Patents
Literature
76 results about "Raman scattering spectra" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
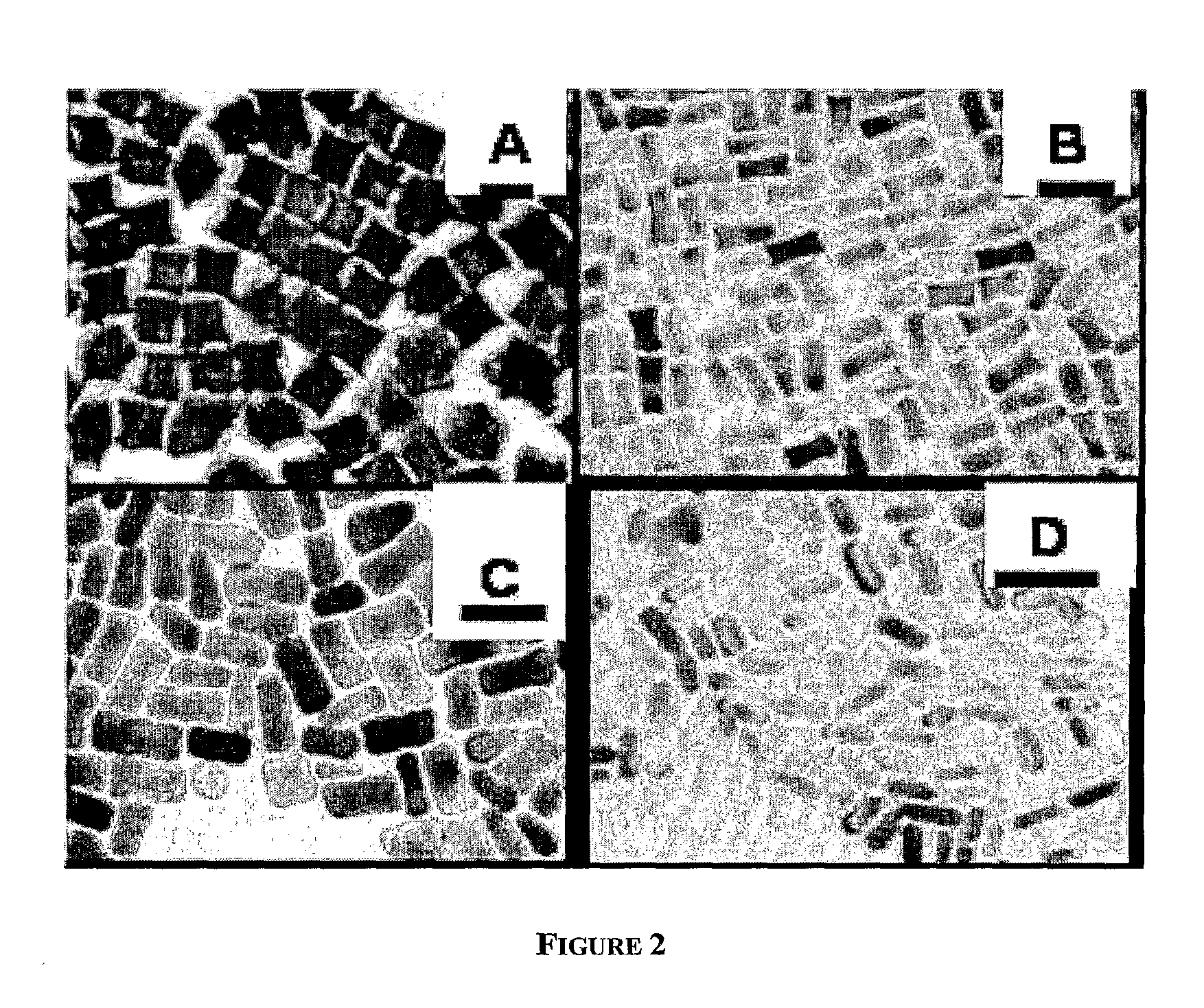
Method for preparing surface for obtaining surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectra of organic compounds
InactiveUS20050077184A1Easy to controlStable structureAnodisationWeather/light/corrosion resistanceSimple Organic CompoundsRaman scattering spectra
A surface-enhanced Raman scattering surface is prepared by anodizing an aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate with reversed polarity current to form pores of anodized oxide on the substrate, and electrodepositing silver or copper into the pores of the anodic oxide film to form needle-shaped metal particles in the pores of the anodic oxide film.
Owner:FETISOV IGOR V
Auto-focus raman spectrometer system
InactiveUS20160091366A1Simple structureFocusRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyExcitation beamLight beam
An autofocus Raman spectrometer system includes a laser probe assembly, a microprocessor, adjustable stages and a driving means. The laser probe assembly includes an excitation means, a focusing optics provided to focus an excitation beam from the excitation means onto a sample and generate Raman scattering spectrum, a collection optics for collecting the Raman scattering spectrum, and a spectrographic detector for generating a Raman spectrum based on the Raman scattering intensity received from the collection optics. The microprocessor receives the Raman spectra signal therefrom. The laser probe assembly is situated on the adjustable stage. The driving means is coupled to the microprocessor and configured to drive the stage to move with respect to the sample. The microprocessor generates a command to the driving means for moving a position of the adjustable stage to achieve an optimal optical focus based on signal intensity of the spectra peaks measured by the spectrographic detector.
Owner:YANG FR JIANN FU
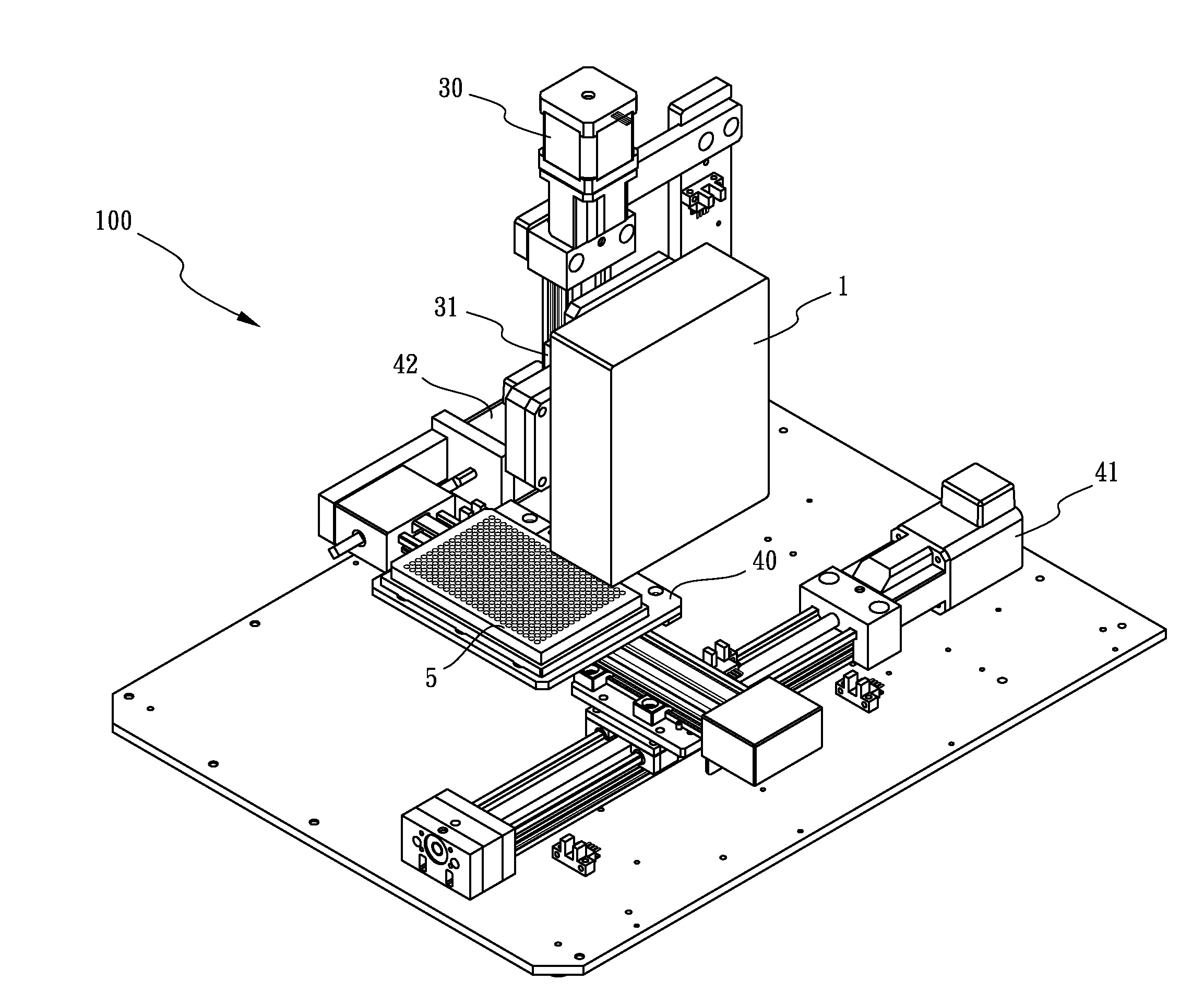
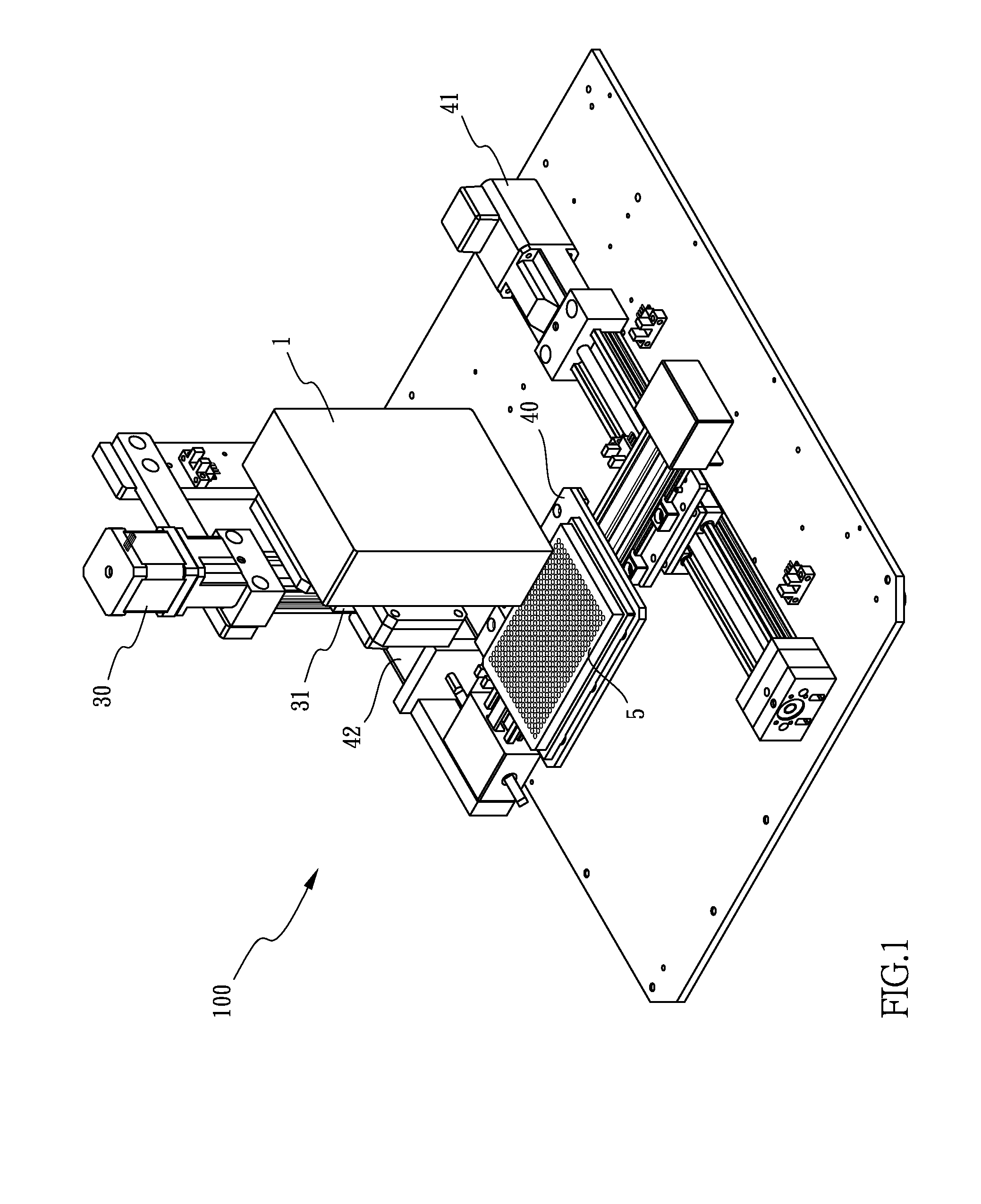
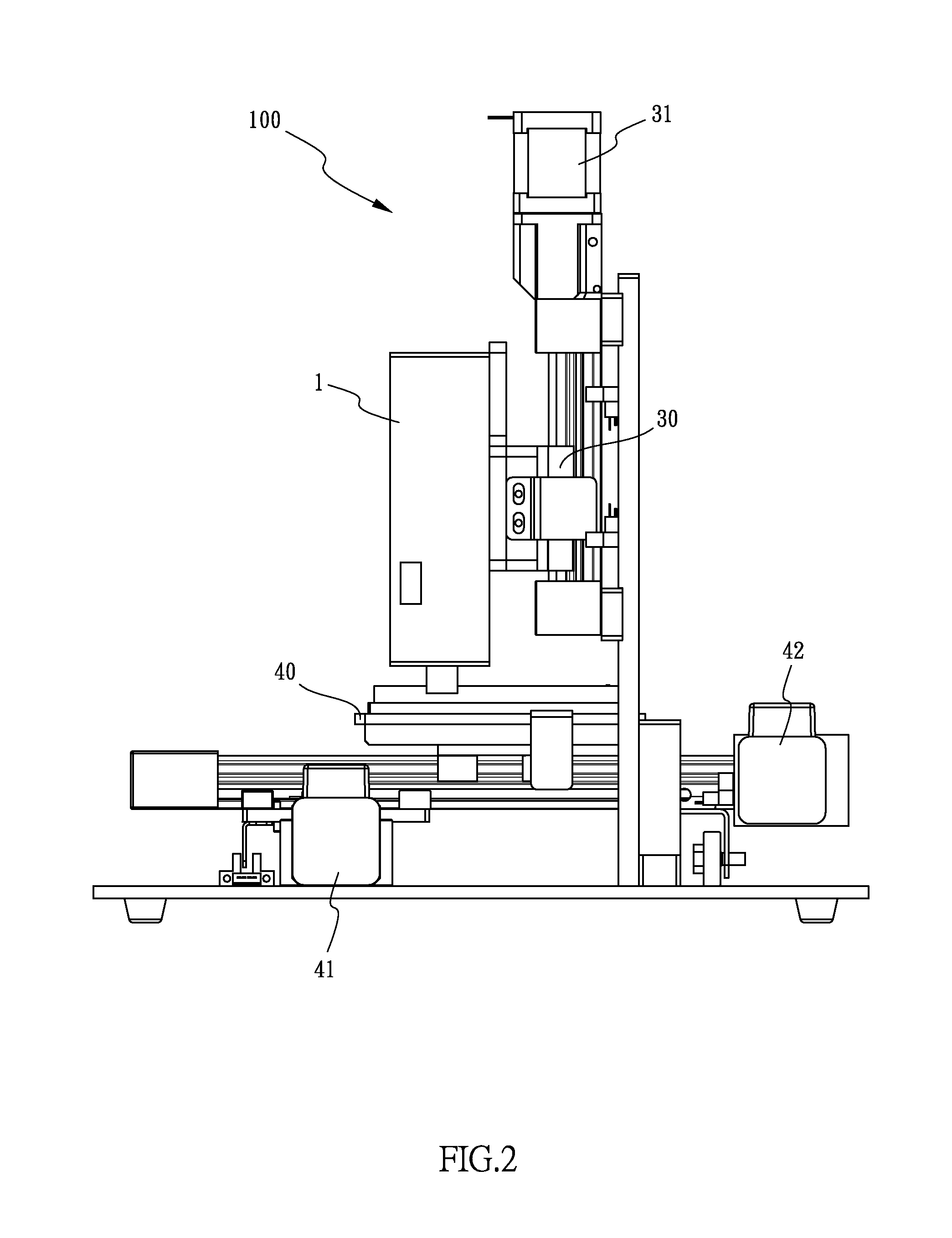
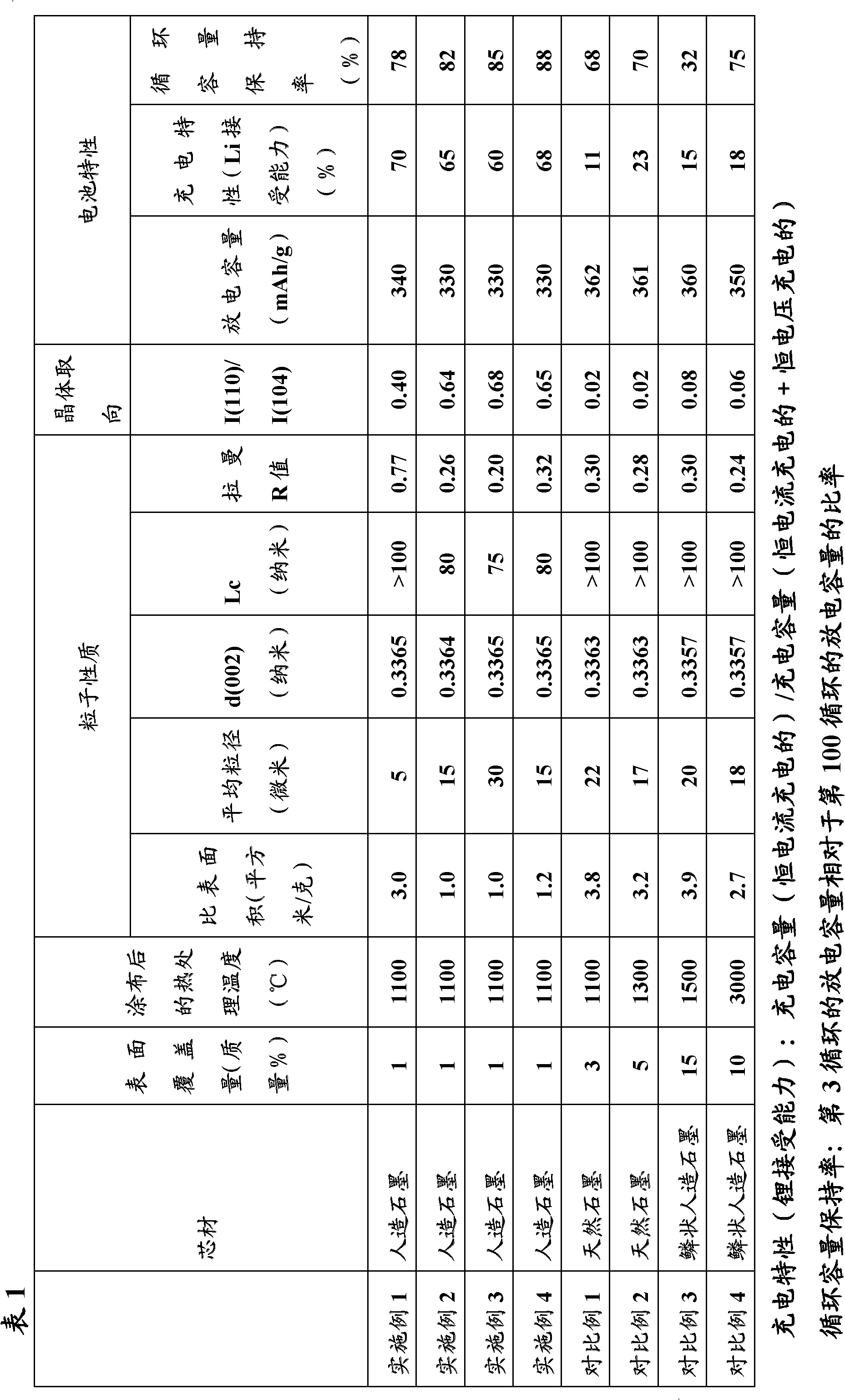
Composite graphite particles and lithium secondary battery using the same
InactiveCN102341346AImprove receptivityImprove featuresGraphiteCell electrodesRaman scattering spectraElectrical battery
The present invention provides composite graphite particles, which are useful for a negative electrode in a secondary battery having high capacitance, good charge- discharge characteristics and good charge-discharge cycle characteristics; and a paste for negative electrode, a negative electrode and a lithium secondary battery which use the composite graphite particles. The composite graphite particles of the present invention comprises a core material consisting of graphite having a interlayer