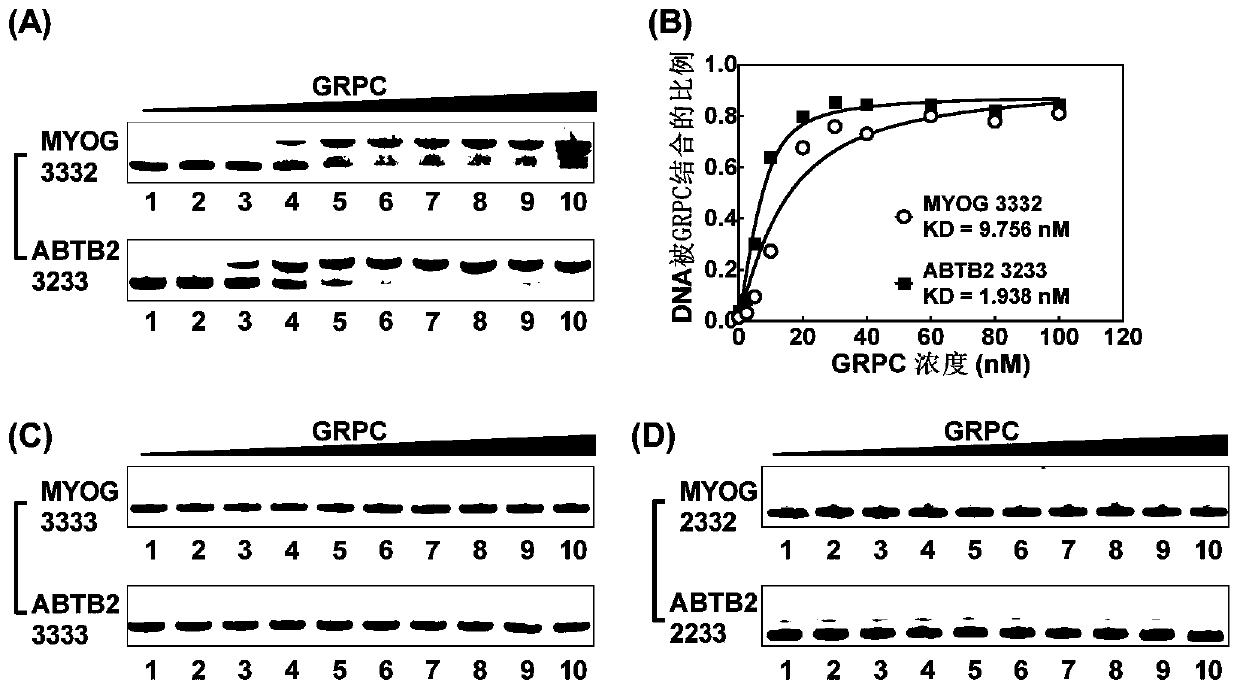
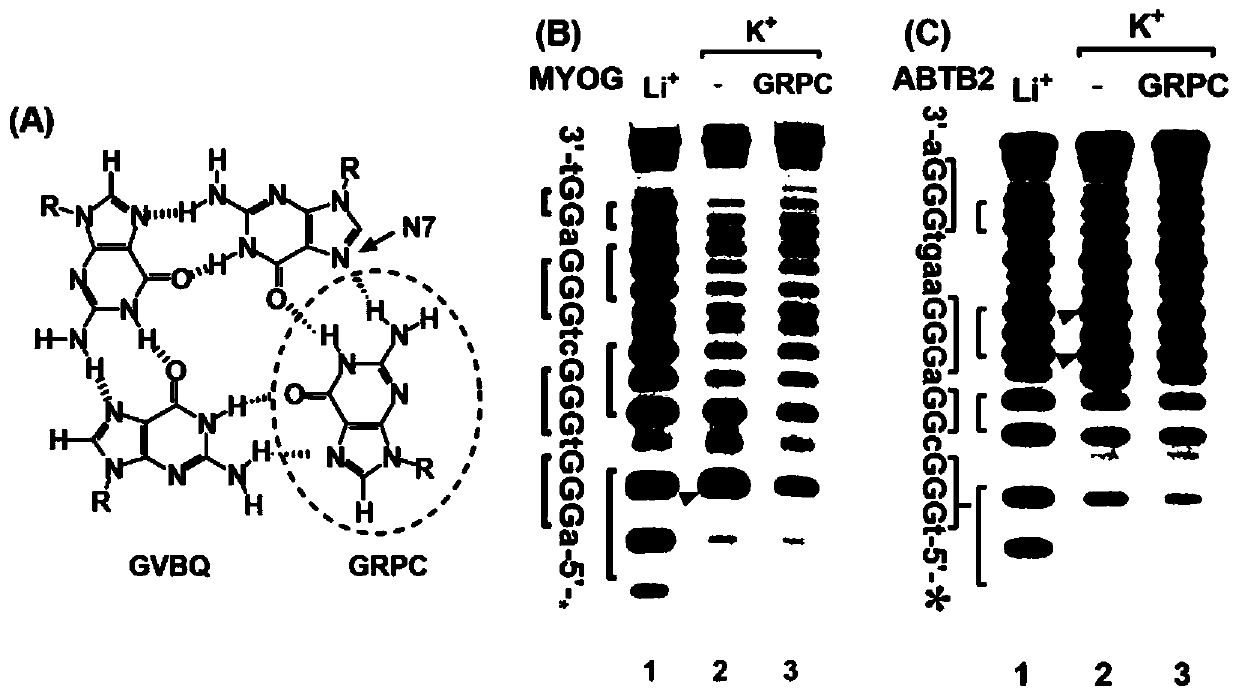
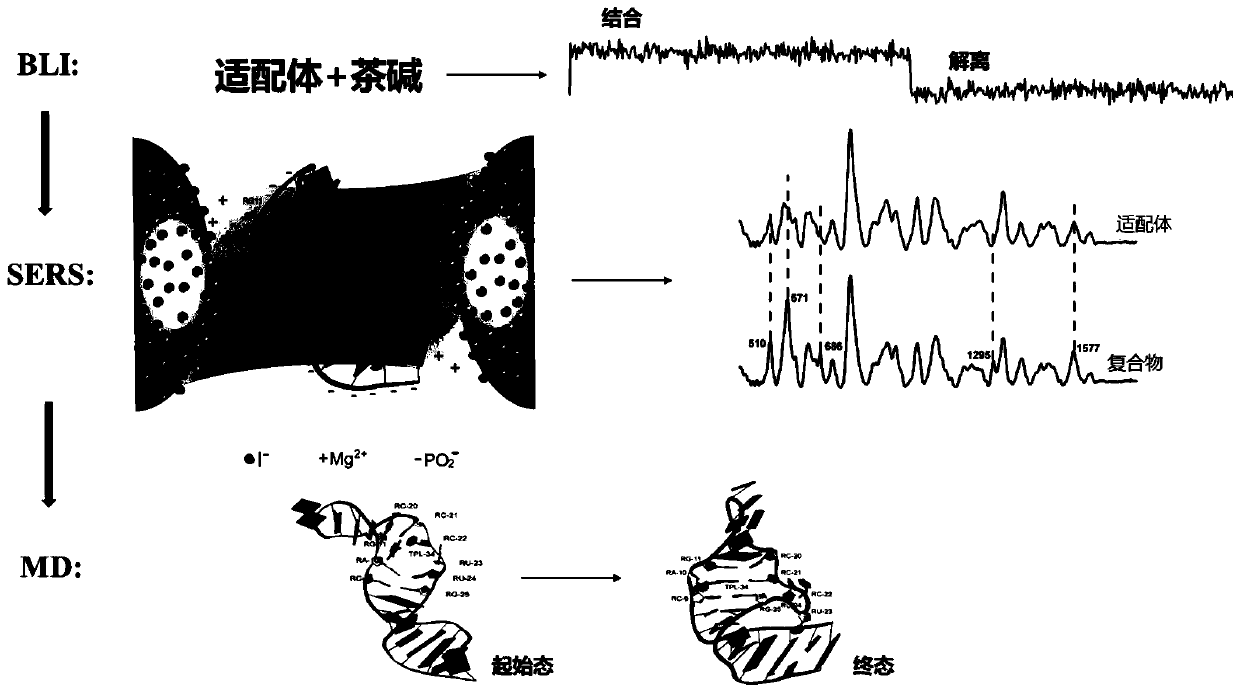
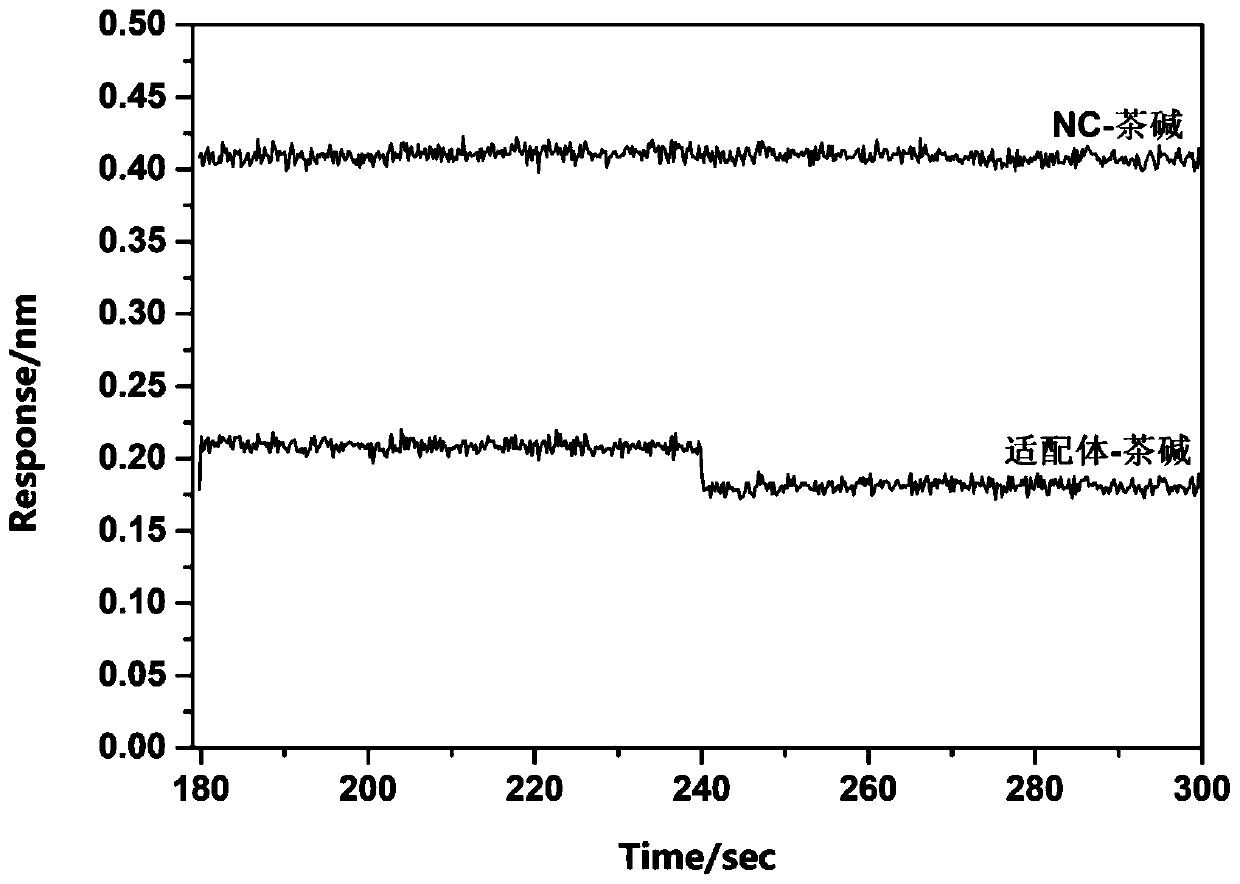
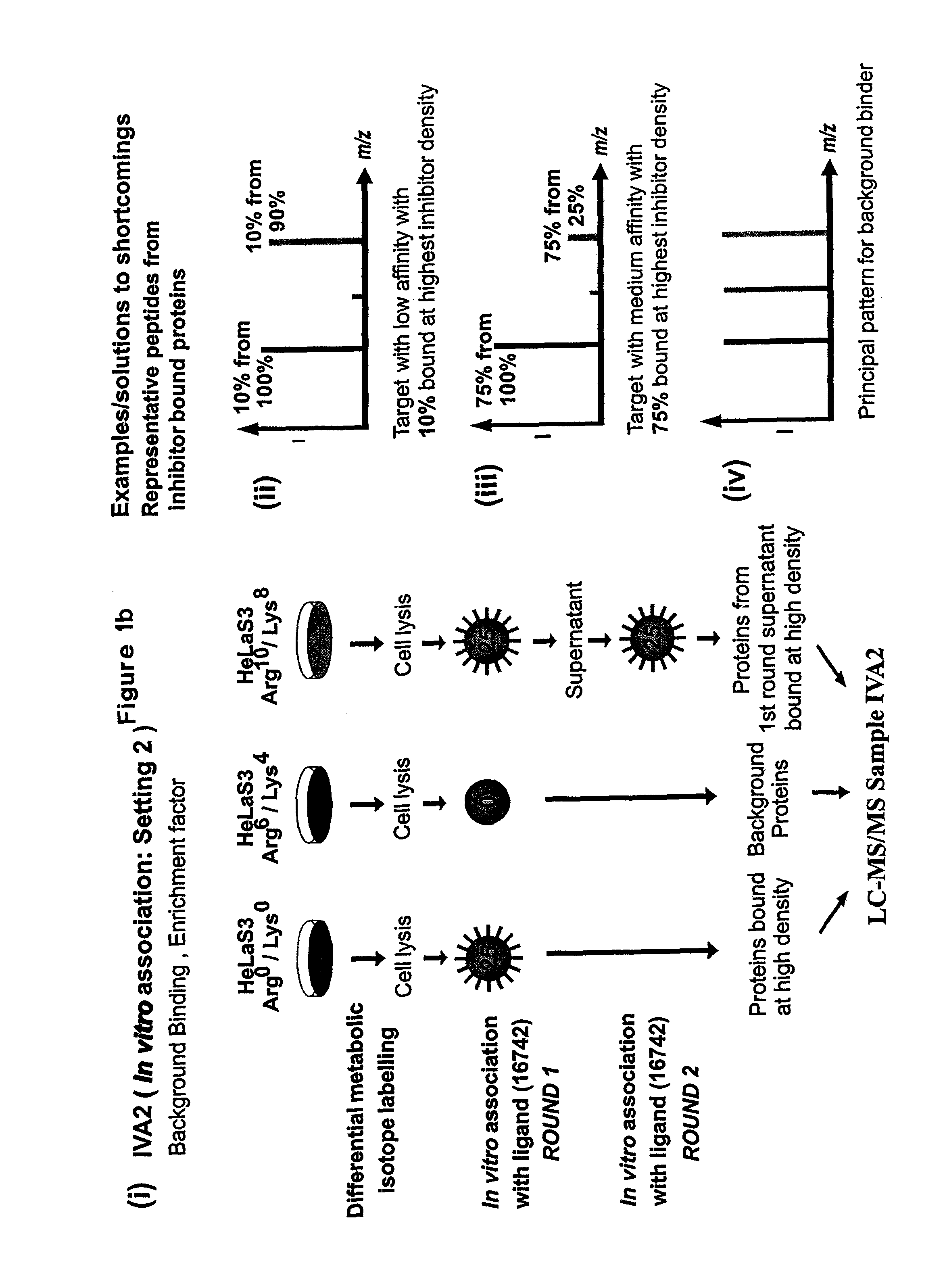
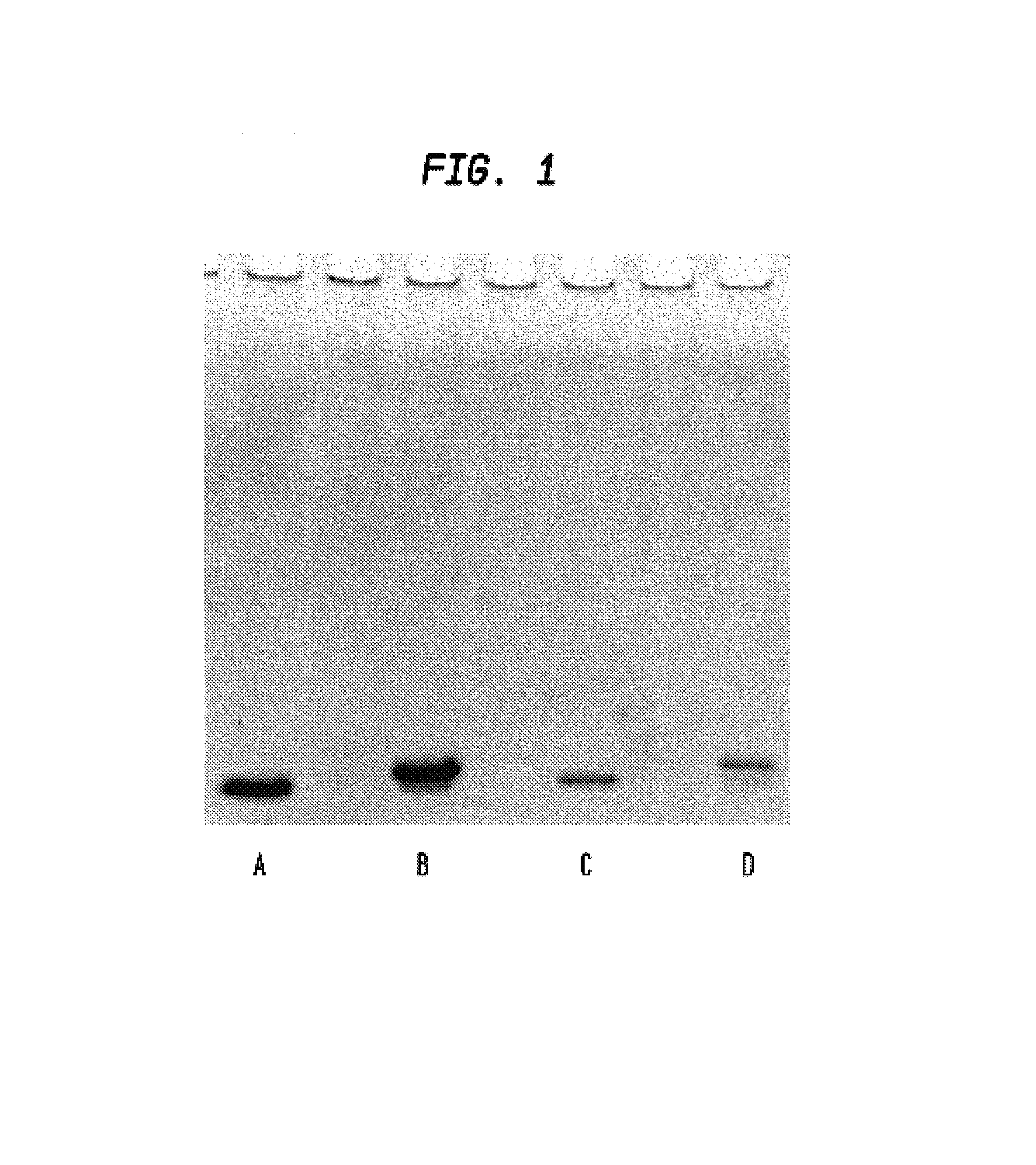
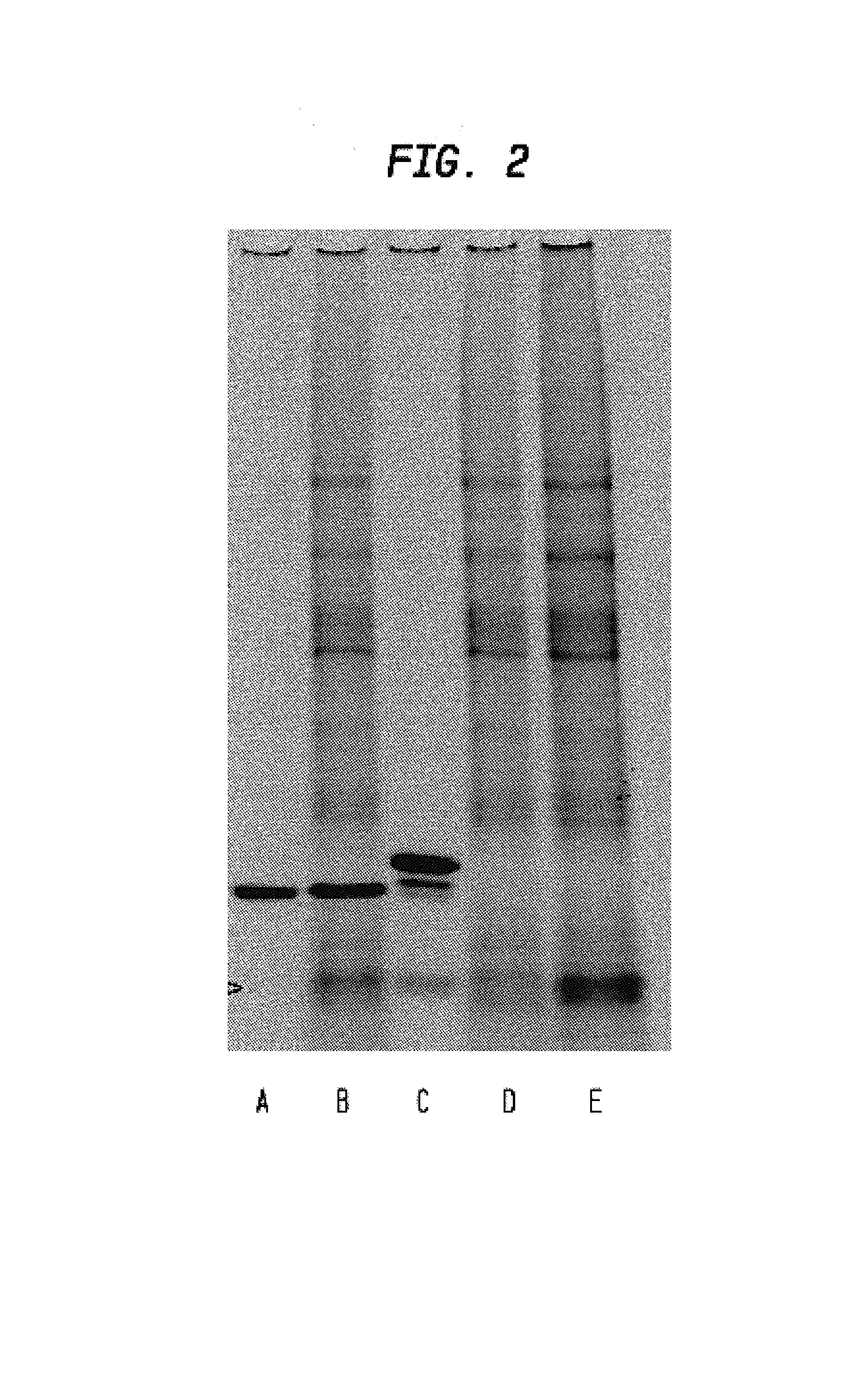
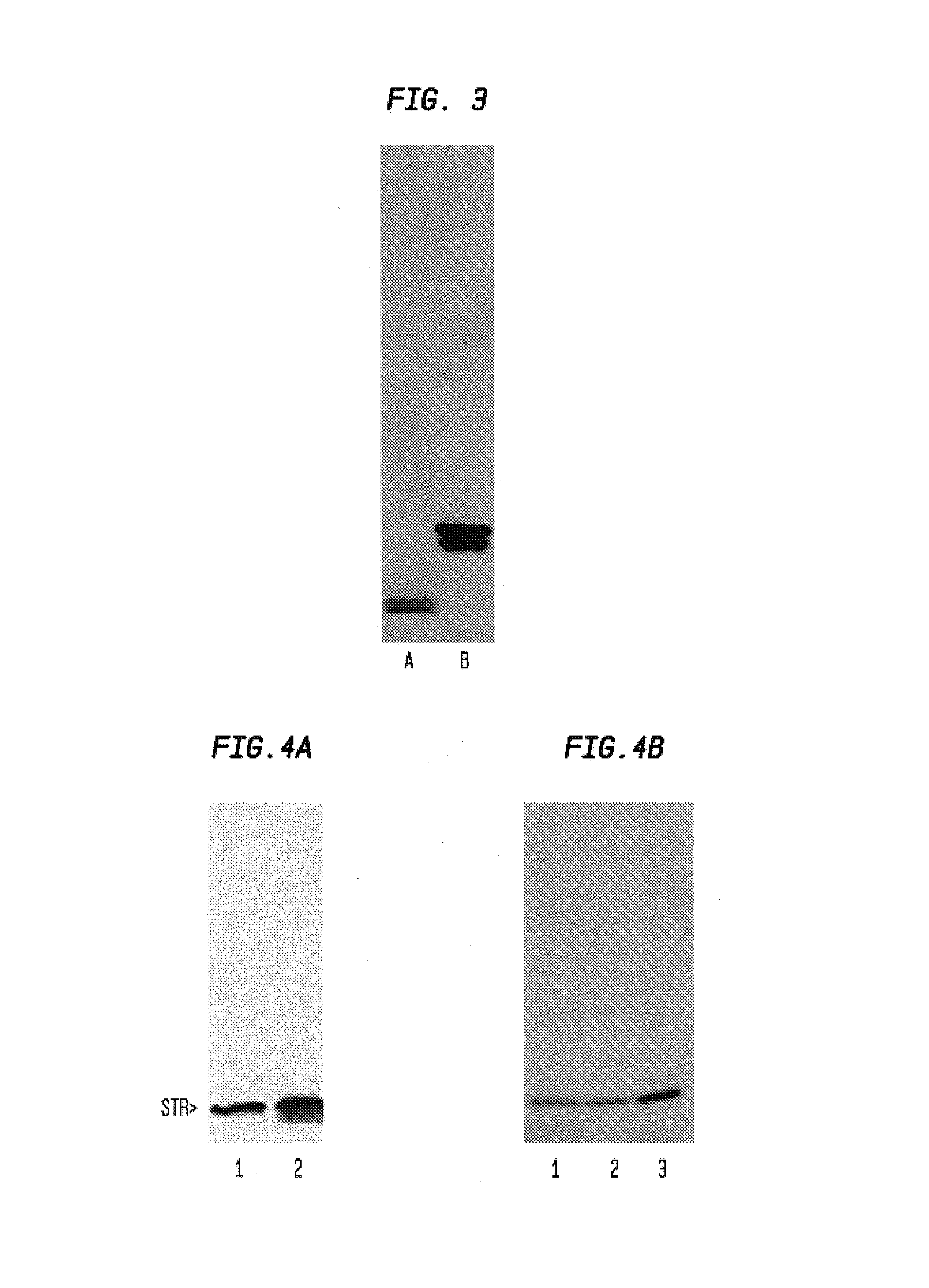
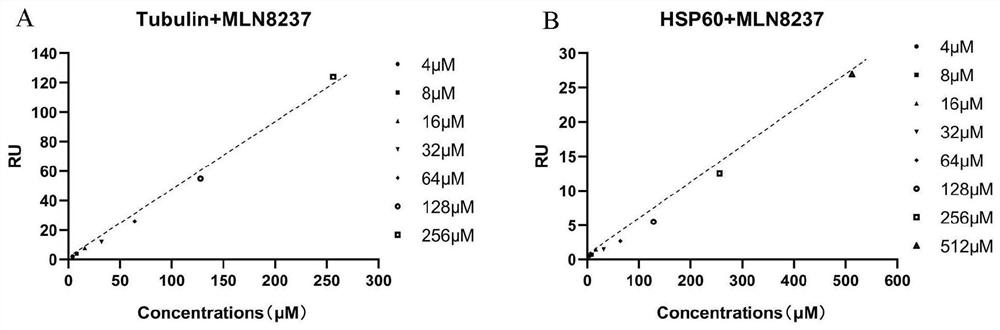
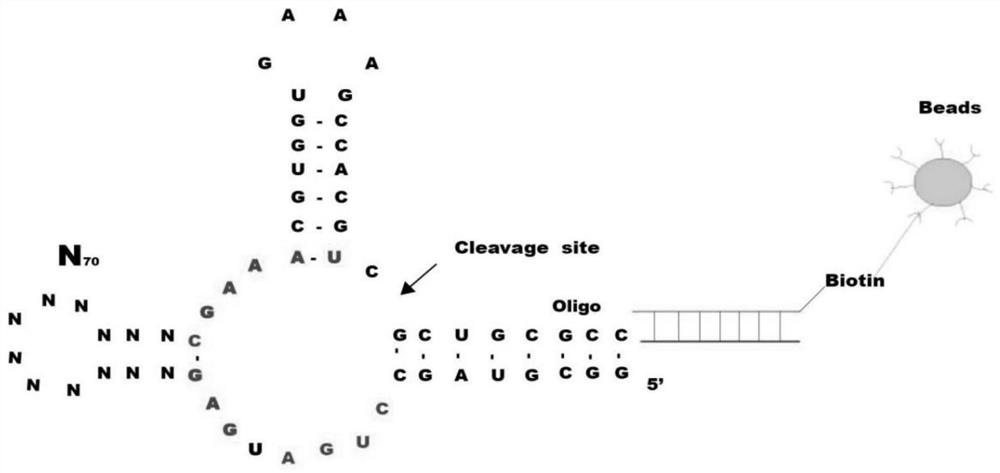
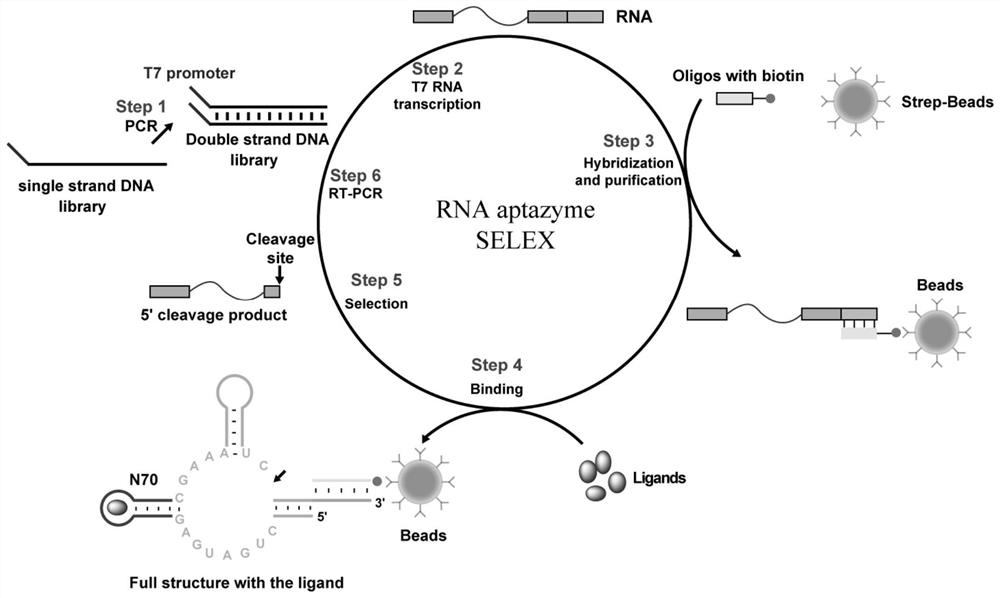
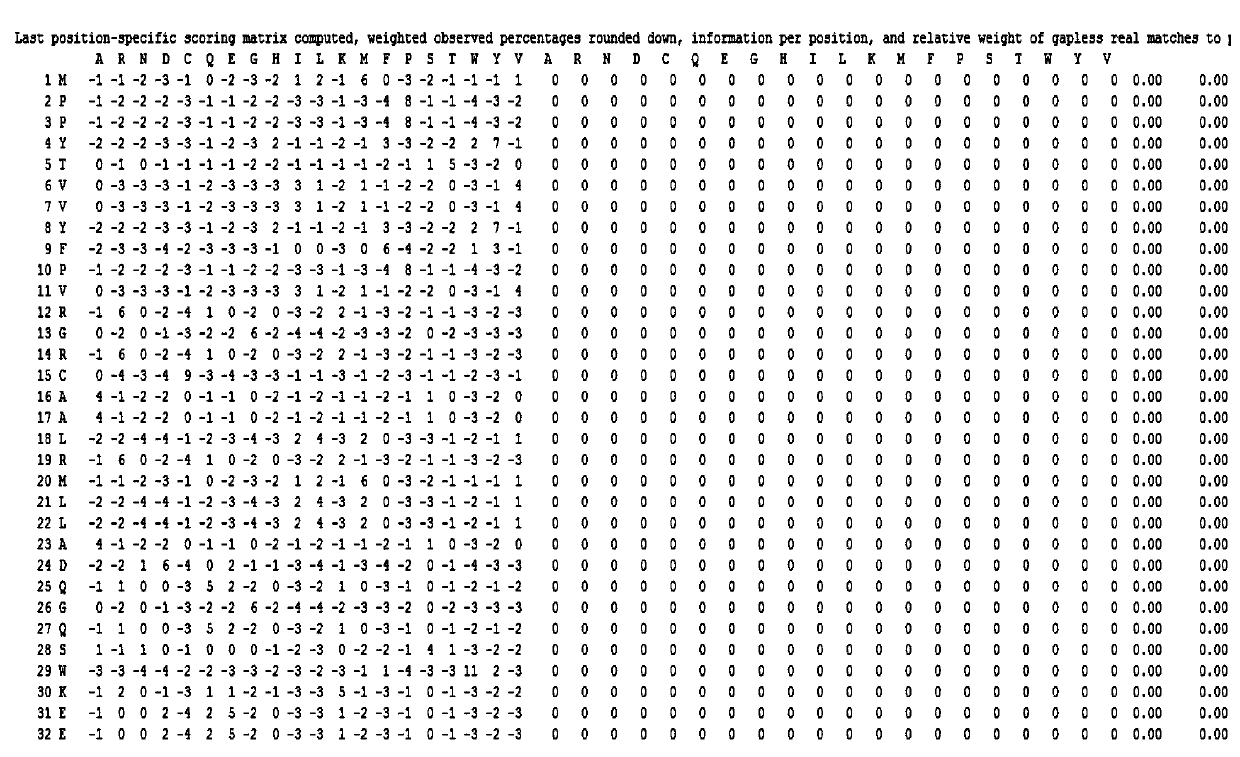
Patents
Literature
57 results about "Small molecule binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with a small molecule, any low molecular weight, monomeric, non-encoded molecule. [GOC:curators, GOC:pde, GOC:pm]
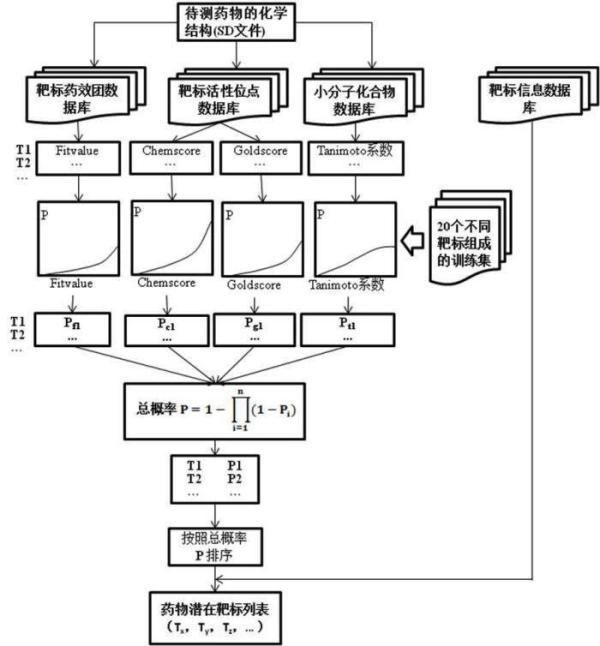
Construction and prediction method of integrated drug target prediction system
InactiveCN102663214AOvercoming the problem of low forecasting accuracySpecial data processing applicationsPharmacophoreEngineering
The invention discloses a construction and prediction method of an integrated drug target prediction system. The method comprises the following steps of: analyzing a protein crystal structure database; selecting the protein bound with the drug-like ligand small molecule or the protein with the small molecule ligand binding potential as a target point, and building a crystal structure database of targets; for these targets, collecting the information of the targets related to diseases, the biology type and the active small molecule ligand information, and integrating a comprehensive target screening database composed of an active site database, a pharmacophore database, a small molecular compound database and a target basic information database. Based on the comprehensive target screening database, the construction of the integrated drug target prediction system is realized through a script program or a PipelinePilot flow, and the probability of target prediction accuracy of the method is provided. The method provided by the invention exerts the three above technical advantages to provide the probability of target prediction, thereby providing effective basis for further experimental verification.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
