Patents
Literature
61results about How to "Extra work" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
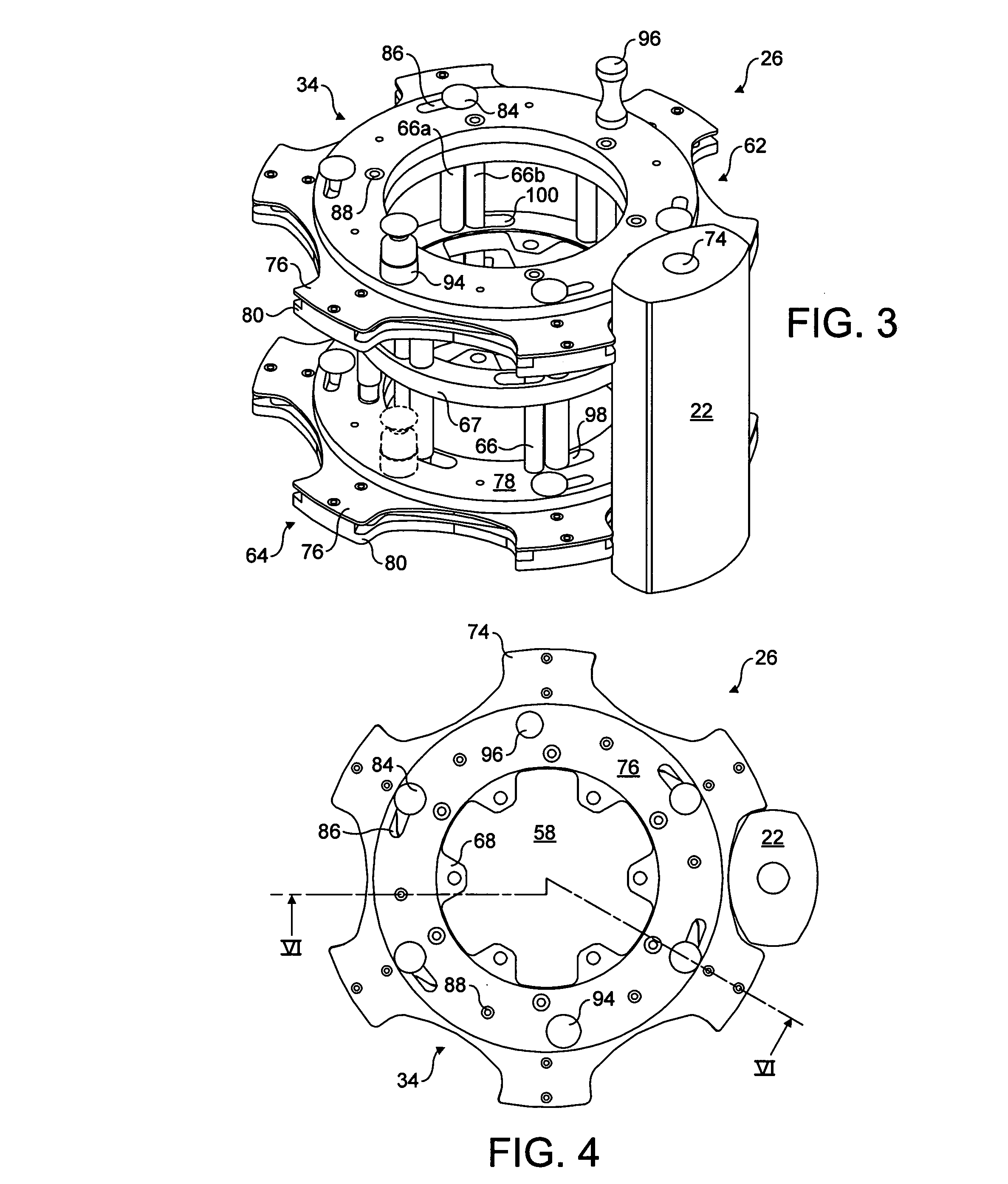
Autonomous working system, an autonomous vehicle and a turning method thereof
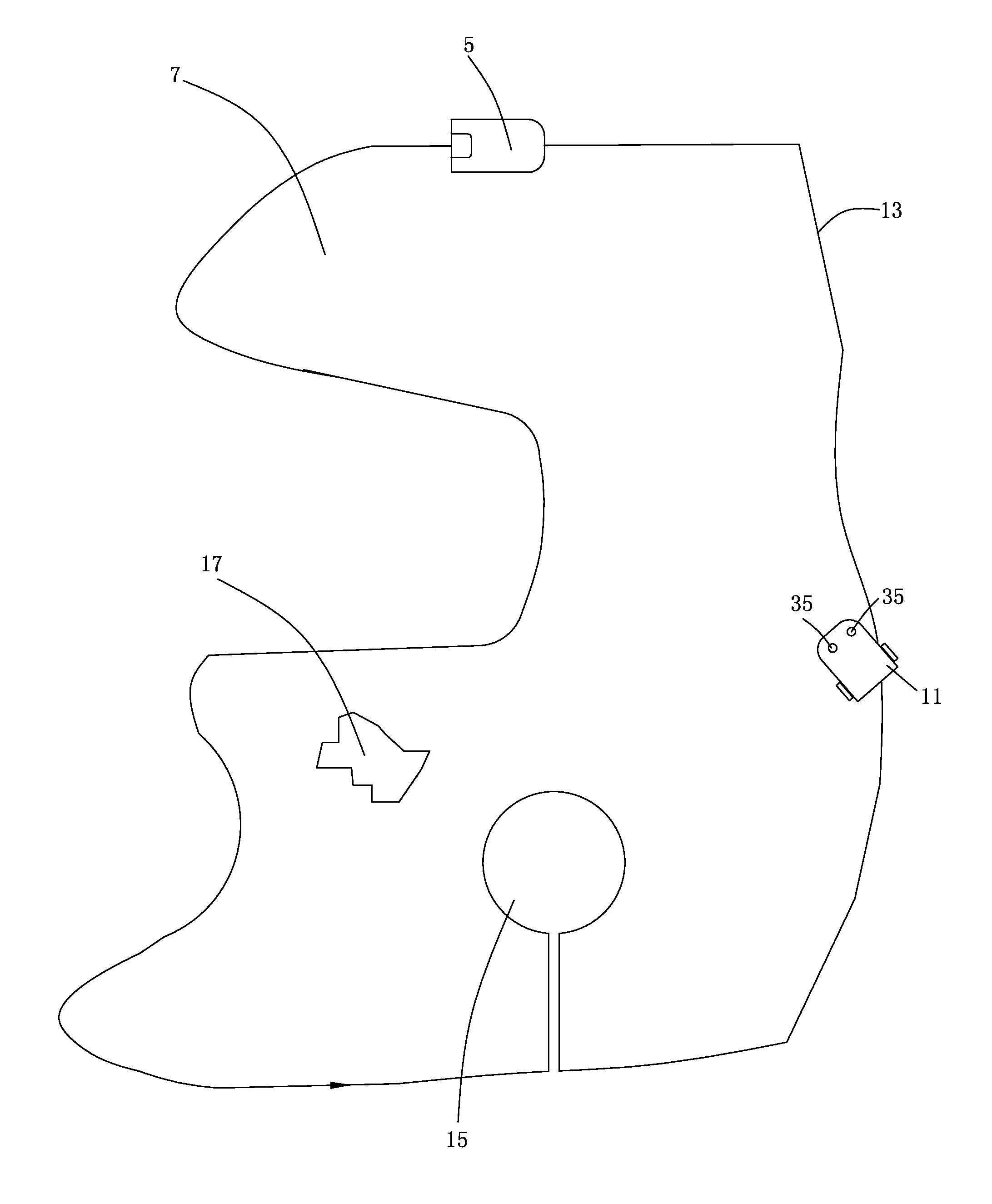
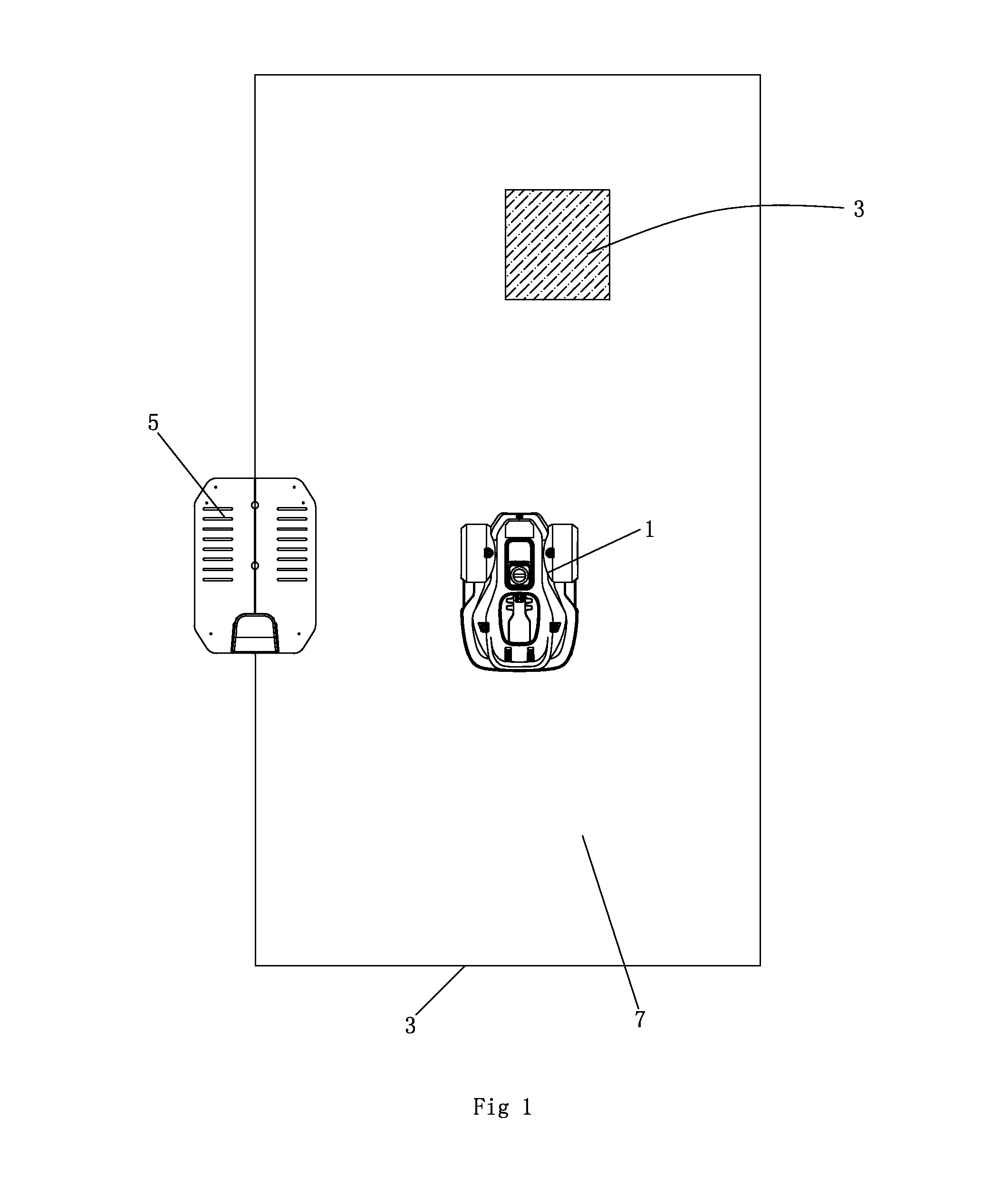
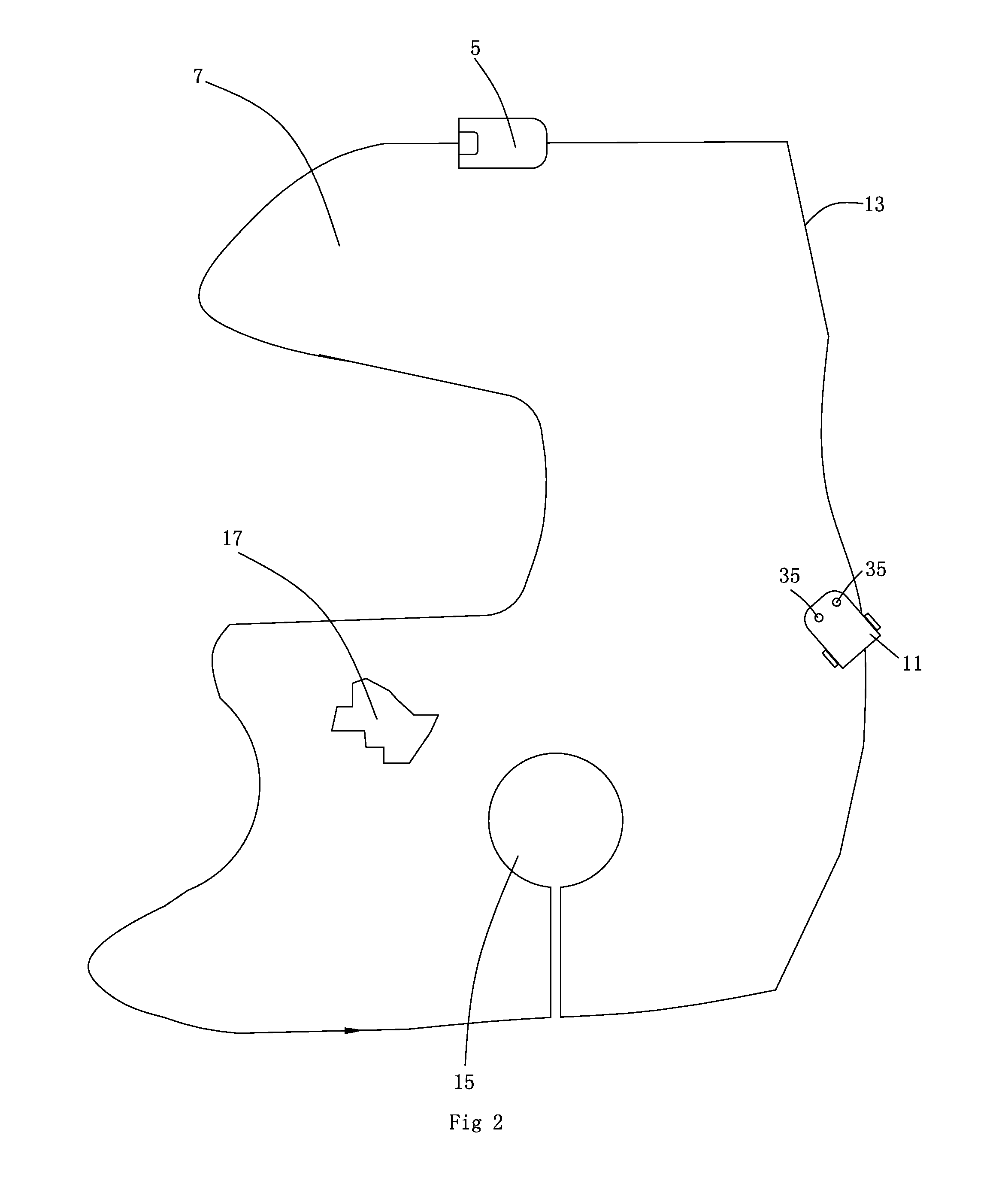
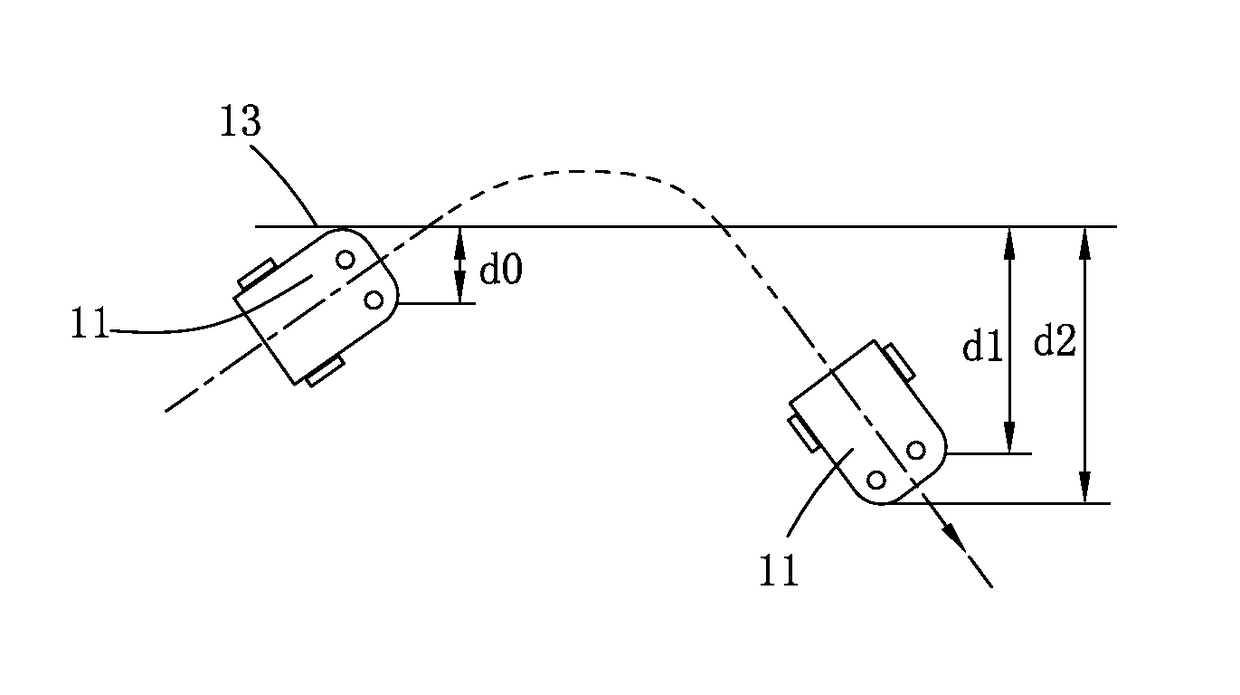
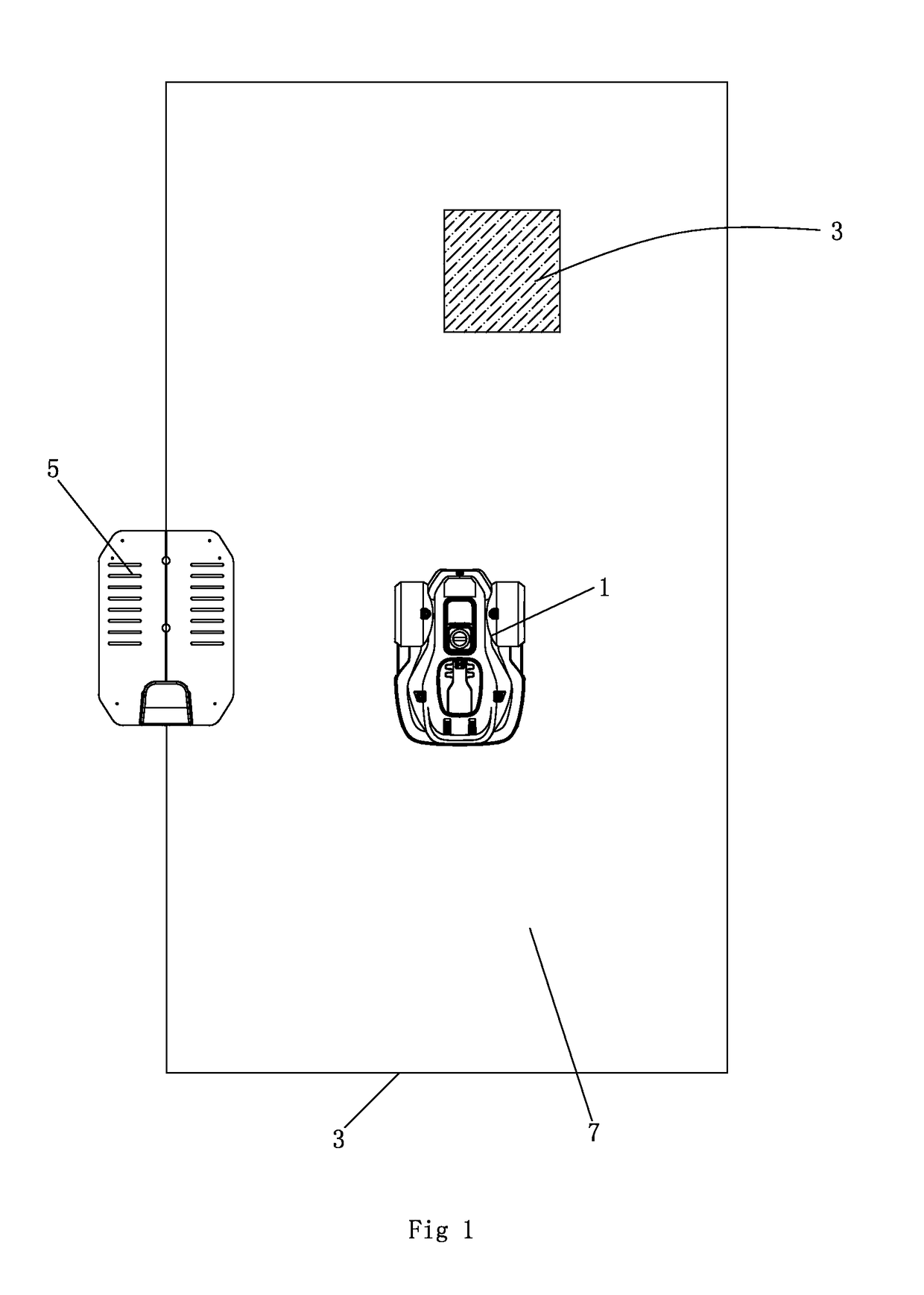
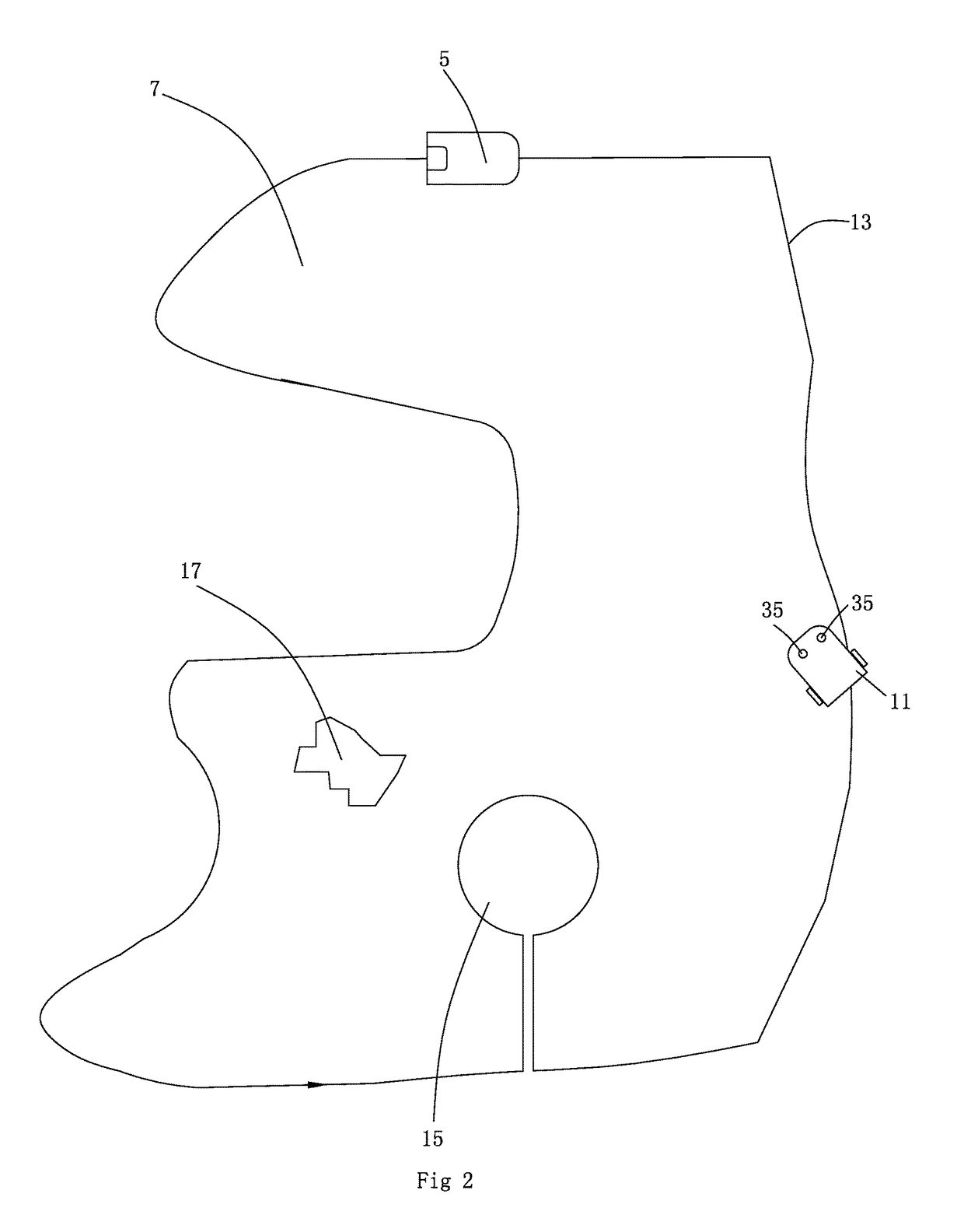
Disclosed in the present invention is an autonomous vehicle (1), which comprises an housing (21), an driving module mounted on the housing (21), an borderline detecting module mounted on the housing for detecting the distance between the autonomous vehicle (1) and the borderline (3), an energy module mounted on the housing for providing energy for the autonomous vehicle, and an control module electrically connected with the driving module and the borderline detecting module. The control module controls the driving module to perform steering based on the signal representing the angle relationship between the autonomous vehicle (1) and the borderline (3) transmitted from the borderline detecting module, so that the axis (33) of the autonomous vehicle (1) always forms an acute angle or an right angle with one side of the borderline (3) while steering is completed, but another side of the borderline (3) forms an acute angle or an right angle with the core axis (33) of the autonomous vehicle (1) when the turning begins. The turning has directivity, so that the autonomous vehicle more easily goes out from the narrow area and the efficiency of area covering is higher; moving is kept during the turning, so that the energy is saved, and the working efficiency is improved.
Owner:POSITEC POWER TOOLS (SUZHOU) CO LTD
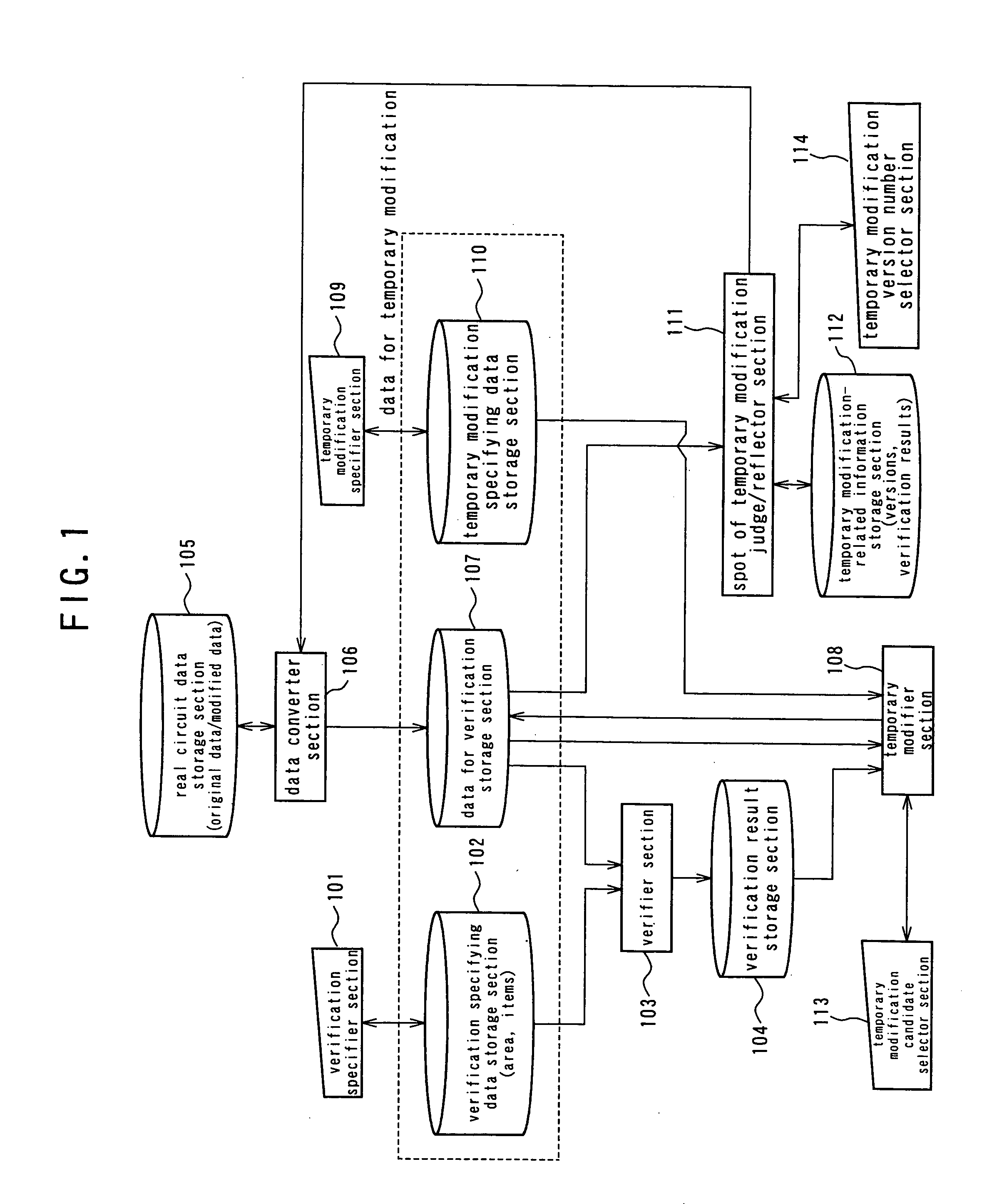
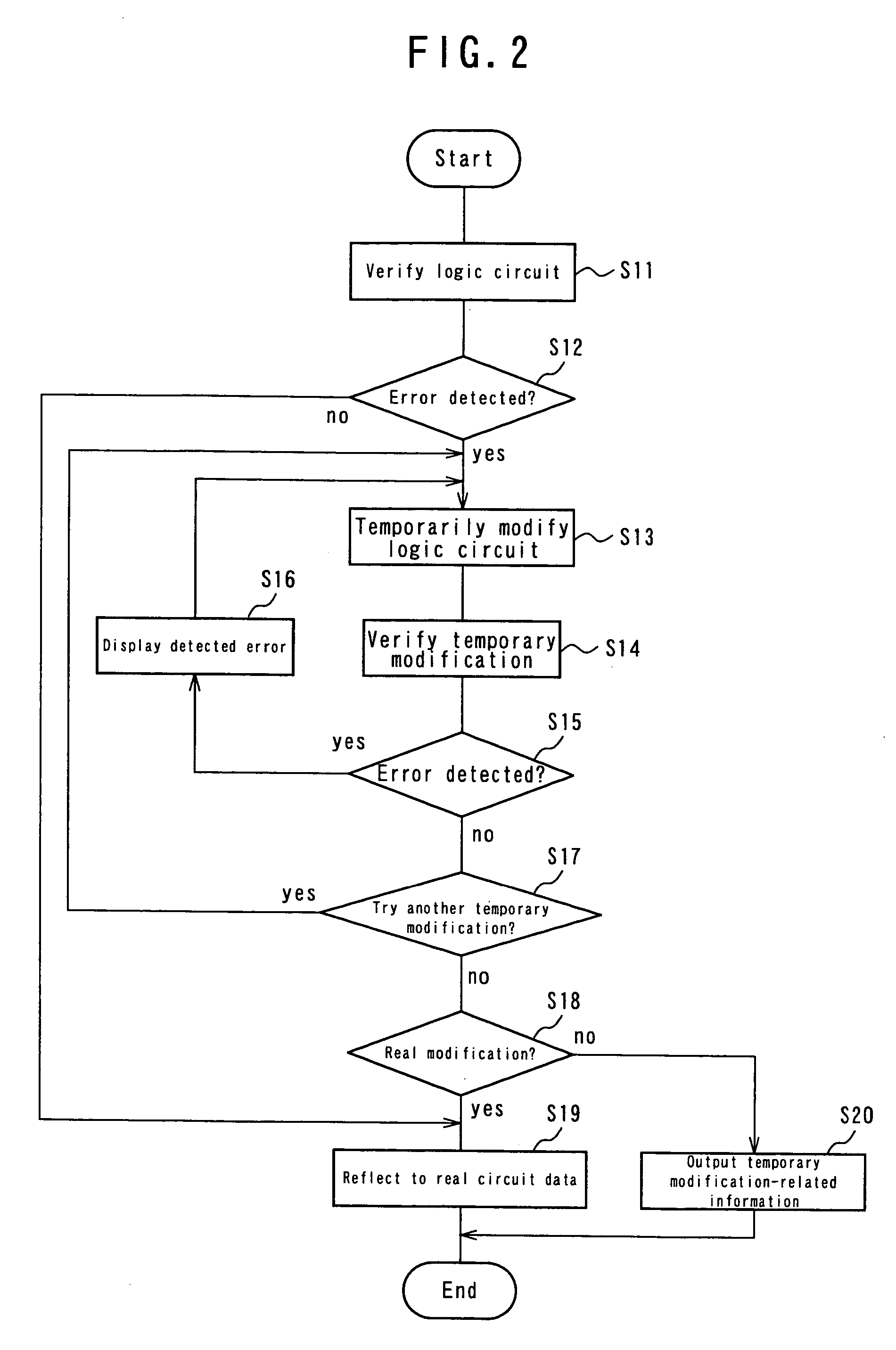
Logic verification device, logic verification method and logic verification computer program
InactiveUS7131086B2Reduce the number of stepsReduce the number of timesDetecting faulty computer hardwareCAD circuit designValidation methodsTheoretical computer science
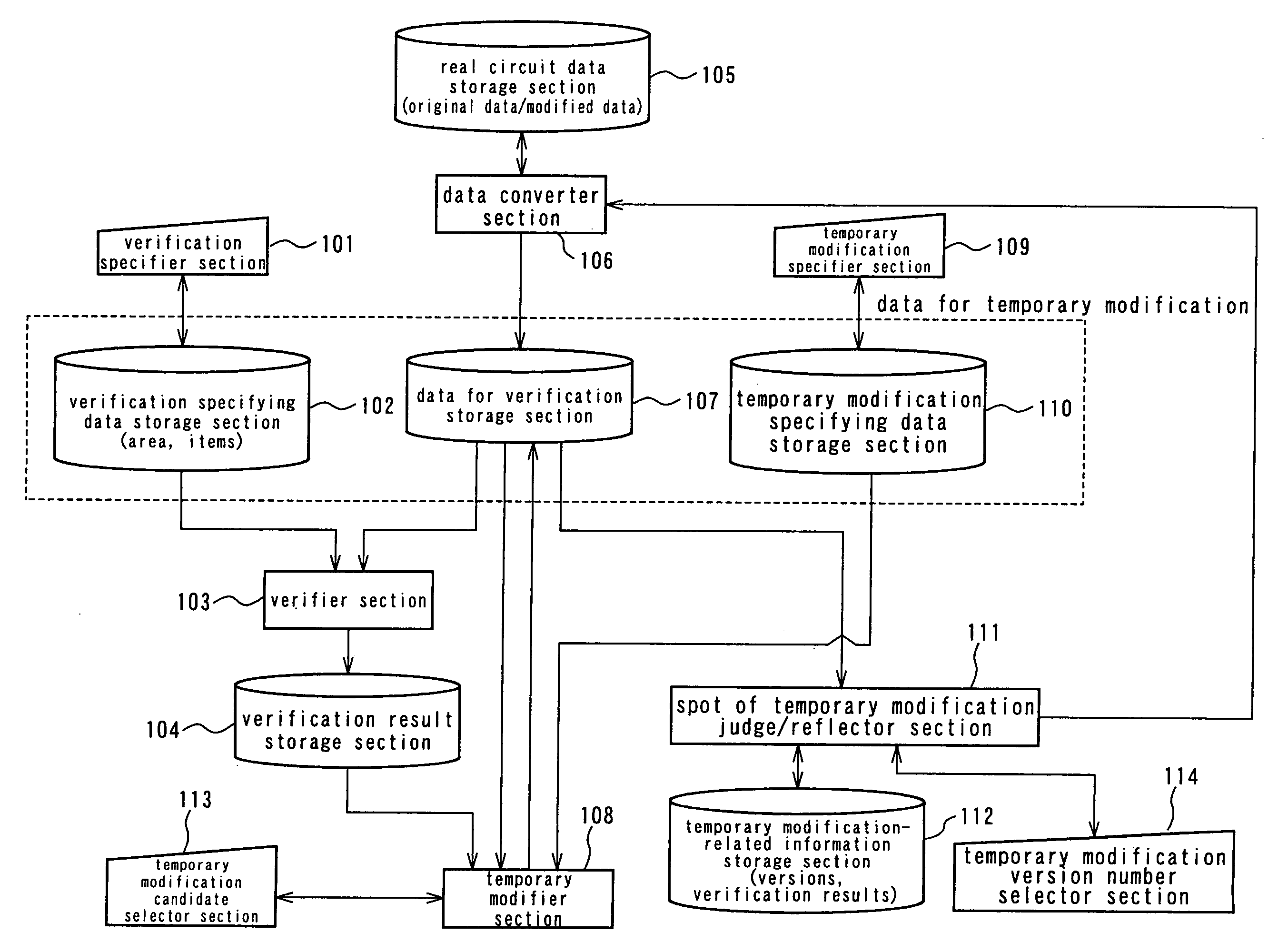
A logic verification device, a logic verification method and a logic verification computer program that can reduce the number of steps involved in designing a logic circuit particularly when the designed logic circuit is subjected to logic verification and modification at the spot where an error is detected. The logic verification device comprises a data converter section adapted to convert real circuit data to be processed for designing a logic circuit into data for verification to be processed for logic verification and vice versa, a verifier section adapted to operate for logic verification of said data for verification and a temporary modifier section adapted to acquire the result of verification of said verifier section and the modification candidate data corresponding to the result of verification of said verifier section and pre-selected as candidate data for modification of said data for verification and modify said data for verification on the basis of said acquired result of verification and said acquired modification candidate data.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
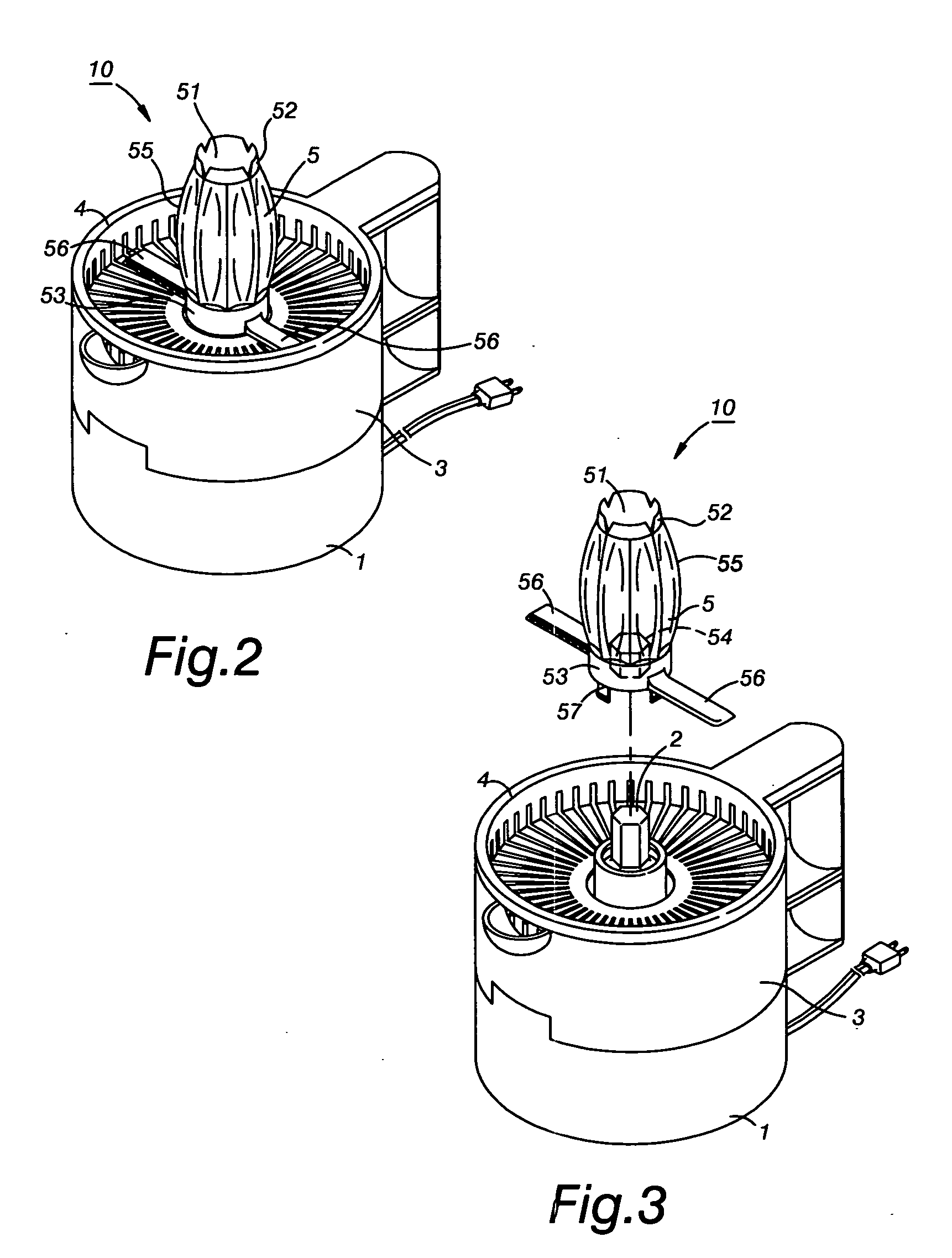
Reamer structure of a juicer
InactiveUS20050081723A1Extra workOperational securityJuice extractionFood preparationEngineeringReamer
A reamer structure of a juicer for extracting juice from a whole fruit comprises an opening provided with a plurality of annularly arranged teeth and a base member with a polygonal locking receptacle for securing an upstanding spindle from a driving unit of a juicer, whereby cutting a fruit in halves is not needed. The reamer is further provided with a plurality of claw shaped projections for extracting juice from fruit flesh. The reamer further includes at least two oppositely and horizontally scrapers extended from its base. The reamer can also be integrally formed with a strainer of a juicer.
