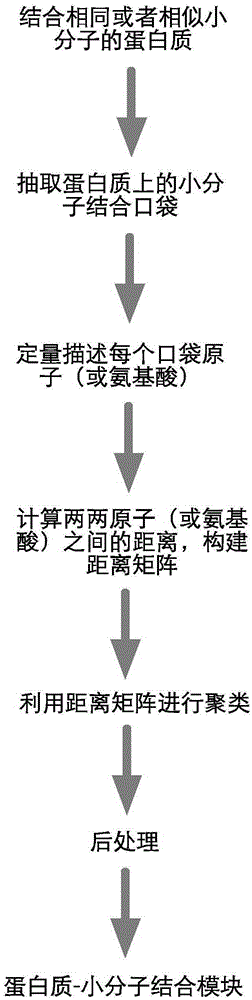
Method for extracting protein-micromolecule interaction module
A technology for small molecules and proteins, applied in the field of protein research, it can solve the problems of general alignment effect and inability to find protein-small molecule interaction modules.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
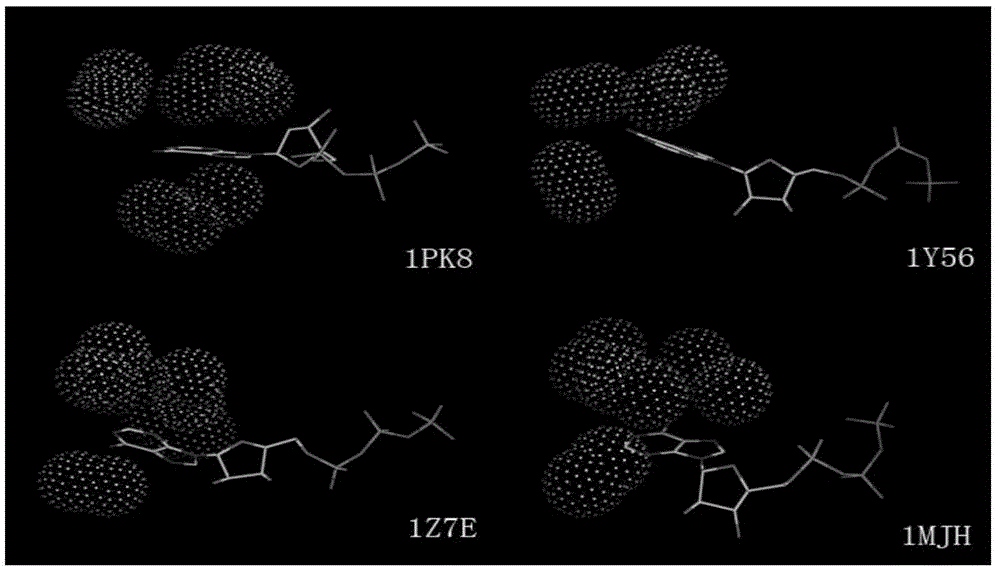
[0063] Example 1: Extraction of interaction modules bound to small molecule ATP and analysis of their biological significance.
[0064] 1.1 Background introduction
[0065] Adenosine triphosphate (referred to as ATP) is an unstable high-energy compound consisting of 1 molecule of adenine, 1 molecule of ribose and 3 molecules of phosphoric acid. Also known as adenosine triphosphate, referred to as ATP. Because ATP can release a large amount of energy when it is hydrolyzed, it is the most direct energy source in the organism. ATP participates in most metabolic processes in the organism and is one of the most important small molecules. Many related studies have shown that proteins of different protein families have conserved binding modules in the ATP-binding pocket. Extracting and analyzing these conserved modules will provide important guidance for understanding the ATP binding mechanism and drug design for ATP-related metabolic diseases significance.
[0066] 1.2 Data proce...
Embodiment 2
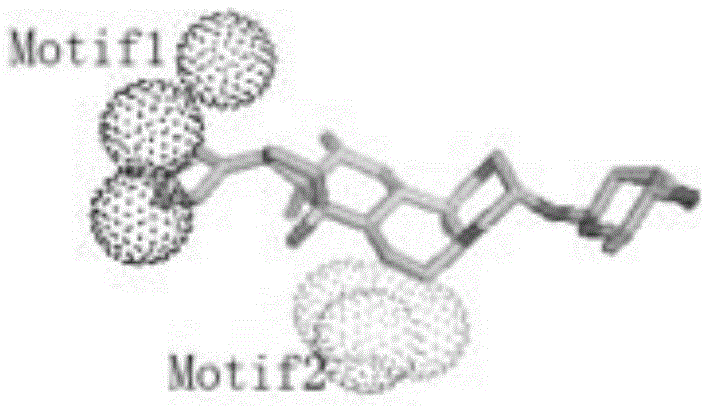
[0071] Example 2: Extraction of interaction modules combined with small molecule DIG and its application in protein design.
[0072] 2.1 Background introduction
[0073] With the rapid development of protein science, the scientific community has a deeper understanding of proteins, and protein design has become an important topic in biology, especially in synthetic biology. One of the most authoritative research teams in this field, David Baker's laboratory at the University of Washington, published a landmark work in the top international academic journal Nature in 2013, that is, the DIG (Chinese name Digaoxin) was obtained through artificial design. , a drug small molecule for the treatment of heart disease) is an artificial protein with high binding activity, showing the unlimited potential of artificially designing various small molecule binding proteins (C.E. :10.1038 / nature12443). In the process of protein design, how to determine the binding pocket or active center of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com