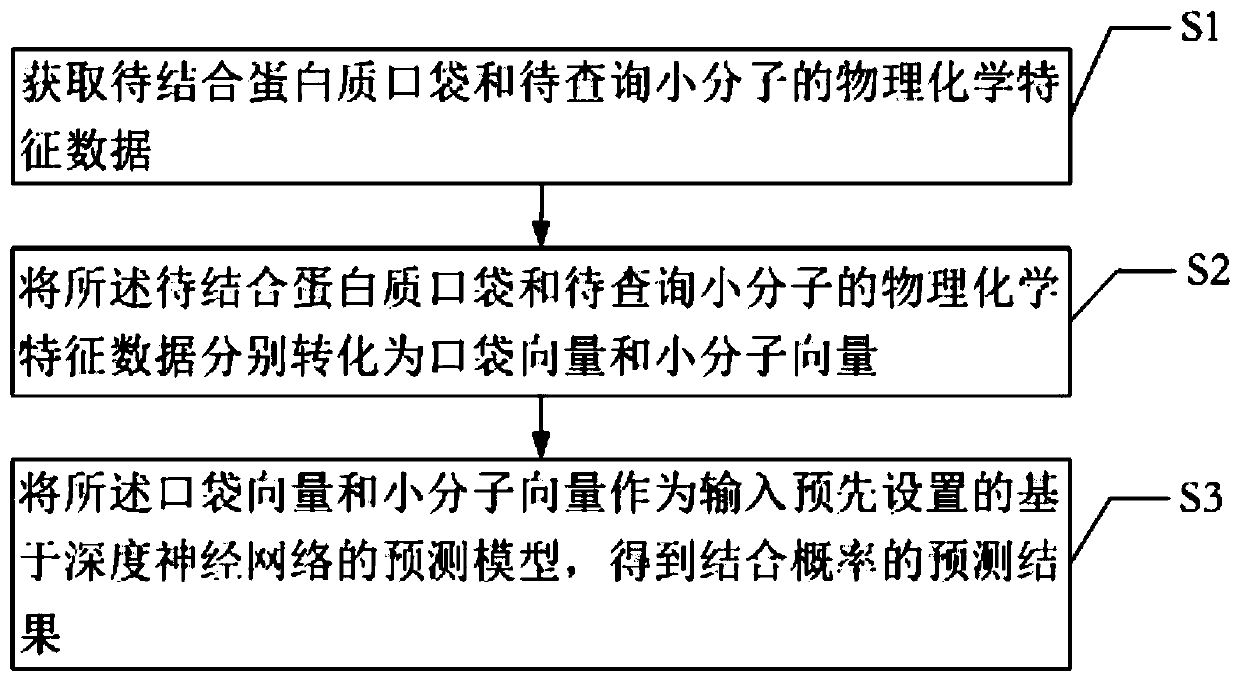
Target protein and micromolecule binding prediction method and system
PendingCN109887541AGood removal effectReduce noiseBiostatisticsProteomicsSystems designProtein target
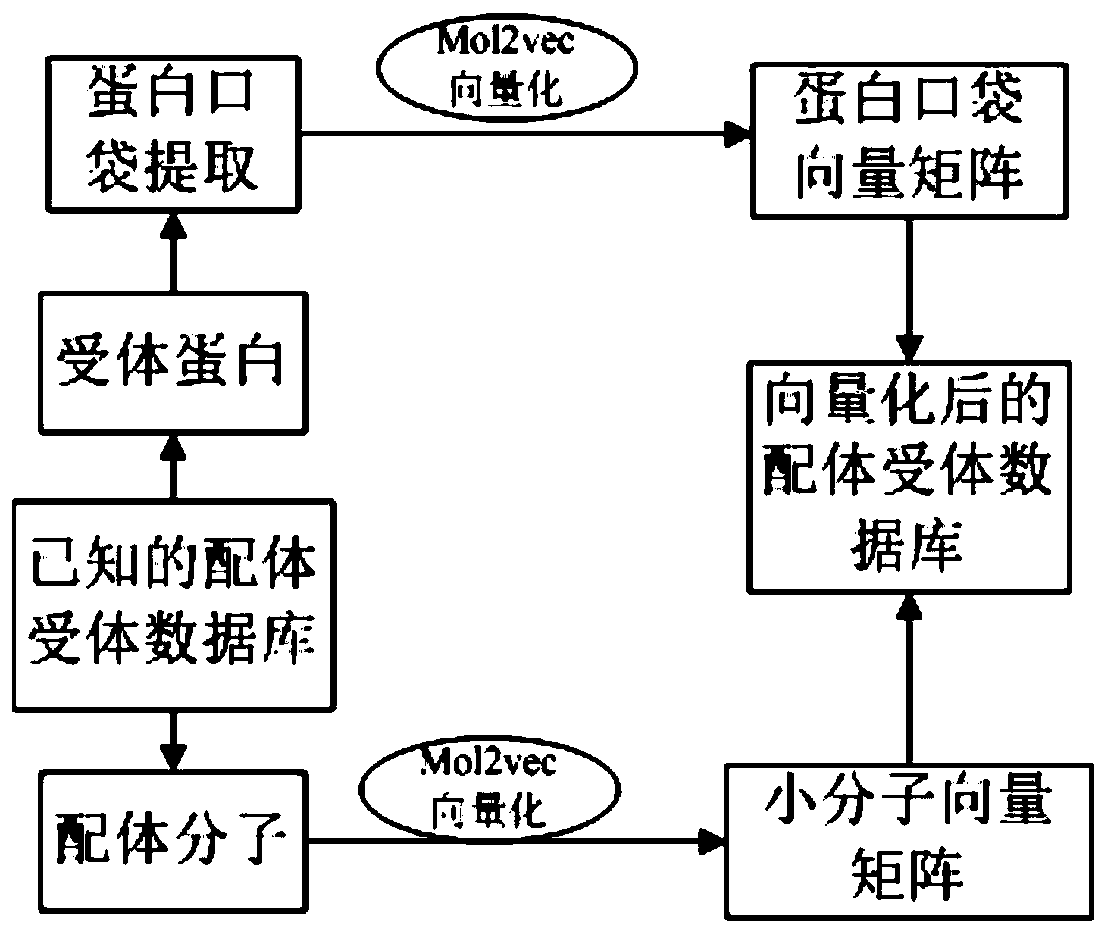
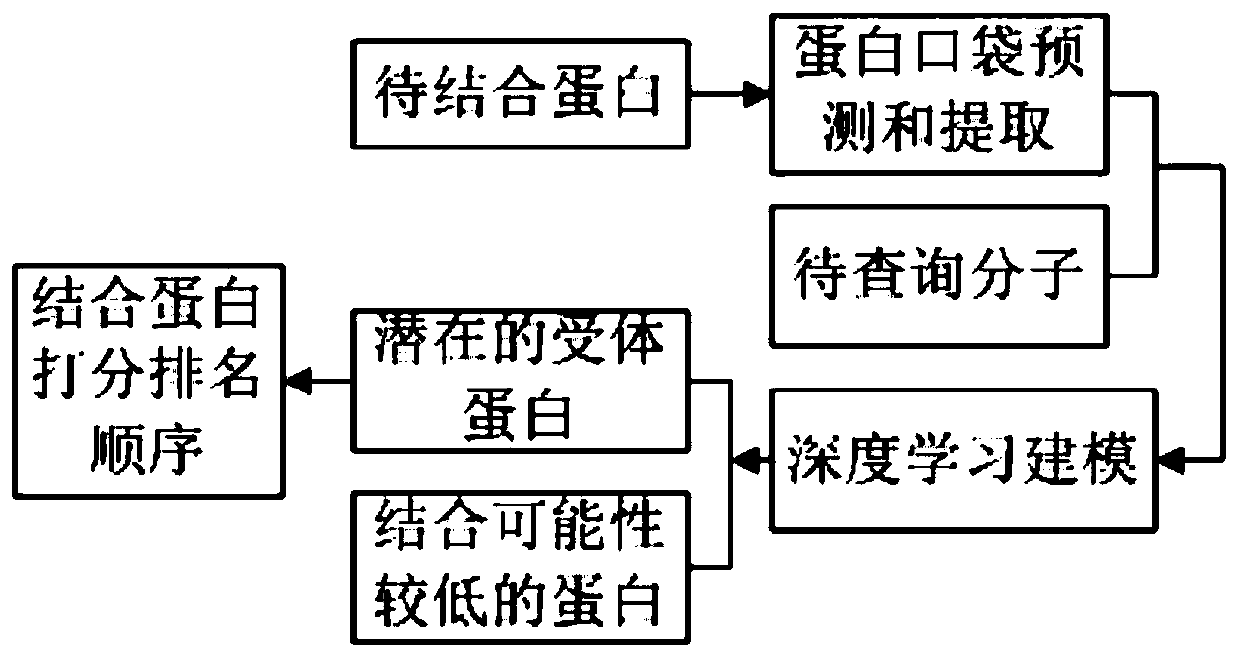
The invention provides a target protein and micromolecule binding prediction method and system. The target protein and micromolecule binding prediction method includes the steps: obtaining physicochemical characteristic data of a protein pocket to be bound and a small molecule to be queried; converting the physicochemical characteristic data of the protein pocket to be bound and the small moleculeto be queried into a pocket vector and a small molecule vector; and respectively inputting the pocket vector and the small molecule vector into a pre-set prediction model based on a deep neural network to obtain a prediction result of the binding probability. The target protein and micromolecule binding prediction method and system extract the active pocket part directly related to the interaction to represent protein, thus being beneficial to removing of non-related information and reduction of noise so as to improve accuracy. In addition, the target protein and micromolecule binding prediction method and system design a neural full-connected layer network model suitable for a learning vector to more easily retain more complete information, and can maintain the key information of the function of the small molecules of the protein by the vector while not depending on the protein small molecule complex conformation for laying the foundation for accurate prediction at high speed.