Owner:LIN KUO I +1
Seismic-protection wheel locational anchorage
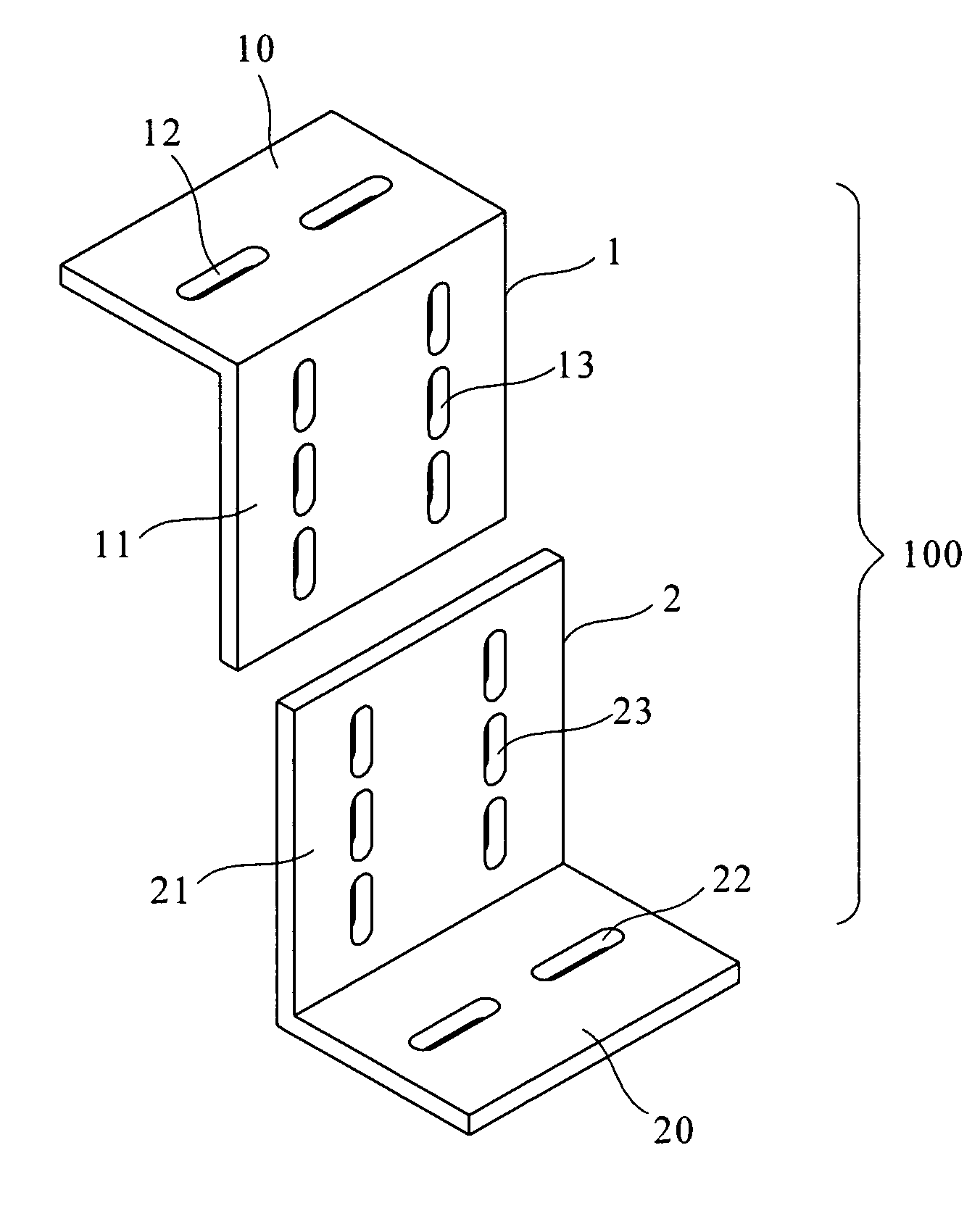
InactiveUS20050284041A1Extra workJoining is strengthenedPortable braking systemMachine framesSeismic protectionEngineering
A seismic-protection wheel locational anchorage is provided. The present seismic-protection wheel locational anchorage includes a first fastening member and a second fastening member. The first fastening member has a first horizontal part and a first perpendicular part vertically and downwardly extending from one end of the first horizontal part. The second fastening member has a second perpendicular part and a second horizontal part extending parallel from a lower end of the second perpendicular part. The first horizontal part of the first fastening member is fastened to the bottom of a machine frame. The second horizontal part is securely fastened to the ground. When the vertical level between the machine frame and the ground is appropriately adjusted, the first perpendicular part and the second perpendicular part are securely joined together so as to provide the seismic-protection wheel locational anchorage for the machine frame.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
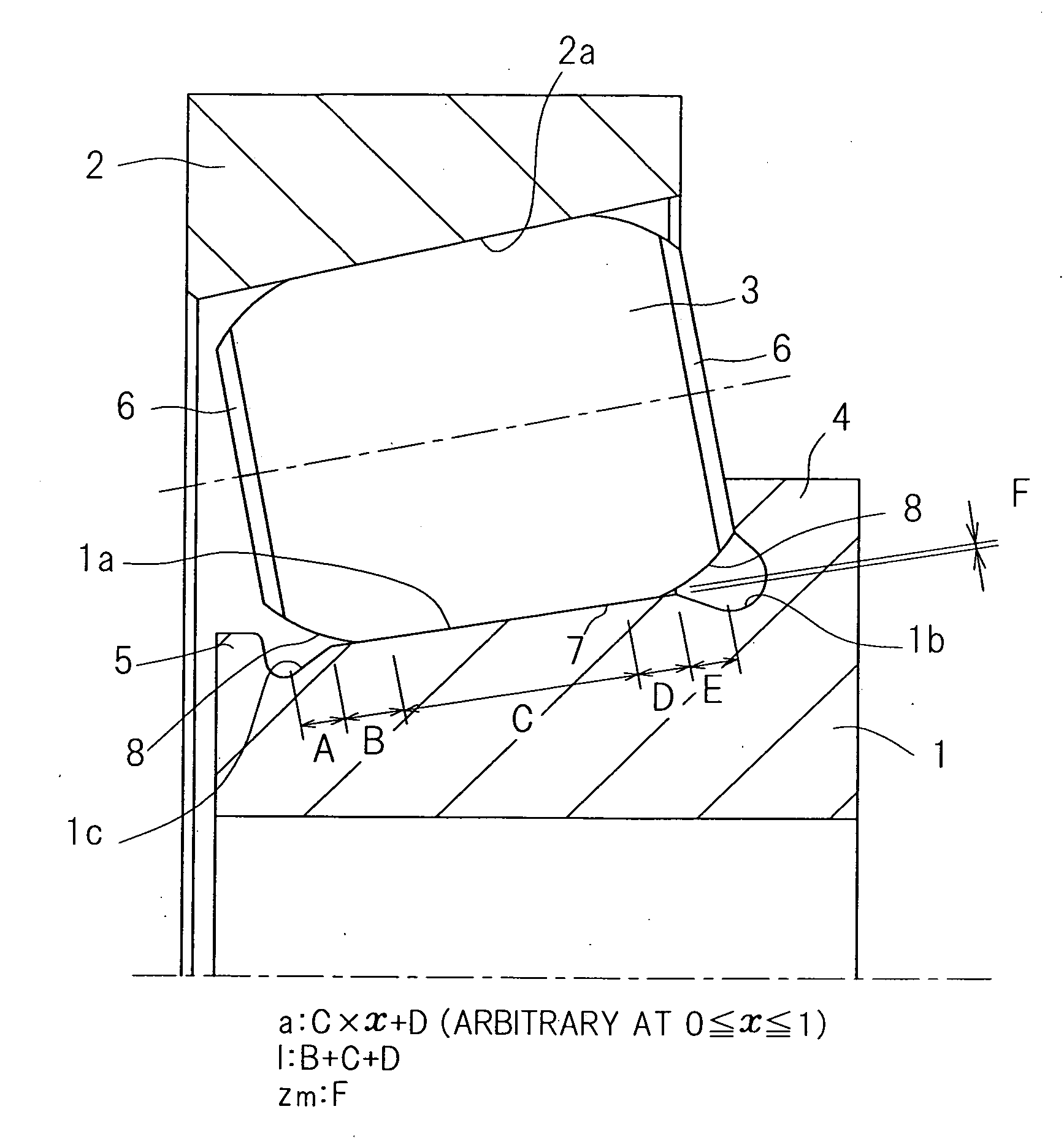
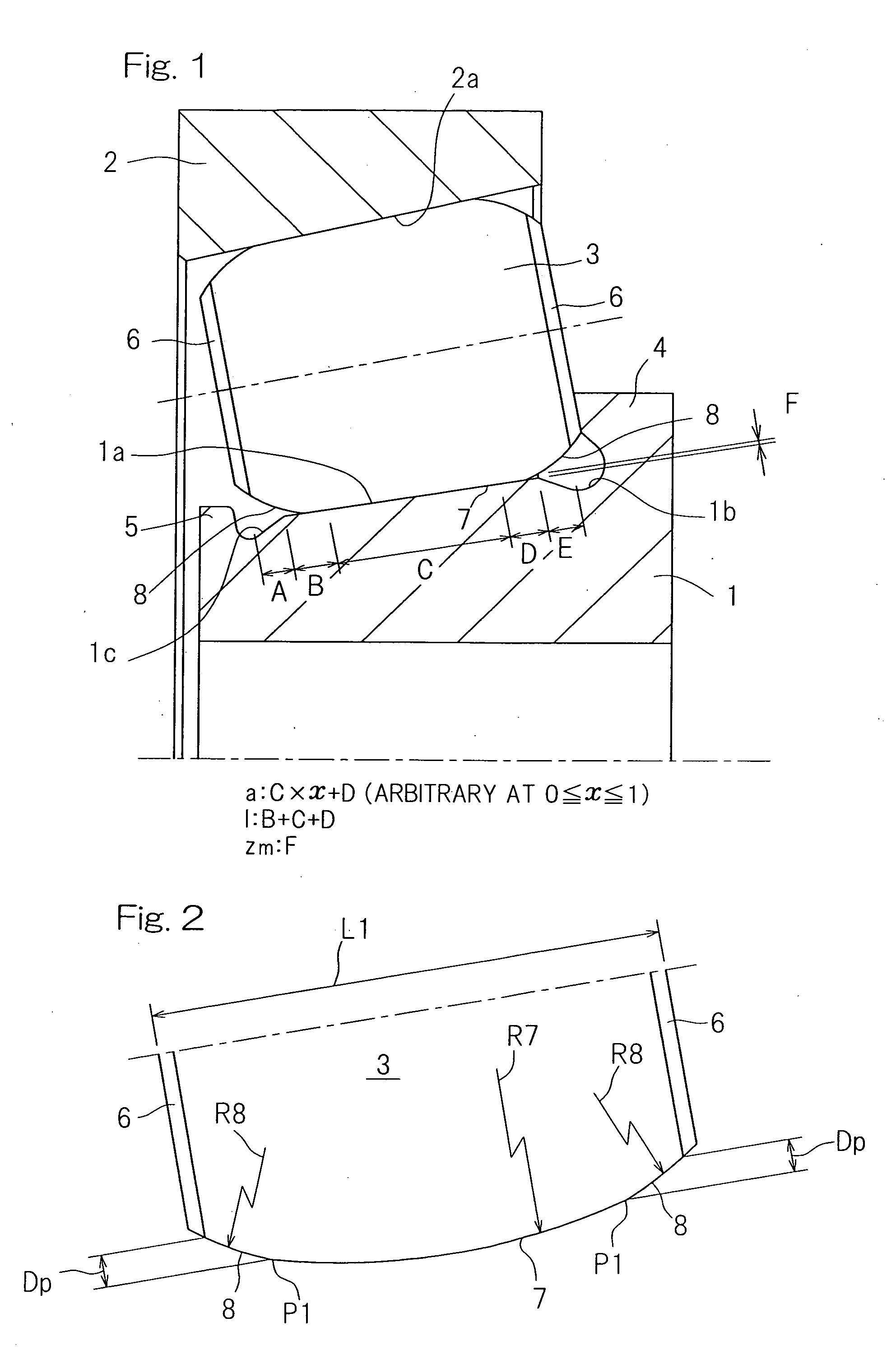
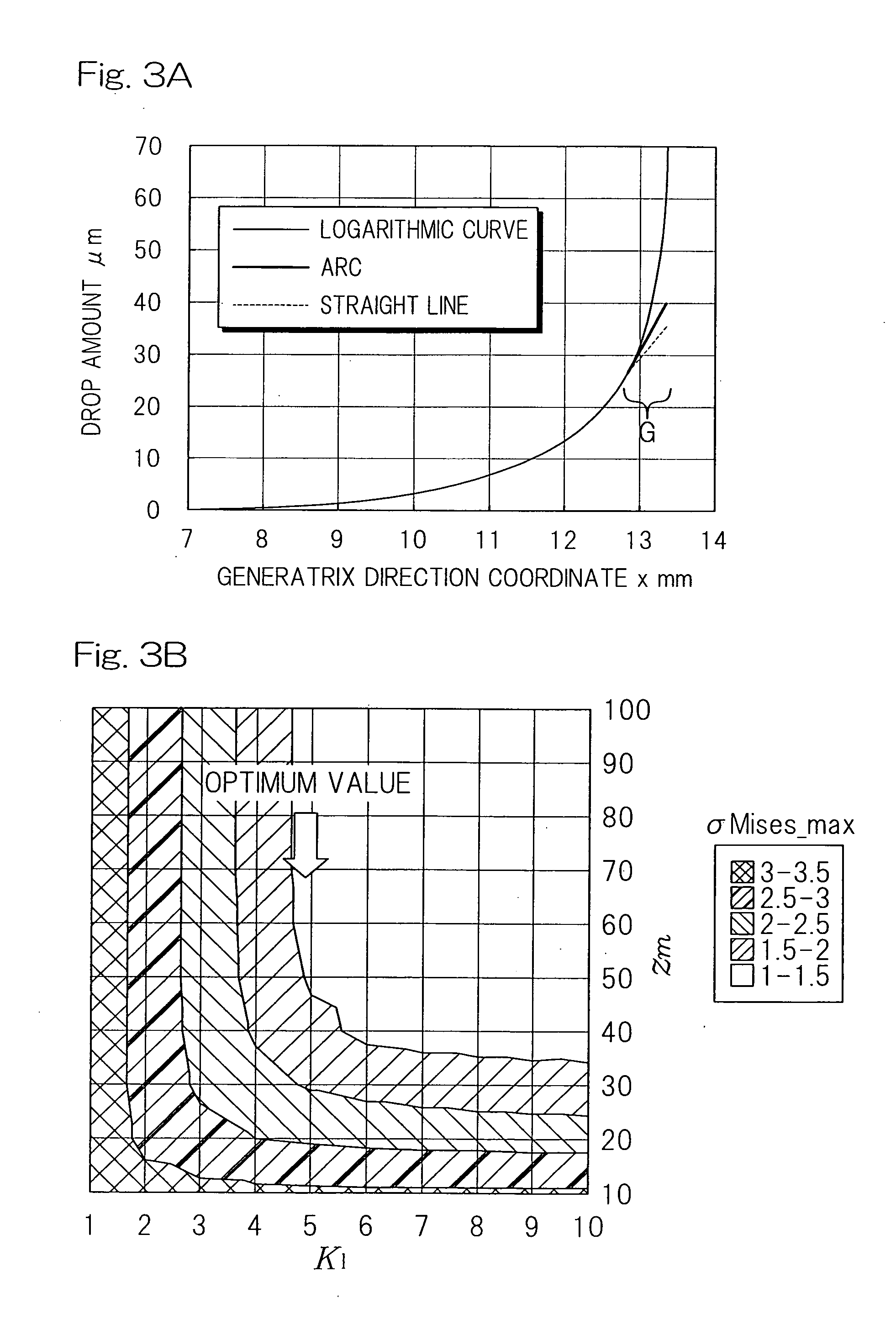
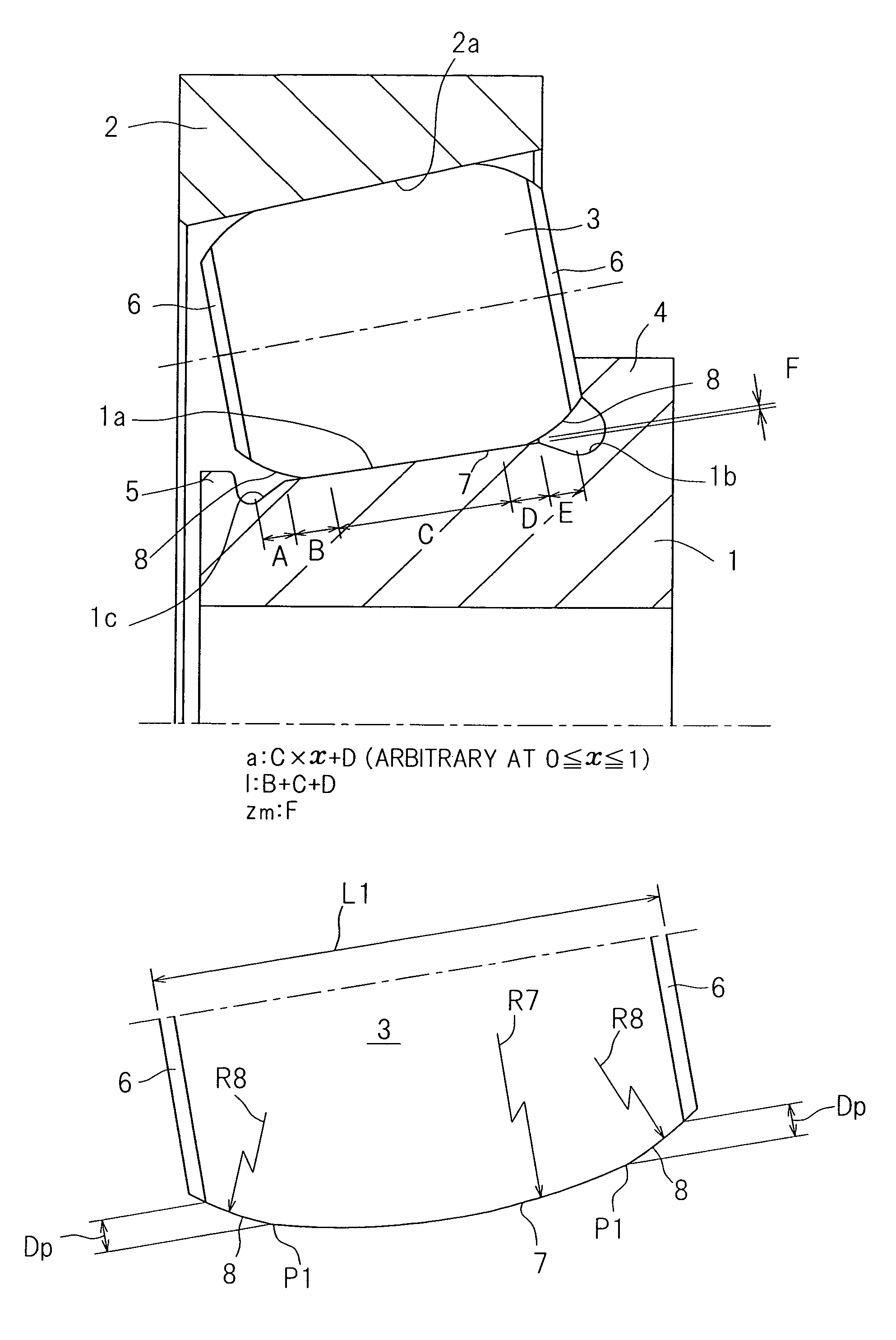
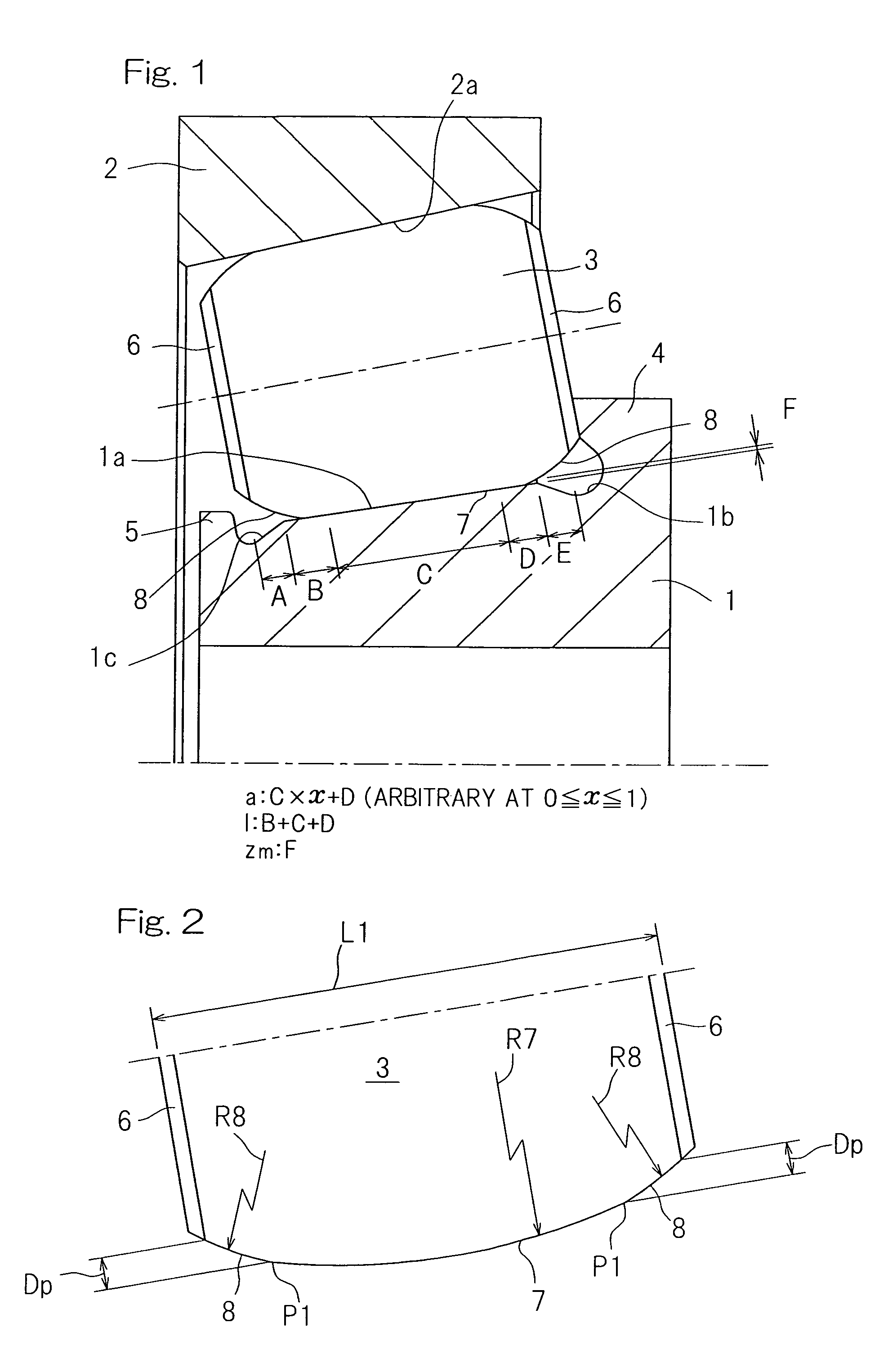
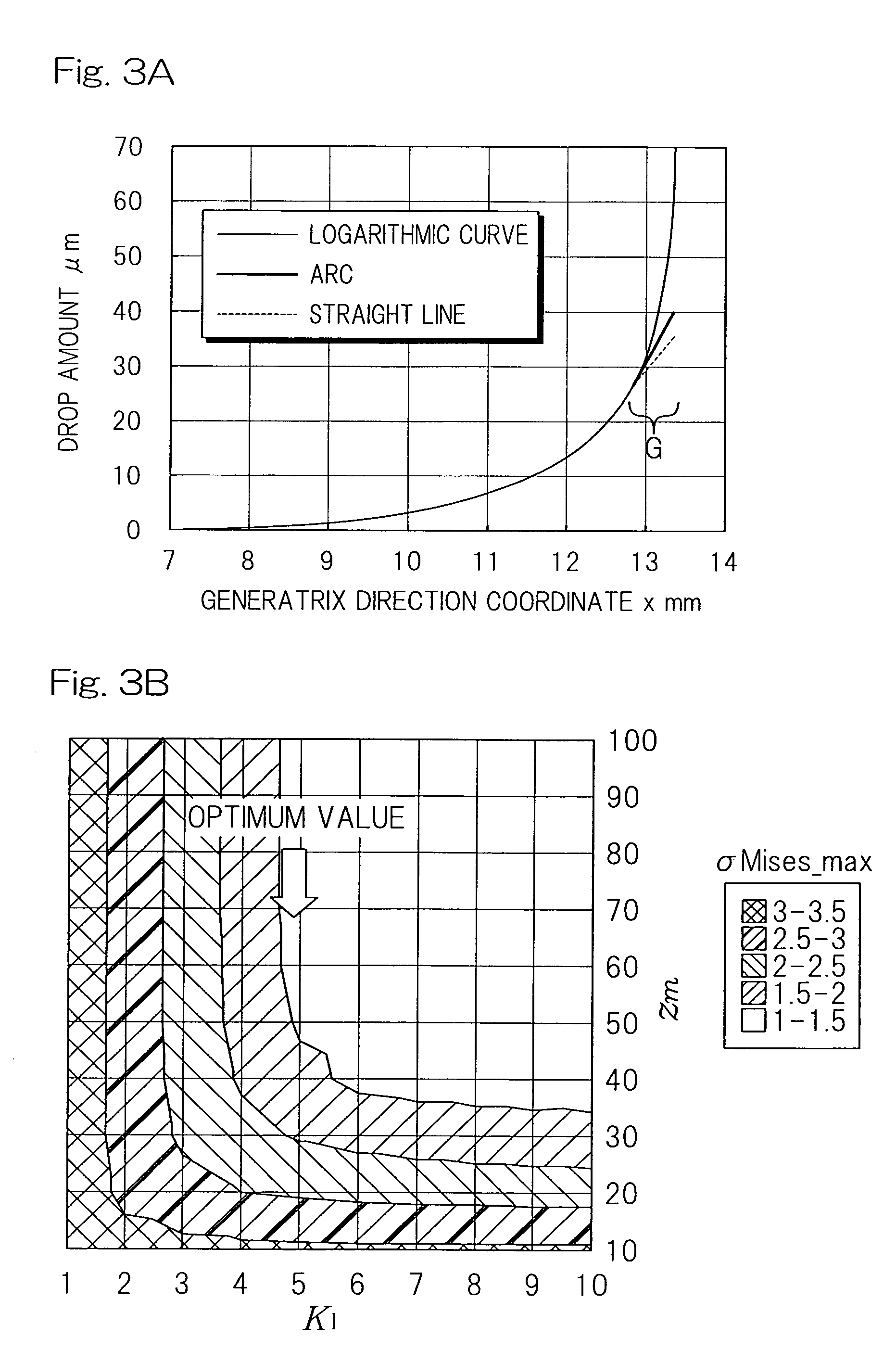
Tapered roller bearing and method of designing the same
ActiveUS20120033909A1Design be relatively longCost reductionRolling contact bearingsShaftsMechanical engineeringContact region
In a tapered roller bearing assembly, a crowning profile formed portion of the roller rolling surface is made up of a contact area crowned portion (7), which is held in contact with an inner ring raceway surface (1a), and a non-contact area crowned portion (8) which is held in non-contact with the inner ring raceway surface (1a). The contact area crowned portion (7) and the non-contact area crowned portion (8) have their generatrices extending in an axial direction of a roller (3), which generatrices are represented by corresponding continuous lines represented by different functions and continued smoothly at a point of connection, and the curvature of the generatrix of the non-contact area crowned portion (8) in the vicinity of the connection point is chosen to be smaller than the curvature of the generatrix of the contact area crowned portion (7).
Owner:NTN CORP
Adjustable star wheel
The present invention provides an adjustable star wheel provided with at least one interchangeable pocket for receiving a container to be conveyed. The star wheel comprises a larger pocket of fixed shape and size, moveable jaws defining a smaller pocket having a fixed shape and size, an actuator disc rotatable about the central axis, and a cam mechanism linking the jaws to the actuator disc to cause radial movement of the jaws. In an extended position, the jaws move the smaller pocket into coincidence with the larger pocket thereby configuring the star wheel to receive containers in the smaller pocket. In the retracted position, the jaws are clear of the larger pocket thereby configuring the star wheel to receive containers in the larger pocket.
Owner:ZEPF TECH UK
Adjustable star wheel
ActiveUS20100193331A1Quick and easy methodEasy to adjustCharge manipulationConveyor partsCamActuator
The present invention provides an adjustable star wheel provided with at least one interchangeable pocket for receiving a container to be conveyed. The star wheel comprises a larger pocket of fixed shape and size, moveable jaws defining a smaller pocket having a fixed shape and size, an actuator disc rotatable about the central axis, and a cam mechanism linking the jaws to the actuator disc to cause radial movement of the jaws. In an extended position, the jaws move the smaller pocket into coincidence with the larger pocket thereby configuring the star wheel to receive containers in the smaller pocket. In the retracted position, the jaws are clear of the larger pocket thereby configuring the star wheel to receive containers in the larger pocket.
Owner:ZEPF TECH UK
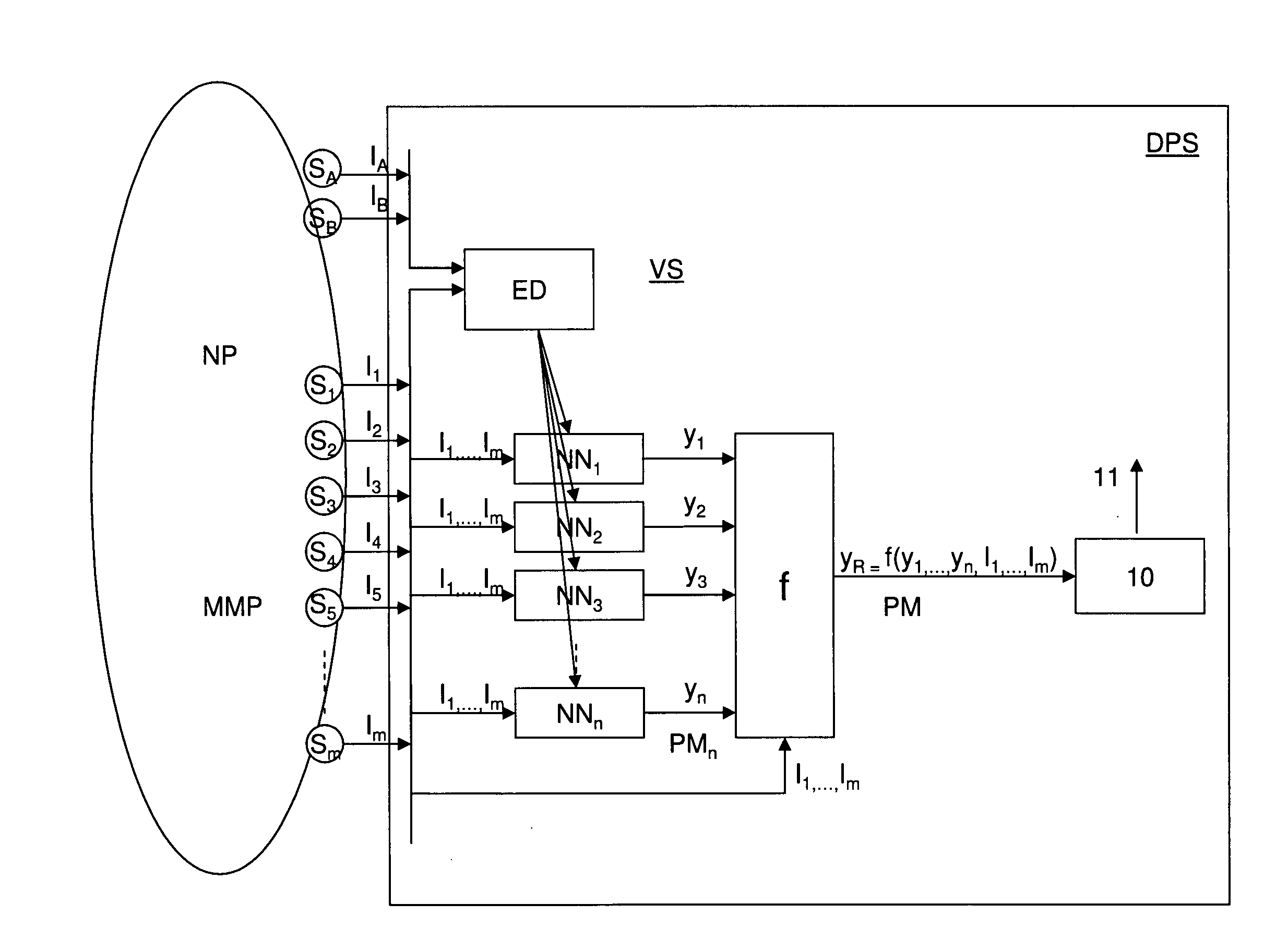
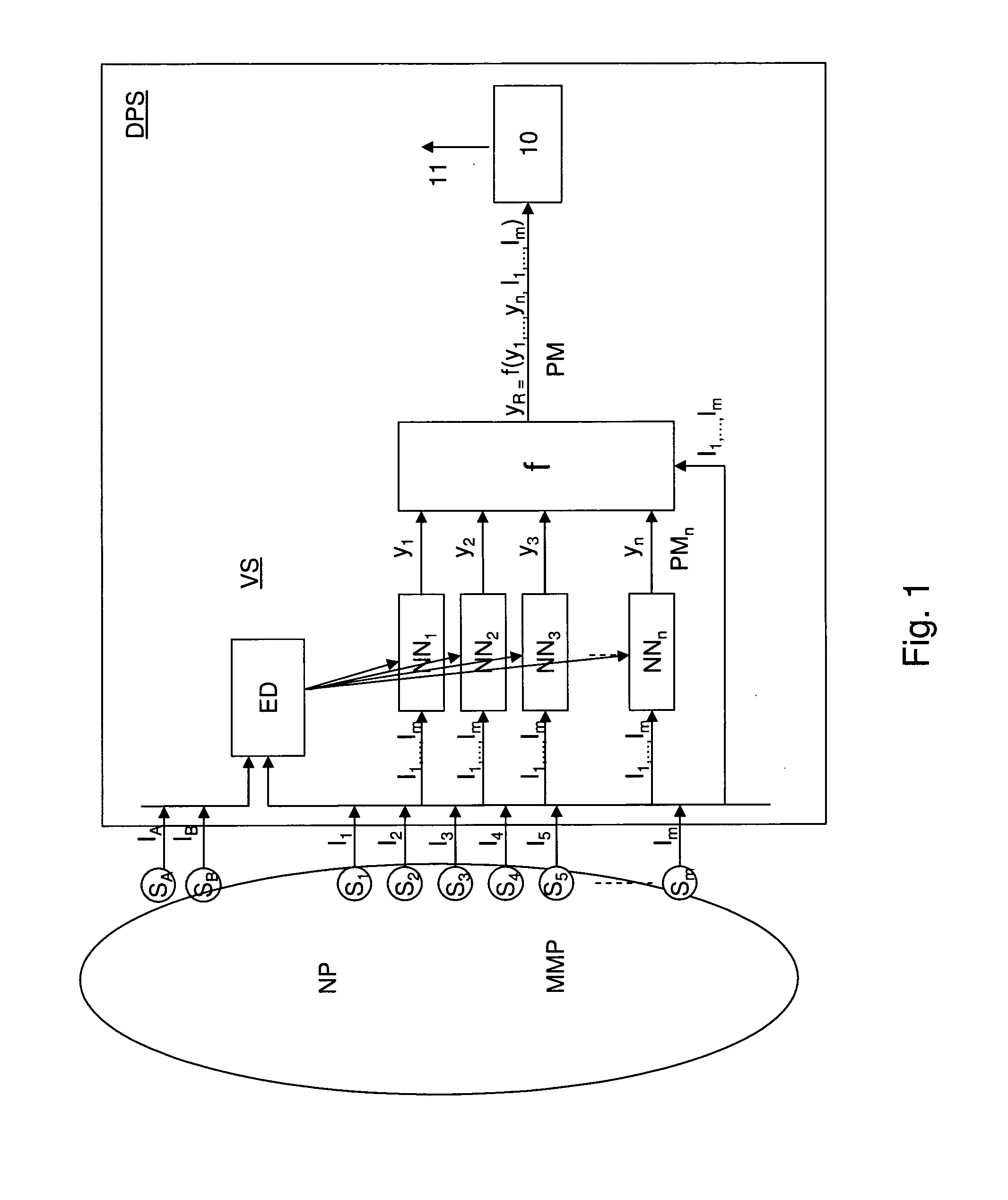
System and method for empirical ensemble-based virtual sensing of particulates
InactiveUS20110313958A1Easy to implementExtra workDigital computer detailsParticle suspension analysisParticulatesVirtual sensors
A virtual sensor system and method for the estimation of an amount or concentration of particulate matter resulting from natural or man made processes comprising two or more empirical models arranged for being trained using empirical data from the processes, for receiving one or more signal input values from one or more sensors of the processes and calculating a signal output value based on the signal input values where the signal output value represents an intermediate amount or concentration of particulate matter. Further a combination function is arranged for receiving the signal output values and continuously calculating the amount or concentration of PM.
