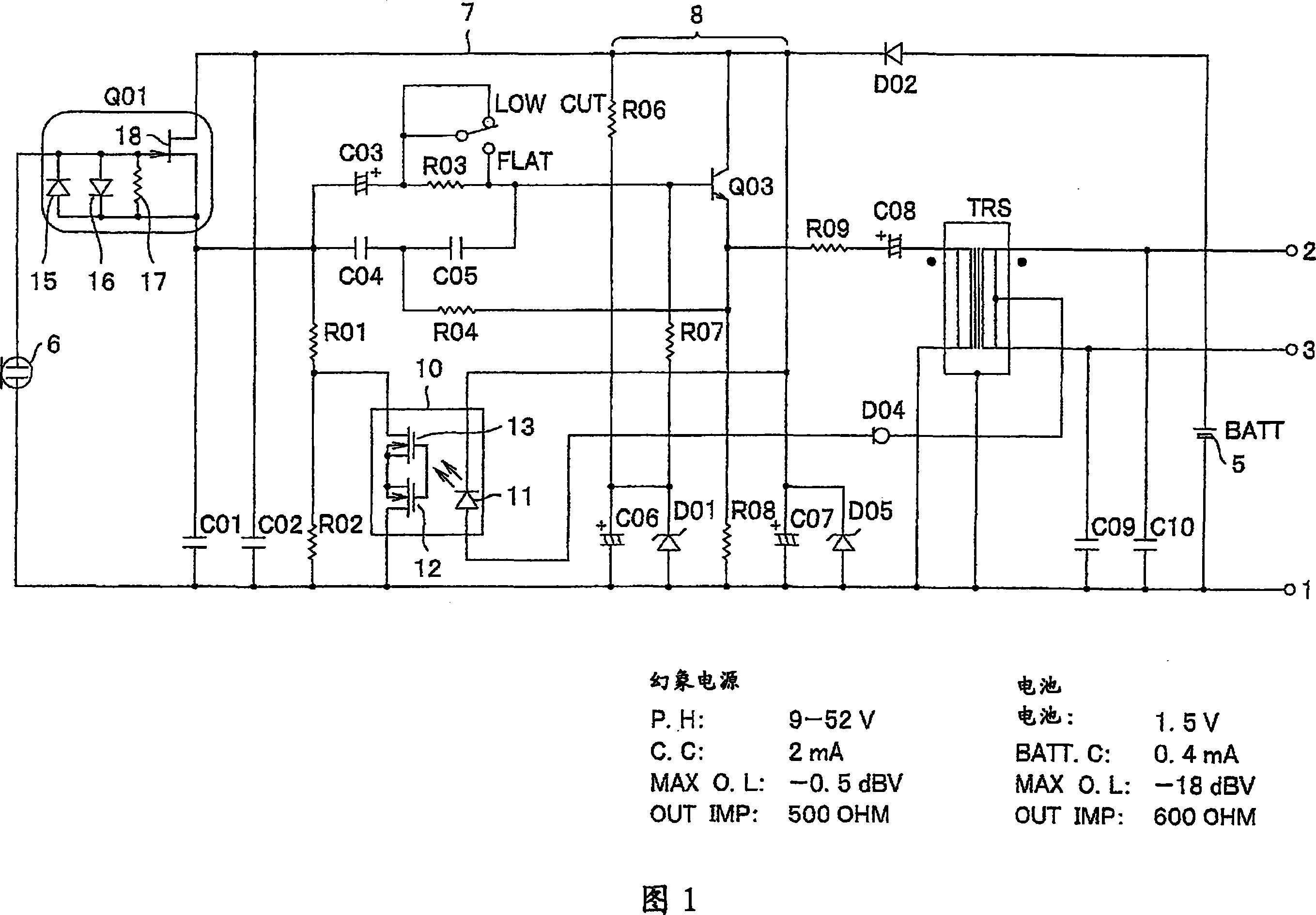
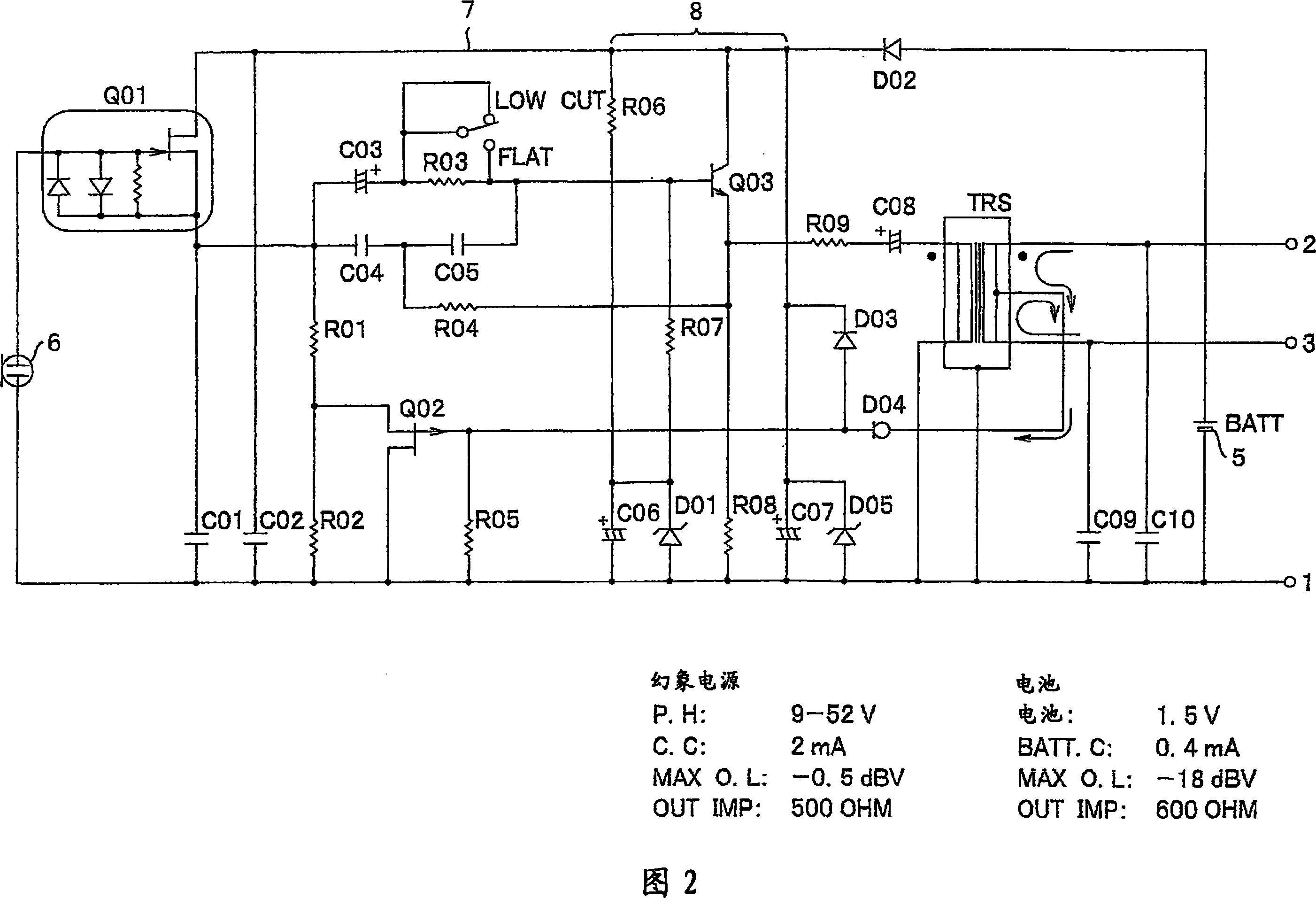
A condenser microphone is obtained, in which the bias of a current amplifier circuit in emitter-follower connection immediately after an impedance converter automatically changes in accordance with the switching of phantom power supply voltages and the maximum output level and the maximum permissible input sound pressure level are increased at any power supply voltage. The condenser microphone comprising a transistor Q2 in emitter-follower connection immediately after an FET 2 that constitutes an impedance converter Q1 has a constant current diode D2 connected to an output transformer TRS that also serves as a transformer for phantom power source supply and resistors R0 and R1 that divide the voltage on the cathode side of the constant current diode D2 into a bias voltage that causes the transistor Q2 to operate.
Owner:AUDIO-TECHNICA
Method and apparatus for detecting a compatible phantom powered device using common mode signaling
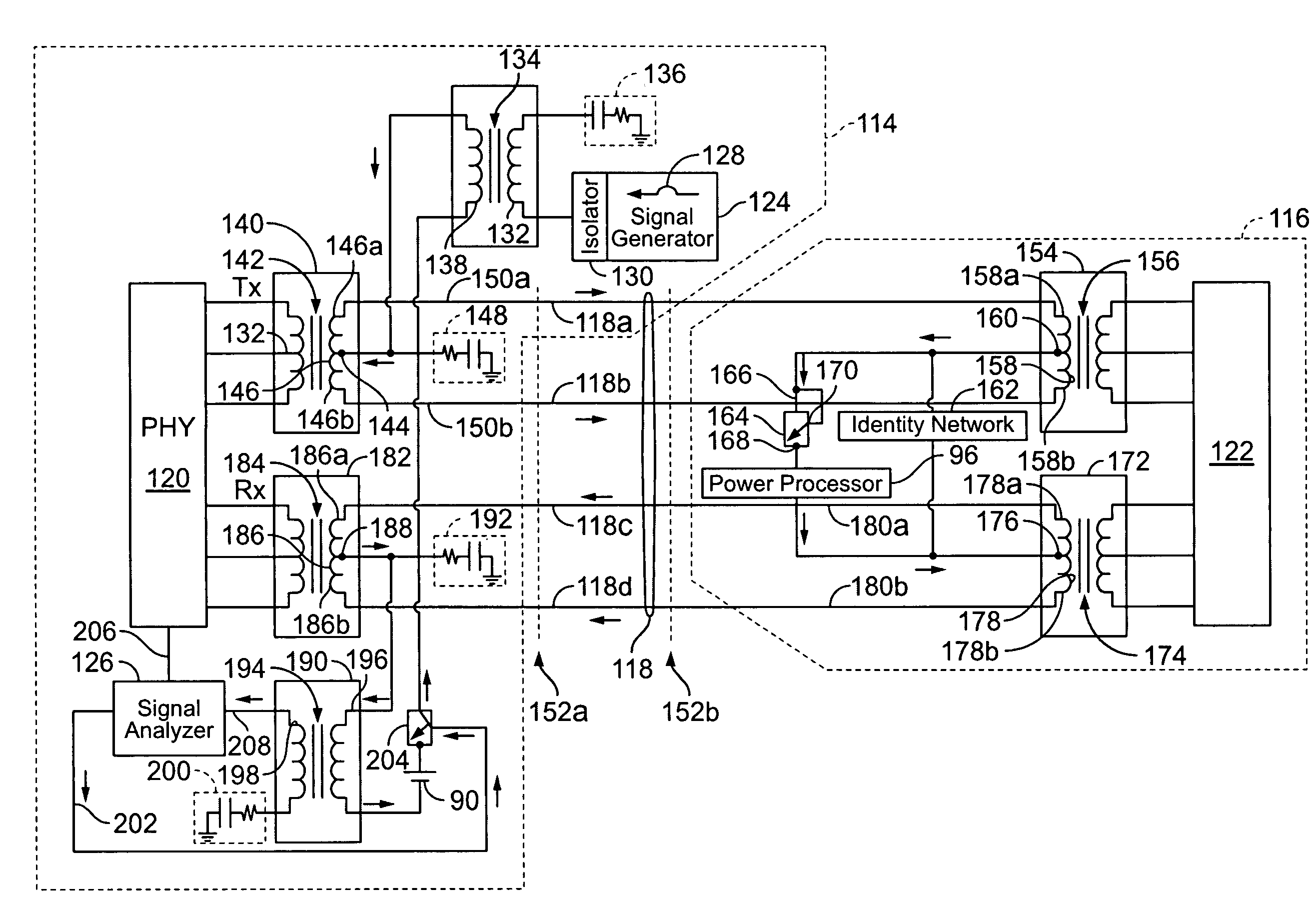
A method and an apparatus provide for determining whether a data terminal equipment (DTE) device represents a compatible device lacking an independent power supply and adapted to be powered using phantom power over a wired connection from a communications device such as a switch. A detection signal may be transmitted from the communications device to an identity network connected to the DTE. A response detection signal may be returned and checked in a receiver at the communications device. A switch may then be closed to provide phantom power if the result of the check indicates that the DTE is a compatible device adapted to receive phantom power. Compatible DTE device may include telephones, Voice over IP (VoIP, IP or Ethernet) telephones, network access devices, computers, and the like.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Phantom powered capacitor microphone and a method of using a vacuum tube in the same
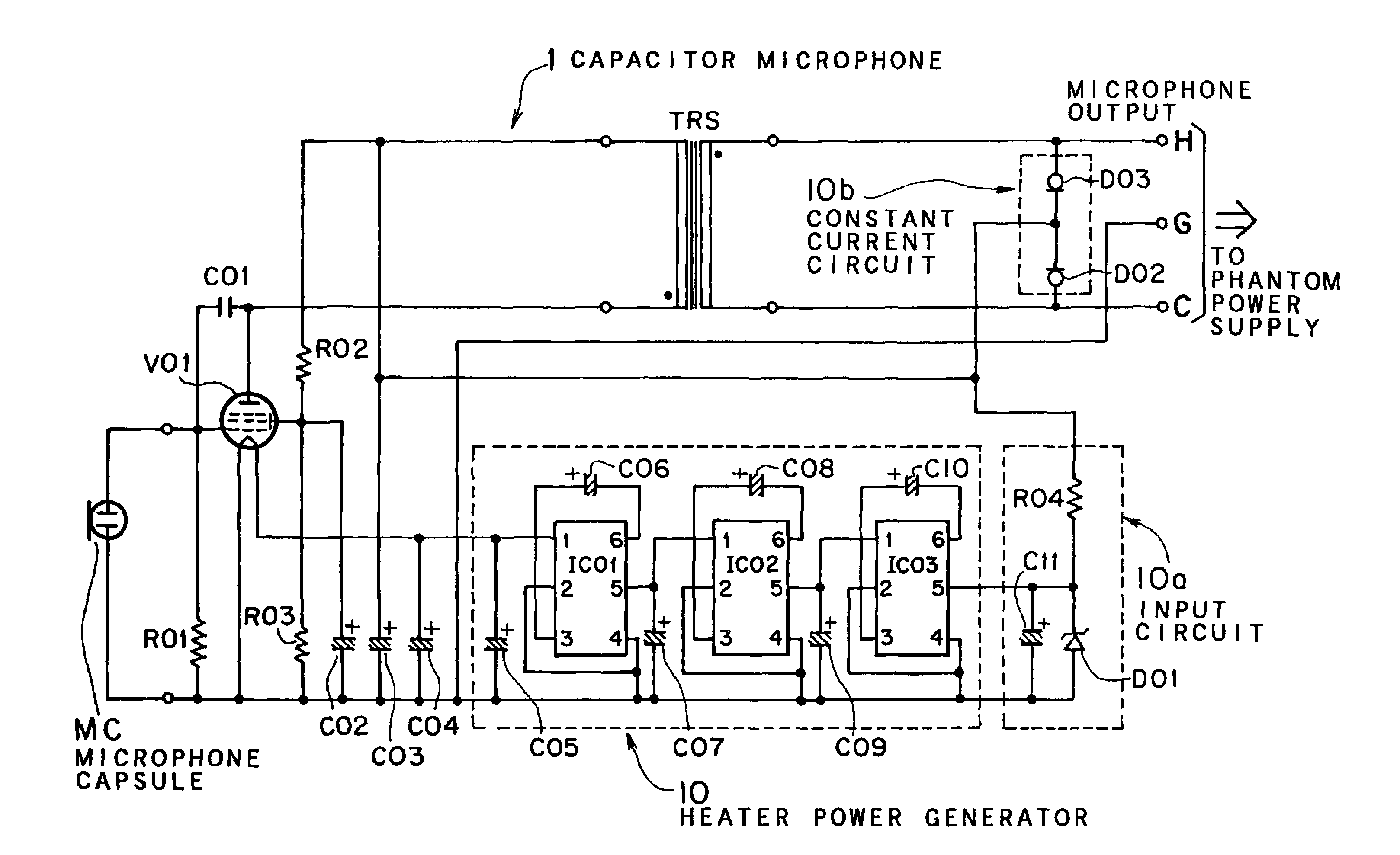
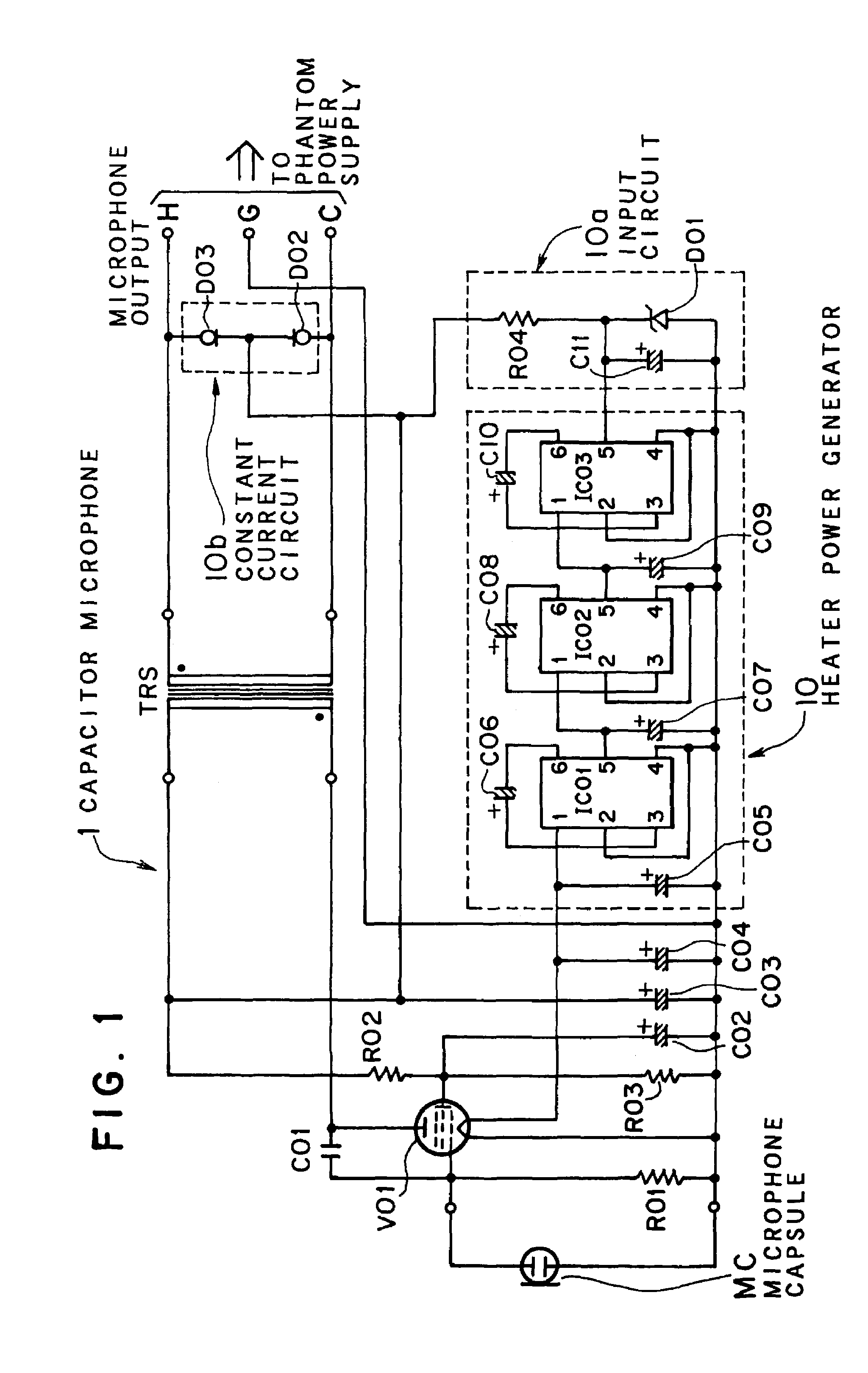
InactiveUS7295675B2Easily-offered in marketNo noisePiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesLow frequency amplifiersLow noiseVoltage converter
