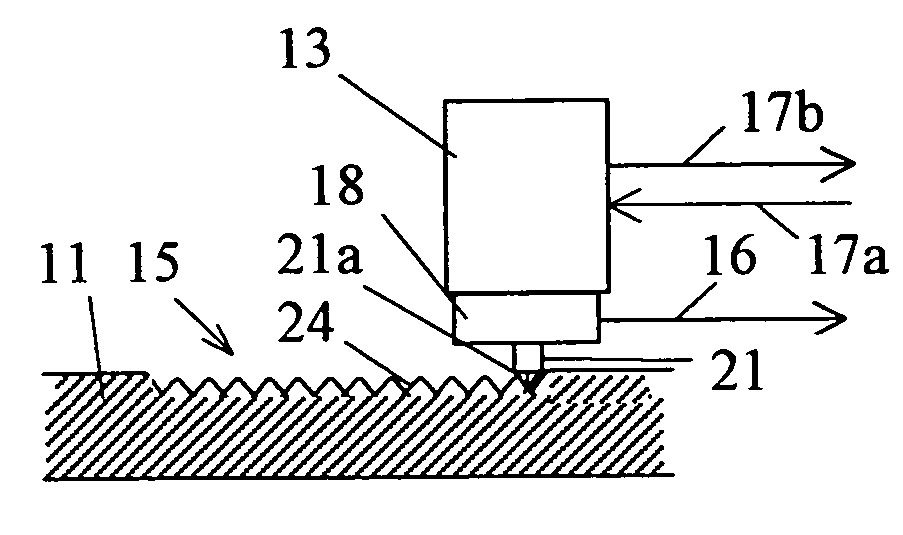
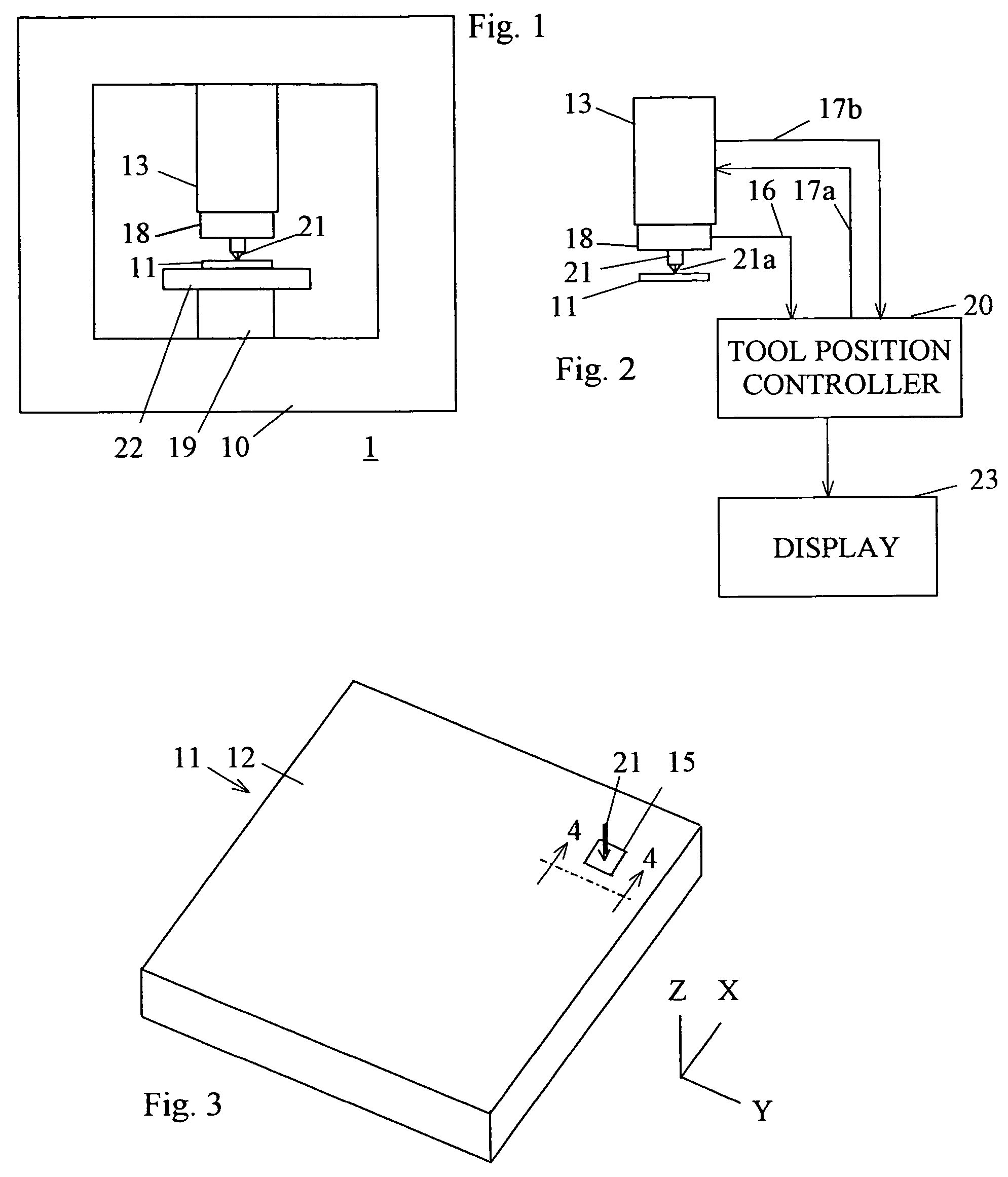
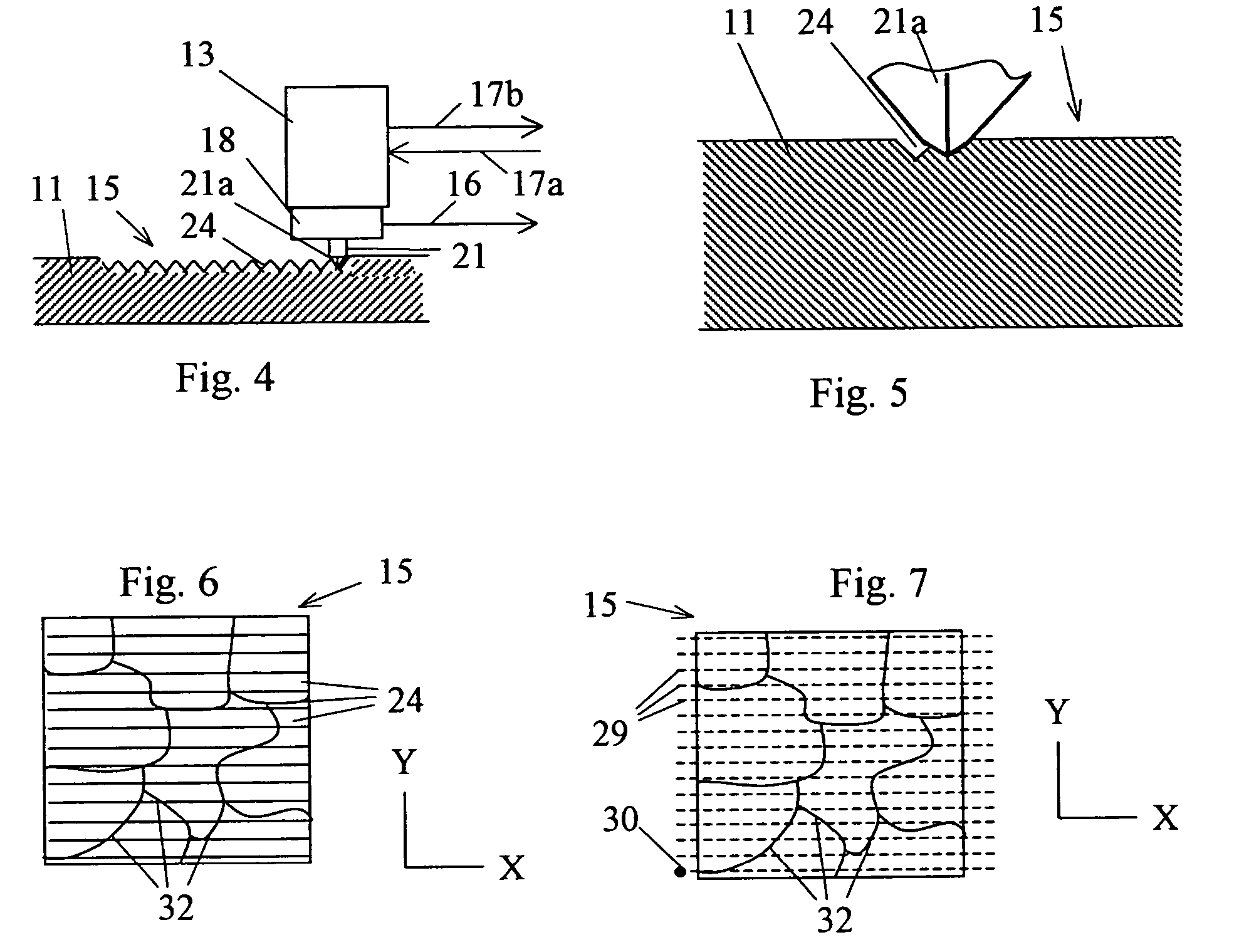
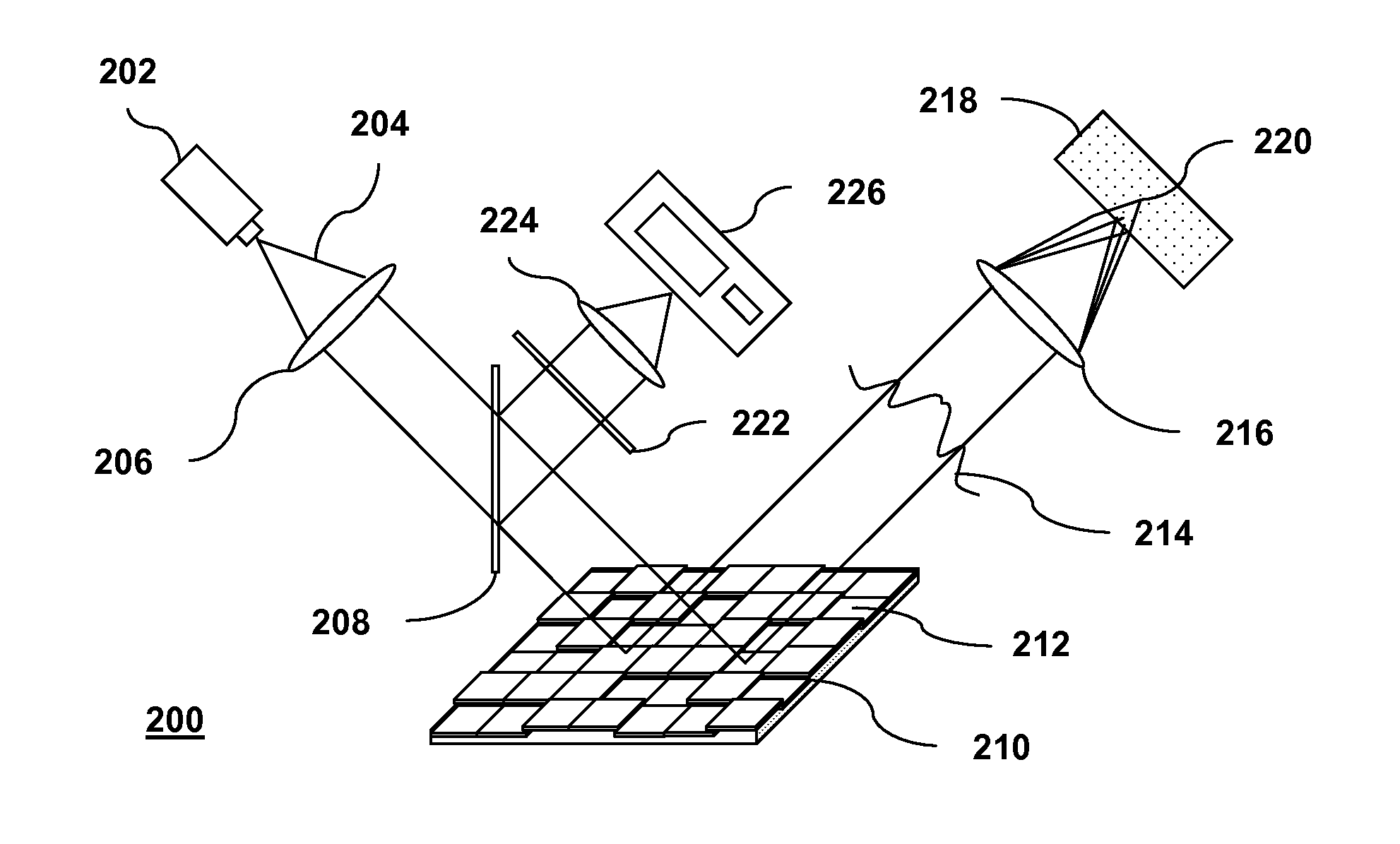
Patents
Literature
86 results about "Inhomogeneous material" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Homogeneous material. A material of uniform composition throughout that cannot be mechanically separated into different materials. NOTE 1 Examples of “homogeneous materials” are certain types of plastics, ceramics, glass, metals, alloys, paper, board, resins, and coatings.
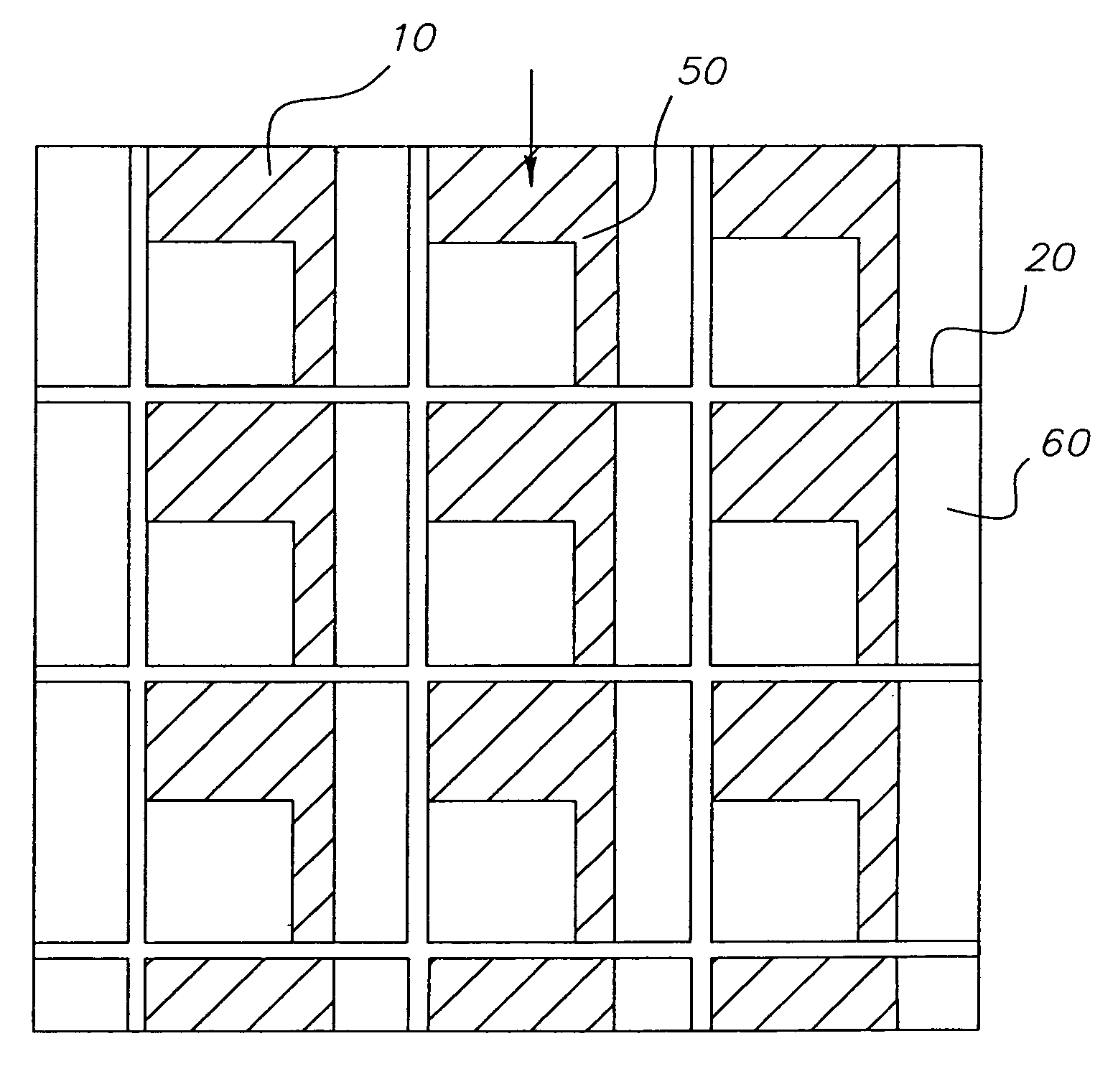
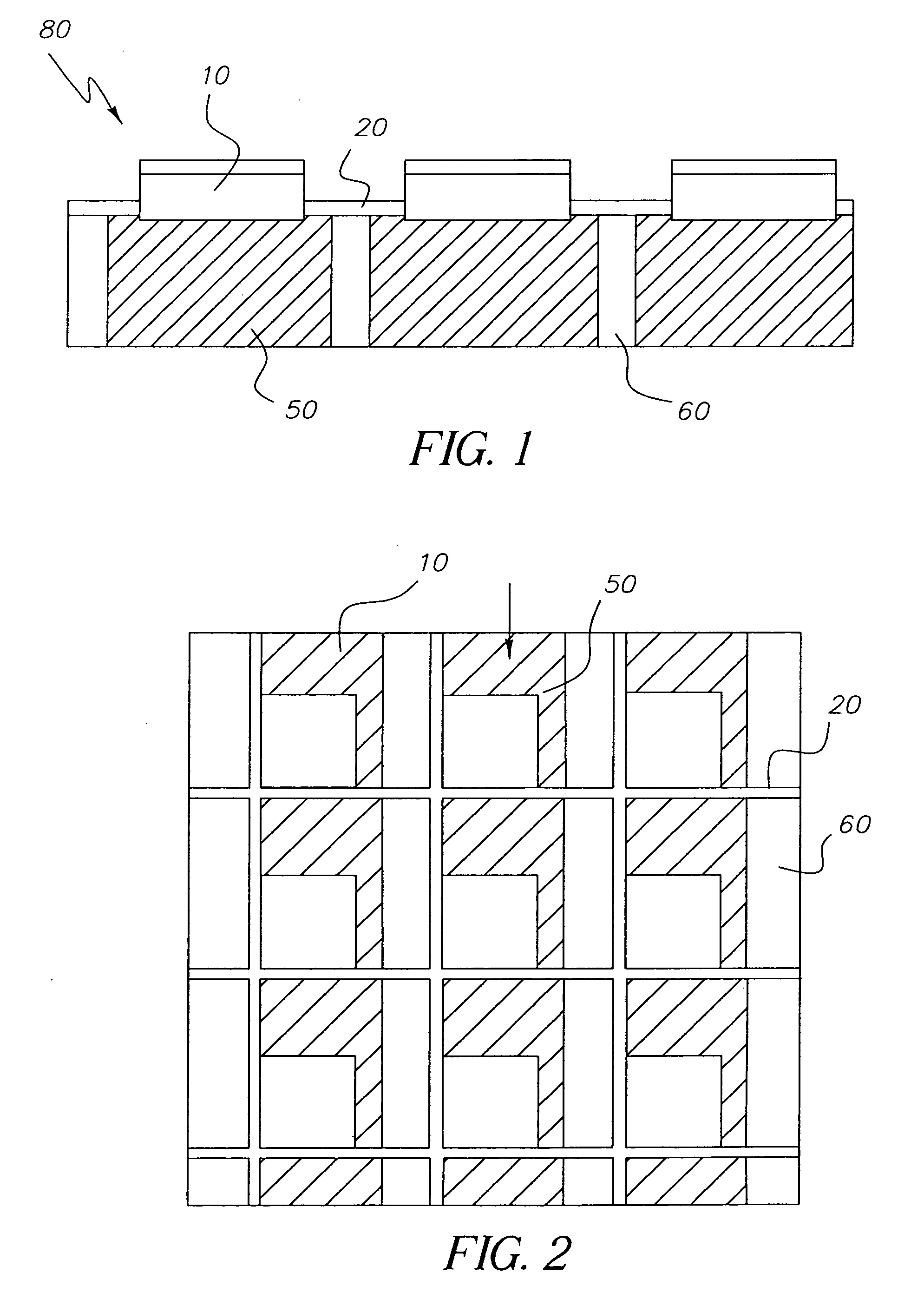
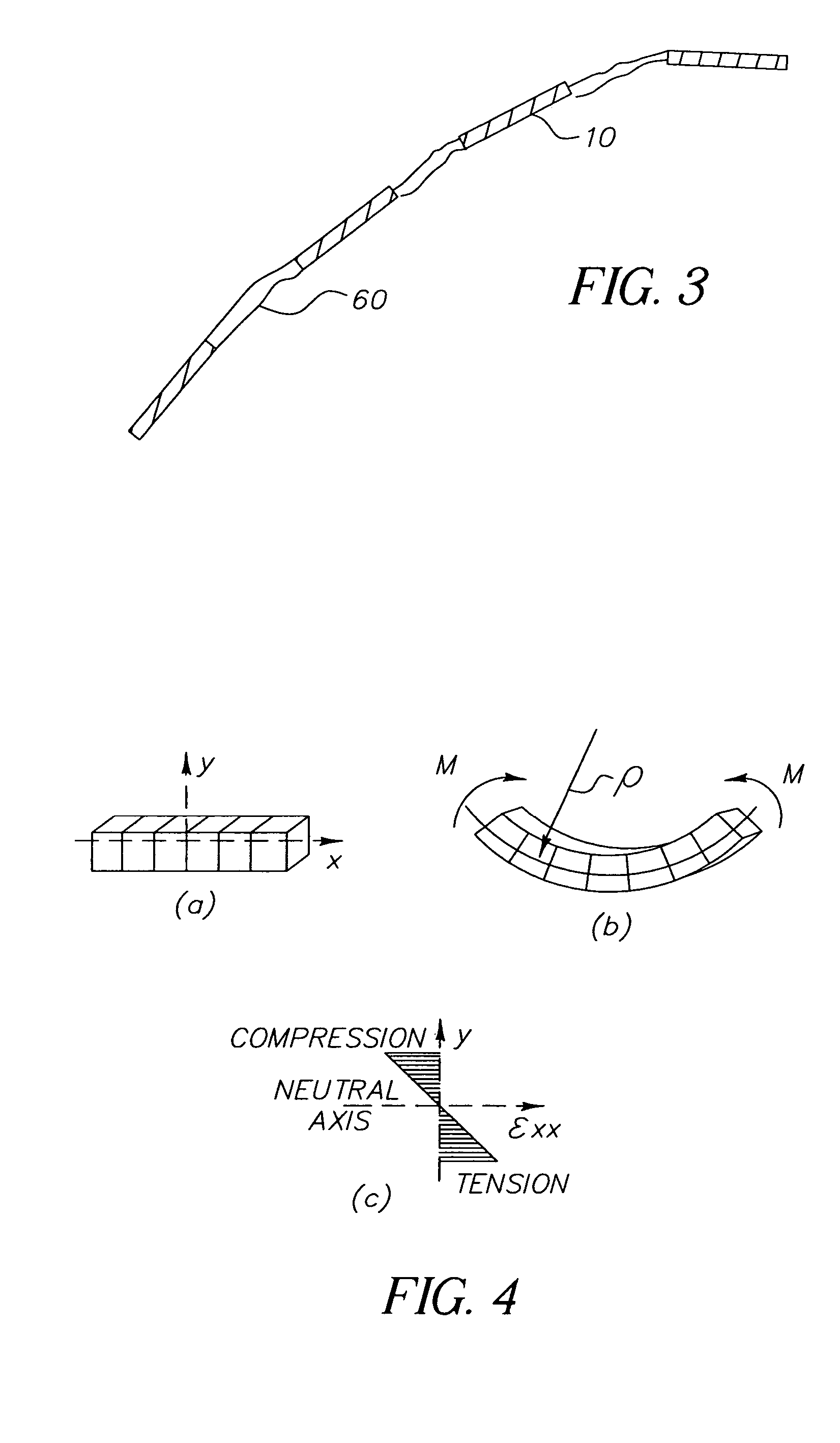
Display device with improved flexibility
InactiveUS20060204675A1Ensures integrity and ease of manufacturingIncrease flexibilityLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingDisplay deviceInhomogeneous material
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
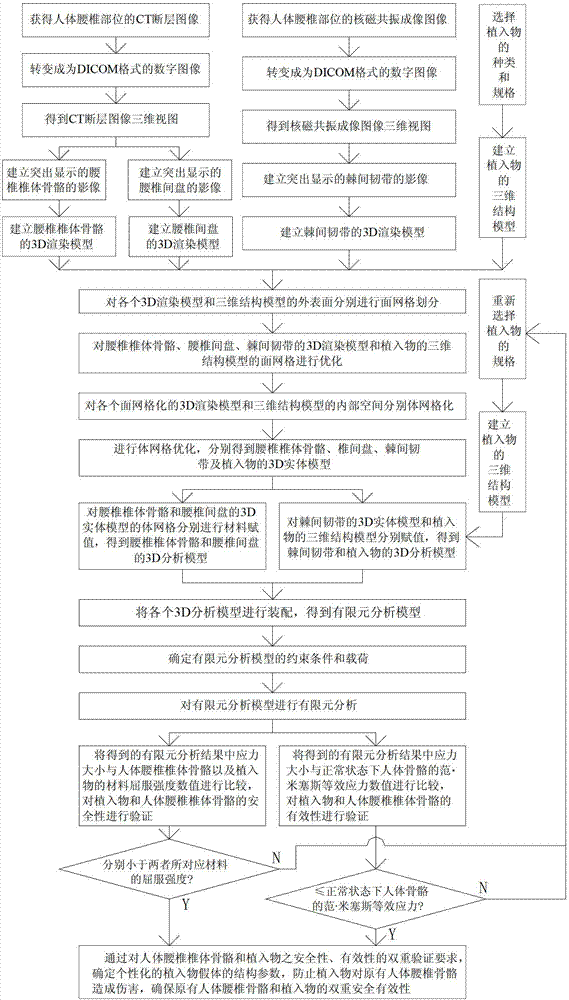
Double safety and effectiveness inspection method of human lumbar bone and implant
InactiveCN102920537AEnsure safetyGuaranteed validityJoint implants3D modellingHuman bodyManufacturing cost reduction
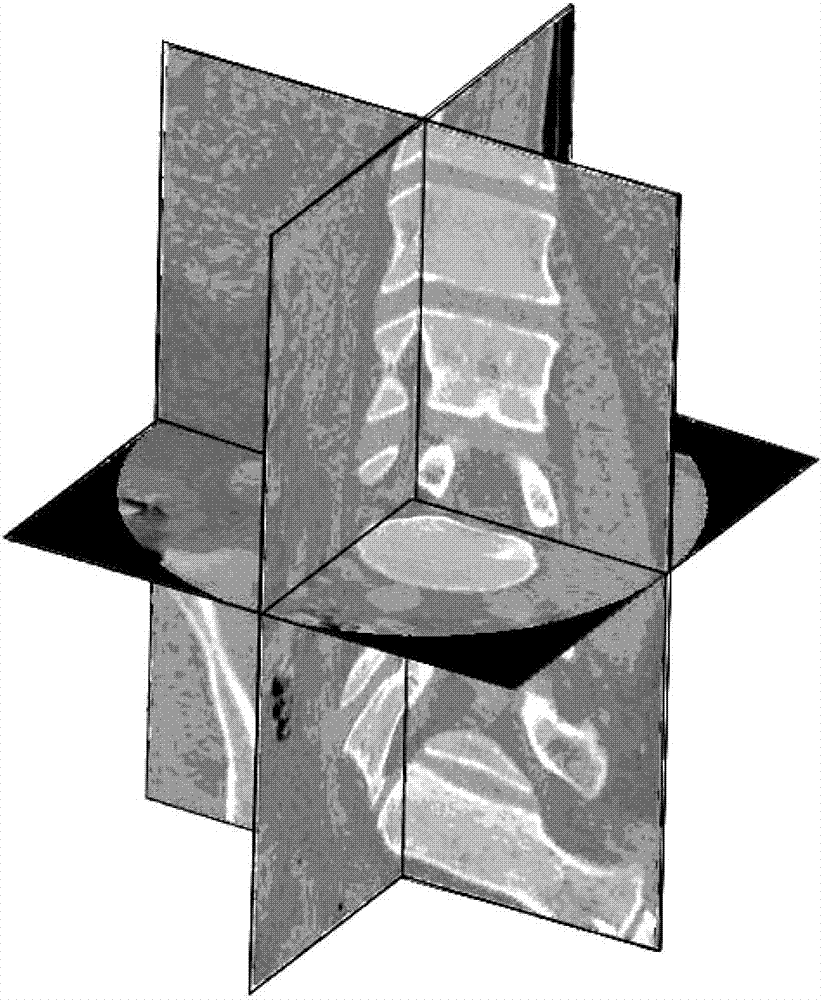
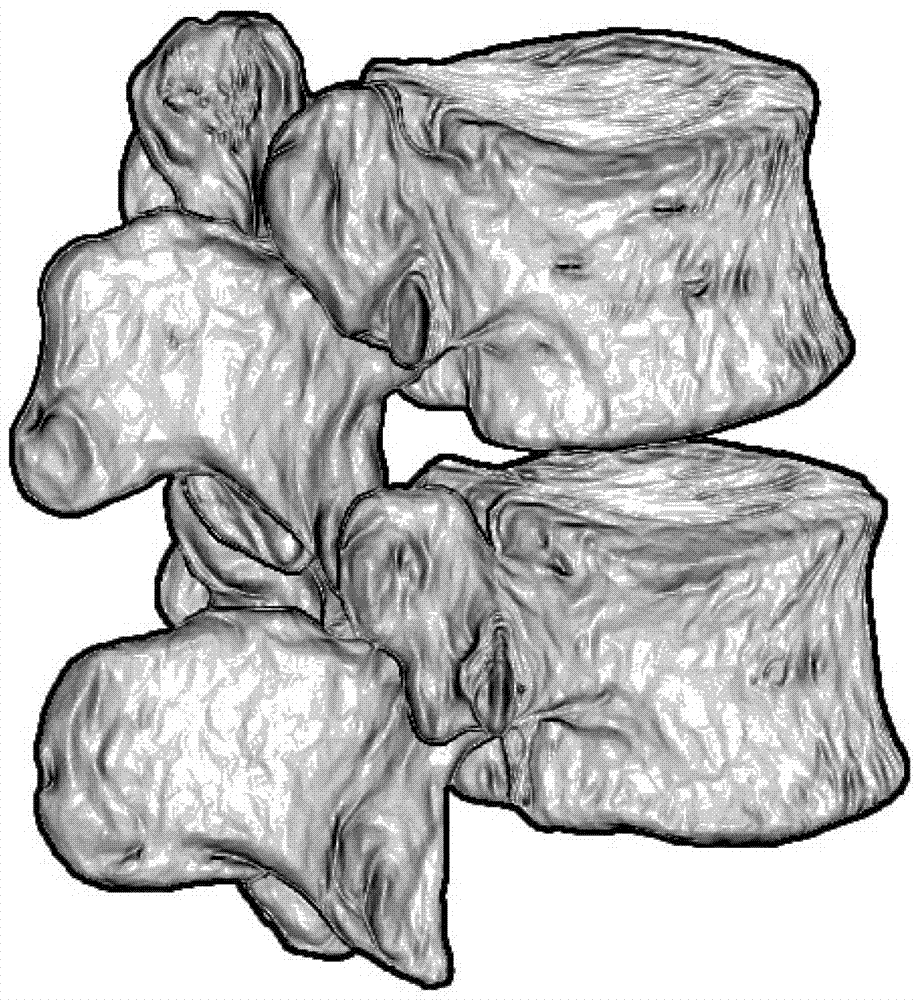
The invention provides a double safety and effectiveness inspection method of human lumbar bone and implant, and belongs to the field of medicine. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a 3D (three-dimensional) rendering model of lumbar body bone, lumbar disc and interspinous ligament by a 3D reconstruction technology; performing 3D grid division to the 3D rendering model, and giving attributes of a heterogeneous material to the 3D rendering model; performing 3D modeling to an implant; assembling the lumbar body bone, the lumbar disc, the interspinous ligament and the implant, and analyzing stress and strain of the assembly by adopting uniformly distributed nodal load through a finite element analysis method; simulating visible finite element analysis by a computer before the implant is implanted into a human body. Therefore, the verification requirement to bone and implant double safety and effectiveness can be fulfilled, the damage of the implant to original human lumbar bones can be prevented, double safety and effectiveness of the bones and implant can be guaranteed, the manufacture cost can be effectively reduced along with convenience and quickness, and individual and industrial manufacturing of a human lumbar bone implant can be realized. The method is applicable in the field of implant stress-strain analysis in the orthopedics department.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Preparation method of SiCf/SiC ceramic matrix composite turbine blades
InactiveCN103113123AMeet preparation requirementsImprove silicon corrosion resistanceYarnStress distribution
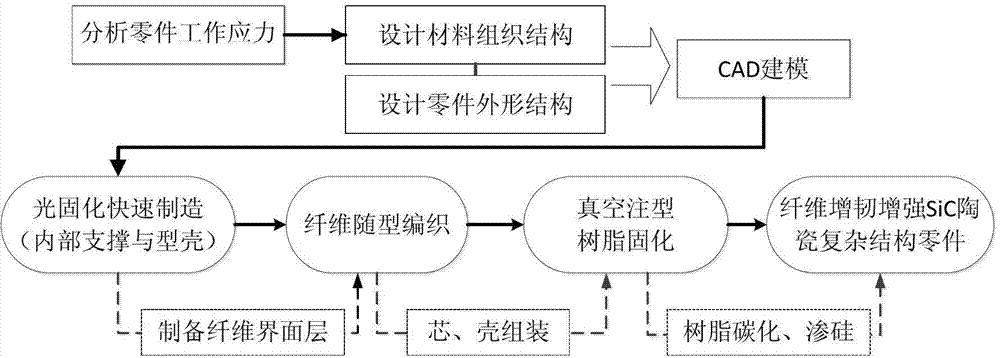
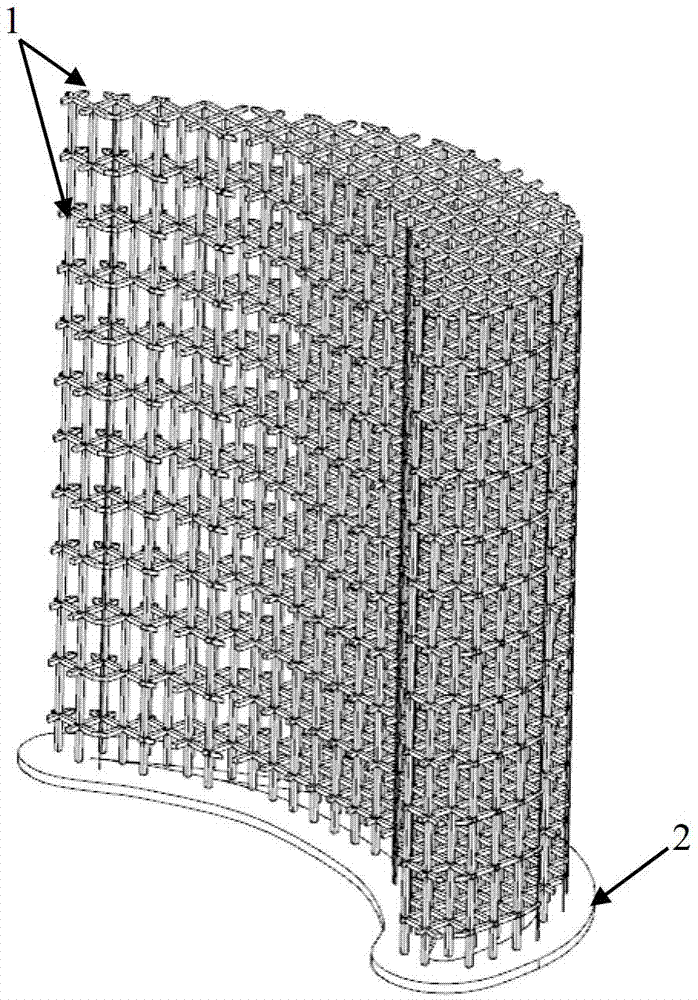
The invention discloses a preparation method of SiCf / SiC ceramic matrix composite turbine blades, which is characterized in that through analyzing the stress distribution of a blade in an application state, based on this point, a performance-controllable SiCf / SiC ceramic matrix composite turbine blade is manufactured through the designing and adopting of processes such as rapid forming, high-performance continuous yarn braiding, gel-casting, reactive sintering, and the like. According to the method, parts such as blades and the like are manufactured by using heterogeneous materials, the contradiction between the uniformity and nonuniform loaded structure of