distance d(002) of 0.337 nm or less in which the intensity ratio ID / IG (R value) between the peak intensity (ID) in a range of 1300 to 1400 cm-1 and the peak intensity ( IG ) in a range of 1580 to 1620 cm-1 as measured by Raman spectroscopy spectra is from 0.01 to 0.1 and a carbonaceous surface layer in which the intensity ratio ID / IG (R value) between the peak intensity (ID) in a range of 1300 to 1400 cm-1 and the peak intensity ( IG) in a range of 1580 to 1620 cm-1 as measured by Raman scattering spectroscopy is 0.2 or higher; wherein the peak intensity ratio I110 / I004 between the peak intensity (I004) of face (110) and the peak intensity (I004 ) of face (004) obtained by XRD measurement on the graphite crystal is 0.2 or higher when the particles are mixed with a binder and pressure-molded to a density of 1.55 to 1.65 g / cm3.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
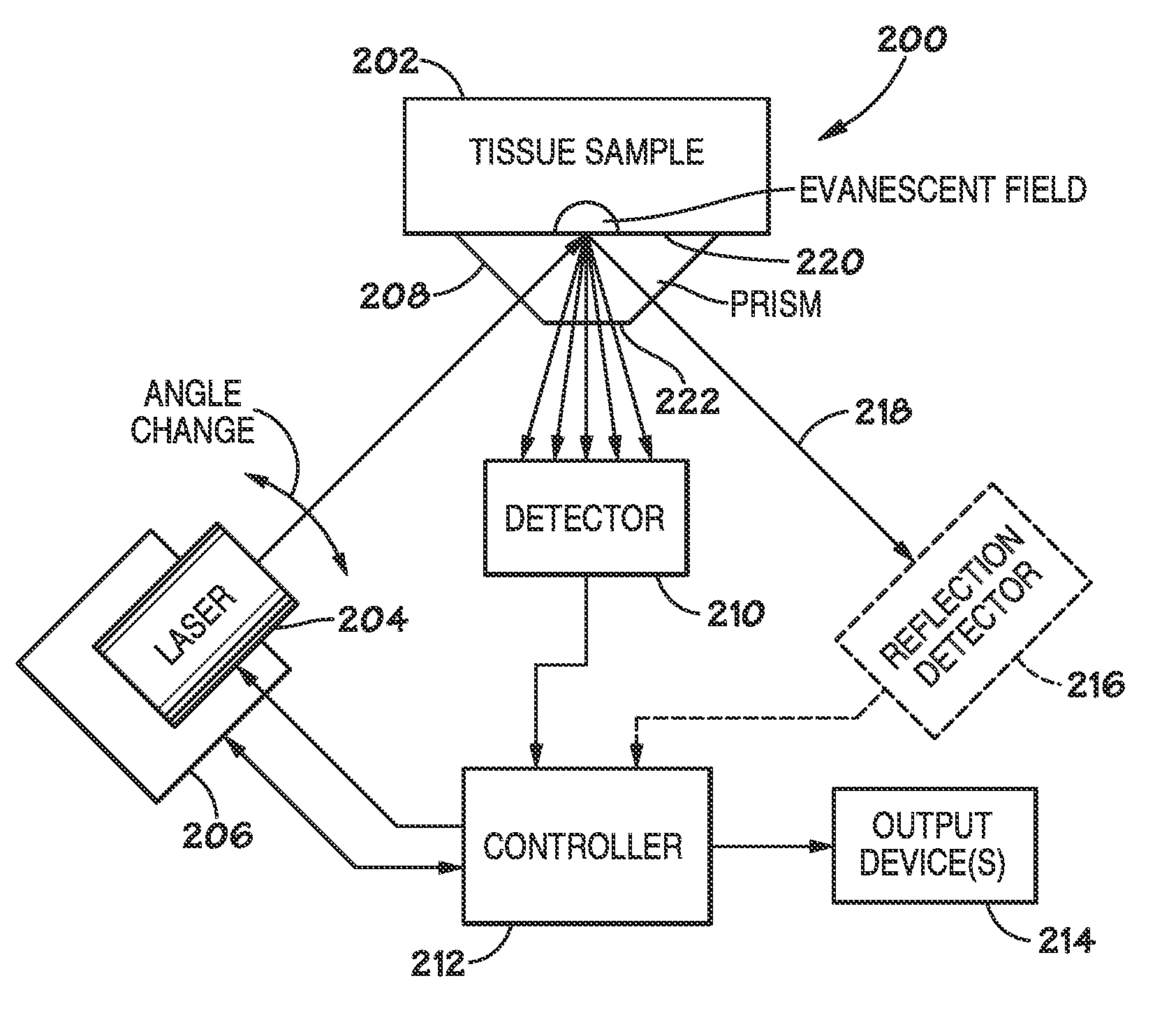
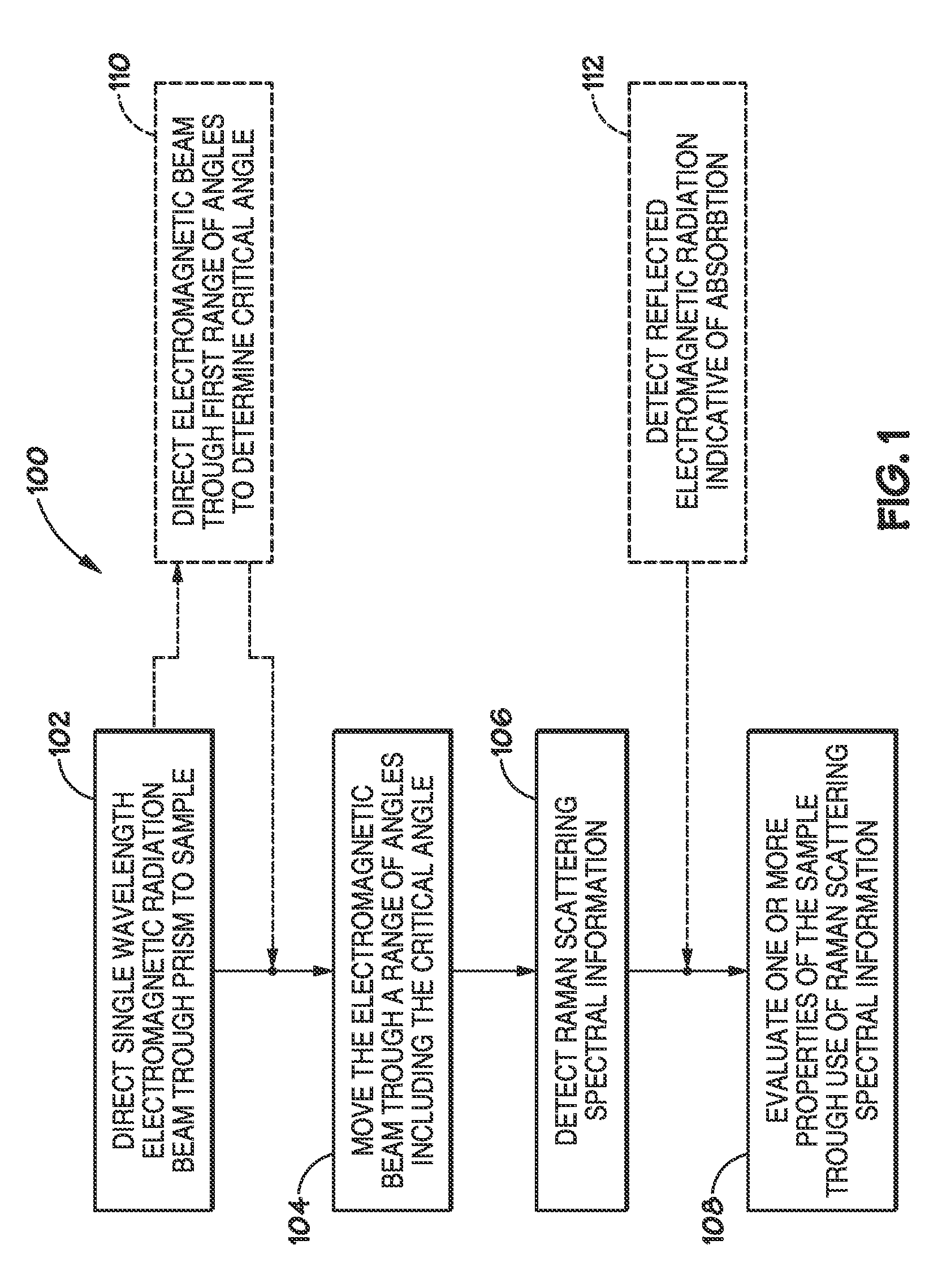
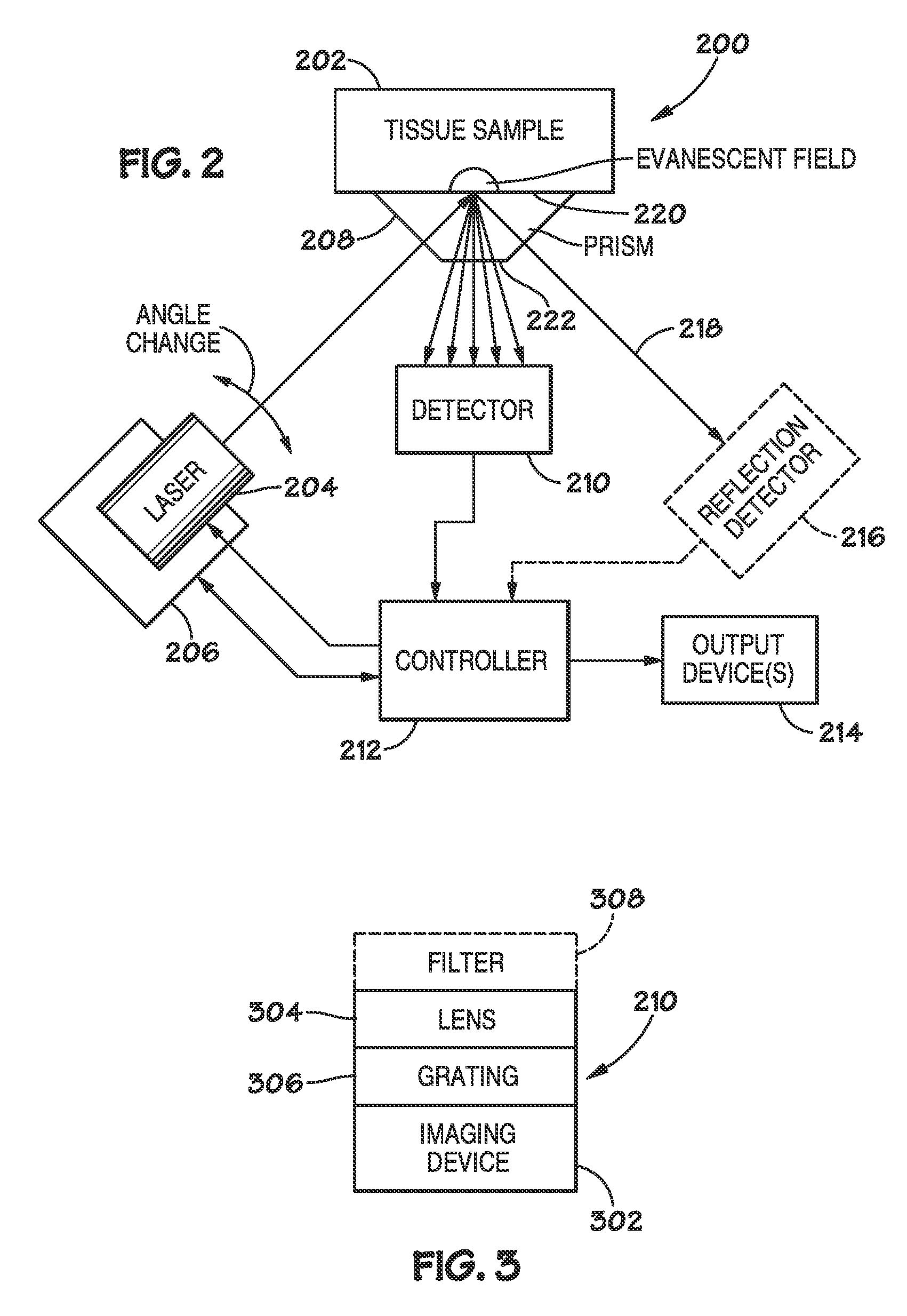
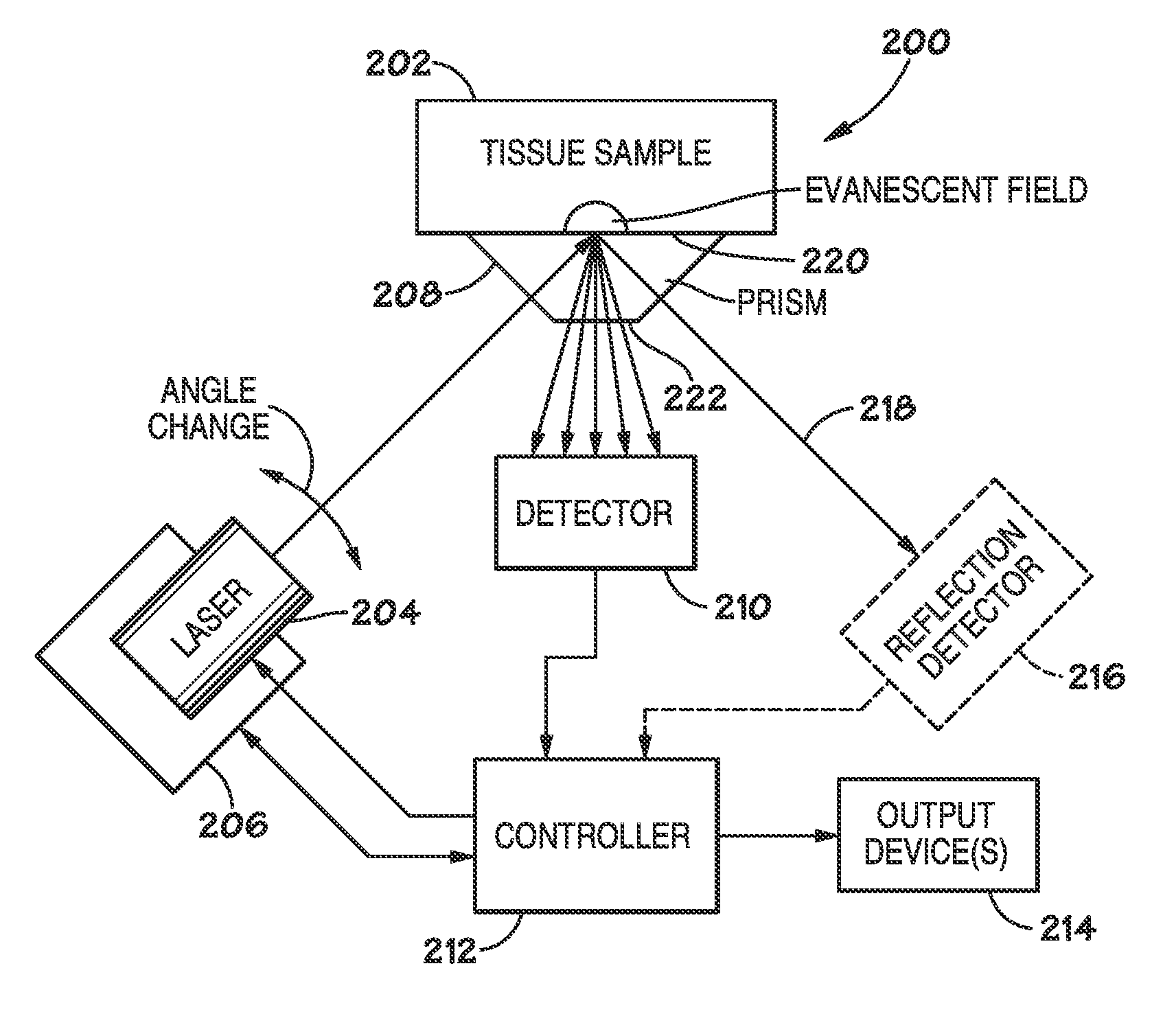
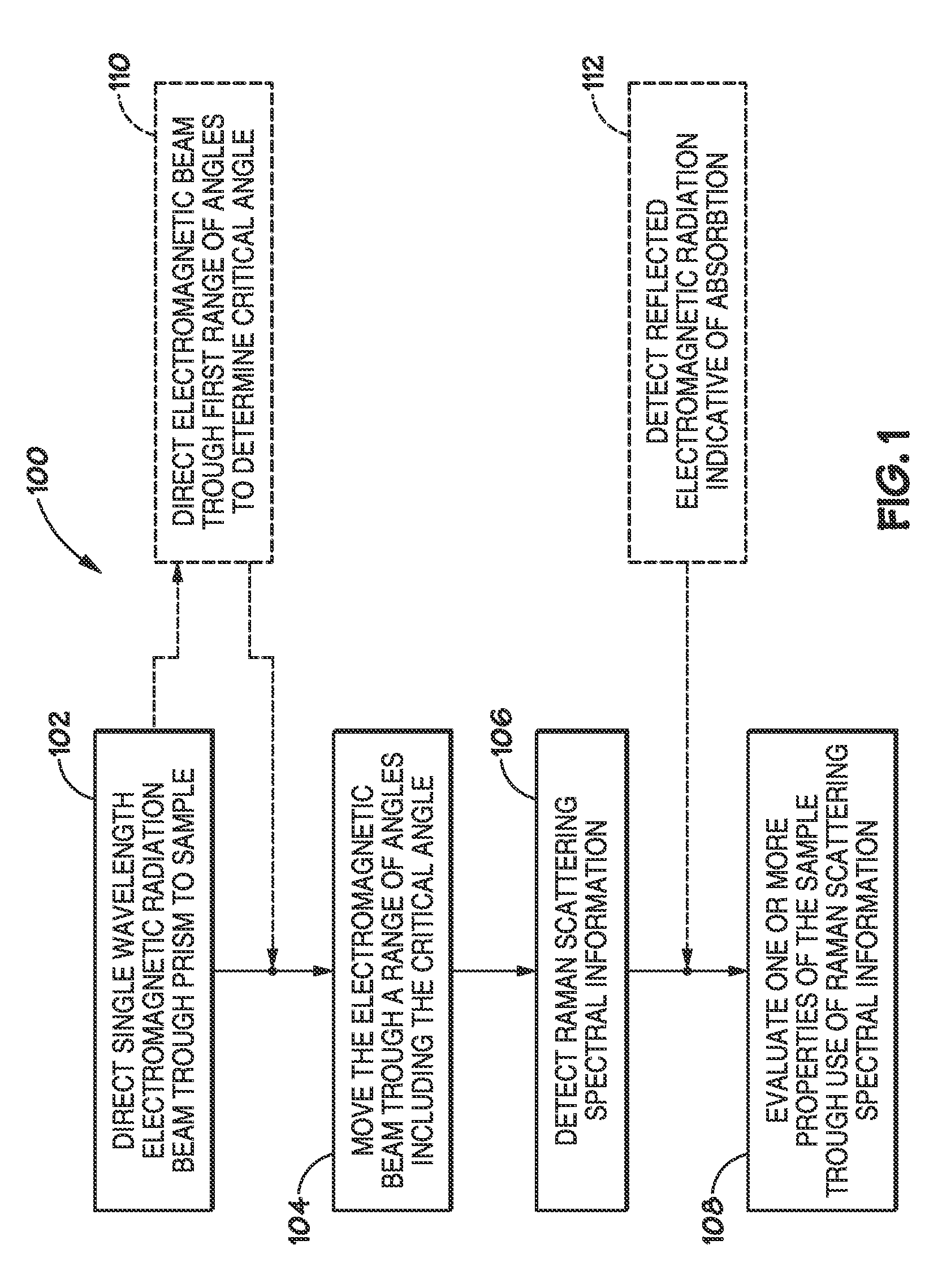
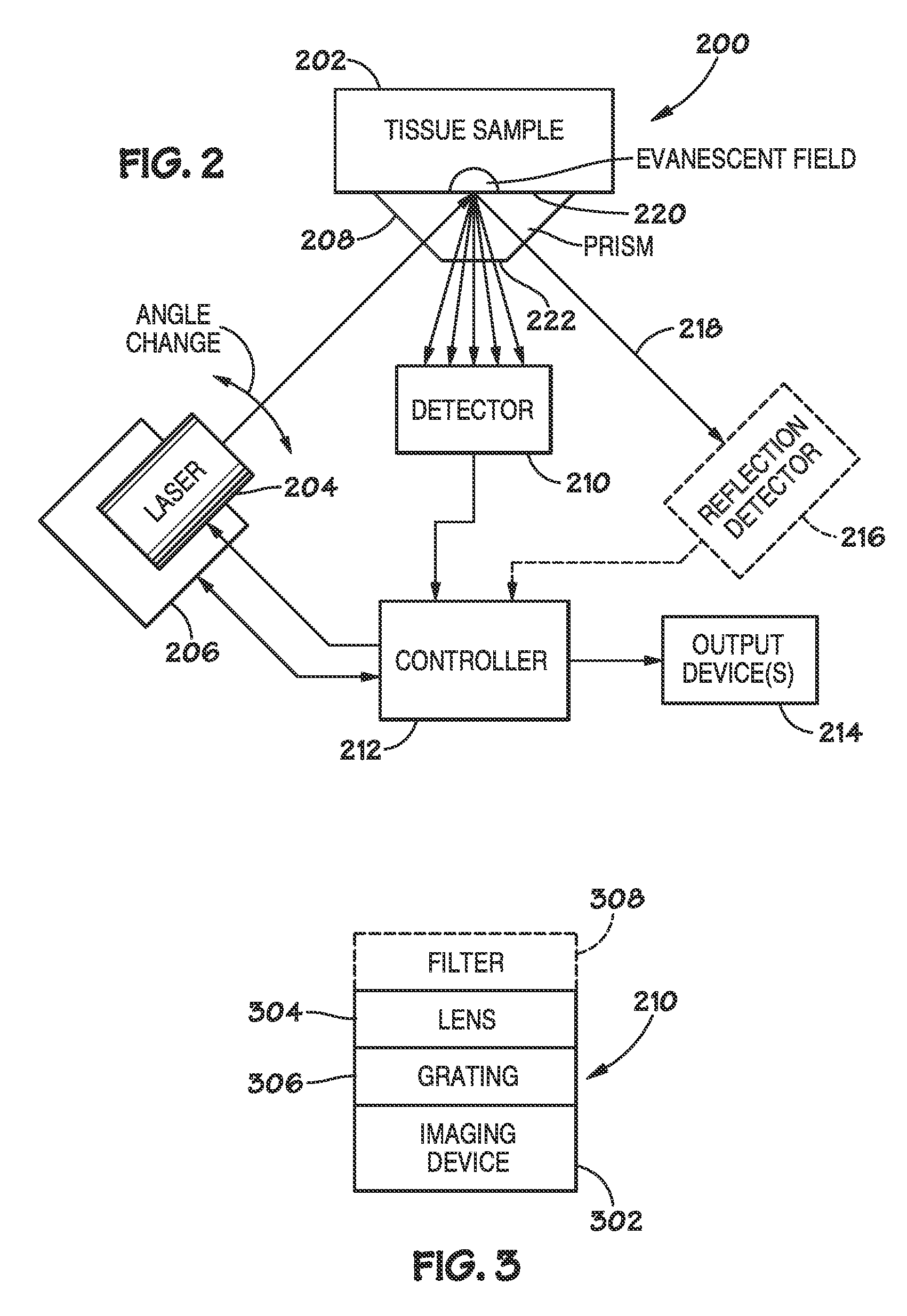
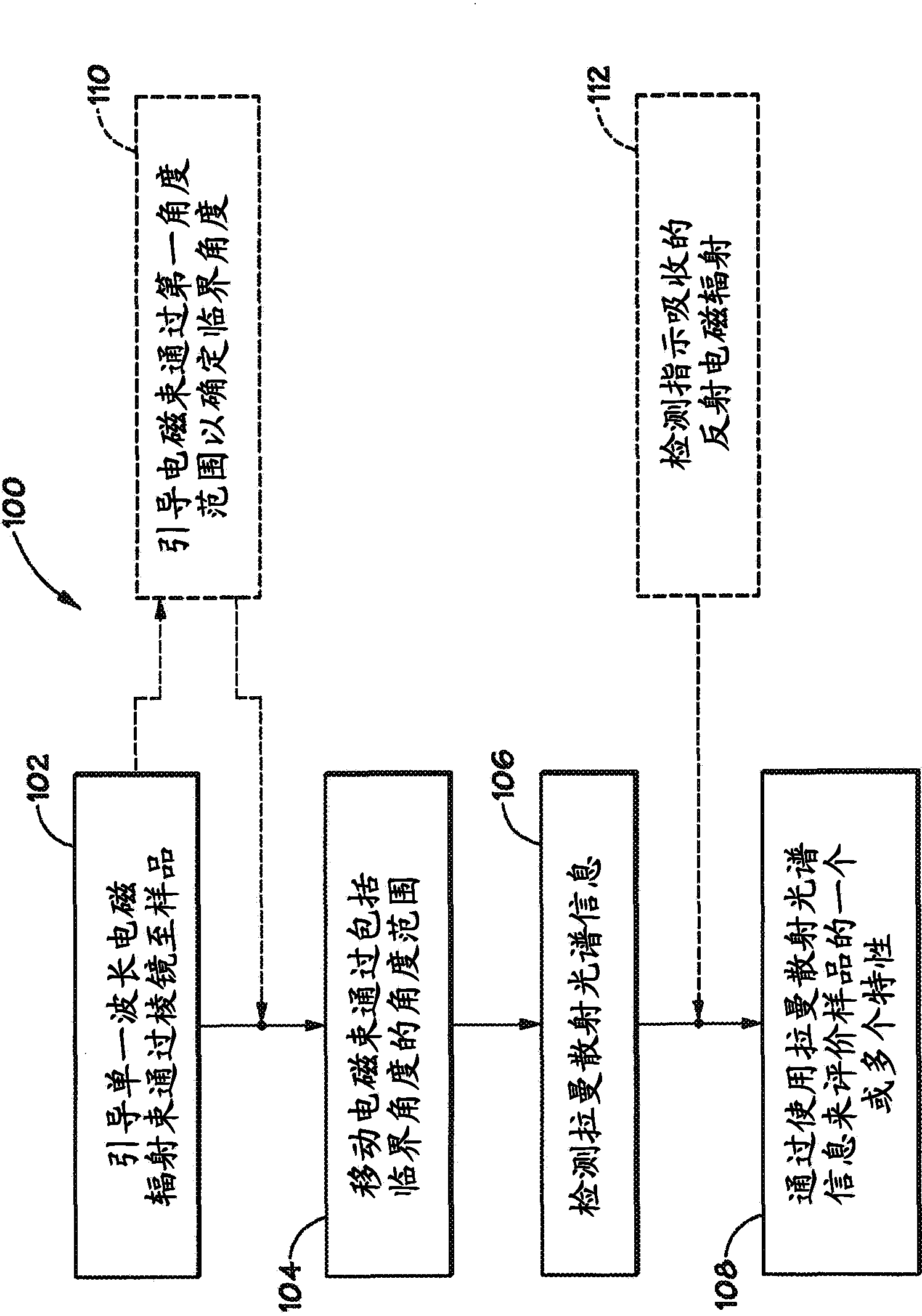
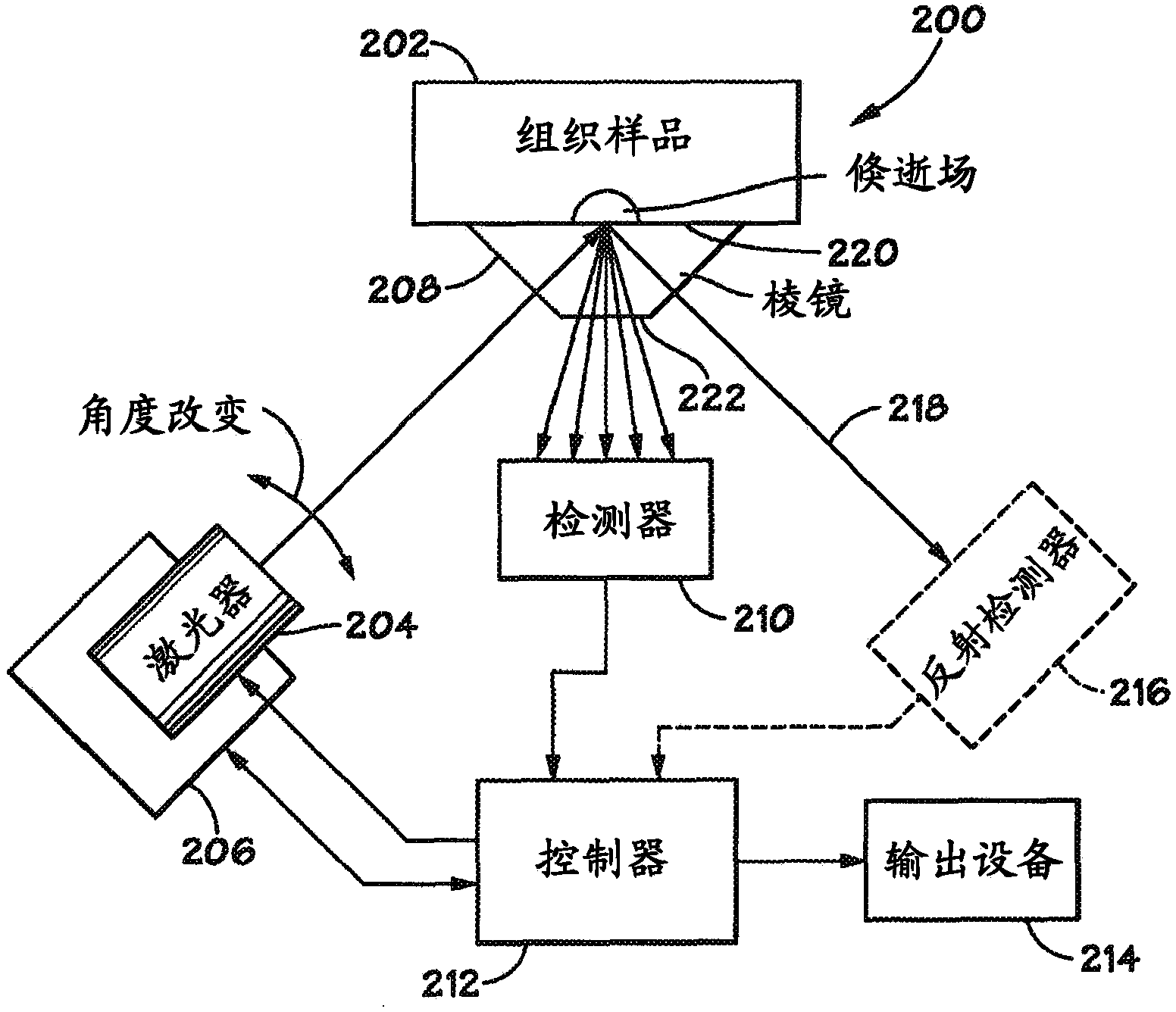
Method and apparatus for evaluating a sample through variable angle raman spectroscopy
InactiveUS20120274934A1Radiation pyrometryRaman scatteringAngle of incidenceRaman scattering spectra
Described are systems and methods for variable angle Raman spectroscopy, in which electromagnetic radiation will be caused to intersect the sample under investigation at a plurality of angles of incidence, so as to provide Raman scattering spectra at each angle. One example use of measuring such spectra at multiple angles of incidence is to enable evaluation at a plurality of depths within the sample. In many implementations, the range of the angles of incidence will include, and extend to either side, of the critical angle.
Owner:AVOLONTE HEALTH
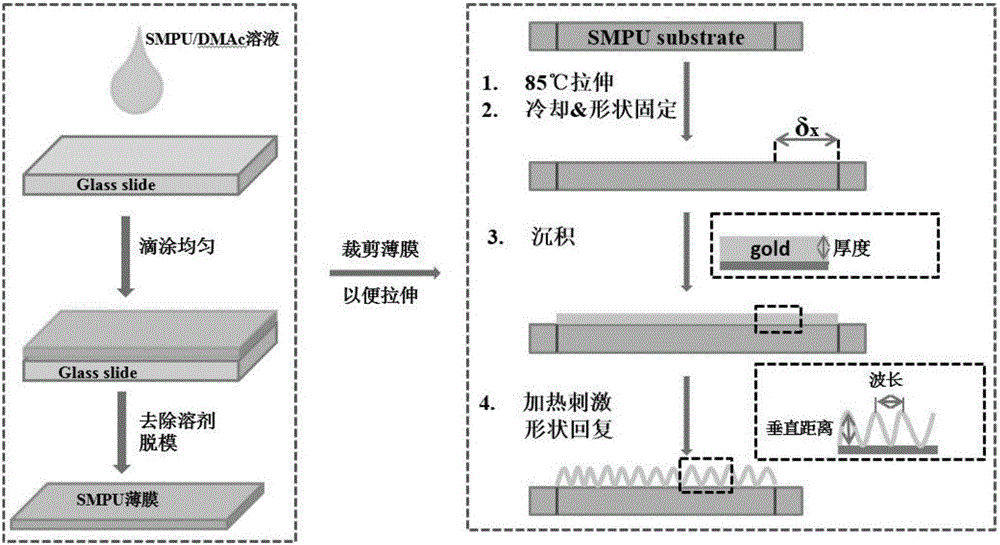
Precious-metal micro-nanometer structure and preparing method and application thereof
InactiveCN105891185AEnhance activity is goodHigh sensitivityMaterial nanotechnologyRaman scatteringRoom temperatureNanostructure
The invention discloses a precious-metal micro-nanometer structure and a preparing method and application thereof. The preparing method includes the steps that a thermotropic shape-memory high-polymer material is dissolved to be coated and dried to obtain a shape-memory high-polymer film; at the specific temperature, the shape-memory high-polymer film is stretched 10% to 30%, the stretched shape-memory high-polymer film is naturally cooled to the room temperature, the shape-memory high-polymer film is kept the stretched state, a precious-metal nanometer particle layer is prepared on the surface of the stretched shape-memory high-polymer