Owner:INSTITUTT FOR ENERGITEKNIKK
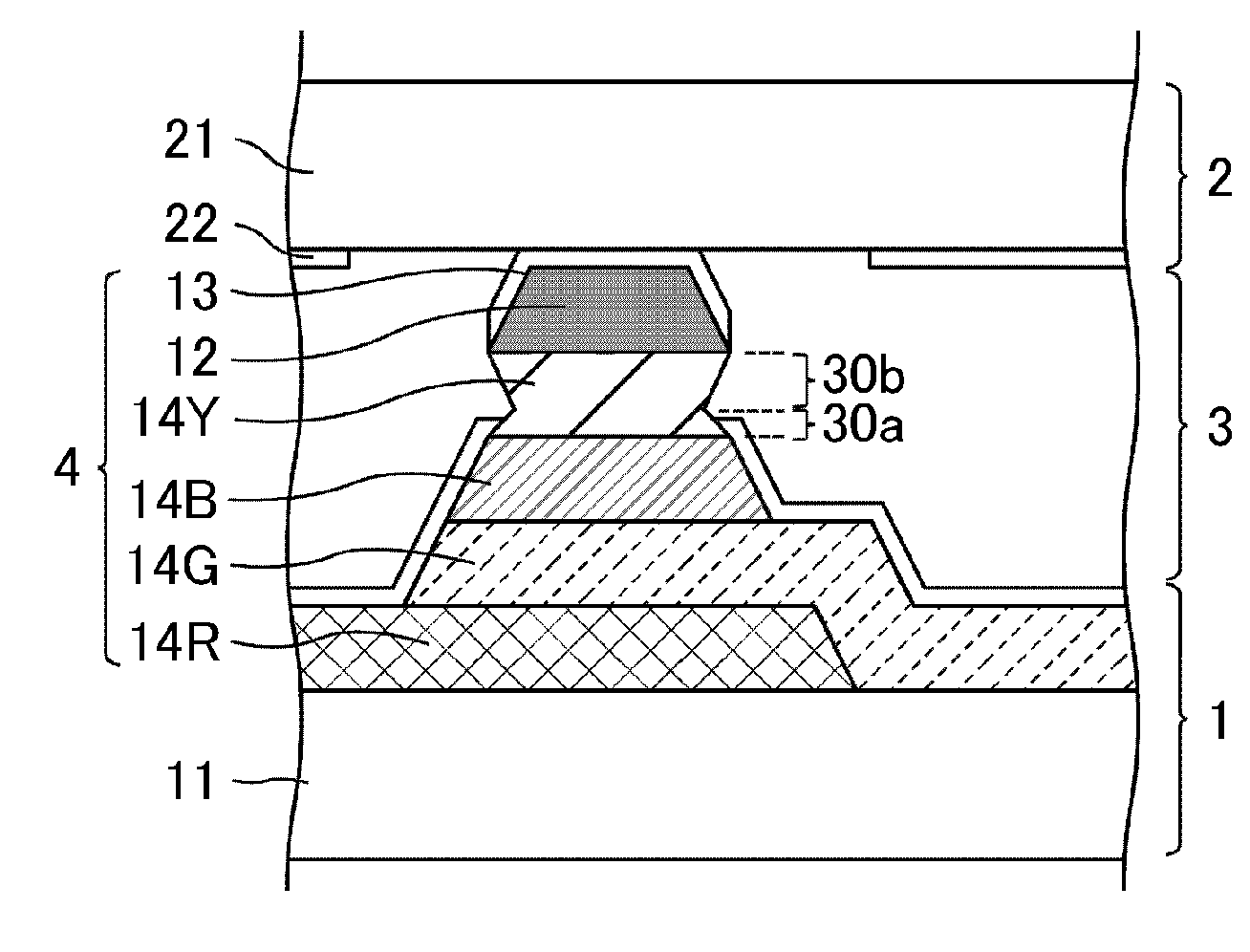
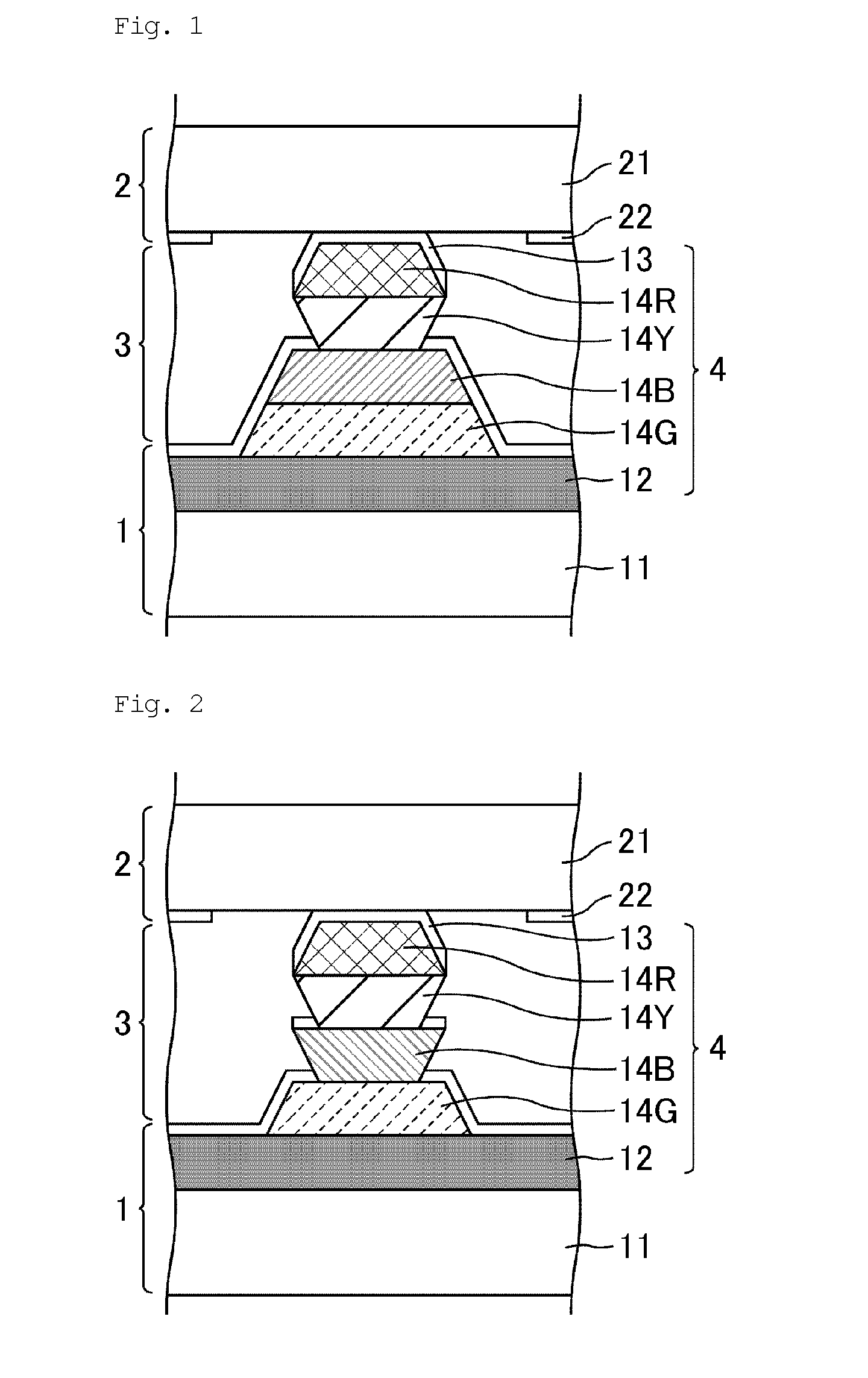
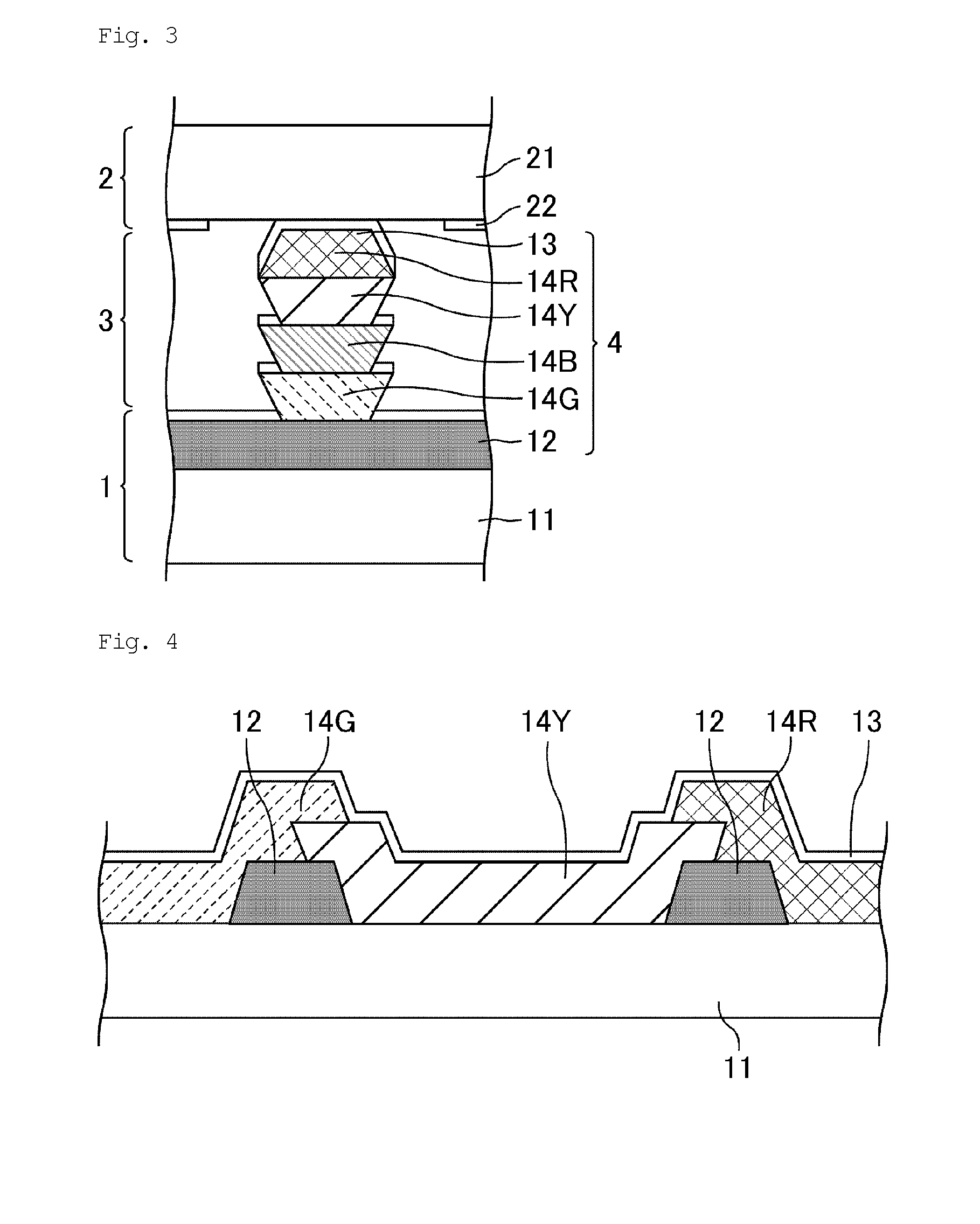
Color filter substrate and liquid crystal display device
The present invention provides a color filter substrate for preventing an electrical short circuit between an electrode and other members at a place upper than the colored transparent layers disposed in a stack, and further preventing electrical disconnection on colored transparent layers other than the colored transparent layers in a stack, in the case where colored transparent layers are disposed in a stack and an electrode is stacked over the entire surface. The color filter substrate of the present invention comprises:colored transparent layers disposed side by side; andcolored transparent layers disposed in a stack,wherein an electrode is disposed at a place upper than the colored transparent layers disposed side by side and an electrode is disposed at a place upper than the colored transparent layers disposed in a stack,the colored transparent layers disposed in a stack include a colored transparent layer having a reverse tapered shape, andthe uppermost layer of the colored transparent layers disposed in a stack has a forward tapered shape.
Owner:SHARP KK
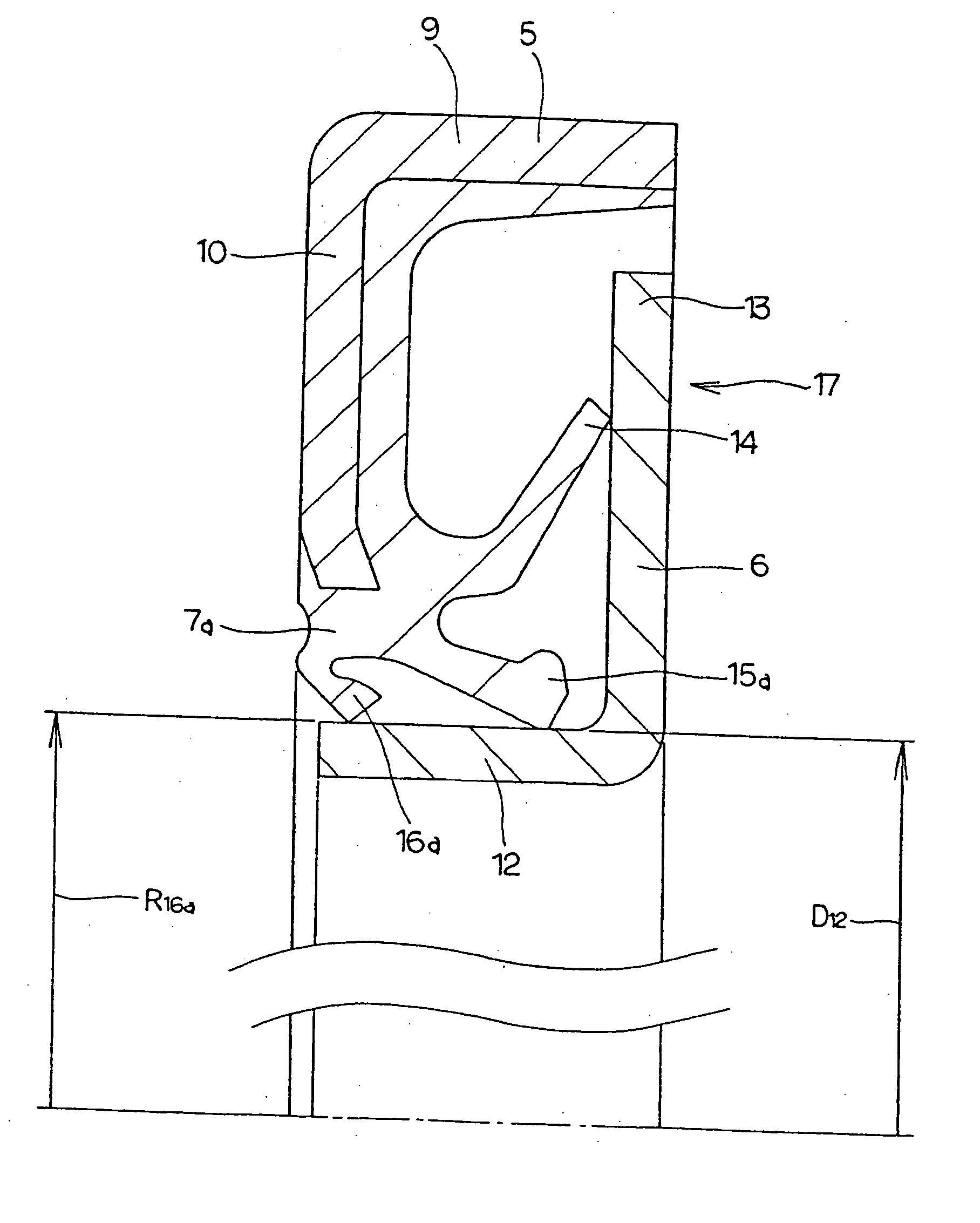
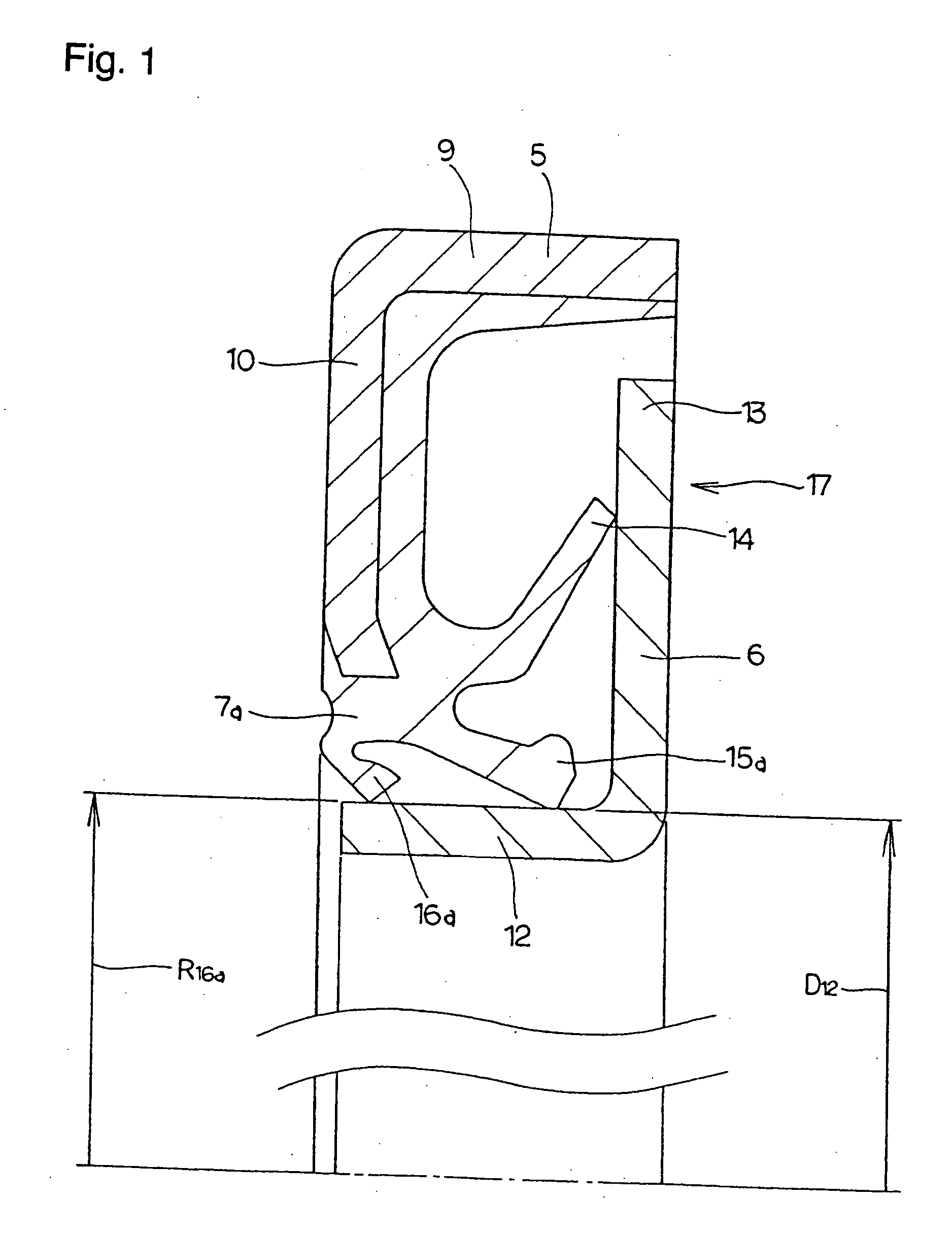
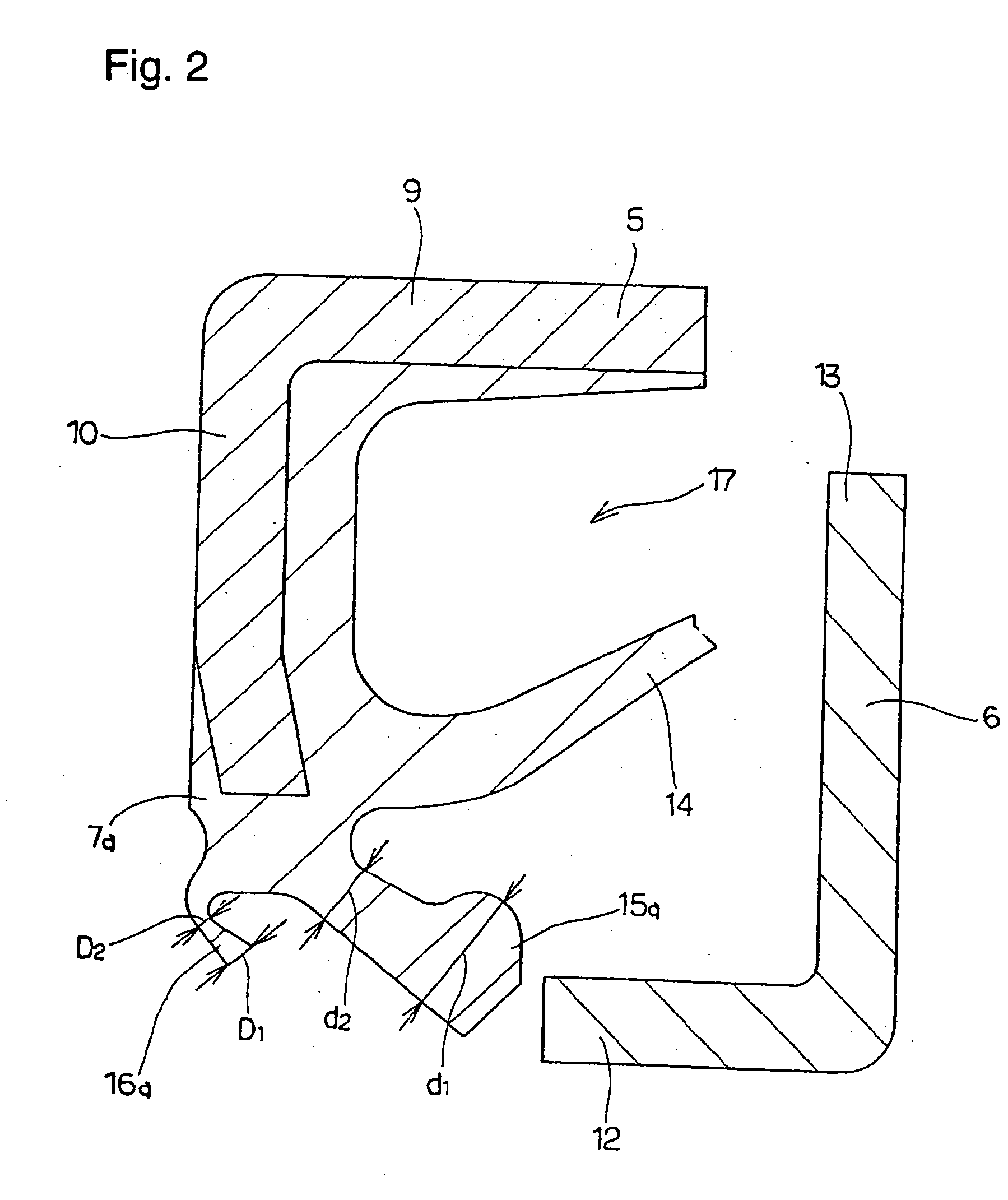
