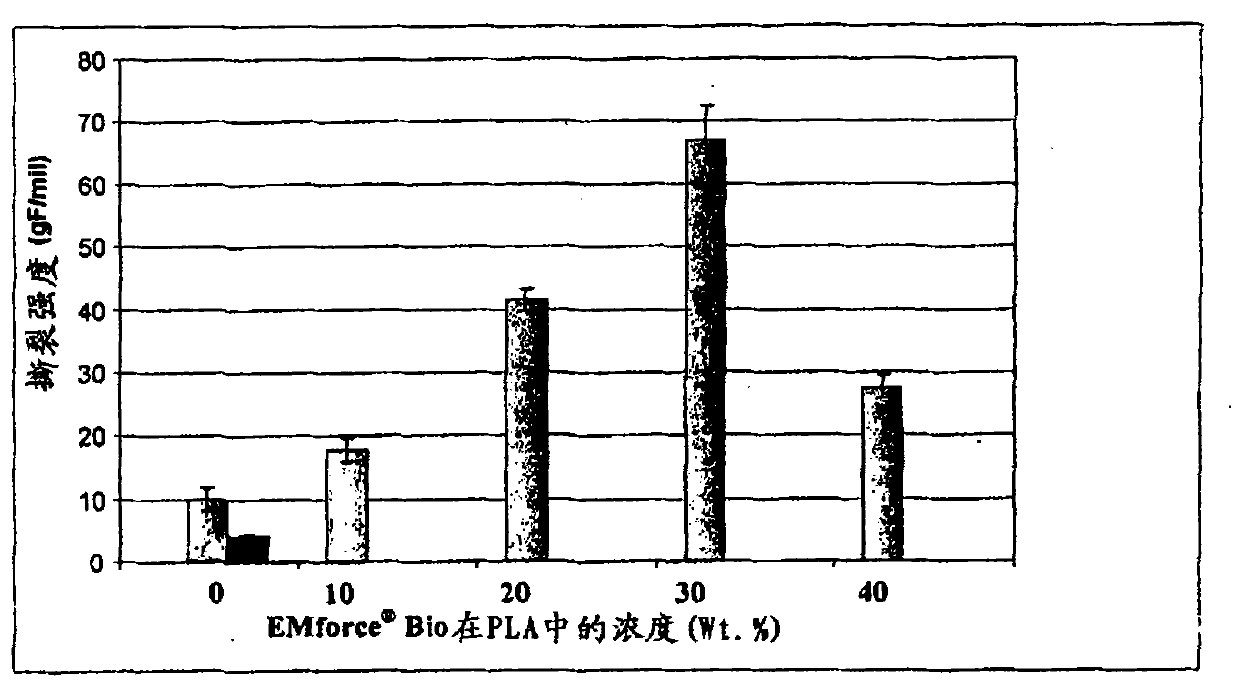
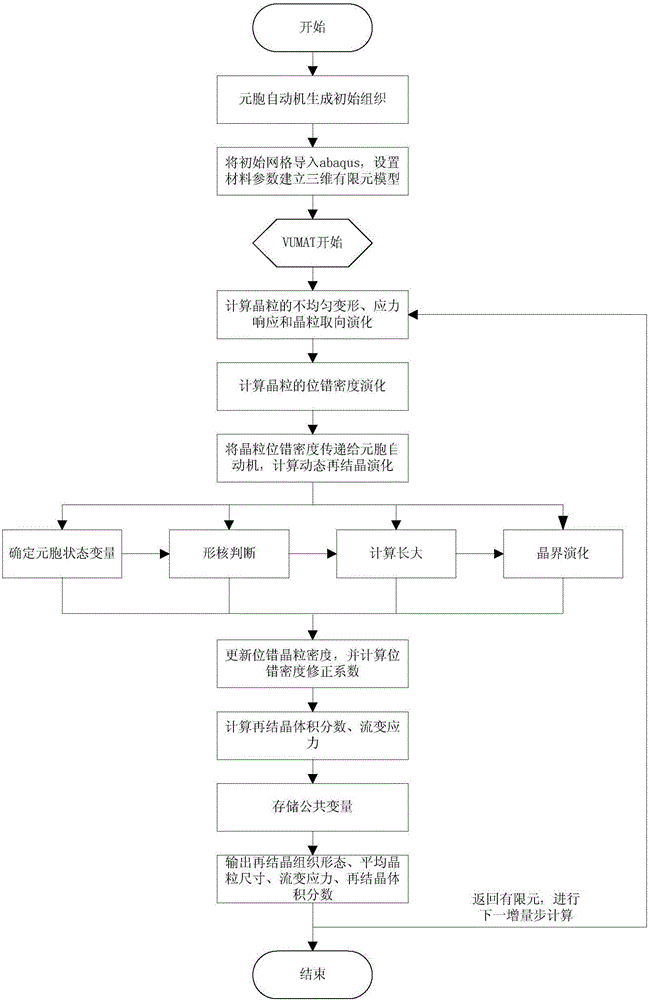
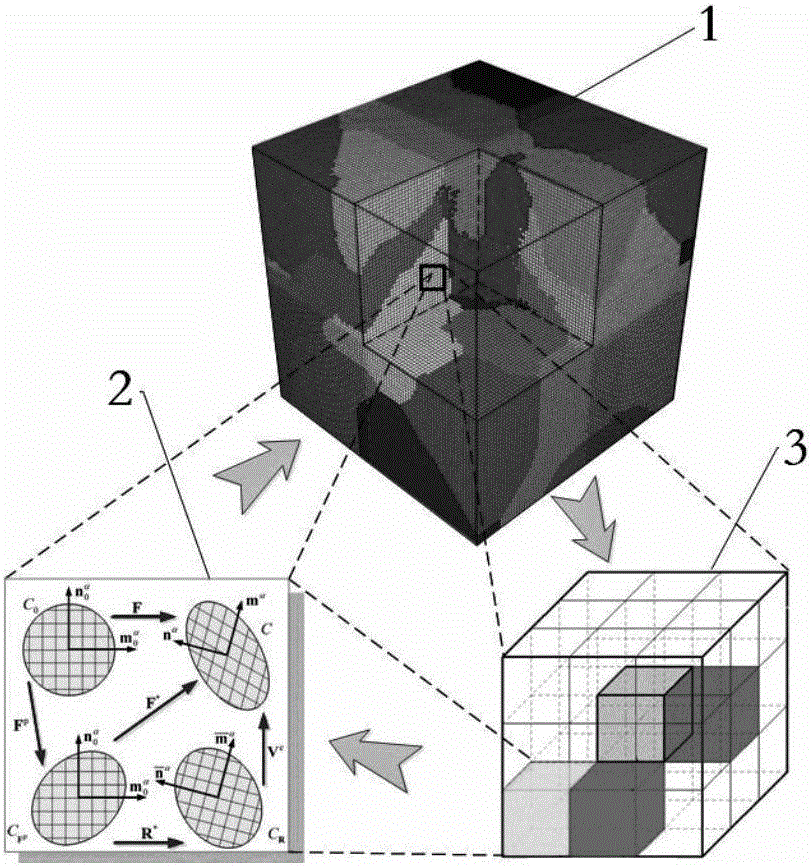
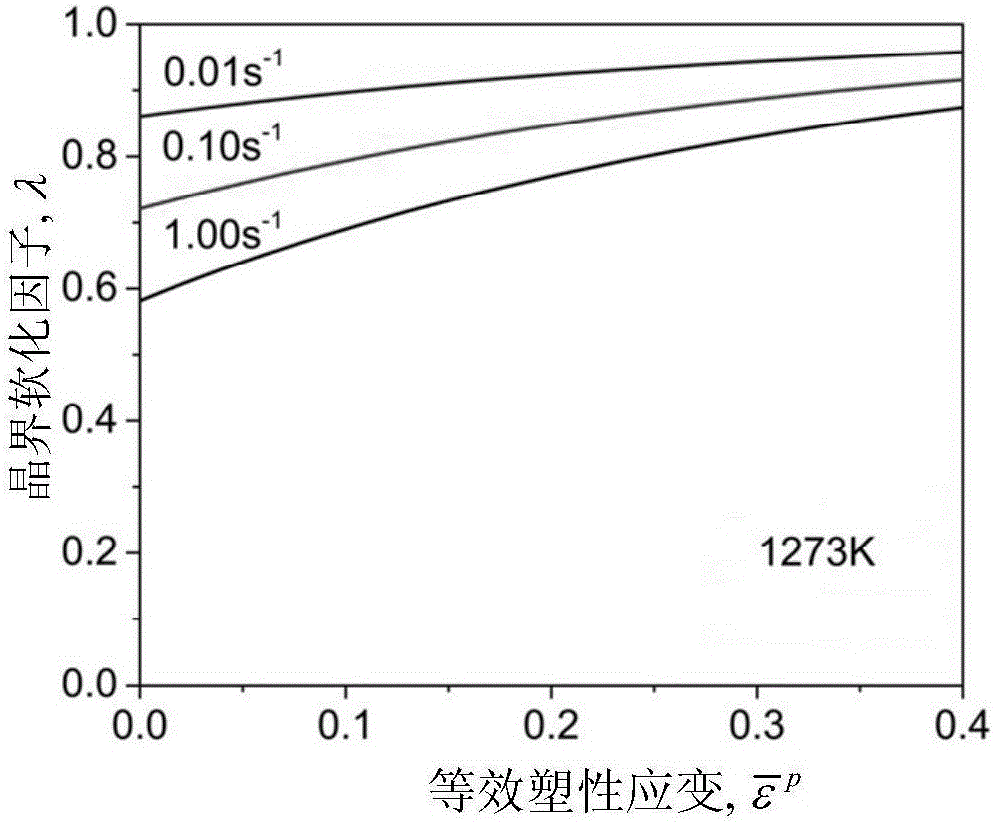
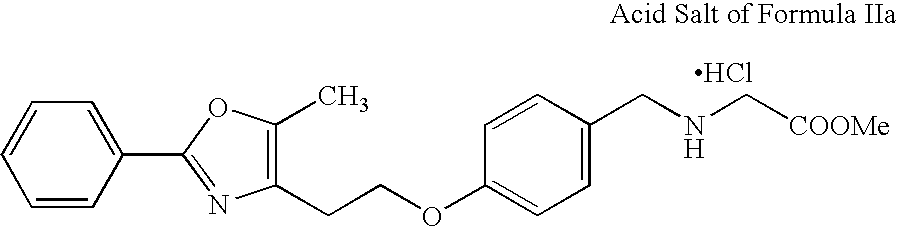
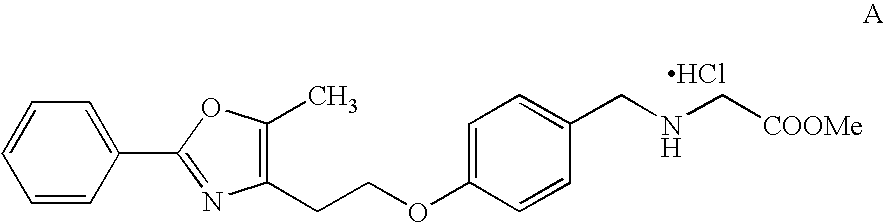
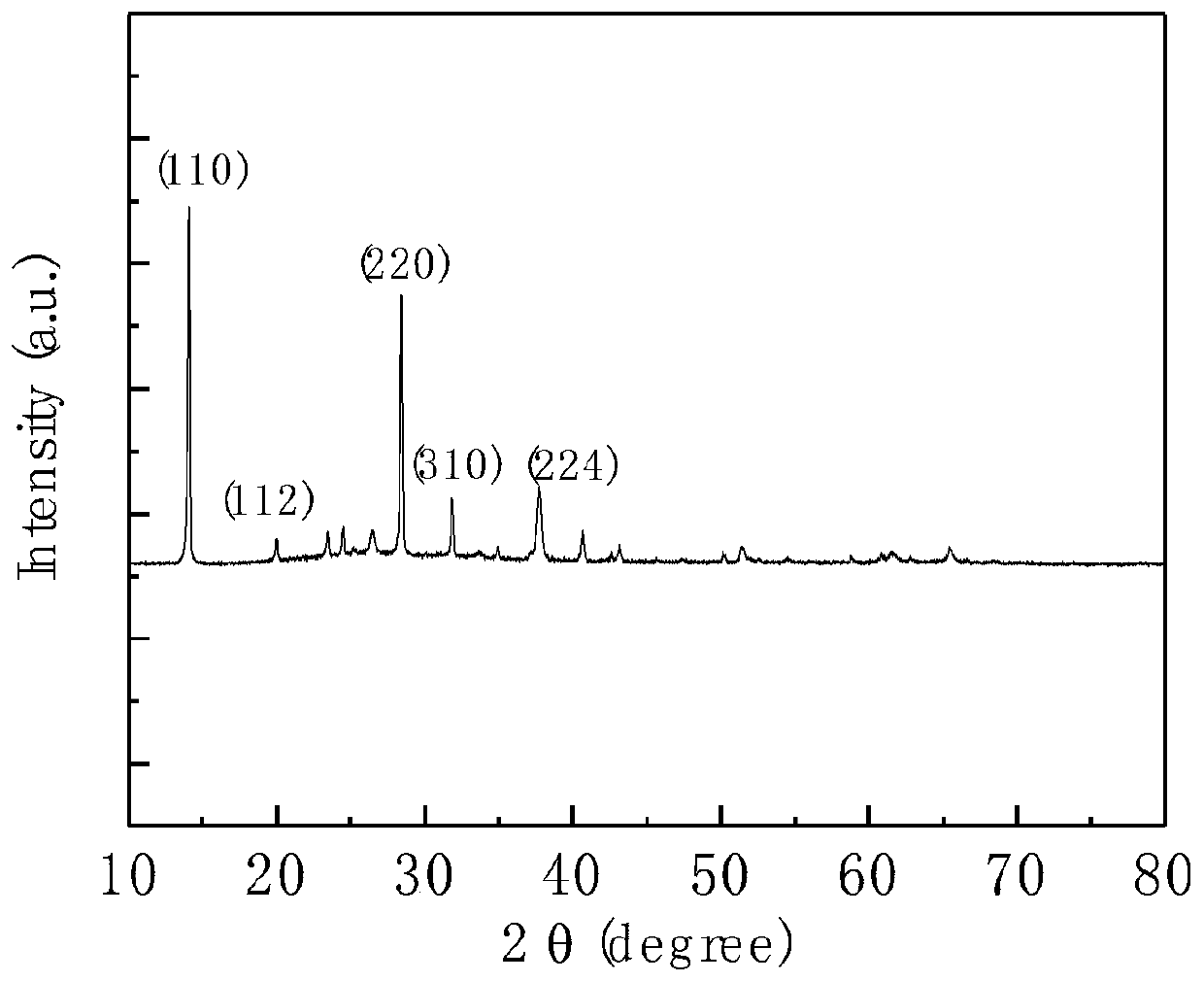
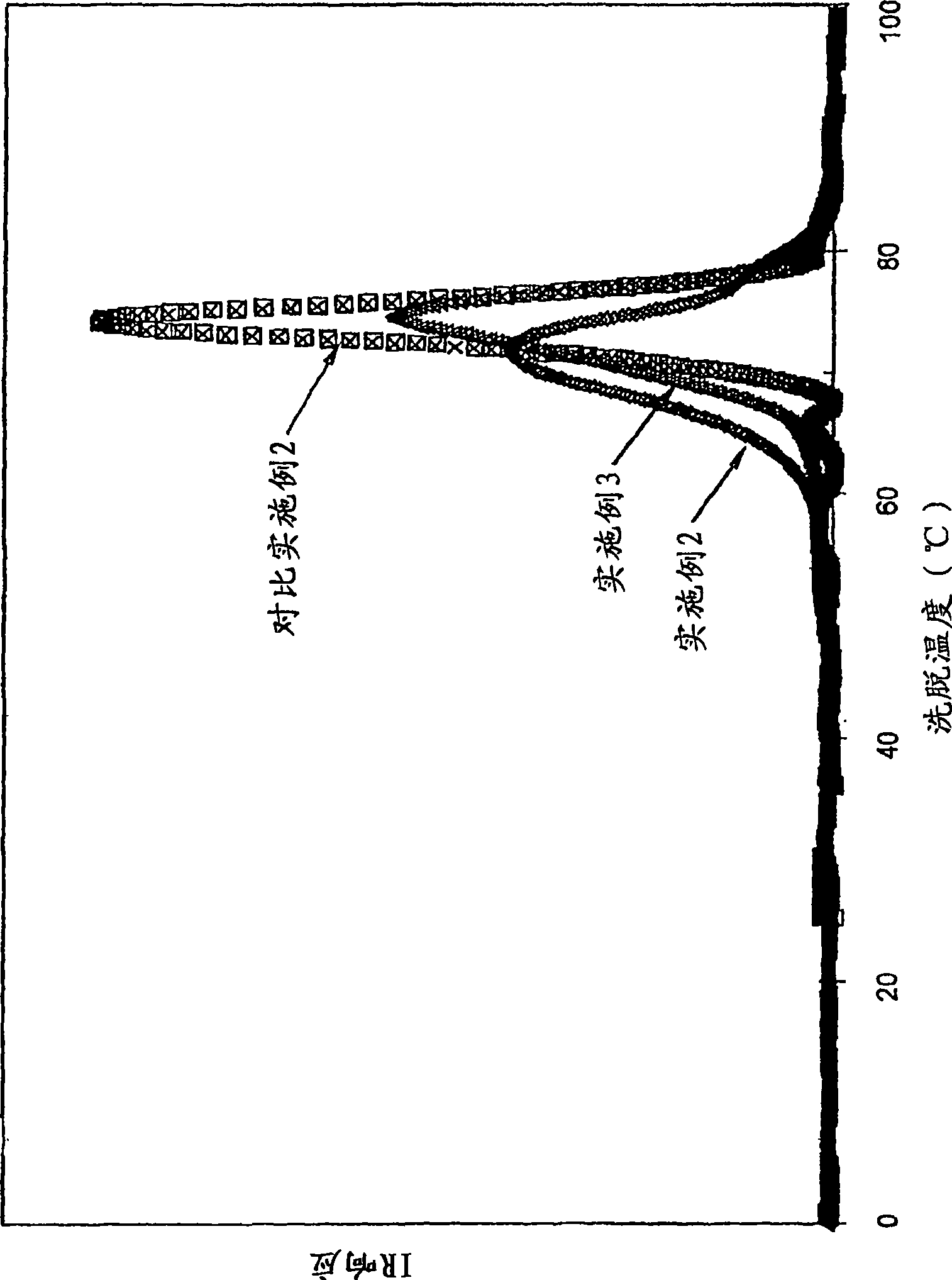
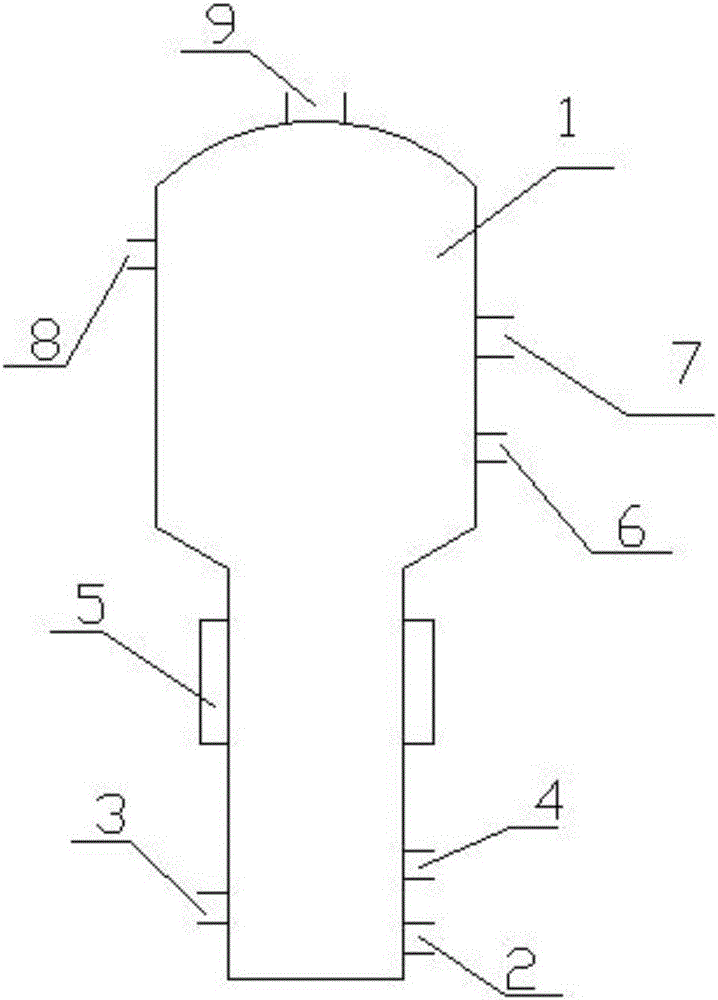
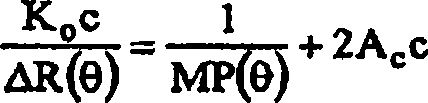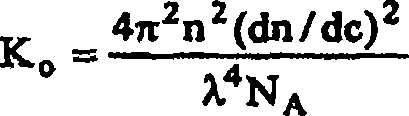Patents
Literature
58 results about "Crystallization kinetics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
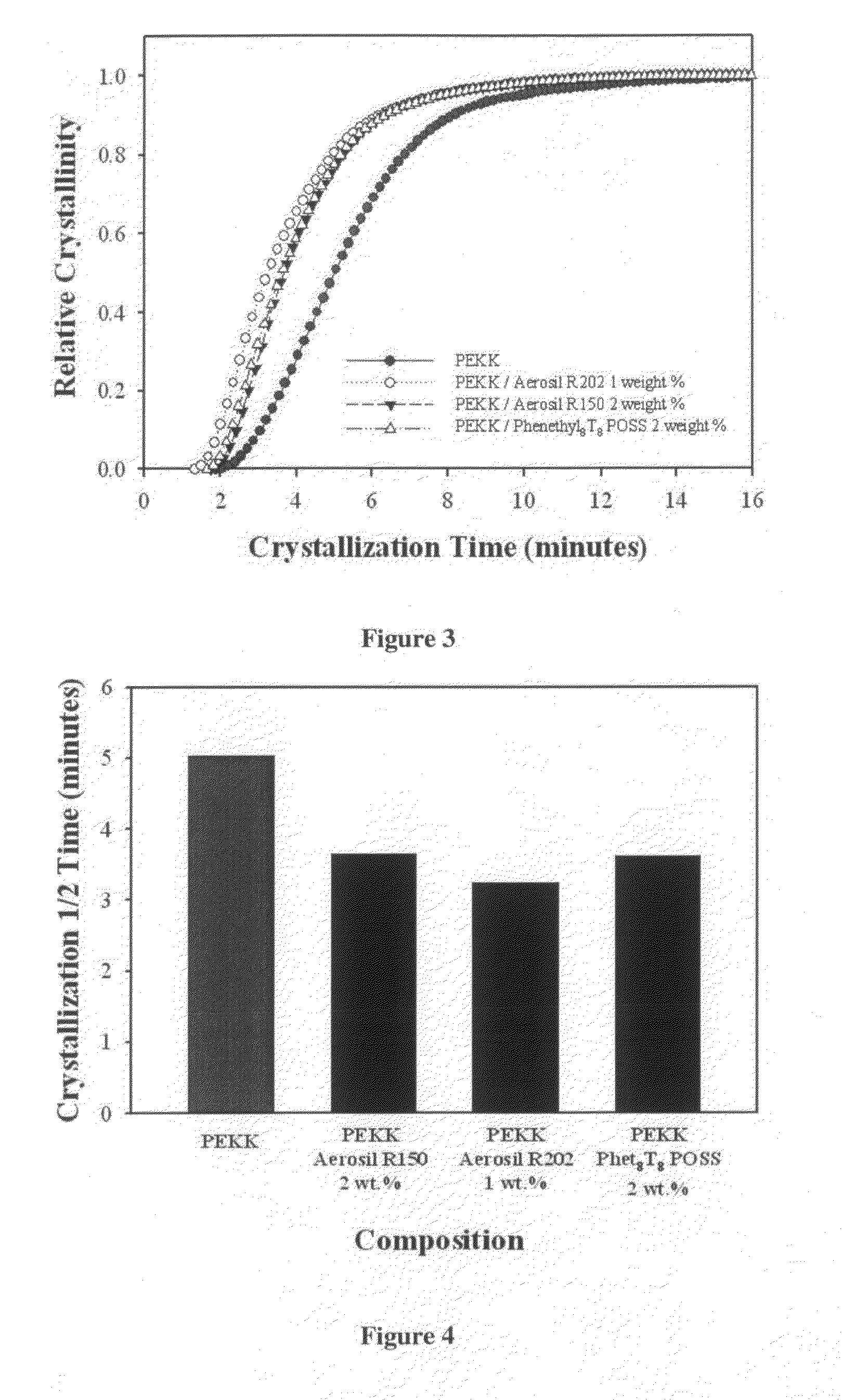
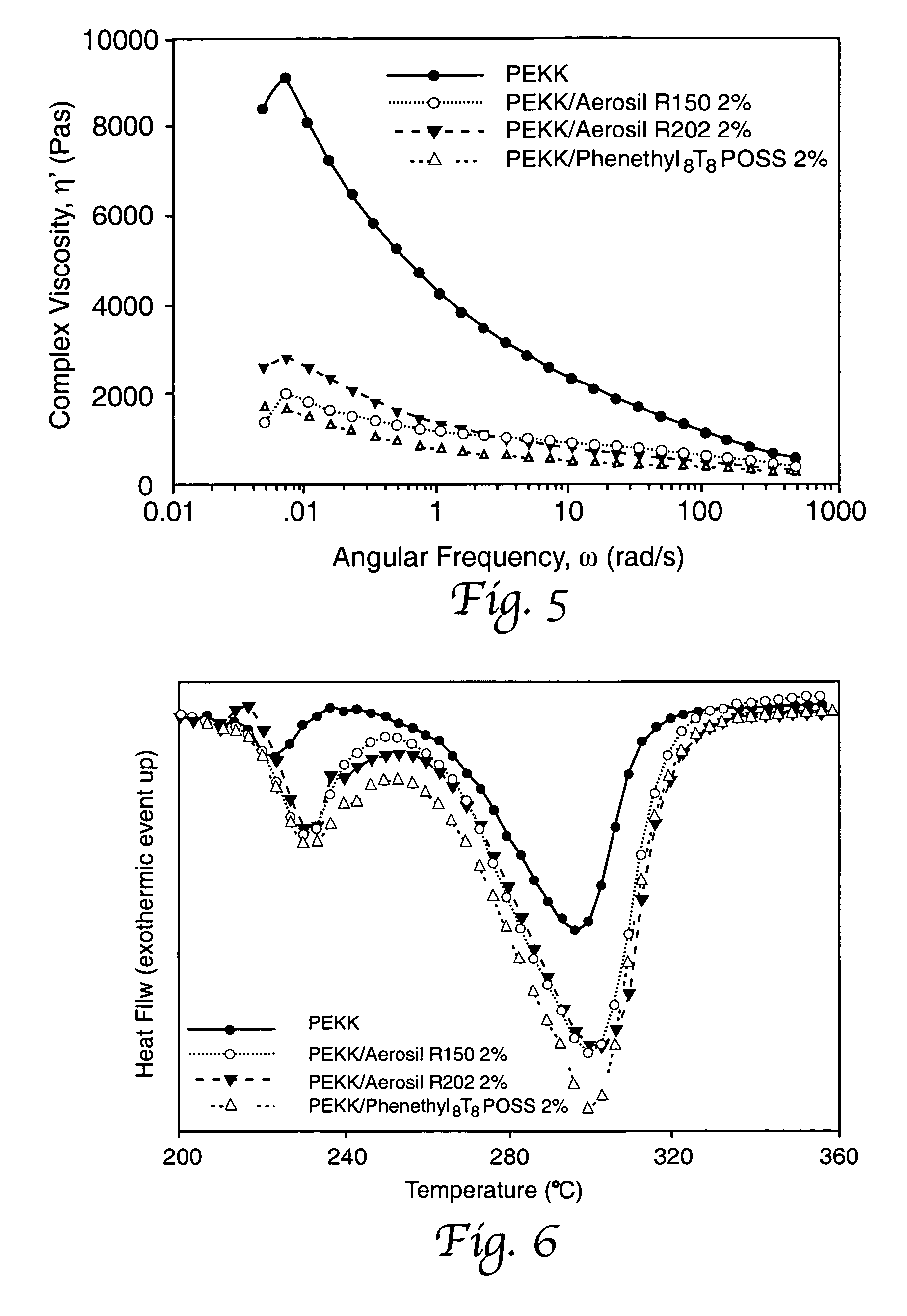
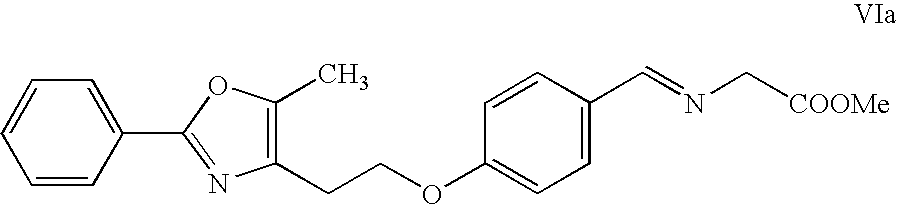
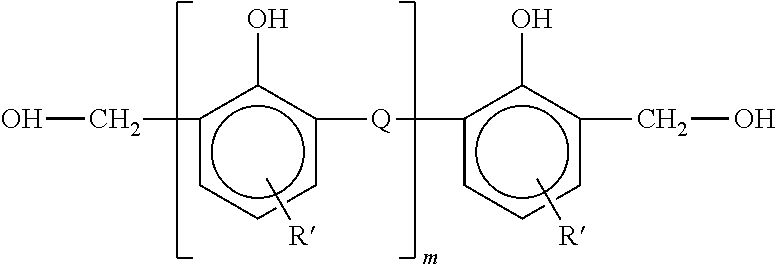
Crystallization kinetics is the area of polymer science that deals with the rate at which randomly ordered chains transform into highly ordered crystals, and includes every aspect of the resultant structure that is dependent on the route that was taken between those different states.
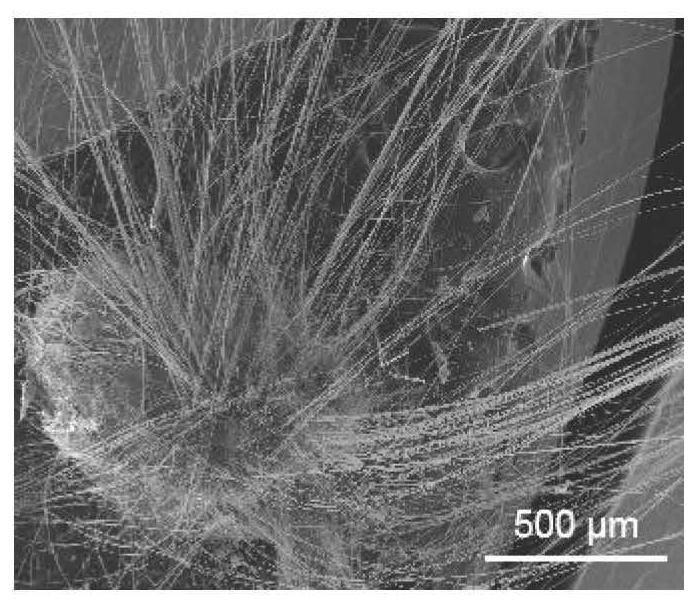
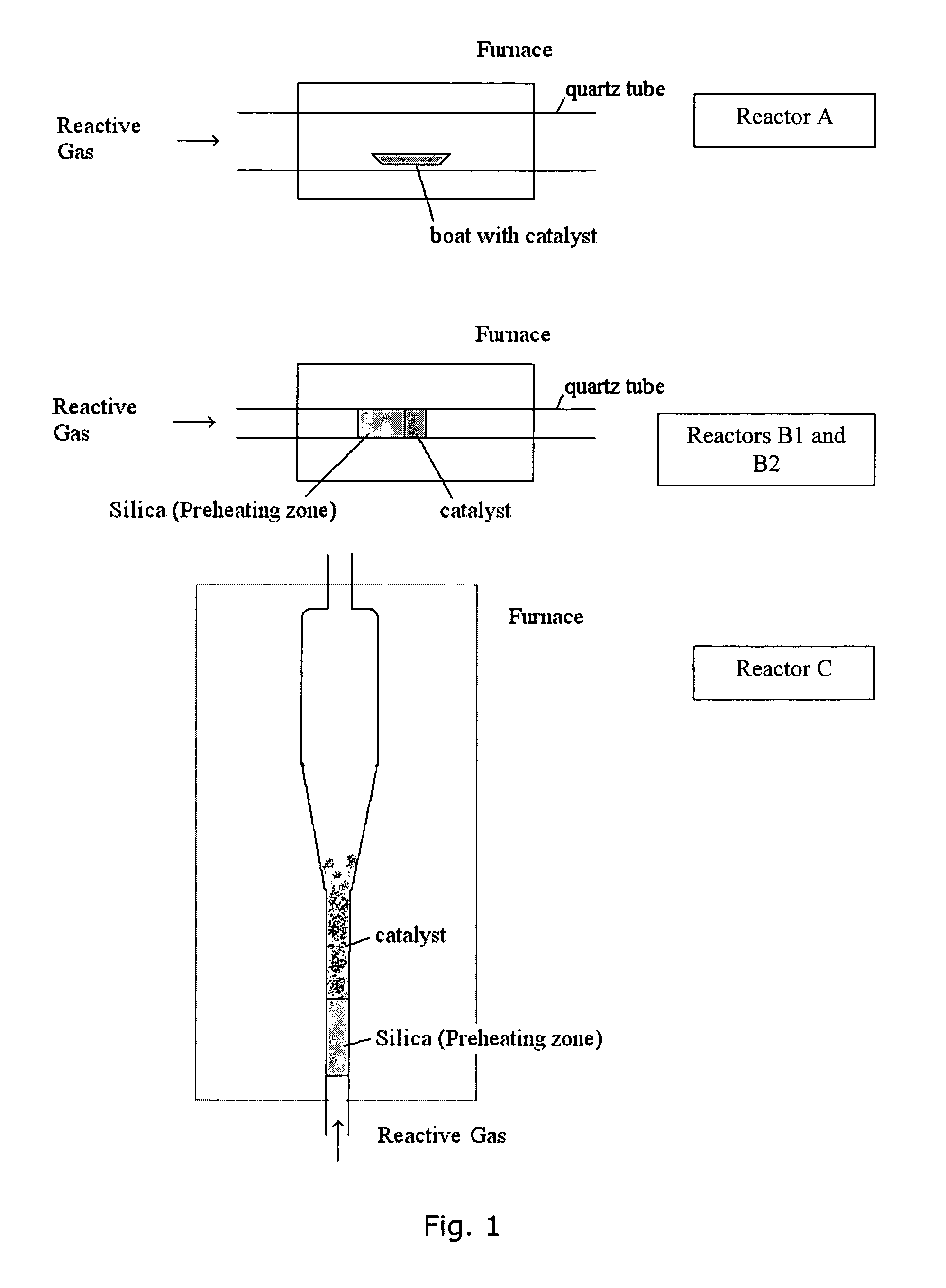
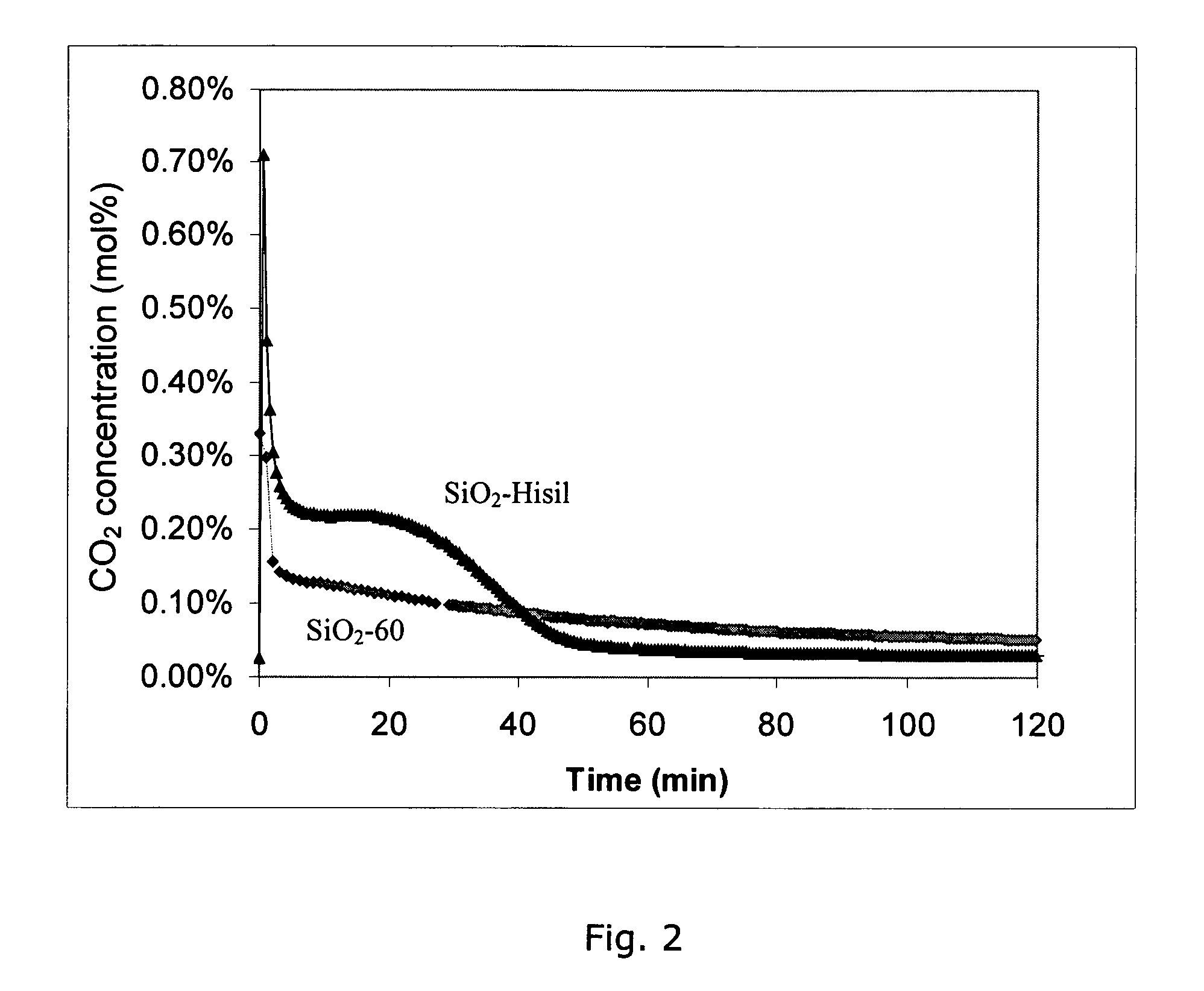
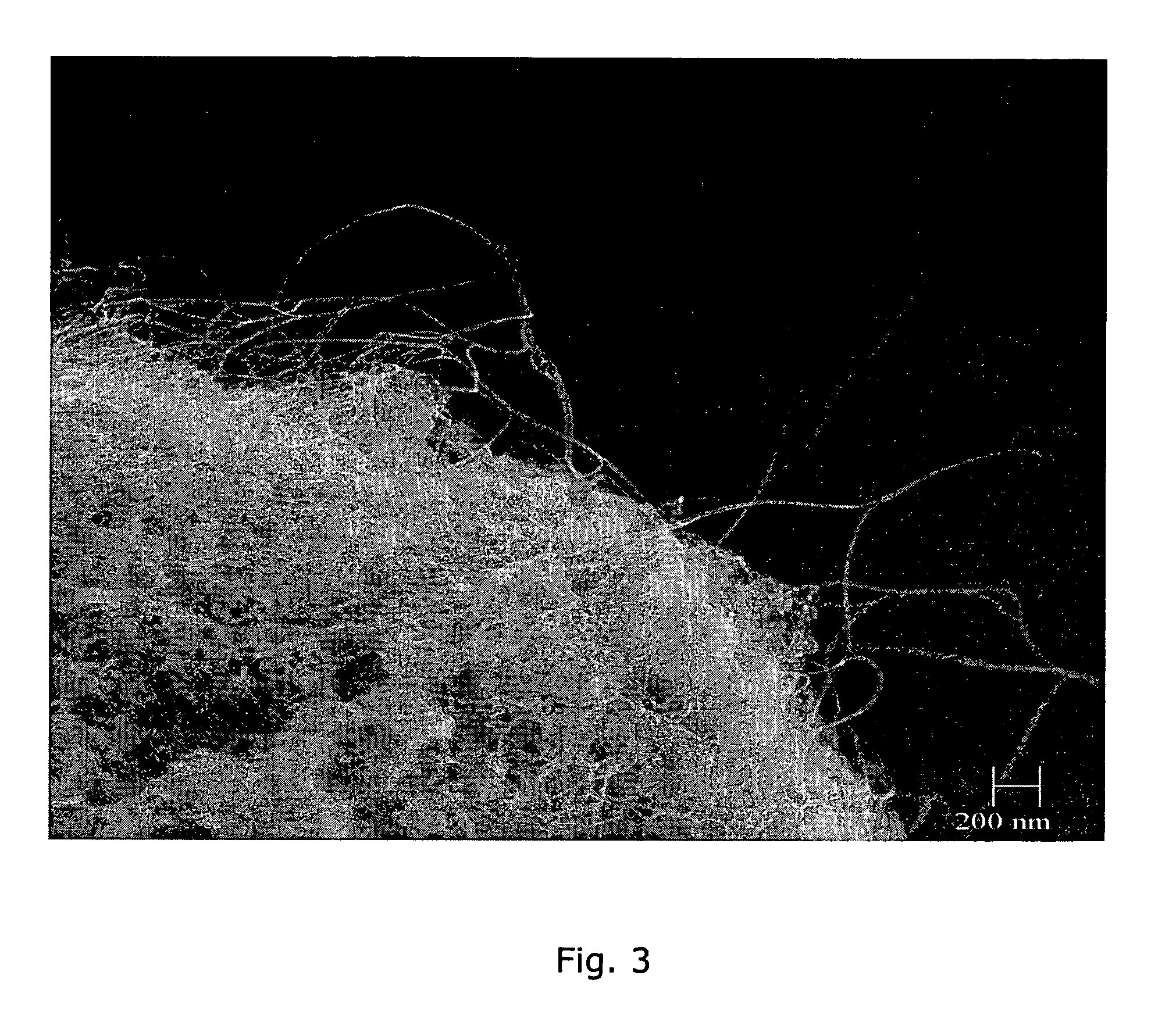
Single-walled carbon nanotube-ceramic composites and methods of use
InactiveUS7816709B2Material nanotechnologyIndividual molecule manipulationField emission deviceCeramic composite
Composites of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) and a ceramic support (e.g., silica) comprising a small amount of catalytic metal, e.g., cobalt and molybdenum, are described. The particle comprising the metal and ceramic support is used as the catalyst for the production of the single-walled carbon