materials is solved, and the performances of materials can be set flexibly according to the bearing needs of manufactured parts; and prepared SiCf / SiC ceramic matrix composite turbine blades have the characteristics of near-net forming variable-cross-section complex structure, controllable material performance, flexible machining, short production cycle, low cost, and the like, and can be applied to the development and manufacturing of high-temperature-resistant complex structured parts for aerospace and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Inhomogeneous materials having physical properties decoupled from desired functions
InactiveUS6873026B1Plastic/resin/waxes insulatorsLiquid organic insulatorsMetal interconnectInhomogeneous material
A composition comprises a first component that provides a predetermined response to radiation, and a second component. Upon curing of the composition, portions of the first component bind together portions of the second component to form an inhomogeneous material having physical properties substantially determined by the second component. The function provided by the first component's response to radiation and the macroscopic properties determined by the second component are largely decoupled and thus may be separately optimized. Some embodiments provide photo-patternable low dielectric constant materials that may be advantageously employed in metal interconnect layers in integrated circuits, for example.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method for observation of microstructural surface features in heterogeneous materials
ActiveUS7107694B2Increase speedLess equipmentWriting aidsMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsConstant forceMachined surface
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Apparatus and Methods for Performing Raman Spectroscopy in Scattering Medium
ActiveUS20120194814A1Enhanced signalEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometrySpatial light modulatorLow distortion
An improved apparatus and method for performing Raman spectroscopy in a scattering medium, where the scattering induced phase modulation is compensated by using a spatial light modulator to shape the wavefront of the laser beam. This allows the laser beam to be focused to a spot inside the inhomogeneous material with low distortion, thus stimulating Raman signal from the focus point for spectral analysis.
Owner:METROHM SPECTRO INC
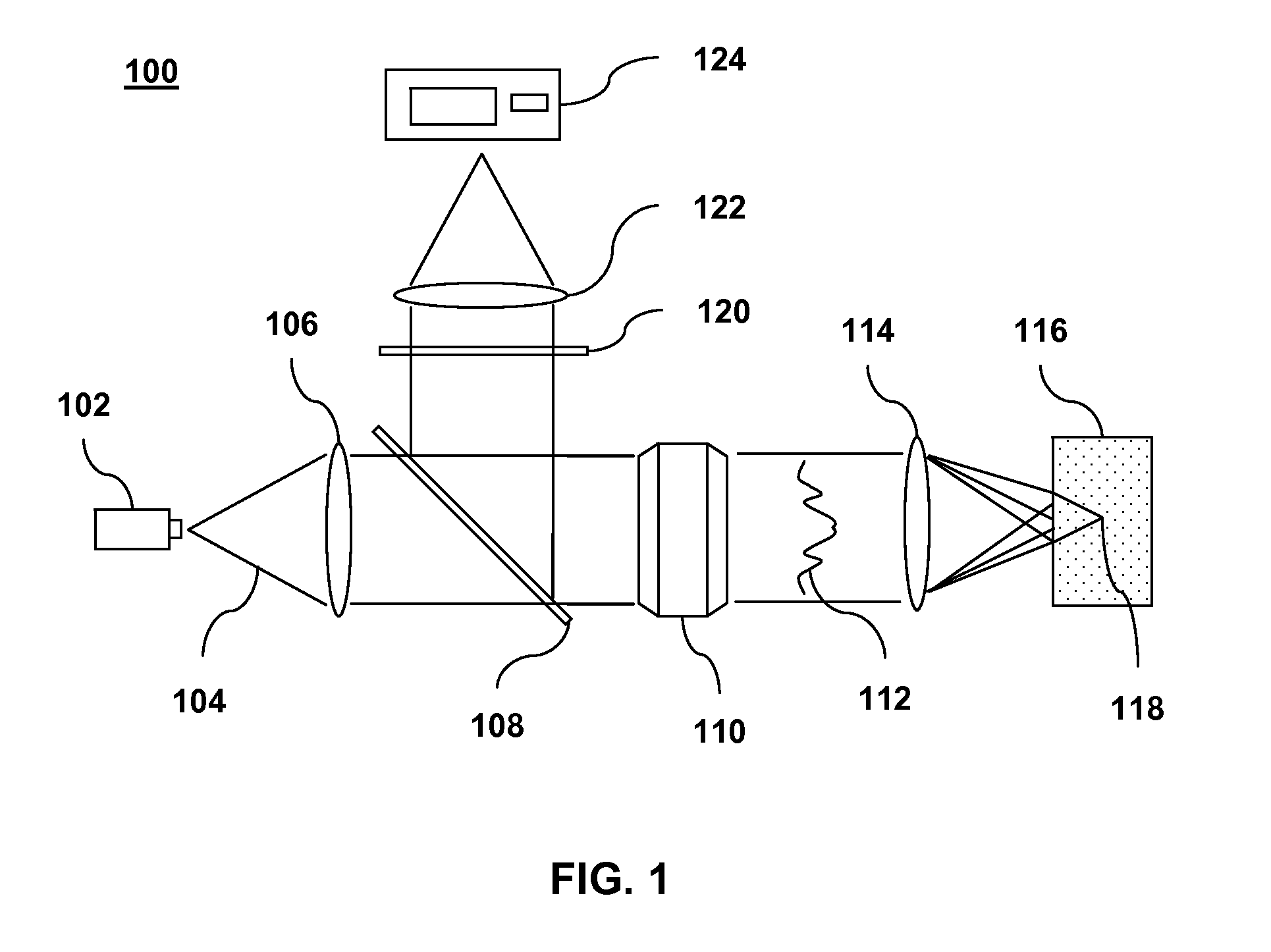
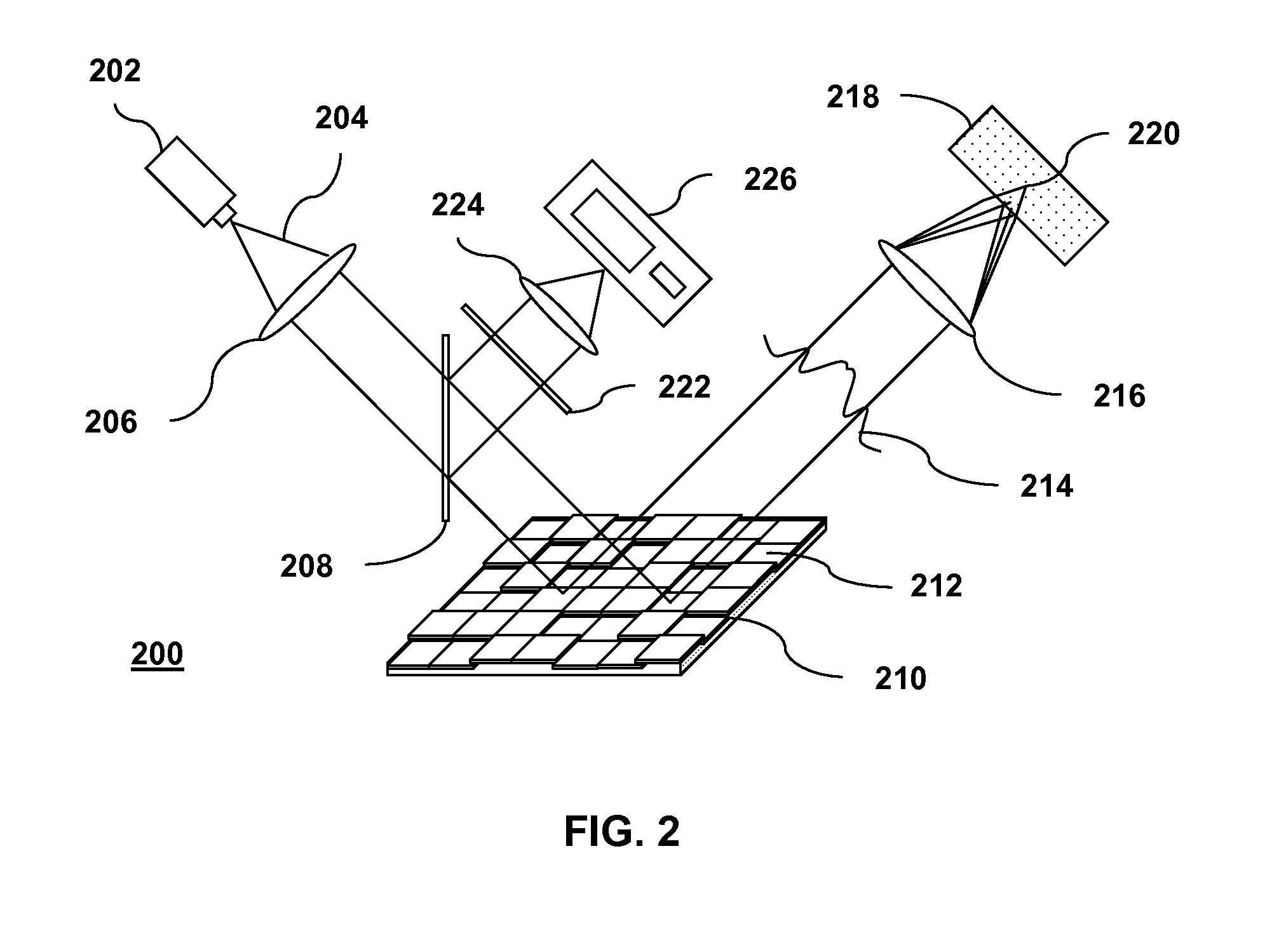
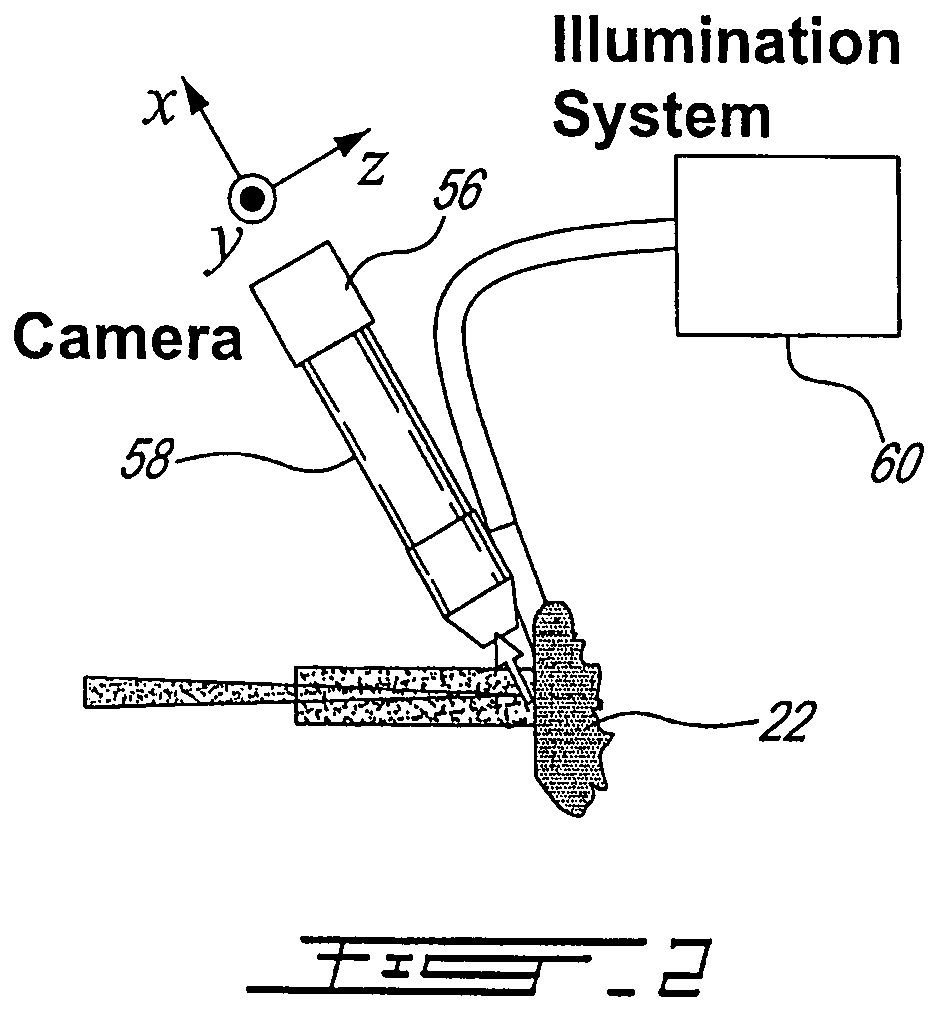
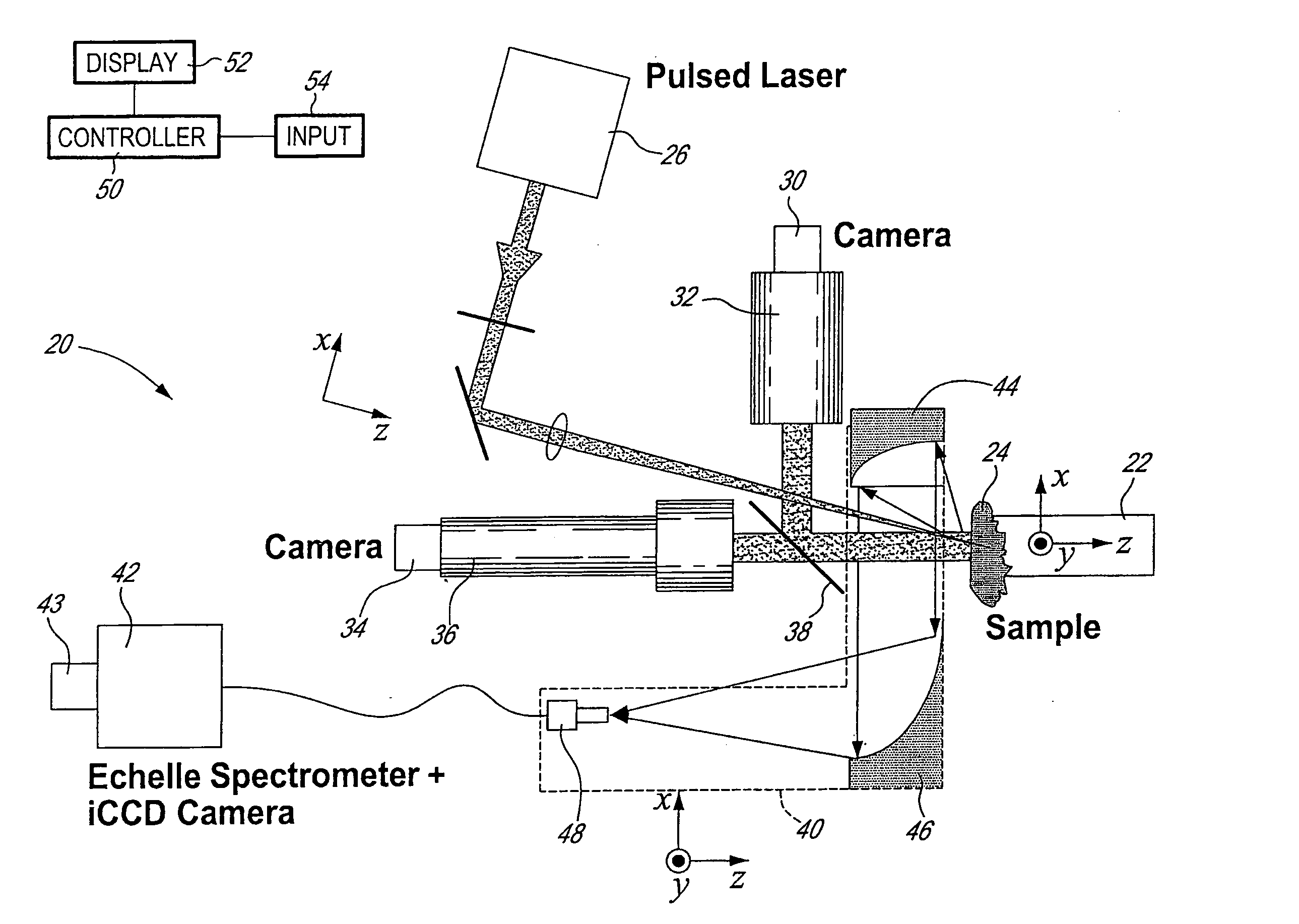
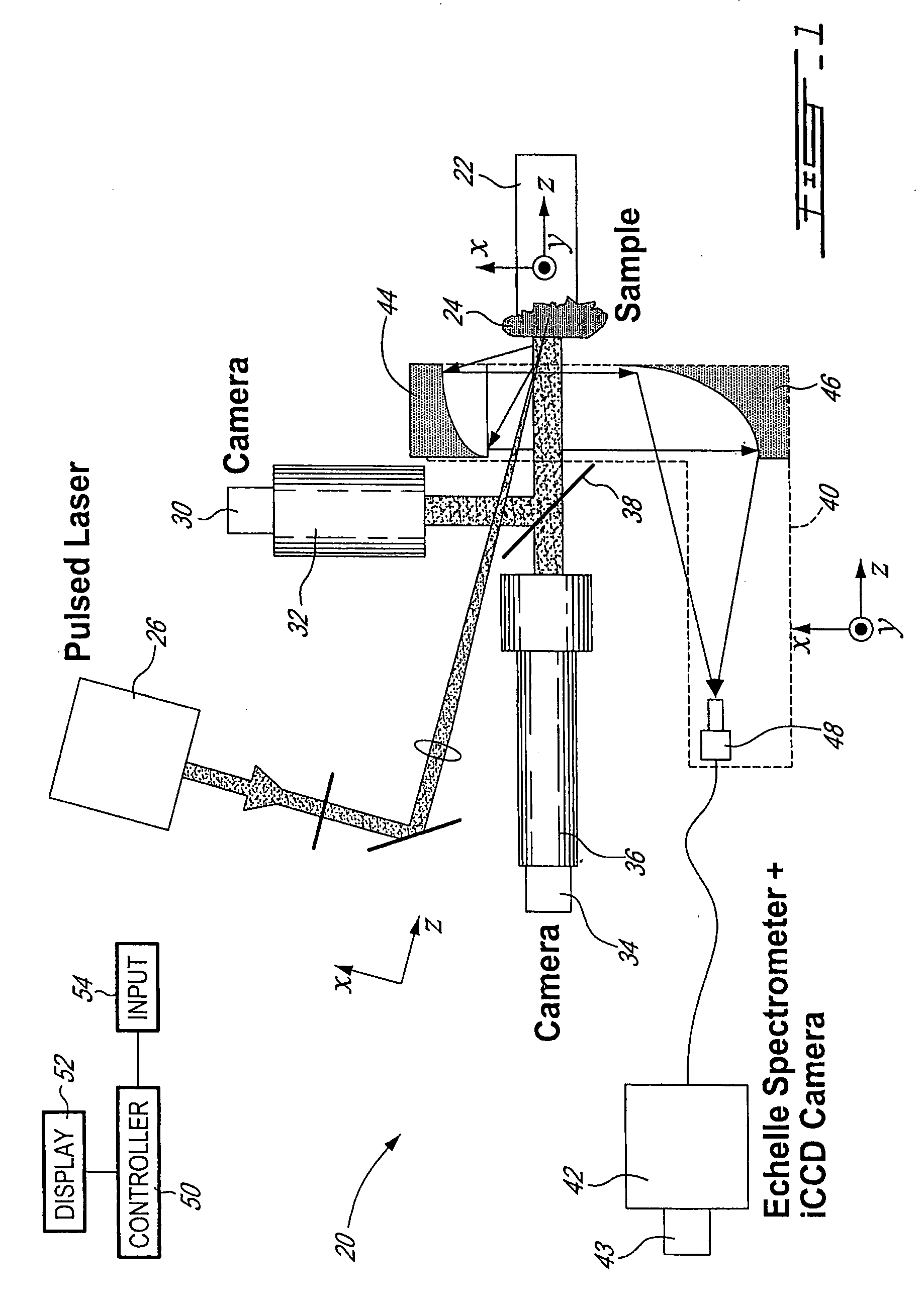
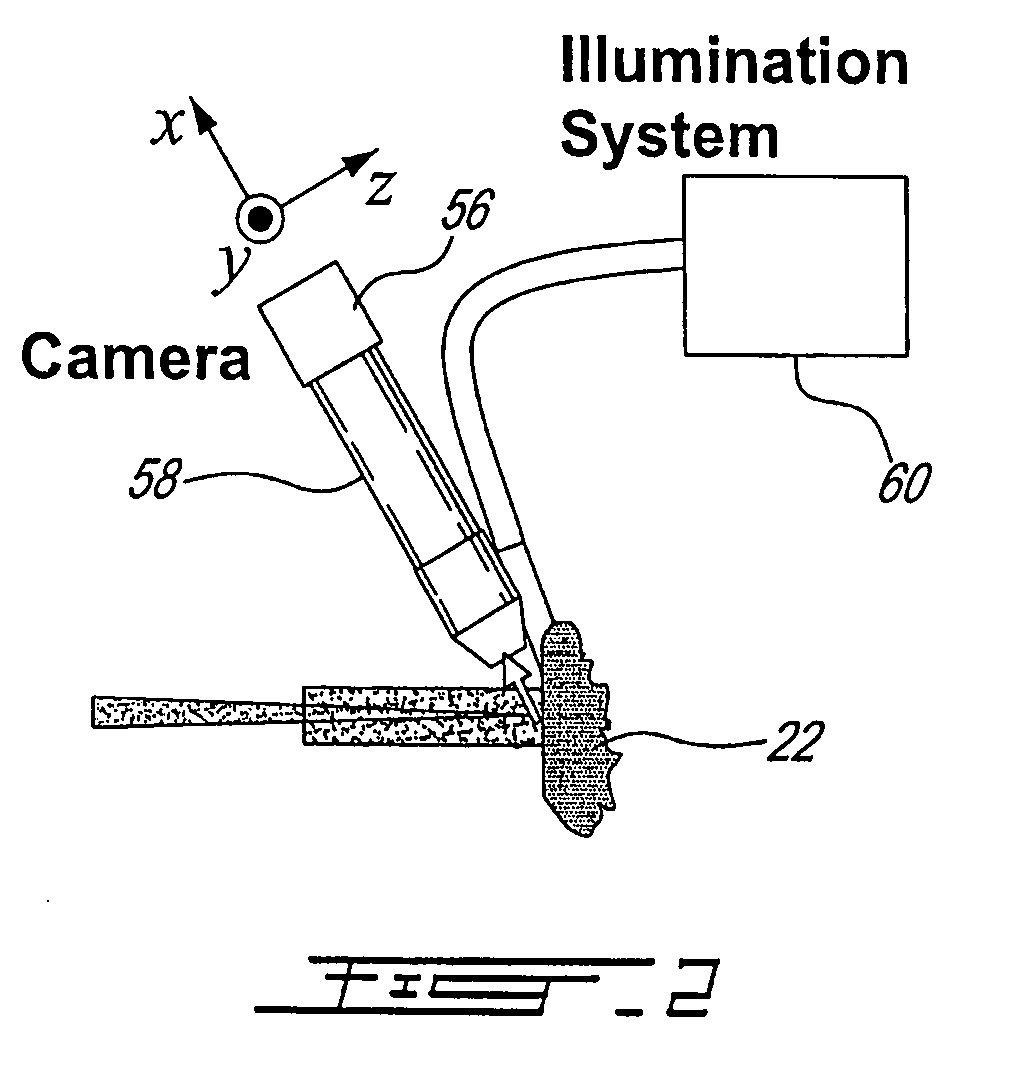
Method and system to measure the concentration of constituent elements in an inhomogeneous material using LIBS
ActiveUS7663749B2Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationInhomogeneous materialVolume concentration
A system and method to improve the accuracy of the measure of constituent element(s) in a sample containing domains potentially including the constituent element(s) are described herein. For each domain, the volume of the domain is estimated and the concentration of the constituent element(s) in the domain is determined using LIBS. When all the domains have been analyzed, the volumetric concentration of the domains is summed and divided by the total volume of the sample. Accordingly, by limiting the concentration analysis to separate domains, it is possible to improve the accuracy of the concentration analysis.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
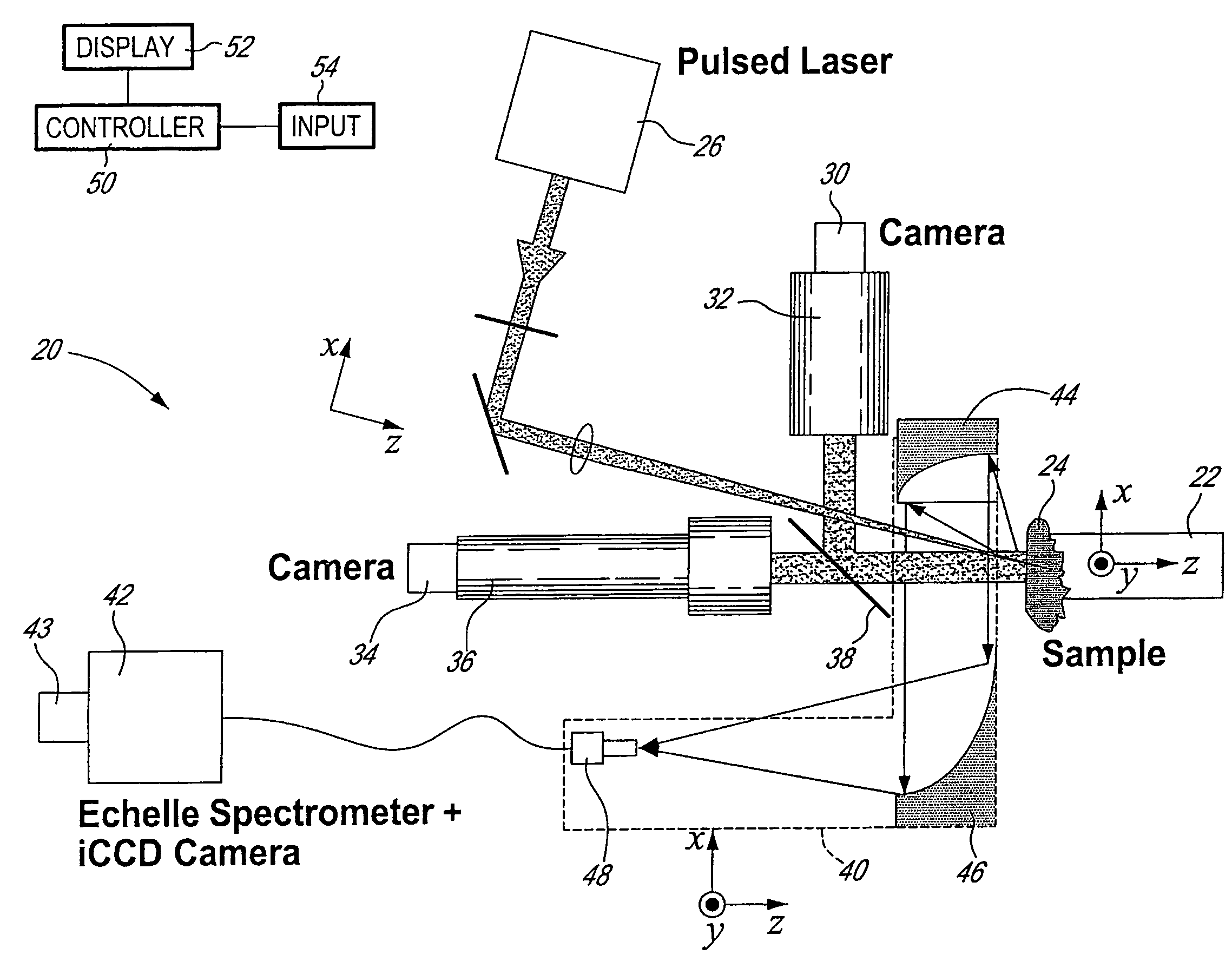
