Method for preparing organic seaweed liquid fertilizer by fermentation and enzymolysis of microorganisms
A seaweed liquid, seaweed technology, applied in the direction of organic fertilizers, etc., can solve problems such as the destruction of active nutrients, and achieve the effects of promoting growth and development, improving photosynthetic efficiency, and improving soil structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
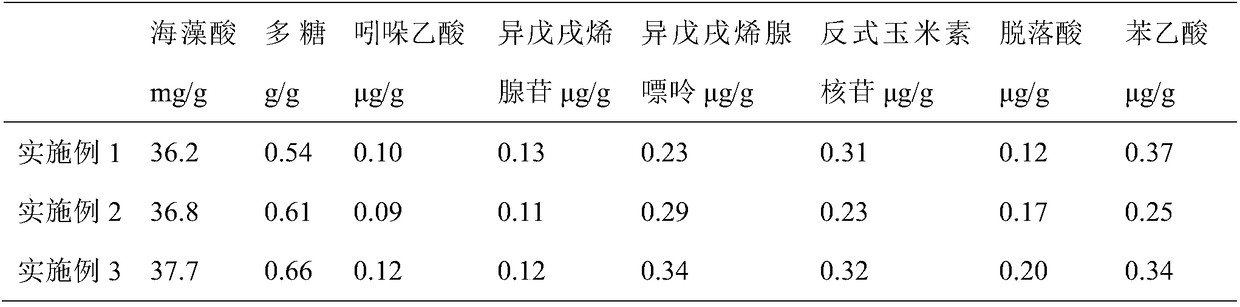
Embodiment 1
[0027] A method for preparing organic seaweed liquid fertilizer by microbial fermentation and enzymolysis, the specific preparation steps are as follows:
[0028] (1) Fresh kelp raw materials are washed with water to remove sand grains and other impurities;
[0029] (2) Add pure fresh water accounting for 1.2 times the quality of kelp to 50 g of washed kelp, crush and grind;
[0030] (3) Put the crushed kelp slurry into the fermentation container, add 2.5×10 9 CFU of Bacillus subtilis and 2.5 x 10 9 CFU of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (the ratio of the bacteria amount is 1:1), after stirring evenly, heat to 37°C, and keep the fermentation for 48h;
[0031] (4) After fermentation, the kelp slurry turns from green to brown, and the pH value is less than 6. Add 0.6g of acid protease and cellulase (2:1) to it, stir evenly, heat to 55°C, and keep it warm for 3 hours. ;
[0032] (5) Filtrate the solution after enzymolysis to obtain a supernatant, and concentrate to obtain an organ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] A method for preparing organic seaweed liquid fertilizer by microbial fermentation and enzymolysis, the specific preparation steps are as follows:
[0035] (1) Fresh kelp and wakame (3:1) are washed with water to remove sand and other impurities;
[0036] (2) Add pure fresh water accounting for 2 times the quality of seaweed to 50 g of mixed seaweed after washing, crush and grind;
[0037] (3) Add the seaweed slurry into the fermentation vessel, add 2.5×10 9 CFU of Bacillus subtilis and 2.5 x 10 9 CFU of Bacillus licheniformis (the ratio of the amount of bacteria is 1:1), stirred evenly, heated to 37°C, and kept for 48 hours of fermentation;
[0038] (4) Add 0.6g of acid protease and pectinase (1:1) to the fermented seaweed slurry, stir evenly, heat to 55°C, and keep warm for 3 hours;
[0039] (5) Filtrate the solution after enzymolysis to obtain a supernatant, and concentrate to obtain an organic seaweed liquid fertilizer.
Embodiment 3
[0041] A method for preparing organic seaweed liquid fertilizer by microbial fermentation and enzymolysis, the specific preparation steps are as follows:
[0042] (1) Wash fresh kelp and Enteromorpha (3:1) raw materials with water to remove sand and other impurities;
[0043] (2) Add pure fresh water accounting for 3 times the quality of seaweed to 50 g of mixed seaweed after washing, crush and grind;
[0044] (3) Add the seaweed slurry to the fermentation vessel, add 4×10 9CFU of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and 4 x 10 9 CFU of Bacillus licheniformis (the ratio of the amount of bacteria is 1:1), stirred evenly, heated to 37°C, and kept for 48 hours of fermentation;
[0045] (4) Add 0.5 g of seaweed quality pectinase and cellulase (3:1) to the fermented seaweed slurry, stir evenly, heat to 55°C, and keep warm for 3 hours;
[0046] (5) Filtrate the solution after enzymolysis to obtain a supernatant, and concentrate to obtain an organic seaweed liquid fertilizer.
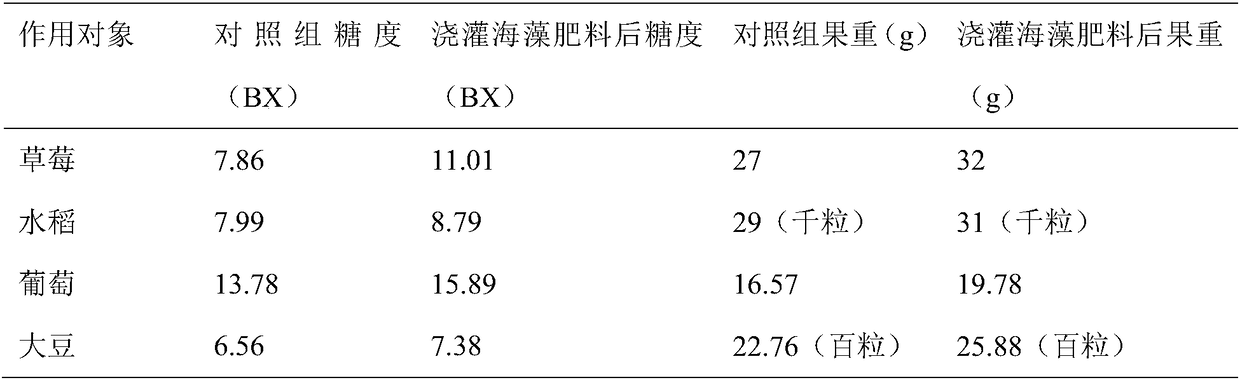
[0047] Acco...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com