Patents
Literature
59results about How to "Increase the output resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
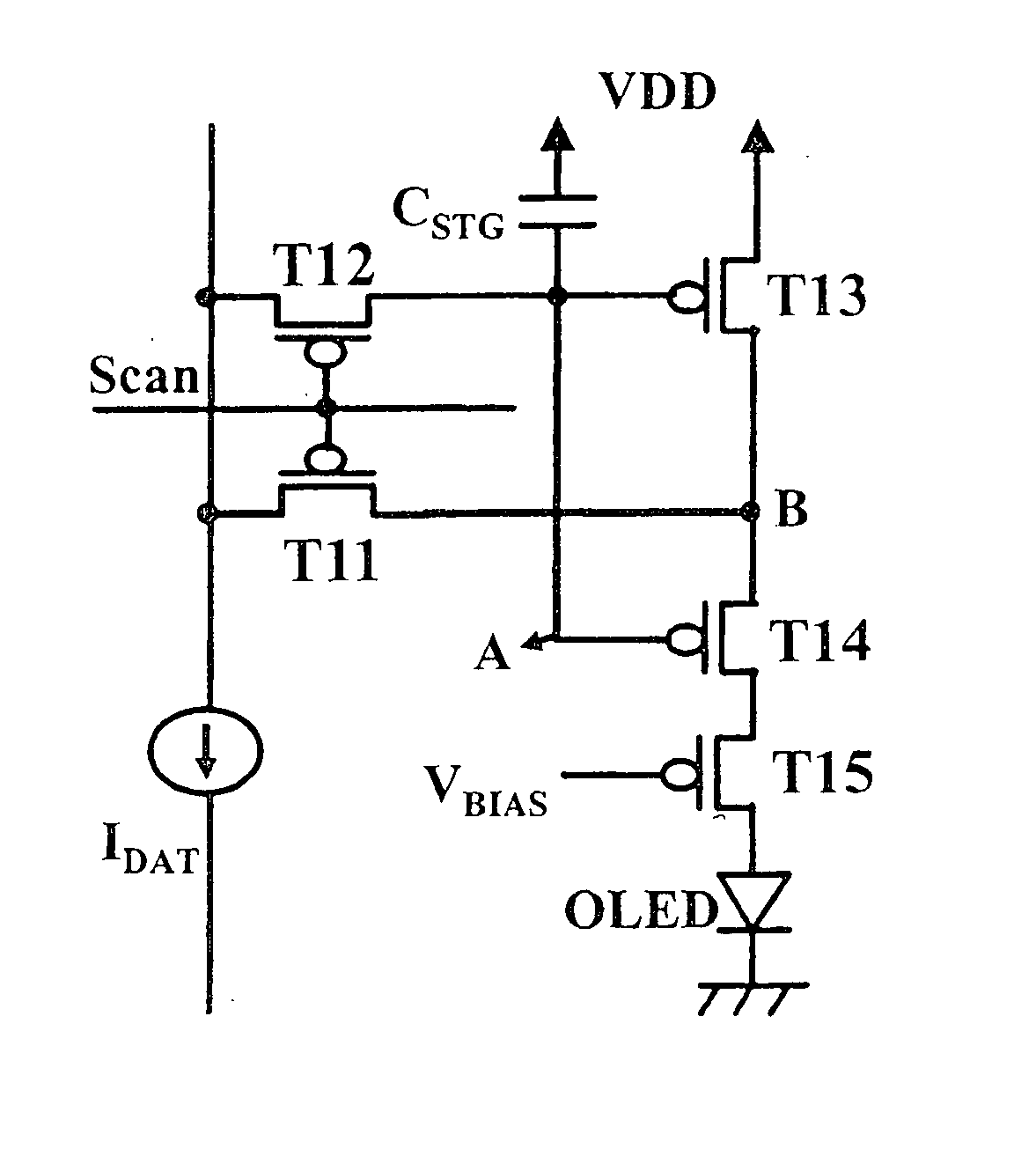
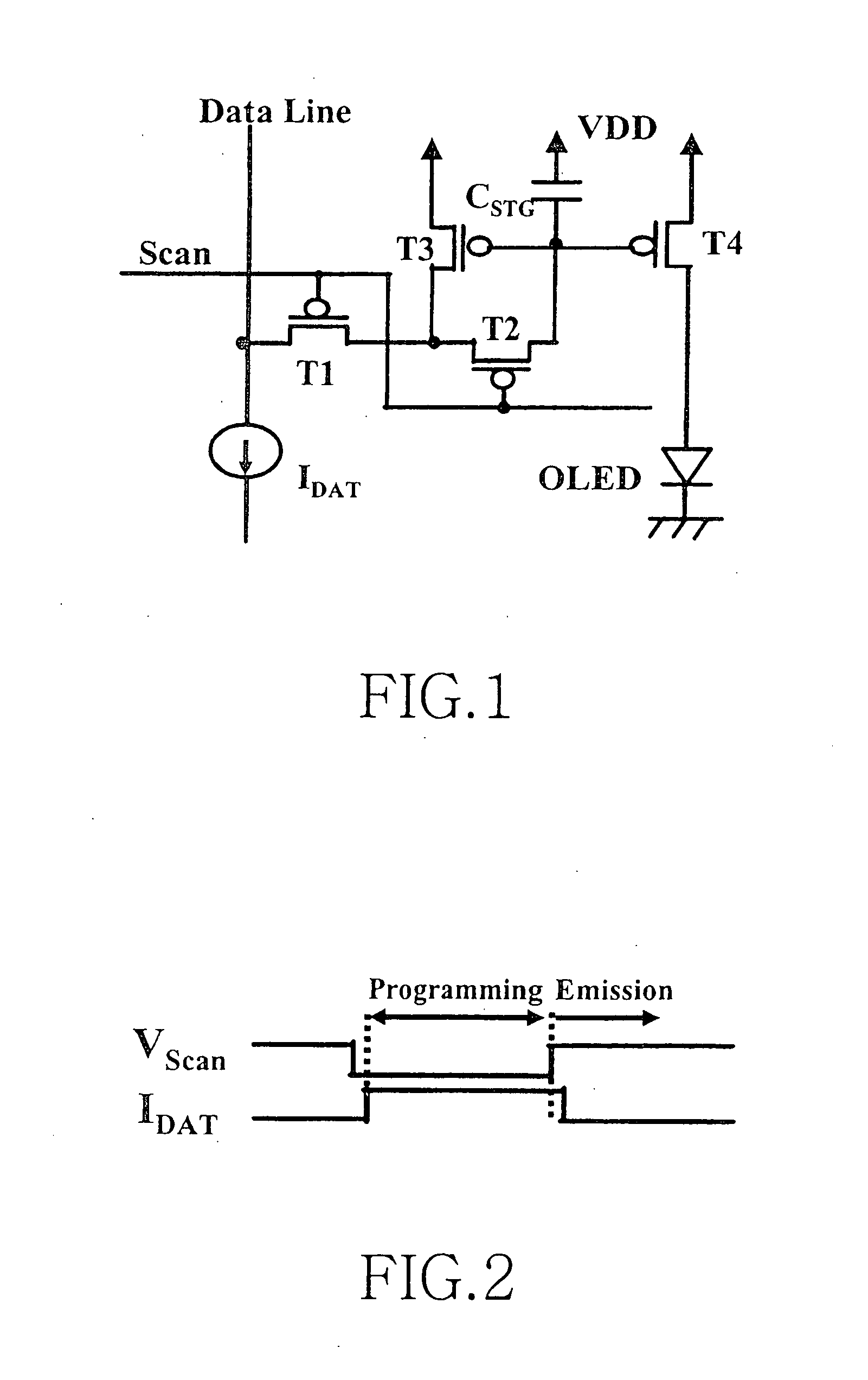
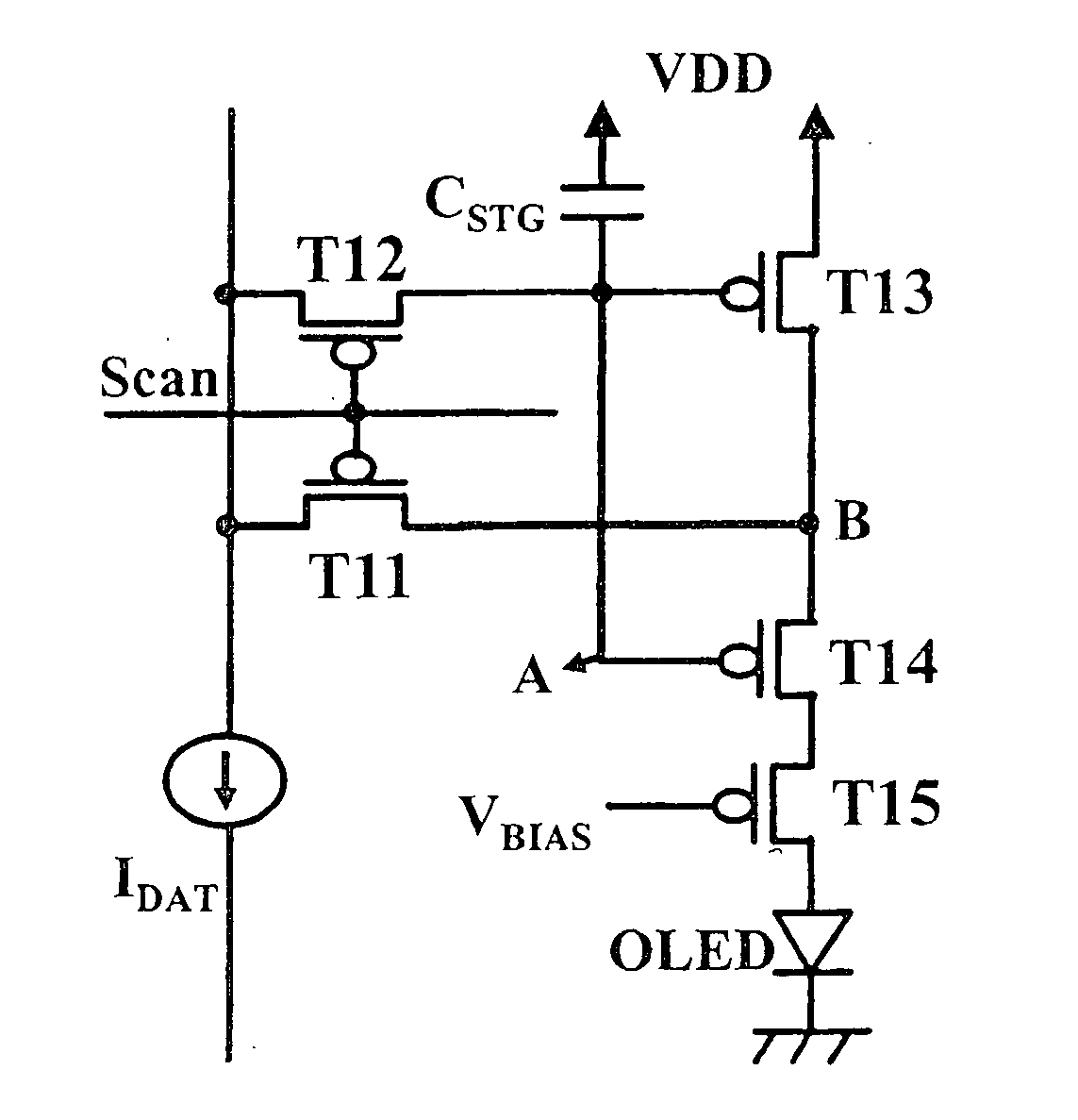
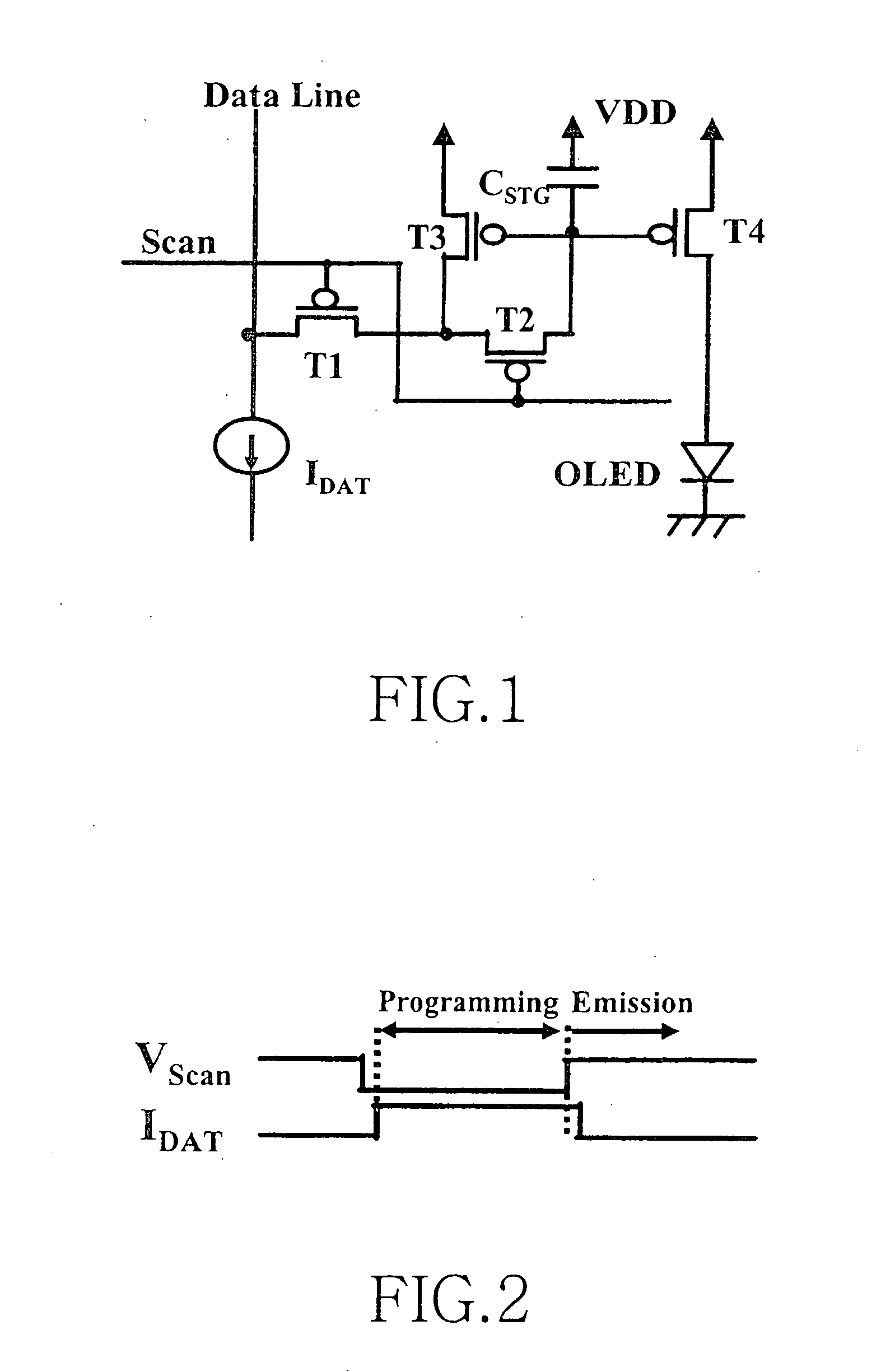
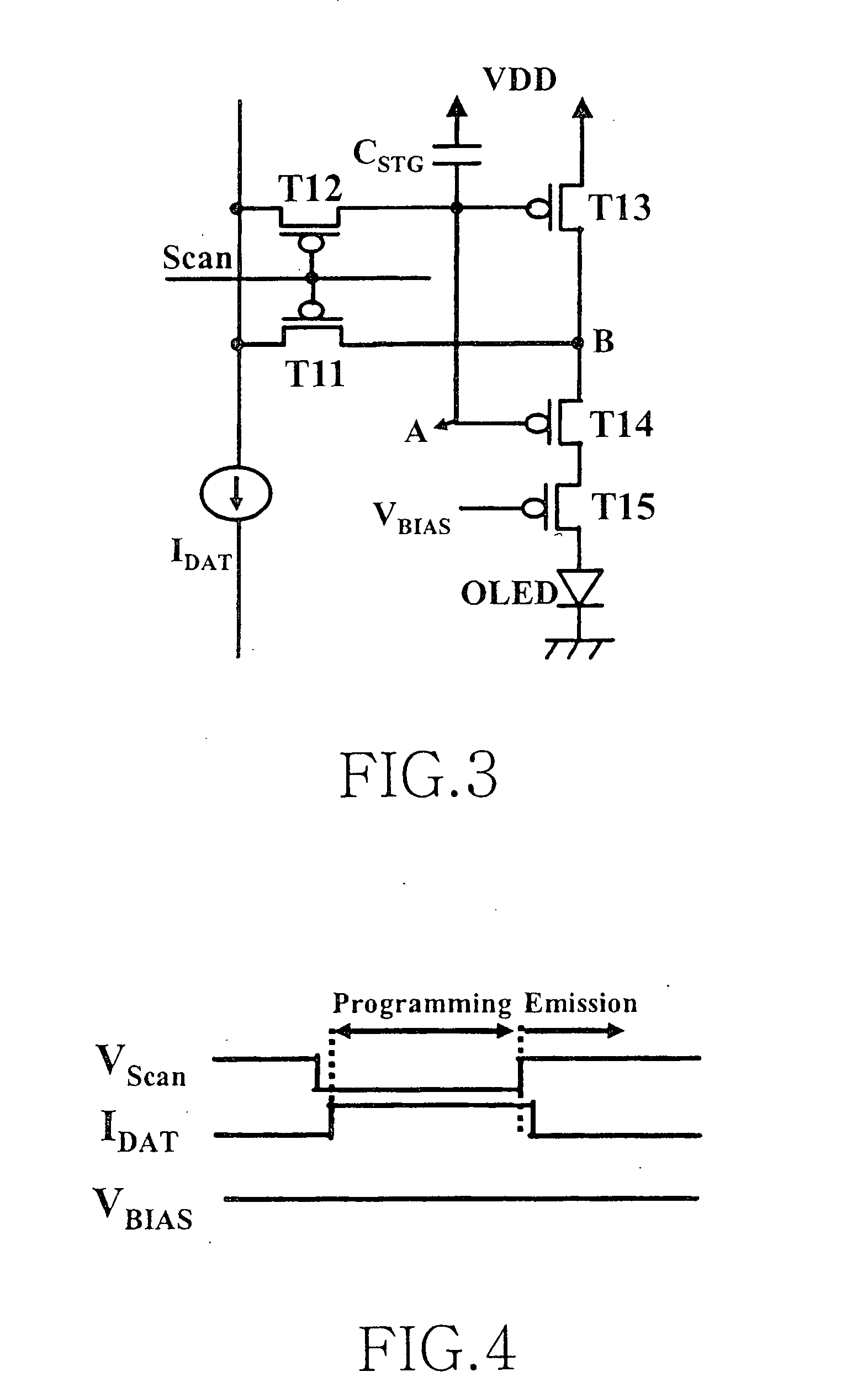
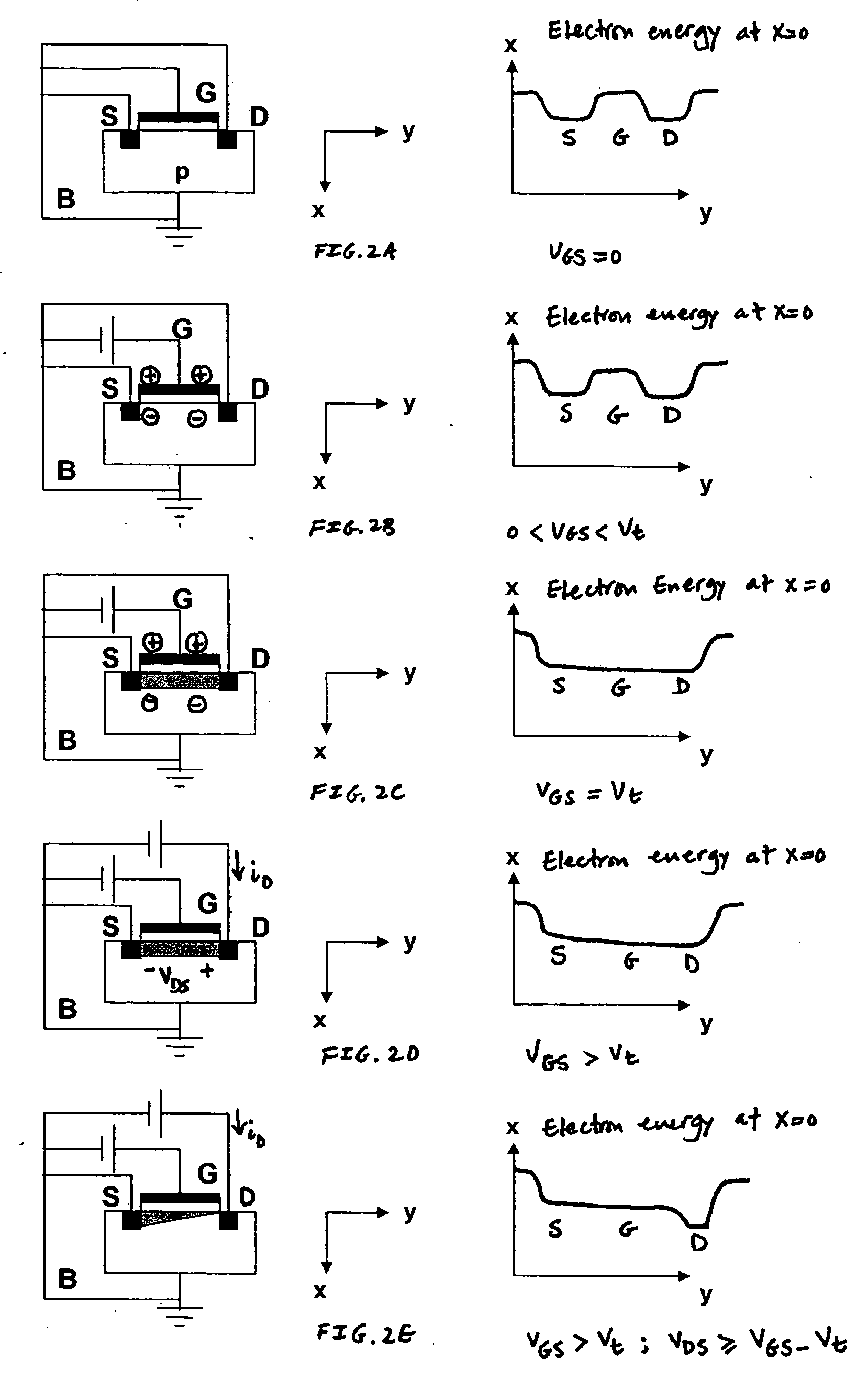
Picture element structure of current programming method type active matrix organic emitting diode display and driving method of data line
ActiveUS20090153459A9Light evenlyIncrease widthStatic indicating devicesActive matrixDevice material
The present invention provides a novel structure of picture elements in current programming-type semiconductor devices, and in particular, the structure of picture elements of an active matrix organic light emitting diode (OLED) display. The device makes a self-compensation for OLED current deviations due to the deterioration in threshold voltage and uneven electric characteristic in thin film transistors. The invention also provides a method for driving a data driver capable of compensating for the uneven electric characteristic of thin film transistors in the driver for driving picture elements in the current programming-type active matrix OLED display device.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
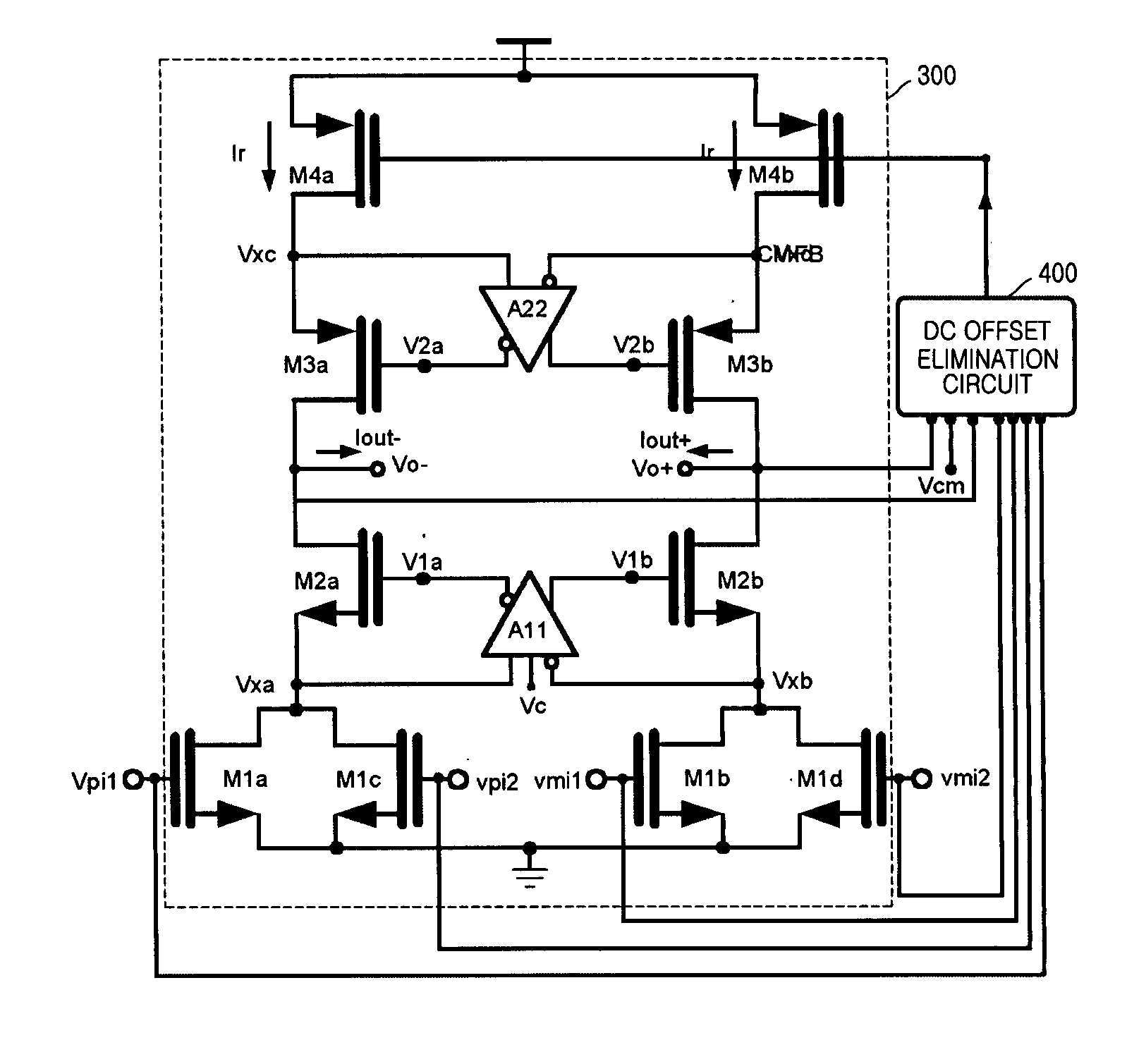
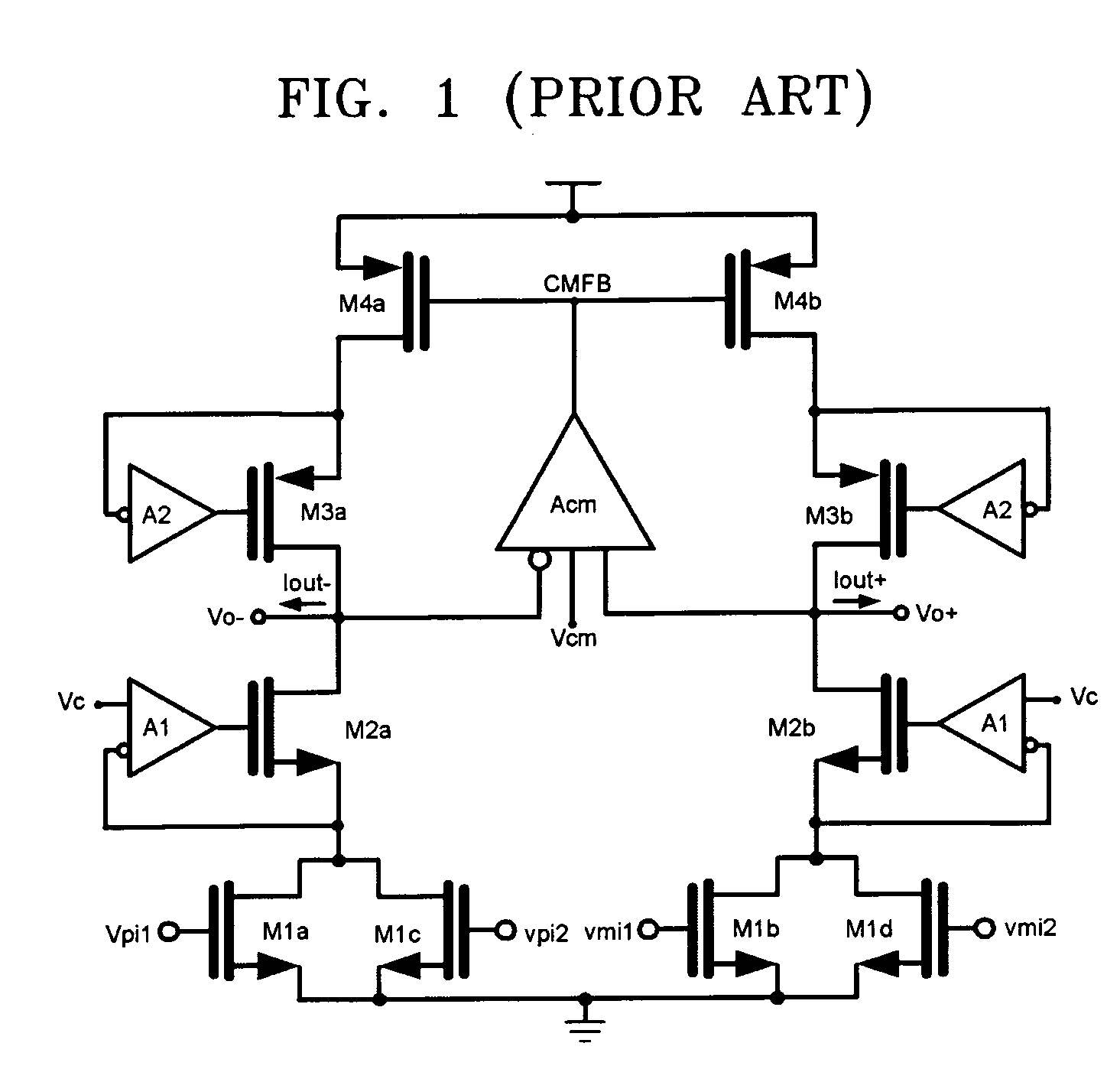
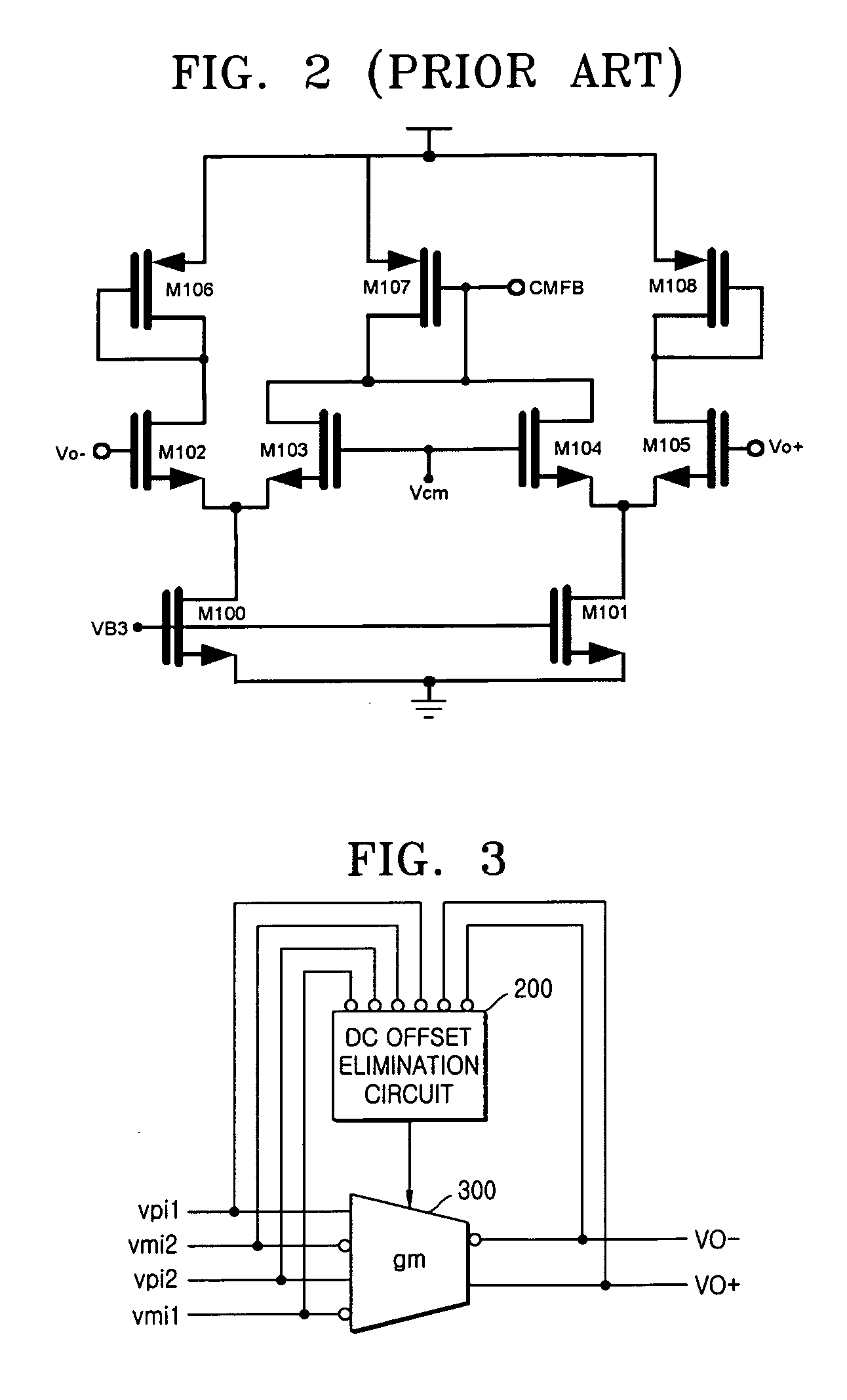
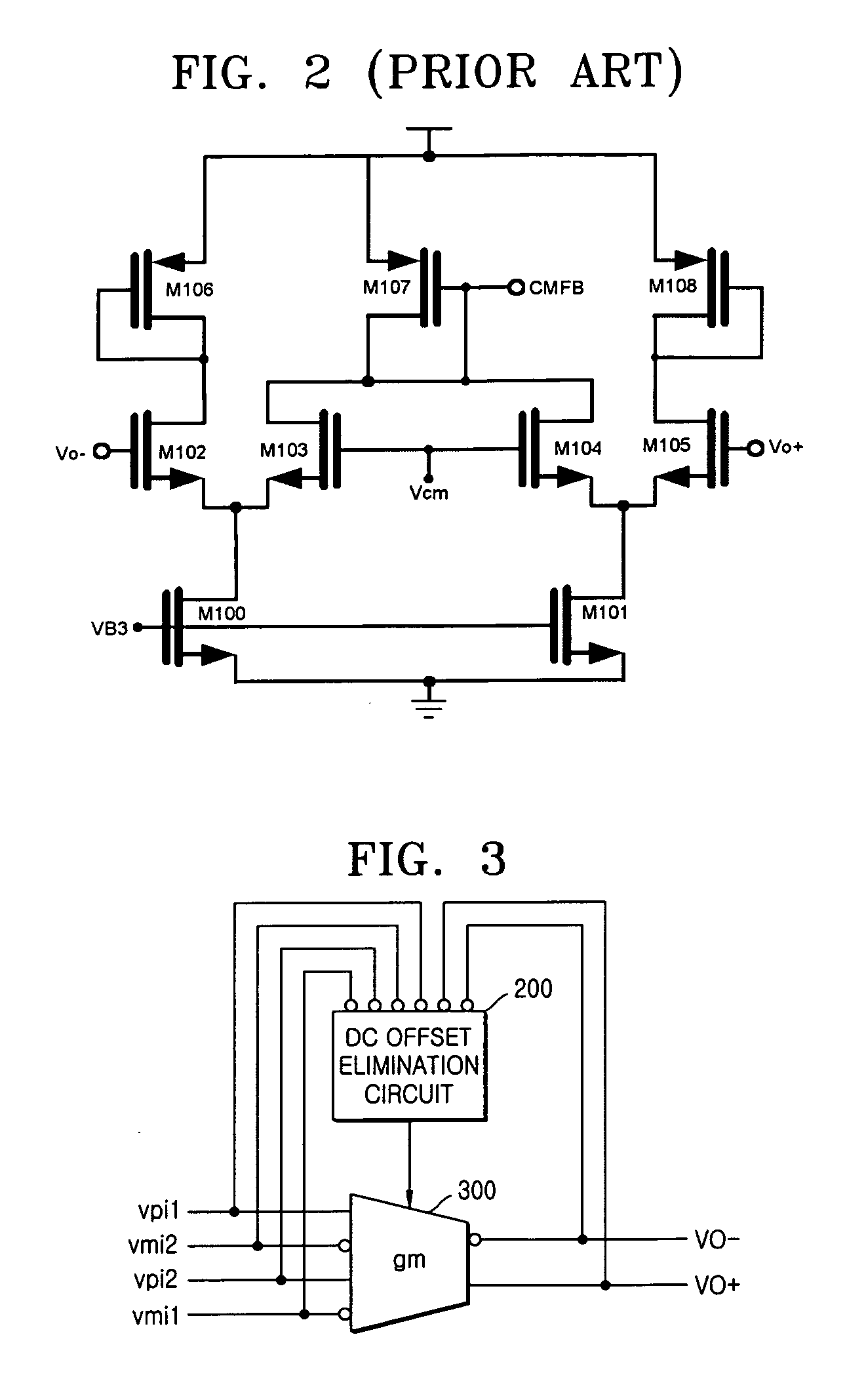
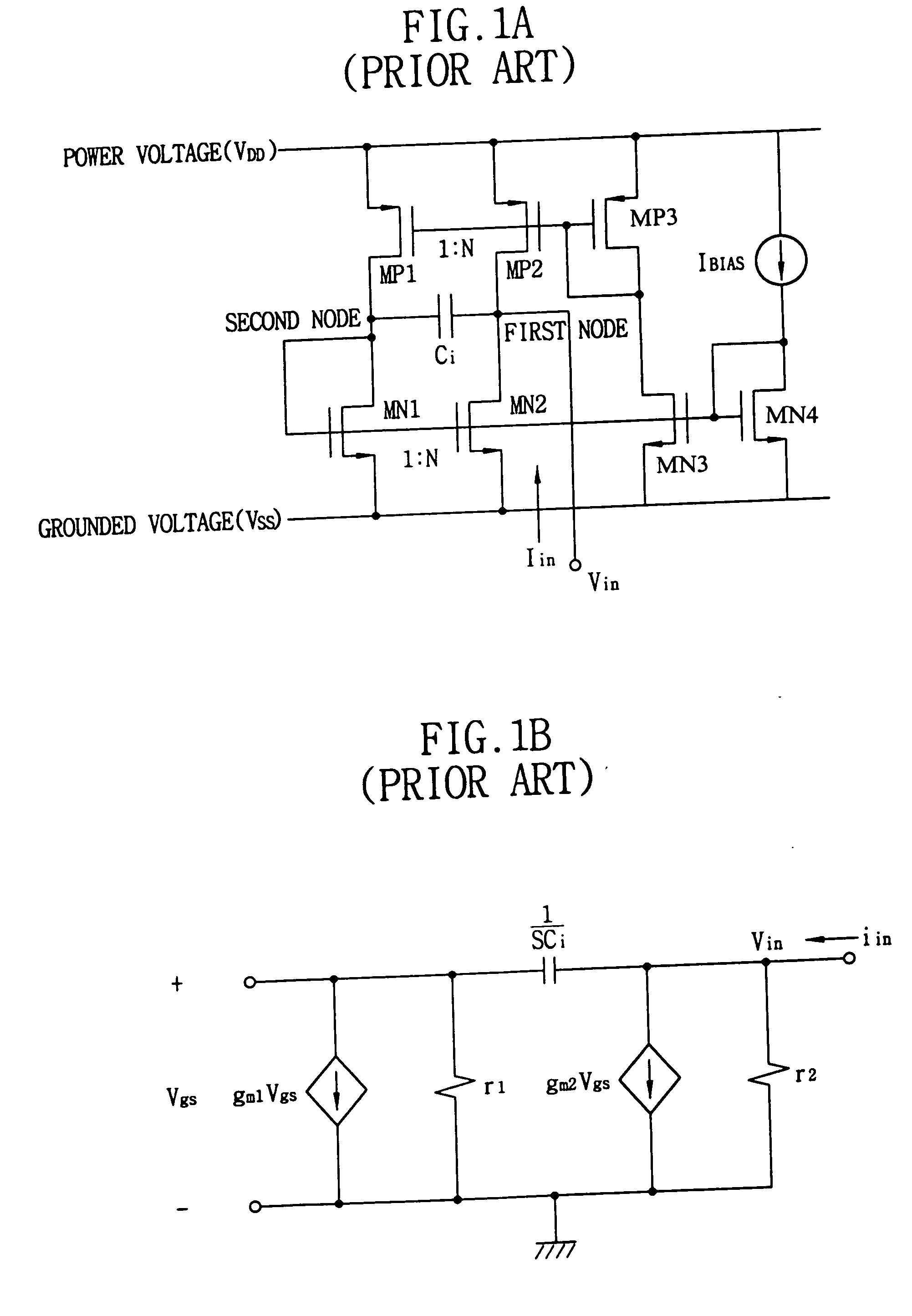
Operational transconductance amplifier with DC offset elimination and low mismatch
ActiveUS20050140445A1Linear rangeLarge output resistance valueDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesAudio power amplifierMode control
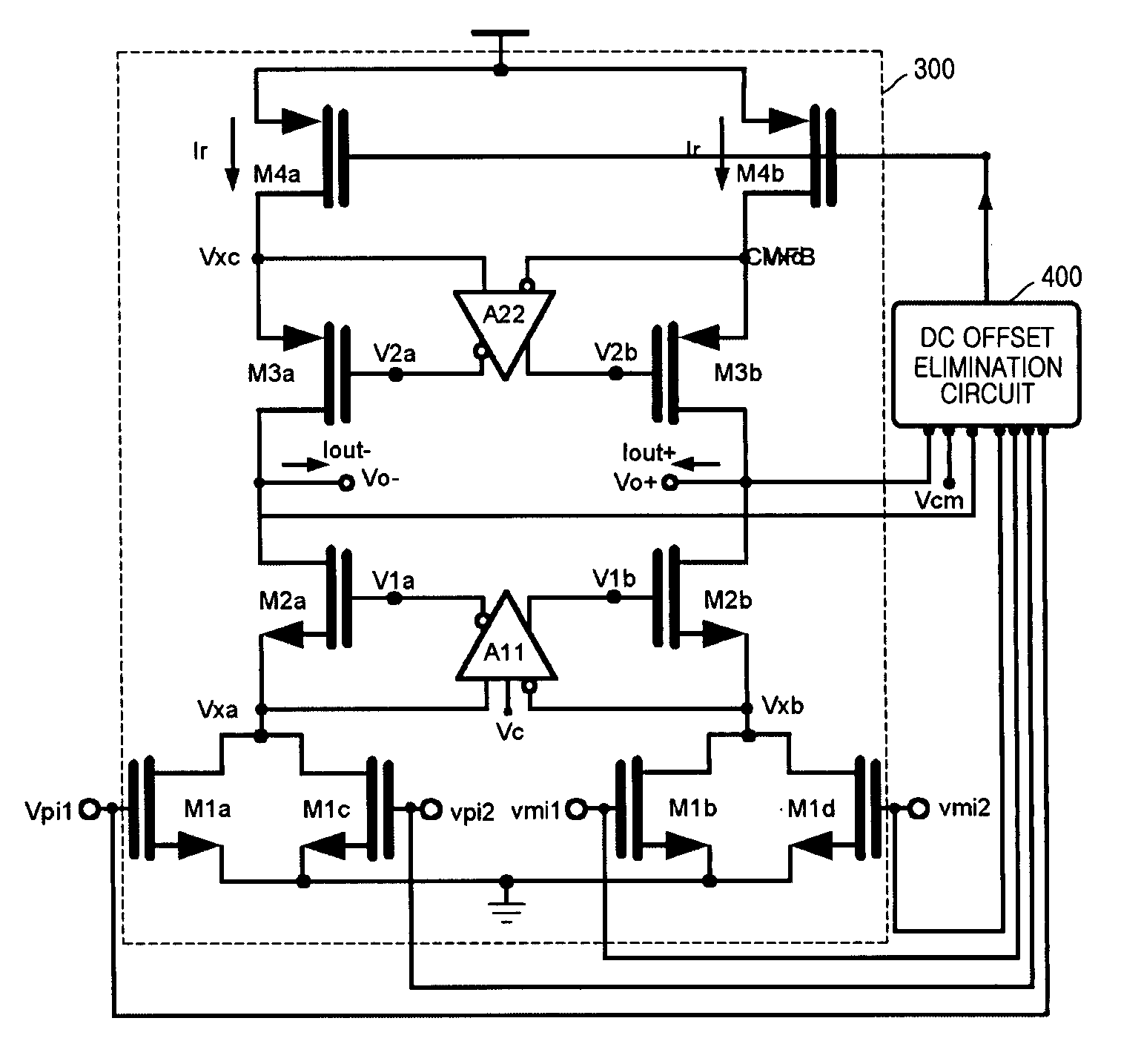
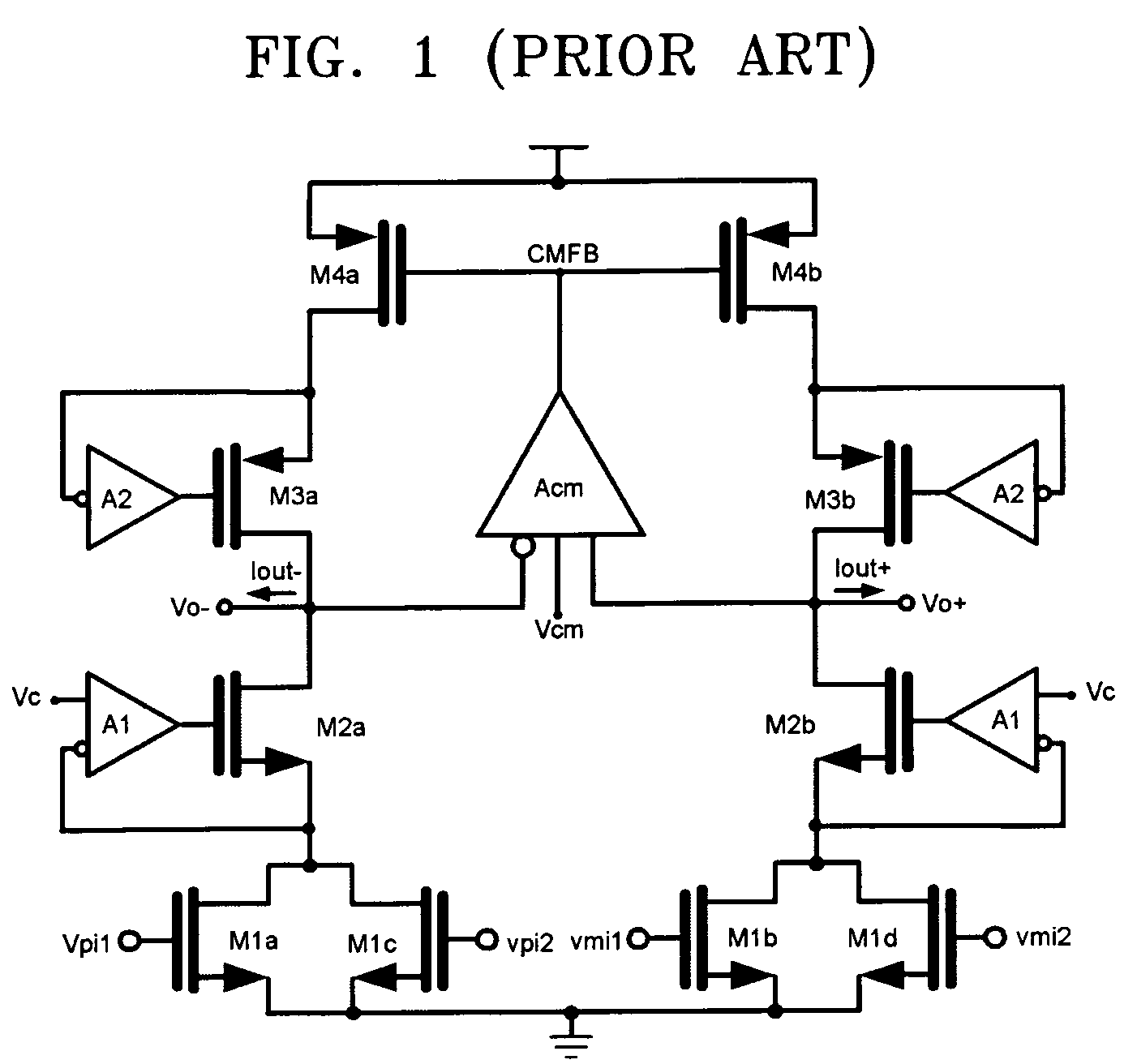
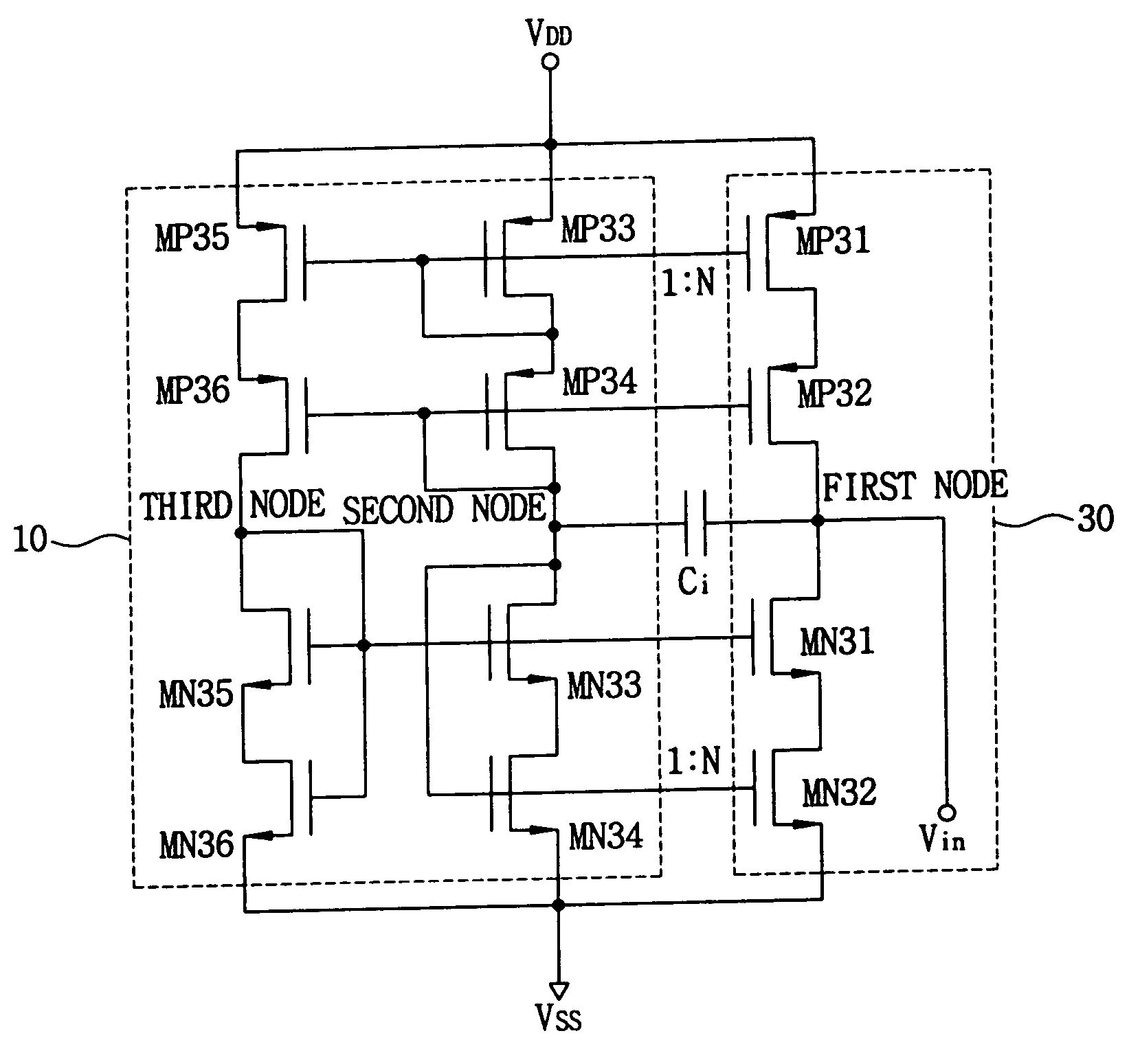
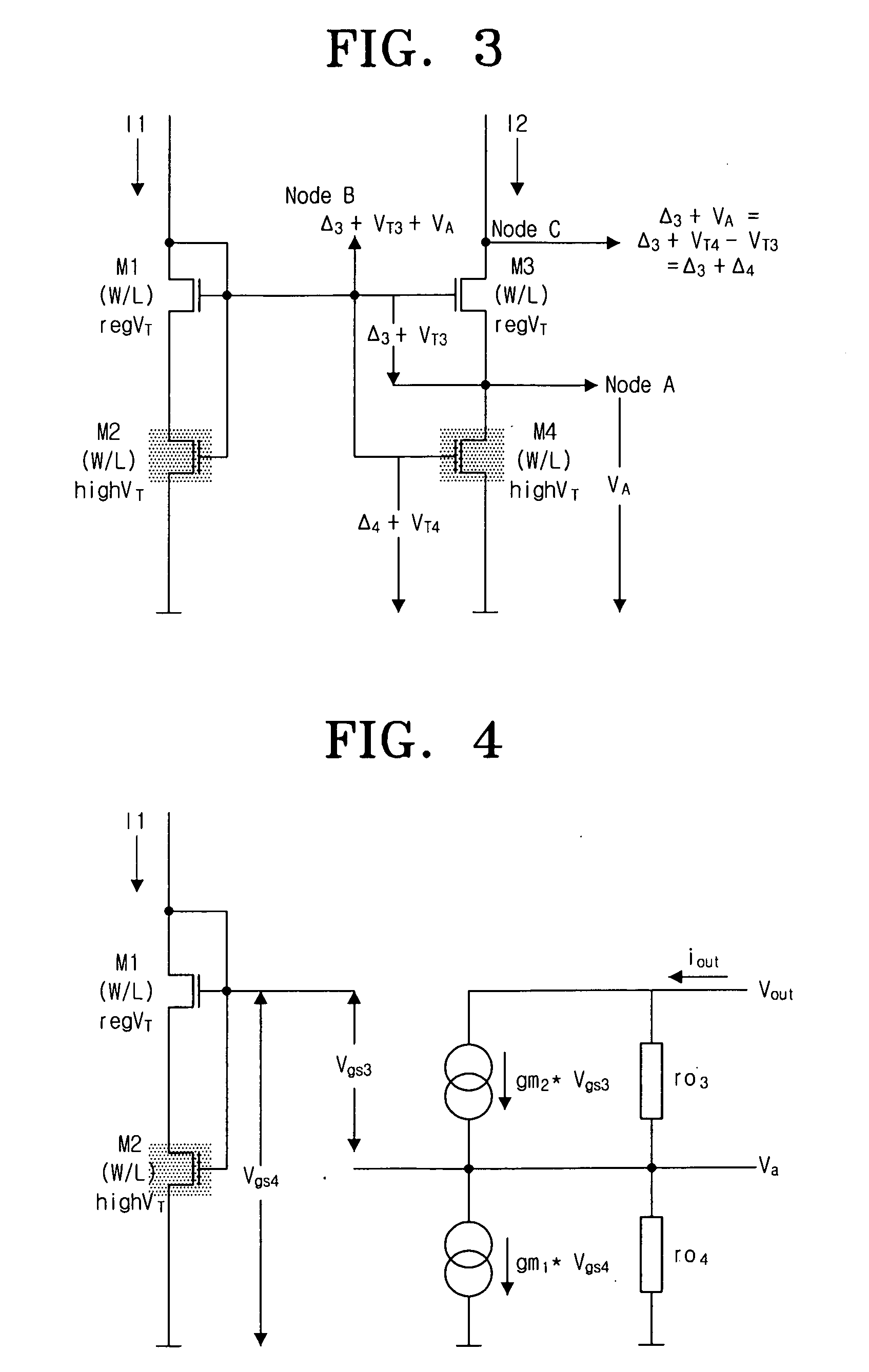