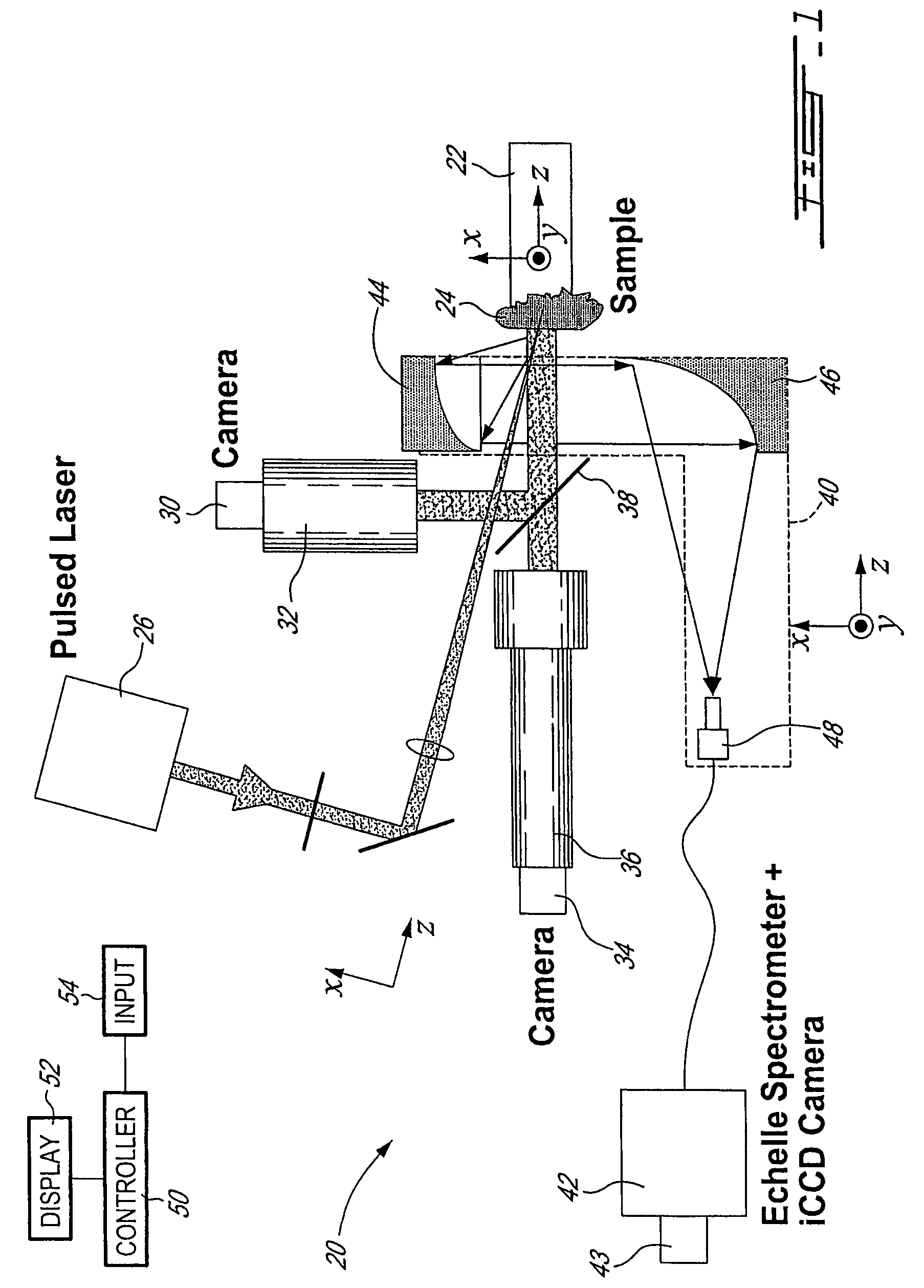
Method and system to measure the concentration of constituent elements in an inhomogeneous material using LIBS
ActiveUS20090091745A1Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationInhomogeneous materialVolume concentration
A system and method to improve the accuracy of the measure of constituent element(s) in a sample containing domains potentially including the constituent element(s) are described herein. For each domain, the volume of the domain is estimated and the concentration of the constituent element(s) in the domain is determined using LIBS. When all the domains have been analyzed, the volumetric concentration of the domains is summed and divided by the total volume of the sample. Accordingly, by limiting the concentration analysis to separate domains, it is possible to improve the accuracy of the concentration analysis.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
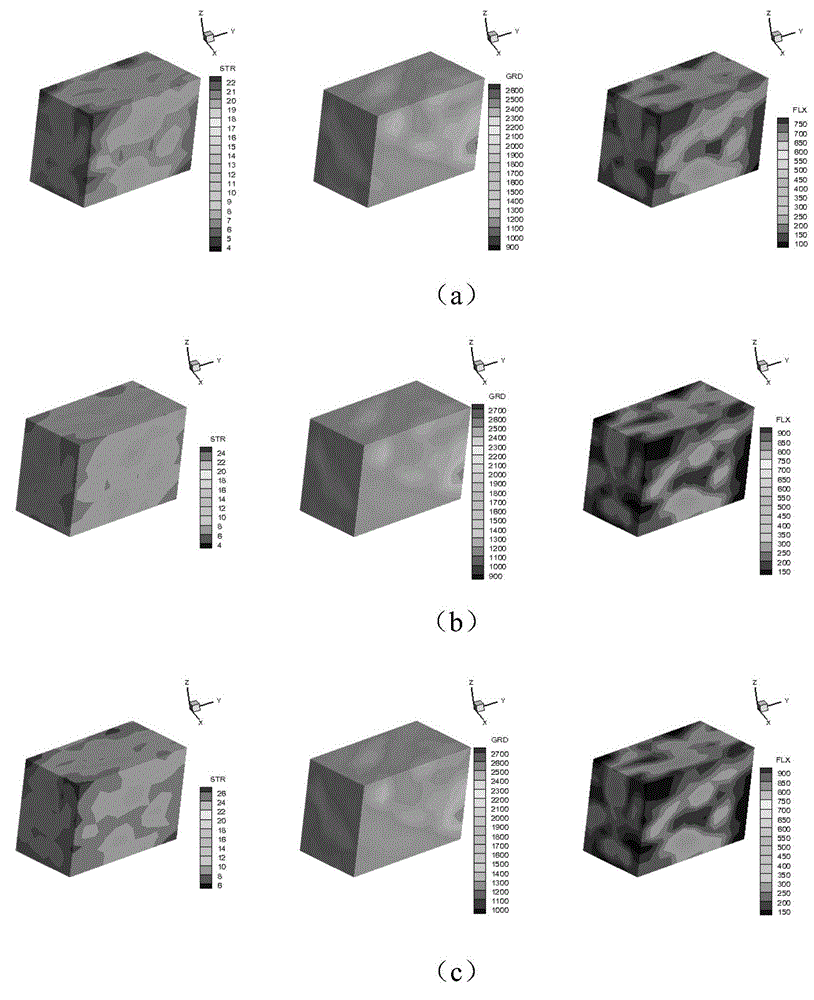
Finite element modeling method of random microstructure of heterogeneous material
InactiveCN102819647AGood macro performanceImprove macro performanceSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelStochastic algorithms
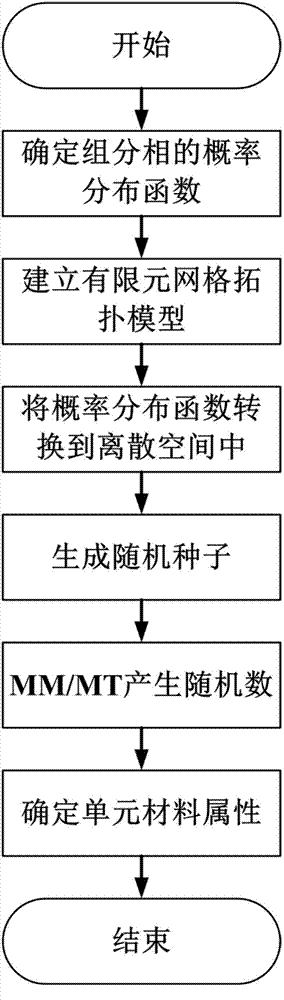
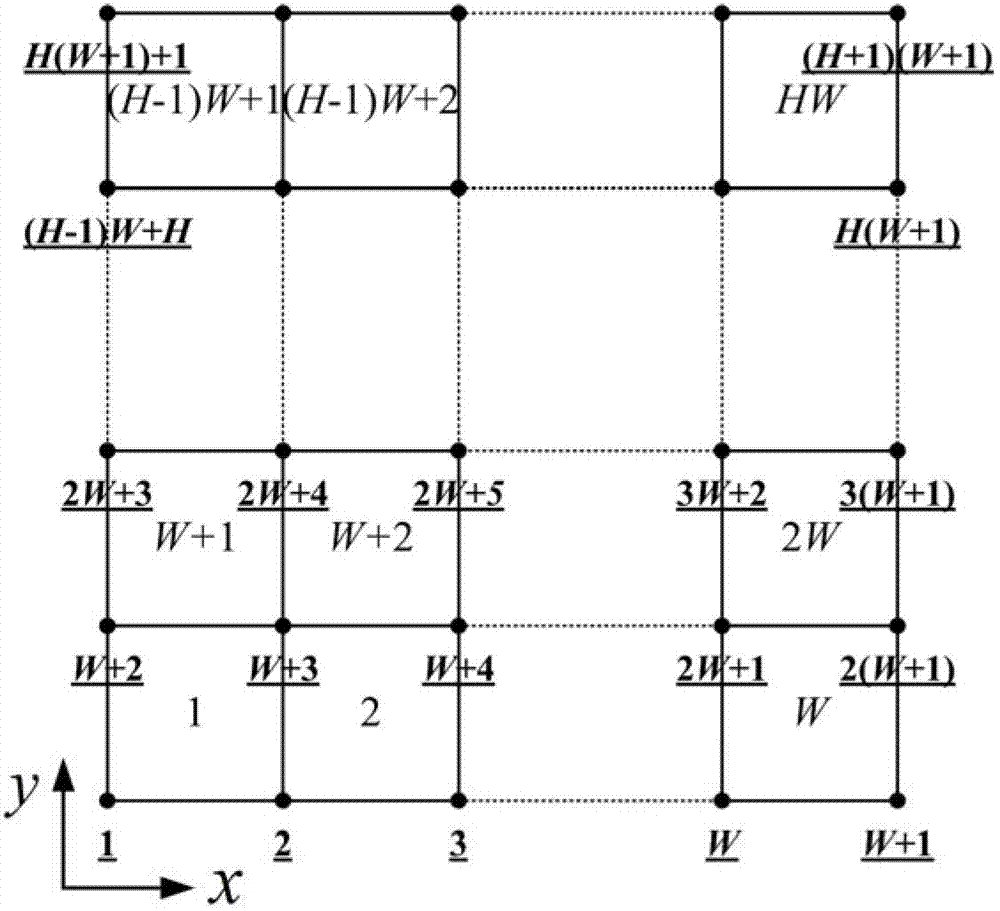
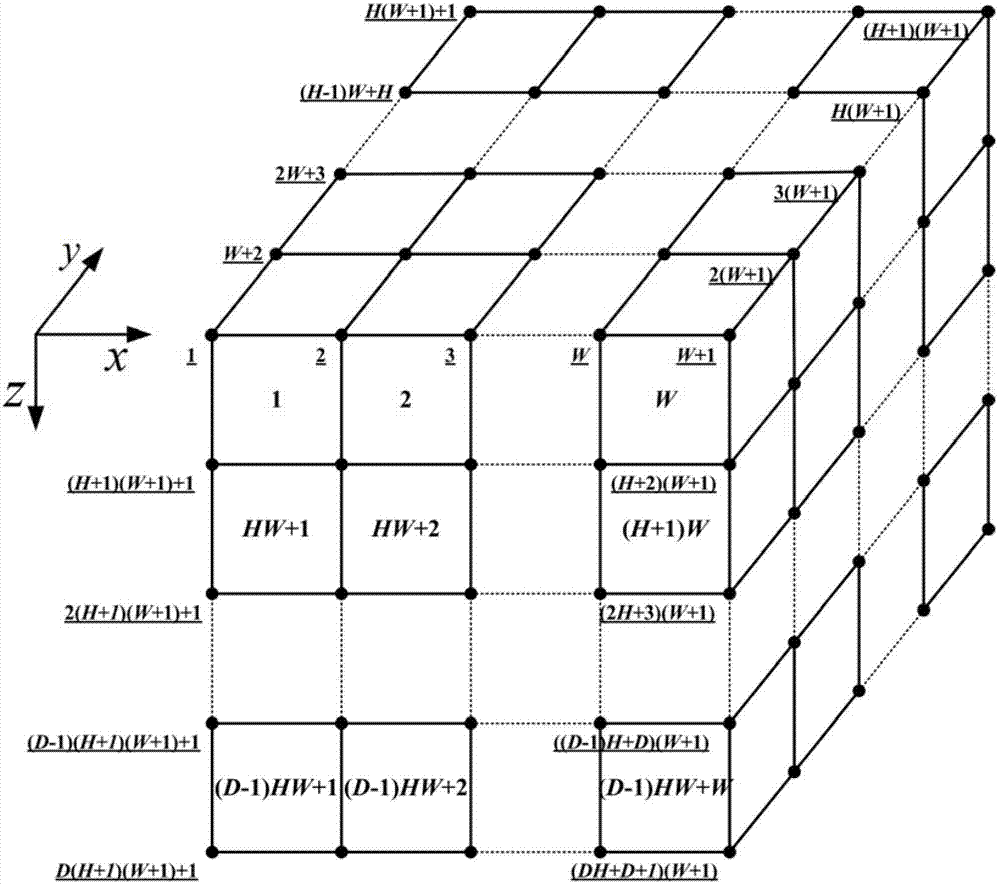
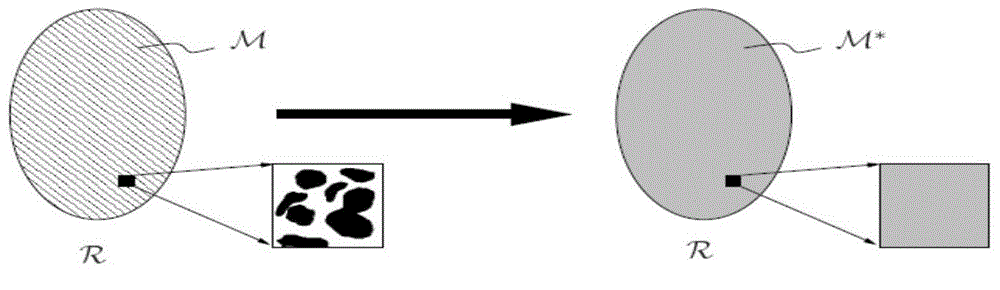
The invention provides a finite element modeling method of a random microstructure of a heterogeneous material, and particularly relates to a method of establishing a finite element network model of the random microstructure of the heterogeneous material based on microstructure probability distribution information and a random algorithm. The method comprises the following steps of: determining a microstructure probability distribution function by using a real or dummy heterogeneous material component phase physical distribution form; converting a probability distribution function into a discrete space of the model on the basis of establishing the finite element network topological model of the material; and determining material attributes of each unit in the definite element model by using random real numbers generated by a pseudo random number generator and consistently distributed in an interval [0, 1], thereby establishing the random microstructure model of the heterogeneous material. The method is suitable for the heterogeneous materials in different modes; the established definite network model can be directly used for analyzing relation among microscopic property, microscopic structure, macroscopic performance of the heterogeneous material; and basis is provided for development and preparation of a new material.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
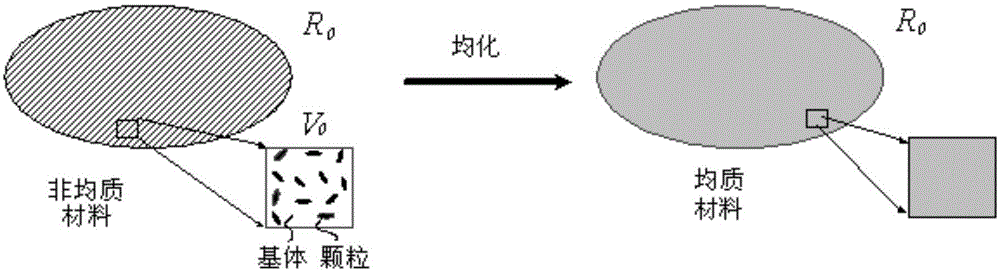
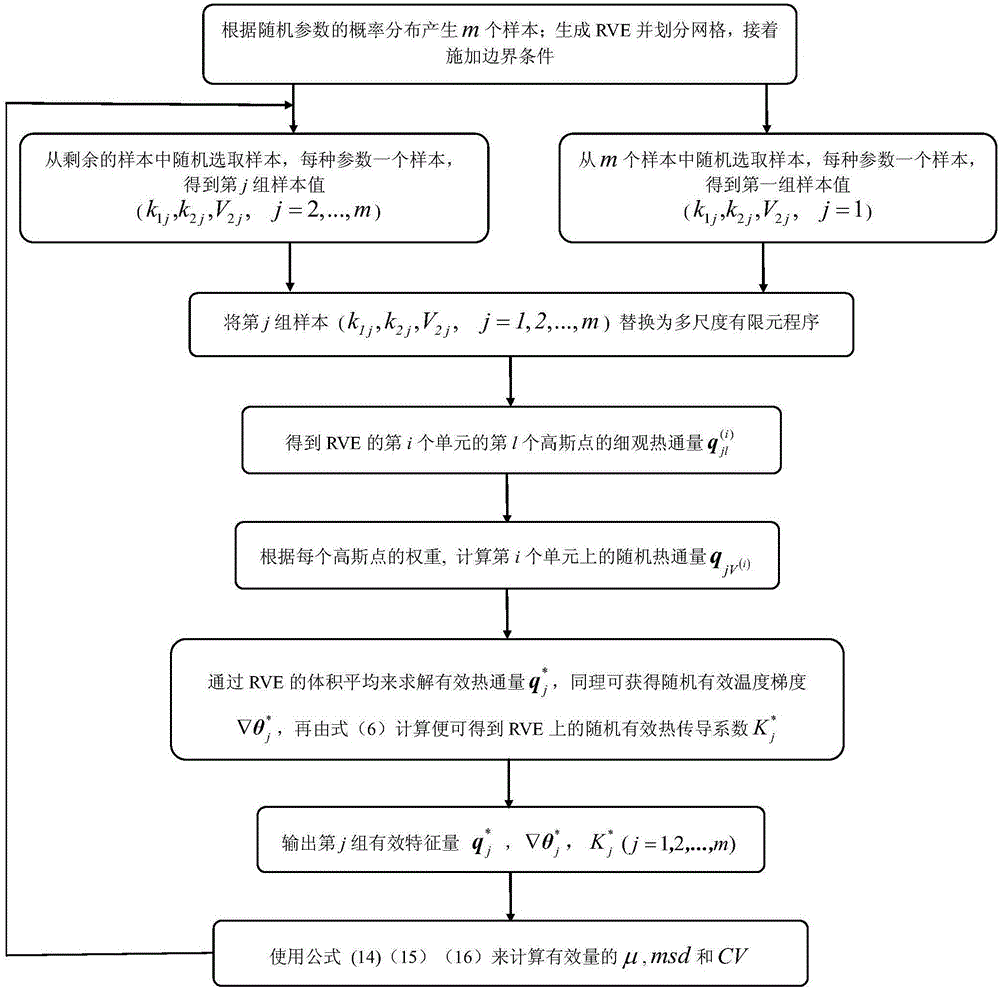
Random thermal homogenizing analysis method of two-phase composite material
ActiveCN105044146ASolving Numerical Modeling ProblemsMaterial heat developmentHeat fluxElement analysis
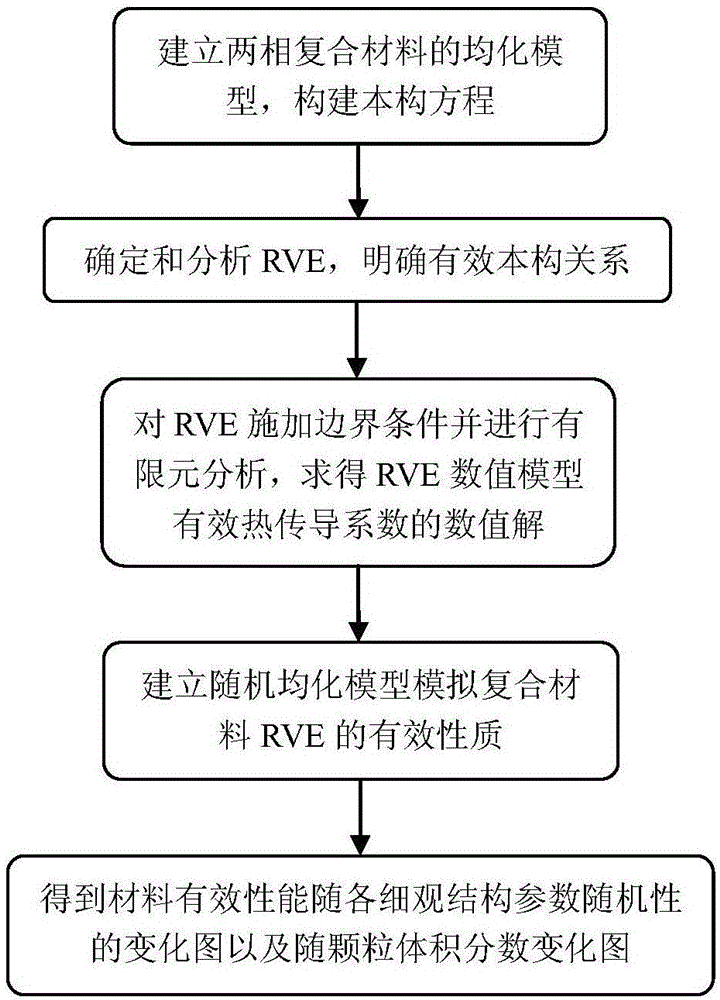
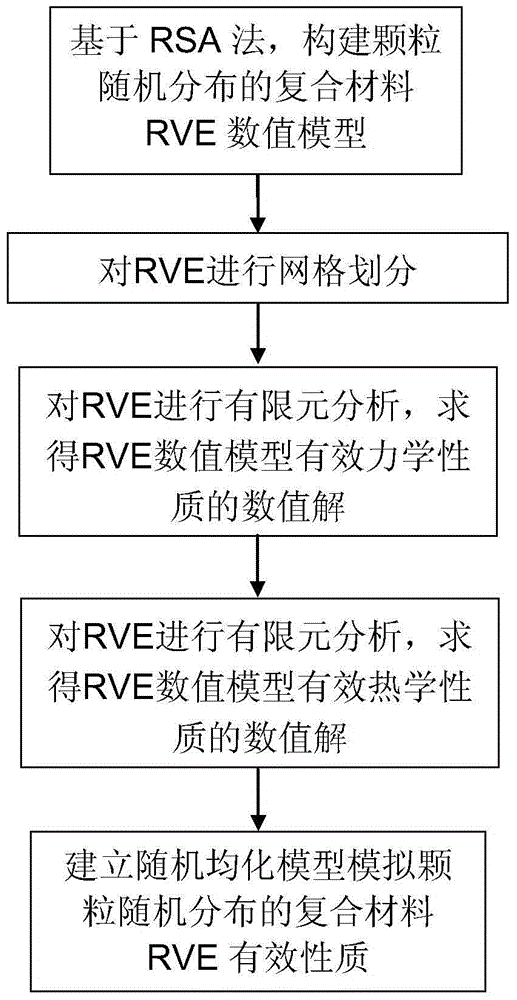