Owner:张海平 +4
Protein degradation target compound, antitumor applications and intermediates thereof, and applications of intermediates
ActiveCN110357889AOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsProtein targetProtein degradation
The present invention relates to a compound represented by a formula (I), antitumor applications and intermediates thereof, and applications of the intermediates, wherein the intermediates are compounds represented by a formula (III) and a formula (IV), the compound represented by the formula (I) has degradation effects on specific target proteins, and mainly comprises three parts, the first partis small molecules binding protein (SMBP), the second part is a link unit (Linker), the third part ubiquitin ligase binding moiety (ULM) is a ligand with ubiquitination function, SMBP and LIN are covalently bound, and LIN is covalently bound to ULM. According to the present invention, a series of the designed and synthesized compounds of the present disclosure have wide pharmacological activities,have function of degradation of specific proteins and / or inhibition of activities, and can be used for related tumor treatment.
Owner:SHANGHAI TECH UNIV
Micro-molecule indirectly labeled dual-antigen sandwich method for determining hepatitis C virus total antibody
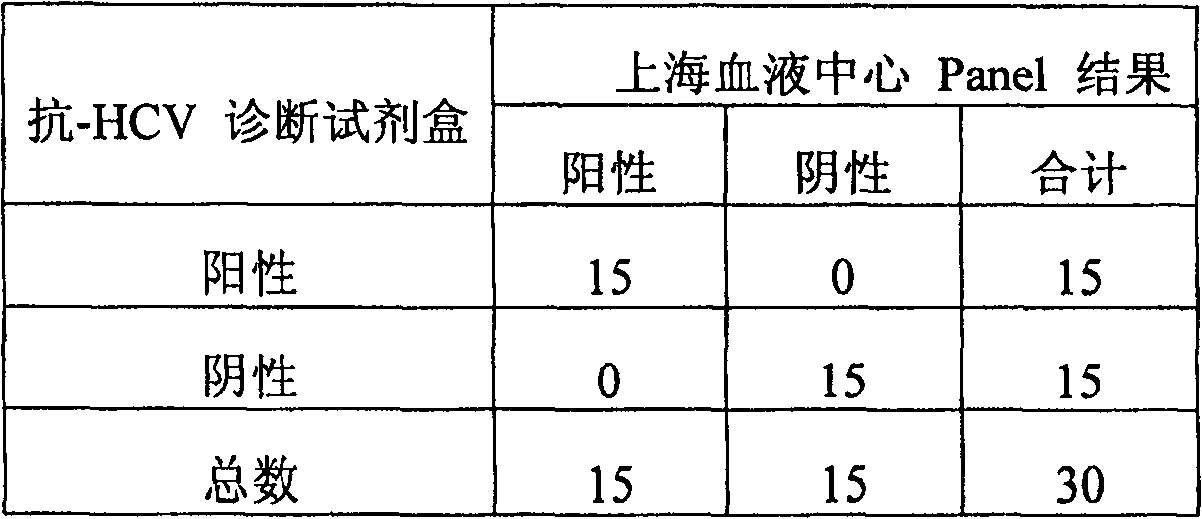
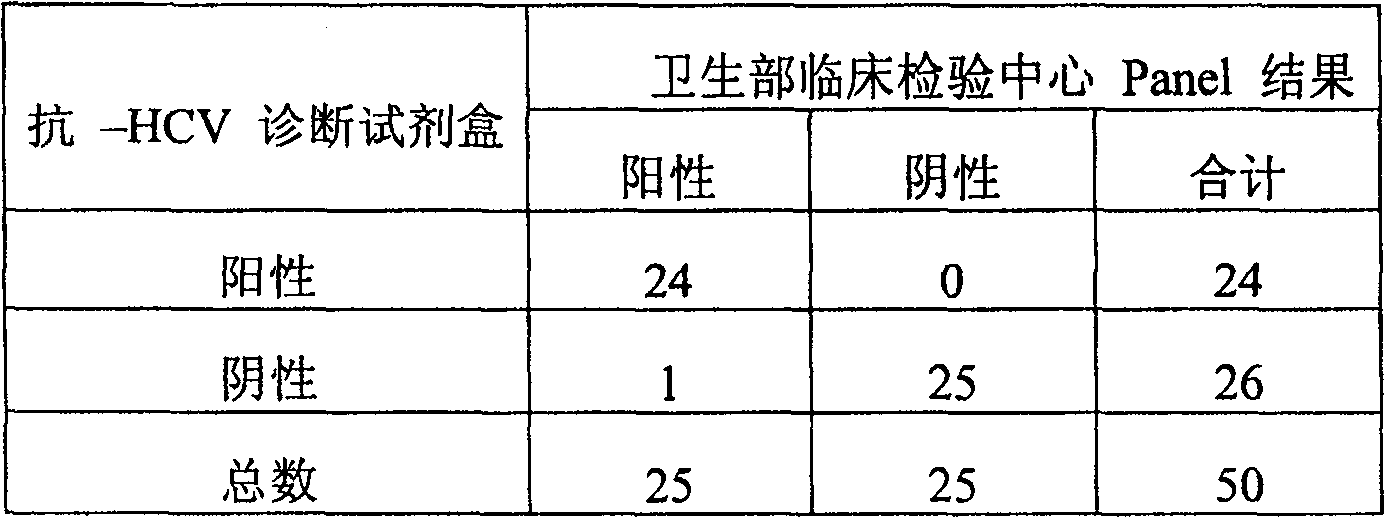
The invention relates to a method for testing the total antibody of hepatitis C virus (HCV), based on dual-antibody interlayer method of small-molecule indirect mark, wherein said method is characterized in that: it uses small molecule matter as mark; uses dual-antigen interlayer method to test the total antibody of sample; and said method comprises: using small molecule material to mark HCV antigen; using HCV antigen to pack solid material; using single generate material to mark small molecule antibody or other material that combined with small molecule; the HCV antibody of sample can be reacted with HCV antigen of solid material surface and small molecule mark, to form dual-antigen interlayer composite; then reacting the small molecule with single report molecule, to make the composite with detected signal generate material. The invention can keep activity of antigen, with signal amplifying function and better specificity of dual-antigen interlayer mode, while it can detect variable kinds of antibodies, to improve the detecting sensitivity and specificity.
Owner:SUZHOU SYM BIO LIFESCI CO LTD
Small molecule binding pockets in nucleic acids
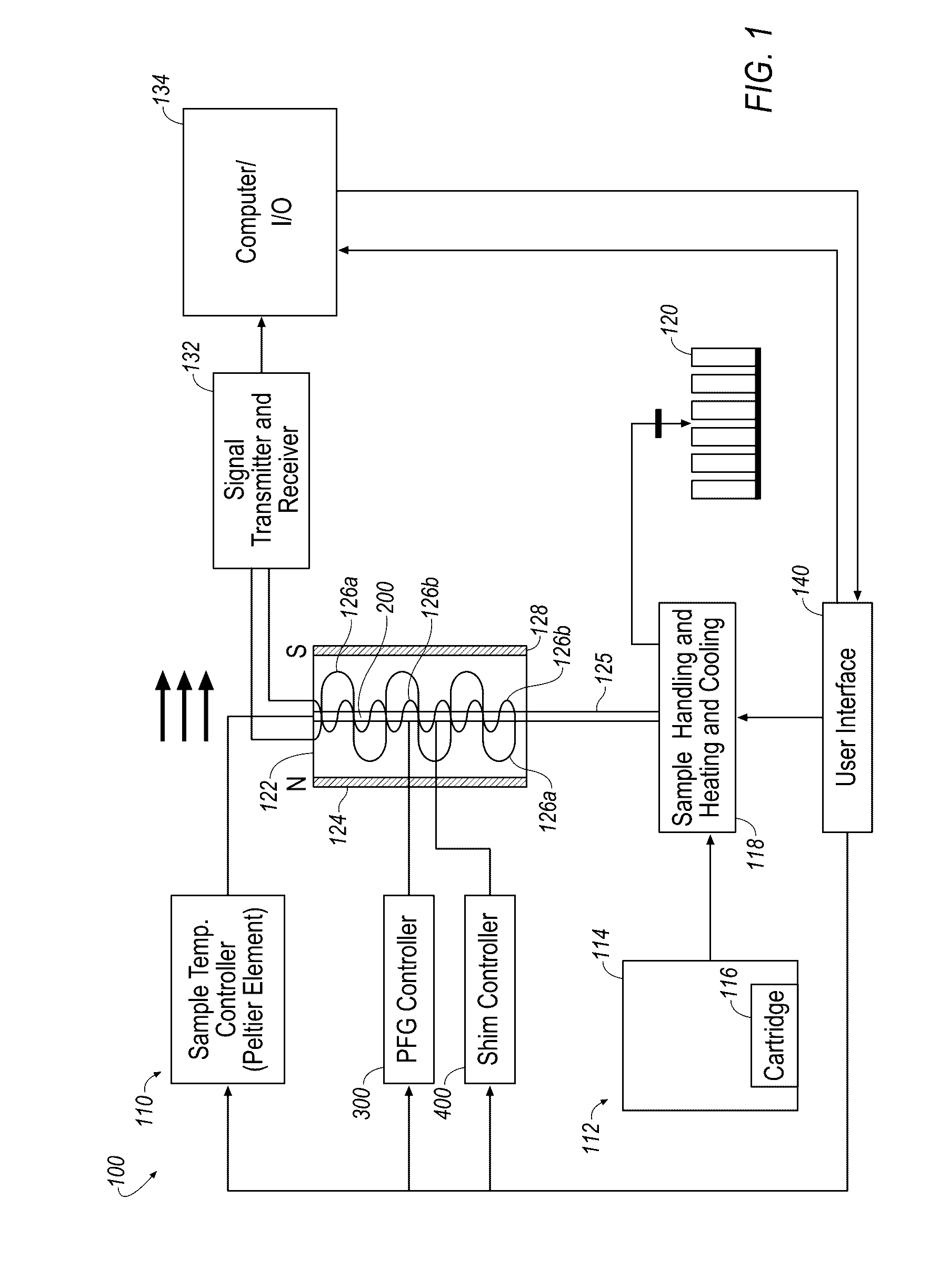
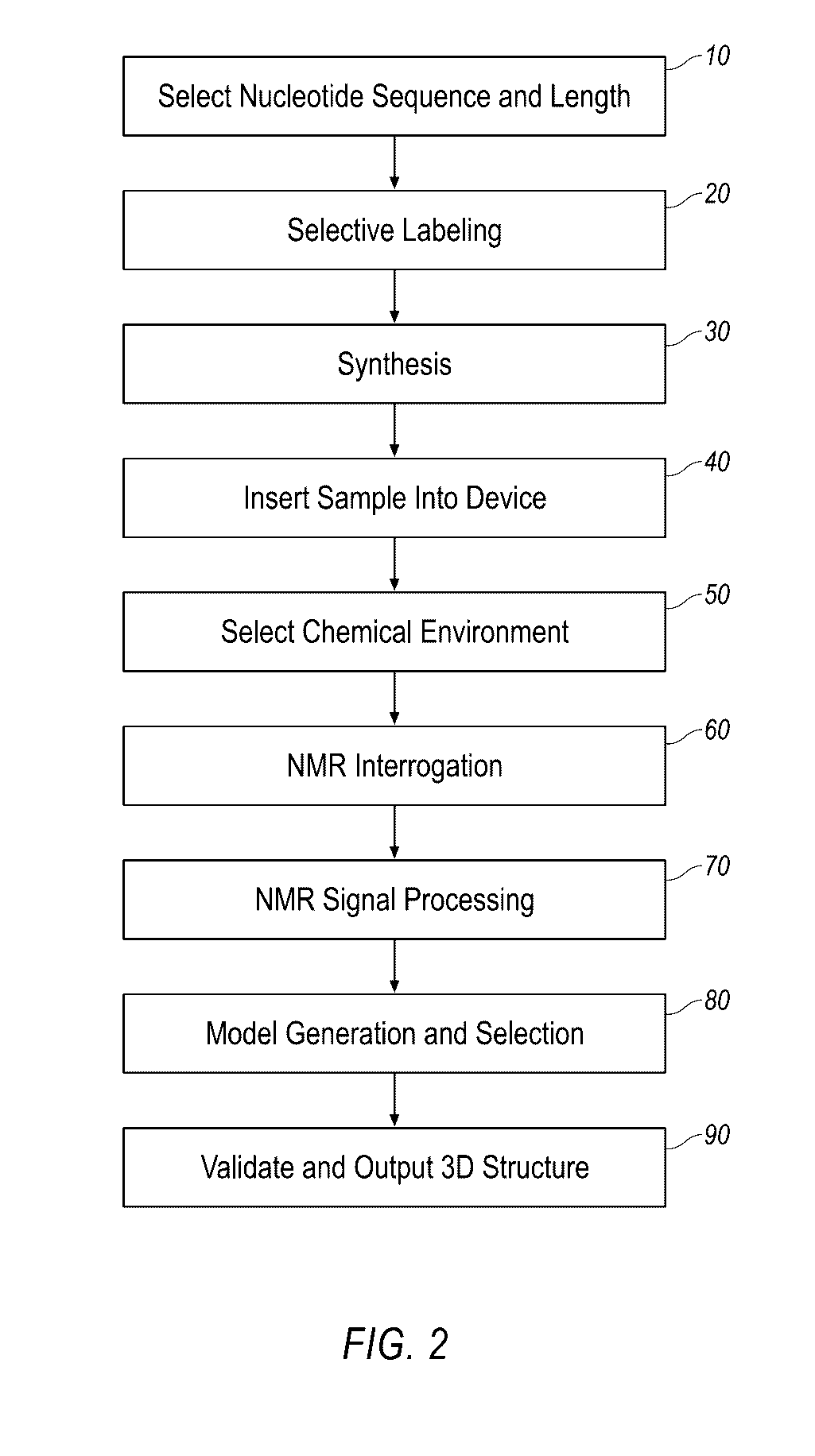
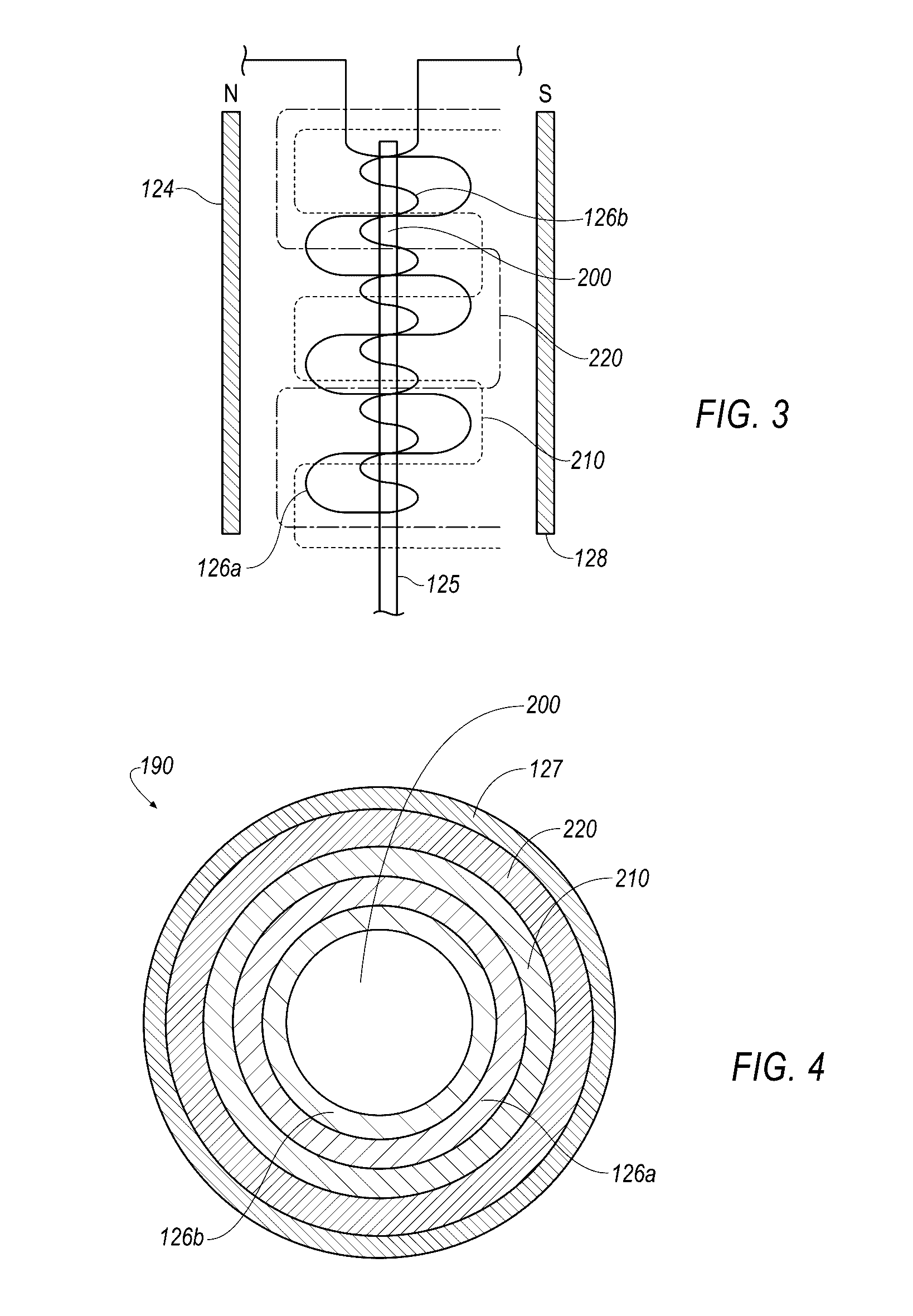
Described herein is technology for determining the 2-D or 3-D atomic resolution structure of a polynucleotide bound to and / or interacting with another molecule, for example a small molecule. In some aspects of the technology, NMR and isotopic labeling strategies are used. The technology described herein is useful for a plurality of applications including but not limited to drug discovery and chemical biology probe discovery.