nanotubes. The nanotube-ceramic composite thus produced can be used “as prepared” without further purification providing significant cost advantages. The nanotube-ceramic composite has also been shown to have improved properties versus those of purified carbon nanotubes in certain applications such as field emission devices. Use of precipitated and fumed silicas has resulted in nanotube-ceramic composites which may synergistically improve the properties of both the ceramic (e.g., silica) and the single-walled carbon nanotubes. Addition of these composites to polymers may improve their properties. These properties include thermal conductivity, thermal stability (tolerance to degradation), electrical conductivity, modification of crystallization kinetics, strength, elasticity modulus, fracture toughness, and other mechanical properties. Other nanotube-ceramic composites may be produced based on Al2O3, MgO and ZrO2, for example, which are suitable for a large variety of applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Surface treated inorganic particle additive for increasing the toughness of polymers
InactiveCN101918485AImproved crystallization kineticsFast crystallizationRefuse receptaclesPolyolefinBiopolymer
A bioplastic composition comprising a biopolymer containing from 10 - 40 wt% of coated inorganic particles; the particles being coated with one or more of fatty acids, fatty acid derivatives, rosins, rosinates, polyolefin based waxes, oligomers and mineral oils, and combinations thereof has improved stiffness and toughness and also has improved crystallisation kinetics rendering it useful for extrusion, injection moulding and thermoforming.