The invention discloses a random thermal homogenizing analysis method of a two-phase composite material. The method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a corresponding microscopic homogenization model of a two-phase composite material composed of a matrix and particles, constructing constitutive equations, and calculating the thermal boundary values of the heterogeneous material; (2) determining and analyzing to obtain one RVE from the two-phase composite material, and determining the effective constitutive relationships among the effective heat conduction coefficient, the volumetric average temperature gradient and the volumetric average heat flux, wherein the volumetric average temperature gradient and the volumetric average heat flux are obtained from RVE; (3) applying boundary conditions on RVE, and at the same time carrying out finite element analysis and calculation to obtain the value of effective heat conduction coefficient of the RVE numerical model; (4) establishing a random homogenizing model to obtain the macroscopic effective quantity of the composite material. In the provided method, a finite element method and Matlab software are used to solve the problem of complicated RVE numerical modeling, the influences of parameter randomness of components of the composite material under three boundary conditions on the macroscopic thermal physical properties are taken into account comprehensively, and thus the provided method has an application value, a certain academic value, and theoretical significance.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Switchable luminescent see-through system
InactiveUS20140286048A1Transparent highImpart luminescent propertyAircraft componentsMechanical apparatusLuminophoreOptical property
The present invention relates to a switchable see-through luminescent system, e.g. for luminous signage, characterized by its mode to exist in two different states, transparent (‘off-state’) and luminescent (‘on-state’), due to the presence of a luminescent material (20), coated on to the transparent surface (10), capable of being excited on command by means of lighting sources (30) (e.g. LEDs) characterized by suitable emission spectra. In the off-state of the luminescent material (20), the surface appears transparent and it is not evident any significant modifications of the optical properties (transparency, color, etc.) of the surface. The excitable luminescent material, from which a large variety of luminophores can be conveniently applied on to a substantially transparent support, of arbitrary geometry, realized with a plurality of homogenous and heterogeneous materials, including laminated glass or double glazed windows, provides a large variety of possible shapes capable of satisfying varied application requirements.
Owner:HELIV GRP SRL
Hydraulic bionic muscle
InactiveCN103802126ANatural movementGood flexibilityJointsRubber layered productsBiomechanicsInhomogeneous material
The invention discloses a hydraulic bionic muscle which comprises an elastic capsule, high pressure oil openings and mounting earrings, wherein the high pressure oil openings are fixedly connected with the two ends of the elastic capsule; the mounting earrings are arranged in the high pressure oil openings; the elastic capsule is a tubular body with tube openings in two ends; the tube wall of the tubular body is formed by compounding an inner layer, a middle layer and a surface layer; the inner layer is an elastic sealed layer; the middle layer is an anisotropic heterogeneous material layer; the surface layer is a grid protection layer woven by an elastic material. The hydraulic bionic muscle is used for a bionic running robot, is equivalent to the muscle between movement bones of the robot, improves the movement flexibility of the bionic running robot, finishes the movement process of the robot through adopting fuzzy control easily, realizes the personated robot movement, has the characteristics of simple and compact structure, and convenience in connection with a system, and also has the characteristic of simulating the biomechanics features of the human muscle.