Owner:NYMIRUM
Determination of Proteins and/or Other Molecules Using Mass Spectroscopy
InactiveUS20070249060A1Material nanotechnologyParticle separator tubesSelf-assembled monolayerSpectroscopy
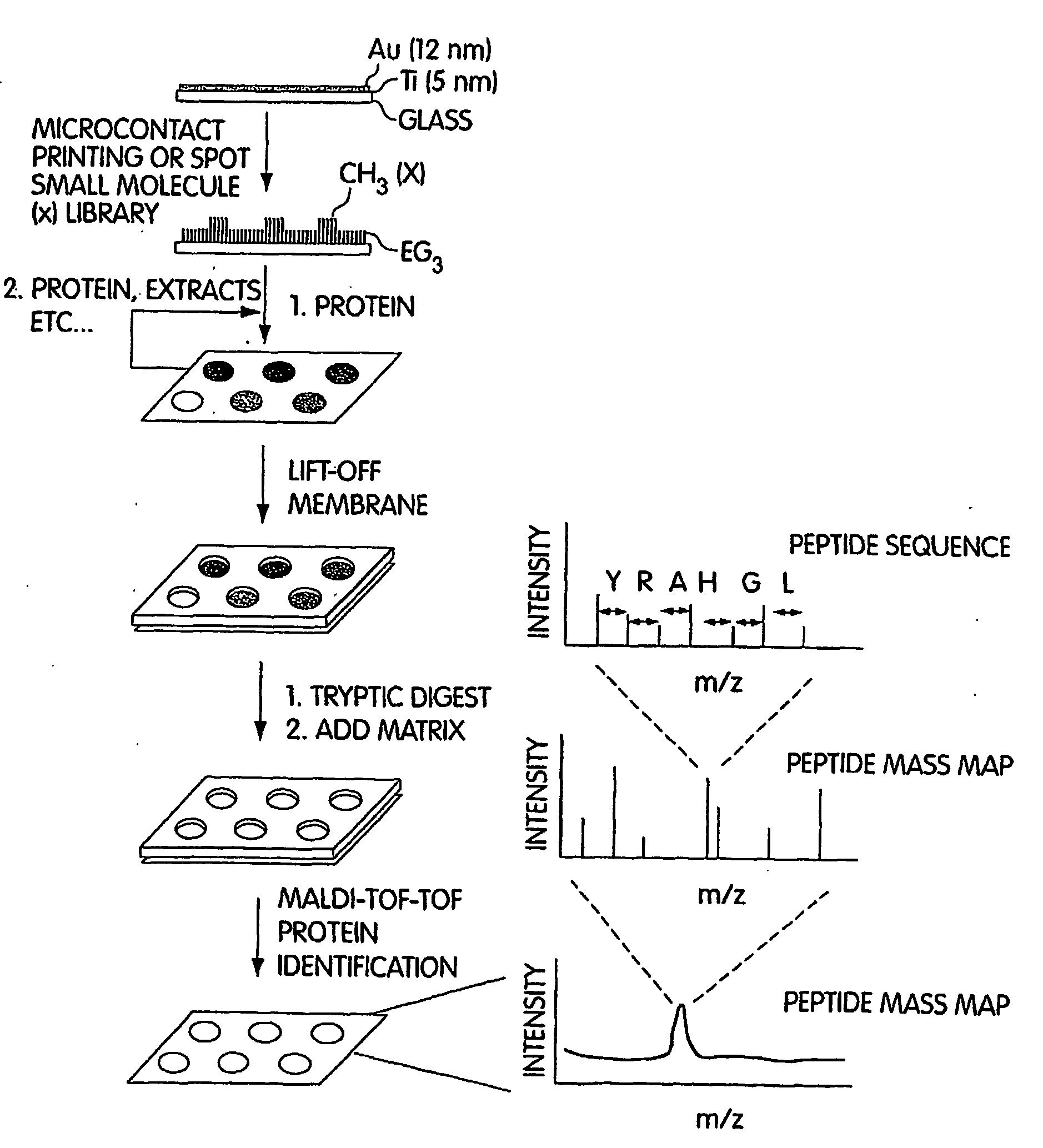
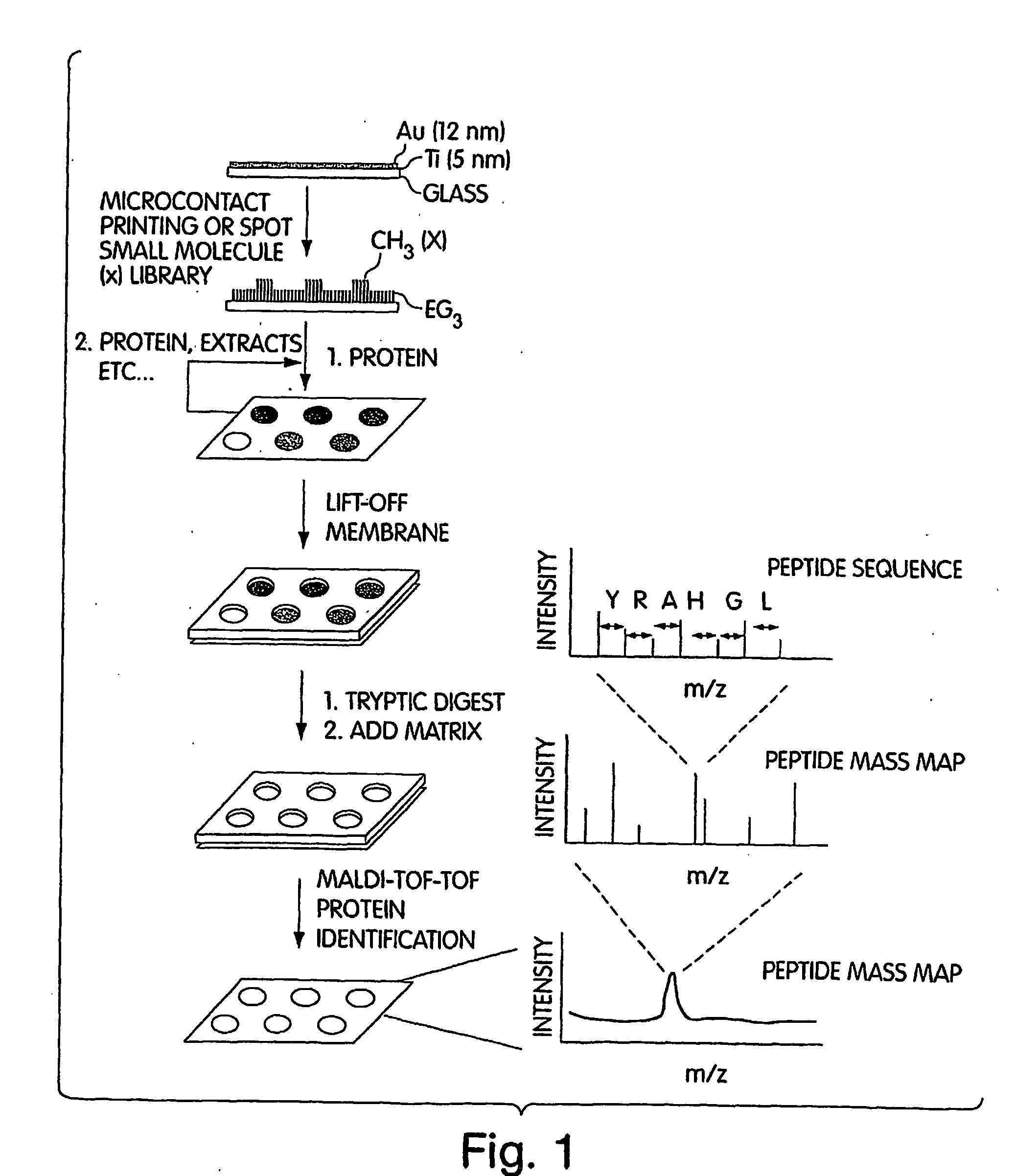
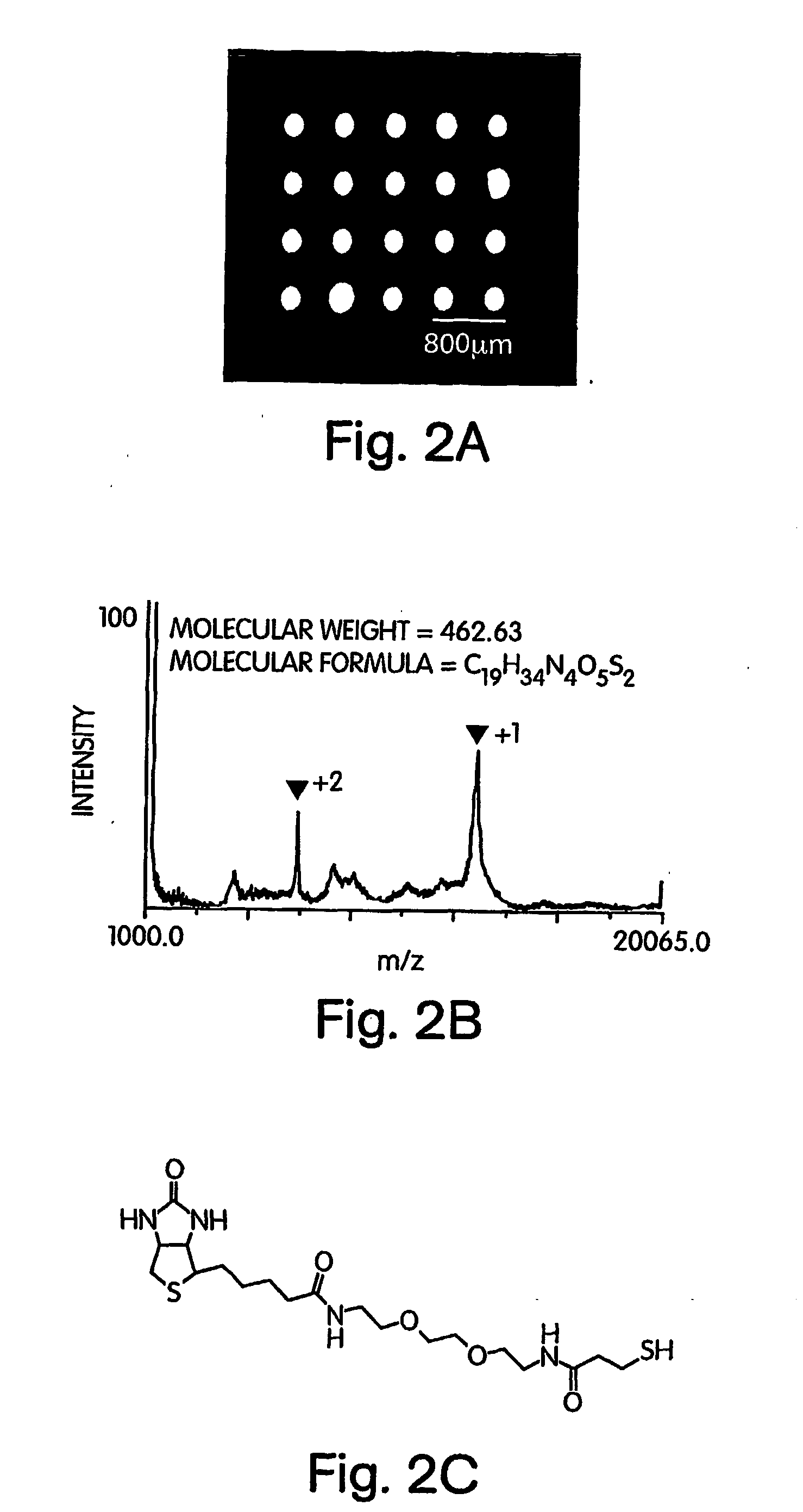
This invention generally relates to the determination of species such as proteins and / or small molecules on self-assembled monolayers using mass spectrometry. In some cases, the proteins and / or small molecules may be arranged on a substrate in an array, for example, in a microarray. In one set of embodiments, the invention relates to methods for determining proteins and / or small molecules bound to self-assembled monolayers using mass spectroscopy techniques such as MALDI and MALDI TOF techniques. This combination allows, for example, the systematic identification of unknown proteins from cell lysates. Identification of novel interactions can be achieved, in some cases, in instances where the binding partner to a particular target species is unknown. In another set of embodiments, the invention relates to methods of attaching a species to a self-assembled monolayer on a substrate such that the substrate can be used in a mass spectrometer, in some cases without requiring additional exposure of the substrate to water. For example, a target species may be detected and / or analysed using mass spectrometry in the presence of similar or “contaminating” species, without first removing the contaminating species.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
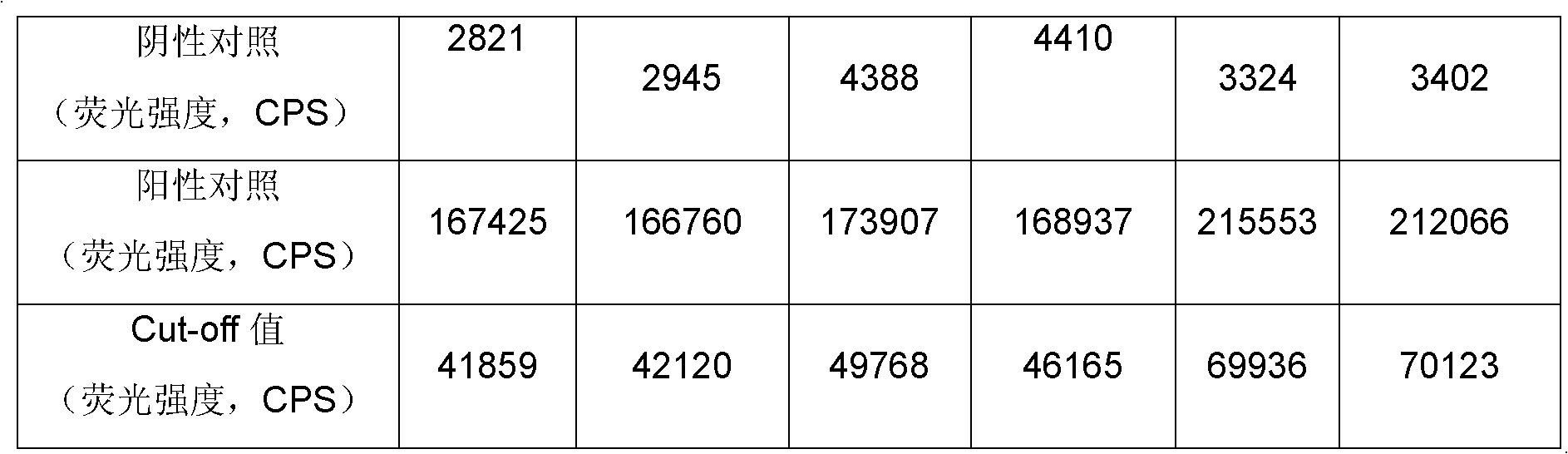
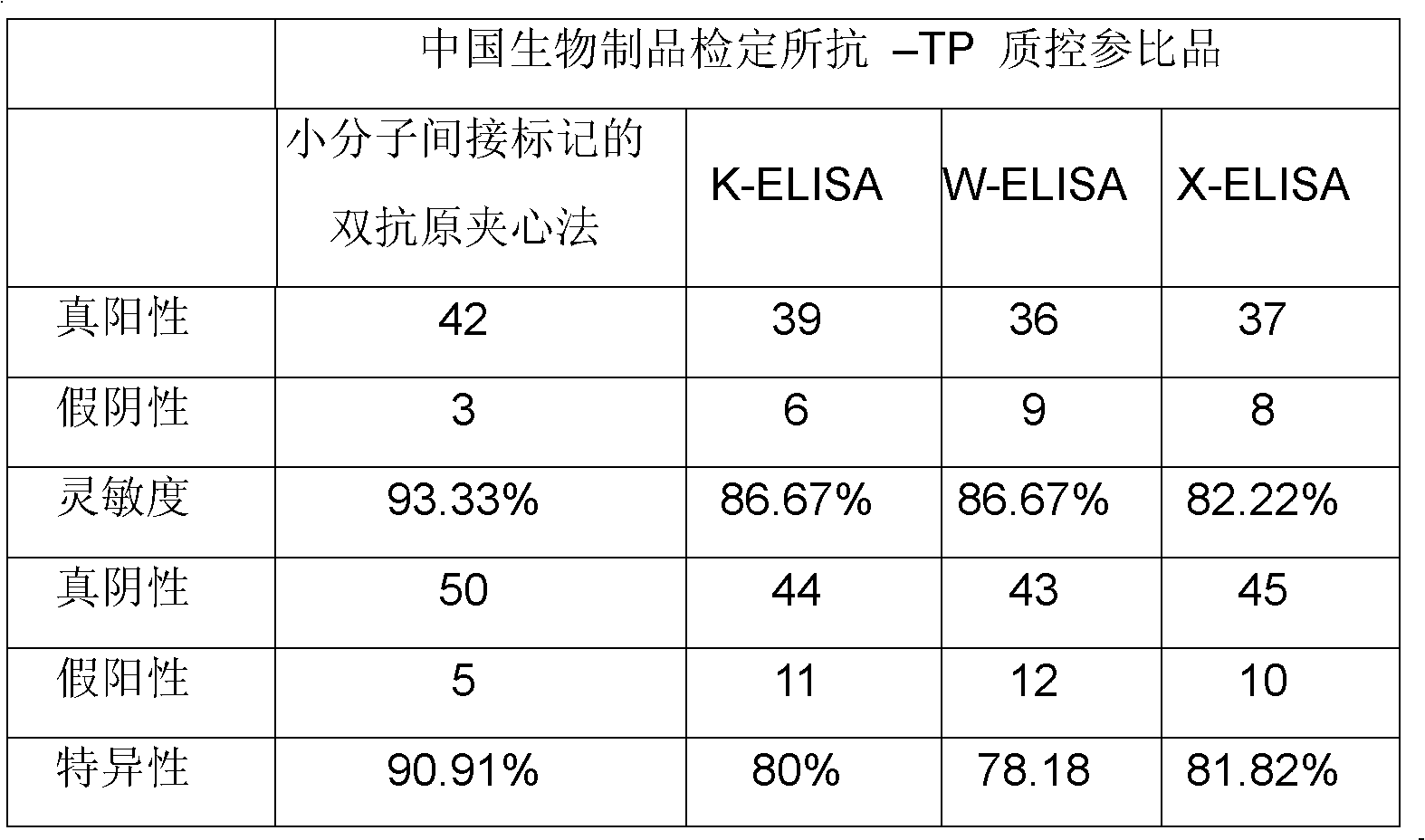
Treponema (TP) antibody detection method and detection kit thereof
The invention discloses a treponema (TP) antibody detection method and a detection kit of the TP antibody detection method. The detection method comprises the following steps of: (a) marking a first TP antigen by a small molecular substance; (b) coating a solid phase material by a second TP antigen; (c) marking an anti-small-molecular substance antibody or other substances capable of being combined with a small molecule by a signal generating substance, and then preparing a signal reporter molecule; (d) carrying out immune reaction between the second TP antigen on the surface of the solid phase material, the first TP antigen marked by the small molecular substance and the TP antibody in a sample, and then carrying out conjugation reaction between the signal reporter molecule and the small molecular substance, thus forming a detachable signal generation substance for detecting the content of the TP antibodies in the sample. The detection kit comprises (a) the first TP antigen marked by the small molecular substance, (b) the solid phase material coated with the second TP antigen, and (c) the signal reporter molecule. By adopting the TP antibody detection method and the detection kit of the TP antibody detection method, the sensitivity and specificity in the detection of the TP antibody can be effectively improved.
Owner:PERKINELMER MEDICAL DIAGNOSTICS PROD SHANGHAI
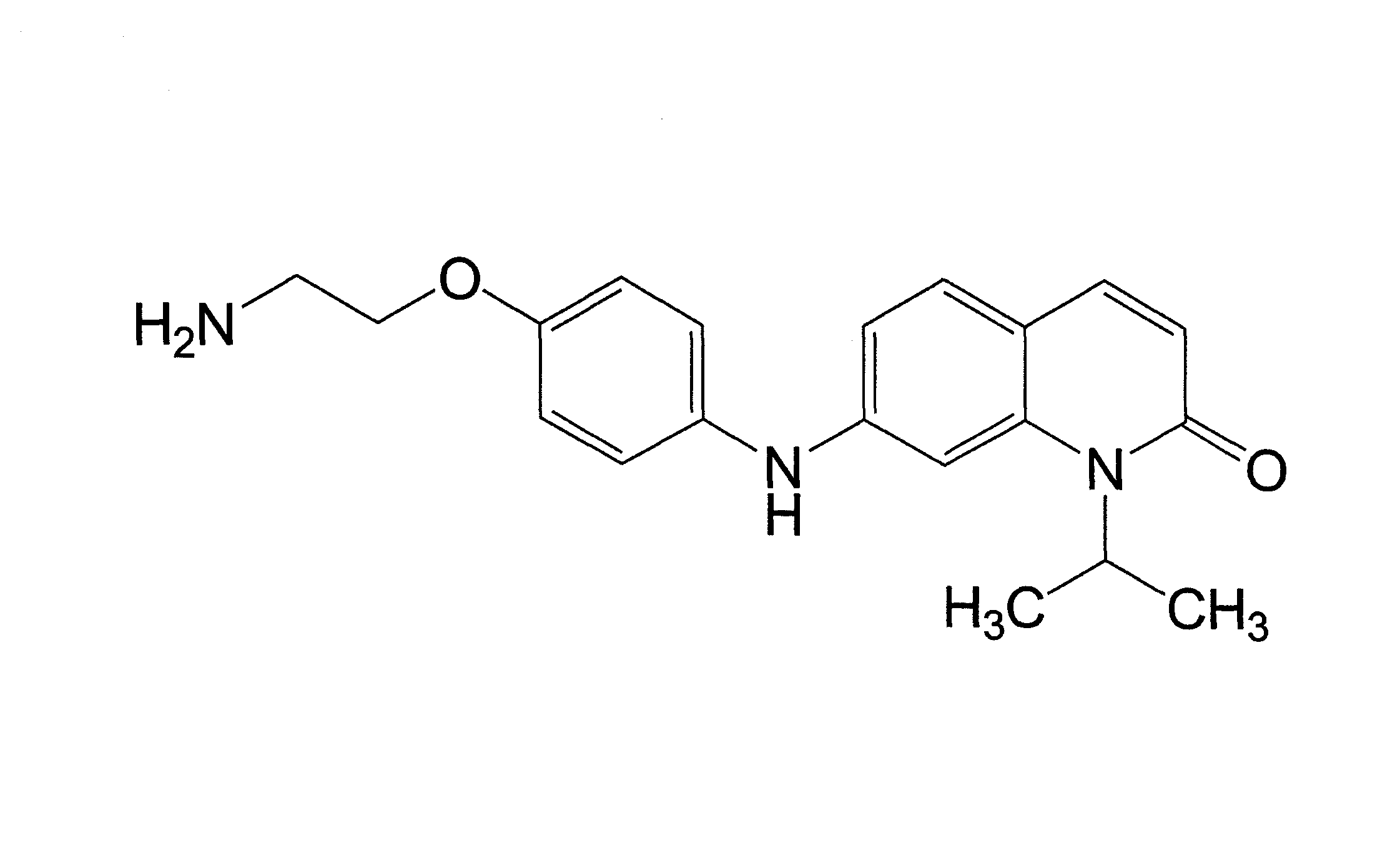
Small molecule Bcl-xL/Bcl-2 binding inhibitors
Owner:OHIO STATE INNOVATION FOUND
Method for extracting protein-micromolecule interaction module
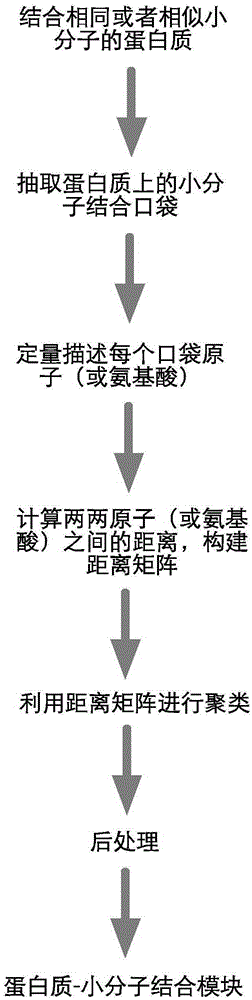
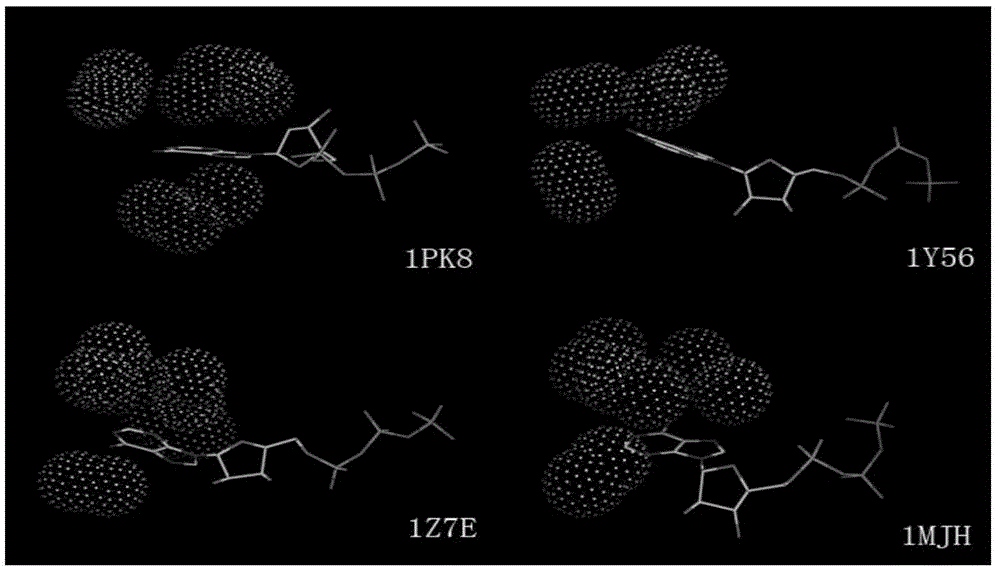
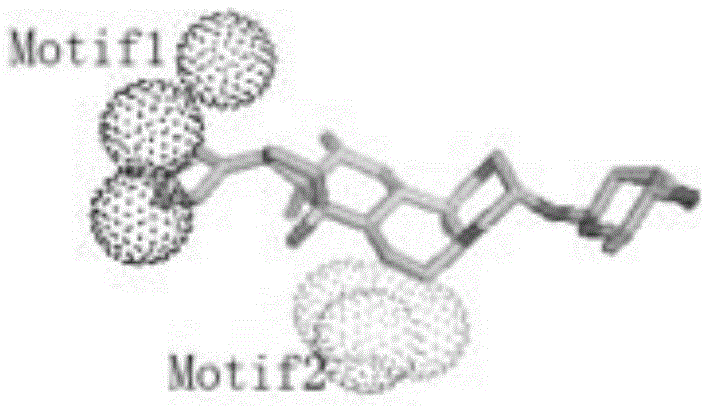
The invention relates to a method for extracting a protein-micromolecule interaction module. The method specifically comprises: firstly, performing quantitative description on atoms (or amino acids) forming a micromolecular binding pocket on protein according to properties of the atoms (or amino acids); secondly, estimating the distance between the every two pocket atoms (or amino acids), and establishing a distance matrix; thirdly, extracting categories of the pocket atoms (or amino acids) with similar properties by utilizing a clustering algorithm; and finally, performing post-processing to obtain the protein-micromolecule interaction module. The method can be applied to multiple aspects of bioinformatics research, protein design, drug screening, micromolecular chemical synthesis and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Exonuclease III/I protection analysis based fluorescent biosensor method for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism
InactiveCN101705292AReduce dosageRapid automation implementationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceDiseasePrenatal diagnosis
The invention discloses an exonuclease protection analysis based fluorescent biosensor method for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism, which comprises allele-specific extension of micromolecule modified single nucleotide, interaction between an oligonucleotide DNA strand primer with micromolecules after extension and binding protein, protection analysis of the exonuclease III / I and fluorescent quantitative detection of a hairpin type oligonucleotide DNA probe primer subjected to end protection based on double-strand indicating dye. The method adopts allele-specific extension of the primer to combine the micromolecule modified single nucleotide at 3' end of a specific primer and then combine the specificity of the binding protein of the micromolecule to protect the primer from being degraded by the exonuclease III / I, and detects single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping through fluorescence of the complex of the protected oligonucleotide DNA primer and double-strand inserting dye. The method features simple and convenient operation, economy, fast speed, sensitivity and strong specificity and is expected to provide a universal technology platform for screening and prenatal diagnosis of the population suffering from gene mutation related genetic diseases.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Structure-based nucleic acid aptamer optimization design method
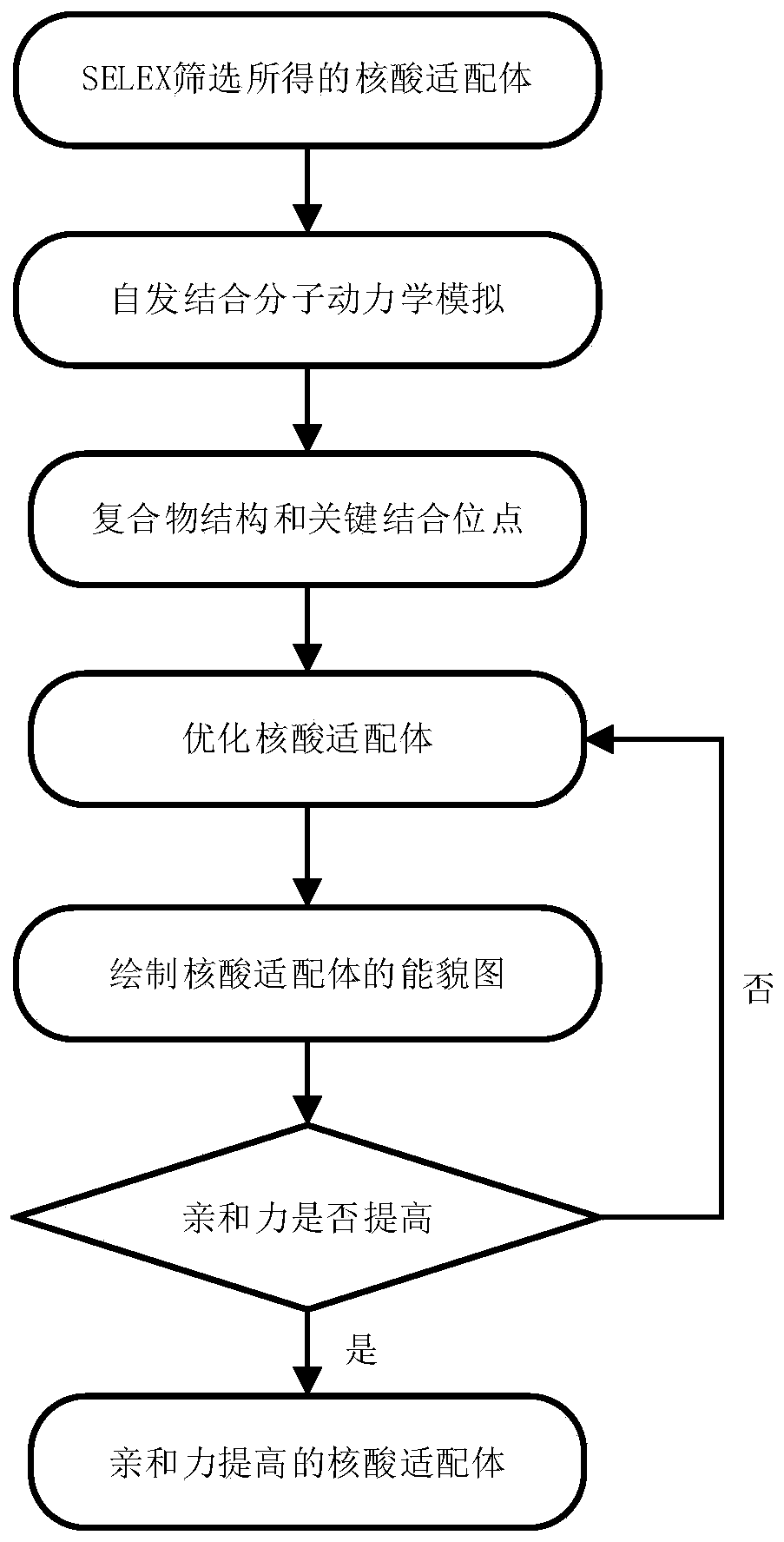
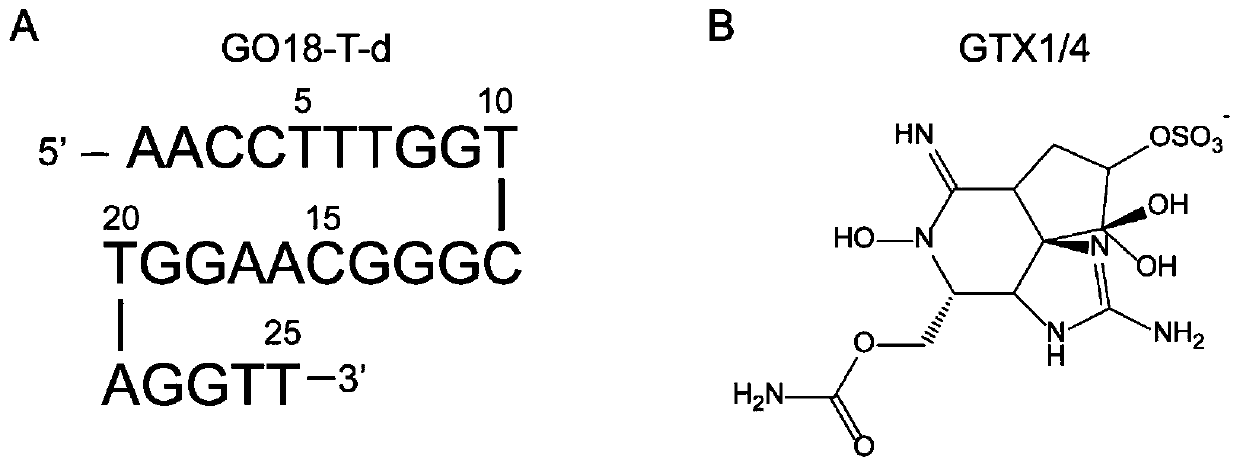
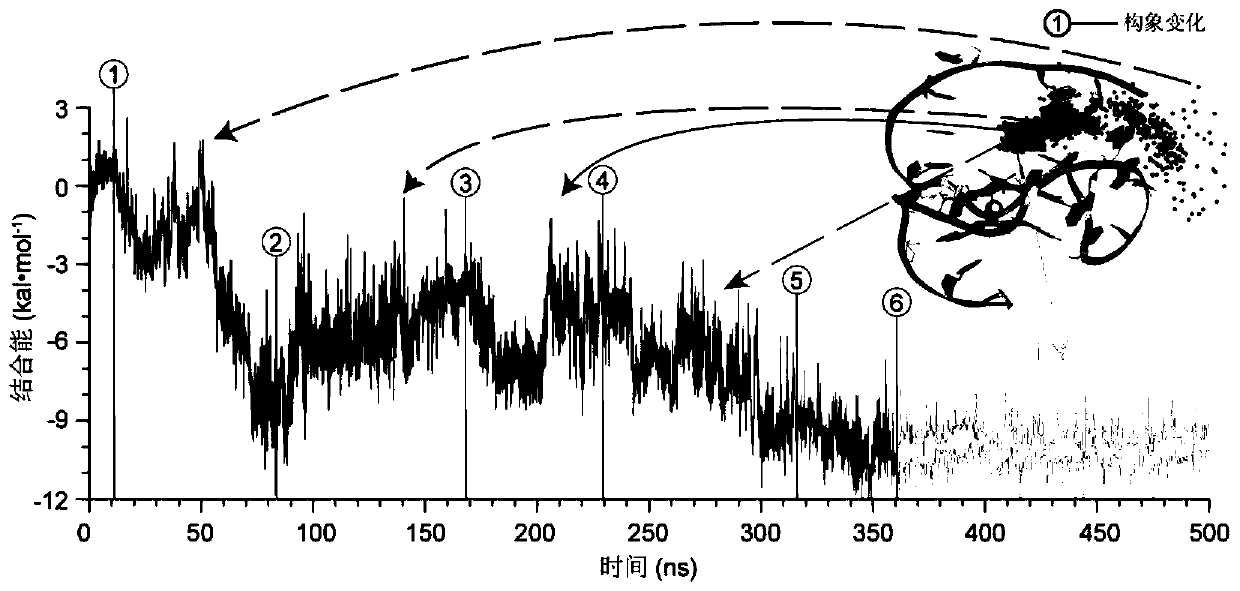
The invention belongs to the technical field of nucleic acid aptamer design and particularly relates to a structure-based nucleic acid aptamer optimization design method. The method is characterized in that starting from a 3D structure of a nucleic acid aptamer screened by the SELEX technology, a 3D structure of a compound formed by combining small molecules with the nucleic acid aptamer is obtained through spontaneous combination simulation; the structure of the compound and key combination sites are analyzed, and optimal design of the high-affinity nucleic acid aptamer is guided by utilizingthe obtained information; a design scheme is evaluated by adopting a performance diagram of nucleic acid aptamer surface combination energy. The method is advantaged in that the method is applied tooptimization design of the nucleic acid aptamer GO18-T-d of specifically combined toxin GTX1 / 4; the nucleic acid aptamer is obtained by screening through the SELEX technology, and affinity is 75.63 nM; a truncated nucleic acid aptamer (GO18-T-d_S) of GO18-T-d is obtained through optimization, and that the affinity of the nucleic acid aptamer is improved by 20 times is verified through an MST experiment, and the optimization method is reasonable and effective.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
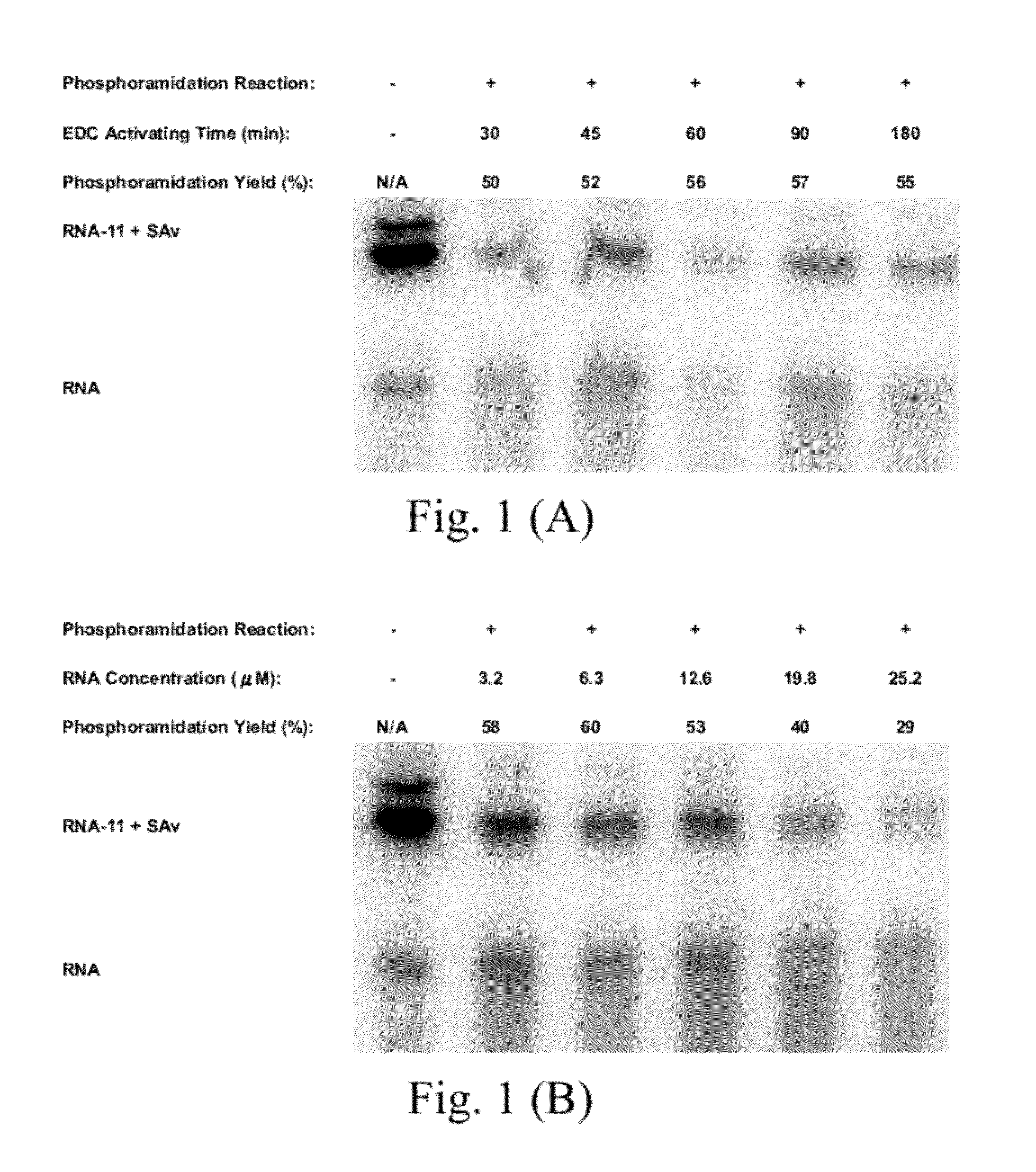
Methods for conjugating nucleic acids with small molecules
A method for conjugating a nucleic acid with a molecule is provided. The method includes steps of (a) reacting the nucleic acid having a 5′-monophosphate with an activating agent in a first buffer to form a solution; (b) mixing an alcohol with the solution formed in the step (a) to obtain an intermediate; and (c) dissolving the intermediate in a second buffer containing an ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and adding a nucleophile thereinto to react the intermediate with the nucleophile.
Owner:KAOHSIUNG MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
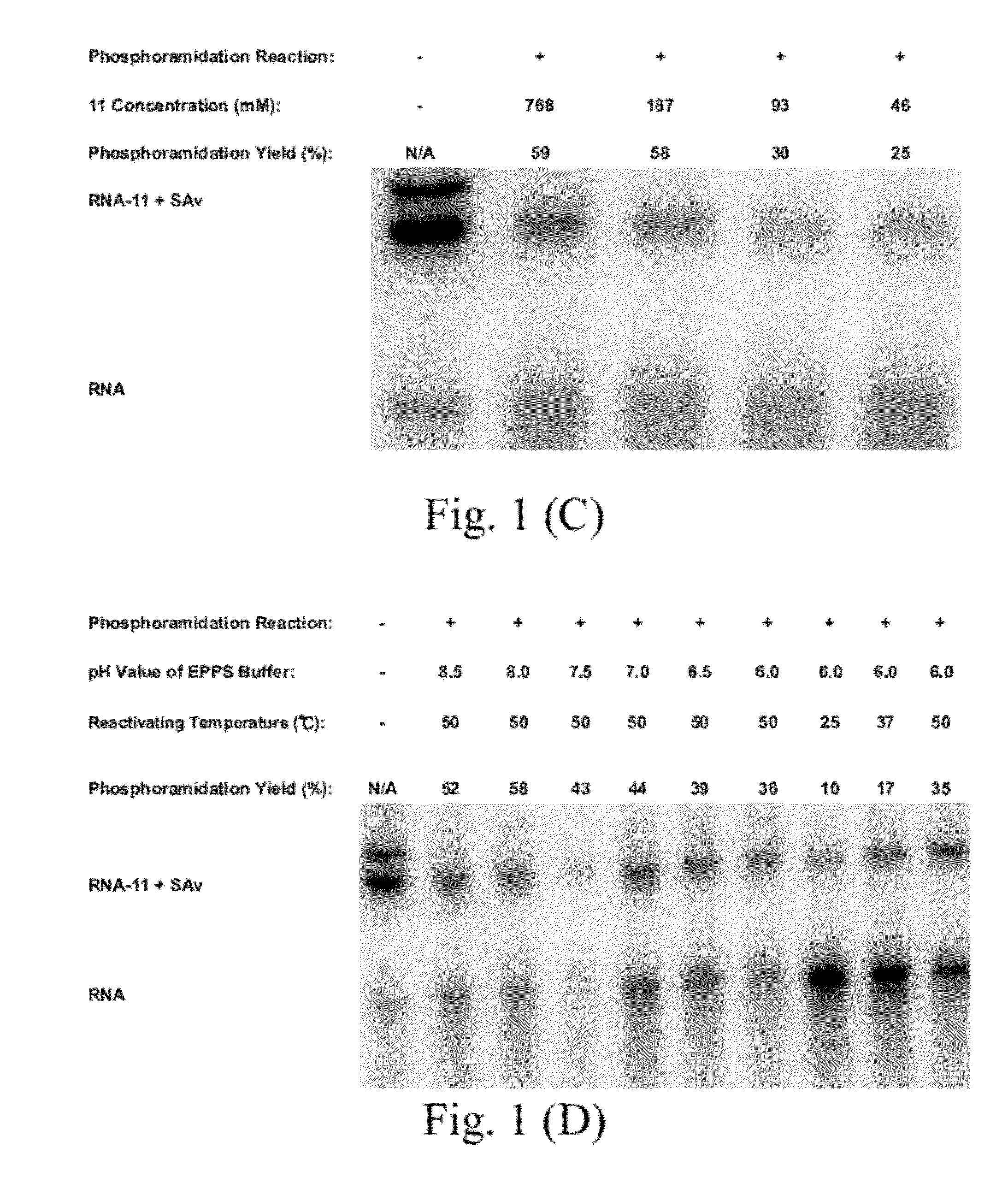
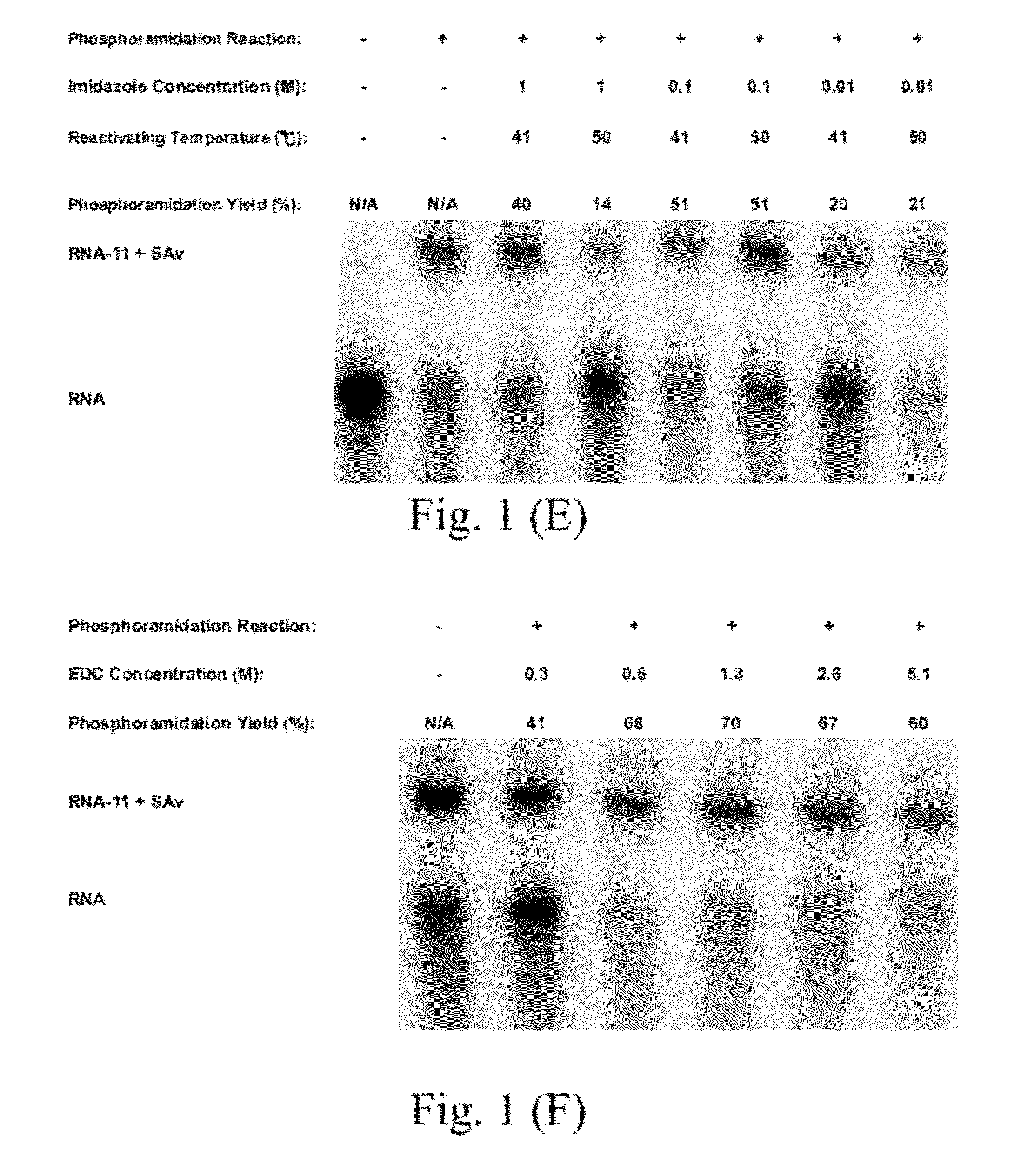
