Target protein and micromolecule binding prediction method and system
A prediction method and small molecule technology, applied in the field of computational biology, can solve problems such as the inability to accurately predict the binding results, achieve the effects of reducing noise, removing irrelevant information, and improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
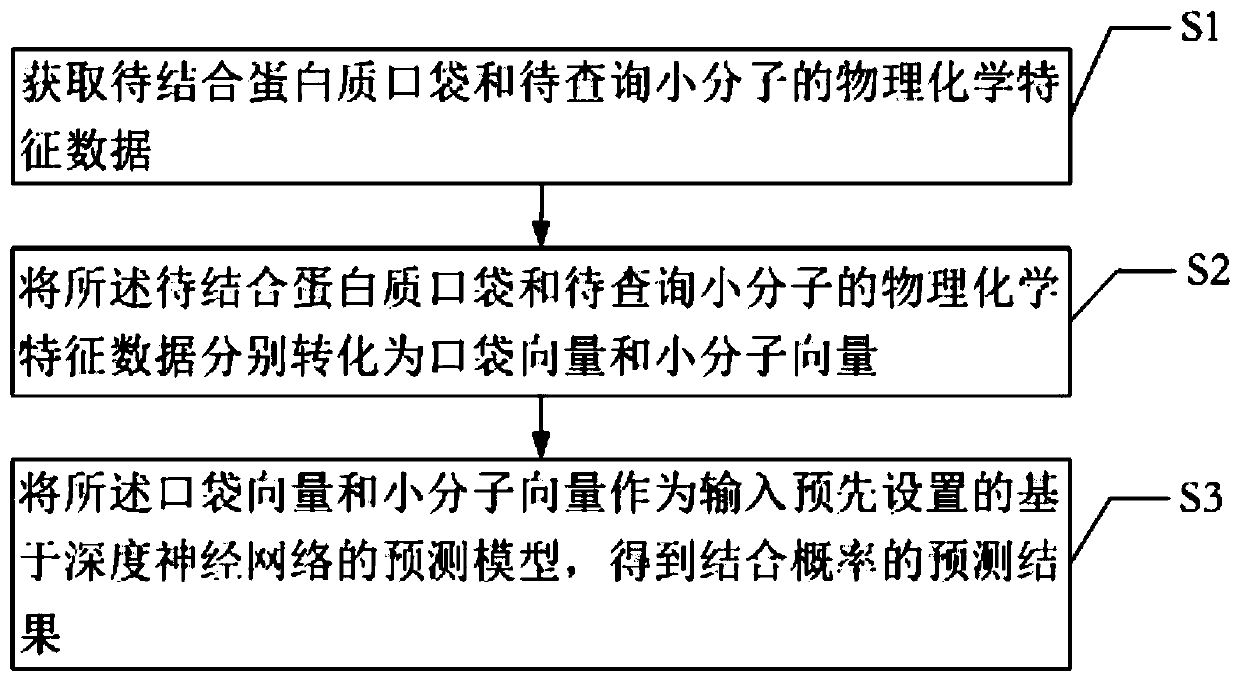
[0044] The first embodiment provided by the present invention is a method for predicting the binding of target proteins and small molecules, such as figure 1 shown, including:
[0045] Step S1, obtaining the physicochemical characteristic data of the protein pocket to be bound and the small molecule to be queried.
[0046]The physical and chemical characteristic data of each target protein used for prediction and the small molecule to be queried that binds to the target protein are obtained. The above data can be directly obtained from various databases of small molecules known to contain protein targets and bind to said protein targets.
[0047] Step S2, converting the physicochemical feature data of the protein pocket to be bound and the small molecule to be queried into pocket vectors and small molecule vectors, respectively.