Owner:当世(上海)智控技术有限公司
Method for observation of microstructural surface features in heterogeneous materials
ActiveUS20050283985A1Increase speedLess equipmentWriting aidsMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsConstant forceMachined surface
A method for forming a topographical image of the heterogeneous variations in a surface of a material has a first machining step and a second scanning step. The preferred machining step uses a preselected scribing tool to scribe a plurality of adjacent grooves in a selected material surface at a preselected constant force. This machining step produces a machined surface whose local elevations relative to a datum plane are dependent on the local hardness or wear resistance of the surface. Then the scanning step shifts the scribing tool across the surface in contact with the surface, and measures the elevation of the tool at a plurality of selected surface coordinates. The measured elevations allow formation of a topological map depicting sub-micron structural features of the surface.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Method and arrangement for measuring flow rate of optically non-homogeneous material
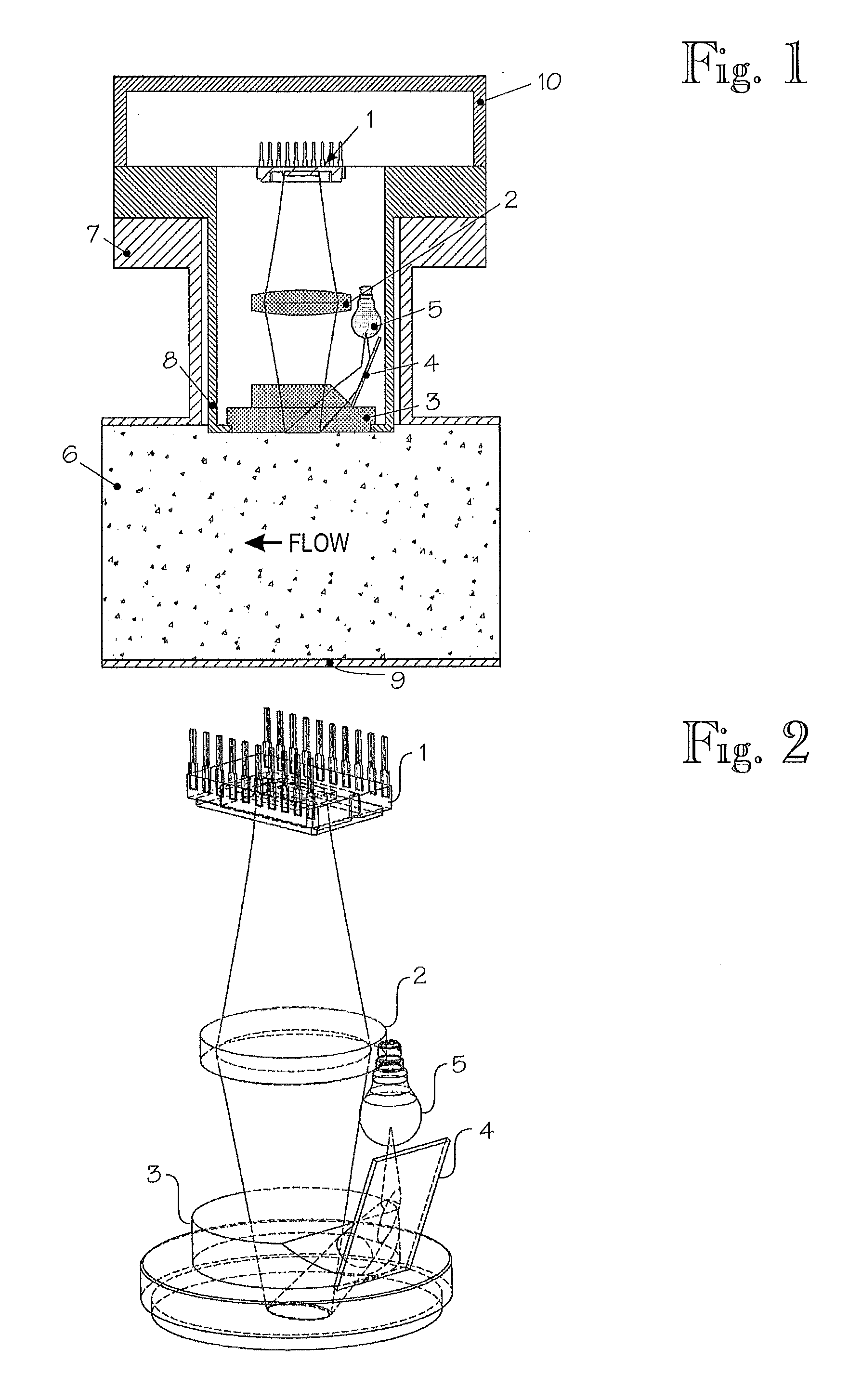
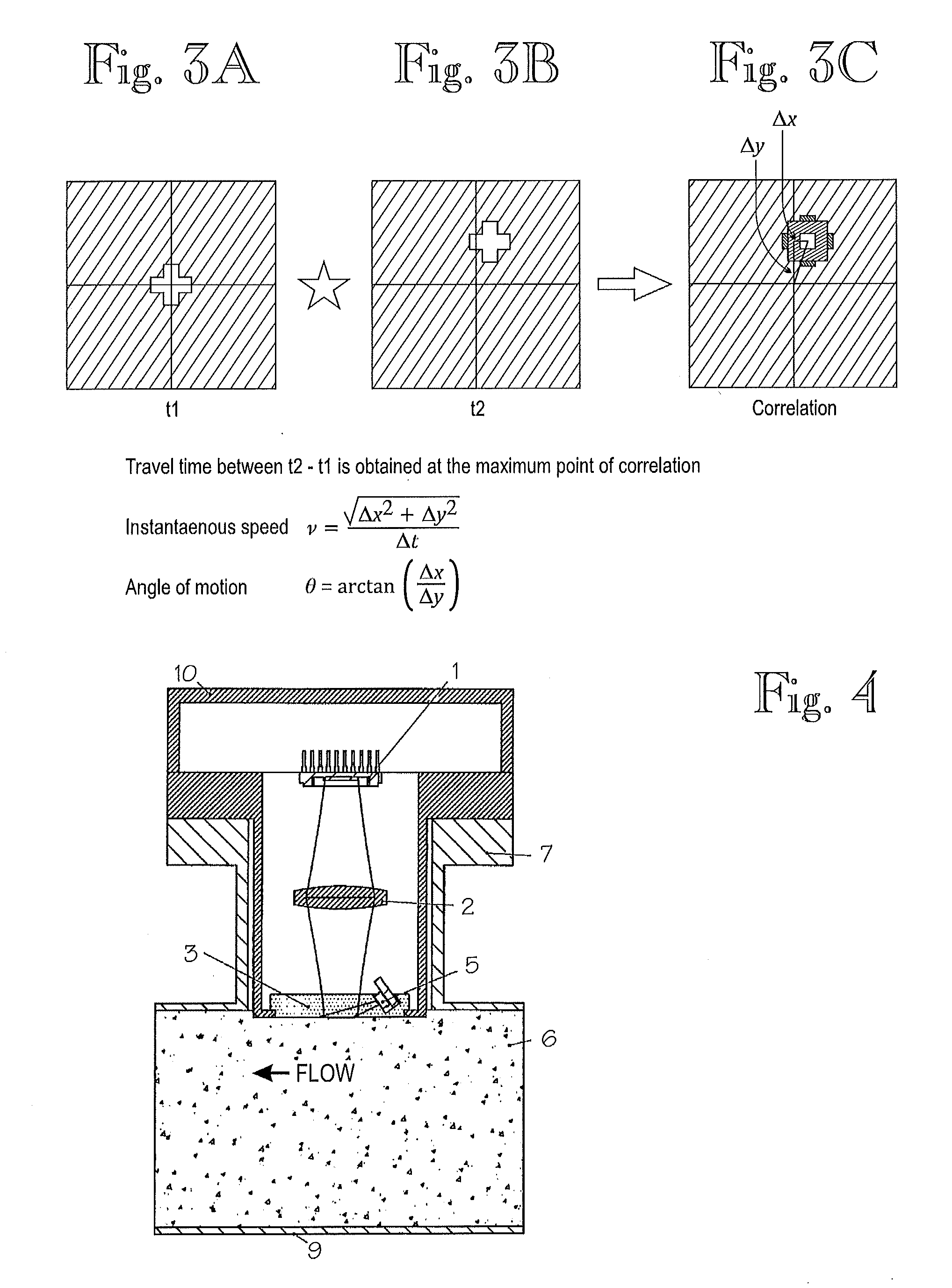
ActiveUS20130057675A1Volume/mass flow measurementColor television detailsInhomogeneous materialTime difference
A method and arrangement are disclosed for measuring a flow rate of optically non-homogeneous material in a process pipe. The non-homogeneous material can be illuminated through a window. Images are taken with a camera, through a window, of illuminated non-homogeneous material. Correlation between temporally successive images determines travel performed by the non-homogeneous material in the process pipe between capture of temporally successive images. Velocity of the non-homogeneous material is determined by the time difference between the successive images and the travel.
Owner:VAISALA
Method for the introduction of an integrated predetermined rupture line in a planar expansive body
InactiveUS20060231536A1Prevent removalIncrease productionPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementMetal working apparatusTear resistanceInhomogeneous material
The invention is directed to a method for introducing an integrated predetermined breaking line in a planar extending article. The method is particularly suitable for introducing an invisible predetermined breaking line with a reproducible, defined tearing resistance by means of a laser in an inhomogeneous material, such as a woven material, which can serve as the decorative layer of an airbag covering. According to the invention, the laser output is controlled depending upon the amount of material along the desired predetermined breaking line.
Owner:GRIEBEL MARTIN +2
Endoscope with at least one reversal system with a non-homogeneous refraction index
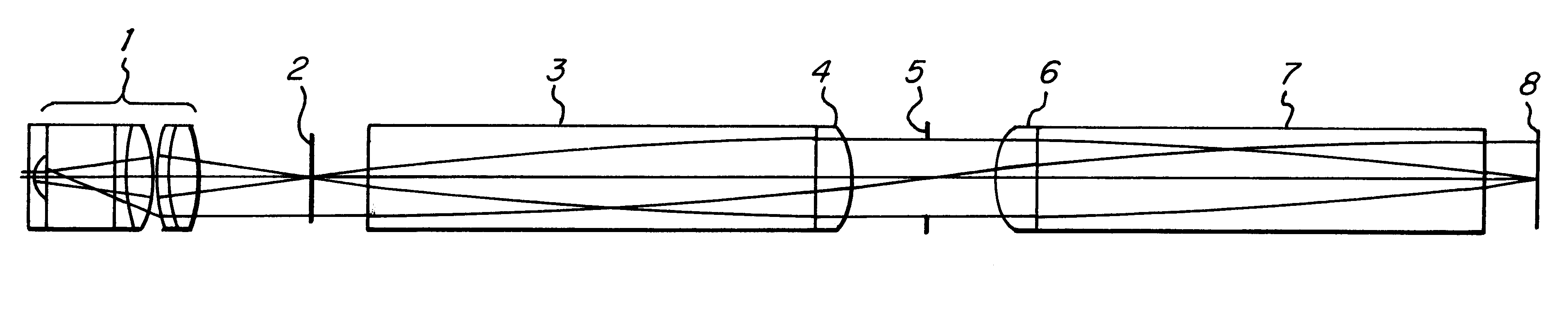
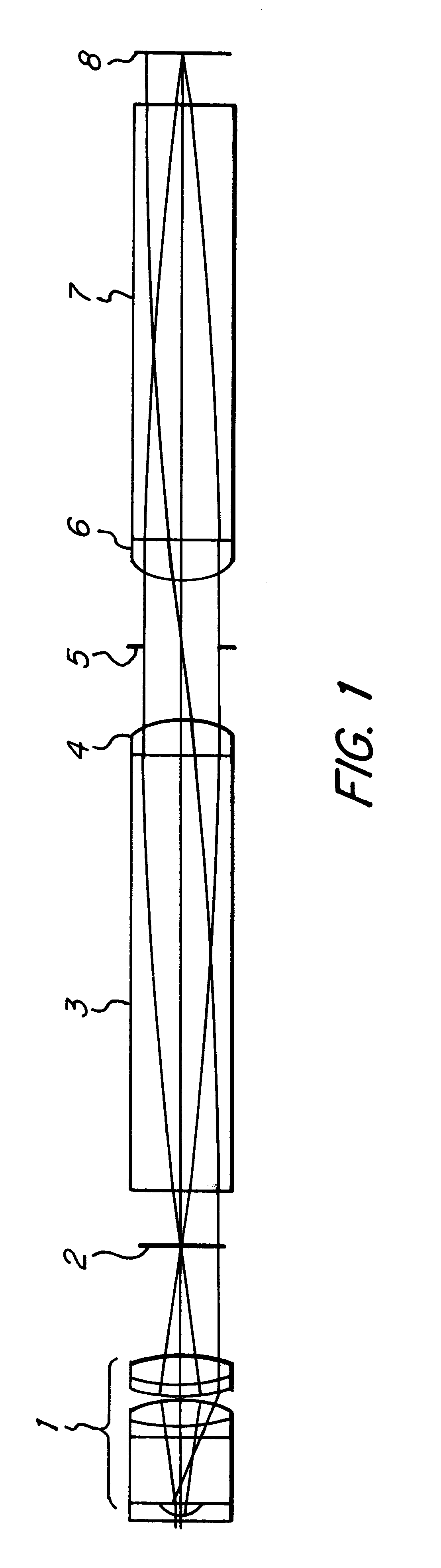
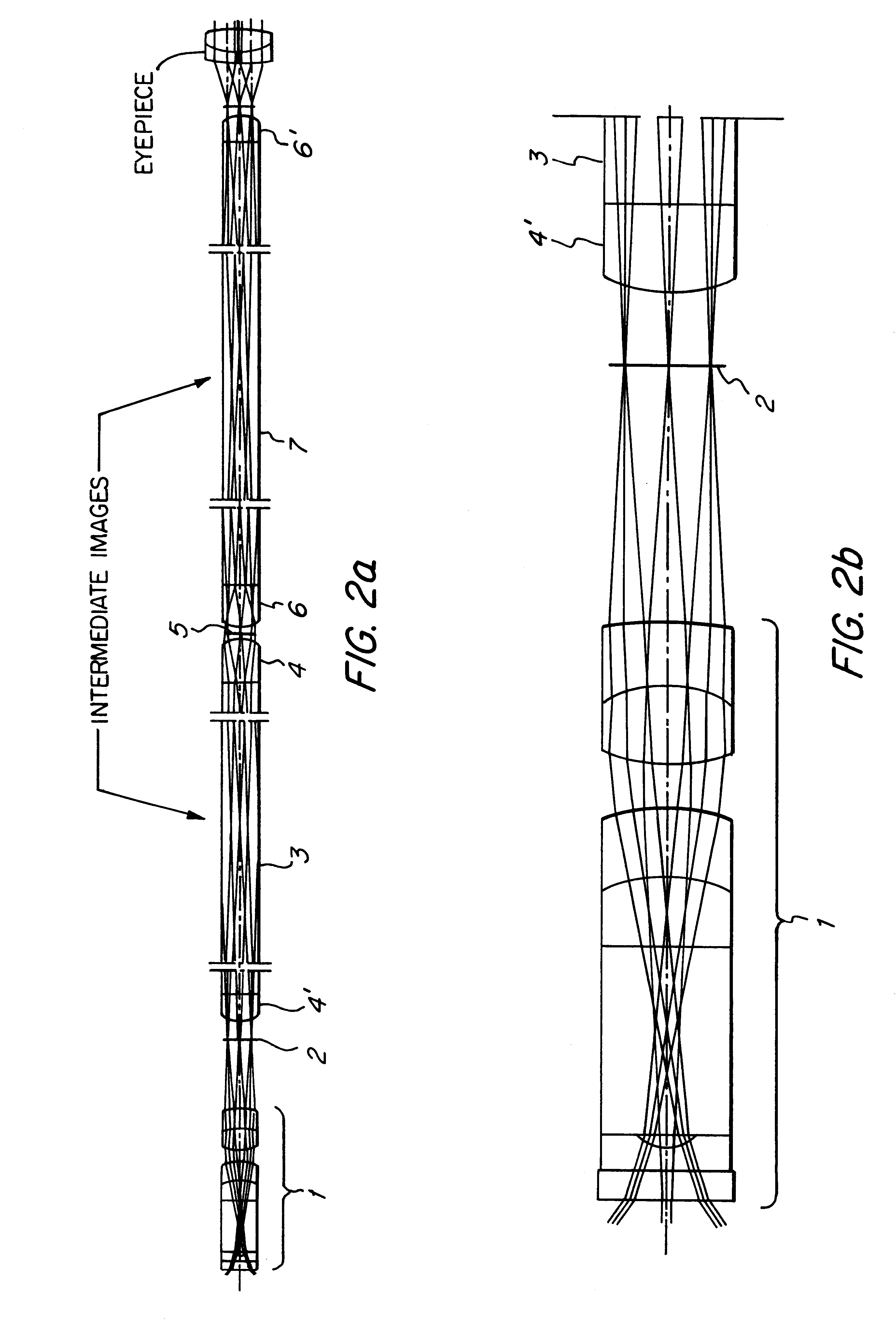
InactiveUS6301043B1Longitudinal chromatic aberrationHinder advantageSurgeryEndoscopesRefractive indexInhomogeneous material
An endoscope having a distally disposed lens and an optical transmission system which transmits the image of the lens to the proximal end of the endoscope is provided. The transmission system includes at least one reversing system, which includes two elements in mutual mirror-inverted arrangement. Each element includes a rod lens with planar faces and at least one optically thin lens having a planar surface. The rod lenses consist of an inhomogeneous material having a positive dispersion and an inhomogeneous refractive index in the radial direction, while the thin lenses are plano-convex lenses.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
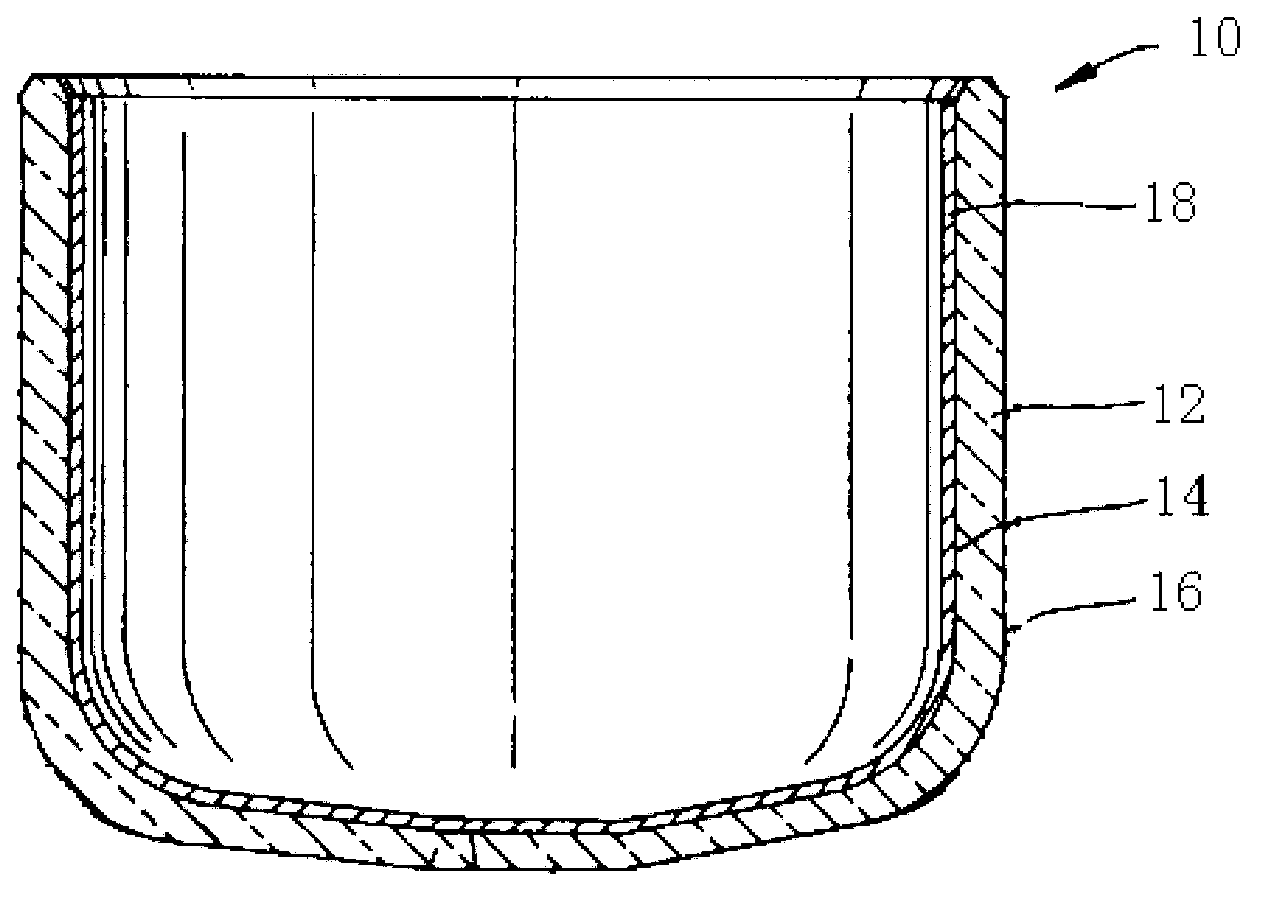
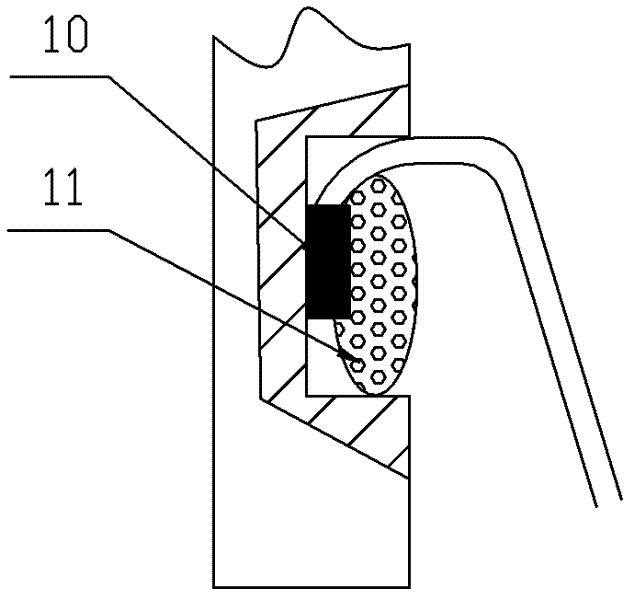
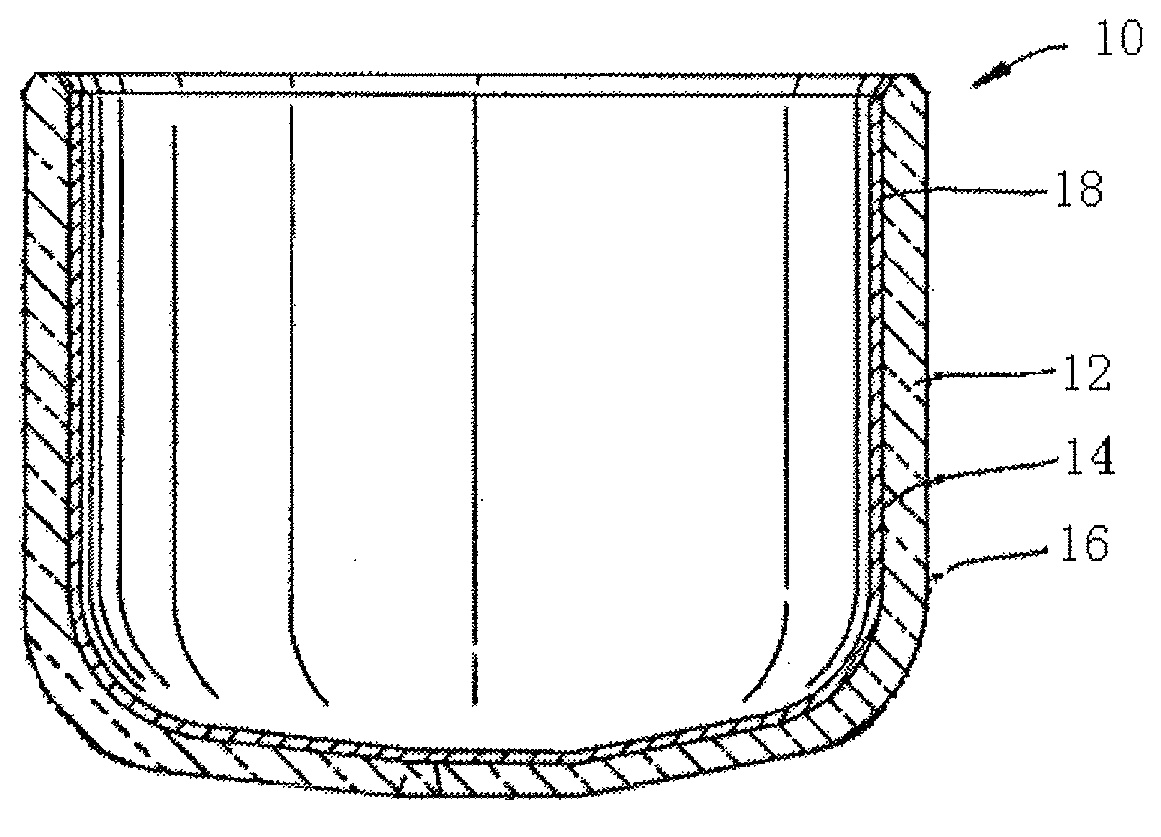
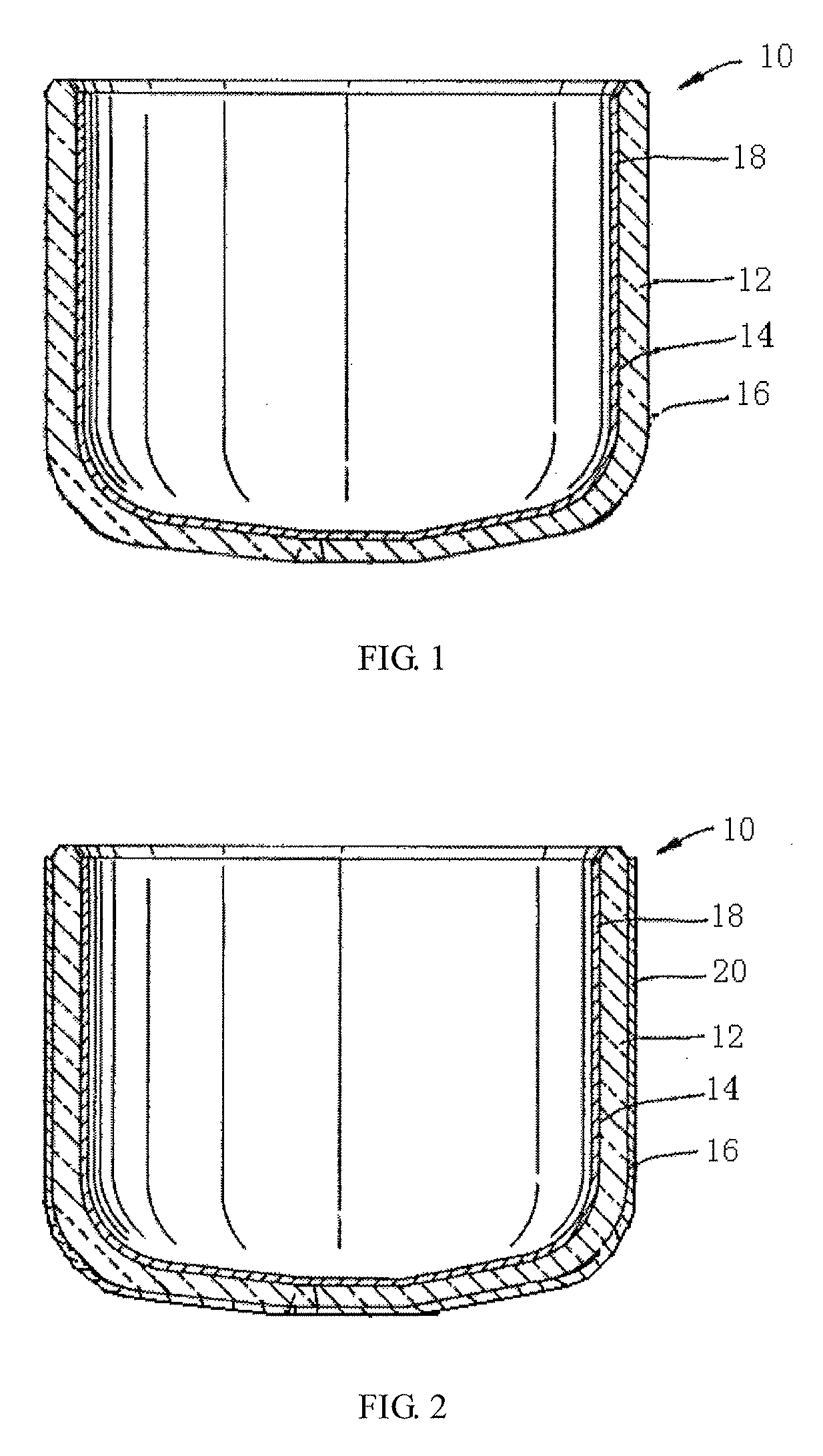
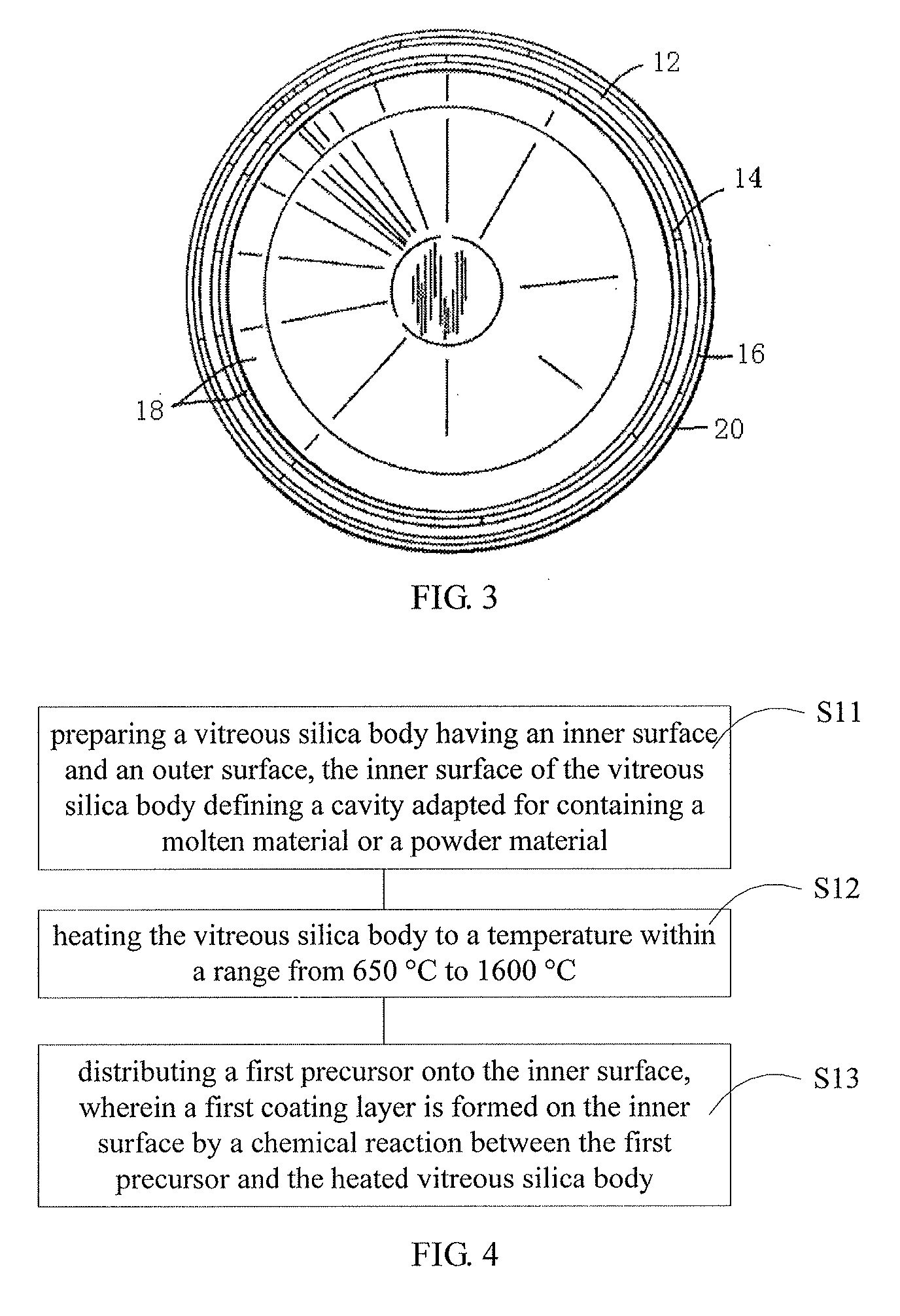
Silica crucible and method for fabricating the same
InactiveCN103154330APromote sheddingHigh mechanical strengthGlass furnace apparatusBy pulling from meltCeriumInhomogeneous material