Owner:SPECIALITY MINERALS (MICHIGAN) INC
Method for predicting coupling responses of isothermal forming and dynamic recrystallization evolution of titanium alloys
ActiveCN106202675AAchieving Unified PredictionTightly deformedDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsCrystallization kineticsTitanium alloy
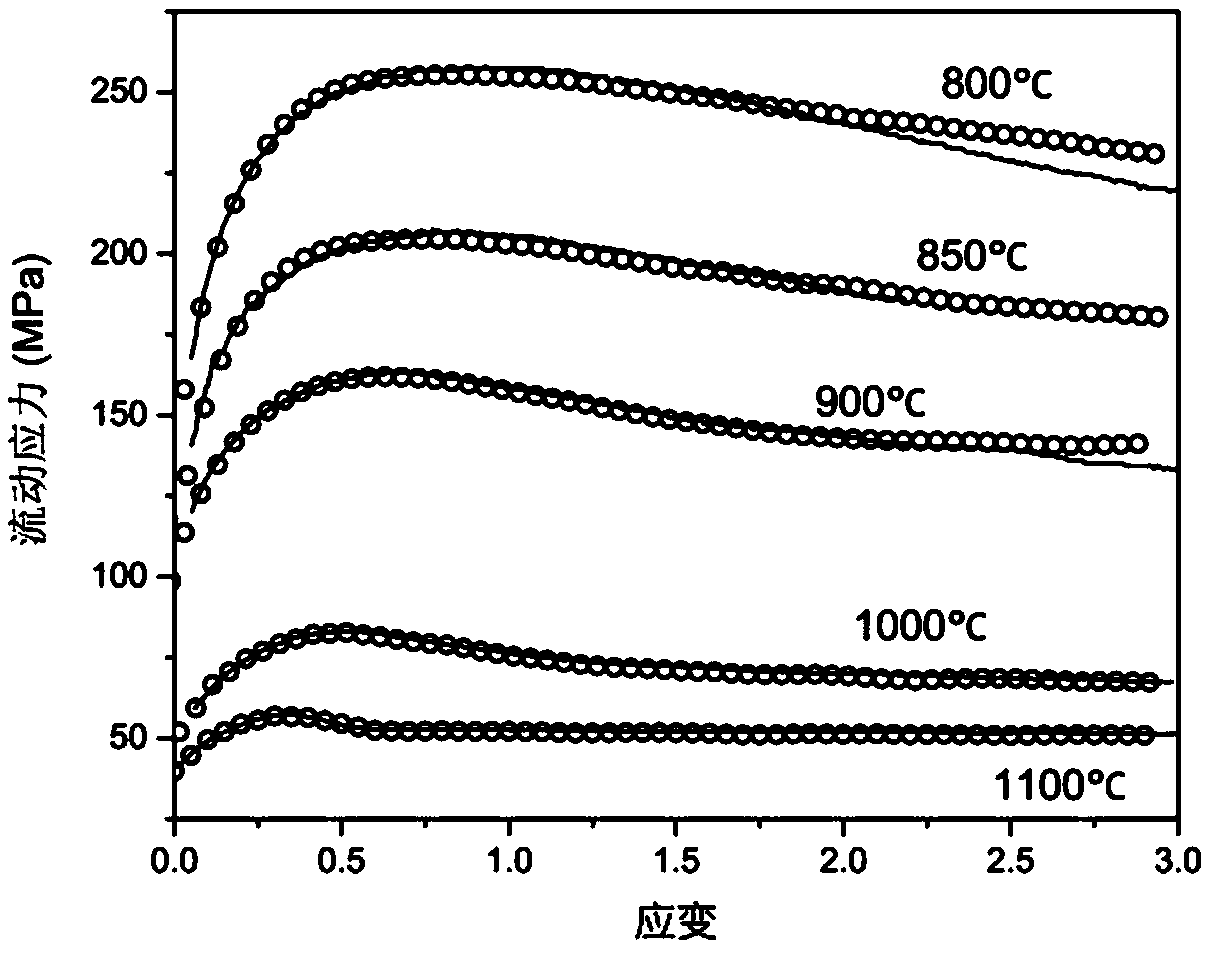
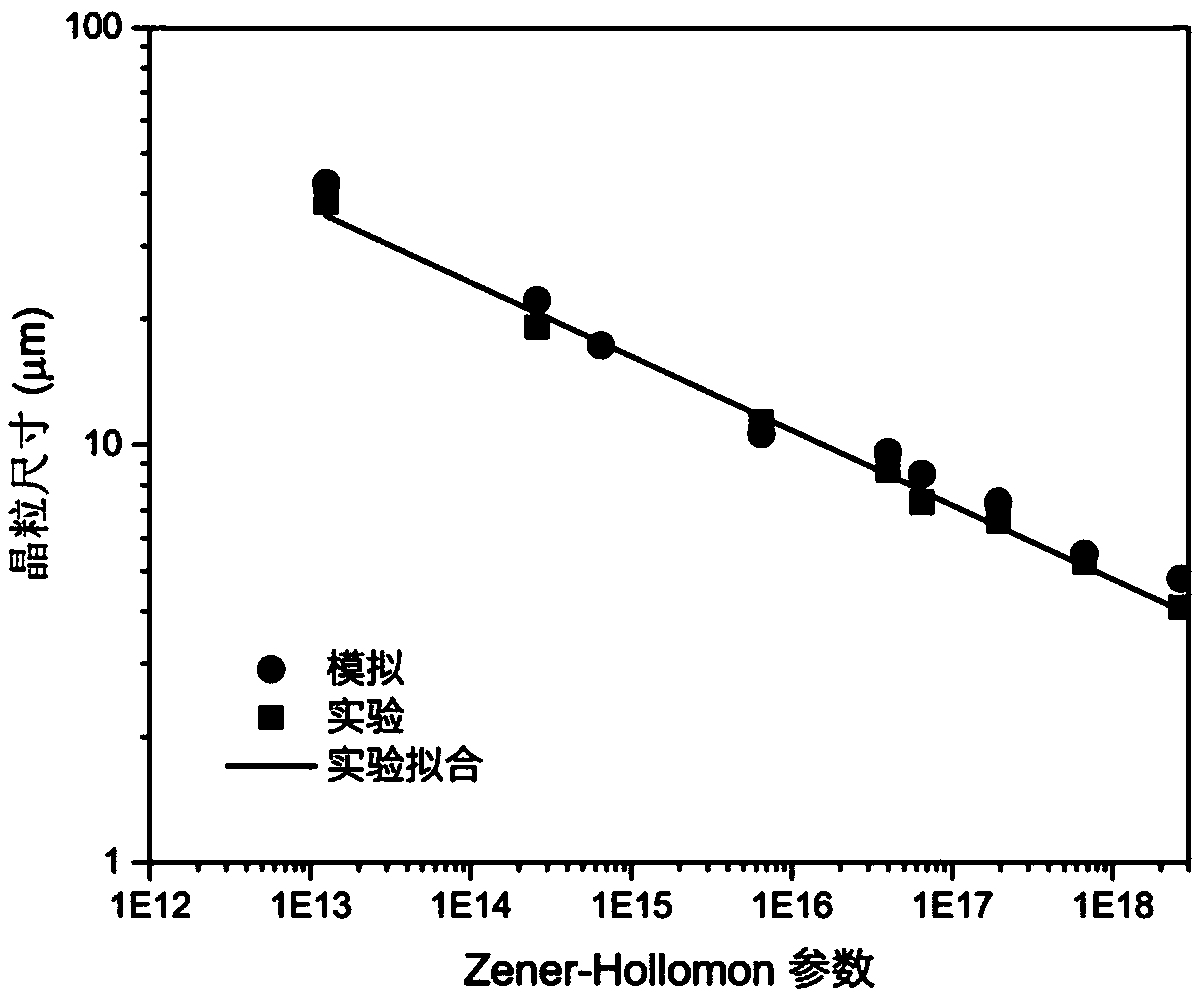
The invention provides a method for predicting coupling responses of isothermal forming and dynamic recrystallization evolution of titanium alloys. Grain stress responses, intercrystalline non-uniform deformation and non-uniform dislocation density caused by intercrystalline non-uniform deformation are obtained in an isothermal forming process of the titanium alloys and are adopted as variables and transmitted to a cellular automaton, dynamic recrystallization evolution of the grain size under the condition of non-uniform size deformation is obtained, and dynamic recrystallization nucleation and grown structure morphology as well as grain boundary evolution and updated dislocation density which are caused by the dynamic recrystallization nucleation and grown structure morphology are obtained. The obtained grain and grain boundary information including dynamic recrystallization nucleation and growth as well as the dislocation density is returned to a crystal plasticity finite element method, dislocation gliding resistance of each grain unit is updated, so that subsequent deformation of the titanium alloys is influenced, and the stress responses of the grain size are calculated according to the constitutive relation. The method realizes synchronous prediction of non-uniform deformation of the grain size in isothermal forming of the titanium alloys, dynamic recrystallization structure morphology evolution, recrystallized grain size evaluation, recrystallization kinetics, deformable bodies and grain flow stress.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Preparation method for high-dispersion zeolite molecular sieves
ActiveCN103204515AReduce condensation agglomerationGood dispersionCrystalline aluminosilicate zeolitesMolecular sieveCrystallization kinetics
The invention relates to a preparation method for high-dispersion zeolite molecular sieves. The preparation method includes preparing gel and performing hydrothermal crystallization on nanometer molecular sieves, pressing organochlorosilane in a crystallization kettle filled with crystallized matter through pressurization of nitrogen under the condition of stirring when the crystallization of the molecular sieves is finished so as to enable the organochlorosilane to fully contact and react with the surfaces of the molecular sieves, and collecting products after reaction of the organochlorosilane and the crystallized matter is finished. The mass ratio of the added organochlorosilane R is R / SIO2=0.01-2, the reaction time is no more than 100 hours, and the reaction temperature ranges from room temperature to 200 DEG C. The organochlorosilane is added when the crystallization of the molecular sieves is finished, and the condensation reaction of the organochlorosilane and the surface hydroxyl groups of the molecular sieves is utilized to block agglomeration among the molecular sieves, so that the defect that prior methods affect crystallization kinetics of the molecular sieves is overcome. Obtained molecular sieve products have good dispersibility and large specific surface areas, and are easy to filter.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Increasing the rate of crystallization of engineering thermoplastics
InactiveUS7790841B1Increase the rate of crystallizationEnhanced crystalline behaviorMaterial nanotechnologyFibre treatmentThermoplasticParticulates
Method for enhancing the crystallization rates of engineering thermoplastics through the use and incorporation of particulate additives with dimensions on the order of 10-1000 nm is described. The presence of nanoparticles at concentrations of, e.g., less than 10 weight percent of the composition, reduces the viscosity of the thermoplastics as compared to the respective homopolymer, thereby increasing polymer chain transport and diffusion to the crystallizing growth front. The prescription of this technology has been shown to reduce crystallization half times of some engineering thermoplastics by as much as 40 percent at optimal crystallization temperatures, an effect that is magnified as the temperature is reduced towards the glassy state of the amorphous phase. Nano-modified engineering thermoplastics with rapid crystallization kinetics and relatively low viscosities can be utilized in component fabrication processes that require rapid processing times, e.g., for the sake of cost efficiency.