The present invention provides a low noise phantom powered capacitor microphone and a method of using a vacuum tube as an impedance converter of the microphone capsule in the capacitor microphone with no exclusive power supply.In the phantom powered capacitor microphone of which a vacuum tube V01 is used as the impedance converter, a part of the voltage supplied from the phantom power supply is converted to a predetermined voltage by one or more switched capacitor voltage converters, for example, by three switched capacitor voltage converters IC01, IC02 and IC03 seriously connected as three stages to obtain the heater voltage of the vacuum tube V01.
Owner:AUDIO-TECHNICA
Phantom power saver power tap
InactiveUS8221166B2UsabilityEliminate consumptionElectric discharge tubesSwitchgear with withdrawable carriageMiniaturizationEngineering
An apparatus, system and method are disclosed for eliminating phantom power wastage utilizing a power tap. An insulation casing creates a receiving space for a printed circuit board which mounts male blades, female receptacles, phantom power indication and a mechanical electrical switching capability is disclosed. The conductive male blades and female receptacles create a cross pattern for a two pronged power tap that allows miniaturization of the power tap so as to allow full access to adjacent electrical outlets. Switching states include normally open which permits zero power flow and normally closed which permits power indication and allows power to flow from conductive male blades to conductive female receiving receptacles.
Owner:ONPLUG INNOVATIONS
Active phantom-powered ribbon microphone with switchable proximity effect response filtering for voice and music applications
ActiveUS9210508B1Increase heightLow frequency responseMicrophone structural associationFrequency response correctionSound sourcesRibbon microphone
Novel active phantom-powered ribbon microphones that provide switchable proximity effect response filtering for voice and music applications are disclosed with unique adjustable interfaces. In one embodiment of the invention, a slider-based full frequency response vs. low frequency response and high pass filtering adjustment interface on a surface of a microphone casing provides a convenient switching between a “Music” mode and a “Voice” mode, wherein the “Voice” mode reduces the undesirable proximity effect in an active phantom-powered ribbon microphone, when a sound source is situated overly close to the active phantom-powered ribbon microphone. Furthermore, in one embodiment of the invention, a slider-based or a knob-based variable voice mode adjustment interface can also be integrated on a surface of a microphone casing to provide various preset levels of low frequency reduction and / or proximity effect response filtering when the “Voice” mode is enabled.