film, the product is put into the environment with the specific temperature, the stretched shape-memory high-polymer film is recovered to the original size in the stretched direction accordingly, and the precious-metal micro-nanometer structure is obtained. According to the preparing method, the precious-metal micro-nanometer structure with the special three-dimensional structure is prepared through the characteristic of the shape-memory high-polymer material, the prepared precious-metal micro-nanometer structure is used as a surface-enhanced-raman-scattering-spectroscopy active substrate, and the detection sensitivity can be remarkably improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
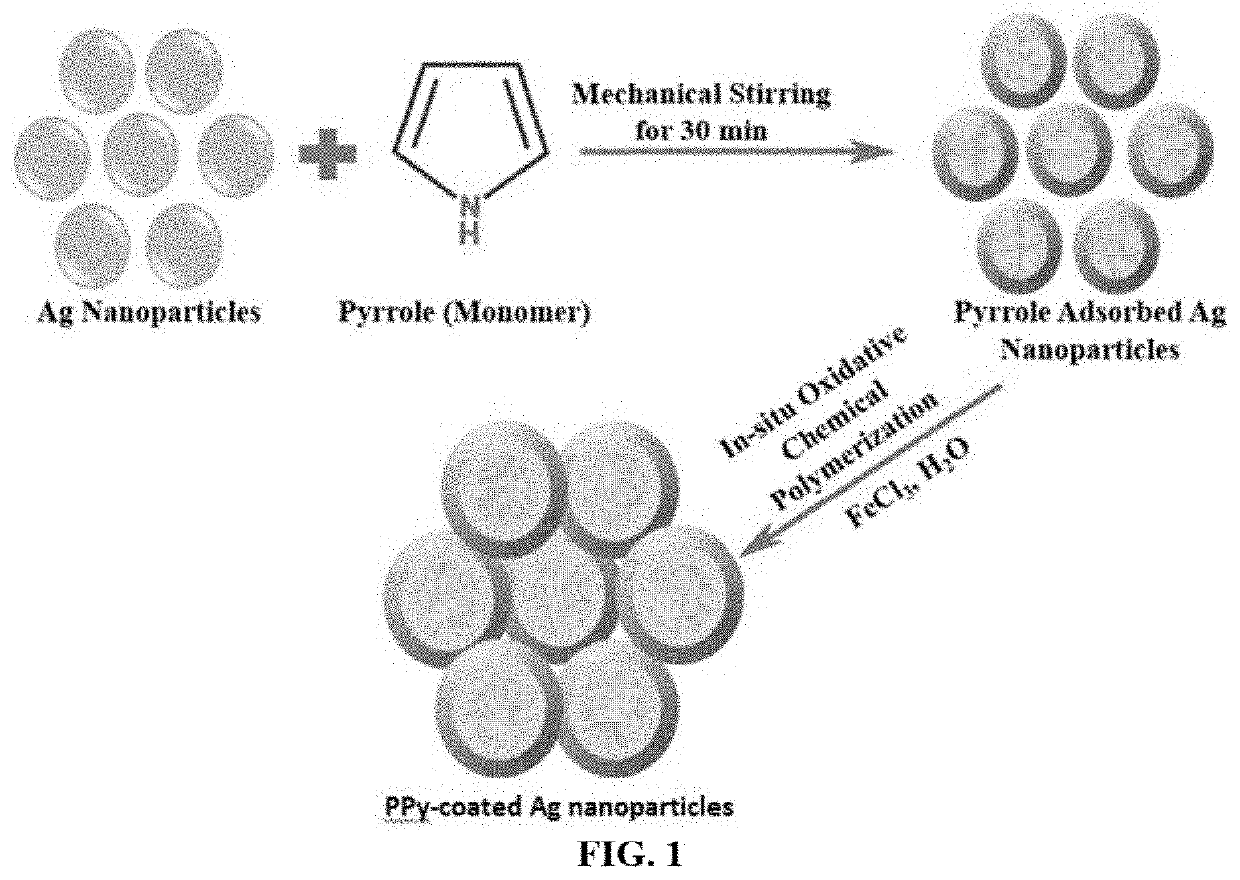
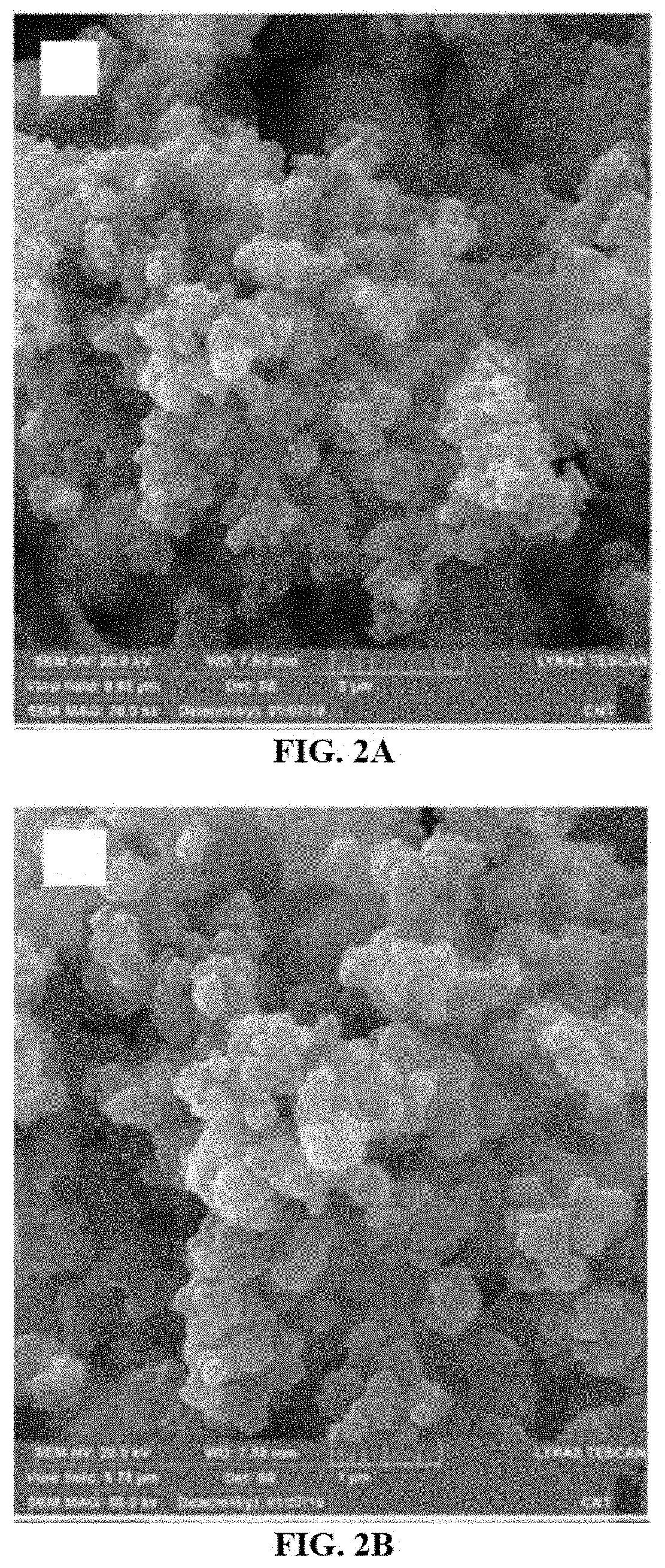
Polypyrrole-coated silver particles for surface enhanced Raman scattering
A method of fabricating polypyrrole-coated silver particles having a core-shell structure via in-situ oxidative polymerization using silver nanoparticles and pyrrole monomers in the presence of an oxidizing agent. A surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) active substrate comprising the polypyrrole-coated silver particles is also disclosed. The surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) active substrate is demonstrated to facilitate the detection and measurement of surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) spectra of analytes with increased Raman signal intensity.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Electrophotographic photoconductor and method for producing the same, image forming apparatus, and process cartridge
InactiveUS20090035017A1Reduction of the residual potentialImprove mobilityElectrographic process apparatusCorona dischargeElectrical conductorRaman scattering spectra
There is provided an electrophotographic photoconductor containing a conductive substrate, and a photosensitive layer, disposed thereon, containing a charge transporting material having a triarylamine structure represented by General Formula 1, and wherein the photosensitive layer satisfies Mathematical Formula 1 when peak heights in raman scattering spectra of the triarylamine structure are measured at a wavenumber of 1,324±2 cm−1 by a confocal raman spectroscopy using z-polarized light:where Ar1, Ar2, and Ar3 are substituted or unsubstituted aromatic hydrocarbon groups, and Ar1 and Ar2, Ar2 and Ar3, and Ar3 and Ar1 are optionally combined to form heterocyclic rings, respectively,ε=I(inside) / I(surface)≧1.1 Mathematical Formula 1where I(inside) represents the peak height in of the raman scattering spectrum obtained at a depth of 5 μm or more from the photosensitive layer surface and I(surface) represents the peak height in the raman scattering spectrum obtained at a depth of less than 5 μm from the photosensitive layer surface.