The invention provides a silica crucible with a coating with a strong adhesion and method for fabricating the same. The silica crucible includes a vitreous silica body having an inner surface and an outer surface, the inner surface of the vitreous silica body defining a cavity adapted for containing a molten material or a powder material; and a first coating layer formed on the inner surface of the vitreous silica body. The first coating layer is formed by pyrolising a composite of aluminum, magnesium, calcium, titanium, zirconium, radium, chromium, selenium, barium, yttrium, cerium, hafnium, tantalum, tin or silicon under a predetermined temperature. The first coating layer is substantially consisted of a nonhomogeneous material, and an interface is defined by the homogeneous material and the nonhomogeneous material between the vitreous silica body and the coating layer. The first coating layer has strong adhesion capability and guarantees the coating layer will not be easily peeled off or removed through hand touching, raw materials loading into the silica crucible or vigorous transportation.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN RES SHANGHAI
Thermoelasticity homogenizing method for three-dimensional random heterogeneous material under finite deformation
ActiveCN105069203ASolving Numerical Modeling ChallengesThe calculation result is accurateSpecial data processing applicationsElement analysisInhomogeneous material
The invention discloses a thermoelasticity homogenizing method for a three-dimensional random heterogeneous material under finite deformation. The method comprises the steps as follows: 1) establishing a composite material representative volume element three-dimensional RVE numerical model with randomly distributed particles based on random sequence adding RSA method and removing a particle overlapping phenomenon while the particle volume fraction is relative large; 2) performing finite element analysis calculation on the composite material three-dimensional RVE numerical model under a thermoelasticity environment to obtain an arithmetic solution of effective property of the RVE numerical model; 3) establishing a random homogenizing model to calculate macroscopic effective property of a composite material and using the macroscopic effective property of the composite material as an actual and effective property. The method of the invention provides a more reliable homogenizing result for the macroscopic effective property of the composite material, and provides sufficient basis for the optimization design of structure and the use of new advanced materials.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Different materials-laminate metal plate and different materials-laminate core, and method of producing the same
InactiveUS20050077798A1Broaden applicationMade firmerMagnetic circuit characterised by magnetic materialsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesMetallurgyInhomogeneous material
The invention is to provide a metal plate of laminated heterogeneous materials, and an iron core of the same, where a plurality of metal plates of different material qualities are easily and stably joined, have characteristics over many applications, may attain low production cost, and provide a making method thereof. That is, a metal plate of laminated heterogeneous materials, which is joined by laminating a plurality of metal plates of different material qualities, is joined by caulking a first material body of the metal plate of the laminated heterogeneous materials having notches at intermediate parts thereof, as well as caulking projections formed by cutting down rows of both ends thereof in the length direction of the notches, and a second material body of the metal plate of the laminated heterogeneous materials formed with caulking holes for inserting the caulking projections, at the caulking projections of said first material body and the caulking holes of the second material body.
Owner:MITSUI HIGH TEC INC
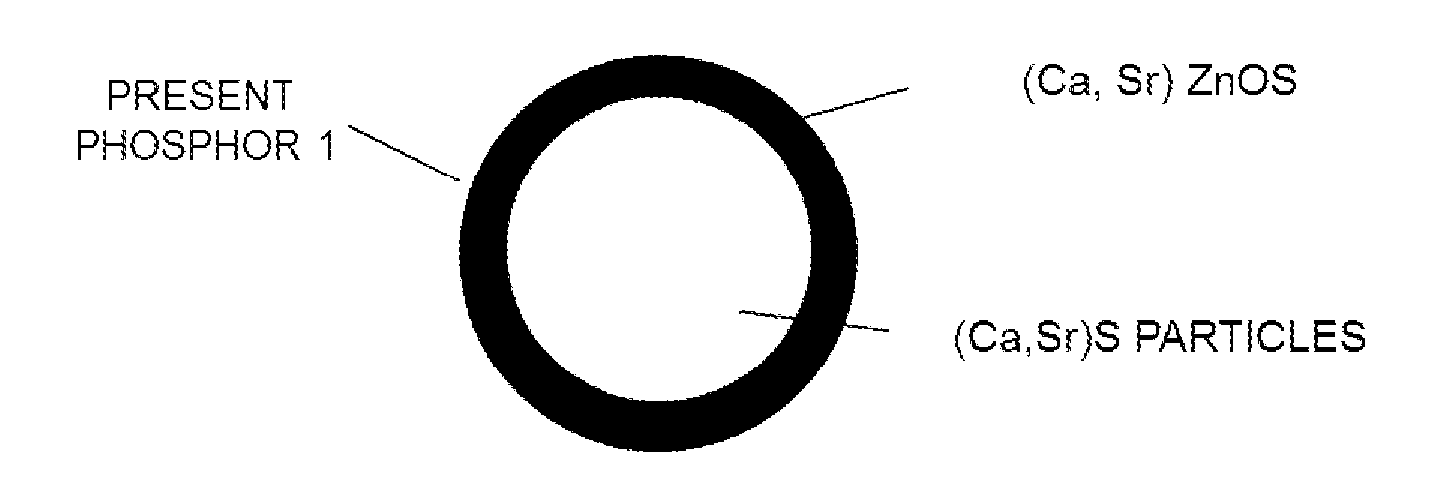
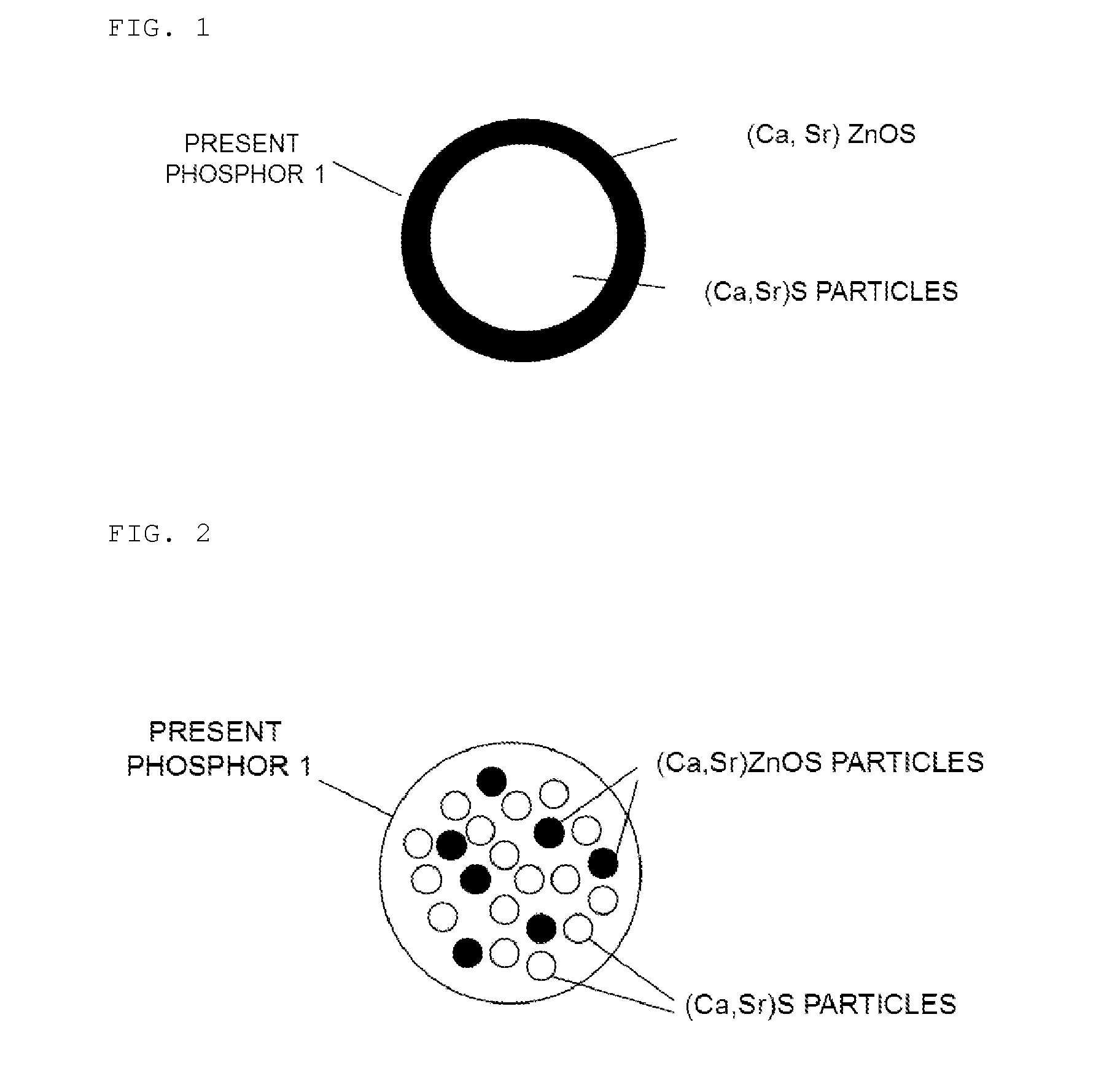
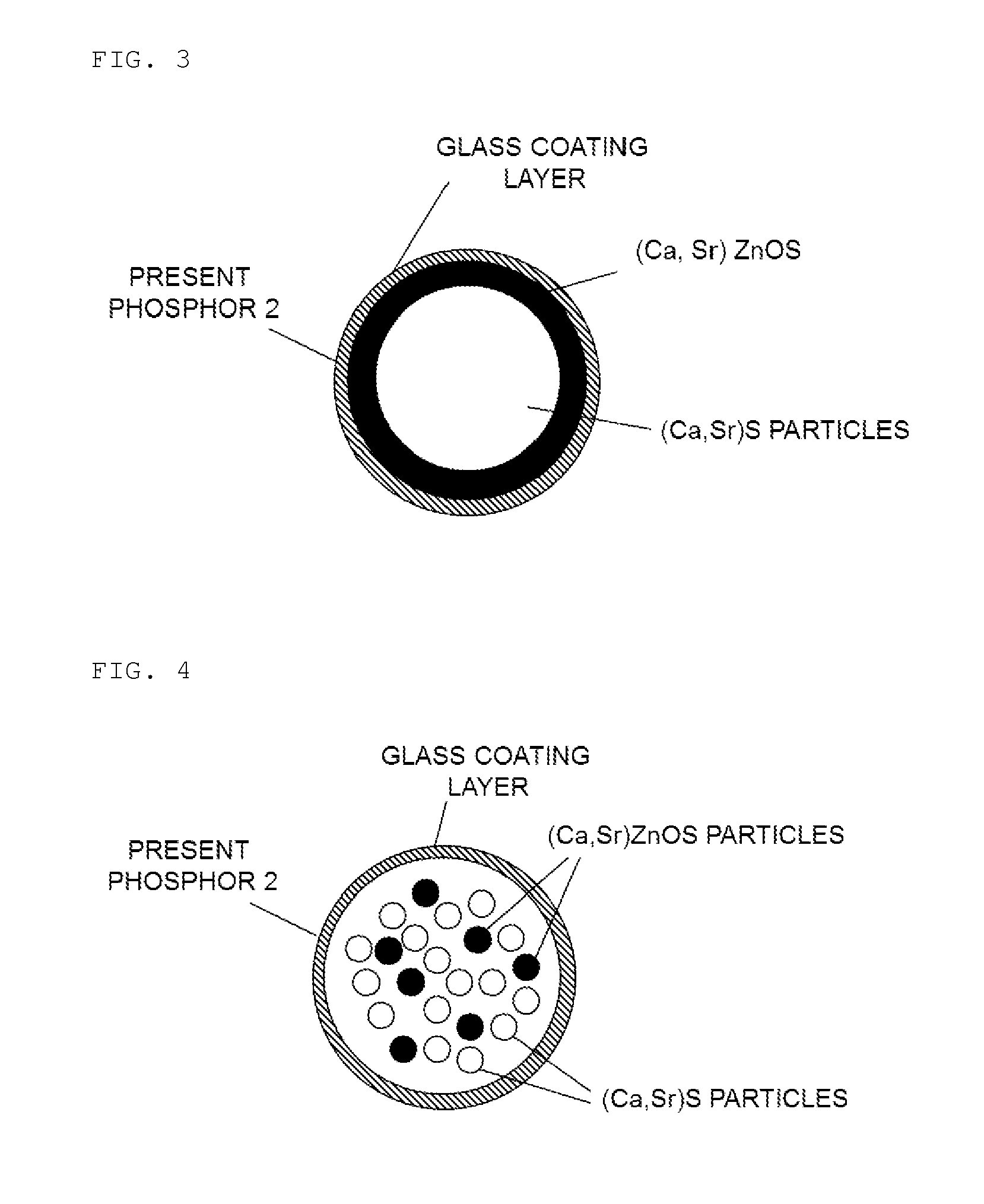
Phosphor, LED Light-Emission Element, and Light Source Device
ActiveUS20150075611A1Inhibitory responseDissimilar material reacting with each other can be suppressedGlass/slag layered productsWater-setting substance layered productChemical reactionPhosphor
Provided is a novel CaS-based phosphor with which chemical reactions can be inhibited even if said CaS-based phosphor is heated with a heterogeneous material. This phosphor includes: a crystalline parent material represented by the composition formula Ca1-xSrxS.yZnO (in the formula, 0≦x<1, 0<y≦0.5); and a luminescent center.