Owner:CLOUD MICROPHONES LLC
Condenser microphone
ActiveUS7970154B2Electrostatic transducer microphonesTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsCapacitanceOutput transformer
Owner:AUDIO-TECHNICA
High-power electromagnetic pulse launcher in well
InactiveUS20120212351A1Small internal resistanceLarge capacityElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAcoustic wave reradiationData acquisitionElectromagnetic pulse
A high-power electromagnetic pulse transmitting device for use in a downhole, the device including a ground instrument and a downhole instrument. The ground instrument, with an industrial control computer as the core, includes a depth / magnetic mark / GPS signal recording module, a Manchester coding and decoding module, and a cable drive module, wherein the depth / magnetic mark recording and the Manchester coding and decoding modules communicate respectively through two serial ports with the industrial control computer, and the cable drive module communication for the downhole instrument through four cables by means of phantom power supply. The downhole instrument includes, in turn, from front to rear: an AC voltage boosting module, a rectifier, an energy storage capacitor, a transmitting coil, and a data acquisition module, and further includes a high-voltage discharge switch and a computer-manipulated controller. Power supply of the downhole instrument is provided by the ground instrument through cables.
Owner:HU WENBAO +14
Ribbon microphone with rounded magnet motor assembly, backwave chamber, and phantom powered JFET circuit
ActiveUS8433090B1Improved and frequency responseReduce acoustic pressureMouthpiece/microphone attachmentsTransducer circuitsPhase cancellationAudio power amplifier
A novel ribbon microphone incorporates rounded-edge magnet motor assembly, a backwave chamber, and a phantom-powered JFET circuit. In one embodiment of the invention, one or more novel rounded-edge magnets may be placed close to a ribbon of the ribbon microphone, wherein the one or more novel rounded-edge magnets reduce or minimize reflected sound wave interferences with the vibration of the ribbon during an operation of the ribbon microphone. Furthermore, in one embodiment of the invention, a novel backwave chamber operatively connected to a backside of the ribbon can minimize acoustic pressure, anomalies in frequency responses, and undesirable phase cancellation and doubling effects. Moreover, in one embodiment of the invention, a novel phantom-powered JFET preamplifier gain circuit can minimize undesirable sound distortions and reduce the cost of producing a conventional preamplifier gain circuit.