Provided is a transconductor capable of eliminating a direct current (DC) offset component of a signal and compensating a mismatch of the signal. The transconductor includes amplifiers of simple circuit structures, and a common mode control DC offset elimination circuit. The transconductor includes a common mode control DC offset elimination circuit unit receiving input / output voltages to stabilize the current supplying and the output DC value, a first amplifier and a second amplifier reducing a mismatch in a transconductor circuit and increasing an output resistance, in order to prevent a signal distortion or a wrong operation of the circuit that is caused by the mismatch signal and unstable DC voltage.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
High voltage gain topology for analog circuits in short channel technologies
InactiveUS7652520B2Reduce leakageImprove noise immunityTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringHigh pressure
A stacked MOS configuration for use in short channel length analog circuit technologies is provided. The stacked MOS configuration comprises a plurality of short-channel MOS transistors coupled in series and sharing a common gate terminal. In an embodiment, a first peripheral transistor provides a drain terminal for the stacked MOS configuration. A second peripheral transistor provides a source terminal for the stacked MOS configuration. Adjacent transistors in the stacked MOS configuration are connected in a drain-to-source configuration.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Differential amplifier and low drop-out regulator with thereof
ActiveUS7173401B1Increase the output resistanceLower overall pressure dropElectric variable regulationEngineeringDifferential amplifier
A differential amplifier having a positive input terminal, a negative input terminal, an output terminal, a bias terminal and a ground terminal is provided. The differential amplifier comprises a differential pair circuit and a current mirror circuit. Wherein, the differential pair circuit is coupled to the positive input terminal, the negative input terminal, the output terminal, and the bias terminal of the differential amplifier. The current