Random thermal homogenizing analysis method of two-phase composite material
A composite material and effective heat technology, which is applied in the field of composite material computational mechanics and can solve the problems of incomplete and unobjective calculation values.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0077] The specific implementation of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and examples.
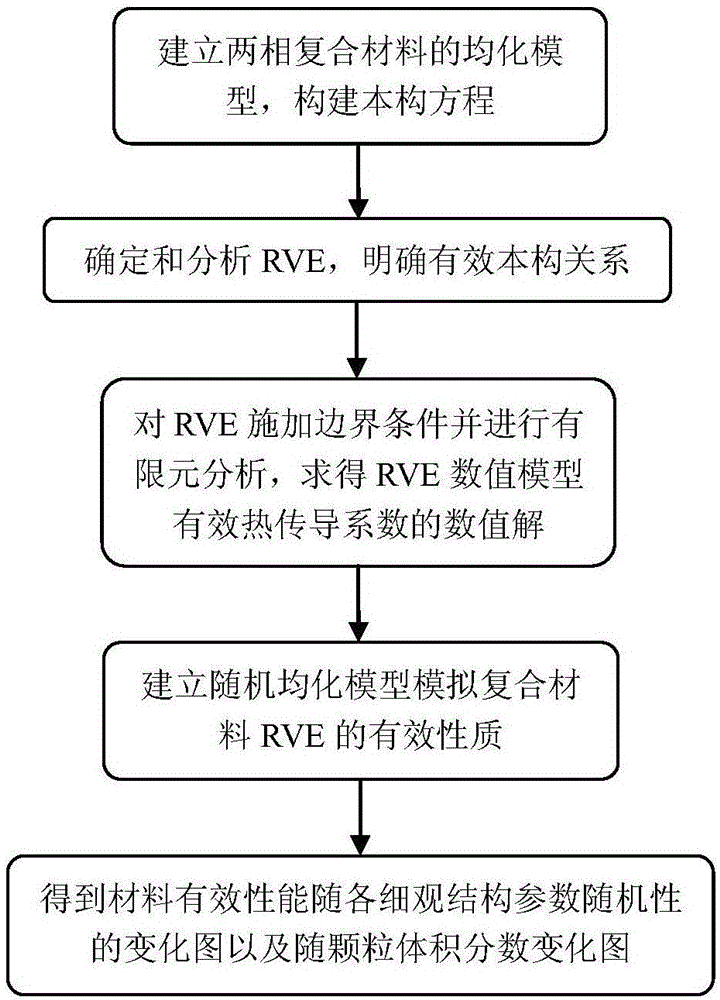
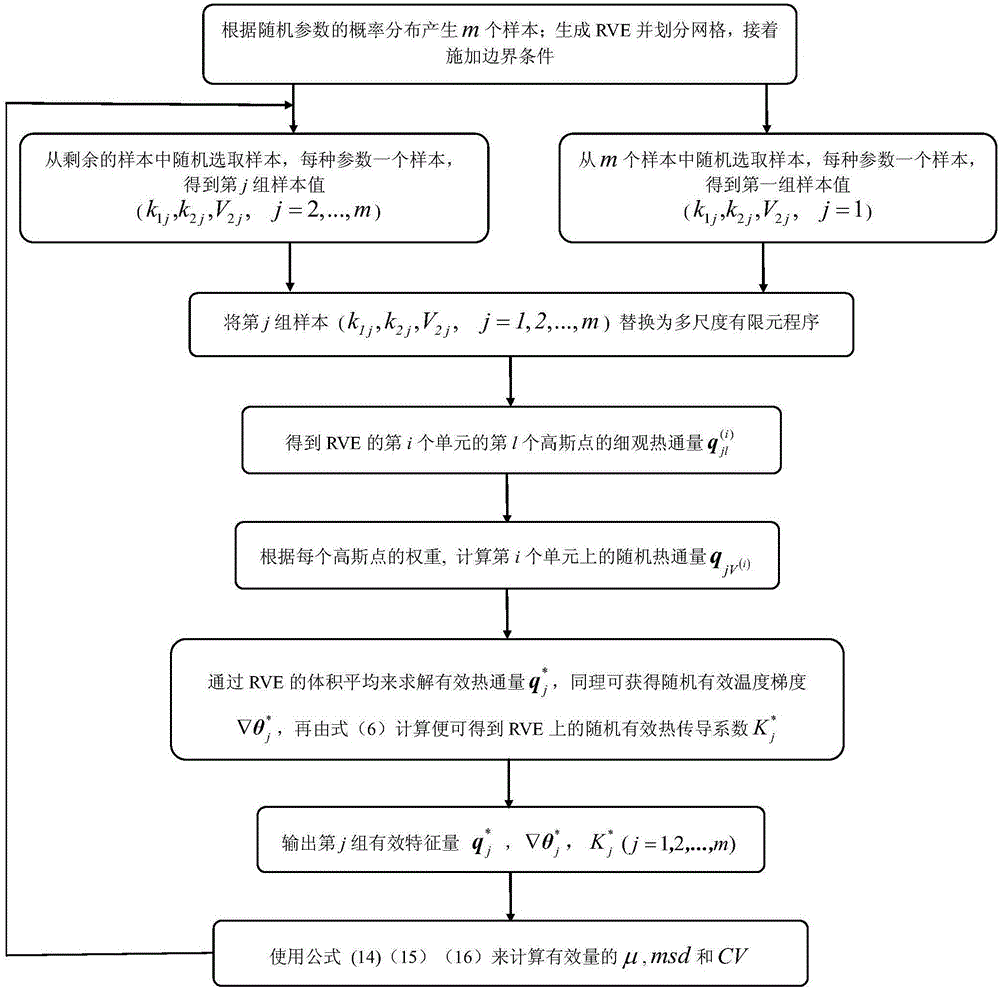
[0078] Such as figure 1 As shown, there are 5 main processes in this embodiment:
[0079] 1 Homogenization analysis
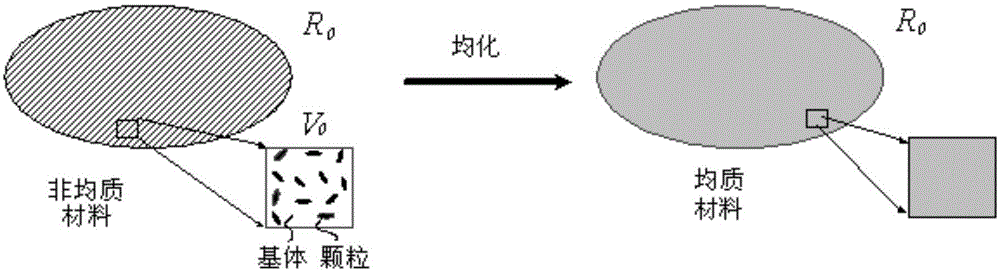
[0080] Assuming a homogeneous isotropic matrix (M 1 ) and particles (M 2 ) two-phase composite material M composed of materials to establish a corresponding mesoscopic homogenization model, such as figure 1 As shown, its reference shape is R 0 , the thermal constitutive equation is
[0081] q=-K·▽θ(1)
[0082] Among them, q represents the heat flux, K represents the thermal conductivity tensor, θ represents the temperature change, and ▽θ represents the temperature gradient. A thermal boundary value problem for this heterogeneous material M is: Solve the temperature function θ(X,t) so that the following equation in R 0 established on
[0083]
[0084] Among them, in The u...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com