Owner:AIR FORCE US SEC
Process employing controlled crystallization in forming crystals of a pharmaceutical
InactiveUS20050256314A1Improve filtration efficiencyImprove washing efficiencyOrganic chemistryCrystallization separationState of artCrystallization kinetics
A process is provided which employs reactive controlled crystallization to produce drug substance having desirable crystal properties which process involves providing reactants A and B in liquid or solution form and adding reactant B to reactant A using a cubic or incremental addition technique to control extent of reaction and thus crystallization kinetics, including supersaturation and nucleation, to produce crystals of drug substance which are generally larger, better quality and with few fines and narrow particle size distribution than normally obtainable employing prior art crystallization techniques. In addition, crystals of drug substance produced by the above process is also provided.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Method for acquiring mobility parameter of re-crystallized structure evolution crystal boundary of metal material
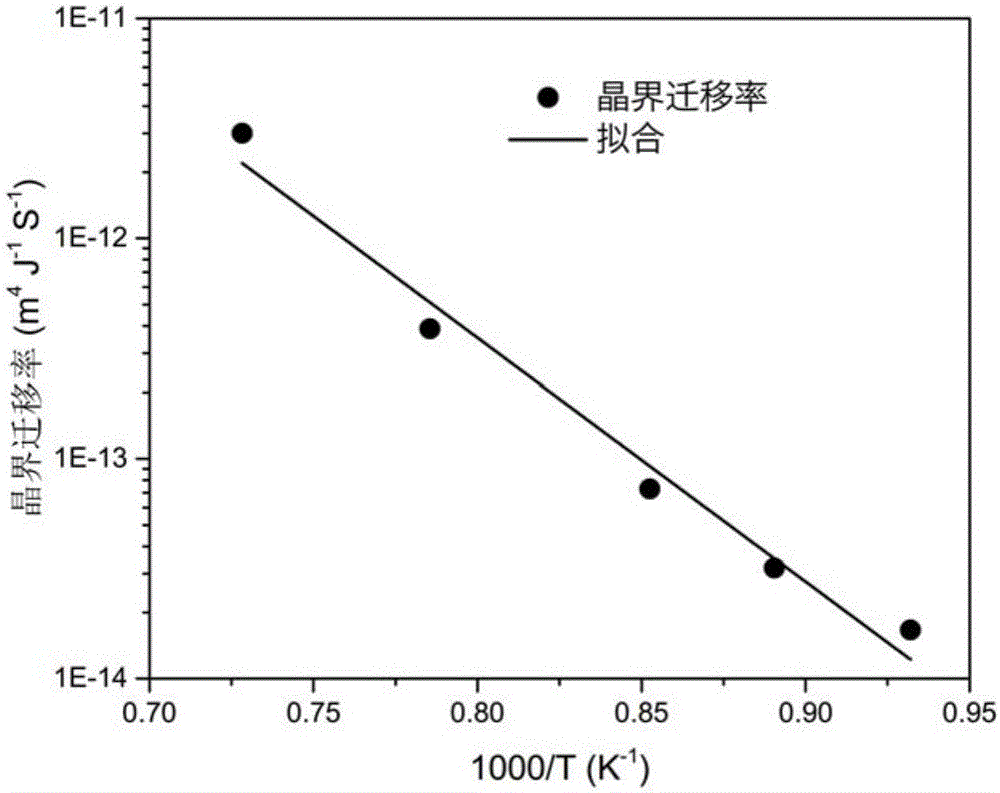
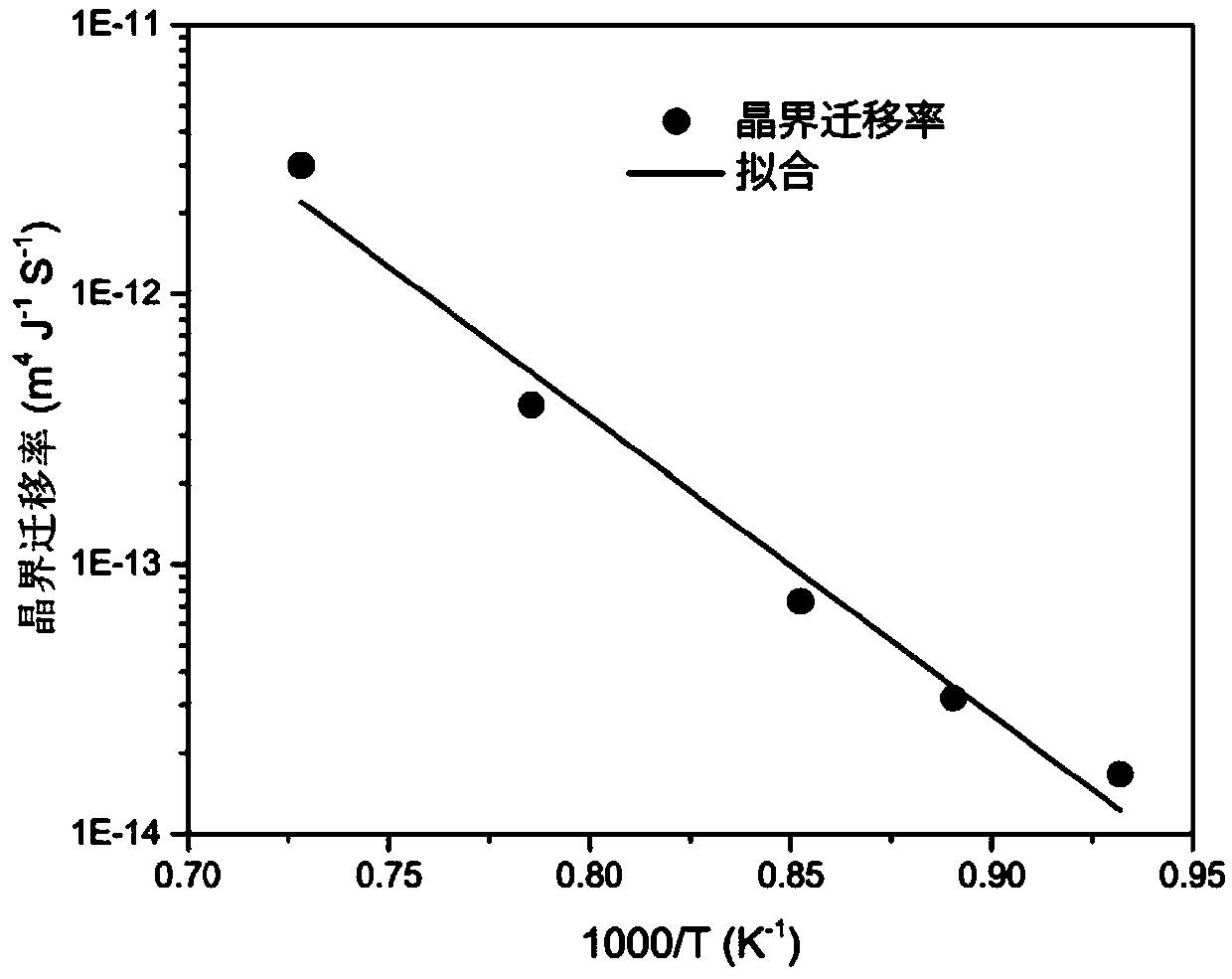
ActiveCN106503397AImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansDesign optimisation/simulationCrystallization kineticsActivation energy
The invention relates to a method for acquiring a mobility parameter of a re-crystallized structure evolution crystal boundary of a metal material. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing static re-crystallization or dynamic re-crystallization physical thermal simulation test on a metal material sample; (2) acquiring an average grain size of static re-crystallization or dynamic re-crystallization of the sample by utilizing a microstructure representation test; (3) establishing a re-crystallization dynamical model on the basis of a structural evolution numerical simulation method, wherein the model includes nucleation and growing sub-models; (4) describing a nucleation rate sub-model through a nucleation rate, excluding the parameters, such as nucleation activation energy, difficult to acquire through the test and the parameters without physical significance; (5) expressing the migration rate of the crystal boundary of a re-crystallization growing sub-model by the product of the driving force and the mobility parameter of the crystal boundary, wherein the mobility parameter of the crystal boundary is a unique fitting parameter in the whole model; (6) adjusting the mobility parameter of the crystal boundary by adopting an inverse optimization algorithm, comparing a numerical simulation result with a test result and confirming the parameter when a difference between the numerical simulation result with the test result is less than a threshold value (0.01-0.1).
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Thermoplastic elastomer compositions, methods of making and articles made from the same
ActiveUS20080081869A1Promote crystallizationReduce and eliminate interferenceOrganic dyesThermoplasticVulcanization