Owner:CLOUD MICROPHONES LLC
Condenser microphone circuit
InactiveCN101048015AElectrets selectrostatic transducerMouthpiece/microphone attachmentsCondenser microphoneTime of use
In a condenser microphone which selectively uses a phantom power supply and a built-in battery power supply, and which switches load resistance elements of an impedance converter corresponding to a selected power supply, a noise due to the high frequencies is prevented from occurring even if a cellular phone or the like is used in the vicinity. The condenser microphone includes: a condenser type electro-acoustic transducer element; an impedance converter that converts an output impedance of the electro-acoustic transducer element; load resistance elements of the impedance converter; a phantom power supply and a built-in battery power supply for operating the impedance converter; a switch that switches the values of the load resistance between at the time of using the phantom power supply and at the time of using the built-in battery power supply, wherein the switch is an optical switch that turns on / off optical coupling. The optical switch is switched so that the value of the load resistance is larger at the time of using the phantom power supply than at the time of using the built-in battery power supply.
Owner:AUDIO-TECHNICA
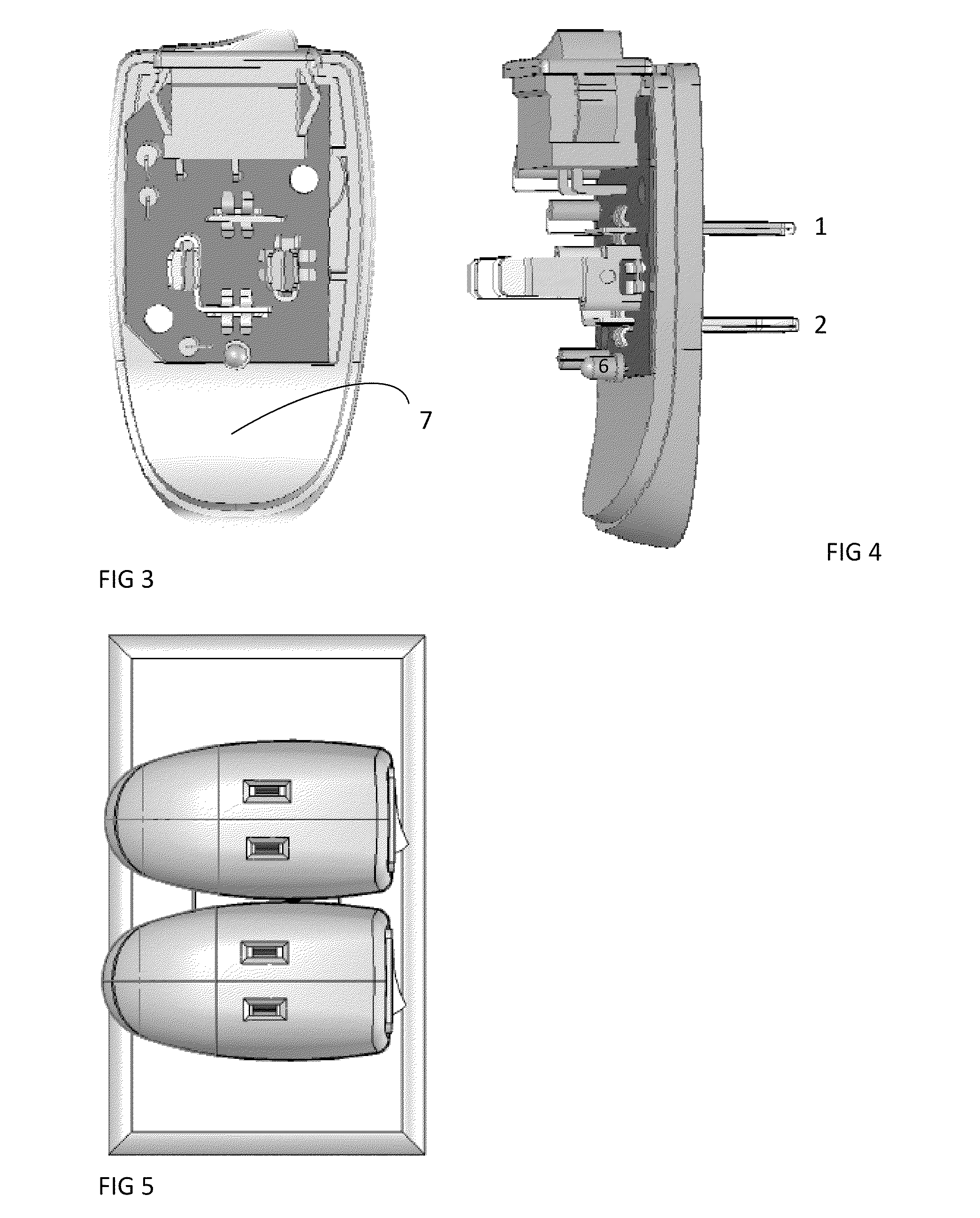
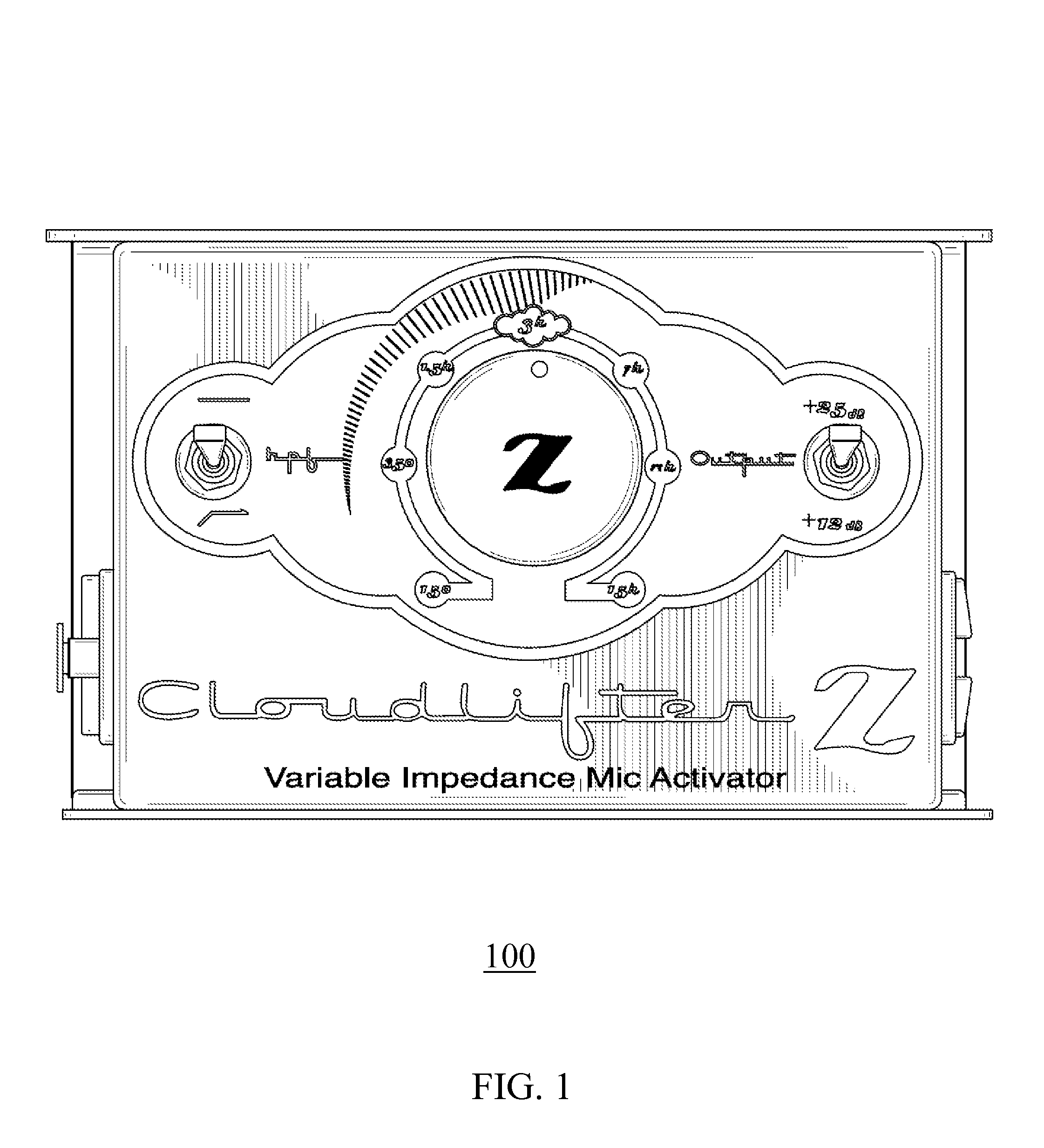
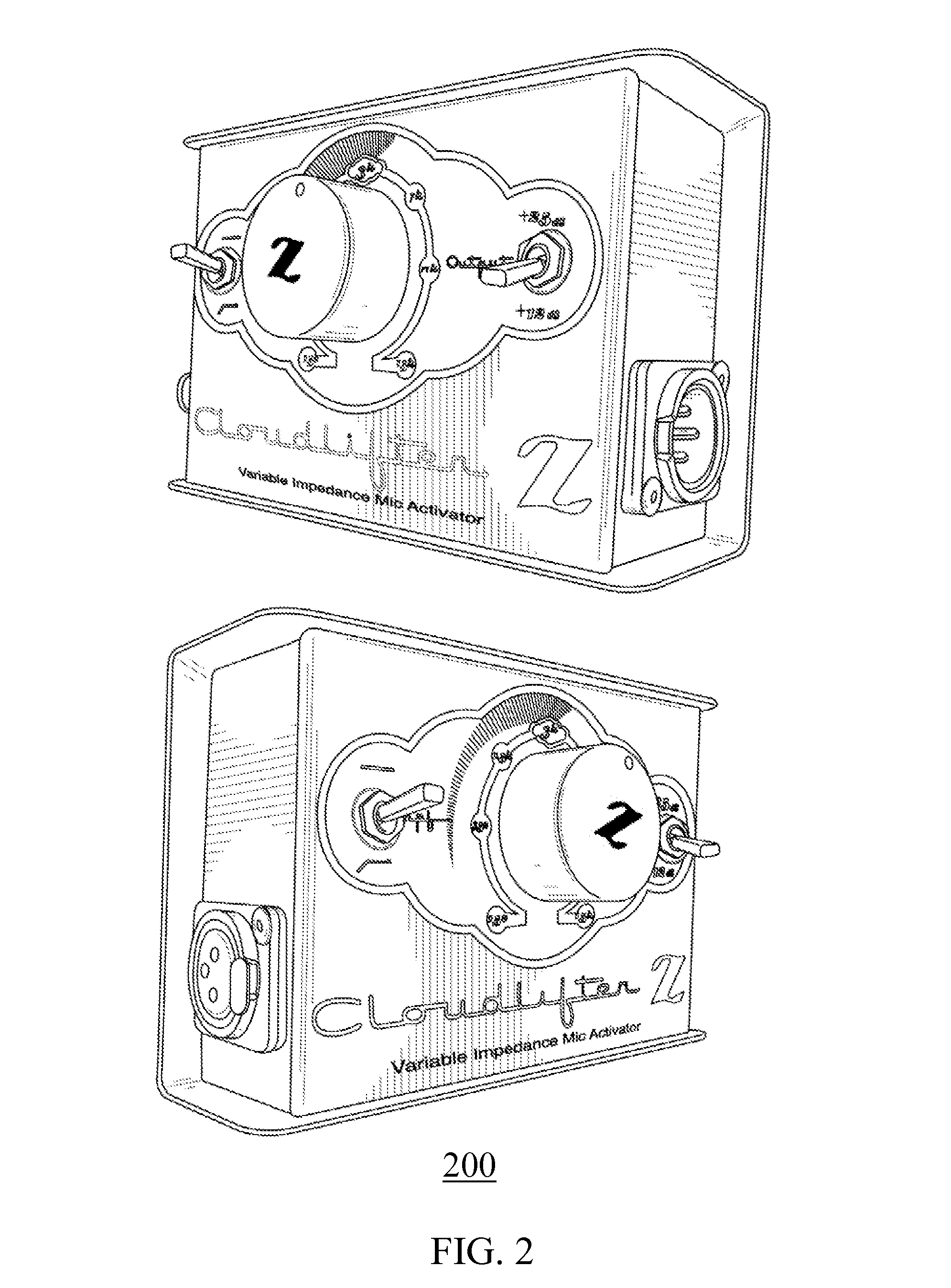
Phantom-powered inline preamplifier with variable impedance loading and adjustable interface
ActiveUS9306519B1Variable impedance loadingManually-operated gain controlMicrophone structural associationSound sourcesAudio power amplifier
Phantom-powered inline preamplifiers capable of variable impedance loading are disclosed with unique adjustable interfaces. By enabling a user to adjust impedance loading from an actively-powered audio preamplifier which takes a microphone electrical signal or another sound source signal as an input, this unique audio preamplifier design with various adjustable impedance loading interface configurations can change sound characteristics according to the user's preference in