mirror circuit receives a constant current from a current source, and mirrors the constant current to the differential pair circuit. The current mirror circuit further connects to the ground terminal of the differential amplifier, and the terminal of the current mirror circuit receiving the constant current is coupled to a first source / drain terminal of a first PMOS transistor. A second source / drain and a gate of the first PMOS transistor are connected to the bias terminal and the output terminal of the differential amplifier, respectively.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
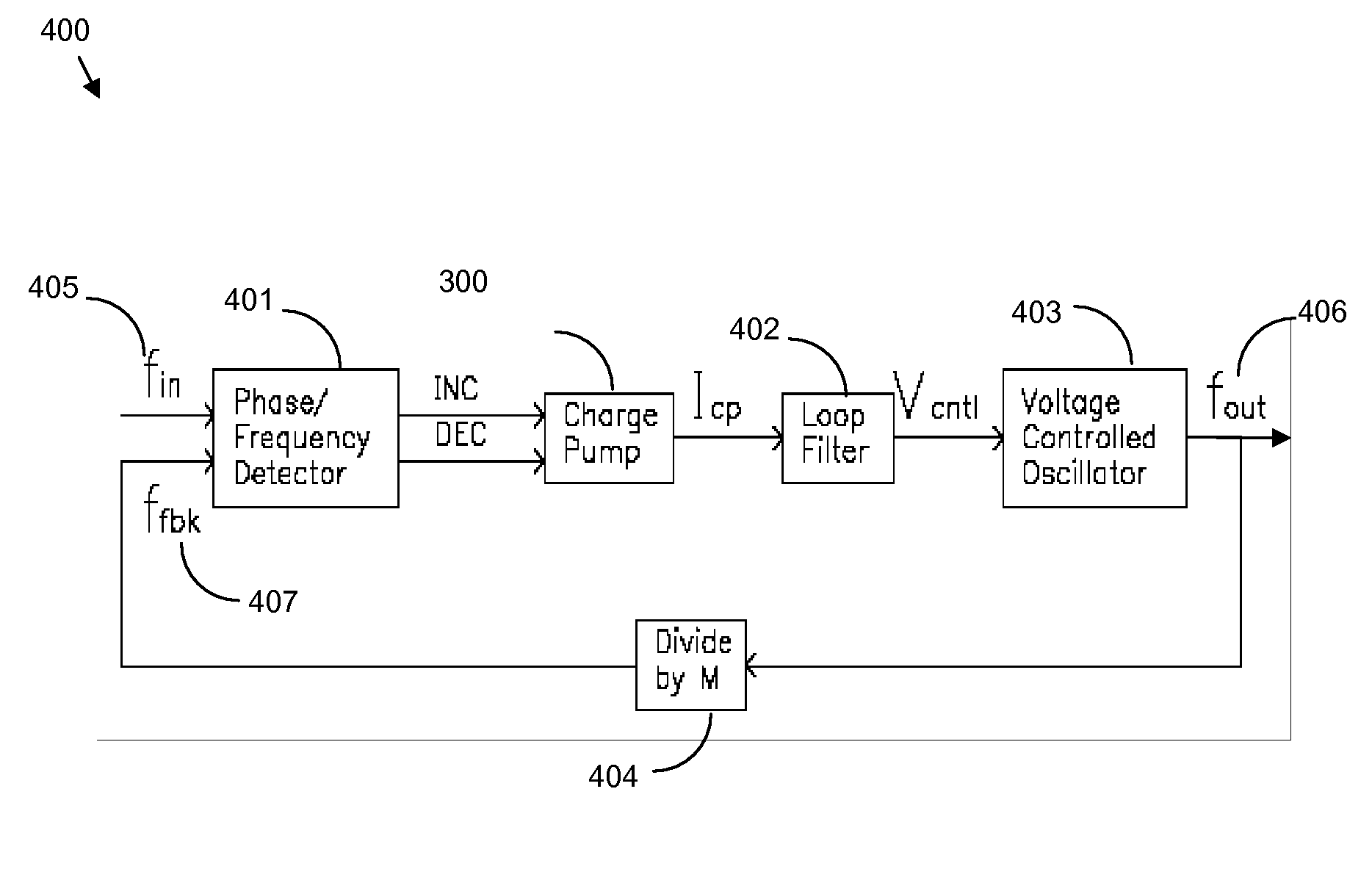
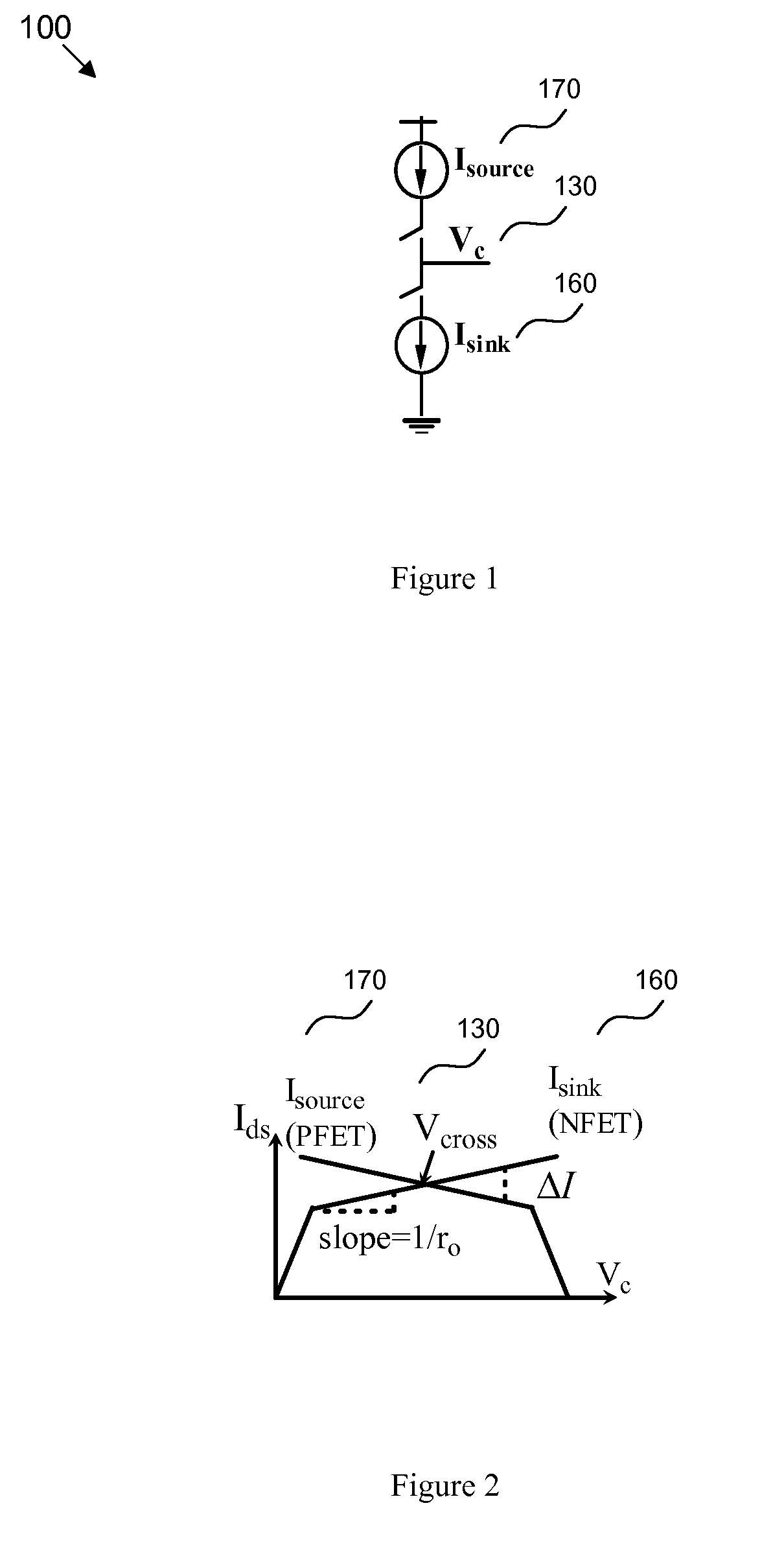
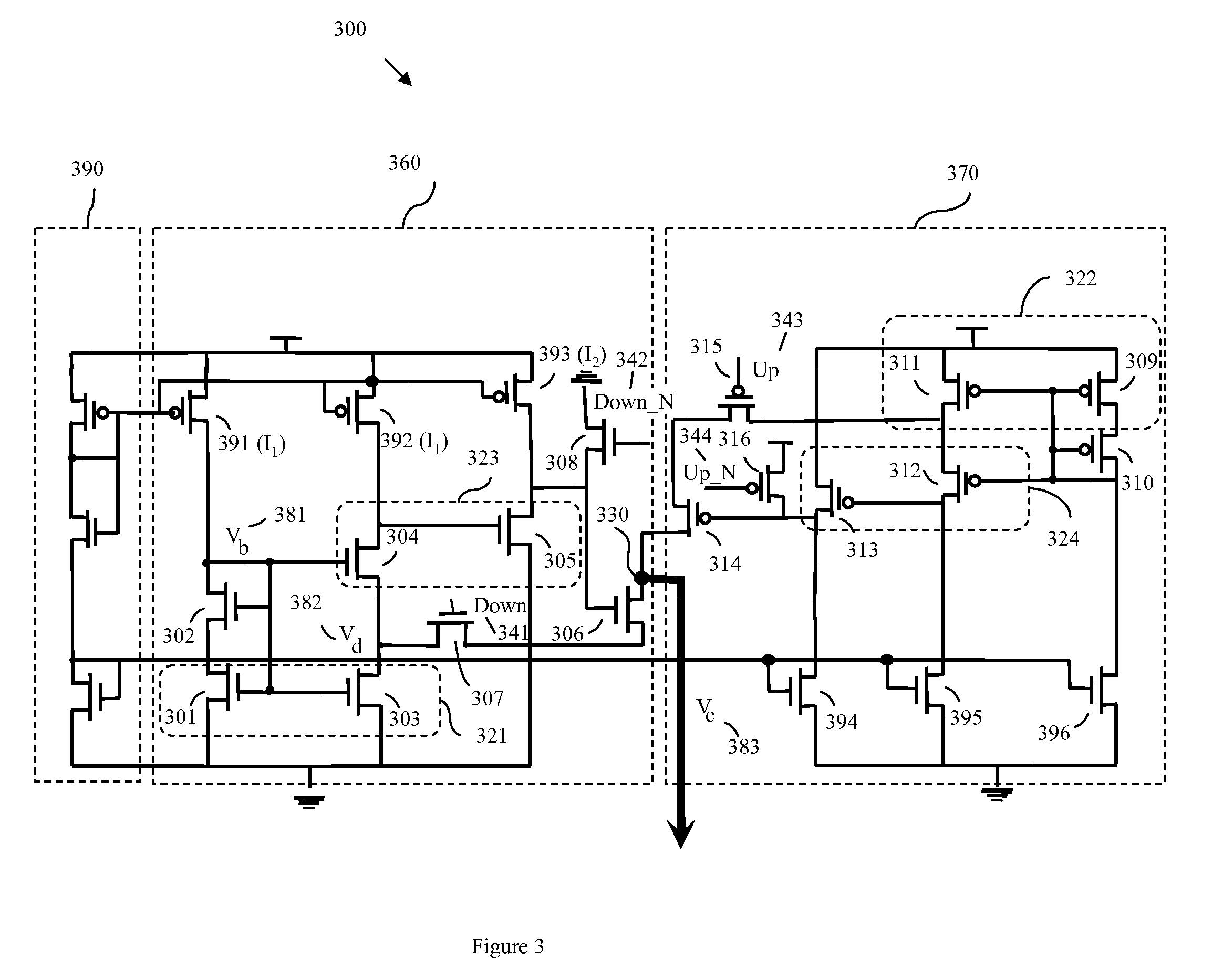
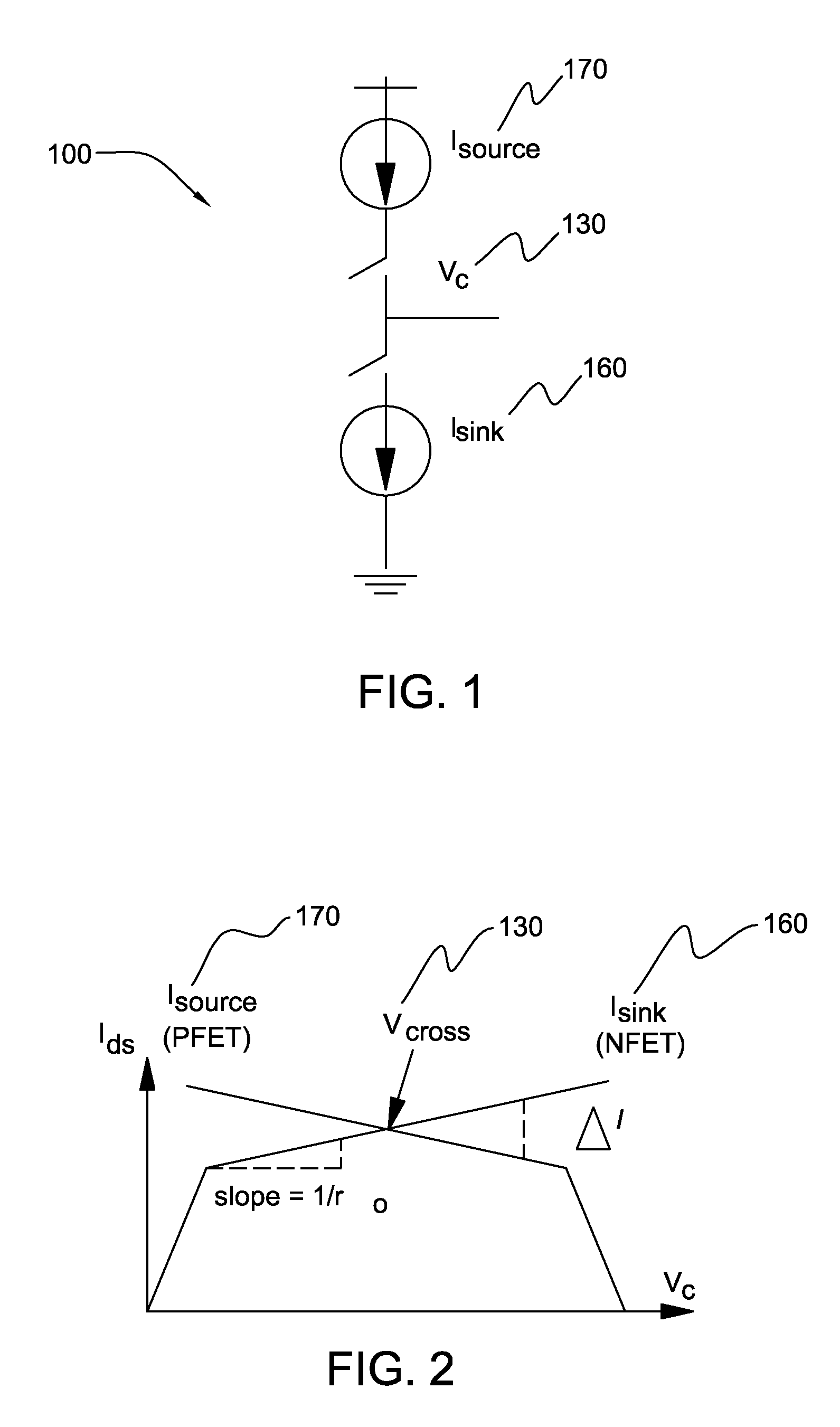
High output resistance, wide swing charge pump
InactiveUS20090033383A1Increase the output resistanceWide operating voltage rangePulse automatic controlApparatus without intermediate ac conversionAudio power amplifierVoltage range
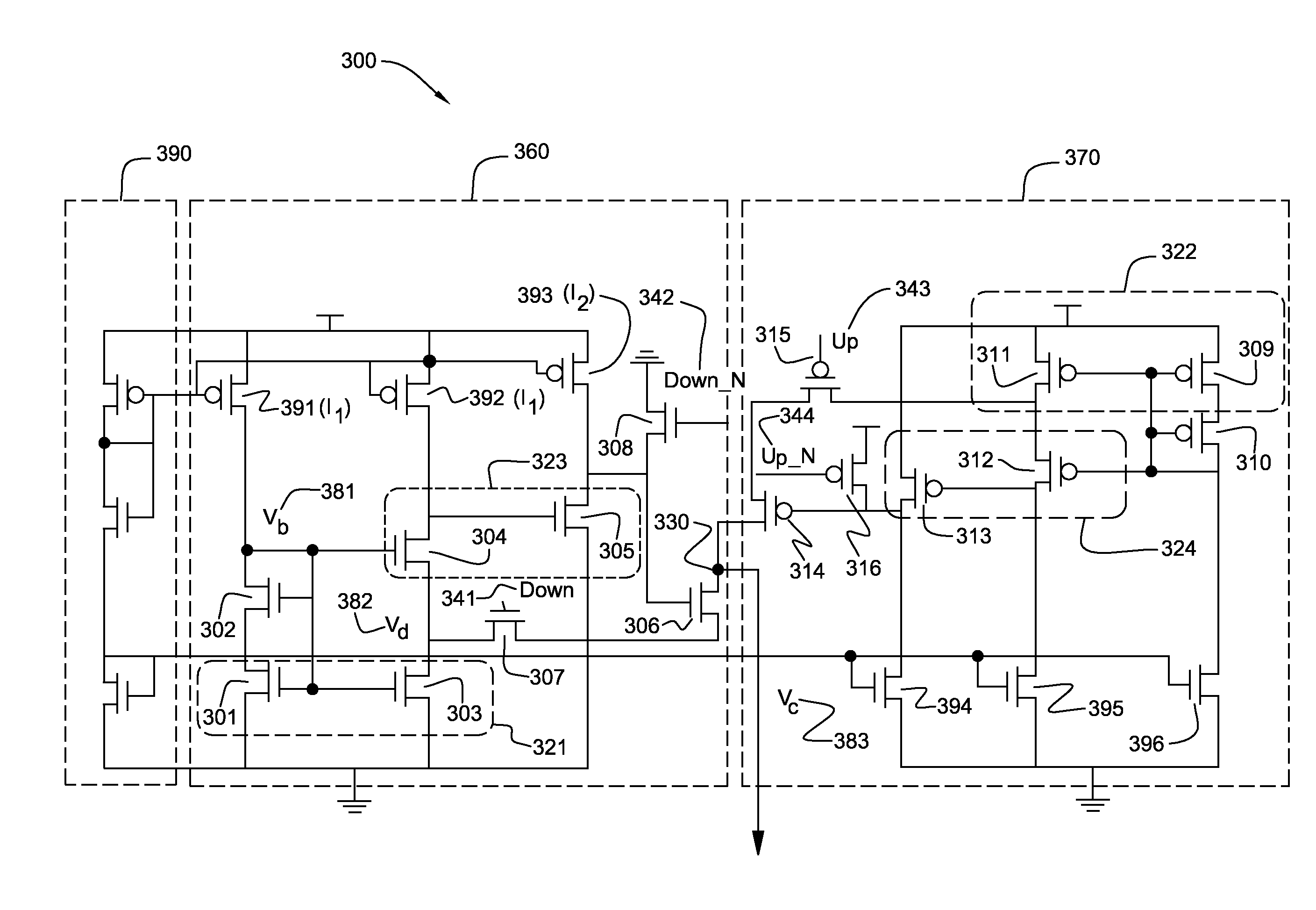
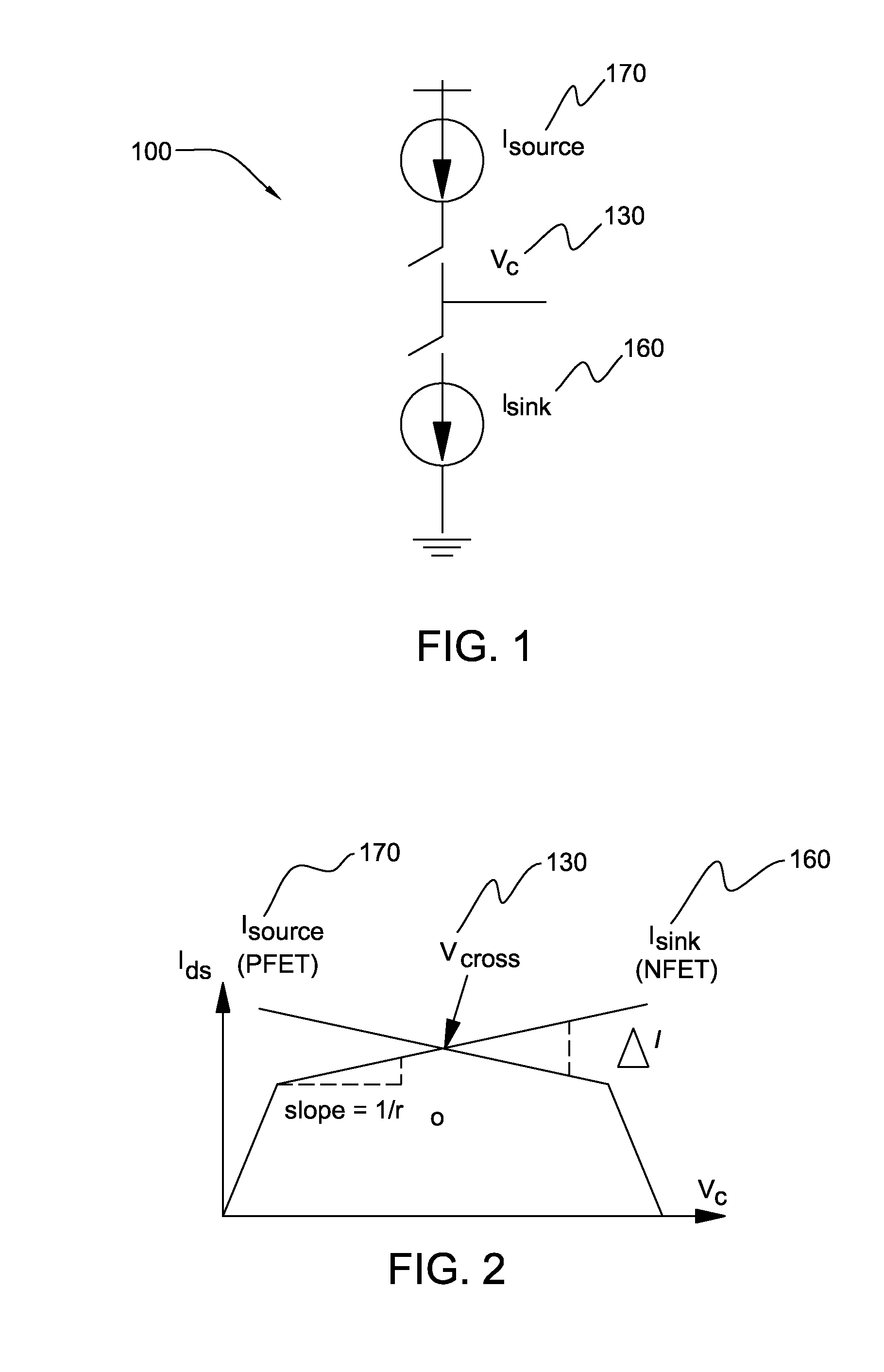
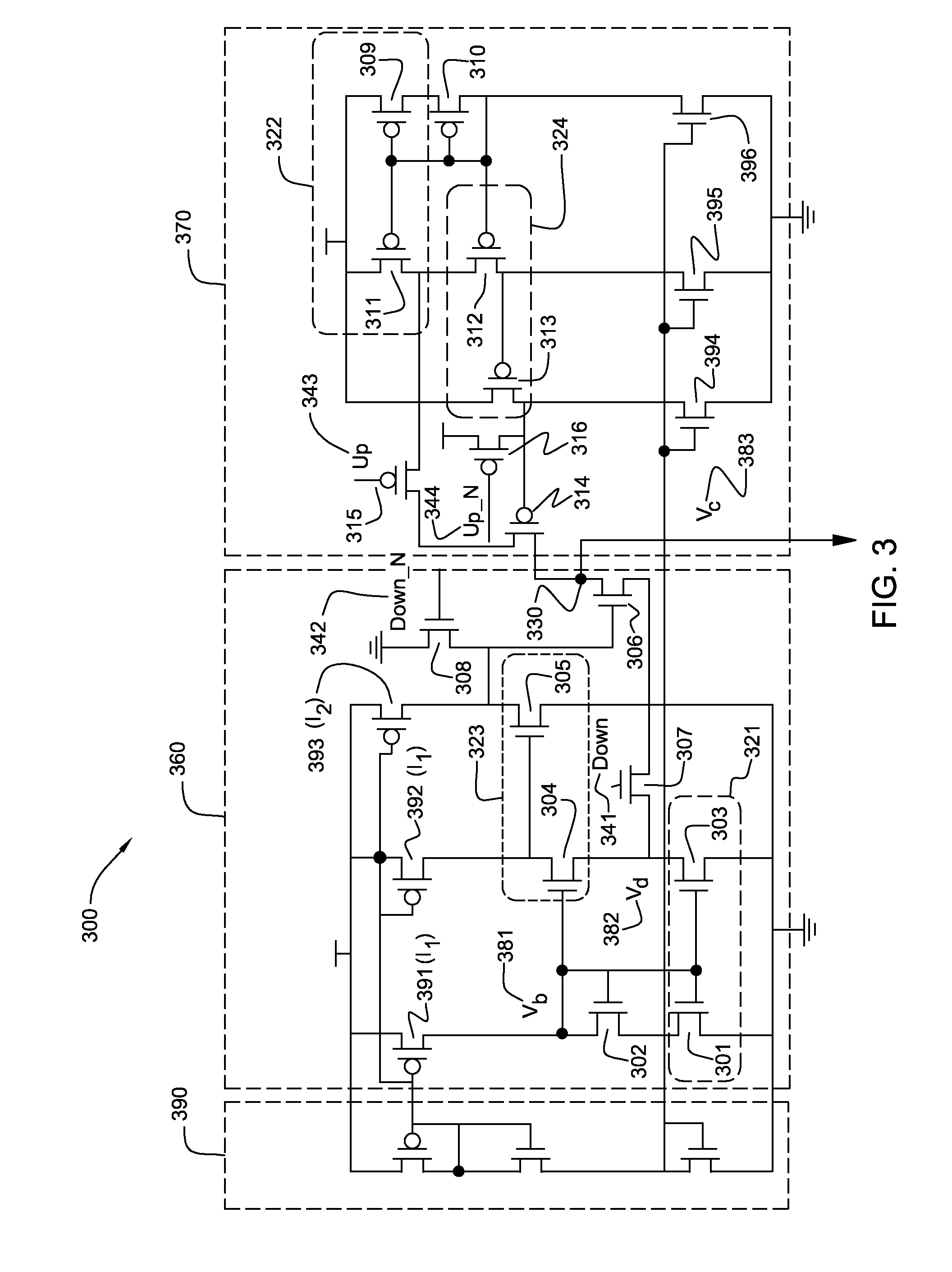
Disclosed are current sink and source circuits, a charge pump that incorporates them, and a phase locked loop that incorporates the charge pump. The current sink and source circuits each have a current mirror that biases a transistor connected to an output node. These circuits each further have a two-stage feedback amplifier to sense the current mirror drain voltage and to control the transistor gate voltage in order to stabilize the current mirror drain voltage independent of output voltage at the output node. The amplifier also increases output resistance at the output node. This configuration allows for a wide operation voltage range and ensures good circuit performance under a very low power supply. A charge pump that incorporates these circuits generates highly matched charging and discharging currents. A PLL that incorporates this charge pump exhibits minimal bandwidth shifts and minimal locking speed and jitter performance degradation.