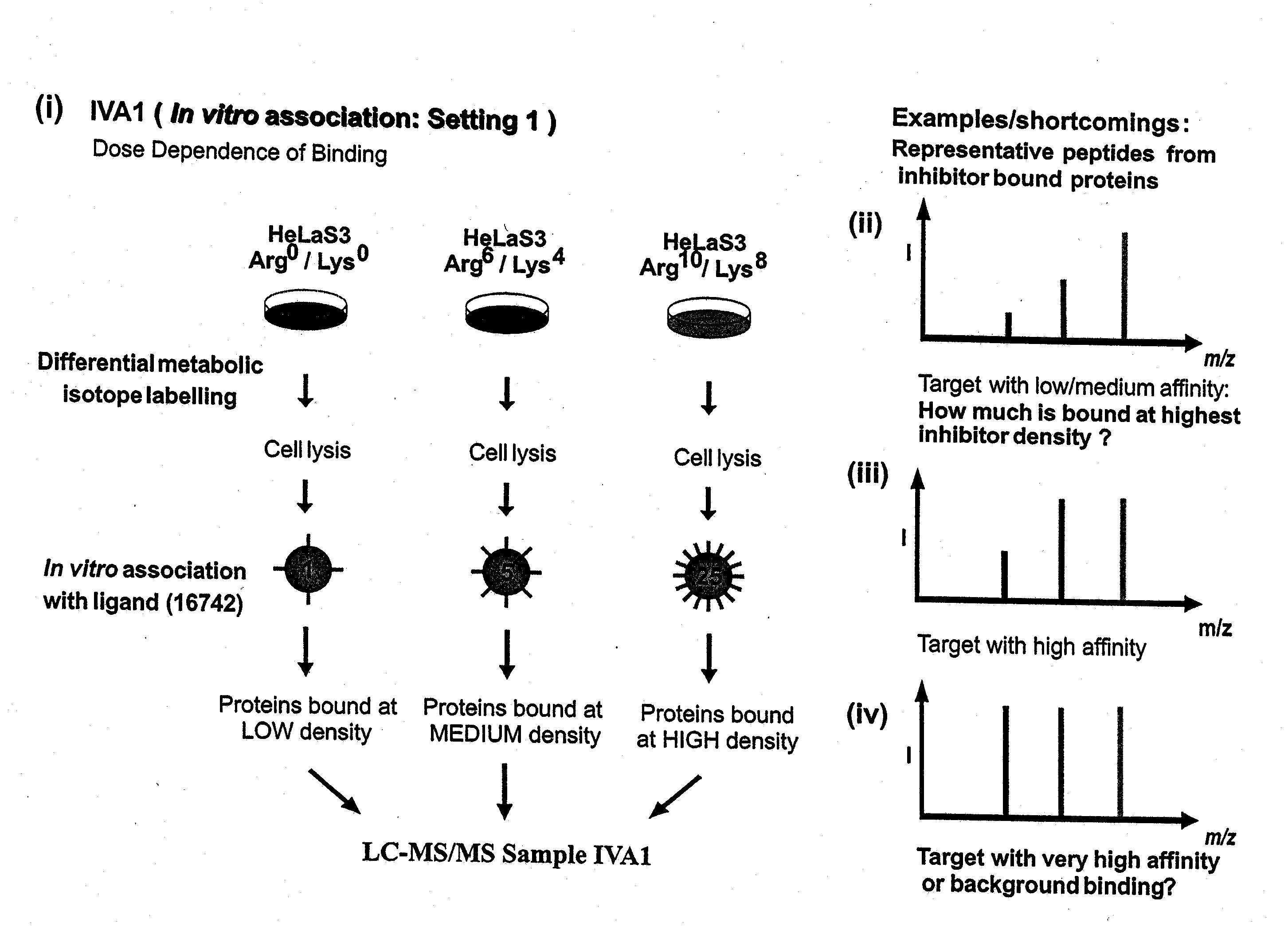
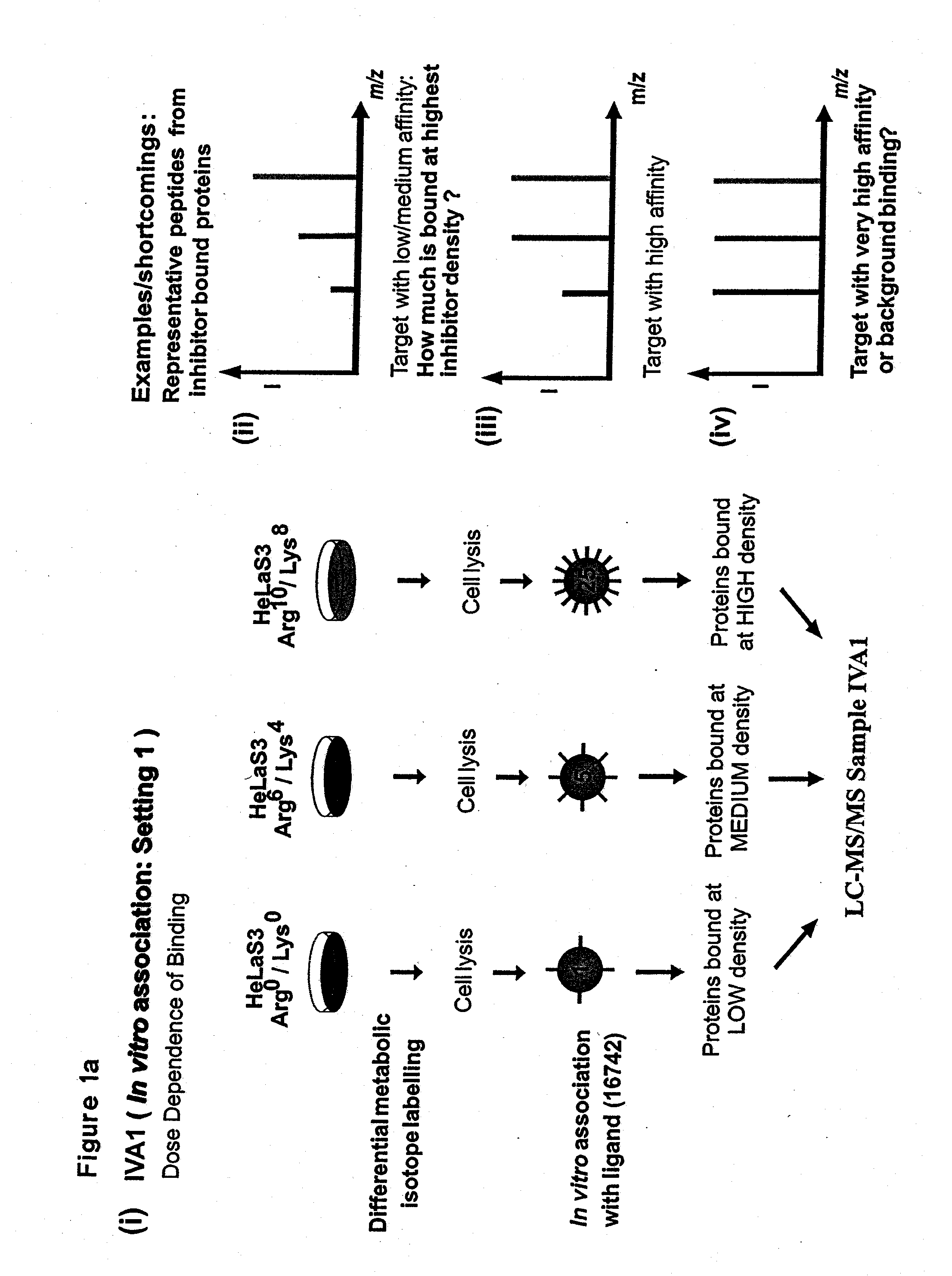
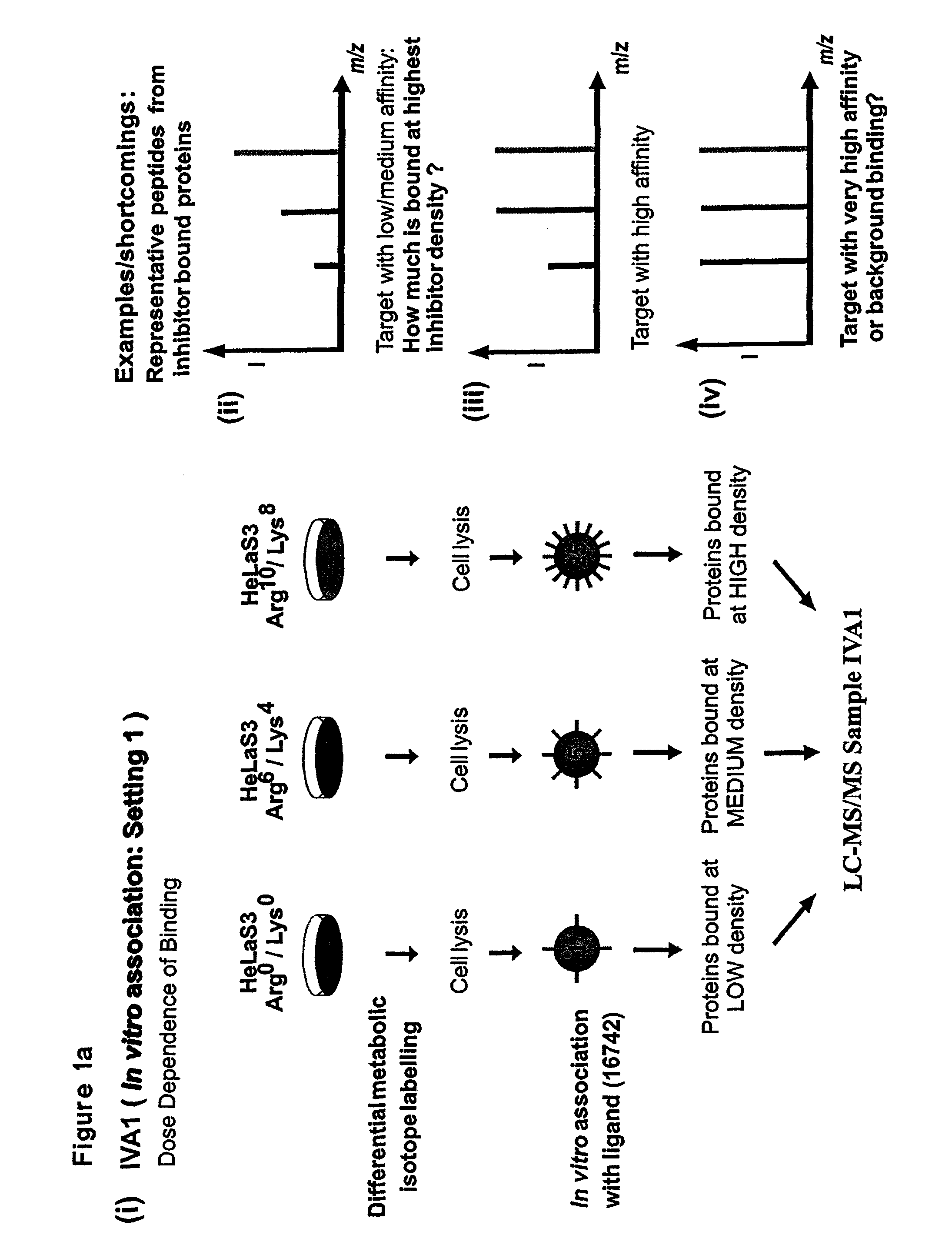
Proteome-Wide Quantification of Small Molecule Binding to Cellular Target Proteins
ActiveUS20100279891A1Simple and rapid characterizationComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein targetProteome
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Predicting method of nucleic acid binding site bound with protein or micromolecule
InactiveCN109979533AImprove prediction success rateUnderstanding Biological MechanismsProteomicsGenomicsMolecular Structure of Nucleic Acids: A Structure for Deoxyribose Nucleic AcidNucleotide
The invention discloses a predicting method of a nucleic acid binding site bound with a protein or a micromolecule, wherein the method belongs to the field of biomolecule interaction predicting researching and development. The method according to the invention comprises the following steps of using the nucleic acid in a nucleic acid molecule structure as a node in a network model, wherein a shortest distance between two non-continuous nucleic acid heavy atoms in a nucleic acid molecule sequence is smaller than the side of the network model, converting the nucleic acid molecule structure to a nucleic acid molecule network model, determining importance of nucleotide in the nucleic acid molecule through calculating centrality of the node of the nucleic acid network, and if the closeness centrality and the degree centrality of a certain node are higher than summation of average values and standard deviations of all nodes in the whole network, determining the nucleotide which corresponds with the node is the nucleic acid binding site. The predicting method has advantages of realizing high predicting success rate which is higher than that of an existing method, realizing simple operationand high practicability, and realizing an important function in understanding a biological mechanism problem of the nucleic acid and related medicament designing.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
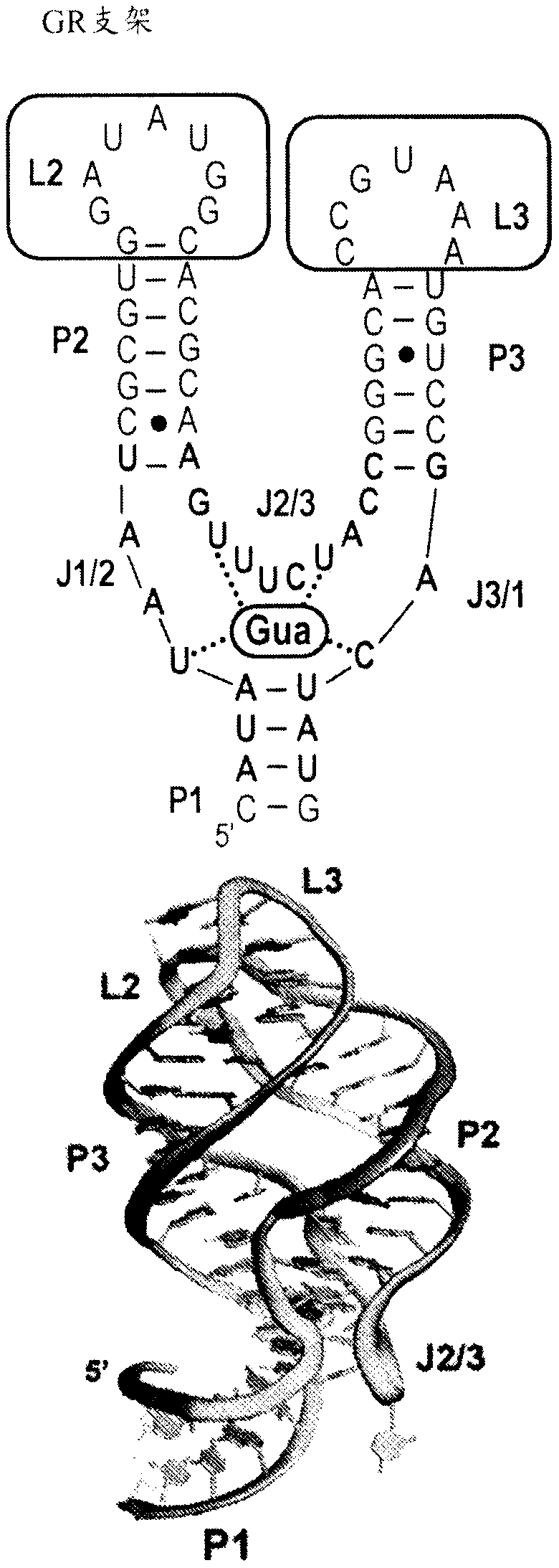
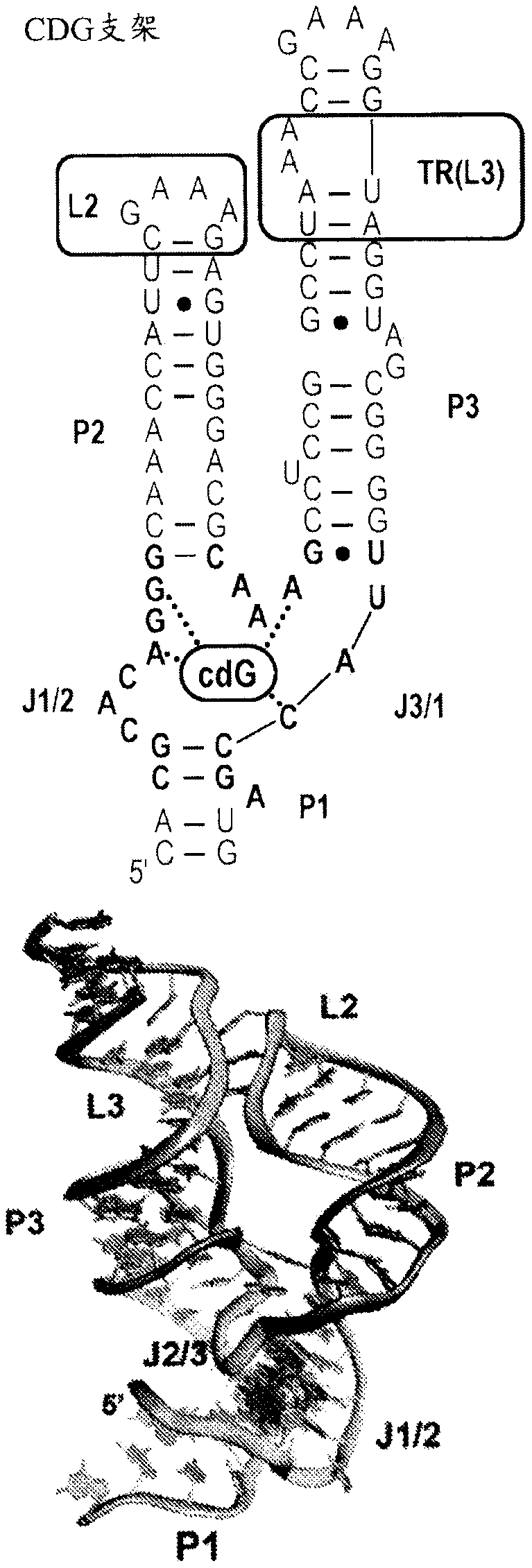
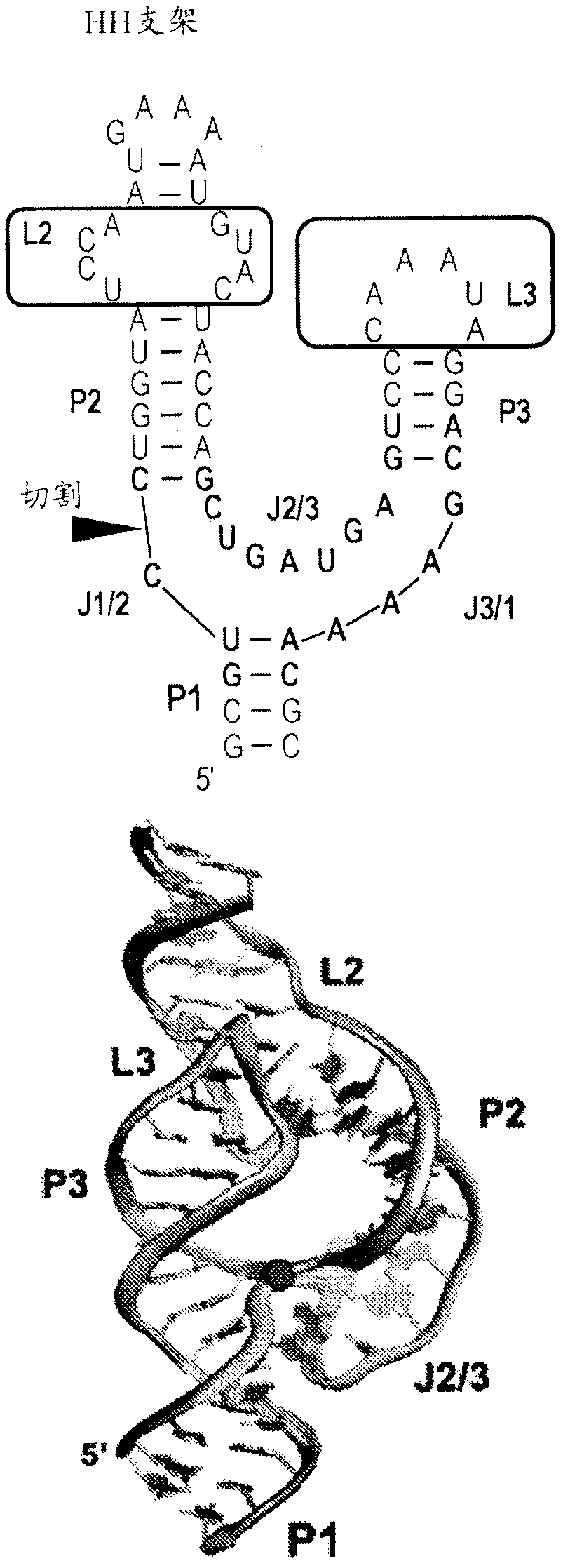
Use of biological RNA scaffolds with in vitro selection to generate robust small molecule binding aptamers for genetically encodable biosensors
Provided herein are libraries of scaffolds derived from riboswitches and small ribozymes and their methods of use. The scaffolds of the invention yield aptamers that are easily identified and characterized by virtue of the structural scaffold. The nature of the scaffold predisposes these RNAs for coupling to readout domains to engineer biosensors that function in vitro and in vivo. Biosensors, synthetic RNA agents and synthetic DNA agents, and their methods of use, are also provided.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Micro-molecule indirectly labeled dual-antigen sandwich method for determining hepatitis C virus total antibody
The invention relates to a method for testing the total antibody of hepatitis C virus (HCV), based on dual-antibody interlayer method of small-molecule indirect mark, wherein said method is characterized in that: it uses small molecule matter as mark; uses dual-antigen interlayer method to test the total antibody of sample; and said method comprises: using small molecule material to mark HCV antigen; using HCV antigen to pack solid material; using single generate material to mark small molecule antibody or other material that combined with small molecule; the HCV antibody of sample can be reacted with HCV antigen of solid material surface and small molecule mark, to form dual-antigen interlayer composite; then reacting the small molecule with single report molecule, to make the composite with detected signal generate material. The invention can keep activity of antigen, with signal amplifying function and better specificity of dual-antigen interlayer mode, while it can detect variable kinds of antibodies, to improve the detecting sensitivity and specificity.
