Surface treated inorganic particle additive for increasing the toughness of polymers
A technology of inorganic particles, biopolymers, applied in applications, household appliances, garbage collection, etc., can solve problems such as poor mechanical strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] In a laboratory experiment, the inventors were able to demonstrate the beneficial effect of fatty acid-coated calcium carbonate additives in improving the toughness of PLA polymers. Specifically, improvements in room- and low-temperature impact toughness as well as improvements in rigidity of PLA were demonstrated.
[0031] The properties of PLA polymers can be controlled by controlling the ratio of stereoisomers comprising PLA. For example, polymerization of predominantly L-form with greater than about 15 mole percent D-form or meso-lactide produces amorphous PLA random copolymers. Polymerization of L-lactic acid instead produces poly-L-lactide (PLLA), which is a semi-crystalline polymer with crystallinity up to 40% or more.
[0032] The inventors used a number of different calcium carbonate-based additives, coated them with stearic acid, and compounded them into PLLA polymer samples to demonstrate the beneficial effect of stearic acid-coated calcium carbonate on the ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Figure 6 Shown against uncoated The coating level of Bio's calcium carbonate precursor particles was studied to determine the results of the optimal coating level. The falling weight impact energy was determined for PLA polymer samples prepared from polymer resin composited with calcium carbonate particles at various coating levels. Calcium carbonate precursor samples were dry coated to each coating level (0.0 to 4.0 wt %) using a laboratory Henschel mixer. However, the coating method is not limited to the dry coating method. Wet coating methods can also be used. Each calcium carbonate material was compounded into PLLA at a target concentration of 25 wt%. Toughness in this test is measured as a falling weight. Figure 6 The resulting curve in shows the classic "S-shaped" curve60, which indicates the minimum coating level required to improve the impact toughness of PLLA. From the sloped portion 62 of the "S-curve" it is estimated that a minimum coating of about 2...
Embodiment 3
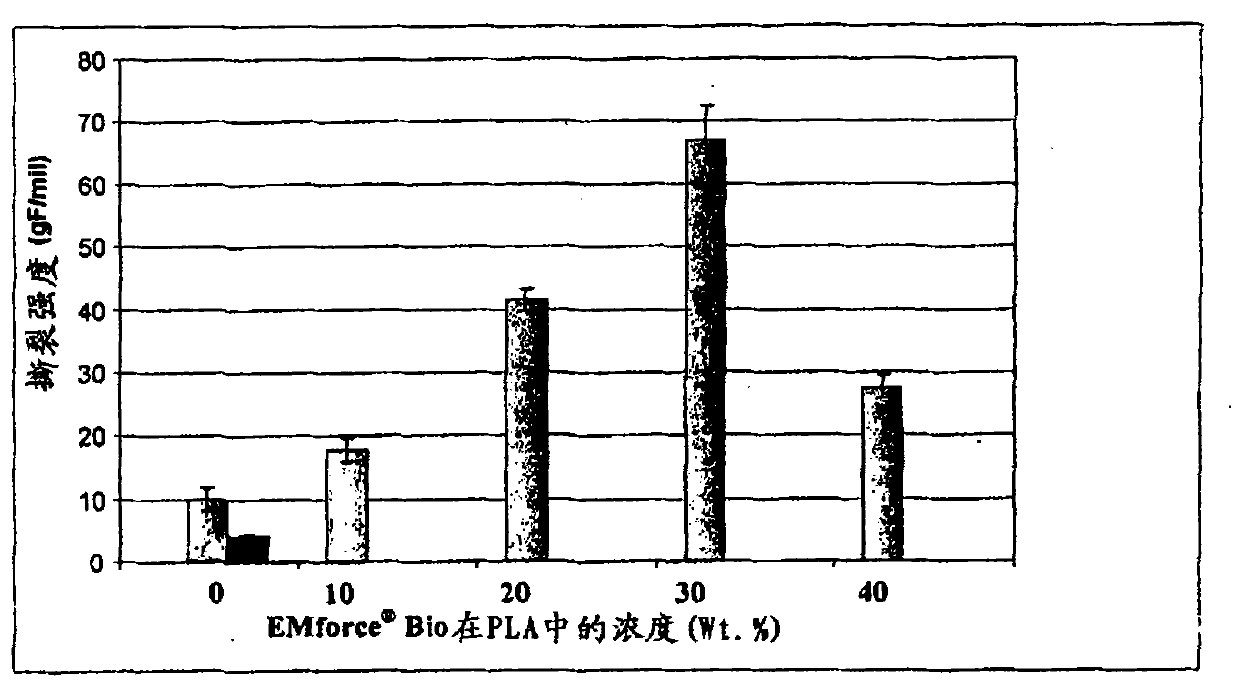
[0062] PLA test pieces of different thicknesses and containing different amounts of coated calcium carbonate were produced on a Brabender Intellitorque using a single-screw extruder with different die gaps and strip pullers at different speeds. Mechanical properties were determined using the Gardner impact test and the Elmendorf tear test at 23°C. The results are shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9 In the results, the filler shows a significant improvement in Gardner impact resistance. Figure 8 The average drop height required for failure of PLA samples containing different amounts of coated filler is shown. Figure 9 The force required to propagate a tear according to the Elmendorf tear test of various PLA samples containing coated fillers is shown, and a significant increase in tear strength is shown in the filled samples.
[0063] The aspect ratio distribution of the material was determined by TEM micrographs described earlier in this paper and at Figure 7 displayed in ....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com