Provided are thermoplastic elastomer compositions, many dynamically vulcanized, with superior crystallization kinetics, methods for making the compositions and articles made therefrom. The thermoplastic elastomer compositions comprise at least a propylene polymer thermoplastic, a rubber and a crystallization additive. The processes for preparation of the thermoplastic elastomer compositions comprises dynamic vulcanization of mixture of a propylene polymer thermoplastic, a rubber and a cure agent followed by addition of a crystallization additive. Further, preparation of articles from the thermoplastic elastomer compositions may be accomplished through traditional thermoforming operations useful with conventional thermoplastics.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Method and device for online representing crystallization kinetic process through ultrasonic wave
InactiveCN103512956AConvenient variable temperature transient testOptimizing the cooling and solidification processAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMolten stateThermal state
The invention discloses a testing method and device for online representing crystallization kinetic process through ultrasonic wave. Temperature and pressure sensors and an ultrasonic probe are mounted in the closed material cavity of a PVT testing device, the material is cooled to perform crystallization, synchronous detection is performed to obtain specific volume and ultrasonic wave sound velocity pair time curves at different pressure and temperature, the thermal state of the material can be classified into solid state, crystalline region and molten state from the inflection points of the curves, and the synchronous ultrasonic wave velocity pair specific volume is plotted and fitted to establish the quantitative relation. The mode that the crystallinity degree in a crystallization kinetic equation is expressed through adopting the specific volume, is changed into the mode that the crystallinity degree in a crystallization kinetic equation is expressed through adopting an ultrasonic wave velocity, the crystallization process is quantificationally analyzed, and the rule of influence of material composition, temperature, pressure and medium on the crystallization is researched. The temperature and pressure sensors and the ultrasonic probe are mounted on a production line or the material cavity of a die, the crystallization process can be online represented conveniently in the normal position and lossless way, feedback can be optimized, the cooling technology and the formula can be controlled, and the product quality can be evaluated. High-pressure online testing and rapid pressure and temperature change testing are performed easily through the method.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
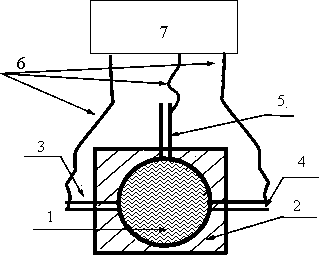
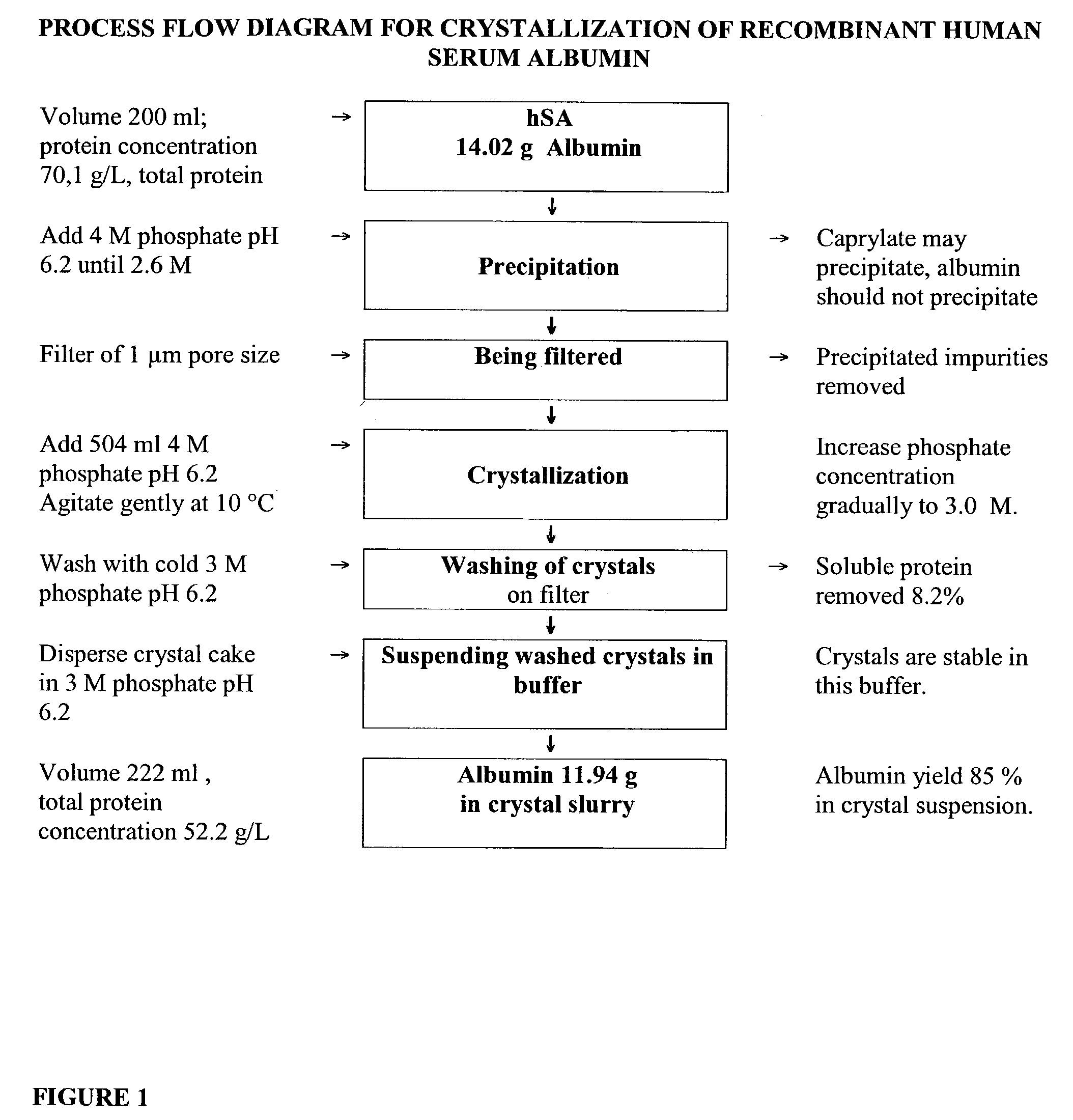
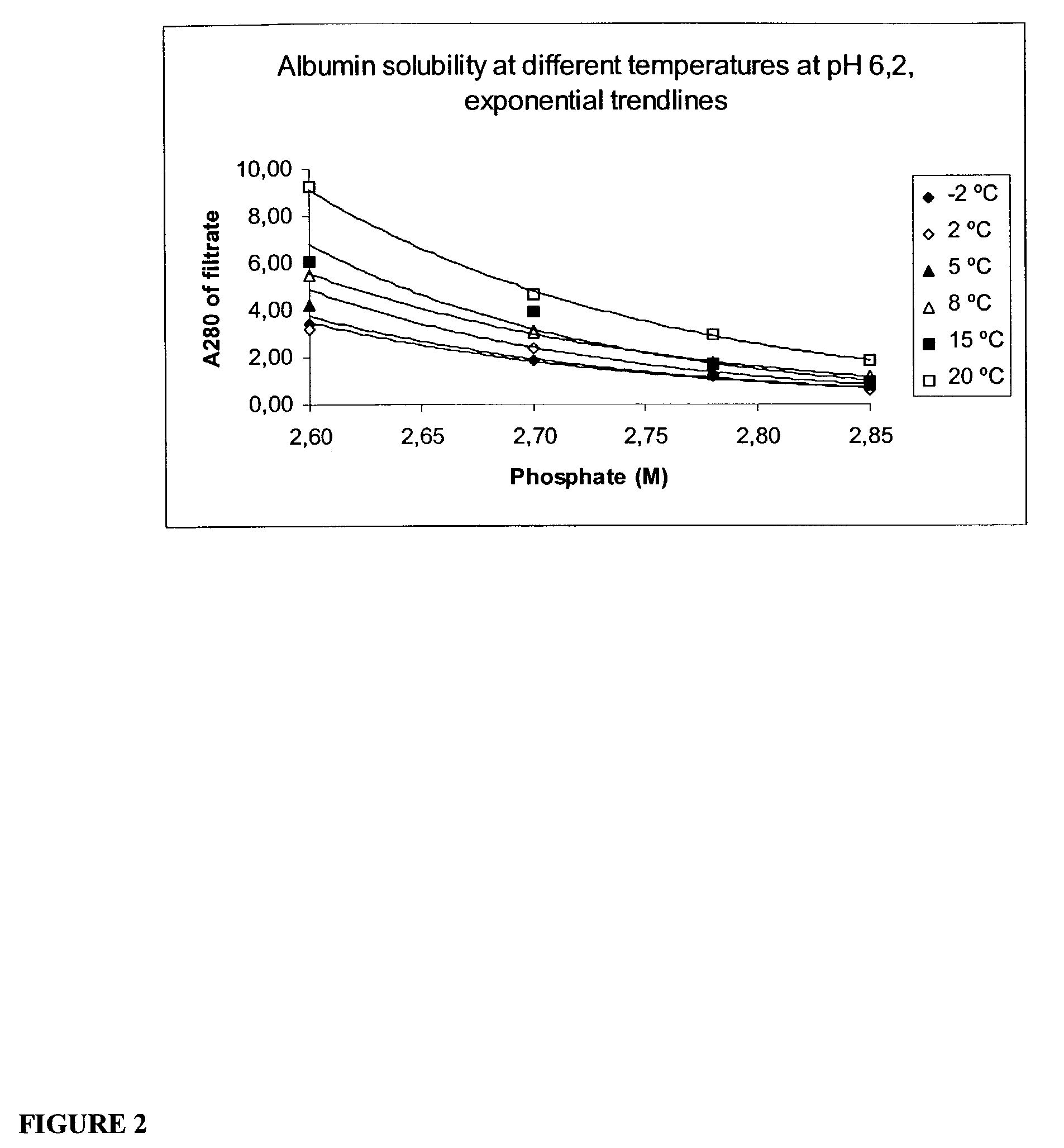
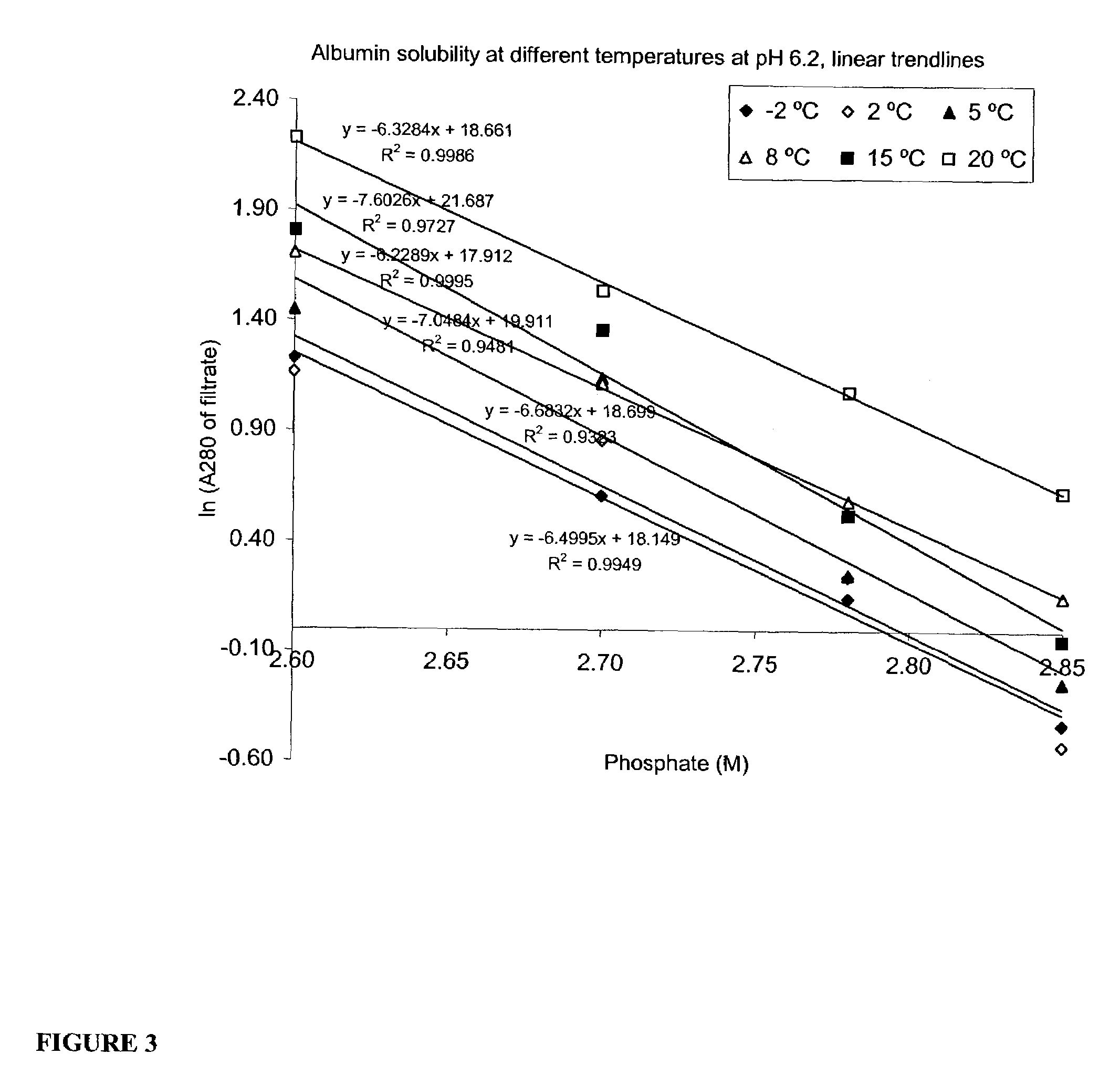
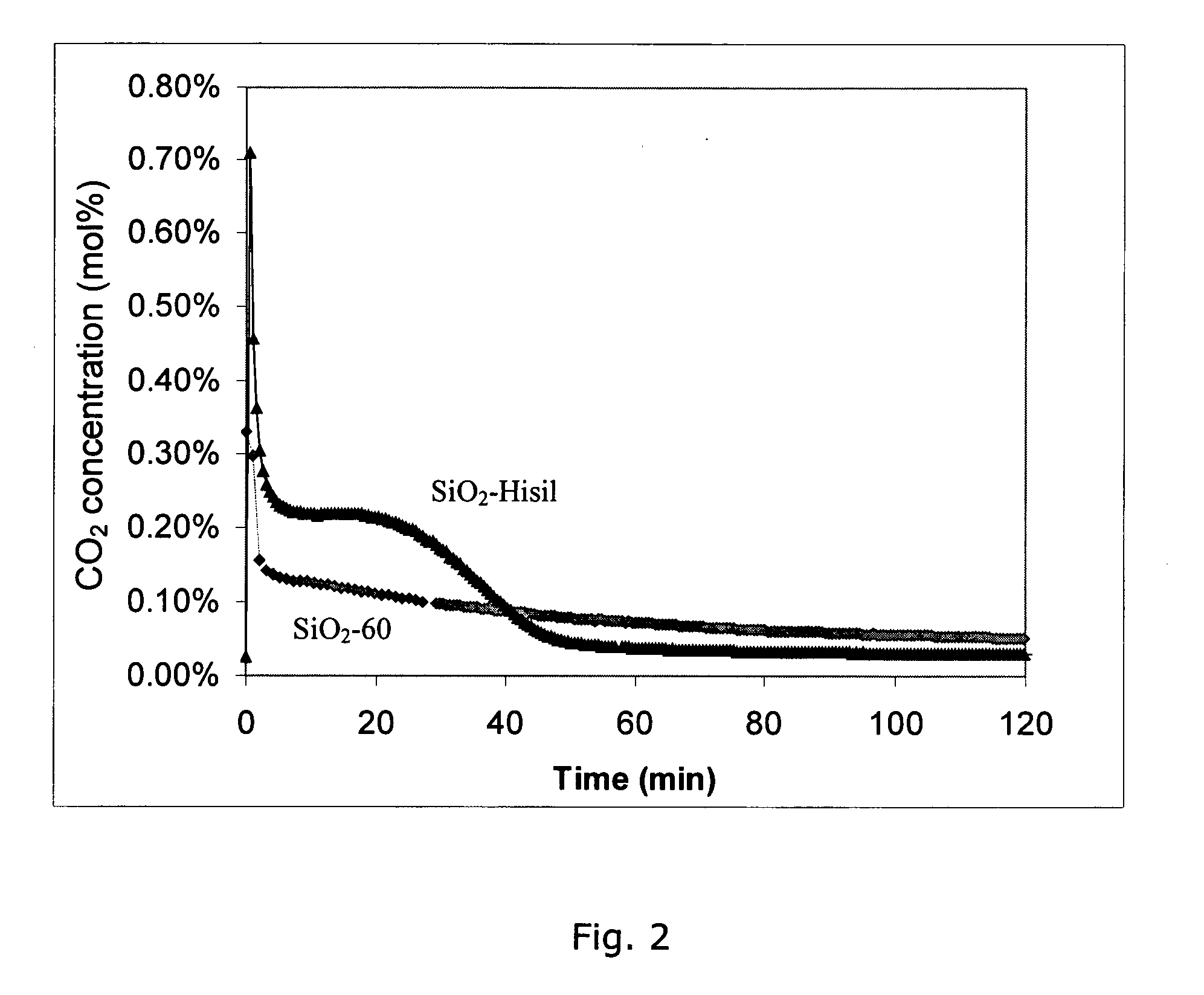
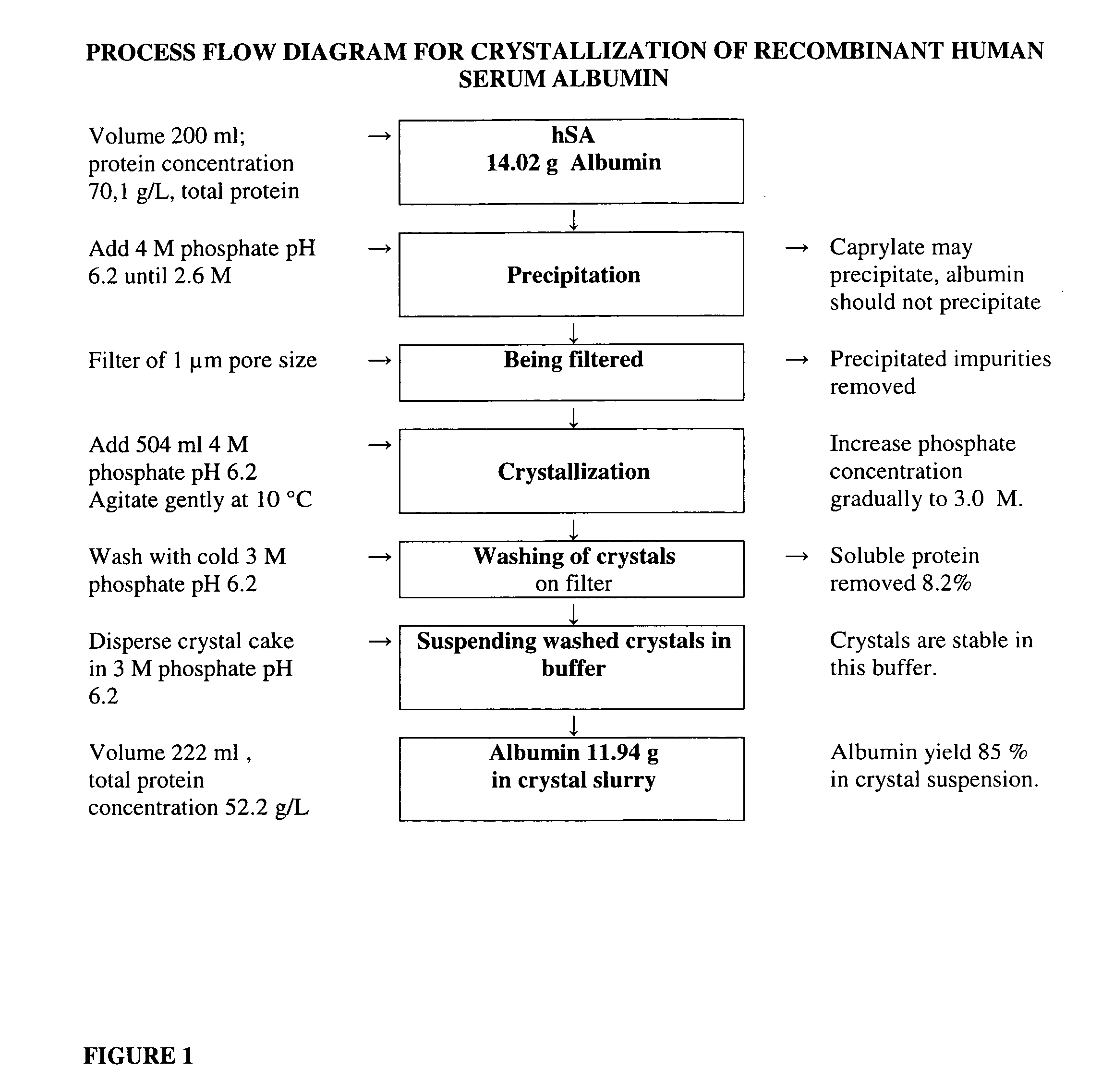
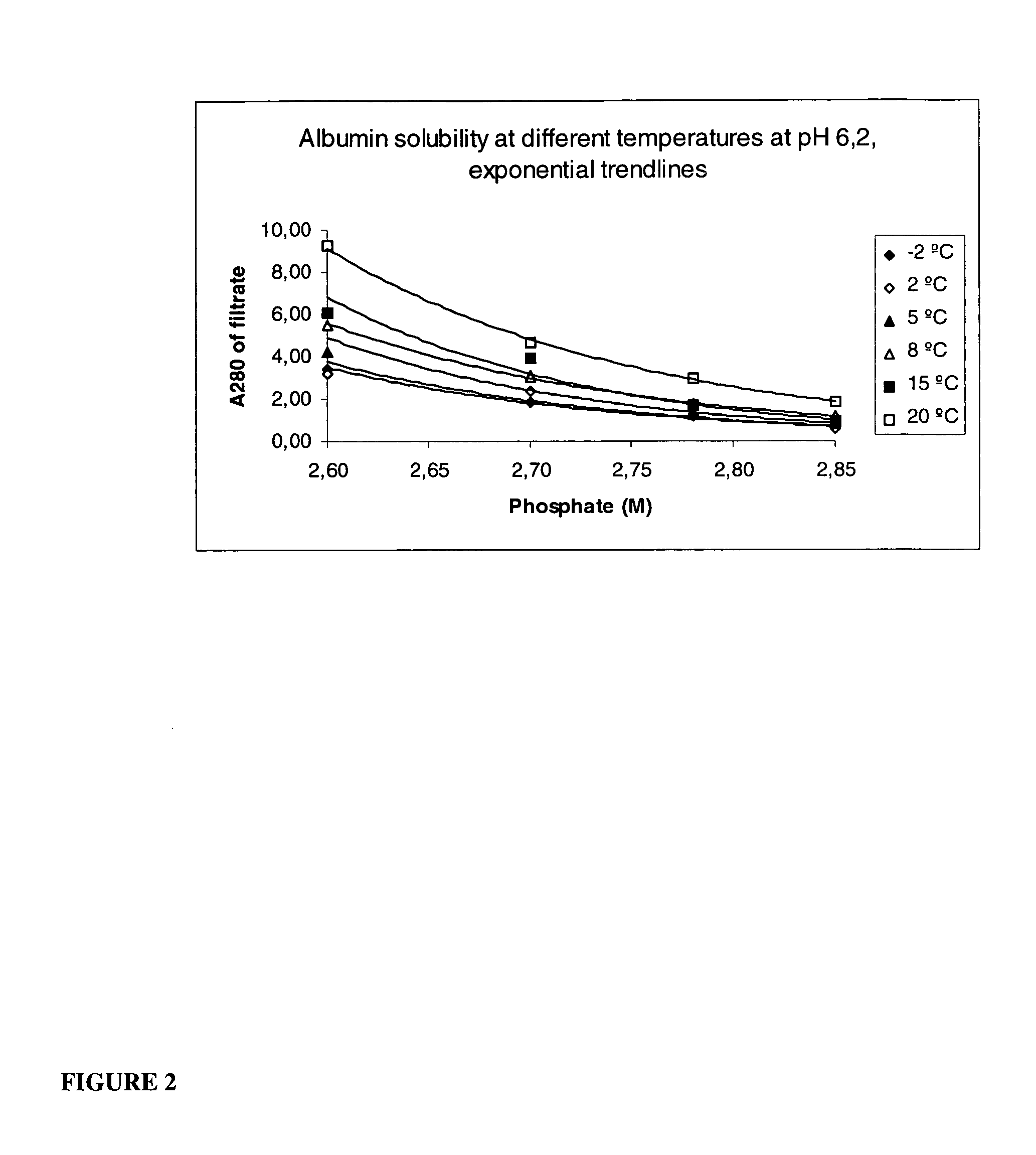
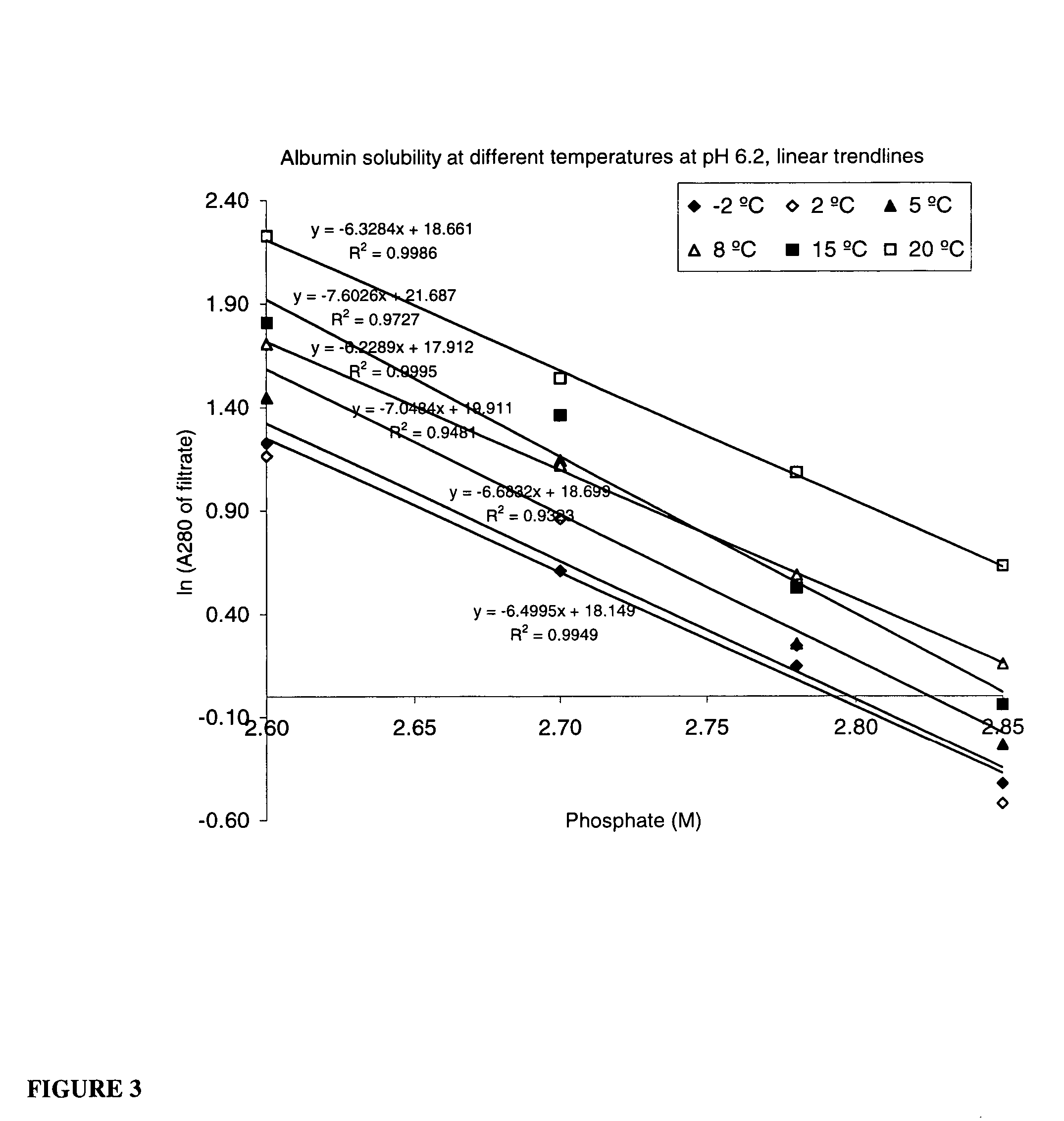
Method for the crystallization of human serum albumin
InactiveUS7087719B2Reduce ionic strengthIncrease ionic strengthPeptide/protein ingredientsSerum albuminPhosphateCrystallization kinetics
The present invention relates to the purification and production of human albumin from various sources through crystallization and repeated crystallization. Basic features of the invented process include providing specific reaction conditions and precipitating reagents to maximize albumin crystallization. Solubility diagrams are utilized as the basis for process control of the invented method. The current invention specifically controls phosphate concentration, pH and temperature to precisely guide crystallization kinetics and crystal yield.