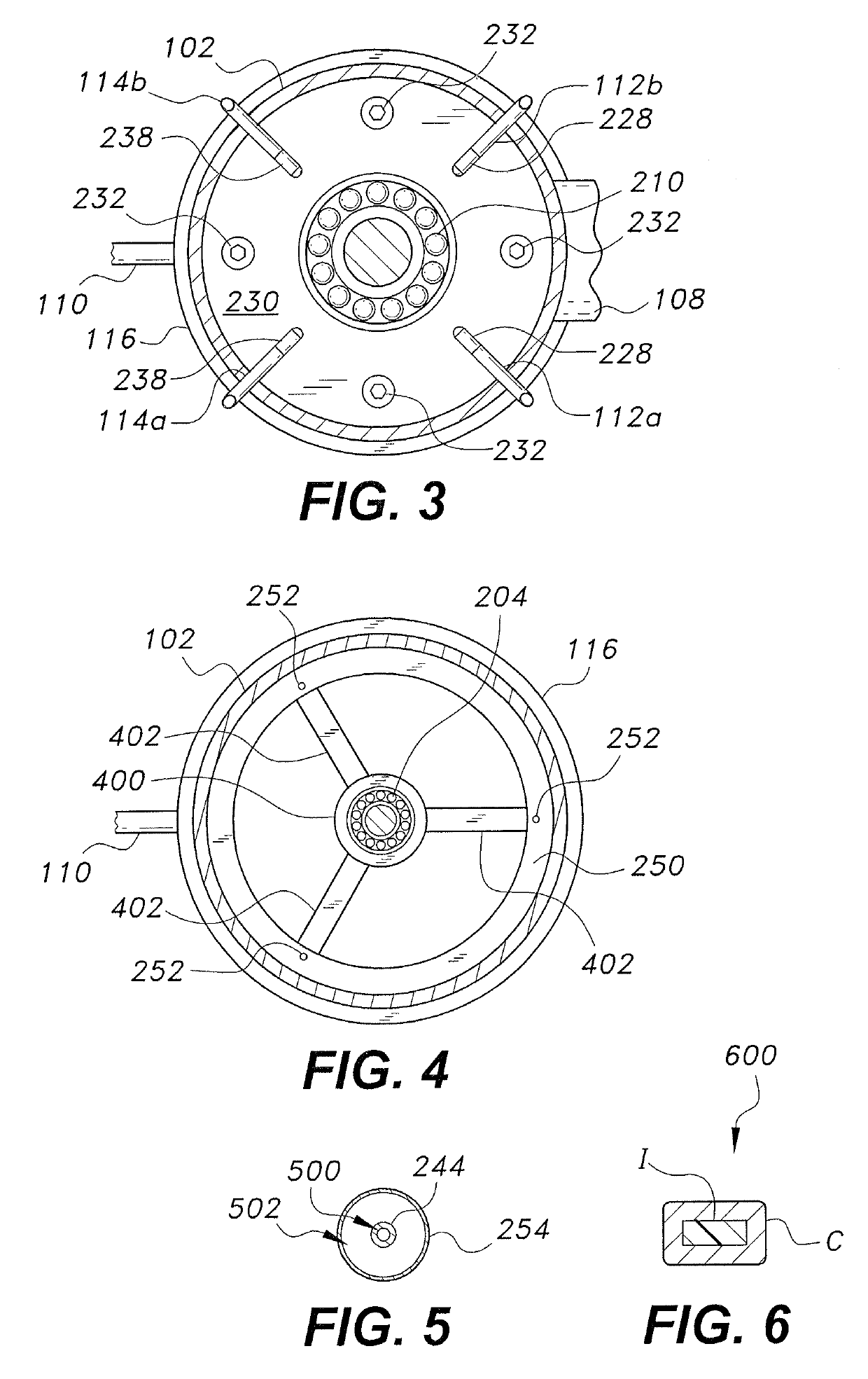
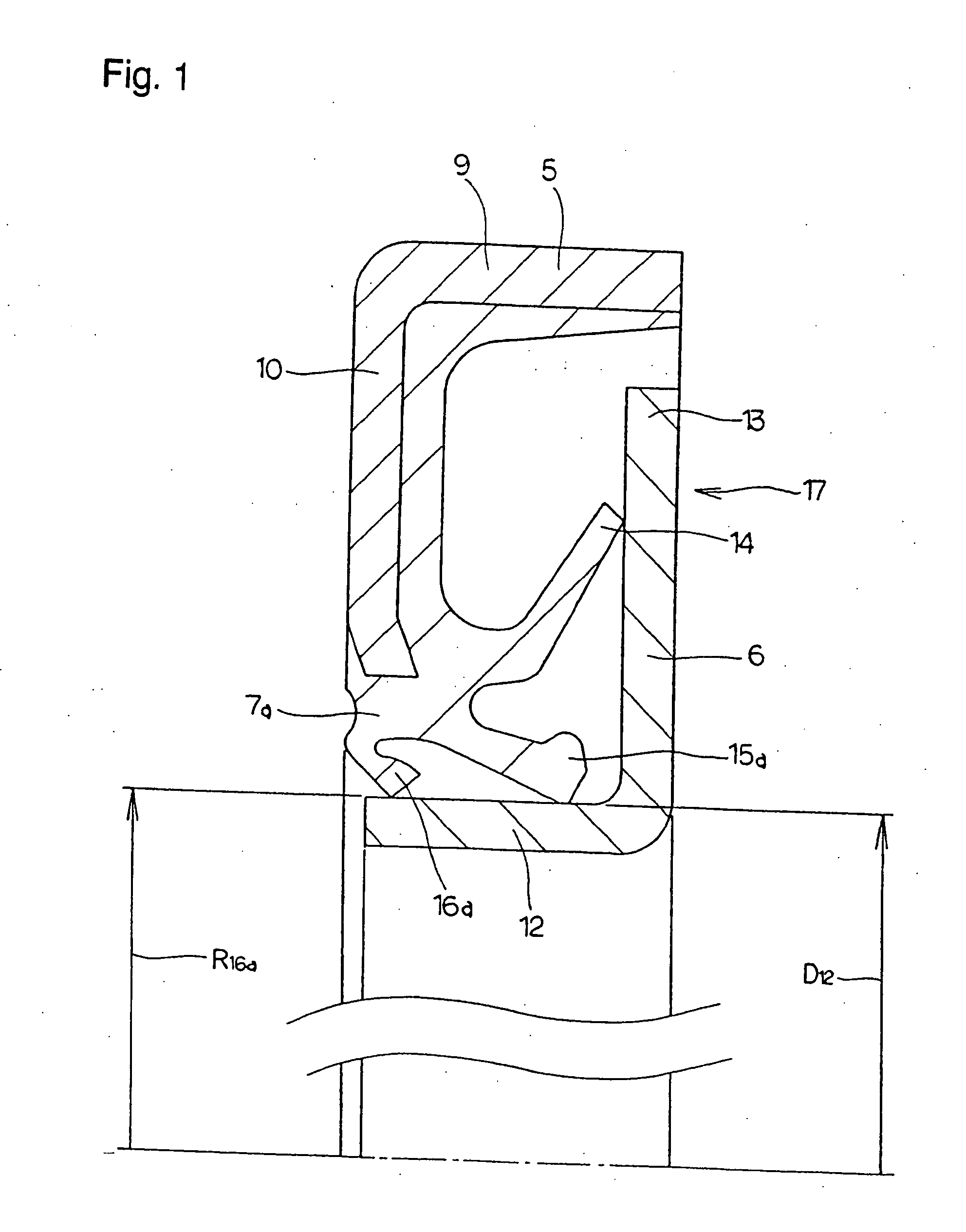
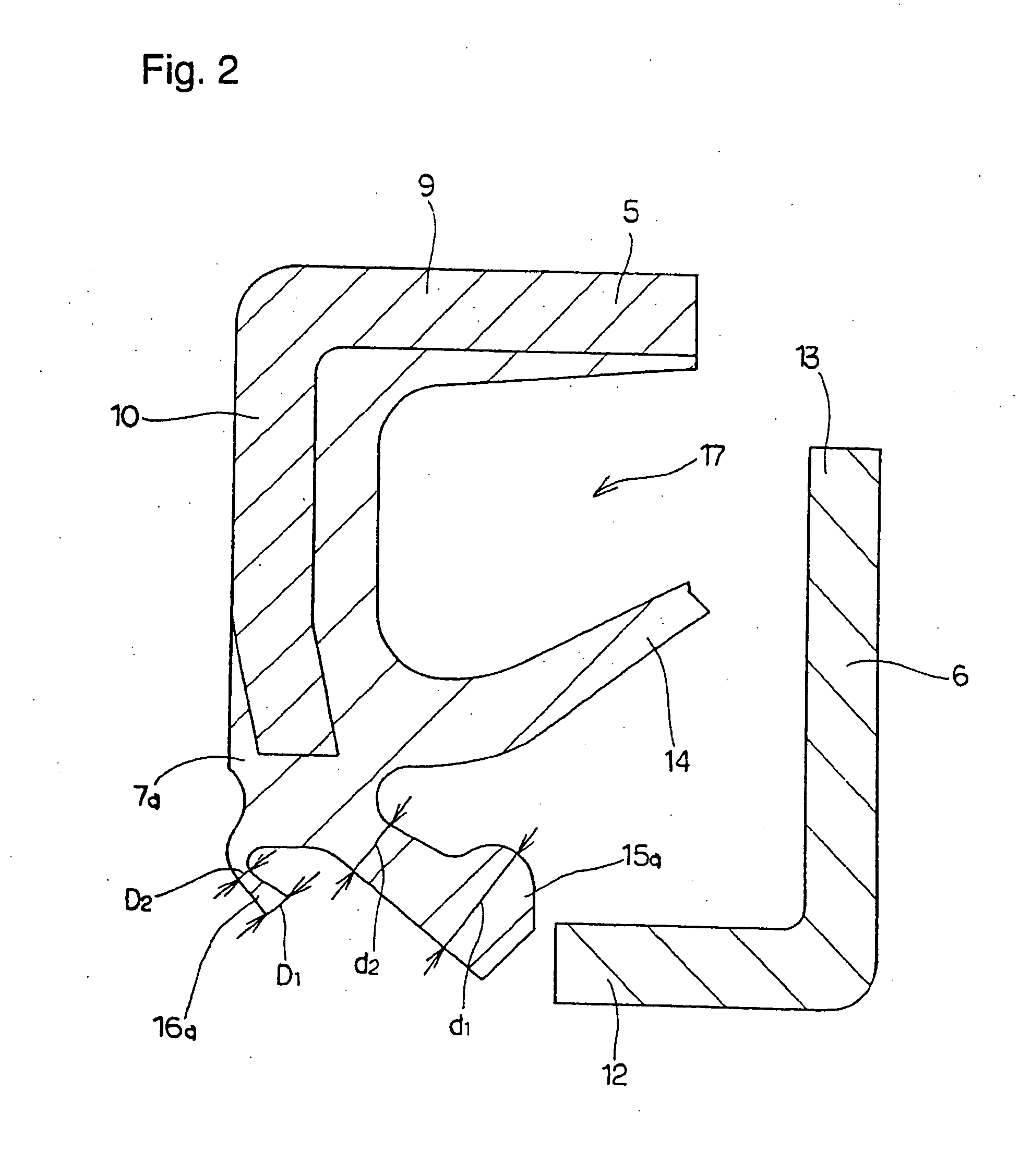
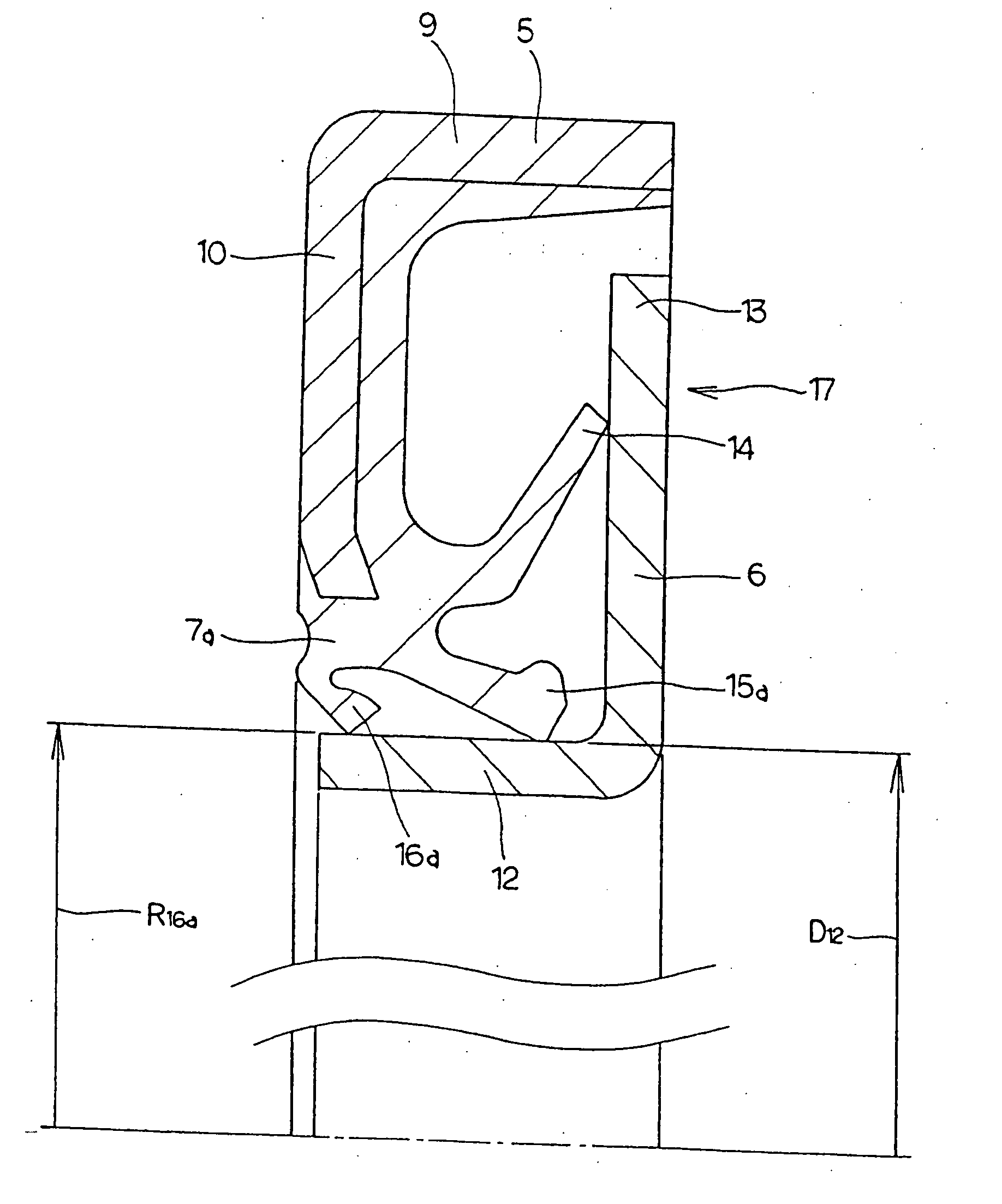
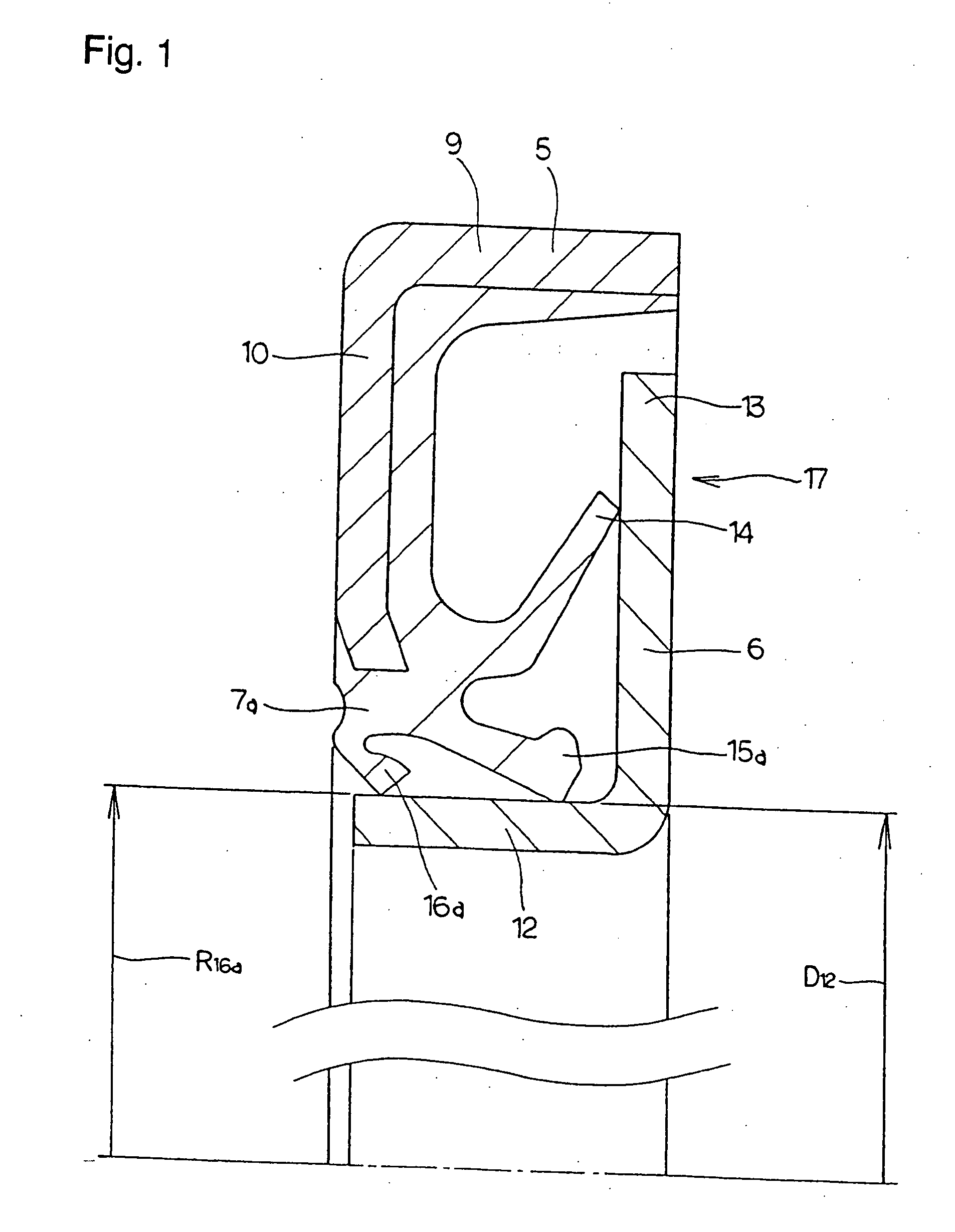
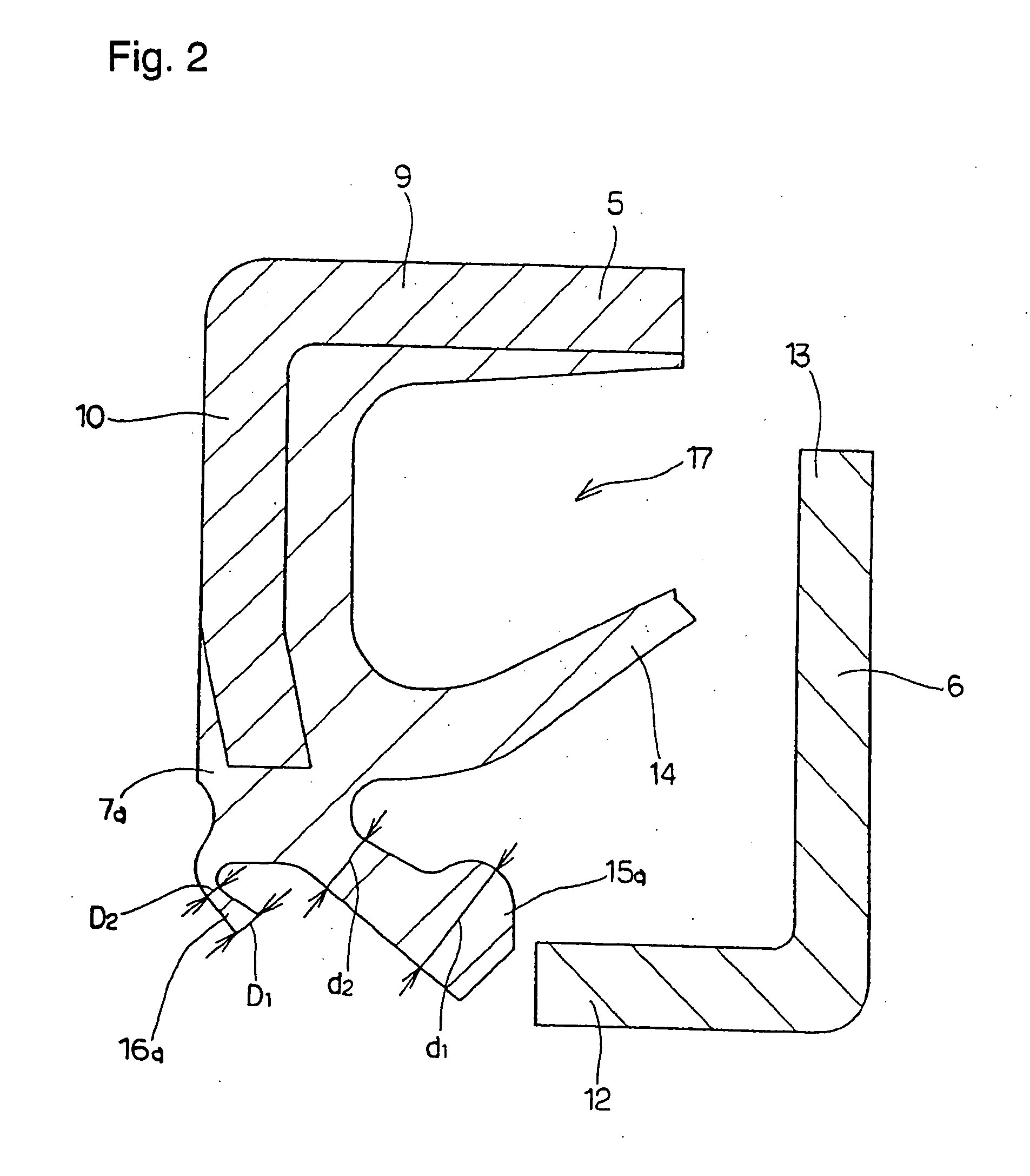
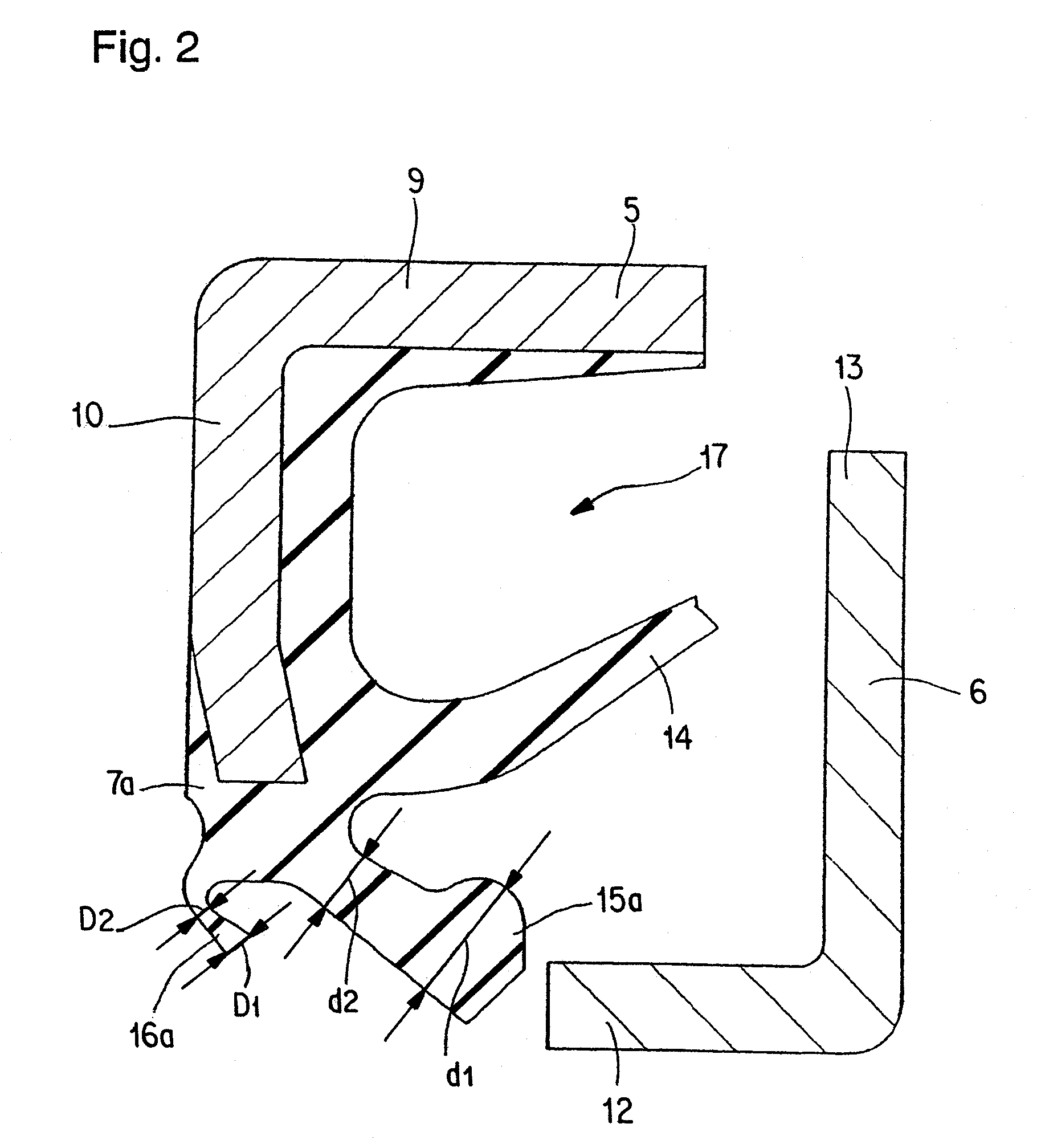
Sealing device, and rolling bearing and hub unit incorporating the sealing unit
InactiveUS20050104302A1Improve sealingLow costEngine sealsRolling contact bearingsRolling-element bearingMechanical engineering
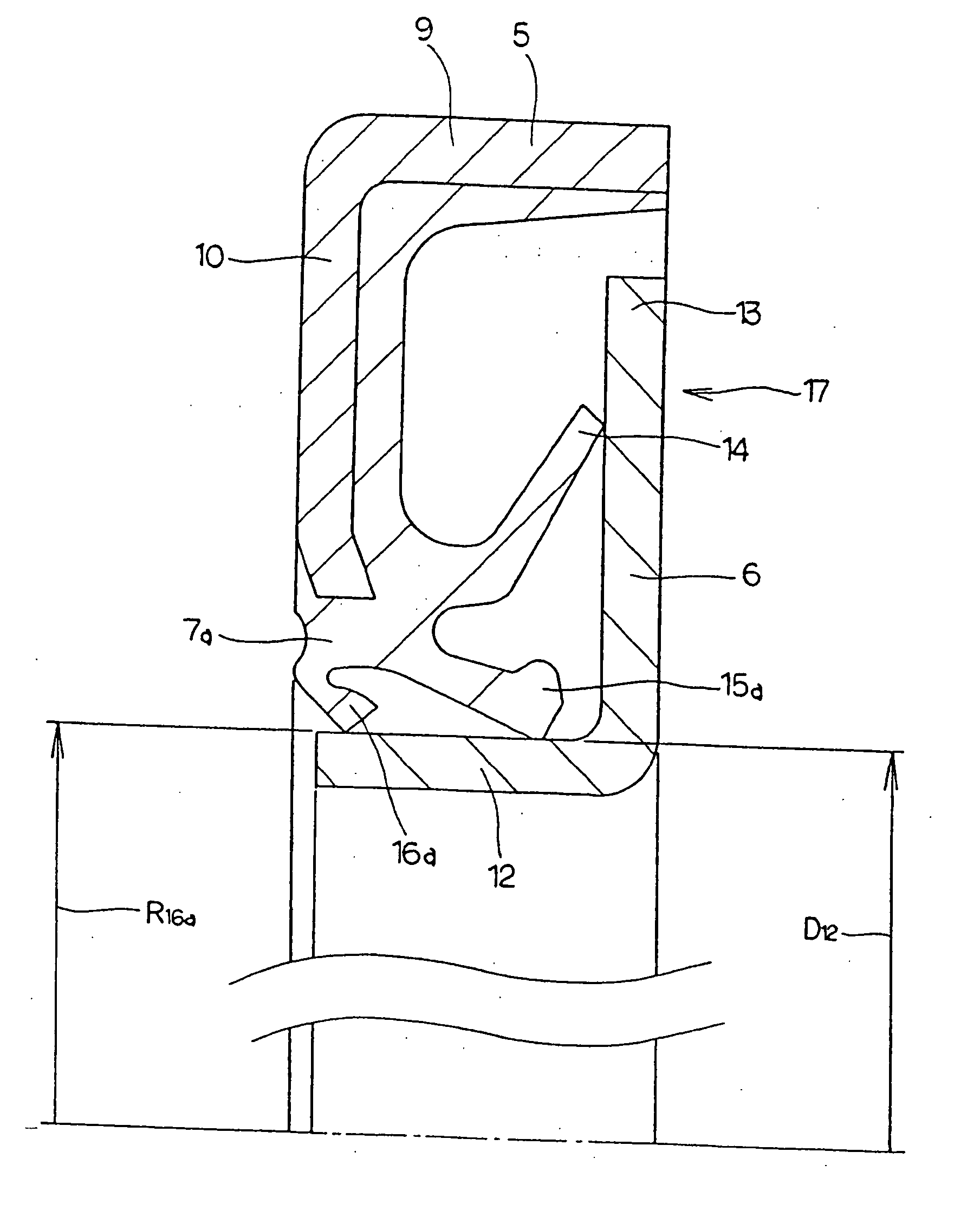
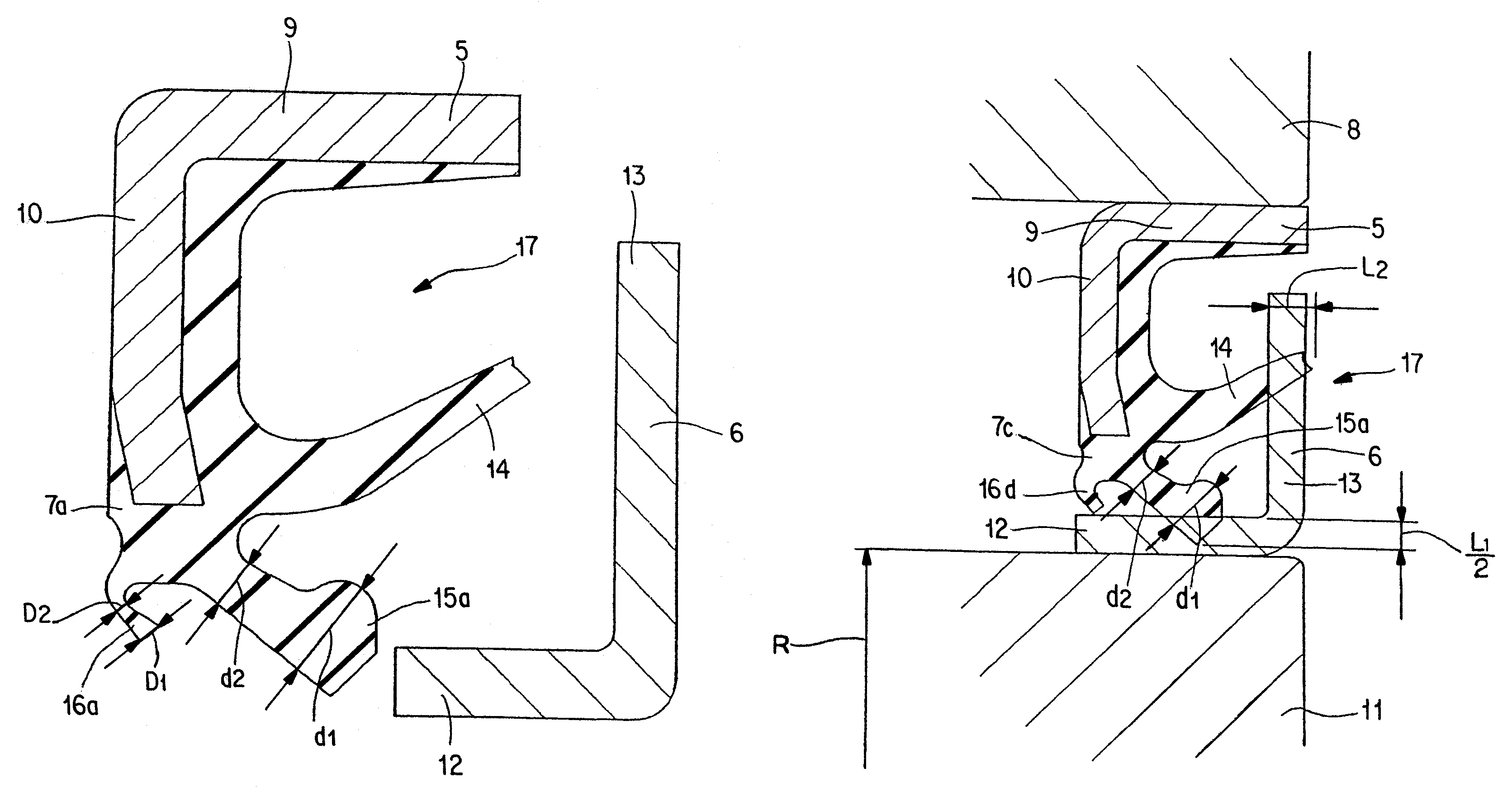
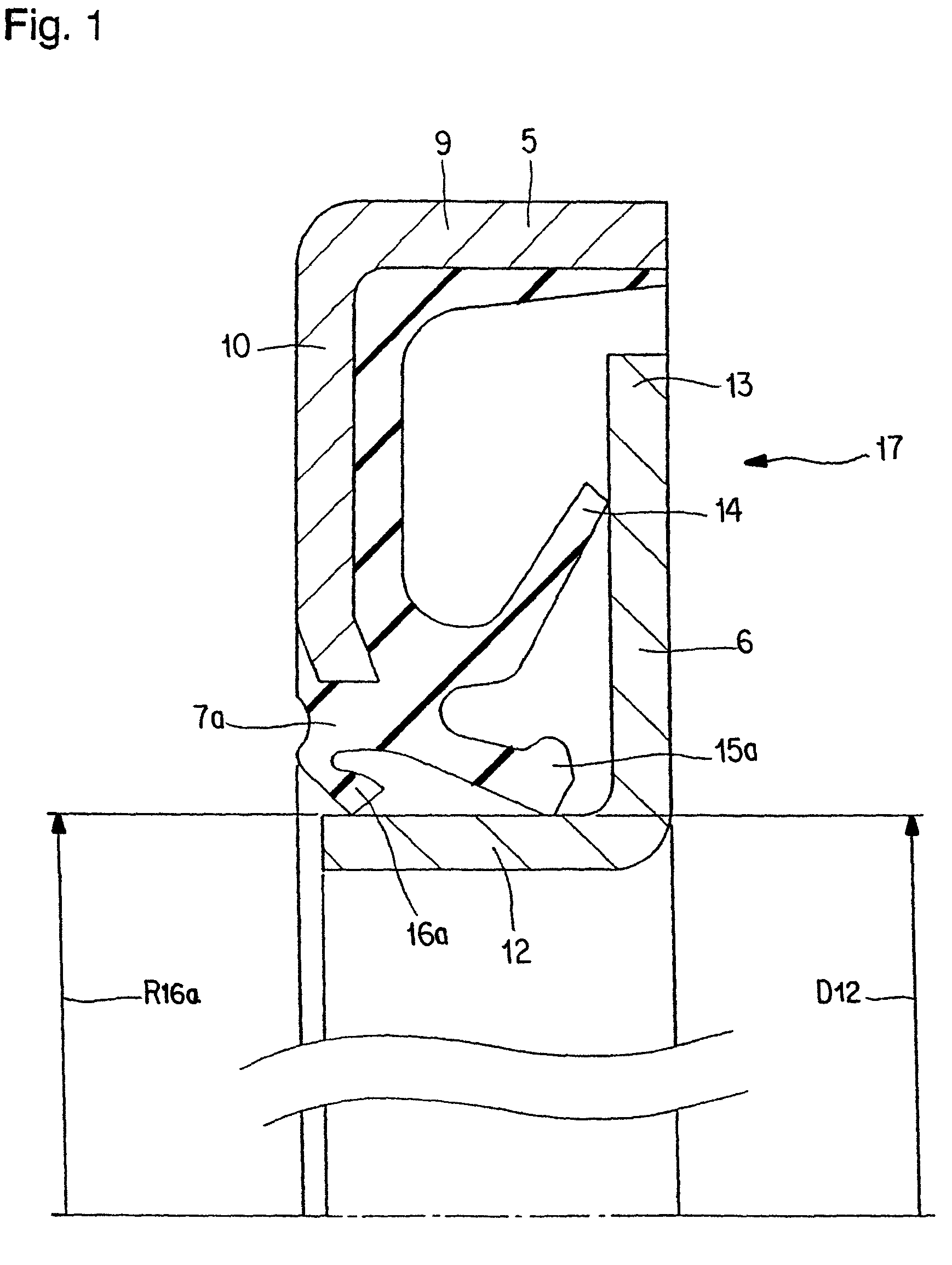
A seal member with its base end connected to a metal core has three seal lips. The thickness of the tip end of the intermediate seal lip in the intermediate position is d1, and the thickness of the base end is d2. The thickness of the tip end of the innermost inner seal lip is D1 and that thickness of the base end is D2. In this case, at least part of the base end of the intermediate seal lip and inner seal lip has its thickness regulated to be 0.2·d1≦d2≦0.8·d1, and 0.5·D1≦D2<D1. The tip edge of the inner seal lip is fitted onto the outer peripheral surface of the radially inside cylindrical portion of a slinger with substantially zero interference. Consequently, even if the slinger and metal core are displaced relative to each other, excellent seal performance is secured while increase of torque is inhibited.