Owner:SUZHOU SYM BIO LIFESCI CO LTD
Polyalkylene glycol acid additives
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
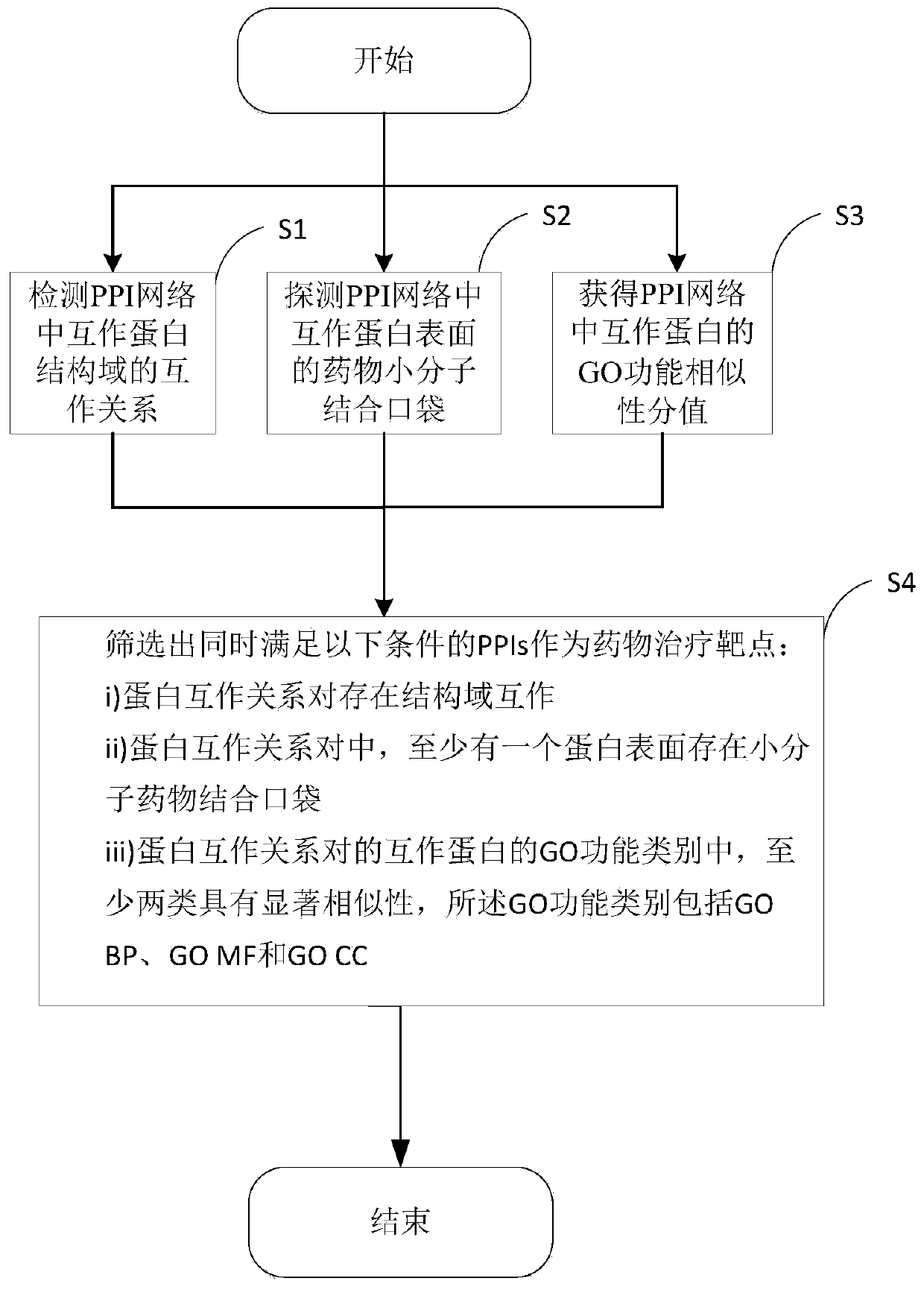
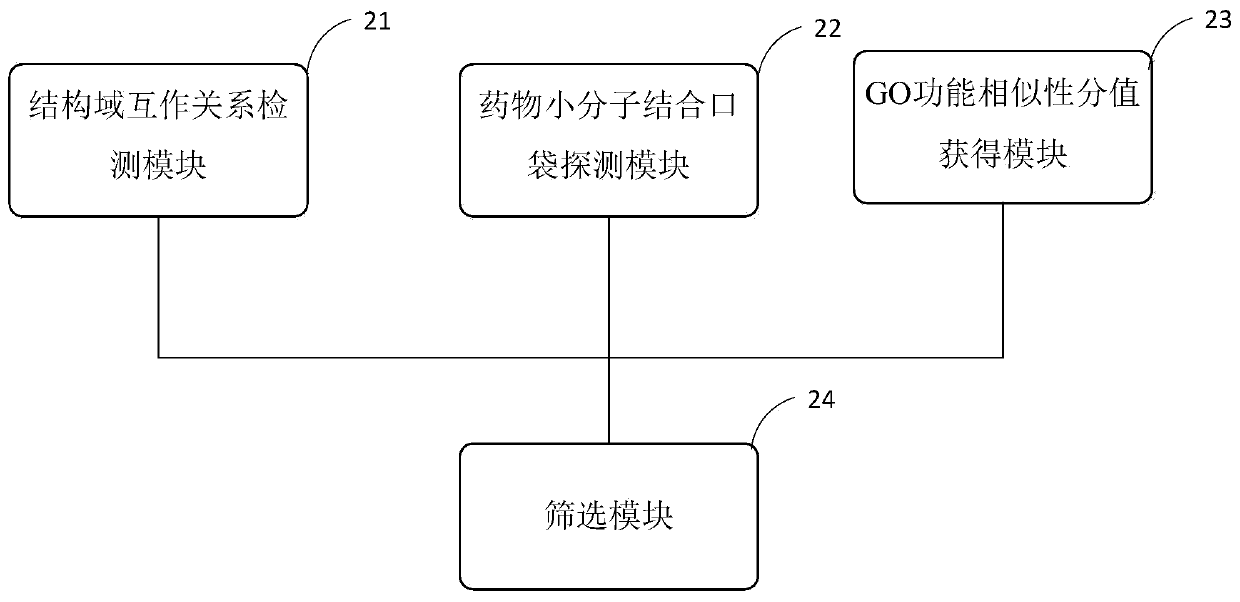
Target PPIs drug property prediction method and device based on protein interaction network
ActiveCN110544506AReliable interactionReduce false positivesProteomicsGenomicsPositive interactionInteractions protein
The invention provides a target PPIs drug property prediction method based on a protein interaction network. The method at least comprises the following steps: S1, detecting the interaction relationship of interaction protein structural domains in the PPI network; S2, detecting a drug small molecule binding pocket on the surface of interaction protein in the PPI network; S3, obtaining a GO function similarity score of the interactive protein in the PPI network; S4, screening out PPIs meeting the following conditions at the same time to serve as drug therapy targets: protein interaction relationship pairs have structural domain interaction; in the protein interaction relationship pair, at least one protein surface has a small molecule drug binding pocket; at least two of the GO function categories of the interaction proteins of the protein interaction relationship pair have significant similarity, and the GO function categories comprise GO BP, GO MF and GO CC. According to the method, three strict mutually independent standards are adopted to comprehensively explore and discover the target PPI, false positive interaction is systematically eliminated, more reliable PPIs are selectedas drug targets, and the calculation result better conforms to objective reality.
Owner:上海源兹生物科技有限公司
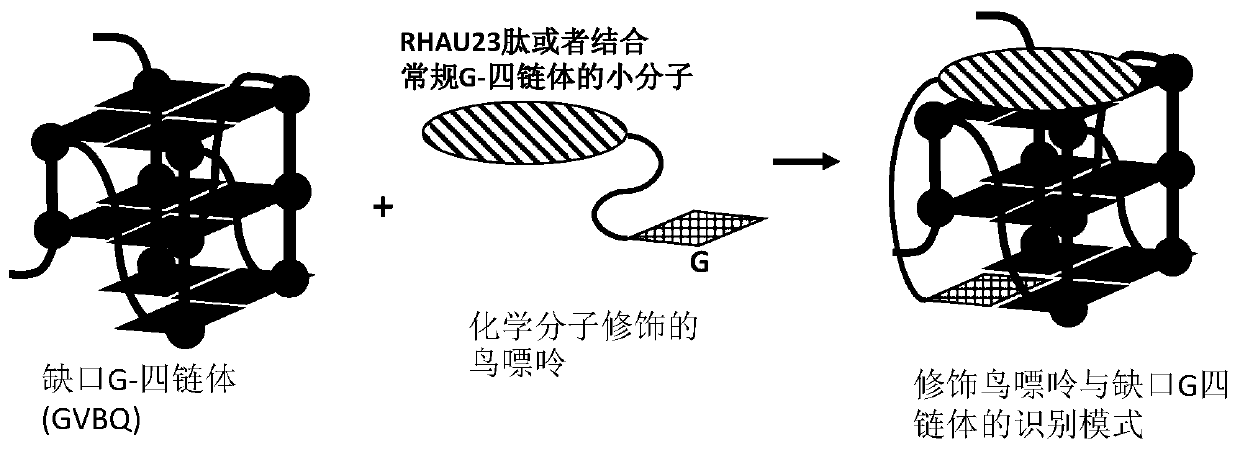
Compound for recognizing notched G-quadruplex, and preparation method and application of compound
InactiveCN111518787AImprove stabilityEnhanced ability to inhibit DNA replicationOrganic chemistryHydrolasesChemical compoundStructural formula
The invention relates to the field of biology, and discloses a compound for recognizing a notched G-quadruplex, and a preparation method and application of the compound. The compound for recognizing the notched G-quadruplex comprises a guanine molecule and a polypeptide or a small molecule capable of recognizing the G-quadruplex, wherein the polypeptide or the small molecule is connected with theguanine molecule through an amido bond, and the structural formula of the compound is shown in the specification. In the structural formula, R1 or R2 is the small molecule or the polypeptide. According to the compound for recognizing the notched G-quadruplex provided by the invention, a notch is filled with guanine to form a hydrogen bond, and the polypeptide or the small molecule is combined witha guanine plane at the tail end of the notched G-quadruplex so as to allow two binding sites to exist between the polypeptide or the small molecule and the notched G-quadruplex, so the notched G-quadruplex can be specifically recognized, the stability of the notched G-quadruplex can be improved, and the DNA replication inhibition ability of the notched G-quadruplex can be enhanced.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for rapidly and effectively detecting conformational change in aptamer and ligand small molecule binding process
The invention relates to the technical field of biological medicine, in particular to a method for rapidly and effectively detecting conformational change in the aptamer and ligand small molecule binding process. The method comprises the following steps: determining the affinity between a selected aptamer and small molecules by applying a biological membrane interference experiment; detecting conformational change before and after the aptamer is combined with the small molecules through a surface enhanced Raman scattering spectrum technology; and visually explaining the binding process of theaptamer and the ligand through molecular dynamics simulation. According to the method, theophylline and the aptamer thereof are taken as examples, it is verified that the method provides new idea forresearch on the reliability of the conformational change of the aptamer and design, modification and screening the high-affinity high-selectivity aptamer, and the method can be applied to the fields of detection, sensing, clinical diagnosis and treatment in a better way.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Targeted mesoporous molecular imaging probe and preparation method thereof
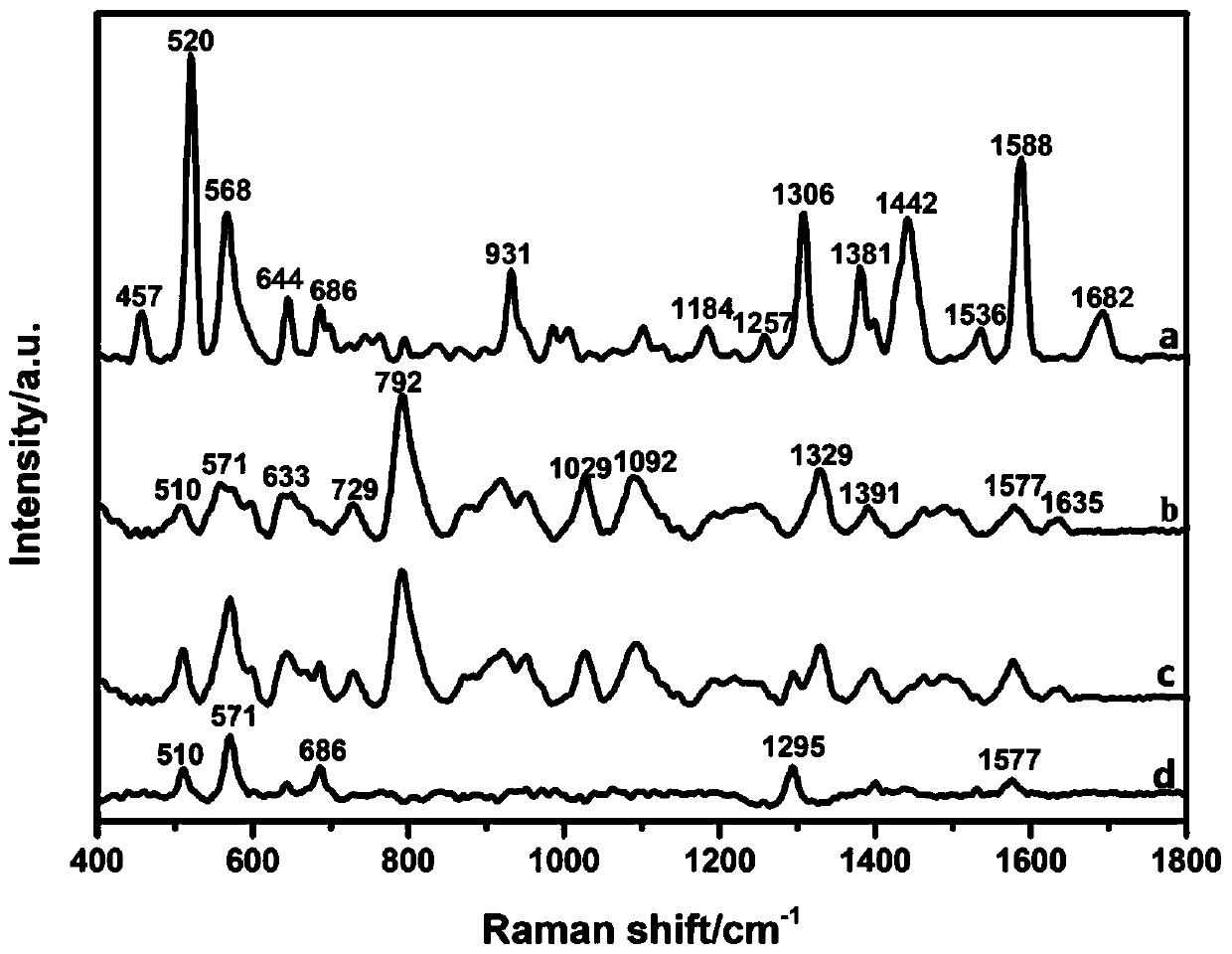
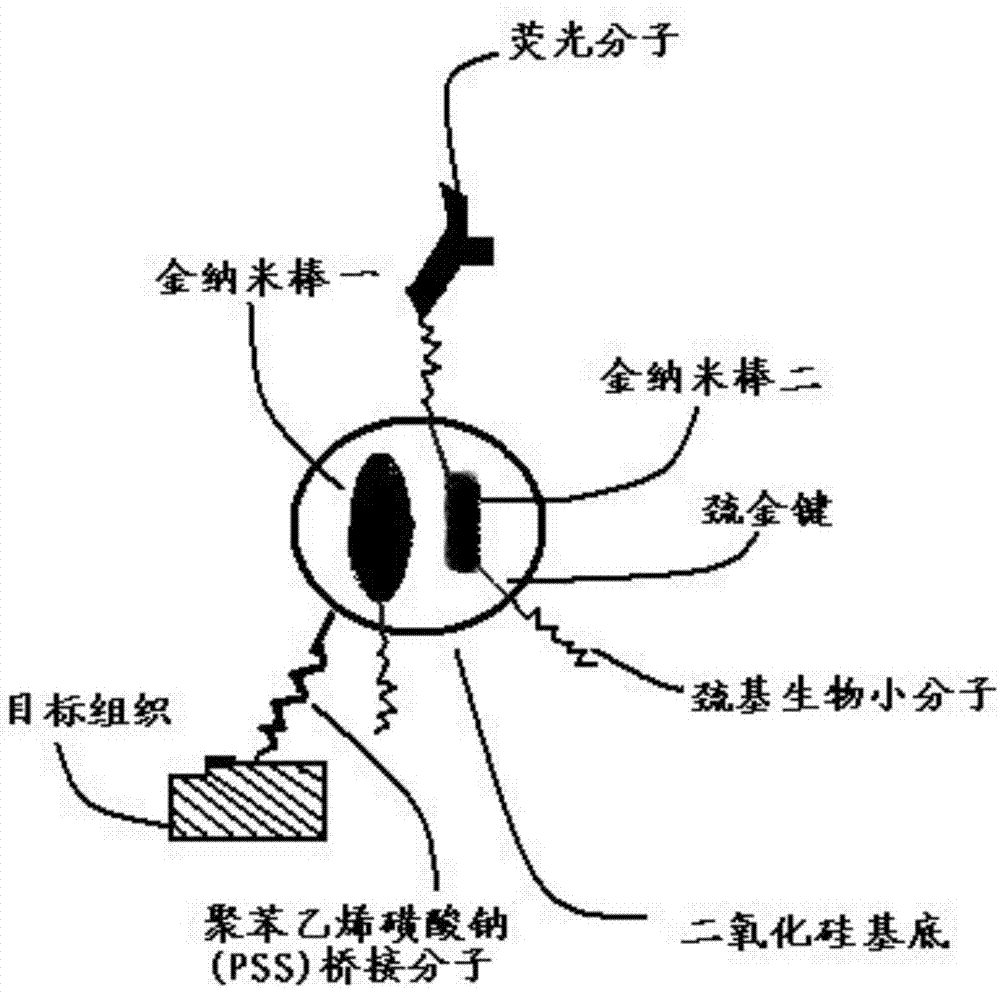
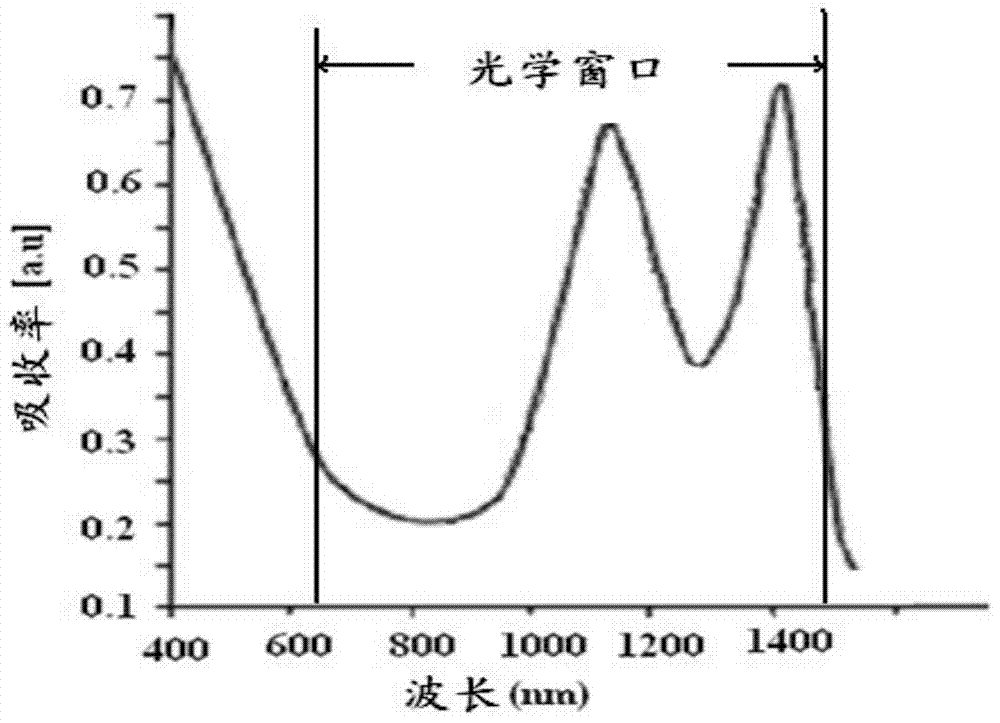
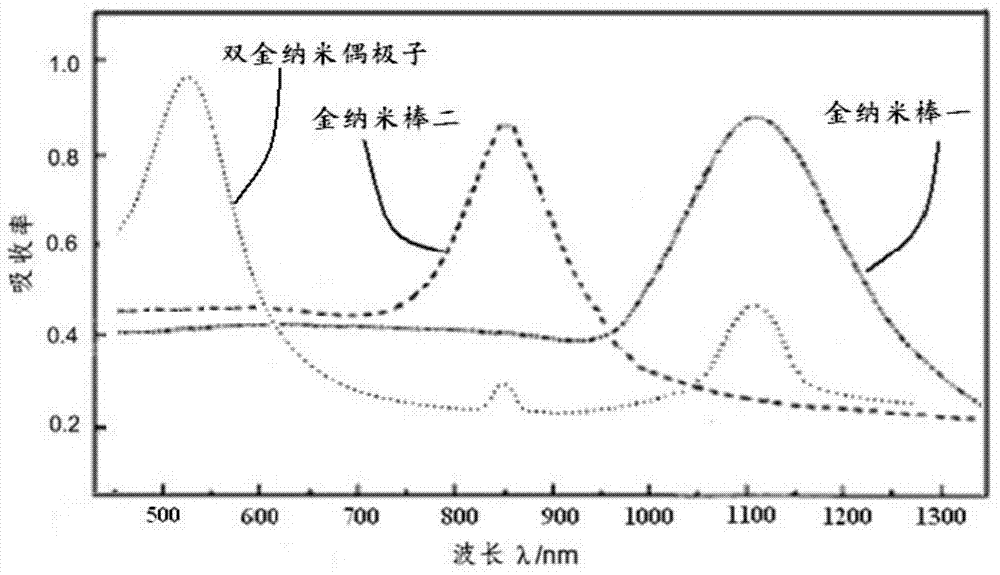
InactiveCN104777140ADecreased fluorescence emission intensityEnhanced fluorescence emission intensityNanotechnologyFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceLuminescence
The invention relates to a targeted mesoporous molecular imaging probe and a preparation method thereof. The targeted mesoporous molecular imaging probe comprises two parts including a surface plasma resonance core layer and a peripheral coating layer, wherein the surface plasma resonance core layer at least comprises a gold nanorod I, a gold nanorod II and substrate nano particles; the peripheral coating layer is formed by fluorescent molecules, sulfydryl small biological molecules and polystyrene sulfonate connectors; the gold nanorod I and the gold nanorod II are cohered on the substrate nano particles, so that the surface plasma resonance core layer can be formed; the distance between the gold nanorod I and the gold nanorod II meets the condition that d is more than or equal to (r1-r2) / 2 and less than or equal to (r1+r2) / 2; the exterior of the core layer is combined with the sulfydryl small biological molecules by a gold sulfhydryl bond, the fluorescent molecules are combined with the sulfydryl small biological molecules by an amide covalent bond, and polystyrene sulfonate is directly connected on a substrate in a bridging way. The invention also provides the preparation method of the targeted mesoporous molecular imaging probe. Blue shift or red shift is generated by surface excitation, and the characteristics of luminescence of a fluorescent structure are matched, so that the brightness is increased by 8-10 orders of magnitude. The targeted mesoporous molecular imaging probe has very high fluorescence characteristic, thus being applied to the diagnosis of tumor fluorescence imaging; the targeted mesoporous molecular imaging probe is especially suitable for detection and diagnosis of tumors in the dark field at the deep part of tissue cells.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
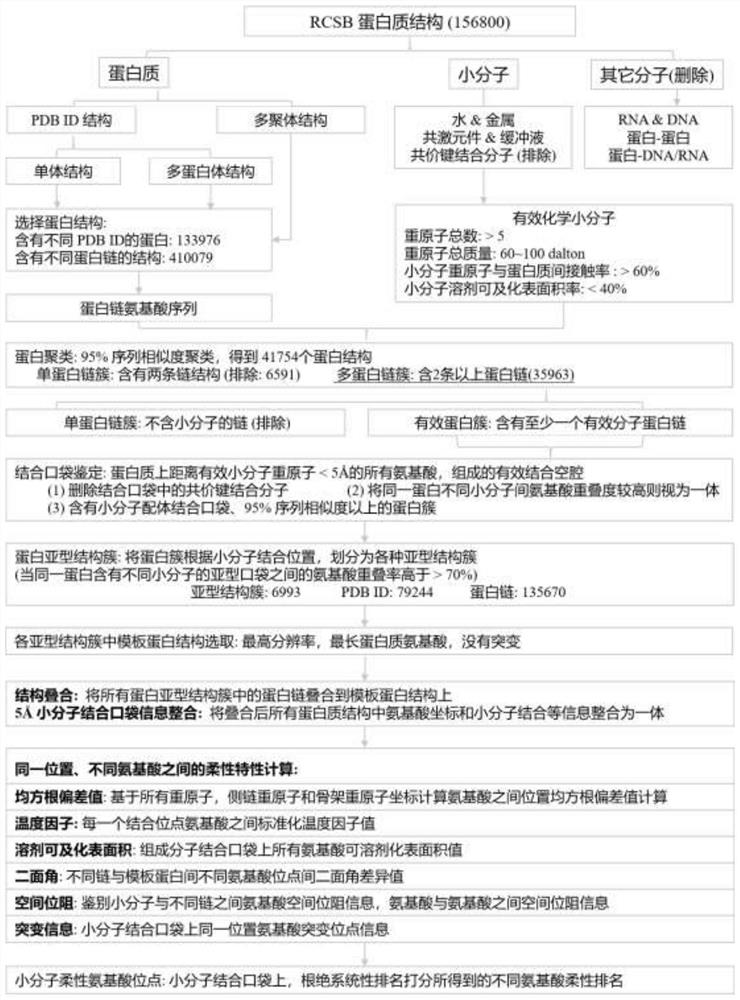
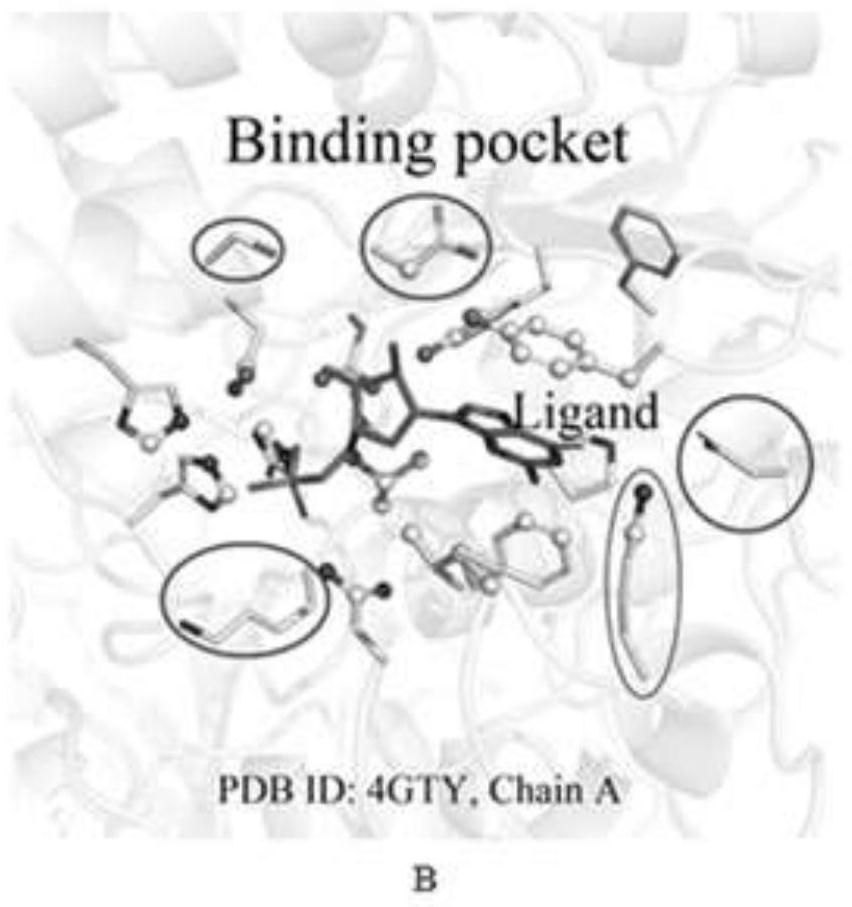
Method for identifying key flexible amino acids on protein small molecule binding pockets
ActiveCN111951884AReducing Rigid Phase Space BarriersImprove virtual screening accuracyBiostatisticsProteomicsProtein structureMolecular binding
The invention relates to a method for identifying key flexible amino acids on a protein small molecule binding pockets. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, in a protein PDB structure, classifying the protein structure into different subtype clusters through 95% sequence similarity; step 2, overlapping all protein structures in the subtype cluster with the same structure by using a clear biological ligand, and accurately identifying small molecule binding pockets on the protein; step 3, dividing the corresponding binding sites in the same structure subtype cluster of the known 3Dstructure into site binding subtypes according to the binding positions of small molecules; step 4, researching the protein flexibility property by calculating physicochemical and structural parameterdifference characterization factors; and step 5, identifying key flexible residues by using the highest score of a system for forming the protein binding pockets. A set of uniform and unbiased research process system is designed, and a set of systematic mathematical statistical formula is developed to determine the structural flexibility of binding site amino acids at the same position of different structural models.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Proteome-wide quantification of small molecule binding to cellular target proteins
ActiveUS8959984B2Simple and rapid characterizationIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationAnalyteProtein target
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Using viruses to detect or purify proteins
InactiveUS7670801B2Easily programmableEasily self-replicatingFungiBacteriaVirusSmall molecule binding
Disclosed are methods of isolating and purifying proteins and other organic small molecules produced in hosts using viruses. Also disclosed are methods of visualizing and / or localizing proteins and other organic small molecules produced in hosts using viruses. Further disclosed are compositions of matter containing the protein or small molecule bound to a virus.