Owner:RICOH KK
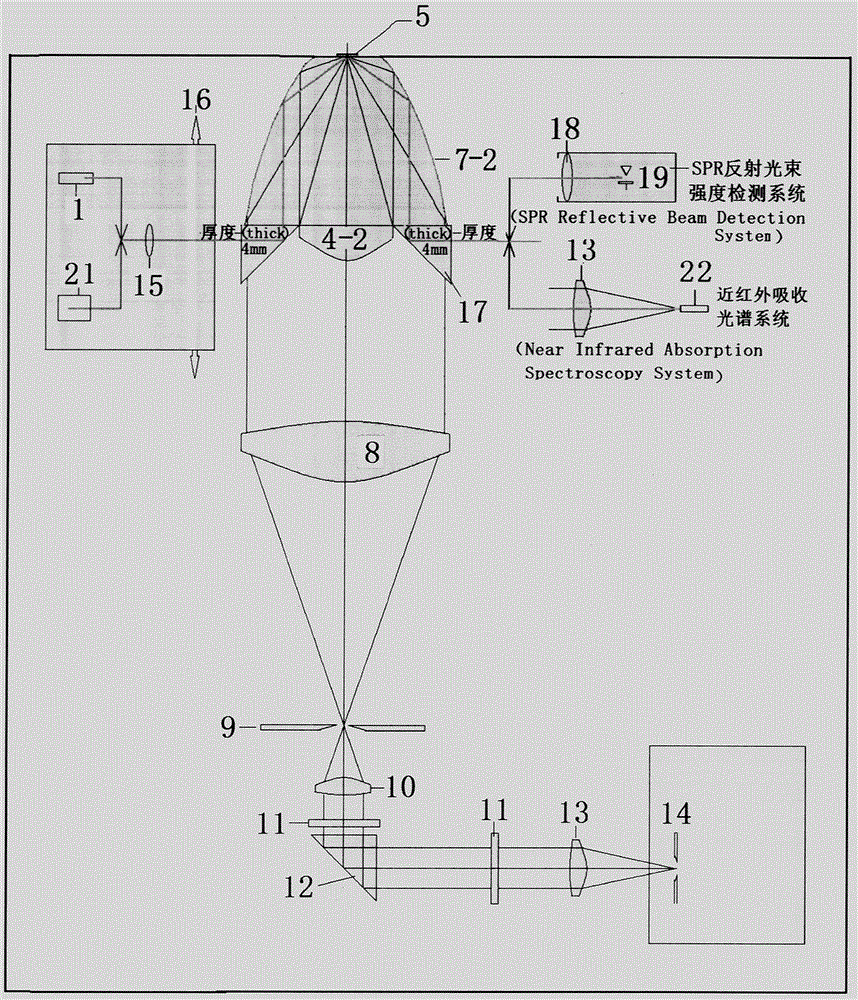
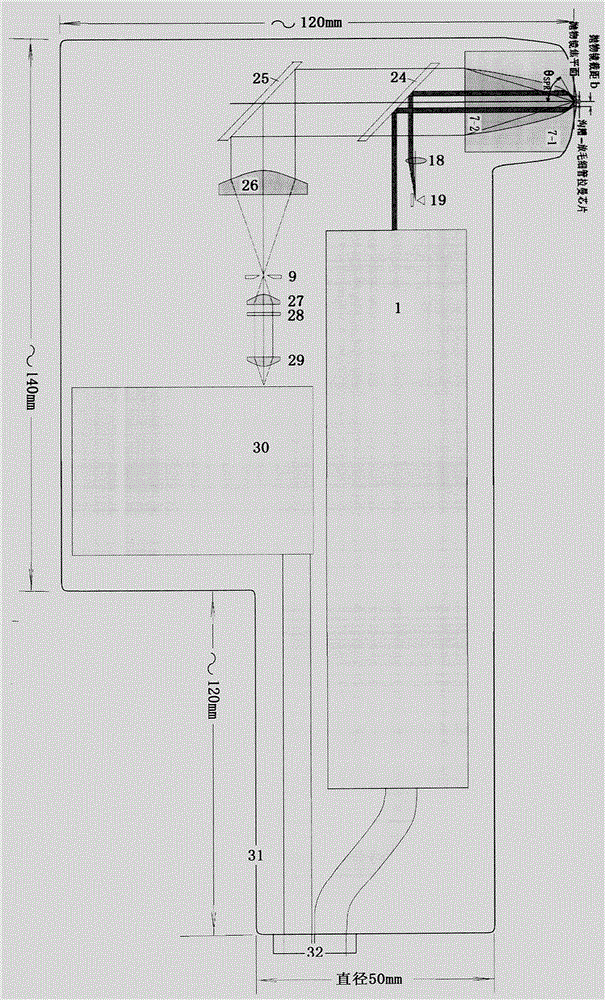
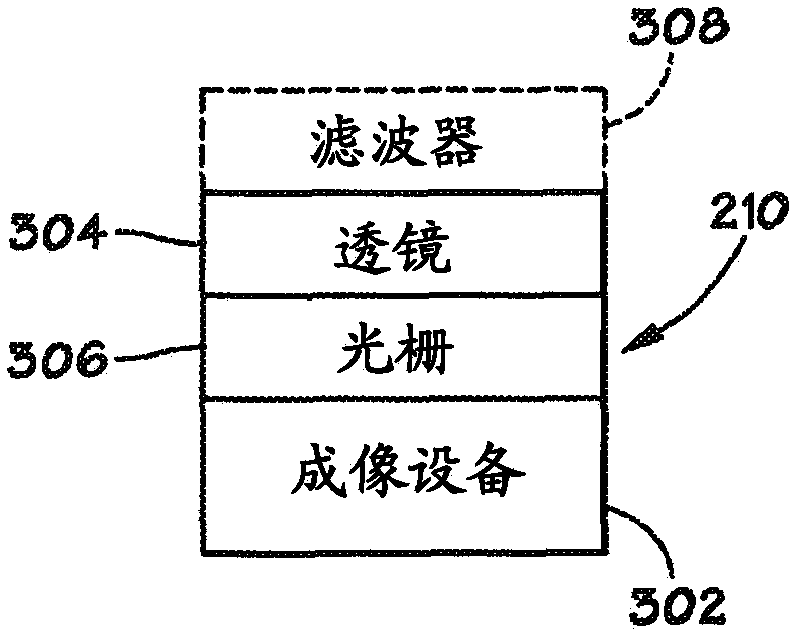
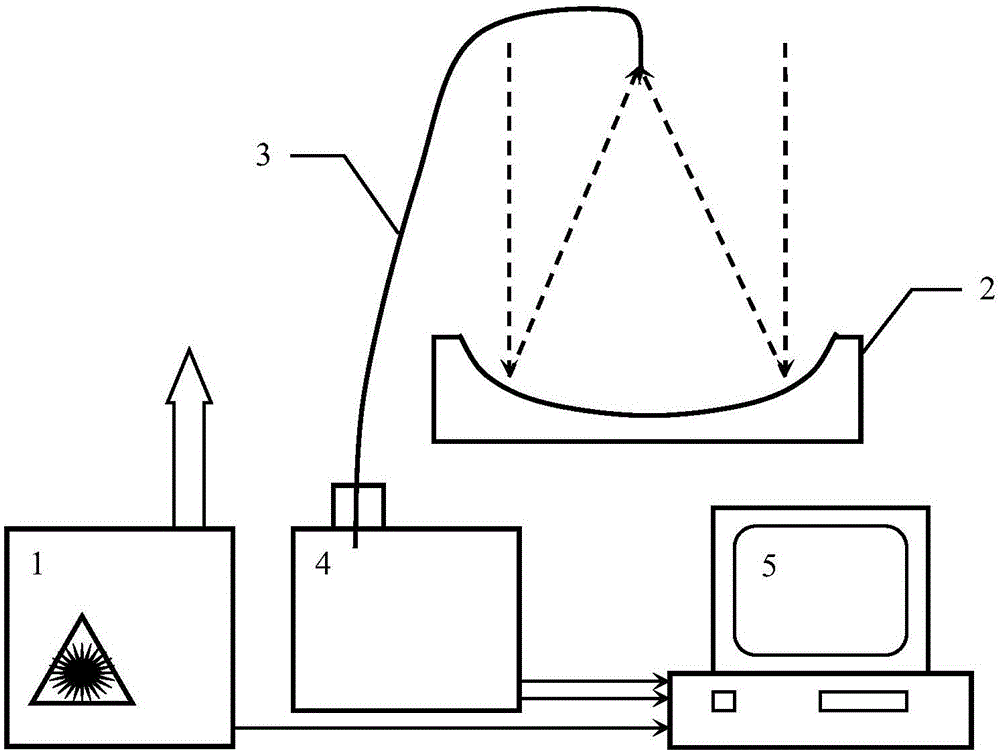
Equipment for using full-aperture angle parabolic mirror to collect surface-enhanced Raman Scattering spectra
The invention relates to the field of Raman spectrographs, and discloses equipment for using a full-aperture angle parabolic mirror to collect surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectra. The invention aims to provide an extra-high sensitive Raman probe for current multiple kinds of portable fiber Raman spectrographs and upgrade the extra-high sensitive Raman probe; to develop a small-size extra-high sensitive SERS Raman spectrograph, an SPR Raman spectrum probe, a spectrograph, an SPR Raman spectrograph with triple functions of Raman / two-spectrum and refractive index absorption, a streaming particle reinforcing Raman analysis probe, and a near-ultraviolet Raman spectrograph. According to the technical scheme, a full-aperture angle of the parabolic mirror is adopted to collect Raman scattering; a high numerical aperture objective lens which is confocal with the parabolic mirror is arranged, a sample is stimulated by a high-quality focusing single-mode laser beam, and an SERS hyper-enhanced factor is guaranteed; Raman enhancement in an SPR mode is achieved, extra-high sensitivity is achieved and the like. The new generation of portable and handheld Raman spectrograph can be widely used in various kinds of trace analysis such as food security screening, cancer screening, environmental monitoring, and war agent detection.
Owner:大连世佩达光谱智能检测科技有限公司
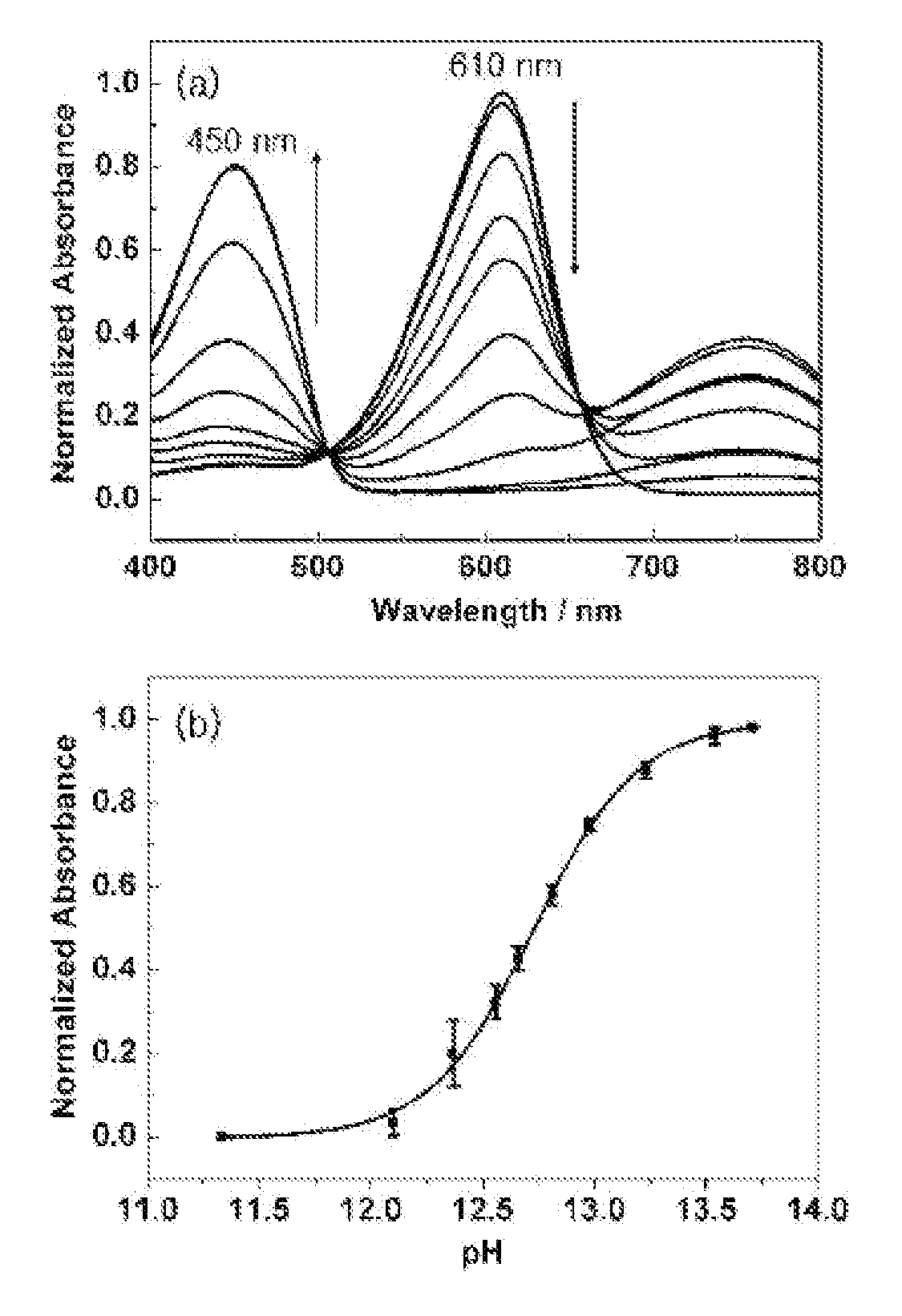
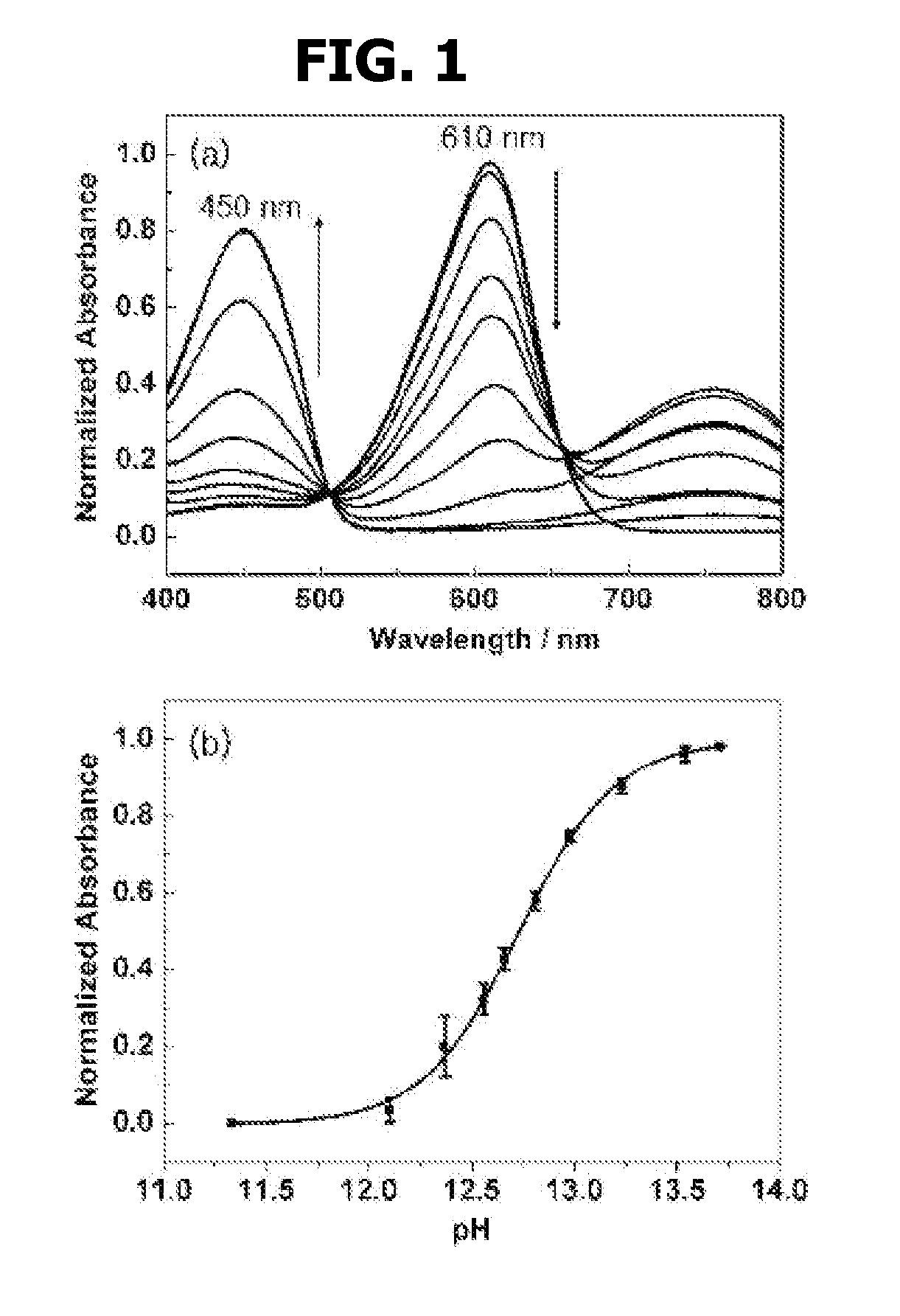
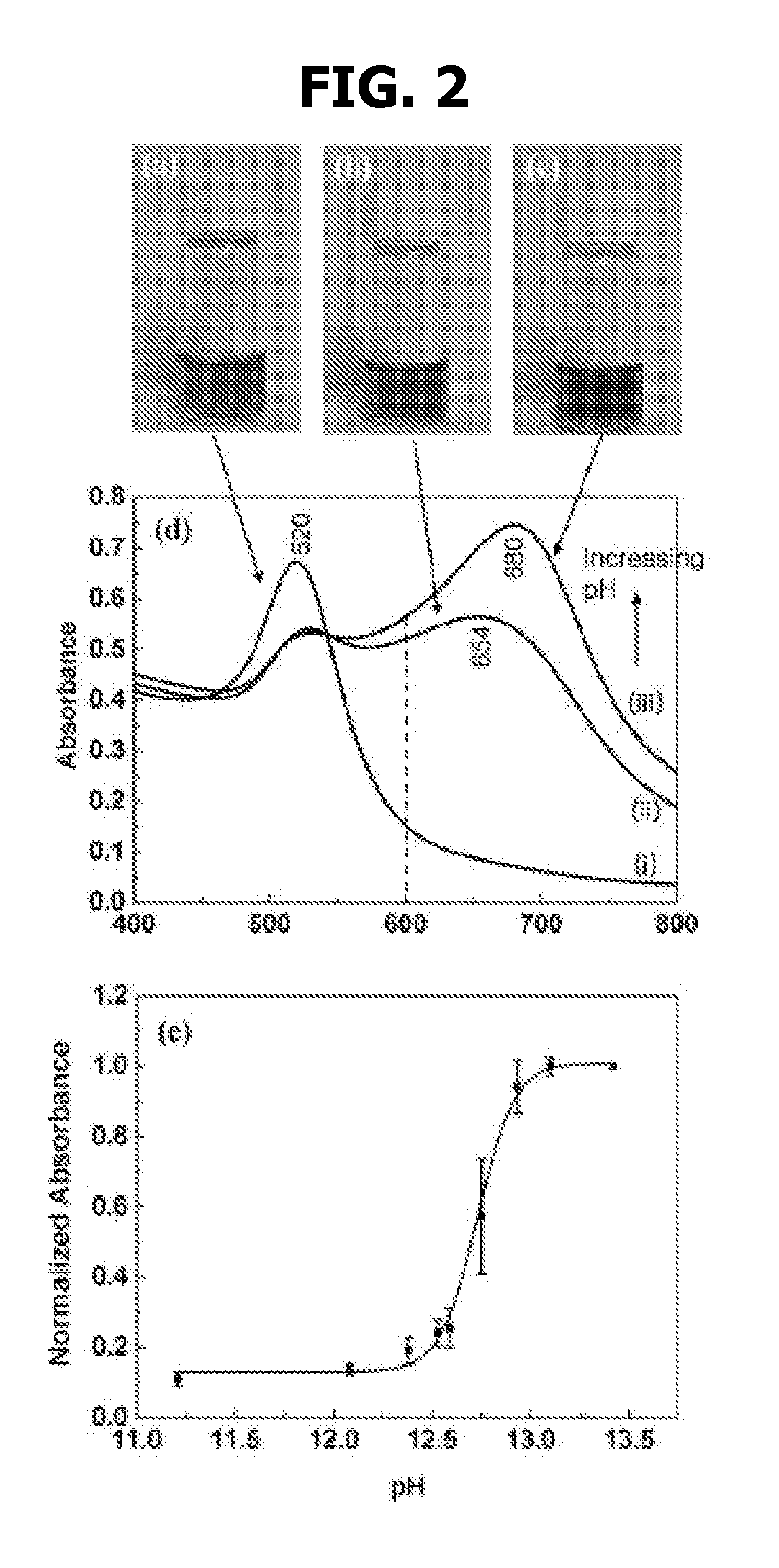
GOLD NANOPARTICLE-BASED pH SENSOR IN HIGHLY ALKALINE REGION BY SURFACE-ENHANCED RAMAN SCATTERING STUDY
InactiveUS20080202195A1Material nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureCITRATE ESTERRaman scattering spectra
Disclosed are a pH sensor for use in a highly alkaline region of pH >11 comprising citrate-reduced gold nanoparticles and a method for calibrating pH of a solution in highly alkaline regions, based on variation in surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectra (SERS).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
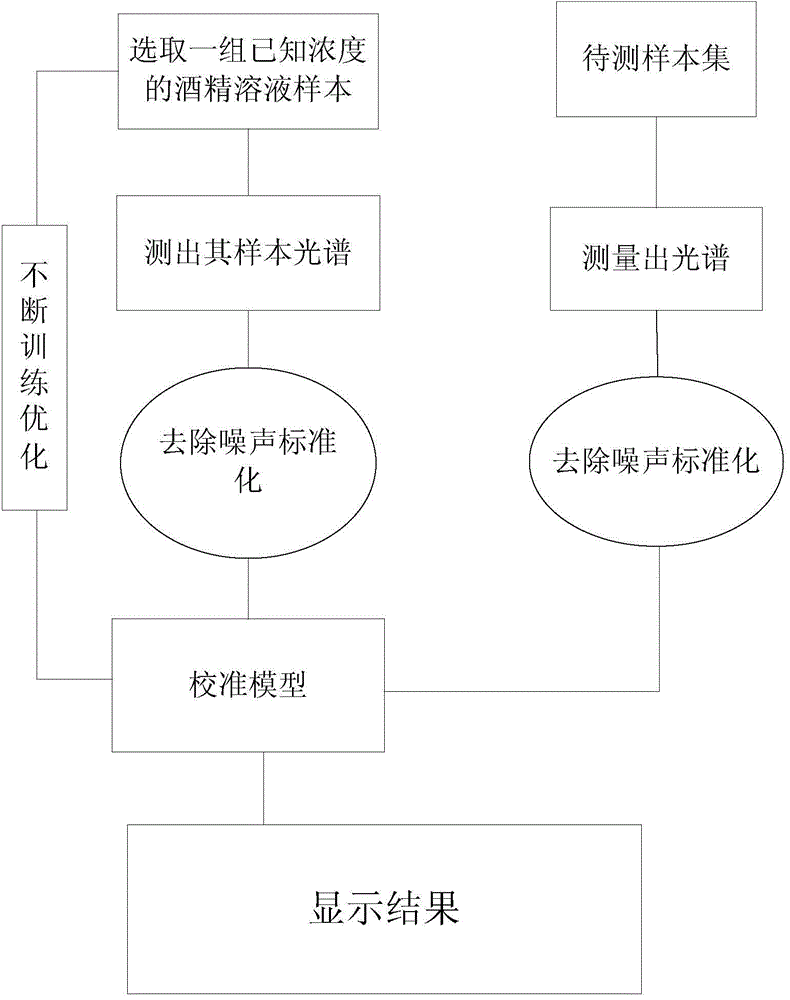
Method and system for noninvasively detecting blood alcohol content based on Raman scattering
The invention relates to a method and a system for noninvasively detecting a blood alcohol content based on Raman scattering. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring Raman scattering spectrum information of one group of alcohol solution blood samples with known concentration by adopting a transmission and reflection manner, establishing a quantitative mathematic relation between a blood alcohol concentration and the Raman peak strength of a Raman scattering spectrum to form a calibrating model; training the calibrating model and obtaining an optimal calibrating model; acquiring Raman scattering spectrum information of to-be-detected blood of a human body by adopting a transmission and reflection manner, and establishing a to-be-tested sample set; and denoising the obtained to-be-tested sample set by using a wavelet analysis method; and obtaining an alcohol concentration predicted value of detecting the blood of the human body by using the to-be-tested sample set as the input of the optical calibrating model. The system comprises a laser emitting module, a signal receiving module, a signal processing module and a digital display module which are sequentially connected. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of rapidness, real time, noninvasive effect and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Method and apparatus for evaluating a sample through variable angle Raman spectroscopy
InactiveUS8970838B2Radiation pyrometryScattering properties measurementsAngle of incidenceRaman scattering spectra
Described are systems and methods for variable angle Raman spectroscopy, in which electromagnetic radiation will be caused to intersect the sample under investigation at a plurality of angles of incidence, so as to provide Raman scattering spectra at each angle. One example use of measuring such spectra at multiple angles of incidence is to enable evaluation at a plurality of depths within the sample. In many implementations, the range of the angles of incidence will include, and extend to either side, of the critical angle.
Owner:AVOLONTE HEALTH
Automatic classification detecting method for multiple analytes based on surface enhancement Raman scattering technology
InactiveCN104535555ASimple and fast operationImprove efficiencyRaman scatteringTarget analysisAnalyte
The invention relates to an automatic classification detecting method for multiple analytes based on the surface enhancement Raman scattering technology. According to the automatic classification detecting method, a nanogold mixed solution formed by integrating three water-soluble polymers which contain Raman active molecules on the surfaces and are capable of specifically recognizing the target analytes serves as a probe, a water solution containing Pb2+ and a water solution containing Ag+ and a water solution containing Cu2+ are mixed with the nanogold mixed solution respectively or at the same time, detecting is carried out through enhancement of a Raman scattering spectrum, efficient automatic classification selectivity for Pb2+, Ag+ and Cu2+ is achieved through the detection, and therefore the three ions and corresponding contents of the three ions can be identified at the same time. According to the automatic classification detecting method, operation is easy and convenient, sensitivity is high, and wide application prospects are achieved in the fields such as biomedicine and environment monitoring.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Method and apparatus for evaluating a sample through variable angle Raman spectroscopy
Described are systems and methods for variable angle Raman spectroscopy, in which electromagnetic radiation will be caused to intersect the sample under investigation at a plurality of angles of incidence, so as to provide Raman scattering spectra at each angle. One example use of measuring such spectra at multiple angles of incidence is to enable evaluation at a plurality of depths within the sample. In many implementations, the range of the angles of incidence will include, and extend to either side, of the critical angle.