Owner:NSK LTD
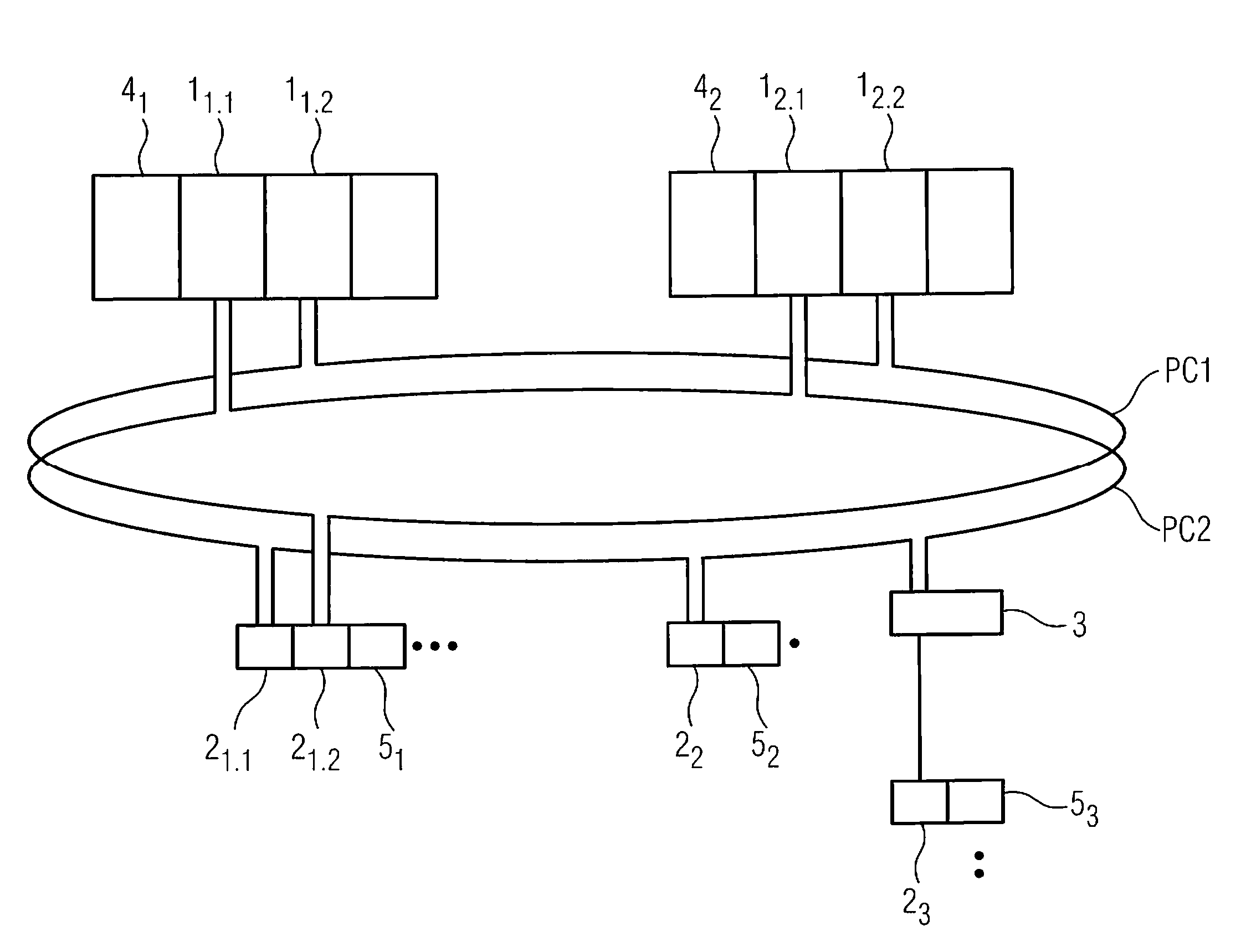
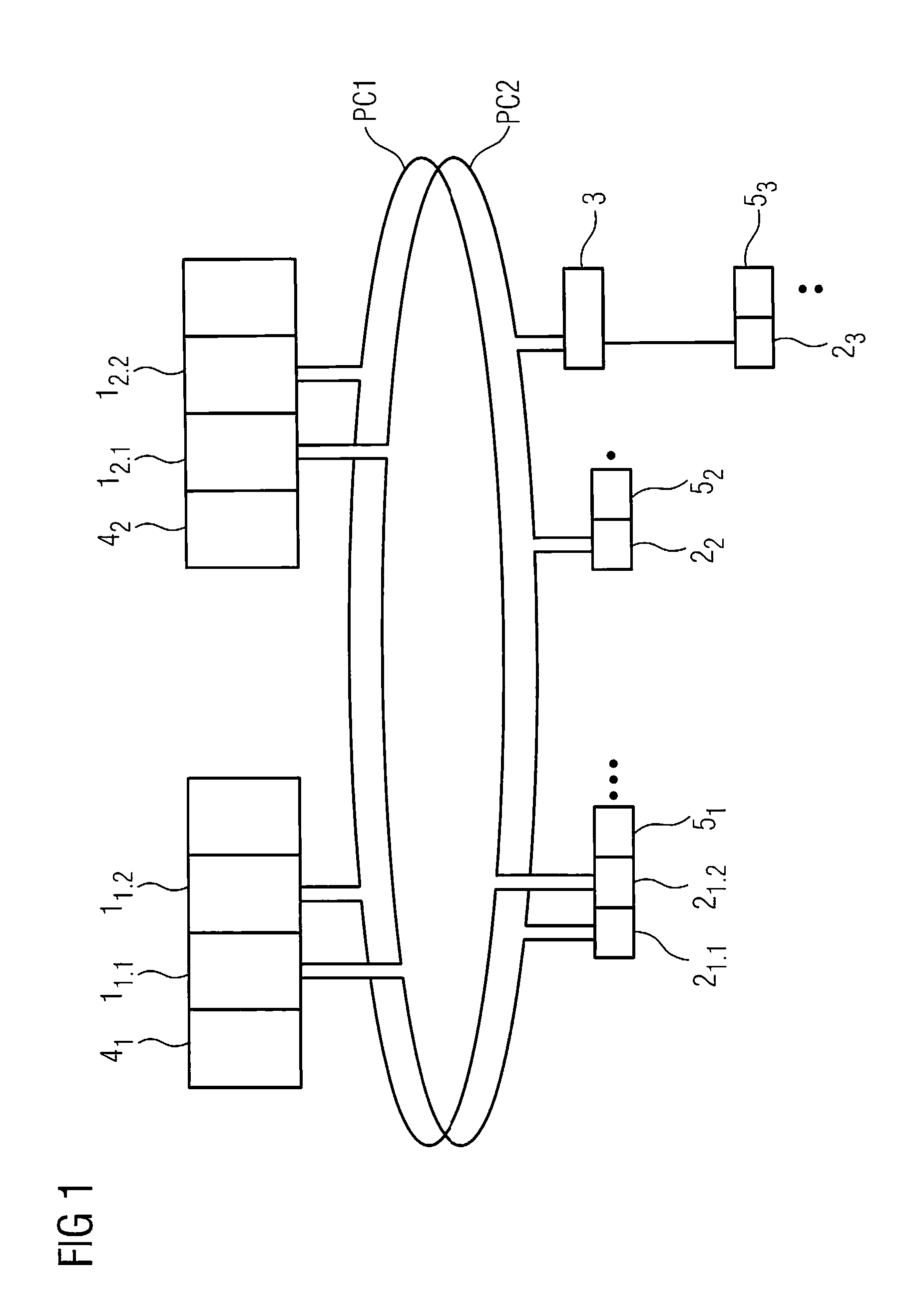
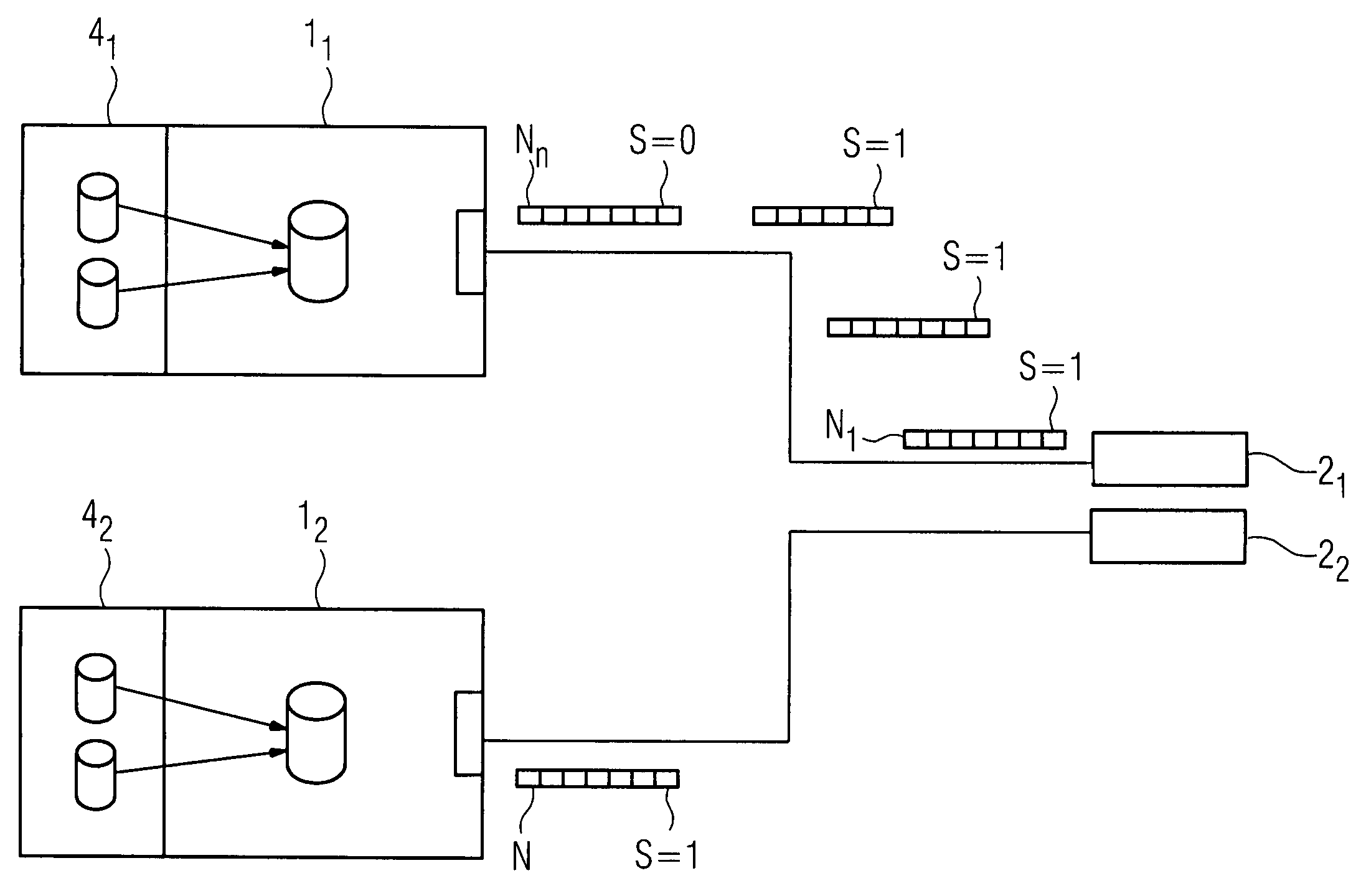
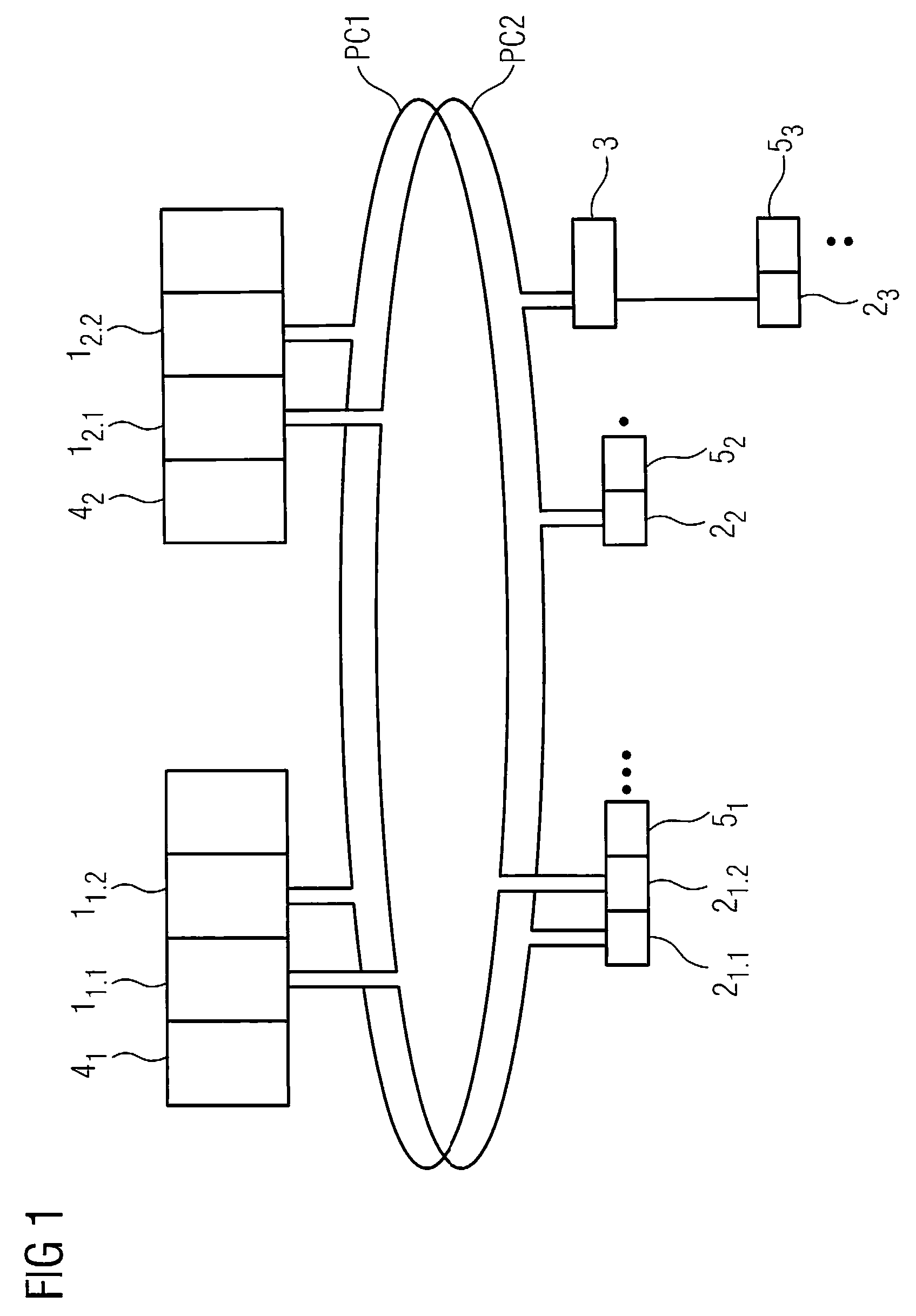
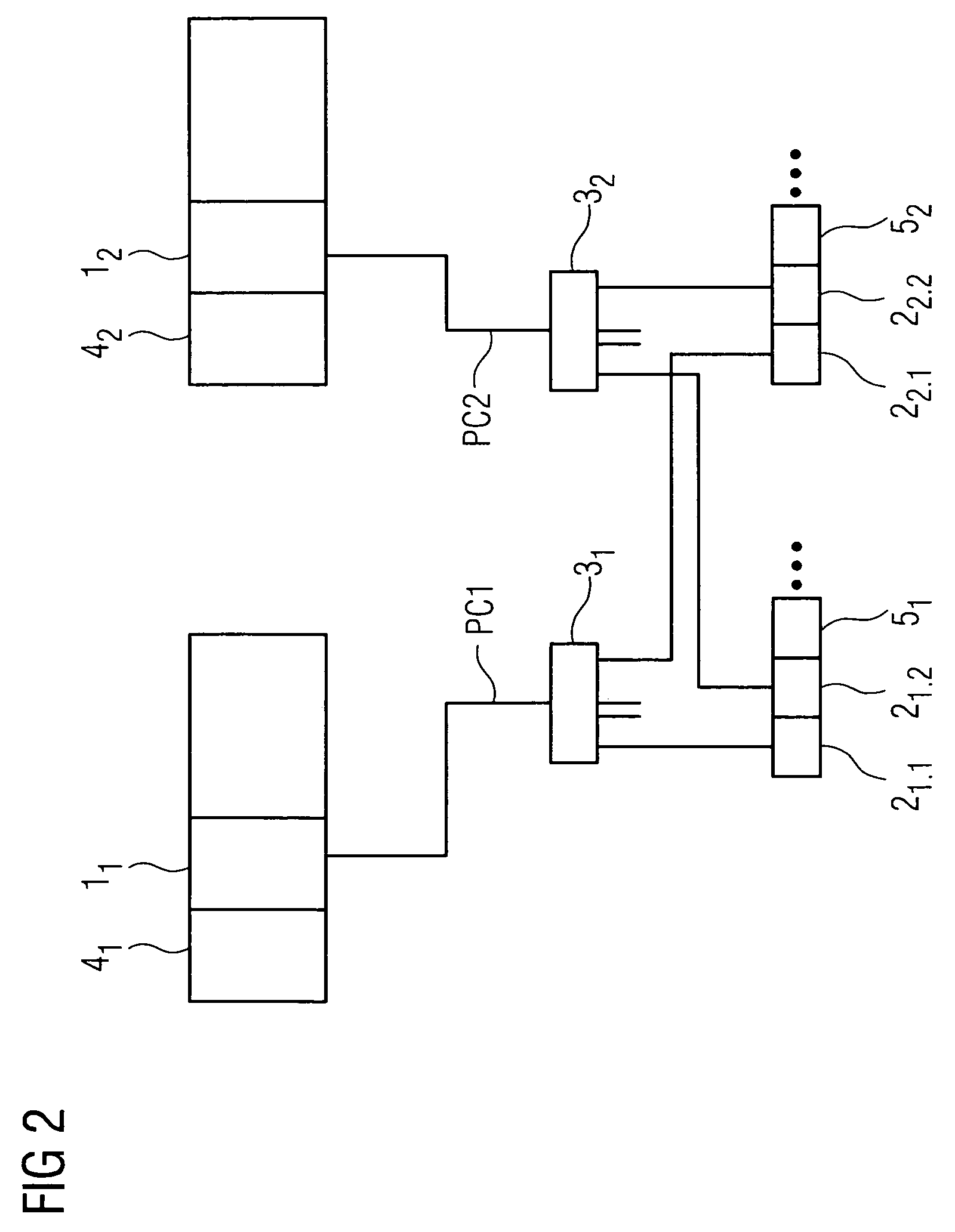
High-availability communication system
ActiveUS20090059947A1Rapid switch backQuick switchProgramme controlError preventionPrimary channelHigh availability
There is described a communication system for reliable communication between communication stations, wherein there is at least one communication connection between the communication stations, wherein the communication connection features at least two channels for transmitting payload data telegrams, wherein only one channel acts as primary channel for the communication at any time, and wherein the other channels are provided as backup channels. A status indicator in the payload data telegram is provided for the indication of information concerning which channel is primary channel or backup channel at a given time point, wherein the communication stations adopt as primary channel that channel for which, during receipt of the payload data telegrams, the most recent status change from backup channel to primary channel was detected by the communication stations.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
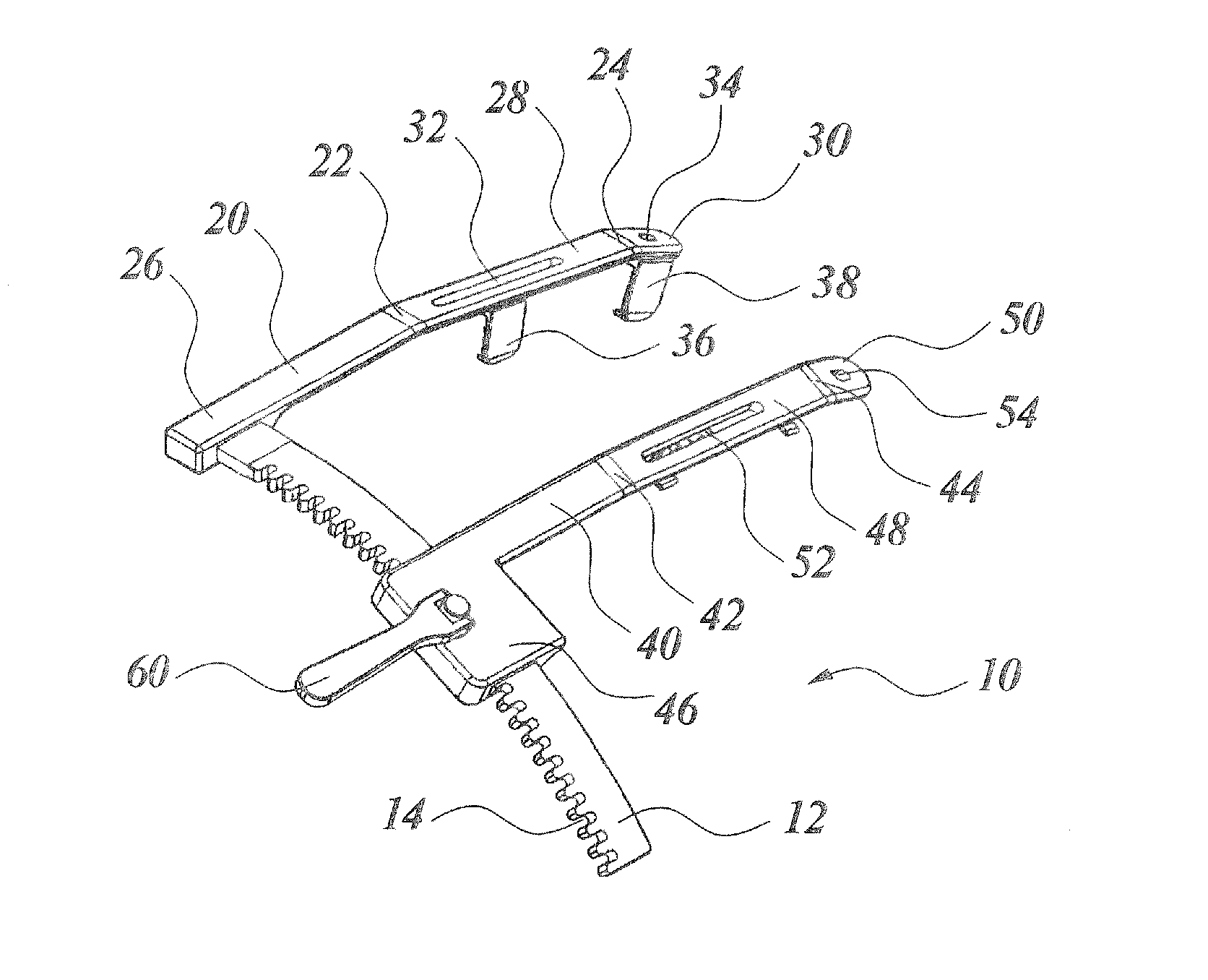
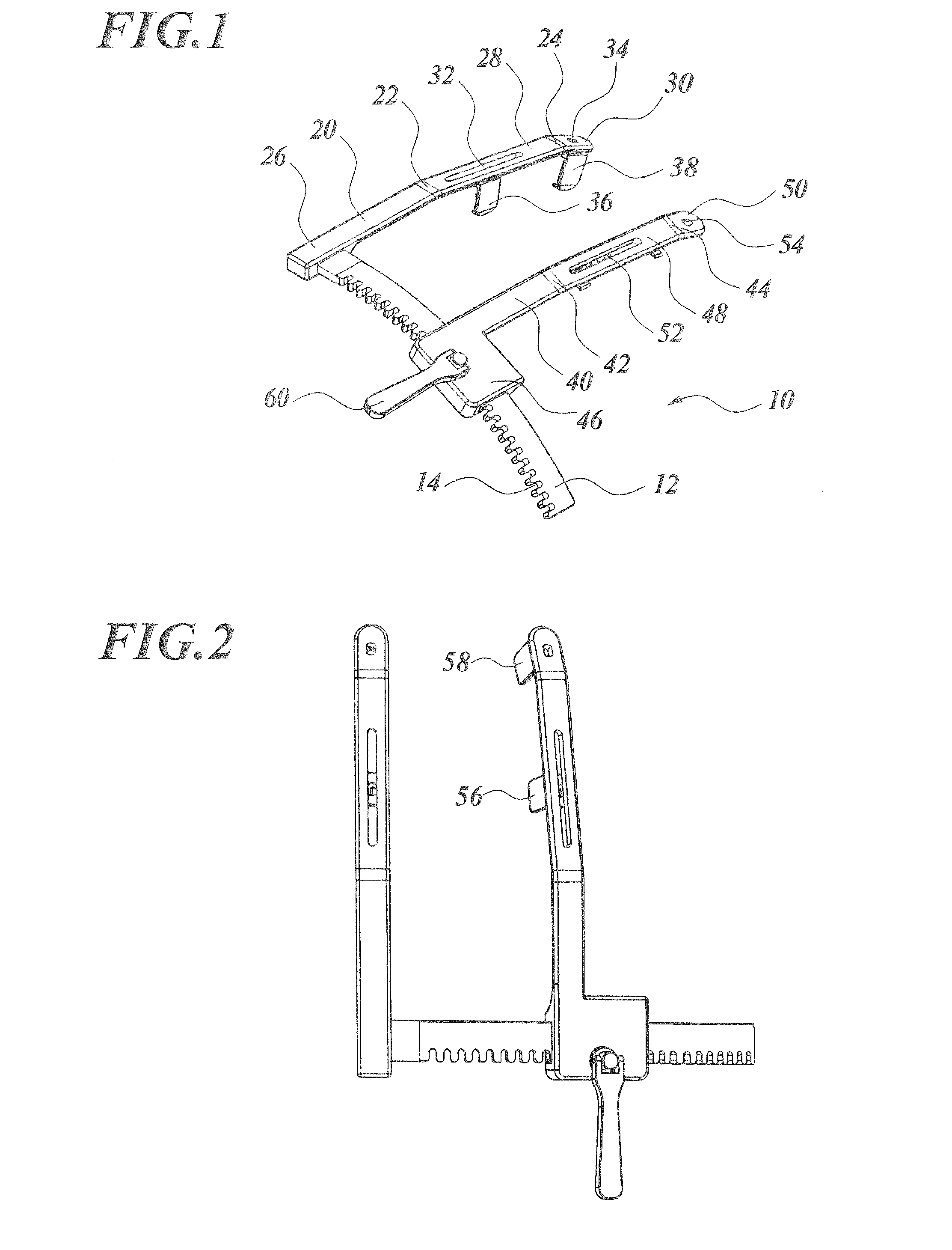
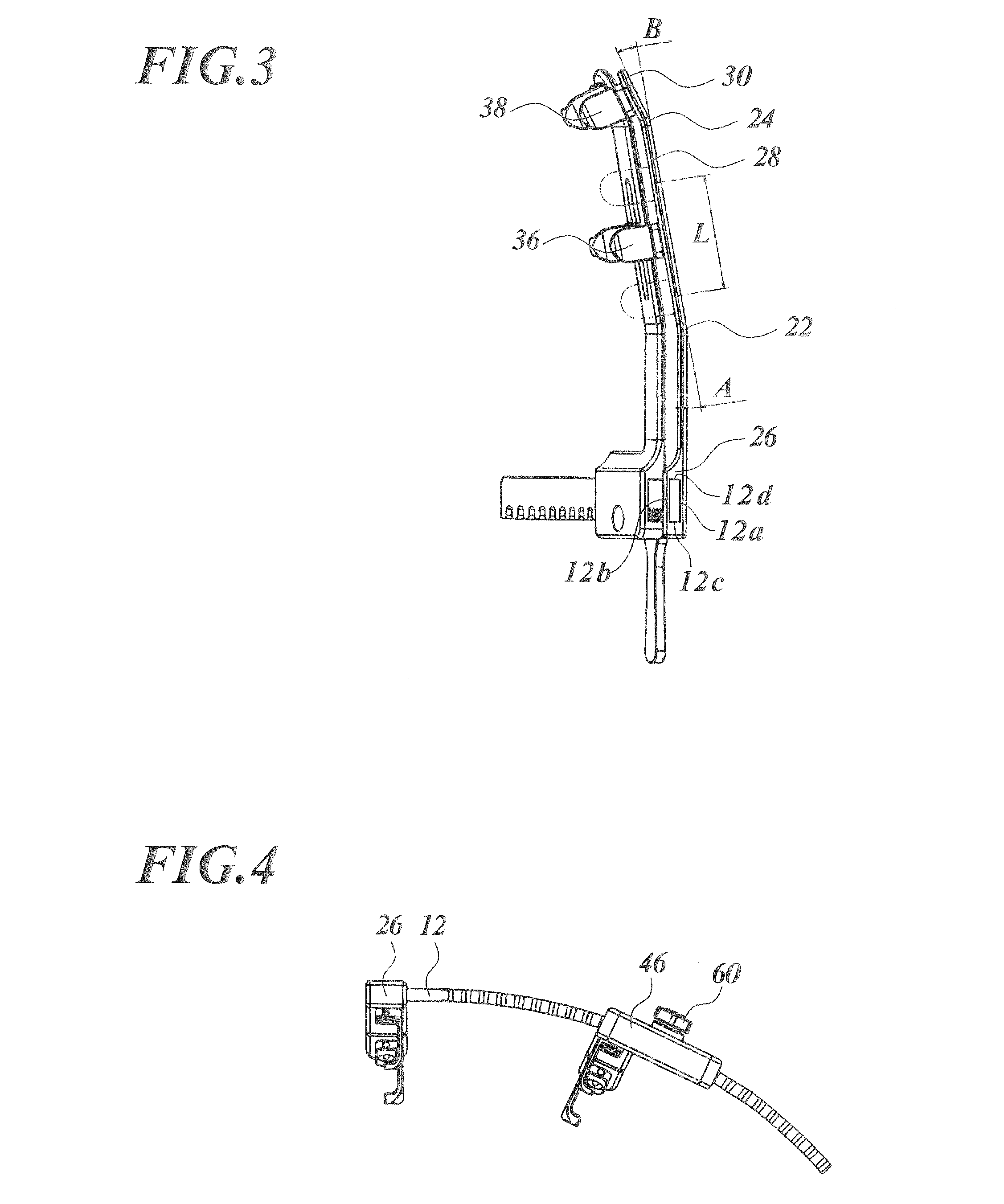
Rib spreader
Disclosed is a rib spreader including a stationary arm having a first bent portion; a first hook having a contact surface to contact with one incision plane of a sternum of human, and attached to the stationary arm ahead of the first bent portion so as to be pivotable over a predetermined angular range; a rack fixed to the base end of the stationary arm at a predetermined angle and curved archwise; a movable arm supported at the base end of the movable arm by the rack so as to be movable along the rack, to thereby vary the distance from the stationary arm; and a second hook having a contact surface to contact with the other incision plane, and is attached to the movable arm ahead of the second bent portion so as to be pivotable over a predetermined angular range.
Owner:MEDICAL PINE
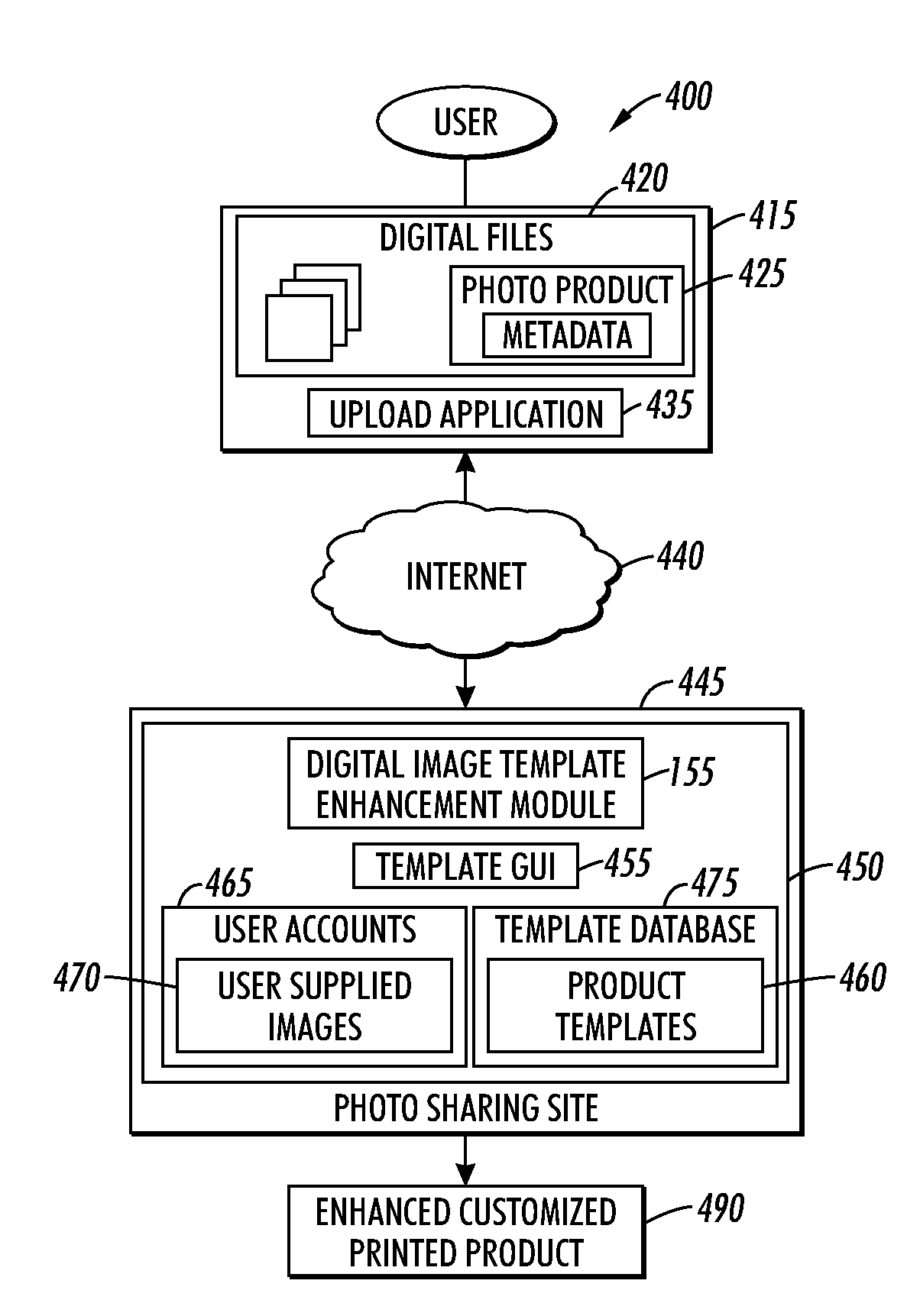
Method and system for processing photo product templates
ActiveUS20100150437A1Reduce numberGreat choiceCharacter and pattern recognitionPictoral communicationPersonalizationImage based
A system and method for processing digital photo product templates to enhance a personalized photo product and to enable greater flexibility when selecting options for the photo product template. One or more photo product templates can be defined as a series of objects, some of which are capable of being colorized by a user. Color sets applicable to the photo product template can be displayed based on a predefined set of colors and / or a user-defined “seed color”. The selected color sets can be automatically applied to the photo product template utilizing a predefined rank. The color sets can be ranked and complementary color set suggestions provided based on the evaluation of the colors in an image.
Owner:XEROX CORP
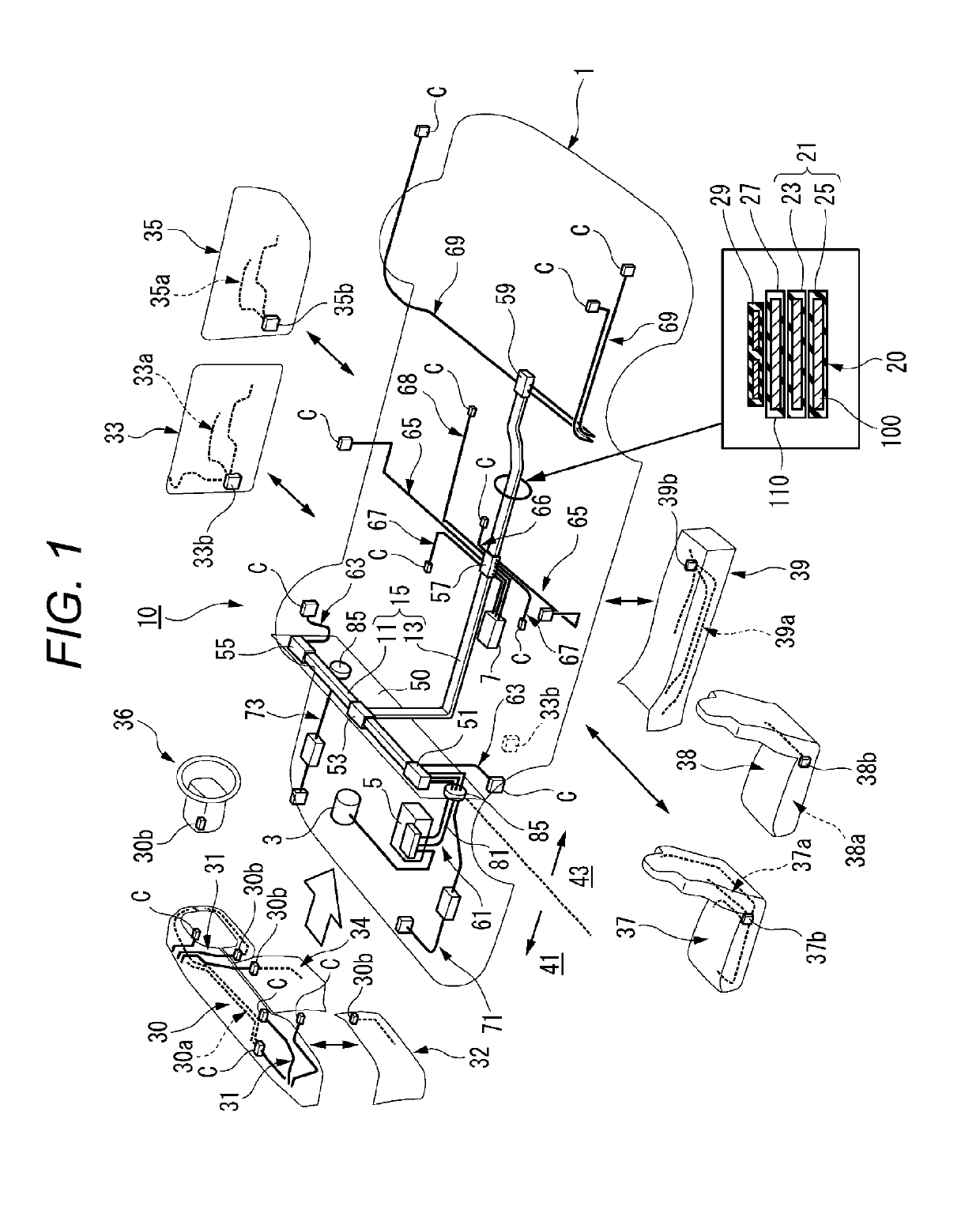
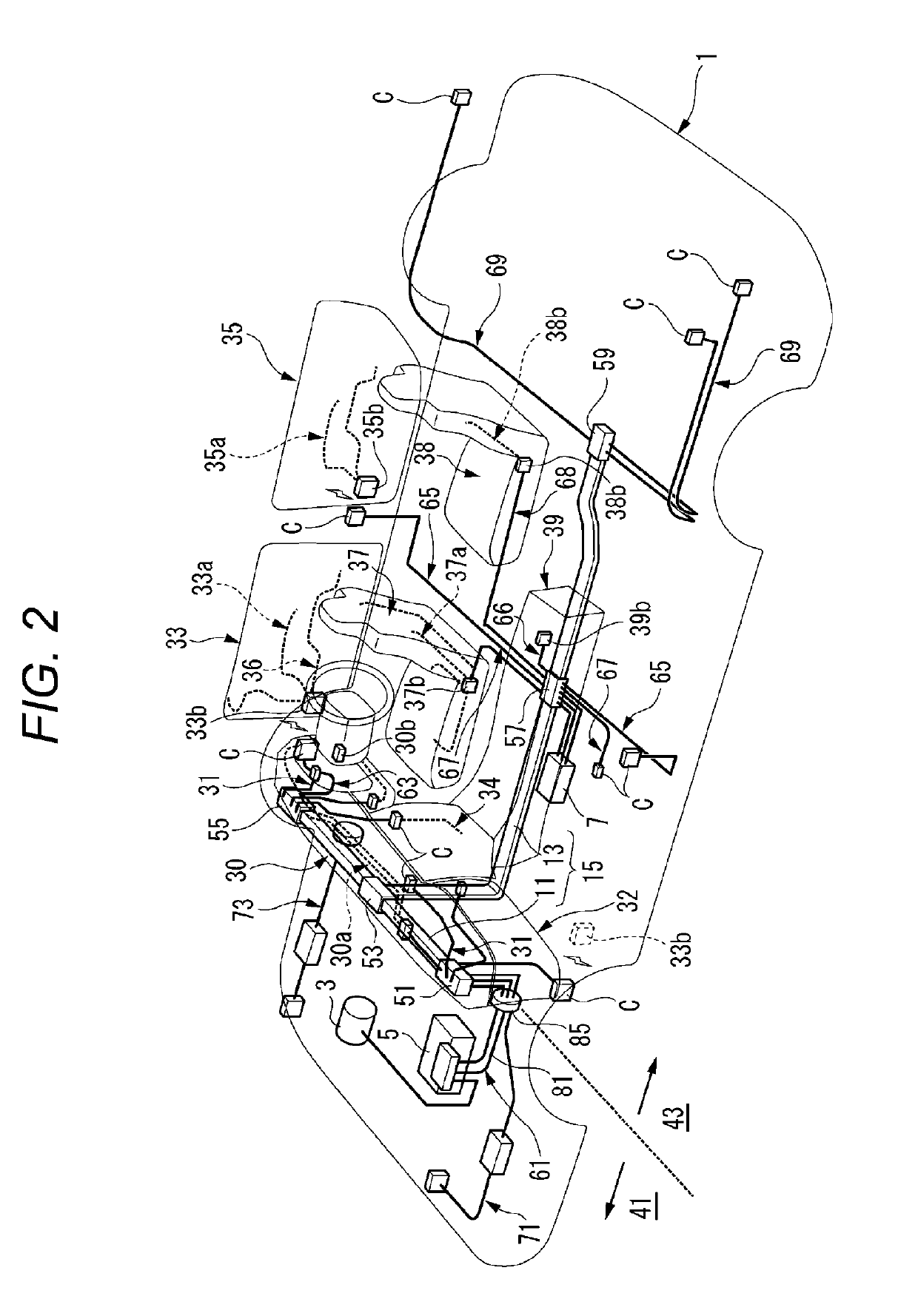
Vehicular circuit body
ActiveUS20190126860A1Reduce voltage fluctuationEasily recoverCoupling device connectionsInsulated cablesRound barElectrical conductor
A vehicular circuit body includes: a trunk line that includes a power source line having a predetermined current capacity and a communication line having a predetermined communication capacity, and that is routed in a vehicle body; a branch line that is connected to an accessory; and a plurality of control boxes that are disposed in a distribution manner along the trunk line, each having a control unit that distributes at least one of power from the power source line, supplied to the trunk line, and a signal from the communication line, to the branch line connected to the trunk line. The trunk line is formed of a routing material having at least one kind of conductor among a flat conductor, a round bar conductor, and a stranded wire.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
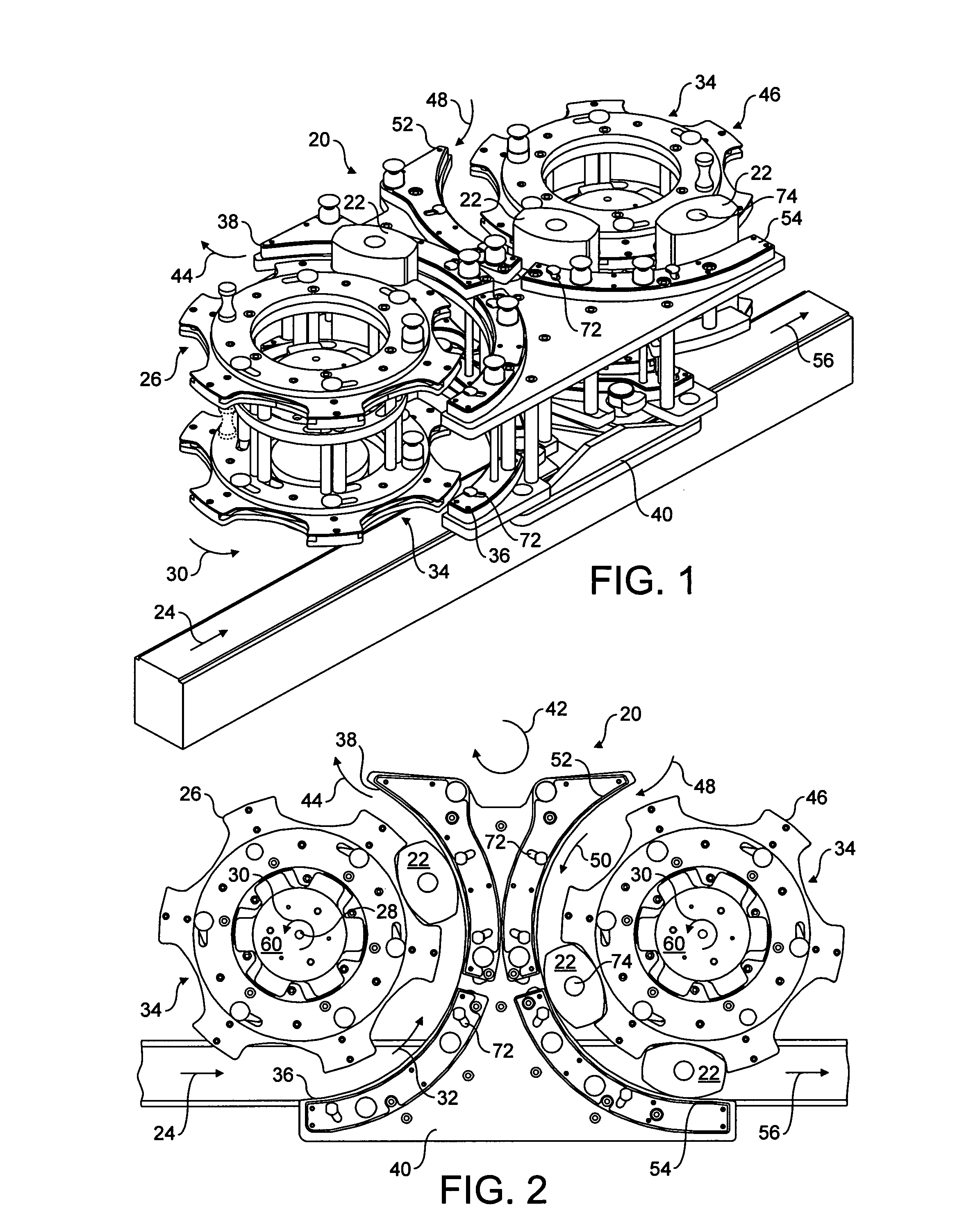
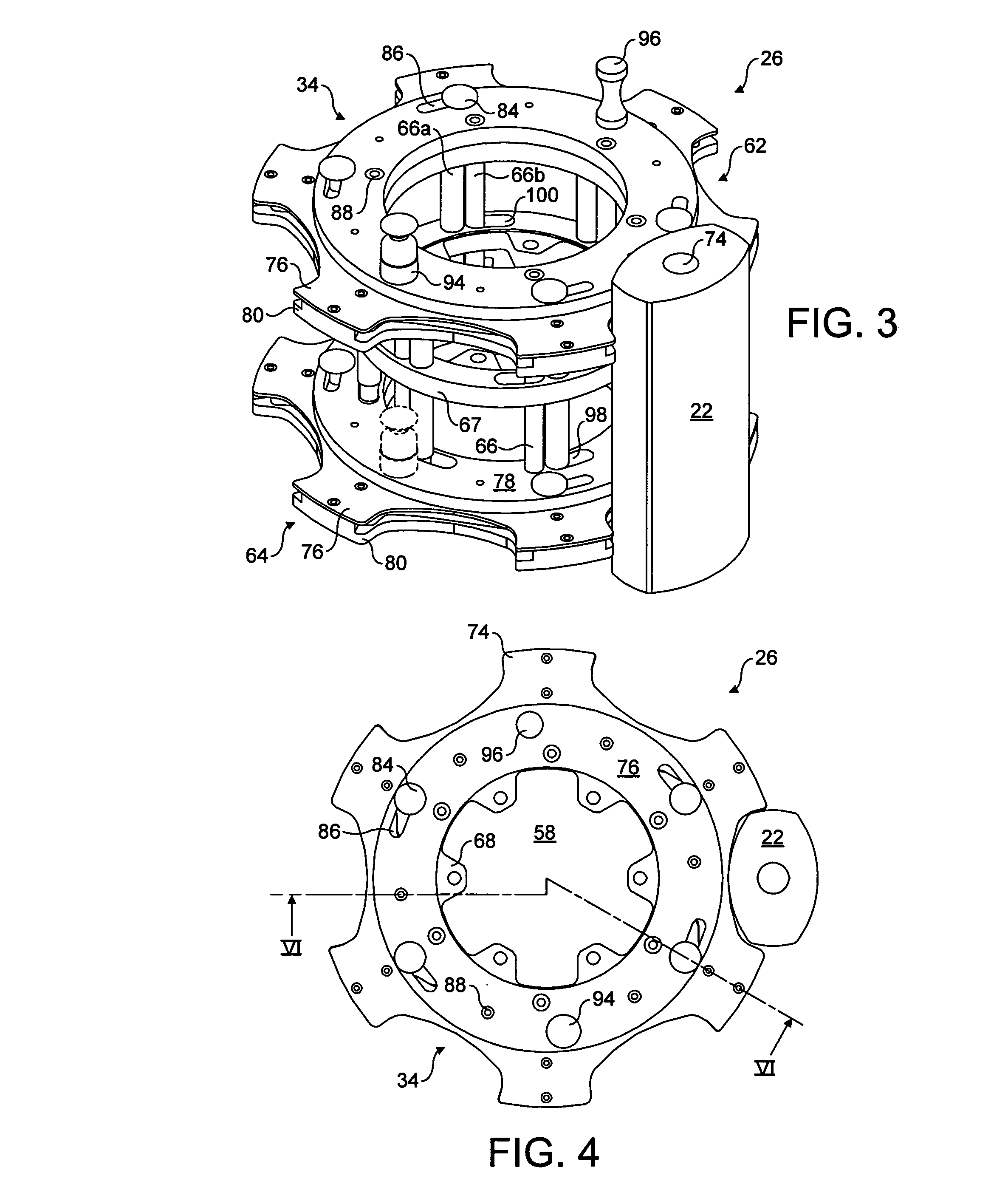
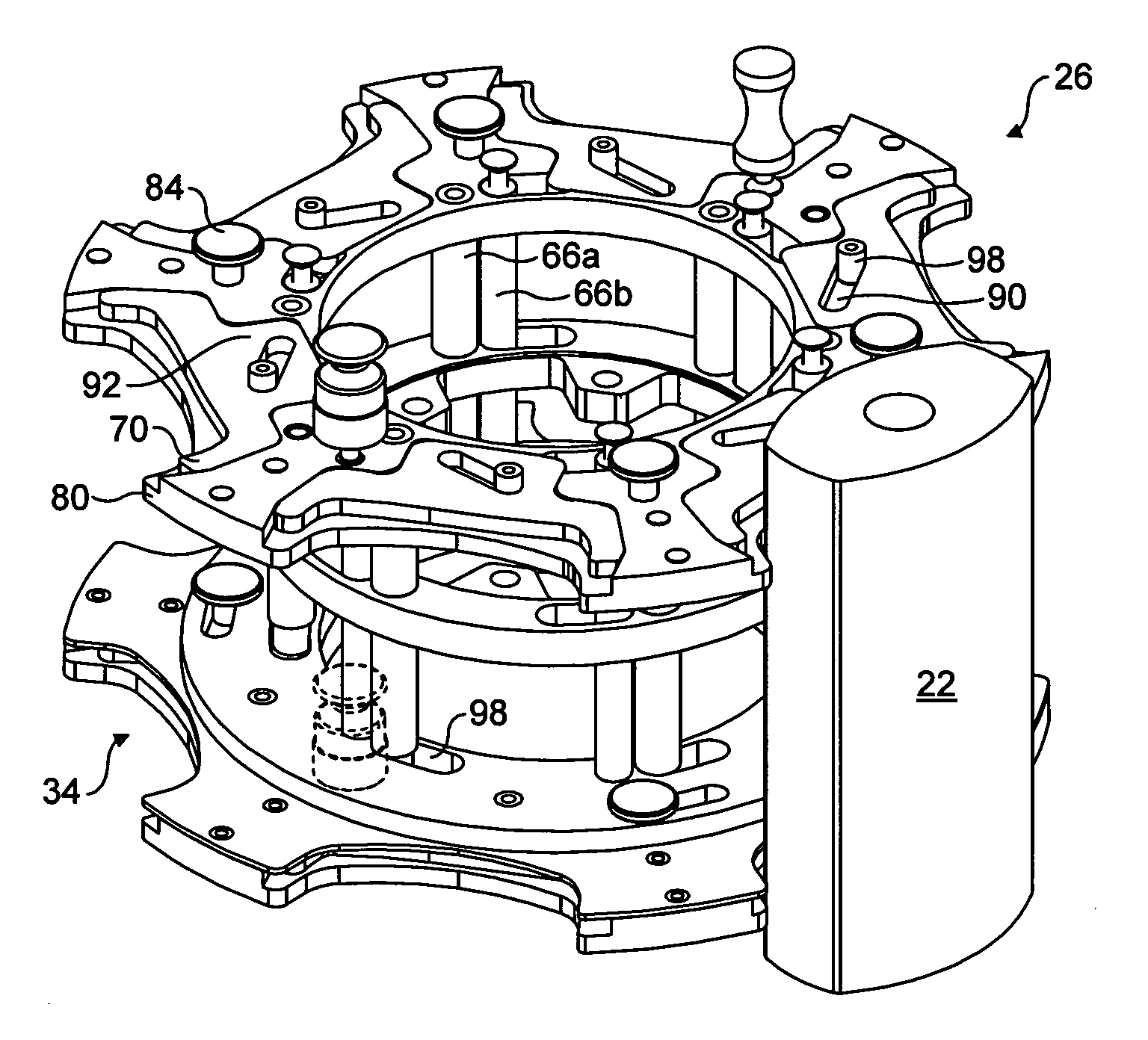
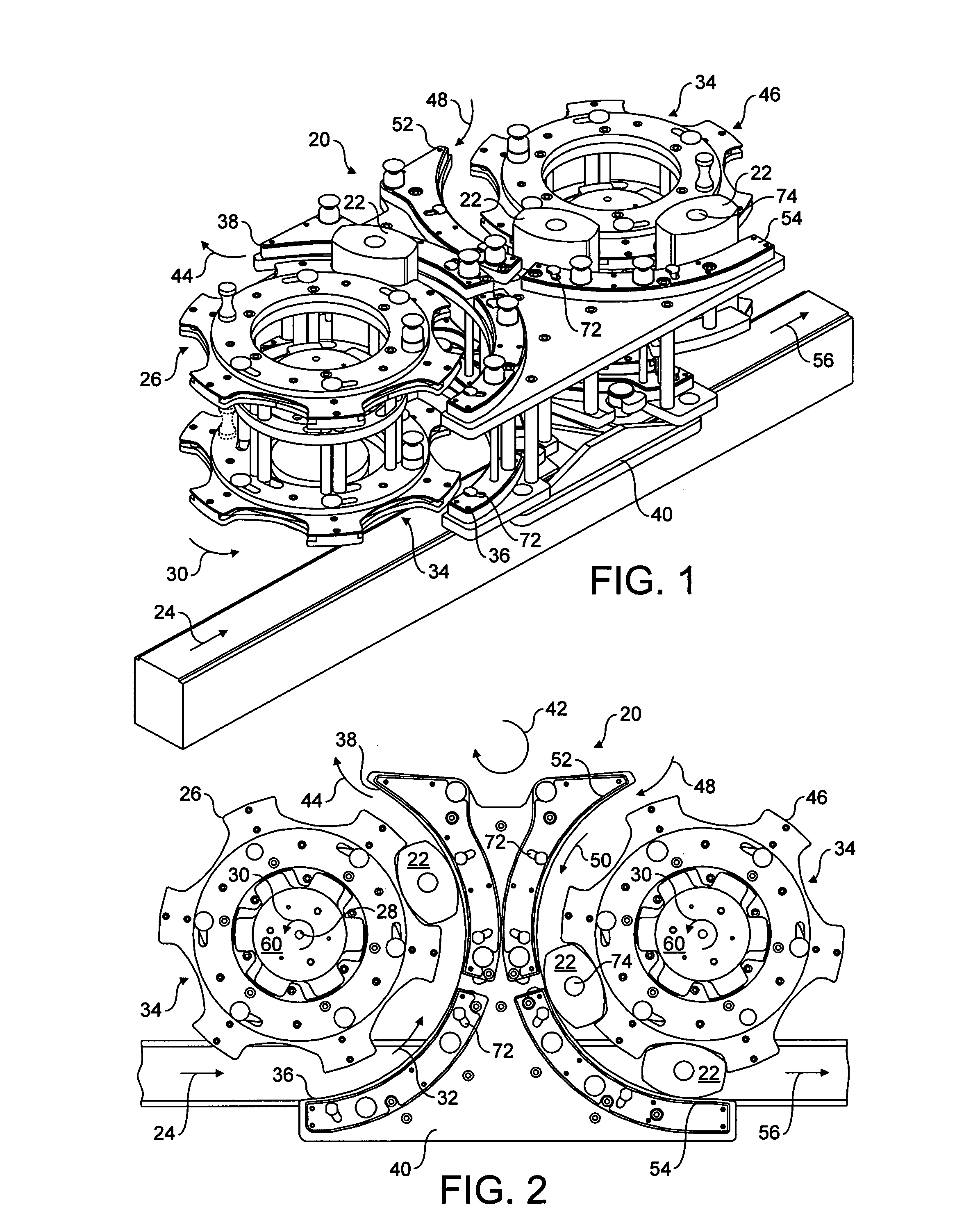
Compound nozzle for cement 3D printer to produce thermally insulated composite cement
ActiveUS10399247B1Eliminating extra workImprove insulation efficiencyAdditive manufacturing apparatusConstruction materialMotor drive3d printer
The compound nozzle for a cement 3D printer to produce thermally insulated composite cement is useful for producing composite thermally insulated cement sections using a 3D printer. The nozzle includes an insulation nozzle concentrically disposed in the central discharge orifice of the compound nozzle to produce a stream of insulation media axially surrounded by a stream of cement mixture extruded from the nozzle to form a wall with a cement exterior and an insulation interior. A motor-driven auger is controlled by a controller, and the cement is supplied from the top either manually or by a concrete pump. The insulating material is supplied to the insulation nozzle by a separate line that uses another pump. The system includes a cleaning mechanism to clean the internal components of the compound nozzle using water jets and a drying system to dry the internal components without disassembling the system.