Owner:IBM CORP
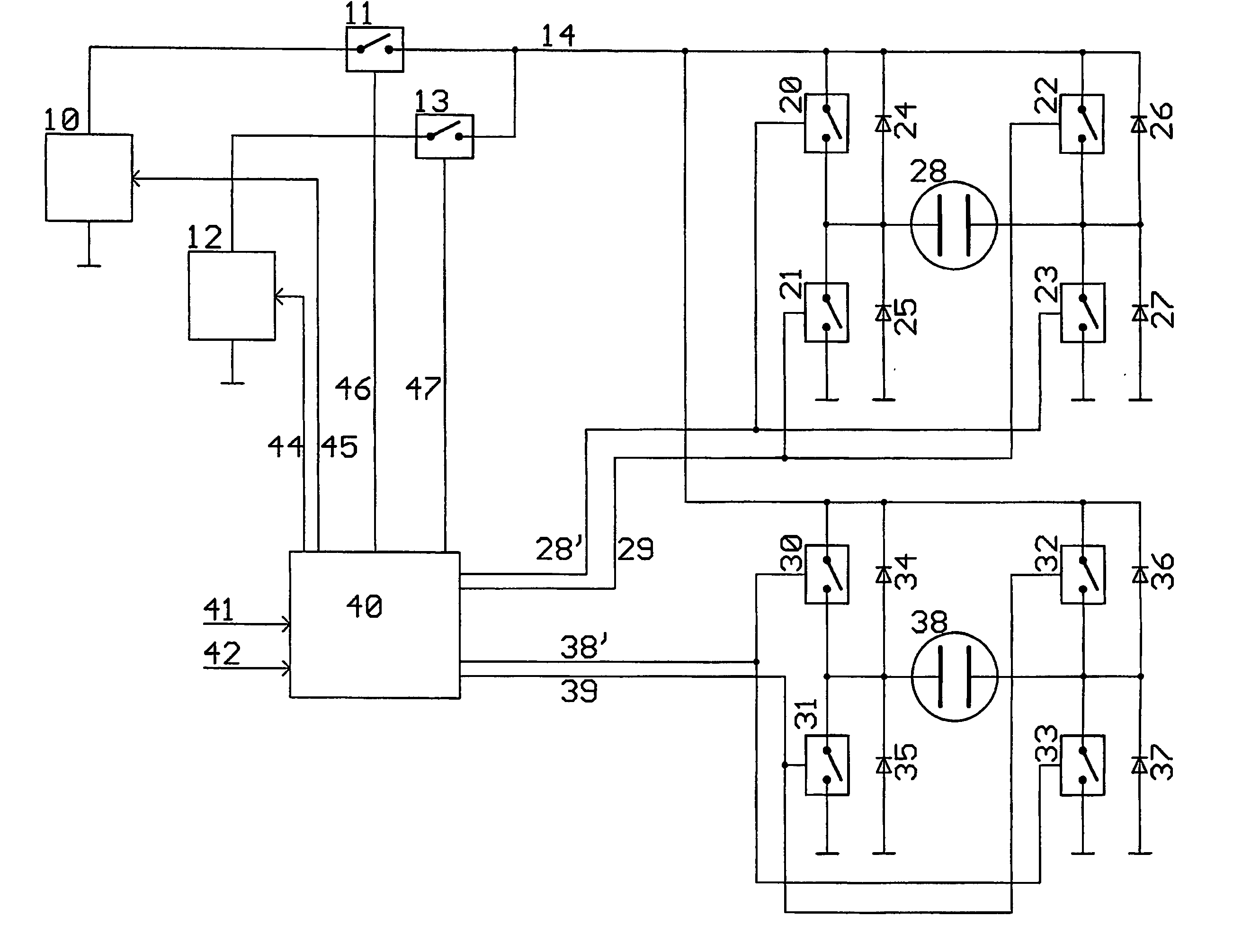
Multiple electroluminescent lamp driver
InactiveUS20070029951A1Increase the output resistanceCharge be relatively smallElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesBrightness perceptionElectroluminescence
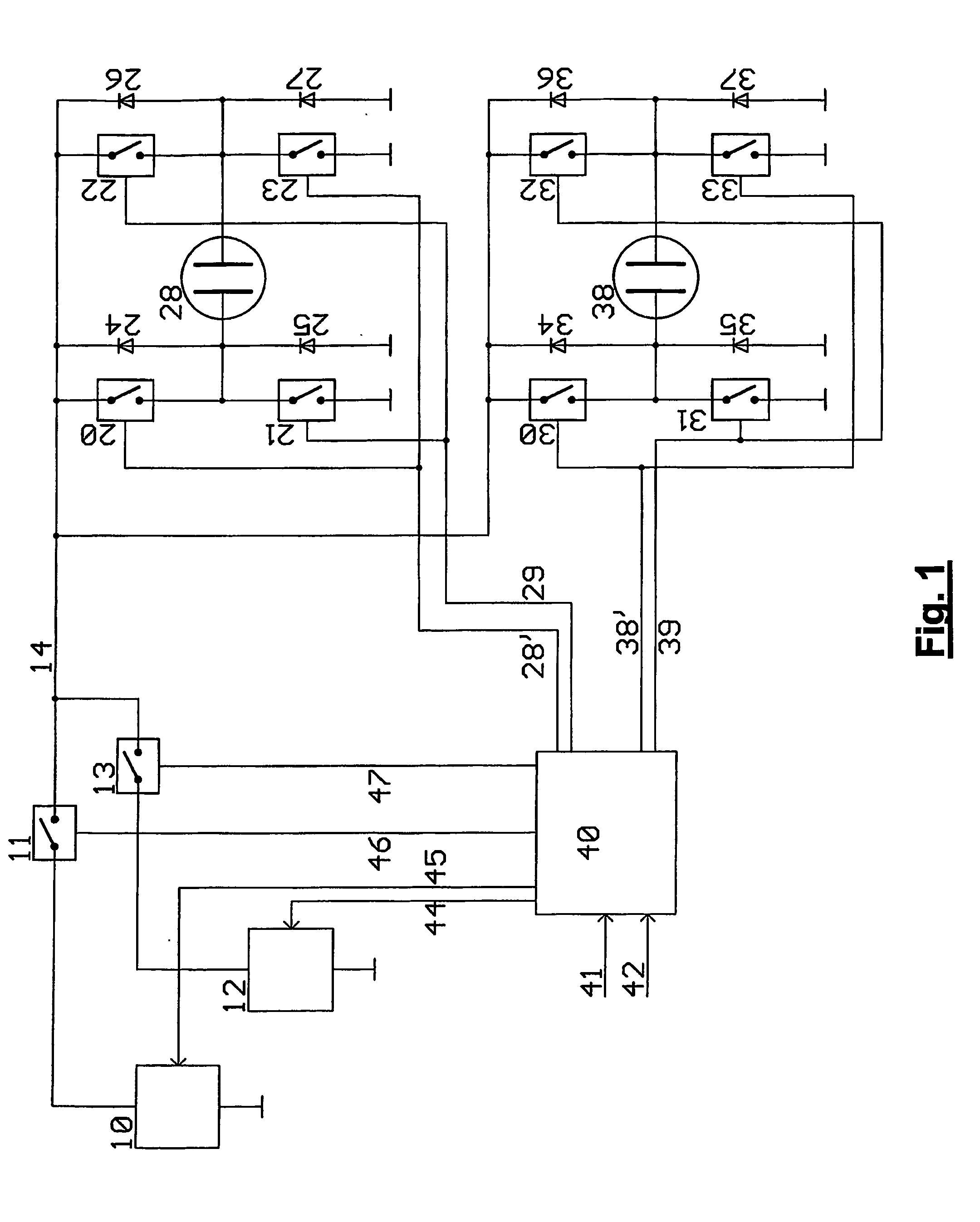
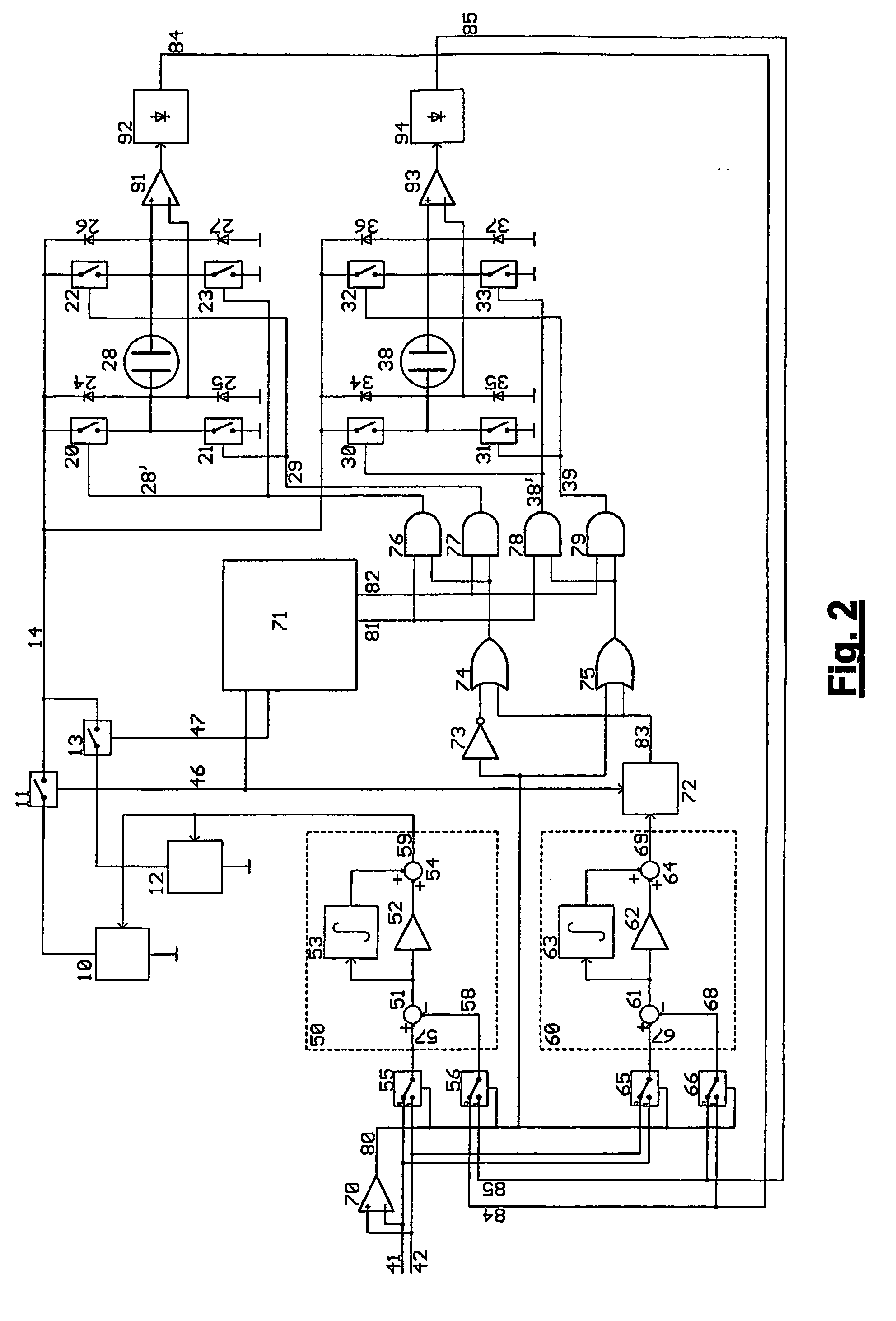
The invention relates to an electroluminescent (EL) lamp driver for controlling the luminescent brightness of at least two EL lamps (28, 38), wherein the driver I is adapted to receive at least two setpoint values corresponding to luminescent brightness of the EL lamps and to create charge waveforms (128, 138) in accordance with the received setpoint values for charging or discharging the EL lamps (28, 38).
Owner:IEE INT ELECTRONICS & ENG SA
Operational transconductance amplifier with DC offset elimination and low mismatch
ActiveUS7193466B2Linear rangeLarge output resistance valueDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesAudio power amplifierMode control
Provided is a transconductor capable of eliminating a direct current (DC) offset component of a signal and compensating a mismatch of the signal. The transconductor includes amplifiers of simple circuit structures, and a common mode control DC offset elimination circuit. The transconductor includes a common mode control DC offset elimination circuit unit receiving input / output voltages to stabilize the current supplying and the output DC value, a first amplifier and a second amplifier reducing a mismatch in a transconductor circuit and increasing an output resistance, in order to prevent a signal distortion or a wrong operation of the circuit that is caused by the mismatch signal and unstable DC voltage.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Micro-grid multi-inverter parallel voltage control method for droop control of robust power
ActiveCN102842921BIncrease the output resistanceSmall output resistanceSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsLow voltageVoltage reference
The invention discloses a micro-grid multi-inverter parallel voltage control method for droop control of robust power. The method comprises the following steps of: specific to each inverter in a micro-grid, computing and synthesizing an inverter output reference voltage by adopting a robust power droop controller; and introducing virtual complex impedance containing a resistance component and an inductive impedance component, and keeping inverter output impedance in a pure resistance state under a power frequency condition by adopting a multi-loop voltage control method based on virtual impedance and quasi-resonance PR (Proportional-Resonant) control, thereby realizing micro-grid multi-inverter parallel running and power equation, wherein the robustness of a micro-grid parallel system on numeric value computing errors, parameter drift, noise interference and the like is enhanced. Due to the adoption of the method, the defects of larger loop current of a parallel system, non-uniform power distribution and the like caused by the inductivity of the impedance output by inverters in the conventional droop method are overcome; and the method is suitable for multi-grid parallel uniform current control in a low-voltage micro-grid.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Biological impedance imaging device
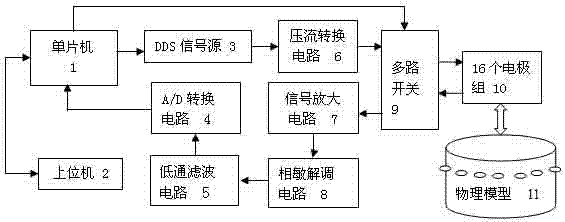
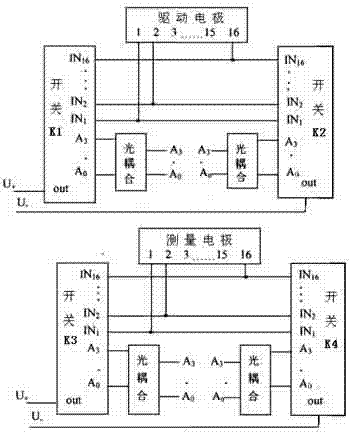
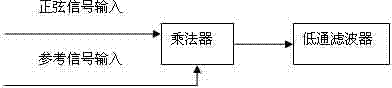
InactiveCN103584860AGuaranteed independenceIncrease the output resistanceDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMicrocontrollerPhysical model
The invention discloses a biological impedance imaging device. The biological impedance imaging device comprises a single-chip microcomputer (1), an upper computer (2), a DDS signal source (3), an A / D conversion circuit (4), a low-pass filtering circuit (5), a voltage-current conversion circuit (6), a signal amplifying circuit (7), a phase-sensitive demodulation circuit (8), multi-way switches (9), a plurality of electrode sets (10) and a physical model (11). The biological impedance imaging device has the advantages that a generated current source has high output resistance, and therefore the independence between output current and load voltage can be guaranteed; each set of switches needs eight-digit IO ports for controlling, the control end of an analog switch is connected with a latch circuit, in this way, two sets of switches can be controlled through an 8+2 digital address line, the number of the IO ports for controlling the single-chip microcomputer is reduced, and then the circuit is simpler and optimized; besides, real part information and imaginary part information of impedance can be obtained through the phase-sensitive demodulation circuit, so that the impedance information obtained through the biological impedance imaging device is more accurate compared with a method for taking the real part information of the impedance only.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
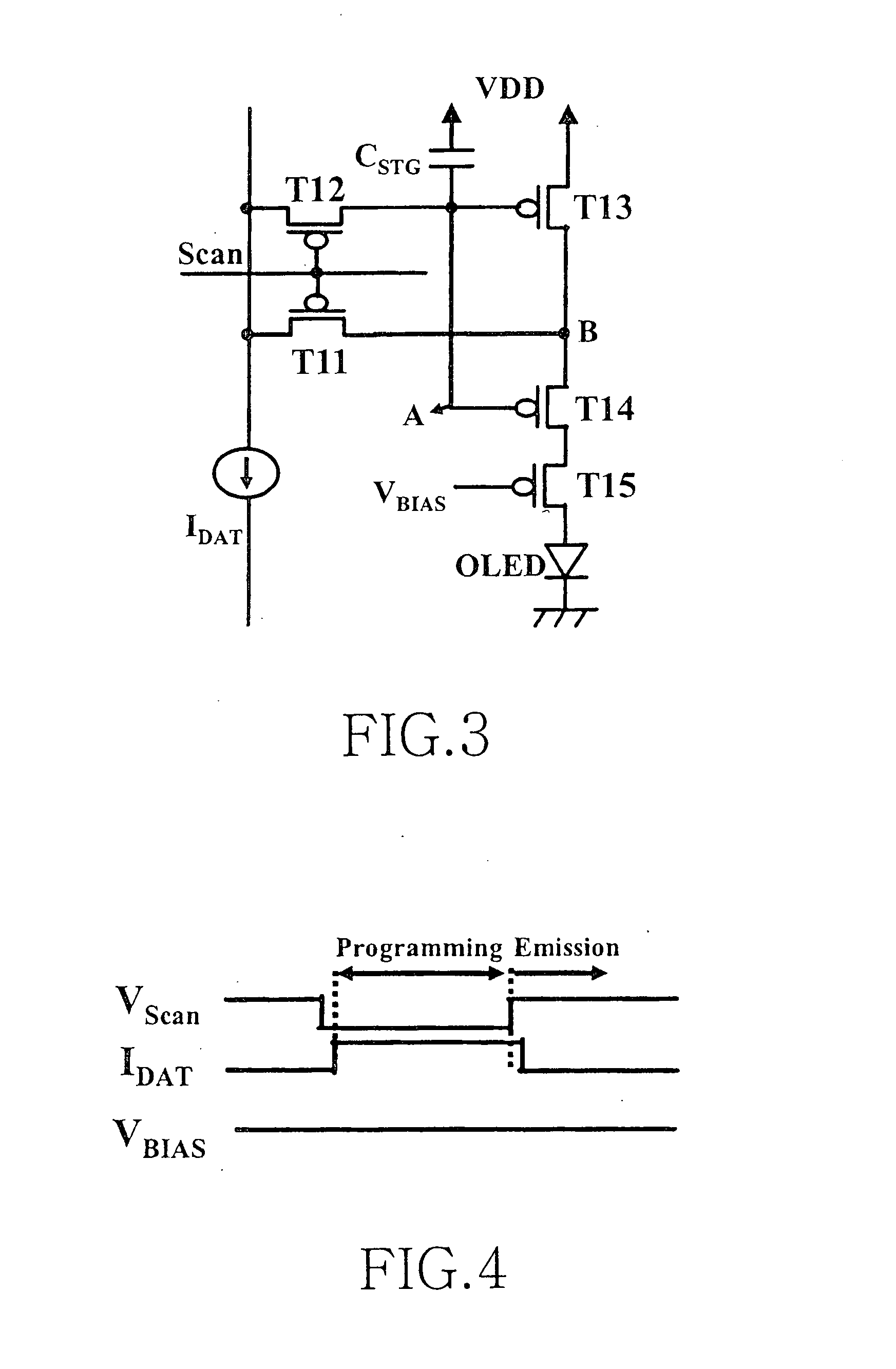
Picture element structure of current programming method type active matrix organic emitting diode display and driving method of data line
ActiveUS20060145989A1Light evenlyIncrease widthStatic indicating devicesActive matrixDevice material
The present invention provides a novel structure of picture elements in current programming-type semiconductor devices, and in particular, the structure of picture elements of an active matrix organic light emitting diode (OLED) display. The device makes a self-compensation for OLED current deviations due to the deterioration in threshold voltage and uneven electric characteristic in thin film transistors. The invention also provides a method for driving a data driver capable of compensating for the uneven electric characteristic of thin film transistors in the driver for driving picture elements in the current programming-type active matrix OLED display device.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Structure for a high output resistance, wide swing charge pump
InactiveUS7701270B2Increase the output resistanceShift in loop bandwidthPulse automatic controlApparatus without intermediate ac conversionAudio power amplifierEngineering
Disclosed are design structures for current sink and source circuits, a charge pump, and a phase locked loop. The current sink and source circuits each have a current mirror that biases a transistor connected to an output node. These circuits each further have a two-stage feedback amplifier to sense the current mirror drain voltage and to control the transistor gate voltage in order to stabilize the current mirror drain voltage independent of output voltage at the output node. The amplifier also increases output resistance at the output node. This configuration allows for a wide operation voltage range and ensures good circuit performance under a very low power supply. A charge pump that incorporates these circuits generates highly matched charging and discharging currents. A PLL that incorporates this charge pump exhibits minimal bandwidth shifts and minimal locking speed and jitter performance degradation.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
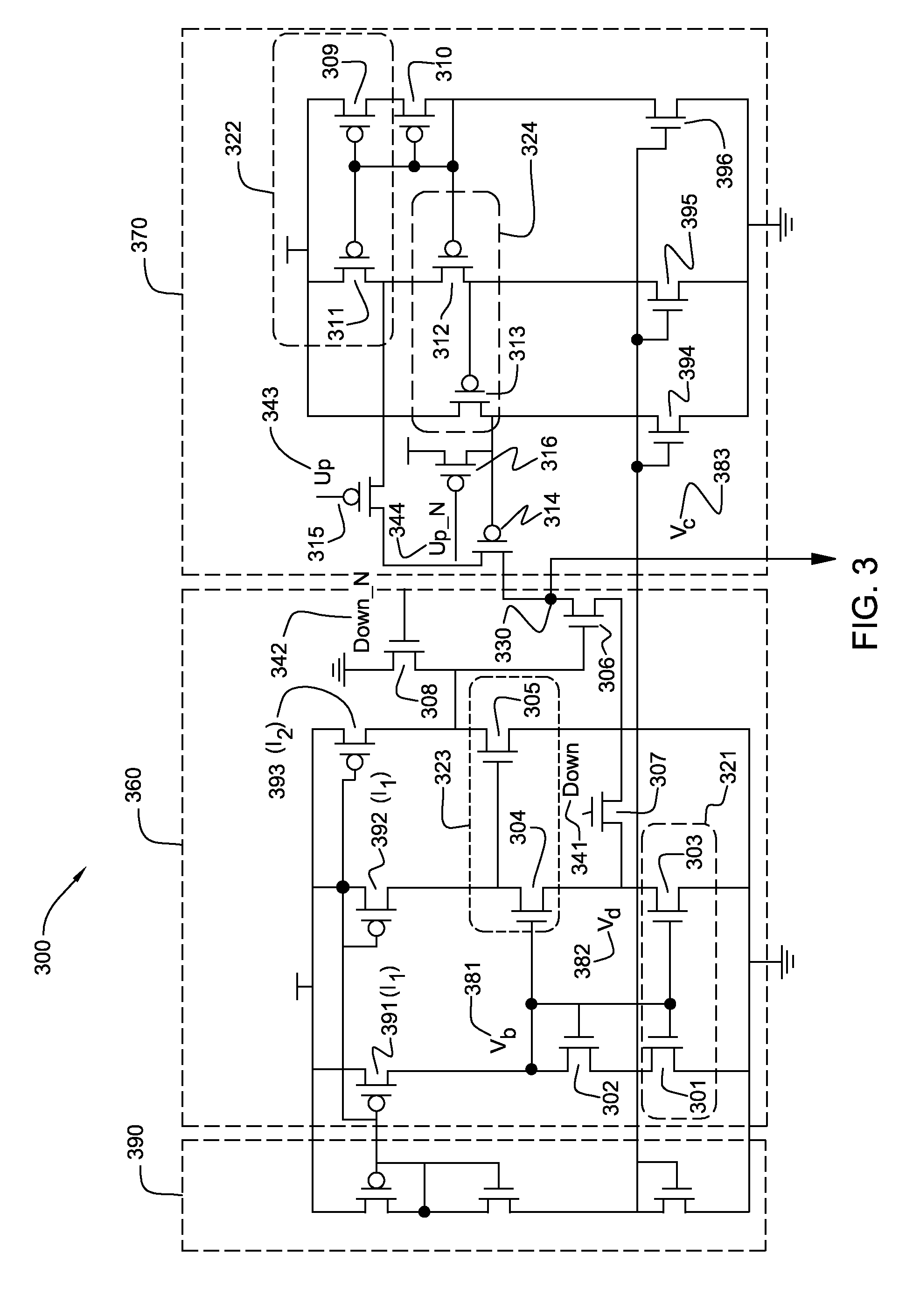
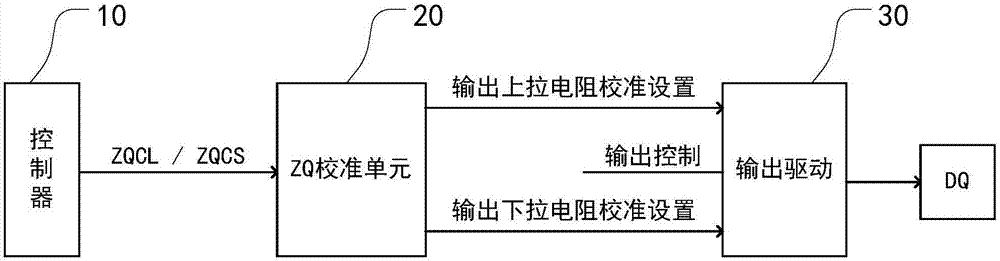
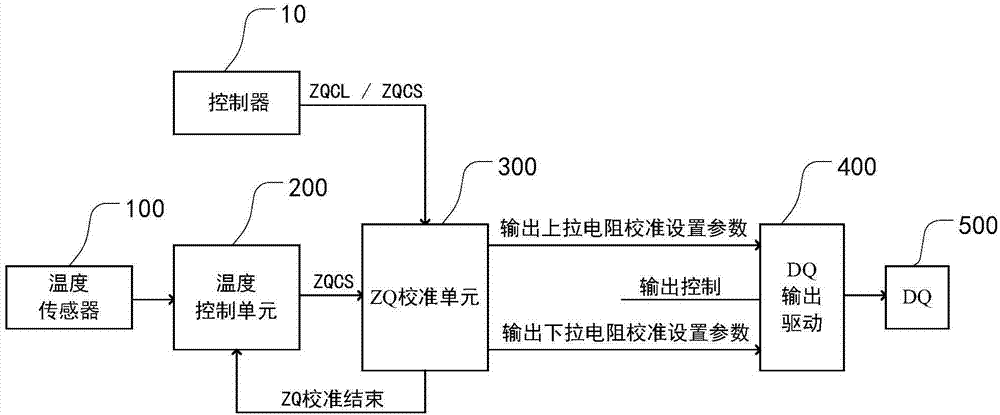
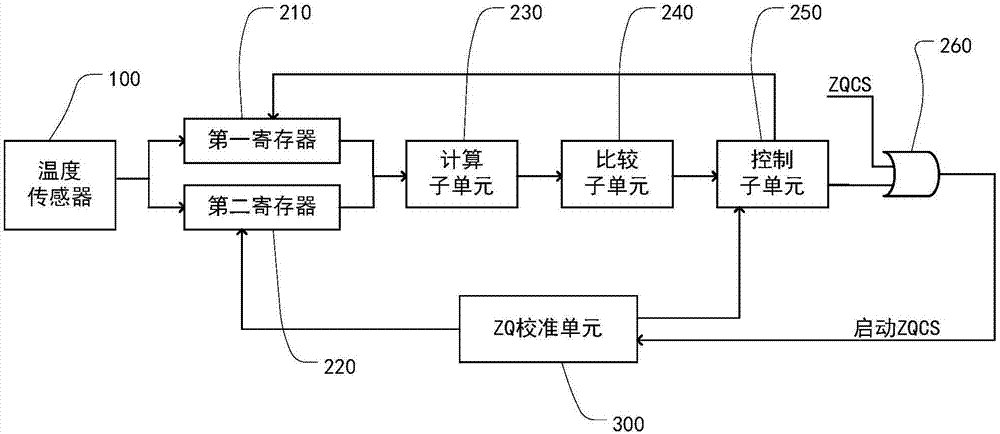
ZQ calibration controller applied to semiconductor memory
The invention provides a ZQ calibration controller applied to a semiconductor memory. The ZQ calibration controller comprises a temperature sensor, a temperature control unit and a ZQ calibration unit, wherein the temperature sensor is used for detecting the temperature of a semiconductor memory; the temperature control unit is used for acquiring and storing a first temperature value and a second temperature value of the semiconductor memory from the temperature sensor, calculating the deviation between the first temperature value and the second temperature value and sending a ZQ calibration starting signal when the deviation exceeds a threshold; and the ZQ calibration unit is used for carrying out ZQ calibration on the semiconductor memory after receiving the ZQ calibration starting signal and sending a ZQ calibration ending signal to the temperature control unit after the ZQ calibration is finished. According to the ZQ calibration controller, by additionally arranging the temperature control unit, the ZQ calibration of the semiconductor memory can be automatically started according to the temperature change of the semiconductor memory, and a resistance value of an output end is improved, so that the integrity of the signal is maintained, the programming burden of the controller is alleviated, the cost is saved, and the power consumption is saved; and an output resistance value of an output port is relatively flexibly and effectively controlled.