a recording, production, or live concert environment. In addition, a high pass filter incorporated in a preamplifier with the variable impedance loading feature allows the user to further customize sound characteristics in the recording environment. This novel inline preamplifier, which may be standalone or integrated into a microphone casing, is powered via a microphone cable from a component (e.g. another preamplifier) providing the phantom power. This inline preamplifier may be connected to a conventional microphone and receive phantom-power into the inline preamplifier from a conventional preamplifier.
Owner:CLOUD RODGER
Audio level compressor
InactiveUS8199934B2Easy to changeEasy to compressGain controlSpeech analysisDynamic range compressionLoad resistance
An audio level compressor for compressing the dynamic range of an input audio signal. The audio level compressor can be part of a microphone, or a separate component. The audio level compressor includes input terminals for receiving the input audio signal, a lamp having a filament resistance that is a function of the input audio signal; a load resistance; a signal gain controller that includes a means for increasing dynamic range compression of the input audio signal, and output terminals for providing an output audio signal that is a function of the input audio signal and the signal gain. The signal gain controller provides a signal gain that is a function of the filament resistance and the load resistance. The audio level compressor can also include an expander circuit or a power conditioning circuit. Power can be provided by an internal source or a phantom power supply.
Owner:OSBORNE GARY T
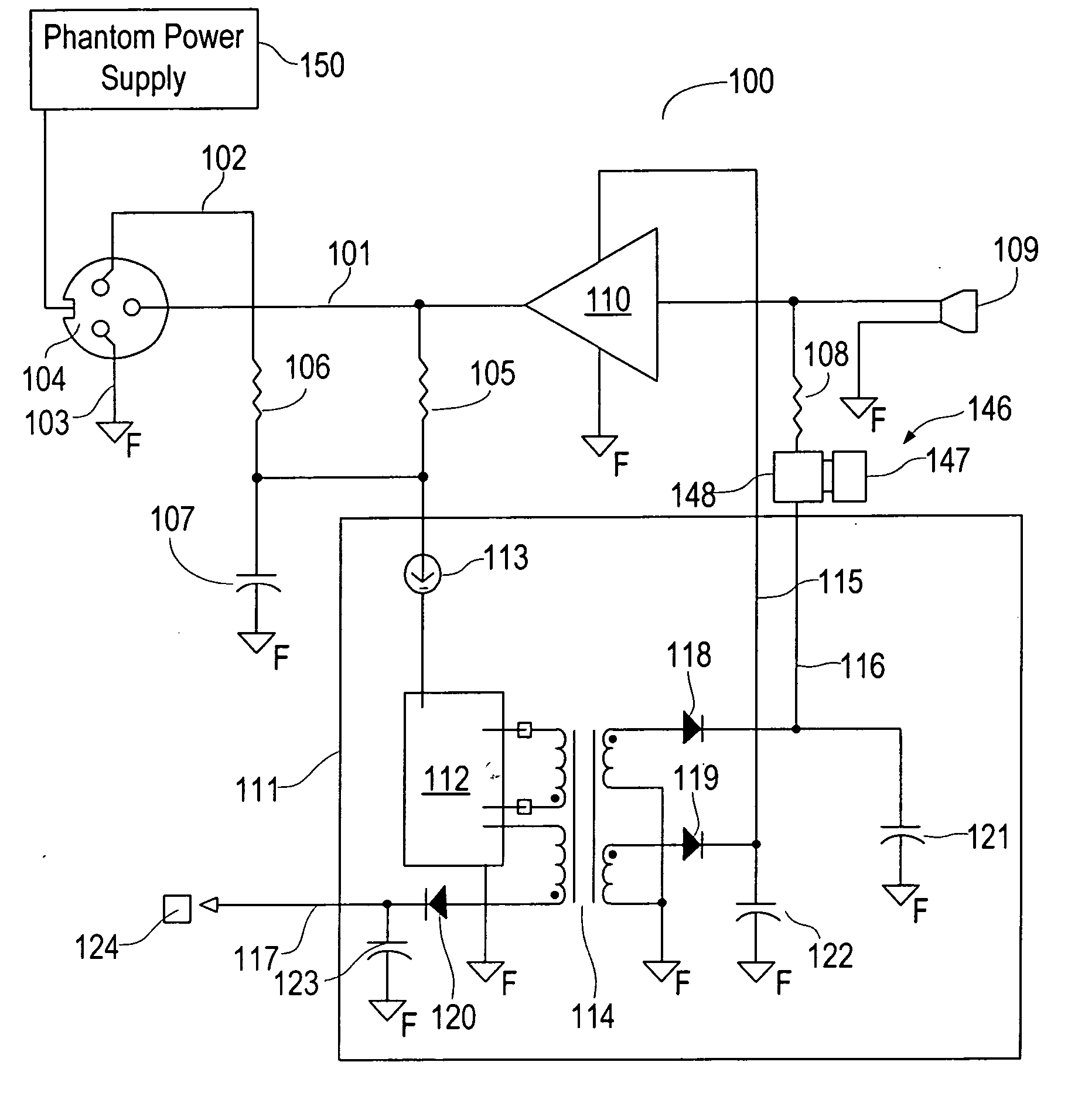
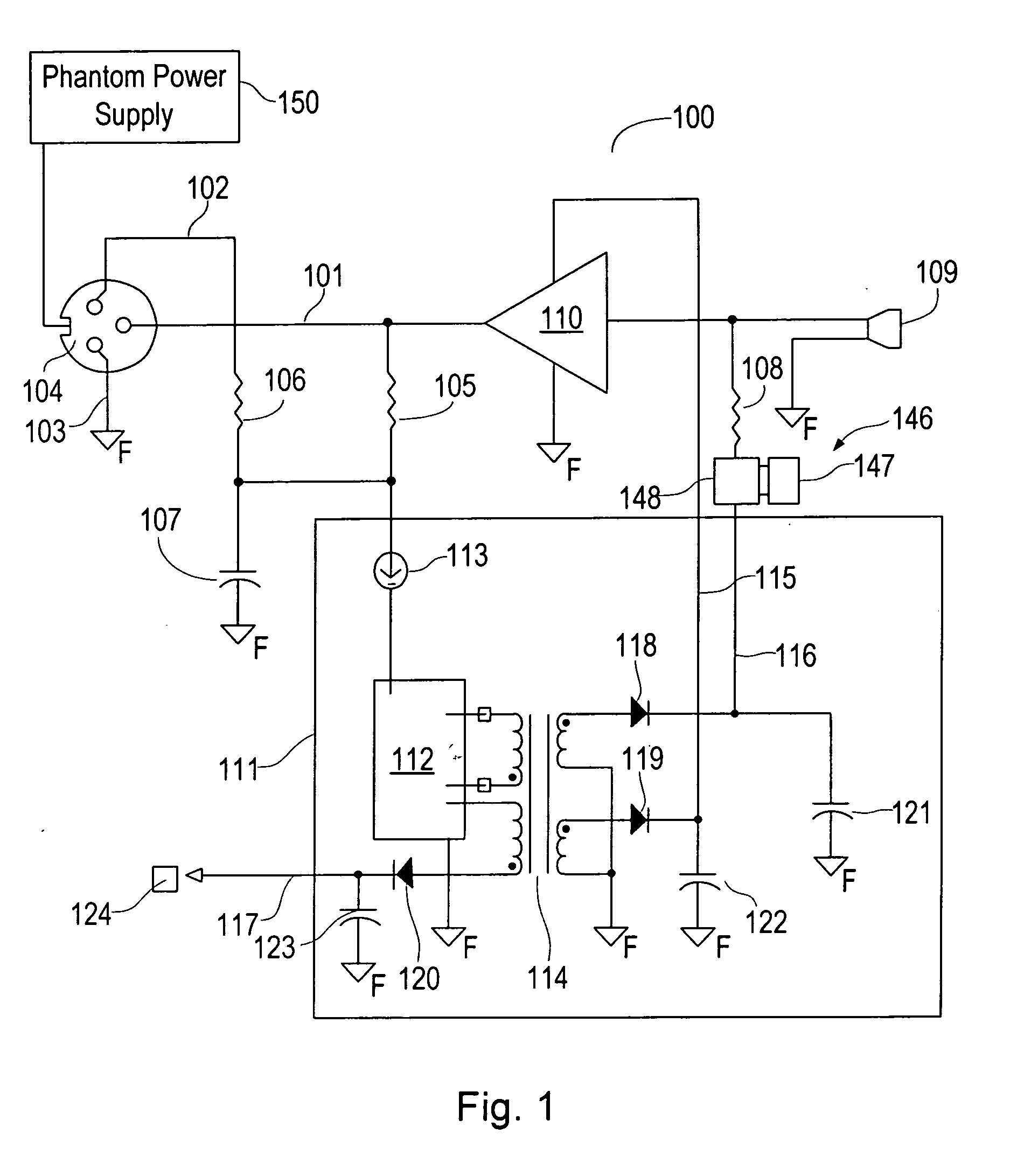
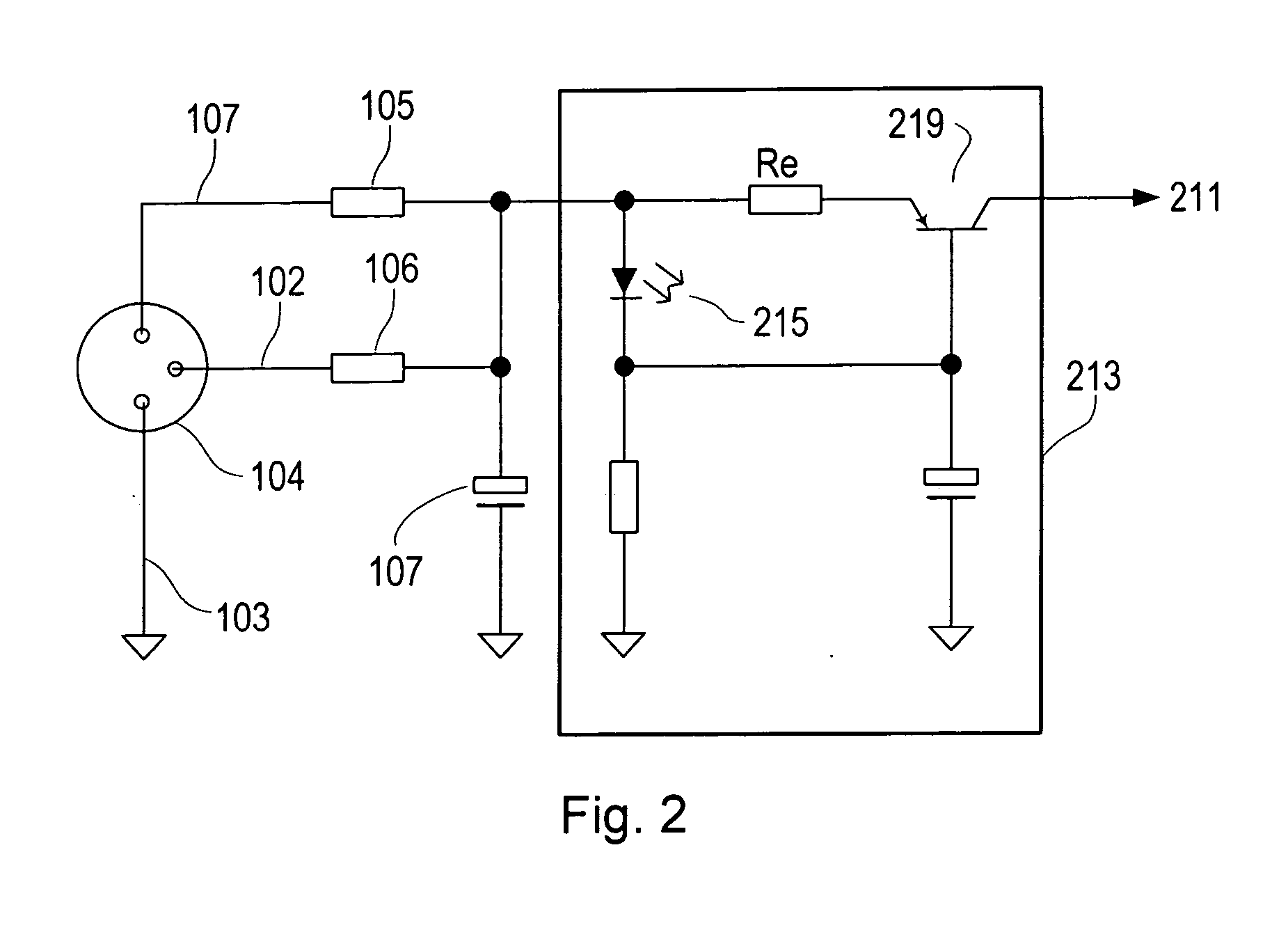
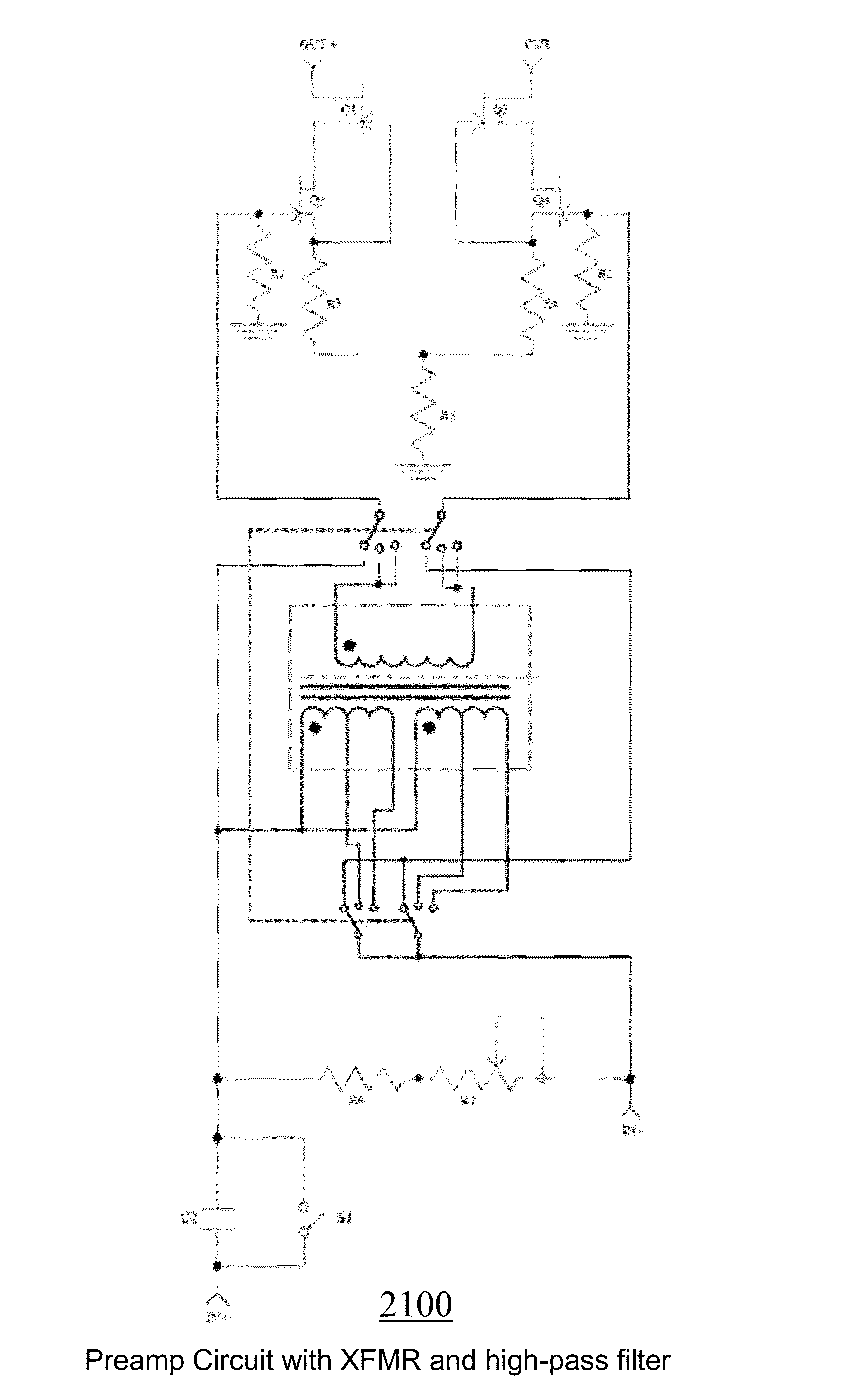
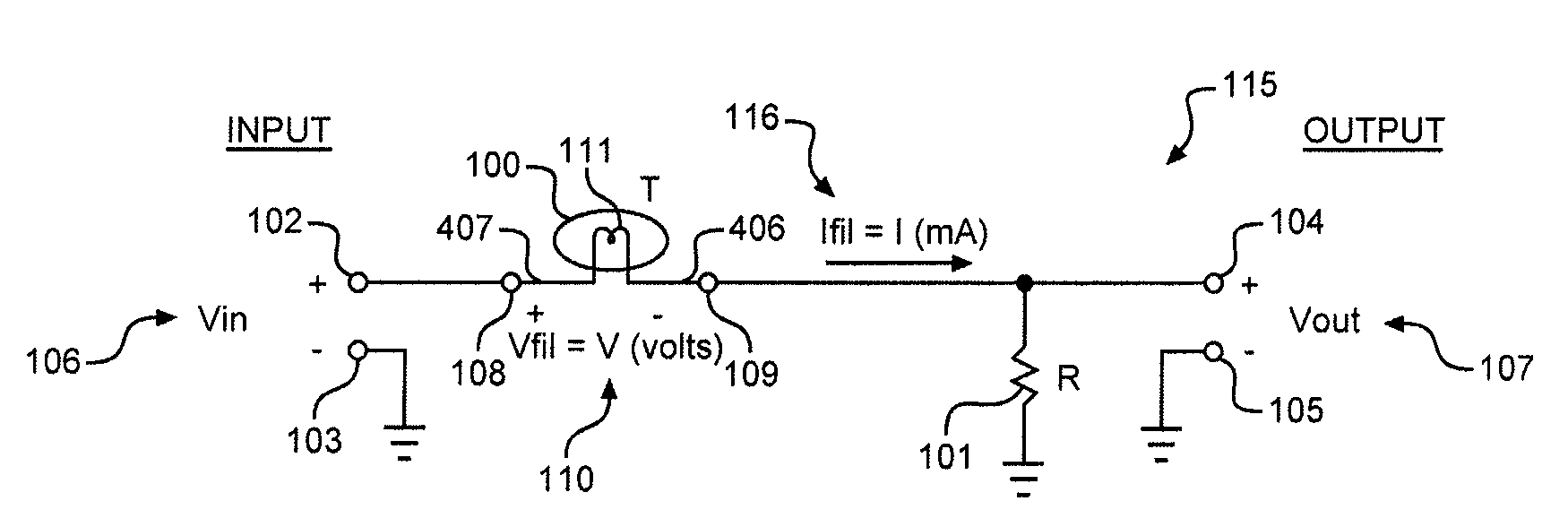
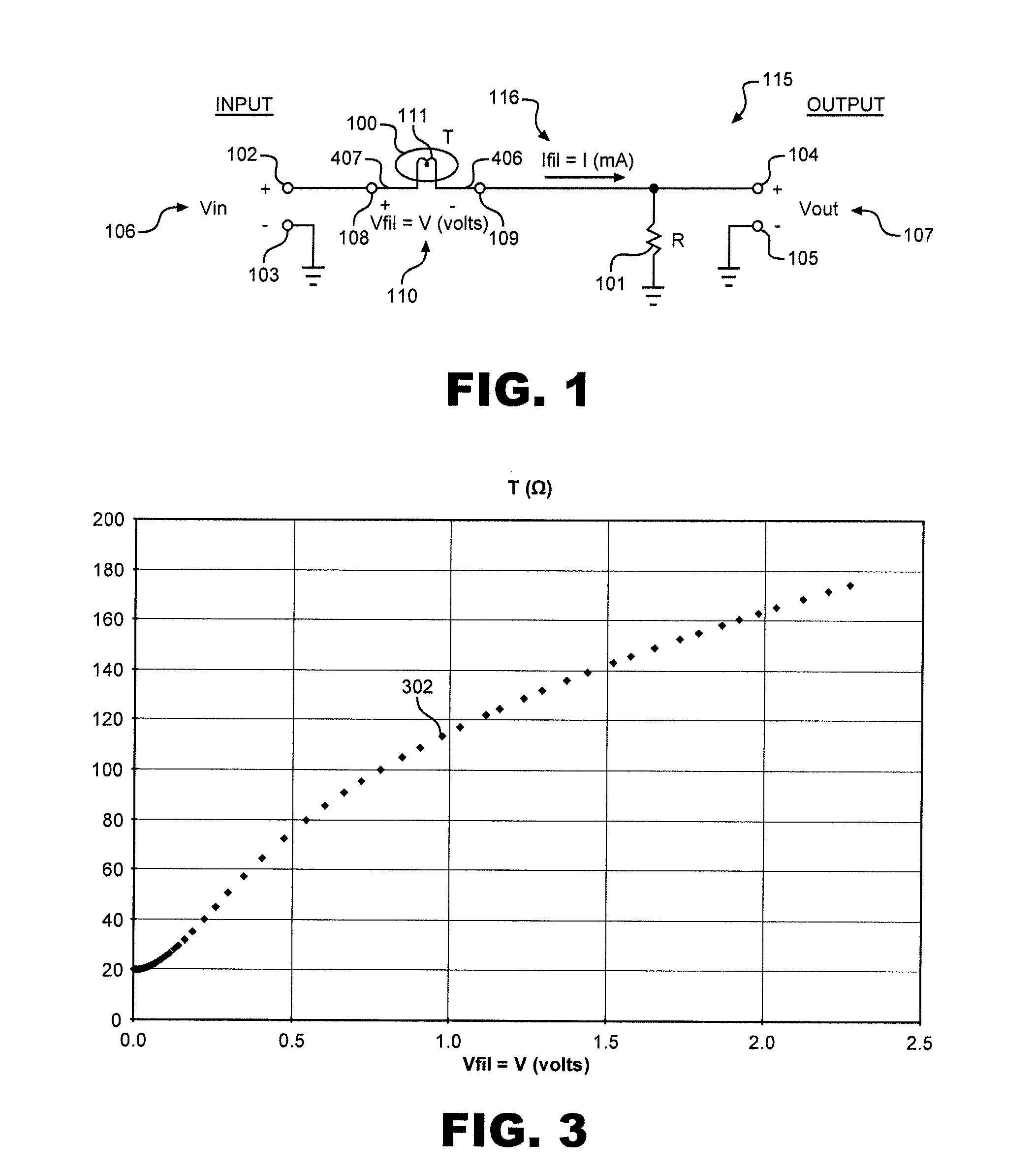
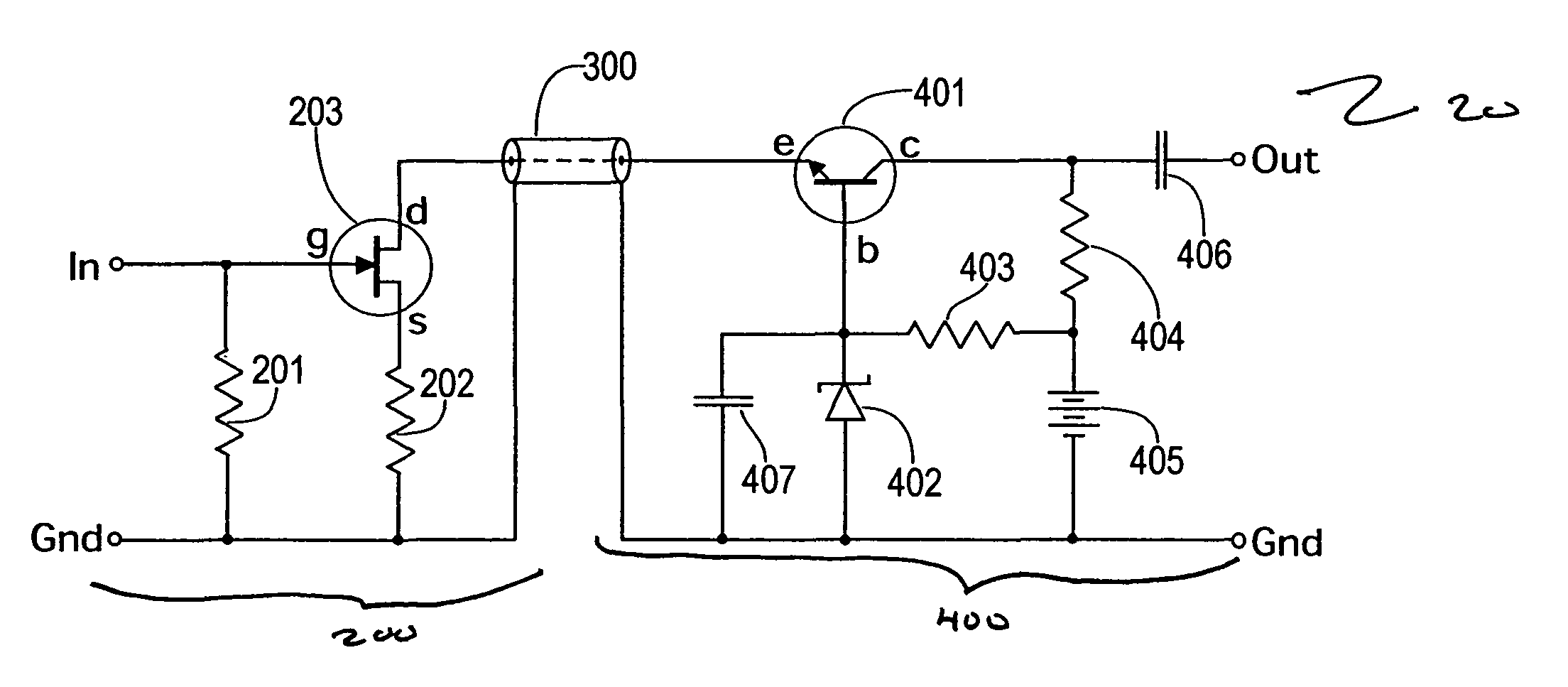
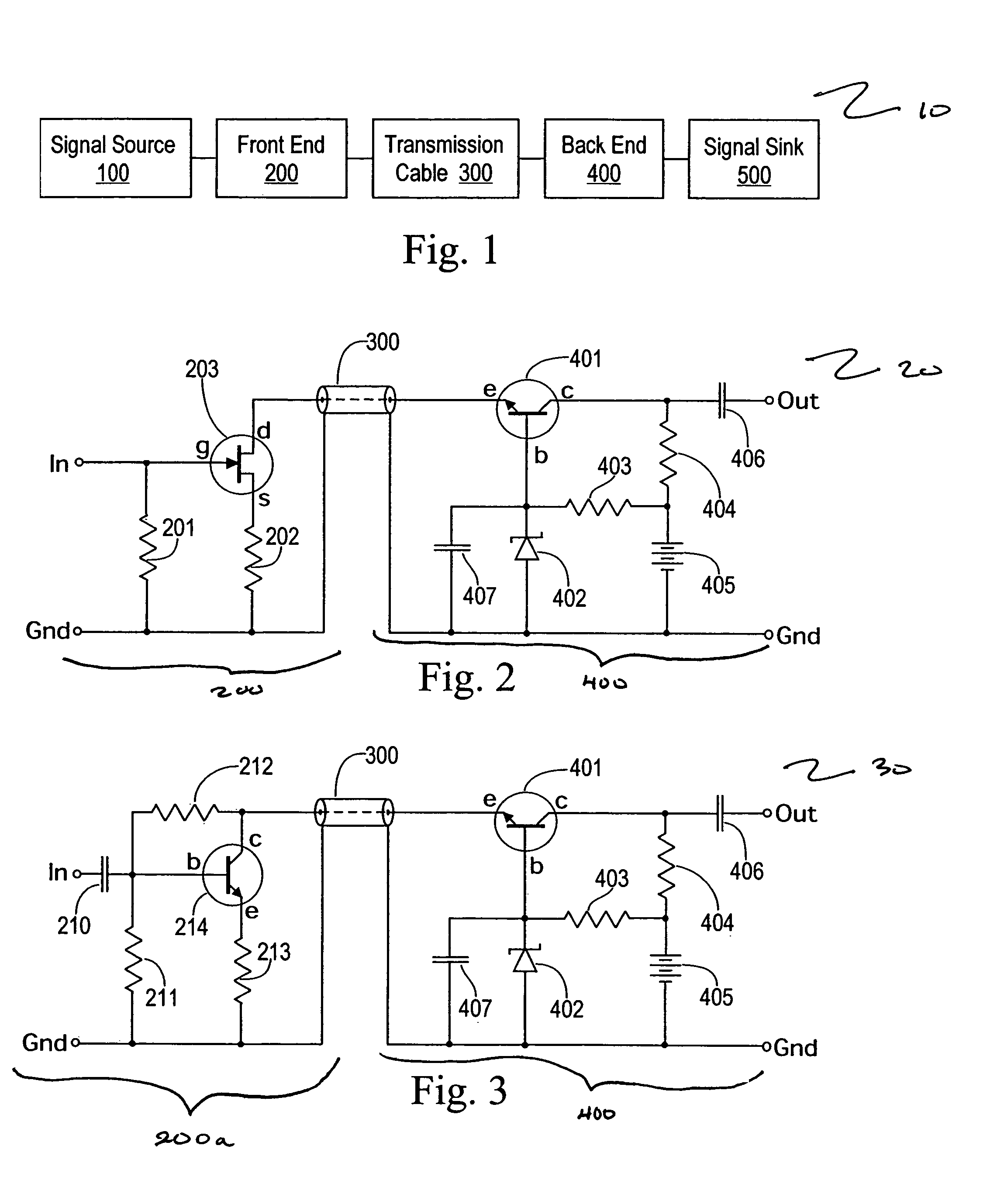
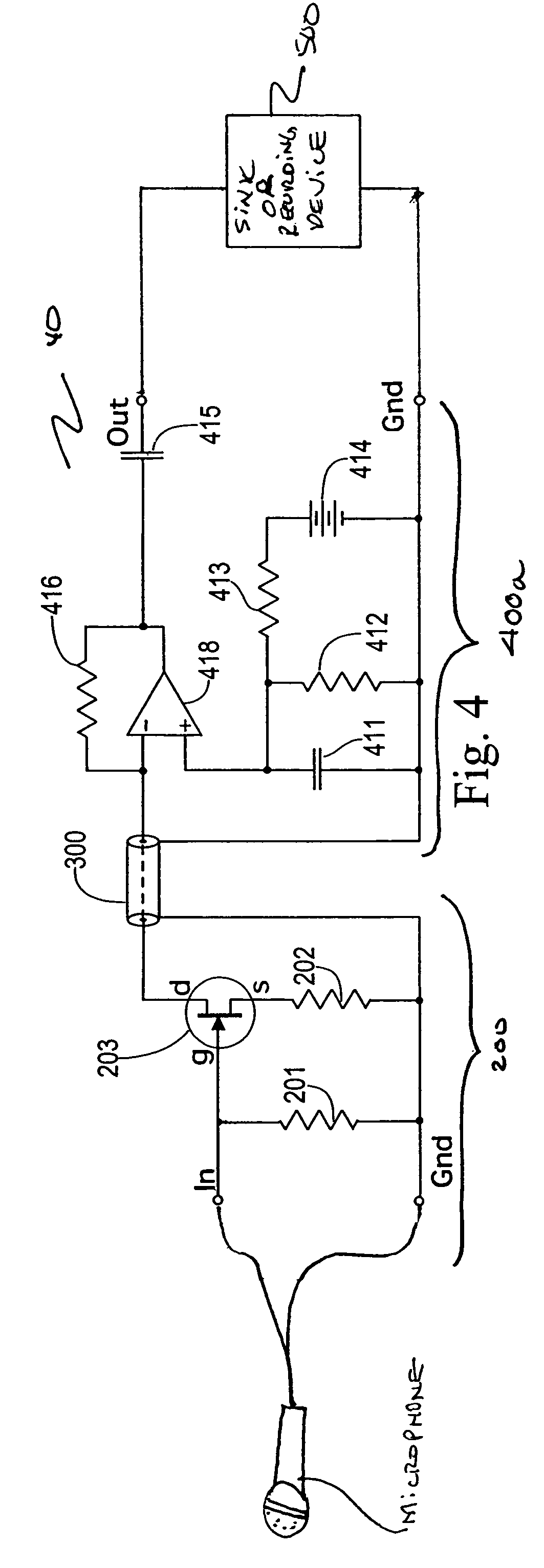
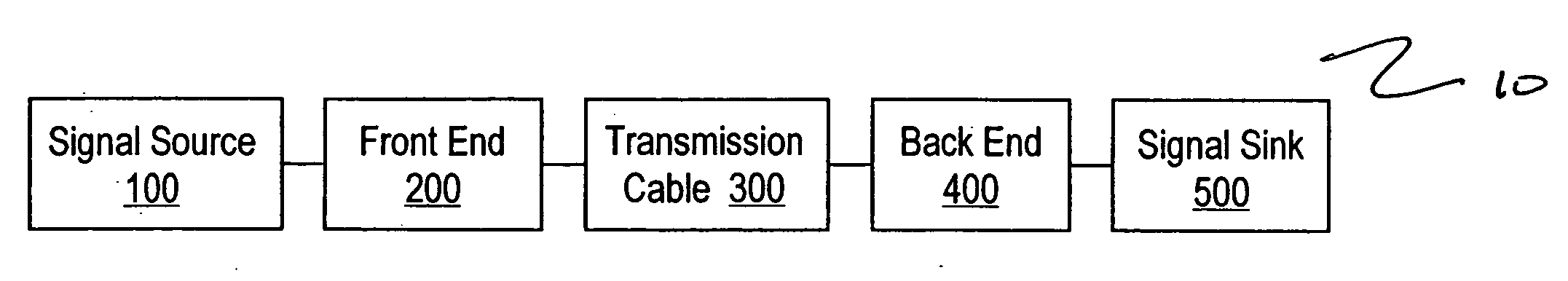
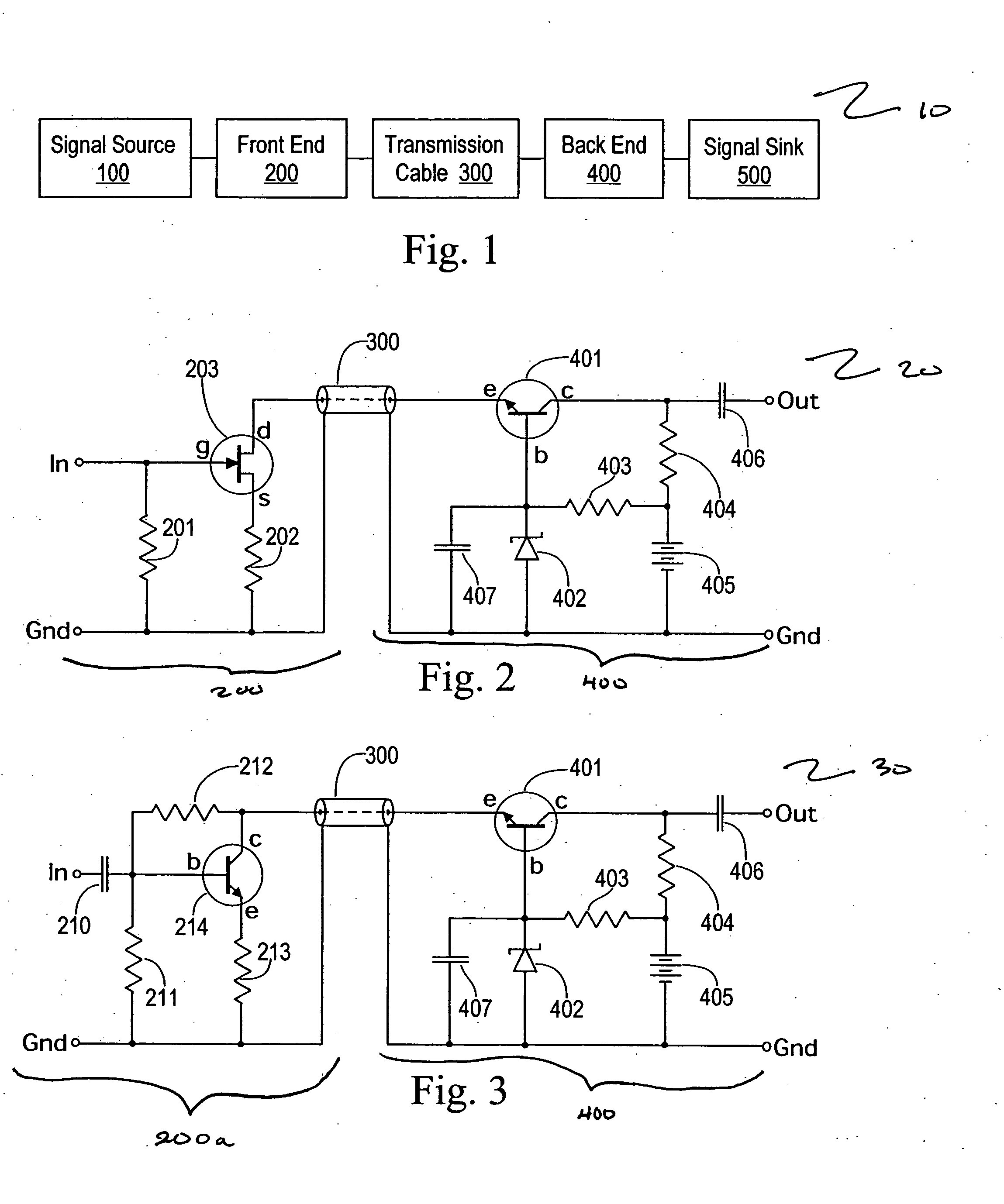
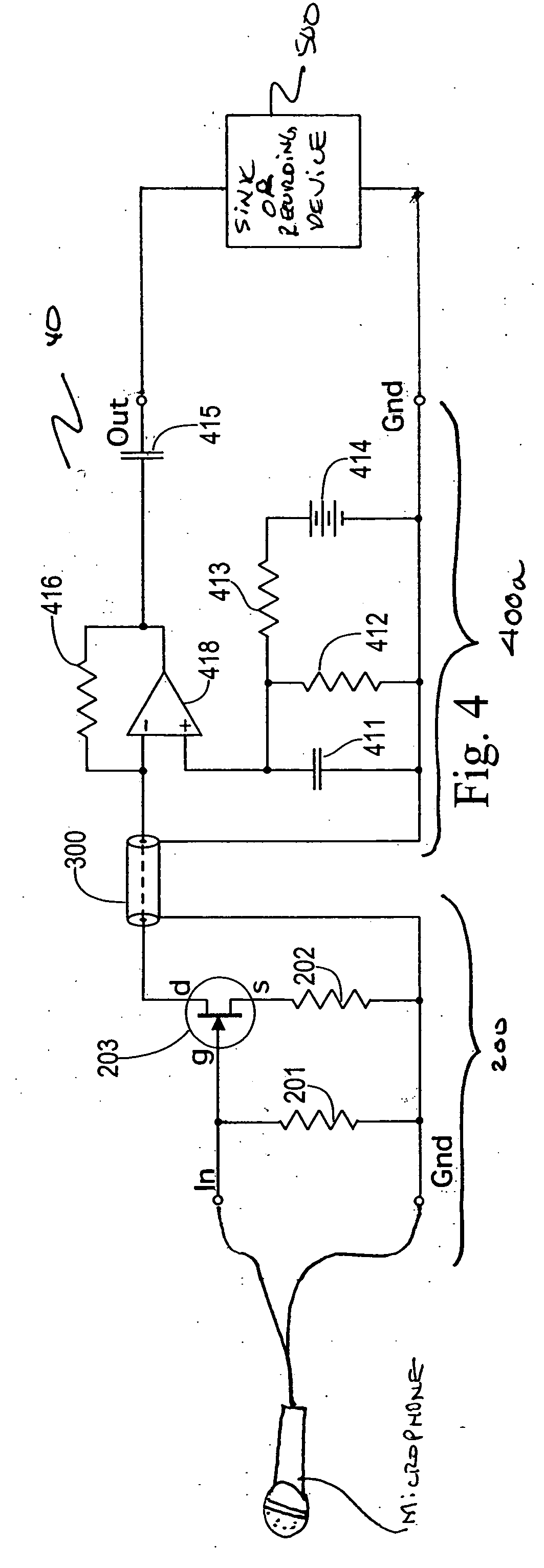
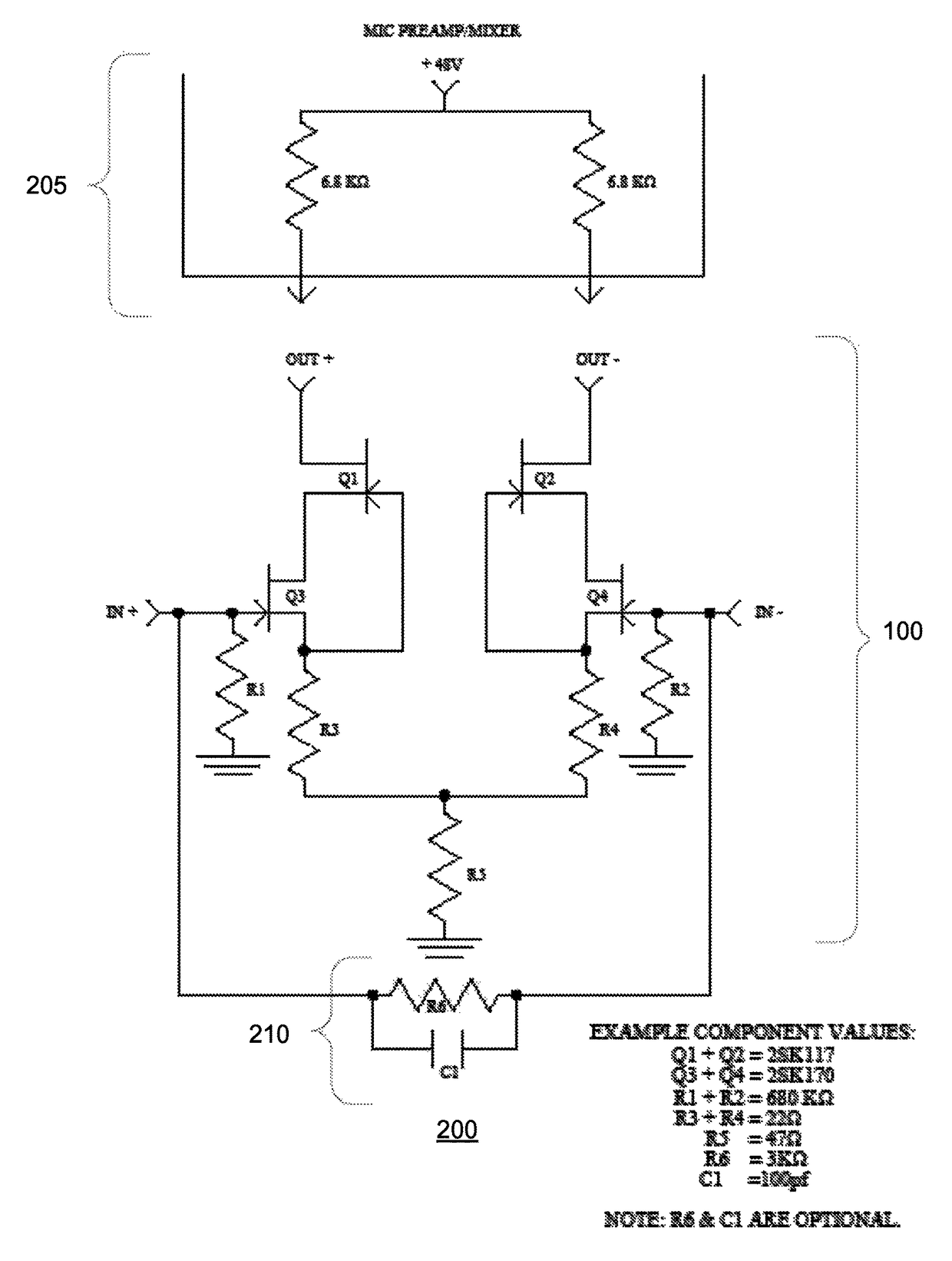
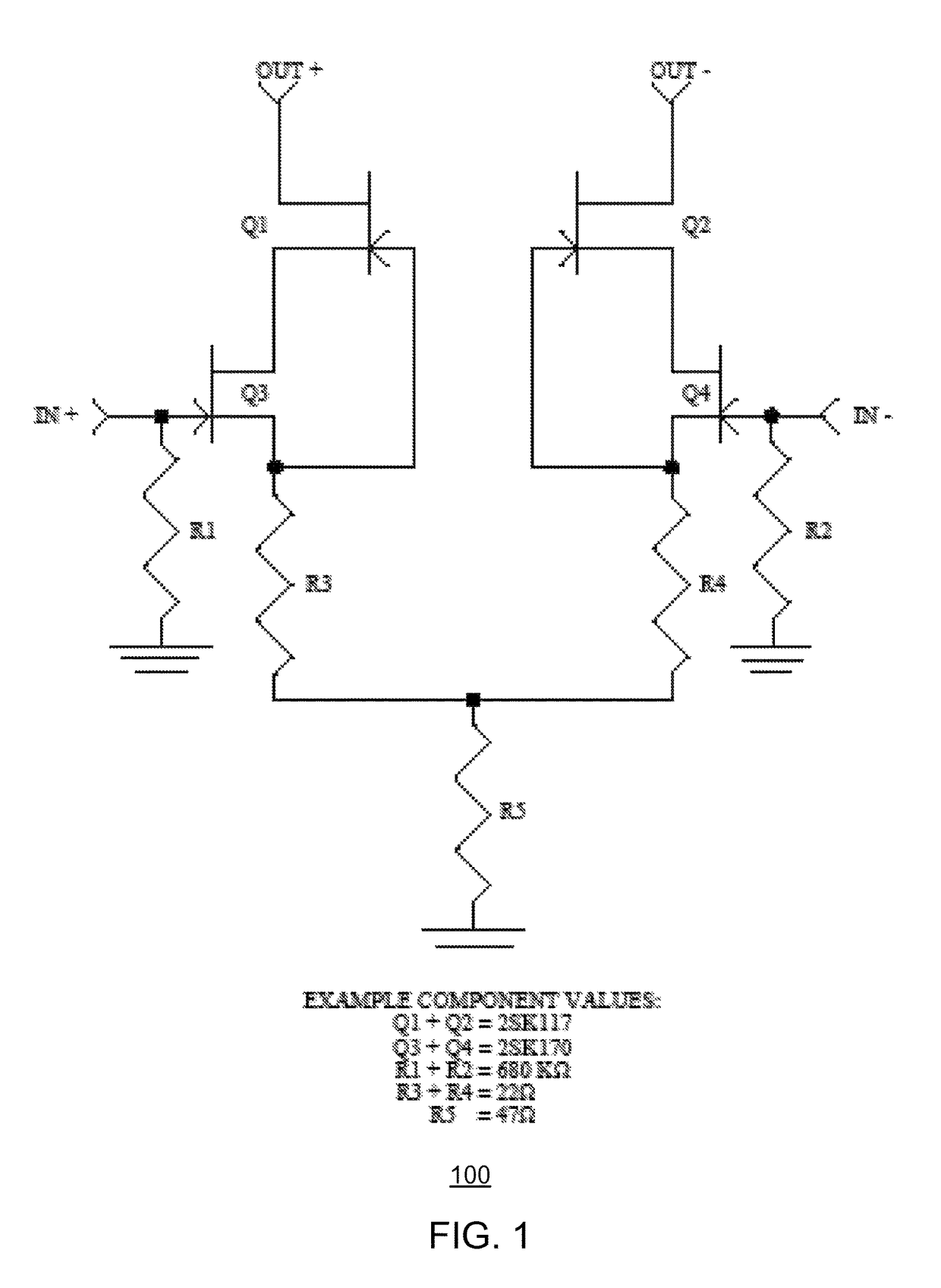
Split cascode line amplifier for current-mode signal transmission
InactiveUS8134385B2Low costIncrease physical strengthMultiple-port networksReliability increasing modificationsElectrical conductorCurrent mode