Owner:AVOLONTE HEALTH
Electrically conducting polymer and production method and use thereof
InactiveUS20070021546A1Threshold value can be loweredHigh aspect ratioNon-metal conductorsConductive materialRaman scatteringMelt viscosity
The invention provides a production method of a conductive polymer, comprising a step of blending a polymer in a state of a melt viscosity of 600 Pa·s or less at a shear rate of 100 s−1 with a vapor grown carbon fiber in 1 to 15 mass at a mixing energy of 1,000 mJ / m3 or less, and a conductive polymer obtained thereby. Preferably, a vapor grown carbon fiber used has an outer fiber diameter of 80 to 500 nm, an aspect ratio of 40 to 1,000, a BET specific surface area of 4: to 30 m2 / g, a do02 of 0.345 nm or less according to an X-ray diffraction method, and a ratio (Id / Ig) of 0.1 to 2 wherein Id and Ig each represent peak heights of a band ranging from 1,341 to 1,349 cm−1 and a band ranging from 1,570 to 1,578 cm−1 respectively, according to a Raman scattering spectrum. According to the invention, an excellent conductivity can be attained by compounding vapor grown carbon fiber in a smaller amount than in a conventional method.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
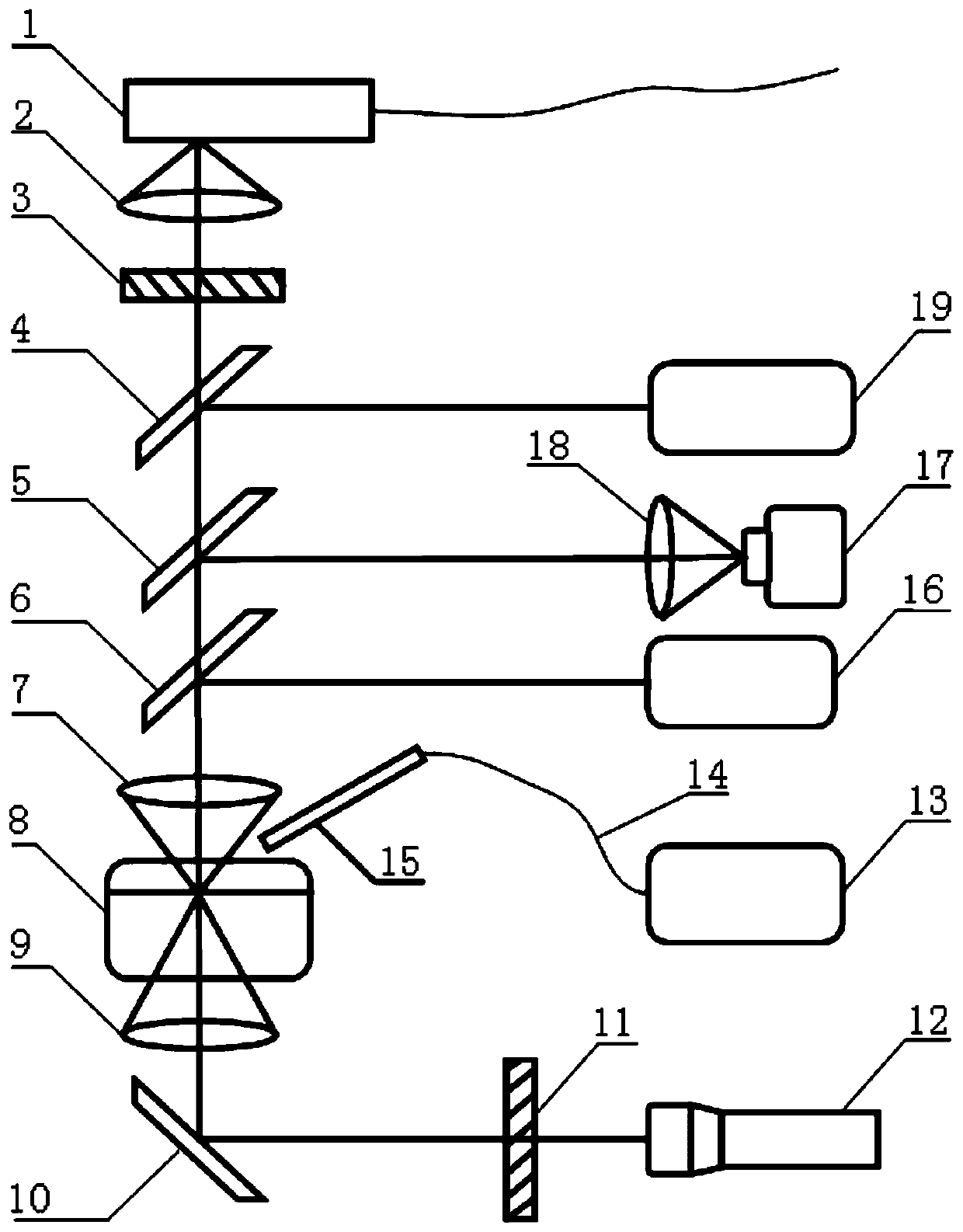
Single-particle detection system based on Raman and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy integration
InactiveCN111077060ANo preprocessing requiredRealize double detection functionRaman scatteringAnalysis by thermal excitationMicro imagingHigh energy
The invention discloses a single-particle detection system based on Raman and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy integration. The single-particle detection system comprises an objective table, an illumination unit, a microscopic imaging unit, a Raman detection unit and a laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy detection unit. Single particles are placed on the objective table, the positions of thesingle particles can be precisely adjusted in a two-dimensional mode, and the microscopic imaging unit collects images of the single particles. The Raman detection unit comprises a continuous operation laser device and a first spectrograph, the continuous operation laser device irradiates the surfaces of the single particles, excites the vibration mode of molecules contained in the single particles and generates scattered photons with the frequency different from that of the exciting light, and the first spectrograph records a Raman scattering spectrum to analyze molecular information of the single particles. The laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy detection unit comprises a pulse laser and a second spectrograph, the pulse laser generates high-energy nanosecond pulses, and a high-intensity electric field of the pulse laser instantly ionizes particles to be detected and generates plasma to emit light; and the second spectrograph is used for detecting plasma luminescence and analyzing the element components of the to-be-detected single particles.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
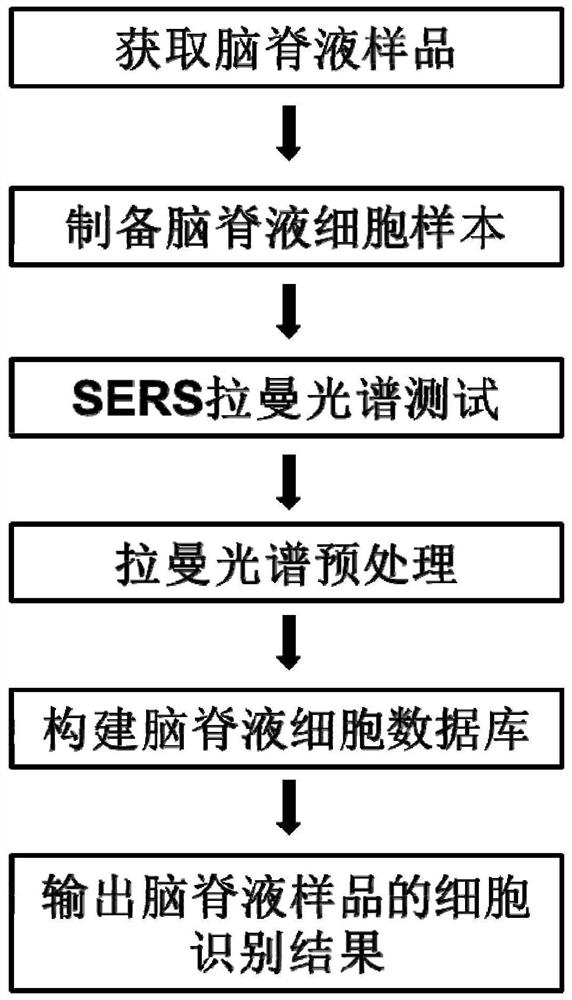
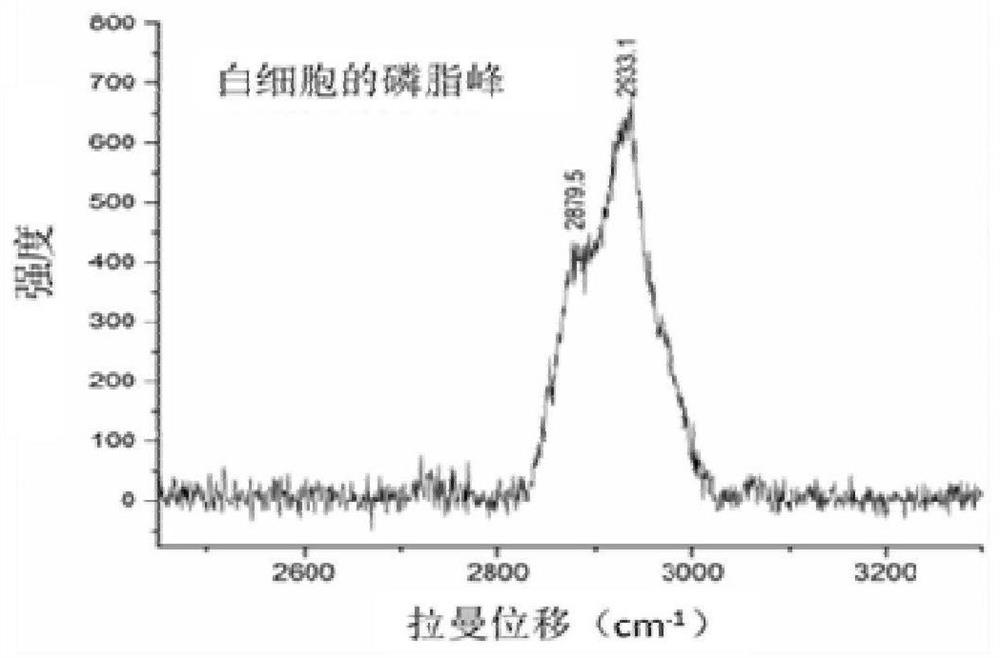
Cerebrospinal fluid cell detection method and system based on Raman scattering spectrum
ActiveCN111707656AReduce labor intensityFast wayRaman scatteringRaman scattering spectraPrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses a cerebrospinal fluid cell detection method and system based on a Raman scattering spectrum. The method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing a cerebrospinal fluid sample; 2, carrying out single-point test and imaging test on cerebrospinal fluid cells on the sample to obtain original Raman spectrum data; 3, processing the original Raman spectrum data obtained in the step 2 to obtain processed Raman spectrum data, wherein the processing comprises the steps of substrate removal preprocessing and normalization processing; and 4, carrying out data analysis on the Raman spectrum data processed in the step 3 by adopting a deep neural network and principal component analysis, and gathering the spectrums of cerebrospinal fluid cells of the same type together with datanodes of the same color to finish classification and detection. According to the method and the system, the detection and judgment accuracy can be improved, and meanwhile, the report issuing efficiency can be improved.
Owner:陕西未来健康科技有限公司
Porous body, production method thereof and composite material using the porous body
A porous material comprising vapor grown carbon fiber in an amount of 10 to 90 mass %, fiber filaments of the carbon fiber forming a three-dimensional network and having a diameter of 1 to 1,000 nm, an aspect ratio of 5 to 15,000, a specific surface area (by BET method) of 2 to 2,000 m2 / g, and the ratio of the intensity of the peak at 1,360 cm−1 in a Raman scattering spectrum of the carbon fiber to that of the peak at 1,580 cm−1 in the spectrum(I1360 / I1580) is 0.1 to 2.0, wherein the porosity of the porous material (V / V0) is 0.50 to 0.99 and a specific surface area is 5 to 1,000 m2 / g; and a production method and use thereof. The vapor grow carbon fiber impregnated in the porous material of the present invention does not contain aggregates and a three-dimensional network is formed between the fiber filaments, wherein length of each of the fiber filaments is maintained. Therefore, the vapor grown carbon fiber enables to readily produce a composite material (porous material), in which even a small amount of addition of vapor grown carbon fiber can exhibit sufficient effect.
Owner:RESONAC HOLDINGS CORPORATION
Noninvasive blood sugar detection device based on raman scattering spectrum and detection method
ActiveCN111227844ARealize non-invasive testingNon-invasive testingDiagnostics using spectroscopySensorsBeam splitterRaman scattering spectra
The invention discloses a noninvasive blood sugar detection device based on a raman scattering spectrum. The noninvasive blood sugar detection device based on a raman scattering spectrum comprises a semiconductor laser, an optical fiber beam splitter, an optical fiber probe, a light filter, a raman spectrometer, a first circuit switch, a second circuit switch, a phase locking amplifier, a heart rate measuring apparatus and a computer. According to the noninvasive blood sugar detection device based on a raman scattering spectrum disclosed by the invention, raman scattering light contains rich molecular vibration information, the characteristics that the raman scattering spectrum having different molecules has different features are utilized, the raman scattering spectrum is used for recognizing molecules; and through the relative value of a glucose characteristic peak at the position of 1125cm-1 in the raman scattering spectrum in pure blood to the hemoglobin characteristic peak value at the position of 1549cm-1, and real-time human body blood sugar concentration data measured by a blood sugar biochemistry instrument, a standard straight line L of the relationship between the relative peak value of the glucose characteristic peak at the position of 1125cm-1 and the human body blood sugar concentration is constructed, and finally noninvasive real-time detection of the human bodyblood sugar is realized. The noninvasive blood sugar detection device disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being high in precision, pollution-free, harmless to human bodies and the like, and has great application prospects in the field of biological noninvasive detection.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
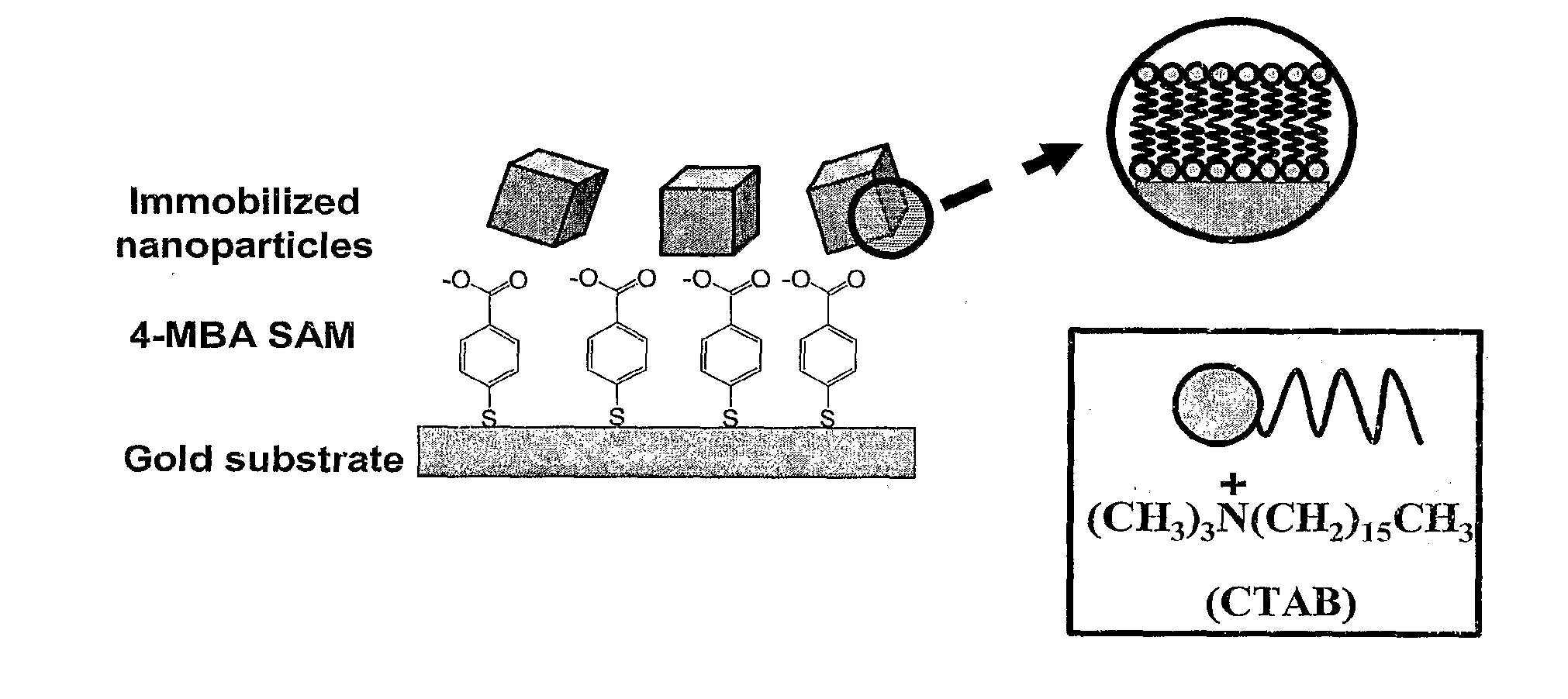
Surface enhanced raman spectroscopy using shaped gold nanoparticles
InactiveUS20110184202A1Enhanced Raman signalMaterial nanotechnologyMaterial analysis by optical meansSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopyElectromagnetic field
Surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) spectra of 4-mercaptobenzoic acid (4-MBA) self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) on gold substrates is presented for SAMs onto which gold nanoparticles of various shapes have been electrostatically immobilized. SERS spectra of 4-MBA SAMs are enhanced in the presence of immobilized gold nanocrystals by a factor of 107-109 relative to 4-MBA in solution. Large enhancement factors are a likely result of plasmon coupling between the nanoparticles (localized surface plasmon) and the smooth gold substrate (surface plasmon polariton), creating large localized electromagnetic fields at their interface, where 4-MBA molecules reside in this sandwich architecture. Moreover, enhancement factors depend on nanoparticle shape, and vary by a factor of 102.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH CAROLINA
Electrophotographic photoconductor and method for producing the same, image forming apparatus, and process cartridge
InactiveUS7955768B2Reduction of the residual potentialImprove mobilityElectrographic process apparatusCorona dischargeElectrical conductorRaman scattering spectra
There is provided an electrophotographic photoconductor containing a conductive substrate, and a photosensitive layer, disposed thereon, containing a charge transporting material having a triarylamine structure represented by General Formula 1, and wherein the photosensitive layer satisfies Mathematical Formula 1 when peak heights in raman scattering spectra of the triarylamine structure are measured at a wavenumber of 1,324±2 cm−1 by a confocal raman spectroscopy using z-polarized light:where Ar1, Ar2, and Ar3 are substituted or unsubstituted aromatic hydrocarbon groups, and Ar1 and Ar2, Ar2 and Ar3, and Ar3 and Ar1 are optionally combined to form heterocyclic rings, respectively,ε=I(inside) / I(surface)≧1.1 Mathematical Formula 1where I(inside) represents the peak height in of the raman scattering spectrum obtained at a depth of 5 μm or more from the photosensitive layer surface and I(surface) represents the peak height in the raman scattering spectrum obtained at a depth of less than 5 μm from the photosensitive layer surface.