Owner:CHANGXIN MEMORY TECH INC
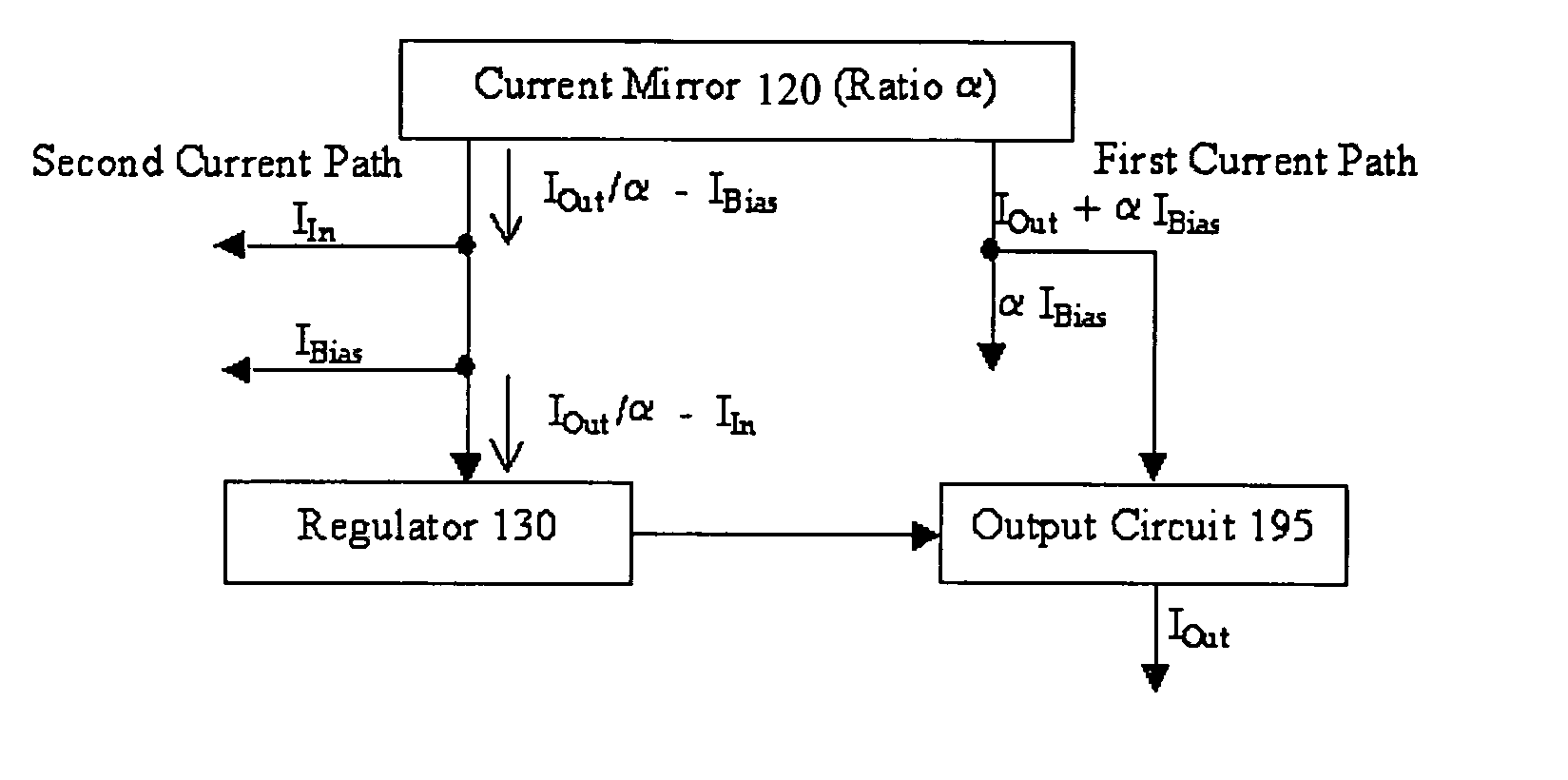
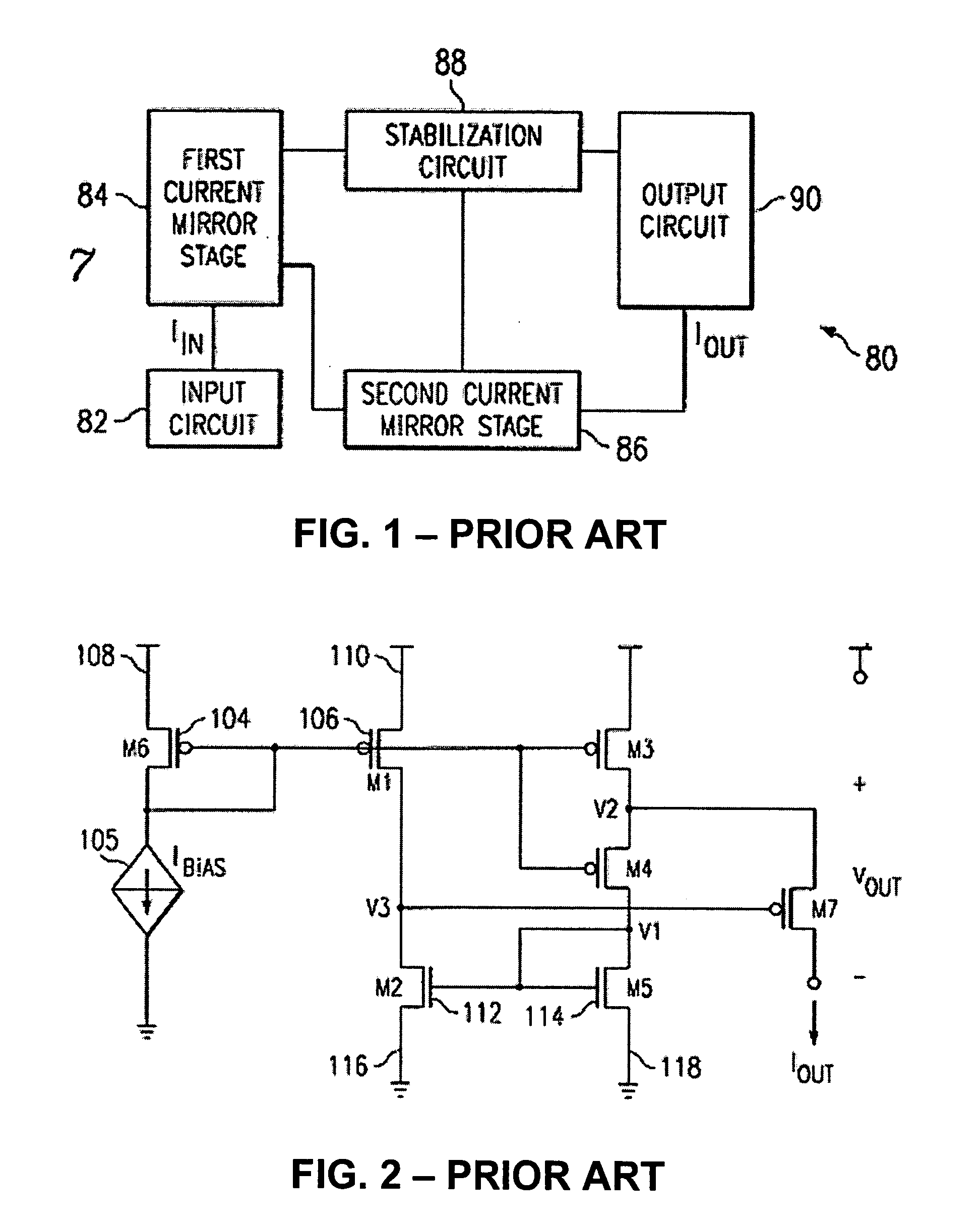
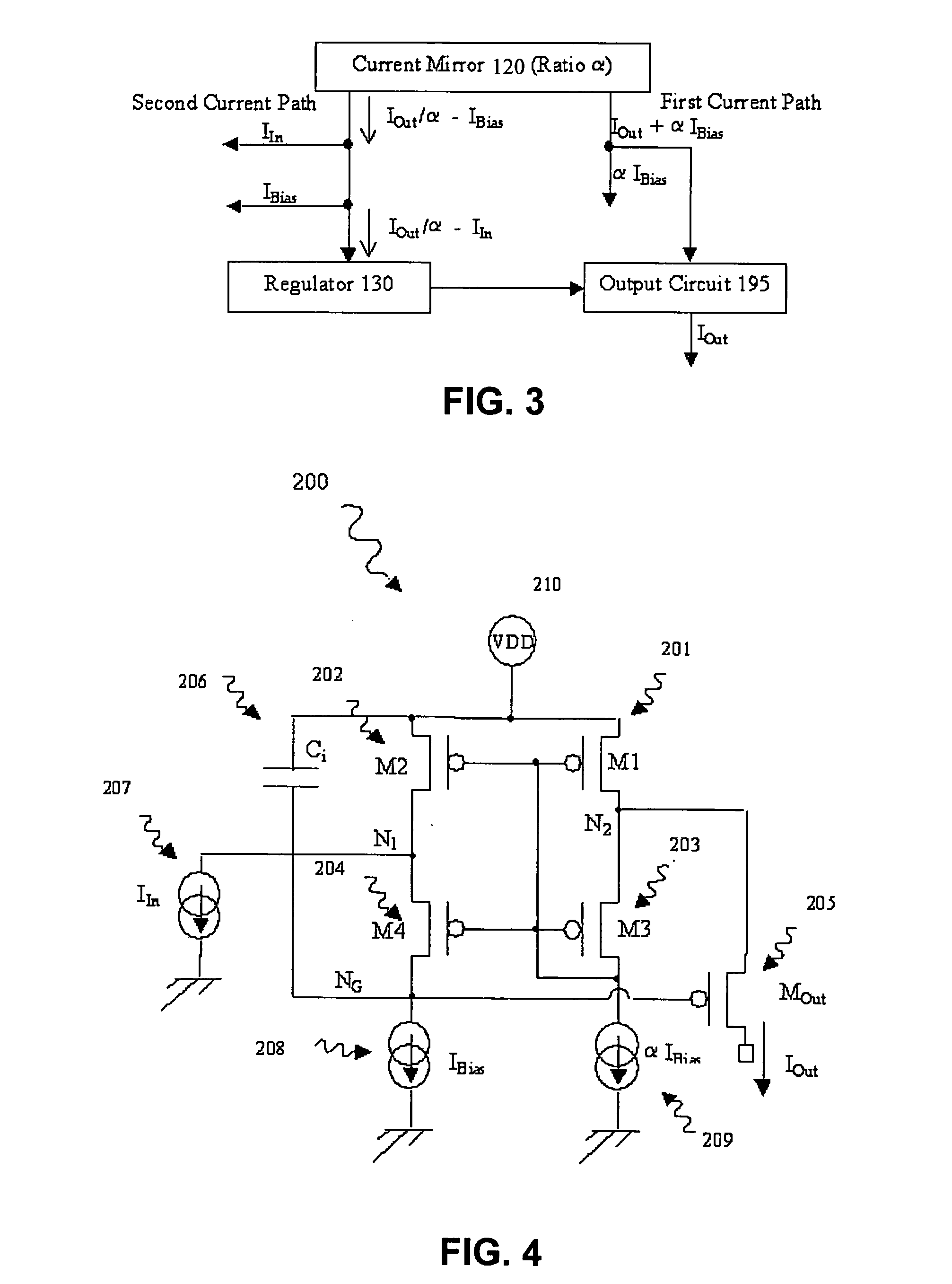
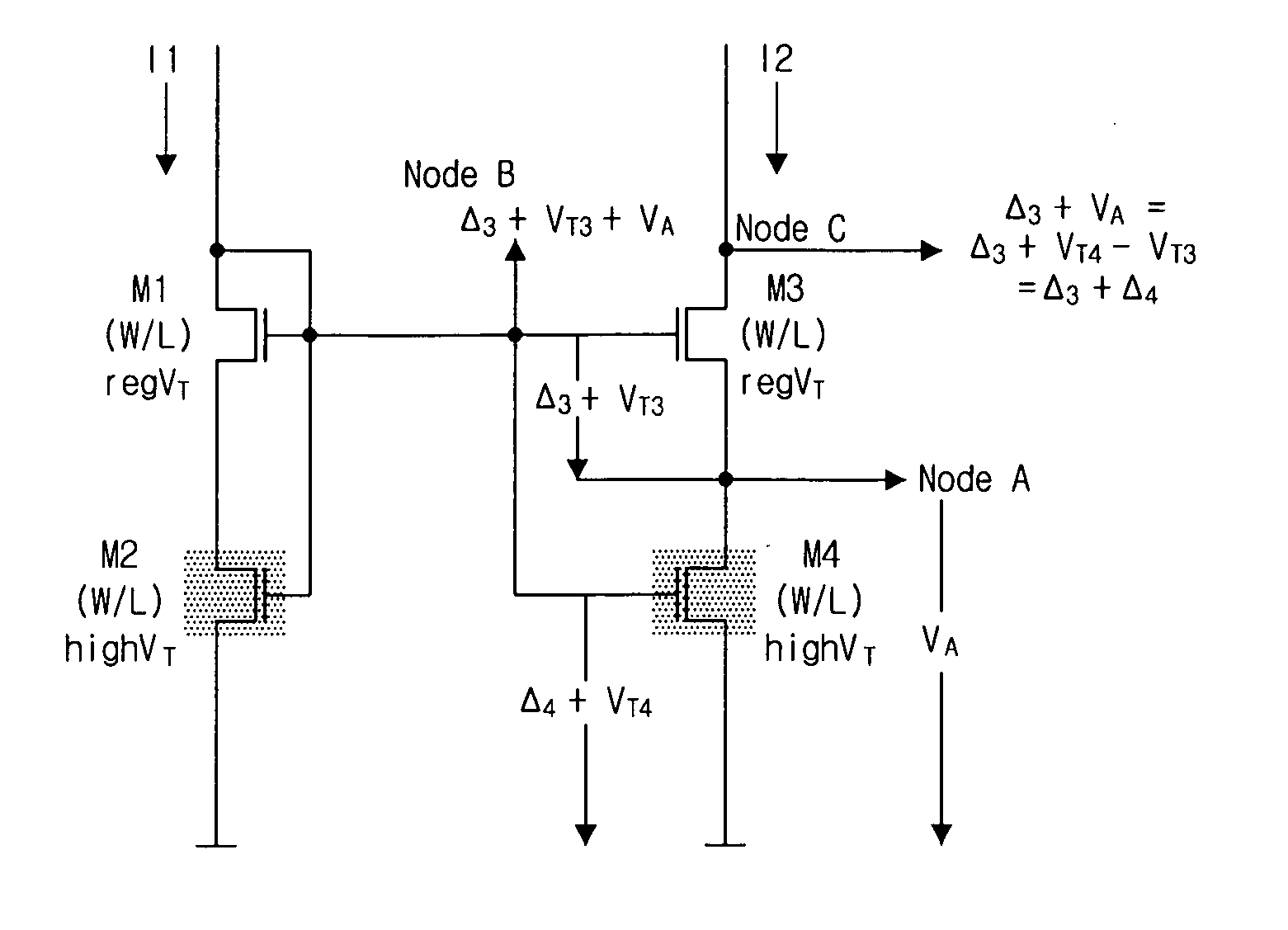
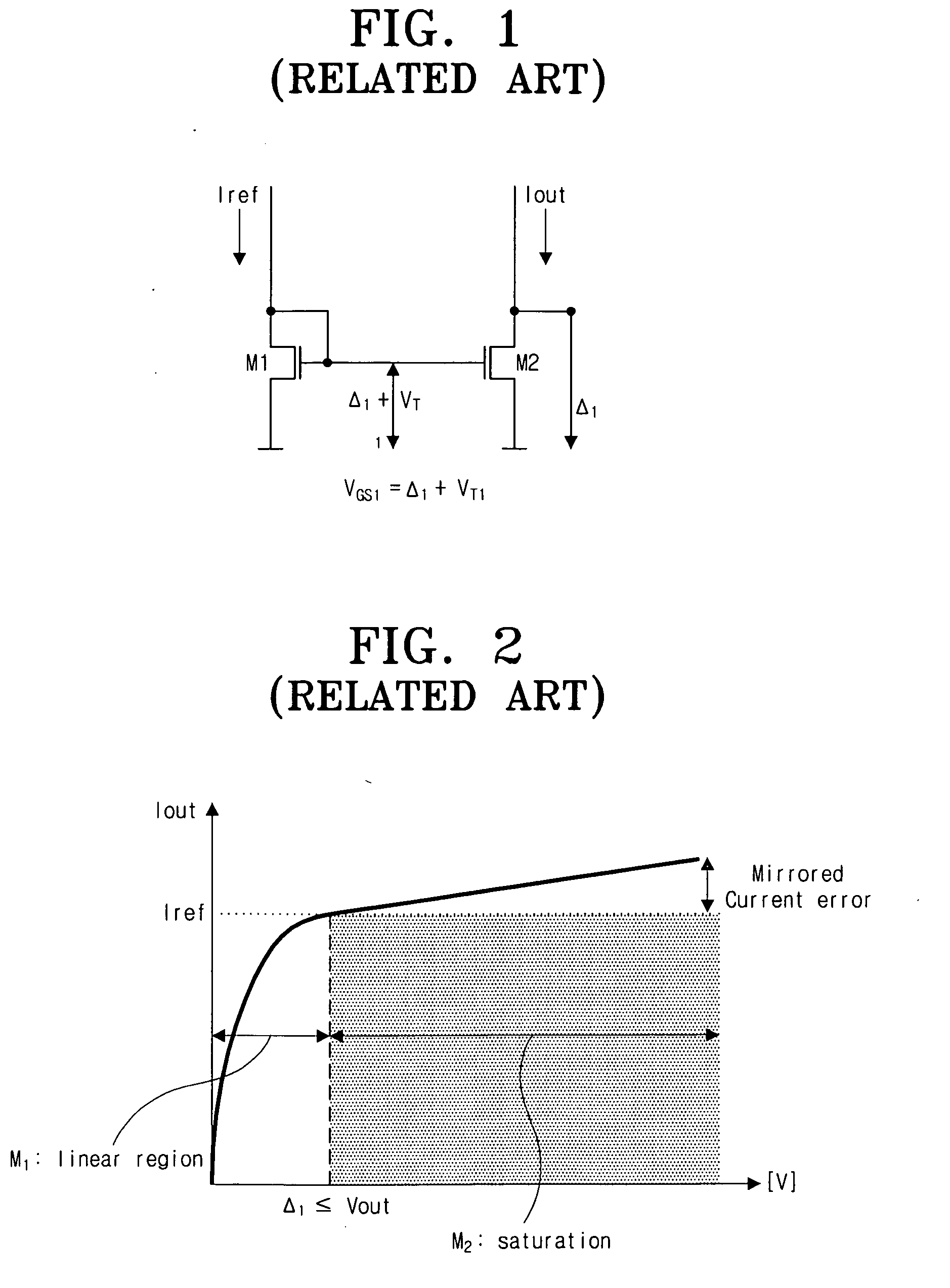
Regulated current mirror
InactiveUS20060113982A1Accurate currentEasy to superviseTransistorMultiple input and output pulse circuitsHigh voltage transistorsHigh pressure
A regulated mirror current source circuit has an output transistor, a regulator for controlling the output circuit, and a current mirror having two or more current paths. The first path of the mirror is coupled in series with a current path of the output circuit, and the second path is coupled to the regulator, to provide feedback. The feedback can provide better precision, or reduced component area. The circuit can include cascode transistors, and the regulator can have integral control. The output transistor gate-source voltage is overdriven to reduce “on” resistance of the output transistor. When the output transistor is a high voltage transistor, its area can be reduced without sacrificing compliance.