Owner:MITSUI MINING & SMELTING CO LTD
Self-adapting stabilized contact electric resistance measuring apparatus
InactiveCN101441234AEvenly distributedImprove distributionResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical resistance and conductanceMeasurement device
A self-adapting stably contacted resistance measurement device comprising an upper conducting substrate and a lower conducting substrate is characterized in that the top of the upper conducting substrate is equipped with a universal-joint spindle. Working surfaces of the upper conducting substrate and the lower conducting substrate are both coated with a soft metal clad which can be fixed on the working surfaces of the upper conducting substrate and the lower conducting substrate by nuts. The device can ensure full contact between the conducting substrates and the end face of a sample and uniform distribution of stable contact resistance and current when passing through the sample and realize accurate measurement. Therefore, the device is applicable to the measurement devices for measuring the resistance and the specific resistance of heterogeneous material.
Owner:BEIJING INSPECT TECH
Thermal deformation tester for cement-emulsified asphalt mortar material
InactiveCN102419341AGuaranteed uniformityEliminate the effects ofMaterial thermal analysisThermal deformationInhomogeneous material
The invention discloses a thermal deformation tester capable of testing a large-size cement-emulsified asphalt mortar material. The tester comprises a fixed bracket, a liquid circulation temperature chamber and a displacement sensor are mounted on the fixed bracket, a heat preservation cavity of the liquid circulation temperature chamber is internally provided with a test piece, the test piece and the displacement sensor are connected through an ejector rod mounted on the fixed bracket, and the test piece is provided with a temperature sensor. Based on the characteristic that the cement-emulsified asphalt mortar is a heterogeneous material, the tester can test the large-size test piece, and can guarantee the accuracy and the representativeness of the test result. The large-size test piece bracket cooperates with the quartz glass ejector rods in different length, which facilitates further study on service behavior of the cement-emulsified asphalt mortar and cracking mechanism of a filled layer of a slab track structure.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Silica crucible and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20130247818A1Strong adhesionEasily peeled offPolycrystalline material growthLiquid surface applicatorsCeriumInhomogeneous material
A silica crucible and a fabricating method thereof are provided. The silica crucible includes a vitreous silica body having an inner surface and an outer surface, the inner surface of the vitreous silica body defining a cavity adapted for containing a molten material or a powder material; and a first coating layer formed on the inner surface of the vitreous silica body. The first coating layer is formed by pyrolysing a composite of aluminum, magnesium, calcium, titanium, zirconium, radium, chromium, selenium, barium, yttrium, cerium, hafnium, tantalum, tin or silicon under a predetermined temperature. The first coating layer substantially includes of a nonhomogeneous material, and an interface is defined by the homogeneous material and the nonhomogeneous material between the vitreous silica body and the coating layer. The first coating layer has strong adhesion capability and guarantees the coating layer will not be easily peeled off or removed.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN RES SHANGHAI
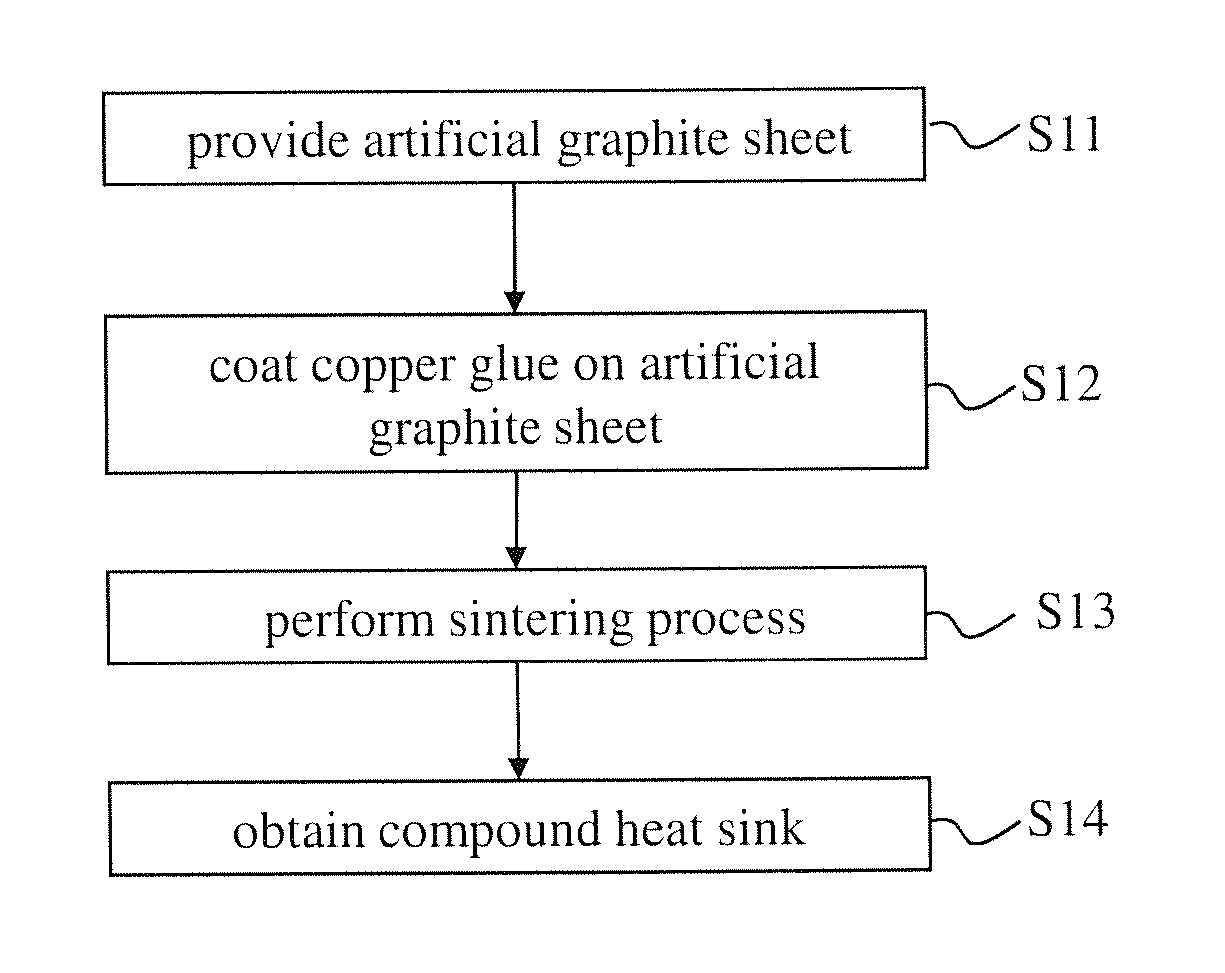
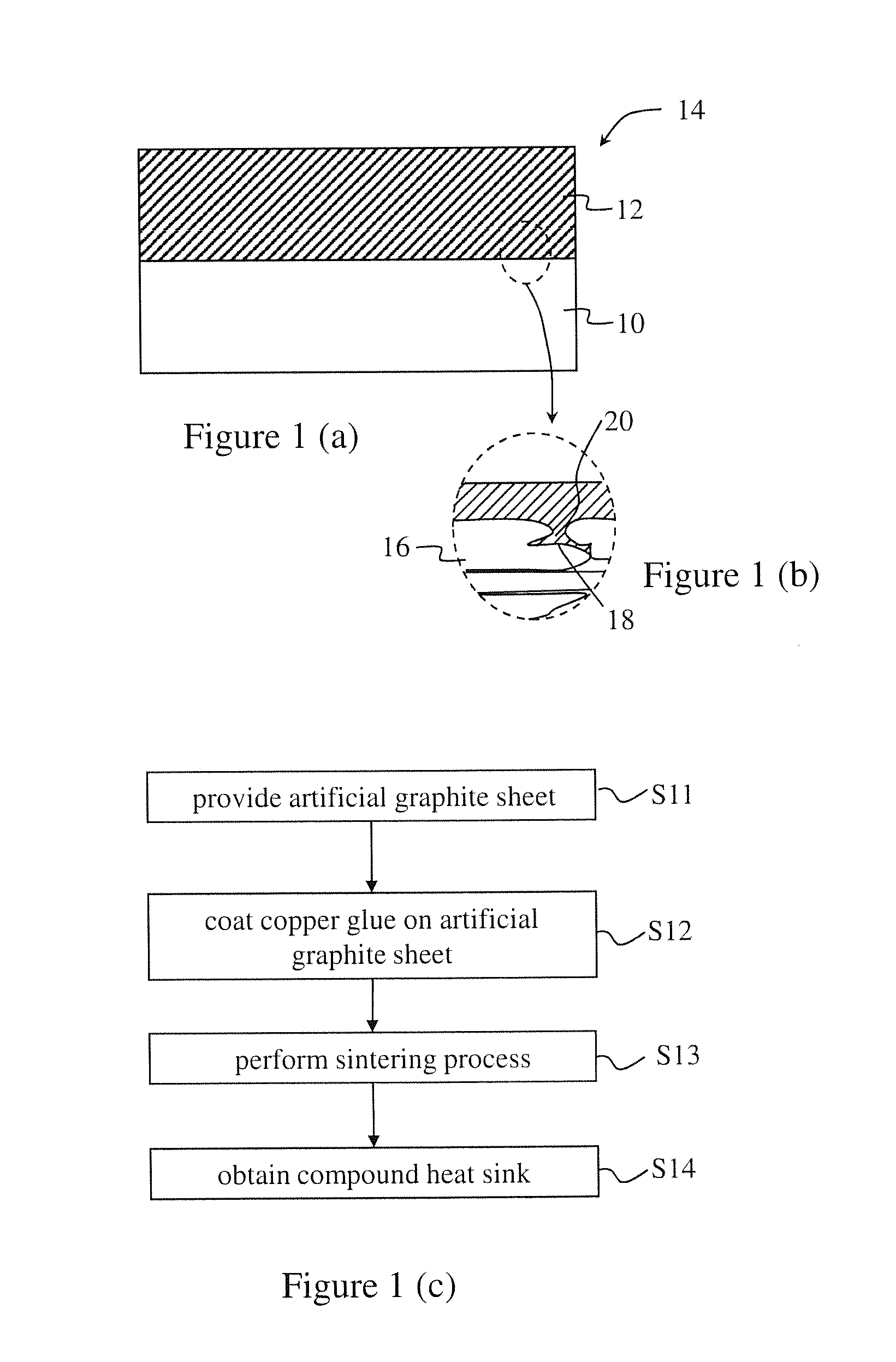
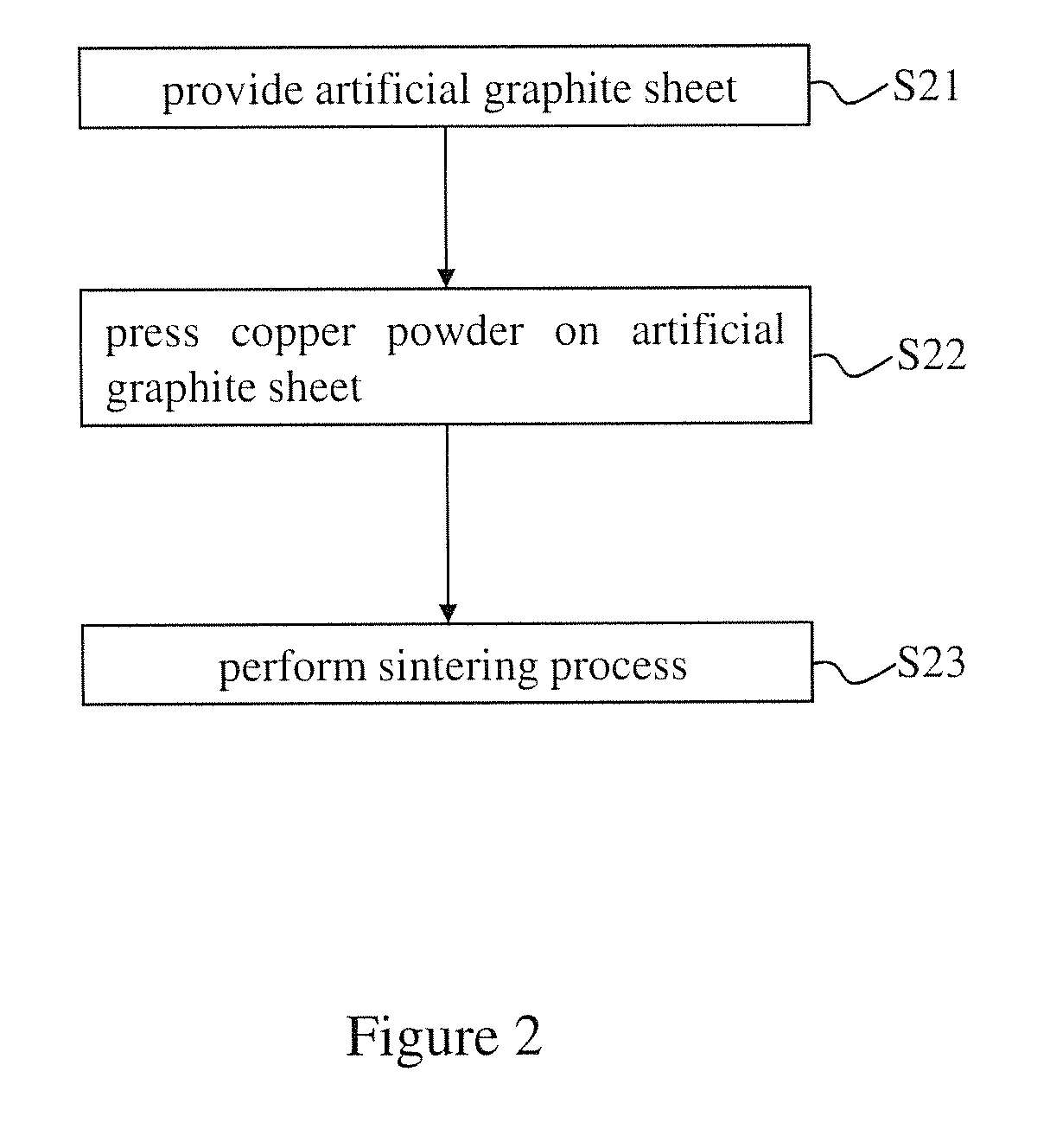
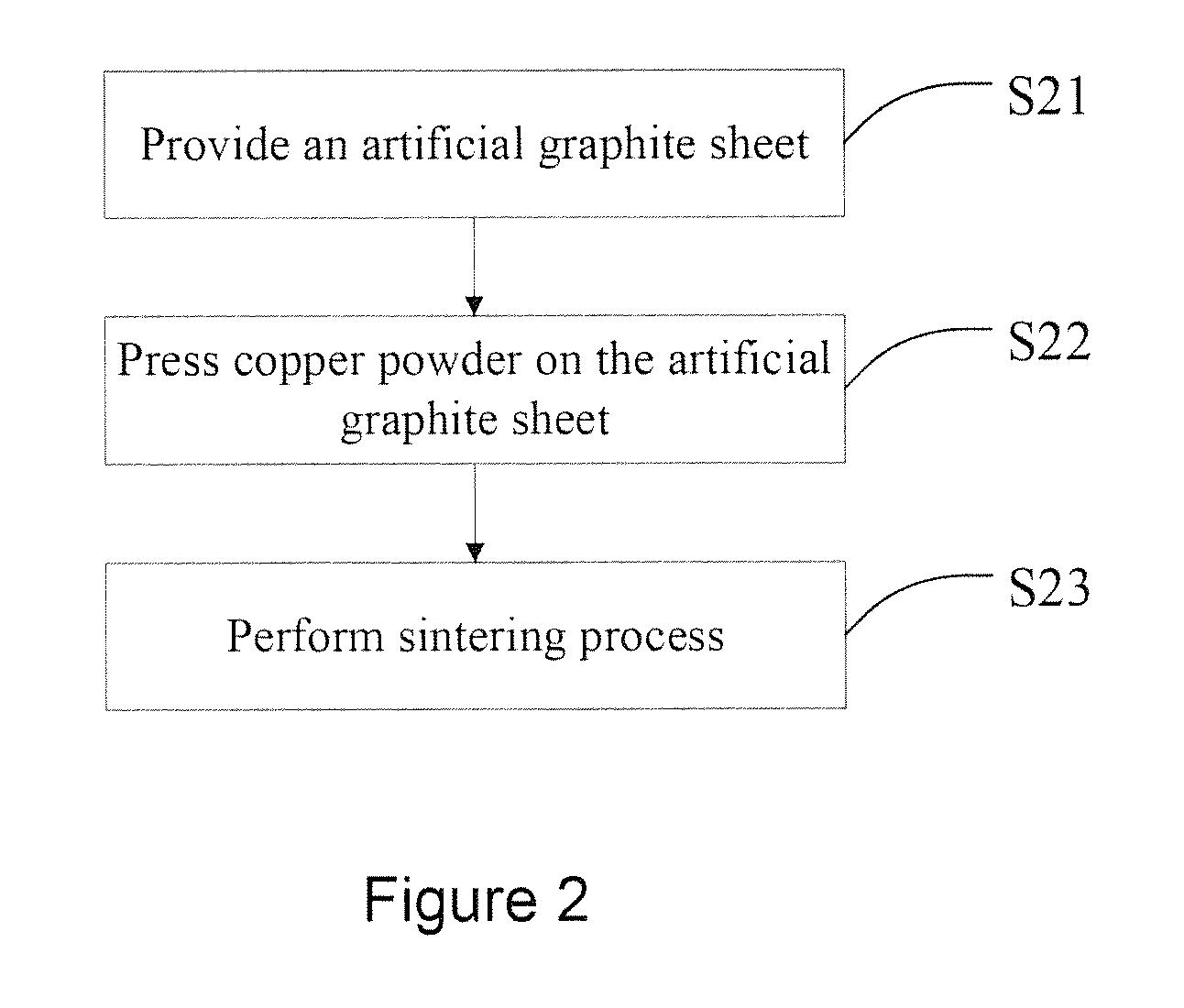
Method for manufacturing compound heat sink
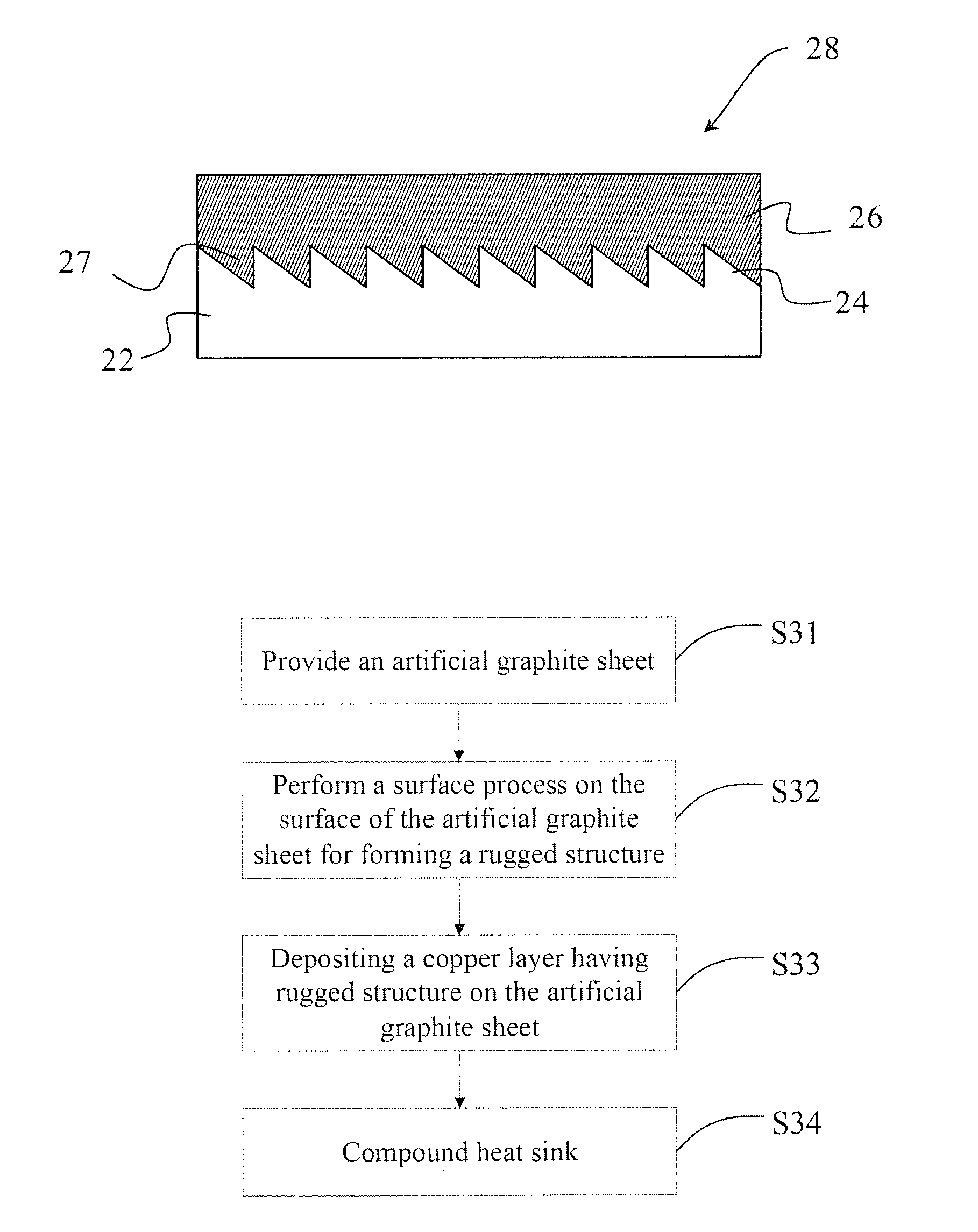
InactiveUS20150136303A1Improve thermal conductivityImprove bond strength and stabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHeat resistanceInhomogeneous material
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing a compound heat sink. Firstly, providing an artificial graphite sheet, and then performing a surface treatment process on the artificial graphite sheet to form a rugged structure on the artificial graphite sheet as a first embedding structure. Finally, forming a metal layer covering the rugged structure, and performing a pressing bonding process to form a second embedding structure corresponding to the first embedding structure to bond the metal layer and the artificial graphite sheet. Namely, the artificial graphite sheet and the metal layer are bonded by the first and second embedding structures for increasing the bonding strength between two heterogeneous materials as well as reducing the interfacial heat resistance. Thereby, the stability of heat dissipation performance can be improved, and a volumetric heat capacity of the compound heat sink from 1.1 to 3.5 J / (cm3·K) is provided.