Current-mode transmission is implemented in a cascode amplifier by splitting a cascode circuit into a front end and a back end to ensure wideband current-mode transmission of an audio signal. A transmission cable is located between the high impedance output of the first end and the low impedance input of the back end. The front end includes a first amplifying device, and the back end includes a second amplifying device. The front end is phantom powered by the back end using the same electrical conductors that carry the current-mode signal over the transmission cable.
Owner:GWINN JOSEPH
Split cascode line amplifier for current-mode signal transmission
InactiveUS20050146389A1Low costIncrease physical strengthReliability increasing modificationsMultiple-port networksElectrical conductorEngineering
Current-mode transmission is implemented in a cascode amplifier by splitting a cascode circuit into a front end and a back end to ensure wideband current-mode transmission of an audio signal. A transmission cable is located between the high impedance output of the first end and the low impedance input of the back end. The front end includes a first amplifying device, and the back end includes a second amplifying device. The front end is phantom powered by the back end using the same electrical conductors that carry the current-mode signal over the transmission cable.
Owner:GWINN JOSEPH
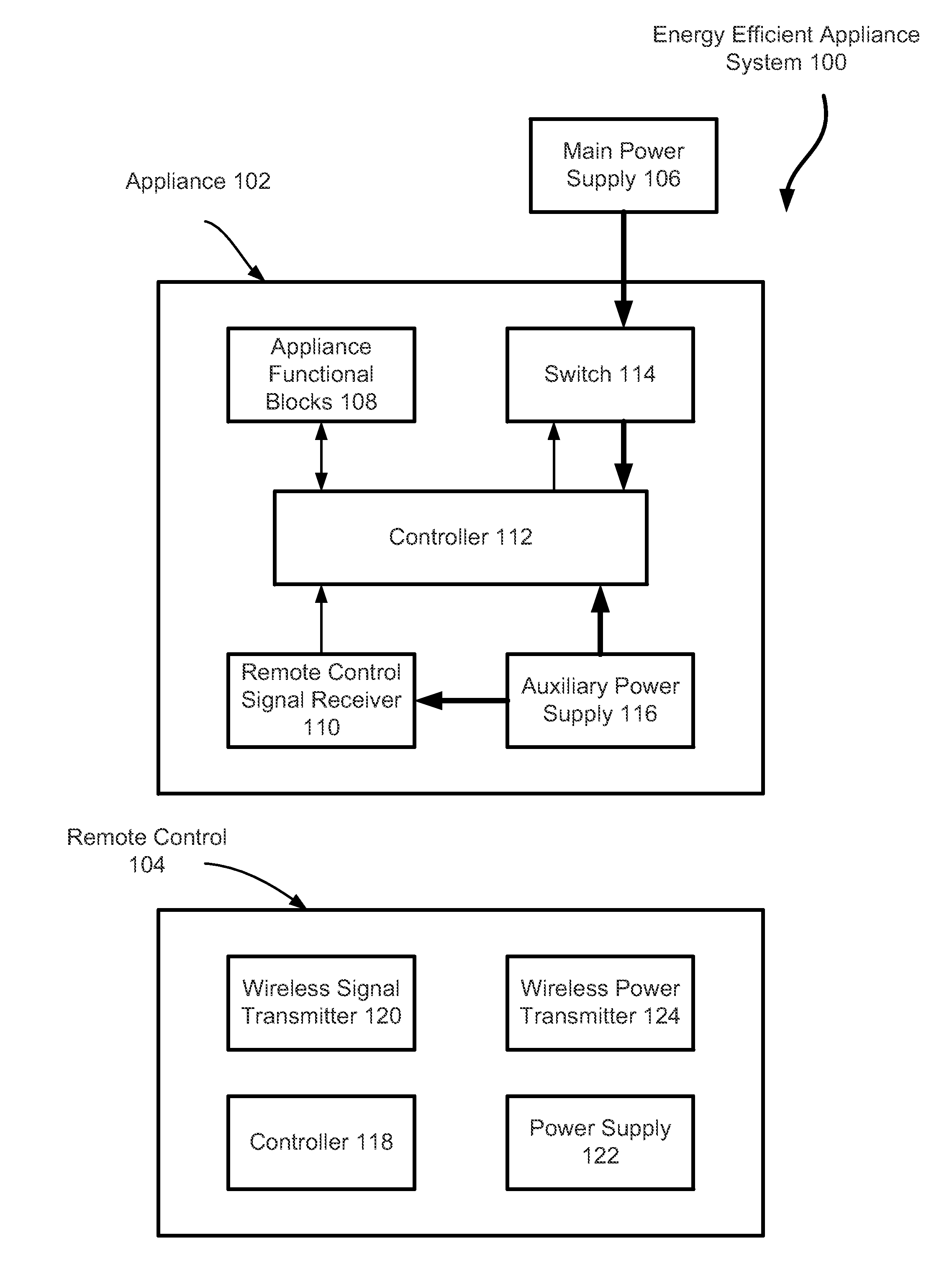
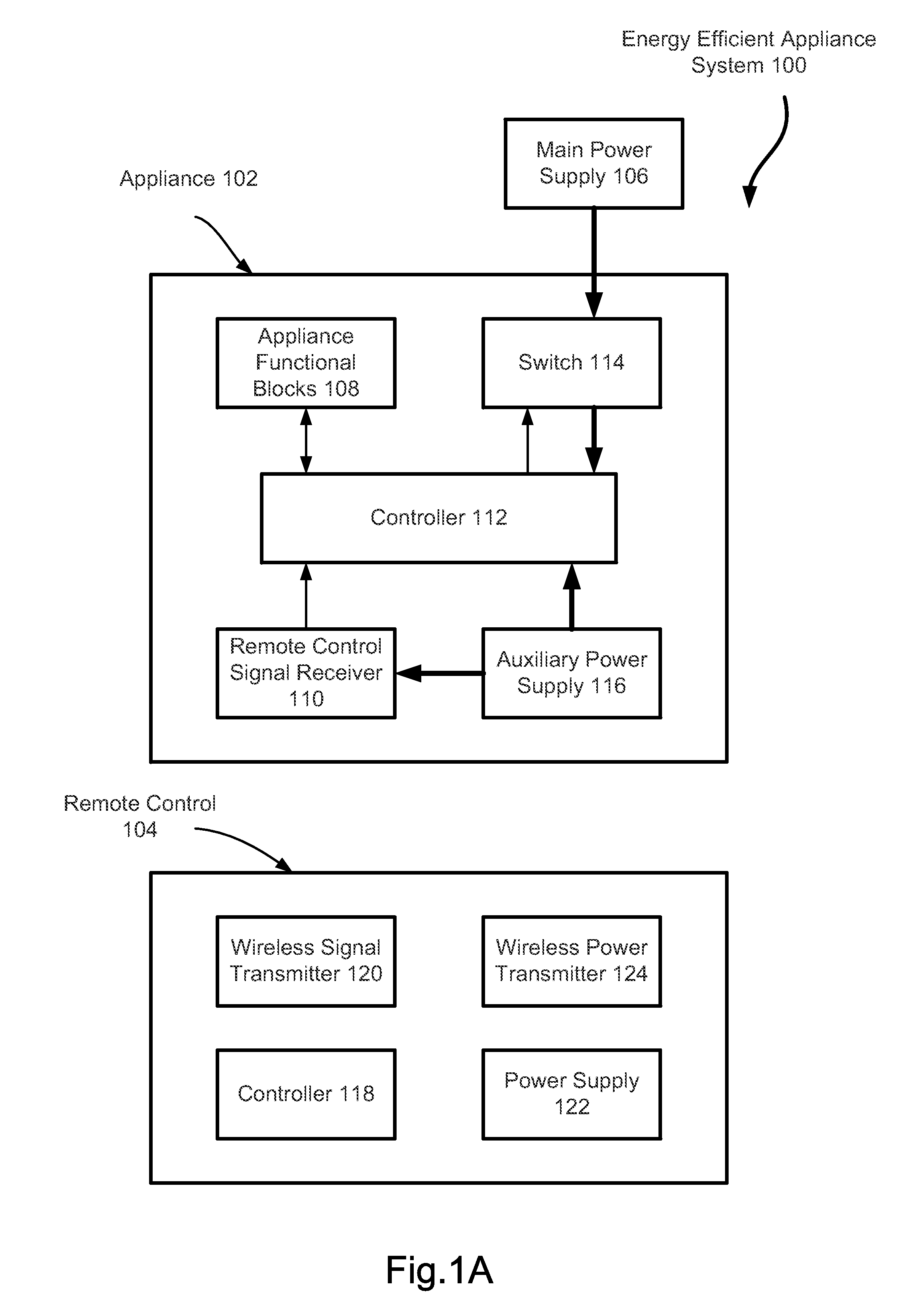
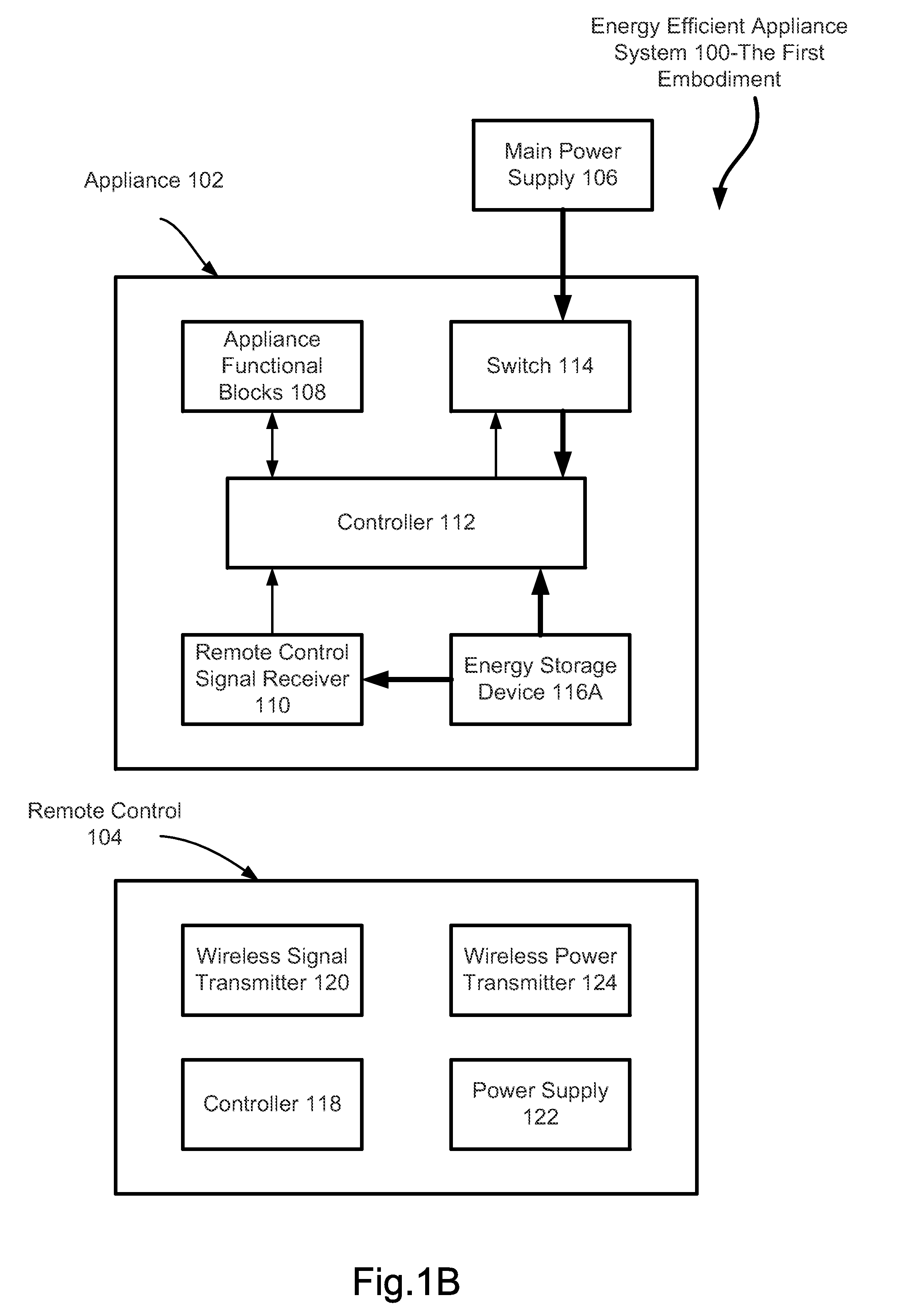
Energy Efficient Electrical Appliance without Phantom Power Consumption
InactiveUS20150288221A1Not consumeEnergy efficiencyElectric signal transmission systemsBatteries circuit arrangementsDigital videoMicrowave oven
An energy efficient appliance is switched off completely from a main power supply when it is not in operation to deliver designed functionalities. An auxiliary power supply is employed to provide power for receiving restarting signal from a remote control device. In one embodiment, the auxiliary power supply receives power wirelessly from the remote control device to switch on the main power supply. In another embodiment, the auxiliary power supply receives power by harvesting energy available in environment. In still another embodiment, the auxiliary power supply is a replaceable or rechargeable battery. The appliance includes televisions, digital video recorders, air conditioners, lighting systems, audio systems and microwave ovens. The appliance may also include a door open system for a home or for an automobile.