Owner:AMI SEMICON BELGIUM
Adaptive series circuit with metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) transistors
ActiveCN102497088AAchieving safe workIncrease the output resistanceDc-dc conversionElectronic switchingLinear regulatorEngineering
The invention discloses an adaptive series circuit with metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) transistors. The on-off motion of a master control MOS transistor is controlled to correspondingly control the adaptive on-off motion of the other MOS transistors, and the MOS transistors are ensured to work safely by utilizing a clamping circuit. The maximum withstand voltage of an equivalent MOS transistor consisting of the MOS transistors is the sum of maximum withstand voltages of all the series-connected MOS transistors. In an actual manufacturing process, limitation on the number of the series-connected MOS transistors is avoided on the premise of not exceeding maximum voltage between the drain of the equivalent MOS transistor and a substrate, so that the limitation of a process on the maximum withstand voltage range of the obtained equivalent MOS transistor is avoided. The adaptive series circuit is applied to places such as a switching regulator and the like requiring quick switching and places such as a light-emitting diode (LED) driving circuit and the like with low requirement for switching speed, and also can be applied to circuits such as a high-voltage step-up regulator, a step-down regulator, a linear regulator and the like.
Owner:SILERGY SEMICON TECH (HANGZHOU) CO LTD
Receiver front-end circuit with external linearity enhanced current mode structure
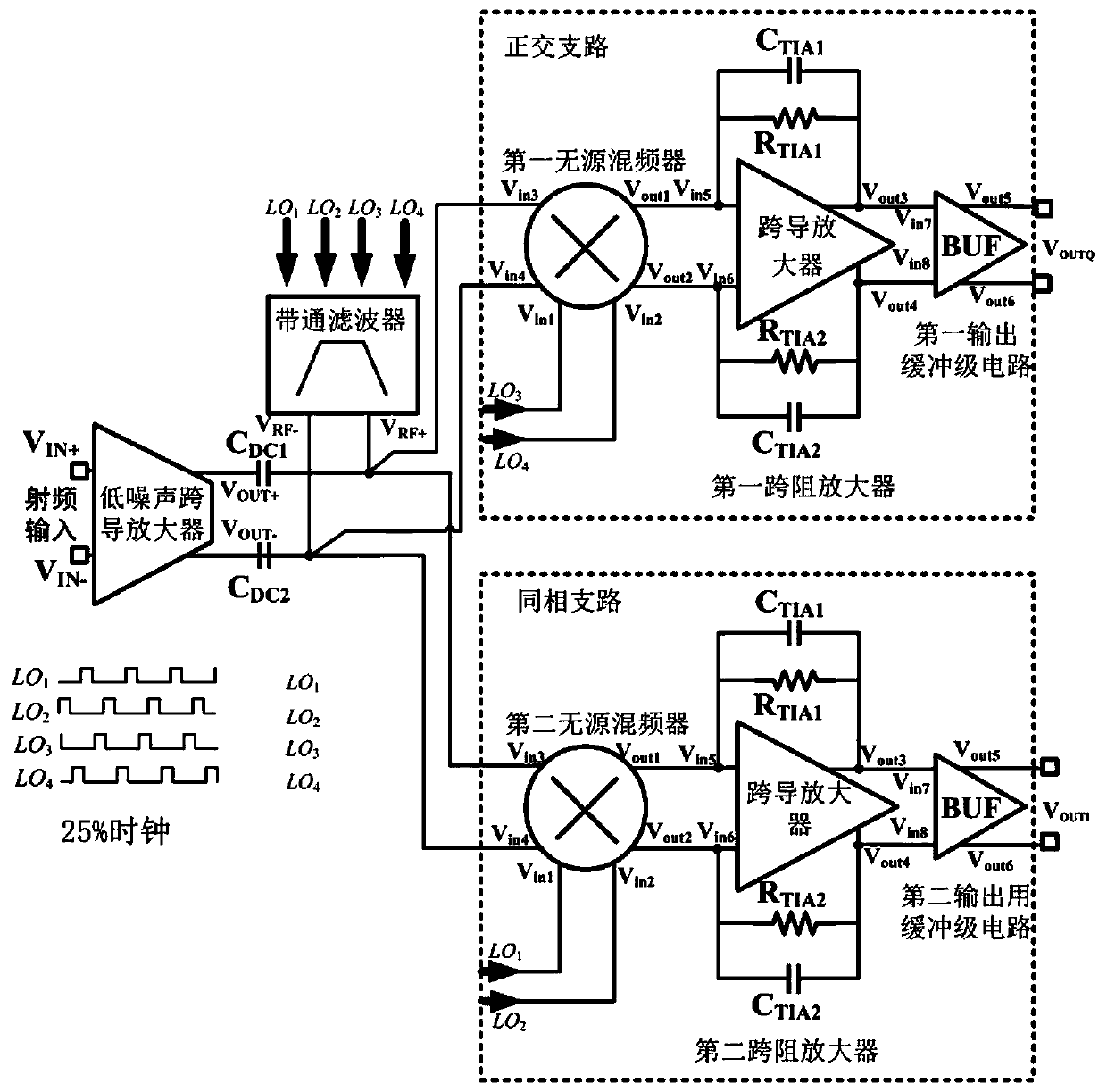
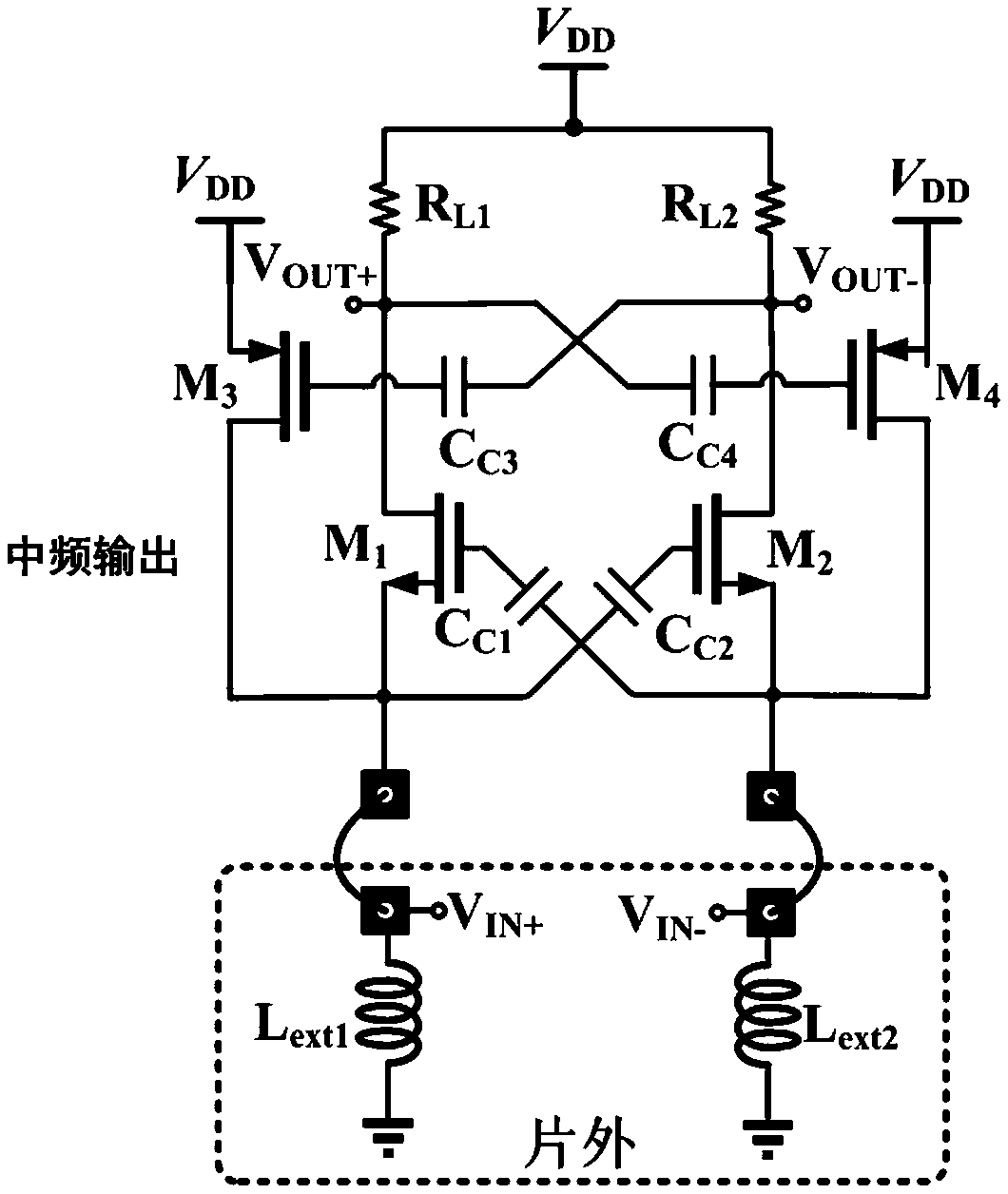
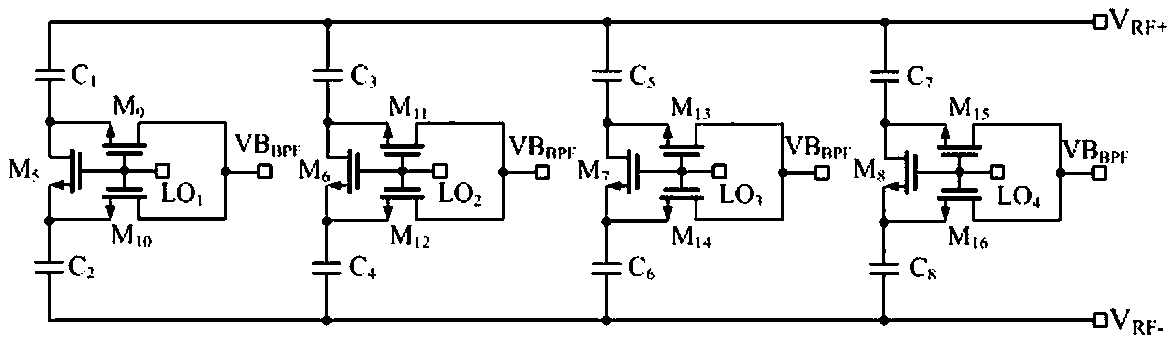
ActiveCN110557130AImprove anti-interference abilityOut-of-band linearity improvementTransmissionAudio power amplifierBand-pass filter
The invention discloses a receiver front-end circuit with an external linearity enhanced current mode structure. The receiver front-end circuit comprises an input low-noise transconductance amplifier,a band-pass filter, a first passive mixer, a first transimpedance amplifier, a first output buffer stage circuit, a second passive mixer, a second transimpedance amplifier and a second output bufferstage circuit. The current mode radio frequency front-end circuit solves the problem that the out-of-band linearity of an existing current mode radio frequency front-end circuit becomes poor.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH +1
Charge pump circuit working at extra low voltage
InactiveCN101710784AImprove matchHigh gainDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationDriving currentAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses a charge pump circuit working at extra low voltage, comprising a common-source common-body body drive current mirror, a first operational amplifier and a second operational amplifier, wherein the common-source common-body body drive current mirror consists of a first N-type MOS tube, a second N-type MOS tube, a third N-type MOS tube, a fourth N-type MOS tube, a first P-type MOS tube, a second P-type MOS tube, a third P-type MOS tube and a fourth P-type MOS tube, the second N-type MOS tube and the fourth N-type MOS tube not only realize the function of pulling down current tubes, but also realizes the function of pulling down the MOS tubes; the second P-type MOS tube and the fourth P-type MOS tube not only realize the function of pulling up the current tubes, but also realizes the function of pulling up the MOS tubes, thereby realizing the parallel connection relation of an MOS switch function and a current mirror function. The goal of increasing gains is achieved through the two operational amplifiers, i.e. the output resistance of the common-source common-body current mirror can be increased under low supply voltage.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
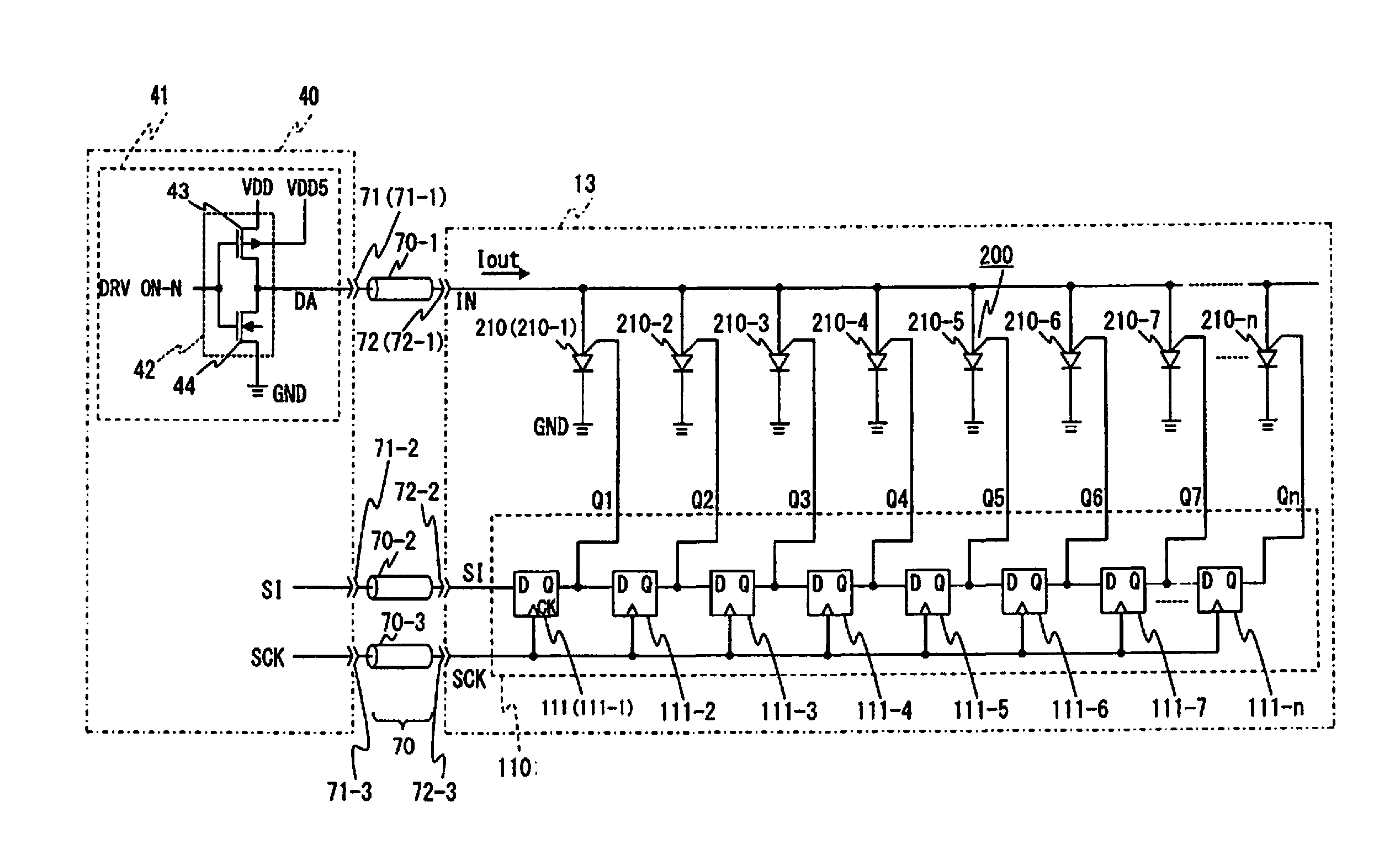
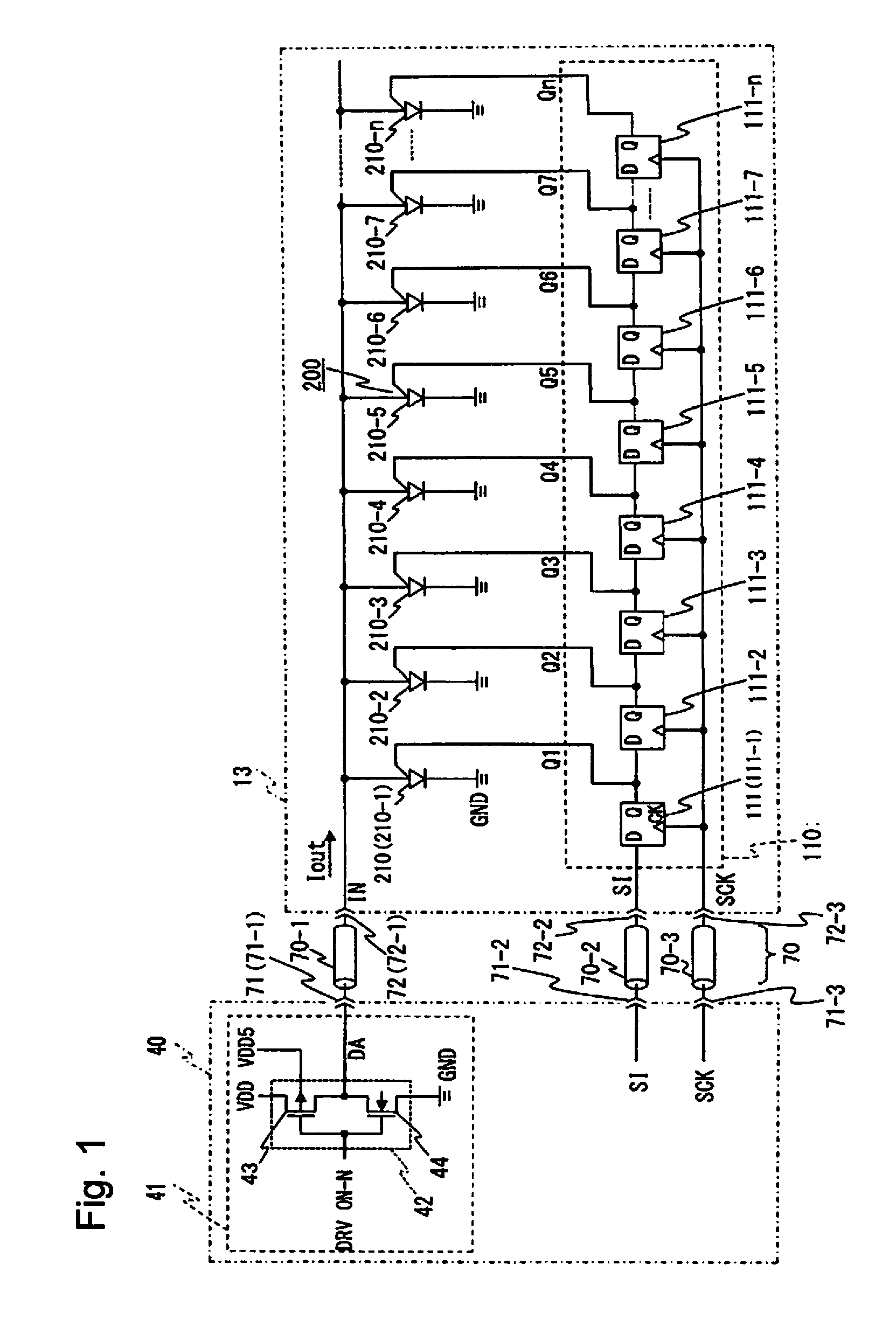
Drive device, print head and image forming apparatus
ActiveUS20110234742A1Increases rising and falling timePreventing high-speed switching controlRecording apparatusElectrical apparatusThreshold voltageDriving circuit
A drive device to drive a plurality of three-terminal light emitting elements, comprising: a drive circuit including a first MOS transistor and configured to drive conducting three-terminal light emitting elements among a plurality of three-terminal light emitting elements based on a received drive signal. The first MOS transistor includes: a third terminal connected to a second power supply having a potential different from a potential of the first power supply; a fourth terminal connected to the second terminals connected in common, a second control terminal configured to control a conduction state between the third terminal and the fourth terminal based on the drive signal; and a substrate terminal set to have a potential different from the potential of the second power supply in a direction of increasing threshold voltage of the first MOS transistor.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
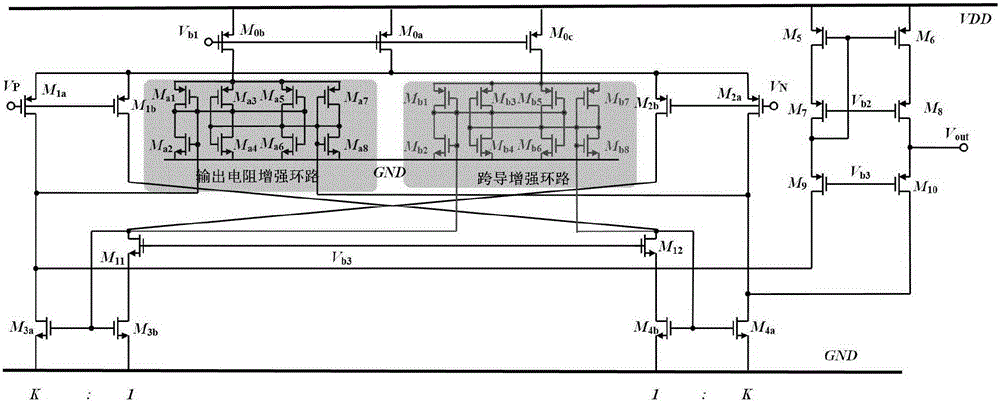
Gain-boosted operational amplifier applicable to TFT-LCD drive circuit
InactiveCN105322897AIncrease the output resistanceIncrease DC GainDifferential amplifiersPositive-feedback-circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierEngineering
The invention relates to large-scale integrated circuits, and aims to boost input transconductance and output resistance of an amplifier, further improve direct current gain of the amplifier and finally realize boost of direct current gain and gain bandwidth product of the amplifier under the condition of same chip area. Therefore, the technical scheme of the invention is a gain-boosted operational amplifier applicable to a TFT-LCD drive circuit. The gain-boosted operational amplifier applicable to the TFT-LCD drive circuit is composed of a Recycling folded cascade amplification stage, an output resistance boosting loop, a transconductance boosting loop and a high swing output stage; differential mode signals Vin- and Vin+ are input through the Recycling folded cascade amplification stage, then, the signals are subjected to the cross positive feedback effect of the output resistance boosting loop stage and the transconductance boosting loop stage and further subjected to current multiplication of a cascade current mirror, and finally, the signals are output to an output end through the high swing output stage. The gain-boosted operational amplifier applicable to the TFT-LCD drive circuit is mainly applied to the large-scale integrated circuits.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Structure for a high output resistance, wide swing charge pump
InactiveUS20090033407A1Increase the output resistanceWide operating voltage rangePulse automatic controlApparatus without intermediate ac conversionHigh resistanceGate voltage
Disclosed are design structures for current sink and source circuits, a charge pump, and a phase locked loop. The current sink and source circuits each have a current mirror that biases a transistor connected to an output node. These circuits each further have a two-stage feedback amplifier to sense the current mirror drain voltage and to control the transistor gate voltage in order to stabilize the current mirror drain voltage independent of output voltage at the output node. The amplifier also increases output resistance at the output node. This configuration allows for a wide operation voltage range and ensures good circuit performance under a very low power supply. A charge pump that incorporates these circuits generates highly matched charging and discharging currents. A PLL that incorporates this charge pump exhibits minimal bandwidth shifts and minimal locking speed and jitter performance degradation.