Owner:UNITED ARAB EMIRATES UNIVERSITY
Connector assembly with variable axial assist
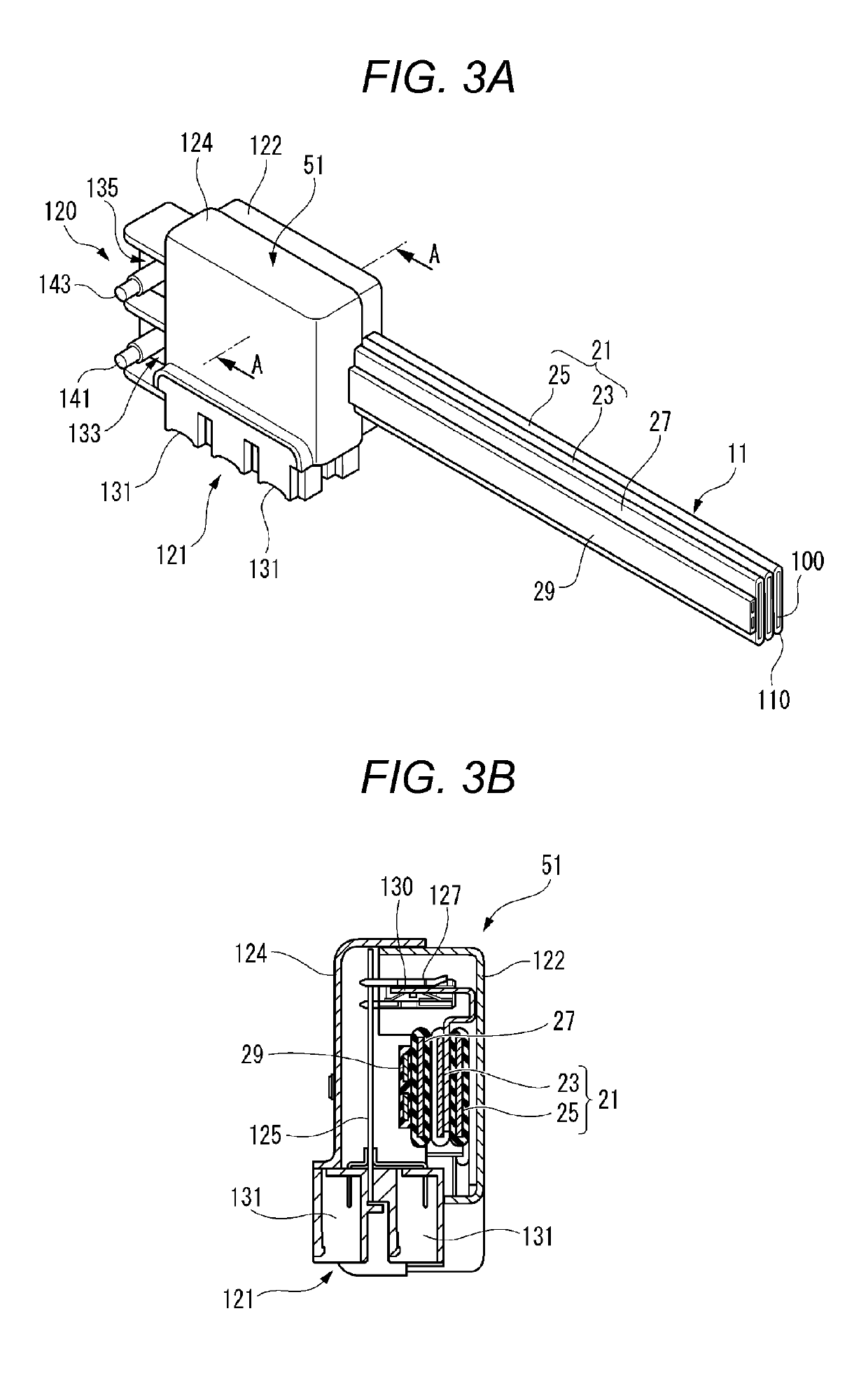
ActiveUS9917402B1Increase frictionReduction of the peak mating-forceEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsEngineeringCam
A connector includes a first-housing, a second-housing, a shroud, and a stacked-gear. The first-housing defines a guide-slot. The second-housing mates with the first-housing. The second-housing includes a linear-gear-rack extending from a second-outer-surface and engages the guide-slot. The shroud is moveable from an unmated-position to a mated-position. The shroud is longitudinally slideably mounted to and surrounding at least a portion of the first-housing. The shroud also includes a curved-gear-rack having a variable-pitch-radius. The stacked-gear is moveably mounted to the first-housing. The stacked-gear has a round-gear and a cam-gear having the variable-pitch-radius in communication with the round-gear. The round-gear engages the linear-gear-rack within the guide-slot. The cam-gear engages the curved-gear-rack such that the cam-gear moves in response to a movement of the shroud from the unmated-position to the mated-position. Rotation of the round-gear engaged with the linear-gear-rack axially pulls the linear-gear-rack into the guide-slot, thereby pulling the second-housing into the first-housing.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
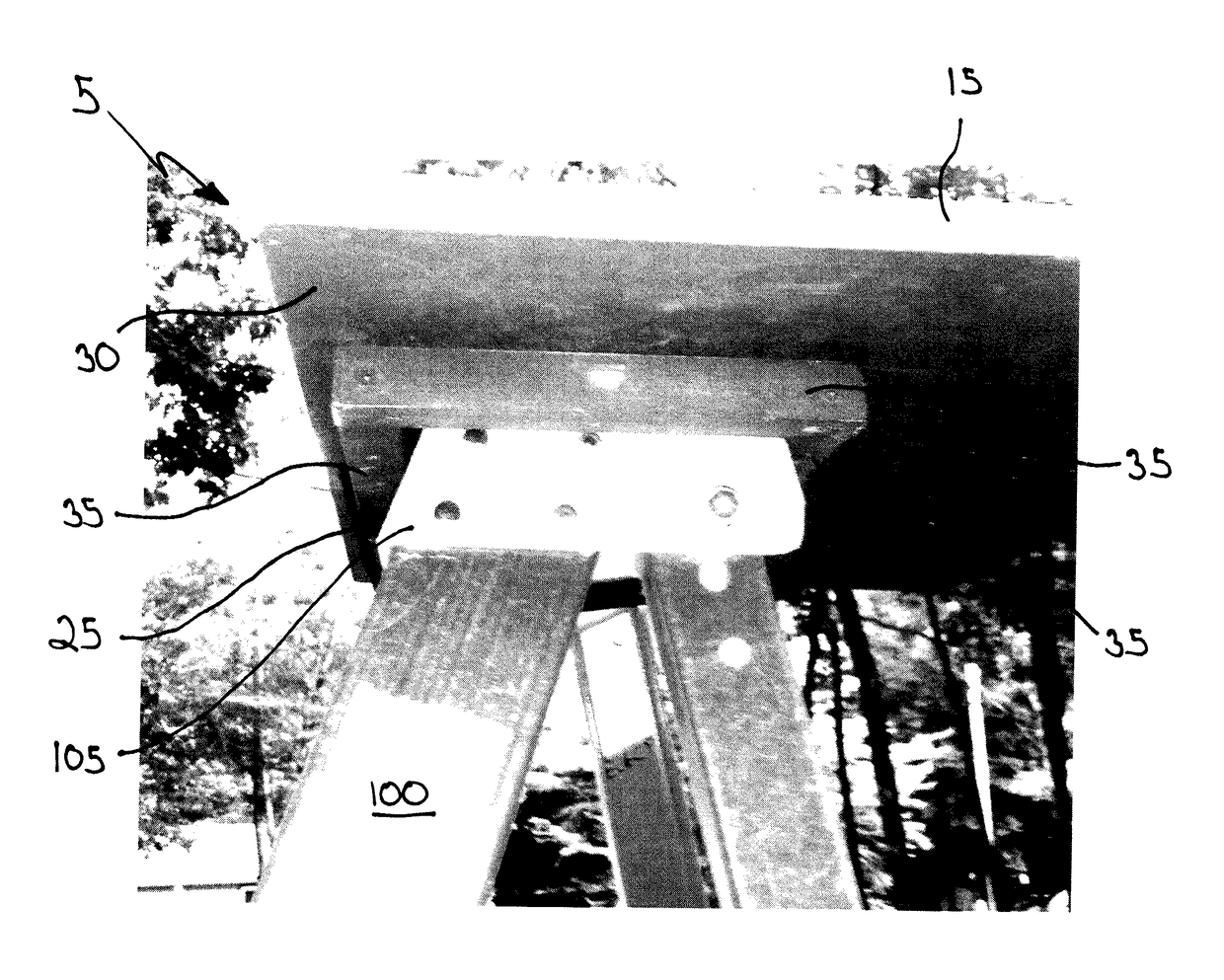
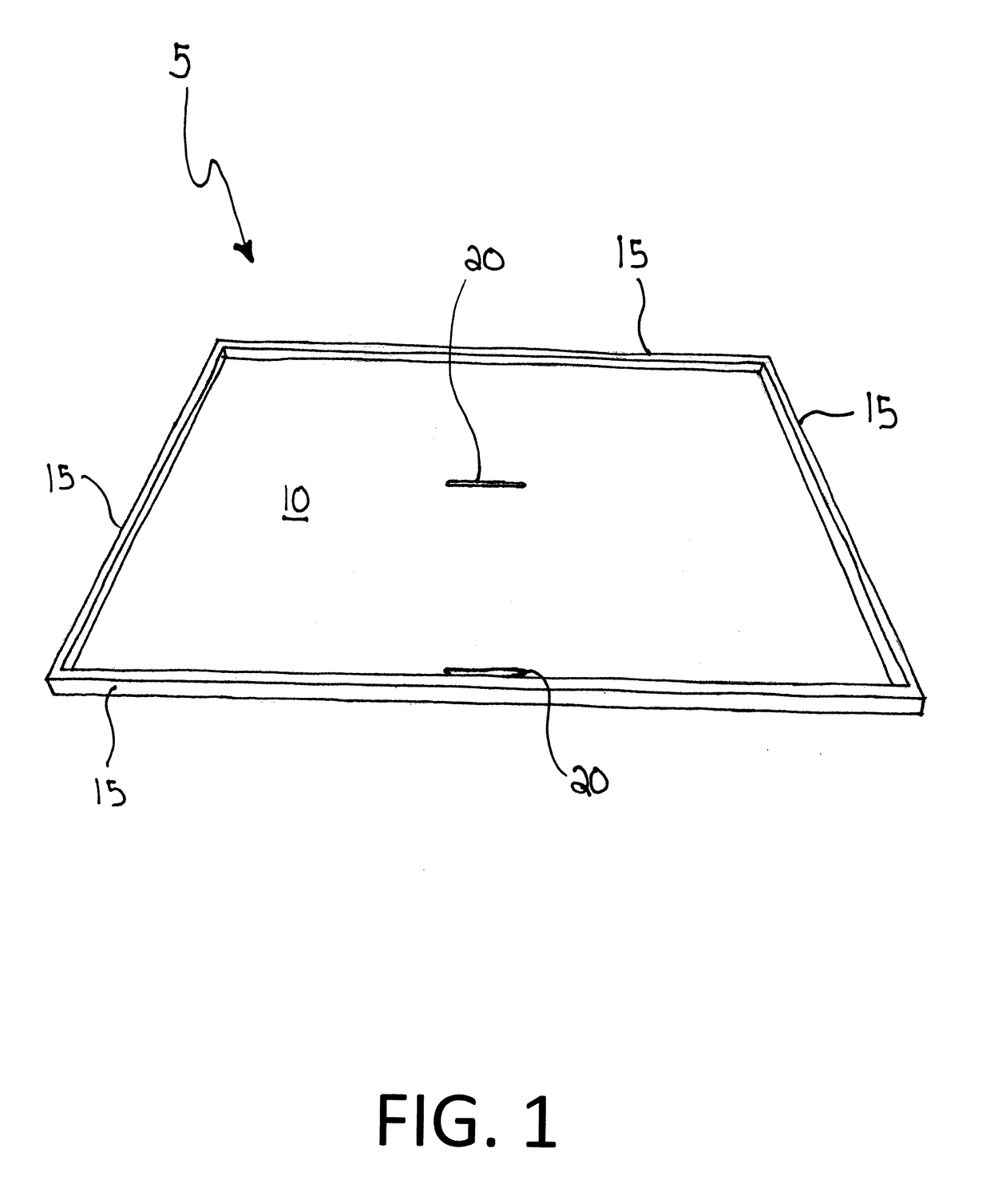
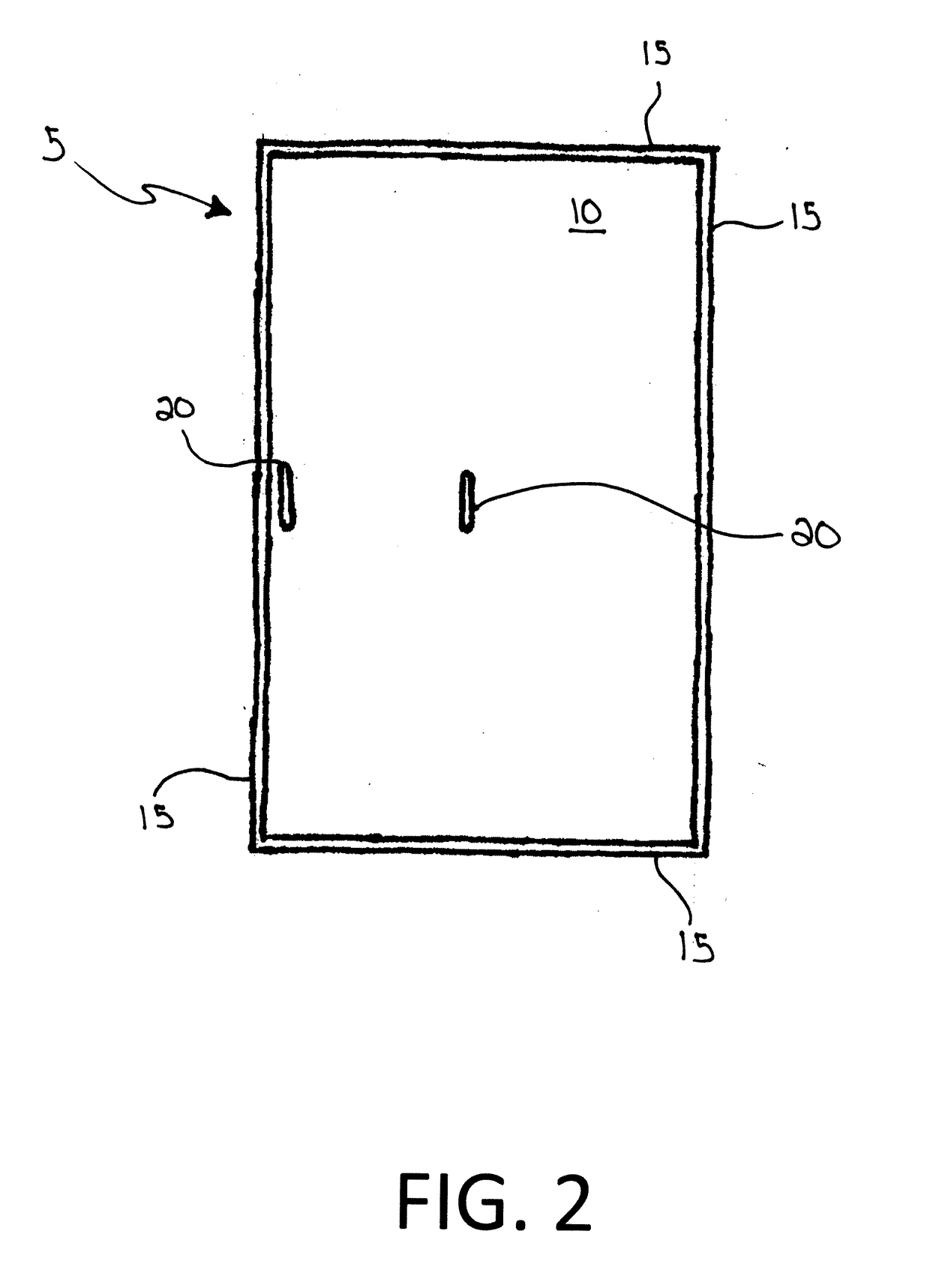
Attachable Platform
An attachable platform providing a work surface affixed to the top cap of the ladder. The device includes a work surface and rails along the exterior edges of the work surface and slots therein. The slots receive an attachment device such as a hook and loop strap to attach the platform to the ladder. Protrusions are found on the back surface of the platform and are designed to accommodate the top cap of a ladder.
Owner:WORKSTATION INTEGRATED LLC
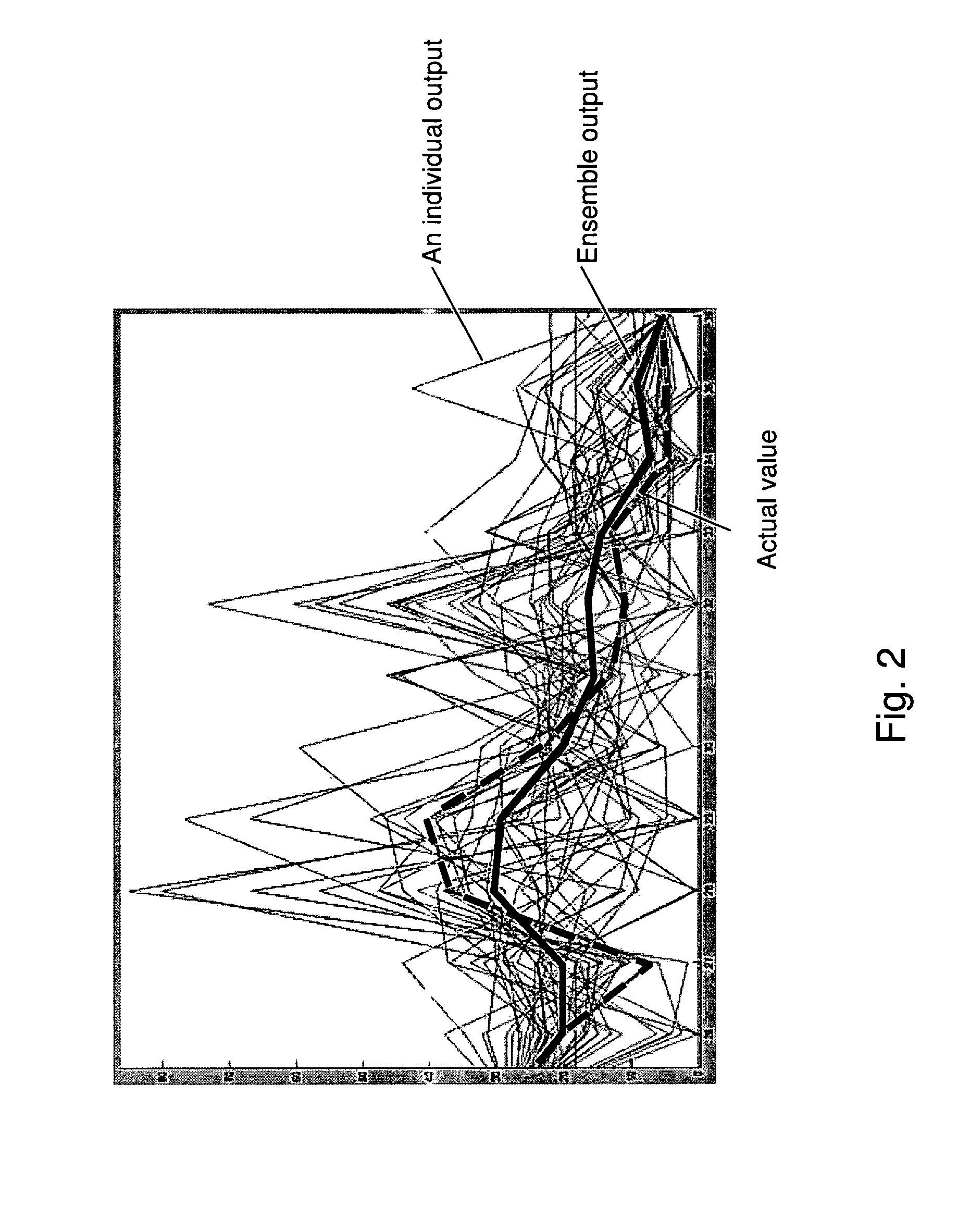
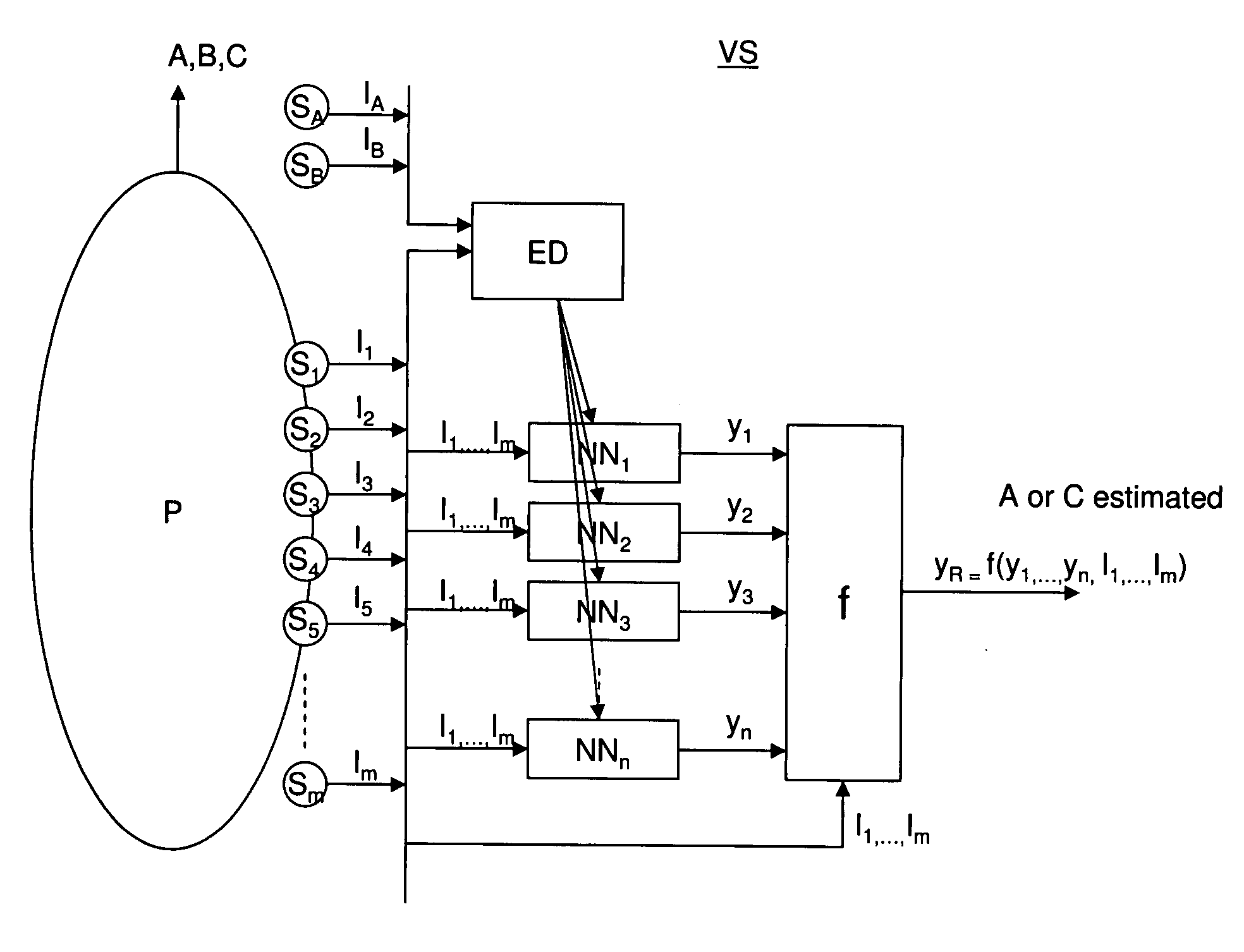
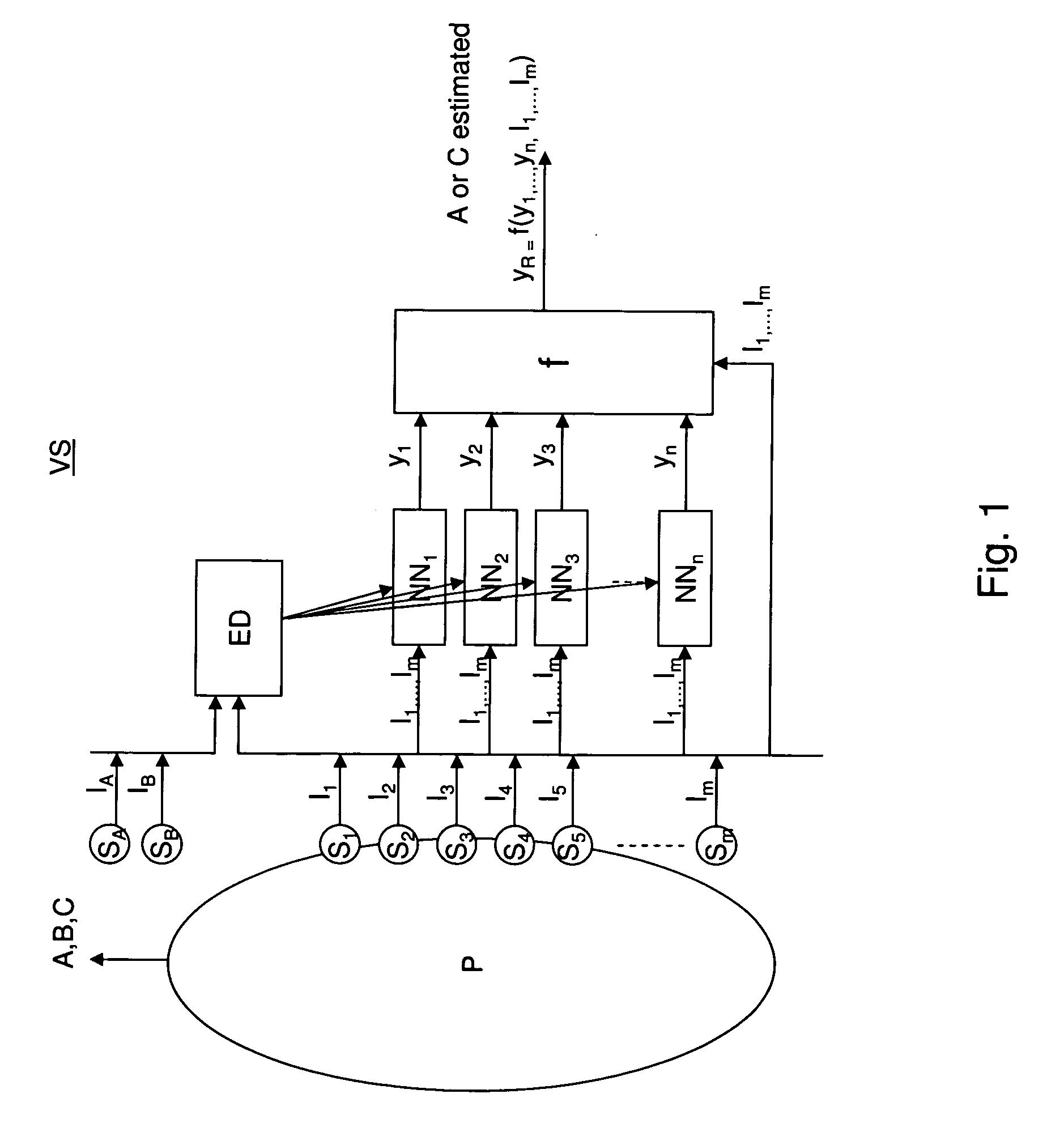
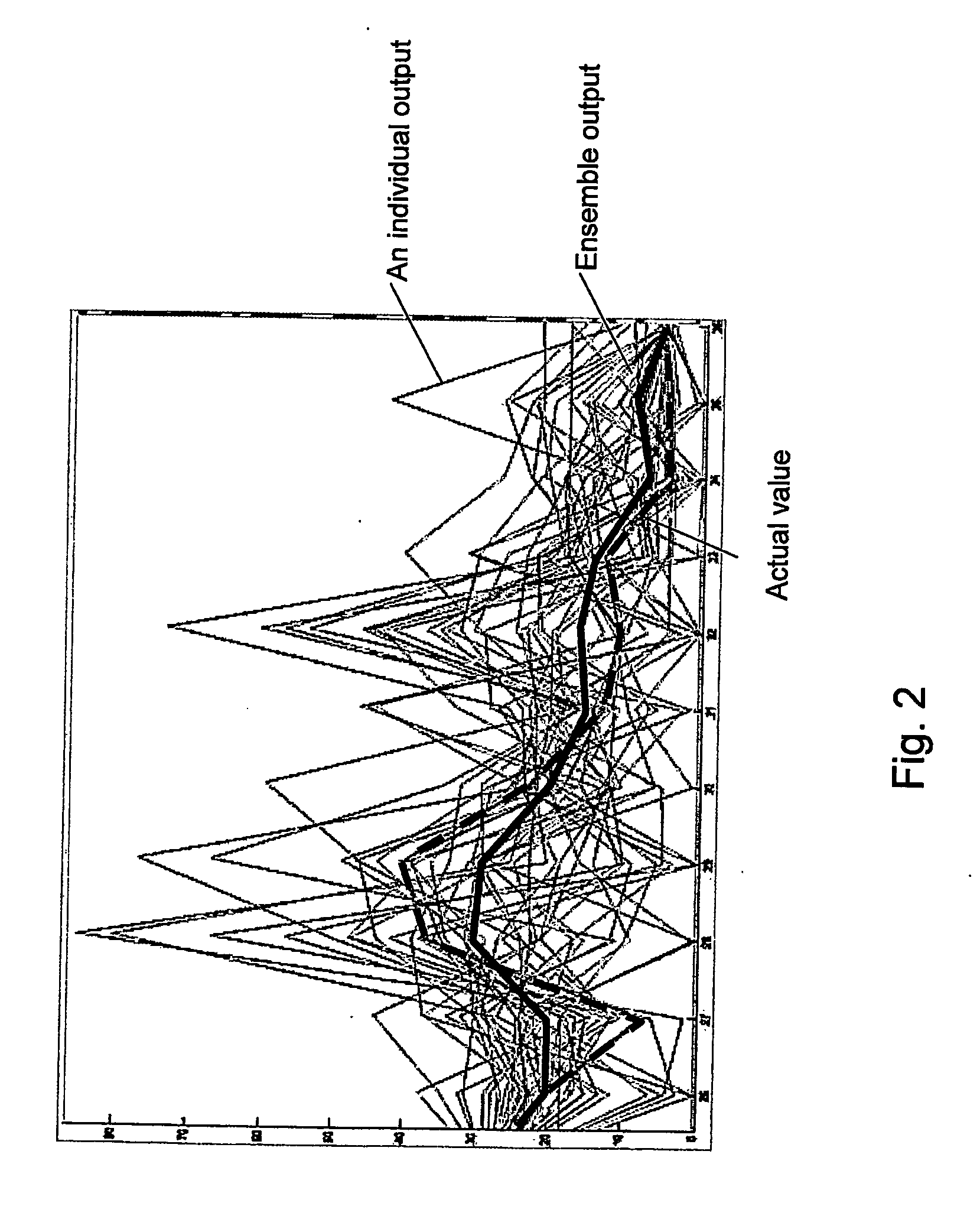
System and method for empirical ensemble- based virtual sensing
InactiveUS20110010318A1Easy to implementAvoid normal workInternal combustion piston enginesDigital computer detailsEngineeringVirtual sensors
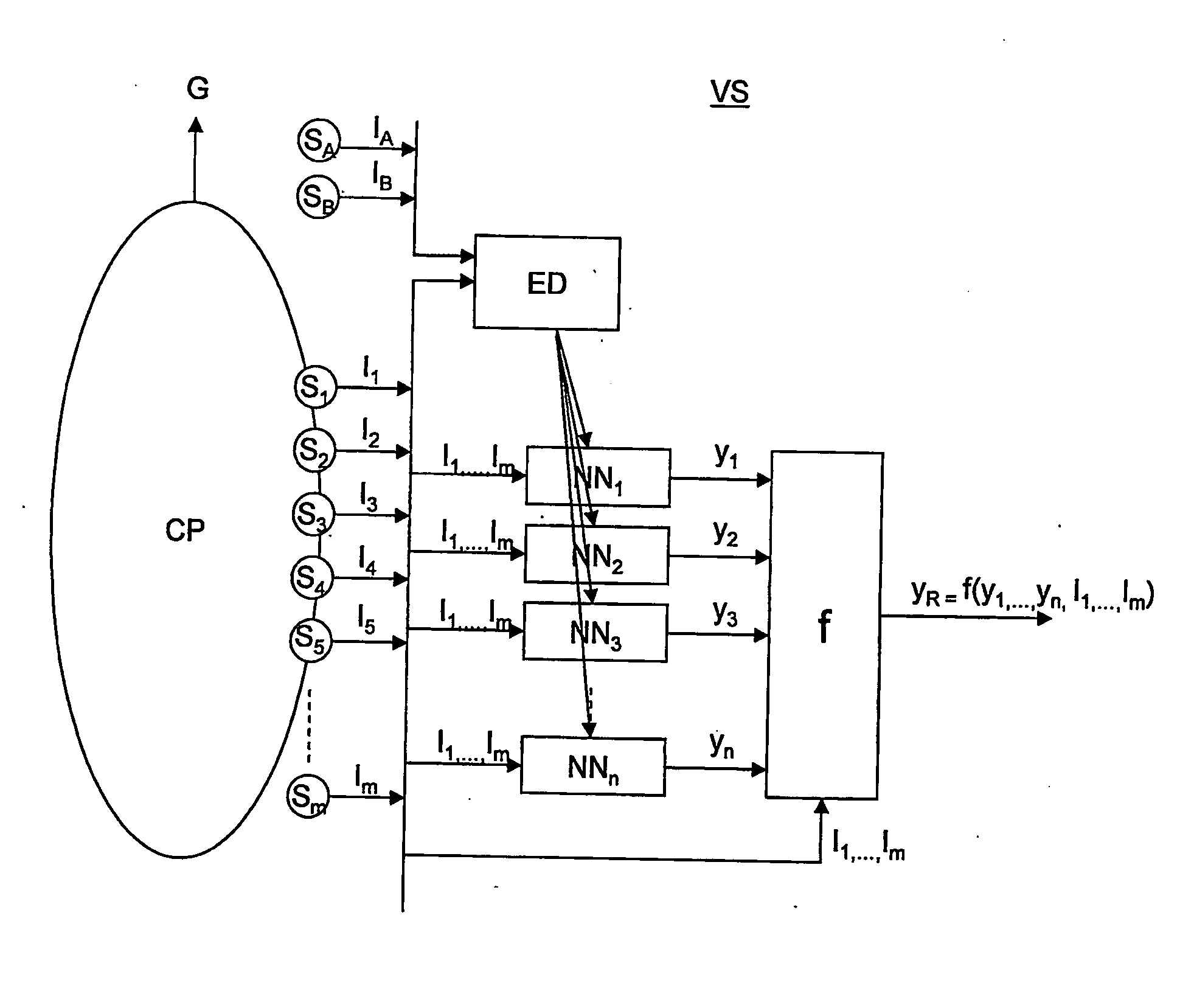
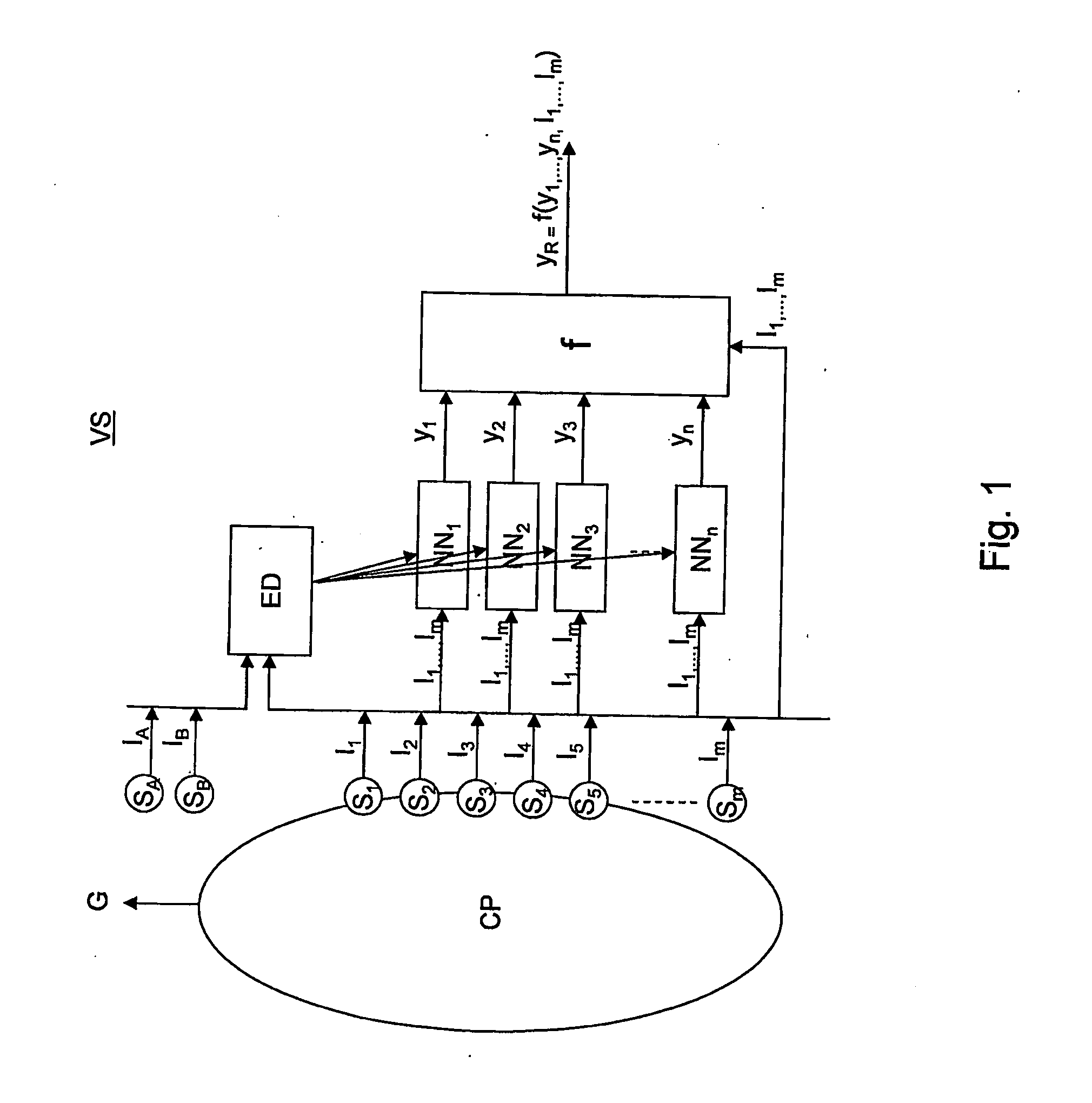
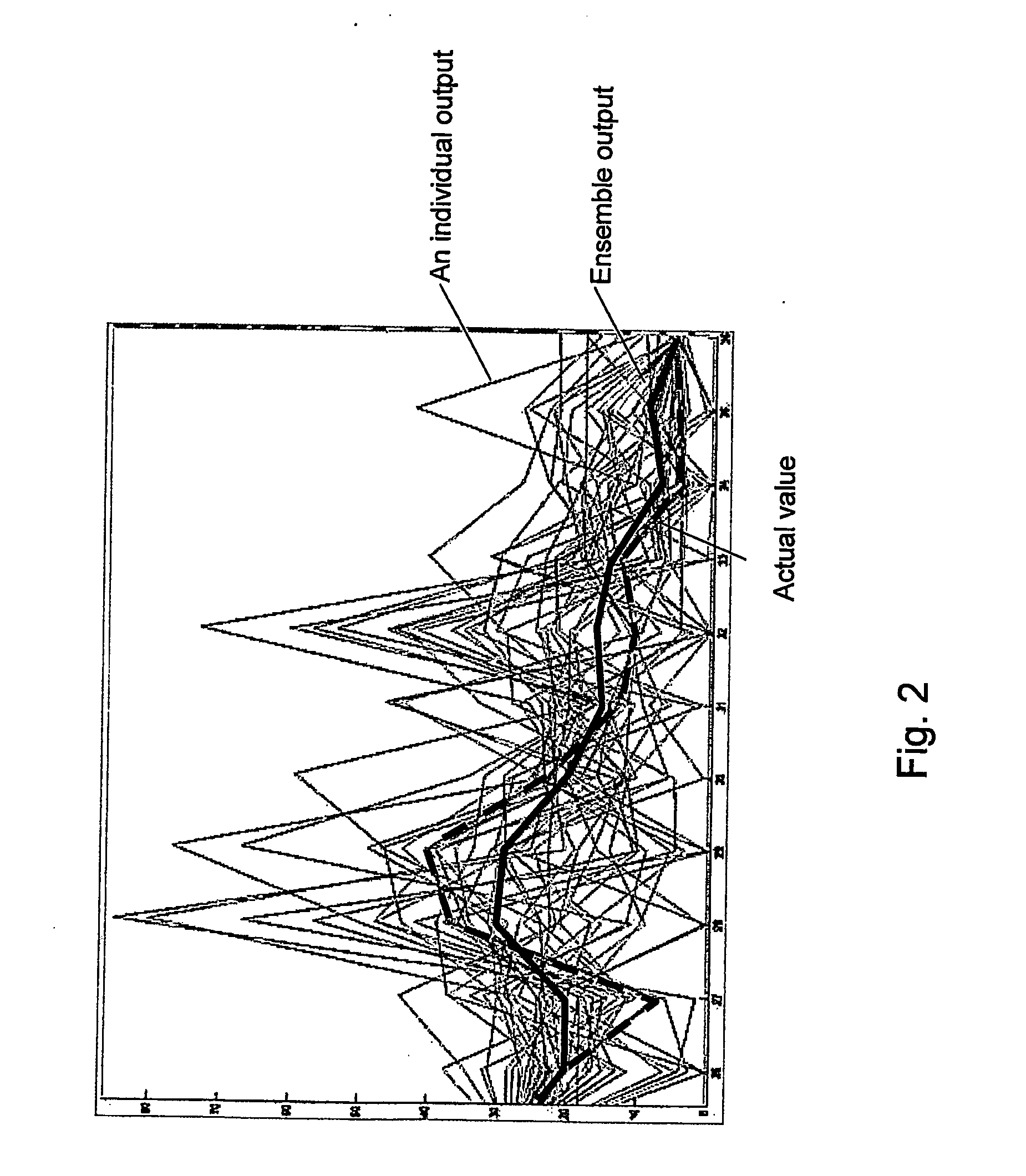
An empirical ensemble based virtual sensor system (VS) for the estimation of an amount of water (C) or oil (A) in a fluid mixture, said virtual sensor comprising two or more empirical models (NN1, NN2, . . . , NNn). The amount is estimated in each of the empirical models (NN1, NN2, . . . , NNn), and a combination function combines (f) the results from the empirical models (NN1, NN2, . . . , NNn) to provide a combined estimate for the amount (yR) that is more accurate than the estimated amount (y1, y2, . . . , yn) from each of the individual empirical models (NN1, NN2, . . . , NNn). The total performance of the virtual sensor system may be increased by increasing the number of empirical models (NN1, NN2, . . . , NNn).
Owner:INSTITUTT FOR ENERGITEKNIKK
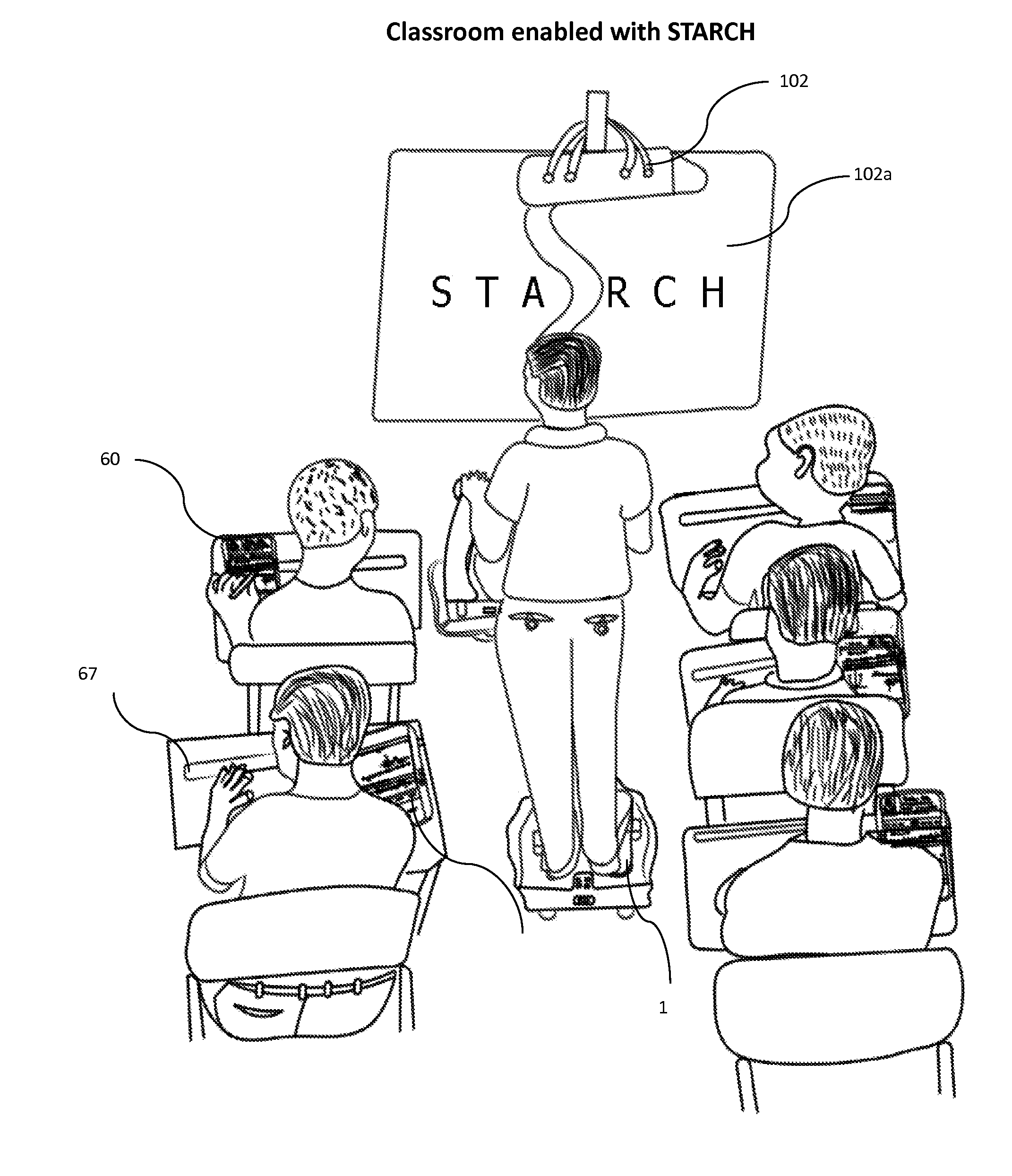
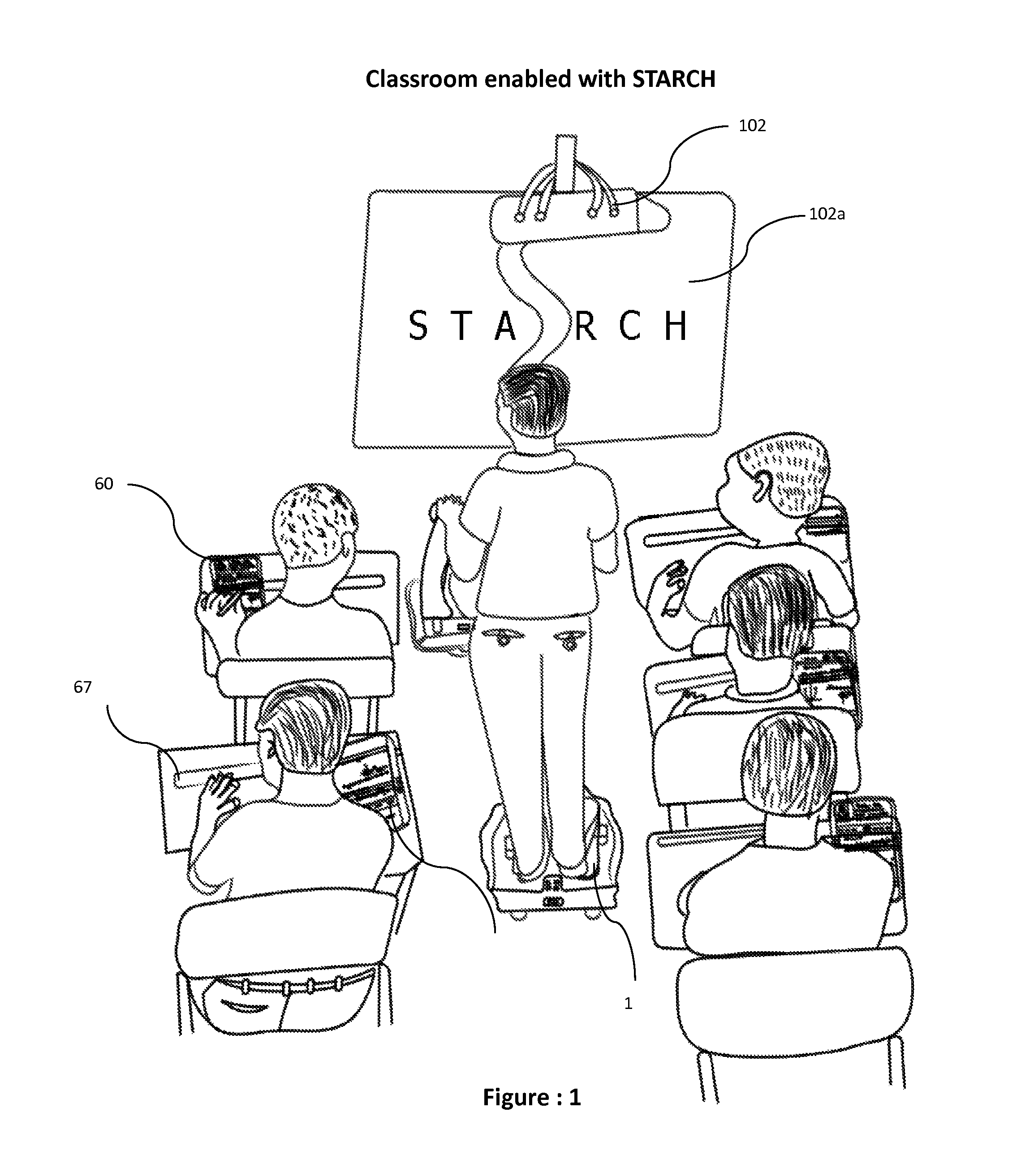
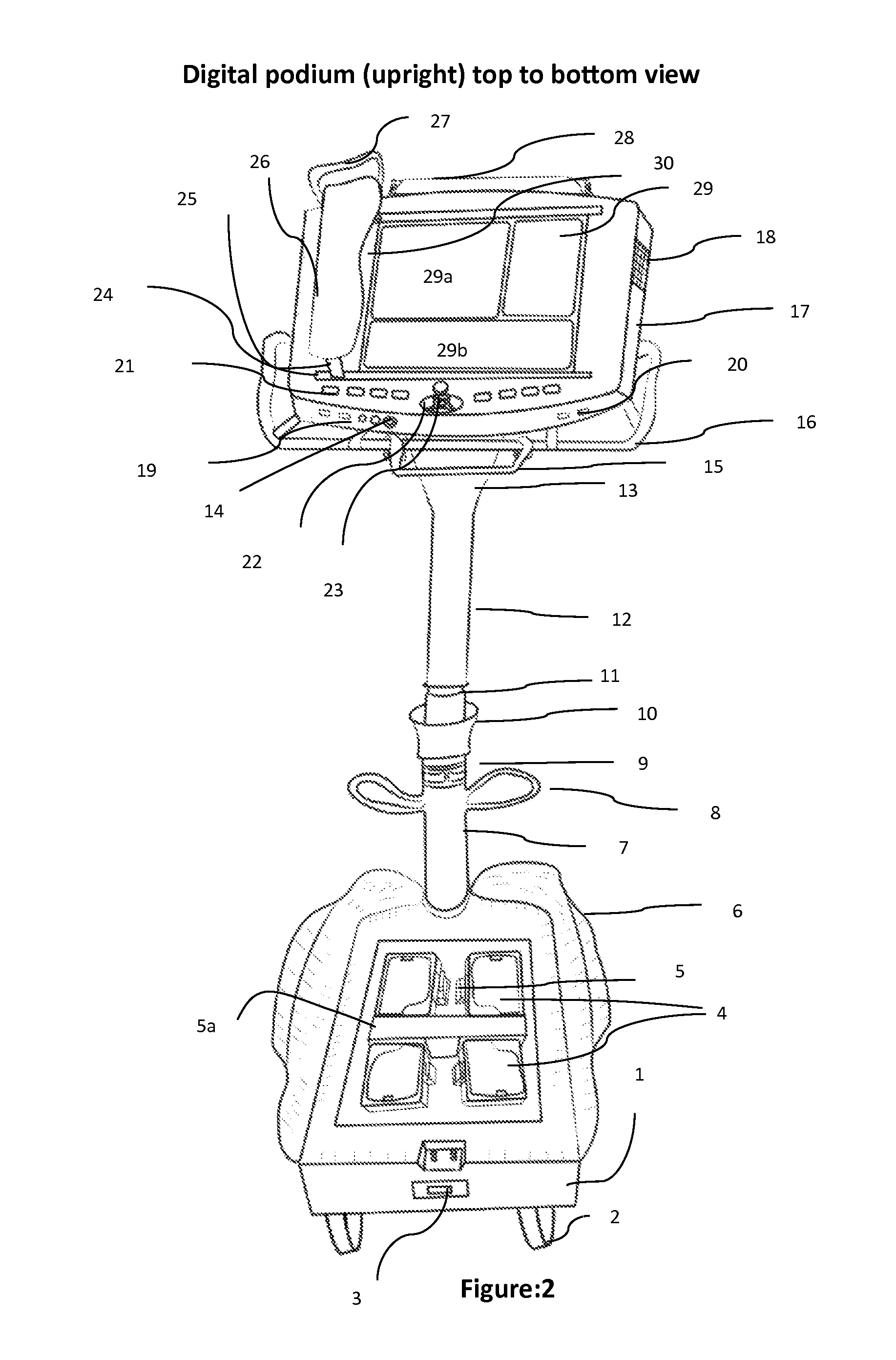
Student, teacher, administrative and research coordinating helper
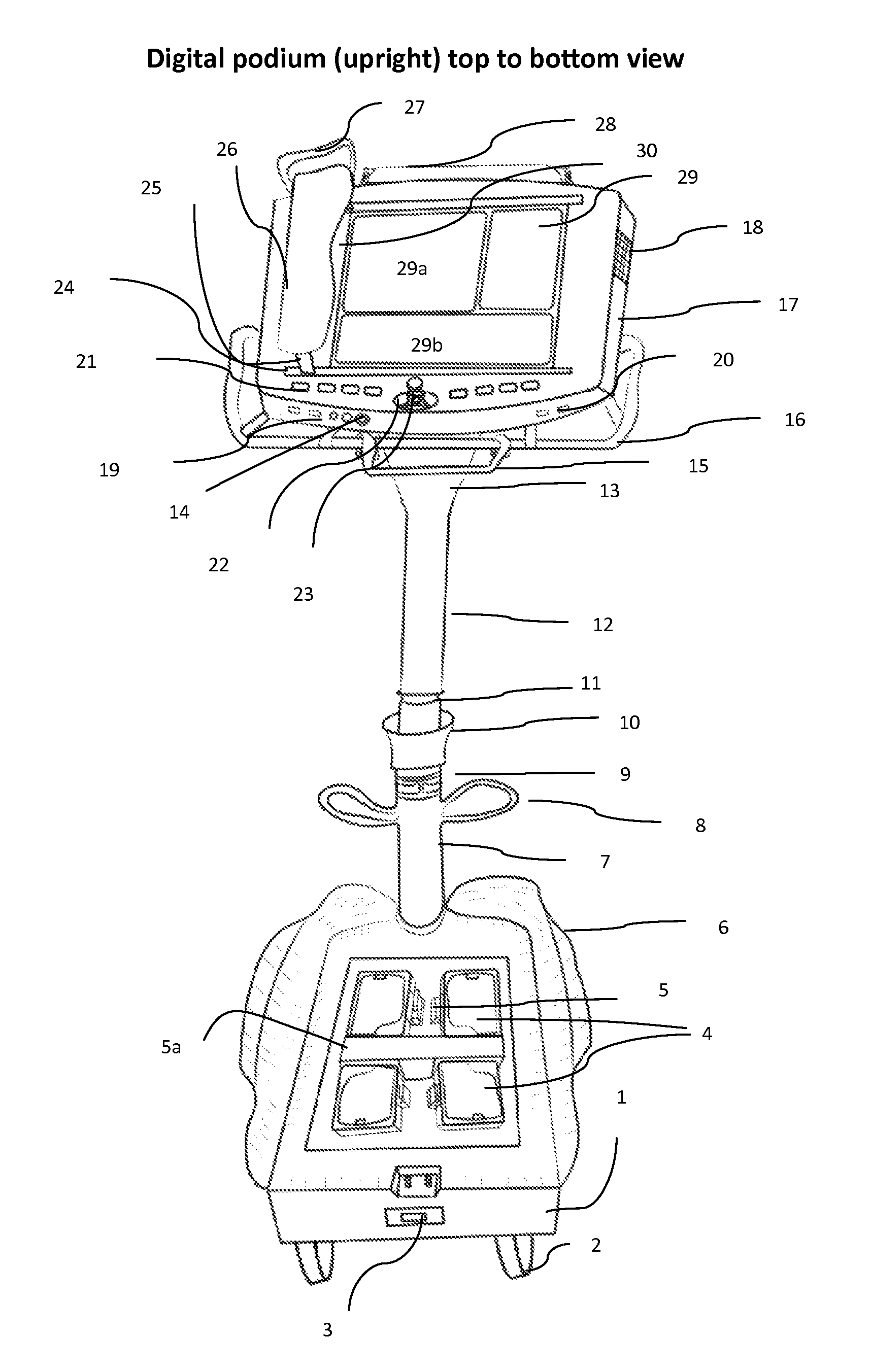
ActiveUS20170061808A1Reduce useReduce consumptionDigital processing power distributionElectrical appliancesLaser projectorEngineering
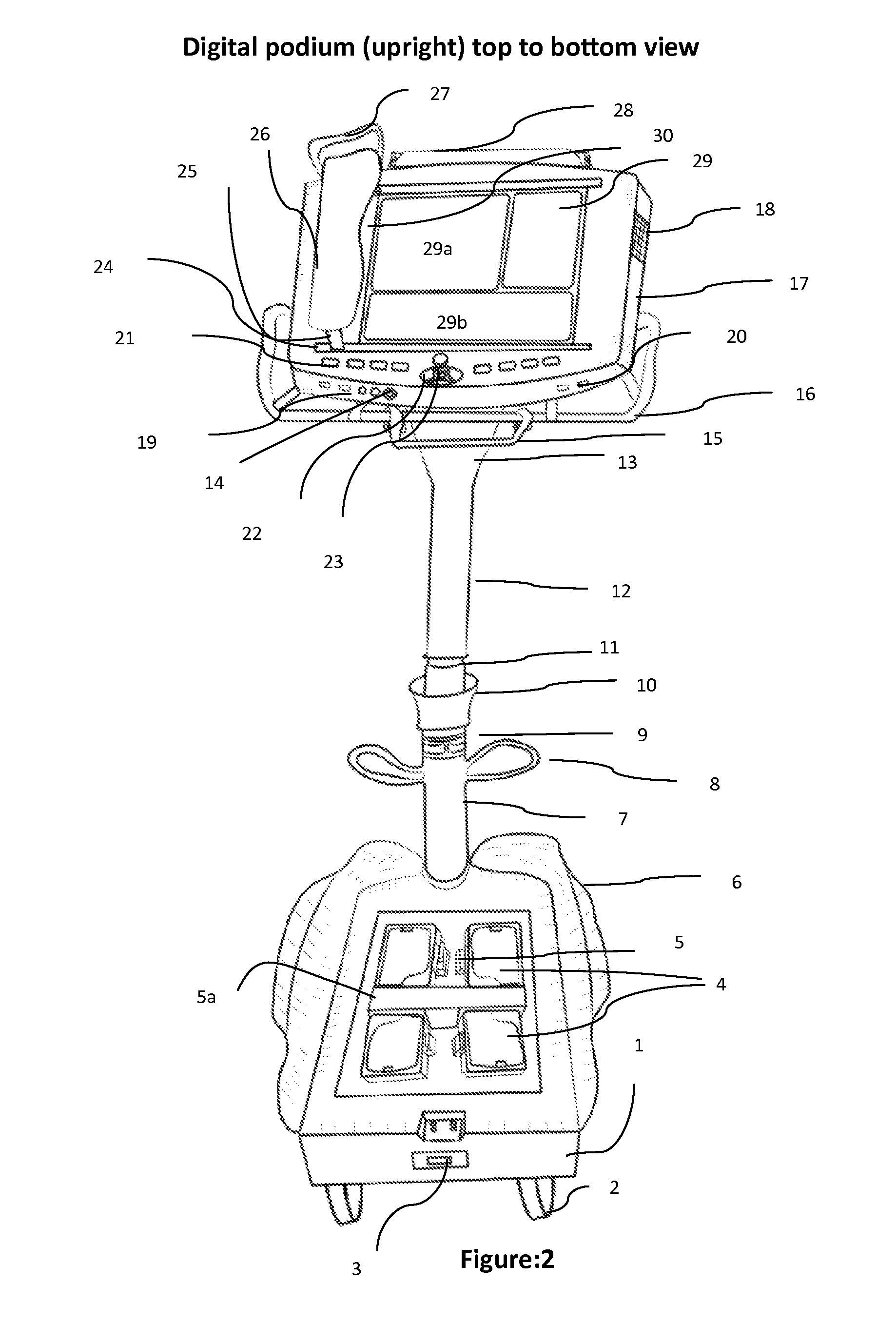
A digital podium apparatus includes: a frame; an extended handle disposed on the digital podium frame with which change of direction of movement is actuated, wherein a user can change direction by rotating the handle; a plurality of computer tablets disposed on the digital podium frame in a multi-tablet podium top; a five-wheel base configured to move the digital podium; a framework having four pedals, wherein the two front pedals are configured to move the podium forward and the two back pedals are configured to move the podium backward; and a divider to prevent the pressure of the standing person, so that to move forward a user uses toes simultaneously by standing on the divider; and wherein the digital podium is configured to project and relay teaching material through a multi-tablet podium into classroom projectors or mini laser projector, and into a dual tablet notebook of each child in classroom.
Owner:CHOPPLA GULSHAN PREM