Owner:HUGETEMP ENERGY
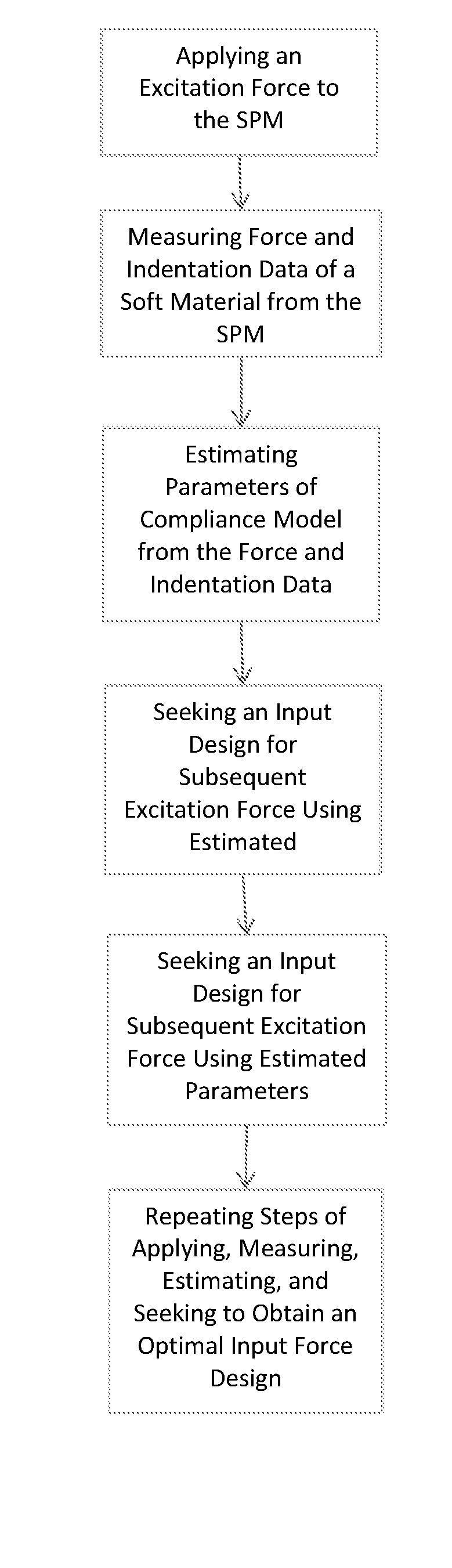
Optimal excitation force design indentation-based rapid broadband nanomechanical spectroscopy
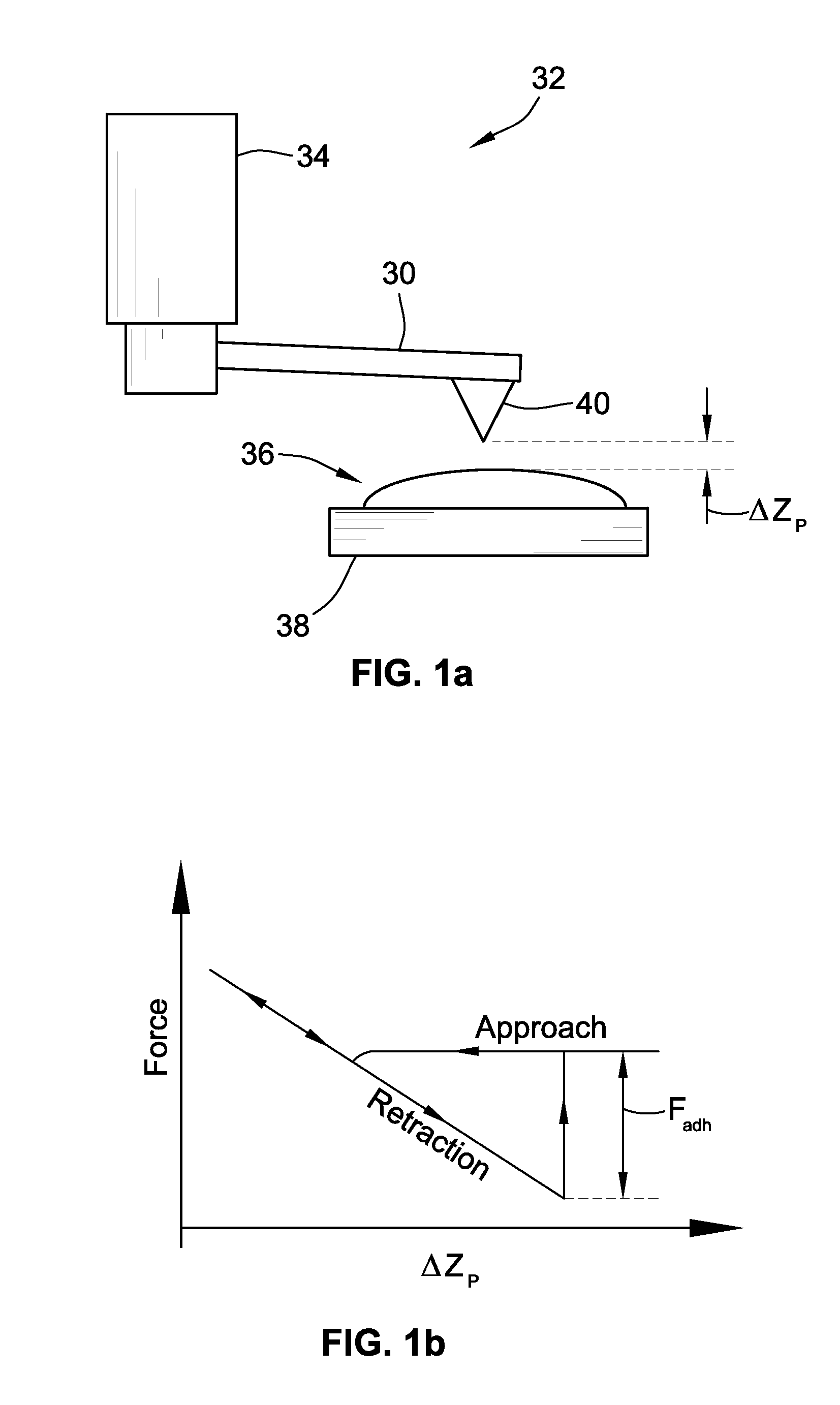
InactiveUS8590061B1Rapid excitationPreventing convolutionNanotechnologyScanning probe microscopySpectroscopyCell Movement Process
An optimal input design method and apparatus to achieve rapid broadband nanomechanical measurements of soft materials using the indentation-based method for the investigation of fast evolving phenomenon, such as the crystallization process of polymers, the nanomechanical measurement of live cell during cell movement, and force volume mapping of nonhomogeneous materials, are presented. The indentation-based nanomechanical measurement provides unique quantification of material properties at specified locations. Particularly, an input force profile with discrete spectrum is optimized to maximize the Fisher information matrix of the linear compliance model of the soft material.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
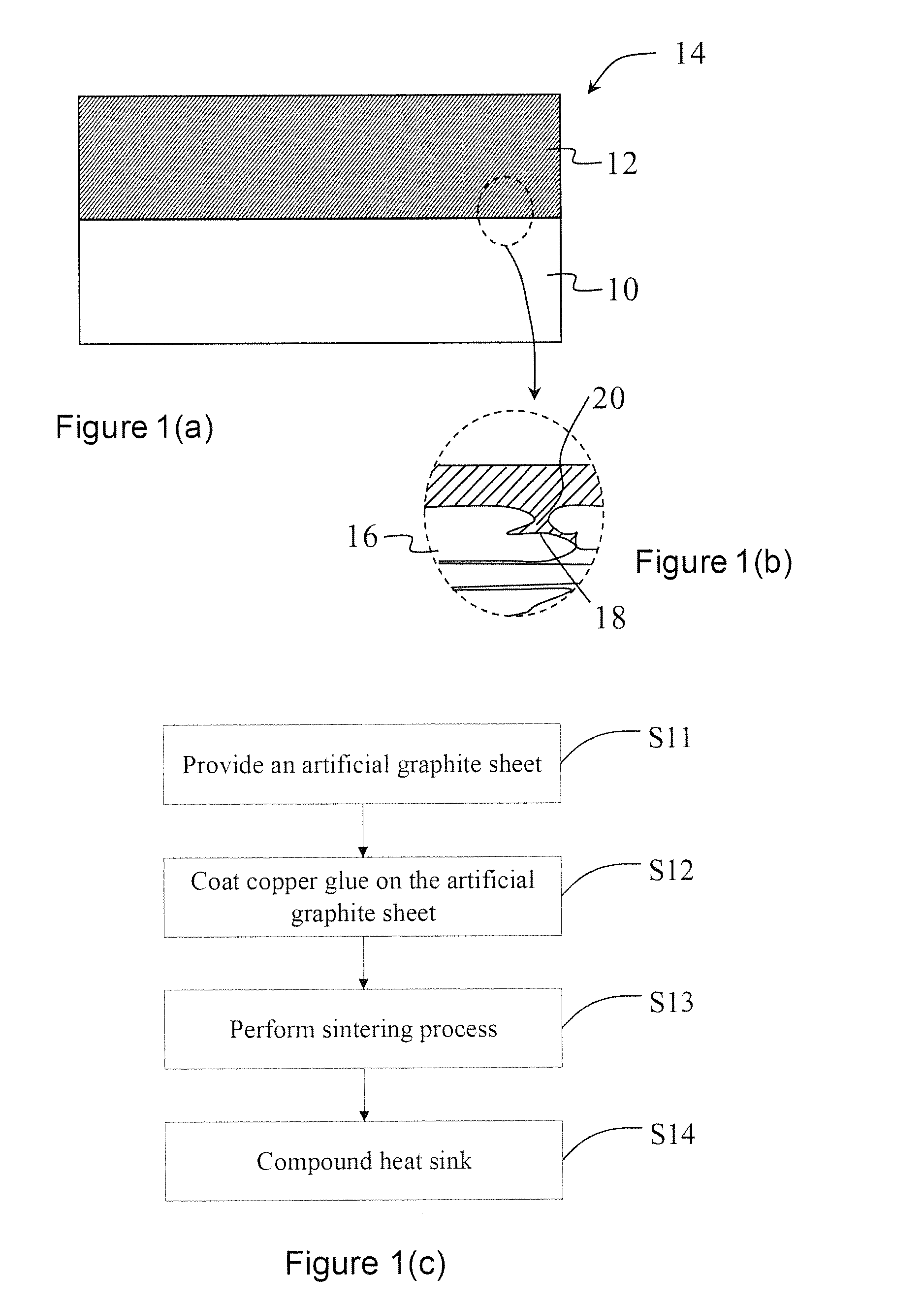
Compound heat sink
InactiveUS20140356580A1Improve bond strength and stabilityImprove thermal conductivityElectrical equipmentThin material handlingHeat resistanceInhomogeneous material
The present invention provides a compound heat sink, mainly comprising a graphite layer and a metal layer. The graphite layer has a first embedding structure on a surface; the metal layer has a second embedding structure on a surface and corresponding to the first embedding structure. The graphite layer and the metal layer are bonded by the first and second embedding structures for increasing the bonding strength between two heterogeneous materials as well as reducing the interfacial heat resistance. Thereby, the stability of heat dissipation performance can be improved.
Owner:HUGETEMP ENERGY
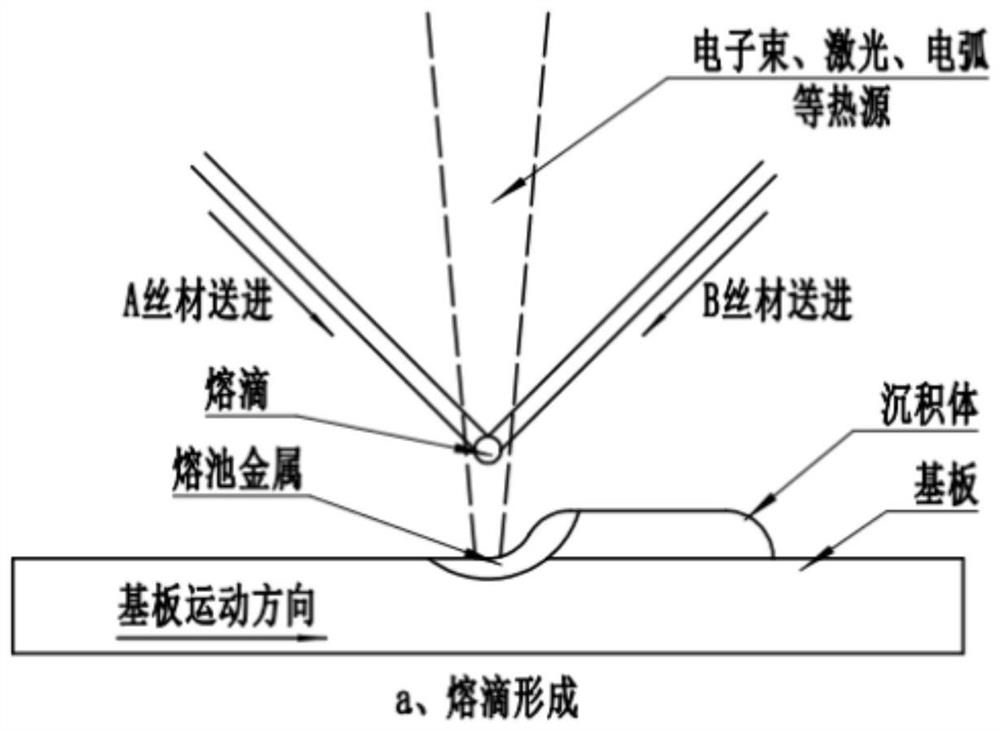
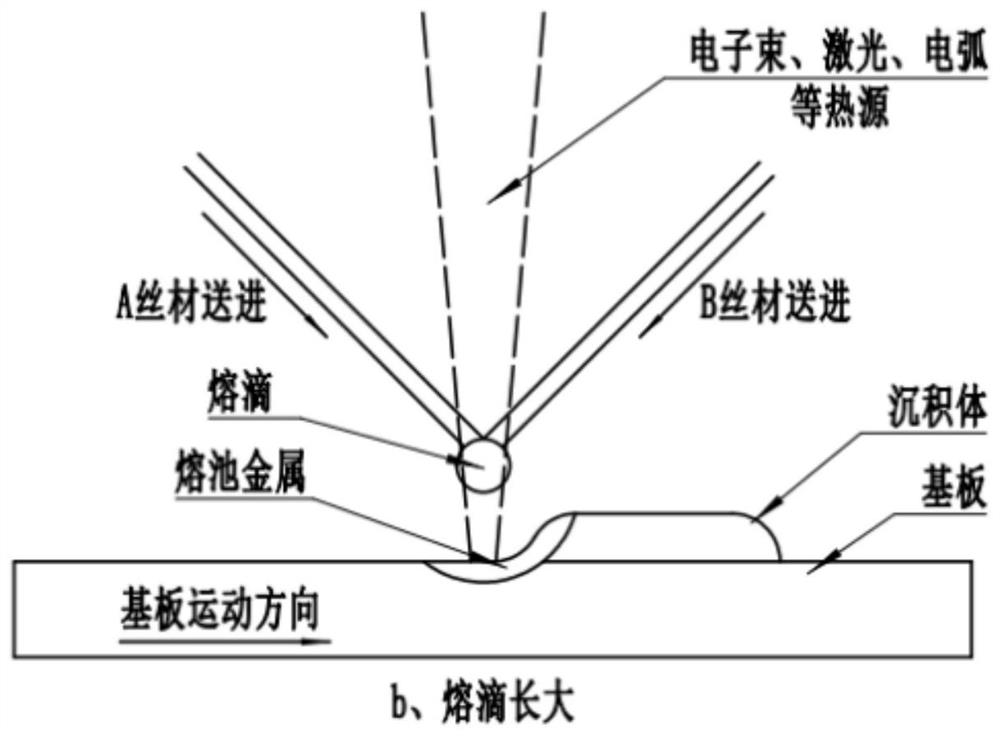
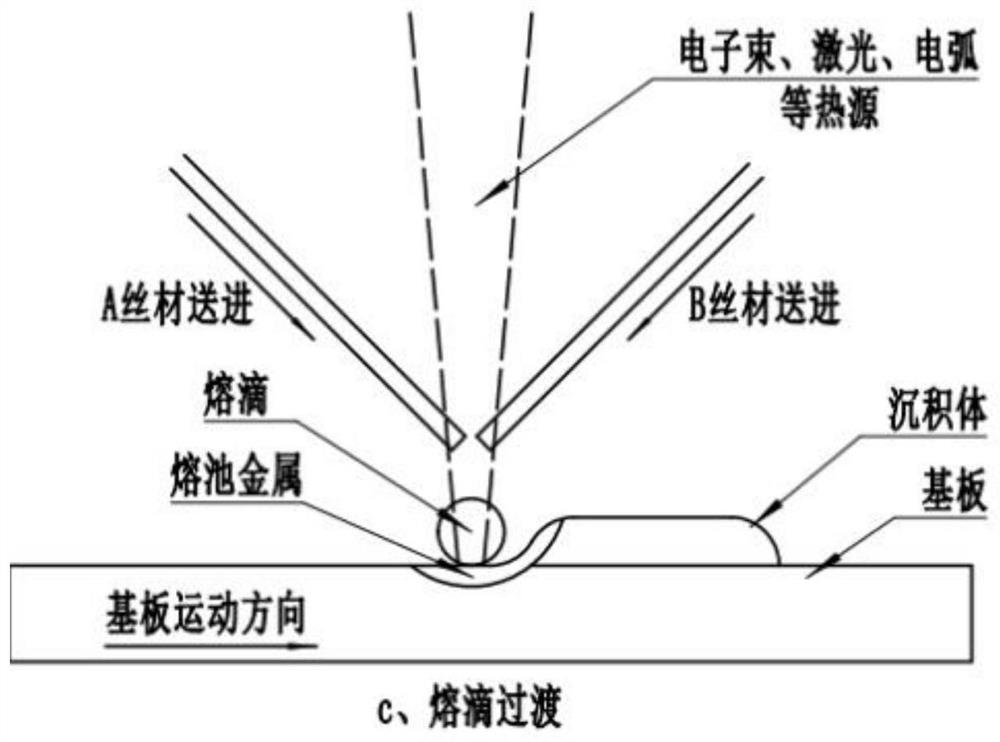
Preparation method of multi-component new alloy and component gradient alloy material part
ActiveCN112935470AIncrease profitImprove forming efficiencyArc welding apparatusElectron beam welding apparatusInhomogeneous materialAlloy
The invention provides a preparation method of a multi-component new alloy and a component gradient alloy material part. Material-forming integration is achieved, and intermediate steps are reduced. According to the method, heterogeneous materials with variable components, gradient and the like are easily realized; compared with powder, wires are used, the material utilization rate is high, and the forming efficiency is high; the wires made of two or more different materials are sequentially melted according to physical characteristics under the effect of a heat source to form a molten drop, then the molten drop is transited to a base body, all components can be uniformly mixed, component segregation can be reduced or even eliminated, the uniformity of a new alloy material in the forming process can be effectively controlled, the stability of the molten drop transition form is higher, and the probability of forming defects is effectively reduced.
Owner:浙江智熔增材制造技术有限公司
System and method for identifying and sorting material
ActiveUS20090251536A1Satisfies needCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsInhomogeneous materialEngineering
An automatic sorting system is for identifying and sorting non-homogenous material. The system includes a conveyor belt and an identification unit cooperable with the conveyor belt and placed above the conveying surface thereof for identifying material traveling therealong. The identification unit includes at least one projector for projecting a beam of light downwardly towards the conveying surface, at a given height above the conveying surface, and onto a given material to be identified, so that a portion of projected light may be reflected back from the given material and upwardly towards the identification unit. The identification unit also includes at least one lens positioned about the identification unit for receiving the portion of reflected light from the given material to be identified. The identification unit also includes a first processing unit operatively linked to the at least one lens for carrying a spectral analysis of the portion of reflected light captured by the at least one lens so as to determine the nature of the given material, and a second processing unit operatively linked to the first processing unit for comparing results of the spectral analysis with corresponding data associated to a variety of different materials stored in a given database of the second processing unit. The present system also includes a sorting unit operatively linked to the second processing unit and operatively cooperating with the second end of the conveyor so as to sort material released from the second end of the conveyor depending on signals received from the second processing unit.
Owner:6511660 CANADA
Real-time rendering method for multilayer inhomogeneous material reflecting object
ActiveCN107204035AIncrease brightnessWide range of brightness3D-image renderingComputer graphics (images)Inhomogeneous material
The invention provides a real-time rendering method for a multilayer inhomogeneous material reflecting object, wherein the method is improved based on a BRDF model. The method comprises the following steps of S10, describing non-uniformity of a ceramic glaze surface in a prepare baking thickness mapping method; S20, obtaining a summit illumination strength calculation formula and an illumination distribution function in the improved BRDF illumination model; and S30, performing brightness adjustment by means of high dynamic range for simulating flexible transition of light on the surface of the ceramic. A model which is rendered through the method accords with an illumination physical characteristic of multilayer inhomogeneous material surface illumination and furthermore can vividly restore a real impression of the multilayer inhomogeneous material object. Furthermore on the condition of relatively large number of sides of the model, high real-time rendering rate can be ensured and a real-time interaction requirement is satisfied.
Owner:桂林大容文化科技有限公司
Different materials-laminate metal plate and different materials-laminate core, and method of producing the same
InactiveUS7268460B2Easily and stably joinedMagnetic circuit characterised by magnetic materialsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesInhomogeneous materialMaterial quality
The invention is to provide a metal plate of laminated heterogeneous materials, and an iron core of the same, where a plurality of metal plates of different material qualities are easily and stably joined, have characteristics over many applications, may attain low production cost, and provide a making method thereof. That is, a metal plate of laminated heterogeneous materials, which is joined by laminating a plurality of metal plates of different material qualities, is joined by caulking a first material body of the metal plate of the laminated heterogeneous materials having notches at intermediate parts thereof, as well as caulking projections formed by cutting down rows of both ends thereof in the length direction of the notches, and a second material body of the metal plate of the laminated heterogeneous materials formed with caulking holes for inserting the caulking projections, at the caulking projections of said first material body and the caulking holes of the second material body.
Owner:MITSUI HIGH TEC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com