Microgrid reactive power balanced allocation method based on impedance composite control
An impedance compounding and balanced distribution technology, applied in the field of microgrid, can solve the problems of impedance measurement accuracy affecting reactive power distribution, harsh impedance matching conditions, and difficulty in meeting multiple VSIs at the same time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
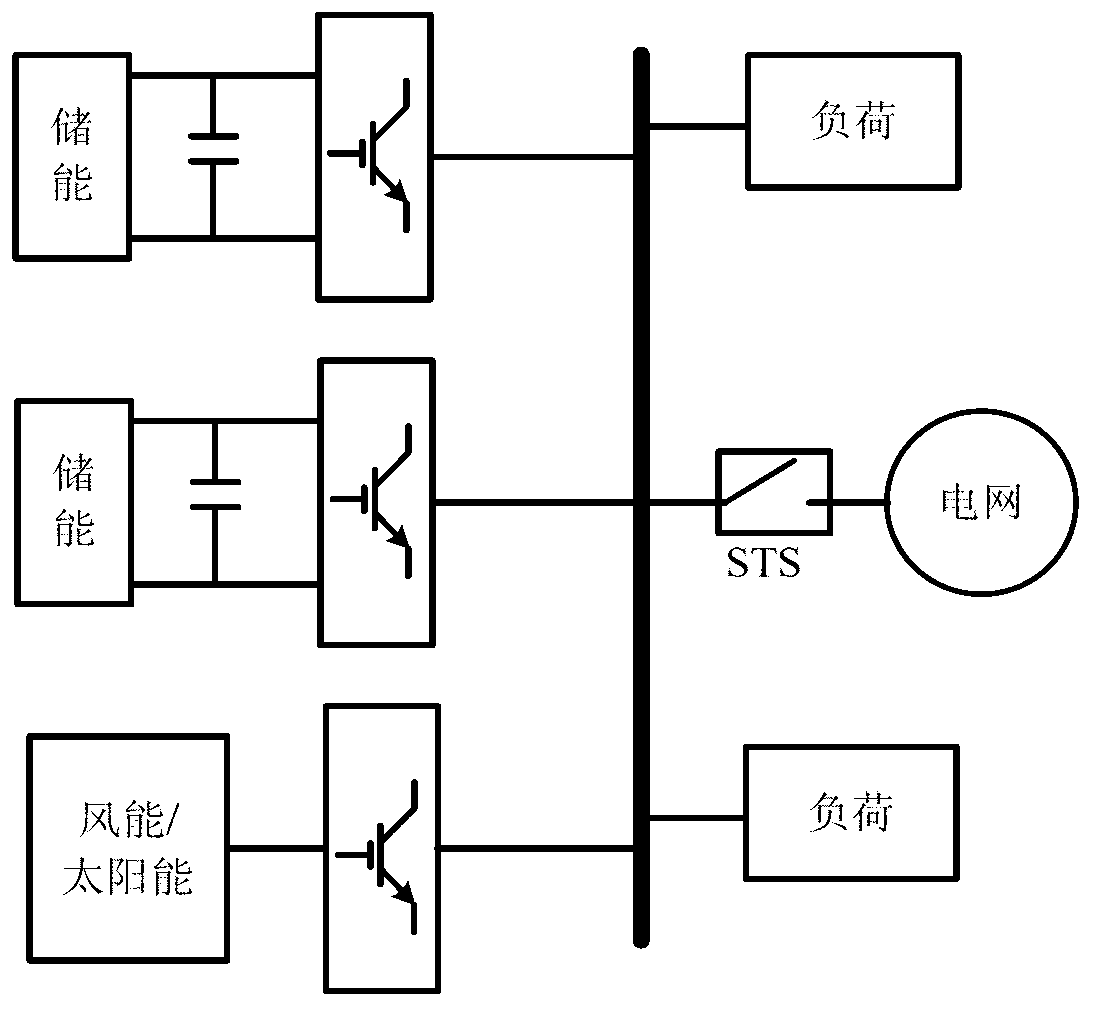
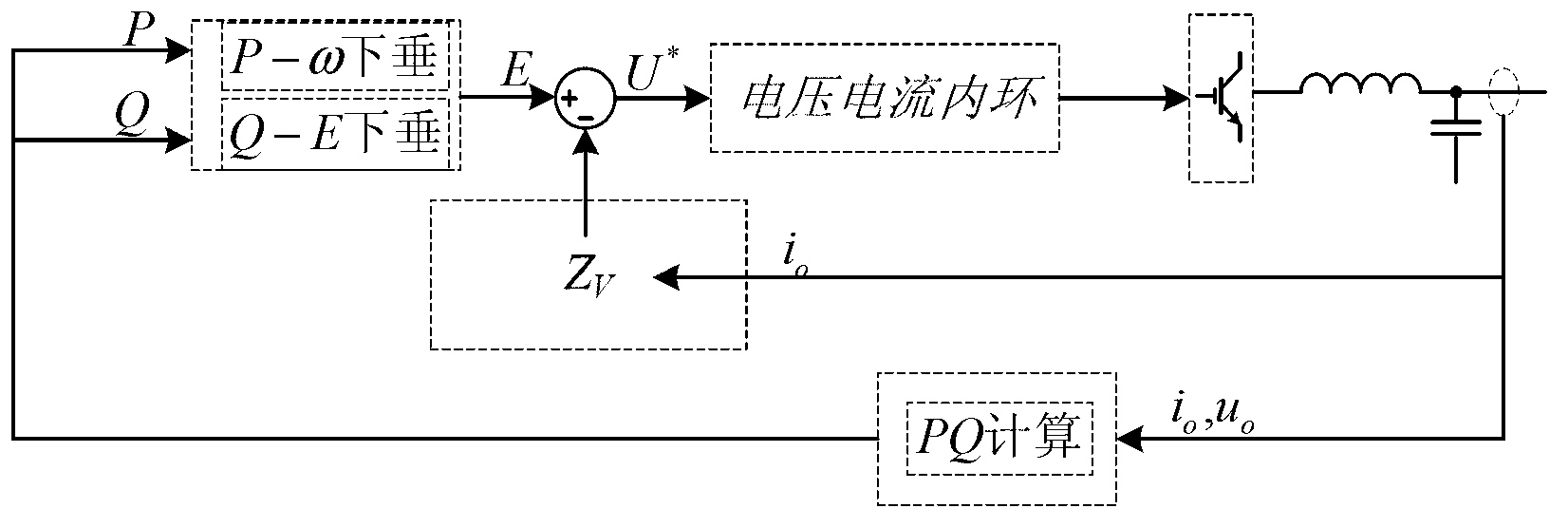
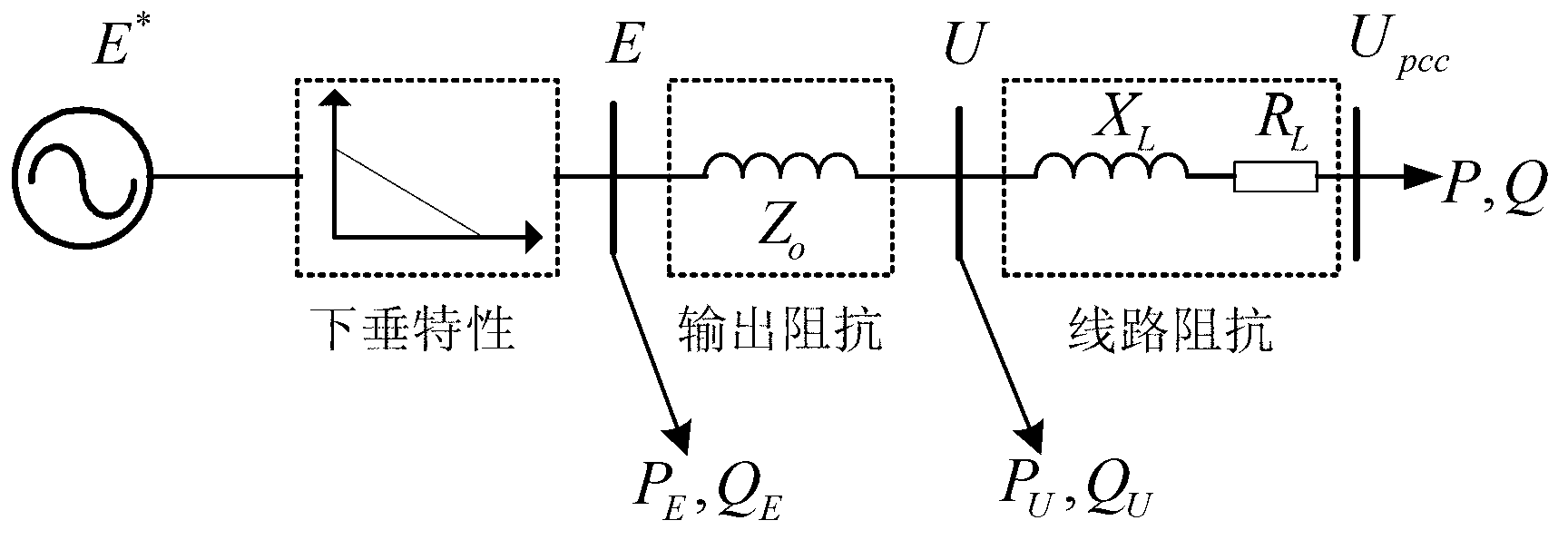
[0047] The technical scheme consists of two parts: a Q-U droop coefficient dynamic adjuster and a Q-U droop control based on virtual impedance compensation. Among them, the Q-U droop coefficient dynamic adjuster dynamically changes the Q-U droop coefficient in real time according to the output active power and reactive power of the VSI; the Q-U droop control based on virtual impedance compensation includes a virtual impedance device, a virtual impedance open-loop compensator and a virtual impedance closed-loop compensator. Part: the virtual impedance adjusts the output impedance of the VSI according to the output current; the virtual impedance open-loop compensator compensates the voltage drop generated by the virtual impedance according to the active and reactive power; the impedance closed-loop compensator uses the PI regulator to control the Q-U droop characteristics.
[0048] The technical scheme of the present invention is, a kind of microgrid reactive power equalization d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com