Owner:RICOH KK
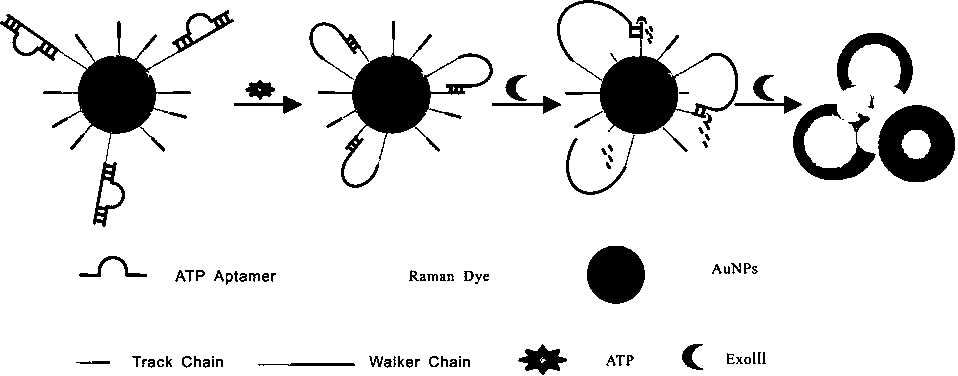
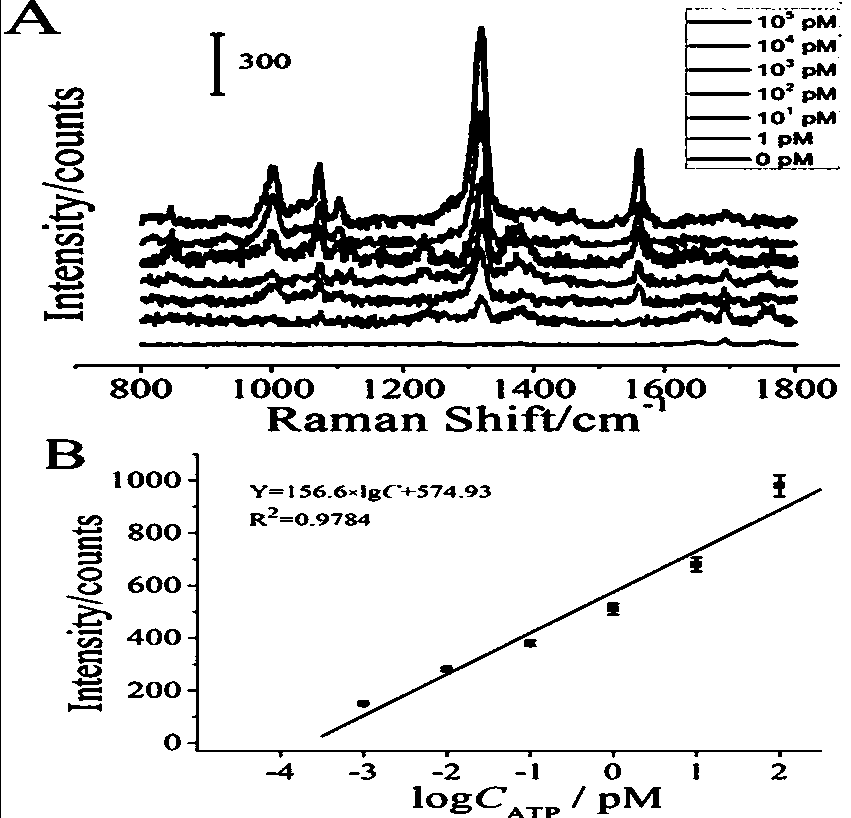
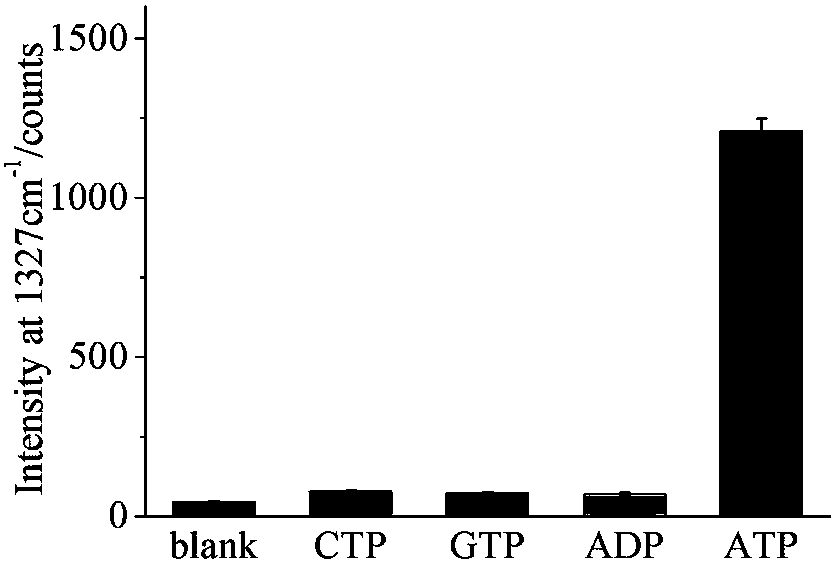
Biosensor for detecting ATP activity and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109507168ARapid ATP Activity AssaySensitive ATP Activity AssayRaman scatteringRaman scattering spectraPlasma resonance
The invention relates to the technical field of biosensors, in particular to a biosensor for detecting ATP (triphosadenine) activity based on surface-enhancement Raman scattering generated by nanogoldparticle aggregation. By means of the characteristic that ATP can be specifically combined with a nucleic acid aptamer of the ATP, Walker Chains of the surfaces of the nanogold particles are released, so that shorter Track Chains on the surfaces of nanogold are catalytically hydrolyzed by means of nuclease, and therefore, the nanogold particles lose nucleic acid protection and are aggregated in ahigh salt buffer solution to generate a surface plasma resonance effect, thereby enhancing the electromagnetic field intensity of the surfaces of the nanogold particles greatly. A Raman dye marked onthe surfaces of the nanogold particles generates a surface-enhancement Raman scattering (SERS) effect and Raman spectra are shown in special positions. When a reaction solution does not contain ATP,Protect Chains cannot be replaced, so that a follow-up nanogold aggregation reaction cannot be carried out, and therefore, no Raman scattering spectra are generated. The biosensor detects the ATP activity quickly, sensitively and safely by taking nucleic acid chains modified on the surfaces of the nanogold particles.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
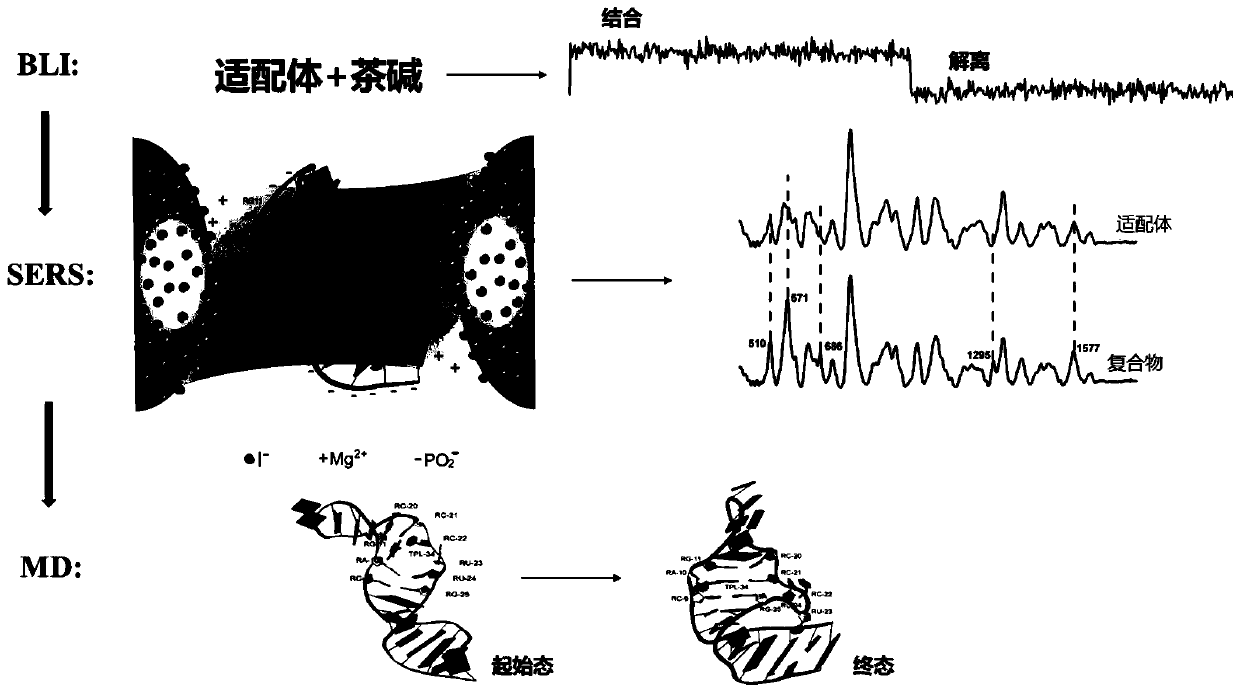
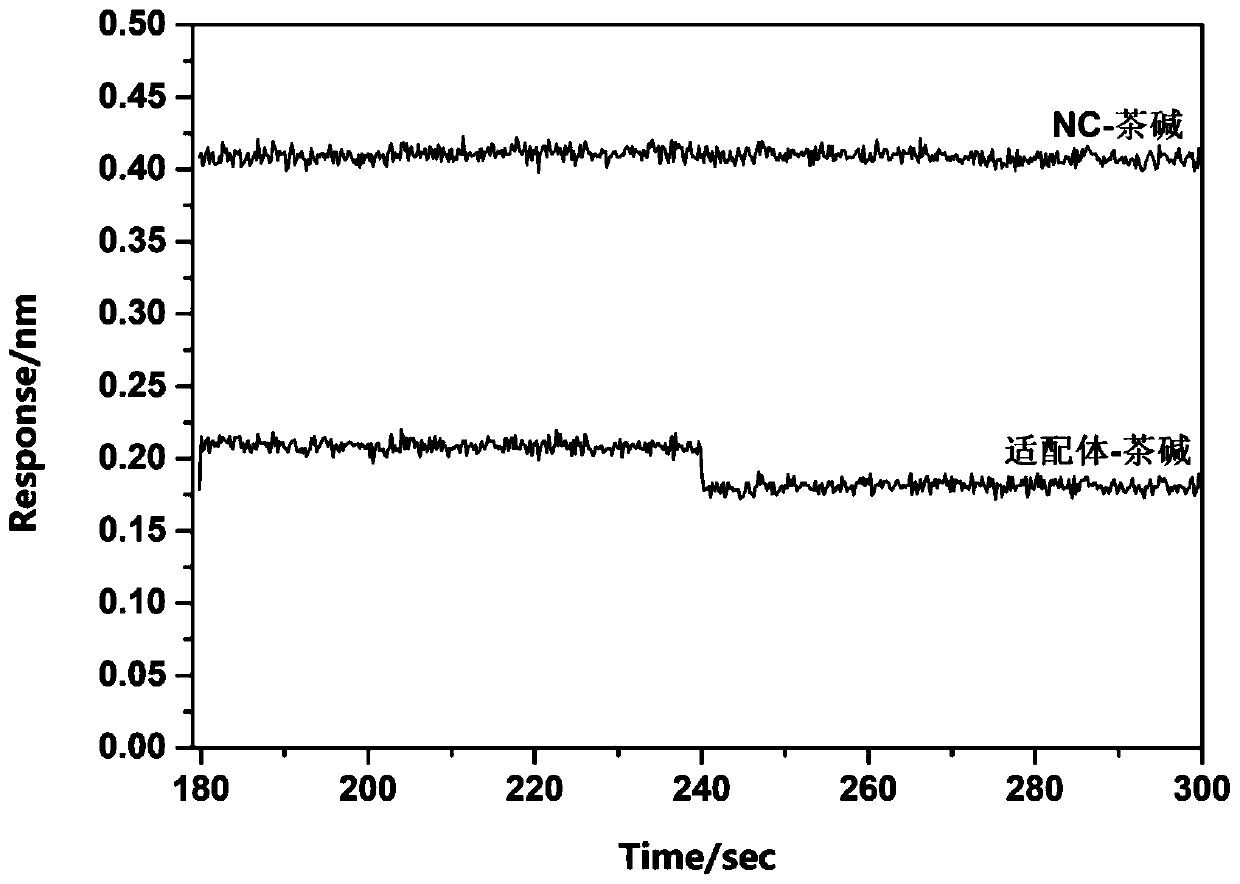
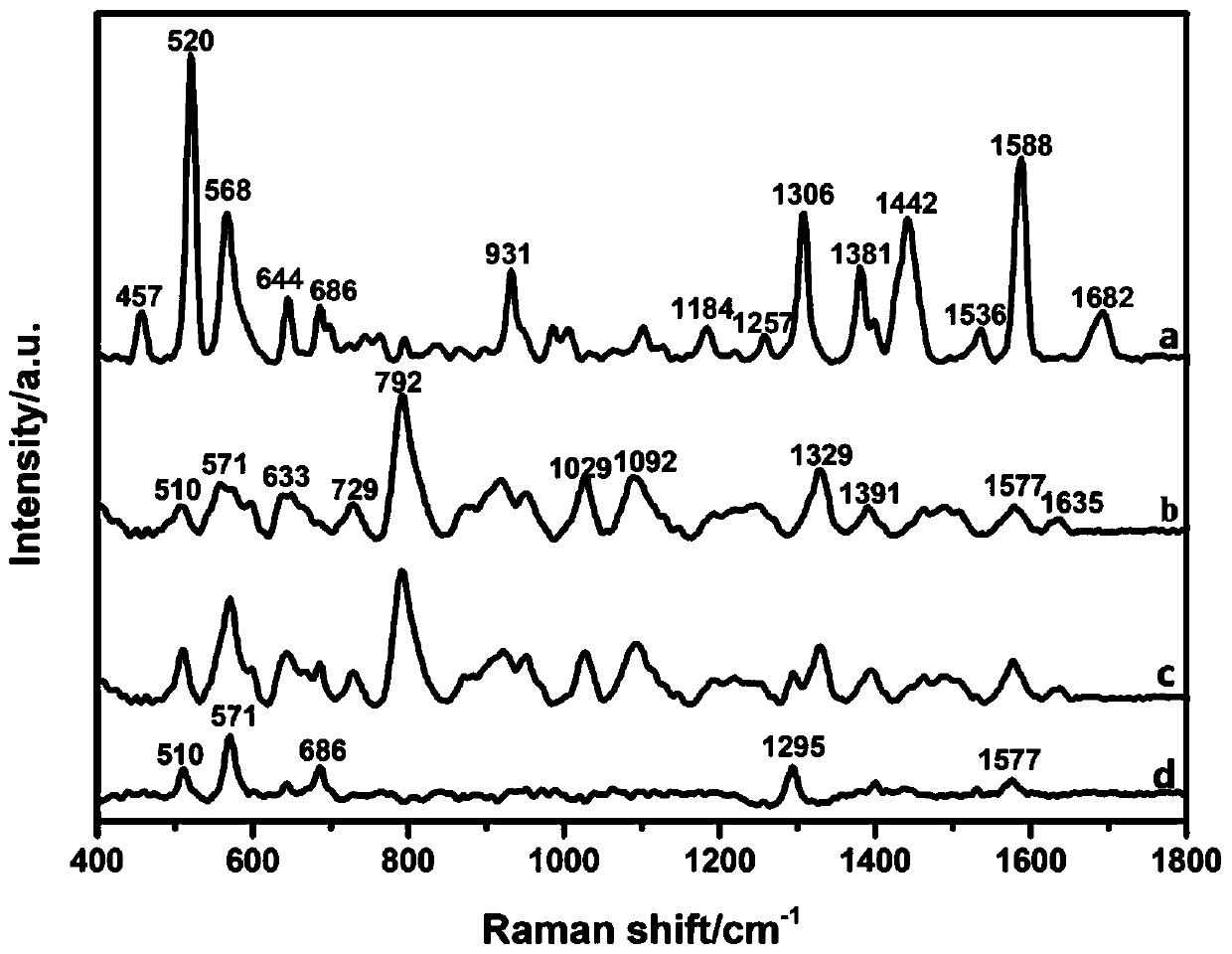
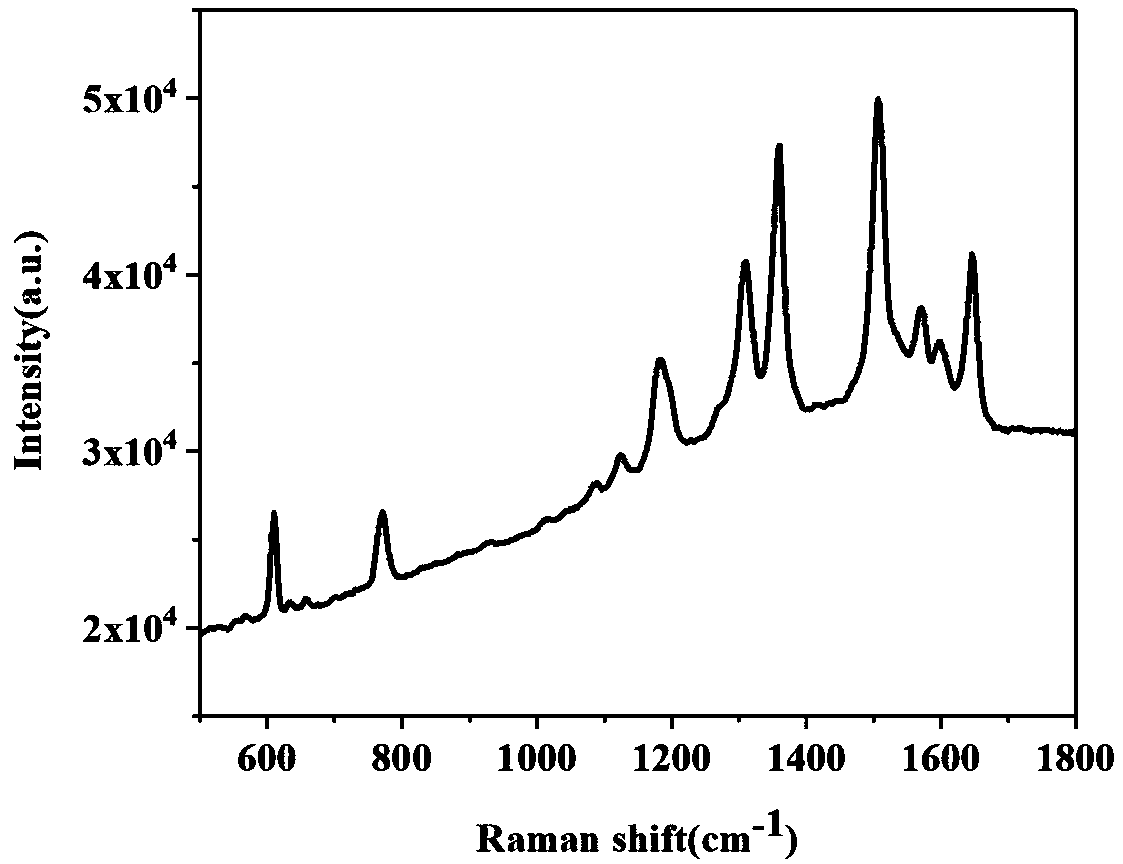
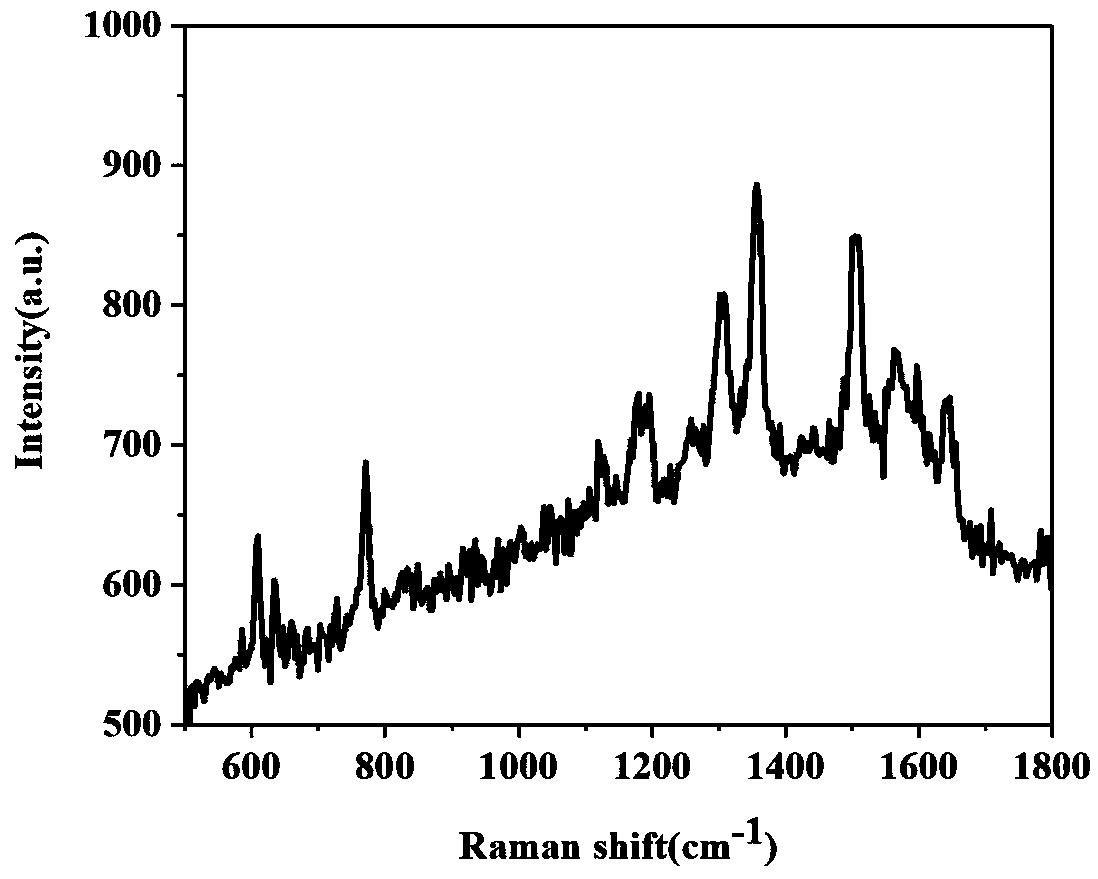
Method for rapidly and effectively detecting conformational change in aptamer and ligand small molecule binding process
The invention relates to the technical field of biological medicine, in particular to a method for rapidly and effectively detecting conformational change in the aptamer and ligand small molecule binding process. The method comprises the following steps: determining the affinity between a selected aptamer and small molecules by applying a biological membrane interference experiment; detecting conformational change before and after the aptamer is combined with the small molecules through a surface enhanced Raman scattering spectrum technology; and visually explaining the binding process of theaptamer and the ligand through molecular dynamics simulation. According to the method, theophylline and the aptamer thereof are taken as examples, it is verified that the method provides new idea forresearch on the reliability of the conformational change of the aptamer and design, modification and screening the high-affinity high-selectivity aptamer, and the method can be applied to the fields of detection, sensing, clinical diagnosis and treatment in a better way.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Low concentration detection SERS (Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering) substrate of PMMA spaced gold nanocube and gold film composite structure
The invention discloses a low concentration detection SERS (Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering) substrate of a PMMA spaced gold nanocube and gold film composite structure, which sequentially comprisesa glass substrate, a titanium film, a gold film, a PMMA film, gold nanocubes and a to-be-detected object adsorbed on the surfaces of the PMMA film and the gold nanocubes. When TM polarized light is normally incident on the surface of the PMMA spaced gold nanocube and gold film composite structure, local surface plasmas and propagation surface plasma are excited, strong resonance coupling occurs between the two kinds of surface plasmas to result in very strong electric field enhancement, and thus a strong surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) spectrum is generated for low-concentration SERSdetection. The low concentration detection SERS substrate has the advantages of easy operation, low cost and high sensitivity, and can be widely applied to low concentration detection.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
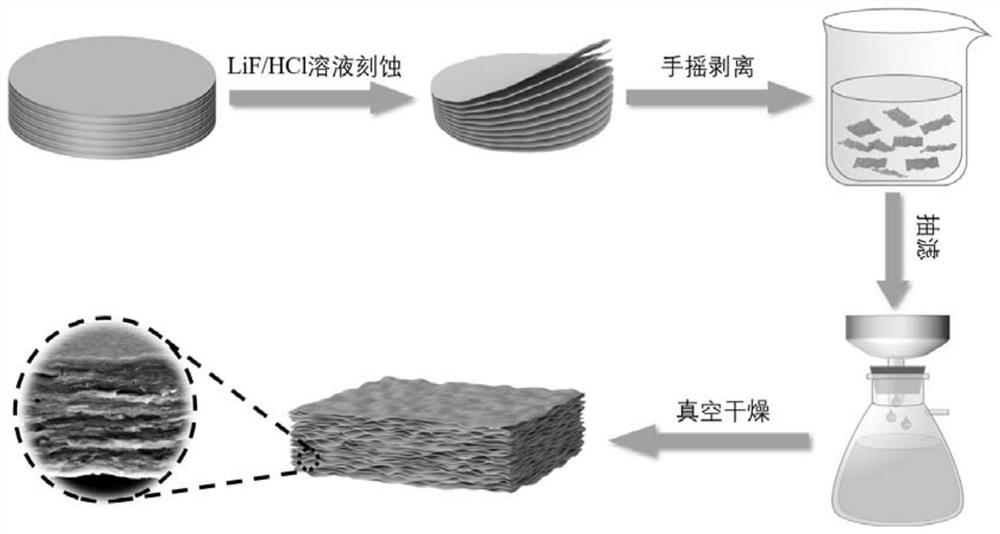
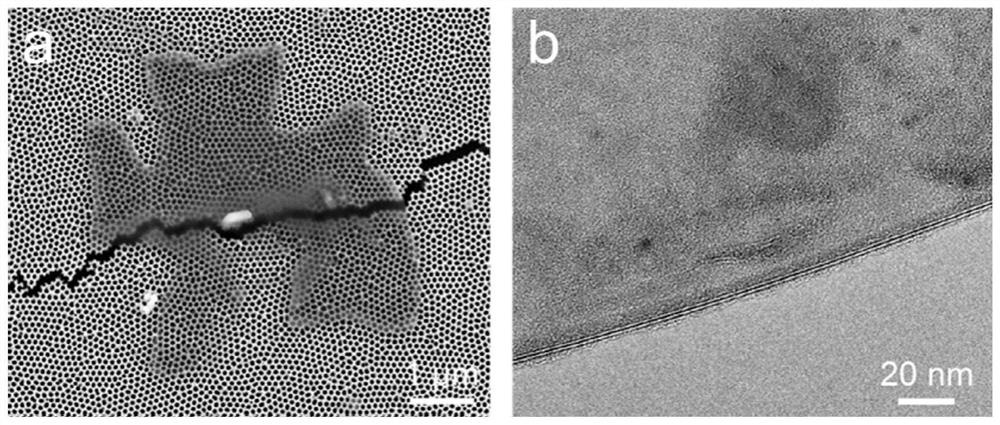
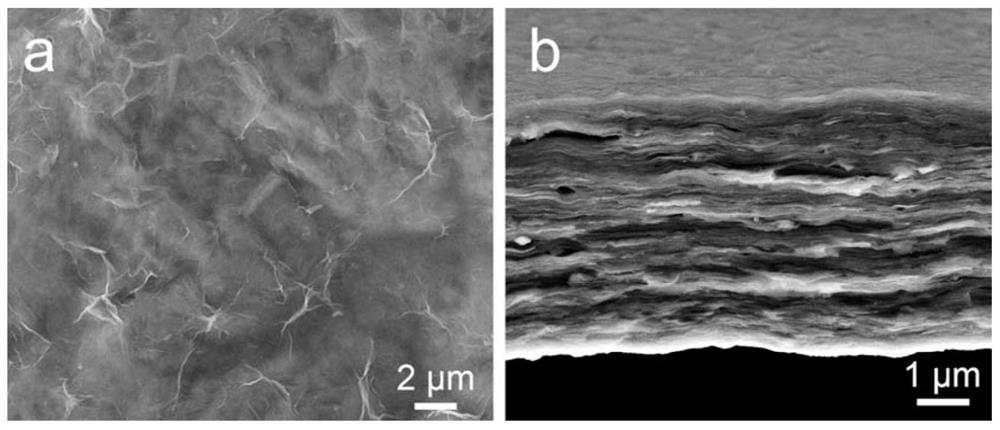