Owner:IBM CORP
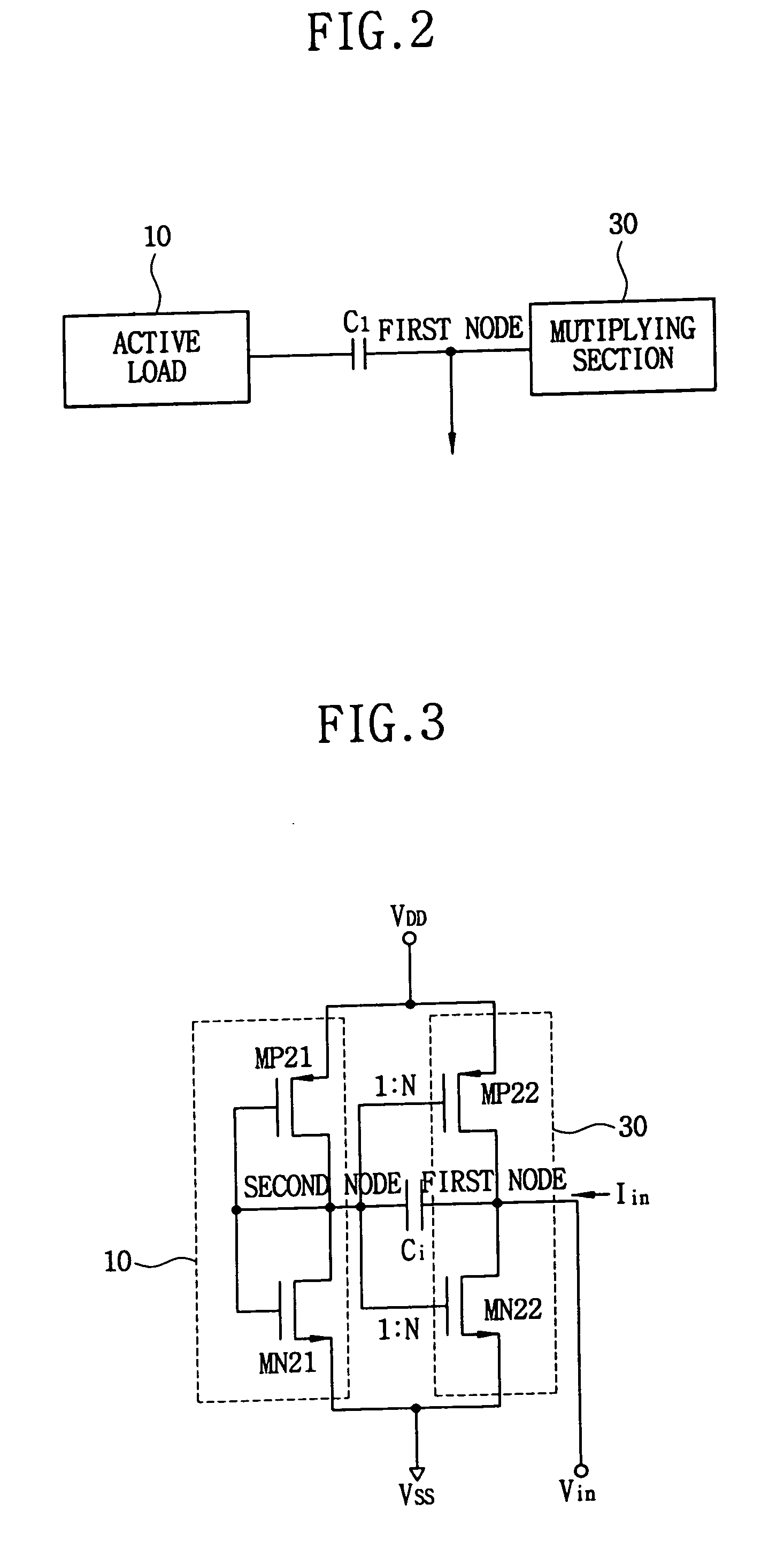
Capacitance multiplier
ActiveUS20050099221A1High bandwidthReduce areaComputations using contact-making devicesNetwork simulating reactancesCapacitanceDischarge efficiency
A capacitance multiplier includes a self-biasing active load for generating a stable bias voltage without a separate current bias. In addition, the capacitance multiplier includes a cascode load within a multiplying section for increasing the output resistance and in turn the charging / discharging efficiency. Furthermore, the capacitance multiplier is implemented with a plurality of multiplying paths to reduce effects of noise for more stable generation of the multiplied capacitance.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Stacked CMOS current mirror using MOSFETs having different threshold voltages
InactiveUS20070109040A1Minimize minimum saturation operating voltageIncrease the output resistanceElectric variable regulationMOSFETOxide semiconductor
A stacked CMOS current mirror using metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) having different threshold voltages is disclosed. The stacked CMOS current mirror includes a first MOSFET having a drain and a gate which are connected to an input current terminal, a second MOSFET having a drain connected to a source of the first MOSFET, a gate connected to the drain and the gate of the first MOSFET, and a source connected to ground, a third MOSFET having a drain connected to an output current terminal and a gate connected to the drain and the gate of the first MOSFET and the gate of the second MOSFET, and a fourth MOSFET having a drain connected to a source of the third MOSFET, a gate connected to the drain and the gate of the first MOSFET, the gate of the second MOSFET and the gate of the third MOSFET, and a source connected to the ground.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Transconductance amplifier adopting signal attenuation technology and method
PendingCN106411273AImprove anti-interference abilityReduce consumptionAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionDifferential amplifiersUltrasound attenuationAudio power amplifier
The invention relates to a transconductance amplifier adopting the signal attenuation technology and a method. The transconductance amplifier comprises differential input-stage input voltages Vin+ and Vin-, and differential input currents are generated. Power voltage VDD is accessed to a signal attenuation circuit, signal attenuation is carried out on the differential input currents, and a current attenuation signal is generated. The power voltage VDD has access to a bias current source, communication is carried out according to the current attenuation signal, and bias currents are output to a first current mirror and a second current mirror. The first current mirror and the second current mirror both copy the bias currents, and copied currents are generated to be transmitted to a third current mirror. The unity-gain bandwidth is increased through the third current mirror, gain amplification is carried out on the copied currents, and an amplifying signal Iout is output. Compared with the prior art, the influence between input and output voltages is low, no additional pole is introduced, and high linearity, high gain and high-precision amplification are achieved.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
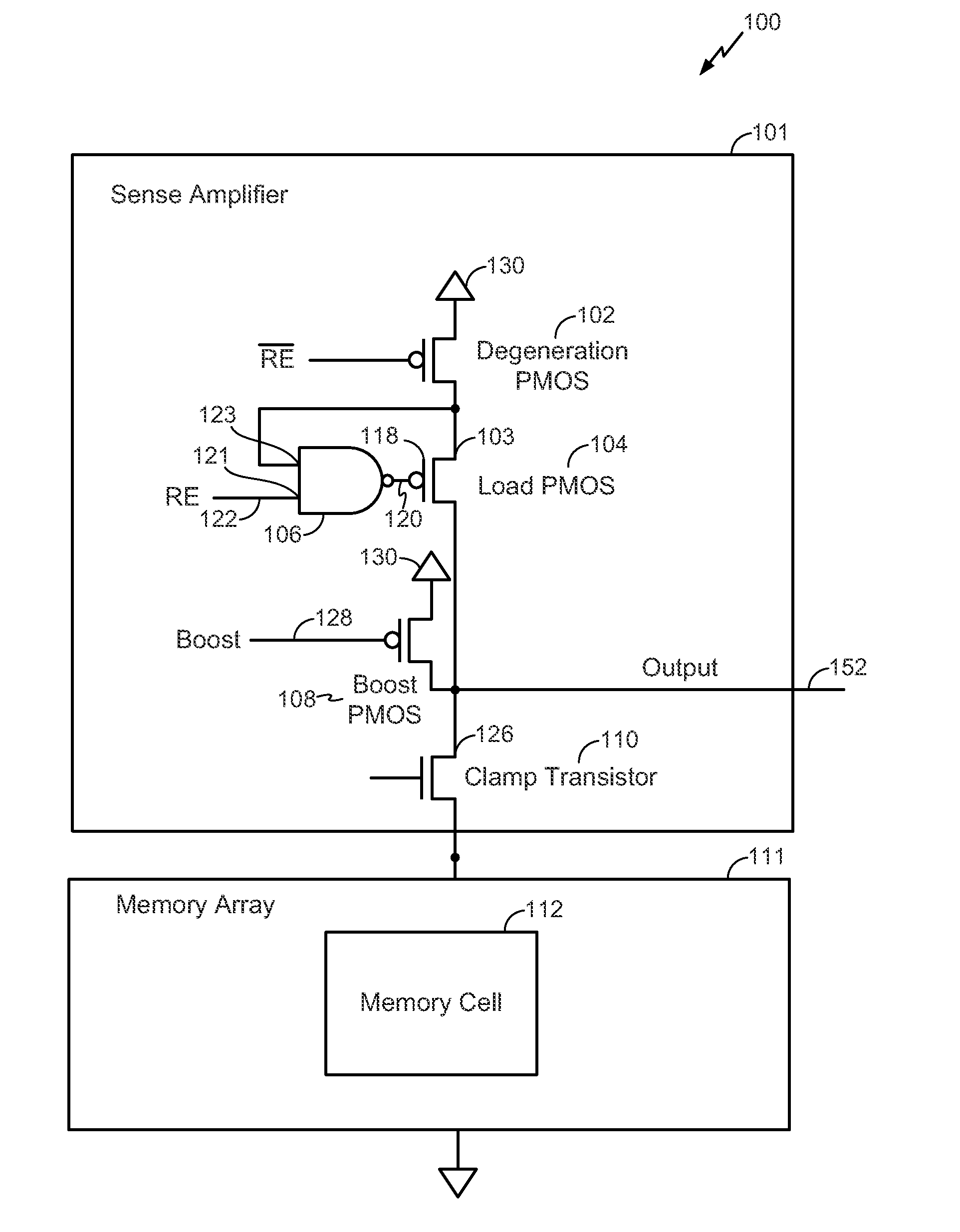
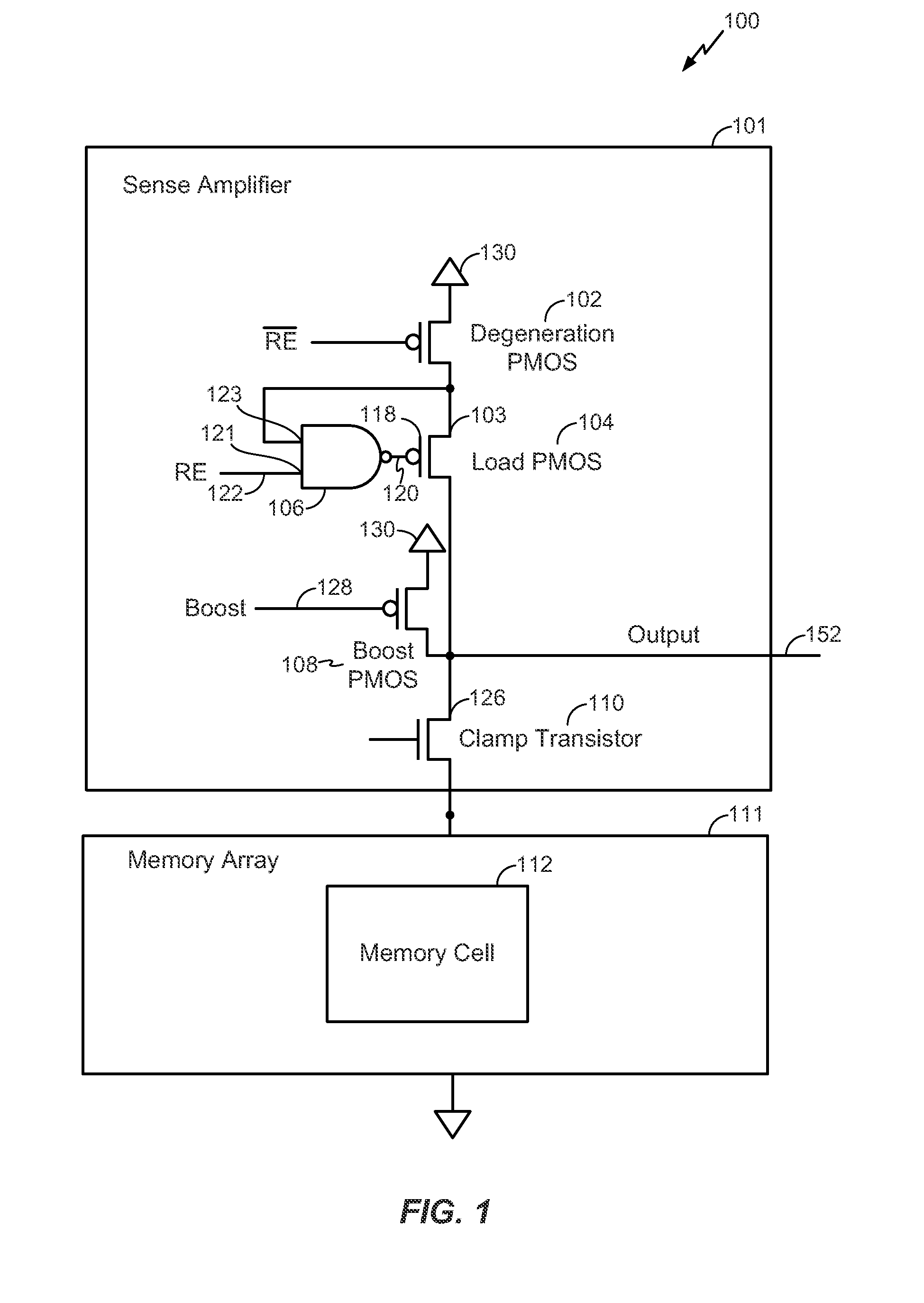
Sensing circuit
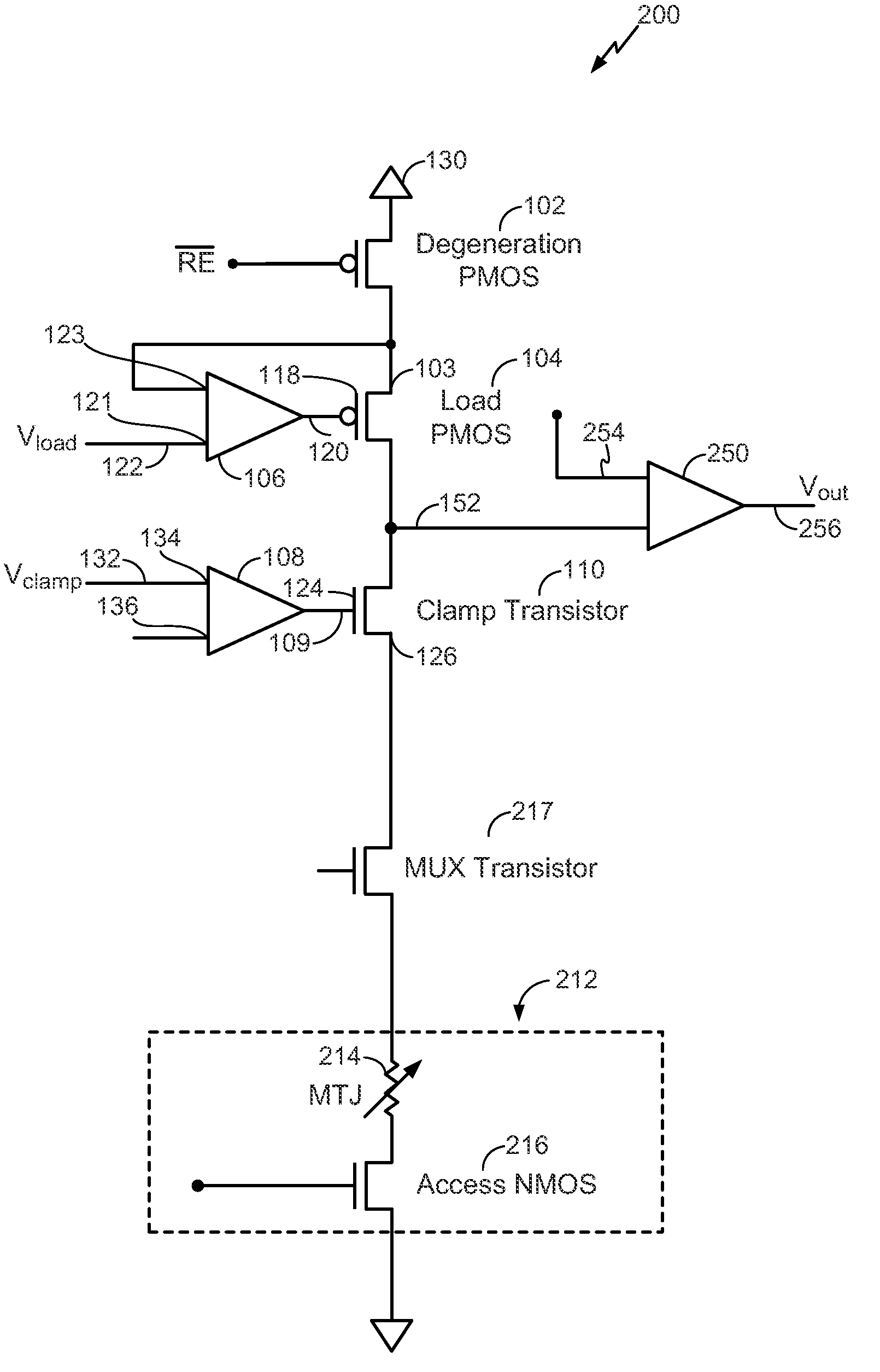
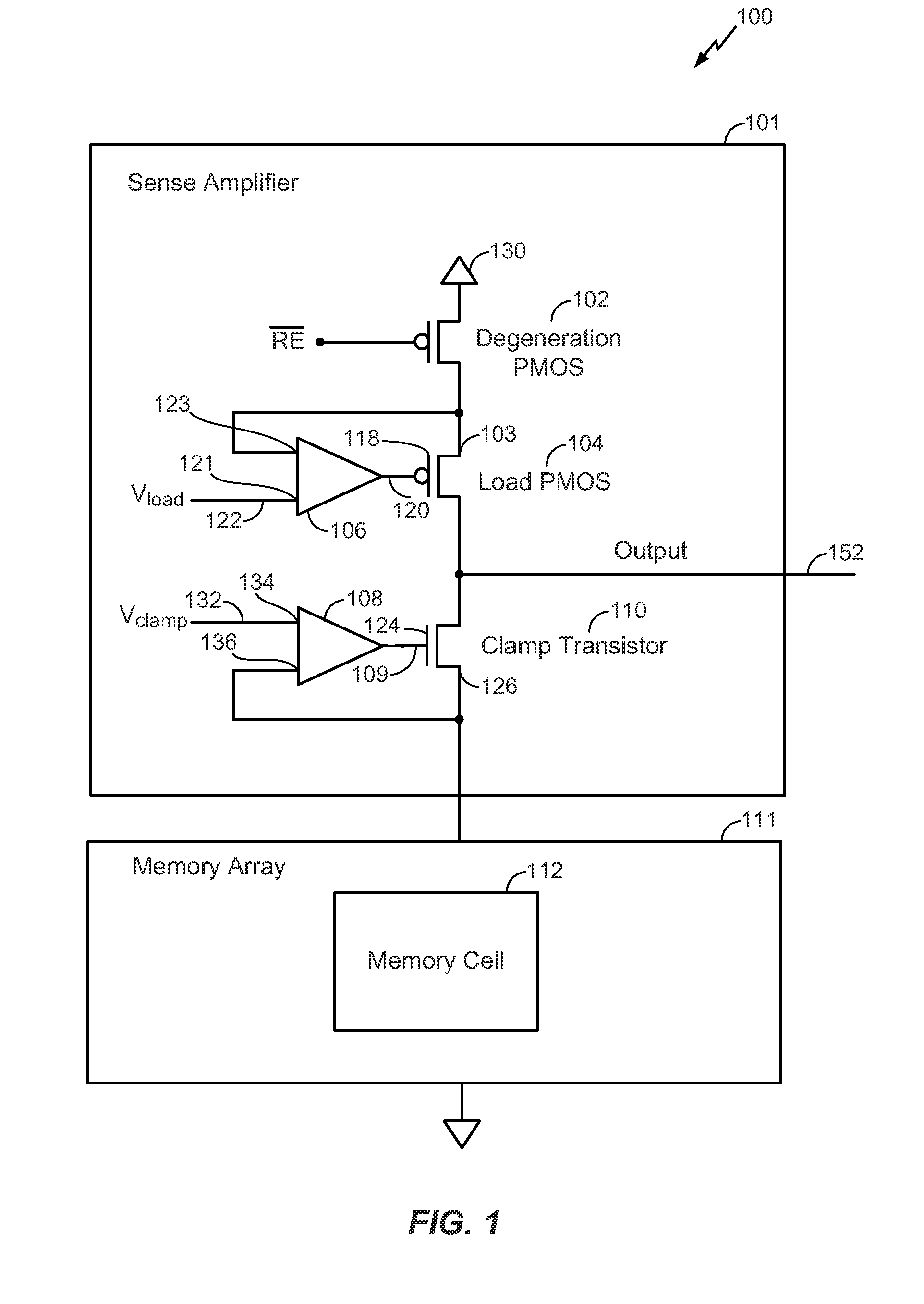
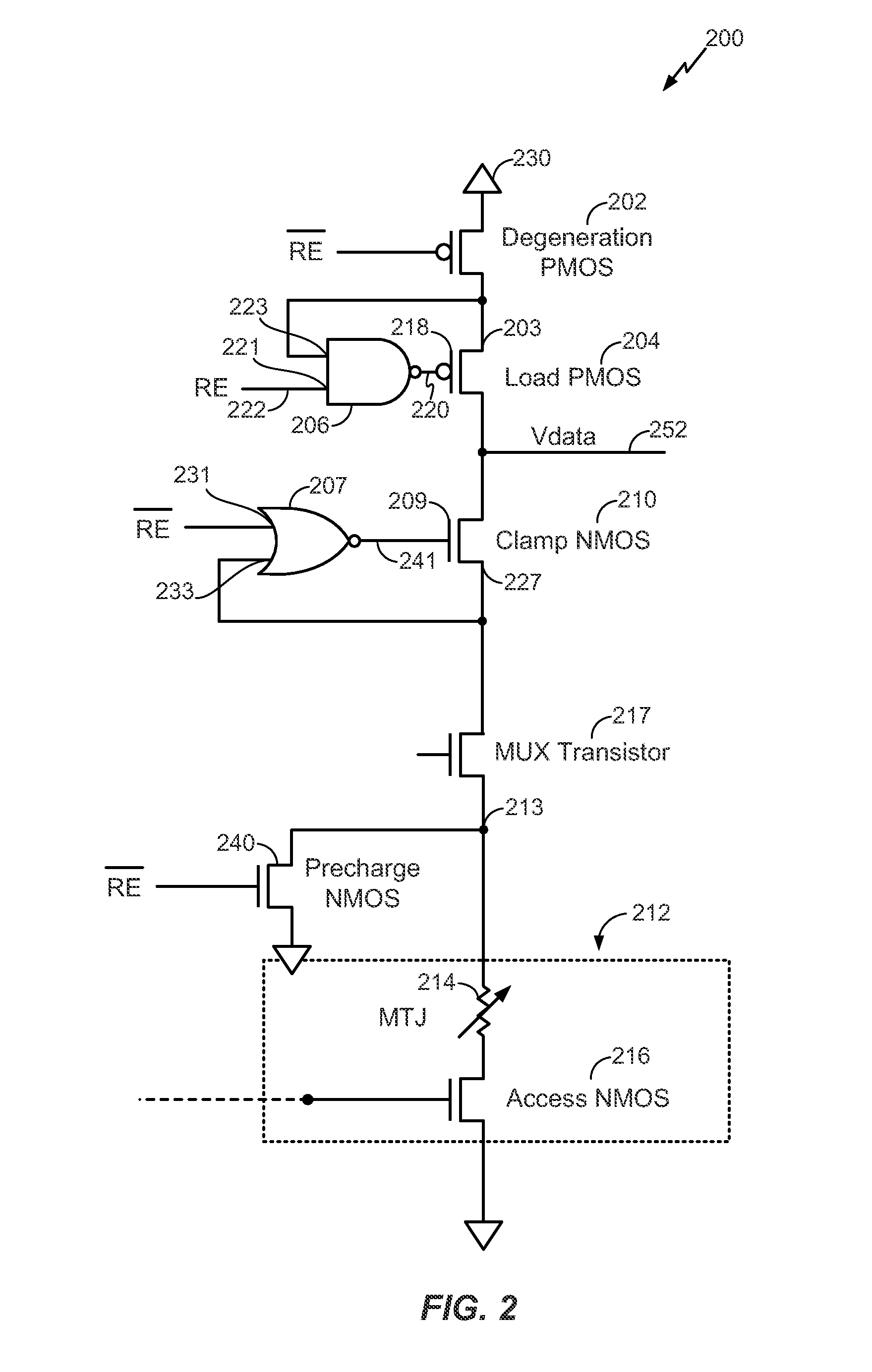
ActiveUS20130002352A1Increase the output resistanceEnhanced sensing marginRead-only memoriesDigital storageAudio power amplifierEngineering
A circuit includes a degeneration p-channel metal-oxide-semiconductor (PMOS) transistor, a load PMOS transistor, and a clamp transistor configured to clamp a voltage applied to a resistance based memory element during a sensing operation. A gate of the load PMOS transistor is controlled by an output of an operational amplifier.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC +1
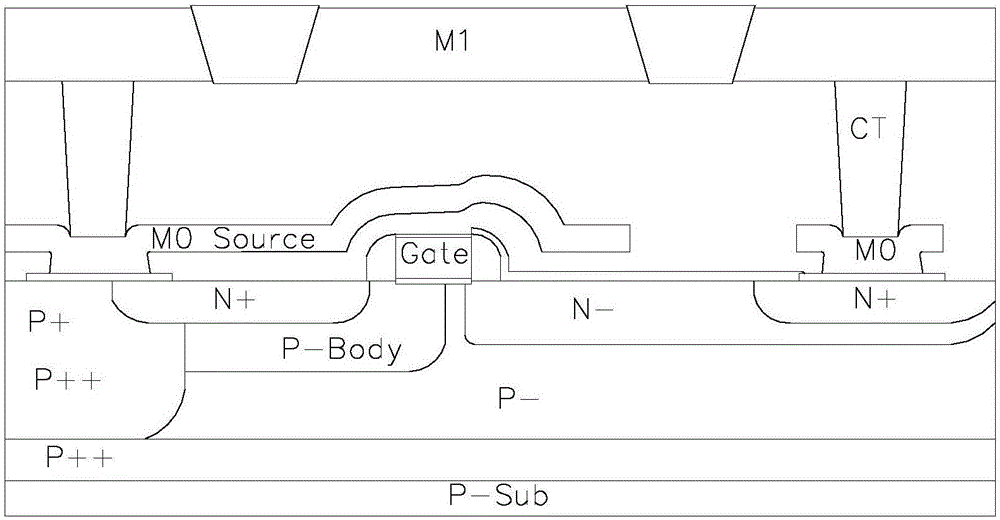
LDMOS with low conduction resistance and relatively low total gate charge and preparation method for LDMOS
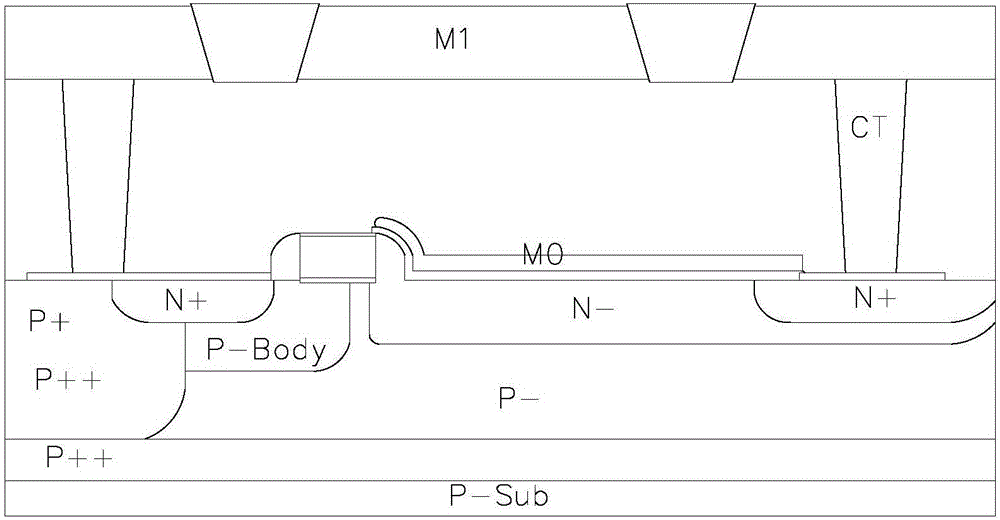
InactiveCN106684150ANot affectedGate Signal Width ReducedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLDMOSCapacitance
The invention provides an LDMOS with low conduction resistance and relatively low total gate charge. The LDMOS comprises a source, a gate, a drain and a metal shielding layer, wherein the metal shielding layer comprises a first metal shielding layer crosses over the upward side of the gate; one end of the first metal shielding layer is positioned below and in contact with the source while a certain distance is formed between the other end of the first metal shielding layer and the drain; the thickness of an insulating dielectric layer between the first metal shielding layer and the gate is used for adjusting the value of a coupling capacitance; and the distance between the other end of the first metal shielding layer and the drain is used for adjusting an electric field between the source and the drain. The technological steps provided by the invention are compatible with a standard CMOS process, an extra mask and a special machine platform are not required; instead, only the ILD thickness and the extension distances of different metal shielding layers M0 need to be adjusted through the process, so that the coupling capacitance is formed between the metal shielding layer and the oxide or silicon nitride SiN and other mediums of the drain; and therefore, different drain electric field coupling is realized, the gate is protected from high voltage impact, and optimization of different voltage devices is realized.
