Preparation method of microorganism immobilization particles for removing residual pesticide in soil
A technology of immobilization of microorganisms and residual pesticides, applied in the field of agricultural biology, can solve the problems of less research on the degradation of organic phosphorus pesticides in pesticide production wastewater, and achieve the effects of good ventilation, low cost and low price
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] A preparation method for removing microbial particles of pesticide residues in soil, according to the following steps:
[0038] (1) Crush the zeolite into particles with a particle size of 60 mesh, dry the corncobs at constant temperature to a constant weight, and then crush them into particles with a particle size of 40 mesh. The core is mixed at a ratio of 1:5 and used as a carrier, dried for later use;
[0039] (2) Fully mix the volume of the Clostridium strain with the weight of the carrier according to the ml:g ratio of 1:0.1, and use glutaraldehyde with a concentration of 0.5% as the cross-linking agent to stir evenly. The volume ratio of the cross-linking agent is 3:7, stir evenly, place at 4°C for 2 hours for cross-linking, prepare immobilized particles with a particle size of 2.5 mm after cross-linking, wash and dry with distilled water, that is, the described Microbial particles.
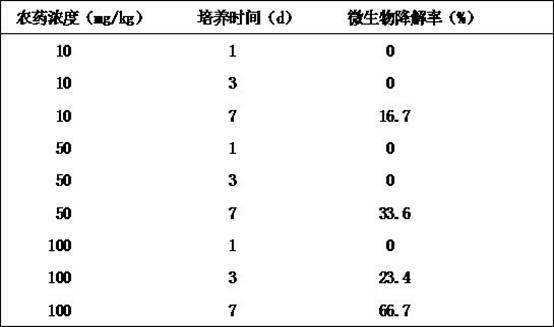
[0040] The composite immobilized microorganisms carried out the soil remediat...
Embodiment 2
[0042] A preparation method for removing microbial particles of pesticide residues in soil, according to the following steps:
[0043] (1) Crush zeolite into particles with a particle size of 60 mesh, dry corncobs at constant temperature to constant weight, and then crush them into particles with a particle size of 80 mesh. The core is 1:1 mixed and used as a carrier, dried for later use;
[0044] (2) Fully mix the volume of the Clostridium strain with the weight of the carrier at a ratio of 1:0.5 in ml:g, and stir evenly with 0.5% glutaraldehyde as the cross-linking agent. The volume ratio of the cross-linking agent is 1:5, stir evenly, place at 4°C for 6 hours for cross-linking, prepare immobilized particles with a particle size of 5.0mm after cross-linking, wash and dry with distilled water, and then make the described Microbial particles.
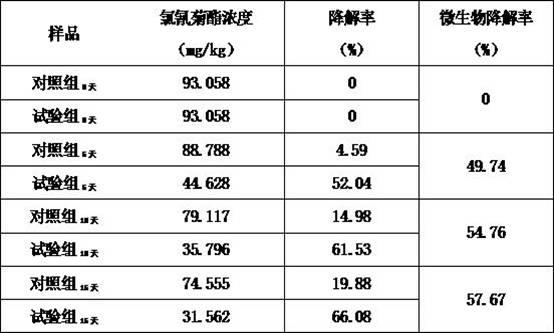
[0045] The composite immobilized microorganisms carried out soil remediation experiments on methyl parathion. The microbial particle...
Embodiment 1 Embodiment 2 and comparative example 1
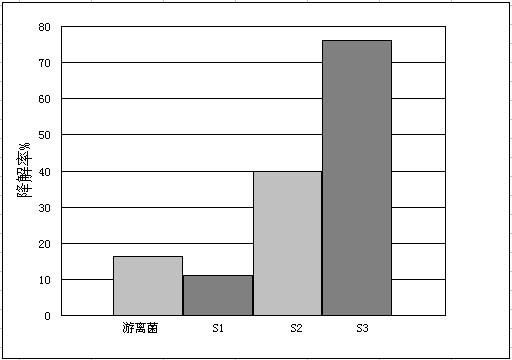
[0049] Example 1, Implementation 2 and Comparative Example 1, the volumes of the bacterial liquid of Clostridium strains were large-diameter corncobs (40 mesh, S2), small-particle-diameter corncobs (80 mesh, S3) and sodium alginate (40 mesh , S1) The effect of different immobilized carriers on the degradation of methyl parathion by Clostridium strain A3 as shown in figure 1 shown. In soil remediation, the degradation effect of bacteria S1 immobilized with sodium alginate was lower than that of bacteria S2 immobilized with large-sized corncobs, while the degradation effect of bacteria S2 immobilized with large-sized corncobs was less than that of bacteria immobilized with small-sized corncobs. Degradation effect of bacteria S3. And as far as the carrier is concerned, the corn cob is non-toxic and harmless to the bacteria and soil, and can be used as a C source in the soil environment, while the sodium alginate carrier is a toxic substance to the soil.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com