High-availability communication system
ActiveUS7944818B2Quick switchExtra workProgramme controlError preventionState variationCommunications system
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Autonomous working system, an autonomous vehicle and a turning method thereof
Disclosed in the present invention is an autonomous vehicle (1), which comprises an housing (21), an driving module mounted on the housing (21), an borderline detecting module mounted on the housing for detecting the distance between the autonomous vehicle (1) and the borderline (3), an energy module mounted on the housing for providing energy for the autonomous vehicle, and an control module electrically connected with the driving module and the borderline detecting module. The control module controls the driving module to perform steering based on the signal representing the angle relationship between the autonomous vehicle (1) and the borderline (3) transmitted from the borderline detecting module, so that the axis (33) of the autonomous vehicle (1) always forms an acute angle or an right angle with one side of the borderline (3) while steering is completed, but another side of the borderline (3) forms an acute angle or an right angle with the core axis (33) of the autonomous vehicle (1) when the turning begins. The turning has directivity, so that the autonomous vehicle more easily goes out from the narrow area and the efficiency of area covering is higher; moving is kept during the turning, so that the energy is saved, and the working efficiency is improved.
Owner:POSITEC POWER TOOLS (SUZHOU) CO LTD
Seal assembly, and rolling bearing and hub unit assembled therewith
InactiveUS20070152404A1Improve sealingLow costEngine sealsRolling contact bearingsRolling-element bearingMechanical engineering
A seal member with its base end connected to a metal core has three seal lips. The thickness of the tip end of the intermediate seal lip in the intermediate position is d1, and the thickness of the base end is d2. The thickness of the tip end of the innermost inner seal lip is D1 and that thickness of the base end is D2. In this case, at least part of the base end of the intermediate seal lip and inner seal lip has its thickness regulated to be 0.2·d1≦d2≦0.8·d1, and 0.5·D1≦D2<D1. The tip edge of the inner seal lip is fitted onto the outer peripheral surface of the radially inside cylindrical portion of a slinger with substantially zero interference. Consequently, even if the slinger and metal core are displaced relative to each other, excellent seal performance is secured while increase of torque is inhibited.
Owner:NSK LTD
Seal assembly, and rolling bearing and hub unit assembled therewith
InactiveUS20070152403A1Improve sealingLow costEngine sealsRolling contact bearingsRolling-element bearingMechanical engineering
A seal member with its base end connected to a metal core has three seal lips. The thickness of the tip end of the intermediate seal lip in the intermediate position is d1, and the thickness of the base end is d2. The thickness of the tip end of the innermost inner seal lip is D1 and that thickness of the base end is D2. In this case, at least part of the base end of the intermediate seal lip and inner seal lip has its thickness regulated to be 0.2 .d1<=D2<=0.8 .D1, and 0.5 .D1 <=D2<D1. The tip edge of the inner seal lip is fitted onto the outer peripheral surface of the radially inside cylindrical portion of a slinger with substantially zero interference. Consequently, even if the slinger and metal core are displaced relative to each other, excellent seal performance is secured while increase of torque is inhibited.
Owner:NSK LTD
Tapered roller bearing and method of designing the same
ActiveUS8858088B2Convenience to workImprove machine efficiencyRoller bearingsShaftsCircular coneEngineering
In a tapered roller bearing assembly, a crowning profile formed portion of the roller rolling surface is made up of a contact area crowned portion, which is held in contact with an inner ring raceway surface, and a non-contact area crowned portion which is held in non-contact with the inner ring raceway surface. The contact area crowned portion and the non-contact area crowned portion have their generatrices extending in an axial direction of a roller, which generatrices are represented by corresponding continuous lines represented by different functions and continued smoothly at a point of connection, and the curvature of the generatrix of the non-contact area crowned portion in the vicinity of the connection point is chosen to be smaller than the curvature of the generatrix of the contact area crowned portion.