Owner:西安阳晓电子科技有限公司
Sensing circuit
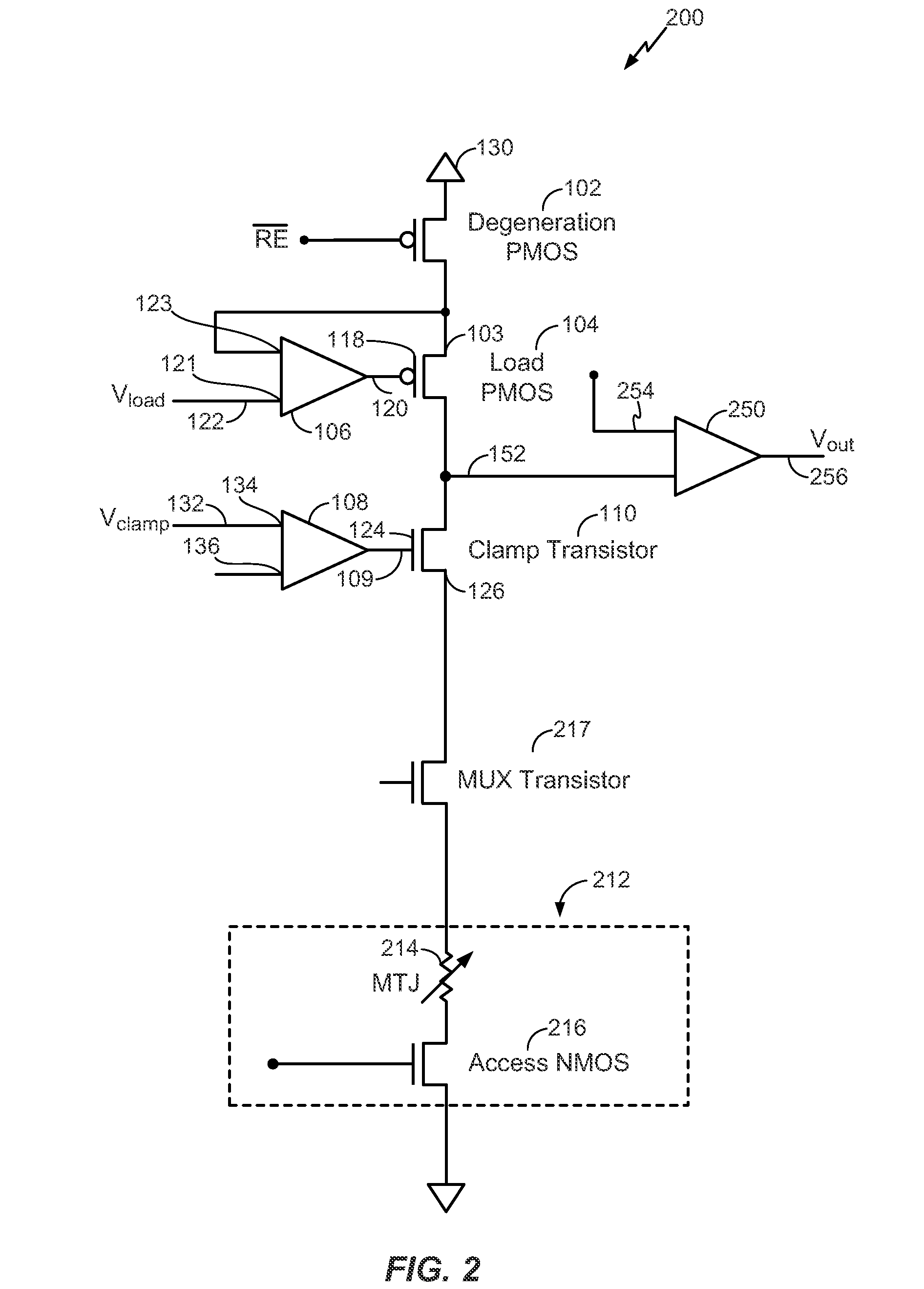
ActiveUS20130003447A1Increase resistanceSensing margin of the sensing circuit may be enhancedPulse automatic controlRead-only memoriesP channelOxide semiconductor
A circuit includes a degeneration p-channel metal-oxide-semiconductor (PMOS) transistor, a load PMOS transistor, and a clamp transistor configured to clamp a voltage applied to a resistance based memory element during a sensing operation. A gate of the load PMOS transistor is controlled by an output of a not-AND (NAND) circuit.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC +1
Constant voltage source with output current limitation
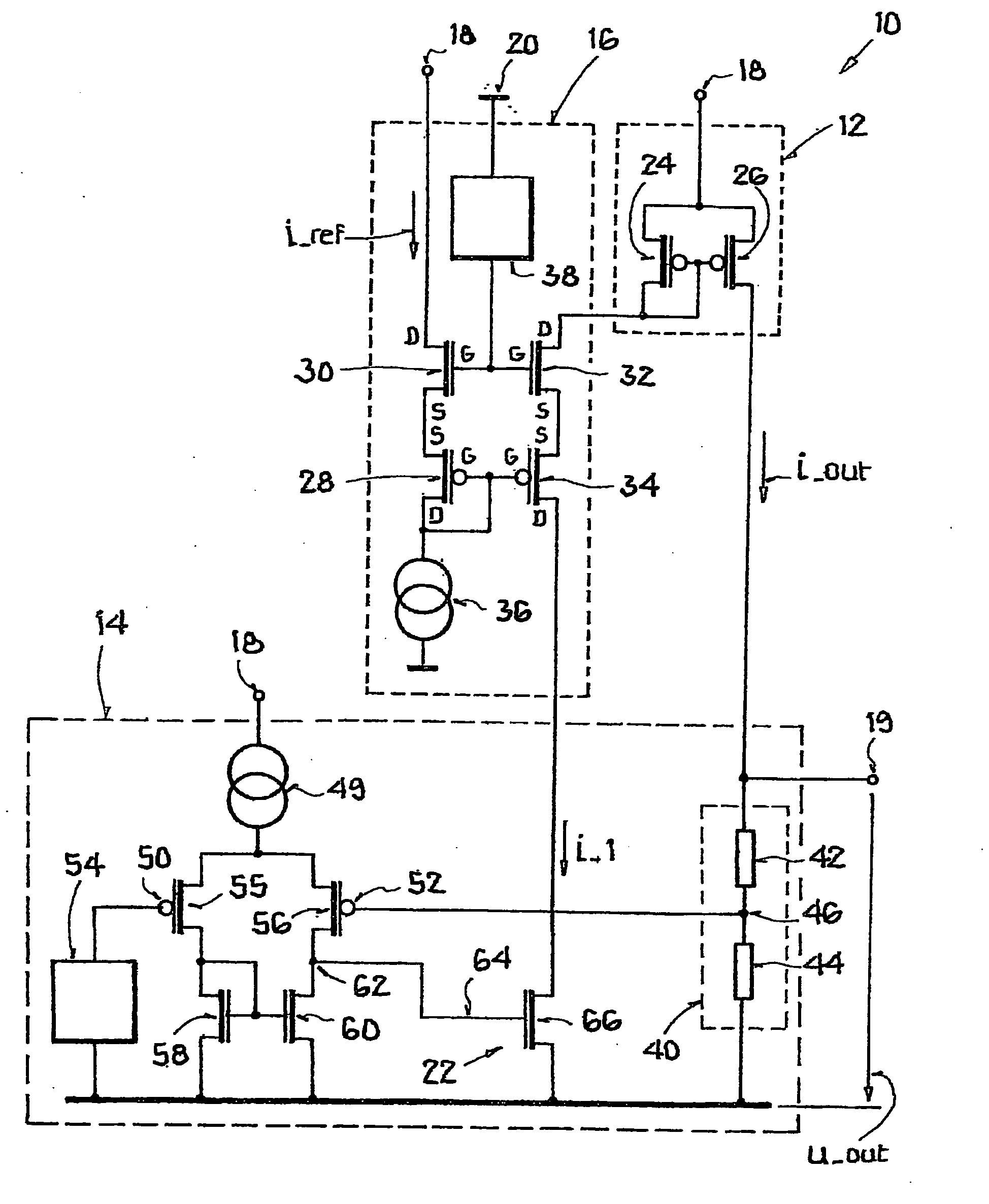
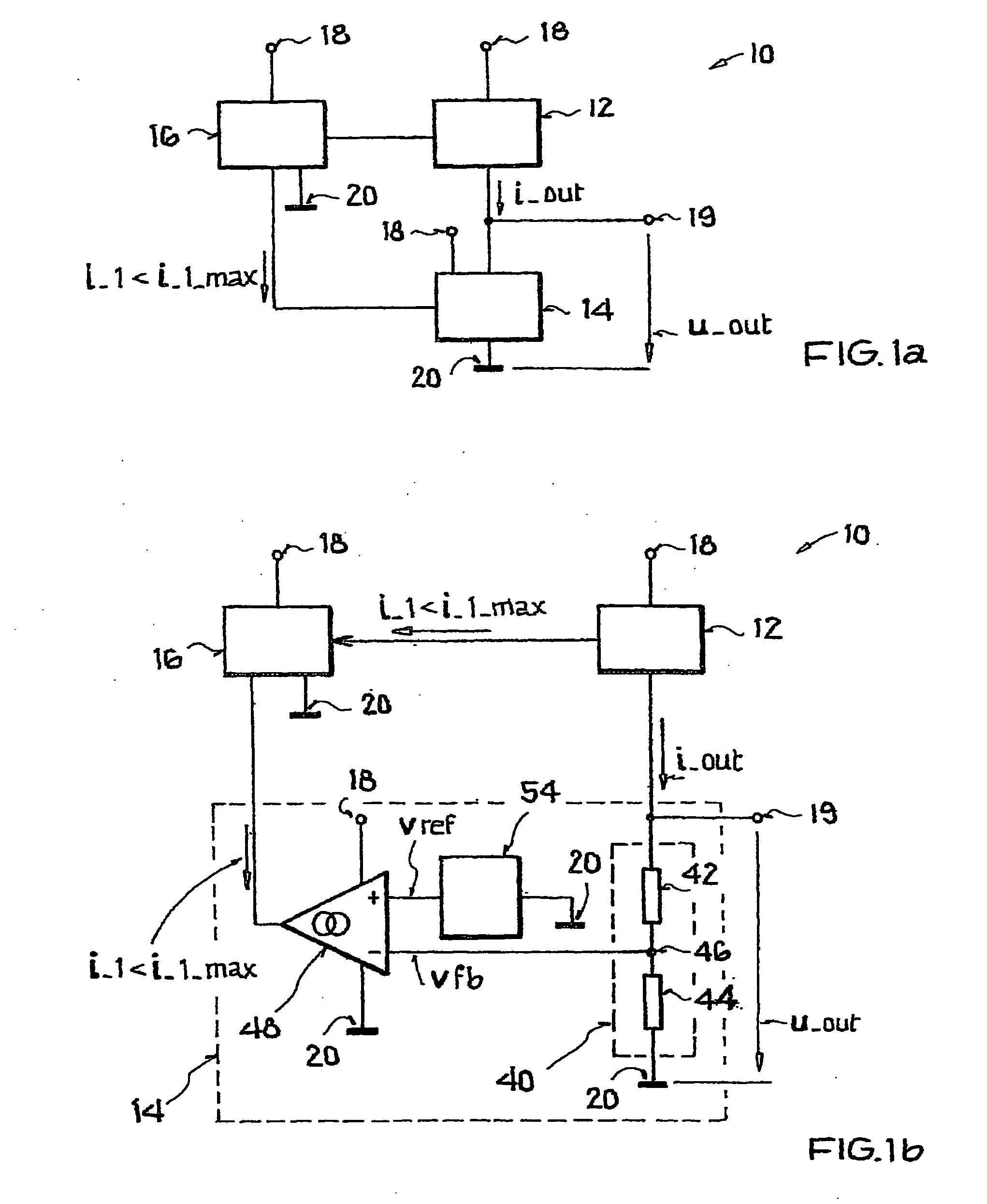
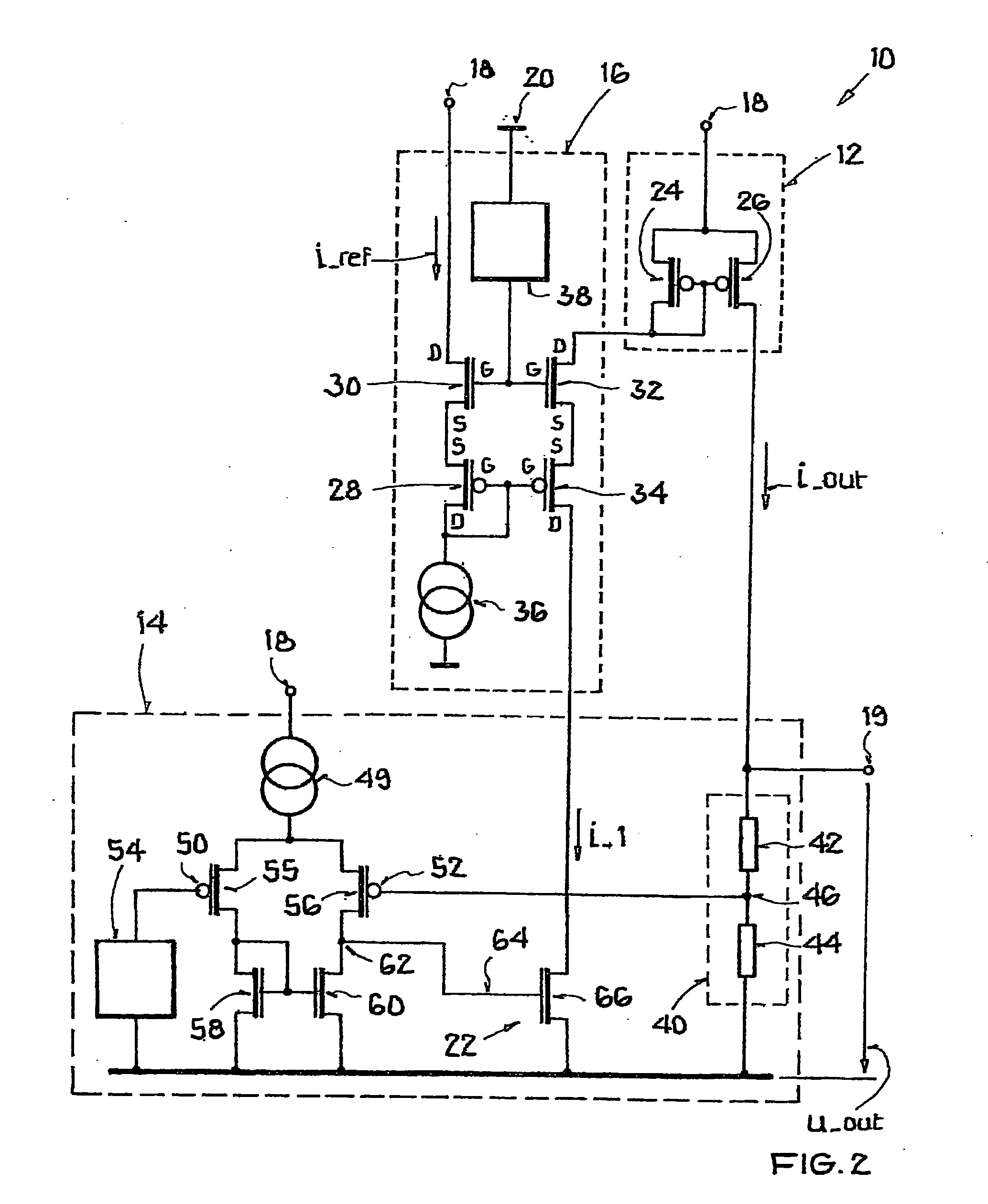
ActiveUS20070132441A1High inputHigh supplyElectric variable regulationCurrent limitingControl signal
A constant voltage source is disclosed having an output current control element, which adjusts an output voltage of the constant voltage source by varying its output current, a control circuit, which acquires a measure for an actual value of the output voltage and processes it to a control signal for the control of the output current control element, and a limiting circuit, which limits the output current to a predefined maximum value by action on the control signal, whereby the limitation is independent of an actual value of the output current. Wherein the limiting circuit has a first pair comprising a first transistor and a second transistor and a second pair comprising a third transistor and a fourth transistor, whereby the first and fourth transistor belong to a first conductivity type, the second and third transistor belong to a second conductivity type, operating current paths of the first pair lie in series between a reference current source and a supply potential, the operating current paths of the second pair are integrated in series into the control branch, control terminals of transistors of the same type are connected to one another, control terminals of transistors of the first conductivity type are connected to the reference current source, and control terminals of transistors of the second conductivity type to a first voltage source. Further, a method for generating a load-independent constant output voltage is disclosed.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
A receiver front-end circuit with current mode structure with enhanced out-of-band linearity
ActiveCN110557130BImprove anti-interference abilityOut-of-band linearity improvementTransmissionLow noiseNoise (radio)
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH +1
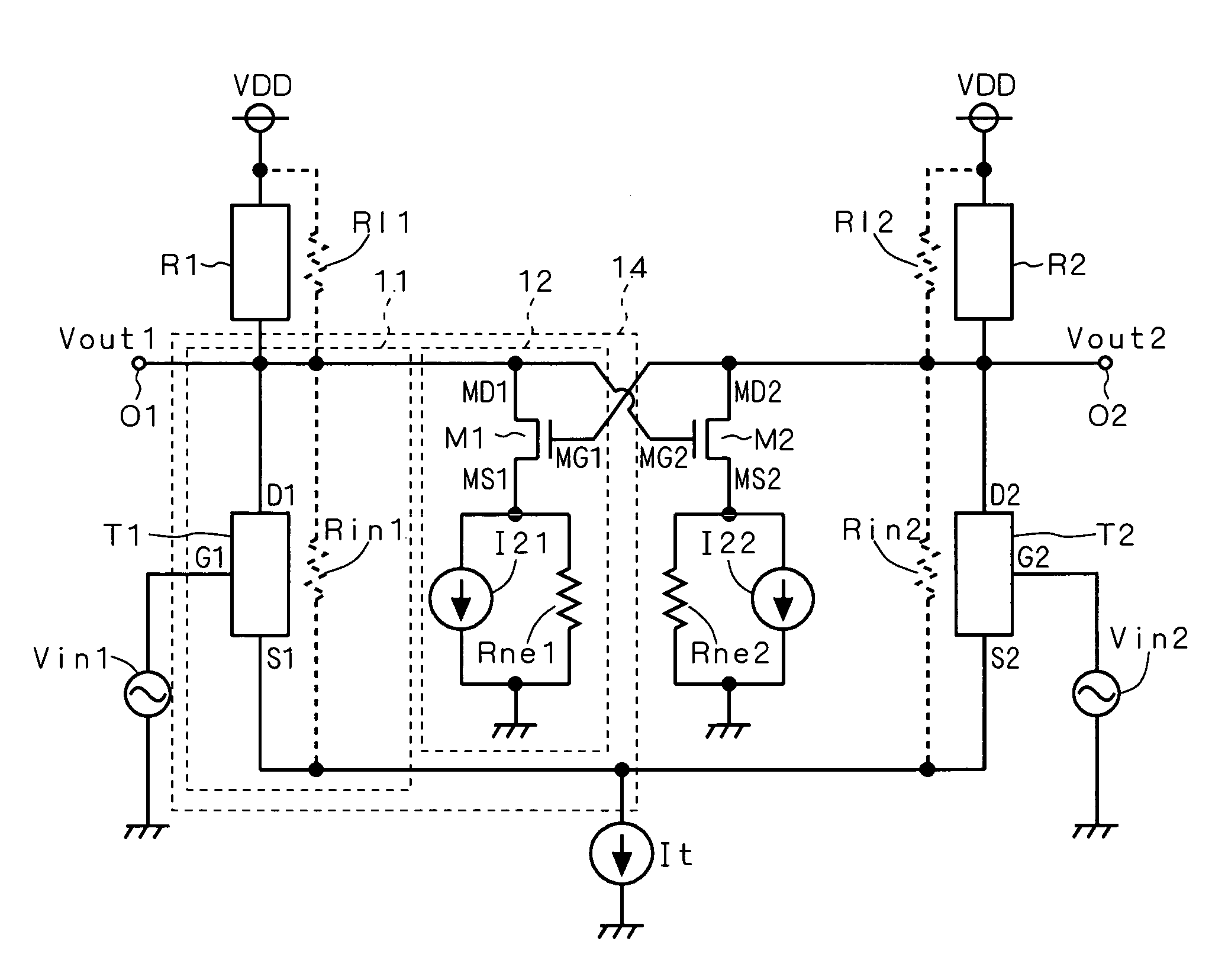
Current source circuit and differential amplifier
InactiveUS7295067B2Increase the output resistanceEasy to provideAmplififers with field-effect devicesDifferential amplifiersElectrical resistance and conductanceDifferential amplifier
A current source block and a negative resistance generation block are connected in parallel. The negative resistance generation block generates a negative resistance in response to the minute variations of an output voltage. Thus the output resistance of a current source circuit is given by the combined resistance of the negative resistance and the resistance of a resistor in the current source block connected in parallel. The resistance of the resistor in the current source block and the negative resistance are controlled to be substantially the same to thereby increase the output resistance of the current source circuit. The current source circuit serves to increase an output resistance when viewed from an differential output terminal. As a result, use of this current source circuit realizes a differential amplifier providing a high gain.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
High voltage gain topology for analog circuits in short channel technologies
InactiveUS20060226464A1Reduce leakageImprove noise immunityTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringHigh pressure
A stacked MOS configuration for use in short channel length analog circuit technologies is provided. The stacked MOS configuration comprises a plurality of short-channel MOS transistors coupled in series and sharing a common gate terminal. In an embodiment, a first peripheral transistor provides a drain terminal for the stacked MOS configuration. A second peripheral transistor provides a source terminal for the stacked MOS configuration. Adjacent transistors in the stacked MOS configuration are connected in a drain-to-source configuration.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
High-definition stereo
InactiveCN101626534AWide Frequency Response CharacteristicsGuaranteed to reproduce the pursuit of nature"Stereophonic circuit arrangementsHigh resistanceMountain stream
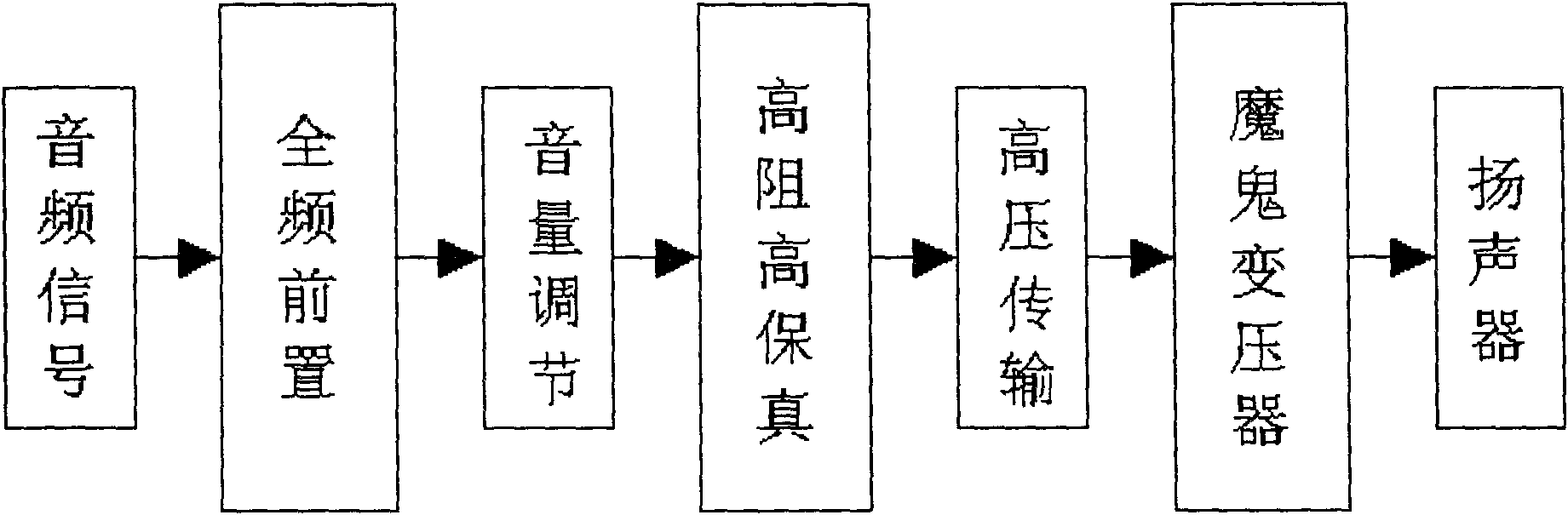
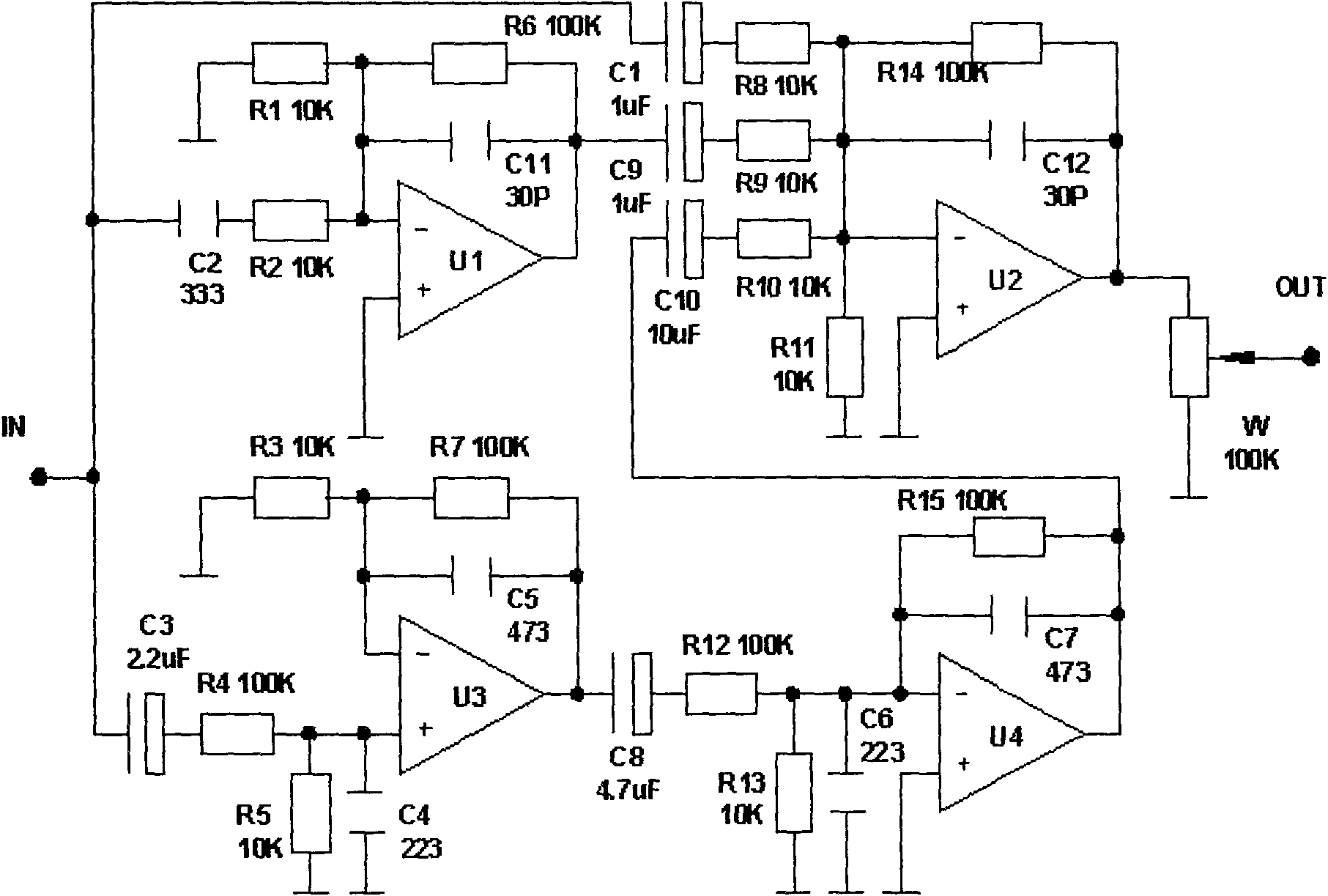
The invention discloses a series of high definition stereo which is characterized by comprising a full-frequency front-end circuit, a high resistance and high fidelity circuit and a devil transformer. The three parts of the high-definition stereo adopt a connecting mode that audio signals are input to the full-frequency front-end circuit, sent to the high resistance and high fidelity circuit through volume adjustment, and sent to the devil transformer through high-voltage transmission to push a loudspeaker to sound. Through the combination, the high-definition stereo has high voltage and super dynamic, and pursues high output impedence R, and the timbre of the high-definition stereo is clear, transparent, round, plump, sweet, real and rich in elasticity, and shows nature again as a mountain stream.
Owner:卢立立
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com