Owner:ICON GENETICS
Ev-mediated delivery of binding protein-small molecule conjugates
PendingUS20190290585A1Overcome problemsEfficient deliveryOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderExtracellular vesicleCrystallography
The present invention relates to extracellular vesicles (EVs) comprising a binding protein which may be used for delivery of protein-drug conjugates comprising the binding protein and a small molecule agent, typically a small molecule drug. The present invention also relates to methods for producing such EVs as well as pharmaceutical compositions and medical uses of such EVs.
Owner:EVOX THERAPEUTICS LTD
Perylene-based small molecular fluorescent probe and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107382814ANovel structureReduce testing costsOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical structureBiological cell
The invention belongs to the technical field of sulfhydryl biological small molecule detection, in particular to a perylene-based small molecular fluorescent probe and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: first performing a nitration reaction on 1-position carbon or 3-position carbon of perylene so as to connect a nitro group, then reducing the nitro group into an amino group, then replacing the amino group with maleic anhydride so as to obtain two small molecular fluorescent probes adopting novel structures, provided by the invention, wherein the two small molecular fluorescent probes adopts the chemical structural formulae shown as a formula (I) or a formula (II). When the small molecular fluorescent probe is combined with a sulfhydryl biological small molecule in a biological cell, green light is emitted, which is significantly different from background blue light of the biological cell; the small molecular fluorescent probe has the advantages of high sensitivity, good selectivity and low biological toxicity; in addition, the preparation process is simple and optimized, and the detection cost of the sulfhydryl biological small molecule is greatly reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
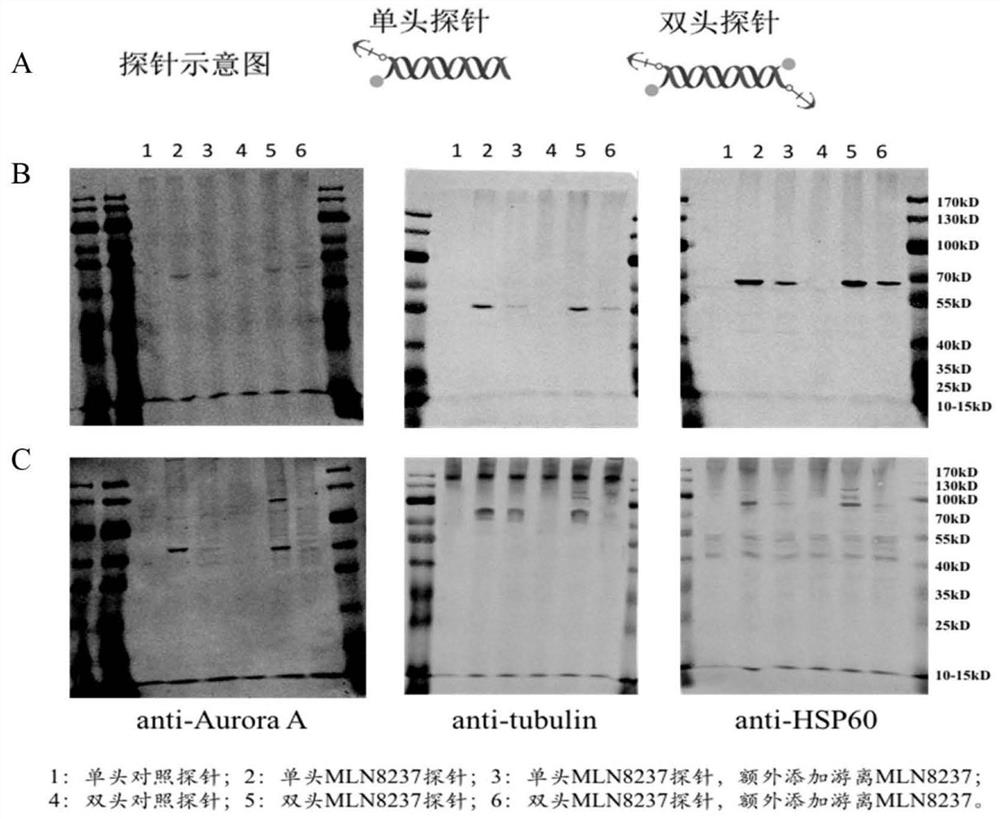
Bioactive molecule binding target identification method based on double-head photoaffinity probe
PendingCN112630446AHigh purityClose to the measured molecular weightBiological testingSeparation technologyUltraviolet lights
The invention relates to the technical field of medicines, and provides a bioactive molecule binding target identification method based on a double-head photoaffinity probe. The method comprises the following three steps: preparing the double-head photoaffinity probe, preparing a protein sample, and capturing, separating and identifying a bioactive small molecule binding target. A double-head photoaffinity probe is used for giving a whole-cell extraction protein compound, and a specific binding target is visible through ultraviolet light capture and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis separation technologies, so the non-specificity of target identification is greatly reduced, and the method can be used for binding target identification research of bioactive small molecules, is beneficial to discovering a brand-new disease binding target, and has good application prospects.
Owner:THE NAVAL MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
Aptamer screening method and application thereof
PendingCN113564155AIngenious designFreedom of choiceMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening processAptamerRiboswitch
The invention discloses an aptamer screening method and application thereof. The method can be used for screening aptamers combined with small molecules. The screening method disclosed by the invention can be used for solving the problems of difficulty in experimental design, complex screening flows and the like in the existing SELEX technology, and more importantly, a RNA aptamer can be obtained by screening by using the method, is an aptamer enzyme on one hand, is an artificial riboswitch on the other hand, and can be applied to the 5'or 3 'end of a gene to directly regulate and control the expression of the gene. In a word, the method disclosed by the invention can be used for generating the aptamers combined with the small molecules, so that the aptamers can be applied to various types of detection, diagnosis assistance and the like, and can also be used for regulating and controlling gene expression as the artificial riboswitch.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
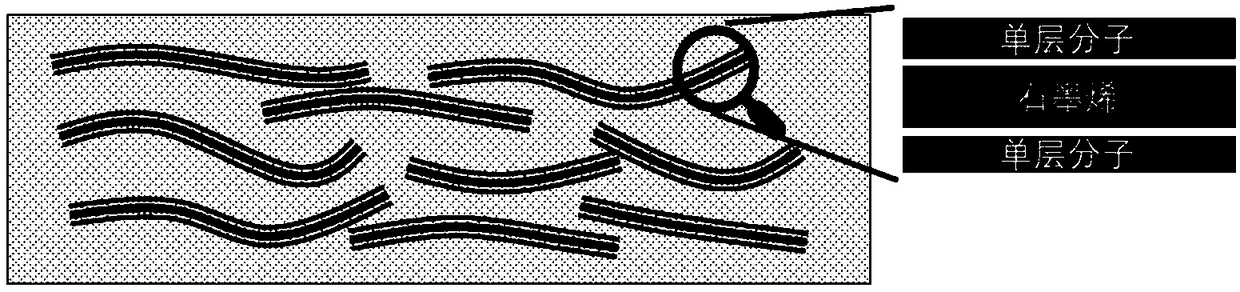
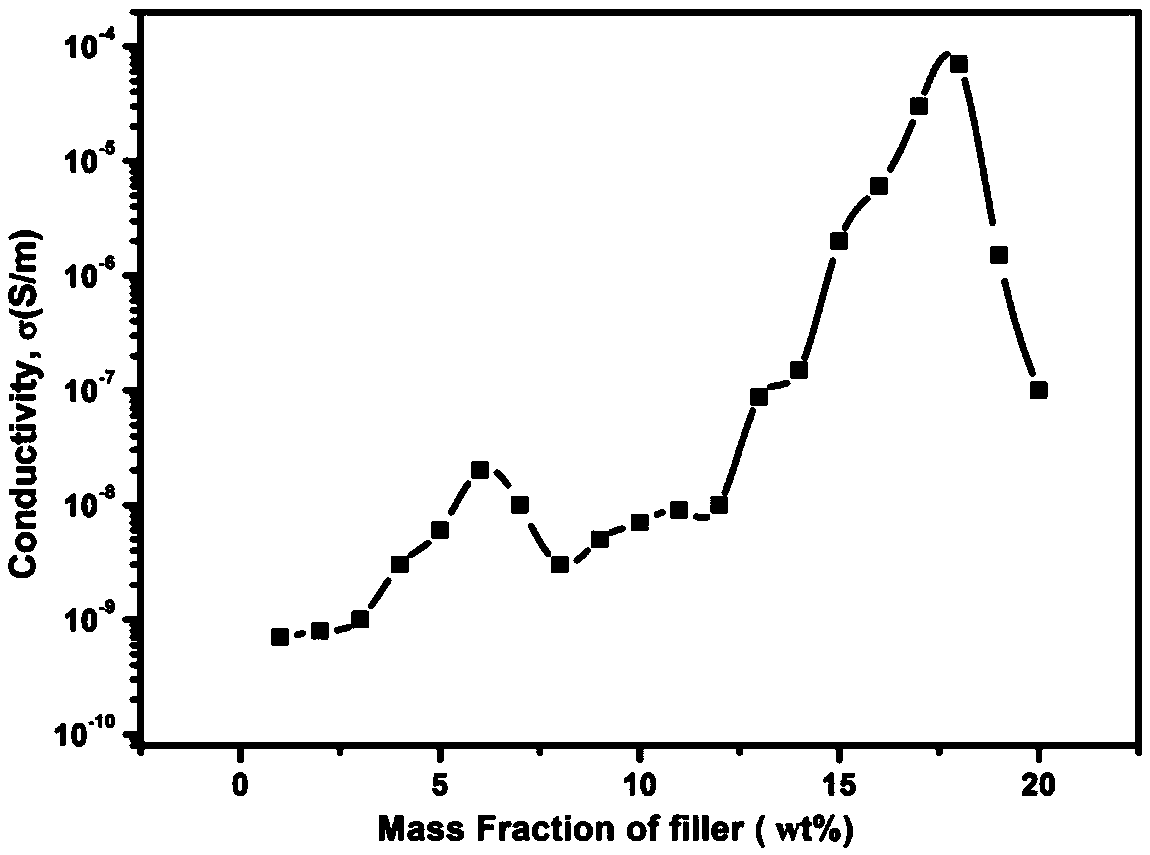
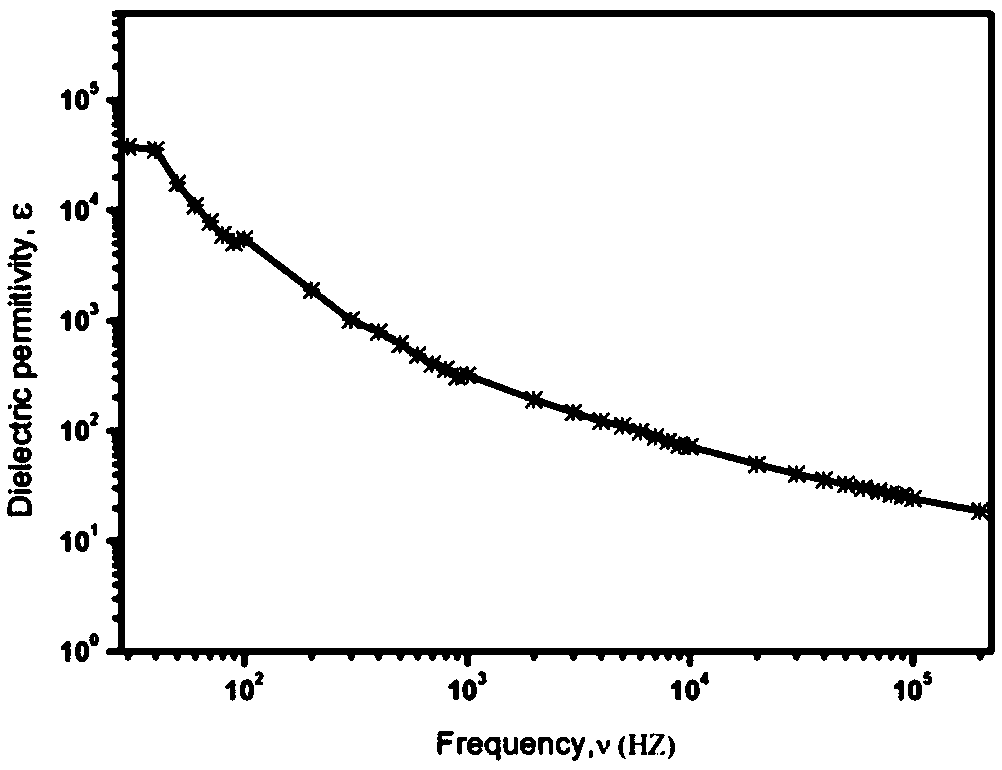
Nanometer composite material with high dielectric constant and low conductivity
The invention belongs to the field of a dielectric composite material and relates to a new method for preparing a nanometer composite material film with high dielectric constant and low conductivity.A dielectric material has wide application in the field of microelectronics, such as a bypass capacitor, an organic field effect transistor, an organic thin layer electroluminescent device, electric field control and an electric energy storage device, but obtaining a material with high dielectric constant, extremely low conductivity and low dielectric loss is still a technical problem. The nanometer composite material film is prepared by combining small-size graphene and aromatic organic micromolecules and filling into a polymer, has high dielectric constant of 10<4> order magnitude and low conductivity of 10<-8> order magnitude, effectively propels the application range of the dielectric material and improves the properties of the material. Organic micromolecules are adsorbed on the surface of the graphene, so that the stacking of graphene sheets and the formation of a conductive network are hindered, and the conductivity can be inhibited while the conductivity of the composite material is improved. The material is simple to form, excellent in performance and favorable for industrialized production.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
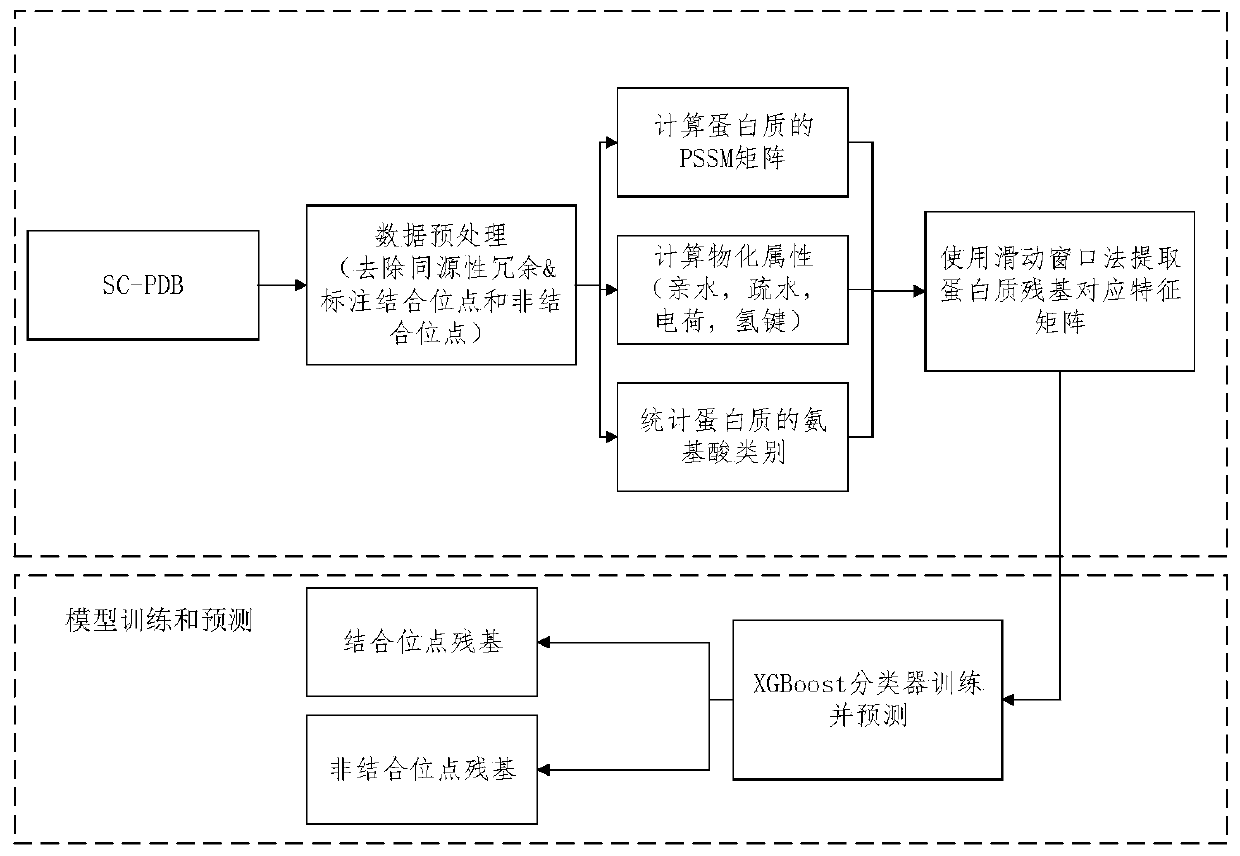
Protein and micromolecule binding site predicting method and predicting device
The invention relates to a protein and micromolecule binding site predicting method and a predicting device, wherein the method and the device belong to the field of micromolecule binding site predicting technology. The invention provides the new protein and micromolecule binding site predicting method. In the method, a sliding sampling window method is used for extracting data. A protein bindingfunction is affect by a binding residue surrounding environment. Therefore the sampling window method is used for extracting data for representing the characteristic of the residue at the central position, thereby realizing better representing effect. After an XGBoost classification model is constructed by means of the extracted characteristic, the classification model has better predicting effect, and the binding site between the protein and the micromolecule can be more accurately predicted.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com