Owner:NTN CORP
Digital information search method and its system
InactiveUS20060146024A1Simple stepsWork lessCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingInformation searchingByte
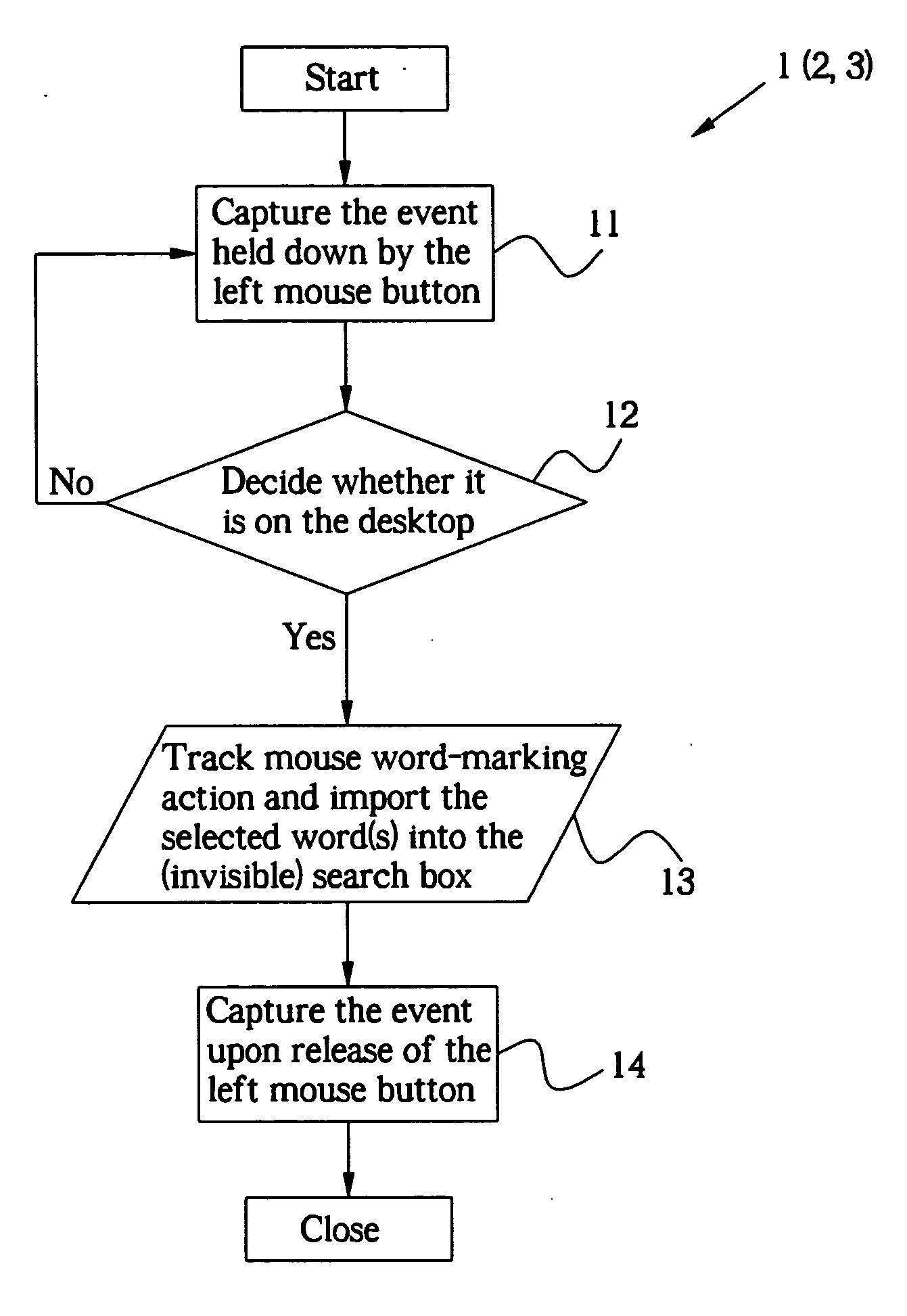
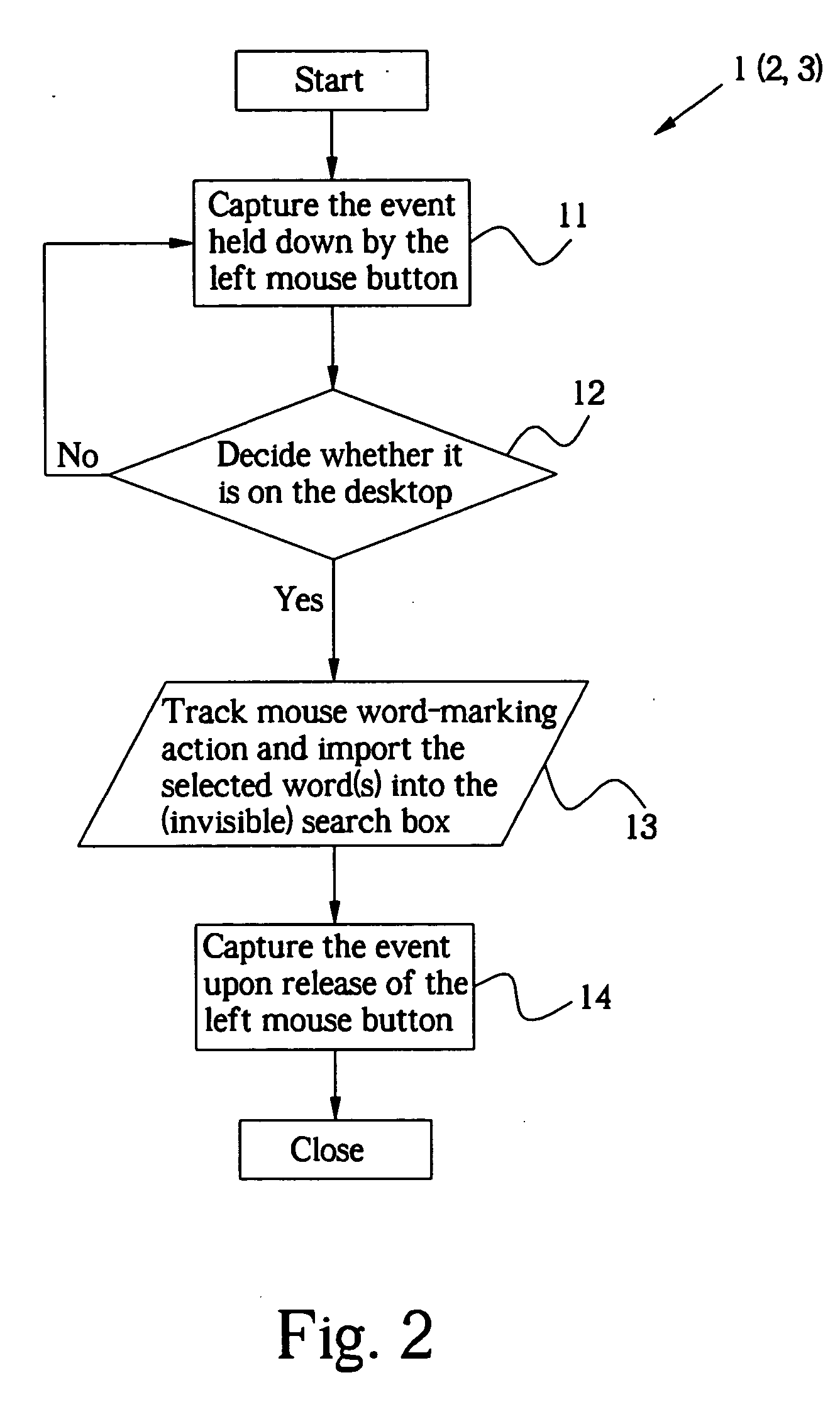
An invention relates to a mouse word-marking method, which is executed in the text fields of all the applications on the desktop, and a system to realize said method. Said method comprises the following steps: 1. The mouse marks and selects the key word(s) from the text fields of any application on the desktop; 2. Decide whether the selected word(s) is on the desktop. If YES, acquire the selected word(s); 3. Further decide whether the bytes of the selected key word(s) are smaller than the set value. If YES, a search button will pop up; 4. Click the button, and the server will execute the search and return the results to the user end; 5. The mouse waits for the next word-marking action on the desktop. The user can also right click the mouse to pop up a menu with search options. Select a search option and the server will execute the search. Alternatively, after acquisition of the selected word(s), drag the mouse at random, and the server will execute the search. Therefore, the user can acquire the searched information simply by using the mouse without opening a browser and inputting key words.
Owner:CHEN PEI
System and method for empirical ensemble-based virtual sensing of gas emission
InactiveUS20100325071A1Easy to implementExtra workInternal combustion piston enginesDigital computer detailsEngineeringGas emissions
An empirical ensemble based virtual sensor system (VS) for the estimation of an amount of a gas (G) resulting from a combustion process (CP) comprising two or more empirical models (NN1, NN2, . . . , NNn). The amount of gas (G) is estimated in each of the empirical models (NN1, NN2, . . . , NNn), and a combination function (f) combines the results from the empirical models (NN1, NN2, . . . , NNn) to provide a combined estimate for the amount of gas (G) that is more accurate than the estimated amount of gas from each of the individual empirical models (y1, y2, . . . , ym). The total performance of the virtual sensor system (VS) may be increased by increasing the number of empirical models (y1, y2, . . . , ym).
Owner:INSTITUTT FOR ENERGITEKNIKK
Seal assembly, and rolling bearing and hub unit assembled therewith
InactiveUS7731200B2Improve sealingLow costEngine sealsRolling contact bearingsRolling-element bearingMechanical engineering
A seal member with its base end connected to a metal core has three seal lips. The thickness of the tip end of the intermediate seal lip in the intermediate position is d1, and the thickness of the base end is d2. The thickness of the tip end of the innermost inner seal lip is D1 and that thickness of the base end is D2. In this case, at least part of the base end of the intermediate seal lip and inner seal lip has its thickness regulated to be 0.2·d1≦d2≦0.8·d1, and 0.5·D1≦D2<D1. The tip edge of the inner seal lip is fitted onto the outer peripheral surface of the radially inside cylindrical portion of a slinger with substantially zero interference. Consequently, even if the slinger and metal core are displaced relative to each other, excellent seal performance is secured while increase of torque is inhibited.
Owner:NSK LTD
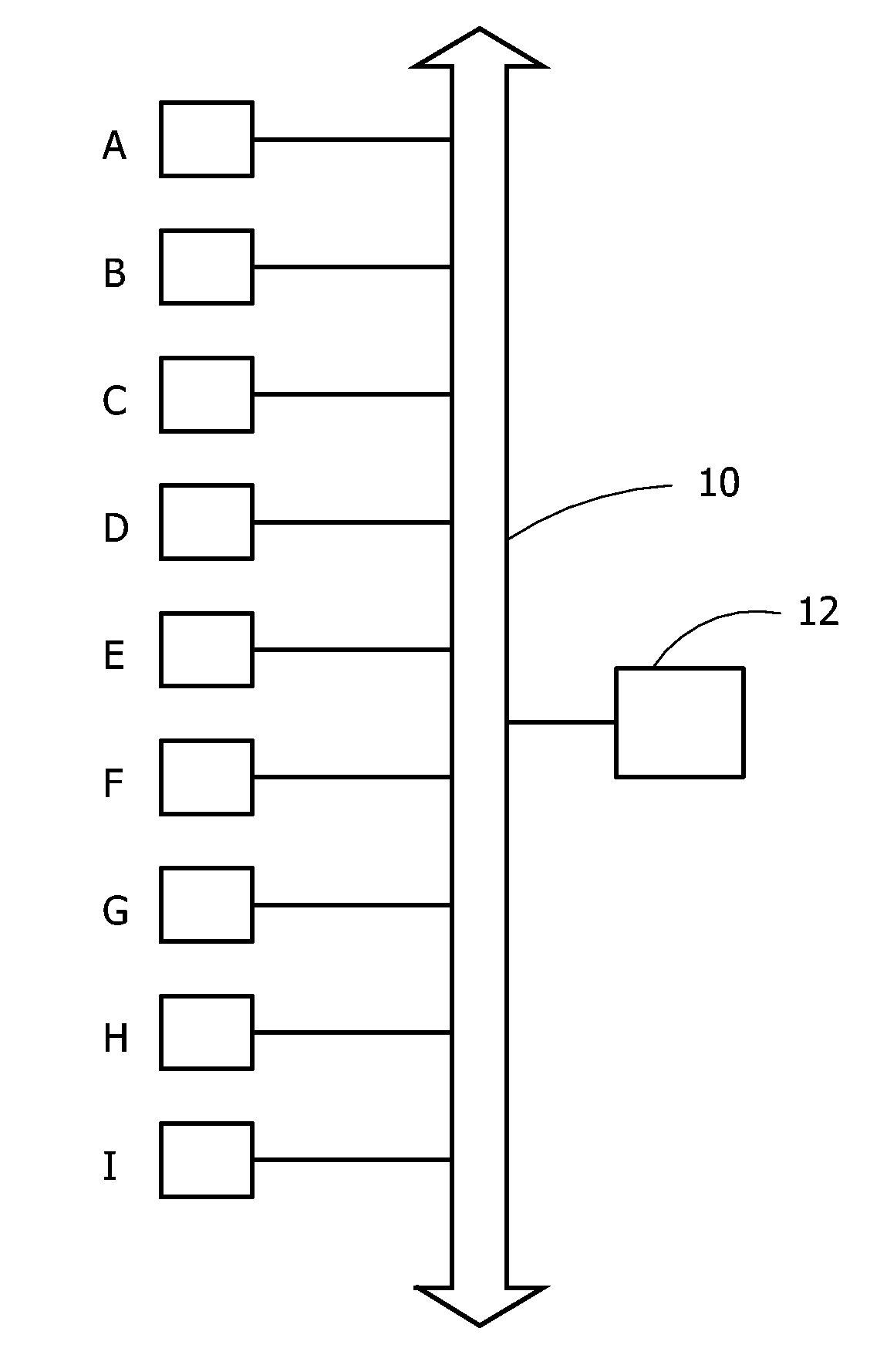
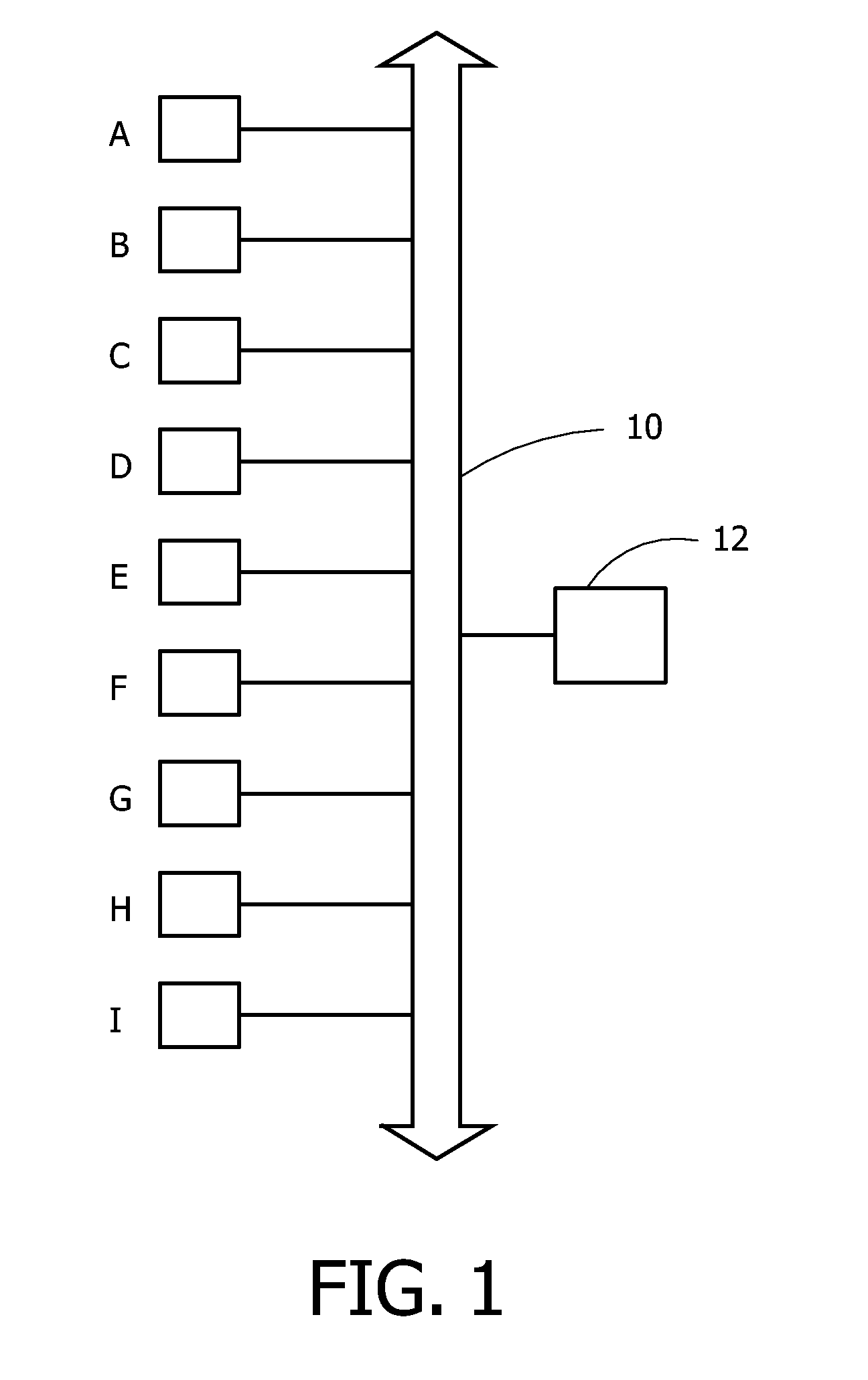
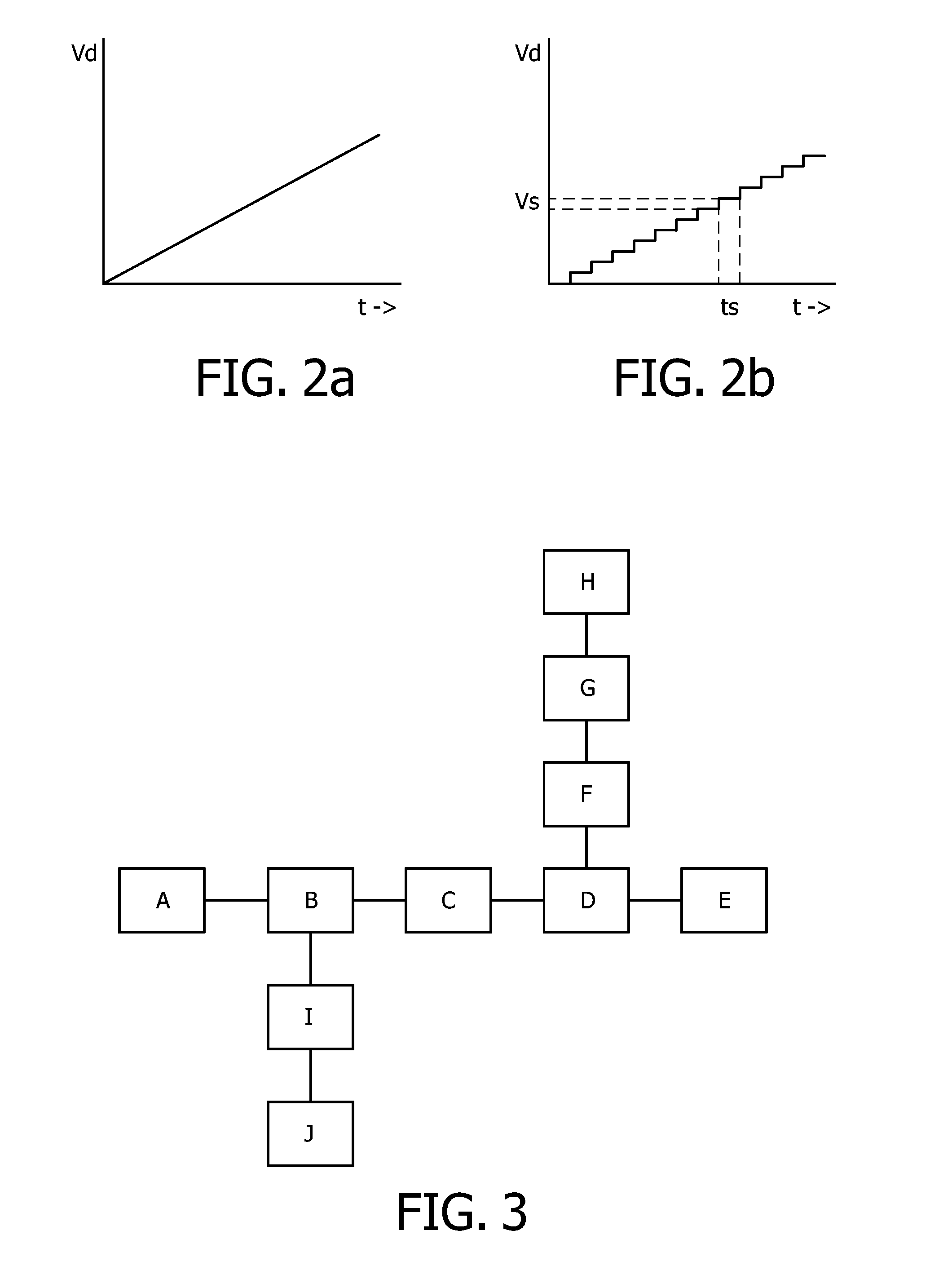
Method to Determine a Relative Position of Devices in a Network and Network of Devices for Carrying Out the Method
InactiveUS20080253303A1Less amount of workExtra workElectric light circuit arrangementData switching by path configurationPresent methodPower cable
The invention discloses a method to determine a relative position of devices in a network, and to a network of devices for carrying out the method. In a network with a power cable (10) connected to a plurality of devices (A-I), one needs to know the physical position thereof in order be able to control them efficiently. This used to be done manually, but the present method proposes to select a device to send a detection signal with increasing amplitude across the network, and to measure the time each of the remaining devices detects the detection signal. Due to signal losses in the network, a more remote device will show a longer detection time. Collecting the various detection times enable a control unit (12) to determine the relative position of all, or at least part of, the devices (A-I).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Hand tool for welding-torch maintenance
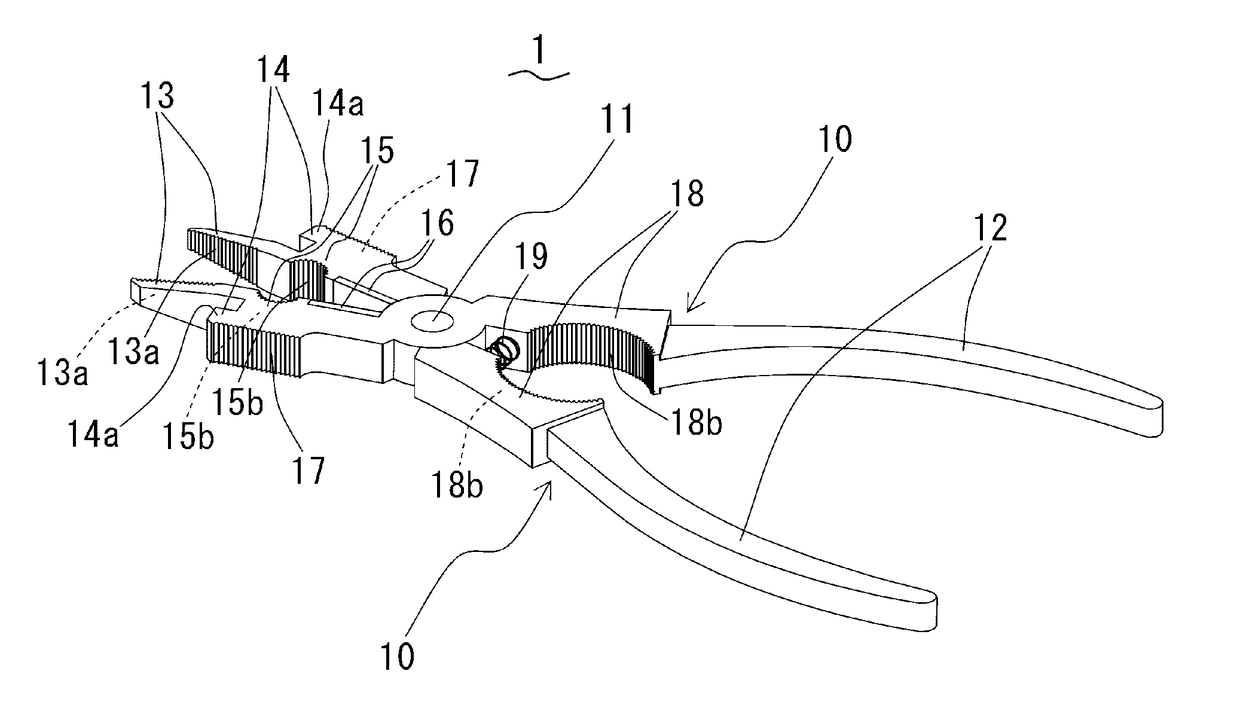
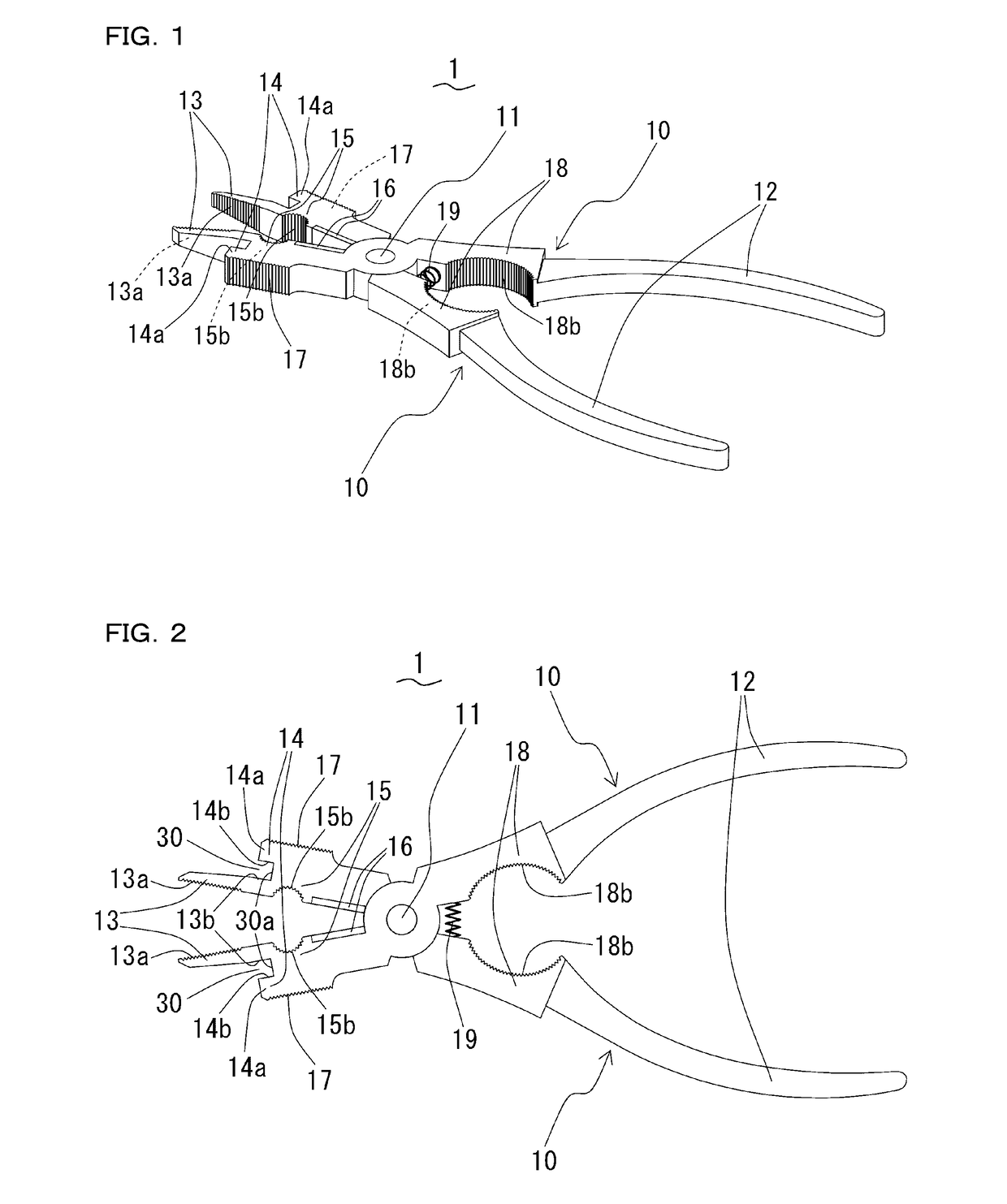
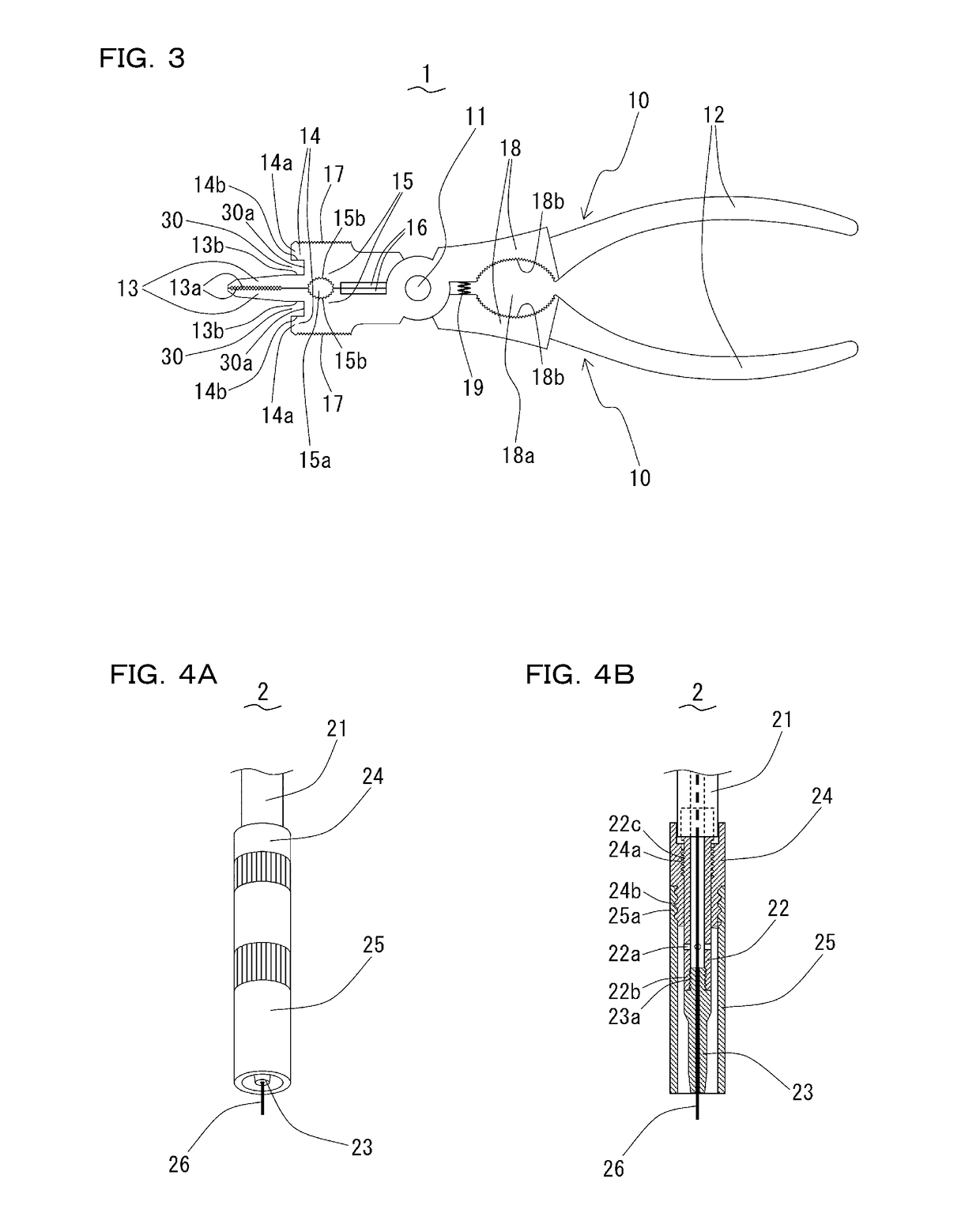
ActiveUS20170182583A1Sufficient working efficiencyExtra workPliersWeld torches cleaningEngineeringWelding torch
A hand tool for welding-torch maintenance, which can remove sputter adhering to a nozzle with sufficient working efficiency. The hand tool has a pair of metal stays turnably supported by a pivoting axis. The metal stays comprises grips handled by a user, 1st pinchings used for pulling a welding-wire, and 2nd pinchings used for removing sputter adhering to the nozzle. The 1st pinchings are configured so as to be inserted into the nozzle when the metal stays are closed. The 2nd pinchings have projections which are extended outside from the backs of the 1st pinchings and thrown out towards heads of the 1st pinchings. The sputter adhering to the inner-and-outer circumferential surfaces and end face of the nozzle are removed by inserting the 1st pinchings into the nozzle, inserting the end of the nozzle between the 2nd pinchings and the 1st pinchings, and moving the tool to scratch the sputter off the inner-and-outer circumferential surfaces and the end face of the nozzle.
Owner:SEVENTY EIGHT CO LTD
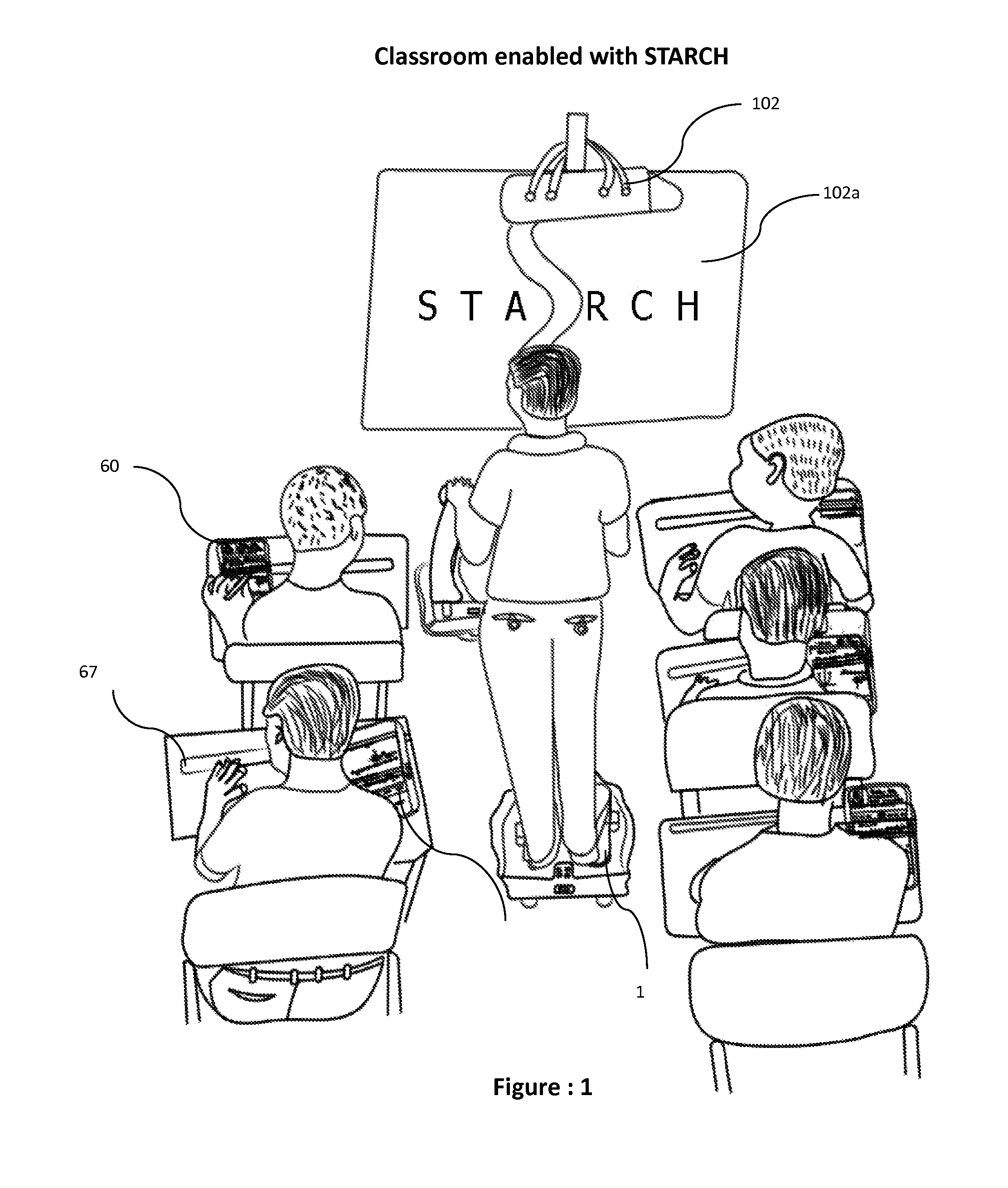
Student, teacher, administrative and research coordinating helper
A digital podium apparatus includes a base, front and rear pairs of wheels and a single wheel at a front of the base. A pair of front pedals can be moved by a user's toes to rotate the front wheels forward and a pair of rear pedals can moved by the user's ankles to rotate the rear wheels backward. A divider is disposed between the front and rear pedals. A height-adjustable pole is coupled to both the single wheel and a digital podium frame. A handle is disposed on the digital podium frame, and the user can change a direction of the base during movement of the digital podium apparatus by rotating the handle. A plurality of computer tablets are disposed on the digital podium frame. The digital podium apparatus may be ridden into a classroom and used to project and relay teaching material to students in the classroom.
Owner:CHOPPLA GULSHAN PREM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com