Owner:PAN YANG
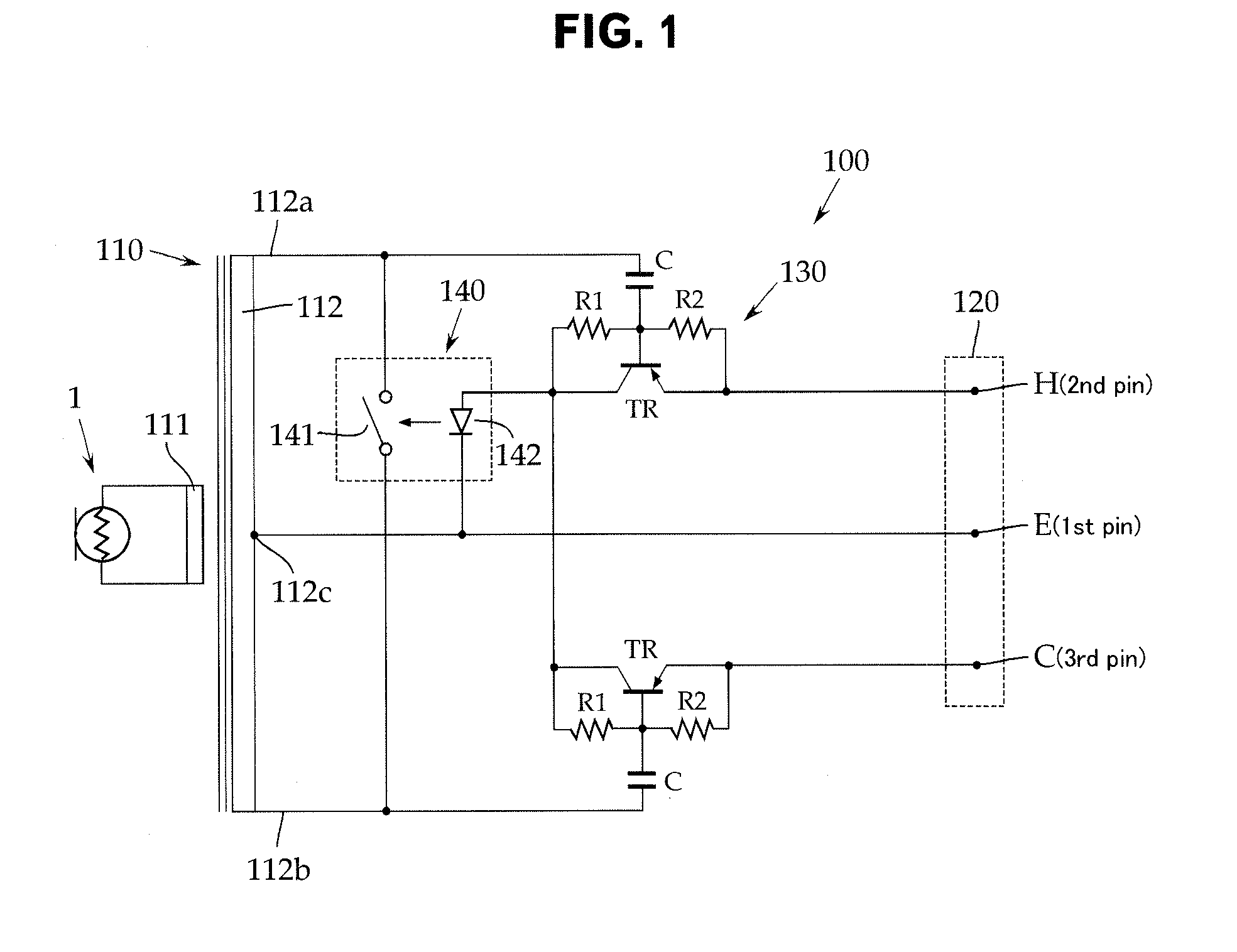
Ribbon microphone
InactiveUS20120189145A1Lower impedanceImprove versatilityTransducer protection circuitsDeaf-aid setsRibbon microphonePhantom power
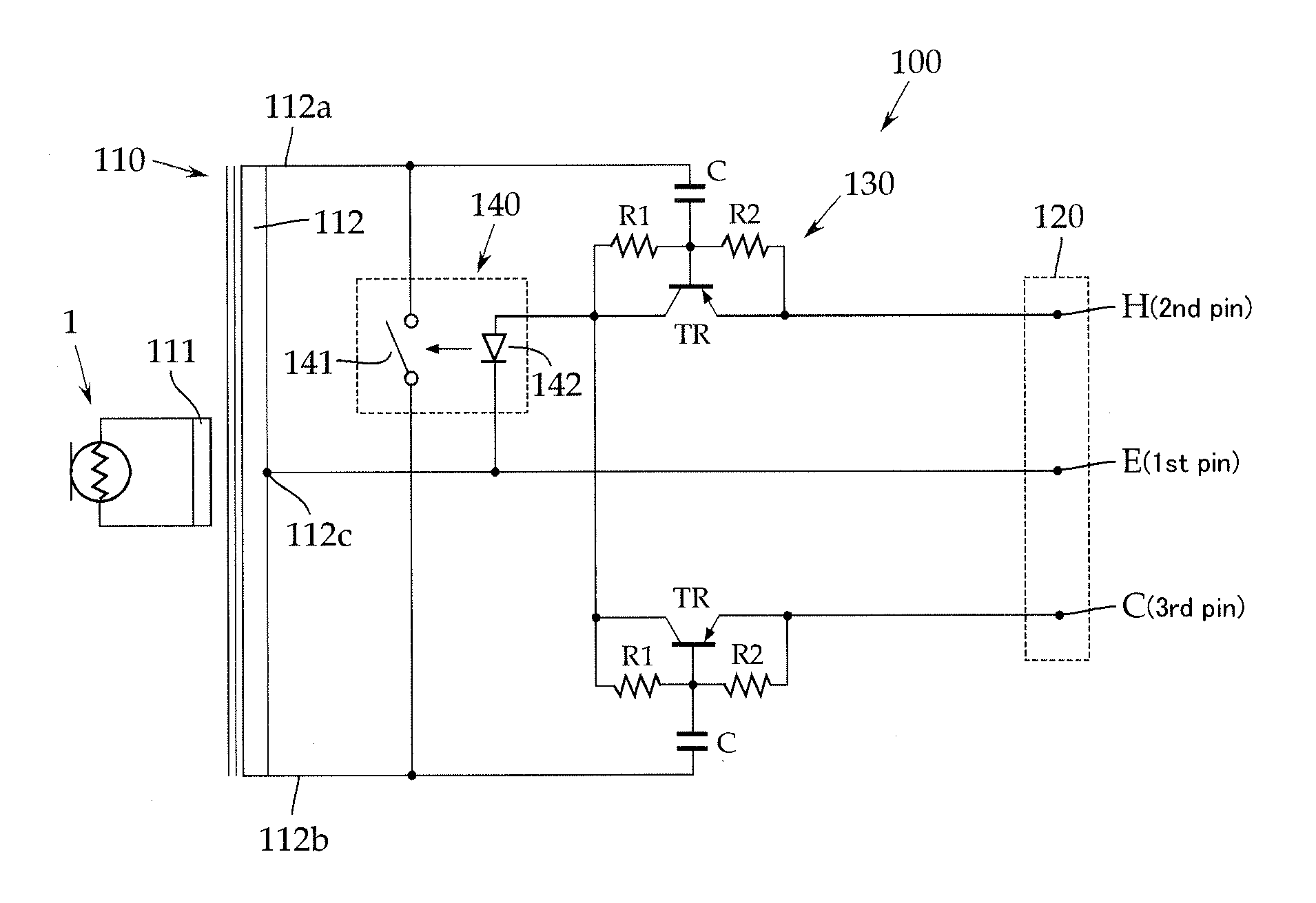
To provide electromagnetic damping without a special output connector for protecting a diaphragm of metallic ribbon foil of a ribbon microphone against shocks. A ribbon microphone operable with a phantom power supply comprises: an acoustic-electric converter 1 including a pair of permanent magnets and a diaphragm of metallic ribbon foil; and a step-up transformer 110 coupled with the diaphragm on a primary winding 111 side and having, on a secondary winding 112 side, an output connector 120 removably connected to a phantom power supply, the step-up transformer 110 increasing a voltage generated by the diaphragm to a predetermined voltage, the voltage then being output to the phantom power supply side through the output connector 120, wherein a switch 141 is connected across the secondary winding 112, the switch 141 being normally closed and being opened by a power supplied from the phantom power supply.
Owner:AUDIO-TECHNICA
Integrated phantom-powered JFET circuit module in portable electronic device for creating hi-fidelity sound characteristics
ActiveUS9668045B1Signal processingAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyEngineeringPhantom power
A novel phantom-powered JFET gain circuit that improves audio clarity and linearity, while reducing a high-gain burden, noise, and distortion from a sole usage of a conventional preamplifier, is disclosed. In one embodiment, the novel phantom-powered JFET gain circuit is encased as a standalone box that connects to a microphone on one end and a conventional preamplifier unit or another conventional audio processing unit on another end. In another embodiment, the novel phantom-powered JFET gain circuit is integrated into a portable electronic device or another consumer electronic device with a microphone to provide an earliest-stage gain in a microphone-captured audio signal processing pathway. Yet in another embodiment, the novel phantom-powered JFET gain circuit is integrated into a preamplifier unit and provides the earliest-stage gain in a microphone-captured audio signal processing pathway, prior to additional and conventional signal amplification by the preamplifier unit.