Owner:TAURUS HSA
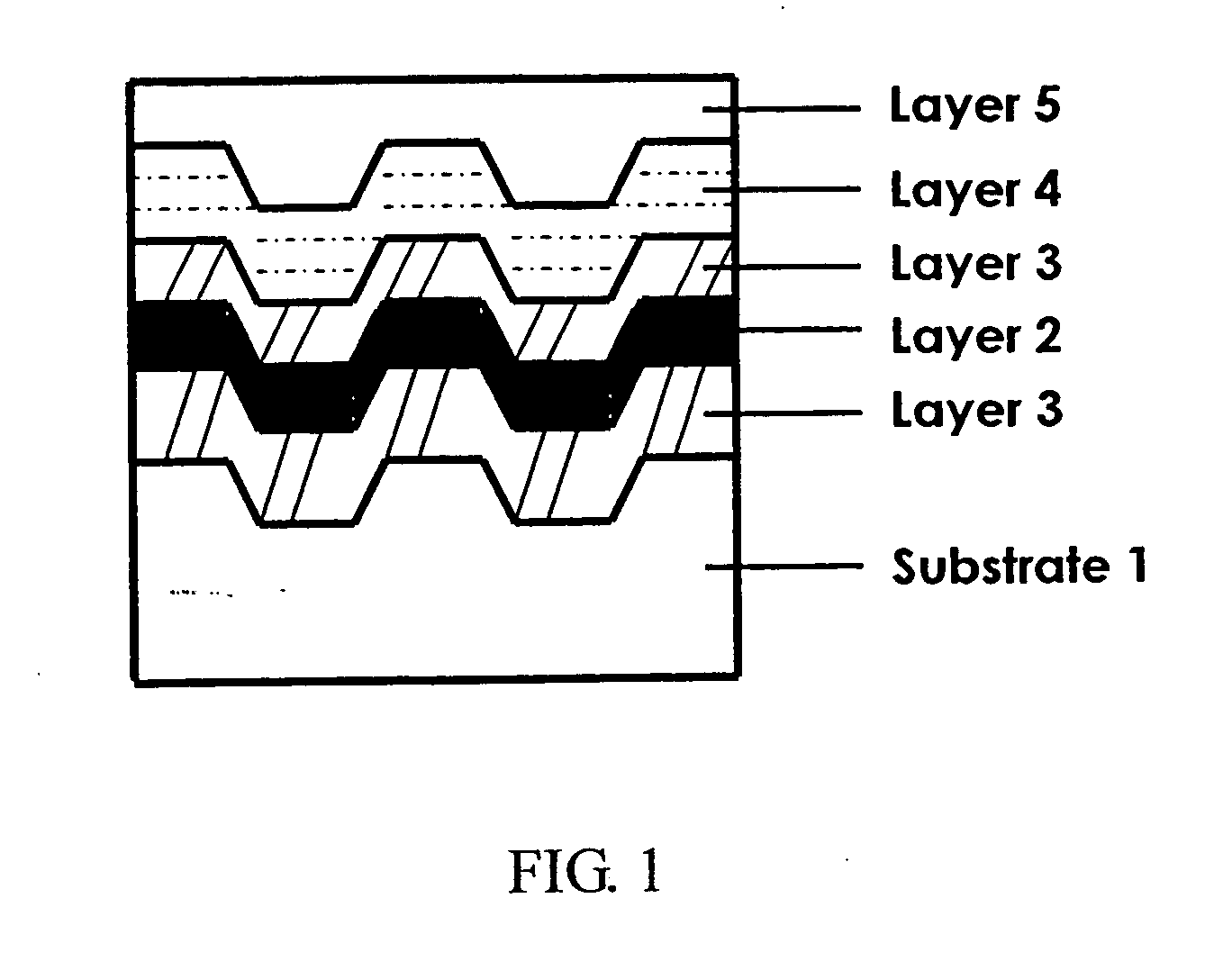
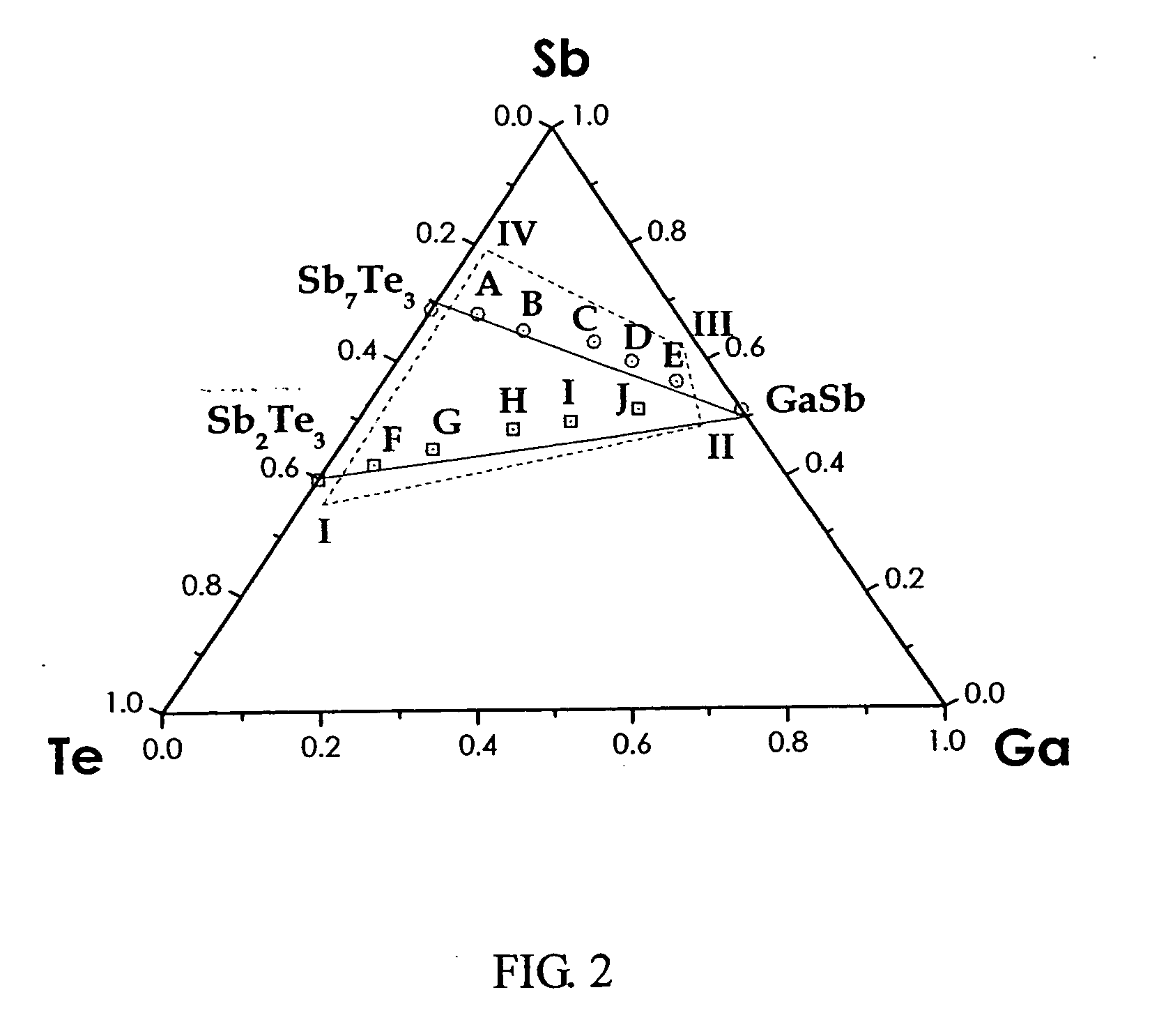
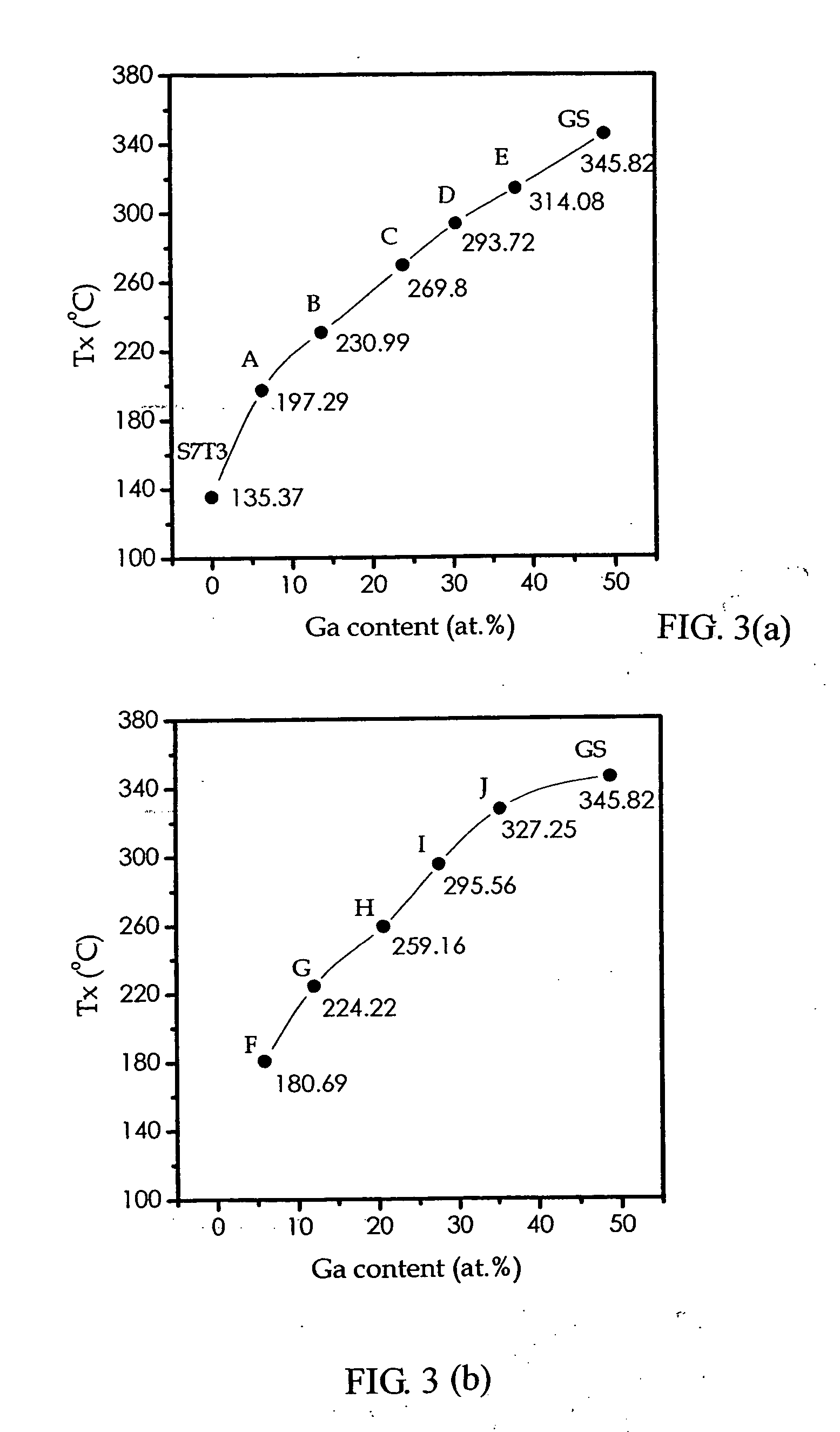
Phase-change recording media based on the Ga-Sb-Te system for ultra-high density optical recording
ActiveUS20050136209A1Improve data transfer rateIncrease rotation speedLayered productsPhotomechanical apparatusHigh rateCrystallization kinetics
This invention discloses a novel rewritable phase-change recording medium for optical data storage, which is based on the GaSbTe ternary alloy system. The designed compositions reside on the Sb7Te3—GaSb and Sb2Te3—GaSb pseudo-binary tielines, and the claimed region can be expressed by the formula (SbxTe100-x)1-z(GaySb100-y)z, 35≦x≦80, 40≦y≦50, 0.05≦z≦0.9. The crystallized phase of the GaSbTe films is a single phase after laser annealing, and the crystal structure is hexagonal with continuous variation in lattice constants. The lattice parameters, a is from 4.255 Å to 4.313 Å and c is from 11.200 Å to 11.657 Å, corresponding to the c / a ratio 2.60 to 2.73. The crystallization kinetics shows increased crystallization temperature (181 to 327° C.) and activation energy (2.8 to 6.5 eV) with increasing GaSb content. The Sb7Te3-rich compositions in the GaSbTe recording media are characteristic of enhanced recrystallization, while those with increasing GaSb content are indicative of higher rate of crystal growth and better erasability. The compositions around Ga2Sb5Te3 exhibit the features of nearly complete erasure and stable cycling performance.
Owner:TSUNG SHUNE CHIN +1
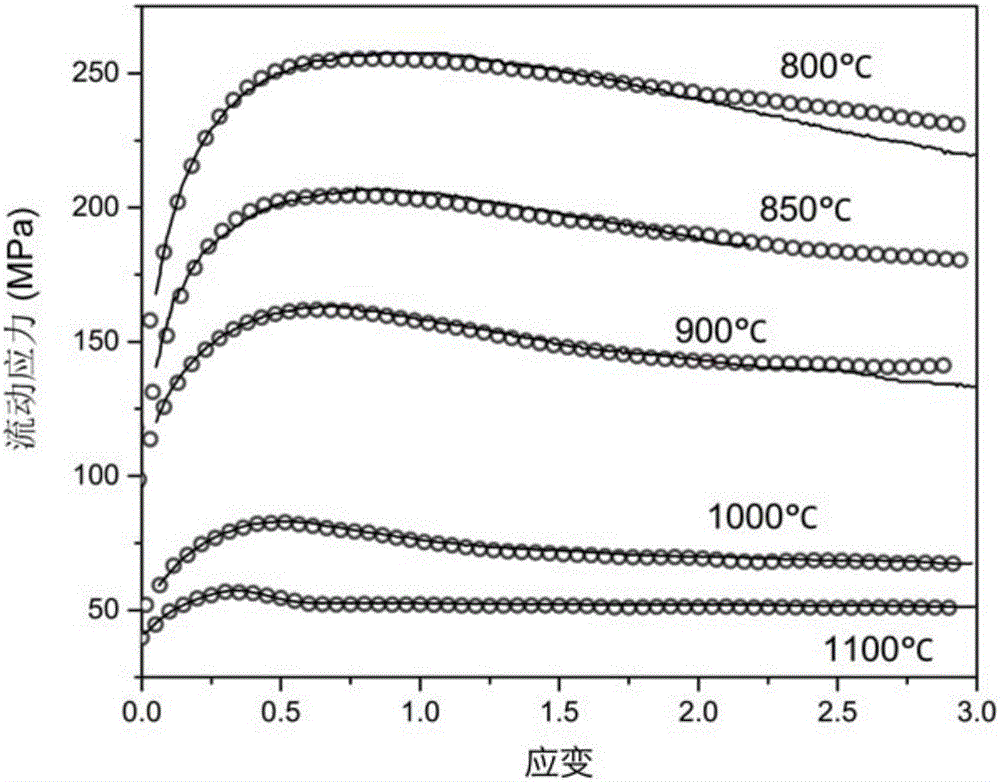
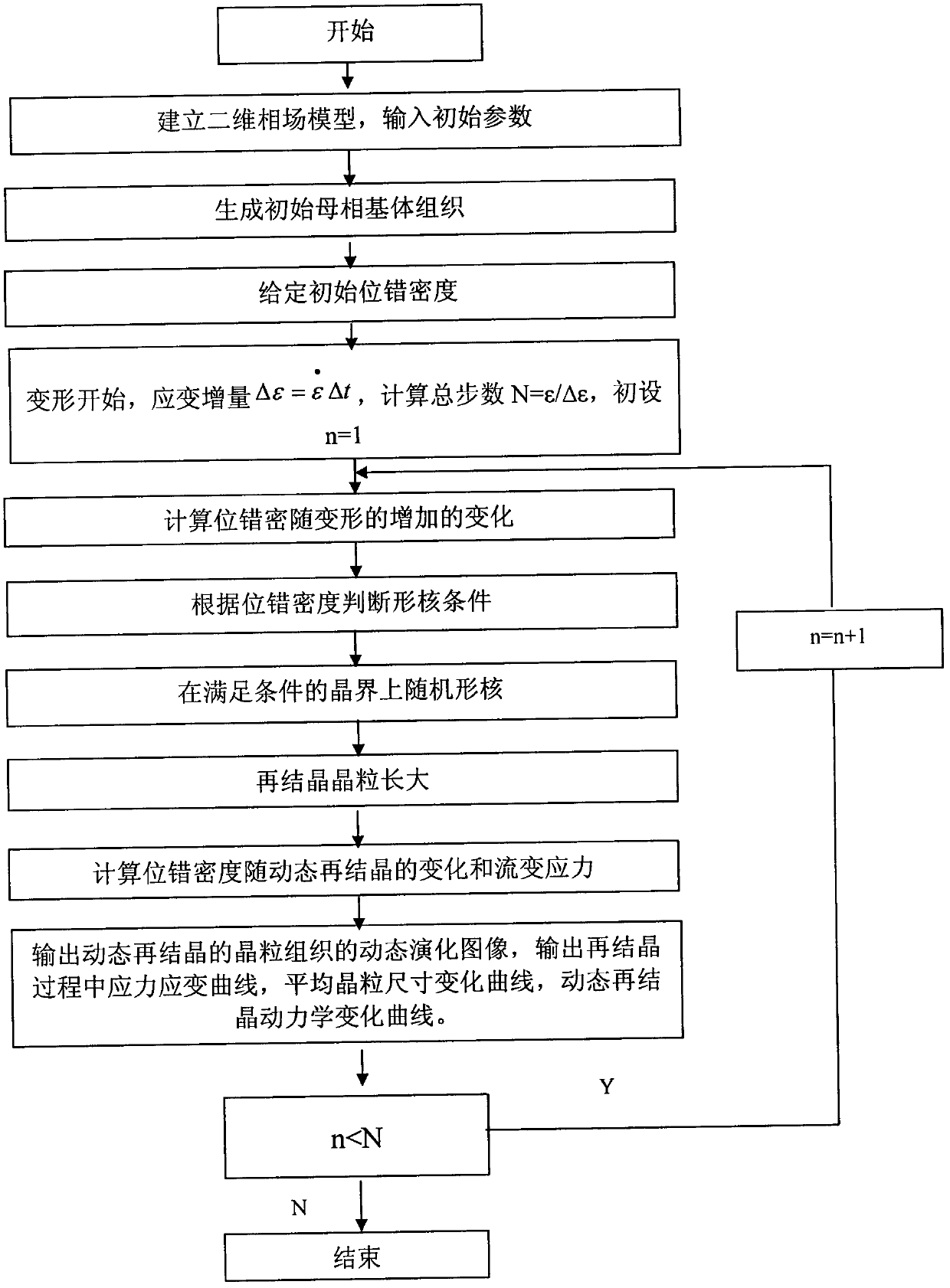
Method for predicting dynamic recrystallization microstructure evolution in thermal deformation process of pure copper
InactiveCN102234716AHelp formulateReduce experiment costHeat treatment process controlPredictive methodsCrystallization kinetics
The invention discloses a method for predicting dynamic recrystallization microstructure evolution in the thermal deformation process of pure copper. In the method, a multi-phase field and dislocation density coupled numerical model is constructed, and related parameters are input, so that the dynamic recrystallization microstructure evolution process, the change of flow stress, dynamic recrystallization conversion fraction and the change condition of average grain size are predicted in real time, the development cost is greatly saved and the development period of new products is shortened. By the method for predicting the dynamic recrystallization microstructure evolution in the thermal deformation process of pure copper, the grain structure in the thermal deformation process is observed in real time, a change rule of a stress strain curve, a kinetic conversion rule of dynamic recrystallization and the conversion form of the grain size along with strain change are obtained, and the method has important significance for reasonably making a processing technology and optimizing the structure and performance of a product.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for predicting dynamic recrystallization fractions of high-alloy materials under time-varying working conditions
The invention discloses a method for predicting dynamic recrystallization fractions of high-alloy materials under time-varying working conditions. The method includes steps of (1), acquiring deformed test specimens of the materials through hot compression simulation experiments; (2), acquiring metallographs of the test specimens through metallographic experiments; (3), counting recrystallization fractions of the test specimens by the aid of Photoshop software; (4), acquiring equivalent strain values and average strain rate values of the test specimens by the aid of finite element simulation; (5), acquiring parameters of the traditional dynamic recrystallization kinetic model by means of regression; (6), improving the traditional dynamic recrystallization kinetic models to obtain novel models capable of predicting the dynamic recrystallization fractions under the time-varying working conditions. The method has the advantages that the method can be used for building the dynamic recrystallization kinetic models for the high-alloy materials and also can be used for predicting the dynamic recrystallization fractions under the time-varying working conditions.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Crystal red phosphorus nanowire and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113174634APromote growthLow internal pressure requirementPolycrystalline material growthFrom solid stateNanowireCrystallization kinetics
The invention discloses a crystal red phosphorus nanowire and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of red phosphorus preparation. The preparation method comprises the following steps: with red phosphorus, iodine and a tin elementary substance as raw materials, controlling a pressure value to be 1.0-5.3 MPa under a vacuum sealing condition, then conducting programmed heating to 612-628 DEG C, carrying out heat treatment, and then cooling to room temperature by sections to obtain the crystal red phosphorus nanowire. According to the method, red phosphorus, iodine and tin are used as raw materials; when the pressure is controlled to be 1.0-5.3 MPa, the instability of crystallization kinetics of the red phosphorus is reduced, the effect of a mineralizer is not enough to reach a lower energy state, and only the crystal red phosphorus nanowire can be formed; and the ultra-long crystal red phosphorus nanowire is obtained, and meanwhile, a foundation is laid for researching a one-dimensional nanomaterial.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A perovskite solar cell doped with potassium thiocyanate and a preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109244251AInhibit migrationImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetallic electrodePotassium thiocyanate
The invention relates to the perovskite solar cell field, which provides a perovskite solar cell doped with potassium thiocyanate and a preparation method thereof. A perovskite battery is composed ofFTO conductive glass, an electron transport layer, a perovskite light absorbing layer, a hole transport layer and a metal electrode from bottom to top. The invention aims at solving the problems of poor crystallinity of perovskite and large lag of perovskite battery. potassium thiocyanate is doped in the perovskite light absorbing layer, which can change the crystallization kinetics of perovskite,promote the grain growth, passivate the internal defect state, stabilize the phase structure of perovskite, restrain the ion migration, thus effectively improve the crystallization quality of perovskite, improve the photoelectric efficiency and stability of perovskite battery, and eliminate the hysteresis effect.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING +1
Single-walled carbon nanotube-ceramic composites and methods of use
InactiveUS20100240529A1Material nanotechnologyOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsField emission deviceCeramic composite
Composites of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) and a ceramic support (e.g., silica) comprising a small amount of catalytic metal, e.g., cobalt and molybdenum, are described. The particle comprising the metal and ceramic support is used as the catalyst for the production of the single-walled carbon nanotubes. The nanotube-ceramic composite thus produced can be used “as prepared” without further purification providing significant cost advantages. The nanotube-ceramic composite has also been shown to have improved properties versus those of purified carbon nanotubes in certain applications such as field emission devices. Use of precipitated and fumed silicas has resulted in nanotube-ceramic composites which may synergistically improve the properties of both the ceramic (e.g., silica) and the single-walled carbon nanotubes. Addition of these composites to polymers may improve their properties. These properties include thermal conductivity, thermal stability (tolerance to degradation), electrical conductivity, modification of crystallization kinetics, strength, elasticity modulus, fracture toughness, and other mechanical properties. Other nanotube-ceramic composites may be produced based on Al2O3, MgO and ZrO2, for example, which are suitable for a large variety of applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Method for the crystallization of human serum albumin
The present invention relates to the purification and production of human albumin from various sources through crystallization and repeated crystallization. Basic features of the invented process include providing specific reaction conditions and precipitating reagents to maximize albumin crystallization. Solubility diagrams are utilized as the basis for process control of the invented method. The current invention specifically controls phosphate concentration, pH and temperature to precisely guide crystallization kinetics and crystal yield.