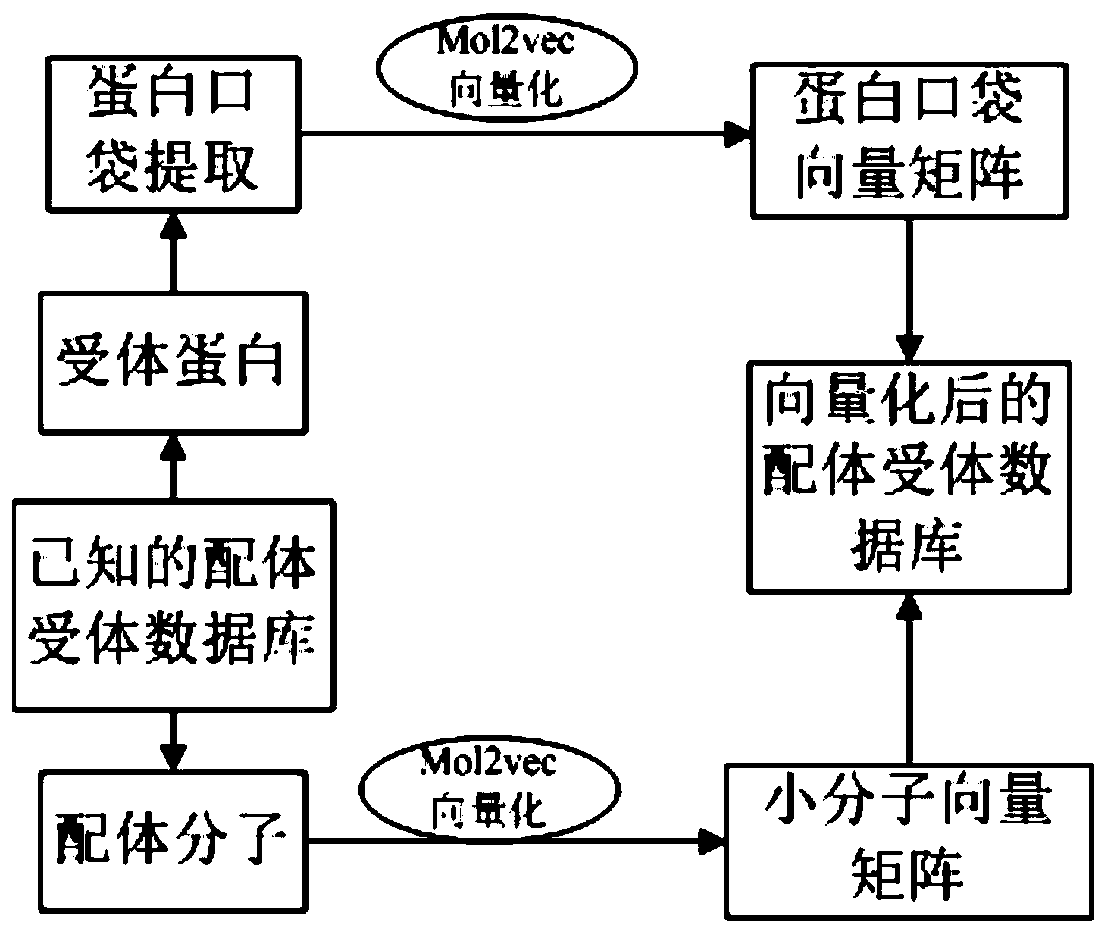
[0048] The relevant data of protein pockets and small molecules obtained in the above step S1 are turned to quantification. Specifically, in order...
Embodiment 2
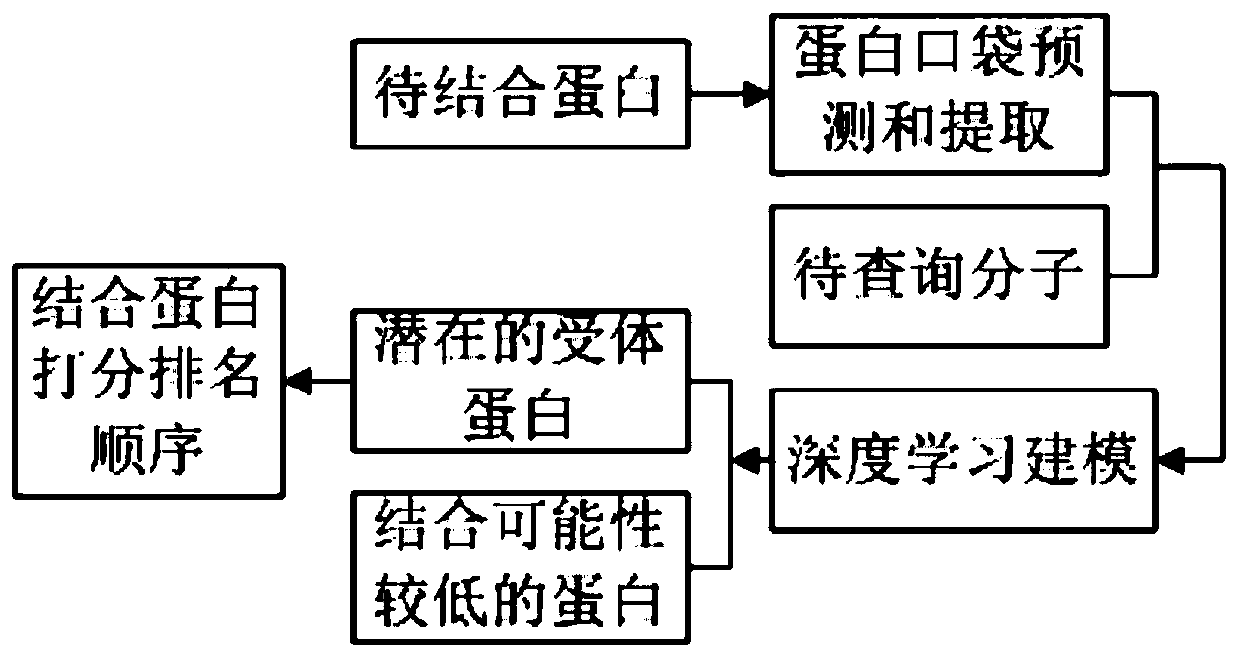
[0123] The second embodiment provided by the present invention is a system for predicting the combination of a target protein and a small molecule, such as Figure 6 shown, including:
[0124] The data acquisition module 610 is used to acquire the physicochemical characteristic data of the protein pocket to be bound and the small molecule to be queried; its function is as described in step S1.
[0125] The vectorization module 620 is used to convert the physicochemical feature data of the pocket of the protein to be bound and the small molecule to be queried into a pocket vector and a small molecule vector respectively; its function is as described in step S2.
[0126] The prediction processing module 630 is configured to use the pocket vector and the small molecule vector as input to a preset prediction model based on a deep neural network to obtain a prediction result of the combination probability, and its function is as described in step S3.
[0127] Specifically, the sys...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com