Improved droop control based microgrid auxiliary master-slave control method
A control method and micro-grid technology, applied in the direction of power network operating system integration, electrical components, circuit devices, etc., can solve problems such as the inability of inverters to achieve output power, frequency deviation, and power distribution limitations.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
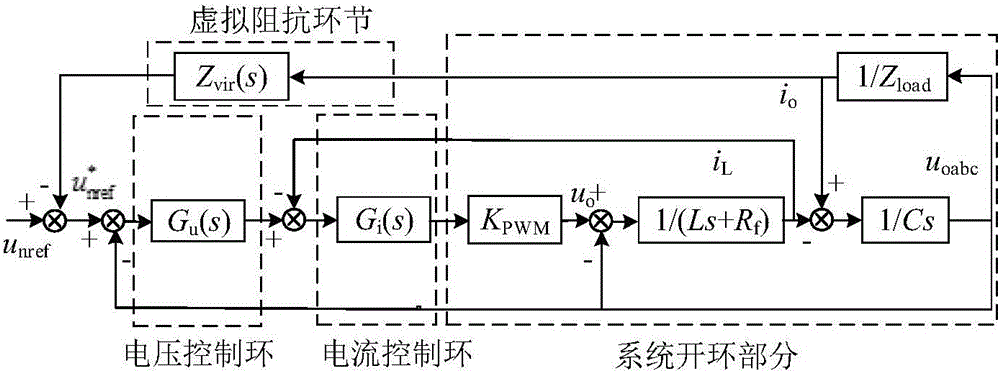
[0049] The new droop control adopted by the present invention: firstly, on the basis of the control principle of the voltage loop and current loop of the loop inverter, the power decoupling is effectively realized by adding a dynamic damping impedance link to serve the power control loop; secondly, the power control link is improved Mainly through the frequency difference f-fn and the voltage difference UU 0 As a feedback signal, in addition to adding a PI control link on the feedback line, it is also necessary to modify the droop coefficient of the feedback line to form a new droop control method. In addition, since there is no integral term in the reactive power expression, In the steady state, there is a static difference in the voltage and poor robustness, so an integral link needs to be added to the reactive power control circuit.
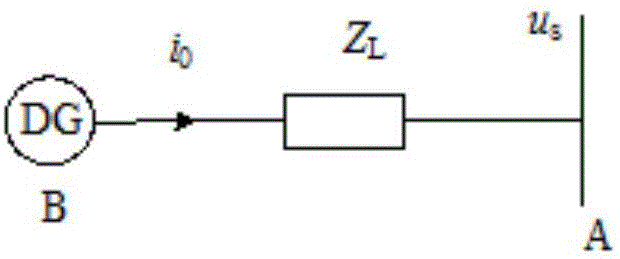
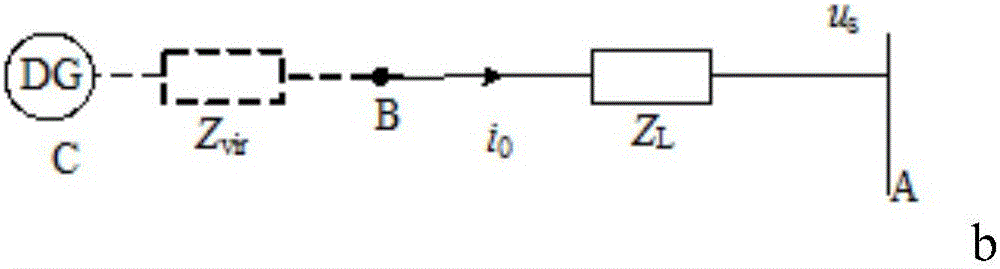
[0050] The above method is called a new type of droop control, which is applied as an auxiliary unit to a master-slave control microgrid system. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com