Owner:GTC BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
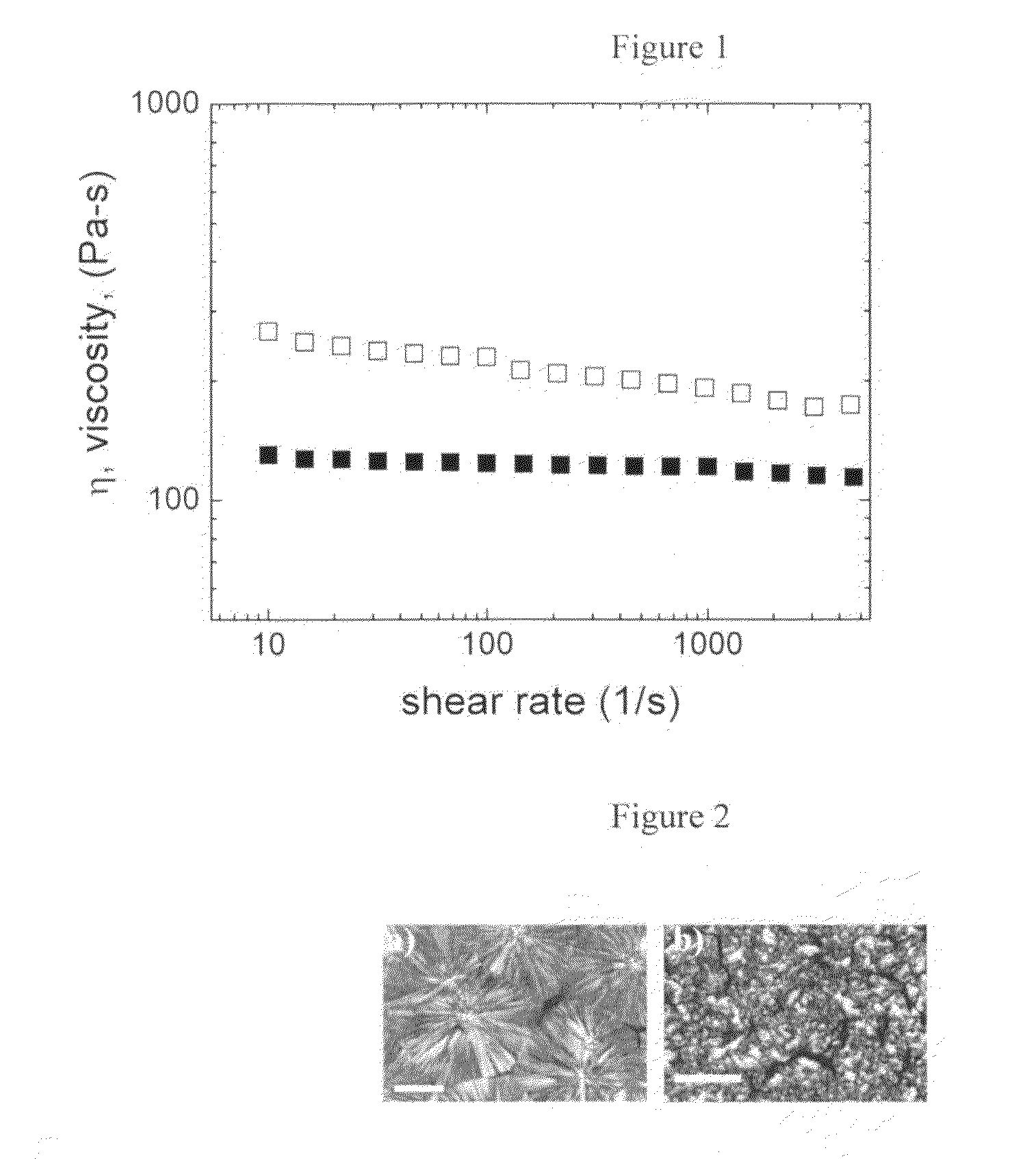
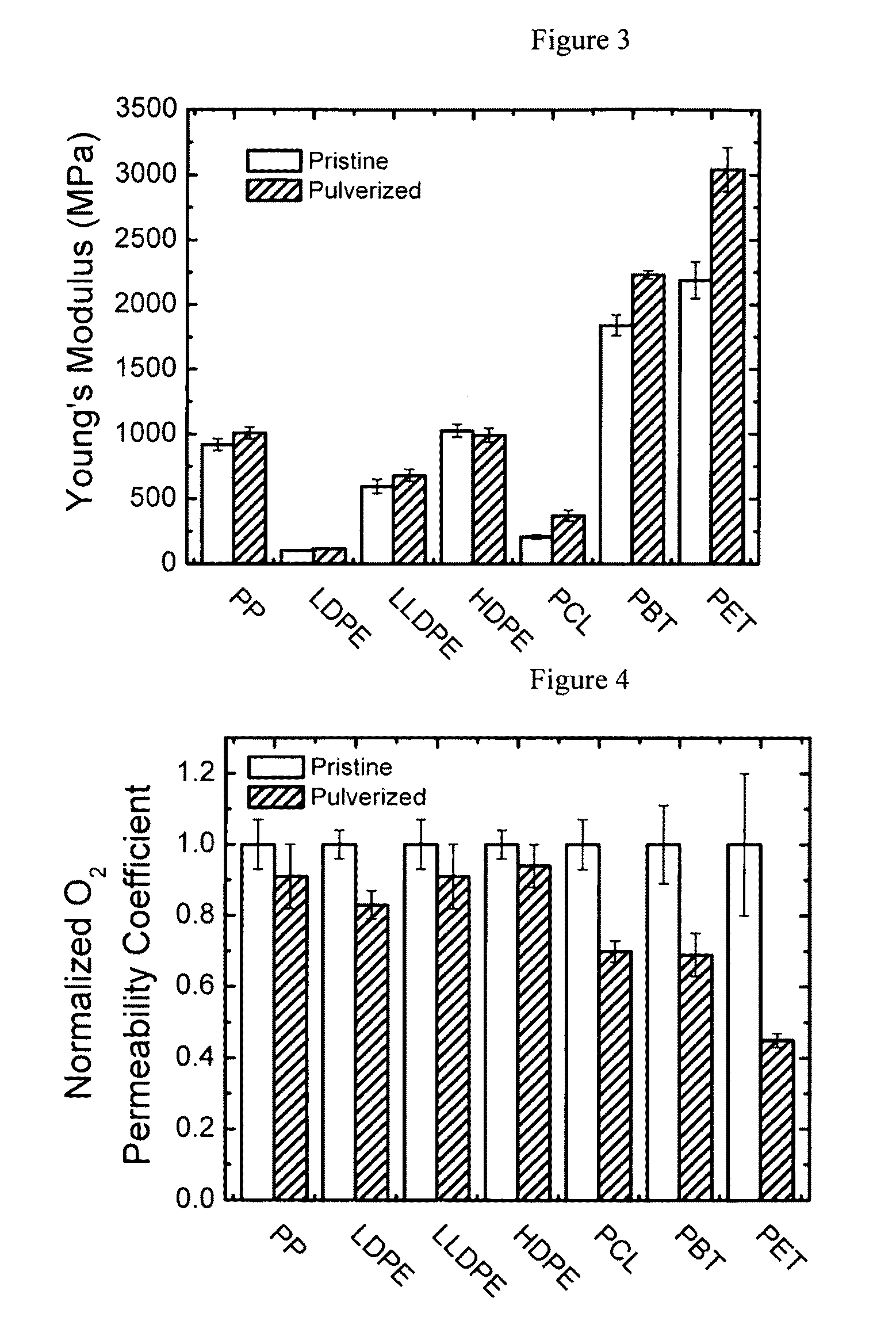
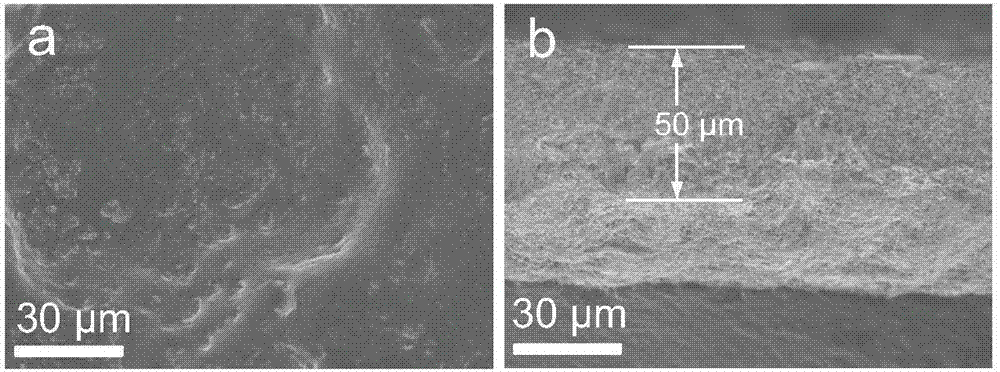
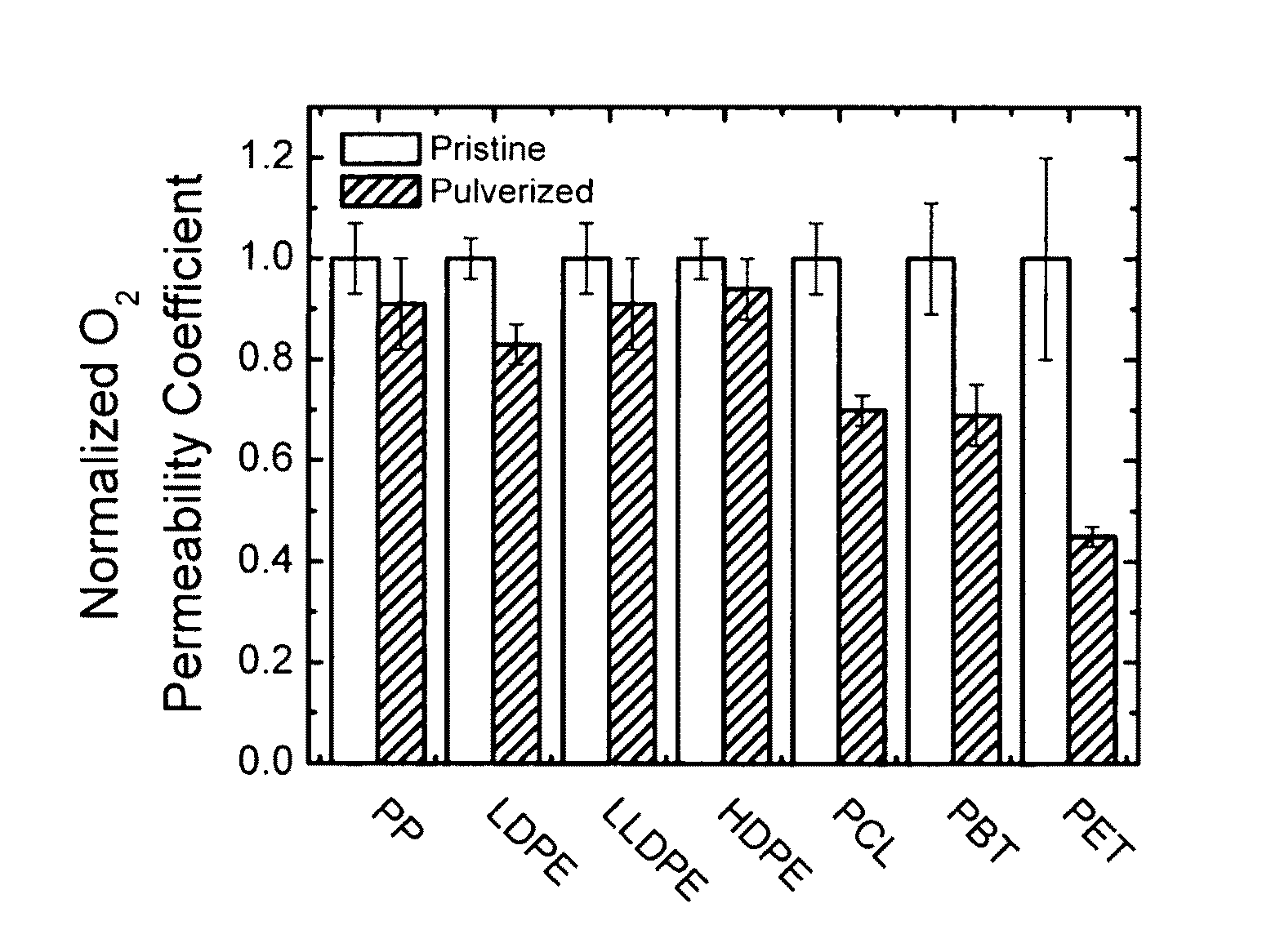
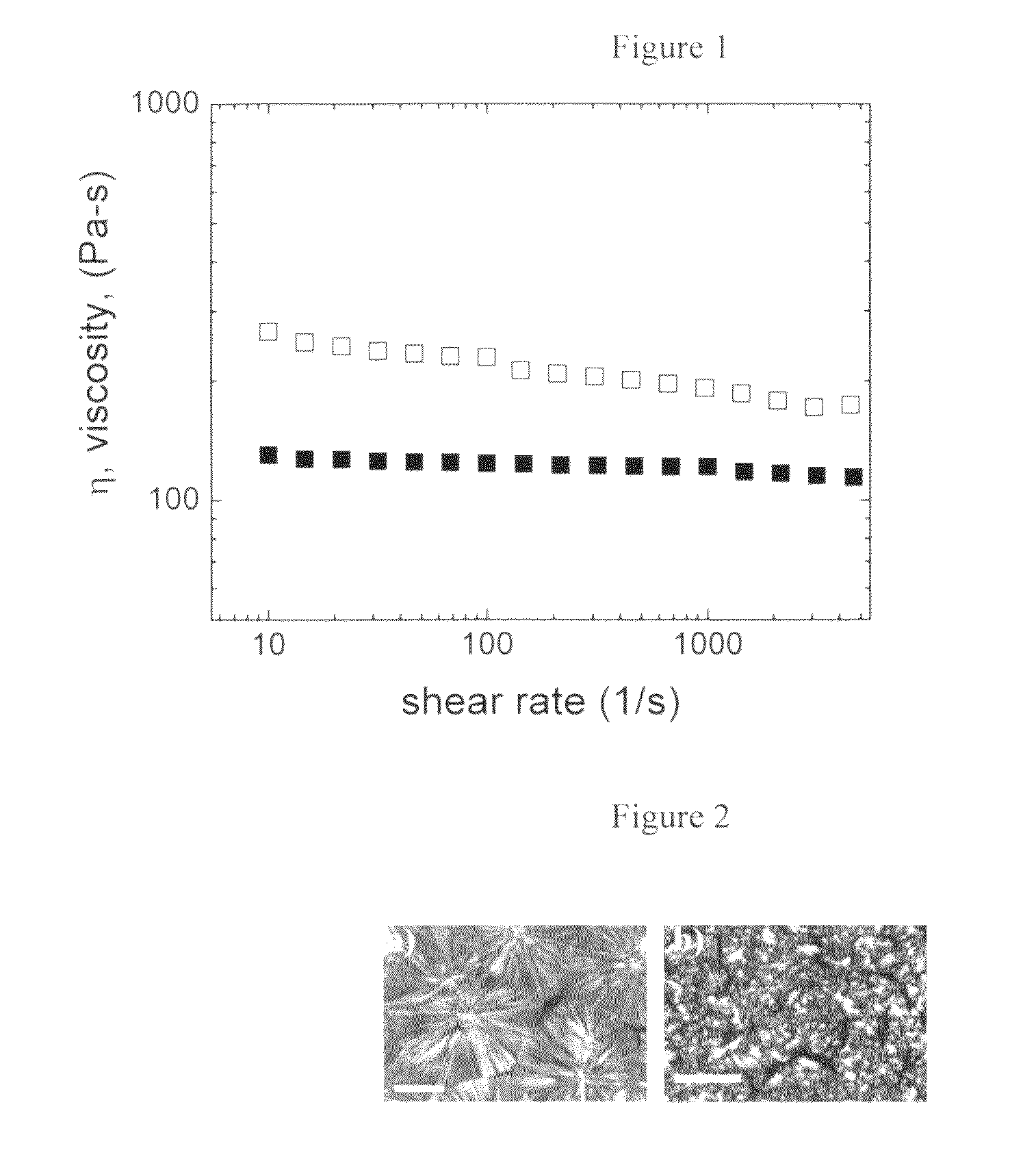
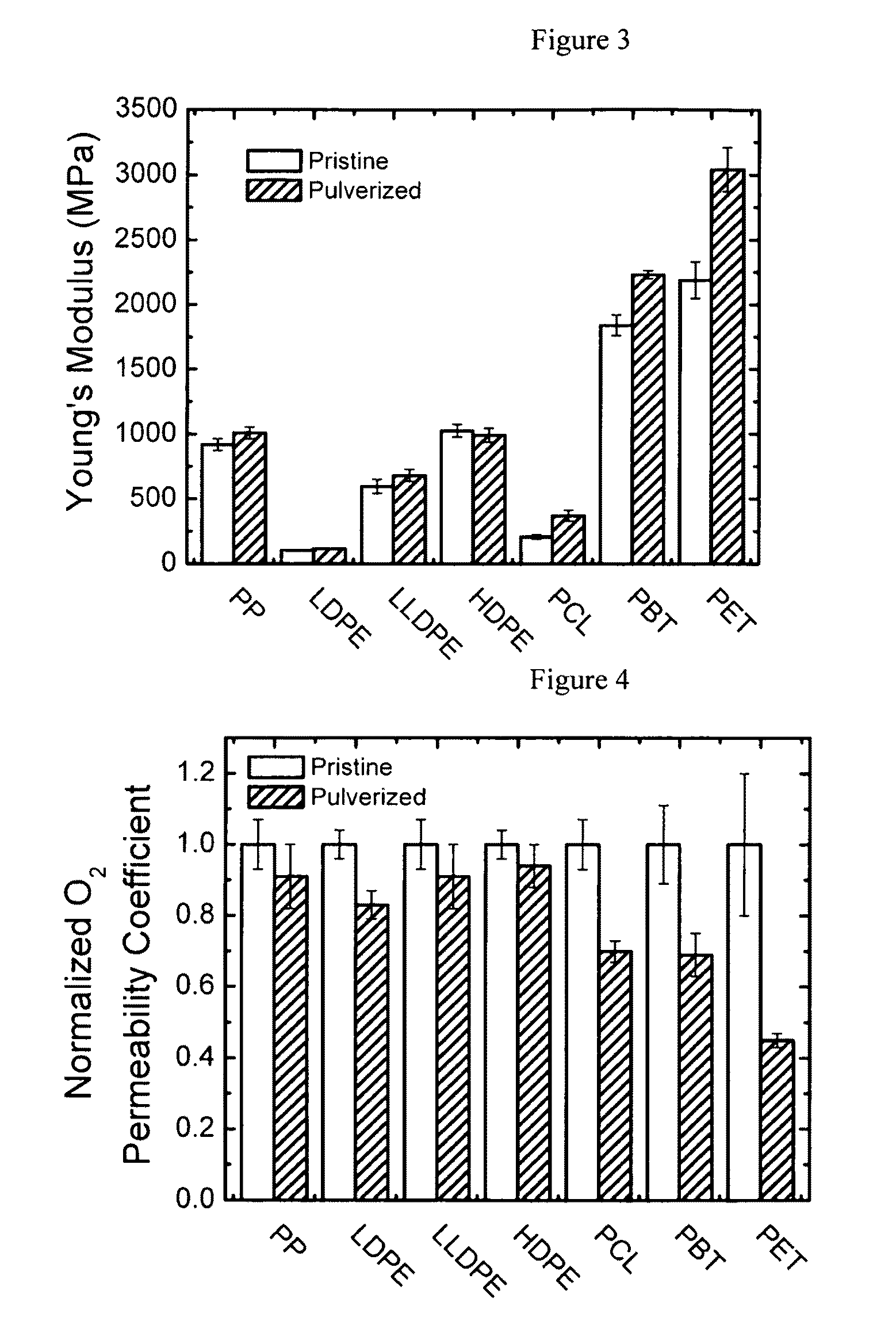
Enhancing the physical properties of semi-crystalline polymers via solid-state shear pulverization
ActiveUS20090198032A1Enhanced crystallization kinetic propertyIncreased onset crystallization temperatureGrain huskingGrain polishingCrystallization kineticsMechanical property
Solid-state shear pulverization of semi-crystalline polymers and copolymers thereof and related methods for enhanced crystallization kinetics and physical / mechanical properties.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Method for in situ preparing of all-solid-state electrolyte
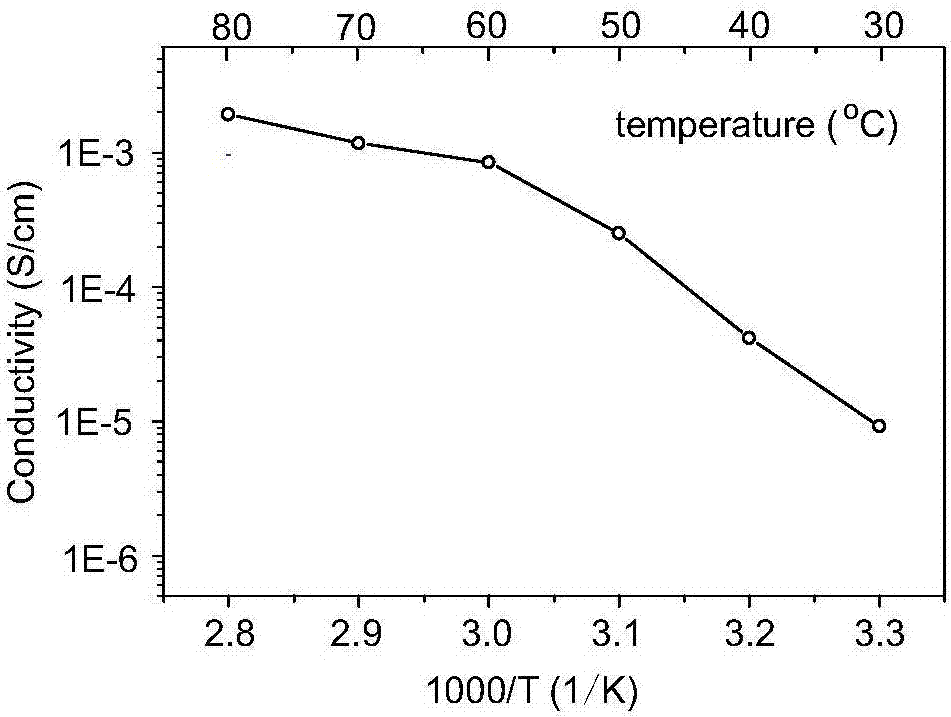
InactiveCN106941189AGood flexibilityHigh specific capacityMaterial nanotechnologySecondary cellsSolid state electrolyteAll solid state
The invention discloses an all-solid-state electrolyte and an in situ preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of all-solid-state electrolytes. The in situ preparation method is simple without involving of any high-risk operations. The all-solid-state electrolyte is characterized in that: SiO2nanoparticles are evenly distributed in a polyethylene oxide skeleton, large anion lithium salt LiBOB is loaded in the skeleton, crystallization kinetics of polyethylene oxide can be effectively inhibited, polymer ionic conductivity is greatly improved, and meanwhile in situ composite SiO2 enhances the mechanical properties of the solid electrolyte. When the all-solid-state electrolyte is used in a lithium secondary battery, better results are obtained. The prepared all-solid-state electrolyte has the advantages of simple process and easy enlarged production, can inhibit lithium dendrite generation, can eliminate flammable and explosive safety hazards, greatly improves the energy density, and provides a solid foundation for commercialization of all-solid-state lithium secondary batteries.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for regulating growth behavior of spinel phase in stainless steel slag
ActiveCN107475468ALarge particle sizeHigh crystallinityRecycling and recovery technologiesMolten stateCrystallization kinetics
The invention belongs to the technical field of metallurgy resource comprehensive utilization and particularly relates to a method for regulating the growth behavior of a spinel phase in stainless steel slag. The method for regulating the growth behavior of the spinel phase in the stainless steel slag includes the following steps that the stainless steel slag is enabled to be in a molten state, and a modifier is added into the stainless steel slag; shearing force is applied to an obtained material, and the stainless steel slag is kept in the molten state while shearing force is applied; and the material is cooled to room temperature to obtain the modified stainless steel slag. By means of the method, the shearing force effect is applied in the stainless steel slag molten modification process, the nucleation-growth behavior of spinel in the high-temperature molten slag is strengthened by improving the crystallization kinetic conditions, formation of large-size spinel crystals is promoted, highly-stable concentration of chromium in the spinel phase is achieved, the risk of oxidation dissolution of chromium in the stainless steel slag is lowered, and conditions are provided for separating and extracting of the spinel phase.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Preparation method of perovskite passivation layer
ActiveCN110620183AQuality improvementReduce the density of defect statesSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCrystallization kineticsField-effect transistor
The invention provides a preparation method of a perovskite passivation layer, and belongs to the technical field of crystal material processing. Aiming at solving the problem that at present, the heterogeneous passivation effect is not ideal, the perovskite homogeneous passivation technology is proposed. The crystallization kinetics process of a passivation layer precursor solution on the surfaceof a perovskite material is adjusted by controlling the temperature, an amorphous passivation layer is promoted to grow, the amorphous passivation layer is used for passivating the defects on the surface and grain boundary of the perovskite material, and the quality of the material is improved. The passivation method provided by the invention is simple in process and easy to implement, the thickness of the passivation layer can be flexibly controlled, the quality of the perovskite material is effectively improved, and the prepared perovskite material has the characteristics of low defect state density and good electrical properties. The method can be widely applied to photoelectronic devices such as light emitting diodes, transistors, field effect transistors, solar cells and lasers.
Owner:JILIN NORMAL UNIV
Anti-frozen-heaving heat pipe
InactiveCN101571362ATo achieve the effect of anti-freeze heaveSolve the defect of frost heave crack pipeSolar heat devicesIndirect heat exchangersSwelling capacityCrystallization kinetics
The invention relates to an anti-frozen-heaving heat pipe. A structure of the heat pipe comprises: a porous medium structure is arranged on the wall surface in an evaporation section of the heat pipe, wherein the porous medium structure is in a porous arrangement; each aperture is between 0.05 and 1.0 mm; and the upper end of the porous medium structure is higher than the liquid level. The invention solves the problems that when the frozen heaving happens, a core heat transfer component of a heat pipe solar water heater, namely the heat pipe may have the phenomenon of pipe cracking to cause that the heat pipe has no effect and the whole solar water heater is damaged and cannot work normally. The heat pipe is analyzed from the angles of crystallization kinetics and material mechanics, and the porous medium structure is arranged on partial positions of the evaporation section of the heat pipe; and the effect of the anti-frozen heaving of the heat pipe is realized in a mode of changing the crystallization of a liquid-phase working medium and in a mode of reducing the phase-transition swell capacity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Thermoplastic elastomer compositions, methods of making and articles made from the same
ActiveUS8207270B2Promote crystallizationReduce and eliminate interferenceOrganic dyesThermoplasticVulcanization
Provided are thermoplastic elastomer compositions, many dynamically vulcanized, with superior crystallization kinetics, methods for making the compositions and articles made therefrom. The thermoplastic elastomer compositions comprise at least a propylene polymer thermoplastic, a rubber and a crystallization additive. The processes for preparation of the thermoplastic elastomer compositions comprises dynamic vulcanization of mixture of a propylene polymer thermoplastic, a rubber and a cure agent followed by addition of a crystallization additive. Further, preparation of articles from the thermoplastic elastomer compositions may be accomplished through traditional thermoforming operations useful with conventional thermoplastics.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Large-area perovskite light-emitting film and light-emitting diode thereof
