Bacillus atrophaeus strain DPPG-28 and application in crop disease control
A technology of DPPG-28 and Bacillus atrophs, applied in the field of agricultural biology, can solve problems such as unsatisfactory effects, achieve good ecological and social benefits, strong adaptability, and improve the effect of plant height at seedling stage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] Example 1 Isolation, purification and screening of disease-preventing and growth-promoting bacterial strains
[0017] (1) Isolation, purification and preservation of rhizosphere microorganisms
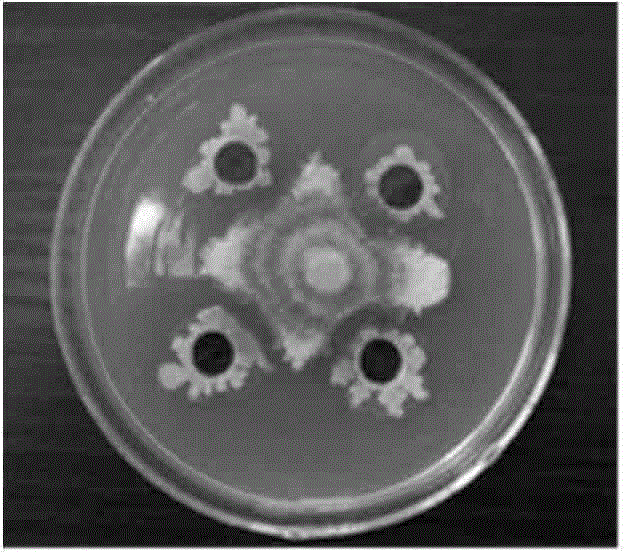
[0018] Weigh 10g of the soil samples collected from the processing tomato production area, add 100ml of sterilized water, then add an appropriate amount of glass beads and shake vigorously for 30min, then let it stand for 10min, take 1ml of the supernatant and add it to a triangle filled with 99ml of sterilized water. bottle, serially diluted to 10 -6 concentration. Add 200 μl of each of the above dilutions to PDA, NA, and Gao’s No. 1 medium plates, spread evenly with a spreader, and after cooling, place them upside down in an incubator at 28°C for cultivation, and repeat twice. After 3-7 days, single colonies of different shapes were picked from each dish and purified on the slant of the test tube for testing. Strains were preserved with distilled water preservation method. ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Identification characteristics of embodiment 2 DPPG-28 bacterial strain
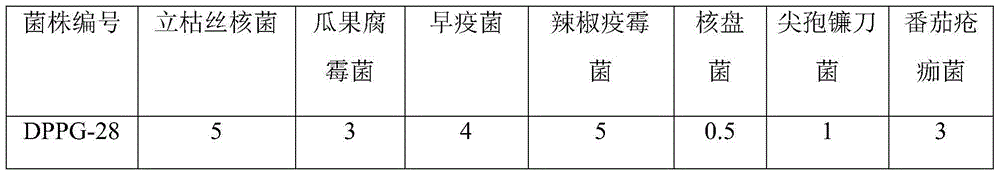
[0035] According to the morphological characteristics of the bacteria, the morphological characteristics of the colony and the results of Gram staining, combined with the eighth edition of Bergey's Manual of Etermitive Bacteriology and the "Manual of Common Bacteria Identification", the physiological and biochemical characteristics of the strain DPPG-28 were analyzed. identification. The results are shown in Table 3. After preliminary identification, the strain DPPG-28 belonged to the genus Bacillus.
[0036] Table 3 Physiological and biochemical characteristics of strain DPPG-28
[0037]
[0038] Note: 10: The reaction is positive or can be grown and utilized; 1: The reaction is negative or cannot be grown and utilized.
[0039] 16S rDNA Identification of Strain DPPG-28
[0040] The 16S rDNA of strain DPPG-28 was sequenced, and the size of the 16S rDNA sequence fragment of DPPG-28 obtained ...
Embodiment 3
[0041] The preparation of embodiment 3 Bacillus atrophaeusDPPG-28 biocontrol agent
[0042] (1) Preparation of seed solution
[0043] After the bacterial strain DPPG-28 obtained in Example 1 was inoculated on NA medium for activation, it was transferred to a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 100mL NA medium, and cultivated at 30°C and 200rpm for 24 hours to obtain a seed solution.
[0044] (2) Preparation of bacterial agent
[0045] Prepare medium, beef extract 5.0g, peptone 10.0g, yeast powder 5.0g, NaCl 5.0g, glucose 10.0g, distilled water 1000mL, sterilize at 121℃ for 20min. The seed solution was inoculated in the fermentation medium at a ratio of 1:100, and cultured at 30°C and 200rpm for 48h. The concentration of viable bacteria in the fermentation broth was 10 8 -10 11 cfu / mL.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com