Preparation method and application of SERS film substrate based on MXene
PendingCN113666373ASimple preparation processLow costCarbon compoundsRaman scatteringTransition metal carbidesRaman scattering spectra
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of an SERS film substrate based on MXene, and relates to the technical field of SERS spectrums. The method comprises the steps of selectively etching away an Al atomic layer in a precursor MAX material by using lithium fluoride-hydrochloric acid as an etching layering agent; repeatedly cleaning the obtained double-transition metal carbide two-dimensional layered material with deionized water, and centrifuging; dispersing in deionized water, shaking, and carrying out centrifugal suction filtration; and obtaining the novel self-supporting SERS film substrate. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple to operate and low in cost, has the advantages of high sensitivity, good Raman enhancement effect, high reproducibility and the like, can be applied to trace detection in the fields of environment, food safety, biomarkers and the like, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
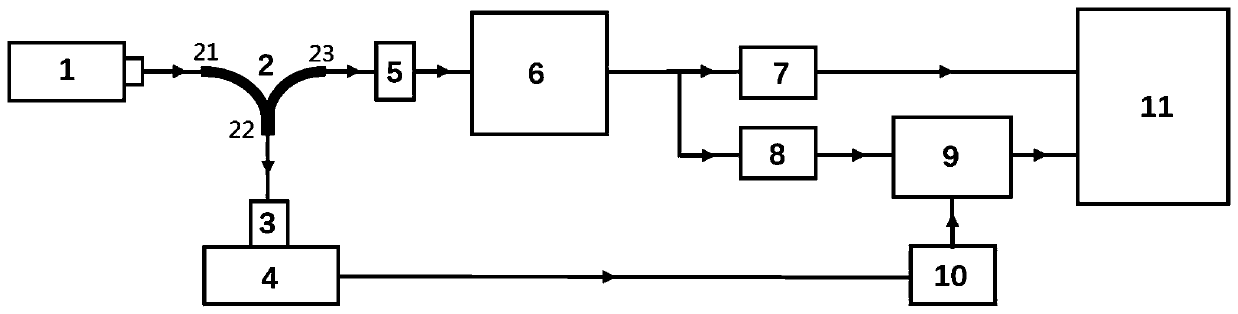
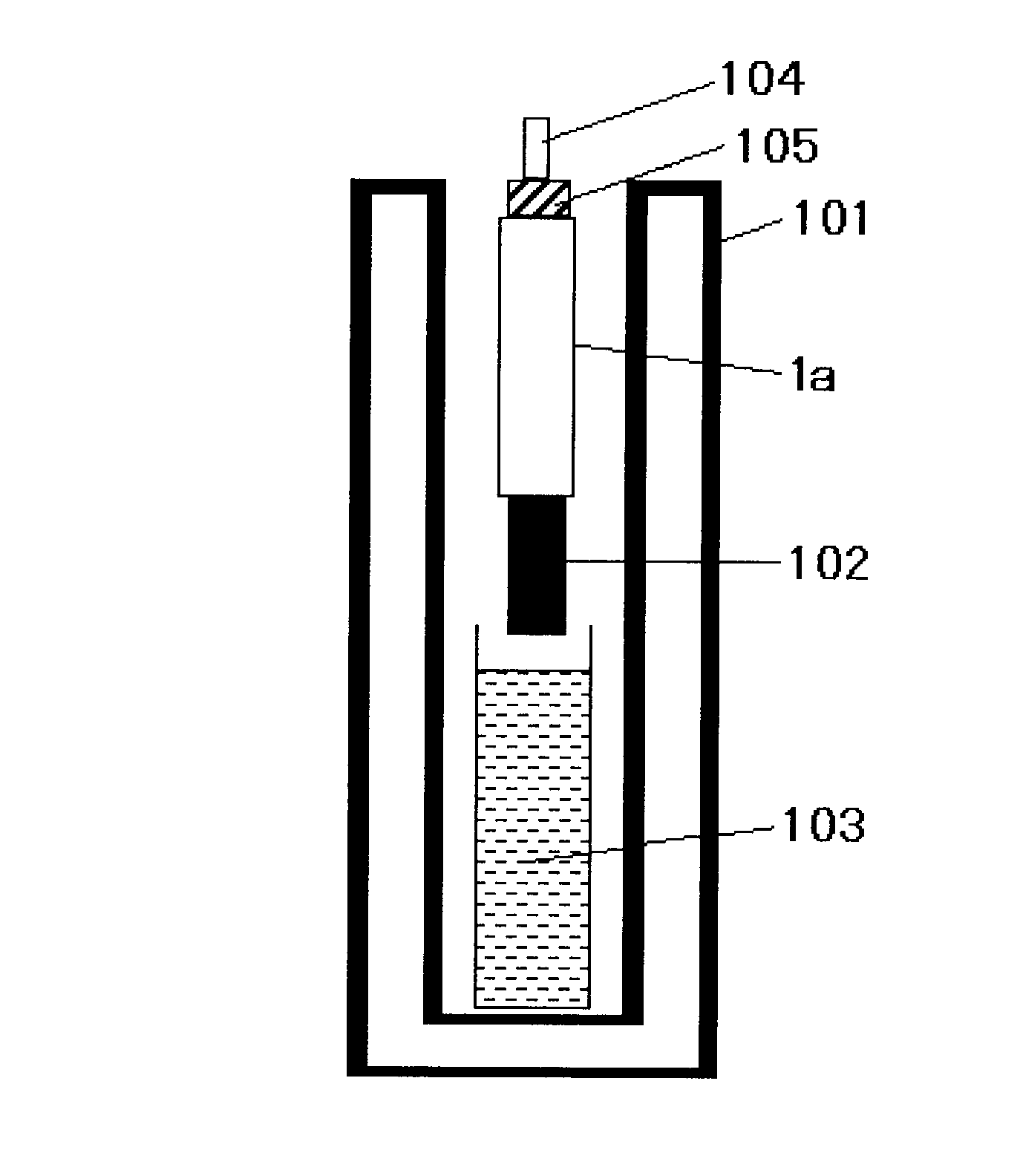
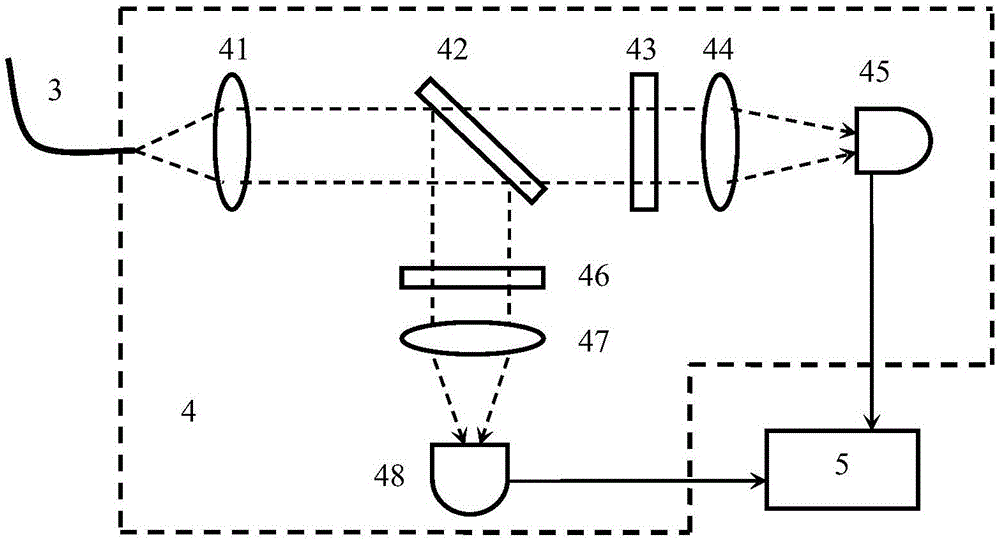
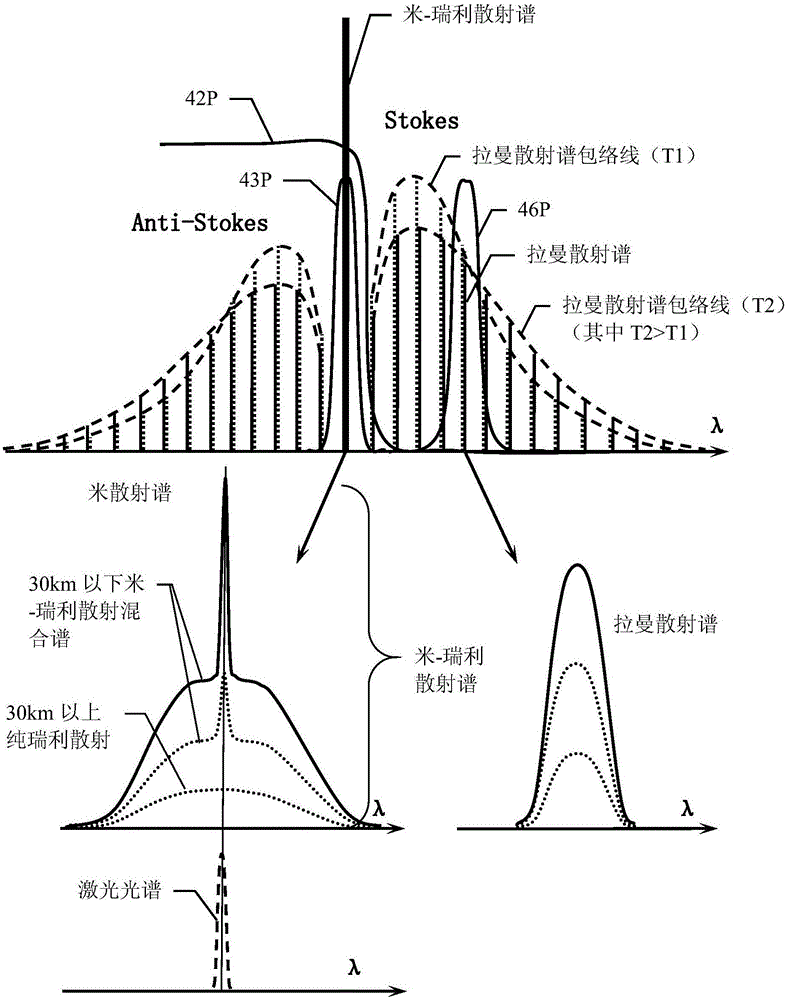
Atmospheric Raman-Rayleigh scattering temperature measurement laser radar and inversion method
ActiveCN106483531AEliminate the effects ofExpand the range of temperature measurement spaceElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationRayleigh scatteringEcho intensity
The invention discloses an atmospheric Raman-Rayleigh scattering temperature measurement laser radar and an inversion method. The laser radar comprises a laser transmitting unit (1), a receiving telescope (2), a receiving optical fiber (3), a signal detecting unit (4) and a signal processing unit (5). A high-resolution spectrum detection method is adopted to measure Rayleigh scattering spectral signals generated on atmospheric molecules by laser higher than 30km or above and Raman scattering spectral signals generated on atmospheric molecules by laser lower than 30km; and inversion is carried out to obtain the temperature of atmosphere at 30km, or above or below can be obtained based on a characteristic that the Raman scattering spectrum is in direct proportion to the Rayleigh scattering spectrum in echo intensity, and therefore, the temperature measurement space range of the Rayleigh scattering temperature measurement laser radar can be expanded. The atmospheric Raman-Rayleigh scattering temperature measurement laser radar has the advantages of wide temperature measurement height range and small temperature measurement error.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
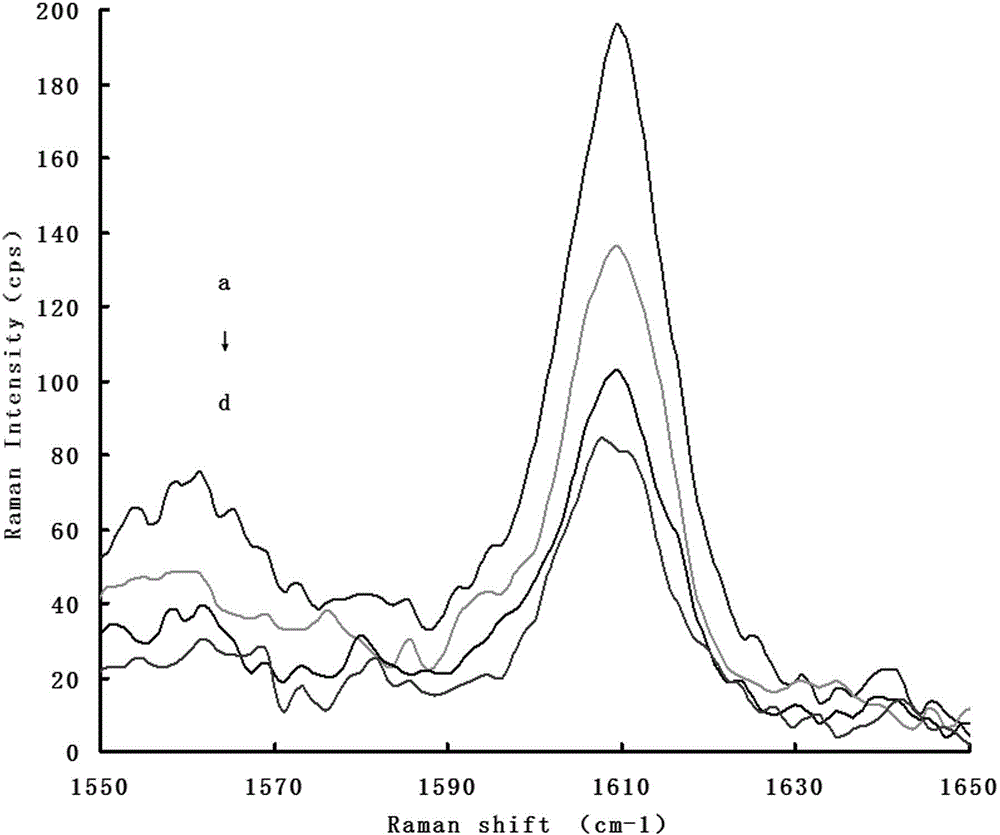
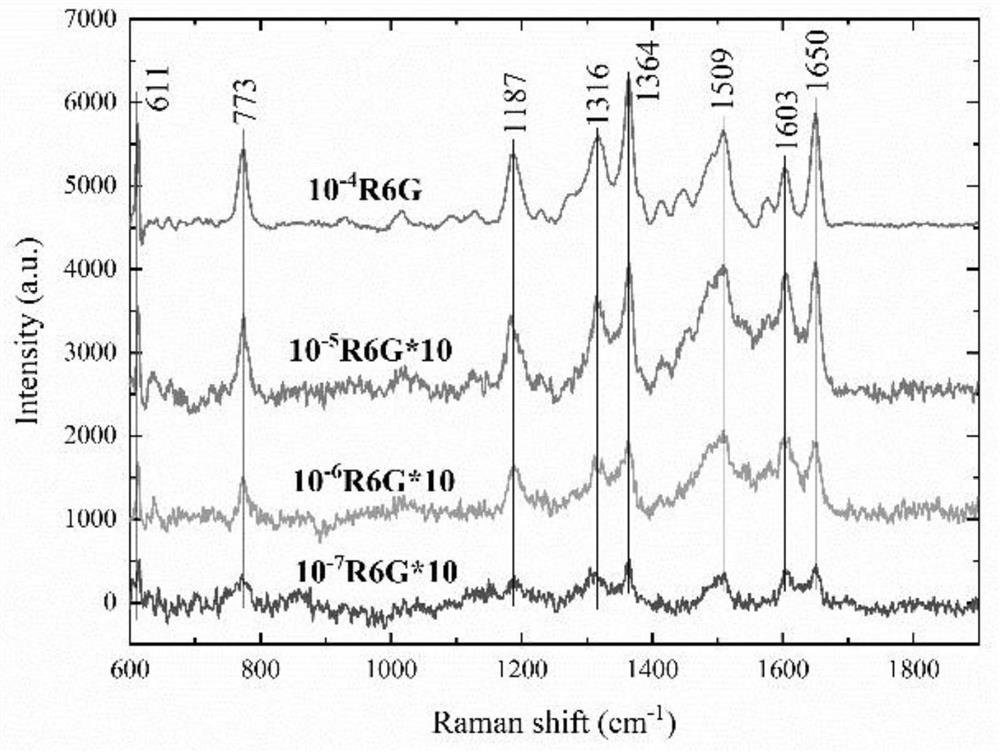
Method for measuring IO3<-> by utilizing surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectrums
InactiveCN104165881AGood choiceImprove system stabilityRaman scatteringRaman scattering spectraControl system
The invention discloses a method for measuring IO3<-> by utilizing surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectrums. The method comprises the steps of (1) preparing an analytic solution with known concentration being IO3<->, and measuring the intensity value I of surface-enhanced Raman scattering peaks at the 1609cm<-1> position; (2) preparing a blank control system without containing a KIO3 standard solution, and measuring the intensity value I0 of the surface-enhanced Raman scattering peaks of the blank control system; (3) calculating according to a formula, namely delta I=I0-I; (4) making a working curve according to the concentration C of the IO3<-> to the delta I; (5) preparing the analytic solution of a measured sample, measuring the intensity value of the surface-enhanced Raman scattering peak as a sample I, and calculating according to a formula, namely delta I sample=I0-sample I; and (6) according to the working curve, calculating the concentration of the IO3<-> in the measured sample. Compared with the existing method, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simplicity in operation, high sensitivity, good selectivity and good system stability.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
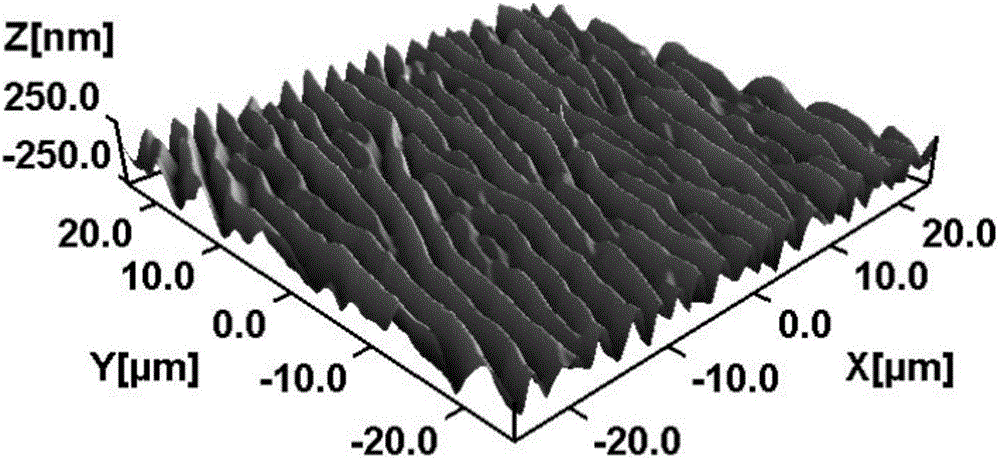
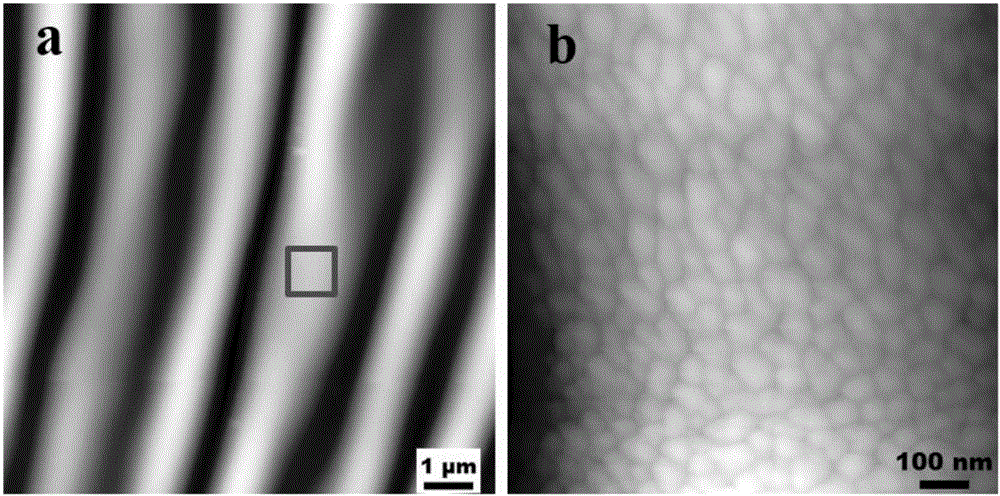
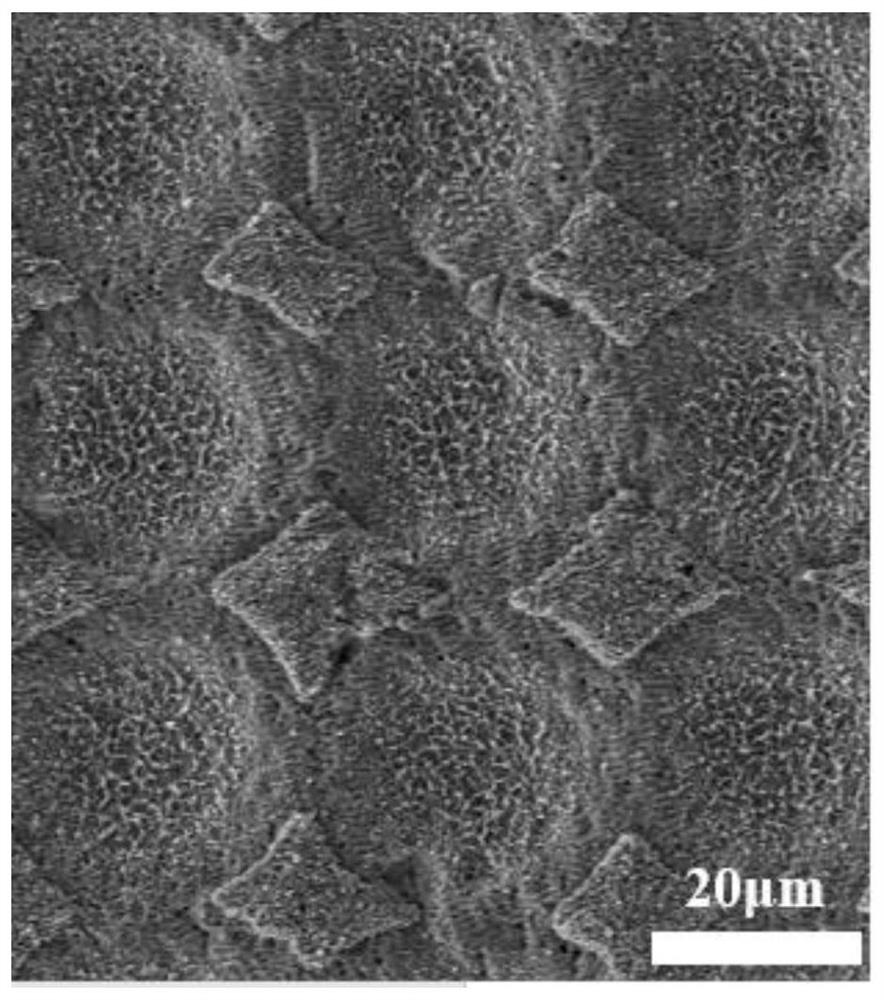