PendingCN113745438AHigh photoluminescence efficiencyFlat surfaceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuantum efficiencyLuminous intensity
The invention discloses a large-area perovskite light-emitting film and a light-emitting diode thereof. The large-area perovskite light-emitting film is highly compact and high in photoluminescence efficiency. According to a printing preparation method of the large-area perovskite light-emitting film, two key steps, namely solvent volatilization of a wet film and thermal annealing crystallization of a perovskite film can be separated through vacuum pretreatment, so that control over crystallization kinetics in the preparation process of the perovskite light-emitting film is achieved, and the problem that a uniform large-area perovskite light-emitting layer cannot be prepared through a traditional spin coating technology is solved. On the basis of the printing preparation process of the large-area perovskite light-emitting film, a large-area perovskite light-emitting diode with uniform light emitting and high external quantum efficiency is prepared, the process for preparing the light-emitting diode is simple in step, the limitation of the current preparation process (such as a spin-coating method and an anti-solvent extraction method) on the preparation size of the perovskite light-emitting diode is solved, and the large-area perovskite light-emitting diode with uniform luminous intensity is obtained.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Propylene polymer compositions and processes for making the same
ActiveCN101490167AWide molecular weight distributionWide composition distributionBulk chemical productionCrystallization kineticsElectron donor
Provided are propylene polymer compositions comprising a propylene copolymer and a propylene homopolymer polymerized in the presence of the propylene copolymer. The propylene polymer compositions exhibit properties such as broad molecular weight distribution, low crystallinity, high solubles and superior crystallization kinetics and are useful in fast cycle-time processing methods such as injection molding, sheet extrusion, thermoforming, and oriented film fabrication. Also provided is a process for preparing the propylene polymer compositions in the presence of a catalyst and at least two electron donors using sequential or parallel polymerization reaction zones. Finally, articles made from the propylene polymer composition are provided, particularly articles requiring high stiffness, high heat deflection temperature, good fatigue resistance and low temperature impact resistance such as appliance parts.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
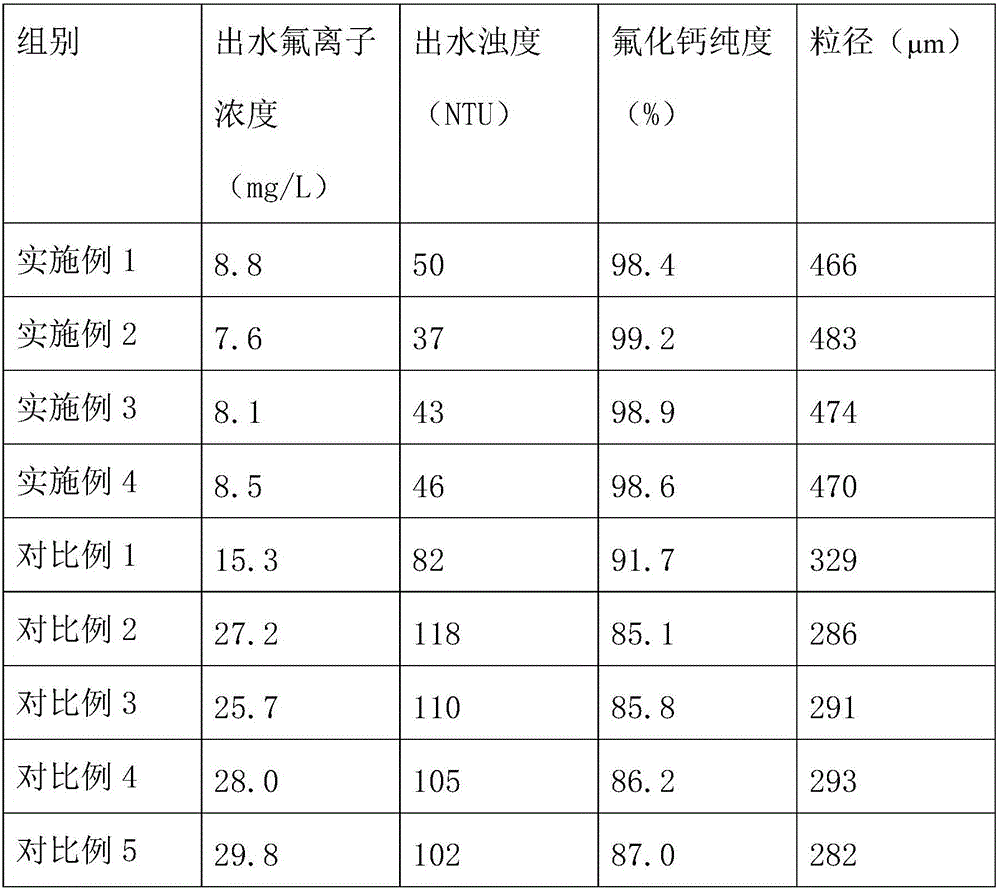
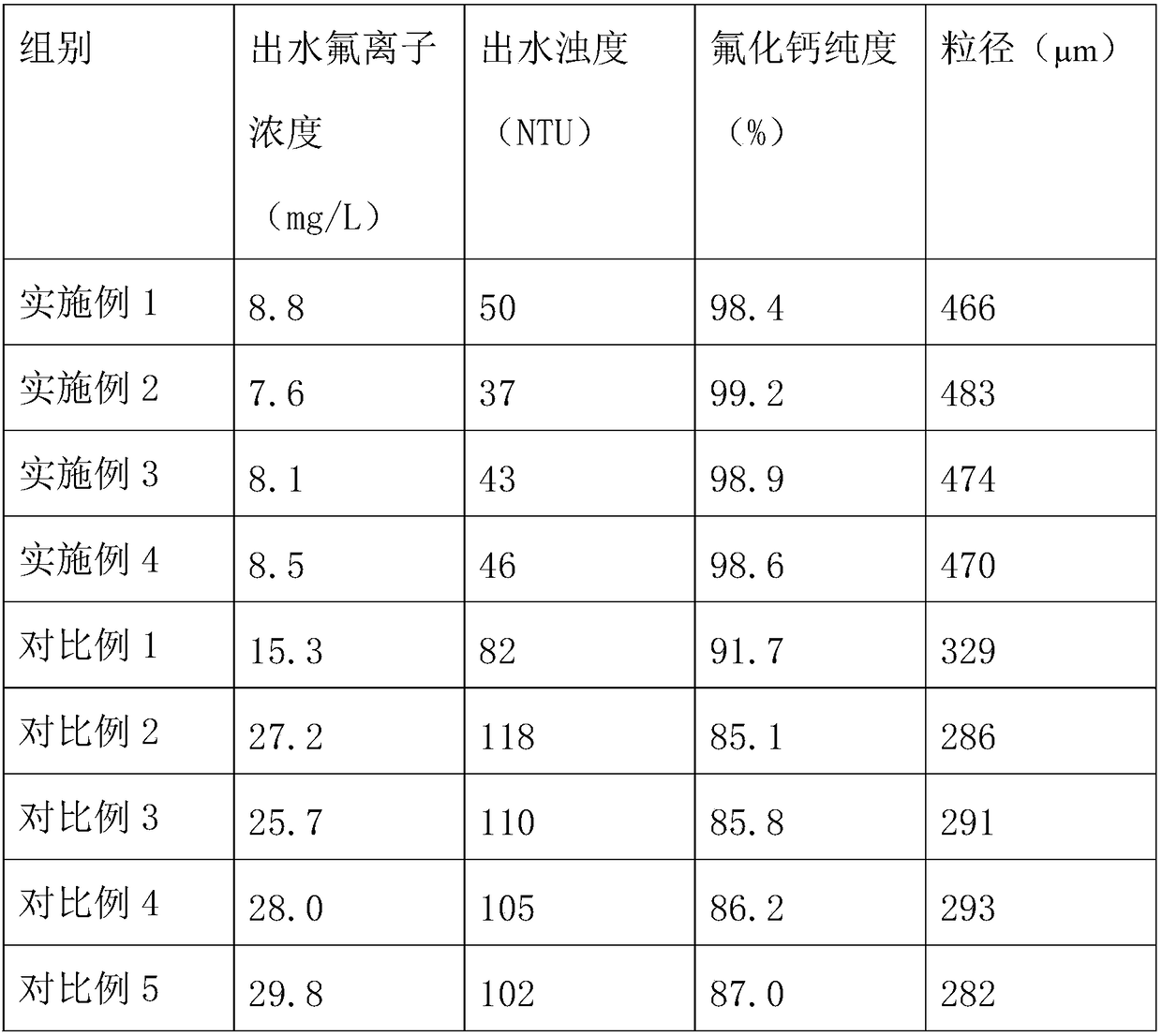
Calcium fluoride (CaF2) induction crystallization process from rare-earth metal smelting high-fluoride wastewater
InactiveCN105836866AImprove liquidityImprove uniformityWater treatment parameter controlWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsHigh fluorideCrystallization kinetics
The invention discloses a calcium fluoride (CaF2) induction crystallization process from rare-earth metal smelting high-fluoride wastewater. The fluidized bed crystallization is used; meanwhile, an electromagnetic field is exerted; under the helium gas atmosphere, through the coupling effect of the fluidized bed crystallization, the electromagnetic field and the helium gas, the crystallization dynamics process parameters such as the crystallization bed process, flow rate, temperature and the like are controlled, so that the CaF2 crystallization velocity is accelerated; the efficient crystallization is realized; the high-purity CaF2 is obtained; the fluorine deep removal and the CaF2 resource recovery are also realized.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Process for inducing crystallization of calcium fluoride in rare earth metal smelting high-fluorine wastewater
InactiveCN105836866BImprove liquidityImprove uniformityWater treatment parameter controlWater/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsHigh fluorideCrystallization kinetics
The invention discloses a process for inducing crystallization of calcium fluoride in rare earth metal smelting high-fluorine wastewater, which adopts fluidized bed crystallization and applies an electromagnetic field at the same time. , temperature and other crystallization kinetic process parameters, accelerate the crystallization rate of CaF2, realize high-efficiency crystallization, and obtain high-purity CaF2, thereby realizing the deep removal of fluorine and the resource utilization of CaF2 at the same time.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
A method for predicting the dynamic recrystallization fraction of highly alloyed materials under time-varying conditions
InactiveCN106053754BSolving the puzzle of dynamic recrystallization behaviorMaterial thermal analysisTesting metalsCrystallization kineticsAlloy
The invention discloses a method for predicting dynamic recrystallization fractions of high-alloy materials under time-varying working conditions. The method includes steps of (1), acquiring deformed test specimens of the materials through hot compression simulation experiments; (2), acquiring metallographs of the test specimens through metallographic experiments; (3), counting recrystallization fractions of the test specimens by the aid of Photoshop software; (4), acquiring equivalent strain values and average strain rate values of the test specimens by the aid of finite element simulation; (5), acquiring parameters of the traditional dynamic recrystallization kinetic model by means of regression; (6), improving the traditional dynamic recrystallization kinetic models to obtain novel models capable of predicting the dynamic recrystallization fractions under the time-varying working conditions. The method has the advantages that the method can be used for building the dynamic recrystallization kinetic models for the high-alloy materials and also can be used for predicting the dynamic recrystallization fractions under the time-varying working conditions.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Enhancing the physical properties of semi-crystalline polymers via solid-state shear pulverization
ActiveUS8410245B2Good physical and mechanical propertiesImprove crystallizationGrain huskingGrain polishingCrystallization kineticsMechanical property
Solid-state shear pulverization of semi-crystalline polymers and copolymers thereof and related methods for enhanced crystallization kinetics and physical / mechanical properties.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
A Method for Obtaining Mobility Parameters of Grain Boundary in Metal Material Recrystallization Microstructure Evolution
ActiveCN106503397BImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansDesign optimisation/simulationCrystallization kineticsActivation energy
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com