Owner:CLOUD RODGER
Digital microphone and power supply unit for a digital microphone
ActiveUS8265306B2Low heat generationPower Loss MinimizationPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesMicrophonesEngineeringPhantom power
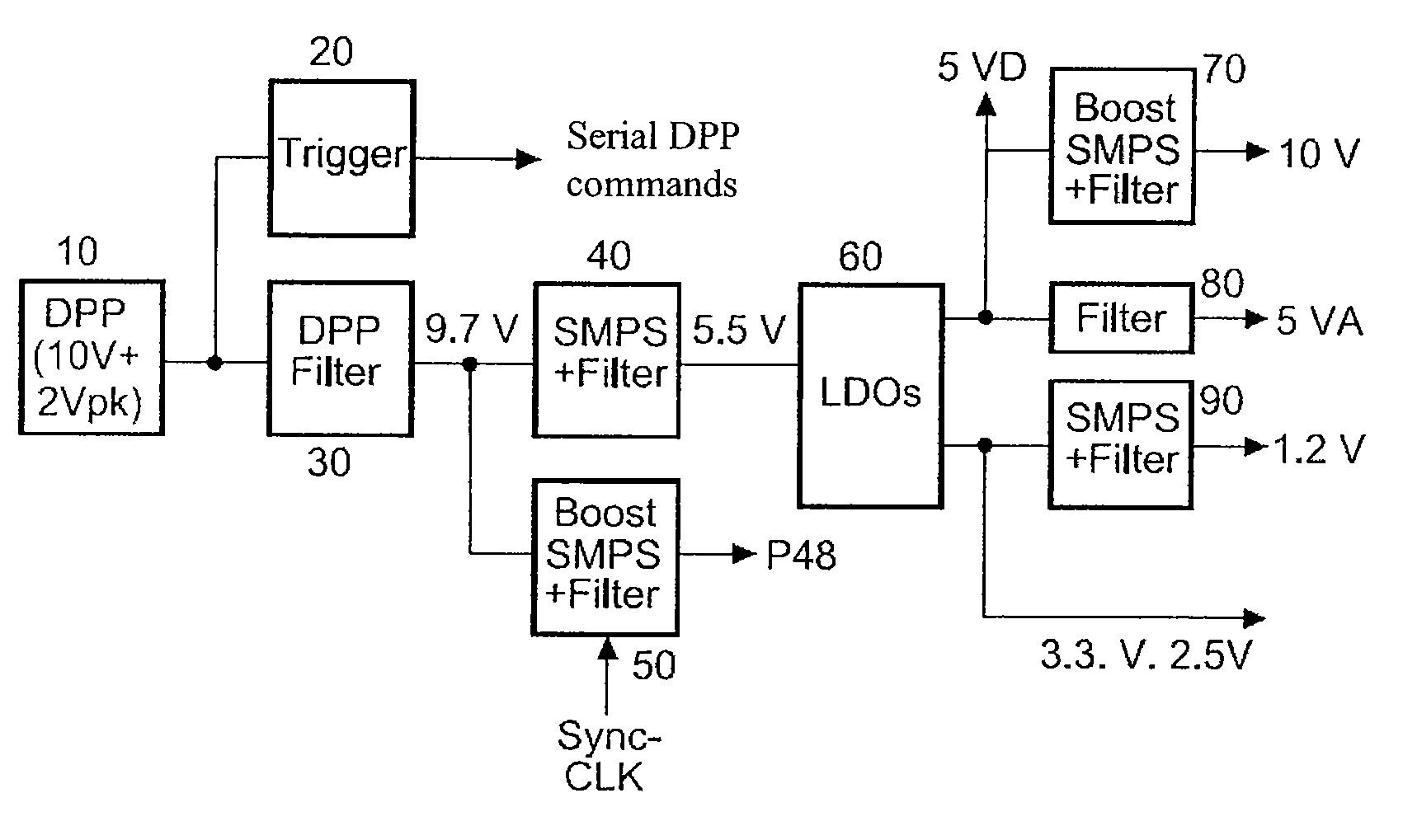
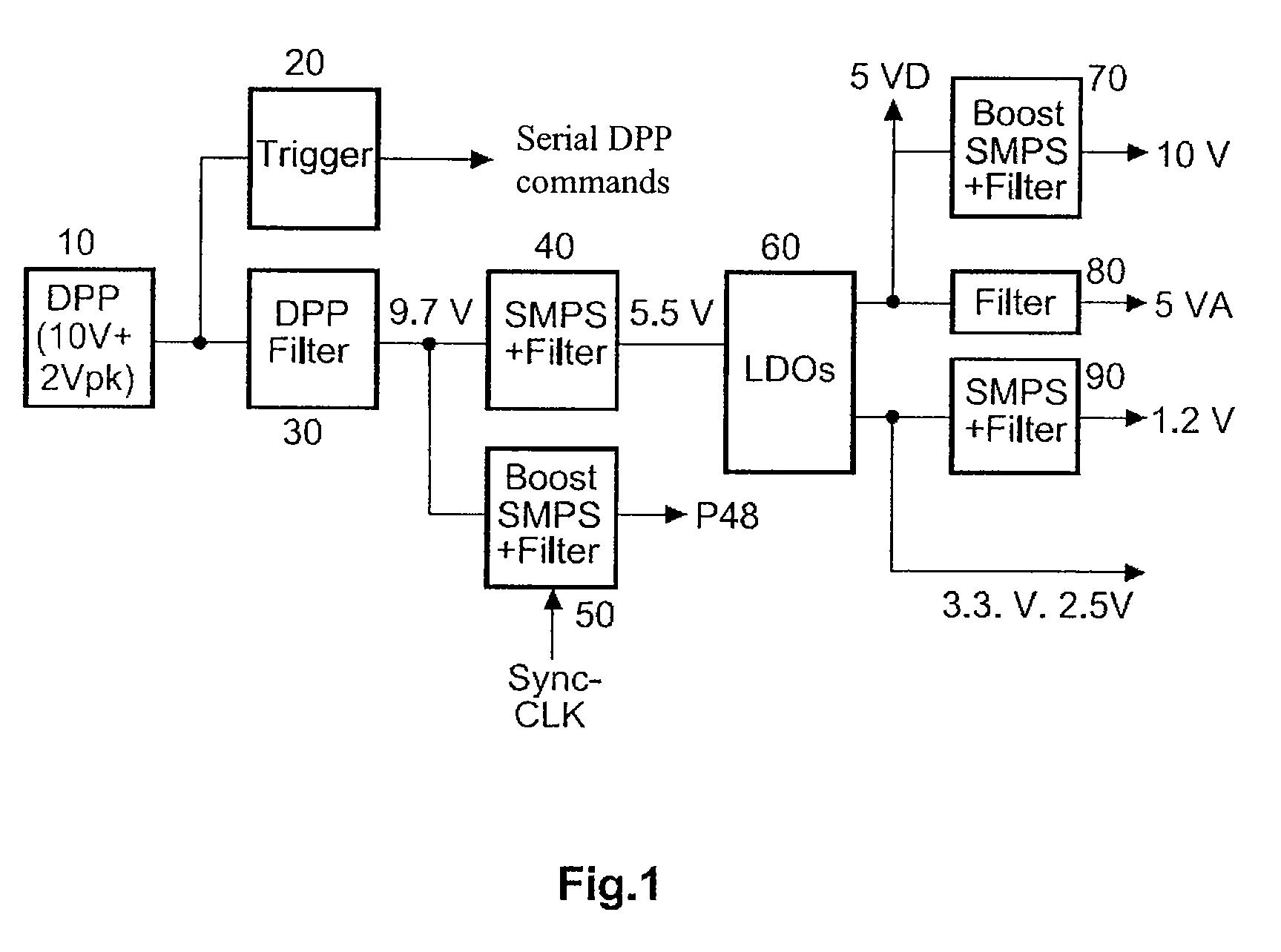
Provided is a digital microphone having a power supply. In this case the power supply is configured so as to provide a P48 V phantom power.
Owner:SENNHEISER ELECTRONICS GMBH & CO KG
Phantom Power Circuit
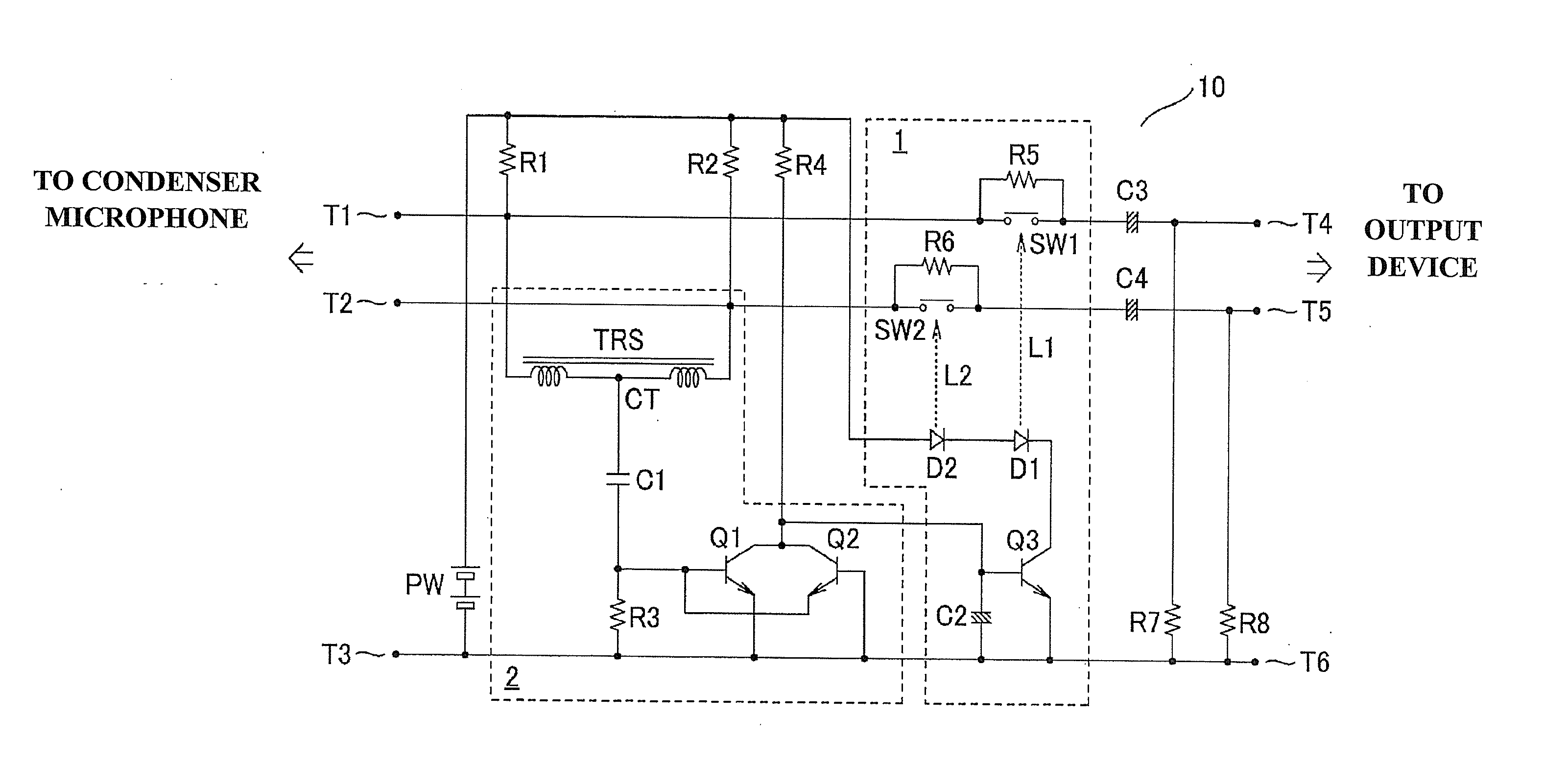
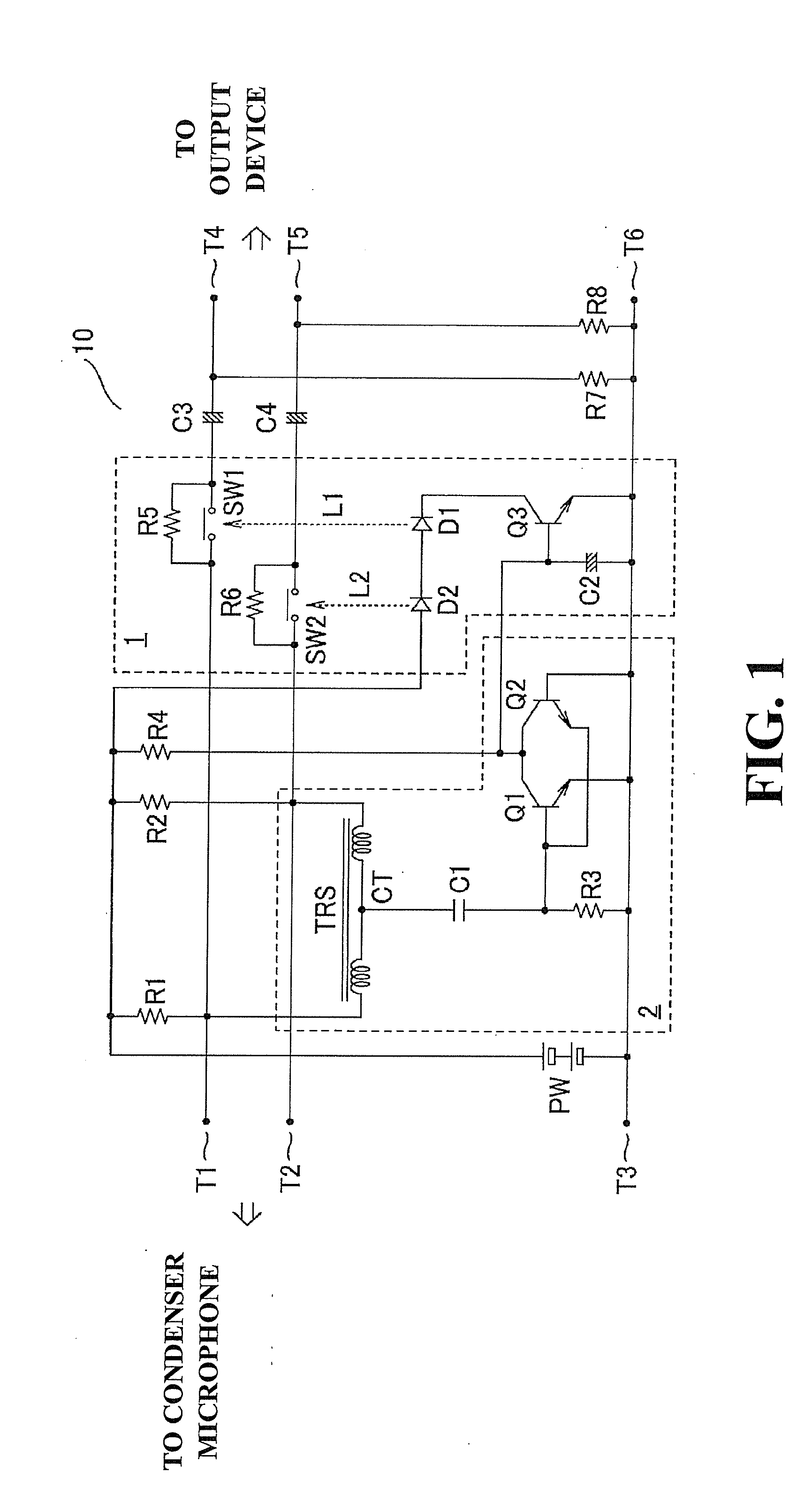
InactiveUS20120076325A1Reduce outputExtra workMicrophone structural associationElectrostatic transducer microphonesPhantom powerCondenser microphone
A phantom power circuit has a detection circuit and a limiting circuit, the detection circuit detecting a pulse current generated in association with connection or disconnection of a condenser microphone, the limiting circuit limiting the output of the condenser microphone. The detection circuit detects a pulse current generated between input terminals of the condenser microphone. The limiting circuit reduces the output from the condenser microphone when the detection circuit detects the pulse current.
Owner:AUDIO-TECHNICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com