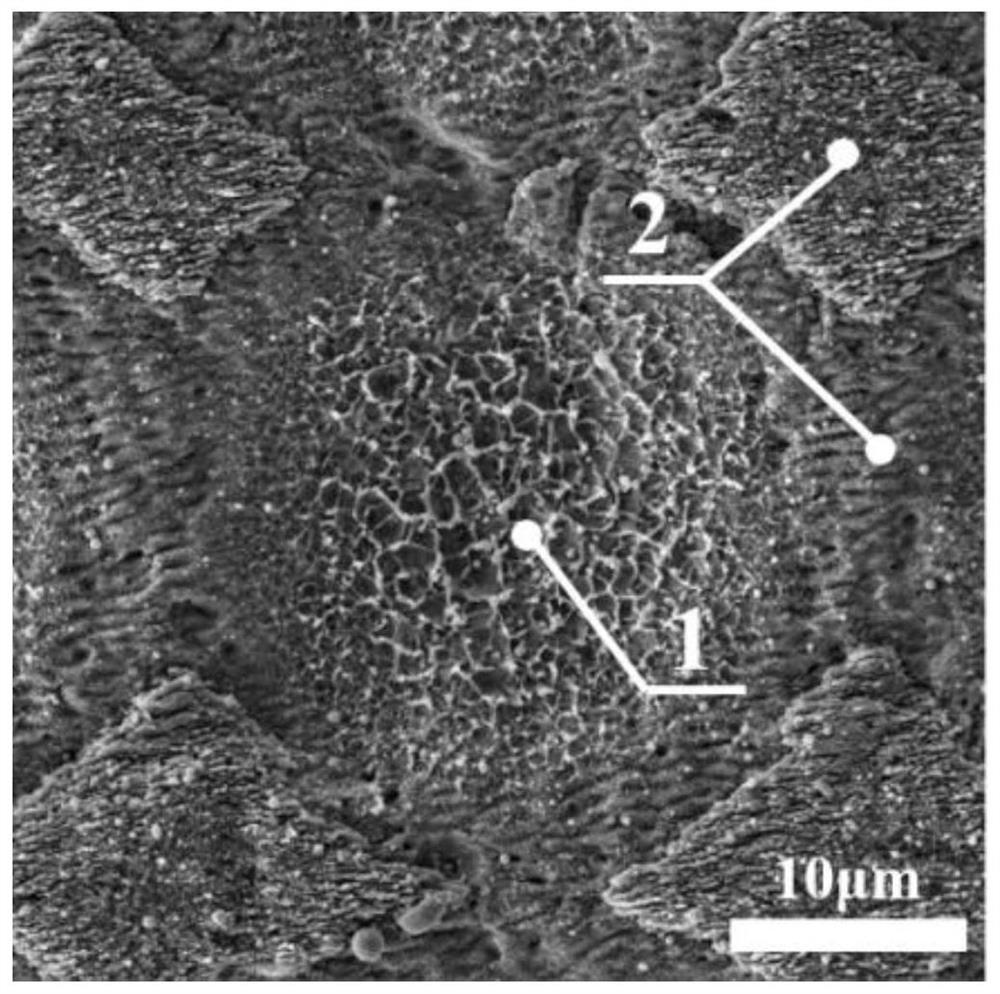
Surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate and preparation method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectrum analysis. The invention provides a surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate, and the surface of the surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate provided by the invention is provided with a multi-stage three-dimensional self-supporting structure of micron pits, nanobelts, nano bulges, nano ripples and nanoparticles. According to the surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate and the preparation method thereof, by controlling laser processing parameters and scanning parameters, controllable preparation of the micro-nano structure on the surface of the material can be achieved, the surface enhanced Raman scattering effect is further improved, the preparation process is simple and practical, and thesurface enhanced Raman scattering substrate and the preparation method thereof are suitable for batch preparation. The invention also provides application of the surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate in surface enhanced Raman scattering, and the surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate provided by the invention has high sensitivity, excellent uniformity and stability, and can be appliedto most detection fields.
Owner:绍兴镭纳激光科技有限公司
Sample rotating rack and Raman spectroscopy detector
InactiveCN110057808ARapid optical exposureRapid Optical Analysis DetectionRaman scatteringSpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsRaman scattering spectraSpectrum analyzer
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
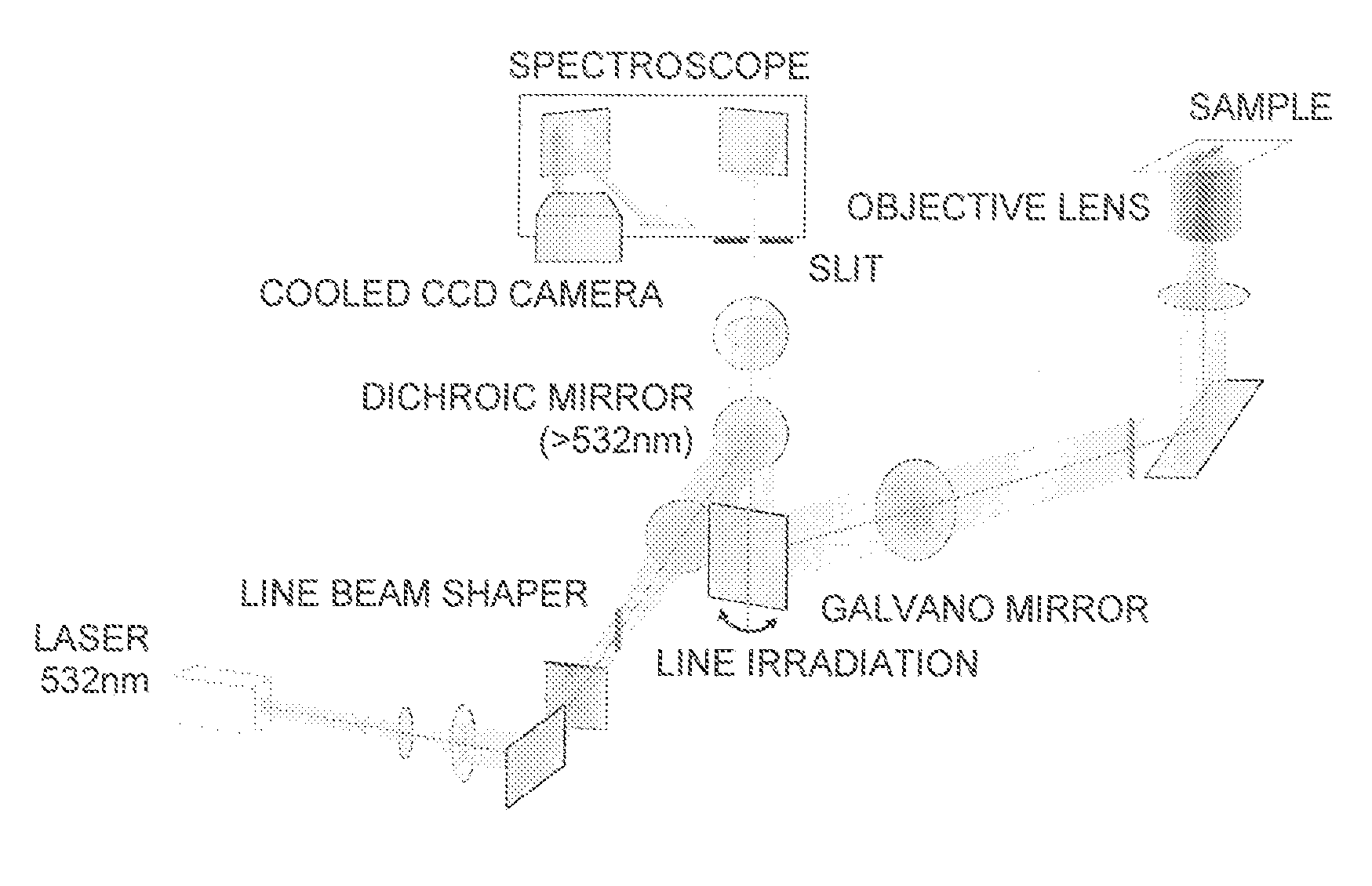
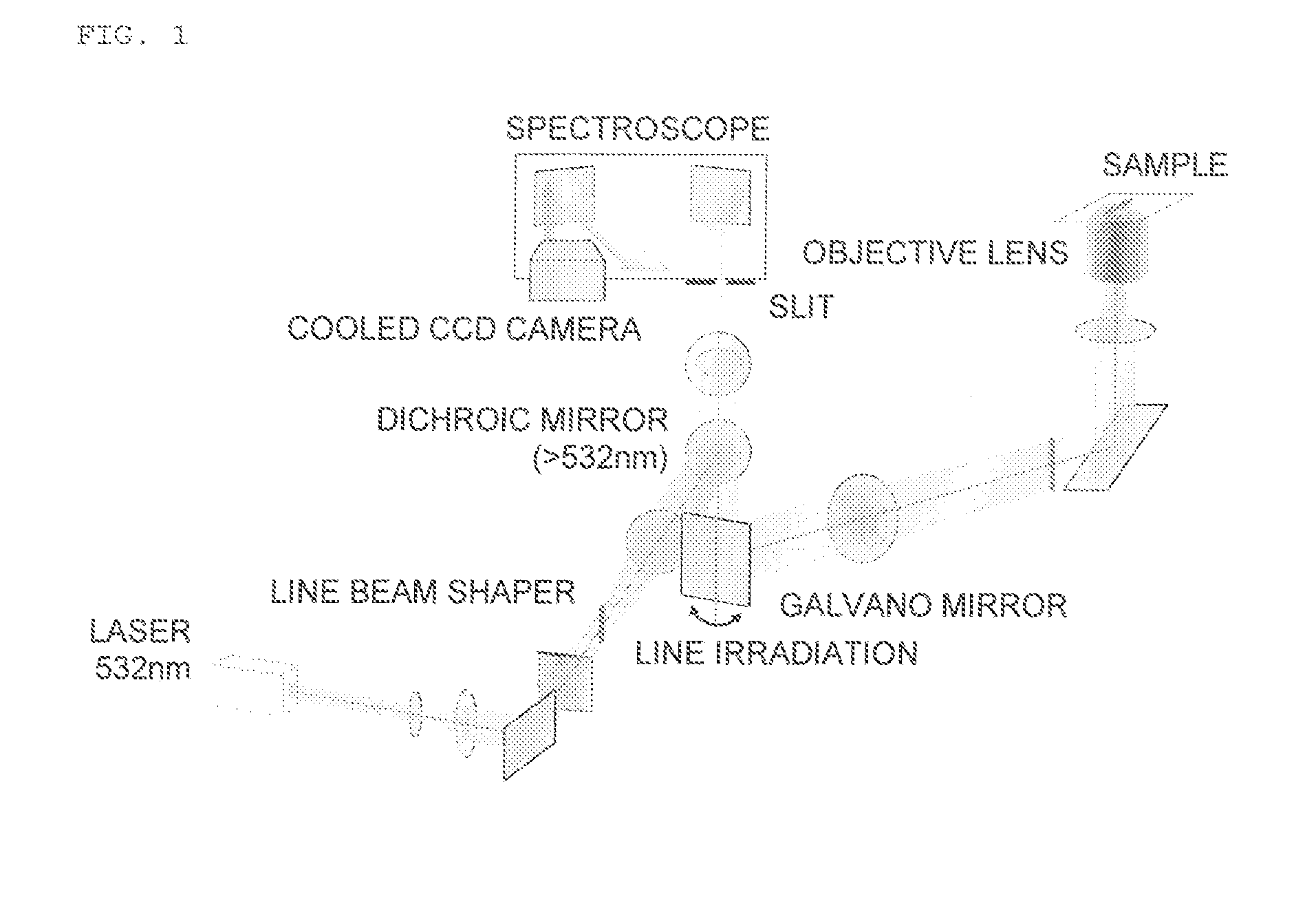
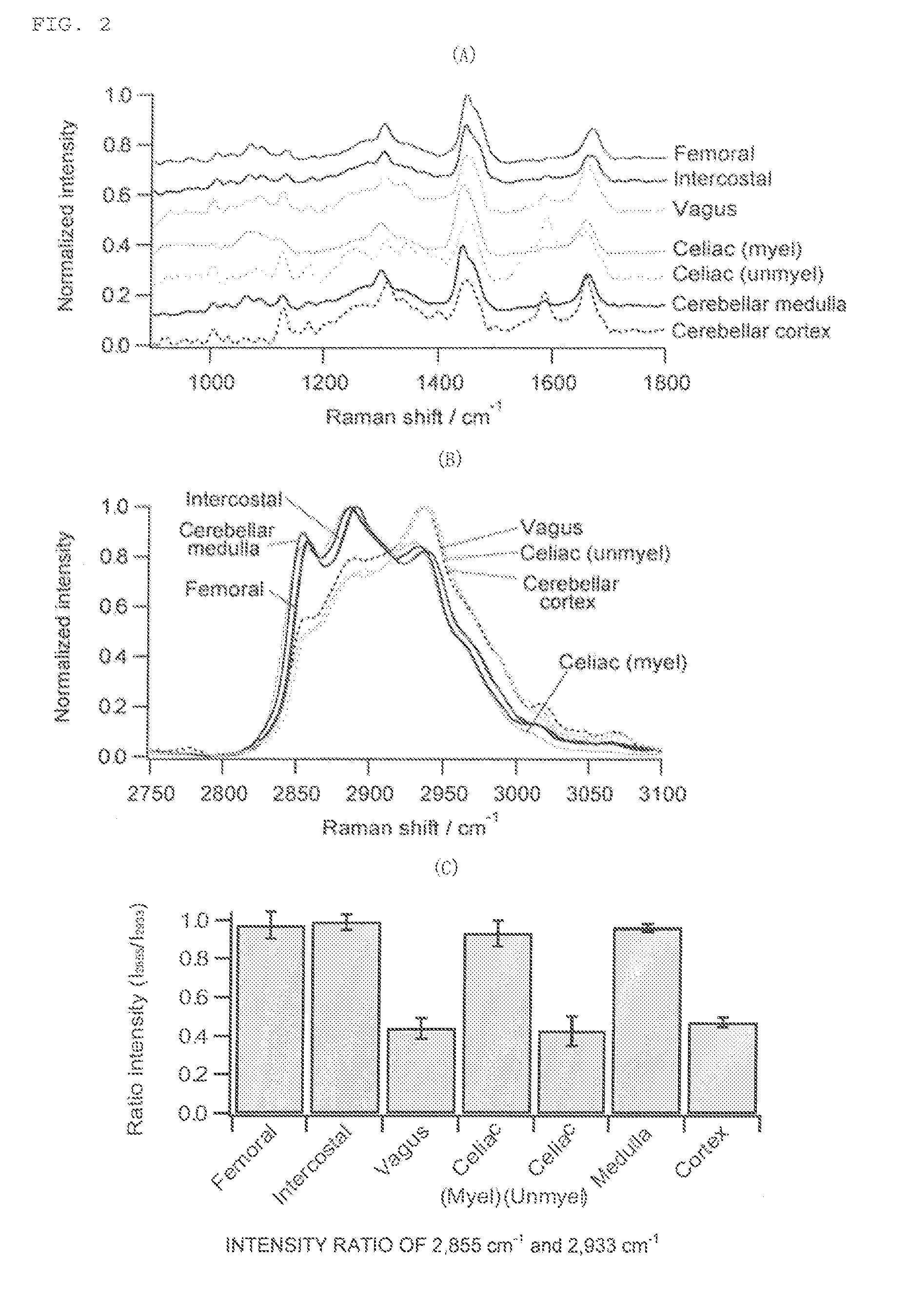
Method for nerve detection by raman scattering spectroscopy
InactiveUS20150297087A1Reduce stepsRadiation pyrometryDiagnostics using spectroscopyRaman scattering spectraStatistical analysis
The present invention provides a method of detecting nerves, including: step 1 of irradiating a sample with excitation light; step 2 of detecting Raman scattering light from the sample; step 3 of calculating an intensity ratio of a wave number within a specific range of the Raman scattering light detected in the step 2 or extracting a feature of the intensity ratio and subjecting the feature to multivariate analysis and / or statistical analysis; and step 4 of specifically displaying nerves containing unmyelinated nerves, using as an index the intensity ratio or a result from the multivariate analysis and / or the statistical analysis.
Owner:KYOTO PREFECTURAL PUBLIC UNIV CORP
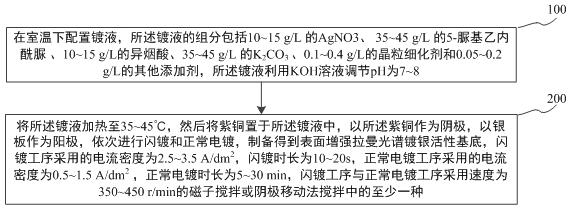
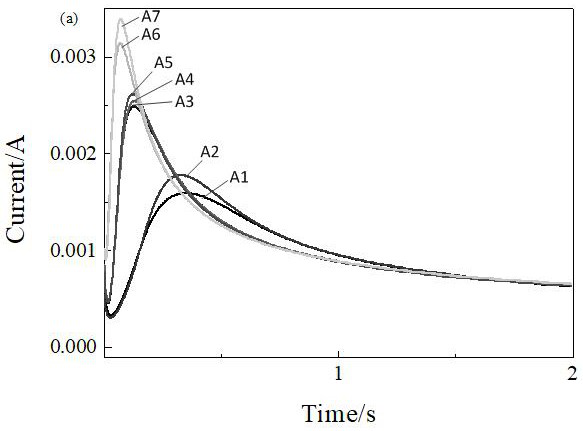
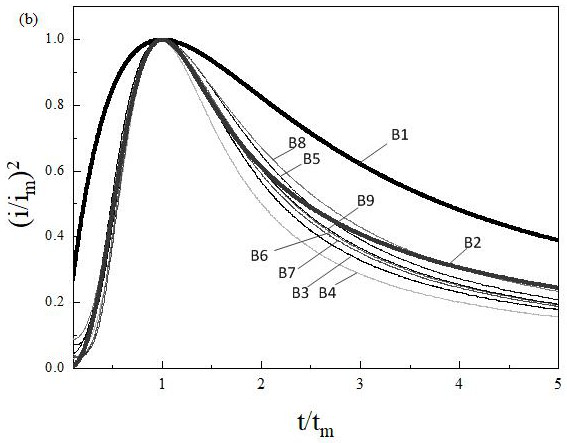
A kind of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy silver-plating active substrate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110016700BEnhancement effect is goodImprove production efficiencyRaman scatteringElectrodesSilver plateRaman scattering spectra
The invention discloses a surface-enhanced Raman spectrum silver-plated active substrate and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the technical field of Raman spectrum detection. The present invention provides a surface-enhanced Raman spectrum silver-plated active substrate and a preparation method thereof. Copper is used as a cathode, a silver plate is used as an anode, and the main complexing agent, auxiliary complexing agent, grain refiner, and Flash plating and subsequent normal electroplating are carried out in the plating solution of conductive salt and other additives. During electroplating, the area ratio of cathode and anode is controlled to prepare a highly active silver-plated substrate. The preparation process is simple, efficient, and environmentally friendly. The surface of the prepared silver-plated active substrate is The silver grains are finely crystallized and uniformly deposited in a large area, and have a good Surface-enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) effect of the Raman scattering spectrum, thereby solving the traditional process of preparing SERS active substrates using silver flakes. High, and the SERS activity of the substrate is poor and other technical problems, so as to improve the preparation efficiency of the SERS active substrate and improve the enhancement effect of the substrate.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com